E-ZPass
| Industry | Electronic toll collection |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1987 |
| Headquarters | , U.S. |
Area served | |
| Website | www |
E-ZPass is an electronic toll collection system used on toll roads, toll bridges, and toll tunnels in the Eastern United States, Midwestern United States, and Southern United States. The E-ZPass Interagency Group (IAG) consists of member agencies in several states, which use the same technology and allow travelers to use the same transponder on toll roads throughout the network.
Since its creation in 1987, various independent systems that use the same technology have been folded into the E-ZPass system, including the I-PASS in Illinois and the NC Quick Pass in North Carolina. Negotiations are ongoing for nationwide interoperability in the United States.
Functionality
[edit]Technology
[edit]




E-ZPass tags are active[1] RFID transponders, historically made by Kapsch TrafficCom (formerly Mark IV Industries Corp—IVHS Division) under a competitively bid contract. They communicate with reader equipment built into lane-based or open-road toll collection lanes by transmitting a unique radio signature. The most common type of tag is an internal tag that can be mounted on the inside of the vehicle's windshield in proximity to the rear-view mirror. Though toll agencies advise adherence to the windshield with mounting strips (usually 3M's Scotch brand "Dual Lock" fasteners), third-party options using trays with suction cups to adhere a pass to a windshield temporarily if used in multiple vehicles are available. Some vehicles have windshields that block RF signals; for those vehicles, historical vehicles, and customers who have aesthetic concerns, an external tag is offered, typically designed to attach to the vehicle's front license plate mounting points.[2]
Although a tag can be used with a motorcycle, usually no official instructions are given for mounting, due to the numerous variations between bike designs and the small area of a motorcycle windshield which could prove a hindrance if the transponder is attached following automobile instructions. Transponders may be put in a shirt or jacket pocket, if necessary.[3]
The E-ZPass transponder works by listening for a signal broadcast by the reader stationed at the toll booth. This 915 MHz signal is sent at 500 kbit/s using the TDM (formerly IAG) protocol in 256-bit packets. Transponders use active Type II read/write technology. In April 2013, Kapsch (purchasers of Mark IV Industries) made the protocol available to all interested parties royalty-free in perpetuity and is granting the right to sublicense the protocol.[4] Transponders are powered by a battery designed to last about 10 years. [5]
Payment and tag types
[edit]Most E-ZPass lanes are converted manual toll lanes and must have fairly low speed limits for safety reasons (between 5 and 15 miles per hour (8 and 24 km/h) is typical), so that E-ZPass vehicles can merge safely with vehicles that stopped to pay a cash toll and, in some cases, to allow toll workers to safely cross the E-ZPass lanes to reach booths accepting cash payments. In some areas, however (typically recently built or retrofitted facilities), there is no need to slow down, because E-ZPass users can utilize dedicated traffic lanes ("Express E-ZPass" or "open road tolling") that are physically separate from the toll-booth lanes. Examples include:
- Delaware Route 1
- Delaware Water Gap Toll Bridge
- Hampton Main toll plaza on I-95 in New Hampshire
- Hooksett Main toll plaza on I-93 in New Hampshire
- Interstate 78 Toll Bridge
- Maine Turnpike at the York, New Gloucester, and West Gardiner mainline toll plazas and at its Scarborough (Exit 44) and Gardiner (Exit 103) interchanges with Interstate 295
- Newark Toll Plaza on the Delaware Turnpike[6]
- Pocahontas Parkway in Virginia
- Atlantic City Expressway
- Four locations on the New Jersey Turnpike: near the Delaware Memorial Bridge (Exit 1), near Exit 18 W, near Exit 18 E, and the Pennsylvania Extension, which connects to the Pennsylvania Turnpike (Exit 6))
- Garden State Parkway
- Ohio Turnpike (mainline toll plazas under reconstruction. Completion date: Spring 2023)[7][needs update]
Other roads in the E-ZPass system have eschewed toll booths altogether, and switched to all-electronic tolling. As vehicles pass at normal speed under toll collection gantries, tolls are collected either through the E-ZPass transponder or by billing the owner of the vehicle via automatic number-plate recognition. Examples include:
Each E-ZPass tag is specifically programmed for a particular class of vehicle; while any valid working tag will be read and accepted in any E-ZPass toll lane, the wrong toll amount will be charged if the tag's programmed vehicle class does not match the vehicle. This will result in a violation and possible large fine assessed to the tag holder, especially if a lower-class (e.g., passenger car) tag is being used in a higher-class vehicle such as a bus or truck. In an attempt to avoid this, E-ZPass tags for commercial vehicles are blue in color, contrasting with the white tags assigned to standard passenger vehicles. The blue E-ZPass is also used in government employee vehicles. In New York, an orange E-ZPass tag is issued to emergency vehicles as well as to employees of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority, Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, and New York State Thruway Authority. New York also offers green-colored E-ZPass tags (and a 10% toll discount plan) to qualifying low-emission and zero-emission vehicles.[9]
For purposes of interoperability, all agencies are connected to each other by a secure network (the "reciprocity network"). This network provides the means to exchange tag data and process toll transactions across the various agencies. Tag data is exchanged among the agencies on a nightly basis. This data can take up to 24 hours on the primary network the unit is issued by (e.g., the New York State Thruway or Illinois Tollway system), but may be delayed by as much as 72 hours on other networks.[10][11]
Expiry
[edit]As of 2022[update] this is a partial list of states that will expire an E-ZPass account for inactivity:
- New Hampshire: 24 months[12]
- North Carolina: at 24 months they start charging a dollar a month and close the account when it runs out of money[13]
- Virginia: 12 months [14][15][16][17]
Retail availability
[edit]
Some issuing agencies offer a packaged E-ZPass transponder preloaded with toll funds sold over-the-counter at a retail setting such as a supermarket or pharmacy service desk that is valid immediately.[18][19] A portion of the balance is available instantly; customers can access the remaining balance when they register their transponders with the issuing E-ZPass agency within several days of first using their E-ZPass.
Usage
[edit]According to the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, 83.4% of vehicles crossing its six bridges and tunnels used E-ZPass for toll payment during all of 2016.[20] As of 2020, about 86% of vehicles along the Pennsylvania Turnpike use E-ZPass for payment of tolls.[21] According to the New Jersey Turnpike Authority, about 90% of vehicles on the New Jersey Turnpike and Garden State Parkway use E-ZPass.[22]
History
[edit]


Creation
[edit]The first E-ZPass system was implemented on December 17, 1996, at all toll collection facilities of Triborough Bridge and Tunnel Authority, including 7 bridges and 2 tunnels. The earliest test of what was then known as the Automatic Vehicle Identification (AVI) was conducted by the Triborough Bridge and Tunnel Authority and the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey. They tested AVI tags on Staten Island and utilized a paper voucher as a control which proved to be far less accurate than the tags. As a result of the test, the two agencies agreed to convene a larger group of the region's toll authorities. Their initial idea was to develop independent systems that did not interfere with each other. TBTA suggested that there be a regionally cooperative system using a single tag, later forming the basis for regional cooperation. The tolling agencies of New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania, which constitute two-thirds of the United States' $3-billion-a-year toll industry, met at an International Bridge, Tunnel and Toll Association (IBTTA) meeting to create a compatible electronic-tolling technology that could be used on the toll roads and bridges of the three states, in an effort to reduce congestion on some of the busiest roadways and toll plazas in the US.
In 1991, the Interagency Committee was created to develop, and involved the participation and cooperation of seven independent toll agencies: the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, the New Jersey Turnpike Authority, the New Jersey Highway Authority (which, at the time, operated the Garden State Parkway), the Triborough Bridge and Tunnel Authority), the New York State Thruway Authority, the Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission, and the South Jersey Transportation Authority (operator of the Atlantic City Expressway).[23] The E-ZPass trademark, however, belongs to the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey.[24] The Port Authority has been aggressive at protecting its trademark, including forcing the Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority to rename the "EZ Pass" regional transit pass to "EZ transit pass" to protect its rights.[25]
The seven agencies started making plans to test two possible technologies for E-ZPass in 1992. The technologies would be installed along the Garden State Parkway and New York State Thruway.[26] E-ZPass was first deployed on the Thruway at the Spring Valley toll plaza on August 3, 1993.[27] Over the following three and a half years, the New York State Thruway Authority (NYSTA) installed electronic toll-collection equipment, in stages, along the Thruway. By December 1996, it was implemented at all of the Thruway's fixed-toll barriers,[28] and by March 1998, E-ZPass was installed at all of the Thruway's mainline exits.[29]
The Triborough Bridge and Tunnel Authority, which maintains all toll bridges and tunnels that begin and end in New York City, is the largest tolling agency by revenue in the United States ($1.9 billion in 2017). It began its E-ZPass implementation in 1995 and completed it at all nine of its toll facilities by January 1997.[30] E-ZPass was popular among motorists who frequently used TBTA crossings, and by August 1996, nearly 2,000 motorists per day were signing up for E-ZPass.[31] The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, which operates all bridges and tunnels between New York City and New Jersey, implemented E-ZPass at the George Washington Bridge in July 1997,[32] and at the Holland Tunnel and Lincoln Tunnel in October 1997.[33]
The Pennsylvania Turnpike planned to adopt E-ZPass by 1998;[34][35] however, implementation of the system was postponed until December 2, 2000,[36] when E-ZPass debuted on the turnpike between Harrisburg West and the Delaware River Bridge.[37] By December 15, 2001, E-ZPass could be used on the entire length of the mainline Pennsylvania Turnpike.[38][39] Commercial vehicles were allowed to use the system beginning on December 14, 2002,[40] and the entire Turnpike system was taking E-ZPass by 2006.[41]
On October 6, 1998, a U.S. patent for an automated toll collection system was issued to Fred Slavin and Randy J. Schafer.[42]
Expansion
[edit]Meanwhile, various other agencies began work on similar electronic toll collecting facilities. This resulted in the emergence of other networks:
- The MassPass system used in Massachusetts, changed to the compatible Fast Lane in 1998 and rebranded E-ZPass in 2012
- The I-Pass system used in Illinois
- The I-Zoom system used in Indiana, rebranded E-ZPass in 2012
- The Smart Tag system used in Virginia, merged with E-ZPass in 2004[43]
- The TransPass system used in Maine, since replaced by the E-ZPass system
- The M-Tag system used in Maryland, integrated into and rebranded E-ZPass in 2001
- The Quick Pass system used in North Carolina, partially integrated in 2013[44] and integrated into Florida's SunPass system
- The E-Pass system in Florida, partially integrated in 2018[45]
- The SunPass system in Florida, partially integrated in 2021[46][47]
- The MnPass system in Minnesota, rebranded into E-ZPass in August 2021[48]
- The PeachPass system used in Georgia, partially integrated with E-ZPass in November 2023.[49]
Originally, these systems were not interchangeable with E-ZPass. However, since most of them use the same technology (or have since converted over to a compatible technology), all of them have been incorporated into the E-ZPass network. Though several still retain their own brand name for their own facilities, users of those systems can use E-ZPass and vice versa. As a result, all E-ZPass holders can use their transponders in any of the states that offer it.
The E-ZPass system continues to expand. The Indiana Toll Road Concession Company upgraded its toll plazas to include E-ZPass functionality on the Indiana East–West Toll Road, while the Ohio Turnpike Commission has upgraded its toll plazas in October 2009 for the Ohio Turnpike (I-76, I-80, I-90).[50] On December 16, 2008, Rhode Island joined the network by activating E-ZPass lanes in the state's only toll booth, at the Claiborne Pell Newport Bridge.[51] The Kentucky Transportation Cabinet, which had a toll road system predating the E-ZPass system which was ended in 2006, announced at the end of July 2015 its entrance into the E-ZPass system as part of the financing for the Louisville-area Ohio River Bridges Project involving the new Abraham Lincoln (paired with the retrofitted Kennedy) and Lewis and Clark bridges.[52]
On November 9, 2017, the Central Florida Expressway Authority (CFX) announced that it was joining the E-ZPass group. CFX began accepting E-ZPass along its toll roads on September 1, 2018.[45][53] On May 28, 2021, the Florida Turnpike Enterprise announced that its SunPass facilities would begin accepting E-ZPass. In addition, E-ZPass facilities began accepting SunPass Pro transponders (but not earlier SunPass transponders).[46][47]
Canada
[edit]E-ZPass is generally not accepted in Canada but several exceptions exist. Until 2005, drivers crossing the Peace Bridge between Fort Erie, Ontario, and Buffalo, New York, paid a toll before crossing to Canada. Following upgrades to the border crossings in 2005, drivers instead pay a toll on the Canadian side of the Peace Bridge after clearing Canadian customs. This is the first E-ZPass toll gantry outside of the United States. The toll goes to the Buffalo and Fort Erie Public Bridge Authority, a bi-national agency responsible for maintaining the international bridge.
On August 11, 2014, E-ZPass began to be accepted at the Lewiston–Queenston Bridge, Rainbow Bridge, and Whirlpool Rapids Bridge.[54] The toll for the Lewiston–Queenston Bridge is paid in Canada after clearing Canadian customs, whereas the toll is paid before leaving the United States at the other two bridges. The toll from these three bridges goes to the Niagara Falls Bridge Commission.
On June 27, 2019, E-ZPass began to be accepted at the Thousand Islands Bridge on both the US side and Canada side.[55]
While these facilities take both U.S. and Canadian cash, E-ZPass is only billable in U.S. dollars.
Out-of-network systems
[edit]E-ZPass ETC transponders do not work on all toll roads in the United States. Currently, the E-ZPass electronic toll-collection system (as well as the other ETC systems that are part of the E-ZPass network) are not compatible with California's FasTrak, Kansas's K-TAG, Oklahoma's Pikepass, Texas's TxTag, Utah's Express Pass, Puerto Rico's AutoExpreso, and Cruise Card, or other ETC systems outside of E-ZPass operating regions. Under MAP-21, passed in 2012, all ETC facilities in the United States were supposed to have some form of interoperability by October 1, 2016; however, no funding was provided for this effort, nor were penalties established for failure to meet this deadline, and as of September 2018[update] this has yet to be accomplished.[56]
In 2009, the Alliance for Toll Interoperability[57] stated that it was exploring the option of using high-speed cameras to take photographs of the cars passing through non-E-ZPass lanes in other states.[58] The Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission, which had been studying going towards all-electronic tolling in order to cut costs, implemented such a system for non-E-ZPass users in 2020 due to the on-going COVID-19 pandemic.[59][60]
Variants
[edit]E-ZPass Plus
[edit]For E-ZPass subscribers who replenish their accounts with a major credit card, the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey offers an E-ZPass option to pay for parking at three Port Authority airports—John F. Kennedy, LaGuardia, and Newark Liberty—through a program known as E-ZPass Plus.[61] This program is also available in New York at Albany International Airport in Albany; Syracuse Hancock International Airport in Syracuse; and the parking lots at the New York State Fair when the fair is in progress; as well as in Atlantic City, New Jersey, at Atlantic City International Airport, the New York Avenue Parking Garage, and the Atlantic City Surface Lot.
The parking payment is debited from the prepaid E-ZPass account if the parking fee is less than $20. If it is $20 or more, the amount is charged directly to the credit card used to replenish the E-ZPass account.[61] The Port Authority reports that drivers save an average of 15 seconds by opting to pay for airport parking using E-ZPass.[citation needed]
Subscribers who replenish their E-ZPass accounts with cash or check cannot participate in this program. Additionally, as of 2013[update], this service is only available to customers of the DelDOT, Delaware River Joint Toll Bridge Commission, Delaware River and Bay Authority, in Delaware; of the New Hampshire DOT; in Maryland; in New Jersey[62] and New York to customers of the PANYNJ, the New York MTA, or the NYS Thruway; and to customers of the Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission.[63]
E-ZPass Flex
[edit]In late 2012, the I-495 HOT (high occupancy toll) lanes in Virginia introduced the E-ZPass Flex transponder.[64] E-ZPass Flex transponders work similarly to regular transponders, but they allow the driver to switch between HOV and toll-paying modes. When a transponder is switched to HOV mode, it is read by the HOT lane's toll equipment, but no toll is charged. E-ZPass Flex also works like a standard E-ZPass on all other toll roads where E-ZPass is accepted, regardless of the position of the switch.[65]
As of 2021[update], E-ZPass Flex devices are currently issued only by Virginia, Maryland,[66] Minnesota,[67] and North Carolina.[68] The following toll roads support E-ZPass Flex in HOV mode:
Minnesota:
- All toll facilities in the system are variable rate HOV lanes and use the Flex transponder. (Free for HOV 2+.)
North Carolina:
- I-77 Express Lanes (free for HOV 3+)
- E-ZPass Flex transponder has an additional one time cost associated[69]
Virginia:
- I-495, I-395 and I-95 Express Lanes (free for HOV 3+)
- I-66 Express Lanes inside and outside the I-495 Beltway (free for HOV 3+)[70]
- I-64 Express Lanes (free for HOV 2+)
Until April 2021, the Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge in New York supported E-ZPass Flex in HOV mode, with a reduced toll for HOV 3+. MTA Bridges and Tunnels only issued the transponders to Staten Island residents. The MTA only offers discounted tolls to holders of New York transponders, so holders of Virginia, Maryland, and North Carolina E-ZPass Flex devices had to pay the full toll regardless of their HOV status.[71]
E-PASS uni
[edit]The Central Florida Expressway Authority offers E-PASS 'uni' (originally E-PASS Xtra[72]), which is compatible with E-ZPass as well as E-PASS, SunPass, LeeWay, PeachPass, NC QuickPass, RiverLink, I-PASS, and FastPass toll systems. It works on E-ZPass toll roads as well as all toll roads in Florida and Georgia.[73] It does not, however, offer the E-ZPass Flex functionality noted above.
SunPass Pro
[edit]The SunPass system in Florida offers the SunPass Pro, with the same toll road compatibility as the E-Pass uni in addition to being accepted in Kansas, Oklahoma, and parts of Texas.[74] It is meant for vehicles with 2 axles. Vehicles with 3 or more axles that will travel outside of Florida are required to purchase a NC Quick Pass instead.[75]
Effects
[edit]Reduced pollution and health improvement
[edit]A study published in the American Economic Journal: Applied Economics, "Traffic Congestion and Infant Health: Evidence from E-ZPass", compared fetal health outcomes for mothers living near congested and uncongested toll plazas on three major highways in Pennsylvania and New Jersey. The researchers focused on areas where toll plazas had instituted E-ZPass, which, because cars travel through more efficiently, diminishes congestion and pollution. The study drew its conclusions by looking at the health outcomes of nearly 30,000 births among mothers who lived within two kilometers of an E-ZPass toll plaza. The researchers state that their findings "suggest that the adoption of E-ZPass was associated with significant improvements of infant health." The study's specific findings were: 1) In areas where E-ZPass was adopted, rates of infant prematurity decreased by between 6.7% and 9.1%; this means that, out of the sample studied, 255 preterm births were likely avoided; 2) Introduction of E-ZPass was correlated with a reduction in the incidence of low birth weight by between 8.5% and 11.3%; that means 275 cases of low birth weight may have been avoided.[76]
Increased home values and subsequent public opinion ramifications
[edit]Another study published in Research in Transportation Economics, "The impact of a transportation intervention on electoral politics: Evidence from E-ZPass", compared changes in home values in areas that switched from manual tolls to E-ZPass compared to similar areas that did not receive the E-ZPass intervention. Using a research design known as difference in differences, the researchers found that traffic indeed was reduced in E-ZPass areas compared to control areas (an average decrease of about 10% in daily commute times). As a consequence, areas near E-ZPasses become more attractive to homeowners, with an estimated resulting increase in home values of $50,185 compared to control areas. The authors then document a 2.37 percentage point decrease in Democratic vote share in the associated E-ZPass areas, which they argue with survey data was largely due to heightened concern around taxation in the areas experiencing the newfound property wealth.[77]
Privacy concerns
[edit]
Civil liberties and privacy rights advocates have expressed concern about how the position data gathered through E-ZPass is used. As of August 2007[update], several states that employ E-ZPass had provided electronic toll information in response to court orders in civil cases, including divorces and other non-criminal matters.[78]
Position data is collected by antennas at locations in addition to fee collection locations. The New York State Department of Transportation (NYSDOT), for example, collect transponder information to provide real-time estimates of travel times between common destinations. By subtracting the time when vehicles pass under the first sign from the current time, the sign can display the expected travel time between the sign and the destination point ahead. This information is also used to determine the best times to schedule maintenance-related lane closures and for other traffic management purposes. According to NYSDOT, the individual tag information is encrypted, and is deleted as soon as the vehicle passes the last reader, and is never made available to the department.[79]
Accounts and agencies
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (April 2008) |
Within the IAG, each member agency has its own billing and customer service center, and each establishes its own fee and discount structures. The agencies also set their own customer account policies. Areas of variation include the refundable deposit or nonrefundable charge for a tag, periodic maintenance fees, paper statement fees, the low account threshold, and replenishment amounts. E-ZPass is usually offered as a debit account: tolls are deducted from prepayments made by the users. Users may opt to have prepayments automatically deposited when their account is low, or they may submit prepayments manually, either by phone or a toll authority's web portal, depending on the agency. For commercial accounts, some agencies allow postpaid plans with a security deposit (which effectively renders them prepaid accounts, with a different replenishment policy).
Fees and discounts by state
[edit]
Some agencies have imposed periodic account maintenance fees on their subscribers. After New Jersey began losing money with the E-ZPass system, a monthly account fee of one dollar was implemented on July 15, 2002[80] and is still in effect for both individual and business accounts.[81] The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey also charges a monthly individual account fee of one dollar.[82] On July 1, 2009, the Maryland Transportation Authority began charging a fee of $1.50 a month to account holders[83] which, as of July 1, 2015[update], only applies to non-residents and is waived if three Maryland E-ZPass tolls were incurred during the previous month.[84]
The Triborough Bridge and Tunnel Authority (TBTA) in New York City once imposed a monthly account fee starting on July 1, 2005, claiming to defray the administrative costs.[85] However, New York State Assembly Bill A06859A in 2005 and 2006 and Senate Bill S6331 in 2006 both considered such a fee threatening the efficiency to move traffic faster with lower tolls and sought to ban it.[86] When the New York State Law started to ban the monthly account fee,[87] the TBTA repealed it on June 1, 2006, and those, especially New Jerseyans, seeking New York accounts and avoiding the monthly fee still imposed by New Jersey and Port Authority, would have to apply for the TBTA or the New York State Thruway accounts at an E-ZPass New York Service Center.[88]
Several agencies offer discounted tolls to E-ZPass customers. The details vary widely, and can include general discounts for all E-ZPass users, variable pricing discounts for off-peak hours, commuter plans with minimum usage levels, flat rate plans offering unlimited use for a period of time, carpool plans for high-occupancy vehicles, and resident plans for those living near particular toll facilities. Many of these plans are available only to customers whose tags are issued by the agency that owns the toll facility in question (reciprocity applies to tag acceptance, not to discounts). Eight authorities in the Northeast (Maine,[89] the Massachusetts Turnpike,[90] the New Hampshire Turnpike,[91] Rhode Island,[92] the New York TBTA,[93] the New York State Thruway,[94] the New Jersey Turnpike,[95] DelDOT[96] and Maryland) restrict their general discounts to their own respective tagholders. While the Delaware Memorial Bridge once restricted its discount plans to New Jersey tags[97] despite its toll plaza being located in Delaware, as of May 2019, all New Jersey and Delaware DoT issued E-ZPass passenger vehicle accounts receive a 25 cent discount at this bridge facility.[98]
Some agencies charge a one-time fee between $20 and $30 for each new transponder, including the Delaware Department of Transportation, the New Hampshire Department of Transportation, and the Maine Turnpike Authority.[99] At least two agencies, the Delaware River and Bay Authority and the Maryland Transportation Authority, once charged multiple fees. In a press release dated July 17, 2007, the DRBA stated: "Beginning January 1, 2008, all DRBA E-ZPass account holders will be charged an account management fee of $1.50 per month. The transponder cost will also be passed on to E-ZPass customers for each new transponder." E-ZPass New York charges a monthly fee of 50 cents for each tag in connection with a business account.[100] The DRBA since merged its service center with New Jersey's E-ZPass service center. On July 1, 2015, a plan put forth by Governor Larry Hogan eliminated Maryland's monthly fee (except accounts without a Maryland address, unless using Maryland toll facilities at least three times in the previous statement period)[101] along with decreasing some toll rates especially for Maryland-issued E-ZPass tags.[102]
E-ZPass users are not required to maintain their account with an agency in their home state (or if in a toll-free state, the closest one to them). Subscribers can open an E-ZPass account with any member of the IAG regardless of residency. This means that users have the option of choosing an agency based on the fees that it charges, effectively allowing them to circumvent transponder and account maintenance fees.[103]
List of places where accepted
[edit]List of agencies
[edit]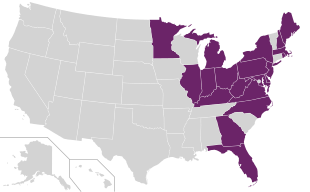
As listed on its website, the E-ZPass Interagency Group includes agencies in 20 states as of 2024[update].[104]
- Buffalo and Fort Erie Public Bridge Authority (New York/Ontario)
- Burlington County Bridge Commission (New Jersey/Pennsylvania)
- Cape May County Bridge Commission (New Jersey)
- Central Florida Expressway Authority
- Cline Avenue Bridge (Indiana)
- Delaware Department of Transportation
- Delaware River and Bay Authority (Delaware/New Jersey)
- Delaware River Joint Toll Bridge Commission (New Jersey/Pennsylvania)
- Delaware River Port Authority (New Jersey/Pennsylvania)
- Florida's Turnpike Enterprise
- Illinois State Toll Highway Authority
- Indiana Toll Road Concession Company
- Kane County Department of Transportation (Illinois)
- Kentucky Public Transportation Infrastructure Authority (see also Ohio River Bridges Project)
- Maine Turnpike Authority
- Maryland Transportation Authority
- Massachusetts Department of Transportation
- Metropolitan Transportation Authority Bridges and Tunnels (New York)
- Minnesota Department of Transportation
- New Hampshire Department of Transportation
- New Jersey Turnpike Authority
- New York State Bridge Authority
- New York State Thruway Authority
- Niagara Falls Bridge Commission (New York/Ontario)
- North Carolina Turnpike Authority
- Ohio Turnpike and Infrastructure Commission
- Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission
- Port Authority of New York and New Jersey (New Jersey/New York)
- Rhode Island Turnpike and Bridge Authority
- Skyway Concessions Company (Illinois)
- South Jersey Transportation Authority (New Jersey)
- State Road and Tollway Authority (Georgia)
- Thousand Islands Bridge Authority (New York)
- United Bridge Partners - Bay City, Michigan
- Virginia Department of Transportation
- West Virginia Parkways Authority
Each of the E-ZPass states operates its own E-ZPass Service Center.[105] NJ E-ZPass manages accounts for the Burlington County Bridge Commission, Delaware River and Bay Authority, Delaware River Joint Toll Bridge Commission and Delaware River Port Authority.[106][107] The E-ZPass New York Service Center operates accounts for the Buffalo and Fort Erie Public Bridge Authority, the Niagara Falls Bridge Commission, the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, and the New York State Thruway Authority.[108] The Virginia Department of Transportation is Virginia's sole member of the E-ZPass Interagency Group, but not all E-ZPass facilities in Virginia are operated by VDOT.[109]
List of roadways, bridges, tunnels, and airports
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (April 2008) |
The following tolled roads, bridges, tunnels, airports, and parking facilities accept E-ZPass. Crossings between jurisdictions are listed in the state where the toll collection point is located, or linked to (in the case of international border crossings).
Delaware
[edit]- Delaware Memorial Bridge/Interstate 295 and U.S. Route 40
- Delaware Turnpike/Interstate 95
- Delaware Route 1
- U.S. Route 301
Florida
[edit]From 2018 to 2021, E-ZPass was only available on the Central Florida Expressway Authority's 125-mile toll road network. Since 2021, the entire state of Florida has accepted E-ZPass.
- Alligator Alley
- Bob Sikes Bridge
- Broad Causeway
- Cape Coral Bridge
- Card Sound Bridge
- Florida's Turnpike
- First Coast (SR 23)
- Airport Expressway
- Florida State Road 408
- Florida State Road 414
- Florida State Road 417
- Florida State Road 429
- Florida State Road 451
- Florida State Road 453
- Florida State Road 528 (Beachline Expressway)
- Poinciana Parkway
- Polk Parkway
- Suncoast Parkway
- Dolphin Expressway
- Don Shula Expressway
- Snapper Creek Expressway
- Gratigny Parkway
- Garcon Point Bridge
- Homestead Extension
- I-4/Selmon Expressway Connector
- I-4 Express Lanes
- I-75 Express Lanes
- I-95 Express Lanes
- I-595 Express Lanes
- Lee Roy Selmon Expressway
- Mid-Bay Bridge
- Midpoint Memorial Bridge
- Orchard Pond Parkway
- Osceola Parkway
- Pinellas Bayway
- Rickenbacker Causeway
- Sanibel Causeway
- Sawgrass Expressway
- Sunshine Skyway Bridge
- Venetian Causeway
- Veterans Expressway
Georgia
[edit]- Peach Pass Express Lanes in the Atlanta region.[110]
Illinois
[edit]- Chicago Skyway/Interstate 90 (separate from I-Pass system)
- Elgin-O'Hare Tollway/Illinois Route 390
- Jane Addams Memorial Tollway/Interstate 39, Interstate 90, and U.S. Route 51
- Ronald Reagan Memorial Tollway/Interstate 88
- Chicago–Kansas City Expressway/Illinois Route 110
- Tri-State Tollway/Interstate 80, Interstate 94, and Interstate 294
- Veterans Memorial Tollway/Interstate 355
Indiana
[edit]- Indiana Toll Road/Interstate 80, Interstate 90
- Lewis and Clark Bridge/Interstate 265 and Kentucky Route 841
- Cline Avenue Bridge/Indiana State Road 912[111][112]
Kentucky
[edit]- Lincoln & Kennedy Bridges/Interstate 65
- Lewis and Clark Bridge/Interstate 265 and Kentucky Route 841
Maine
[edit]Maryland
[edit]- Baltimore Harbor Tunnel/Interstate 895
- Fort McHenry Tunnel/Interstate 95
- Francis Scott Key Bridge/Interstate 695
- Bridge collapsed and impassable as of March 2024
- Maryland Route 200 (Intercounty Connector)
- John F. Kennedy Memorial Highway/Interstate 95
- William Preston Lane Jr. Memorial Bridge (aka the Chesapeake Bay Bridge)/U.S. Route 50 and U.S. Route 301
- Governor Harry W. Nice Memorial Bridge/U.S. Route 301
- Thomas J. Hatem Memorial Bridge/U.S. Route 40
- Bicycling is conditionally allowed since 2016 on weekends and state holidays[113]
Massachusetts
[edit]- Callahan Tunnel/Massachusetts Route 1A
- Massachusetts Turnpike/Interstate 90
- Route 128 station parking garage
- Sumner Tunnel/Massachusetts Route 1A
- Ted Williams Tunnel/Interstate 90
- Tobin Bridge/U.S. Route 1
Michigan
[edit]- Liberty Bridge (Bay City, Michigan)[114]
- Independence Bridge (coming soon)
Minnesota
[edit]- Interstate 394/U.S. Route 12 (HOT lanes)
- Interstate 35W (HOT lanes)
- Interstate 35E (HOT lanes)
New Hampshire
[edit]- Everett Turnpike/U.S. Route 3, Interstate 293, New Hampshire Route 3A, and Interstate 93
- New Hampshire Turnpike (Blue Star Turnpike)/Interstate 95
- Spaulding Turnpike/New Hampshire Route 16
New Jersey
[edit]- Atlantic Avenue Parking Lot, Atlantic City
- Atlantic City Expressway
- Atlantic City International Airport
- Benjamin Franklin Bridge/Interstate 676 and U.S. Route 30
- Betsy Ross Bridge/New Jersey Route 90
- Burlington-Bristol Bridge/New Jersey Route 413 and Pennsylvania Route 413
- Commodore Barry Bridge/U.S. Route 322
- Easton–Phillipsburg Toll Bridge/U.S. Route 22
- Garden State Parkway
- George Washington Bridge/Interstate 95
- Holland Tunnel/Interstate 78
- Lincoln Tunnel/New Jersey Route 495, New York State Route 495
- New Jersey Turnpike/Interstate 95 and Interstate 78
- New York Avenue Garage, Atlantic City
- Newark Liberty International Airport
- Ocean Drive[115]
- Tacony–Palmyra Bridge/New Jersey Route 73 and Pennsylvania Route 73
New York
[edit]- Albany International Airport
- Atlantic Beach Bridge/New York State Route 878[116]
- Bayonne Bridge/New Jersey Route 440 and New York State Route 440
- Bear Mountain Bridge/U.S. Route 6 and U.S. Route 202
- Bronx–Whitestone Bridge/Interstate 678
- Brooklyn–Battery Tunnel/Interstate 478
- Cross Bay Veterans Memorial Bridge
- Goethals Bridge/Interstate 278
- Henry Hudson Bridge/Henry Hudson Parkway and New York State Route 9A
- International Bridges between New York State, US and Ontario, Canada[117]
- Peace Bridge
- Lewiston–Queenston Bridge
- Rainbow Bridge (Niagara Falls)
- Whirlpool Rapids Bridge (NEXUS Only)
- Thousand Islands Bridge (New York/Ontario)
- John F. Kennedy International Airport
- Kingston–Rhinecliff Bridge/New York State Route 199
- LaGuardia Airport
- Marine Parkway–Gil Hodges Memorial Bridge
- Mid-Hudson Bridge/U.S. Route 44 and New York State Route 55
- New England Thruway/Interstate 95
- Newburgh–Beacon Bridge/Interstate 84 and New York State Route 52
- New York State Thruway/Interstate 87, Interstate 287, and Interstate 90
- Outerbridge Crossing/New Jersey Route 440 and New York State Route 440
- Queens–Midtown Tunnel/Interstate 495
- Rip Van Winkle Bridge/New York State Route 23
- North Grand Island Bridge/Interstate 190
- South Grand Island Bridge/Interstate 190
- Syracuse Hancock International Airport
- Tappan Zee Bridge/Interstate 87 and Interstate 287
- Throgs Neck Bridge/Interstate 295
- Robert F. Kennedy (Triborough) Bridge/Interstate 278
- Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge/Interstate 278
North Carolina
[edit]- I-77 Express on Interstate 77 (HOT lanes)
- Monroe Expressway/U.S. Route 74 Bypass
- Triangle Expressway/North Carolina Highway 540 and North Carolina Highway 885
Ohio
[edit]- Memorial Bridge
- Ohio Turnpike (sections of Interstate 76, Interstate 80, and Interstate 90)
Pennsylvania
[edit]- Amos K. Hutchinson Bypass/PA Turnpike 66
- Delaware River–Turnpike Toll Bridge/Interstate 95
- Delaware Water Gap Toll Bridge/Interstate 80
- Interstate 78 Toll Bridge/Interstate 78
- James E. Ross Highway/Interstate 376
- Milford–Montague Toll Bridge/U.S. Route 206
- Mon–Fayette Expressway/PA Turnpike 43
- New Hope–Lambertville Toll Bridge/U.S. Route 202
- Pennsylvania Turnpike/Interstate 76, Interstate 70, Interstate 276, Interstate 476, and Interstate 95
- Pittsburgh International Airport[118]
- Portland–Columbia Toll Bridge
- Scudder Falls Bridge/Interstate 295
- Southern Beltway/PA Turnpike 576
- Trenton–Morrisville Toll Bridge/U.S. Route 1
- Walt Whitman Bridge/Interstate 76
Rhode Island
[edit]- Pell Bridge/Rhode Island Route 138
- Statewide truck-only tolling program (implemented 2018; paused 2022 per court order) [119]
Virginia
[edit]- Boulevard Bridge/Virginia State Route 161
- Dulles Toll Road/Virginia State Route 267
- Dulles Greenway/Virginia State Route 267
- 495 Express Lanes/Interstate 495 (HOT lanes)
- 395 Express Lanes/Interstate 395 (HOT lanes)
- Powhite Parkway/Virginia State Route 76
- Downtown Expressway/Virginia State Route 195
- George P. Coleman Memorial Bridge/U.S. Route 17
- Chesapeake Expressway/Virginia State Route 168
- Chesapeake Bay Bridge-Tunnel/U.S. Route 13
- Pocahontas Parkway/Virginia State Route 895
- South Norfolk Jordan Bridge/Virginia State Route 337
- Downtown Tunnel/Interstate 264
- Midtown Tunnel/U.S. Route 58
- 95 Express Lanes on Interstate 95 (HOT lanes)
- Dominion Boulevard Veterans Bridge/U.S. Route 17
- Interstate 66 (Inside the Beltway)
- Interstate 66 (Outside the Beltway) (HOT lanes)
- 64 Express Lanes on Interstate 64 (HOT lanes)
West Virginia
[edit]Parking
[edit]Although not part of the E-ZPass-Plus program, E-ZPass users may also pay for parking at Pittsburgh International Airport. The E-ZPass transponder is used for identification only. The Southern Beltway, which also uses E-ZPass, has its western terminus at the airport.
The New York State Fair offered E-ZPass Plus as a payment option at two of its parking lots for the first time in 2007,[120] and offered the service again for subsequent seasons.[121] The service was administered by the New York State Thruway Authority (NYSTA), and motorists' E-ZPass accounts were charged the same $5 parking fee that cash customers were charged. Unlike other E-ZPass Plus implementations, the State Fair systems charged motorists at the parking lot entrances; drivers opting to pay by E-ZPass Plus used dedicated "E- ZPass Plus Only" lanes. Since the lots only charge for parking during the twelve days of the State Fair, mobile, self-contained E-ZPass units were used to process vehicles. The units were mounted on trailers with a collapsible gantry for the E-ZPass antennas, used a cellular wireless connection to send transactions to the NYSTA back-office system, and were powered by batteries that were kept replenished by photovoltaic solar panels, with a generator for backup.[122] This service seems to be still existent (as the E-ZPass website lists the State Fair as part of its Plus program).[123]
E-ZPass can be used to pay for parking at the Route 128 station in Westwood, Massachusetts; this is available for Massachusetts customers only.[citation needed] E-ZPass can also be used to pay for parking at John F. Kennedy International Airport and LaGuardia Airport in New York City as well as Newark Liberty International Airport.[123]
Drive-thru retail
[edit]E-ZPass was tested in a since-discontinued program by some McDonald's restaurants on Long Island, New York, at which drive-through customers were given the option to pay using their E-ZPass accounts to test out cardless payment platforms.[124][125] In late 2013, Wendy's started a similar system called drive-thru that is E-ZPass compatible, and it underwent testing at five Staten Island Wendy's locations.[125] In 2018, a one-year pilot project with the startup Verdeva was announced to test drive-thru and gas station payments via separate accounts set up with the E-ZPass system.[126]
In December 2021, PayByCar launched a pilot program to accept E-ZPass (or its own RFID stickers) at 27 Alltown gas stations in the Boston area.[127]
Non-transactional traffic monitoring
[edit]E-ZPass transponders are also used to monitor traffic. A transponder-reader is placed above the roadway at various intervals, and the time a particular tag takes between scans at each interval provides information about the speed of traffic between those points. This transit time information is often relayed back to motorists via electronic signs on the roadway or via traffic reporting agencies who use the information as part of radio and television traffic reports.[128] The individual tag data is not collected or used for ticketing purposes, as some sources have suggested.[129]
Toll facilities that do not accept E-ZPass in E-ZPass states and provinces
[edit]There are many toll facilities, mostly bridges run by independent authorities, that are not part of the E-ZPass network even though they are in a state that is in the E-ZPass region. With Congress seeking a national electronic toll-collection system in place for federal highways, E-ZPass officials are talking to other states that have electronic tolls "to find a common way to do business".[130] However, the congressional legislation did not include any penalties for agencies and states that failed to comply with the implementation of such a system. As of 2021[update], most Florida and Minnesota toll facilities had become compatible with E-ZPass. Georgia toll roads were in the process of becoming compatible by 2022. Other states, like Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, California, and Washington were not scheduled to become compatible with E-ZPass in the near future.[131]
List of facilities
[edit]- Anderson Ferry (Ohio/Kentucky)
- Augusta Ferry (Ohio/Kentucky)
- Cape May–Lewes Ferry (Delaware/New Jersey)
- Downbeach Express (New Jersey)
- Dingman's Ferry Bridge (New Jersey/Pennsylvania)
- Fort Frances–International Falls International Bridge (Minnesota/Ontario) - cash only toll booth paid by Canada bound vehicles on US side before crossing bridge
- Fort Madison Toll Bridge (Illinois/Iowa)
- Gasparilla Bridge (Florida)
- Greenspring Low Water Toll Bridge (West Virginia/Maryland)
- Hammock Dunes Bridge (Florida)
- Highway 407 (Ontario) - utilizes their own transponder-based system
- Moseywood Road (Lake Harmony, Pennsylvania) – Toll paid upon entry to community. Provides a shortcut to Lake Harmony from Pennsylvania Route 940 to Pennsylvania Route 903
- Ogdensburg-Prescott International Bridge (New York/Ontario) - toll booth on US side after passing CBP control point
- Seaway International Bridge (New York/Ontario) - toll booth found in Canada for in bound traffic from US and US bound traffic from Canada.
- St. Francisville Bridge – Old Wabash Cannonball Railroad (Illinois-Indiana)[132]
- Wayne Six Toll Bridge (West Virginia/Ohio) – Privately owned
In Michigan, the Ambassador Bridge, Detroit-Windsor Tunnel, Blue Water Bridge, Mackinac Bridge, International Bridge, and Grosse Ile Toll Bridge do not use E-ZPass.
See also
[edit]- Drivewyze – weigh station bypassing of commercial vehicles at participating state highway locations
- List of electronic toll collection systems
- List of toll bridges
- List of toll roads
- NORPASS – weigh station bypassing, partner of E-ZPass
- PrePass – weigh station bypassing, commercial vehicles at participating state highway locations
References
[edit]- ^ "NJTA-E-ZPass". State.NJ.US. December 13, 2007. Archived from the original on December 13, 2007.
- ^ "Tags". E-ZPass New York. Retrieved July 23, 2013.
- ^ "E-ZPass MA Frequently Asked Questions". Highway Division - MassDOT. Archived from the original on 2013-07-19.
- ^ "Press Kit". Kapsch.net. April 25, 2013. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved July 23, 2013.
- ^ "FAQs". E-ZPass Group. Retrieved 9 August 2024.
- ^ "I-95 High-Speed E-ZPass lanes open in Hampton". Fosters.com. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ^ "Some big changes coming to the Ohio Turnpike". News 5 Cleveland WEWS. 25 June 2021.
- ^ Hu, Winnie (2019-07-23). "The Last Toll Collectors". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2021-07-21.
- ^ "Green Pass Discount Plan - New York State Thruway". thruway.ny.gov. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- ^ "File Specifications". E-ZPass Group. Retrieved July 23, 2013.
- ^ "E-ZPass MA Frequently Asked Questions". Highway Division – MassDOT. Archived from the original on July 19, 2013. Retrieved July 23, 2013.
- ^ "E-ZPass Customer Agreement – Private Account Terms and Conditions" (PDF). ezpassnh.com. 2021-06-25. Retrieved 2022-03-17.
- ^ "NC Quick Pass Terms and Conditions" (PDF). ncquickpass.com. 2022-12-19. Retrieved 2023-07-25.
- ^ "Maybe Set A Calendar Reminder For Summer: Your Virginia E-Z Pass May Be Inactive". NPR.org. February 3, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "Virginia pauses deactivation of idle E-ZPass accounts amid pandemic". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved 2021-07-21.
- ^ Ley, Ana (February 2, 2021). "Virginia will stop canceling E-ZPasses for 6 months as pandemic continues". pilotonline.com. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ Pascale, Jordan (May 1, 2018). "Virginia is among the only states that deactivate an E-ZPass for inactivity. Users say that's ridiculous". pilotonline.com. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "E-ZPass On-the-Go". getezpass.com. Archived from the original on 2009-04-15. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ "E-ZPass Retail". PATurnpike.com.
- ^ "2016 Monthly Traffic and Percent of E-ZPass Usage" (PDF). Port Authority of NY and NJ. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 28, 2018. Retrieved November 5, 2016.
- ^ Southwick, Ron (July 21, 2020). "Pa. Turnpike raising tolls again in 2021; those without E-ZPass will pay much more". PennLive. Retrieved January 15, 2021.
- ^ "Why not E-ZPass?". New Jersey Turnpike Authority. Retrieved March 17, 2024.
- ^ Sims, Calvin (1991-04-04). "No-Stop Tolls: 3 States Agree To Automation". The New York Times. Retrieved 2018-04-12.
- ^ "Latest Status Info". tdsr.uspto.gov.
- ^ Daily Brief, Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority, February 15, 2008
- ^ Rifkin, Glenn (1992-09-09). "BUSINESS TECHNOLOGY; Electronic Toll-Taking Is Being Put to the Test". The New York Times. Retrieved 2018-04-12.
- ^ "Altered E-ZPass system in gear". The Journal News. 1993-08-03. pp. 9, 10. Retrieved 2021-07-21.
- ^ New York State Thruway Authority (2002). "The New York State Thruway: 1991–2000". Thruway Chronology. New York State Thruway Authority. Archived from the original on August 15, 2016. Retrieved November 18, 2010.
- ^ Preston, Jennifer (1998-03-12). "Installation of E-Z Pass System on Turnpike and Parkway Is Expected to Take 2 Years". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2021-07-21.
- ^ Gross, Jane (1997-03-25). "Electronic Tolls Are Catching On, And Commuters Are Catching Up". The New York Times. Retrieved 2018-04-06.
- ^ Holloway, Lynette (1996-08-21). "With Triborough Bridge Debut, A Test for E-Z Pass Toll System". The New York Times. Retrieved 2018-04-06.
- ^ Pristin, Terry (1997-07-16). "A Few Glitches in E-Z Pass". The New York Times. Retrieved 2018-04-06.
- ^ Pristin, Terry (1997-10-29). "New Jersey Daily Briefing; E-Z Pass Exceeds Expectation". The New York Times. Retrieved 2018-04-06.
- ^ "Electronic tolls coming to Pa. Turnpike by 1998". Lancaster New Era. Associated Press. March 22, 1994. p. A3.
- ^ Gilbert, Pat R. (March 22, 1994). "7 Agencies OK Electronic Toll-Collection Firm: Project Expected to Speed Traffic on Parkway, Turnpike". The Record. Bergen County, NJ. p. A3.
- ^ Wyckoff, P.L. (March 12, 1998). "E-ZPass to debut on Atlantic City highway: But 2000 is target for Turnpike and Parkway". The Star-Ledger. Newark, NJ. p. 22.
- ^ "E-ZPass not so easy for drivers on first day". Erie Times-News. Associated Press. December 3, 2000.
- ^ "Pennsylvania Turnpike extends E-ZPass service". The Express-Times. Easton, PA. December 15, 2001.
- ^ Fuoco, Michael A. (December 22, 2001). "Turnpike E-ZPass Will Get More Lanes". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. p. D6.
- ^ Therolf, Garrett (December 15, 2002). "E-ZPass making life harder for bridge users". The Morning Call. Allentown, PA. p. B1.
- ^ Agnello, Joe (March 16, 2006). "E-ZPASS, Other Enhancements Coming This Year to Greensburg and Beaver Valley Expressways" (Press release). Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission. Archived from the original on October 14, 2008. Retrieved March 15, 2012.
- ^ "Toll collection system – U.S. Patent 5819234 Abstract". Patentstorm.us. Archived from the original on 2010-12-17. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- ^ "Va. Joins E-ZPass Fast Lane (washingtonpost.com)". The Washington Post.
- ^ "North Carolina and E-ZPass interoperable from January 3, 2013 - Toll Roads News". Archived from the original on September 16, 2013.
- ^ a b "Central Florida Expressway Authority Joins E-ZPass Group" (Press release). Central Florida Expressway Authority. November 9, 2017. Retrieved August 31, 2018.
- ^ a b "Newest SunPass transponders will work with other states' E-ZPass toll readers". FOX 13 Tampa Bay. 2021-05-28. Retrieved 2021-05-28.
- ^ a b "Florida Turnpike Teams Up With Multi-State E-ZPass System". Miami News, Weather, Sports From CBS4 WFOR – News, Sports, Weather, Traffic and Miami's Best. 2021-05-28. Retrieved 2021-05-28.
- ^ Thiede, Dana (July 15, 2021). "MnPass express lane system to become E-ZPass". Minneapolis, MN: KARE-TV. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ^ Davis, Jason (November 6, 2023). "Peach Pass partners with E-ZPass, expands toll access across 8 states". WSB-TV. Retrieved 26 November 2023.
- ^ Samuel, Peter (21 March 2007). "Indiana to have I-Zoom transponder brand". TollRoadsNews.com. Archived from the original on 7 February 2012.
- ^ "E-ZPass Lanes open". WBZ News Radio. Associated Press. 16 December 2008. Archived from the original on 12 July 2012. Retrieved 2008-12-16.
- ^ Green, Marcus (July 29, 2015). "Kentucky joins E-Z Pass for Ohio River Bridges Project". Louisville, KY: WDRB. Retrieved September 17, 2015.
- ^ Williams, Kevin (August 2, 2018). "E-ZPass is coming to some local toll roads starting Sept. 1". Orlando, FL: WFTV. Retrieved August 31, 2018.
- ^ "Niagara Falls Bridge Commission Introduces E-ZPass Toll Program at Rainbow, Whirlpool, and Lewiston-Queenston Bridge Crossings" (Press release). Niagara Falls Bridge Commission. June 2, 2014. Archived from the original on July 14, 2014. Retrieved June 11, 2014.
- ^ Benoit, Katie (June 27, 2019). "E-ZPass comes to Thousand Islands Bridge". WWNY-TV.
- ^ Elliott, Christopher (27 September 2018). "When will we have a nationwide toll transponder system?". USA TODAY. Gannett Company. Retrieved 28 August 2019.
- ^ ATI – Alliance for Toll Interoperability. Tollinterop.org (2013-07-19). Retrieved on 2013-07-23.
- ^ "Toll Payment in Other States May Get Easier". .tbo.com. 2009-02-06. Archived from the original on 2009-12-19. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- ^ Thompson, Charles (March 6, 2012). "Caution: All-E-Z Pass turnpike ahead". The Patriot-News. Harrisburg, PA. p. A1.
- ^ PA Turnpike Commission (2021-08-25). "Toll By Plate Factsheet" (PDF). PATurnpike. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-09-15. Retrieved 2021-08-25.
- ^ a b "The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey - Press Release". panynj.gov. Archived from the original on December 3, 2008.
- ^ "Ezpass NJ availability types and methods to get discounts". PayPticket. 2018-11-03. Archived from the original on 2018-11-08. Retrieved 2018-11-08.
- ^ "NH E-ZPass". Ezpassnh.com. Retrieved July 23, 2013.
- ^ "video interview with Pierce Coffee, I-495 Express Lanes Project Marketing Director". WUSA-TV. 13 March 2012. Archived from the original on 17 December 2013. Retrieved 1 June 2012.
- ^ "VDOT :: E-ZPass Flex". ezpassva.com. Retrieved 2015-05-25.
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions About the 495 Express Lanes". NBC4 Washington (WRC). 16 November 2012. Retrieved 2020-02-20.
- ^ "Tags - E-ZPass".
- ^ "NC Quick Pass Transponders". NC Turnpike Authority. Archived from the original on 2018-06-12. Retrieved 2020-02-20.
- ^ "Transponder Options". NC Quick Pass. Retrieved 2023-10-26.
- ^ "Transform 66". Archived from the original on 2022-12-05. Retrieved 2022-12-05.
- ^ "S.I. resident discount on Verrazzano to stay at $2.75". Staten Island Advance. 2021-04-07. Retrieved 2021-07-20.
- ^ Harper, Ryan (November 14, 2018). "Extra On Getting There: New E-Pass Transponder Works in 18 States". News 13. Retrieved August 5, 2021.
- ^ "Uni – One Toll Pass. 19 States. | Central Florida Expressway Authority".
- ^ "Sunpass PRO".
- ^ "Sunpass: 3-Plus Axel Transponder".
- ^ "Traffic Congestion, Infant Health, and E-ZPass". Journalist's Resource.org. 2 May 2011.
- ^ Jerzak, Connor T.; Libgober, Brian (1 May 2020). "The impact of a transportation intervention on electoral politics: Evidence from E-ZPass". Research in Transportation Economics. 80: 100809. doi:10.1016/j.retrec.2019.100809. S2CID 212898558.
- ^ Newmarker, Chris (8 October 2007). "E-ZPass Records Out Cheaters in Divorce Court". NBC News. Archived from the original on October 2, 2013. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- ^ "NYSDOT Announces Travel Time Signs in Staten Island". New York State Department of Transportation. 2007-07-10. Retrieved 30 April 2010.
- ^ "Mobilizing the Region 386, E-ZPass Gains New Customers". Tri-State Transportation Campaign. Archived from the original on 2017-06-28.
- ^ New Jersey E-ZPass – Individual and Business Terms and Conditions[permanent dead link]
- ^ "E-ZPass New York - Terms & Conditions - Individual Accounts".
- ^ "Cost-Recovery Efforts Approved for Maryland's Toll Facilities". 29 January 2009. Retrieved 2009-06-04.
- ^ "MDTA News Releases".
- ^ "Triborough Bridge and Tunnel Authority statement to E-ZPass account holders". Archived from the original on 2005-06-09. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- ^ "New York State Legislature Bill Status". Public.leginfo.state.ny.us. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- ^ "Public Authorities Law Section 2855". Public.leginfo.state.ny.us. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- ^ AAA New York: Car and Travel: March 2007[permanent dead link]
- ^ Maine Turnpike: Toll Charts Archived 2012-05-11 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Massachusetts Turnpike Toll / Mileage Calculator Archived 2012-09-04 at archive.today shows that E-ZPass discount tolls are limited to FAST LANE Archived 2011-02-26 at the Wayback Machine users.
- ^ "New Hampshire Turnpike System Toll Rate Schedule" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-06-05. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- ^ "Newport/Pell Bridge Toll Rates". Ritba.org. 2010-02-15. Archived from the original on 2010-11-27. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- ^ MTA Bridges and Tunnels Crossing Charges limit E-ZPass discounts for tags issued by New York E-ZPass Customer Service Center only.
- ^ Toll and Distance Frequently Asked Questions Archived 2018-09-10 at the Wayback Machine limit E-ZPass discounts for tags issued by New York E-ZPass Customer Service Center only.
- ^ "New Jersey Turnpike Authority: Toll Rates". State.nj.us. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- ^ The Frequent User Plan Archived 2015-02-19 at the Wayback Machine is limited to Delaware tags. Otherwise, the cash and E-ZPass tolls are the same.
- ^ "Plan Descriptions and Discounts (Delaware Memorial Bridge) (Tag Specific)". NJ E-ZPass. 2012. Retrieved 2015-07-14.
- ^ "Delaware Memorial Bridge toll hike to start later, E-ZPass discount added". Press of Atlantic City. 2019-02-20. Retrieved 2023-04-01.
- ^ "How Much Does a Maine Turnpike E-ZPass Tag Cost?". EZPassMaineTurnpike.com. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ^ "E-ZPass New York - Terms & Conditions - Business Accounts".
- ^ "Private Account Terms and Conditions, Section II.h" (PDF). Ezpassmd.com. 2015-07-01. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-07-15. Retrieved 2015-07-14.
- ^ "New Lower Toll Rates Effective July 1" (PDF). Ezpassmd.com. 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-07-04. Retrieved 2015-07-14.
- ^ Laura Northrup (March 2, 2011). "You Don't Have to Buy an E-ZPass from the State Where You Live".
- ^ "About Us – Members". E-ZPass Group. E-ZPass Interagency Group. Retrieved May 29, 2021.
- ^ "E-ZPass Group – Get E-ZPass". E-ZPass Interagency Group. Retrieved 4 December 2013.
- ^ "NJ E-ZPass". E-ZPass New Jersey. Retrieved 4 December 2013.
- ^ "COMMISSION MOVES TO MERGE E-ZPASS CUSTOMER SERVICE OPERATIONS WITH NEW JERSEY ELECTRONIC TOLL COLLECTION GROUP". DRTJBC – Current Press Releases. Delaware River Joint Toll Bridge Commission. Archived from the original on 5 July 2015. Retrieved 4 July 2015.
- ^ "E-ZPass New York". E-ZPass New York. Retrieved 4 December 2013.
- ^ "Toll Facilities". VDOT. Virginia Department of Transportation. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
- ^ "Peach Pass users gain access to E-ZPass in eight more states". 11Alive.com. November 7, 2023. Retrieved December 14, 2023.
- ^ "Cline Avenue Bridge homepage".
- ^ Avila, Larry (December 16, 2020). "Cline Avenue Bridge will reopen to traffic following Dec. 23 ribbon cutting". Northwest Indiana Business Magazine. Linker Media Group.
- ^ Anderson, David (August 24, 2016). "Hatem Bridge bike riders will be limited to weekends, holidays starting Sept. 6". The Aegis. Baltimore Sun Media Group. Archived from the original on September 29, 2016. Retrieved September 18, 2016.
- ^ Sevilla, Dominic (7 January 2023). "What Bay City's new toll bridges mean for non-residents". Huron Daily Tribune.
- ^ Wittkowski, Donald (April 26, 2018). "E-Z Pass set to go live on Cape May County bridges". The Press of Atlantic City. Retrieved May 20, 2018.
- ^ Asbury, John (December 12, 2023). "E-ZPass accepted at Atlantic Beach Bridge starting Wednesday". Newsday. Retrieved December 14, 2023.
- ^ Note: Some toll plazas are in New York and some are in Ontario.
- ^ "Grant Oliver Launches Online Sign Up for Go Fast Pass". PRNewswire. Pittsburgh. March 24, 2010. Retrieved July 23, 2013.
- ^ "The RhodeWorks Tolling Program". dot.ri.gov.
- ^ "E-ZPass Tested at State Fair as Way To Clear Traffic – August 30, 2007". New York Sun. 30 August 2007. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- ^ "Parking & Transportation". New York State Fair. Retrieved November 5, 2022.
- ^ "Mobile E-ZPass reader deployed by NYSTA for Fair parking – Rent a Reader opportunity". TOLLROADSnews. 29 August 2007. Archived from the original on 5 February 2011. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- ^ a b "E-ZPass Plus". E-ZPass Group. Retrieved June 20, 2022.
- ^ "McDonald's Testing E-Payment System". USA Today. 29 May 2001. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ a b E-ZPass for Fast Food iDriveThru Available at Wendy's • Fast Food Drive-Thrus Are Getting E-ZPass System So You Don't Have to Exhaust Yourself Digging for Change Time (12/26/2013)
- ^ "You may soon be able to use E-ZPass to pay at the pump and at drive-throughs - the Boston Globe". The Boston Globe.
- ^ Hiawatha Bray (December 13, 2021). "Now you can save money on gas with an E-ZPass".
- ^ "E-ZPass Monitors Being Set Up to Observe City Traffic". Gothamist. 11 April 2011. Retrieved 2011-09-27.
- ^ "E-ZPass Speeding Tickets False". Snopes. 7 April 2011. Retrieved 2011-09-27.
- ^ Donald Wittkowski. "As E-ZPass turns 20, electronic toll system could link more states". The Press of Atlantic City. Retrieved 16 December 2013.
- ^ Pransky, Noah (2021-05-27). "Why Are 34 States Ignoring a Law Designed to Make Your Road Trip Easier?". NBC 5 Dallas-Fort Worth. Retrieved 2021-05-28.
- ^ "Toll Facilities in the United States". Federal Highway Administration. Retrieved 4 December 2013.
