Michael W. Young
Michael W. Young | |
|---|---|
 Michael W. Young in Nobel Prize press conference in Stockholm, December 2017 | |
| Born | Michael Warren Young March 28, 1949 |
| Education | University of Texas, Austin (BA, PhD[1]) |
| Known for | Circadian rhythms |
| Awards | Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (2017) |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Chronobiology Biology |
| Institutions | University of Texas, Austin Stanford University School of Medicine Rockefeller University |
| Thesis | Non-essential sequences, genes, and the polytene chromosome bands of drosophila melanogaster (1975) |
| Doctoral advisor | Burke Judd |
| Doctoral students | Leslie B. Vosshall |
Michael Warren Young (born March 28, 1949) is an American biologist and geneticist. He has dedicated over three decades to research studying genetically controlled patterns of sleep and wakefulness within Drosophila melanogaster.[2]
At Rockefeller University, his lab has made significant contributions in the field of chronobiology by identifying key genes associated with regulation of the internal clock responsible for circadian rhythms. He was able to elucidate the function of the period gene, which is necessary for the fly to exhibit normal sleep cycles. Young's lab is also attributed with the discovery of the timeless and doubletime genes, which makes proteins that are also necessary for circadian rhythm. He was awarded the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine along with Jeffrey C. Hall and Michael Rosbash "for their discoveries of molecular mechanisms controlling the circadian rhythm".[3][4]
Life[edit]
Early life[edit]
Michael W. Young was born in Miami, Florida, on March 28, 1949.[5] His father worked for Olin Mathieson Chemical Corporation managing aluminum ingot sales for the south eastern United States. His mother worked for a law firm as a secretary. Despite no history of science or medicine in either of their backgrounds, Young’s parents were supportive of his interest in science and provided the means of scientific exploration through microscopes and telescopes. They lived in an environment close to private zoos, where occasionally some of the animals would escape into their backyard and spark Young's scientific interest.[6]
Michael Young grew up in and around Miami, Florida.[2] Then, his family moved near Dallas, Texas, where he graduated from L. D. Bell High School.[7] In his early teens, Michael’s parents gifted him one of Darwin’s books on evolution and biological mysteries. The book described biological clocks as the reason why a strange plant he had seen years earlier produced flowers that closed during the day and opened at night. The location and composition of these clocks were unknown, and this sparked Michael Young’s interest at an early age.[6]
Family life[edit]
While working as a graduate student at the University of Texas at Austin, Michael Young met his future wife Laurel Eckhardt. Later, both moved to Stanford University, where Michael worked as a postdoctoral fellow and Laurel pursued her PhD with Len Herzenberg. Today, she is a Professor of Biology at Hunter College. Michael and Laurel still work close to each other. Together, they have two daughters, Natalie and Arissa.[6]
Academic career[edit]
Young earned his undergraduate degree in biology from University of Texas at Austin in 1971.[2] After a summer of research with Burke Judd on the Drosophila genome, Young stayed at the UT to complete a Ph.D. in genetics in 1975.[5] It was during his time here that Young became fascinated with research focused on Drosophila.[6] During his graduate work, he learned of Ron Konopka and Seymour Benzer’s work with Drosophila circadian mutants, which led to his future work in cloning the period gene.[6]
Michael Young continued his studies through postdoctoral training at Stanford University School of Medicine with an interest in molecular genetics and particular focus on transposable elements.[2] He worked in Dave Hogness’ lab and became familiar with the methods of recombinant DNA.[6] Two years later, he joined Rockefeller University as an assistant professor. From 1978 on he was involved in the University, serving as associate professor in 1984 and later named professor in 1988.[8] In 2004, Young was appointed Vice President for Academic Affairs and was also granted the Richard and Jeanne Fisher Chair.[5]
Scientific career[edit]
Discovery of PER[edit]
At The Rockefeller University in the early 1980s, Young and his two lab members, Ted Bargiello and Rob Jackson, further investigated the circadian period gene in Drosophila. They constructed segments of recombinant Drosophila DNA, amplified them in bacteria, and injected them in per mutant animals. A locomotor behavior monitor was used to assay behavioral activity. The team watched and recorded fly activity through the day and night to show that the fly restored circadian behavioral rhythms by transferring a functional per gene.[9] Later, by determining the sequence of the gene on the X chromosome, they found that the arrhythmic mutation produced a functionless protein, while long-period and short-period mutants of per changed the amino acid sequence of a still functional protein.[10][11]
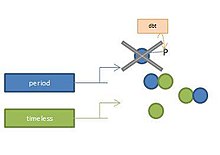
Discovery of timeless[edit]
Following the discovery of per, the Young lab looked for additional circadian genes. In late 1980s, Amita Sehgal, Jeff Price, Bernice Man helped Young use forward genetics to screen for additional mutations that altered fly rhythms. A new gene located on chromosome 2 was named timeless (tim) and was successfully cloned and sequenced. They found strong functional connections between tim and per. Tim mutants interfered with per mRNA cycling. In 1994, Leslie Vosshall, a graduate student in Young's lab, discovered that if PER proteins were protected from degradation, they would accumulate without TIM, but could not move to the nuclei. Later Young and others found that TIM proteins did not accumulate in nuclei in per mutants. They concluded that PER and TIM worked together.[12] Another lab member Lino Saez, saw that PER and TIM associate with each other to stabilize each other and to allow their nuclear accumulation.[13] Later studies by the Young, Sehgal, and Edery labs revealed that light causes the rapid degradation of TIM and resets of the phase of the circadian rhythm.[14][15]
Doubletime phosphorylation[edit]
In 1998, Jeff Price from the Young lab discovered a kinase called doubletime (Casein kinase 1) that phosphorylates PER on certain serine residues. This signal marks it for degradation. When PER and TIM are bound, doubletime does not seem to be able to phosphorylate PER, allowing it to accumulate.[16] Young’s discovery of doubletime mutants in 1998 was soon followed by the 2001 discovery of a form of Familial Advanced Sleep Phase Syndrome (FASPS) in humans, which is linked to an hPer2 polymorphism that removes a serine normally phosphorylated by Casein kinase 1.[17] Other forms of FASPS are caused by mutations that alter the Casein kinase 1 gene. Doubletime mutations in Drosophila alter the phosphorylation and degradation of PER protein. This affects the regularity in period of the organism. This discovery solidified doubletime as a necessary part of the circadian clock.[18]
Positions and honors[edit]
- 1978: Andre and Bella Meyer Foundation fellowship[2]
- 2006: Pittendrigh/Aschoff Award from the Society for Research on Biological Rhythms[2]
- 2007: Fellow of the American Academy of Microbiology[2]
- 2007: Member of the National Academy of Sciences[2]
- 2009: Gruber Prize in Neuroscience (with Michael Rosbash and Jeffrey C. Hall)[19]
- 2011: Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize (with Michael Rosbash and Jeffrey C. Hall)[8]
- 2012: Massry Prize (with Michael Rosbash and Jeffrey C. Hall)[8]
- 2012: Canada Gairdner International Award (with Michael Rosbash and Jeffrey C. Hall)[8]
- 2013: Shaw Prize in Life Science and Medicine (with Michael Rosbash and Jeffrey C. Hall)[8]
- 2013: Wiley Prize in Biomedical Sciences (with Michael Rosbash and Jeffrey C. Hall)[20]
- 2017: Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (with Michael Rosbash and Jeffrey C. Hall)[21]
- 2018: Member of the American Philosophical Society[22]
References[edit]
- ^ "University of Texas at Austin Alum Michael W. Young Awarded Nobel Prize".
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h "2009 Neuroscience Prize- Michael W. Young". Biology. Gruber Foundation. Retrieved April 6, 2015.
- ^ Cha, Arlene Eujung (October 2, 2017). "Nobel in physiology, medicine awarded to three Americans for discovery of 'clock genes'". Washington Post. Retrieved October 2, 2017.
- ^ "The 2017 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine – Press Release". The Nobel Foundation. October 2, 2017. Retrieved October 2, 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Biographical Notes of Laureates". Biology. The Shaw Foundation. Retrieved April 6, 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f "Autobiography of Michael Young". Biology. The Shaw Foundation. Retrieved April 6, 2015.
- ^ Tom Uhler (October 4, 2017). "This North Texas high school claims a Nobel Prize winner". Fort Worth Star-Telegram. Retrieved November 14, 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "Mike Young to Receive Shaw Prize". The Rockefeller University. Retrieved October 2, 2017.
- ^ Bargiello, Thaddeus; Rob Jackson; Michael Young (1984). "Restoration of circadian behavioral rhythms by gene transfer in Drosophila". Nature. 312 (5996): 752–754. Bibcode:1984Natur.312..752B. doi:10.1038/312752a0. PMID 6440029. S2CID 4259316.
- ^ Jackson, Rob; Thaddeus Bargiello; Suk-Hyeon Yun; Michael Young (1986). "Product of per locus of Drosophila shares homology with proteoglycans". Nature. 320 (6058): 185–188. Bibcode:1986Natur.320..185J. doi:10.1038/320185a0. PMID 3081818. S2CID 4305720.
- ^ Baylies, Mary; Thaddeus Bargiello; Rob Jackson; Michael Young (1986). "Changes in the abundance or structure of the per gene product can affect the periodicity of the Drosophila clock". Nature. 326 (6111): 390–392. doi:10.1038/326390a0. PMID 2436052. S2CID 4253390.
- ^ Sehgal, Amita; Adrian Rothenfluh-Hilfiker; Melissa Hunter-Ensor; Yifeng Chen; Michael Myers; Michael Young (1995). "Rhythmic expression of timeless: a basis for promoting circadian cycles in period gene autoregulation". Science. 270 (5237): 808–810. Bibcode:1995Sci...270..808S. doi:10.1126/science.270.5237.808. PMID 7481772. S2CID 38151127.
- ^ Saez, Lino; Michael Young (1996). "Regulation of nuclear entry of the Drosophila clock proteins period and timeless". Neuron. 17 (5): 808–810. doi:10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80222-6. PMID 8938123. S2CID 2106981.
- ^ Myers, Michael; Karen Smith; Adrian Hilfiker; Michael Young (1996). "Light-induced degradation of TIMELESS and entrainment of the Drosophila circadian clock". Science. 271 (5256): 1736–1740. Bibcode:1996Sci...271.1736M. doi:10.1126/science.271.5256.1736. PMID 8596937. S2CID 6811496.
- ^ Lee, Choogon; Vaishali Parikh; Tomoko Itsukaichi; Kiho Bae; Isaac Edery (1996). "Resetting the Drosophila clock by photic regulation of PER and a PER-TIM complex". Science. 271 (5256): 1740–1744. Bibcode:1996Sci...271.1740L. doi:10.1126/science.271.5256.1740. PMID 8596938. S2CID 24416627.
- ^ Price, Jeffrey; Justin Blau; Adrian Rothenfluh; Marla Abodeely; Brian Kloss; Michael Young (1998). "double-time Is a Novel Drosophila Clock Gene that Regulates PERIOD Protein Accumulation". Cell. 94 (1): 83–95. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81224-6. PMID 9674430. S2CID 14764407.
- ^ Toh, Kong; Christopher Jones; Yan He; Erik Eide; William Hinz; David Virshup; Louis Ptacek; Ying Fu (2001). "An hPer2 phosphorylation site mutation in familial advanced sleep phase syndrome". Science. 291 (5506): 1040–1043. Bibcode:2001Sci...291.1040T. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.722.460. doi:10.1126/science.1057499. PMID 11232563. S2CID 1848310.
- ^ Kloss, Brian; Jeffrey L. Price; Lino Saez; Justin Blau; Adrian Rothenfluh; Cedric S. Wesley; Michael W. Young (1998). "The Drosophila Clock Gene double-time Encodes a Protein Closely Related to Human Casein Kinase Iε". Cell. 94 (1): 97–107. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81225-8. PMID 9674431. S2CID 15931992.
- ^ "Michael W. Young | The Gruber Foundation". gruber.yale.edu. Retrieved October 2, 2017.
- ^ "Wiley: Twelfth Annual Wiley Prize in Biomedical Sciences Awarded to Dr. Michael Young, Dr. Jeffrey Hall and Dr. Michael Rosbash". Biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Retrieved April 6, 2015.
- ^ Sample, Ian (October 2, 2017). "Jeffrey C Hall, Michael Rosbash and Michael W Young win 2017 Nobel prize in physiology or medicine – as it happened". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved October 2, 2017.
- ^ "Election of New Members at the 2018 Spring Meeting | American Philosophical Society".
External links[edit]
- Michael W. Young's Rockefeller Lab Page
- Michael Young describes his work with Drosophila genes and specific mutations that produce changes in the sleep-wake cycle. Young goes on to discuss the implications of his findings in the medical field. on YouTube
- Michael W. Young on Nobelprize.org including the Nobel Lecture 7 December 2017 Time Travels: A 40 Year Journey from Drosophila’s Clock Mutants to Human Circadian Disorders
- 1949 births
- American geneticists
- American Nobel laureates
- Chronobiologists
- Living people
- Massry Prize recipients
- Members of the United States National Academy of Sciences
- Nobel laureates in Physiology or Medicine
- University of Texas at Austin College of Natural Sciences alumni
- Rockefeller University faculty
- Scientists from Miami
- 21st-century American scientists
- 20th-century American biologists
- 21st-century biologists
- Members of the American Philosophical Society
