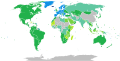
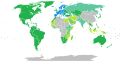
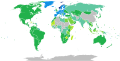
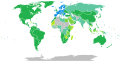
Visa requirements for EFTA nationals
This article needs to be updated. (November 2017) |
Visa requirements for EFTA nationals | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Member states | |
Website efta | |
Visa requirements for EFTA nationals are administrative entry restrictions by the authorities of other states placed on citizens of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) member states.
Current member states of EFTA are Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland.
Member states' citizens enjoy freedom of movement in each other's territories in accordance with the EFTA convention.[1] EFTA nationals also enjoy freedom of movement in the European Union (EU). Currently, in practice, EFTA nationals and EU citizens and are not only visa-exempt but are legally entitled to enter and reside in each other's countries. The Citizens’ Rights Directive[2] (also sometimes called the "Free Movement Directive") defines the right of free movement for citizens of the European Economic Area (EEA),[3] which includes the three EFTA members Iceland, Norway and Liechtenstein and the member states of the EU. Switzerland, which is a member of EFTA but not of the EEA, is not bound by the Directive but rather has a separate bilateral agreement on free movement with the EU.[4]
Visa requirements maps
[edit]Visa free access
[edit]This table lists all countries, as of this date with source information as it is cited inline, for which citizens of at least one EFTA member state may enter without a visa on an ordinary passport. Information regarding visas on arrival and on exit fees is not listed in the table, regarding which, see the relevant section below.
| Africa | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Visa not required | Visa required | Notes |
| All states.[5][6][7][8] | 90 days within 12 months. | ||
| All states.[9] | 30 days. | ||
| Norway, Switzerland.[10] | Iceland, Liechtenstein | 30 days. | |
| All states.[11][12][13][14] | 90 days. | ||
| All others.[15] | Liechtenstein[16] | 14 days. | |
| All states.[17][18][19][20] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[21][22][23][24] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[25] | 3 months within a calendar year. | ||
| All states.[26] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[27] | 3 months. | ||
| All states.[28] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[29] | 3 months | ||
| Caribbean | |||
| Country | Visa not required | Visa required | Notes |
| All states.[30] | 3 months. | ||
| All states.[31] | 3 months. | ||
| All states.[32] | 3 months. | ||
| All states.[33][34][35] | 21 days (90 days for Norway). | ||
| All states.[36] | 90 days (30-day tourist cards required). | ||
| All states.[37][38] | 3 months. | ||
| All states.[39] | 3 months. | ||
| All states. | 90 days | ||
| All states.[40] | 3 months. | ||
| All states. | 6 weeks. | ||
| All states. | 1 month. | ||
| All states. | 90 days within any 180 day period. | ||
| Central and North America | |||
| Country | Visa not required | Visa required | Notes |
| All states.[41] | 1 month for Switzerland. | ||
| All states. | 6 months, eTA required if arriving by air.[42] | ||
| All states.[43] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[44] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[45] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[46] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[47] | 180 days. | ||
| All states.[48] | 90 days (30-day tourist cards required). | ||
| All states.[49] | 180 days. | ||
| All states (VWP) | 90 days on every arrival from overseas, ESTA (issued for 2 years) required when arriving by air and cruise ship. | ||
| South America | |||
| Country | Visa not required | Visa required | Notes |
| All states.[50] | 90 days. | ||
| All states. | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[51] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[52] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[53] | 90 days - extendable up to 180-days stay within a one-year period. | ||
| All states.[54] | 90 days. | ||
| Norway, Switzerland.[55] | Iceland, Liechtenstein | 3 months. | |
| All states.[56] | 90 days. | ||
| All states. | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[57] | 90 days, extendable once. | ||
| All states.[58] | 90 days, extendable once. | ||
| Asia | |||
| Country | Visa not required | Visa required | Notes |
| All states.[59] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[60] | 30 days. | ||
| All states.[61] | 90 days. | ||
| All others.[62] | Liechtenstein | 30 days. | |
| All states | 60 days. | ||
| Switzerland | All others. | 15 days. | |
| All states.[63] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[64] | 30 days. | ||
| All states.[65] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[66] | 90 days (30 days for Iceland and Liechtenstein). | ||
| All states. | 30 days, extendable once. | ||
| All states | 90 days. | ||
| All states. | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[67][68][69][70] | 30 days. | ||
| Norway.[71][72] | All others. | 15 days. | |
| Middle East and Caucasus | |||
| Country | Visa not required | Visa required | Notes |
| All states.[73][74] | 180 days. | ||
| All states.[75][76] | 1 year. | ||
| All states.[77][78] | 3 months. | ||
| Europe | |||
| Country | Visa not required | Visa required | Notes |
| All states.[79] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[80] | |||
| All states.[81][82] | 5 days. Must enter through the Minsk National Airport. | ||
| All states.[83] | 90 days within 180 days. | ||
| All states. | Freedom of movement. | ||
| All states.[84] | 90 days within 180 days. | ||
| All states.[85] | 90 days within 180 days. | ||
| All states.[86] | 90 days within 180 days. | ||
| All states.[87] | |||
| All states.[88] | |||
| All states.[89] | 90 days within 180 days. | ||
| All states.[90] | 90 days within 180 days. | ||
| All states.[91] | 90 days within 180 days. | ||
| All states.[92][93] | 6 months.[94] | ||
| All states. | |||
| Oceania | |||
| Country | Visa not required | Visa required | Notes |
| All states (eVisitor).[95] | 90 days on each visit in 12-month period if granted. | ||
| All states.[96] | 4 months. | ||
| All states.[97] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[98] | 90 days within 180 days. | ||
| All states.[99] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[100] | 90 days. | ||
| All states.[101] | 90 days within any 180 day period. | ||
| All states.[102] | 90 days. | ||
| All states[citation needed] | 90 days. | ||
| All states. | 90 days. | ||
| All others.[103] | Iceland | 90 days. | |
All EFTA nationals can visit the following partially recognised countries or territories with autonomous immigration policies without a visa:
|
|
Reciprocity
[edit]
The EFTA member states are all part of the Schengen Area, an area comprising 29 European states that have eliminated border controls with other Schengen members and strengthened border controls with non-Schengen countries. The Schengen area mostly functions as a single country for international travel purposes, with a common visa policy. Since 2001, the European Union has issued two lists regarding visas for the Schengen Area: a white list of countries whose nationals do not require visas (Annex II)[114] and a black list of countries whose nationals do require visas (Annex I).[115] As per Regulation No 539/2001 (amended by Regulation No 1289/2013)[116] reciprocity is required from all Annex II countries and territories. That means that these countries must offer visa-free access for 90 days to citizens of the 29 Schengen member states.
When this is not the case, the affected Schengen member state is expected to notify the European Commission. Starting six months after the notification, the Commission may adopt an implementing act to suspend the visa-free regime for certain categories of nationals of the third country concerned, for a period of up to six months, with a possible prolongation by further periods of up to six months. If the Commission decides not to adopt such an act, it has to present a report explaining the reasons why it did not propose the measure. If after two years from the notification the third country is still requiring visas from citizens of one or more Member States, the Commission shall adopt a delegated act to re-impose the visa obligation on all citizens of the third country, for a period of 12 months. Either the European Parliament or the Council could oppose the entry into force of the delegated acts.[116] All of the states that implement the common visa rules – including Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, Switzerland, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus and Romania – may notify the European Commission about non-compliant third states.[117]
According to a report from April 2015,[118] the Commission dismissed notifications by both Bulgaria and Romania of a general visa requirement by Australia.[119] It concluded that the Australian electronic visa 'manual processing' treatment should not be considered as equivalent to the Schengen visa application procedures and consequently will not be covered by the reciprocity mechanism.[118] In its previous report,[120] the Commission also committed to assessing certain provisions of the US electronic visa system — such as the application fee. In its previous report,[120] the Commission also committed to assessing certain provisions of the US ESTA system — such as the application fee — and the Australian eVisitor system.
Special requirements
[edit]The following countries require electronic registrations for all EFTA nationals:
- Australia requires EFTA nationals to obtain an eVisitor, which is issued free of charge.
- Canada requires EFTA nationals to obtain an eTA. The application fee is 7 CAD.
- New Zealand requires EFTA nationals to obtain an NZeTA and IVL if arriving by air. The application fee is NZD 9 or 12 and NZD 35.
- United States requires EFTA nationals to obtain an ESTA. The application fee is US$21.
-
Visa policy of the Schengen Area
Visa on arrival
[edit]The following countries provide visa on arrival to EFTA nationals. Some countries may not provide visa on arrival facilities at all entry points.
| Visa on arrival for citizens of all EFTA states |
Notes |
|---|---|
| 14 days. BD 25.[122] | |
| 30 days. Fees vary per country. Extensions are possible.[125] | |
| 1 month, extension possible. XOF 47,000 to XOF 61,000.[126] | |
| 30 days. USD 20.[127] | |
| EUR 25.[129] | |
| 50 USD. EUR 30.[131] | |
| 1 month. EUR 75.[133] | |
| 30 days. USD 25.[134] | |
| 90 days. EUR 85.[136] | |
| 30 days. USD 35.[137] | |
| 30 days. EUR 30–80.[139] | |
| 30 days. Free of charge.[142][143] | |
| 3 months, extendable once. USD 50.[145] | |
| 3 months. KWD 3.[146] | |
| 30 days. USD 30.[149] | |
| 1 month extendable for 2 additional months.[152] | |
| 30 days. Free of charge.[154] | |
| 30 days. Extendable up to 90 days. Fees vary. | |
| 30 days. Free of charge. Extendable up to 90 days, MVR 750.[157] | |
| 30 days, extendable up to 60 days.[citation needed] | |
| 90 days. USD 25-100.[162] | |
| 3 months. OMR 5-20.[164] | |
| 60 days. Free of charge.[165][166] | |
| 59 days. USD 50.[167] | |
| 1 month. QAR 50-150.[169] | |
| 30 days, extendable up to 150 days. Fees vary.[170] | |
| 90 days. USD 20.[173] | |
| USD 50 - USD 100.[175] | |
| 7 days, extendable for 90 days. XOF 10,000-90,000.[176] | |
| USD 100.[178] | |
| 90 days. USD 50 - USD 80.[176] | |
| 3 months. USD 30 - USD 70.[180] |
| Visa on arrival available to the citizens of some EFTA countries. Some countries may not provide visa on arrival facilities at all entry points. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Country | Visa on arrival available to citizens of | Notes |
| Norway, Switzerland[182] | USD 20.[183] | |
| Iceland, Norway, Switzerland[184] | USD 100 | |
Limited visa on arrival
[edit] Burundi - Visas are issued on arrival if an Entry Authorisation letter was issued by the authorities of Burundi.[185]
Burundi - Visas are issued on arrival if an Entry Authorisation letter was issued by the authorities of Burundi.[185] Iraq – Holders of ordinary passports of all EFTA member states except Switzerland may obtain a visa on arrival for Iraqi Kurdistan valid for 15 days when arriving through the Erbil International Airport or Sulaimaniyah International Airport.[186]
Iraq – Holders of ordinary passports of all EFTA member states except Switzerland may obtain a visa on arrival for Iraqi Kurdistan valid for 15 days when arriving through the Erbil International Airport or Sulaimaniyah International Airport.[186] Pakistan - Nationals from Norway and Switzerland may obtain visa on arrival when travelling on business. They must have a local sponsor who must obtain an approval from the immigration authorities at the port of arrival (Islamabad, Lahore, Peshawar, Quetta or Karachi airports) and a recommendation letter from country of residence or invitation letter from Pakistan.[187] Nationals of Iceland and Norway may obtain a visa on arrival for a maximum stay of 30 days, if they are travelling as part of a group through a designated tour operator.[188]
Pakistan - Nationals from Norway and Switzerland may obtain visa on arrival when travelling on business. They must have a local sponsor who must obtain an approval from the immigration authorities at the port of arrival (Islamabad, Lahore, Peshawar, Quetta or Karachi airports) and a recommendation letter from country of residence or invitation letter from Pakistan.[187] Nationals of Iceland and Norway may obtain a visa on arrival for a maximum stay of 30 days, if they are travelling as part of a group through a designated tour operator.[188] Somalia - Visas are issued on arrival for 30 days (extendable once) provided an invitation letter issued by the sponsor has been submitted to the Airport Immigration Department at least 2 days before arrival.[189]
Somalia - Visas are issued on arrival for 30 days (extendable once) provided an invitation letter issued by the sponsor has been submitted to the Airport Immigration Department at least 2 days before arrival.[189] Vietnam - Visitors can obtain a visa on arrival for a maximum stay of 1 or 3 months if they are holders of an approval letter issued and stamped by the Vietnamese Immigration Department (obtainable online through travel agencies for a fee) and if arriving only at airports in Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City or Da Nang.[190] All travellers can visit Phú Quốc without a visa for up to 30 days.[191][192]
Vietnam - Visitors can obtain a visa on arrival for a maximum stay of 1 or 3 months if they are holders of an approval letter issued and stamped by the Vietnamese Immigration Department (obtainable online through travel agencies for a fee) and if arriving only at airports in Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City or Da Nang.[190] All travellers can visit Phú Quốc without a visa for up to 30 days.[191][192]
Online visas
[edit]The following countries provide electronic visas to EFTA nationals.
| Electronic visas available to citizens of the EFTA states |
Notes |
|---|---|
| Available to all EFTA nationals. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals.Visa on arrival also available. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. Visa on arrival also available. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. Visa on arrival also available. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. Visa on arrival also available. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. Visa on arrival also available. | |
| Available to citizens of Iceland, Norway and Switzerland. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. Visa on arrival also available. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. Visa on arrival also available. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. Visa on arrival also available. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. Visa on arrival also available. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. Visa on arrival also available. | |
| Available to the citizens of Norway. However, Norwegian citizens do not require a visa for visits up to 15 days. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. Visa on arrival also available. | |
| Available to all EFTA nationals. Visa on arrival also available. |
Prearranged visa required
[edit]All EFTA citizens must always arrange the visa prior to travel to (as of March 2017) the following countries.
| Prearranged visa required for citizens of all EFTA states |
Notes |
|---|---|
| Except short term visits in transit and Hainan. | |
| Can be obtained in travel agencies or airlines. | |
| Outside Iraqi Kurdistan | |
| 15 days visa-free within the territory covered by the agreement for holders of a border traffic permit. (Eligible inhabitants of the border regions in Norway and Russia).[217][218][219] | |
Other
[edit] China – Citizens of Iceland and Switzerland transiting through People's Republic of China at one of the following airports and other ports of entry may visit the city for up to: 72 hours – Changsha, Chengdu, Chongqing, Dalian, Guangzhou, Guilin, Harbin, Kunming, Qingdao, Shenyang, Tianjin, Wuhan, Xi'an and Xiamen, 144 hours – Beijing's Capital International airport and West Railway station, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Shanghai's Hongqiao and Pudong international airports, railway station and port, Shijiazhuang Zhengding International Airport, Tianjin's Binhai International Airport and International Cruise Homeport and Qinhuangdao Port.[220][221][222] Visa-free access to Hainan Island as long as the visit lasts 15 days or less and is part of a tour group organised by a National Tourism Administration of China-approved travel agency based in Hainan is granted to the following EFTA nationals - Norway and Switzerland.[223]
China – Citizens of Iceland and Switzerland transiting through People's Republic of China at one of the following airports and other ports of entry may visit the city for up to: 72 hours – Changsha, Chengdu, Chongqing, Dalian, Guangzhou, Guilin, Harbin, Kunming, Qingdao, Shenyang, Tianjin, Wuhan, Xi'an and Xiamen, 144 hours – Beijing's Capital International airport and West Railway station, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Shanghai's Hongqiao and Pudong international airports, railway station and port, Shijiazhuang Zhengding International Airport, Tianjin's Binhai International Airport and International Cruise Homeport and Qinhuangdao Port.[220][221][222] Visa-free access to Hainan Island as long as the visit lasts 15 days or less and is part of a tour group organised by a National Tourism Administration of China-approved travel agency based in Hainan is granted to the following EFTA nationals - Norway and Switzerland.[223] Nauru – Simplified visa procedure for citizens of Iceland and Norway. Unlike other visitors, they do not have to submit a criminal record certificate and a certificate of medical fitness together with visa application.[224]
Nauru – Simplified visa procedure for citizens of Iceland and Norway. Unlike other visitors, they do not have to submit a criminal record certificate and a certificate of medical fitness together with visa application.[224] Russia - all EFTA nationals are eligible for eVisa access to Kaliningrad Oblast for up to 8 days.[225]
Russia - all EFTA nationals are eligible for eVisa access to Kaliningrad Oblast for up to 8 days.[225] Uzbekistan – Simplified visa procedure that waives invitation letter requirement is in force for the citizens of Switzerland.[226]
Uzbekistan – Simplified visa procedure that waives invitation letter requirement is in force for the citizens of Switzerland.[226] Zambia /
Zambia /  Zimbabwe - a universal KAZA visa that is valid for both countries can be issued on arrival to citizens of all EFTA member states.[227][228][229]
Zimbabwe - a universal KAZA visa that is valid for both countries can be issued on arrival to citizens of all EFTA member states.[227][228][229] Kenya /
Kenya /  Rwanda /
Rwanda /  Uganda - an East Africa Borderless Visa: Travelers from any country can obtain a multiple entry visa that allows entry to these three countries for tourism over period of 90 days. Visa must be first used in the country that issued it.[230]
Uganda - an East Africa Borderless Visa: Travelers from any country can obtain a multiple entry visa that allows entry to these three countries for tourism over period of 90 days. Visa must be first used in the country that issued it.[230]
Non-ordinary passports
[edit]In addition to visa requirements for normal passport holders certain countries have specific visa requirements towards diplomatic and various official passport holders:
| Country | Visa-free access |
|---|---|
| Russia (diplomatic passports) | |
| Russia (diplomatic passports), Thailand (diplomatic or official passports), | |
| Azerbaijan (diplomatic passports), India (diplomatic passports), Kazakhstan (diplomatic passports), Mexico (diplomatic, official or service passports), Pakistan (diplomatic passports), Philippines (diplomatic, official or service passports), Russia (diplomatic passports), Turkey (diplomatic passports) | |
| Algeria (diplomatic or official passports), Angola (diplomatic passports), China (diplomatic passports), Cuba (diplomatic passports), India (diplomatic passports), Indonesia (diplomatic or service passports), Iran (diplomatic passports), Kazakhstan (diplomatic passports), Kuwait (diplomatic or official passports), Qatar (diplomatic or official passports), Russia (diplomatic passports), Thailand (diplomatic or official passports), Vietnam (diplomatic passports) |
Cape Verde, Ethiopia, Mali and Zimbabwe grant visa-free access to holders of diplomatic or service passports issued to nationals of any country. Mauritania and Senegal grant visa-free access to holders of diplomatic passports issued to nationals of any country (except Italy for Mauritania). Bahrain, Bangladesh, Burkina Faso, Cambodia and South Sudan allow holders of diplomatic, official, service and special passports issued to nationals of any country to obtain a visa on arrival.
Non-visa restrictions
[edit]Blank passport pages
[edit]Many countries require a minimum number of blank pages to be available in the passport being presented, typically one or two pages.[231] Endorsement pages, which often appear after the visa pages, are not counted as being valid or available.
Vaccination
[edit]
Many African countries, including Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone and Togo, South Sudan, Uganda, and Zambia, require all incoming passengers older than nine months to one year[232] to have a current International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis, as does the South American territory of French Guiana.[233]
Some other countries require vaccination only if the passenger is coming from an infected area or has visited one recently or has transited for 12 hours in those countries: Algeria, Botswana, Cabo Verde, Chad, Djibouti, Egypt, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Lesotho, Libya, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritania, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, Papua New Guinea, Seychelles, Somalia, South Africa, Sudan, Tunisia, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe.[234][235]
Passport validity length
[edit]Very few countries, such as Paraguay, just require a valid passport on arrival.
However many countries and groupings now require only an identity card – especially from their neighbours. Other countries may have special bilateral arrangements that depart from the generality of their passport validity length policies to shorten the period of passport validity required for each other's citizens[236][237] or even accept passports that have already expired (but not been cancelled).[238]
Some countries, such as Japan,[239] Ireland and the United Kingdom,[240] require a passport valid throughout the period of the intended stay.
In the absence of specific bilateral agreements, countries requiring passports to be valid for at least 6 more months on arrival include Afghanistan, Algeria, Anguilla, Bahrain,[241] Bhutan, Botswana, British Virgin Islands, Brunei, Cambodia, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Cayman Islands, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Costa Rica, Côte d'Ivoire, Curaçao, Ecuador, Egypt, El Salvador, Equatorial Guinea, Fiji, Gabon, Guinea Bissau, Guyana, Haiti, India, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Israel,[242] Jordan, Kenya, Kiribati, Kuwait, Laos, Madagascar, Malaysia, Marshall Islands, Mongolia, Myanmar, Namibia, Nepal, Nicaragua, Nigeria, Oman, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Peru,[243] Philippines,[244] Qatar, Rwanda, Samoa, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Solomon Islands, Somalia, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Suriname, Tanzania, Thailand, Timor-Leste, Tokelau, Tonga, Turkey, Tuvalu, Uganda, United Arab Emirates, Vanuatu, Venezuela, and Vietnam.[245]
Countries requiring passports valid for at least 4 months on arrival include Micronesia and Zambia.
Countries requiring passports with a validity of at least 3 months beyond the date of intended departure include Azerbaijan, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Honduras, Montenegro, Nauru, Moldova and New Zealand. Similarly, the EEA countries of Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, all European Union countries (except Ireland) together with Switzerland also require 3 months validity beyond the date of the bearer's intended departure unless the bearer is an EEA or Swiss national.
Countries requiring passports valid for at least 3 months on arrival include Albania, North Macedonia, Panama, and Senegal.
Bermuda requires passports to be valid for at least 45 days upon entry.
Countries that require a passport validity of at least one month beyond the date of intended departure include Eritrea, Hong Kong, Lebanon, Macau, the Maldives[246] and South Africa.
Criminal record
[edit]Some countries, including Australia, Canada, Fiji, New Zealand and the United States,[247] routinely deny entry to non-citizens who have a criminal record while others impose restrictions depending on the type of conviction and the length of the sentence.
Persona non grata
[edit]The government of a country can declare a diplomat persona non grata, banning him from entering the country or expelling him if he has already entered. In non-diplomatic use, the authorities of a country may also declare a foreigner persona non grata permanently or temporarily, usually because of unlawful activity.[248]
Israeli stamps
[edit]
Kuwait,[249] Lebanon,[250] Libya,[251] Syria,[252] and Yemen[253] do not allow entry to people with passport stamps from Israel or whose passports have either a used or an unused Israeli visa, or where there is evidence of previous travel to Israel such as entry or exit stamps from neighbouring border posts in transit countries such as Jordan and Egypt.
To circumvent this Arab League boycott of Israel, the Israeli immigration services have now mostly ceased to stamp foreign nationals' passports on either entry to or exit from Israel (unless the entry is for some work-related purposes). Since 15 January 2013, Israel no longer stamps foreign passports at Ben Gurion Airport. Passports are still (as of 22 June 2017[update]) stamped at Erez when passing into and out of Gaza.[citation needed]
Iran refuses admission to holders of passports containing an Israeli visa or stamp that is less than 12 months old.
Biometrics
[edit]Several countries mandate that all travellers, or all foreign travellers, be fingerprinted on arrival and will refuse admission to or even arrest travellers who refuse to comply. In some countries, such as the United States, this may apply even to transit passengers who merely wish to change planes rather than go landside.[254]
Fingerprinting countries/regions include Afghanistan,[255][256] Argentina,[257] Brunei, Cambodia,[258] China,[259] Ethiopia,[260] Ghana, Guinea,[261] India, Japan,[262][263] Kenya (both fingerprints and a photo are taken),[264] Malaysia upon entry and departure,[265] Mongolia, Saudi Arabia,[266] Singapore, South Korea,[267] Taiwan, Thailand,[268] Uganda,[269] the United Arab Emirates and the United States.
Many countries also require a photo be taken of people entering the country. The United States, which does not fully implement exit control formalities at its land frontiers (although long mandated by its own legislation),[270][271][272] intends to implement facial recognition for passengers departing from international airports to identify people who overstay their visa.[273]
Together with fingerprint and face recognition, iris scanning is one of three biometric identification technologies internationally standardised since 2006 by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) for use in e-passports[274] and the United Arab Emirates conducts iris scanning on visitors who need to apply for a visa.[275][276] The United States Department of Homeland Security has announced plans to greatly increase the biometric data it collects at US borders.[277] In 2018, Singapore began trials of iris scanning at three land and maritime immigration checkpoints.[278][279]
Passport rankings
[edit]Passport rankings by the number of countries and territories their holders could visit without a visa or by obtaining visa on arrival as of 5 October 2021[update] were as follows: Swiss — 186 countries and territories (ranked 6th) Norwegian — 185 (7th); Icelandic — 180 (12th), and Liechtenstein — 178 (14th), according to the Henley Passport Index.[280]
Freedom of movement within EFTA and the EEA
[edit]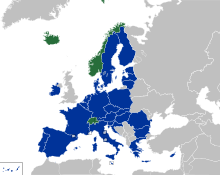
EFTA member states' citizens enjoy freedom of movement in each other's territories in accordance with the EFTA convention.[1] EFTA nationals also enjoy freedom of movement in the European Union (EU). EFTA nationals and EU citizens and are not only visa-exempt but are legally entitled to enter and reside in each other's countries. The Citizens’ Rights Directive[2] (also sometimes called the "Free Movement Directive") defines the right of free movement for citizens of the European Economic Area (EEA),[3] which includes the three EFTA members Iceland, Norway and Liechtenstein and the member states of the EU. Switzerland, which is a member of EFTA but not of the EEA, is not bound by the Directive but rather has a separate bilateral agreement on free movement with the EU.
As a result, de facto, a citizen of an EFTA country can live and work in all the other EFTA countries and in all the EU countries, and a citizen of an EU country can live and work in all the EFTA countries (but for voting and working in sensitive fields, such as government / police / military, citizenship is often required, and non-citizens may not have the same rights to welfare and unemployment benefits as citizens).[281]
As an alternative to holding a passport, a valid national identity card can also be used to exercise the right of free movement within EFTA[282] and the EU/EEA[2][4] Travellers should still bring a passport or national identity card, as one may be required. Strictly speaking, it is not necessary for an EEA or Swiss citizen to possess a valid passport or national identity card to enter the EEA or Switzerland. In theory, if an EEA or Swiss citizen outside of both the EEA and Switzerland can prove his/her nationality by any other means (e.g. by presenting an expired passport or national identity card, or a citizenship certificate), he/she must be permitted to enter the EEA or Switzerland. An EEA or Swiss citizen who is unable to demonstrate his/her nationality satisfactorily must nonetheless be given 'every reasonable opportunity' to obtain the necessary documents or to have them delivered within a reasonable period of time or corroborate or prove by other means that he/she is covered by the right of free movement.[283][284][285]
However, EEA member states and Switzerland can refuse entry to an EEA/Swiss national on public policy, public security or public health grounds where the person presents a "genuine, present and sufficiently serious threat affecting one of the fundamental interests of society".[286] If the person has obtained permanent residence in the country where he/she seeks entry (a status which is normally attained after 5 years of residence), the member state can only expel him/her on serious grounds of public policy or public security. Where the person has resided for 10 years or is a minor, the member state can only expel him/her on imperative grounds of public security (and, in the case of minors, if expulsion is necessary in the best interests of the child, as provided for in the Convention on the Rights of the Child).[287] Expulsion on public health grounds must relate to diseases with 'epidemic potential' which have occurred less than 3 months from the person's the date of arrival in the Member State where he/she seeks entry.[288]
A family member of an EEA/Swiss citizen who is in possession of a residence permit indicating their status is exempt from the requirement to hold a visa when entering the European Economic Area or Switzerland when they are accompanying their EEA/Swiss family member or are seeking to join them.[289] However the UK requires family members to obtain a special permit in order to enter the United Kingdom.[290] Non-EEA family members will need a Schengen Visa before they travel to Switzerland even if they possess a UK residence permit that clearly mentions that they are the family member of an EEA citizen.
Consular protection of EFTA nationals abroad
[edit]When in a foreign country, Norwegian and Icelandic citizens can seek help from the mission of any of the Nordic countries if their own country does not have a diplomatic mission in the country they are visiting. This is according to the Helsinki Treaty, which state that public officials in the foreign services of any of the Nordic countries are to assist citizens of another Nordic country if that country is not represented in the territory concerned.[291][292]
The Principality of Liechtenstein maintains a very small network of diplomatic missions. Switzerland is representing Liechtenstein in those countries wherein Liechtenstein itself does not maintain consular representation.[293]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b "Short Overview of the EFTA Convention". Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- ^ a b c "EUR-Lex - 32004L0038R(01) - EN - EUR-Lex". Eur-lex.europa.eu. 29 June 2004. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ a b Decision of the EEA Joint Committee No 158/2007 of 7 December 2007 amending Annex V (Free movement of workers) and Annex VIII (Right of establishment) to the EEA Agreement, 2008-05-08, retrieved 2021-01-01
- ^ a b "EUR-Lex - 22002A0430(01) - EN". Official Journal L 114, 30/04/2002 P. 0006 - 0072. Retrieved 2020-12-19.
- ^ Requirements for visa application, Government of Botswana.
- ^ Requirements for visa application, Government of Botswana.
- ^ Requirements for visa application, Government of Botswana.
- ^ Requirements for visa application, Government of Botswana.
- ^ Visa policy of Cape Verde
- ^ "Eswatini Government". www.gov.sz. Retrieved 2020-10-28.
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ "Visa Exemptions". Lesotho E-Visa. 2017-03-28. Retrieved 2020-10-28.
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ "Foreign Nationals | Embassy of the Republic of Namibia in Washington, D.C." www.namibiaembassyusa.org. Retrieved 2020-10-28.
- ^ "Visa Information—Senegal". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 30 October 2015. Archived from the original on 19 December 2019. Retrieved 30 October 2015.
- ^ "EUR-Lex - 22009A0630(05) - EN". Europa.eu. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Department of Home Affairs - Exempt Countries". www.dha.gov.za. Retrieved 2020-10-28.
- ^ airport, Tunis international. "Visas and entry conditions in Tunisia". www.aeroportdetunis.com. Retrieved 2020-10-28.
- ^ "Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Antigua and Barbuda". 18 April 2010. Archived from the original on 18 April 2010. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions". Bahamashclondon.net. Archived from the original on 30 June 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Microsoft Word - 1. Visa List - June 2012.doc" (PDF). Foreign.gov.bb. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-02-15. Retrieved 2017-03-03.
- ^ "AGREEMENT BETWEEN THE EUROPEAN UNION AND THE COMMONWEALTH OF DOMINICA ON THE SHORT-STAY VISA WAIVER" (PDF). Data.consilium.europa.eu. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Entry Requirements : Discover Dominica, the Nature Island". Dominica.dm. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Do I Need a Visa to Enter into Dominica? - Government of the Commonwealth of Dominica". 13 February 2013. Archived from the original on 13 February 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Embassy of the Dominican Republic, in the United States". Domrep.org. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "AGREEMENT BETWEEN THE EUROPEAN UNION AND GRENADA ON THE SHORT-STAY VISA WAIVER" (PDF). Data.consilium.europa.eu. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Citizens Of The Following Countries Do Not Need A Visa To Enter Grenada" (PDF). 18 October 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 October 2014. Retrieved 2023-04-02.
- ^ "Embassy of Haiti – Washington, DC". Haiti.org. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Countries that need Visas to Travel to St. Kitts and Nevis - Ministry of Foreign Affairs". Govt.kn. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Exempted Countries". ins.gov.bz. Retrieved 2020-10-27.
- ^ Branch, Government of Canada, Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada, Communications (15 April 2015). "Electronic Travel Authorization (eTA)". Canada.ca. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Costa Rica Tourism Official Website. Hotels, travel agencies, car rental and tours". Visitcostarica.com. Archived from the original on 3 March 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Ministerio de Relaciones Exteriores de El Salvador - Inicio". Rree.gob.sv. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Ministerio de Relaciones Exteriores de Guatemala". Minex.gob.gt. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Secretaría de Relaciones Exteriores de Honduras". Sre.gob.hn. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Instituto Nacional de Migración - Gobierno - gob.mx". Inm.gob.mx. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "MINISTERIO DE RELACIONES EXTERIORES-CONFERENCIA UN". 6 June 2007. Archived from the original on 6 June 2007. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Authorized Visa" (PDF). 29 December 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 December 2009. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Dirección Nacional de Migraciones - Accesible". Migraciones.gov.ar. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Entrance Visas in Brazil" (PDF). Sistemas.mre.gov.br. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Ministerio de Relaciones Exteriores de Chile - Visas". Minrel.gob.cl. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Agreement - Consilium". Europa.eu. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Ministerio de Relaciones Exteriores y Movilidad Humana – Ecuador". Cancilleria.gob.ec. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa Entry Requirements (countries) – Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation| Co-operative Republic of Guyana". Archived from the original on 2018-09-12. Retrieved 2020-10-27.
- ^ "ACUERDOS BILATERALES SUSCRITOS POR EL PARAGUAY EN MATERIA DE "SUPRESIÓN DE VISAS"" (PDF). Mre.gov.py. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 November 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "..:: Dirección Nacional de Migración ::." 18 December 2008. Archived from the original on 18 December 2008. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Home". 25 October 2007. Archived from the original on 25 October 2007. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information". Mofat.gov.bn. Archived from the original on 28 July 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Warga Dari 75 Negara Ini Bebas Lakukan Kunjungan Wisata Ke Indonesia Tanpa Visa". Setkab.go.id. 7 October 2015. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Exemption of Visa (Short-Term Stay)". Mofa.go.jp. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ KMI. "45 countries with 30 days visa-free regime". Mfa.kz. Archived from the original on 30 December 2016. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa Requirement by Country". Imi.gov.my. Archived from the original on 28 November 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Guidelines on the Entry of Temporary Visitors to the Philippines". Dfa.gov.ph. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ Korea, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of. "Visit to Korea > Visa". Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 24 August 2013. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Countries/Regions Requiring Visa". Ica.gov.sg. Archived from the original on 16 October 2015. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ "BaiViet - EXEMPTION OF ENTRY VISA TO VIETNAM". 6 October 2010. Archived from the original on 6 October 2010. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ Newspaper, Tuoi Tre (7 June 2016). "Official: Vietnam to scrap visas for five European countries in July". Tuoitrenews.vn. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Who does not need visa to travel to Armenia?" (PDF). 15 January 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 January 2013. Retrieved 2023-04-02.
- ^ "Visafree List" (PDF). 16 January 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Ministry Of Foreign Affairs Of Georgia - Interviews". 13 August 2008. Archived from the original on 13 August 2008. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ Georgia, Civil. "Civil.Ge - Georgia Restores One-Year Visa-Free Rules". Civil.ge. Archived from the original on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Tourist Visa Table" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 May 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ German citizens born before January 1, 1928 need a visa for Israel, which will be issued for free if one was not a member of the Nazi party or involved in crimes committed during the time of the Nazi Germany.
- ^ "Ministria e Punëve të Jashtme" (PDF). Punetejashtme.gov.al. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Turisme d'Andorra. Useful information on the Principality". Visitandorra.com. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Information on visa-free travel via the checkpoint "Minsk National Airport" - Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Belarus". Mfa.gov.by. Archived from the original on 16 January 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "List of States which citizens can visit Belarus for 5-days visa-free" (PDF). Mfa.gov.by. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Vize". Mfa.ba. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Ministry of Foreign Affairs and European Integration of the RM". Gov.md. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Overview of visa regimes for foreign citizens". Mvpei.gov.me. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa Regime". 18 January 2013. Archived from the original on 18 January 2013. Retrieved 2023-04-02.
- ^ "FAQ Monaco". Visitmonaco.com. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Border formalities - Ufficio di Stato per il Turismo". visitsanmarino.com. Archived from the original on 24 July 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Consular countries". mfa.gov.rs. Archived from the original on 27 July 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "From Rep. Of Türkiye Ministry of Foreign Affairs". www.mfa.gov.tr. Retrieved 2020-03-04.
- ^ "Entry regime and visa requirements for foreigners entering Ukraine - MFA of Ukraine". mfa.gov.ua. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visiting the UK: information for EU, EEA and Swiss citizens". GOV.UK. Retrieved 2020-02-01.
- ^ "UK visa requirements (accessible version)". GOV.UK. Retrieved 2021-01-01.
- ^ "The UK's points-based immigration system: information for EU citizens". GOV.UK. Retrieved 2020-12-29.
- ^ "EVisitor (Subclass 651)". Archived from the original on 2013-09-26. Retrieved 2013-09-25.
- ^ "Visa". 6 June 2012. Archived from the original on 6 June 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "EU and Republic of Kiribati sign agreement - Fiji Times Online". Fijitimes.com. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Federated States of Micronesia -YAP, CHUUK, POHNPEI, KOSRAE-". Visit-micronesia.fm. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "New Zealand Visas - Immigration New Zealand". Glossary.immigration.govt.nz. Archived from the original on 12 January 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Palau enters visa waiver deal with European Union". Guampdn.com. 9 December 2015. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Agreement between the European Union and the independent State of Samoa on the short-stay visa waiver". Data.consilium.europa.eu. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Concessional entry arrangement countries". Solomon Islands Gazette. 2017-01-26.
- ^ "Visa Exempt". Immigration.gov.vu. Retrieved 2022-03-07.
- ^ "入 境 事 務 處". immd.gov.hk. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Public Security Police Force". fsm.gov.mo. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Tonga". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "Bureau of Consular Affairs, Ministry of Foreign Affairs". 31 October 2009. Archived from the original on 31 October 2009. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Special Categories Exempted From Visa Requirements - For Foreign Citizens - Consular Services - Ministry of Foreign Affairs - Republic of Kosovo". mfa-ks.net. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "VISA Regulations". 4 March 2014. Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- ^ "О визах - Министерство иностранных дел". mfa-rso.su. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Procedure of the Entry to the Territory of the Republic of South Ossetia - Министерство иностранных дел". mfa-rso.su. Archived from the original on 15 October 2013. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Transnistria useful information, warnings, visas, border crossings, budget accommodation". 5 February 2007. Archived from the original on 5 February 2007. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Rules and recommendations - Transnistria tour". Transnistria-tour.com. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ As listed in Annex II of the Council Regulation 539/2001.
- ^ As listed in annex I of the Council Regulation 539/2001.
- ^ a b "EUR-Lex - 32013R1289 - EN - EUR-Lex". new.eur-lex.europa.eu. Archived from the original on 3 February 2014. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ State of play and the possible ways forward as regards the situation of non-reciprocity with certain third countries in the area of visa policy, European Commission, 12 April 2016.
- ^ a b "Report from the Commission of 22.4.2015 assessing the situation of non-reciprocity with certain third countries in the area of visa policy" (PDF). European Commission. 22 April 2015. Retrieved 2 May 2015.
- ^ "Information from the Commission about notifications by the Member States of cases of non-reciprocity in accordance with Article 1(4)(a) of Council Regulation (EC) No 539/2001 as amended by Regulation (EU) No 1289/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council". European Commission. 12 April 2014. Retrieved 14 April 2014.
- ^ a b "Seventh report on certain third countries' maintenance of visa requirements in breach of the principle of reciprocity" (PDF). European Commission. 26 November 2012. Retrieved 27 November 2012.
- ^ "Bahrain Electronic Visa Service". Evisa.gov.bh. Archived from the original on 12 July 2018. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Bahrain". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ Available at Shahjalal International Airport, Shah Amanat International Airport and Osmani International Airport only.
- ^ Amin, Sandy Riopel, Ash. "Consulate General of the People's Republic of Bangladesh, Los Angeles, California". bangladeshconsulatela.com. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Visa Information—Bangladesh". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "Visa Information—Burkina Faso". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 17 December 2013. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ^ a b "Visa Information—Cambodia". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ Obtainable at Nelson Mandela International Airport, Cesária Évora Airport, Amílcar Cabral International Airport and Aristides Pereira International Airport.
- ^ a b "Visa Information—Cape Verde". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "Présidence de l'Union des Comores [Site officiel]". 5 December 2004. Archived from the original on 5 December 2004. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ a b "Visa Information—Comoros". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ Obtainable at Djibouti–Ambouli International Airport.[citation needed]
- ^ a b "Visa Information—Djibouti". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ a b "Visa Information—Egypt". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ Visa not required for up to 15 days in Sinai resorts.[according to whom?][citation needed]
- ^ a b "Visa Information—Guinea Bissau". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "Visa Information—Indonesia". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Obtainable at the airports in Chah-Bahar, Qeshm, Kish, Mashad, Esfahan, Shiraz, Tabriz and Tehran international airports.
- ^ "Visa Information—Iran". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 17 December 2013. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ^ Visa on arrival obtainable at most international ports of entry and at most international land border crossings (except King Hussein/Allenby Bridge crossing).
- ^ Board, Welcome to Jordan Tourism. "Visas To Jordan". visitjordan.com. Archived from the original on 6 May 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Jordan". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "Jordan axes visa fee to encourage tourists - News - Travel Trade Gazette". 8 May 2015. Archived from the original on 8 May 2015. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ Wakhusama, Ernest Wamboye. "A brief guide on getting a Kenya Visa on arrival - Xplorato Ventures". xplorato.com. Archived from the original on 4 March 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Kenya". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "Visa Information—Kuwait". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 17 December 2013. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ^ Available at international airports Wattay Vientiane, Pakse Savannakhet and Luang Prabang, and at land borders Friendship Bridge, Vientiane and Savannakhet; Nam Heuang Friendship Bridge, Sayabouly Province; and border crossings at Boten-Mohan, Dansavan-Lao Bao, Houaysay-Chiang Khong, Thakhek-Nakhon Phanom, Nong Haet-Nam Kan, Nam Phao-Kao Cheo, Veun Kham-Dong Calor, and Vangtao-Chong Mek as well as Tha Naleng train station in Vientiane, which connects to the train station in Nongkhai, Thailand. Entry points Napao-Chalo, Taichang-Sophoun, Pakxan-Bungkan, and Xiengkok are open only to visa holders.
- ^ "Visa-on-arrival". tourismlaos.org. Archived from the original on 27 March 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Laos". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ Obtainable at the land border with Syria, the port of Beirut, or Beirut International Airport.
- ^ "sub4". 11 August 2013. Archived from the original on 11 August 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Lebanon". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "Madagascar Visa Information, How To Obtain a Visa". madagascar-consulate.org. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Madagascar". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "Visa Information—Malawi". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ Beney. "Maldives Immigration". immigration.gov.mv. Archived from the original on 19 February 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Maldives". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "Visa Information—Mauritania". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Visa Information—Mozambique". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ Obtainable at Tribhuvan International Airport and certain land borders.
- ^ "Welcome to Department of Immigration, Nepal". 6 January 2002. Archived from the original on 6 January 2002. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Nepal". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "Welcome to OAMC". 13 August 2007. Archived from the original on 13 August 2007. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Oman". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "Visa Information—Papua New Guinea". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "Nationals from the following countries MUST obtain an Entry Permit from a PNG Mission" (PDF). Immigration.gov.png. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 March 2014. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Philippines". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ Available only at Doha International Airport.
- ^ "Visa Information—Qatar". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 17 December 2013. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ^ a b "Visa Information—Sri Lanka". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ ETA obtainable on arrival or online prior to arrival.
- ^ Obtainable at Johan Adolf Pengel International Airport.
- ^ "Visa Information—Suriname". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 17 December 2013. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ^ "Immigration Services Department of United Republic of Tanzania". 16 September 2012. Archived from the original on 16 September 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Tanzania". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ a b c "Visa Information—Togo". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "REQUIREMENTS FOR ENTRY INTO UGANDA - Ministry of Internal Affairs". 19 December 2012. Archived from the original on 19 December 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Uganda". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 26 November 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ "Zambia Visa & Immigration". zambiatourism.com. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Zimbabwe". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 17 December 2013. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ^ Obtainable at Addis Ababa Bole International Airport.
- ^ "Consular Service". ethiopianembassy.org. Archived from the original on 7 November 2013. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Ethiopia". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 17 December 2013. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ^ "Summary of countries entitled for visa exemption/waiver or visitor visa on arrival". Republic of the Marshall Islands, Ministry of Justice, Immigration & Labor, Division of Immigration. May 2018. Retrieved 6 January 2019.
- ^ "Visa Information—Burundi". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 17 December 2013. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ^ "Visa Information—Iraq". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 17 December 2013. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ^ "Visa Information—Pakistan". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 17 December 2013. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ^ "Directorate General of Immigration & Passports, Ministry of Interior, Government of Pakistan". dgip.gov.pk. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa Information—Somalia". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 17 December 2013. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ^ "Visa Information—Vietnam". timaticweb.com. Montreal, CAN: International Air Transport Association. 17 December 2013. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ^ html, www.sitecreation.com.au - web design, sydney, design, freelance. "Discover Phu Quoc - island paradise in the Gulf of Thailand, secluded and beautiful beaches, resorts and hotels on Phu Quoc island, Vietnam..." discoverphuquoc.com. Archived from the original on 23 February 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "No visa required for tourists to Phu Quoc on short stay - Vietsea Tourist - Travel to Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia and Thailand - Vietnam Travel Tours". vietseatourist.vn. Archived from the original on 1 July 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Home Page - The Electronic Visa System of Azerbaijan Republic". Evisa.gov.az. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Bahrain Electronic Visa Service". Evisa.gov.bh. Archived from the original on 11 August 2022. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Kingdom of Cambodia - Ministry of Foreign Affairs & International Cooperation". Evisa.gov.kh. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Gabon e-Visa". Dgdi.ga. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Indian e-Tourist Visa". indianvisaonline.gov.in. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ BESSIN, Effi Marcel. ":::SNEDAI:::". snedai.com. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ eCitizen. "eCitizen - Gateway to All Government Services". ecitizen.go.ke. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Kuwait e-Visa". Moi.gov.kw. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ International Air Transport Association (IATA), Travel Information Manual
- ^ a b "Myanmar eVisa (Official Government Website)". evisa.moip.gov.mm. Archived from the original on 2018-02-18.
- ^ "Nepal eVisa". nepalimmigration.gov.np. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "شرطة عمان السلطانية". www.rop.gov.om. Archived from the original on November 30, 2016.
- ^ "Characteristics of the unified e-visa and conditions for its issuance". Russian Consular Affairs. Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Russia.
- ^ "VISA". Migration.gov.rw. 2013-09-10. Retrieved 2013-10-22.
- ^ "Virtual Visa". www.smf.st. Archived from the original on 2015-05-21. Retrieved 2023-04-02.
- ^ "Online Visa Application". Eta.gov.lk. Retrieved 2013-10-22.
- ^ "Tajikistan e-Visa". Republic of Tajikistan Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 2016-06-05.
- ^ "Uganda e-Visa". immigration.go.ug. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Vietnam evisa - National portal on Immigration". Archived from the original on February 2, 2017.
- ^ Company, Alfa XP Software. "e-Visa". Zambiaimmigration.gov.zm. Archived from the original on 28 July 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Home". Evisa.gov.zw. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Visa-free zone between Norway and Russia". Visahouse.com. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Соглашение между Правительством Российской Федерации и Правительством Королевства Норвегия об упрощении порядка взаимных поездок жителей приграничных территорий Российской Федерации и Королевства Норвегия (с изменениями на 20 января 2016 года), Международное соглашение от 02 ноября 2010 года". Docs.cntd.ru. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Протокол о внесении изменений в приложение к Соглашению между Правительством Российской Федерации и Правительством Королевства Норвегия об упрощении порядка взаимных поездок жителей приграничных территорий Российской Федерации и Королевства Норвегия от 2 ноября 2010 года, Международный протокол от 20 января 2016 года". Docs.cntd.ru. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ Ministry of Public Security. "上海、江苏、浙江三省市实行部分国家外国人144小时过境免签政策及常遇边检问题解答". Archived from the original on 2016-11-05. Retrieved 2017-03-21.
- ^ "China's Yangtze River Delta Now Offers 144-hour Visa-free Entry". Mps.gov.cn. Archived from the original on January 27, 2016. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ L_204232. "京津冀对53国外国人实施144小时过境免签政策 - 资讯 - 海外网". news.haiwainet.cn. Retrieved 2018-01-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Hainan Regulated Visa Waiver Policy-Immigration Regulations--Website of Hainan International Tourism Island". en.visithainan.gov.cn. Archived from the original on 16 December 2013. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ "Immigration Regulations 2014 SL No. 2 of 2014" (PDF). Pacliii.org. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "The list of foreign States whose nationals can apply for e-visa". Consular Department of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation. Retrieved 1 July 2019.
- ^ "Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Uzbekistan — Visa of the Republic of Uzbekistan". Mfa.uz. Archived from the original on 8 February 2018. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "KAZA Visa for Zambia and Zimbabwe". kazavisa.info. Archived from the original on 21 July 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ "Kaza Visa Launch – Flame of Africa". 29 November 2014. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "KAZA UNIVISA Launch 2014 - Book Namibia". Booknamibia.com. 28 November 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Three countries, one visa". Safari-uganda.com. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ Baker, Vicky (20 June 2013). "Passport expiry dates and blank pages: what are the rules?". The Guardian. Retrieved 13 January 2024.
The number of remaining blank pages a passport should have is also an issue. Some travellers have reported arriving with one or less than one full page left and waiting for hours at immigration, until an official reluctantly grants them entry. The FCO lists no hard and fast rules because, in many cases, there aren't any.
- ^ "Yellow Fever". Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC). African Union. Retrieved 23 August 2021.
African countries that requires (sic) Yellow Fever vaccination certificate: Countries that require vaccination for all travellers older that 9 months or 1 year: Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameron, Central African Republic, Congo, Côte d'lvoire, DRC, Gabon, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Liberia, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, Niger, Togo.
- ^ "Fièvre jaune" (in French). September 2, 2018. Retrieved August 27, 2019.
- ^ "Yellow Fever". Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC). African Union. Retrieved 23 August 2021.
African countries that requires Yellow Fever vaccination certificate: Countries that requires (sic) vaccination for travellers from countries with risk of yellow fever transmission or transit for 12 hours in those countries: Algeria, Botswana, Cabo Verde, Chad, Djibouti, Egypt, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Lesotho, Libya, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritania, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, Papua New Guinea, Seychelles, Somalia, South Africa, Sudan, Tunisia, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe.
- ^ Country list - Yellow fever vaccination requirements and recommendations; and malaria situation; and other vaccination requirement
- ^ "Foreign Affairs Manual, 9 FAM 403.9-3(B)(2) f". U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 10 October 2017.
- ^ "Visitor Visa". travel.state.gov. US Department of State. Retrieved 13 January 2024.
Passport valid for travel to the United States – Your passport must be valid for at least six months beyond your period of stay in the United States (unless exempt by country-specific agreements). Each individual who needs a visa must submit a separate application, including any family members listed in your passport.
- ^ "Countries whose citizens are allowed to enter Turkey with their expired passports". Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Republic of Turkey. Archived from the original on 8 October 2015. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
Countries whose citizens are allowed to enter Turkey with their expired passports: 1. Germany – Passports expired within the last year / ID's expired within the last year, 2. Belgium - Passports expired within the last 5 years, 3. France - Passports expired within the last 5 years, 4. Spain - Passports expired within the last 5 years, 5. Switzerland - Passports expired within the last 5 years, 6. Luxemburg - Passports expired within the last 5 years, 7. Portugal - Passports expired within the last 5 years, 8. Bulgaria – Valid ordinary passport
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions". Embassy of Japan in Malaysia. Retrieved 13 January 2024.
Q: Do I need at least 6 months passport validity in order to enter Japan? A: Japan does not have any regulations relating to passport validity, so long as your passport will be valid until after you leave Japan.
- ^ "Entering the UK". Gov.UK. Retrieved 17 March 2021.
You're not from an EEA country: you must have a valid passport to enter the UK. It should be valid for the whole of your stay.
- ^ Bahrain government website
- ^ "Passports and Visa | GoIsrael - the Official Website of Tourism to Israel".
- ^ "Government Of Peru Requires Six-Month Validity On Passports To Enter Peru". Traveling & Living in Peru. 2 January 2019. Retrieved 17 March 2021.
- ^ "Bureau of Immigration of the Republic of the Philippines". Retrieved 17 March 2021.
- ^ Timatic
- ^ "Maldives Reduces Passport Validity Requirement of Minimum 6 Months to Just 1 Month". Corporate Maldives. 24 October 2020. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- ^ Government of Canada -- Overcome criminal convictions
- ^ "No entry for Modi into US: visa denied | India News - Times of India". The Times of India. Mar 18, 2005. Retrieved 2020-09-29.
- ^ "Travel Report - Kuwait". Voyage.gc.ca. 2012-11-16. Retrieved 2013-07-01.
- ^ Travel Advice for Lebanon - Australian Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade Archived 2008-12-24 at the Wayback Machine and Lebanese Ministry of Tourism Archived 2009-03-27 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Travel Advice for Libya - Australian Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade". Smartraveller.gov.au. Archived from the original on 2013-06-22. Retrieved 2013-07-01.
- ^ Travel Advice for Syria - Australian Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade Archived 2008-12-19 at the Wayback Machine and Syrian Ministry of Tourism
- ^ "Travel Advice for Yemen - Australian Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade". Smartraveller.gov.au. Archived from the original on 2011-08-20. Retrieved 2013-07-01.
- ^ Calder, Simon (24 April 2017). "Airline lobbying for a relaxation of draconian rules for London-Auckland travellers". The Independent. Archived from the original on 21 June 2022. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
Travellers heading west from the UK to New Zealand may soon be able to avoid the onerous requirement to clear US border control during the refuelling stop at Los Angeles airport (LAX). Unlike almost every other country in the world, the US insists on a full immigration check even for passengers who simply intend to re-board their plane to continue onwards to a foreign destination. Air New Zealand, which flies daily from Heathrow via Los Angeles to Auckland, says there are currently "strict requirements for travellers" in transit at LAX. Through passengers to Auckland on flight NZ1 or Heathrow on NZ2 must apply in advance for an ESTA (online visa) even though they have no intention of staying in the US. They also have to undergo screening by the Transportation Security Administration.
- ^ "How to enter Afghanistan. The Entry Requirements for Afghanistan - CountryReports". Countryreports.org.
- ^ Nordland, Rod (19 November 2011). "In Afghanistan, Big Plans to Gather Biometric Data". The New York Times.
- ^ "Argentina strengthens migratory control". Archived from the original on 2 December 2013.
- ^ "Cambodia Foreign Entry Requirements". Us-passport-information.com.
- ^ "China to Start Fingerprinting Foreign Visitors". Air Canada. 31 Jan 2019. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
Effective April 27, 2018, border control authorities at all of China's ports of entry, including its airports, will start collecting the fingerprints of all foreign visitors aged between 14 and 70. Diplomatic passport holders and beneficiaries of reciprocal agreements are exempted..
- ^ "Äthiopien: Reise- und Sicherheitshinweise". Auswaertiges-amt.de.
- ^ "Visa". paf.gov.gn.
- ^ "Japan fingerprints foreigners as anti-terror move". Reuters. 20 November 2016. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Anger as Japan moves to fingerprint foreigners - World". Theage.com.au. 2007-10-26.
- ^ "Immigration & Visas FAQs". Kenya Airports Authority. Retrieved 6 May 2019.
Will visitors still have their digital photo and fingerprints taken at the immigration desk on arrival? Yes, the need to have photos and fingerprints taken upon arrival is to authenticate that the person who applied for the Visa is the same person at the port of entry
- ^ "Malaysia". CountryReports. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia mandates fingerprints and biometrics for foreigners - SecureIDNews". secureidnews.com. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "S Korea to scan fingerprints of suspicious foreign visitors - People's Daily Online". peopledaily.com.cn. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "National News Bureau of Thailand".
- ^ AfricaNews (2019-01-14). "Gemalto awarded Uganda's new e-Immigration solution with fast-track border crossing eKiosks at Entebbe Airport". Africanews. Retrieved 2019-04-24.
- ^ Brown, Theresa Cardinal (9 May 2016). "Biometric Entry-Exit Update: CBP Developing Land Border Process". Bipartisan Policy Center. Retrieved 25 April 2019.
While a requirement for a biometric entry-exit system has been in law for over a decade, it is not yet a reality. Many reasons for the long gestating development have been documented in BPC's 2014 report Entry-Exit System: Progress, Challenges, and Outlook, including the technological, operational, and cost challenges of creating exit systems and infrastructure where none exist today. However, many critics, especially in Congress, simply accused the Department of Homeland security of dragging its feet... the major operational, logistical, and technical challenge in implementing exit capability at our ports has been the land borders. Unlike airports and seaports, the land border environment is not physically controlled, there is no means to get advance information on who is arriving, and the sheer volume of travel—both vehicular and pedestrian—creates challenges in any system to not further exacerbate delays. While biometric exit for land vehicular traffic is still in the "what if" stage, CBP is moving ahead and piloting systems and technology to use with the large population of pedestrian crossers at the U.S.-Mexico border.
- ^ Lipton, Eric (21 May 2013). "U.S. Quietly Monitors Foreigners' Departures at the Canadian Border". The New York Times. Retrieved 25 April 2019.
Long demanded by lawmakers in Congress, it is considered a critical step to developing a coherent program to curb illegal immigration, as historically about 30 percent to 40 percent of illegal immigrants in the United States arrived on tourist visas or other legal means and then never left, according to estimates by Homeland Security officials.
- ^ Lipton, Eric (15 December 2006). "Administration to Drop Effort to Track if Visitors Leave". The New York Times. Retrieved 25 April 2019.
Efforts to determine whether visitors actually leave have faltered. Departure monitoring would help officials hunt for foreigners who have not left, if necessary. Domestic security officials say, however, it would be too expensive to conduct fingerprint or facial recognition scans for land departures.
- ^ Campoy, Ana (17 April 2019). "The US wants to scan the faces of all air passengers leaving the country". Quartz. Retrieved 2019-04-24.
- ^ "ICAO Document 9303: Machine Readable Travel Documents, Part 9: Deployment of Biometric Identification and Electronic Storage of Data in MRTDs, 7th edition" (PDF). 2015. Retrieved 23 April 2019.
- ^ "Iris Scan Implemented at Doha International Airport". Archived from the original on 8 January 2012.
- ^ "Iris Scanner Could Replace Emirates ID In UAE". SimplyDXB. 11 June 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
The breach of privacy is probably the biggest threat to the biometric technique of iris recognition. Secondly, a device error can false reject or false accept the identity which can also have some heinous consequences. Lastly, the method isn't the most cost-effective one. It is complex and therefore expensive. Furthermore, the maintenance of devices and data can also be relatively burdensome. However, thanks to the oil money and spending ability of Dubai, they are economically equipped to effectively embrace this system.
- ^ Roberts, Jeff John (12 September 2016). "Homeland Security Plans to Expand Fingerprint and Eye Scanning at Borders". Fortune. Fortune Media IP Limited. Retrieved 24 April 2019.
Unlike with documents, it's very hard for a traveler to present a forged copy of a fingerprint or iris. That's why the U.S. Department of Homeland Security plans to vastly expand the amount of biometric data it collects at the borders. According to Passcode, a new program will ramp up a process to scan fingers and eyes in order to stop people entering and exiting the country on someone else's passport.
- ^ "Singapore tests eye scans at immigration checkpoints". Reuters. 6 August 2018. Retrieved 24 April 2019.
Singapore has started scanning travellers' eyes at some of its border checkpoints, its immigration authority said on Monday, in a trial of expensive technology that could one day replace fingerprint verification.
- ^ Lee, Vivien (6 August 2018). "5 Reasons We Prefer Iris Scans To Fingerprint Checks At Our Borders In Singapore". Retrieved 24 April 2019.
The iris technology could potentially scan irises covertly, as opposed to the scanning of thumbprints which necessitates active participation.
- ^ "Henley Passport Index" (PDF). Henley and Partners. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ "What is an EEA country? What is an EFTA country?". Livingingreece.gr. Retrieved 2017-05-08.
- ^ "APPENDIX 1 Movement of persons (Art. 20)" (PDF). ARTICLE 1.
- ^ Article 6.3.2 of the Practical Handbook for Border Guards (C (2006) 5186)
- ^ Judgement of the European Court of Justice of 17 February 2005, Case C 215/03, Salah Oulane vs. Ministervoor Vreemdelingenzaken en Integratie
- ^ "UK Border Force Operations Manual: Processing British and EEA Passengers without a valid Passport or Travel Document" (PDF). Ukba.homeoffice.gov.uk. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-08-08.
- ^ Article 27 of Directive 2004/38/EC (Directive 2004/38/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 on the right of citizens of the Union and their family members to move and reside freely within the territory of the Member States).
- ^ Article 28 of Directive 2004/38/EC (Directive 2004/38/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 on the right of citizens of the Union and their family members to move and reside freely within the territory of the Member States).
- ^ Article 29 of Directive 2004/38/EC (Directive 2004/38/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 on the right of citizens of the Union and their family members to move and reside freely within the territory of the Member States).
- ^ Articles 3(1) and 5(2) of the Directive 2004/38/EC (Directive 2004/38/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 on the right of citizens of the Union and their family members to move and reside freely within the territory of the Member States).
- ^ UK Border Agency. "EEA family permits". Retrieved 11 February 2013.
- ^ "Meld. St. 12 (2010–2011)". April 2011.
- ^ Article 34 of the Helsinky Treaty (Article 34 p. 8)
- ^ "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Education and Sport". www.regierung.li. Archived from the original on 2021-09-26. Retrieved 2020-03-05.
External links
[edit]- Timatic service giving subscribers up-to-date information on visa requirements(subscription required)