Islet cell transplantation
| Islet cell transplantation | |
|---|---|
 Microscopic image of an islet of Langerhans (lighter area) surrounded by exocrine pancreas tissue (darker staining). | |
| MeSH | D016381 |
Islet transplantation is the transplantation of isolated islets from a donor pancreas into another person. It is a treatment for type 1 diabetes.[1] Once transplanted, the islets begin to produce insulin, actively regulating the level of glucose in the blood.
Islets are usually infused into the person's liver.[2] If the cells are not from a genetically identical donor the person's body will recognize them as foreign and the immune system will begin to attack them as with any transplant rejection. To prevent this immunosuppressant drugs are used. A study from 2005 showed that islet transplantation has progressed to the point that 58% of the people were insulin independent one year after the operation.[3] A review published 2016 reported a 50 – 70% rate of insulin independence after five years, in five studies from leading transplant centers published 2005 – 2012.[4]
In the period from 1999 to 2004, 471 people with type 1 diabetes received islet transplants at 43 institutions worldwide.[5]
Donislecel (Lantidra) allogeneic (donor) pancreatic islet cellular therapy was approved for medical use in the United States in June 2023.[6]
History
[edit]The concept of islet transplantation is not new.[7] Investigators as early as the English surgeon Charles Pybus (1882–1975) attempted to graft pancreatic tissue to cure diabetes.[citation needed]
Goals
[edit]The goal of islet transplantation is to infuse enough islets to control the blood glucose level removing the need for insulin injections. For an average-size person (70 kg), a typical transplant requires about one million islets, isolated from two donor pancreases. Because good control of blood glucose can slow or prevent the progression of complications associated with diabetes, such as nerve or eye damage, a successful transplant may reduce the risk of these complications. But a transplant recipient will need to take immunosuppressive drugs that stop the immune system from rejecting the transplanted islets.[citation needed]
Newer studies have focused their attention towards reducing severe hypoglycemic events, a life-threatening state in type 1 diabetes, rather than focus on removing the need for insulin injections entirely.[8][9]
Procedure
[edit]
Researchers use a mixture of highly purified enzymes (Collagenase) to isolate islets from the pancreas of a deceased donor. Collagenase solution is injected into the pancreatic duct which runs through the head, body and tail of the pancreas. Delivered this way, the enzyme solution causes distension of the pancreas, which is subsequently cut into small chunks and transferred into so-called Ricordi's chamber, where digestion takes place until the islets are liberated and removed from the solution. Isolated islets are then separated from the exocrine tissue and debris in a process called purification.
During the transplant, a radiologist uses ultrasound and radiography to guide placement of a catheter through the upper abdomen and into the portal vein of the liver. The islets are then infused through the catheter into the liver. The person will receive a local anesthetic. If a person cannot tolerate local anesthesia, the surgeon may use general anesthesia and do the transplant through a small incision. Possible risks of the procedure include bleeding or blood clots.
It takes time for the islets to attach to new blood vessels and begin releasing insulin. The doctor will order many tests to check blood glucose levels after the transplant, and insulin may be needed until control is achieved.
-
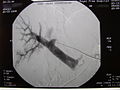
Radiographic image of the portal vein and its branches in the transplant recipient before infusion of isolated islets.
-
Post-transplant radiographic image of the recipient's portal tree.
Immunosuppression
[edit]The Edmonton protocol uses a combination of immunosuppressive drugs, including daclizumab (Zenapax), sirolimus (Rapamune) and tacrolimus (Prograf). Daclizumab is given intravenously right after the transplant and then discontinued. Sirolimus and tacrolimus, the two main drugs that keep the immune system from destroying the transplanted islets, must be taken for life.[citation needed]
Limitations
[edit]While significant progress has been made in the islet transplantation field,[10] many obstacles remain that currently preclude its widespread application. Two of the most important limitations are the currently inadequate means for preventing islet rejection, and the limited supply of islets for transplantation. Current immunosuppressive regimens are capable of preventing islet failure for months to years, but the agents used in these treatments are expensive and may increase the risk for specific malignancies and opportunistic infections. In addition, and somewhat ironically, the most commonly used agents (like calcineurin inhibitors and rapamycin) are also known to impair normal islet function and/or insulin action. Further, like all medications, the agents have other associated toxicities, with side effects such as oral ulcers, peripheral edema, anemia, weight loss, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diarrhea and fatigue.[11] Perhaps of greatest concern to the person and physician is the harmful effect of certain widely employed immunosuppressive agents on renal function. For the person with diabetes, renal function is a crucial factor in determining long-term outcome, and calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and ciclosporin) are significantly nephrotoxic. Thus, while some people with a pancreas transplant tolerate the immunosuppressive agents well, and for such people diabetic nephropathy can gradually improve, in other people the net effect (decreased risk due to the improved blood glucose control, increased risk from the immunosuppressive agents) may worsen kidney function. Indeed, Ojo et al. have published an analysis indicating that among people receiving other-than-kidney allografts, 7%–21% end up with kidney failure as a result of the transplant and/or subsequent immunosuppression.[12]
Another limitation to the islet transplantation process is the inflammatory response of the liver. Dr. Melena Bellin is an associate professor of pediatric endocrinology and surgery and director of research for the islet autotransplant program at the University of Minnesota Medical Center and Masonic Children's Hospital. Her research centers on making islet transplants safer and more effective for type one diabetics. The process of infusing islet cells into the liver can trigger an inflammatory response in the body. This reaction leads to a large amount of the newly transplanted islets being destroyed. Losing islet cells decreases the probability of successful insulin production and increases the likelihood of type one diabetes developing again in the patient. Dr. Bellin is currently testing two anti-inflammatory drugs that are already on the market to see if they may be useful in preventing inflammation that destroys islet cells.[13]
References
[edit]- ^ Health Quality Ontario (2015). "Pancreas Islet Transplantation for Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Clinical Evidence Review". Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series. 15 (16): 1–84. ISSN 1915-7398. PMC 4664938. PMID 26644812.
- ^ Lakey JR, Burridge PW, Shapiro AM (September 2003). "Technical aspects of islet preparation and transplantation". Transplant International. 16 (9): 613–32. doi:10.1111/j.1432-2277.2003.tb00361.x. PMID 12928769.
- ^ Close NC, Hering BJ, Eggerman TL (March 2005). "Results from the inaugural year of the Collaborative Islet Transplant Registry". Transplantation Proceedings. 37 (2): 1305–8. doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2004.12.117. PMID 15848704.
- ^ Shapiro, A. M. James; Pokrywczynska, Marta; Ricordi, Camillo (2016-11-11). "Clinical pancreatic islet transplantation". Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 13 (5): 268–277. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2016.178. ISSN 1759-5037. PMID 27834384. S2CID 28784928.
- ^ Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Paty BW, Senior PA, Bigam DL, Ryan EA (May 2005). "Strategic opportunities in clinical islet transplantation". Transplantation. 79 (10): 1304–7. doi:10.1097/01.TP.0000157300.53976.2A. PMID 15912095.
- ^ "FDA Approves First Cellular Therapy to Treat Patients with Type 1 Diabetes". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 28 June 2023. Retrieved 28 June 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Piemonti L, Pileggi A (2013). "25 Years of the Ricordi Automated Method for Islet Isolation" (PDF). CellR4. 1 (1): 8–22. PMC 6267808. PMID 30505878.
- ^ Hering BJ, Clarke WR, Bridges ND, Eggerman TL, Alejandro R, Bellin MD, Chaloner K, Czarniecki CW, Goldstein JS, Hunsicker LG, Kaufman DB, Korsgren O, Larsen CP, Luo X, Markmann JF, Naji A, Oberholzer J, Posselt AM, Rickels MR, Ricordi C, Robien MA, Senior PA, Shapiro AM, Stock PG, Turgeon NA (July 2016). "Phase 3 Trial of Transplantation of Human Islets in Type 1 Diabetes Complicated by Severe Hypoglycemia". Diabetes Care. 39 (7): 1230–40. doi:10.2337/dc15-1988. PMC 5317236. PMID 27208344.
- ^ Gerber PA, Hochuli M, Benediktsdottir BD, Zuellig RA, Tschopp O, Glenck M, de Rougemont O, Oberkofler C, Spinas GA, Lehmann R (January 2018). "Islet transplantation as safe and efficacious method to restore glycemic control and to avoid severe hypoglycemia after donor organ failure in pancreas transplantation" (PDF). Clinical Transplantation. 32 (1): e13153. doi:10.1111/ctr.13153. PMID 29140547. S2CID 22996728.
- ^ Robertson RP (February 2004). "Islet transplantation as a treatment for diabetes - a work in progress". The New England Journal of Medicine. 350 (7): 694–705. doi:10.1056/NEJMra032425. PMID 14960745. S2CID 1307522.
- ^ Hirshberg B, Rother KI, Digon BJ, Lee J, Gaglia JL, Hines K, Read EJ, Chang R, Wood BJ, Harlan DM (December 2003). "Benefits and risks of solitary islet transplantation for type 1 diabetes using steroid-sparing immunosuppression: the National Institutes of Health experience". Diabetes Care. 26 (12): 3288–95. doi:10.2337/diacare.26.12.3288. PMID 14633816. Full text
- ^ Ojo AO, Held PJ, Port FK, Wolfe RA, Leichtman AB, Young EW, Arndorfer J, Christensen L, Merion RM (September 2003). "Chronic renal failure after transplantation of a nonrenal organ". The New England Journal of Medicine. 349 (10): 931–40. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa021744. PMID 12954741. S2CID 12270800.
- ^ Brody, Barbara. "Making Islet Cell Transplants Safer". Diabetes Forecast.