Kingdom of Damot
Kingdom of Damot | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 960–1316 | |||||||||
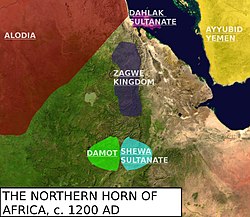 The kingdom of Damot and its neighbours circa 1200 AD | |||||||||
| Capital | Maldarede 9°23′N 37°34′E / 9.39°N 37.56°E | ||||||||
| Common languages | Gonga, and other Omotic languages | ||||||||
| Religion | Paganism, Christianity | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Motalami | |||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 960 | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 1316 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The Kingdom of Damot (Amharic: ዳሞት) was a medieval kingdom in what is now western Ethiopia.[1] The territory was positioned below the Blue Nile.[2] It was a powerful state that forced the Sultanate of Showa (also called Shewa) to pay tributes. It also annihilated the armies of the Zagwe dynasty that were sent to subdue its territory. Damot conquered several Muslim and Christian territories.[3] The Muslim state Showa and the new Christian state under Yekuno Amlak formed an alliance to counter the influence of Damot in the region.[4]
History
[edit]The kings of Damot, who bore the title motalami, resided in a town which, according to the hagiography of Tekle Haymanot, was called Maldarede.[5] Damot was conquered by Emperor Amda Seyon in 1316/7. His royal chronicle recounted that "all the people of Damot [came] into my hands; its king, its princes, its rulers, and its people, men and women without number, whom I exiled into another area."[6] Amda Seyon seemingly left the Damotian royal family in power, for the title motälämi continued to be used until the 15th century.[7] al-Mufaddal ibn Abi al-Fada'il in the fourteenth century writes that Damot alongside Harla Kingdom were forced to pay tribute to Abyssinia.[8]
Originally located south of the Abay and west of the Muger River,[9] under the pressure of Oromo attacks the rulers were forced to resettle north of the Abay in southern Gojjam between 1574 and 1606.[10]
Their territory extended east beyond the Muger as far as the Jamma.[9] The province of Damot remained part of the Ethiopian Empire well after the Zemene Mesafint began, unlike other southern regions. The ruler of Damot was typically from Gojjam and held the title Ras.
Religion
[edit]The population of Damot adherred to its own religion dominated by a deity called Däsk. This continued on even well after being conquered by the Christian Empire, which repeatedly led to conflict between the locals and the Christian garrison troops.[11] Parts of the population seemingly remained pagan until the late 16th century.[12]
It is claimed in the Hagiography of Tekle Haymanot that the latter managed to convert the ruler of Damot to Christianity.[13]
References
[edit]- ^ Shinn, David (2013). Historical Dictionary of Ethiopia. Scarecrow Press. p. 111. ISBN 9780810874572.
- ^ Shillington, Kevin (4 July 2013). Encyclopedia of African History 3-Volume Set. Routledge. ISBN 9781135456696.
- ^ Bounga, Ayda (2014). The kingdom of Damot: An Inquiry into Political and Economic Power in the Horn of Africa (13th c.). Annales D'ethiopie. p. 262.
- ^ Hassen, Mohammed. Oromo of Ethiopia (PDF). University of London. p. 4.
- ^ Bouanga 2014, pp. 33–37.
- ^ Ayenachew, Deresse (2020). "Territorial Expansion and Administrative Evolution under the "Solomonic" Dynasty". In Samantha Kelly (ed.). A Companion to Medieval Ethiopia and Eritrea. Brill. p. 65.
- ^ Ayenachew, Deresse (2020). "Territorial Expansion and Administrative Evolution under the "Solomonic" Dynasty". In Samantha Kelly (ed.). A Companion to Medieval Ethiopia and Eritrea. Brill. p. 71.
- ^ Harla. Encyclopedia Aethiopica.
- ^ a b G.W.B. Huntingford, Historical Geography of Ethiopia from the first century AD to 1704 (London: British Academy, 1989), p. 69
- ^ The dates for this movement are discussed by Huntingford in his Historical Geography, at pp. 143f
- ^ Ayenachew, Deresse (2020). "Territorial Expansion and Administrative Evolution under the "Solomonic" Dynasty". In Samantha Kelly (ed.). A Companion to Medieval Ethiopia and Eritrea. Brill. p. 80.
- ^ Fauvelle, François-Xavier (2020). "Of Conversion and Conversation: Followers of Local Religions in Medieval Ethiopia". In Samantha Kelly (ed.). A Companion to Medieval Ethiopia and Eritrea. Brill. p. 140.
- ^ Lusini, Gianfrancesco (2020). "The Ancient and Medieval History of Eritrean and Ethiopian Monasticism: An Outline". In Samantha Kelly (ed.). A Companion to Medieval Ethiopia and Eritrea. Brill. p. 207.
Further reading
[edit]- Bouanga, Ayda (2013). Le Damot dans l'histoire de l'Ethiopie (XIIIe-XXe siècles) : recompositions religieuses, politiques et historiographiques (in French). Université Panthéon-Sorbonn.
- Bouanga, Ayda (2014). "Le royaume du Damot : enquête sur une puissance politique et économique de la Corne de l'Afrique (XIIIe siècle)" (PDF). Annales d'Ethiopie (in French). 29: 27–58. doi:10.3406/ethio.2014.1557.
