Mamberamo River
| Mamberamo | |
|---|---|
 Mamberamo River, aerial view in 2017. | |
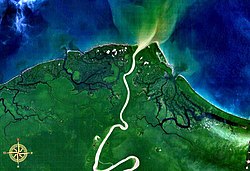 Mamberamo, entering the sea, seen from space. | |
| Location | |
| Country | Indonesia |
| Region | Papua |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | confluence of Tariku and Taritatu |
| • coordinates | 2°55′30″S 138°26′30″E / 2.92500°S 138.44167°E |
| Mouth | |
• location | Pacific Ocean, Indonesian, New Guinea |
• coordinates | 1°28′S 137°54′E / 1.467°S 137.900°E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 1,112 km (691 mi) |
| Basin size | 78,992 km2 (30,499 sq mi)[1] |
| Depth | |
| • minimum | 8 m (26 ft) |
| • maximum | 33 m (108 ft) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Mamberamo Delta, Pacific Ocean |
| • average | 5,500 m3/s (190,000 cu ft/s)[2] 5,922.9 m3/s (209,170 cu ft/s)[3] |
| • maximum | 25,000 m3/s (880,000 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Tariku River |
| • right | Taritatu River |
The Mamberamo (Indonesian: Sungai Mamberamo) is the second-longest river on the island of New Guinea, after Sepik River (1,146 km) and the third largest in Oceania by discharge (5,500 m3/s) volume after Fly River (7,500 m3/s) and Sepik (7,000 m3/s). It is located in the Indonesian province of Papua. It is the second largest river in Indonesia by volume of discharge after Kapuas River (6,500 m3/s) and also the widest.[4]
The river is formed from the confluence of its upper tributaries, the Tariku and Taritatu Rivers in the Lakes Plains region, an interior basin with extensive freshwater swamp forests and grasslands. It flows northwards between the Van Rees Range (Pegunungan Van Rees) and Foja Mountains through a series of rapids and gorges. The last 160 km of the river are navigable.[5] In the coastal lowlands, the river is lined with marshes and forms a broad river delta. The Mamberamo discharges into the Pacific Ocean at the northern point of Point D'Urville or Cape Narwaku (Tanjung Narwaku).
The river's huge valley is home to various uncontacted peoples and incredible biodiversity. In the 1990s, the Indonesian Government had plans to construct a large hydroelectric dam on the Mamberamo that would have submerged much of the area. This plan was shelved after the Indonesian financial crisis from 1998 to 1999, but there are concerns by environmental groups that it could be resurrected sometime in the future. At present, the Mamberamo remains the second largest river in the world to be completely unfragmented by dams in its catchment, behind only the relatively nearby Fly.[4]
The Mamberamo area also broadly refers to several nearby mountain ranges, including the Van Rees and Foja Mountains (also known as Foya), which were the subject of a recent rapid biological assessment conducted by Conservation International, the Indonesian Institute of Sciences, and Cenderawasih University. The scientific team discovered the first new bird species from New Guinea in 60 years, and a wealth of other new plants and animals. The Foya Mountains appear to be a globally outstanding repository of biodiversity.
Tributary
[edit]Mamberamo River List of Tributaries by Length.
- Taritatu River 808 km (502 mi)
- Tariku River 488 km (303 mi)
History
[edit]
In 1545, the Spanish navigator Iñigo Ortiz de Retes sailed along the northern coast of the island as far as the mouth of this river that he charted as San Agustín. At this spot, on 20 June 1545, he claimed the territory for the Spanish Crown, and in the process bestowed the name to the island (Nueva Guinea) by which it is known today.
The first European to enter the mouth of the Mamberamo was Dutchman Dr D. F. van Braam Morris in 1883. The residents from the northern Moluccas (Ternate) rowed up the river to ascertain that it was navigable by steamer.[6] The following year in 1884 Van Braam Morris returned to the steamship Havik and travelled 60 mi (97 km) (as the crow flies) along its course.[7]

Mamberamo Foja Wildlife Reserve
[edit]The Mamberamo Foja Wildlife Reserve covers an area of 16,610 km2, extending along the Mamberamo and its major tributaries from the Central Range foothills to the Pacific Ocean. It encompasses the central Lakes Plains region and extends southwards along the eastern side of the river to include the Foya Mountains, the river delta, and the sea.[8]
Mamberamo Bridge
[edit]The Mamberamo Bridge was the second longest cable-stayed span in Indonesia after Kutai Kartanegara Bridge with 235 meters and 270 meters respectively until the latter bridge collapsed in November 2011.
See also
[edit]- List of drainage basins of Indonesia
- Mekong-Mamberamo linguistic area
- Lower Mamberamo languages
- Kwerba Mamberamo language
References
[edit]- ^ Joesron, Loebis. "Country Report Implementation of Demonstration Project Mamberamo River Basin INDONESIA".
- ^ Joesron, Loebis. "Country Report Implementation of Demonstration Project Mamberamo River Basin INDONESIA".
- ^ Rendy, Firmansyah. "Grafik Neraca Air Pulau Papua".
- ^ a b "Fragmentation and Flow Regulation of the World's Large River Systems" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-30. Retrieved 2013-01-12.
- ^ "Mamberamo River". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Accessed 7 June 2020
- ^ Souter (1963) p. 145
- ^ (in Dutch) 'Nieuw Guinea', in de De Locomotief, donderdag 5 maart 1885 no. 57. Visited 2 July 2013
- ^ Petocz, Ronald G. (1989). Conservation and Development in Irian Jaya: A Strategy for Rational Resource Utilization. Brill, 1989.
External links
[edit]- Souter, Gavin (1963). New Guinea: The Last Unknown. Angus & Robertson. ISBN 0-207-94627-2.
