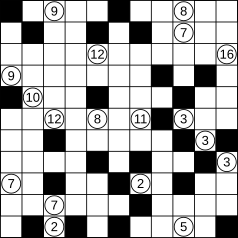
Kuromasu
Where are the black cells? (Japanese: 黒枡はどこだ?, Hepburn: Kuromasu wa doko da?), abbreviated Kuromasu (黒マス) or Kurodoko (黒どこ), is a binary-determination logic puzzle published by Nikoli. As of 2005[update], one book consisting entirely of Kuromasu puzzles has been published by Nikoli.
Rules
[edit]Kuromasu is played on a rectangular grid. Some of these cells have numbers in them. Each cell may be either black or white. The object is to determine what type each cell is.
The following rules determine which cells are which:
- Each number on the board represents the number of white cells that can be seen from that cell, including itself. A cell can be seen from another cell if both cells are within the same row or column, and there are no black cells between them in that row or column.
- Numbered cells must not be black.
- No two black cells must be horizontally or vertically adjacent.
- All the white cells must be connected horizontally or vertically.
Solution methods
[edit]A number of methods of solving Kuromasu puzzles exist.
Any cell with a number in it must be white; this is very important. For example, a 2 cell with another numbered cell next to it would be visible from the 2 cell, and no other cells can be visible from the 2 cell. Therefore, all neighbouring cells to the 2 cell must be black. The cell beyond the other numbered cell must also be black. This is one method of starting some Kuromasu puzzles.
Another method of beginning some Kuromasu puzzles starts from a 2 cell and another numbered cell or white cell in the same row or column, with just one space between them. The cell in the middle must be black, as if it were white, the 2 cell would be able to see at least 3 cells.
If the number inside a cell is equal to the maximum number of cells it could possibly see, then all those cells must be white in order for that maximum to be possible. For example, in a 7×7 puzzle, the maximum number that can be had in any cell is 13 (the cell itself, plus six others in the row, plus six other in the column). If a 13 appears in a cell of a 7×7 puzzle, all cells in the same row or column as the 13 must be white. This is often represented by placing dots in those cells.
Deciding if a Kuromasu puzzle is solvable is NP-complete.[1]
History
[edit]Kuromasu is an original puzzle of Nikoli; it first appeared in Puzzle Communication Nikoli #34 (June 1991). The English language Nikoli website uses Engrish to translate the name as "Where is Black Cells".
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Kölker, Jonas (2012). "Kurodoko is NP-complete". Journal of Information Processing. 20 (3): 694–706. doi:10.2197/ipsjjip.20.694.
External links
[edit]- 0hn0.com Popular web version
- Where is Black Cells page on Nikoli site
- Comparing Methods for Solving Kuromasu Puzzles
- Kuromasu Solver using Java
- Kuromasu for Android on Google Play