Minimally invasive procedure
| Minimally invasive procedure | |
|---|---|
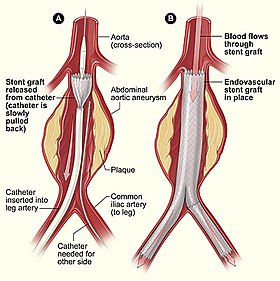 Endovascular aneurysm repair - example of minimally invasive procedure | |
| MeSH | D019060 |
| eMedicine | 938198 |
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definition is invasive, and many operations requiring incisions of some size are referred to as open surgery. Incisions made during open surgery can sometimes leave large wounds that may be painful and take a long time to heal. Advancements in medical technologies have enabled the development and regular use of minimally invasive procedures. For example, endovascular aneurysm repair, a minimally invasive surgery, has become the most common method of repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in the US as of 2003. The procedure involves much smaller incisions than the corresponding open surgery procedure of open aortic surgery.[1]
Interventional radiologists were the forerunners of minimally invasive procedures. Using imaging techniques, radiologists were able to direct interventional instruments through the body by way of catheters instead of the large incisions needed in traditional surgery. As a result, many conditions once requiring surgery can now be treated non-surgically.[2]
Diagnostic techniques that do not involve incisions, puncturing the skin, or the introduction of foreign objects or materials into the body are known as non-invasive procedures.[3] Several treatment procedures are classified as non-invasive. A major example of a non-invasive alternative treatment to surgery is radiation therapy, also called radiotherapy.[4]
Medical uses
[edit]
Minimally invasive procedures were pioneered by interventional radiologists who had first introduced angioplasty and the catheter-delivered stent. Many other minimally invasive procedures have followed where images of all parts of the body can be obtained and used to direct interventional instruments by way of catheters (needles and fine tubes), so that many conditions once requiring open surgery can now be treated non-surgically.[2] A minimally invasive procedure typically involves the use of arthroscopic (for joints and the spine) or laparoscopic devices and remote-control manipulation of instruments with indirect observation of the surgical field through an endoscope or large scale display panel, and is carried out through the skin or through a body cavity or anatomical opening. Interventional radiology now offers many techniques that avoid the need for surgery.[2]
By use of a minimally invasive procedure, a patient may require only an adhesive bandage on the incision, rather than multiple stitches or staples to close a large incision. This usually results in less infection, a quicker recovery time and shorter hospital stays, or allow outpatient treatment.[5] However, the safety and effectiveness of each procedure must be demonstrated with randomized controlled trials. The term was coined by John E. A. Wickham in 1984, who wrote of it in British Medical Journal in 1987.[6]
Specific procedures
[edit]
Many medical procedures are called minimally invasive; those that involve small incisions through which an endoscope is inserted, end in the suffix -oscopy, such as endoscopy, laparoscopy, arthroscopy. Other examples of minimally invasive procedures include the use of hypodermic injection, and air-pressure injection, subdermal implants, refractive surgery, percutaneous surgery, cryosurgery, microsurgery, keyhole surgery, endovascular surgery using interventional radiology (such as angioplasty or embolization), coronary catheterization, permanent placement of spinal and brain electrodes, stereotactic surgery, the Nuss procedure, radioactivity-based medical imaging methods, such as gamma camera, positron emission tomography and SPECT (single photon emission tomography). Related procedures are image-guided surgery, and robot-assisted surgery.[7]
Equipment
[edit]Special medical equipment may be used, such as fiber optic cables, miniature video cameras and special surgical instruments handled via tubes inserted into the body through small openings in its surface. The images of the interior of the body are transmitted to an external video monitor and the surgeon has the possibility of making a diagnosis, visually identifying internal features and acting surgically on them.[8]
Benefits
[edit]Minimally invasive surgery should have less operative trauma, other complications and adverse effects than an equivalent open surgery. It may be more or less expensive (for dental implants, a minimally invasive method reduces the cost of installed implants and shortens the implant-prosthetic rehabilitation time with four–six months[9]). Operative time is longer, but hospitalization time is shorter. It causes less pain and scarring, speeds recovery, and reduces the incidence of post-surgical complications, such as adhesions and wound rupture. Some studies have compared heart surgery.[10]
Risks
[edit]Risks and complications of minimally invasive procedures are the same as for any other surgical operation, among the risks are: death, bleeding, infection, organ injury, and thromboembolic disease.[11]
There may be an increased risk of hypothermia and peritoneal trauma due to increased exposure to cold, dry gases during insufflation. The use of surgical humidification therapy, which is the use of heated and humidified CO2 for insufflation, may reduce this risk.[12]
Invasive procedures
[edit]
Sometimes the use of non-invasive methods is not an option, so that the next level of minimally invasive techniques are looked to. These include the use of hypodermic injection (using the syringe), an endoscope, percutaneous surgery which involves needle puncture of the skin, laparoscopic surgery commonly called keyhole surgery, a coronary catheter, angioplasty and stereotactic surgery.[citation needed]
Open surgery
[edit]"Open surgery" is any surgical procedure where the incision made is enough to allow the surgery to take place. With tissues and structures exposed to the air, the procedure can be performed either with the unaided vision of the surgeon or with the use of loupes or microscopes. Some examples of open surgery used are for herniated disc commonly called a "slipped disc", and most types of cardiac surgery and neurosurgery.[medical citation needed]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Sethi RK, Henry AJ, Hevelone ND, Lipsitz SR, Belkin M, Nguyen LL (September 2013). "Impact of hospital market competition on endovascular aneurysm repair adoption and outcomes". J. Vasc. Surg. 58 (3): 596–606. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2013.02.014. PMID 23684424.
- ^ a b c "Global Statement Defining Interventional Radiology" (PDF). Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology. 21 (8): 1147–1149. Aug 2010. doi:10.1016/j.jvir.2010.05.006. Archived from the original (PDF) on Jul 28, 2011.
- ^ Dorland's (2012). Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary (32nd ed.). Elsevier. p. 955. ISBN 978-1-4160-6257-8.
- ^ Daniel Albert (2012). Dorland's illustrated medical dictionary (32nd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Saunders/Elsevier. p. 1573. ISBN 978-1-4160-6257-8.
- ^ "Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedures". MeSH - NCBI. Archived from the original on Sep 29, 2023.
- ^ Wickham JE' (1987-12-19). "The new surgery". Br Med J. 295 (6613): 1581–1582. doi:10.1136/bmj.295.6613.1581. PMC 1257475. PMID 3121078.
- ^ Ahmed K, Khan MS, Vats A, et al. (October 2009). "Current status of robotic assisted pelvic surgery and future developments". International Journal of Surgery. 7 (5): 431–40. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2009.08.008. PMID 19735746.
- ^ Belzberg, Micah; Mahapatra, Smruti; Perdomo-Pantoja, Alexander; Chavez, Francisco; Morrison, Kyle; Xiong, K. Timothy; Gamo, Nao J.; Restaino, Stephen A.; Thakor, Nitish; Yazdi, Youseph; Iyer, Rajiv; Tyler, Betty; Theodore, Nicholas; Luciano, Mark G.; Brem, Henry; Groves, Mari; Cohen, Alan R.; Manbachi, Amir (2020). "Minimally invasive therapeutic ultrasound: Ultrasound-guided ultrasound ablation in neuro-oncology". Ultrasonics. 108 (12): 106210. doi:10.1016/j.ultras.2020.106210. PMC 8895244. PMID 32619834.
- ^ Topalo V, Chele N (March 2012). "Minimally invasive method of early dental implant placement in two surgical steps". Revista de chirurgie oro-maxilo-facială și implantologie (in Romanian). 3 (1): 16–23. ISSN 2069-3850. 60. Archived from the original on 2016-04-02. Retrieved 2012-08-19.(webpage has a translation button)
- ^ Kilger E, Weis FC, Goetz AE, et al. (March 2001). "Intensive care after minimally invasive and conventional coronary surgery: a prospective comparison". Intensive Care Medicine. 27 (3): 534–9. doi:10.1007/s001340000788. PMID 11355122. S2CID 23157051.
- ^ "Minimally Invasive Surgery. Keyhole Surgery information". patient.info. Retrieved 2017-05-25.
- ^ Peng Y, Zheng M, Ye Q, Chen X, Yu B, Liu B (January 2009). "Heated and humidified CO2 prevents hypothermia, peritoneal injury, and intra-abdominal adhesions during prolonged laparoscopic insufflations". The Journal of Surgical Research. 151 (1): 40–7. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2008.03.039. PMID 18639246.
Further reading
[edit]- "Minimally Invasive Cancer Treatments Highlighted". www.sciencedaily.com. November 28, 2005. Retrieved 2015-08-03.
- Tachibana K (March 2004). "Emerging technologies in therapeutic ultrasound: thermal ablation to gene delivery". Human Cell. 17 (1): 7–15. doi:10.1111/j.1749-0774.2004.tb00015.x. PMID 15369132. S2CID 19482620.
- Kim PE, Singh M (July 2003). "Functional magnetic resonance imaging for brain mapping in neurosurgery". Neurosurgical Focus. 15 (1): E1. doi:10.3171/foc.2003.15.1.1. PMID 15355003.
- Richie RC (2002). "Non-invasive assessment of the risk of coronary heart disease". Journal of Insurance Medicine. 34 (1): 31–42. PMID 15303592.
- Golder W (June 2004). "Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in clinical oncology". Onkologie. 27 (3): 304–9. doi:10.1159/000077983. PMID 15249722. S2CID 20644834.
- Cherry SR (February 2004). "In vivo molecular and genomic imaging: new challenges for imaging physics". Physics in Medicine and Biology. 49 (3): R13–48. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/49/3/R01. PMID 15012005. S2CID 250810092.
- Lymberis A, Olsson S (2003). "Intelligent biomedical clothing for personal health and disease management: state of the art and future vision". Telemedicine Journal and e-Health. 9 (4): 379–86. doi:10.1089/153056203772744716. PMID 14980096.
- Söling A, Rainov NG (October 2003). "Bioluminescence imaging in vivo - application to cancer research". Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 3 (7): 1163–72. doi:10.1517/14712598.3.7.1163. PMID 14519079. S2CID 28865110.
- Rohrscheib M, Robinson R, Eaton RP (September 2003). "Non-invasive glucose sensors and improved informatics--the future of diabetes management". Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism. 5 (5): 280–4. doi:10.1046/j.1463-1326.2003.00275.x. PMID 12940864. S2CID 7192060.
- Jacobs AH, Winkeler A, Dittmar C, Hilker R, Heiss WD (2002). "Prospects of molecular imaging in neurology". Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. Supplement. 39: 98–109. doi:10.1002/jcb.10414. PMID 12552609. S2CID 8618818.
- Malhi GS, Valenzuela M, Wen W, Sachdev P (February 2002). "Magnetic resonance spectroscopy and its applications in psychiatry". The Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 36 (1): 31–43. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1614.2002.00992.x. PMID 11929436. S2CID 15981685.
- Jacobs A, Heiss WD (April 2002). "Towards non-invasive imaging of HSV-1 vector-mediated gene expression by positron emission tomography". Veterinary Microbiology. 86 (1–2): 27–36. doi:10.1016/S0378-1135(01)00488-6. PMID 11888687.
- Leman JA, Morton CA (January 2002). "Photodynamic therapy: applications in dermatology". Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 2 (1): 45–53. doi:10.1517/14712598.2.1.45. PMID 11772339. S2CID 40893453.
- Richter JE (November 1997). "Ambulatory esophageal pH monitoring". The American Journal of Medicine. 103 (5A): 130S–134S. doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(97)00338-0. PMID 9422638.
External links
[edit]- Minimally invasive heart surgery. Medical Encyclopedia, MedlinePlus.
