Major trauma
| Major trauma | |
|---|---|
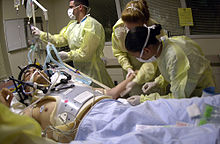 | |
| Health care providers attending to a person on a stretcher with a gunshot wound to the head; the patient is intubated, and a mechanical ventilator is visible in the background | |
| Specialty | Emergency medicine, trauma surgery |
Major trauma is any injury that has the potential to cause prolonged disability or death.[1] There are many causes of major trauma, blunt and penetrating, including falls, motor vehicle collisions, stabbing wounds, and gunshot wounds. Depending on the severity of injury, quickness of management, and transportation to an appropriate medical facility (called a trauma center) may be necessary to prevent loss of life or limb. The initial assessment is critical, and involves a physical evaluation and also may include the use of imaging tools to determine the types of injuries accurately and to formulate a course of treatment.[citation needed]
In 2002, unintentional and intentional injuries were the fifth and seventh leading causes of deaths worldwide, accounting for 6.23% and 2.84% of all deaths. For research purposes the definition often is based on an Injury Severity Score (ISS) of greater than 15.[2]
Classification
[edit]Injuries generally are classified by either severity, the location of damage, or a combination of both.[3] Trauma also may be classified by demographic group, such as age or gender.[4] It also may be classified by the type of force applied to the body, such as blunt trauma or penetrating trauma. For research purposes injury may be classified using the Barell matrix, which is based on ICD-9-CM. The purpose of the matrix is for international standardization of the classification of trauma.[5] Major trauma sometimes is classified by body area; injuries affecting 40% are polytrauma, 30% head injuries, 20% chest trauma, 10%, abdominal trauma, and 2%, extremity trauma.[4][6]
Various scales exist to provide a quantifiable metric to measure the severity of injuries. The value may be used for triaging a patient or for statistical analysis. Injury scales measure damage to anatomical parts, physiological values (blood pressure etc.), comorbidities, or a combination of those. The Abbreviated Injury Scale and the Glasgow Coma Scale are used commonly to quantify injuries for the purpose of triaging and allow a system to monitor or "trend" a patient's condition in a clinical setting.[7] The data also may be used in epidemiological investigations and for research purposes.[8]
Approximately 2% of those who have experienced significant trauma have a spinal cord injury.[9]
Causes
[edit]Injuries may be caused by any combination of external forces that act physically against the body.[10] The leading causes of traumatic death are blunt trauma, motor vehicle collisions, and falls, followed by penetrating trauma such as stab wounds or impaled objects.[11] Subsets of blunt trauma are both the number one and two causes of traumatic death.[12]
For statistical purposes, injuries are classified as either intentional such as suicide, or unintentional, such as a motor vehicle collision. Intentional injury is a common cause of traumas.[13] Penetrating trauma is caused when a foreign body such as a bullet or a knife enters the body tissue, creating an open wound. In the United States, most deaths caused by penetrating trauma occur in urban areas and 80% of these deaths are caused by firearms.[14] Blast injury is a complex cause of trauma because it commonly includes both blunt and penetrating trauma, and also may be accompanied by a burn injury. Trauma also may be associated with a particular activity, such as an occupational or sports injury.[15]
Pathophysiology
[edit]The body responds to traumatic injury both systemically and at the injury site.[16] This response attempts to protect vital organs such as the liver, to allow further cell duplication and to heal the damage.[17] The healing time of an injury depends on various factors including sex, age, and the severity of injury.[18]
The symptoms of injury may manifest in many different ways, including:[19]
- Altered mental status
- Fever
- Increased heart rate
- Generalized edema
- Increased cardiac output
- Increased rate of metabolism
Various organ systems respond to injury to restore homeostasis by maintaining perfusion to the heart and brain.[20] Inflammation after injury occurs to protect against further damage and starts the healing process. Prolonged inflammation may cause multiple organ dysfunction syndrome or systemic inflammatory response syndrome.[21] Immediately after injury, the body increases production of glucose through gluconeogenesis and its consumption of fat via lipolysis. Next, the body tries to replenish its energy stores of glucose and protein via anabolism. In this state the body will temporarily increase its maximum expenditure for the purpose of healing injured cells.[18][22]
Diagnosis
[edit]
The initial assessment is critical in determining the extent of injuries and what will be needed to manage an injury, and for treating immediate life threats.
Physical examination
[edit]Primary physical examination is undertaken to identify any life-threatening problems, after which the secondary examination is carried out. This may occur during transportation or upon arrival at the hospital. The secondary examination consists of a systematic assessment of the abdominal, pelvic, and thoracic areas, a complete inspection of the body surface to find all injuries, and a neurological examination. Injuries that may manifest themselves later may be missed during the initial assessment, such as when a patient is brought into a hospital's emergency department.[23] Generally, the physical examination is performed in a systematic way that first checks for any immediate life threats (primary survey), and then taking a more in-depth examination (secondary survey).[24]
Imaging
[edit]
Persons with major trauma commonly have chest and pelvic x-rays taken,[6] and, depending on the mechanism of injury and presentation, a focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) exam to check for internal bleeding. For those with relatively stable blood pressure, heart rate, and sufficient oxygenation, CT scans are useful.[6][25] Full-body CT scans, known as pan-scans, improve the survival rate of those who have suffered major trauma.[26][27] These scans use intravenous injections for the radiocontrast agent, but not oral administration.[28] There are concerns that intravenous contrast administration in trauma situations without confirming adequate renal function may cause damage to kidneys, but this does not appear to be significant.[25]
In the U.S., CT or MRI scans are performed on 15% of those with trauma in emergency departments.[29] Where blood pressure is low or the heart rate is increased—likely from bleeding in the abdomen—immediate surgery bypassing a CT scan is recommended.[30] Modern 64-slice CT scans are able to rule out, with a high degree of accuracy, significant injuries to the neck following blunt trauma.[31]
Surgical techniques
[edit]Surgical techniques, using a tube or catheter to drain fluid from the peritoneum, chest, or the pericardium around the heart, often are used in cases of severe blunt trauma to the chest or abdomen, especially when a person is experiencing early signs of shock. In those with low blood-pressure, likely because of bleeding in the abdominal cavity, cutting through the abdominal wall surgically is indicated.[6]
Prevention
[edit]By identifying risk factors present within a community and creating solutions to decrease the incidence of injury, trauma referral systems may help to enhance the overall health of a population.[32] Injury prevention strategies are commonly used to prevent injuries in children, who are a high risk population.[33] Injury prevention strategies generally involve educating the general public about specific risk factors and developing strategies to avoid or reduce injuries.[34] Legislation intended to prevent injury typically involves seatbelts, child car-seats, helmets, alcohol control, and increased enforcement of the legislation.[citation needed] Other controllable factors, such as the use of drugs including alcohol or cocaine, increases the risk of trauma by increasing the likelihood of traffic collisions, violence, and abuse occurring.[6] Prescription drugs such as benzodiazepines may increase the risk of trauma in elderly people.[6]
The care of acutely injured people in a public health system requires the involvement of bystanders, community members, health care professionals, and health care systems. It encompasses pre-hospital trauma assessment and care by emergency medical services personnel, emergency department assessment, treatment, stabilization, and in-hospital care among all age groups.[35] An established trauma system network is also an important component of community disaster preparedness, facilitating the care of people who have been involved in disasters that cause large numbers of casualties, such as earthquakes.[32]
Management
[edit]

Pre-hospital
[edit]The pre-hospital use of stabilization techniques improves the chances of a person surviving the journey to the nearest trauma-equipped hospital. Emergency medicine services determines which people need treatment at a trauma center as well as provide primary stabilization by checking and treating airway, breathing, and circulation as well as assessing for disability and gaining exposure to check for other injuries.[23]
Spinal motion restriction by securing the neck with a cervical collar and placing the person on a long spine board was of high importance in the pre-hospital setting, but due to lack of evidence to support its use, the practice is losing favor. Instead, it is recommended that more exclusive criteria be met such as age and neurological deficits to indicate the need of these adjuncts.[36][37] This may be accomplished with other medical transport devices, such as a Kendrick extrication device, before moving the person.[38] It is important to quickly control severe bleeding with direct pressure to the wound and consider the use of hemostatic agents or tourniquets if the bleeding continues.[39] Conditions such as impending airway obstruction, enlargening neck hematoma, or unconsciousness require intubation. It is unclear, however, if this is best performed before reaching hospital or in the hospital.[40]
Rapid transportation of severely injured patients improves the outcome in trauma.[6][23] Helicopter EMS transport reduces mortality compared to ground-based transport in adult trauma patients.[41] Before arrival at the hospital, the availability of advanced life support does not greatly improve the outcome for major trauma when compared to the administration of basic life support.[42][43] Evidence is inconclusive in determining support for pre-hospital intravenous fluid resuscitation while some evidence has found it may be harmful.[44] Hospitals with designated trauma centers have improved outcomes when compared to hospitals without them,[6] and outcomes may improve when persons who have experienced trauma are transferred directly to a trauma center.[45]
Improvements in pre-hospital care have led to "unexpected survivors", where patients survive trauma when they would have previously been expected to die.[46] However these patients may struggle to rehabilitate.[47]
In-hospital
[edit]Management of those with trauma often requires the help of many healthcare specialists including physicians, nurses, respiratory therapists, and social workers. Cooperation allows many actions to be completed at once. Generally, the first step of managing trauma is to perform a primary survey that evaluates a person's airway, breathing, circulation, and neurologic status.[48] These steps may happen simultaneously or depend on the most pressing concern such as a tension pneumothorax or major arterial bleed. The primary survey generally includes assessment of the cervical spine, though clearing it is often not possible until after imaging, or the person has improved. After immediate life threats are controlled, a person is either moved into an operating room for immediate surgical correction of the injuries, or a secondary survey is performed that is a more detailed head-to-toe assessment of the person.[49]
Indications for intubation include airway obstruction, inability to protect the airway, and respiratory failure.[50] Examples of these indications include penetrating neck trauma, expanding neck hematoma, and being unconscious. In general, the method of intubation used is rapid sequence intubation followed by ventilation, though intubating in shock due to bleeding can lead to arrest, and should be done after some resuscitation whenever possible. Trauma resuscitation includes control of active bleeding. When a person is first brought in, vital signs are checked, an ECG is performed, and, if needed, vascular access is obtained. Other tests should be performed to get a baseline measurement of their current blood chemistry, such as an arterial blood gas or thromboelastography.[51] In those with cardiac arrest due to trauma chest compressions are considered futile, but still recommended.[52] Correcting the underlying cause such as a pneumothorax or pericardial tamponade, if present, may help.[52]
A FAST exam may help assess for internal bleeding. In certain traumas, such as maxillofacial trauma, it may be beneficial to have a highly trained health care provider available to maintain airway, breathing, and circulation.[53]
Intravenous fluids
[edit]Traditionally, high-volume intravenous fluids were given to people who had poor perfusion due to trauma.[54] This is still appropriate in cases with isolated extremity trauma, thermal trauma, or head injuries.[55] In general, however, giving lots of fluids appears to increase the risk of death.[56] Current evidence supports limiting the use of fluids for penetrating thorax and abdominal injuries, allowing mild hypotension to persist.[4][55] Targets include a mean arterial pressure of 60 mmHg, a systolic blood pressure of 70–90 mmHg,[54][57] or the re-establishment of peripheral pulses and adequate ability to think.[54] Hypertonic saline has been studied and found to be of little difference from normal saline.[58]
As no intravenous fluids used for initial resuscitation have been shown to be superior, warmed Lactated Ringer's solution continues to be the solution of choice.[54] If blood products are needed, a greater use of fresh frozen plasma and platelets instead of only packed red blood cells has been found to improve survival and lower overall blood product use;[59] a ratio of 1:1:1 is recommended.[57] The success of platelets has been attributed to the fact that they may prevent coagulopathy from developing.[60] Cell salvage and autotransfusion also may be used.[54]
Blood substitutes such as hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers are in development; however, as of 2013 there are none available for commercial use in North America or Europe.[54][61][62] These products are only available for general use in South Africa and Russia.[61]
Medications
[edit]Tranexamic acid decreases death in people who are having ongoing bleeding due to trauma, as well as those with mild to moderate traumatic brain injury and evidence of intracranial bleeding on CT scan.[63][64][65] It only appears to be beneficial, however, if administered within the first three hours after trauma.[66] For severe bleeding, for example from bleeding disorders, recombinant factor VIIa—a protein that assists blood clotting—may be appropriate.[6][55] While it decreases blood use, it does not appear to decrease the mortality rate.[67] In those without previous factor VII deficiency, its use is not recommended outside of trial situations.[68]
Other medications may be used in conjunction with other procedures to stabilize a person who has sustained a significant injury.[4] While positive inotropic medications such as norepinephrine sometimes are used in hemorrhagic shock as a result of trauma, there is a lack of evidence for their use.[69] Therefore, as of 2012 they have not been recommended.[58] Allowing a low blood pressure may be preferred in some situations.[70]
Surgery
[edit]The decision whether to perform surgery is determined by the extent of the damage and the anatomical location of the injury. Bleeding must be controlled before definitive repair may occur.[71] Damage control surgery is used to manage severe trauma in which there is a cycle of metabolic acidosis, hypothermia, and hypotension that may lead to death, if not corrected.[6] The main principle of the procedure involves performing the fewest procedures to save life and limb; less critical procedures are left until the victim is more stable.[6] Approximately 15% of all people with trauma have abdominal injuries, and approximately 25% of these require exploratory surgery. The majority of preventable deaths from trauma result from unrecognised intra-abdominal bleeding.[72]
Prognosis
[edit]Trauma deaths occur in immediate, early, or late stages. Immediate deaths usually are due to apnea, severe brain or high spinal cord injury, or rupture of the heart or of large blood vessels. Early deaths occur within minutes to hours and often are due to hemorrhages in the outer meningeal layer of the brain, torn arteries, blood around the lungs, air around the lungs, ruptured spleen, liver laceration, or pelvic fracture. Immediate access to care may be crucial to prevent death in persons experiencing major trauma. Late deaths occur days or weeks after the injury[23] and often are related to infection.[73] Prognosis is better in countries with a dedicated trauma system where injured persons are provided quick and effective access to proper treatment facilities.[6]
Long-term prognosis frequently is complicated by pain; more than half of trauma patients have moderate to severe pain one year after injury.[74] Many also experience a reduced quality of life years after an injury,[75] with 20% of victims sustaining some form of disability.[76] Physical trauma may lead to development of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).[77] One study has found no correlation between the severity of trauma and the development of PTSD.[78]
Epidemiology
[edit]
| no data < 25 25–50 50–75 75–100 100–125 125–150 | 150–175 175–200 200–225 225–250 250–275 > 275 |
Trauma is the sixth leading cause of death worldwide, resulting in five million or 10% of all deaths annually.[80][81] It is the fifth leading cause of significant disability.[80] About half of trauma deaths are in people aged between 15 and 45 years and trauma is the leading cause of death in this age group.[81] Injury affects more males; 68% of injuries occur in males[82] and death from trauma is twice as common in males as it is in females, this is believed to be because males are much more willing to engage in risk-taking activities.[81] Teenagers and young adults are more likely to need hospitalization from injuries than other age groups.[83] While elderly persons are less likely to be injured, they are more likely to die from injuries sustained due to various physiological differences that make it more difficult for the body to compensate for the injuries.[83] The primary causes of traumatic death are central nervous system injuries and substantial blood loss.[80] Various classification scales exist for use with trauma to determine the severity of injuries, which are used to determine the resources used and, for statistical collection.
History
[edit]The human remains discovered at the site of Nataruk in Turkana, Kenya, are claimed to show major trauma—both blunt and penetrating—caused by violent trauma to the head, neck, ribs, knees, and hands, which has been interpreted by some researchers as establishing the existence of warfare between two groups of hunter-gatherers 10,000 years ago.[84] The evidence for blunt-force trauma at Nataruk has been challenged, however, and the interpretation that the site represents an early example of warfare has been questioned.[85]
Society and culture
[edit]Economics
[edit]The financial cost of trauma includes both the amount of money spent on treatment and the loss of potential economic gain through absence from work. The average financial cost for the treatment of traumatic injury in the United States is approximately US$334,000 per person, making it costlier than the treatment of cancer and cardiovascular diseases.[86] One reason for the high cost of the treatment for trauma is the increased possibility of complications, which leads to the need for more interventions.[87] Maintaining a trauma center is costly because they are open continuously and maintain a state of readiness to receive patients, even if there are none.[88] In addition to the direct costs of the treatment, there also is a burden on the economy due to lost wages and productivity, which in 2009, accounted for approximately US$693.5 billion in the United States.[89]
Low- and middle-income countries
[edit]Citizens of low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) often have higher mortality rates from injury. These countries accounted for 89% of all deaths from injury worldwide.[82] Many of these countries do not have access to sufficient surgical care and many do not have a trauma system in place. In addition, most LMICs do not have a pre-hospital care system that treats injured persons initially and transports them to hospital quickly, resulting in most casualty patients being transported by private vehicles. Also, their hospitals lack the appropriate equipment, organizational resources, or trained staff.[90][91] By 2020, the amount of trauma-related deaths is expected to decline in high-income countries, while in low- to middle-income countries it is expected to increase.[citation needed]
Special populations
[edit]Children
[edit]| Cause | Deaths per year |
|---|---|
| Traffic collision |
260,000 |
| Drowning |
175,000 |
| Burns |
96,000 |
| Falls |
47,000 |
| Toxins |
45,000 |
Due to anatomical and physiological differences, injuries in children need to be approached differently from those in adults.[92] Accidents are the leading cause of death in children between 1 and 14 years old.[76] In the United States, approximately sixteen million children go to an emergency department due to some form of injury every year,[76] with boys being more frequently injured than girls by a ratio of 2:1.[76] The world's five most common unintentional injuries in children as of 2008 are road crashes, drowning, burns, falls, and poisoning.[93]
Weight estimation is an important part of managing trauma in children because the accurate dosing of medicine may be critical for resuscitative efforts.[94] A number of methods to estimate weight, including the Broselow tape, Leffler formula, and Theron formula exist.[95]
Pregnancy
[edit]Trauma occurs in approximately 5% of all pregnancies,[96] and is the leading cause of maternal death. Additionally, pregnant women may experience placental abruption, pre-term labor, and uterine rupture.[96] There are diagnostic issues during pregnancy; ionizing radiation has been shown to cause birth defects,[4] although the doses used for typical exams generally are considered safe.[96] Due to normal physiological changes that occur during pregnancy, shock may be more difficult to diagnose.[4][97] Where the woman is more than 23 weeks pregnant, it is recommended that the fetus be monitored for at least four hours by cardiotocography.[96]
A number of treatments beyond typical trauma care may be needed when the patient is pregnant. Because the weight of the uterus on the inferior vena cava may decrease blood return to the heart, it may be very beneficial to lay a woman in late pregnancy on her left side.[96] also recommended are Rho(D) immune globulin in those who are rh negative, corticosteroids in those who are 24 to 34 weeks and may need delivery or a caesarean section in the event of cardiac arrest.[96]
Research
[edit]Most research on trauma occurs during war and military conflicts as militaries will increase trauma research spending in order to prevent combat related deaths.[98] Some research is being conducted on patients who were admitted into an intensive care unit or trauma center, and received a trauma diagnosis that caused a negative change in their health-related quality of life, with a potential to create anxiety and symptoms of depression.[99] New preserved blood products also are being researched for use in pre-hospital care; it is impractical to use the currently available blood products in a timely fashion in remote, rural settings or in theaters of war.[100]
References
[edit]- ^ "Glossary". National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. Retrieved 26 March 2014.
- ^ Palmer, C (2007). "Major trauma and the injury severity score—where should we set the bar?". Annual Proceedings of the Association for the Advancement of Automotive Medicine. 51: 13–29. PMC 3217501. PMID 18184482.
- ^ Moore 2013, p. 77[full citation needed]
- ^ a b c d e f Marx, J (2010). Rosen's emergency medicine: concepts and clinical practice (7th ed.). Philadelphia: Mosby/Elsevier. pp. 243–842. ISBN 978-0323054720.
- ^ "The Barell Injury Diagnosis Matrix, Classification by Body Region and Nature of the Injury". Center for Disease Control. Retrieved 19 June 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Bonatti, H; Calland, JF (2008). "Trauma". Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America. 26 (3): 625–48. doi:10.1016/j.emc.2008.05.001. PMID 18655938.
- ^ Moore 2013, pp. 77–98[full citation needed]
- ^ Discussion document on injury severity measurement in administrative datasets (PDF). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. September 2004. pp. 1–3. Retrieved 2013-05-24.
- ^ Ahn, H; Singh, J; Nathens, A; MacDonald, RD; Travers, A; Tallon, J; Fehlings, MG; Yee, A (Aug 2011). "Pre-hospital care management of a potential spinal cord injured patient: a systematic review of the literature and evidence-based guidelines". Journal of Neurotrauma. 28 (8): 1341–61. doi:10.1089/neu.2009.1168. PMC 3143405. PMID 20175667.
- ^ Moore 2013, p. 2[full citation needed]
- ^ DiPrima Jr., PA (2008-03-21). EMT-Basic. McGraw-Hill. pp. 227–33. ISBN 978-0071496797.
- ^ Dickenson ET, Limmer D, O'Keefe MF (2009). Emergency Care. ISBN 978-0135005231.
- ^ Jeff Garner; Greaves, Ian; Ryan, James R.; Porter, Keith R. (2009). Trauma care manual. London: Hodder Arnold. ISBN 978-0340928264.
- ^ Medzon R, Mitchell EJ (2005). Introduction to Emergency Medicine. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Willkins. pp. 393–431. ISBN 978-0781732000.
- ^ Kannus, P.; Parkkari, J.; Jarvinen, T.; Jarvinen, A.; Jarvinen, M. (June 2003). "Basic science and clinical studies coincide: active treatment approach is needed after a sports injury". Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports. 13 (3): 150–54. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0838.2003.02225.x. PMID 12753486. S2CID 11161742.
- ^ Boffard, Kenneth (2007). Manual of Definitive Surgical Trauma Care. London, England: Hodder Arnold Publishers. ISBN 978-0340947647.
- ^ Winterborn, R. J.; Cook, T. A. (2003). "The Pathophysiology of Severe Trauma". Surgery. 21 (9): 240a. doi:10.1383/surg.21.9.240.16923.
- ^ a b Sutin, Kenneth M; Marino, Paul L. (2007). The ICU book. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0781748025.
- ^ Pietzman 2002, p. 21[full citation needed]
- ^ Pietzman 2002, p. 17[full citation needed]
- ^ Pietzman 2002, p. 19[full citation needed]
- ^ Keel M, Trentz O (June 2005). "Pathophysiology of polytrauma". Injury. 36 (6): 691–709. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2004.12.037. PMID 15910820.
- ^ a b c d Committee on Trauma, American College of Surgeons (2008). ATLS: Advanced Trauma Life Support Program for Doctors (8th ed.). Chicago: American College of Surgeons. ISBN 978-1880696316.
- ^ Moore 2013, p[full citation needed]
- ^ a b McGillicuddy EA, Schuster KM, Kaplan LJ, et al. (2010). "Contrast-induced nephropathy in elderly trauma patients". J Trauma. 68 (2): 294–97. doi:10.1097/TA.0b013e3181cf7e40. PMID 20154540.
- ^ Huber-Wagner S, Lefering R, Qvick LM, et al. (2009). "Effect of whole-body CT during trauma resuscitation on survival: a retrospective, multicentre study". Lancet. 373 (9673): 1455–61. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60232-4. PMID 19321199. S2CID 45335697.
- ^ Jiang, L; Ma, Y; Jiang, S; Ye, L; Zheng, Z; Xu, Y; Zhang, M (September 2, 2014). "Comparison of whole-body computed tomography vs selective radiological imaging on outcomes in major trauma patients: a meta-analysis". Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine. 22 (1): 54. doi:10.1186/s13049-014-0054-2. PMC 4347587. PMID 25178942.
- ^ Allen TL, Mueller MT, Bonk RT, Harker CP, Duffy OH, Stevens MH (2004). "Computed tomographic scanning without oral contrast solution for blunt bowel and mesenteric injuries in abdominal trauma". J Trauma. 56 (2): 314–22. doi:10.1097/01.TA.0000058118.86614.51. PMID 14960973.
- ^ Korley FK, Pham JC, Kirsch TD (2010). "Use of advanced radiology during visits to US emergency departments for injury-related conditions,1998–2007". JAMA. 304 (13): 1465–71. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.1408. PMID 20924012.
- ^ Neal MD, Peitzman AB, Forsythe RM, et al. (February 2011). "Over reliance on computed tomography imaging in patients with severe abdominal injury: is the delay worth the risk?". J Trauma. 70 (2): 278–84. doi:10.1097/TA.0b013e31820930f9. PMID 21307722.
- ^ Kanji, HD; Neitzel, A; Sekhon, M; McCallum, J; Griesdale, DE (Apr 2014). "Sixty-four-slice computed tomographic scanner to clear traumatic cervical spine injury: systematic review of the literature". Journal of Critical Care. 29 (2): 314.e9–13. doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.10.022. PMID 24393410.
- ^ a b Hoyt, DB; Coimbra, R (2007). "Trauma systems". Surgical Clinics of North America. 87 (1): 21–35, v–vi. doi:10.1016/j.suc.2006.09.012. PMID 17127121.
- ^ Walker, Bonnie (1996). Injury Prevention for Young Children: A Research Guide. Greenwood. p. 2. ISBN 978-0313296864.
- ^ CDC Injury Fact Book. Atlanta, Georgia: National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Atlanta, Georgia. 2006. pp. 35–101.
- ^ "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Injury Prevention and Control: Injury Response: Acute Injury Care". Archived from the original on 2015-09-24. Retrieved 2017-09-09.
- ^ Sundstrøm, Terje; Asbjørnsen, Helge; Habiba, Samer; Sunde, Geir Arne; Wester, Knut (2013-08-20). "Prehospital Use of Cervical Collars in Trauma Patients: A Critical Review". Journal of Neurotrauma. 31 (6): 531–40. doi:10.1089/neu.2013.3094. ISSN 0897-7151. PMC 3949434. PMID 23962031.
- ^ Singletary, Eunice M.; Charlton, Nathan P.; Epstein, Jonathan L.; Ferguson, Jeffrey D.; Jensen, Jan L.; MacPherson, Andrew I.; Pellegrino, Jeffrey L.; Smith, William “Will” R.; Swain, Janel M. (2015-11-03). "Part 15: First Aid". Circulation. 132 (18 suppl 2): S574–89. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000269. ISSN 0009-7322. PMID 26473003.
- ^ Karbi, OA; Caspari, DA; Tator, CH (1988). "Extrication, immobilization and radiologic investigation of patients with cervical spine injuries". Canadian Medical Association Journal. 139 (7): 617–21. PMC 1268249. PMID 3046734.
- ^ Moore 2013, pp. 154–66[full citation needed]
- ^ Bulger, EM; Maier, RV (Feb 2007). "Prehospital care of the injured: what's new". The Surgical Clinics of North America. 87 (1): 37–53, vi. doi:10.1016/j.suc.2006.09.009. PMID 17127122.
- ^ Sullivent, EE; Faul, M; Wald, MM (Jul–Sep 2011). "Reduced mortality in injured adults transported by helicopter emergency medical services". Prehospital Emergency Care. 15 (3): 295–302. doi:10.3109/10903127.2011.569849. PMID 21524205. S2CID 26089433.
- ^ Stiell IG, Nesbitt LP, Pickett W, et al. (2008). "The OPALS Major Trauma Study: impact of advanced life-support on survival and morbidity". CMAJ. 178 (9): 1141–52. doi:10.1503/cmaj.071154. PMC 2292763. PMID 18427089.
- ^ Liberman M, Roudsari BS (2007). "Prehospital trauma care: what do we really know?". Curr Opin Crit Care. 13 (6): 691–96. doi:10.1097/MCC.0b013e3282f1e77e. PMID 17975392. S2CID 44694756.
- ^ Dretzke J, Sandercock J, Bayliss S, Burls A (2004). "Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prehospital intravenous fluids in trauma patients". Health Technol Assess. 8 (23): iii, 1–103. doi:10.3310/hta8230. PMID 15193210.
- ^ Nirula R, Maier R, Moore E, Sperry J, Gentilello L (2010). "Scoop and run to the trauma center or stay and play at the local hospital: hospital transfer's effect on mortality". J Trauma. 69 (3): 595–99, discussion 599–601. doi:10.1097/TA.0b013e3181ee6e32. PMID 20838131.
- ^ Anes - Combat Anesthesia: The First 24 Hours https://medcoeckapwstorprd01.blob.core.usgovcloudapi.net/pfw-images/dbimages/Anes%20%20Ch%203.pdf
- ^ Royal Society Trauma recovery: new science and technology for mental and physical health https://royalsociety.org/-/media/about-us/industry/tof-conference-reports/trauma-recovery-report-2020.pdf
- ^ Moore 2013, p. 160[full citation needed]
- ^ Moore 2013, p. 163[full citation needed]
- ^ Nemeth, J; Maghraby, N; Kazim, S (May 2012). "Emergency airway management: the difficult airway". Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America. 30 (2): 401–20, ix. doi:10.1016/j.emc.2011.12.005. PMID 22487112.
- ^ Moore 2013, p. 161[full citation needed]
- ^ a b Vanden Hoek TL, Morrison LJ, Shuster M, Donnino M, Sinz E, Lavonas EJ, Jeejeebhoy FM, Gabrielli A (2010-11-02). "Part 12: cardiac arrest in special situations: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care". Circulation. 122 (18 Suppl 3): S829–61. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.971069. PMID 20956228.
- ^ Krausz AA, El-Naaj IA, Barak M (2009). "Maxillofacial trauma patient: coping with the difficult airway". World Journal of Emergency Surgery. 4: 21. doi:10.1186/1749-7922-4-21. PMC 2693512. PMID 19473497.
- ^ a b c d e f Cherkas, David (Nov 2011). "Traumatic Hemorrhagic Shock: Advances In Fluid Management". Emergency Medicine Practice. 13 (11): 1–19, quiz 19-20. PMID 22164397. Archived from the original on 2012-01-18.
- ^ a b c Roppolo LP, Wigginton JG, Pepe PE (2010). "Intravenous fluid resuscitation for the trauma patient". Curr Opin Crit Care. 16 (4): 283–88. doi:10.1097/MCC.0b013e32833bf774. PMID 20601865. S2CID 22449600.
- ^ Wang, CH; Hsieh, WH; Chou, HC; Huang, YS; Shen, JH; Yeo, YH; Chang, HE; Chen, SC; Lee, CC (Dec 11, 2013). "Liberal Versus Restricted Fluid Resuscitation Strategies in Trauma Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Observational Studies". Critical Care Medicine. 42 (4): 954–61. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000000050. PMID 24335443. S2CID 44411659.
- ^ a b Tintinalli, Judith E. (2010). Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide (Emergency Medicine (Tintinalli)). New York: McGraw-Hill Companies. p. 176. ISBN 978-0071484800.
- ^ a b Kobayashi, L; Costantini, TW; Coimbra, R (Dec 2012). "Hypovolemic shock resuscitation". The Surgical Clinics of North America. 92 (6): 1403–23. doi:10.1016/j.suc.2012.08.006. PMID 23153876.
- ^ Greer SE, Rhynhart KK, Gupta R, Corwin HL (2010). "New developments in massive transfusion in trauma". Curr Opin Anesthesiol. 23 (2): 246–50. doi:10.1097/ACO.0b013e328336ea59. PMID 20104173. S2CID 35694962.
- ^ "In Medical Triumph, Homicides Fall Despite Soaring Gun Violence". Wall street Journal. 8 December 2012. Retrieved 2012-12-09.
- ^ a b "UpToDate Inc". Retrieved 2010-11-13.
- ^ Spahn DR, Kocian R (2005). "Artificial O2 carriers: status in 2005". Curr. Pharm. Des. 11 (31): 4099–114. doi:10.2174/138161205774913354. PMID 16378514. Archived from the original on 2012-07-24.
- ^ Shakur H, Roberts I, Bautista R, Caballero J, Coats T, Dewan Y, El-Sayed H, Gogichaishvili T, et al. (CRASH-2 trial) (2010). "Effects of tranexamic acid on death, vascular occlusive events, and blood transfusion in trauma patients with significant haemorrhage (CRASH-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial". The Lancet. 376 (9734): 23–32. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60835-5. hdl:20.500.12959/415. PMID 20554319. S2CID 10407122.
- ^ Cap AP, Baer DG, Orman JA, Aden J, Ryan K, Blackbourne LH (July 2011). "Tranexamic acid for trauma patients: a critical review of the literature". The Journal of Trauma. 71 (1 Suppl): S9–14. doi:10.1097/TA.0b013e31822114af. PMID 21795884.
- ^ CRASH-3 trial collaborators (2019-11-09). "Effects of tranexamic acid on death, disability, vascular occlusive events and other morbidities in patients with acute traumatic brain injury (CRASH-3): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial". The Lancet. 394 (10210): 1713–1723. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32233-0. ISSN 0140-6736. PMC 6853170. PMID 31623894.
- ^ Napolitano, LM; Cohen, MJ; Cotton, BA; Schreiber, MA; Moore, EE (June 2013). "Tranexamic acid in trauma: how should we use it?". The Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery. 74 (6): 1575–86. doi:10.1097/ta.0b013e318292cc54. PMID 23694890. S2CID 9569603.
- ^ Hauser CJ, Boffard K, Dutton R, et al. (September 2010). "Results of the CONTROL trial: efficacy and safety of recombinant activated Factor VII in the management of refractory traumatic hemorrhage". J Trauma. 69 (3): 489–500. doi:10.1097/TA.0b013e3181edf36e. PMID 20838118.
- ^ Simpson, E; Lin, Y; Stanworth, S; Birchall, J; Doree, C; Hyde, C (Mar 14, 2012). "Recombinant factor VIIa for the prevention and treatment of bleeding in patients without haemophilia". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 3 (3): CD005011. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005011.pub4. hdl:10871/13808. PMID 22419303.
- ^ Senz, A; Nunnink, L (Oct 2009). "Review article: inotrope and vasopressor use in the emergency department". Emergency Medicine Australasia. 21 (5): 342–51. doi:10.1111/j.1742-6723.2009.01210.x. PMID 19694785. S2CID 20328839.
- ^ "Vasopressor and Inotrope Usage in Shock" (PDF). Department of Surgical Education, Orlando Regional Medical Center. Apr 19, 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2014.
- ^ Andrew B., MD Peitzman; Andrew B. Peitzman; Michael, MD Sabom; Donald M., MD Yearly; Timothy C., MD Fabian (2002). The trauma manual. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0781726412.
- ^ Fitzgerald, J.E.F.; Larvin, Mike (2009). "Chapter 15: Management of Abdominal Trauma". In Baker, Qassim; Aldoori, Munther (eds.). Clinical Surgery: A Practical Guide. CRC Press. pp. 192–204. ISBN 978-1444109627.
- ^ Moore 2013, p. 330[full citation needed]
- ^ Rivara FP, Mackenzie EJ, Jurkovich GJ, Nathens AB, Wang J, Scharfstein DO (2008). "Prevalence of pain in patients 1 year after major trauma". Arch Surg. 143 (3): 282–87, discussion 288. doi:10.1001/archsurg.2007.61. PMID 18347276.
- ^ Ulvik A, Kvåle R, Wentzel-Larsen T, Flaatten H (2008). "Quality of life 2–7 years after major trauma". Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 52 (2): 195–201. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2007.01533.x. PMID 18005377. S2CID 13256047.
- ^ a b c d Peitzman AB, Rhodes M, Schwab CW, Yealy DM, Fabian TC, eds. (2008). "Pediatric Trauma". The Trauma Manual (3rd ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 499–514. ISBN 978-0781762755.
- ^ "309.81 Posttraumatic Stress Disorder". Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (fourth ed.). Washington, USA: American Psychiatric Association. 1994. pp. 424–29.
- ^ Feinstein, A; Dolan, Ray (1991). "Predictors of post-traumatic stress disorder following physical trauma: an examination of the stressor criterion". Psychological Medicine. 21 (1). Cambridge University Press: 85–91. doi:10.1017/S0033291700014689. hdl:21.11116/0000-0001-A23A-7. PMID 2047509. S2CID 28663482.
- ^ "Death and DALY estimates for 2004 by cause for WHO Member States" (xls). World Health Organization. 2004. Retrieved 2010-11-13.
- ^ a b c Søreide K (2009). "Epidemiology of major trauma". The British Journal of Surgery. 96 (7): 697–98. doi:10.1002/bjs.6643. PMID 19526611. S2CID 10670345.
- ^ a b c Jason Smith; Ian Greaves; Keith Porter, eds. (2010). Major trauma (1. publ. ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-0199543328.
- ^ a b Norton R, Kobusingye O (May 2013). "Injuries". The New England Journal of Medicine. 368 (18): 1723–30. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1109343. PMID 23635052.
- ^ a b Moore 2013, p. 23[full citation needed]
- ^ Lahr, M. Mirazón; Rivera, F.; Power, R. K.; Mounier, A.; Copsey, B.; Crivellaro, F.; Edung, J. E.; Fernandez, J. M. Maillo; Kiarie, C. (2016). "Inter-group violence among early Holocene hunter-gatherers of West Turkana, Kenya". Nature. 529 (7586): 394–98. Bibcode:2016Natur.529..394L. doi:10.1038/nature16477. PMID 26791728. S2CID 4462435.
- ^ Stojanowski, Christopher M.; Seidel, Andrew C.; Fulginiti, Laura C.; Johnson, Kent M.; Buikstra, Jane E. (24 Nov 2016). "Contesting the Massacre at Nataruk". Nature. 539 (7630): E8–E10. doi:10.1038/nature19778. PMID 27882979. S2CID 205250945.
- ^ PHTLS: Prehospital Trauma Life Support. Mosby/JEMS. 2010. ISBN 978-0323065023.
- ^ Hemmila MR, Jakubus JL, Maggio PM, et al. (August 2008). "Real money: complications and hospital costs in trauma patients". Surgery. 144 (2): 307–16. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2008.05.003. PMC 2583342. PMID 18656640.
- ^ Taheri PA, Butz DA, Lottenberg L, Clawson A, Flint LM (January 2004). "The cost of trauma center readiness". American Journal of Surgery. 187 (1): 7–13. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2003.06.002. PMID 14706578.
- ^ "Injury Facts" (PDF). National Safety Council. Retrieved July 17, 2012.
- ^ Sakran JV, Greer SE, Werline EC, McCunn M (September 2012). "Care of the injured worldwide: trauma still the neglected disease of modern society". Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine. 20 (1): 64. doi:10.1186/1757-7241-20-64. PMC 3518175. PMID 22980446.
- ^ Mock C, Quansah R, Krishnan R, Arreola-Risa C, Rivara F (June 2004). "Strengthening the prevention and care of injuries worldwide". Lancet. 363 (9427): 2172–79. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16510-0. PMID 15220042. S2CID 33390855.
- ^ Dickinson E, Limmer D, O'Keefe MF, Grant HD, Murray R (2008). Emergency Care (11th ed.). Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice Hall. pp. 848–52. ISBN 978-0135005248.
- ^ BBC News Online (December 10, 2008). "UN raises child accidents alarm". London: BBC. BBC News. Retrieved 2010-10-31.
- ^ Rosenberg M, Greenberger S, Rawal A, Latimer-Pierson J, Thundiyil J (June 2011). "Comparison of Broselow tape measurements versus physician estimations of pediatric weights". The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 29 (5): 482–8–8. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2009.12.002. PMID 20825816.
- ^ So TY, Farrington E, Absher RK (2009). "Evaluation of the accuracy of different methods used to estimate weights in the pediatric population". Pediatrics. 123 (6): e1045–51. doi:10.1542/peds.2008-1968. PMID 19482737. S2CID 6009482.
- ^ a b c d e f Tibbles, Carrie (July 2008). "Trauma In Pregnancy: Double Jeopardy". Emergency Medicine Practice. 10 (7).
- ^ Campbell, John Creighton (2000). Basic trauma life support for paramedics and other advanced providers. Upper Saddle River, N.J: Brady/Prentice Hall Health. pp. 239–47. ISBN 978-0130845849.
- ^ Gulland A (May 2008). "Emergency Medicine: Lessons from the battlefield". BMJ. 336 (7653): 1098–100. doi:10.1136/bmj.39568.496424.94. PMC 2386631. PMID 18483051.
- ^ Ringdal M, Plos K, Lundberg D, Johansson L, Bergbom I (2009). "Outcome after injury: memories, health-related quality of life, anxiety, and symptoms of depression after intensive care". J Trauma. 66 (4): 1226–33. doi:10.1097/TA.0b013e318181b8e3. PMID 19088550.
- ^ Alam HB, Velmahos GC (August 2011). "New trends in resuscitation". Current Problems in Surgery. 48 (8): 531–64. doi:10.1067/j.cpsurg.2011.04.002. PMC 3128790. PMID 21718901.
Bibliography
[edit]- Jeff Garner; Greaves, Ian; Ryan, James R.; Porter, Keith R. (2009). Trauma Care Manual. London, England: Hodder Arnold. ISBN 978-0340928264.
- Feliciano, David V.; Mattox, Kenneth L.; Moore, Ernest J (2012). Trauma, Seventh Edition (Trauma (Moore)). McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0071663519.
- Andrew B., Peitzman; Michael, MD Sabom; Donald M., MD Yearly; Timothy C., MD Fabian (2002). The trauma manual. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0781726412.
Further reading
[edit]- Editorial Board, Army Medical Department Center & School, ed. (2004). Emergency War Surgery (3rd ed.). Washington, DC: Borden Institute. Archived from the original on 2011-06-23. Retrieved 2010-10-31.
- Zajtchuk, R; Bellamy, RF; Grande, CM, eds. (1995). Textbook of Military Medicine, Part IV: Surgical Combat Casualty Care. Vol. 1: Anesthesia and Perioperative Care of the Combat Casualty. Washington, DC: Borden Institute. Archived from the original on 2011-06-22. Retrieved 2010-10-31.
External links
[edit]- Emergency Medicine Research and Perspectives (emergency medicine procedure videos)
