Folklore of the United States
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2007) |
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Culture of the United States |
|---|
 |
| Society |
| Arts and literature |
| Other |
| Symbols |
|
United States portal |
American folklore encompasses the folklore that has evolved in the present-day United States mostly since the European colonization of the Americas. It also contains folklore that dates back to the Pre-Columbian era.
Folklore consists of legends, music, oral history, proverbs, jokes, popular beliefs, fairy tales, stories, tall tales, and customs that are the traditions of a culture, subculture, or group. It is also the set of practices through which those expressive genres are shared.
Native American folklore[edit]
Native American cultures are rich in myths and legends that explain natural phenomena and the relationship between humans and the spirit world. According to Barre Toelken, feathers, beadwork, dance steps and music, the events in a story, the shape of a dwelling, or items of traditional food can be viewed as icons of cultural meaning.[1]
Native American cultures are numerous and diverse. Though some neighboring cultures hold similar beliefs, others can be quite different from one another. The most common myths are the creation myths, which tell a story to explain how the earth was formed, and where humans and other beings came from. Others may include explanations about the Sun, Moon, constellations, specific animals, seasons, and weather. This is one of the ways that many tribes have kept, and continue to keep, their cultures alive; these stories are told as a way of preserving and transmitting the nation, tribe, or band's particular beliefs, history, customs, spirituality, and traditional way of life. According to Barre Toelken, "Stories not only entertain but also embody Native behavioral and ethical values."[1]
Although individual tribes have their own sacred beliefs and myths, many stories have much in common. Myths about floods are almost universal amongst Plains tribes, stories of a flooded earth being restored. There are many "hero stories" immortalising the adventures of heroes with supernatural powers, who right wrongs and defeat evils. Animal tales are common, some explaining how features of certain animals occurred, some using animal characters for narration, and others using animals symbolically. There are also myths where supernatural beings appear in the form of animals, with the bear, elk, eagle, owl, and snake frequently referred to.[2]
Founding myths[edit]
The founding of the United States is often surrounded by national myths, legends, and tall tales. Many stories have developed since the founding long ago to become a part of America's folklore and cultural awareness, and non-Native American folklore especially includes any narrative which has contributed to the shaping of American culture and belief systems. These narratives have varying levels of historical accuracy; the veracity of the stories is not a determining factor.[citation needed]
Christopher Columbus[edit]
Christopher Columbus, as a hero and symbol to the then-immigrants, is an important figure in the body of American myth. His status, not unlike most American icons, is representative not of his own accomplishments, but the self-perception of the society which chose him as a hero. Having effected a separation from England and its cultural icons, the United States was left without history—or heroes on which to base a shared sense of their social selves. Washington Irving was instrumental in popularizing Columbus. His version of Columbus' life, published in 1829, was more a romance than a biography.[3] The book was very popular, and contributed to an image of the discoverer as a solitary individual who challenged the unknown sea, as triumphant Americans contemplated the dangers and promise of their own wilderness frontier. As a consequence of his vision and audacity, there was now a land free from kings, a vast continent for new beginnings. In the years following the Revolution the poetic device "Columbia" was used as a symbol of both Columbus and America. King's College of New York changed its name in 1792 to Columbia, and the new capital in Washington was subtitled District of Columbia.[3]
Jamestown[edit]
In May 1607, the Susan Constant, the Discovery, and the Godspeed sailed through Chesapeake Bay and thirty miles up the James River settlers built Jamestown, Virginia, England's first permanent colony. Too late in the season to plant crops, many were not accustomed to manual labor. Within a few months, some settlers died of famine and disease. Only thirty-eight made it through their first year in the New World. Captain John Smith, a pirate turned gentleman, turned the settlers into foragers and successful traders with the Native Americans, who taught the English how to plant corn and other crops. Smith led expeditions to explore the regions surrounding Jamestown, and it was during one of these that the chief of the Powhatan Native Americans captured Smith. According to an account Smith published in 1624, he was going to be put to death until the chief's daughter, Pocahontas, saved him. From this, the legend of Pocahontas sprang forth, becoming part of American folklore, children's books, and movies.[4]
Pilgrims[edit]

Plymouth Rock is the traditional site of disembarkation of William Bradford and the Mayflower Pilgrims who founded Plymouth Colony in 1620, and an important symbol in American history. There are no contemporary references to the Pilgrims' landing on a rock at Plymouth. The first written reference to the Pilgrims landing on a rock is found 121 years after they landed. The Rock, or one traditionally identified as it, has long been memorialized on the shore of Plymouth Harbor in Plymouth, Massachusetts. The holiday of Thanksgiving is said to have begun with the Pilgrims in 1621.[5] They had come to America to escape religious persecution, but then nearly starved to death. Some friendly Native Americans, including Squanto, helped the Pilgrims survive through the first winter. The perseverance of the Pilgrims is celebrated during the annual Thanksgiving festival.
Revolutionary War figures[edit]
George Washington[edit]
George Washington (February 22, 1732 – December 14, 1799), the country's first president, is the most preeminent of American historical and folkloric figures, as he holds the place of "Pater Patriae". Apocryphal stories about Washington's childhood include a claim that he skipped a silver dollar across the Rappahannock River at Ferry Farm. Another tale claims that as a young child, Washington chopped down his father's cherry tree. His angry father confronted the young Washington, who proclaimed "I cannot tell a lie" and admitted to the transgression, thus illuminating his honesty. Parson Mason Locke Weems mentions the first citation of this legend in his 1806 book, The Life of George Washington: With Curious Anecdotes, Equally Honorable to Himself and Exemplary to His Young Countrymen. This anecdote cannot be independently verified. Samuel Clemens, also known as Mark Twain, is also known to have spread the story while lecturing, personalizing it by adding "I have a higher and greater standard of principle. Washington could not lie. I can lie but I won't."[citation needed]
Patrick Henry[edit]
Patrick Henry (May 29, 1736 – June 6, 1799) was an attorney, planter and politician who became known as an orator during the movement for independence in Virginia in the 1770s. Patrick Henry is best known for the speech he made in the House of Burgesses on March 23, 1775, in Saint John's Church in Richmond, Virginia. With the House undecided on whether to mobilize for military action against the encroaching British military force, Henry argued in favor of mobilization. Forty-two years later, Henry's first biographer, William Wirt, working from oral histories, tried to reconstruct what Henry said. According to Wirt, Henry ended his speech with words that have since become immortalized: "I know not what course others may take; but as for me, Give me Liberty, or give me Death!" The crowd, by Wirt's account, jumped up and shouted "To Arms! To Arms!". For 160 years Wirt's account was taken at face value. In the 1970s, historians began to question the authenticity of Wirt's reconstruction.[citation needed]

Betsy Ross[edit]
Betsy Ross (January 1, 1752 – January 30, 1836) is widely credited with making the first American flag. There is, however, no credible historical evidence that the story is true. Research conducted by the National Museum of American History notes that the story of Betsy Ross making the first American flag for General George Washington entered into American consciousness about the time of the 1876 centennial celebrations. In the 2008 book The Star-Spangled Banner: The Making of an American Icon,[6] Smithsonian experts point out that accounts of the event appealed to Americans eager for stories about the revolution and its heroes and heroines. Betsy Ross was promoted as a patriotic role model for young girls and a symbol of women's contributions to American history.[7]
Other Revolutionary War heroes who became figures of American folklore include: Benedict Arnold, Benjamin Franklin, Nathan Hale, John Hancock, John Paul Jones and Francis Marion.[8]
Tall tales[edit]
The tall tale is a fundamental element of American folk literature. The tall tale's origins are seen in the bragging contests that often occurred when men of the American frontier gathered. A tall tale is a story with unbelievable elements, relayed as if it were true and factual. Some such stories are exaggerations of actual events; others are completely fictional tales set in a familiar setting, such as the American Old West, or the beginning of the Industrial Revolution. They are usually humorous or good-natured. The line between myth and tall tale is distinguished primarily by age; many myths exaggerate the exploits of their heroes, but in tall tales, the exaggeration looms large, to the extent of becoming the whole of the story.[9]
Based on historical figures[edit]
- John Chapman (September 26, 1774 – March 18, 1845), widely known as Johnny Appleseed, was an American pioneer nurseryman who introduced apple trees to large parts of Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, and Illinois. He became an American legend while still alive, largely because of his kind and generous ways, and the symbolic importance he attributed to apples. Johnny Appleseed is remembered in American popular culture by his traveling song or Swedenborgian hymn ("The Lord is good to me...").
- Daniel Boone (November 2, 1734 [O.S. October 22] – September 26, 1820) was an American pioneer, explorer, and frontiersman whose frontier exploits made him one of the first folk heroes of the United States.
- Davy Crockett (August 17, 1786 – March 6, 1836) was a 19th-century American folk hero, frontiersman, soldier and politician. He is commonly referred to in popular culture by the epithet, "King of the Wild Frontier". He represented Tennessee in the U.S. House of Representatives, served in the Texas Revolution, and died at the Battle of the Alamo.
- Mike Fink (c. 1770/1780 – c. 1823) called "king of the keelboaters", was a semi-legendary brawler and river boatman who exemplified the tough and hard-drinking men who ran keelboats up and down the Ohio and Mississippi Rivers.
- Martha Jane Canary (May 1, 1852 – August 1, 1903), better known as Calamity Jane, was an American frontierswoman, and professional scout best known for her claim of being an acquaintance of Wild Bill Hickok. She is said to have also exhibited kindness and compassion, especially to the sick and needy. It was from her that Bret Harte took his famous character of Cherokee Sal in The Luck of Roaring Camp.
- Jigger Johnson (1871–1935), was a lumberjack and log driver from northern New England who is known for his numerous off-the-job exploits, such as catching bobcats alive with his bare hands, and drunken brawls.[10][11]
- John Henry was an African-American railroad worker who is said to have worked as a "steel-driving man"—a man tasked with hammering a steel drill into rock to make holes for explosives to blast the rock away in constructing a railroad tunnel. According to legend, John Henry's prowess as a steel-driver was measured in a race against a steam-powered hammer, which he won, only to die in victory with his hammer in his hand and his heart giving out from stress. The "Ballad of John Henry" is a musical rendition of his story.
- Molly Pitcher was a nickname given to a woman said to have fought in the American Battle of Monmouth, who is generally believed to have been Mary Hays. Since various Molly Pitcher tales grew in the telling, many historians regard Molly Pitcher as folklore rather than history, or suggest that Molly Pitcher may be a composite image inspired by the actions of a number of real women. The name itself may have originated as a nickname given to women who carried water to men on the battlefield during the war.
Other historical figures include Titanic survivor Molly Brown, Wild West showman Buffalo Bill Cody, and sharpshooter Annie Oakley.
Fictional characters[edit]
- Paul Bunyan is a lumberjack figure in North American folklore and tradition. One of the most famous and popular North American folklore heroes, he is usually described as a giant as well as a lumberjack of unusual skill, and is often accompanied in stories by his animal companion, Babe the Blue Ox. The character originated in folktales circulated among lumberjacks in the Northeastern United States and eastern Canada, first appearing in print in a story published by Northern Michigan journalist James MacGillivray in 1906.
- Cordwood Pete is said to be the younger brother of legendary lumberjack Paul Bunyan.
- The Lone Ranger is a fictional hero of the west who fought raiders and robbers in the Texas area. The sole survivor of a group of six rangers, he set out to bring the criminals who killed his brother to justice. The Lone Ranger is said to have been based on Bass Reeves by Historian Art Burton but that is in dispute.[12][13]
- Johnny Kaw is a mythical Kansas settler whose exploits created elements of the Kansas landscape and helped establish wheat and sunflowers as major crops. The character dates to the 1955 centennial of Kansas and has been explored in numerous books.
- John the Conqueror also known as High John the Conqueror, and many other folk variants, is a folk hero from African-American folklore. John the Conqueror was an African prince who was sold as a slave in the Americas. Despite his enslavement, his spirit was never broken and he survived in folklore as a sort of a trickster figure, because of the tricks he played to evade his masters. Joel Chandler Harris's 'Br'er Rabbit' of the Uncle Remus stories is said to be patterned after High John the Conqueror.
- Pecos Bill is an American cowboy, apocryphally immortalized in numerous tall tales of the Old West during American westward expansion into the Southwest of Texas, New Mexico, Southern California, and Arizona

- Captain Stormalong was an American folk hero and the subject of numerous nautical-themed tall tales originating in Massachusetts. Stormalong was said to be a sailor and a giant, some 30 feet tall; he was the master of a huge clipper ship known in various sources as either the Courser or the Tuscarora, a ship so tall that it had hinged masts to avoid catching on the moon.[14]
Legendary and folkloric creatures[edit]
- Bigfoot, also known as "Sasquatch", is the name given to an ape-like creature that some believe inhabit mostly forests in the Pacific Northwest region of, and throughout the entirety of, North America. Bigfoot is usually described as a large, hairy, bipedal humanoid, although descriptions vary depending on location. The height range is about 6 to 10 feet tall with black, dark brown, or dark reddish hair.[15][16] One of the most famous accounts of Bigfoot is the Patterson-Gimlin film, where a supposedly female Bigfoot marches across the screen with giant strides, turns to face the camera, then marches off up a steep hill and into the forest.[17] There are more than 100 sightings reported yearly. Among these reporters are veterans, campers, hikers, explorers, hunters, and more. There are several websites, podcasts and organizations related to Bigfoot.
- Champ is the name given to a reputed lake monster living in Lake Champlain, a natural freshwater lake in North America. The lake crosses the Canada–United States border, located partially in the Canadian province of Quebec and partially in the U.S. states of Vermont and New York. There is no scientific evidence for Champ's existence, though there have been over 300 reported sightings.[18]
- Punxsutawney Phil is a semi-mythical groundhog central to the most well-known Groundhog Day ceremony, a Pennsylvania Dutch superstition that claims to predict the arrival of spring. According to tradition, the same groundhog has made predictions ever since the 1800s.
- The Jersey Devil is a legendary creature said to inhabit the New Jersey Pine Barrens of Southern New Jersey in the United States. The creature is often described as a flying biped with hooves, but there are many different variations. The most common description is that of a kangaroo-like creature with the face of a horse, the head of a dog, leathery bat-like wings, horns, small arms with clawed hands, red eyes, cloven hooves and a forked tail. It has been reported to move quickly, as to avoid human contact, and often is described as emitting a "blood-curdling scream".[19][20] The legend goes as such: a woman named Mother Leeds gave birth to her 13th child on a dark, stormy night. Mother Leed is said to be a witch and her 13th child was born the Devil. It soon grew wings and hooves, killed the midwife, and took off into the night.
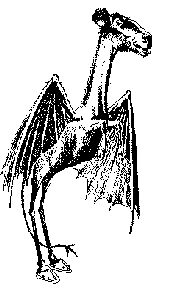
The Jersey Devil - The White Lady is a type of female ghost reportedly seen in rural areas and associated with some local legend of tragedy. Common to many of them is the theme of losing or being betrayed by a husband or fiancé. They are often associated with an individual family line or said to be a harbinger of death, similar to a banshee.
- Mothman is a mythical creature from Point Pleasant, West Virginia described as a large humanoid with glowing red eyes on its face and large bird-like wings with fur covering its body. Mothman has been blamed for the collapse of the Silver Bridge.
- The Hodag is a mythical beast that is said to inhabit the forests of Northern Wisconsin, particularly around the city of Rhinelander. The Hodag has a reptilian body with the horns of a bull and is said to have a penchant for mischief.
- Old Black Eyes is a spectral hound said to frequent an area known as the Baker Rocks, located near the top of the Black Mountains of North Carolina. Old Black Eyes is said to be the spirit of Jim Baker, who lived at the rocks and was regarded as a witch with supernatural powers by the local mountain people. According to legend, Jim Baker performed some sort of ritual at an old Indian cemetery, near the Black Mountains, where he proceeded to sell his soul to the Devil. The Devil proceeded to turn Baker's pupils "unnaturally black" as a sign of their deal and hell's claim on his soul. Upon his death, Baker was said to take the spirit of a "devil dog", identifiable by the large black pupils of its eyes, that people feared to approach, believing it was surrounded in black magic. It was said the only way to get rid of Old Black Eyes was to draw its picture, pin it to a tree, and then shoot it with a gun.[21]
- In North American folklore, Fearsome critters were tall tale animals jokingly said to inhabit the wilderness in or around logging camps, especially in the Great Lakes region. Today, the term may also be applied to similar fabulous beasts.
Other folkloric creatures include the Chupacabra, Jackalope, the Nain Rouge of Detroit, Michigan, the Hide-behind, Wendigo of Minnesota and Chessie, a legendary sea monster said to live in Chesapeake Bay.[22]
Literature[edit]
Santa Claus, also known as Saint Nicholas, Father Christmas, or simply "Santa", is a figure with legendary, mythical, historical and folkloric origins. The modern figure of Santa Claus was derived from the Dutch figure, Sinterklaas, which may, in turn, have its origins in the hagiographical tales concerning the Christian Saint Nicholas. "A Visit from St. Nicholas", also known as "The Night Before Christmas" is a poem first published anonymously in 1823 and generally attributed to Clement Clarke Moore. The poem, which has been called "arguably the best-known verses ever written by an American",[23] is largely responsible for the conception of Santa Claus from the mid-nineteenth century to today, including his physical appearance, the night of his visit, his mode of transportation, the number and names of his reindeer, as well as the tradition that he brings toys to children. The poem has influenced ideas about St. Nicholas and Santa Claus from the United States to the rest of the English-speaking world and beyond. Is There a Santa Claus? was the title of an editorial appearing in the September 21, 1897, edition of The (New York) Sun. The editorial, which included the famous reply "Yes, Virginia, there is a Santa Claus", has become a part of popular Christmas folklore in the United States and Canada.[24]
The Headless Horseman is a fictional character from the short story "The Legend of Sleepy Hollow" by American author Washington Irving. The story, from Irving's collection of short stories, entitled The Sketch Book of Geoffrey Crayon, has worked itself into known American folklore/legend through literature and film.[25]
"Rip Van Winkle" is a short story by the American author Washington Irving, first published in 1819. It follows a Dutch-American villager in colonial America named Rip Van Winkle who meets mysterious Dutchmen, imbibes their liquor and falls asleep in the Catskill Mountains. He awakes 20 years later to a very changed world, having missed the American Revolution.
Inspired by a conversation on nostalgia with his American expatriate brother-in-law, Irving wrote the story while temporarily living in Birmingham, England. It was published in his collection, The Sketch Book of Geoffrey Crayon, Gent. While the story is set in New York's Catskill Mountains near where Irving later took up residence, he admitted, "When I wrote the story, I had never been on the Catskills."[26]
Folk music[edit]
Native Americans were the earliest inhabitants of the land that is today known as the United States and played its first music. Beginning in the 17th century, immigrants from the United Kingdom, Ireland, Spain, Germany and France began arriving in large numbers, bringing with them new styles and instruments. African slaves brought musical traditions, and each subsequent wave of immigrants contributes to a melting pot. Folk music includes both traditional music and the genre that evolved from it during the 20th-century folk revival. The term originated in the 19th century but is often applied to music that is older than that.[citation needed]
The earliest American scholars were with The American Folklore Society (AFS), which emerged in the late 1800s. Their studies expanded to include Native American music but still treated folk music as a historical item preserved in isolated societies. In North America, during the 1930s and 1940s, the Library of Congress worked through the offices of traditional music collectors Robert Winslow Gordon, Alan Lomax and others to capture as much North American field material as possible. Lomax was the first prominent scholar to study distinctly American folk music such as that of cowboys and southern blacks. His first major published work was in 1911, Cowboy Songs and Other Frontier Ballads, and was arguably the most prominent US folk music scholar of his time, notably during the beginnings of the folk music revival in the 1930s and early 1940s.[citation needed]
The American folk music revival was a phenomenon in the United States that began during the 1940s and peaked in popularity in the mid-1960s. Its roots went earlier, and performers like Burl Ives, Woody Guthrie, Lead Belly, and Oscar Brand had enjoyed a limited general popularity in the 1930s and 1940s. The revival brought forward musical styles that had, in earlier times, contributed to the development of country & western, jazz, and rock and roll music.[citation needed]
African-American music[edit]
Slavery was introduced to the Thirteen Colonies beginning in the early 17th century in Virginia. The ancestors of today's African-American population were brought from hundreds of tribes across West Africa and brought with them certain traits of West African music. This included call and response vocals, complex rhythmic music, syncopated beats, shifting accents, incorporation of hums and moans, which are sounds with no distinct meaning, and a combination of sound and body movements. The African musical focus on rhythmic singing and dancing was brought to the New World, where it became part of a distinct folk culture that helped Africans "retain continuity with their past through music."[citation needed] Along with retaining many African elements, there was also a continuation of instruments. Enslaved Africans would either take with them African instruments or reconstructed them once in the New World. The first slaves in the United States sang work songs and field hollers. However, slave music was used for a variety of reasons. Music was included in religious ceremonies and celebrations, used to coordinate work, and to conceal hidden messages, like when they were commenting on slave owners. African American slave songs can be divided into three groups: religious, work, and recreational songs.[27][28][29]
Spirituals[edit]
Protestant hymns written mostly by New England preachers became a feature of camp meetings held among devout Christians across the South. Most slaves were typically animists or were a part of some other form of African Religion. To destroy any remnants of African culture or make more people disciples, slaves would be encouraged and taken to church. They became attracted to the grace and freedom that was preached within the church, which was very different from the lives they were living. Slaves would learn the same hymns that their masters sang, and when they came together they developed and sang adapted versions of these hymns, they were called Negro spirituals. It was from these roots, of spiritual songs, work songs, and field hollers, that blues, jazz, and gospel developed. Negro spirituals were primarily expressions of religious faith. These songs provided them a voice for their longing for freedom and to experience it. Around the 1840s, slaves knew that in the northern states, slavery was illegal, and some northerners wanted the complete abolishment of slavery. So when they sang about heaven, it was also about possibly escaping north. In the early 19th century the Underground Railroad was developed, containing a network of secret routes and safe houses, and it greatly impacted slaves' religious music. When there was any mention of trains, stations, etc. in spirituals they were directly referencing the Underground Railroad, such as the song "Swing Low, Sweet Chariot". These songs were designed so that slave owners thought that slaves were only singing about heaven.[30][31]
Work songs[edit]
Work Songs at least had two functions: one to benefit the slaves and another to benefit overseers. When a group of slaves had to work together on a hard task, like carrying a heavy load, singing would provide a rhythm that allowed them to coordinate their movements. When picking crops, music was not necessary, but when there was silence it would be uncomfortable for the overseers. Even though there was a presence of melancholy in songs, Southern slave owners would interpret that their slaves were happy and content, possibly because of their singing.[31]
Recreational songs[edit]
Even if slave owners attempted to forbid things like drums or remnants of African culture, they did not seem to mind them learning European instruments and music. In some cases, black string players would be invited to play to entertain white audiences. Between the week of Christmas and New Years’, owners would give their slaves a holiday. This provided a chance for slave families who had different masters to come together, otherwise, they would not go anywhere. Some slaves would craft items, but masters detested industrious slaves. So most slaves would spend their recreational time doing other things, like dancing and singing. Masters approved of such activities, but they may not have listened carefully to the songs that were performed.[31]
Folk songs[edit]
The original Thirteen Colonies of the United States were all former British possessions, and Anglo culture became a major foundation for American folk and popular music. Many American folk songs are identical to British songs in arrangements, but with new lyrics, often as parodies of the original material. Anglo-American traditional music also includes a variety of broadside ballads, humorous stories and tall tales, and disaster songs regarding mining, shipwrecks and murder.[32] Folk songs may be classified by subject matter, such as: drinking songs, sporting songs, train songs, work songs, war songs, and ballads.
- The Star-Spangled Banner's tune was adapted from an old English drinking song by John Stafford Smith called "To Anacreon in Heaven."
- "The Ballad of Casey Jones" is a traditional song about railroad engineer Casey Jones and his death at the controls of the train he was driving. It tells of how Jones and his fireman Sim Webb raced their locomotive to make up for lost time, but discovered another train ahead of them on the line, and how Jones remained on board to try to stop the train as Webb jumped to safety.
- "When Johnny Comes Marching Home" (sometimes "When Johnny Comes Marching Home Again") is a popular song of the American Civil War that expressed people's longing for the return of their friends and relatives who were fighting in the war. The Irish anti-war song "Johnny I Hardly Knew Ye" and "When Johnny Comes Marching Home" share the same melodic material. Based on internal textual references, "Johnny I Hardly Knew Ye" apparently dates from the early 1820s, while When Johnny Comes Marching Home was first published in 1863. "Johnny I Hardly Knew Ye" is a popular traditional Irish anti-war and anti-recruiting song. It is generally dated to the early 19th century, when soldiers from Athy, County Kildare served the British East India Company.
- "Oh My Darling, Clementine" (1884) is an American western folk ballad believed to have been based on another song called Down by the River Liv'd a Maiden (1863). The words are those of a bereaved lover singing about his darling, the daughter of a miner in the 1849 California Gold Rush. He loses her in a drowning accident. The song plays during the opening credits for the highly acclaimed John Ford movie "My Darling Clementine". It also runs as a background score all through the movie.
- "The Yellow Rose of Texas" is a traditional folk song. The original love song has become associated with the legend that Emily D. West, a biracial indentured servant, "helped win the Battle of San Jacinto, the decisive battle in the Texas Revolution".
- "Take Me Out to the Ball Game" is a 1908 Tin Pan Alley song by Jack Norworth and Albert Von Tilzer which has become the unofficial anthem of baseball, although neither of its authors had attended a game prior to writing the song. The song is traditionally sung during the seventh-inning stretch of a baseball game. Fans are generally encouraged to sing along.
Other American folksongs include: "She'll Be Coming 'Round the Mountain", "Skewball", "Big Bad John", "Stagger Lee", "Camptown Races" and "The Battle Hymn of the Republic".
Sea shanties[edit]
Work songs sung by sailors between the 18th and 20th centuries are known as sea shanties. The shanty was a distinct type of work song, developed especially in American-style merchant vessels that had come to prominence in decades prior to the American Civil War. These songs were typically performed while adjusting the rigging, raising anchor, and other tasks where men would need to pull in rhythm. These songs usually have a very punctuated rhythm precisely for this reason, along with a call-and-answer format. Well before the 19th century, sea songs were common on rowing vessels. Such songs were also very rhythmic in order to keep the rowers together.[33]
They were notably influenced by songs of African Americans, such as those sung whilst manually loading vessels with cotton in ports of the southern United States. The work contexts in which African-Americans sang songs comparable to shanties included: boat-rowing on rivers of the southeastern U.S. and Caribbean; the work of stokers or "firemen", who cast wood into the furnaces of steamboats plying great American rivers;and stevedoring on the U.S. eastern seaboard, the Gulf Coast, and the Caribbean—including "cotton-screwing": the loading of ships with cotton in ports of the American South. During the first half of the 19th century, some of the songs African Americans sang also began to appear in use for shipboard tasks, i.e. as shanties.
Shanty repertoire borrowed from the contemporary popular music enjoyed by sailors, including minstrel music, popular marches, and land-based folk songs, which were adapted to suit musical forms matching the various labor tasks required to operate a sailing ship. Such tasks, which usually required a coordinated group effort in either a pulling or pushing action, included weighing anchor and setting sail.
"Poor Paddy Works on the Railway" is a popular Irish and American folk song. Historically, it was often sung as a sea chanty. The song portrays an Irish worker working on a railroad. There are numerous titles of the song including, "Pat Works on the Railway" and "Paddy on the Railway". "Paddy Works on the Erie" is another version of the song. "Paddy on the Railway" is attested as a chanty in the earliest known published work to use the word "chanty", G. E. Clark's Seven Years of a Sailor's Life (1867). Clark recounted experiences fishing on the Grand Banks of Newfoundland, in a vessel out of Provincetown, Mass. c. 1865–66. At one point, the crew is getting up the anchor in a storm, by means of a pump-style windlass. One of the chanties the men sing while performing this task is mentioned by title, "Paddy on the Railway."
Shaker music[edit]
 |
| Music |
|---|
|
| Works inspired by Simple Gifts |
|
| Works inspired by Shakers |
|
The Shakers are a religious sect founded in 18th-century England upon the teachings of Ann Lee. Shakers today are most known for their cultural contributions, especially style of music and furniture. The Shakers composed thousands of songs, and also created many dances; both were an important part of the Shaker worship services. In Shaker society, a spiritual "gift" could also be a musical revelation, and they considered it important to record musical inspirations as they occurred. "Simple Gifts" was composed by Elder Joseph Brackett and originated in the Alfred Shaker community in Maine in 1848. Aaron Copland's iconic 1944 ballet score Appalachian Spring, uses the now famous Shaker tune "Simple Gifts" as the basis of its finale.[34]
Folk dancing[edit]
Folk dances of British origin include the square dance, descended from the quadrille, combined with the American innovation of a caller instructing the dancers. The religious communal society known as the Shakers emigrated from England during the 18th century and developed their own folk dance style.[35]
Locations and landmarks[edit]
- the "Lost Colony" of Roanoke Island: In 1587, Sir Walter Raleigh recruited over 100 men, women and children to journey from England to Roanoke Island on North Carolina's coast and establish the first English settlement in America under the direction of John White as governor. Virginia Dare (born August 18, 1587) was the first child born in the Americas to English parents, Ananias and Eleanor White Dare in the short-lived Roanoke Colony. The fact of her birth is known because the governor of the settlement, Virginia Dare's grandfather, John White, returned to England in 1587 to seek fresh supplies. When White eventually returned three years later, Virginia and the other colonists were gone. During the past four hundred years, Virginia Dare has become a prominent figure in American myth and folklore, symbolizing different things to different groups of people. She is the subject of a poem (Peregrine White and Virginia Dare) by Rosemary and Stephen Vincent Benét, and the North Carolina Legend of the White Doe. While often cited as an indigenous legend, the white doe seems to have its roots in English folklore. White deer are common in English legends and often used as symbols of Christian virtue. A similar story of a young girl transformed into a white deer can be found in Yorkshire, where it formed the basis for Wordsworth's poem The White Doe of Rylstone. In the four centuries since their disappearance, the Roanoke colonists have been the subject of a mystery that still challenges historians and archaeologists as one of America's oldest.[36]
- Bennington Triangle is an area of southwestern Vermont within which a number of people went missing between 1945 and 1950. The area shares characteristics with the Bridgewater Triangle in Southeastern Massachusetts.
- The Bridgewater Triangle is an area of about 200 square miles (520 km2) within southeastern Massachusetts in the United States, claimed to be a site of alleged paranormal phenomena, ranging from UFOs to poltergeists, orbs, balls of fire and other spectral phenomena, various bigfoot-like sightings, giant snakes and thunderbirds. The term was coined by New England-based cryptozoologist Loren Coleman.
- Times Square is a major commercial intersection in Midtown Manhattan, New York City, at the junction of Broadway and Seventh Avenue and stretching from West 42nd to West 47th Streets. Times Square – iconified as "The Crossroads of the World" is the brightly illuminated hub of the Broadway Theater District. Formerly Longacre Square, Times Square was renamed in April 1904 after The New York Times moved its headquarters to the newly erected Times Building site of the annual ball drop on New Year's Eve. The northern triangle of Times Square is technically Duffy Square, dedicated in 1937 to Chaplain Francis P. Duffy of New York City's "Fighting 69th" Infantry Regiment; a memorial to Duffy is located there, along with a statue of George M. Cohan. The Duffy Statue and the square were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2001.

- Empire State Building is a 102-story skyscraper located in New York City at the intersection of Fifth Avenue and West 34th Street. Its name is derived from the nickname for New York, the Empire State. It stood as the world's tallest building for 40 years, from its completion in 1931. The Empire State Building is generally thought of as an American cultural icon. The project involved 3,400 workers, mostly immigrants from Europe, along with hundreds of Mohawk ironworkers, many from the Kahnawake reserve near Montreal. Perhaps the most famous popular culture representation of the building is in the 1933 film King Kong, in which the title character, a giant ape, climbs to the top to escape his captors but falls to his death after being attacked by airplanes. The 1957 romantic drama film An Affair to Remember involves a couple who plan to meet atop the Empire State Building, a rendezvous that is averted by an automobile accident. The 1993 film Sleepless in Seattle, a romantic comedy partially inspired by An Affair to Remember, climaxes with a scene at the Empire State observatory.
Other locations and landmarks that have become part of American folklore include: Independence Hall, Monument Valley, Ellis Island, Hoover Dam, Pearl Harbor, the Vietnam War Memorial, and the Grand Canyon.[citation needed]
Cultural icons[edit]
- The Liberty Bell is an iconic symbol of American independence, located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The bell was commissioned from the London firm of Lester and Pack in 1752, and was cast with the lettering (part of Leviticus 25:10) "Proclaim LIBERTY throughout all the land unto all the inhabitants thereof." In the 1830s, the bell was adopted as a symbol by abolitionist societies, who dubbed it the "Liberty Bell". It acquired its distinctive large crack sometime in the early 19th century—a widespread story claims it cracked while ringing after the death of Chief Justice John Marshall in 1835.[citation needed]
- The Statue of Liberty a colossal neoclassical sculpture on Liberty Island in New York Harbor, designed by Frédéric Bartholdi and dedicated on October 28, 1886. The statue, a gift to the United States from the people of France, is of a robed female figure representing Libertas, the Roman goddess of freedom, who bears a torch and a tablet upon which is inscribed the date of the American Declaration of Independence, July 4, 1776. The statue is an icon of freedom and of the United States: a welcoming signal to immigrants arriving from abroad.
- Uncle Sam (initials U.S.) is a common national personification of the American government and came into use during the War of 1812. According to legend, Samuel Wilson, a meatpacker in New York, supplied rations for the soldiers and stamped the letters U.S. on the boxes, which stood for United States but was jokingly said to be the initials of Uncle Sam. An Uncle Sam is mentioned as early as 1775, in the original "Yankee Doodle" lyrics of the Revolutionary War [citation needed]. "Columbia", who first appeared in 1738 and sometimes was associated with liberty, is the personification of the American nation, while Uncle Sam is a personification of the government; they are some times shown working together or disputing with one another over political issues, especially in the political cartoons of Puck. With the American Revolutionary War came Brother Jonathan as a personification of the American Everyman; but it wasn't until after the War of 1812 Uncle Sam appeared. Brother Jonathan saw full literary development into the personification of American national character through the 1825 novel Brother Jonathan by John Neal.[37][38]
- Shark Mouth nose art on military aircraft: Although originally from Austria this stylistic design was applied to the American Volunteer Group in Asia known more commonly as "The Flying Tigers". This design was painted on the units' P-40 fighters around the large air intake near the front of the plane. This image has since been placed on various aircraft such as American UH-1 and AH-1 helicopters during the Vietnam War as well as the modern-day A-10 Thunderbolt II, A-29 Supertucano and AT-6 Wolverine, and other vehicles both military and civilian alike.
Other cultural icons include Rosie the Riveter, the United States Constitution, the Colt Single Action Army, Smokey Bear, the Boeing B-52 Stratofortress, and apple pie.
History[edit]
Historical events that form a part of American folklore include: the Boston Massacre, the Boston Tea Party, Paul Revere's Ride, the Battle of the Alamo, the Salem witch trials, the Gunfight at the O.K. Corral, the California Gold Rush, the Battle of the Little Bighorn, the Battle of Gettysburg, the Attack on Pearl Harbor, and the September 11th attacks.[39]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Toelken, Barre.The Anguish of Snails, Utah State University Press, 2003 ISBN 0-87421-555-2
- ^ "Native American Mythology & Legends – Legends of America". www.legendsofamerica.com. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Columbus in History". Xroads.virginia.edu. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ^ McGeehan, John R. (2011-02-23). "McGeehan, John R., Jamestown Settlement". Netplaces.com. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ^ Aspen Design, Westbrook, CT (2012-11-08). "Pilgrim Hall Museum". Pilgrimhall.org. Archived from the original on 2010-06-20. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "NMAH | Resources: FAQs". amhistory.si.edu. Retrieved 2022-10-17.
- ^ Snell, Rachel A. (2018). ""God, Home, and Country": Women, Historical Memory, and National Identity in English Canada and the United States". American Review of Canadian Studies. 48 (2): 244–255. doi:10.1080/02722011.2018.1472946. S2CID 149523167. Retrieved 2022-07-02.
- ^ Crawford, Amy. "The Swamp Fox". Smithsonian. Retrieved 2019-02-24.
- ^ Paquette, Dan. "LibGuides: ENG 225 - Children's Literature (Fairy Tales, Folklore, Myths, and Legends): Definitions". libguides.stcc.edu. Retrieved 2021-07-21.
- ^ Appalachia Appalachian Mountain Club, 1964.
- ^ Monahan, Robert. "Jigger Johnson", New Hampshire Profiles magazine, Northeast Publications, Concord, New Hampshire, April, 1957.
- ^ Burton, Art; Boardman, Mark. "Once And For All, Is The Lone Ranger Based on Bass Reeves?". True West Magazine. Retrieved 2022-11-01.
- ^ LaCapria, Kim. "Was the Original 'Lone Ranger' a Black Man? - Truth or Fiction?". Retrieved 2022-11-01.
- ^ Fee, Christopher R.; Webb, Jeffrey B. (2016-08-29). American Myths, Legends, and Tall Tales: An Encyclopedia of American Folklore [3 volumes]. Bloomsbury Publishing USA. ISBN 978-1-61069-568-8.
- ^ "Bigfoot [a.k.a. Abominable Snowman of the Himalayas, Mapinguari (the Amazon), Sasquatch, Yowie (Australia) and Yeti (Asia)]". The Skeptic's Dictionary. Archived from the original on September 14, 2008. Retrieved August 17, 2008.
- ^ "Sasquatch". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2008.
- ^ Roger Patterson & Chris Murphy (2005) [1966]. The Bigfoot Film Controversy (contains Patterson's 1966 book, Do Abominable Snowmen of America Really Exist?). Illustrated by Roger Patterson. Hancock House. ISBN 0-88839-581-7.
- ^ "Champ, the Lake Champlain Monster". Lake Champlain Region. 2011-07-19. Retrieved 2021-11-29.
- ^ The Jersey Devil, by James F. McCloy and Ray Miller Jr., Middle Atlantic Press. ISBN 0-912608-11-0
- ^ "The Jersey Devil & Pine Barrens Folklore – New Jersey Pine Barrens". Pinelands Preservation Alliance. Archived from the original on 2013-12-04. Retrieved 2014-01-04.
- ^ Curran, Bob (2010). Mysterious Celtic Mythology In American Folklore. Gretna, Louisiana: Pelican Publishing Company, Inc. pp. 265–266. ISBN 978-1-58980-743-3.
- ^ Kappatos, Nicole (August 30, 2018). "From the Archives: Chessie, the Chesapeake Bay sea monster". Richmond Times-Dispatch. Retrieved 2021-02-03.
- ^ Burrows, Edwin G. & Wallace, Mike. Gotham: A History of New York City to 1898. New York: Oxford University Press, 1999. pp. 462–463 ISBN 0-19-511634-8
- ^ "Holiday podcast: Yes, Virginia, There is a Santa Claus (re-aired)". Journalism History journal. 2020-12-14. Retrieved 2022-10-17.
- ^ Hischak, Thomas S. (2017-03-06). 100 Greatest American Plays. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-1-4422-5606-4.
- ^ Pierre M. Irving, The Life and Letters of Washington Irving, G. P. Putnam's Sons, 1883, vol. 2, p. 176.
- ^ Bronner, Simon J. (2017-03-29). "Folklore in the United States". Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Literature. doi:10.1093/acrefore/9780190201098.013.88. ISBN 978-0-19-020109-8. Retrieved 2021-02-23.
- ^ "Roots of African American Music". Smithsonian Music. Retrieved 2021-02-23.
- ^ "Digital History". www.digitalhistory.uh.edu. Retrieved 2021-04-07.
- ^ "African American Spirituals". The Library of Congress. Retrieved 25 June 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Guion, David (2012-06-25). "Slave music and the Civil War". Musicology for Everyone. Retrieved 2021-04-07.
- ^ Kip Lornell, Exploring American Folk Music: Ethnic, Grassroots, and Regional Traditions in the United States (Oxford MS: Univ. Press of Mississippi, 2012), 82-117. ISBN 1617032662; and Duncan Emrich, ed., Anglo-American Songs and Ballads (Washington DC: Library of Congress, 1947); available online at https://www.loc.gov/folklife/LP/AFS_L12.pdf
- ^ Early Naval Ballads of England (1841), Printed for the Percy society by C. Richards, 2019-06-11
- ^ Pollack, Howard (1999). Aaron Copland: The Life and Work of an Uncommon Man. New York, New York: Henry Holt and Company. pp. 398–399. ISBN 0-8050-4909-6.
- ^ R.C. Opdahl, V.E. Woodruff Opdahl, A Shaker Musical Legacy, A Shaker Musical Legacy, (London: U. Press of New England) 2004, pp. 24, 279. "’Let Us Labor’: The Evolution of Shaker Dance", Shaker Heritage Society, https://shakerheritage.wordpress.com/2012/04/04/let-us-labor-the-evolution-of-shaker-dance/
- ^ "Hause, Eric The Lost Colony". Coastalguide.com. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ^ Morgan, Winifred (1988). An American Icon: Brother Jonathan and American Identity. Newark, New Jersey: University of Delaware Press. p. 143. ISBN 0-87413-307-6.
- ^ Kayorie, James Stephen Merritt (2019). "John Neal (1793–1876)". In Baumgartner, Jody C. (ed.). American Political Humor: Masters of Satire and Their Impact on U.S. Policy and Culture. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. p. 88. ISBN 978-1-4408-5486-6.
- ^ e.g. Vincent Kelly Pollard, "Pearl Harbor", in Nadeau, Kathleen M.., Lee, Jonathan H. X., eds. Encyclopedia of Asian American Folklore and Folklife, vol. 1 (Santa Barbara CA: ABC-CLIO, 2011), 630-31. ISBN 9780313350665
Further reading[edit]
- Baughman, Ernest Warren. Type And Motif-index of the Folktales of England And North America. The Hague: Mouton & Co., 1966–1967.
- Coffin, Tristram P.; Cohen, Hennig, (editors), Folklore in America; tales, songs, superstitions, proverbs, riddles, games, folk drama and folk festivals, Garden City, N.Y. : Doubleday, 1966. Selections from the Journal of American folklore.
- Ed Cray and Marilyn Eisenberg Herzog (January 1967). "The Absurd Elephant: A Recent Riddle Fad". Western Folklore. 26 (1). Western Folklore, Vol. 26, No. 1: 27–36. doi:10.2307/1498485. JSTOR 1498485.—the evolution of the Elephant Riddle that entered U.S. folklore in California in 1963
- Cox, William T. with Latin Classifications by George B. Sudworth. Fearsome Creatures of the Lumberwoods. Washington, D.C.: Judd & Detweiler Inc., 1910.
External links[edit]
- American Folklore Society
- American Myth Today: O Brother, Where Art Thou? American Studies at the University of Virginia

