Naming conventions in Eritrea and Ethiopia
This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2013) |
The naming convention used in Eritrea and Ethiopia does not have family names and typically consists of an individual personal name and a separate patronymic.[1][2] This is similar to Arabic, Icelandic, and Somali naming conventions. Traditionally for Ethiopians and Eritreans the lineage is traced paternally; legislation has been passed in Eritrea that allows for this to be done on the maternal side as well.
In this convention, children are given a name at birth, by which name they will be known.[2] To differentiate from others in the same generation with the same name, their father's first name and sometimes grandfather's first name is added. This may continue ad infinitum.[3] Outside Ethiopia, this is often mistaken for a surname or middle name but unlike European names, different generations do not have the same second or third names.[4]
In marriage, unlike in some Western societies, women do not change their maiden name, as the second name is not a surname.[1]
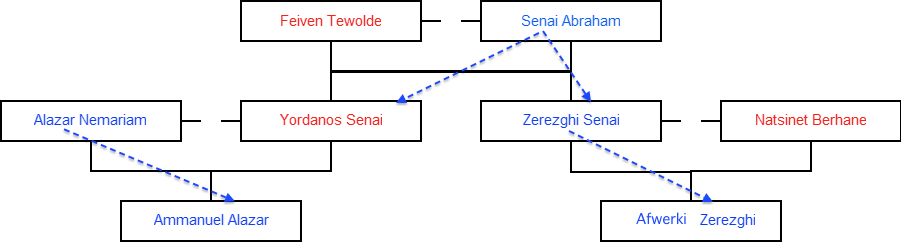
In the example above, the progenitors, Feiven and Senai, may be differentiated from others in their generation by their father's name. In this example, Feiven's and Senai's fathers' first names are Tewolde and Abraham respectively.
Feiven and Senai have a daughter and a son, each of whom is married and has a child. The first to have a child (a son) is their daughter, Yordanos Senai; she and her husband name the boy Ammanuel. The next sibling to have a child is Yordanos' brother, Zerezghi Senai; this child is also a son, named Afwerki. Ammanuel and Afwerki would each get their father's first name for their last.
In contemporary post-independence Eritrea, a person's legal name consists of his or her given name, followed by the given name of one of the parents (written name position equivalent to a "middle name" in Western naming conventions) then the given name of a grandparent (position equivalent to a "last name" in Western naming conventions). In modern Ethiopia, a person's legal name includes both the father and the individual's given names, so that the father's given name becomes the child's "last name", there is no actual middle name. In Ethiopia, and traditionally in Eritrea, the naming conventions follow the father's line of descent while certain exemptions can be made in Eritrea in which the family may choose to use the mother's line of descent. Usually in both countries the grandparent's name of the person is omitted in a similar way to how the middle name is omitted in Western naming conventions excluding important legal documents.
Ethiopians and Eritreans in the diaspora who have to legally adopt Western naming conventions usually convert their father's or grandfather's given name into an official last name or surname, with the ones who choose their grandfather's name additionally repurposing their father's name as an official middle name.[5][4]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Evason, Nina. "Ethiopian Culture > Naming". Artarmon, New South Wales: Special Broadcasting Service. Retrieved 2023-11-25.
- ^ a b Tesfagiorgis G., Mussie (2010). Eritrea. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. p. 236. ISBN 978-1-59884-231-9.
- ^ Spencer, John H (2006). Ethiopia at bay : a personal account of the Haile Selassie years. Hollywood, CA: Tsehai. p. 26. ISBN 1-59907-000-6.
- ^ a b Helebo, Fikru. "Ethiopian Naming System". Retrieved 9 January 2013.
- ^ Tesfagiorgis, Mussie G. (October 29, 2010). Eritrea. ABC-CLIO. p. 236. ISBN 978-1598842319.
