GQM
GQM, the initialism for goal, question, metric, is an established goal-oriented approach to software metrics to improve and measure software quality.[1]
History[edit]
GQM has been promoted by Victor Basili of the University of Maryland, College Park and the Software Engineering Laboratory at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center[2] after supervising a Ph.D. thesis by Dr. David M. Weiss.[3] Dr. Weiss' work was inspired by the work of Albert Endres at IBM Germany.[4][5][6]
Method[edit]
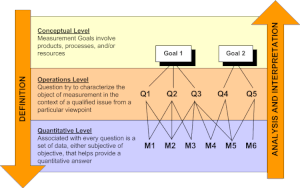
GQM defines a measurement model on three levels:[7]
- 1. Conceptual level (Goal)
- A goal is defined for an object, for a variety of reasons, with respect to various models of quality, from various points of view and relative to a particular environment.
- 2. Operational level (Question)
- A set of questions is used to define models of the object of study and then focuses on that object to characterize the assessment or achievement of a specific goal.
- 3. Quantitative level (Metric)[8]
- A set of metrics, based on the models, is associated with every question in order to answer it in a measurable way.
GQM stepwise[edit]
Another interpretation of the procedure is:[9]
- Planning
- Definition
- Data collection
- Interpretation
Sub-steps[edit]
Sub-steps are needed for each phases. To complete the definition phase, an eleven-step procedure is proposed:[9]
- Define measurement goals
- Review or produce software process models
- Conduct GQM interviews
- Define questions and hypotheses
- Review questions and hypotheses
- Define metrics
- Check metrics on consistency and completeness
- Produce GQM plan
- Produce measurement plan
- Produce analysis plan
- Review plans
Recent developments[edit]
The GQM+Strategies approach was developed by Victor Basili and a group of researchers from the Fraunhofer Society.[10] It is based on the Goal Question Metric paradigm and adds the capability to create measurement programs that ensure alignment between business goals and strategies, software-specific goals, and measurement goals.
Novel application of GQM towards business data are described.[11] Specifically in the software engineering areas of Quality assurance and Testing, GQM is used.[12]
Further reading[edit]
- Victor R. Basili's contributions to software quality (IEEE Software, 2006)
- Solingen/Berghout: The Goal/Question/Metric Method: A Practical Guide for Quality Improvement of Software Development (PDF, 2015)
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ "Goal/Question/Metric (GQM) – The Making of Software". Retrieved 2021-03-18.
- ^ "Software Engineering Division/Code 580". sed.gsfc.nasa.gov. Retrieved 2021-03-18.
- ^ Basili, V. R.; Weiss, D. M. (November 1984). "A Methodology for Collecting Valid Software Engineering Data". IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering. SE-10 (6): 728–738. doi:10.1109/TSE.1984.5010301. hdl:1903/7513. ISSN 1939-3520. S2CID 10114944.
- ^ "Homepage Albert Endres". www.aendres.de. Retrieved 2021-03-18.
- ^ Endres, Albert (2003). A handbook of software and systems engineering : empirical observations, laws, and theories. H. Dieter Rombach. Harlow, England: Pearson Addison Wesley. ISBN 0-321-15420-7. OCLC 50417309.
- ^ Endres, Albert (1975-04-01). "An analysis of errors and their causes in system programs". ACM SIGPLAN Notices. 10 (6): 327–336. doi:10.1145/390016.808455. ISSN 0362-1340.
- ^ Basili, V.; Caldiera, G.; Rombach, H. D. (1994). "The Goal Question Metric Approach". S2CID 13884048.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help) - ^ Huether, Derek (2020). Metrics Cookbook. p. 11. ISBN 9798586916082.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Solingen, Rini van (1999). The goal/question/metric method : a practical guide for quality improvement of software development. Egon Berghout. London: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-709553-7. OCLC 43551689.
- ^ Basili, V.R.; J. Heidrich; M. Lindvall; J. Münch; C.B. Seaman; M. Regardie; A. Trendowicz (2009). "Determining the impact of business strategies using principles from goal-oriented measurement". Business Services: Konzepte, Technologien, Anwendungen. 9. Internationale Tagung Wirtschaftsinformatik. Books OCG. Vienna, Austria: Österreichische Computer Gesellschaft. ISBN 978-3-85403-246-5.
- ^ Southekal, Prashanth H. (2017). Data for business performance : the Goal-Question-Metric (GQM) model to transform business data into an enterprise asset. Basking Ridge, NJ. ISBN 978-1-63462-184-7. OCLC 970616125.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Witte, Frank (2018), Witte, Frank (ed.), "Goal Question Metric", Metriken für das Testreporting: Analyse und Reporting für wirkungsvolles Testmanagement (in German), Wiesbaden: Springer Fachmedien, pp. 145–150, doi:10.1007/978-3-658-19845-9_22, ISBN 978-3-658-19845-9, retrieved 2021-03-18
