Religion in France
Religion in France (2021)[1]


The majority of the religious population in France identifies as Christian. Catholicism is the most prominent denomination in France, but has long lost the state religion status it held prior to the 1789 French Revolution and during various non-republican regimes of the 19th century, including the Restoration, the July Monarchy and the Second French Empire.
Religion in France is diverse, which could be attributed to the country's adherence to secularism, freedom of religion and freedom of thought, as guaranteed by the 1789 Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen. The Republic is based on the principle of laïcité (or "freedom of conscience") established by the 1880s Jules Ferry laws and the 1905 French law on the Separation of the Churches and the State.
The major religions practiced in France include Christianity (about 50% of the overall population,[1] with denominations including Catholicism, various branches of Protestantism, Eastern Orthodoxy, Armenian Orthodoxy), Islam, Judaism, Buddhism, Hinduism, and Sikhism among others, making it a multiconfessional country. About 40% of the population is non-religious. Sunday Mass attendance has fallen to 5% for Catholics, and the overall level of religious observance is generally lower than in the past.[2][3]
Demographics[edit]
Chronological statistics[edit]
Note that these are from different sources and likely have different methodologies, which makes survey to survey comparisons uncertain.
| Religious group |
Population % 1986[4] |
Population % 1987[5] |
Population % 1994[4] |
Population % 2001[5] |
Population % 2004[6] |
Population % 2006[7] |
Population % 2010[5] |
Population % 2012[8] |
Population % 2016[9] |
ages 18-59 % 2019-2020[10] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Christianity | 82% | 76% | 69% | 71% | 66.2% | 66.1% | 67% | 59% | 51.1% | - |
| –Catholicism | 81% | 75% | 67% | 69% | 64.3% | 64.0% | 64% | 56% | - | 29% |
| –Protestantism | 1% | 1% | 2% | 2% | 1.9% | 2.1% | 3% | 3% | - | - |
| –Other and unaffiliated Christians | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Islam | - | - | - | - | 4.3% | 3.0% | - | - | 5.6% | 10% |
| Judaism | - | - | - | - | 0.6% | 0.6% | - | - | 0.8% | |
| Other religions | 2.5% | 3% | 8% | 6% | 1.9% | 2.3% | 5% | 8% | 2.5% | 10% |
| Not religious | 15.5% | 21% | 23% | 23% | 27.0% | 27.6% | 28% | 32% | 39.6% | 51% |
Survey data[edit]
In 2015, the Eurobarometer, a survey funded by the European Union, found that Christianity was the religion of 54.3% of the respondents, with Catholicism being the main denomination with 47.8%, followed by other Christians with 4.1% (Protestants with 1.8% and the Eastern Orthodox with 0.6%). Muslims were found to comprise 3.3%, Jews were 0.4%, and members of the other religions were 1.6%. Unaffiliated people were 40.4%; 22.8% declared to be atheists, and 17.6% declared to be agnostics.[11]
In 2017, the Pew Research Center found in their Global Attitudes Survey that 54.2% of the French regarded themselves as Christians, with 47.4% belonging to the Catholic Church, 3.6% being unaffiliated Christians, 2.2% being Protestants, and 1.0% being Eastern Orthodox. The 37.8% of unaffiliated people were divided into 24.8% atheists, 8.2% of nothing in particular, and 4.8% of agnostics. Muslims made up 5.0% of the population, Jews made up 0.4%, and members of other religions made up 1.4%. 1.1% were either undecided or didn't answer the question.[12]
In May 2019, the Eurobarometer conducted a survey in France. It was published in September 2019 within Special Eurobarometer 493, showing the following outcome: Christians made up 47% of the population, with Catholics making up 41%, Orthodox Christians making up 2%, Protestants making up 2%, and other Christians making up 2% each. Muslims were found to be 5%, Jews 1%, and Buddhists 1%. Atheists (21%) and nonbelievers (or agnostics) (19%) made up 40% of unaffiliated people. People of other religions made up 5% of the population, while those who refused to answer made up 1%.[13]
| Source
(year) |
Christianity | Christian denominations | No religion | Other religions | Unanswered | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catholicism | Protestants | Orthodox | Other denominations | Islam | Judaism | Buddhism | Other religions | ||||
| Eurobarometer (2019)[14] | 47% | 41% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 40% | 5% | 1% | 1% | 5% | 1% |
| Observatoire de la laïcité (2018)[15] | 52% | 48% | 3% | 1% | 34% | 3% | 1% | 2% | 1% | 7% | |
| Eurobarometer (2018)[16] | 54.9% | 49.9% | 2.0% | 0.8% | 2.2% | 37.9% | 4.9% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.9% | |
| Ofre, Institut Randstad (2018) [17] | 51.5% | 49.5% | 2% | 37.5% | 8.5% | 2% | 1% | ||||
| Ipsos survey (2017) [18] | 61.0% | 57.5% | 3.1% | 0.4% | 35.0% | 3.0% | 1.0% | ||||
| Pew Research Center Western Europe survey (2017)[19] | 63.6% | 59.4% | 2.3% | 1.9% | 28.3% | 7.5% | 0.2% | ||||
| Pew Research Center Global Attitudes (2017)[12] | 54.2% | 47.4% | 2.2% | 1.0% | 3.6% | 37.8% | 5.0% | 0.4% | 1.4% | 1.1% | |
| IFOP, Institut Montaigne (2016)[9] | 51.1% | 51.1% | 39.6% | 5.6% | 0.8% | 2.5% | 0.4% | ||||
| Eurobarometer (2015)[11] | 54.3% | 47.8% | 1.8% | 0.6% | 4.1% | 40.4% | 3.3% | 0.4% | 0.7% | 0.9% | |
Religion among the youth[edit]
| Religion by country |
|---|
|
|

According to the European Value Survey, between 2010 and 2012, 47% of French youth declared themselves Christians, while according to an IFOP study based on a sample of 406, around 52% of 11- to 15-year-olds declared themselves Catholics, and according to a CSA poll, around 65.4% of 18- to 24-year-old French declared themselves as Christians.[20][21]
A 2010 Pew Research Center survey found that 60% of French people (7 million) between the ages of 15 and 29 identified themselves as Christians.[22]
In 2018, a study by the French polling agency OpinionWay, which was paid for by three Catholic institutions, found that 41% of French adults between the ages of 18 and 30 said they were Catholics, 3% said they were Protestants, 8% said they were Muslims, 1% said they were Buddhists, 1% said they were Jews, and 3% said they were part of other religions.
52 percent of those who believed in God thought that his existence was either certain or likely, 28% thought it was unlikely, and 19% thought it was impossible.[23]
In the same year, a study was done by the Benedict XVI Centre for Religion and Society at London's St. Mary's University and the Institut Catholique de Paris. The study also used data from the European Social Survey for 2014 and 2016, with a sample size of 600 people aged 16 to 29. Of these 600 people, 25% were Christians (23% Catholic and 2% Protestant), 10% were Muslims, 1% were of other religions, and 64% were not religious.[24]
The information came from two questions: "Do you think of yourself as a member of any particular religion or denomination?" was asked to the whole sample, and "Which one?" was asked to the sample that said "Yes."[25]
Pew Research says that the average number of children born to non-Muslims in Europe (but not specifically in France) is 1.6, while the average number of children born to Muslims is 2.6. This is why there are so many more young Muslims than other groups.[26]
History[edit]
France guarantees freedom of religion as a constitutional right, and the government generally respects this right in practice. Because of a long history of anticlericalism, the state cut its institutional ties with the Catholic Church in 1905 and made a strong promise to keep the public sector free of religion.[27]
Catholicism as a state religion[edit]
Catholicism is the largest religion in France. During the pre-1789 Ancien Régime, France was traditionally considered the Church's eldest daughter, and the King of France always maintained close links to the Pope. However, the "Gallicanism" policy meant that the king selected bishops.
French Wars of Religion (1562–1598)[edit]
A strong Protestant population resided in France, primarily of Reformed confession. The government usually opposed this but at times, tolerated more. This supppression continued throughout the 16th century, culminating in the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre, until the 1598 Edict of Nantes issued by Henry IV.
For the first time, the state considered Huguenots something other than mere heretics. The Edict of Nantes thus opened a path for secularism and tolerance. In addition to offering general freedom of conscience to subjects, the edict offered many specific concessions to the Huguenots, including amnesty and the reinstatement of their civil rights, the right to work for the state or in any field, and to bring grievances directly to the king.[28]
Post–Edict of Nantes (1598–1789)[edit]
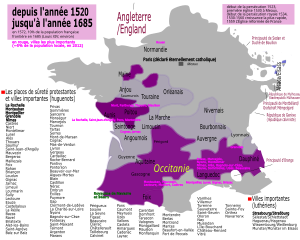
The 1598 Edict also granted the Protestants places of safety (places de sûreté), military strongholds such as La Rochelle (for which the king paid 180,000 écus a year), along with a further 150 emergency forts (places de refuge), to be maintained at the Huguenots' own expense. Such an innovative act of toleration stood virtually alone in a Europe (except for the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth) where standard practice forced the subjects of a ruler to follow whatever religion that the ruler formally adopted – the application of the principle of cuius regio, eius religio.
Religious conflicts resumed at the end of the 17th century, when Louis XIV, the "Sun King," initiated the persecution of Huguenots by introducing the dragonnades in 1681. This wave of violence intimidated the Protestants into converting to Catholicism. He made the policy official with the 1685 revocation of the Edict of Nantes. As a result, a large number of Protestants—estimates range from 200,000 to 500,000—left France during the following two decades, seeking asylum in England, the United Provinces, Denmark, the Protestant states of the Holy Roman Empire (Hesse, Brandenburg-Prussia, etc.), and in European colonies in North America and South Africa.[29]
The revocation returned France to a state of affairs similar to that of virtually every other European country of the period, in which only the state religion was tolerated. Europe's experiment with religious tolerance was effectively over for the time being. In practice, the revocation caused France to suffer a brain drain, as it lost a large number of skilled craftsmen, including key designers such as Daniel Marot.[30]
French Revolution[edit]
The French Revolution stripped the Catholic Church of most of its wealth, power, and influence.[31] The early revolutionaries sought to secularize all of French society, an effort inspired in part by the writings and philosophy of Voltaire.[32] In August 1789, the new National Assembly abolished tithes, the mandatory 10% income tax which all Frenchmen (including non-Catholics) paid to the Catholic Church. In November 1789, they voted to expropriate the vast wealth of the Church in endowments, lands and buildings.[33] In 1790, the Assembly abolished monastic religious orders. Statues and saints were rejected in a burst of iconoclasm, and most religious instruction ended.[34]
The Civil Constitution of the Clergy of 1790 put the Catholic Church under state control. It upended the traditional authority of the Church by required priests and bishops to be elected by their parishioners. The Republic legalized divorce and transferred birth, death, and marriage registrations to the state.[33] The Catholic clergy was persecuted by the Paris Commune of 1792 to 1795 and by some of the Représentants en mission. Most notably, Jean-Baptiste Carrier conducted large-scale drownings of priests and nuns in the river Loire.[35]
In 1793, the government established a secular Republican Calendar. Church tradition had set aside every Sunday, together with many saint's days and other religious holidays, as days for celebration and relaxation but the government tried to end all that and to increase the total number of working days. It instituted a 10-day week, allowing one day in 10 for relaxation. Workers and peasants felt cheated and overworked. The new system disrupted daily routines and ended cherished celebrations. When the reformers were overthrown or executed, their radical new calendar was quickly abandoned.[36][37]


Religious minorities—Protestants and Jews—were granted full civil and political rights, which represented a shift towards a more secular government to some, and an attack on the Catholic Church to others.[33] New religions and philosophies were allowed to compete with Catholicism. The introduction of the prominent cults during the revolutionary period – the Cult of Reason and the Cult of the Supreme Being – responded to the belief that religion and politics should be seamlessly fused together. This is a shift from the original Enlightenment ideals of the Revolution that advocated for a secular government with tolerance for various religious beliefs.[38] While Maximilien Robespierre favored a religious foundation to the Republic, he maintained a hard stance against Catholicism because of its association with corruption and the counterrevolution.[33]
The cults sought to erase the old ways of religion by closing churches, confiscating church bells, and implementing a new Republican Calendar that excluded any days for religious practice. Many churches were converted into Temples of Reason. The Cult of Reason was first to de-emphasize the existence of God, and instead focus on deism, featuring not the sacred, divine, nor eternal, but the natural, earthy, and temporal existence.[38] To tie the church and the state together, the cults transformed traditional religious ideology into politics. The Cult of the Supreme Being used religion as political leverage. Robespierre accused political opponents of hiding behind God and using religion to justify their oppositional stance against the Revolution. It was a shift in ideology that allowed for the cult to use the new deistic beliefs for political momentum.[38]
Following the Thermidorian Reaction the persecutions of Catholic clergy ceased and the role of new cults practically ended.
Napoleon and concordat with the Vatican[edit]
The Catholic Church was badly hurt by the Revolution.[31] By 1800 it was poor, dilapidated and disorganized, with a depleted and aging clergy. The younger generation had received little religious instruction, and was unfamiliar with traditional worship. However, in response to the external pressures of foreign wars, religious fervor was strong, especially among women.[39]
Napoleon, who took control in a coup by 1800, decided that religious divisiveness had to be minimized to unite France. The Concordat of 1801 was an agreement between Napoleon and Pope Pius VII, signed in July 1801 that remained in effect until 1905. It sought national reconciliation between revolutionaries and Catholics and solidified the Roman Catholic Church as the majority church of France, with most of its civil status restored. The hostility of devout Catholics against the state had then largely been resolved. It did not restore the vast church lands and endowments that had been seized upon during the revolution and sold off. Catholic clergy returned from exile, or from hiding, and resumed their traditional positions in their traditional churches. Very few parishes continued to employ the priests who had accepted the Civil Constitution of the Clergy of the Revolutionary regime. While the Concordat restored much power to the papacy, the balance of church-state relations tilted firmly in Napoleon's favour. He selected the bishops and supervised church finances.[40]
Bourbon Restoration (1814-1830)[edit]
The Bourbon Restoration made the Catholic Church again the state religion of France. Other religions were tolerated, but Catholicism was favored both financially and politically. Its lands and financial endowments were not returned, but the government now paid salaries and maintenance costs for church activities. The bishops had regained control of Catholic affairs and of education. While the aristocracy before the Revolution did not place a high priority on religious doctrine or practice, the decades of exile created an alliance of throne and altar. The royalists who returned were much more devout, and much more aware of their need for a close alliance with the Church. They had discarded skepticism and now promoted the wave of Catholic religiosity that was sweeping Europe, with a new regard to the Virgin Mary, the Saints, and popular religious rituals such as saying the rosary. Devotionalism was far stronger in rural areas, and much less noticeable in Paris and the other cities. The population of 32 million included about 680,000 Protestants, and 60,000 Jews. They were tolerated. Anti-clericalism of the sort promoted by the Enlightenment and writers such as Voltaire had not disappeared, but it was in recession and repressed by the ultra-conservative Bourbon government.[41]
At the elite level, the intellectual climate changed dramatically from the intellectually oriented classicism to emotionally based romanticism. A book by François-René de Chateaubriand entitled Génie du christianisme ("The Genius of Christianity") (1802) had an enormous influence in reshaping French literature and intellectual life. It emphasized the power of religion in creating European high culture. Chateaubriand's book did more than any other single work to restore the credibility and prestige of Christianity in intellectual circles and launched a fashionable rediscovery of the Middle Ages and their Christian civilisation. The revival was by no means confined to an intellectual elite, however, but was evident in the real, if uneven, rechristianisation of the French countryside.[42]
Napoleon III (1848-1870)[edit]
Napoleon III strongly supported Catholic interests, financing the church and supporting Catholic missionaries in the emerging French Empire. His primary goal was the conciliation of religious and anti-religious interests in France to avoid the conflicts that took place during the revolution and that reappeared after he lost power.[43][44]
In terms of foreign policy, the French army stopped the anti-clerical Kingdom of Italy from taking full control of Rome after it was formed in 1860 and took over parts of the papal states. In Paris, the conservative Gallican bishops helped the Emperor control the French people, while liberal Catholic intellectuals wanted to use the Church as an instrument of reform. A problem arose with Pope Pius IX, who reigned from 1846 to 1878. He started out as a liberal but suddenly, in the 1860s, became the leading champion of reactionary politics in Europe, in opposition to all forms of modern liberalism. He demanded complete autonomy for the church and its religious and educational affairs and had the First Vatican Council (1869–70) decree papal infallibility. Napoleon III's foreign policy was too tied to Rome's support for him to break with the Pope, but his close relationship with the Pope made him very weak at home. When he declared war on Prussia in 1870, he brought his army home, and the kingdom of Italy swallowed up the papal domains, and the Pope became a prisoner of the Vatican. When the Vatican spoke out against progress, industrialization, capitalism, socialism, and almost every new idea, it upset liberal and conservative Catholics in France. It also energized secular liberals, including many professionals, and the anti-clerical socialist movement. They stepped up their attacks on church control of schools.[45]
Third Republic (1870–1940)[edit]
Throughout its lifetime, the Third Republic (1870–1940) saw battles over the status of the Catholic Church in France between the republicans and the monarchists and other authoritarians (such as the Napoleonists). The French Catholic clergy and bishops were closely associated with the monarchists, and its higher hierarchy was largely drawn from noble families. The republicans' power base was the anti-clerical middle class, which saw the Church's alliance with the monarchists as both a political threat to the republic and a threat to the modern spirit of progress. The republicans detested the Church for its political and class affiliations; for them, the Church represented the Ancien Régime, a time in French history most republicans hoped was long behind them. The Republicans were strengthened by Protestant and Jewish support. Numerous laws successively weakened the Catholic Church. In 1879, priests were excluded from the administrative committees of hospitals and boards of charity; in 1880, new measures were directed against the religious congregations; from 1880 to 1890, lay women replaced nuns in many hospitals; and in 1882, the Ferry school laws were passed. Napoleon's Concordat of 1801 continued to ensure state funding of the church, but in 1881, the government cut off salaries to priests, which it disliked.[46]
Republicans feared that religious orders in control of schools—especially the Jesuits and Assumptionists—indoctrinated anti-republicanism into children. Determined to root this out, republicans insisted the state needed control of the schools for France to achieve economic and militaristic progress. (Republicans felt one of the primary reasons for the German victory in 1870 was their superior education system.)
The early anti-Catholic laws were largely the work of republican Jules Ferry in 1882. Religious instruction was pushed out of all schools, and religious orders were forbidden to teach in them. Funds were appropriated from religious schools to build more state schools. Later in the century, other laws passed by Ferry's successors further weakened the Church's position in French society. Civil marriage became the only legal one, divorce was introduced, and chaplains were removed from the army.[47]
When Leo XIII became pope in 1878, he tried to calm Church-State relations. In 1884, he told French bishops not to act in a hostile manner toward the State ('Nobilissima Gallorum Gens'[48]). In 1892, he issued an encyclical advising French Catholics to rally to the Republic and defend the Church by participating in republican politics ('Au milieu des sollicitudes'[49]). This attempt at improving the relationship failed. Deep-rooted suspicions remained on both sides and were inflamed by the Dreyfus Affair (1894–1906). Catholics were for the most part anti-Dreyfusard. The Assumptionists published anti-Semitic and anti-republican articles in their journal La Croix. This infuriated republican politicians, who were eager to take revenge. Often they worked in alliance with Masonic lodges. The Waldeck-Rousseau Ministry (1899–1902) and the Combes Ministry (1902–05) fought with the Vatican over the appointment of bishops. Chaplains were removed from naval and military hospitals in the years 1903 and 1904, and soldiers were ordered not to frequent Catholic clubs in 1904.
Emile Combes, when elected Prime Minister in 1902, was determined to defeat Catholicism thoroughly. Shortly after taking office, he closed down all parochial schools in France. Then he had parliament reject authorisation of all religious orders. This meant that all fifty-four orders in France were dissolved and about 20,000 members immediately left France, many for Spain.[50] The Combes government worked with Masonic lodges to create a secret surveillance of all army officers to make sure that devout Catholics would not be promoted. Exposed as the Affaire Des Fiches, the scandal undermined support for the Combes government, and he resigned. It also undermined morale in the army, as officers realized that hostile spies examining their private lives were more important to their careers than their own professional accomplishments.[51]
1905: Separation of Church and State[edit]
Radicals (as they called themselves) achieved their main goals in 1905: they repealed Napoleon's 1801 Concordat. Church and State were finally separated. All Church property was confiscated. Religious personnel were no longer paid by the State. Public worship was given over to associations of Catholic laymen who controlled access to churches. However, in practice, masses and rituals continued to be performed.[52]
A 1905 law instituted the separation of Church and State and prohibited the government from recognising, salarying, or subsidising any religion. The 1926 Briand-Ceretti Agreement subsequently restored for a while a formal role for the state in the appointment of Catholic bishops, but evidence for its exercise is not easily obtained. Prior to 1905, the 1801–1808 Concordat compelled the State to support the Catholic Church, the Lutheran Church, the Calvinist Church, and the Jewish religion, and to fund public religious education in those established religions.
For historical reasons, this situation is still current in Alsace-Moselle, which was a German region in 1905 and only joined France again in 1918. Alsace-Moselle maintains a local law of pre-1918 statutes which include the Concordat: the national government pays, as state civil servants, the clergy of the Catholic diocese of Metz and of Strasbourg, of the Lutheran Protestant Church of Augsburg Confession of Alsace and Lorraine, of the Protestant Reformed Church of Alsace and Lorraine, and of the three regional Israelite consistories, and it provides for now non-compulsory religious education in those religions in public schools and universities. Also for historical reasons, Catholic priests in French Guiana are civil servants of the local government.
Religious buildings built prior to 1905 at taxpayers' expense are retained by the local or national government, and may be used at no expense by religious organisations. As a consequence, most Catholic churches, Protestant temples, and Jewish synagogues are owned and maintained by the government but are assigned by the government to their respective religious communities for "legal, exclusive, free, perpetual use."[53] The government, since 1905, has been prohibited from funding any post-1905 religious edifice, and thus religions must build and support all new religious buildings at their own expense. Some local governments de facto subsidise prayer rooms as part of greater "cultural associations".
Recent tensions[edit]
An ongoing topic of controversy is whether the separation of Church and State should be weakened so that the government would be able to subsidise Muslim prayer rooms and the training of imams. Advocates of such measures, such as Nicolas Sarkozy at times, declare that they would encourage the Muslim population to better integrate into the fabric of French society. Opponents contend that the state should not fund religions.[citation needed] Furthermore, the state ban on wearing conspicuous religious symbols, such as the Islamic female headscarf, in public schools has alienated some French Muslims, provoked minor street protests and drawn some international criticism.[citation needed]
In the late 1950s after the end of the Algerian war, hundreds of thousands of Muslims, including some who had supported France (Harkis), settled permanently to France. They went to the larger cities where they lived in subsidized public housing, and suffered very high unemployment rates.[54] In October 2005, the predominantly Arab-immigrant suburbs of Paris, Lyon, Lille, and other French cities erupted in rioting by socially alienated young people, many of them second- or third-generation immigrants.[55][56]
American University professor C. Schneider says:
For the next three convulsive weeks, riots spread from suburb to suburb, affecting more than three hundred towns....Nine thousand vehicles were torched, hundreds of public and commercial buildings destroyed, four thousand rioters arrested, and 125 police officers wounded.[57]
Traditional interpretations say the riots were spurred by radical Muslims or unemployed youth. Another view states that the riots reflected broader problem of racism and police violence in France.[57]
In March 2012, a Muslim radical named Mohammed Merah shot three French soldiers and four Jewish citizens, including children in Toulouse and Montauban.
In January 2015, the satirical newspaper Charlie Hebdo, that had ridiculed Muhammad, and a Jewish grocery store came under attack from radicalized Muslims who had been born and raised in the Paris region. World leaders rallied to Paris to show their support for free speech. Analysts agree that the episode had a profound impact on France. The New York Times summarized the ongoing debate:
So as France grieves, it is also faced with profound questions about its future: How large is the radicalized part of the country's Muslim population, the largest in Europe? How deep is the rift between France's values of secularism, of individual, sexual and religious freedom, of freedom of the press and the freedom to shock, and a growing Muslim conservatism that rejects many of these values in the name of religion?[58]
Religions[edit]
Christianity[edit]

Christianity is the largest group of religions of France, but has recently stopped being a majority of the overall population. According to a survey held by Institut français d'opinion publique (Ifop) for the centre-right Institut Montaigne think-tank, 51.1% of the total population of France was Christian in 2016.[9] The following year, a survey by Ipsos focused on Protestants and based on 31,155 interviews found that 57.5% of the total population of France declared to be Catholic and 3.1% declared to be Protestant.[59]
In 2016, Ipsos Global Trends, a multi-nation survey held by Ipsos and based on approximately 1,000 interviews, found that Christianity is the religion of 45% of the working-age, internet connected population of France; 42% stated they were Catholic, 2% stated that they were Protestants, and 1% declared to belong to any Orthodox church.[60]
In 2019, the Eurobarometer, a survey funded by the European Union, found that Christianity was the religion of 47% of the French, with Catholicism being the main denomination with 41%, followed by Orthodox Christian, Protestants and other Christians with 2% each one.[13]
France is home to a number of Marian shrines, notably the Cathedrale Notre-Dame de Chartres in Chartres, Notre Dame de la Salette in La Salette, Notre Dame de Paris in Paris, and the Sanctuary of Our Lady of Lourdes. It is also home to the Taizé Community, an ecumenical Christian monastic fraternity in Taizé, Saône-et-Loire, Burgundy. All are important pilgrimage sites. The Sanctuary of Our Lady of Lourdes appeals to a broader demographic, with 6 million people a year (before the pandemic) visiting Lourdes.[61] With a focus on youth, Taize Community, on the other hand, has become one of the world's most important sites of Christian pilgrimage with over 100,000 young people from around the world converging each year for prayer, Bible study, sharing, and communal work.[62][undue weight? – discuss]
Islam[edit]

A 2016 survey held by Institut Montaigne and Ifop found that 5.6% of the French population had an Islamic background, while 5.3% declared they were Muslims by faith. According to the same survey 84.9% of surveyed people who had at least one Muslim parent said were Muslims, 3.4% were Christians, 10.0% were not religious and 1.3% belonged to other religions.[9]
According to Pew Research, in 2050 France will be 12.7% Muslim in the zero migration scenario (no migration to or from Europe), 17.4% in the medium migration scenario (regular migration continues and refugee flows cease), or 18% in the high migration scenario (2014 to mid-2016 refugee inflow patterns continue as well as regular migration).[63]
Judaism[edit]

In 2016, 0.8% of the total population of France, or about 535,000 people, were religious Jews.[9] In the 21st century, France has the largest Jewish population in Europe and the third-largest Jewish population in the world (after Israel and the United States).[64]
Jewish presence in France is documented since the early Middle Ages. France was a center of Jewish learning in the Middle Ages, but persecution increased as the Middle Ages wore on, including multiple expulsions and returns. During the late 18th-century French Revolution, France was the first country in Europe to emancipate its Jewish population. Antisemitism nonetheless persisted despite legal equality, manifested for instance in the Dreyfus affair of the late 19th century.
During World War II, the Vichy government collaborated with Nazi occupiers to deport numerous French Jews and foreign Jewish refugees to concentration camps.[65] 75% of the local Jewish population in France nonetheless survived the Holocaust,[66][67] but a much higher percentage of the foreign Jewish refugees who had more recently arrived to France were deported and killed.
The majority of French Jews in the 21st century are Sephardi and Mizrahi North African Jews, many of whom (or their parents) emigrated from former French colonies of North Africa after those countries became independent in the 1950s and 1960s. They migrated to France in the second half of the 20th century. French Jews span a wide range of religious affiliations, from the ultra-Orthodox Haredi communities to the large segment of Jews who are entirely secular and who commonly marry outside the Jewish community.[68]
Buddhism[edit]

As of the 2000s, Buddhism in France was estimated to have between 1 million (Ministry of the Interior) strict adherents and 5 million people influenced by Buddhist doctrines,[69] very large numbers for a Western country. Many French Buddhists do not consider themselves "religious".[70] According to scholar Dennis Gira, who was the director of the Institute of Science and Theology of Religions of Paris, Buddhism in France has a missionary nature and is undergoing a process of "inculturation" that may represent a new turning of the "Wheel of the Dharma", similar to those that it underwent in China and Japan, from which a new incarnation of the doctrine — a "French Buddhism" — will possibly arise.[69]
In 2012, the European headquarters of the Fo Guang Shan monastic order opened in France, near Paris. It was the largest Buddhist temple in Europe at that time.[71] The Plum Village Tradition school of Buddhism was developed in France with the Plum Village Monastery located in the Dordogne.[72][73]
Hinduism[edit]
Hinduism is a minority religion followed in France by 0.25% of total population,[74] mainly by Indians and Sri Lankans, in whom Tamils community forms a major group in the country.[75] Hinduism is most influential in the French Overseas department of Réunion where estimates of practicing Hindus vary from 6.7%[76] to 10.7%.[77] and most of the large towns have a functioning Hindu temple.[78]
Though being in very small number, the Hindu culture has deeply influenced the society of France by Yoga, Meditation and in recent times organizations like ISKCON have played a major role.[79][80][81] Notably, French-Indian Mirra Alfassa known to her followers as The Mother or La Mère founded the Sri Aurobindo Ashram and was highly influential on the philosophy of Integral Yoga.[82][83]
Paganism[edit]

Paganism, in the sense of Contemporary paganism, in France included a broad variety of traditions and movements. As with neopaganism in other countries, these traditions sit somewhere on a gradient, with one side represented by reconstructionist religious movements and on the other side by a variety of witchcraft and shamanic traditions with a focus on personal revelation. Pagans and pagan movements often blend elements of both influences. The term "pagan" (Latin paganus), used by Christians to define those who maintained polytheistic religions, originally meant "rural person, countryfolk, civilian", as a dweller of a pagus (rural district).[84]
The more identitary and reconstructionist Pagan movements are the majority and are represented by Celtic Druidry and Germanic Heathenry, while Wicca is an example of a non-identitary Pagan movement. Polytheism, nature worship, animism and pantheism are common features in Pagan theology. Rituals take place in both public and in private domestic settings. Academic research has placed the Pagan movement along a spectrum, with eclecticism on one end and polytheistic reconstructionism on the other.[85]
All Pagan movements place great emphasis on the divinity of nature as a primary source of divine will, and on humanity's membership of the natural world, bound in kinship to all life and the Earth itself. The animistic aspects of Pagan theology assert that all things have a soul - not just humans or organic life - so this bond is held with mountains and rivers as well as trees and wild animals. As a result, Pagans believe the essence of their spirituality is both ancient and timeless, regardless of the age of specific religious movements. Places of natural beauty are therefore treated as sacred and ideal for ritual, like the nemetons of the ancient Celts.[86][85]
Many Pagans hold that different lands (and/or cultures) have their own natural religion, with many legitimate interpretations of divinity, and therefore reject religious exclusivism.
While the Pagan community has tremendous variety in political views spanning the whole of the political spectrum, environmentalism is often a common feature.[87]
Other religions[edit]
Groups such as Antoinism, Aumism, Christian Science, Invitation to Life, Raelism, and the International Society for Krishna Consciousness, have over 1000 members, whereas the Unification Church has approximately 400 members. In 1995, France created the first French parliamentary commission on cult activities, which led to a report registering a number of religious groups considered socially disruptive and/or dangerous. Some of these groups have been banned, including the Children of God.[88]
According to the French sociologist Régis Dericquebourg, in 2003 the main small religious minorities were the Jehovah's Witnesses (130,000, though the European Court on Human Rights reckoned the number at 249,918 "regular and occasional" Jehovah's Witnesses),[89] Adventists, Evangelicals, Mormons (31,000 members), and Soka Gakkai Buddhists.
According to the 2005 Association of Religion Data Archives data there were close to 4,400 Baháʼís in France.[90]
According to the 2007 edition of the Quid, other notable religious minorities included the New Apostolic Church (20,000), the Universal White Brotherhood (20,000), Sukyo Mahikari (15,000–20,000), the New Acropolis (10,000), the Universal Alliance (1,000), and the Grail Movement (950).[91]
-
Statue of a Chinese goddess Shui Wei Sheng Niang during a procession for the Lunar New Year in Paris.
-
Antoinist temple of Tours, Indre-et-Loire.
Controversies and incidents[edit]
Growth of Islam and conflict with laïcité[edit]

In Paris and the surrounding Île-de-France region, French Muslims tend to be more educated and religious, and the vast majority of them consider themselves loyal to France.[92][93] Among Muslims in Paris in the early 2010s, 77% disagreed when asked whether violence is an acceptable moral response for a noble cause or not; 73% said that they were loyal to France; and 18% believed homosexuality to be acceptable.[92]
In 2015, there were 2,500 mosques in France, up from 2,000 in 2011. In 2015, Dalil Boubakeur, rector of the Grand Mosque of Paris, said the number should be doubled to accommodate the large and growing population of French Muslims.[94]
Financing the construction of mosques was a problematic issue for a long time; French authorities were concerned that foreign capital could be used to acquire influence in France, and so in the late 1980s it was decided to favour the formation of a "French Islam", though the 1905 law on religions forbids the funding of religious groups by the state. According to Salah Bariki, advisor to the mayor of Marseille in 2001, at a Koranic school in Nièvre, only three percent of the books were written in French, and everything was financed from abroad. She supported the public's participation in financing an Islamic cultural centre in Marseille to encourage Muslims to develop and use French learning materials in order to thwart foreign indoctrination. Even secular Muslims and members of civil society were to be represented by the centre.[95] Local authorities have financed the construction of mosques, sometimes without minarets, and called them Islamic "cultural centres" or municipal halls rented to "civil associations". In the case of the plans to build the Mosque of Marseille, due to protests and a tribunal decision by the National Rally, the National Republican Movement, and the Mouvement pour la France, the rent of an 8,000 m2 (86,111 sq ft) terrain for the mosque was increased from €300/year to €24,000/year and the renting period was reduced from 99 to 50 years.[95]
Charlie Hebdo shooting[edit]
This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2020) |
France came to an uproar in January 2015, when eight writers and cartoonists were shot dead by two terrorists who raided the French satirical magazine Charlie Hebdo. For years, it had been threatened by Muslim fundamentalists for publishing cartoons criticizing Muhammad. While condemnation of this attack was unanimous in the West and among the internationally recognized governments of the Muslim world, some militants approved, stating that it was right to kill those who insulted Muhammad. [citation needed]
Freedom of religion[edit]
In 2023, the country was scored 3 out of 4 for religious freedom by Freedom House.[96]
See also[edit]
- 1905 French law on the Separation of the Churches and the State
- Anti-clericalism
- Dechristianisation of France during the French Revolution
- Freedom of religion in France
- Irreligion in France
- Jules Ferry laws
- Laïcité
References[edit]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Etat des lieux de la laïcité en France - 2021" (PDF) (official statistics) (in French). Observatoire de la laïcité, Government of France. p. 37. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 January 2024.
- ^ Knox, Noelle (11 August 2005). "Religion takes a back seat in Western Europe". USA Today.
- ^ "France – church attendance". Via Integra. 10 June 2010. Retrieved 23 February 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Catholicisme et protestantisme en France – Analyses sociologiques et données de l'Institut CSA pour La Croix" [Catholicism and Protestantism in France – Sociological analysis and data from the CSA Institute for La Croix] (PDF) (in French). CSA. 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 September 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Le catholicisme en France en 2010" (PDF). IFOP. August 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-02-11.
- ^ "Sondage CSA: Les Francais et la religion" (PDF). La Croix. 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-11-08. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ "Éléments d'analyse géographique de l'implantation des religions en France" (PDF). IFOP. December 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-09-24.
- ^ "Le catholicisme en France" (PDF). CSA. March 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-02-22.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "A French Islam is possible" (PDF). Institut Montaigne. 2016. p. 13. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 September 2017.
- ^ Insee Références (2023). "Immigrés et descendants d'immigrés en France" [Immigrants and descendants of immigrants in France] (PDF). Insee Références (in French): 39.
En 2019‑2020, 29 % des personnes âgées de 18 à 59 ans se déclarent catholiques, 10 % musulmaneset 10 % se déclarent affiliées à d'autres religions, tandis que les 51 % autres se disent sans religion.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "DISCRIMINATION IN THE EU IN 2015", Special Eurobarometer, 437, European Union: European Commission, 2015, archived from the original on 29 January 2020, retrieved 15 October 2017 – via GESIS
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Spring 2017 Survey Data". Pew Research Center's Global Attitudes Project. Retrieved 2018-10-23.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Special Eurobarometer 493, European Union: European Commission, September 2019, pages 229-230 Retrieved 17 January 2020. The question asked was "Do you consider yourself to be...?" With a card showing: Catholic, Orthodox Christian, Protestant, Other Christian, Jewish, Muslim - Shia, Muslim - Sunni, Other Muslim, Sikh, Buddhist, Hindu, Atheist, Non believer/Agnostic and Other. Also space was given for Refusal (SPONTANEOUS) and Don't Know. On the other hand, Sikh and Hindu did not reach the 1% threshold.
- ^ "Special Eurobarometer 493, pages 229-230". European Union: European Commission. September 2019.
- ^ "État des lieux de la laïcité en France" (PDF). Observatoire de la Laïcité. January 2019. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-01-10. Retrieved 2019-04-07.
- ^ Eurobarometer 90.4: Attitudes of Europeans towards Biodiversity, Awareness and Perceptions of EU customs, and Perceptions of Antisemitism. European Commission. Retrieved 9 August 2019 – via GESIS.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Religion en entreprise: des conflits rares mais en légère hausse, selon une enquête". La Croix (in French). 2018-09-26. ISSN 0242-6056. Retrieved 2019-04-08.
- ^ "Sondage "Les protestants en France en 2017" (1) : qui sont les protestants ?". Reforme.net (in French). 2017-10-26. Archived from the original on 2020-03-05. Retrieved 2019-04-12.
- ^ "Western Europe Survey Dataset". Pew Research Center. Retrieved 2019-04-07.
- ^ Dieu existe, pour la majorité des jeunes Français
- ^ Change in religious affiliations especially for youth
- ^ "France". Archived from the original on 2018-02-12. Retrieved 2019-02-17.
- ^ La-Croix.com (2018-03-23). "Dieu existe, pour la majorité des jeunes Français". La Croix (in French). Retrieved 2018-08-15.
- ^ Bullivant, Stephen (2018). "Europe's Young Adults and Religion: Findings from the European Social Survey (2014-16) to inform the 2018 Synod of Bishops" (PDF). St Mary's University's Benedict XVI Centre for Religion and Society; Institut Catholique de Paris. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 March 2018.
- ^ "European Social Survey, Online Analysis". nesstar.ess.nsd.uib.no. Archived from the original on 2019-02-17. Retrieved 2018-05-14.
- ^ Hackett, Conrad. "5 facts about the Muslim population in Europe". Pew Research Center. Retrieved 2022-01-07.
- ^ Baubérot, Jean (15 March 2001). "The Secular Principle". Embassy of France in the US. Archived from the original on 22 February 2008.
- ^ Ruth Whelan, and Carol Baxter, eds. Toleration and religious identity: the Edict of Nantes and its implications in France, Britain and Ireland (Four Courts PressLtd, 2003).
- ^ Spielvogel, Jackson J. (2003). Western Civilization – Volume II: Since 1500 (5th ed.). p. 410.
- ^ Joutard, Philippe (1985). "The Revocation of the Edict of Nantes: End or Renewal of French Protestantism?". In Prestwich, Menna (ed.). International Calvinism, 1541-1715. Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-0-19-821933-0.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Betros, Gemma (December 2010). "The French Revolution and the Catholic Church". History Review (68): 16–21. ProQuest 818499173.
- ^ Gliozzo, Charles A. (1971). "The Philosophes and Religion: Intellectual Origins of the Dechristianization Movement in the French Revolution". Church History. 40 (3): 273–283. doi:10.2307/3163003. JSTOR 3163003.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Popkin, Jeremy D (2015). A Short History of the French Revolution. Sixth ed. 2015
- ^ Idzerda, Stanley J. (1954). "Iconoclasm during the French Revolution". The American Historical Review. 60 (1): 13–26. doi:10.2307/1842743. JSTOR 1842743.
- ^ R.R. Palmer,. Twelve Who Ruled: The Year of the Terror in the French Revolution (1941) pp 220-22.
- ^ Perovic, Sanja (March 2012). "The French Republican Calendar: Time, History and the Revolutionary Event: The French Republican Calendar". Journal for Eighteenth-Century Studies. 35 (1): 1–16. doi:10.1111/j.1754-0208.2011.00408.x.
- ^ Zerubavel, Eviatar (1977). "The French Republican Calendar: A Case Study in the Sociology of Time". American Sociological Review. 42 (6): 868–877. doi:10.2307/2094573. JSTOR 2094573.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Stevenson, Shandi (2013). Religions of Revolution: The Merging of Religious and Political in the Cult of Reason and the Cult of the Supreme being in France 1793–1794 (Thesis). ProQuest 1461390217.
- ^ Robert Tombs, France: 1814-1914 (1996) p 241
- ^ Nigel Aston, Religion and revolution in France, 1780-1804 (Catholic University of America Press, 2000) pp 279-335.
- ^ Frederick B. Artz, France under the Bourbon Restoration, 1814-1830 (1931) pp 99-171.
- ^ James McMillan, "Catholic Christianity in France from the Restoration to the separation of church and state, 1815-1905." in Sheridan Gilley and Brian Stanley, eds., The Cambridge history of Christianity (2014) 8: 217-232
- ^ Isser, Natalie (1988). "Protestants and Proselytization During the Second French Empire". Journal of Church and State. 30 (1): 51–70. doi:10.1093/jcs/30.1.51. JSTOR 23917715.
- ^ Roger L. Williams, Gaslight and Shadow the World of Napoleon III 1851 1870 (1957), pp 70-96, 194-95.
- ^ Theodore Zeldin, France, 1848-1945: volume II: Intellect, Taste and Anxiety (1977) pp 986-1015.
- ^ Rigoulot, Philippe (2009). "Protestants and the French nation under the Third Republic: Between recognition and assimilation". National Identities. 11 (1): 45–57. doi:10.1080/14608940802680961. S2CID 145338843.
- ^ Harrigan, Patrick J. (2001). "Church, State, and Education in France From the Falloux to the Ferry Laws: A Reassessment". Canadian Journal of History. 36 (1): 51–83. doi:10.3138/cjh.36.1.51.
- ^ "Leo XIII – Nobilissima Gallorum Gens". vatican.va. (full text)
- ^ "Leo XIII – Au milieu des sollicitudes". vatican.va. (full text)
- ^ Tallett, Frank; Atkin, Nicholas (1991). Religion, society, and politics in France since 1789. London: Hambledon Press. p. 152. ISBN 1-85285-057-4.
- ^ Porch, Douglas (2003). The March to the Marne: The French Army 1871–1914. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 92–104. ISBN 0-521-54592-7., is the most thorough account in English.
- ^ Maurice Larkin, Church and state after the Dreyfus affair: The separation issue in France (1974).
- ^ "Medieval Abbey church saved from TV auction, The Tablet, 15, January, 2022, p.28.
- ^ Haddad, Yvonne Yazbeck; Balz, Michael J. (June 2006). "The October Riots in France: A Failed Immigration Policy or the Empire Strikes Back?". International Migration. 44 (2): 23–34. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2435.2006.00362.x.
- ^ "Special Report: Riots in France". BBC News. 9 November 2005. Retrieved 17 November 2007.
- ^ Mucchielli, Laurent (May 2009). "Autumn 2005: A Review of the Most Important Riot in the History of French Contemporary Society". Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies. 35 (5): 731–751. doi:10.1080/13691830902826137. S2CID 144434973.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Cathy Lisa Schneider, "Police Power and Race Riots in Paris," Politics & Society (2008) 36#1 pp 133–159 on p. 136
- ^ Erlanger, Steven (10 January 2015). "Days of Sirens, Fear and Blood: 'France Is Turned Upside Down'". The New York Times. Retrieved 1 July 2021.
- ^ "Sondage "Les protestants en France en 2017" (1): qui sont les protestants?" [Survey "Protestants in France in 2017" (1): Who are the Protestants?]. Reforme.net (in French). 26 October 2017. Archived from the original on 19 October 2017. Retrieved 1 December 2017.
- ^ "Religion, Ipsos Global Trends". Ipsos. 2017. Archived from the original on 5 September 2017. About Ipsos Global Trends survey
- ^ Susan Spano, "Lourdes celebrates 150th anniversary of Bernadette's Visions," Los Angeles Times, Travel section, Sept. 7, 2008.
- ^ "Profound and unique experience in Taize for Yorkshire teenagers". 27 July 2017. Retrieved 4 October 2019.
- ^ "Europe's Growing Muslim Population". Pew Research Center. 2017.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help) - ^ "Jews". Pew Research Center. December 18, 2012.
- ^ "France". Holocaust Encyclopedia. United States Holocaust Memorial Museum.
- ^ "Le Bilan de la Shoah en France (Le régime de Vichy)" [The Report of the Holocaust in France (The Vichy regime)]. BS Encyclopédie.
- ^ Croes, M. (1 January 2006). "The Holocaust in the Netherlands and the Rate of Jewish Survival". Holocaust and Genocide Studies. 20 (3): 474–499. doi:10.1093/hgs/dcl022. S2CID 37573804.
- ^ "France : Un portrait de la population juive". Religioscope.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gira, Dennis (2011–2012). "The "Inculturation" of Buddhism in France". Études. 415. S.E.R.: 641–652. ISSN 0014-1941.
- ^ What place for Buddhism in secular France? (Video). AFPTV. 12 September 2016. Archived from the original on 2021-12-21. See the section with a speech by Marion Dapsance.
- ^ Anning, Caroline (22 June 2012). "Europe's largest Buddhist temple to open". BBC News.
- ^ "The Plum Village Tradition".
- ^ "Thich Nhat Hanh – The Mindfulness Bell". www.parallax.org. Retrieved 2023-02-24.
- ^ "European Countries With The Highest Number Of Hindus: 2010 To 2050". WorldAtlas. Retrieved 2021-06-06.
- ^ "World Tamil Population | Tamilo: Watch Tamil TV Serial Shows Online and Tamil Videos". tamilo.tv. Archived from the original on 2021-06-06. Retrieved 2021-06-06.
- ^ "Indian diaspora" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-08-21. Retrieved 2018-08-10.
- ^ "Country Profile: Reunion (Department of Reunion)". Archived from the original on 13 October 2007. Retrieved 2015-02-14.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Peoples of Africa: Réunion-Somalia. Marshall Cavendish. 2001. pp. 412–. ISBN 978-0-7614-7166-0.
- ^ Mallipattana, Suman V. "The Influence of Hinduism on Literature – Asian American and Asian Research Institute". Retrieved 2021-06-06.
- ^ "Bhakti yoga, eco farm help in Luçay-le-Mâle, France". www.workaway.info. Retrieved 2021-06-06.
- ^ "Vedic Federation Strengthens ISKCON's Position in France". ISKCON News. Retrieved 2021-06-06.
- ^ Allard, Syama (2023-01-10). "All about Mirra Alfassa: the Mother". Hindu American Foundation. Retrieved 2023-02-24.
- ^ "The Mother | Auroville". auroville.org. Retrieved 2023-02-24.
- ^ "Pagan". Dictionary.com. Retrieved December 18, 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Neo-Paganism". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved December 18, 2019.
- ^ "Animism". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved December 18, 2019.
- ^ Moreton, Cole (June 22, 2009). "Everyone's A Pagan Now". The Guardian. Retrieved December 18, 2019.
- ^ Dericquebourg, Régis (9–12 April 2003). De la MILS à la MIVILUDES: la politique envers les sectes en France après la chute du governement [sic] socialiste [From MILS to MIVILUDES: Policies towards sects in France after the fall of the socialist government]. CENSUR International Conference (in French). Vilnius (Lithuanie): CESNUR.
- ^ "Fédération Chrétienne des Témoins de Jéhovah de France v. France". Reports of Judgments and Decisions 2001. Vol. XI. European Court of Human Rights.
- ^ "Most Bahá'í Nations (2005)". The Association of Religion Data Archives. 2005. Archived from the original on 2018-12-26. Retrieved 2012-08-24.
- ^ "Les sectes en France: Nombre d'adeptes ou sympathisants" [Sects in France: Number of followers or sympathisers]. Quid (in French). Archived from the original on 6 August 2009.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Tajuddin, Razia. "Islam in Paris". Euro-Islam: News and Analysis on Islam in Europe and North America. Archived from the original on 4 November 2011.
- ^ Cole, Juan (1 July 2015). "Sharpening Contradictions: Why al-Qaeda attacked Satirists in Paris". Informed Comment.
- ^ Porter, Tim (16 June 2015). "French Muslim leader Dalil Boubaker calls for empty Catholic churches to be turned into mosques". International Business Times.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Maussen, M. J. M. (2009). "Constructing mosques: The governance of Islam in France and the Netherlands". UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository), University of Amsterdam. pp. 155, 186, 172.
- ^ Freedom House website, France page, retrieved 2023-08-28