Voter identification laws in the United States
Voter ID laws in the United States are laws that require a person to provide some form of official identification before they are permitted to register to vote, receive a ballot for an election, or to actually vote in elections in the United States.

| Part of the Politics series |
| Voting |
|---|
|
|
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of the United States |
|---|
 |
At the federal level, the Help America Vote Act of 2002 requires a voter ID for all new voters in federal elections who registered by mail and who did not provide a driver's license number or the last four digits of a Social Security number that was matched against government records.[1] Though state laws requiring some sort of identification at voting polls go back to 1950, no state required a voter to produce a government-issued photo ID as a condition for voting before the 2006 elections. Indiana became the first state to enact a strict photo ID law, which was upheld two years later by the U.S. Supreme Court.[2][3] As of 2021, 36 states have enacted some form of voter ID requirement.[2][4] Lawsuits have been filed against many of the voter ID requirements on the basis that they are discriminatory with an intent to reduce voting.[5] The proliferation of voter ID laws has prompted non-partisan, non-profit organizations like League of Women Voters and VoteRiders to work with and for U.S. citizens so that everyone who is eligible to cast a vote can do so.[6][7]
Proponents of voter ID laws argue that they reduce electoral fraud while placing only little burden on voters. Opponents argue that voter ID laws are unnecessary due to the fact that voter impersonation is extremely rare in the United States and has been shown to be unlikely to result in any plausible impact on the outcome of elections.[8][9][10]
While research has shown mixed results, studies have generally found that voter ID laws have negligible, if any, impact on voter turnout, including that of racial minorities.[11] Research has also shown that Republican legislators in swing states, states with rapidly diversifying populations, and districts with sizable black, Latino, or immigrant populations have pushed the hardest for voter ID laws.[12][13][14] Parts of voter ID laws in several states have been overturned by courts.[15][16][17]
State-by-state requirements
[edit]The National Conference of State Legislatures (NCSL) provides a web page and a map with ID requirements for voting in each state.[18] In states with strict ID laws, the voter is required to take additional action after the provisional ballot is cast to verify ID. The NCSL website describes strict states as follows:
In the "strict" states, a voter cannot cast a valid ballot without first presenting ID. Voters who are unable to show ID at the polls are given a provisional ballot. Those provisional ballots are kept separate from the regular ballots. If the voter returns to election officials within a short period of time after the election (generally a few days) and presents acceptable ID, the provisional ballot is counted. If the voter does not come back to show ID, that provisional ballot is never counted.[19]
In states with non-strict voter ID laws, other methods of validation are allowed, which vary by state. Possible alternatives are: signing an affidavit, having a poll worker vouch for voter, having election officials verify a voter's identity after the vote is cast, or having the voter return an inquiry mailed to their reported address.
The NCSL categorizes state-level voter ID laws as follows:[20]
- Photo ID required (strict): Arkansas, Georgia, Indiana, Kansas, Mississippi, Ohio, Tennessee, and Wisconsin.
- Photo ID requested (non-strict): Alabama, Florida, Hawaii, Idaho, Louisiana, Michigan, Montana, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, and Texas.
- Non-photo ID required (strict): Arizona, North Dakota, and Wyoming.
- Non-photo ID requested (non-strict): Alaska, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Iowa, Kentucky, Missouri, New Hampshire, Oklahoma, Utah, Washington, Virginia, and West Virginia.
- No ID required to vote at ballot box: California, Illinois, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Nebraska, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Vermont, and Washington, D.C.
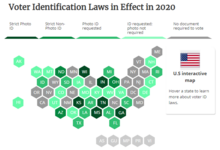
2020 Voter ID law map
History
[edit]This section may be in need of reorganization to comply with Wikipedia's layout guidelines. (August 2023) |
Voter ID laws go back to 1950, when South Carolina became the first state to start requesting identification from voters at the polls. The identification document did not have to include a picture; any document with the name of the voter sufficed. In 1970, Hawaii joined in requiring ID, and Texas a year later. Florida was next in 1977, and Alaska in 1980 to become the first five states in the United States to request identification of some sort from voters at the polls.[21]
In 1999, Virginia Governor Jim Gilmore attempted to start a pilot program that required voters to show IDs at the polls. His initiative was blocked by Democrats and the NAACP, and was stopped by court order. His administration had spent and mailed $275,000 worth of free voter ID cards to residents in Arlington and Fairfax counties.[22][23]
Afterward Republican-dominated states have worked to pass laws for voter IDs, ostensibly to prevent "voter fraud", which studies have shown is "vanishingly rare."[16] Opponents say that many of the provisions of such laws are a conspiracy designed to disadvantage minorities, poor and elderly, many of whom have tended in recent years to vote Democratic, so the Republicans are deriving political benefits from their voter ID campaign. In 2002, President George W. Bush signed the Help America Vote Act into law, which required all first-time voters in federal elections to show photo or non-photo ID upon either registration or arrival at the polling place.[24]
In 2004, Arizona passed a law requiring voters to bring a state-issued photo ID to the polling place. Similar proposals were discussed in various other states and were passed in some cases. In several states, a person's citizenship status is noted on their photo ID.[25][26]
An Indiana law requiring a photo ID be shown by all voters before casting ballots went into effect on July 1, 2005.[27] Civil rights groups in Indiana launched a lawsuit, Crawford v. Marion County Election Board, that reached the Supreme Court in 2008. The Court ruled that the law was constitutional, paving the way for expanded ID laws in other states.[28][29]
In 2011, Wisconsin Governor Scott Walker (WI Act 23) and Ohio Governor John Kasich enacted similar laws. Texas Governor Rick Perry placed a voter ID bill as an "emergency item" in 2011, allowing legislators to rush it through the process.[30] Jurisdiction over Texas election procedure had been given to the Department of Justice, which was required to pre-clear the law for approval. The Texas law recognized government-issued photo identification and weapons permits but not college IDs, resulting in criticism that the law was unfavorable to young voters, who trend liberal, while favorable to gun owners, who trend conservative.[31] Rhode Island passed a voter ID law in 2011; it is the only state with a Democratic-controlled legislature to do so.[32]
In South Carolina, Gov. Nikki Haley enacted a 2011 law requiring government-issued IDs at the polls, which included provisions for the issuance of free IDs. Haley made a one-time offer to arrange for voter ID applicants to be driven to issuing locations.[33] The ID requirement was blocked by the Justice Department.[34]
Wisconsin's Voter ID law in 2011 provided free IDs to people who did not have them. But in practice, state employees at the DMV were instructed to provide the IDs for free only if people specifically asked to have their fee waived.[35] The requirement to show photo ID had been declared in violation of the Wisconsin Constitution and blocked by state and federal judges, but those decisions were overturned by the Wisconsin Supreme Court and later the 7th Circuit Court of Appeals.[36] Weeks later, the U.S. Supreme Court again blocked the law for 2014.[37] On March 23, 2015, the U.S. Supreme Court rejected an appeal by the ACLU, effectively upholding the 7th Circuit's decision Wisconsin's voter ID law as constitutional.[38]
Pennsylvania's voter ID law allowed various forms of photo identification cards, including those held by drivers, government employees, in-state college students, and residents of elder-care facilities. Voters who do not possess these forms of identification can obtain voting-only photo IDs issued by the Pennsylvania Department of State through the Pennsylvania Department of Transportation (PennDOT).[39] A judicial order on October 2, 2012, blocked enforcement of Pennsylvania's law until after the 2012 Presidential election. Following a trial in the summer of 2013 and a six-month delay, Commonwealth Court Judge Bernard L. McGinley struck down Pennsylvania's voter ID law on January 17, 2014, as violative of the constitutional rights of state voters.
He noted that required alternative voter IDs were available only through 71 PennDOT Drivers Licensing Centers across the state. Five of the 71 DLCs are located in Philadelphia, nine counties have no DLCs at all, and DLCs have limited hours: in nine counties they are open only one day per week, and in 13 counties they are open only two days per week. The court ruled that the Pennsylvania Department of State provided too little access, no financial support to provide IDs to those without access, and no alternatives to obtaining the required IDs. Judge McGinley found that this leaves about half of Pennsylvania without DLCs for five days a week, imposing a significant barrier to obtaining Pennsylvania's "free ID".[40] Photo IDs are not required to vote in PA.[41]
Voters in Minnesota rejected a voter ID proposal on the 2012 general election ballot by a margin of 54–46%.[42] It is the only such ballot defeat for a voter ID law in the country.
Push for photo ID requirements
[edit]Since the late 20th century, the Republican Party has led efforts to create more stringent voter ID laws for the stated objective of preventing voter fraud. Twelve states now require voters to show some form of photo identification (see table below) with approximately the same number currently pursuing similar legislation. Republican members of ALEC often introduced the laws, which were then signed by Republican governors.[43]

Some states pursuing new photo identification requirements had been required by the Voting Rights Act of 1965 to get federal preclearance prior to enacting new election laws. However, in the 2013 case Shelby County v. Holder, the United States Supreme Court struck down section 4(b) of the Act, which contained the formula that determined, based on historic racial discrimination, which states were required to seek preclearance. The court ruled the section unconstitutional, finding that although the provision had been rational and necessary at the time it had been enacted, changing demographics had rendered its formula inaccurate and no longer applicable. As a result, in states previously required to have preclearance, statutes requiring voter ID were able to immediately take effect .[44]
According to a 2021 report by the Brennan Center for Justice, the states of Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Montana, New Hampshire, Texas, and Wyoming all enacted restrictive Voter ID requirements which make it harder for Americans to vote.[45]
Court challenges
[edit]The practical effect of striking out section 4(b) of the Voting Rights Act in the Shelby County case was that a challenge to electoral law changes in covered states could no longer be determined by a federal administrative or judicial officer, instead having to be litigated in a court of law on a case-by-case basis, a much more costly and time-consuming process.
By the end of August 2017, federal courts had struck down voter ID laws in Ohio, Texas, North Carolina and Wisconsin. All the cases are likely to be heard ultimately by the US Supreme Court.[15] The court ruled that the legislature's ending of Ohio's "Golden Week" imposed a "modest burden" on the right to vote of African Americans and said that the state's justifications for the law "fail to outweigh that burden."[15] This week had been a period of time when residents could "register to vote and cast an early ballot at the same location."[15]
In 2017, the Texas law was initially struck down at the District level on the grounds that it intended discriminate against black and Hispanic voters, but the decision was reversed by the 5th Circuit.[46][47] A North Carolina law was overturned as "its provisions deliberately target African-Americans with almost surgical precision … in an effort to depress black turnout at the polls."[16] North Carolina appealed to the US Supreme Court, which declined to hear the appeal, allowing the prior federal court decision to stand.[48] Parts of Wisconsin's voter ID laws were ruled to be unconstitutional and it was advised to accept more forms of identification for the fall 2016 election cycle.[16]
Shelby County v. Holder
[edit]On June 25, 2013, the US Supreme Court declared, by a 5–4 decision, in Shelby County v. Holder that Section 4(b) of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 was unconstitutional. Previously, states with a history of proven voter discrimination were required to obtain preclearance from a federal court before making changes to their voting laws.[49] Section 4 of the Act contained the formula for determining which states or political subdivisions were covered by Section 5.[50] The majority opinion argued that the formula used to determine which jurisdictions required federal oversight or preclearance had not been updated to reflect current social conditions, including a decline in institutionalized discrimination and direct voter suppression.[49] The states previously covered under section 5 were: Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, South Carolina, Texas, and Virginia, as well as parts of California, Florida, Michigan, New York, North Carolina, and South Dakota.[51] By ruling these restrictions to be unconstitutional, it rendered section 5 unenforceable under the current formula.[52]
Since the Court's decision, several states passed new voter ID laws and other restrictions on registration and on voting. Within 24 hours of the Shelby County verdict, Texas, North Carolina, Mississippi, and Alabama, four states that were previously covered by Section 5 of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 began to implement or stated intentions to implement strict photo ID policies.[53] Texas' proposed policy required a voter to show their passport, driver license or other form of photo ID before they could cast their ballot. However, this policy was found to be discriminatory to black and Hispanic voters, and so it was adapted to include the provision for voters to be able to cast a ballot if they signed an affidavit explaining why they could not obtain a form of photo ID and showed an alternate form of ID, such as a utility bill.[54] According to a 2018 Brennan Center report, states that previously needed preclearance have purged voters off their rolls at a much higher rate than other states.[55] Additionally, according to another Brennan Center 2018 Poll on the State of Voting, most of the states that were previously covered by Section 5, have recently enacted laws or other measures that restricted voting rights.
Edward K. Olds argues in his December 2017 Columbia Law Review Article "More than "Rarely Used": A Post-"Shelby" Judicial Standard For Section 3 Preclearance" that in the wake of the defeat of Section 5 of the Voting Rights Act, which was struck down by Shelby County v. Holder, Section 3 could take on a very similar role. Section 3 states that a federal judge can require a jurisdiction to seek pre approval for future policies if it found to be in violation of the Fourteenth or Fifteenth Amendments, however, states that this is unlikely in the current political climate.[56]
In the 2015 Phylon article "A Response to Shelby County, Alabama v. Holder: Energizing, Educating and Empowering Voters," June Gary Hopps and Dorcas Davis Bowles argue that by eliminating section 5 of the Voting Rights Act, Shelby County v. Holder decreased the participation of minorities and that "The participation of these groups is not only important because of the implications for ensuring civil rights, but also for developing social capital within neighborhoods, and increasing positive inter-group relations." This article also states that combined with the Citizens United Supreme Court decision, there is an extreme potential for erosion to civil rights gains, that could "further alienate disenfranchised people."[57]
In the Berkeley Journal of African-American Law & Policy article "The Blinding Color of Race: Elections and Democracy in the Post-Shelby County Era" Sahar Aziz that "the majority in Shelby County lost sight of the objective of the VRA. This historic law was not merely about preventing the most extreme levels or forms of discrimination, but rather having in place a regime that is preventative in nature so as to ensure discrimination continues to decrease and eliminates the possibility of returning to a period of systemic disenfranchisement."[58]
Desmond S. King and Rogers M. Smith argue in their Du Bois Review article "The Last Stand?" that although Shelby v. Holder represents a barrier to African-American political participation, efforts to disproportionately decrease the political power of minorities will long-term, fail to prevent increases in political gains for minorities. However, "they threaten to foster severe conflicts in American politics for years to come."[59]
Studies and analysis
[edit]A 2005 report by former President Jimmy Carter and former Secretary of State James Baker concluded that concerns of both those who support and oppose strengthened voter ID laws were legitimate. It recommended voter ID requirements be enacted, to be slowly phased in over a period of five years, and accompanied by the issuance of free ID cards provided by mobile ID vans that would visit traditionally underserved communities.[60] In 2007, a report prepared by the staff of the federal Election Assistance Commission concluded "there is a great deal of debate on the pervasiveness of fraud."[61] Some studies have also found that ID laws can disproportionately disenfranchise low-income voters and voter of color.[62]
Cost of voter identification cards
[edit]According to a Harvard study, "the expenses for documentation, travel, and waiting time [for obtaining voter identification cards] are significant—especially for minority group and low-income voters—typically ranging from about $75 to $175. When legal fees are added to these numbers, the costs range as high as $1,500."[63][64] So even if the cards themselves may be free, the costs associated with obtaining the card can be expensive.[63] The author of the study notes that the costs associated with obtaining the card far exceeds the $1.50 poll tax (equivalent to $11.00 in 2023[65]) outlawed by the 24th amendment in 1964.[64]
Fraud prevention
[edit]The vast majority of voter ID laws in the United States target only voter impersonation, of which there are only 31 documented cases (some possibly involving multiple voters) in the United States from the 2000–2014 period.[66] According to PolitiFact, "in-person voter fraud—the kind targeted by the ID law—remains extremely rare".[67] The available research and evidence point to the type of fraud that would be prevented by voter ID laws as "very rare" or "extremely rare".[68] PolitiFact finds the suggestion that "voter fraud is rampant" false, giving it its "Pants on Fire" rating.[67] Most cases of alleged voter fraud involving dead voters have been shown to be a result of incorrect matching of voter rolls and death records, such as when someone died after they voted rather than before.[69] Writing in 2009, Harvard political scientist Stephen Ansolabehere noted that despite the common belief "that fraud occurs at least somewhat often in elections … social scientists have been unable to develop unambiguous measures of the incidence of fraud, and legal cases find very little hard evidence on the matter."[70] In a 2012 analysis, News21 of the Walter Cronkite School of Journalism surveyed thousands of election officials in 50 states regarding all instances of fraud relating to elections since 2000, and concluded that in-person voter impersonation is virtually non-existent, amounting to one out of about every 15 million prospective voters.[71]
A 2021 study in the Quarterly Journal of Economics by University of Bologna and Harvard Business School economists Enrico Cantoni and Vincent Pons found no evidence that strict voter ID laws had any effect on fraud – actual or perceived.[72]
Proponents of voter ID laws cite the registration of dead and out-of-state voters as a vulnerability in the electoral system. A 2012 report by the Pew Center showed that more than 1.8 million deceased people remain registered to vote nationwide. The same report found 3 million voters registered in multiple states, presumably due to changes of residency.[73] David Becker, the director of Election Initiatives for Pew, said this study's results pointed to the need to improve voter registration, rather than to evidence of voter fraud or suppression.[74]
Proponents of voter ID laws fear that motivated individuals could exploit registration irregularities to impersonate dead voters or impersonate former state residents, casting multiple fraudulent ballots. Critics of such laws note that they only prevent one kind of fraud, namely voter impersonation. They say that this form of fraud is illogical, as the risks (a fine of up to $10,000 and/or 5 years in prison) far outweigh the benefits (casting one extra vote for the voter's desired candidate).[75] Democrats have alleged that the scale of impersonation fraud has been greatly exaggerated by Republicans for political reasons.[76]
A 2012 investigation of 207 alleged dead voters in South Carolina found only five instances unexplained by clerical errors. For instance, sometimes a son with the same name as his dead father was accidentally recorded as voting under the father's name.[77] A study of dead voters in the 2006 Georgia midterm election concluded that only fifteen of the 66 alleged instances of dead voting were potentially fraudulent. All but four of the dead votes were cast absentee, and most of the absentee voters in question cast early ballots but died before the election, giving the impression of voter fraud.[78] A 2013 study testing for additional cases of electoral fraud in addition to two cases that had already been documented found no additional cases of such fraud.[79]
A 2007 report by the liberal Brennan Center for Justice concluded that voter impersonation was rarer than being struck by lightning. The author of this report, Justin Levitt, later reported in 2014 that he had identified only thirty-one credible instances of voter impersonation since 2000, involving a total of 241 ballots, out of a billion ballots cast.[80][81] Also, in 2007, Lorraine Minnite released a report for Project Vote concluding that voter fraud was "extremely rare" in the United States.[82] In 2014, a survey was published concluding that there was no evidence of widespread voter impersonation in the 2012 U.S. general election.[83]
Proponents of voter ID laws have pointed to a 2014 study by Old Dominion University professors Jesse Richman and David Earnest as justification. The study, which used data developed by the Cooperative Congressional Election Study, concluded that more than 14 percent of self-identified non-citizens in 2008 and 2010 indicated that they were registered to vote, approximately 6.4% of surveyed non-citizens voted in 2008, and 2.2% of surveyed non-citizens voted in 2010.[84][85] However, the study also concluded that voter ID requirements would be ineffective at reducing non-citizen voting.[86] This study has been criticized by numerous academics.[87][88][89] A 2015 study by the managers of the Cooperative Congressional Election Study found that Richman and Earnest's study was "almost certainly flawed" and that, in fact, it was most likely that 0% of non-citizens had voted in recent American elections.[88] Richman and Earnest's findings were the result of measurement error; some individuals who answered the survey checked the wrong boxes in surveys. Richman and Earnest therefore extrapolated from a handful of wrongfully classified cases to achieve an exaggerated number of individuals who appeared to be non-citizen voters.[88] Richman later conceded that "the response error issues … may have biased our numbers".[90] Richman has also rebuked President Trump for claiming that millions voted illegally in 2016.[90] Brian Schaffner, Professor of Political Science at University of Massachusetts, Amherst, who was part of the team that debunked Richman and Earnest's study said that the study
… is not only wrong, it is irresponsible social science and should never have been published in the first place. There is no evidence that non-citizens have voted in recent U.S. elections... It is bad research, because it fails to understand basic facts about the data it uses. Indeed, it took me and my colleagues only a few hours to figure out why the authors' findings were wrong and to produce the evidence needed to prove as much. The authors were essentially basing their claims on two pieces of data associated with the large survey—a question that asks people whether they are citizens and official vote records to which each respondent has been matched to determine whether he or she had voted. Both these pieces of information include some small amounts of measurement error, as is true of all survey questions. What the authors failed to consider is that measurement error was entirely responsible for their results. In fact, once my colleagues and I accounted for that error, we found that there were essentially zero non-citizens who voted in recent elections.
— Brian Schaffner[89]
Support for voter ID laws correlates with perceived prevalence of voter fraud.[91] Although absentee ballot fraud is more common[quantify] than voter impersonation, only six of the 31 states with voter ID laws also impose similar requirements on people who mail in absentee ballots.[92]
Perception of electoral systems
[edit]Lorraine Minnite of Demos has criticized proponents of voter ID laws for shifting their arguments in favor of such laws from voter fraud to electoral integrity. In an expert report prepared for the ACLU, she argued that "Calling the problem "electoral integrity" does not change the fact that the only threat to electoral integrity addressed by photo ID laws is in-person voter fraud," and that because such fraud is extremely rare, voter ID laws are not justified to prevent this problem.[93] But in 2005, American University's Commission on Federal Election Reform, co-chaired by former President Jimmy Carter and former Secretary of State James Baker, wrote:
The electoral system cannot inspire public confidence if no safeguards exist to deter or detect fraud or to confirm the identity of voters. Photo IDs currently are needed to board a plane, enter federal buildings, and cash a check. Voting is equally important.
— The Commission on Federal Election Reform[94]
The Commission concluded that, although proven voter impersonation is minimal, a photo ID requirement will ensure election integrity and safeguard public perception of the nation's voting system at little cost to anyone.[94]
However, among certain demographics, voter ID laws lower electoral confidence. A 2016 study concluded that Democrats in states with strict ID laws have reduced faith in the electoral system. It said that negative politicization by the Democratic Party may be to blame.[95] On the other hand, Republicans living in strict photo identification states were more confident in their elections, though possibly due to similar politicization by Republican elites.[95] Another 2015 study found that voters living in states with voter ID laws were not more confident in elections than voters who lived in states without such laws.[96] A 2016 study found that people living in states with voter ID laws were no more confident in their elections than people in states without such laws, nor did they perceive lower rates of voter impersonation fraud.[97] A 2017 study found similar results for both national and local election outcomes.[98]
Turnout
[edit]Studies of the effects of voter ID laws on turnout in the United States have generally found that such laws have little, if any, effect on turnout.[72][99][14] This may be because these laws do not reduce turnout very much; it may also be because the strictest voter ID laws have the largest effect on turnout, and they have only been enacted relatively recently.[13] Although most Americans possess a government-issued photo ID, those without ID may have trouble acquiring the proper credentials, lowering their turnout. The most comprehensive study of voter IDs, a 2017 study by Harvard political scientist Stephen Ansolabehere and Tufts political scientist Eitan Hersh, found that in Texas, 1.5% of those who showed up to vote in the 2012 election lacked the kinds of IDs that are targeted by voter ID laws, 4.5% of the total eligible population lacked them, 7.5% of black registered voters lack them.[100][101] The numbers are likely higher in states with more urban areas, as fewer voters have driving licenses.[100][101] A 2011 study by New York University's Brennan Center estimated that of the US population that is of voting age, 6–11% lack government-issued photo ID.[102] The Heritage Foundation, a conservative think tank, disputed the methodology of the study, citing a question in which 14 percent of respondents said they had both a U.S. birth certificate and naturalization papers.[103]
Since some legitimate voters lack the kind of IDs demanded by voter ID laws, some commentators have argued that strict voter ID laws reduce voter turnout, especially among poor, black, elderly, disabled, and minority-language voters, and voters who have changed their names.[104] However, the results of studies assessing the effect (or lack thereof) of these laws on turnout have been inconclusive.[105]: 945 For example, a 2012 study found that a stricter voter ID law in Georgia lowered turnout by about 0.4% in 2008 compared to 2004.[106] A 2006 study also found that voter ID laws decreased aggregate turnout by between 3 and 4 percent.[107] In contrast, several other studies have failed to demonstrate significant turnout reductions.[70][108] A 2010 study found that 1.2% of registered voters in three states with voter ID laws (Indiana, Maryland, and Mississippi) lacked an ID that complied with the law.[109] A 2011 study found that photo ID laws were correlated with a 1.6% decline in turnout, and non-photo ID laws were correlated with a 2.2% decline.[110] In a 2014 review by the Government Accountability Office of the academic literature, five studies out of ten found that voter ID laws had no significant effect on overall turnout, four studies found that voter ID laws decreased overall turnout, and one study found that the laws increased overall turnout.[111]
A 2014 Rice University study reported that Texas's voter ID law decreased turnout mainly among people who incorrectly thought they did not have the type of ID needed to comply with the law. The authors of this study also suggested that an education campaign aimed at clearly communicating what types of ID are acceptable in Texas would be beneficial.[112]
A 2016 study argued that, although no clear-cut relationship exists between strict voter ID laws and voter turnout, the disenfranchising impact of voter ID laws may be hidden by Democratic voter mobilization.[113] Strong negative reactions to voter ID laws among Democratic constituencies could, in theory, boost Democratic turnout enough to compensate for effects of the laws themselves.[113] A 2007 report found a small increase in Democratic turnout in places with new voter ID laws.[114]
A 2017 study found that 474 people tried to vote in Virginia's 2014 Senate election, but could not do so because they lacked the proper ID to comply with the state's voter ID law. The same study found that turnout was higher in parts of the state where registered voters were less likely to have a driver's license. The authors suggested that "This unexpected relationship might be explained by a targeted Department of Elections mailing, suggesting that the initial impact of voter ID laws may hinge on efforts to notify voters likely to be affected."[115]
A 2019 paper by Brown University economists found that the implementation of a photo ID law in Rhode Island led to a decline in turnout, registration, and voting among individuals who did not have drivers' licenses.[116]
Disparate impact
[edit]Charges of racial discrimination in voter ID laws are founded in the disparate impact doctrine of constitutional law, which claims that any action—intentional or unintentional—that statistically disadvantages a protected class constitutes discrimination. Disparate impact is most often discussed in the context of African Americans. The moral validity and constitutionality of this doctrine is hotly debated.[117] This is relevant to voter ID laws because of accusations that these laws disproportionately reduce turnout among minority voters.[118] According to an assessment of the existing research on voter ID laws by University of Pennsylvania political scientist Dan Hopkins, the research indicates that voter ID laws do disproportionately disenfranchise minority voters.[14] Research also shows that racial minorities are less likely to possess IDs.[119]
Federal appeals courts have struck down strict voter-ID laws in Texas and North Carolina, citing intent by the legislatures to discriminate against minority voters.[120] The appeals court noted that the North Carolina Legislature "requested data on the use, by race, of a number of voting practices"—then, data in hand, "enacted legislation that restricted voting and registration in five different ways, all of which disproportionately affected African Americans."[121] The changes to the voting process "target African Americans with almost surgical precision," and "impose cures for problems that did not exist."[121]
A 2008 study found that the strictest voter ID laws reduced voter turnout relative to the most lax form of such laws (stating one's name). The same study reported that "the stricter voter identification requirements depress turnout to a greater extent for less educated and lower income populations, for both minorities and non-minorities."[122] A 2009 study found that 84% of white registered voters in Indiana had access to photo ID to comply with that state's ID law, as compared to 78% of black voters on the rolls there.[123] A 2008 study found that African Americans, Hispanics, and the elderly were less likely to have a voter ID that complied with Georgia's voter ID law.[124]
A 2012 analysis by Nate Silver found that voter ID laws seem to decrease turnout by between 0.8% and 2.4%, depending on how strict they are, and tend to cause a shift towards the Republican candidate of between 0.4% and 1.2%. Silver found that the statistical reasoning was flawed in a number of studies which had found small effects but had described them as not statistically significant.[125]
In 2012, an investigation by Reuters found that voter ID laws in Georgia and Indiana had not led to lower turnout of minorities and concluded that concerns about this "are probably overstated".[126] In a 2014 review by the Government Accountability Office of the academic literature, three studies out of five found that voter ID laws reduced minority turnout whereas two studies found no significant impact.[111]
A 2014 study by the Government Accountability Office reported that voter ID laws in Kansas and Tennessee reduced turnout in these states by 1.9 and 2.2 percent, respectively, compared to four states that did not pass voter ID laws—Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, and Maine. The study indicates that young people, black people, and newly registered voters were most likely to have their turnout reduced. But Tennessee officials suggested that the reduced turnout may have been due to a lack of compelling ballot measures in 2012, and Kansas officials dismissed the drop in black voters as a product of high random variance in a small population. Tennessee officials questioned the reproducibility of this report, given its reliance on data from Catalist, which they claimed was a progressive political group.[127]
A 2014 study from the University of Iowa found no evidence that strict voter ID laws reduce minority turnout.[128] A 2012 study found that, although the Georgia voter ID laws lowered overall turnout by 0.4%, there was no racial or ethnic component to the suppression effect.[106]
Disparate impact may also be reflected in access to information about voter ID laws. A 2015 experimental study found that election officials queried about voter ID laws were slightly more likely to respond to emails from a non-Latino Anglo or European name (70.5% response rate) than a Latino name (64.8% response rate), though response accuracy was similar across those groups.[129]
Studies have also analyzed racial differences in ID requests rates. A 2012 study in the city of Boston found strong evidence that non-white voters were more likely to be asked for ID during the 2008 election. According to exit polls, 23% of whites, 33% of Asians, 33% of blacks, and 38% of Hispanics were asked for ID, though this effect is partially attributed to black and Hispanics preferring non-peak voting hours when election officials inspected a greater portion of IDs. Precinct differences confound the data, as black and Hispanic voters tended to vote at black and Hispanic-majority precincts.[130]
A 2010 study of the 2006 midterm election in New Mexico found that election officials asked Hispanics for ID more often than they did early voters, women, and non-Hispanics.[131] A 2009 study of the 2006 midterm elections nationwide found that 47% of white voters reported being asked to show photo identification at the polls, compared with 54% of Hispanics and 55% of African Americans."[70] Very few people were denied the chance to vote as a result of voter identification requests.[70] A 2015 study found that turnout among blacks in Georgia was generally higher since the state began enforcing its strict voter ID law.[132]
A 2017 study in the Journal of Politics "shows that strict identification laws have a differentially negative impact on the turnout of racial and ethnic minorities in primaries and general elections. We also find that voter ID laws skew democracy toward those on the political right."[133] The results of this study were challenged in a paper by Stanford political scientist Justin Grimmer and four other political scientists.[134] The paper says that the findings in the aforementioned study "a product of data inaccuracies, the presented evidence does not support the stated conclusion, and alternative model specifications produce highly variable results. When errors are corrected, one can recover positive, negative, or null estimates of the effect of voter ID laws on turnout, precluding firm conclusions."[134] In a response, the authors of the original study dismissed the aforementioned criticisms, and stood by the findings of the original article.[135] Columbia University statistician and political scientist Andrew Gelman said that the response by the authors of the original study "did not seem convincing" and that the finding of racial discrepancies in the original study does not stand.[136]
A 2017 report by Civis Analytics for the liberal super PAC Priorities USA purported to show that Hillary Clinton lost Wisconsin the 2016 presidential election due to voter suppression brought on by Wisconsin's strict voter ID laws.[137] Political scientists expressed serious skepticism of the report's methodology; Yale University political scientist Eitan Hersh said the report "does not meet acceptable evidence standards."[137] A 2017 paper by University of Wisconsin-Madison political scientists Kenneth Mayer and Michael DeCrescenzo also purported to show that voter suppression swayed Wisconsin from Clinton; this paper was also rebutted by other political scientists on the basis of poor methodology.[138]
A 2021 paper by University of Bologna and Harvard Business School economists Enrico Cantoni and Vincent Pons found that voter ID laws had "no negative effect on registration or turnout, overall or for any group defined by race, gender, age, or party affiliation."[72]
A 2019 study in the journal Electoral Studies found that the implementation of voter ID laws in South Carolina reduced overall turnout but did not have a disparate impact.[139] 2019 studies in Political Science Quarterly and the Atlantic Economic Journal found no evidence that voter ID laws have a disproportionate influence on minorities.[140][141]
A 2022 study found that Black and Latino voters were disproportionately likely to vote without ID.[142]
International comparisons
[edit]Many nations require some form of voter identification at the polling place, but specific details of the requirement vary widely.[143] In Spain, Greece, France, Belgium, India, and Italy, a government-issued photo ID is required to cast a ballot.[143] Mexico has a similar system, with all registered voters receiving a photo ID upon completing the registration process.[143] Several Western democracies do not require identification for voting, such as Denmark, Australia, and New Zealand.[143] In Ireland and Switzerland, poll workers reserve the right to request identification but are not required to do so.[143] In Canada, identification is required, but voters can provide any two forms of ID from a list of 45 possibilities. Canada's system is more stringent than the 17 U.S. states that do not require ID but less stringent than the 22 U.S. states with strict requirements. The strict Indiana ID system, for instance, accepts only five forms of ID: an Indiana driver's license, an Indiana ID card, a military ID, a US passport, or a student ID card from an in-state college or university.[143] Conversely, some countries, like Australia, require no form of identification at any election.[144] This position is similar to the situation in New York and California.[citation needed]
Several developing nations have instituted voter ID laws. Many Arab nations require voters to leave a fingerprint upon casting a ballot, allowing quick detection of fraud.[145] In 2012, the head of Libya's national election commission expressed surprise that the American system "depends so much on trust and the good faith of election officials and voters alike".[145] The Gambia gives each voter a single marble to cast, ensuring that no one can vote multiple times.[145]
Public opinion
[edit]Public opinion polls have shown broad support for voter ID laws among voters in the United States. A 2011 Rasmussen poll found that 75% of likely voters "believe voters should be required to show photo identification, such as a driver's license, before being allowed to vote."[146] A 2012 Fox News poll produced similar results, revealing that 87% of Republicans, 74% of independent voters, and 52% of Democrats supported new voter ID laws.[147] More recently, a 2021 Pew Research poll showed that 93% of Republicans and 61% of Democrats[a] favor requirements that voters show government-issued photo ID to vote.[148]
Although all major political demographics support voter ID laws, a 2013 study showed significant divergence in opinion between conservative-affiliated demographics, which are staunch supporters, and liberal-affiliated demographics, which are less supportive.[91] The study also showed that support depends on survey framing: when questions biased against voter ID laws are asked, support drops 15% compared to when questions favorable to voter ID laws are asked.[91] A 2016 study showed that emphasizing the adverse effects of voter ID laws on eligible voters decreased popular support for such laws.[149] Another 2016 study found that white people with high levels of implicit racism, but not explicit racism, were more supportive of voter ID laws when they were exposed to a fear-eliciting condition.[150] A 2016 study found that partisan affiliation is a major determinant of support for voter ID laws and that Republicans are much more likely than Democrats to be concerned about voter fraud.[151] Research shows that individuals who hold hostile views towards nonwhite immigrants are most likely to believe that voter fraud is rampant.[152]
Former Attorney General Eric Holder and others have compared the laws to a poll tax, in which southern states during the Jim Crow Era imposed voting fees, which discourage black and even some poor whites until the passage of grandfather clauses from voting.[153]
Politicization of voter ID issues
[edit]In 2014, a study released by the Congressional Research Service concluded that, in the absence of systematic risk analyses, it is difficult to determine what points in the election process—voter registration, voting systems, polling place location and hours, poll worker training, voter identification, vote tabulation, or other steps—involve the greatest potential risks to election integrity and therefore warrant the greatest attention.[154] Another 2014 study argued that careful voter roll maintenance is probably a more effective method for preventing voter fraud than voter ID laws.[79]
A 2015 study found that local coverage of voter fraud during the 2012 elections was greatest in presidential swing states and states that passed strict vote ID laws prior to the 2012 election. There was no evidence that the reporting was related to the actual rate of voter fraud in each state. Based on this data, the authors concluded that "parties and campaigns sought to place voter fraud on the political agenda in strategically important states to motivate their voting base ahead of the election".[155] Another 2015 study found a similar correlation between the enactment of voter ID laws and a state's electoral competitiveness, suggesting electioneering motives.[156]
A 2016 study found polarization over voter ID laws was less stark in state legislatures where electoral competition was not intense.[157] The same 2016 study found a notable relationship between the racial composition of a member's district, region, and electoral competition, and the likelihood that a state lawmaker supported a voter ID bill.[157] The study found that "Democratic lawmakers representing substantial black district populations are more opposed to restrictive voter ID laws, whereas Republican legislators with substantial black district populations are more supportive."[157] Southern lawmakers (particularly Democrats) were more opposed to restrictive voter ID legislation.[157] Black legislators in the South were the least supportive of restrictive voter ID bills.[157] A 2018 experimental study in Legislative Studies Quarterly, which sent messages from Latino and white constituents to lawmakers, found that lawmakers who supported voter ID laws were less likely to respond to messages sent by Latino constituents.[158]
A 2017 study in American Politics Research found that the adoption of voter ID laws is most likely when control of the governor's office and state legislature switches to Republicans, and when the size of black and Latino populations in the state increases.[159] Another 2017 study found that the different advertising strategies used to advertise Kansas' voter ID laws by different county clerks influenced the effect of these laws on turnout.[160]
A 2018 study by the Williams Institute found that 137,000 transgender people who have transitioned were eligible to vote in the 2018 US elections in states with strict voter ID laws. An estimated 57% of them may not have identification or documentation that states their preferred gender. Eight states currently have strict voter ID laws that require voters to provide a government-issued photo ID in order to vote at the polls. In these states, election officials and poll workers decide whether a voter's identification accurately identifies the voter and matches the information listed in the voter registration rolls.[161]
Several states controlled by Democrats maintain voter ID laws. For instance, Hawaii has required a state-issued photo ID for decades.[162] In 2011, the Rhode Island legislature enacted a photo ID requirement, which was signed by governor Lincoln Chafee, making Rhode Island the most recent state controlled by Democrats to pass such legislation.[163] However, both Hawaii and Rhode Island are "non-strict photo ID states", meaning that, in some circumstances, an affidavit or other legal measure can satisfy the ID requirement.[19] In 2021, many Democrats, including Joe Manchin, Stacey Abrams and Raphael Warnock signalled a general openness to voter ID laws in the context of the For the People Act. The Washington Post observed an "evolution" by many Democrats on the issue, some of whom were no longer as strongly opposed to voter ID, and in a few cases, went on record to say they had never really been opposed to it.[164][165]
Registration and election day voter ID laws by state
[edit]This section needs to be updated. (July 2022) |
| State | Original Date Enacted | Type of Law | Key Dates and Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 2014 | Photo ID (non-strict) | Law tightened in 2011 to require photo ID as of 2014,[166][167] but it had not obtained federal preclearance.[168] Following the US Supreme Court ruling in the case of Shelby County v. Holder, (2013), suspending the provision for pre-clearance, the state attorney general believed the voter ID law could be implemented in 2014.[169] The state of Alabama issues free voter ID cards to voters who need them.[170] These photo IDs are issued by driver license bureaus. The state closed driver license bureaus in eight of the ten counties with the highest percentages of nonwhite voters, and in every county in which blacks made up more than 75 percent of registered voters.[171] However, the Board of Registrars' offices were kept open in all counties, and mobile ID locations remain active.[172] Two election officials can sign sworn statements saying they know the voter as an alternative to showing a photo ID. |
| Alaska | Non Photo ID required (non-strict) | A Photo ID law was drafted by Rep. Bob Lynn; it was referred to the State Affairs and Judiciary Committees on January 7, 2013.[173][174] | |
| Arizona | 2004 | Strict Non Photo ID | Non-photographic forms of ID are accepted at polling places as of 2013[175] |
| Arkansas | 2013 | Non Photo ID required (non-strict) | Photo ID bill passed by lawmakers in 2013, and survived a veto by the Governor to become Act 595 of 2013. On May 2, 2014, Pulaski County Circuit Judge Tim Fox ruled Act 595 unconstitutional, but stayed his ruling pending an appeal.[176] The week before early voting began for the 2014 midterm elections, the Arkansas Supreme Court affirmed Judge Fox's decision declaring Arkansas Act 595 of 2013 to be unconstitutional on its face.[177] |
| California | Multiple ID sources accepted, including Photo ID's | In most cases, California voters are not required to show identification before they cast ballots.[178][179] | |
| Colorado | 2003 | Non-Photo ID required (non-strict) | Non-photographic forms of ID allowed at polling places as of 2013.[180] |
| Connecticut | Non Photo ID required (non-strict) | Non-photographic forms of ID allowed at polling places.[181] | |
| Delaware | Non Photo ID required (non-strict) | Non-photographic forms of ID allowed at polling places as of 2013.[182] | |
| Florida | 1977 | Photo ID (non-strict) | Photo ID required when voting in person.[183] |
| Georgia | 1977 | Strict Photo ID | Existing law tightened in 2005 to require a photo ID; in 2006, passed a law providing for the issuance of voter ID cards on request at no cost to registered voters who do not have a driver's license or state-issued ID card. Photo ID was required to vote in the 2012 elections.[184] Photo ID required for absentee voting as of 2021, pending legal challenges.[185] |
| Hawaii | 1978 | Photo ID (non-strict) | Photo ID required when voting in person.[162][186] |
| Idaho | 2010 | Photo ID (non-strict) | Voters may sign a Personal Identification Affidavit if they do not possess a Photo ID at the polls.[187] |
| Illinois | No ID required | Republican Senators authoring a bill for Photo ID.[188] | |
| Indiana | 2005 | Strict Photo ID | Photo ID required when voting in person, enacted in 2008 after Supreme Court clearance.[189] The Indiana law was upheld by the U.S. Supreme Court in Crawford v. Marion County Election Board. |
| Iowa | 2017 | ID required | Iowa voters are required to show a voter ID card, driver's license, non-driver's ID, military/veterans ID, passport, or tribal document at the polls before they vote.[190] |
| Kansas | 2011 | Strict Photo ID | Photo ID required for in person voting; registration requires proof of citizenship, i.e., passport, birth certificate.[191] The state suggested that federal registration ID could be used only for federal elections, and voters would need proof of citizenship for local and state elections. In July 2016 a federal court struck this down, and said the state had to allow more forms of ID for voting in November 2016. [citation needed] The Tenth Circuit struct down the requirement of proof of citizenship to register in April 2020.[192] |
| Kentucky | Non Photo ID required (non-strict) | A citizen may vote if they have Photo ID, or if a precinct officer can vouch for the voter.[193] | |
| Louisiana | Photo ID (non-strict) | Voters may also use non-photographic identification at the polling place.[194] | |
| Maine | No ID required | No ID needed at polling place if registered to vote at least one day prior to election. However an ID is required to vote if person was registered to vote on the day of the election[195] | |
| Maryland | 2013 | No ID required | Republicans sponsored a House Bill requiring Photo ID in 2013.[196] |
| Massachusetts | No ID required | Non-photographic ID is accepted at polling stations.[197] | |
| Michigan | Photo ID (non-strict) | Passed in 1996, but ruled invalid until a State Supreme Court ruling in 2007. Voters are requested to show photo ID or sign a statement saying they do not have valid ID in their possession at the time. Either way, the voter will not be turned away.[198] | |
| Minnesota | Multiple ID sources accepted, including Photo ID's | Minnesota registration can be done in advance online or on paper, which requires state drivers license or MN ID numbers (both are photo ID's) or partial Social Security number. Election day registration has been in place in Minnesota since 1974.[199] On election day, previously registered voters must sign their name on the precinct voter list but are not required to provide a photo ID. For voters who register on election day there are seven options to prove identity and residency in the voting precinct, including ID with current name and address (examples use photos), other approved photo ID's, a list of approved documents, another registered voter vouching for address, college ID (normally includes photo), valid registration in same precinct, notice of late registration, staff person of residential facility.[200][201] Some, mostly urban Minnesota precincts, use computer poll book software that, as an option, can read the bar code of a Minnesota drivers license and quickly match the voter with their electronically stored registration, a feature that speeds up voting.
The National Conference of State Legislatures (NCSL) March 2023 update of "Voter ID Laws" misrepresents Minnesota's election rules by labeling them as "No document required to vote".[202] While documentation is not required for voters who have preregistered up to two years prior to and 21 days before election day (and voted in the last four years), a comprehensive list of identity documents (including photo ID's) and alternatives are required to preregister, and the same list applies to voters registering on election day. Minnesota also allows voters to register by checking a box when they apply for or renew their state driver’s license or state ID (both are photo ID's). | |
| Mississippi | 2011 | Strict Photo ID | Governor signed Photo ID bill into law in 2012. The bill was required to go through Pre-Clearance check from the federal government.[203] The US Supreme Court ruling in Shelby v. Holder (2013) suspended this provision. Mississippi was expected to enact its new Photo ID requirement in 2014.[204]
Photo ID is now required to vote in 2018.[205] |
| Missouri | 2002 | Non-Photo ID required (non-strict) | In 2006, the existing law was tightened to require photo ID. In 2006, State Supreme Court blocks law. In 2013, State House passes Voter ID law, needing approval by both State Senate and voters in November 2014 elections.[206] State House passes an additional version of Photo ID law in 2016. State Senate passes Photo ID law in 2016. Vote held to amend the state constitution in regards to Photo ID requirement in summer of 2016, resulting in Photo ID law being enacted.[207] |
| Montana | 2003 | Non-Photo ID required (non-strict) | Montana Voter ID Bill tabled in committee in 2013 by both Republicans and Democrats. Voter impersonation fraud was not substantiated as a problem in the state.[208] |
| Nebraska | Photo Id and other options | Online, mail in, Department of Motor Vehicles in-office and personal messenger/agent voter registration must be completed by third Friday prior to election. In person at local County Clerk's office by 2nd Friday prior. Registration requires a copy of a current and valid photo ID, or a copy of a utility bill, bank statement, government check, paycheck or other government document which is dated within 60 days immediately prior to the date of presentation showing the same name and residence address provided on the voter registration application.[209] | |
| Nevada | No ID required | Secretary of State sponsors a bill for Photo ID in 2012.[210] | |
| New Hampshire | 2015 | Photo ID (non-strict) | Voters may sign an affidavit and have their photograph taken in lieu of showing a photo ID. (Voters who object to having their photo taken for religious reasons may sign an additional religious affidavit in lieu of the photograph.) |
| New Jersey | No ID required | Non-photographic forms of ID are accepted at the polls.[211] | |
| New Mexico | 2008 | No ID required | In 2008, the existing voter ID law was relaxed, and now allows a voter to satisfy the ID requirement by stating his/her name, address as registered, and year of birth.[citation needed] |
| New York | No ID required | Non-photographic ID accepted at polling stations[212] | |
| North Carolina | 2018 | Photo ID (strict) | In 2013, the state House passed a bill that requires voters to show a photo ID issued by North Carolina, a passport, or a military identification card when they go to the polls by 2016. Out-of-state drivers licenses are accepted only if the voter registered within 90 days of the election, and university photo identification is never acceptable.[213] In July 2016, a three-judge panel of the United States Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit reversed a trial court decision in a number of consolidated actions and struck down the law's photo ID requirement, finding that the new voting provisions targeted African Americans "with almost surgical precision," and that the legislators had acted with clear "discriminatory intent" in enacting strict election rules, shaping the rules based on data they received about African-American registration and voting patterns.[214][215][216][217] The U.S. Supreme Court let this decision stand without review in May 2017.[218][219][220] In response, the General Assembly proposed, and the voters passed, a voter ID requirement in the state constitution. Enabling legislation is set to take effect in 2020.[221] A judge temporarily blocked the law on December 27, 2019.[222] Democratic Attorney General Josh Stein has decided to appeal.[223] The General Assembly, through the joint action of North Carolina's Speaker of the House and President pro tempore of the Senate, have filed for an emergency stay.[needs update] |
| North Dakota | 2003 | Strict Non-Photo ID | ND Senate passes bill that would require Photo identification OR a person with Photo ID to vouch for a voter without ID. 2003 law amended in 2013, and moved to a strict non-photo requirement.[citation needed] On August 1, 2016, a federal judge blocked the law, citing "undisputed evidence … that Native Americans face substantial and disproportionate burdens in obtaining each form of ID deemed acceptable".[17] Specifically, the state had said that tribal cards without street addresses of the resident were unacceptable, but many Native Americans use post office boxes and do not have street addresses on reservations. The state revised the law in April 2017. The law was again put on hold by the district court in April 2018. This decision was appealed to the Eighth Circuit Court of Appeals and on July 31, 2019, the law was upheld.[224] |
| Ohio | 2006 | Strict Photo ID | Non-photographic forms of ID are accepted at polling stations.[225] With strong Republican majorities in Ohio House and Senate, the Photo ID bill was expected to be revisited following the ruling in Shelby v. Holder (2013).[226] The legislature rescinded the practice of a "Golden Week," during which voters could both register and vote early. In July 2016 the court ruled that this change put an undue burden on African-American voters, as the state had not proved justification through documented instances of fraud.
Ohio House Bill 458, enacting a strict photo ID requirement and limitations on mail-in voting and in-person early voting was signed into law by Gov. Mike DeWine on Jan. 6, 2023. The law requires voters to present a photo ID in order to cast their ballots. Furthermore, the ID requirement also applies to voter registration.[227] |
| Oklahoma | 2009 | Non-Photo ID required (non-strict) | Oklahoma voters approved a voter Photo ID proposal proposed by the Legislature in 2010. The only non-photo form of ID accepted at the polls is the voter's registration card.[228] |
| Oregon | Mail Ballots Only | Oregon has no polling stations, and ballots are mailed in. Non-photographic forms of ID are accepted for voting registration. Ballot envelopes must be signed and signatures are compared to voter registration card.[229] | |
| Pennsylvania | No ID required | Law struck down by Commonwealth Court Judge Bernard L. McGinley on January 17, 2014, as "violative of the constitutional rights of state voters" after first full evidentiary trial since Shelby v Holder (2013). The law was found, by preponderance of evidence, to place undue burden on hundreds of thousands of already registered voters due to a lack of infrastructure and state support for obtaining required IDs.[40][230] | |
| Rhode Island | 2014 | Photo ID (non-strict) | RI requires Photo ID at the polls in 2014.[231] |
| South Carolina | 1988 | Photo ID (non-strict) | Law tightened in 2011.[166] U.S. Justice Department rejected South Carolina's law as placing an undue burden disproportionately on minority voters.[34] On October 10, 2012, the U.S. District Court upheld South Carolina's Voter ID law, though the law did not take effect until 2013.[232][233] As of January 2016, a photo ID is requested, but a voter registration card will be accepted if there is a "reasonable impediment" in possessing a photo ID.[234] |
| South Dakota | 2003 | Photo ID (non-strict) | If a voter does not possess a photo ID at the polling place, then the voter may complete an affidavit of personal identification.[235] |
| Tennessee | 2011 | Strict Photo ID | Law tightened in 2011.[166] Tennessee voters were required to show Photo ID during the 2012 elections.[236] |
| Texas | 1990 | Strict Photo ID | Law tightened in 2011.[166] U.S. Justice Department rejected the Texas law as placing an undue burden disproportionately on minority voters.[237] The 2013 US Supreme Court ruling in Shelby County v. Holder (2013) suspended the provision for pre-clearance absent an updated model.[238] On October 9, 2014, a U.S. District Judge struck down the law.[239] On October 14, 2014, a panel for the 5th Circuit Court of Appeals issued a preliminary injunction against the ruling of the District Court, which was confirmed 6-3 by the U.S. Supreme Court on October 18; it sent the law back to the lower courts. Therefore, the state will implement this law for the 2014 elections.[240] On August 5, 2015, the 5th Circuit Court of Appeals found the law to violate Section 2 of the Voting Rights Act and sent it back to the U.S. District Court.[241] In July 2016, the 5th Circuit Court of Appeals found the law discriminatory against minorities and ordered the lower court to come up with a fix before the November 2016 elections.[242] In February 2017, U.S. Attorney General Jeff Sessions dropped the lawsuit against the 2011 voter ID legislation.[243] |
| Utah | 2009 | Non-Photo ID required (non-strict) | Non-photographic forms of ID are accepted at polling stations.[244] |
| Vermont | No ID required | No ID required to vote at polling stations.[245] | |
| Virginia | 2020 | No photo ID required | Lawmakers passed a Voter ID bill in 2010, and the then Governor implemented it in a way that allows non-photo IDs. After the 2012 election, the Virginia legislature passed a new law stipulating that non-photo IDs cannot be used. The governor signed a law to require photo IDs in 2013. (Acceptable forms of voter ID include a permit for a concealed handgun but not a Social Security card or utility bill.)[246] The law would have needed to pass "pre-clearance" by the U.S. Department of Justice under the 1965 Voting Rights Act (certain states and jurisdictions, mostly in Southern states were required to wait for pre-clearance before changing voting laws).[247] The US Supreme Court ruling in the case of Shelby County v. Holder, (2013), suspended the provision for pre-clearance, clearing the way for Virginia to enact the new Photo ID requirement in 2014.[248] Governor Northam signed legislation repealing the photo ID requirement on April 12, 2020.[249][250] |
| Washington | 2005 | Non-Photo ID required (non-strict) | Washington has no polling stations. Ballots are mailed in.[251] |
| West Virginia | 2017 | Non-Photo ID requested (non-strict) | Republicans were preparing a Photo ID bill in 2013.[252] West Virginia now requests a non-photo ID to vote in 2017.[253] |
| Wisconsin | 2011 | Strict Photo ID | Following two 2012 rulings by Dane County circuit judges that blocked implementation of the 2011 Wisconsin Act 23 law requiring Voter ID, on July 31, 2014, the Wisconsin Supreme Court upheld the law.[254] On September 12, the Seventh Circuit Court of Appeals allowed the law to be put into effect 54 days before the 2014 elections, overturning a previous ruling in federal court.[255] On October 9, 2014, the state was barred from implementing the Voter ID law for 2014 by the U.S. Supreme Court.[256][257] On March 23, 2015, the United States Supreme Court rejected an appeal by the ACLU against Wisconsin's voter ID law, effectively upholding the Seventh Circuit's ruling that it is constitutional.[38] The law went into effect with the local/state primary vote on February 16, 2016.[258] The case was remanded back to Judge Adelman of the federal Eastern District of Wisconsin for further proceedings. He gathered evidence as to the burden of the law. In July 2016 he issued an injunction against the voter ID law, "ruling citizens without an official ID may still cast ballots after signing an affidavit affirming their identity."[259] This ruling was appealed to the Seventh Circuit and subsequently put on hold in August 2016. Oral arguments were held in February 2017.[224] A decision is still pending.[260] |
| Wyoming | 2021 | Strict Non Photo ID | Acceptable identification includes a Wyoming driver's license, a U.S. passport, or a Medicaid or Medicare insurance card.[261][262] |
| Washington, D.C. | No ID required | No ID needed at polling stations.[263] |
See also
[edit]- Election Integrity Commission
- Identity documents in the United States
- Transgender disenfranchisement in the United States#Voter ID history
- Voter fraud in the United States
- Voter identification laws
- Voter suppression in the United States
 Politics portal
Politics portal United States portal
United States portal
Notes
[edit]- ^ Figures include Independents who reported leaning towards either party.
References
[edit]- ^ Tokaji, Daniel P. "The Help America Vote Act: An Overview". The E-Book on Election Law: An Online Reference Guide. Moritz College of Law. Retrieved March 13, 2013.
- ^ a b "Everything You've Ever Wanted to Know About Voter ID Laws". ProPublica. Retrieved October 2, 2012.
- ^ Greenhouse, Linda (April 29, 2008). "In a 6-to-3 Vote, Justices Uphold a Voter ID Law". The New York Times.
- ^ "Voter Identification Requirements – Voter ID Laws". National Conference of State Legislatures. Retrieved November 5, 2014.
- ^ shanton, karen (May 2014). "voter id in the courts" (PDF). Retrieved July 10, 2021.
- ^ Heinz, Ethan (September 24, 2022). "NAACP and League of Women Voters sues over voter ID laws". ABC17NEWS. Retrieved October 24, 2022.
- ^ Mills, Shamane (March 2, 2016). "National Group Steps In To Help Madison Voters With ID Requirements". Wisconsin Public Radio. Retrieved October 24, 2022.
- ^ Gilbert, Michael D. (September 5, 2014). "The Problem of Voter Fraud". Columbia Law Review. 115 (3): 739–75.Virginia Public Law and Legal Theory Research Paper No. 2014-56; Virginia Law and Economics Research Paper No. 2014-15.
- ^ Farrell, Henry (November 14, 2013). "Trump's commission should investigate alien abductions, not voter fraud. There's as much survey evidence for both". The Washington Post. Retrieved May 12, 2017.
- ^ Cottrell, David; Herron, Michael C.; Westwood, Sean J. (October 26, 2017). "An exploration of Donald Trump's allegations of massive voter fraud in the 2016 General Election". Electoral Studies. 51: 123–142. doi:10.1016/j.electstud.2017.09.002.
- ^ Skelley, Geoffrey (May 17, 2021). "How The Republican Push To Restrict Voting Could Affect Our Elections". FiveThirtyEight. Retrieved May 17, 2021.
- ^ Hicks, William; McKee, Seth; Smith, Daniel (February 21, 2016). "The Determinants of State Legislator Support for Restrictive Voter ID Laws". State Politics & Policy Quarterly. 16 (4): 411–431. doi:10.1177/1532440016630752. S2CID 27742794.
- ^ a b Highton, Benjamin (2017). "Voter Identification Laws and Turnout in the United States". Annual Review of Political Science. 20: 149–167. doi:10.1146/annurev-polisci-051215-022822.
- ^ a b c Hopkins, Dan (August 21, 2018). "What We Know About Voter ID Laws". FiveThirtyEight. Retrieved August 21, 2018.
- ^ a b c d Ariane de Vogue, "Voting challenges head toward the Supreme Court: 4 cases to watch", CNN, July 19, 2016; accessed July 30, 2016
- ^ a b c d Wines, Michael; Blinder, Alan (July 30, 2016). "Voter ID Laws Take a Beating in U.S. Courts". The New York Times. p. 1.
- ^ a b Rober Barnes (August 1, 2016). "Federal judge blocks N. Dakota's voter-ID law, calling it unfair to Native Americans". The Washington Post. Retrieved August 2, 2016.
- ^ "Voter ID". National Conference of State Legislatures. Retrieved September 15, 2016.
- ^ a b "Voter ID: State Requirements". National Conference of State Legislatures. October 21, 2014.
- ^ EL. "Voter Identification Requirements". National Conference of State Legislatures.
- ^ "Voter ID History". National Conference of State Legislatures. Retrieved November 5, 2014.
- ^ "Va. High Court Panel Bars Voter ID Plan". The Washington Post. October 23, 1999. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ "Voters in 10 Localities to Receive ID Cards". Pqasb.pqarchiver.com. October 2, 1999. Archived from the original on November 8, 2012. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ Eviatar, Daphne (October 1, 2008). "Florida 2000 Redux?". The Washington Independent. American Independent Institute. Archived from the original on August 8, 2011. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ Urbina, Ian (May 12, 2008). "Voter ID Battle Shifts to Proof of Citizenship". The New York Times. Missouri;Florida;Kansas;Oklahoma;South Carolina;Arizona;Indiana. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ "More states may copy Arizona's proof-of-citizenship voter requirement". Tucson Citizen. January 16, 2008. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ Barnes, Robert (April 29, 2008). "High Court Upholds Indiana Law On Voter ID". The Washington Post. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ "Supreme Court Hears Indiana Voter ID Case". NPR. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ Biskupic, Joan (January 6, 2008). "Voter ID case could affect election laws". USA Today. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ "After Six-Year Fight, Perry Signs Voter ID into Law". The Texas Observer. May 27, 2011. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ "Voter identification: First, show your face". The Economist. September 17, 2011. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ "Providence Journal article". The Providence Journal. August 23, 2011. Retrieved November 12, 2011.[dead link]
- ^ Smith, Gina. "Free rides to DMV offered for photo IDs". The State. Archived from the original on January 24, 2012. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ a b Kinnard, Meg (December 23, 2011). "HuffPost, 23 December 2011: South Carolina Voter ID Law: Justice Department Blocks Controversial Legislation". The Huffington Post. Retrieved October 2, 2012.
- ^ Venegren, Jessica; Doherty, Shawn (September 7, 2011). "Top DOT official tells staff not to mention free voter ID cards to the public — unless they ask". Capital Times. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- ^ "LEAGUE OF WOMEN VOTERS OF WISCONSIN EDUCATION NETWORK, INC. AND MELANIE G. RAMEY, PLAINTIFFS-RESPONDENTS,† V. SCOTT WALKER, THOMAS BARLAND, GERALD C. NICHOL, MICHAEL BRENNAN, THOMAS CANE, DAVID G. DEININGER AND TIMOTHY VOCKE, DEFENDANTS-APPELLANTS, DOROTHY JANIS, JAMES JANIS, AND MATTHEW AUGUSTINE, INTERVENORS-CO-APPELLANTS" (PDF). Court of Appeals of Wisconsin. Retrieved October 28, 2019.
- ^ "High court blocks Wisconsin voter ID law". WPLG. October 9, 2014. Archived from the original on October 16, 2014. Retrieved October 10, 2014.
- ^ a b Hurley, Lawrence (March 23, 2015) – "U.S. top court rejects challenge to Wisconsin voter ID law". Reuters. Retrieved March 24, 2015.
- ^ "Challenges loom for Pennsylvania's new voter ID law". The Patriot-News. Associated Press. March 15, 2012. Retrieved October 2, 2012.
- ^ a b "The Uncertain Future of Voter ID Laws". The Atlantic. January 18, 2014. Retrieved January 18, 2014.
- ^ Karen Langley (October 2, 2012). "Judge blocks enforcement of portion of Pa. voter ID law". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. Retrieved October 2, 2012.
- ^ Ragsdale, Jim (November 7, 2012). "Voter ID drive rejected". Star Tribune. Retrieved March 20, 2013.
- ^ "Flurry of Voter ID laws tied to conservative group ALEC". NBC News. May 13, 2016. Retrieved May 14, 2016.
- ^ "Texas Voter ID Law "Will Take..."". Dallas News. Archived from the original on June 26, 2013. Retrieved June 26, 2013.
- ^ Brennan Center for Justice, October 2021
- ^ Fernandez, Manny (April 10, 2017). "Federal Judge Says Texas Voter ID Law Intentionally Discriminates". The New York Times. Retrieved August 14, 2018.
- ^ Ura, Alexa (April 27, 2018). "Federal appellate court upholds embattled Texas voter ID law". The Texas Tribune. Retrieved August 29, 2021.
- ^ Liptak, Adam; Wines, Michael (May 15, 2017). "Strict North Carolina Voter ID Law Thwarted After Supreme Court Rejects Case". The New York Times. Retrieved August 14, 2018.
- ^ a b "Shelby County v. Holder, 570 U.S. ___ (2013)". Retrieved December 8, 2018 – via Justia.
- ^ "Supreme Court Rules on Voting Rights Act: June 25, 2013." In Historic Documents of 2013, 284–98. Washington, DC: CQ Press, 2014. doi:10.4135/9781483347851.n31
- ^ Fuller, Jaime. "How has voting changed since Shelby County v. Holder?". The Washington Post. Retrieved November 16, 2018.
- ^ "ABA panel examines the effects of Shelby County v. Holder". American Bar Association. September 17, 2014. Archived from the original on December 15, 2018. Retrieved November 16, 2018.
- ^ "Effects of Shelby County v. Holder". Brennan Center for Justice. August 6, 2018. Retrieved November 16, 2018.
- ^ Fernandez, Manny (April 27, 2018). "Texas' Voter ID Law Does Not Discriminate and Can Stand, Appeals Panel Rules". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved December 8, 2018.
- ^ "Purges: A Growing Threat to the Right to Vote" (PDF).
- ^ Olds, Edward K. (2017). "More Than "rarely Used": A Post–"shelby" Judicial Standard for Section 3 Preclearance". Columbia Law Review. 117 (8): 2185–2223. JSTOR 44464881.
- ^ Hopps, June Gary; Bowles, Dorcas Davis (2015). "A Response to Shelby County, Alabama v. Holder: Energizing, Educating and Empowering Voters". Phylon. 52 (2): 1–23. JSTOR 43681951.
- ^ Aziz, Sahar (April 2014). "The Blinding Color of Race: Elections and Democracy after Shelby". Berkeley Journal of African American Law and Policy.
- ^ King, Desmond S.; Smith, Rogers M. (Spring 2016). "THE LAST STAND?". Du Bois Review. 13 (1): 25–44. doi:10.1017/S1742058X1500017X. S2CID 148230193. ProQuest 1801833400.
- ^ Carter, Jimmy; Baker, James (February 3, 2008). "A Clearer Picture on Voter ID". Carter Center. Retrieved May 14, 2014.
- ^ Urbina, Ian (April 11, 2007). "Panel Said to Alter Finding on Voter Fraud". The New York Times. Retrieved December 17, 2011.
- ^ Milford, Sean. "Photo identification at the ballot: election protection or voter suppression?". Missouri Law Review. 80 (1): 297.
- ^ a b "'Free' voter IDs are costly, Harvard Law report finds – Harvard Law Today". Harvard Law Today. Retrieved January 11, 2017.
- ^ a b "The High Cost of 'Free' Photo Voter Identification Cards" (PDF).
- ^ Johnston, Louis; Williamson, Samuel H. (2023). "What Was the U.S. GDP Then?". MeasuringWorth. Retrieved November 30, 2023. United States Gross Domestic Product deflator figures follow the MeasuringWorth series.
- ^ Bump, Philip (October 13, 2014). "The disconnect between voter ID laws and voter fraud". The Fix. The Washington Post. Retrieved July 26, 2016.
- ^ a b "PolitiFact - Light a match to Greg Abbott's ridiculous claim about 'rampant voter fraud'". Retrieved August 3, 2016.
- ^
- Cassidy, Chrstina A.; Moreno, Ivan (May 14, 2017). "In Wisconsin, ID law proved insurmountable for many voters". Associated Press. Retrieved May 14, 2017.
- Liptak, Adam (March 23, 2015). "Wisconsin Decides Not to Enforce Voter ID Law". The New York Times. Retrieved May 14, 2017.
- "Despite Court Ruling, Voting Rights Fight Continues In North Carolina". NPR. Retrieved May 14, 2017.
- "Trump's Bogus Voter Fraud Claims". FactCheck.org. October 19, 2016. Retrieved May 14, 2017.
- Vitali, Ali; Peter Alexander; Kelly O'Donnell (May 11, 2017). "Trump establishes vote fraud commission". CNBC. Retrieved May 14, 2017.
- Colvin, Jill (October 18, 2016). "trump-wrongly-insists-voter-fraud-is-very-very-common". U.S. News & World Report. Associated Press. Archived from the original on October 20, 2016.
- "Trump voter fraud claim was '800lb gorilla in jury box' at Texas trial". The Guardian. Associated Press. February 11, 2017. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved May 14, 2017.
- ^ "The 'Voter Fraud' Myth Debunked". Rolling Stone. June 12, 2012. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- ^ a b c d Ansolabehere, Stephen (January 1, 2009). "Effects of Identification Requirements on Voting: Evidence from the Experiences of Voters on Election Day". PS: Political Science & Politics. 42 (1): 127–130. doi:10.1017/S1049096509090313. ISSN 1537-5935. S2CID 15315808.
- ^ "Who Can Vote? - A News21 2012 National Project". votingrights.news21.com. Retrieved August 14, 2018.
- ^ a b c Cantoni, Enrico; Pons, Vincent (2021). "Strict ID Laws Don't Stop Voters: Evidence from a U.S. Nationwide Panel, 2008–2018". The Quarterly Journal of Economics. 136 (4): 2615–2660. doi:10.1093/qje/qjab019. hdl:11585/821494. ISSN 0033-5533.
- ^ Pam Fessler (February 14, 2012). "Study: 1.8 Million Dead People Still Registered to Vote". NPR. Retrieved January 18, 2016.
- ^ Weinger, Mackenzie (February 14, 2012). "Report: 1.8M dead registered to vote". Politico. Retrieved March 28, 2016.
- ^ Bingham, Amy (September 12, 2012). "Voter Fraud: Non-Existent Problem or Election-Threatening Epidemic?". ABC News. Retrieved March 30, 2016.
- ^ "Voter ID Laws Target Rarely Occurring Voter Fraud". Fox News. Associated Press. September 24, 2011. Retrieved March 30, 2016.
- ^ Kessler, Glenn (July 24, 2013). "The case of 'zombie' voters in South Carolina". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved February 15, 2016.
- ^ Hood, M. V.; Gillespie, William (March 1, 2012). "They Just Do Not Vote Like They Used To: A Methodology to Empirically Assess Election Fraud". Social Science Quarterly. 93 (1): 76–94. doi:10.1111/j.1540-6237.2011.00837.x. ISSN 1540-6237.
- ^ a b Christensen, Ray; Schultz, Thomas J. (March 1, 2014). "Identifying Election Fraud Using Orphan and Low Propensity Voters". American Politics Research. 42 (2): 311–37. doi:10.1177/1532673X13498411. ISSN 1532-673X. S2CID 154343482.
- ^ Diallo, Amadou (February 10, 2016). "Republicans champion voter ID laws absent credible evidence of fraud". Al Jazeera America. Retrieved March 28, 2016.
- ^ Bump, Philip (August 3, 2016). "Here's how rare in-person voter fraud is". The Washington Post. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- ^ Minnite, Lorraine (2007). "The Politics of Voter Fraud" (PDF). Project Vote. Retrieved March 29, 2016.
- ^ Ahlquist, John S.; Mayer, Kenneth R.; Jackman, Simon (2014). "Alien Abduction and Voter Impersonation in the 2012 U.S. General Election: Evidence from a Survey List Experiment". Election Law Journal: Rules, Politics, and Policy. 13 (4): 460–475. doi:10.1089/elj.2013.0231.
- ^ Richman, Jesse (October 24, 2014). "Washington Post: Could non-citizens decide the November election?". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 18, 2015.
- ^ Richman, Jesse T.; Chattha, Gulshan A.; Earnest, David C. (December 1, 2014). "Do non-citizens vote in U.S. elections?". Electoral Studies. 36: 149–157. doi:10.1016/j.electstud.2014.09.001.
- ^ Hiltzik, Michael (October 31, 2014). "Today's voting freakout: noncitizens are coming to steal your election". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved March 28, 2016.
- ^ Bump, Philip (October 27, 2014). "Methodological challenges affect study of non-citizens' voting". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 7, 2016.
- ^ a b c Ansolabehere, Stephen; Luks, Samantha; Schaffner, Brian F. (December 2015). "The perils of cherry picking low frequency events in large sample surveys". Electoral Studies. 40: 409–10. doi:10.1016/j.electstud.2015.07.002.
- ^ a b "Trump's Claims About Illegal Votes Are Nonsense. I Debunked the Study He Cites as 'Evidence.'". POLITICO Magazine. Retrieved January 27, 2017.
- ^ a b Cohn, Nate (January 26, 2017). "Illegal Voting Claims, and Why They Don't Hold Up". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved January 26, 2017.
- ^ a b c Wilson, David C.; Brewer, Paul R. (December 21, 2013). "The Foundations of Public Opinion on Voter ID Laws Political Predispositions, Racial Resentment, and Information Effects". Public Opinion Quarterly. 77 (4): 962–84. doi:10.1093/poq/nft026. ISSN 0033-362X.
- ^ Childress, Sarah (October 20, 2014). "Why Voter ID Laws Aren't Really about Fraud". Frontline. PBS. Retrieved April 14, 2016.
- ^ "Expert Report of Lorraine C. Minnite" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on September 9, 2016. Retrieved July 22, 2016.
- ^ a b The Commission on Federal Election Reform (September 2005). "Building Confidence in U.S. Elections" (PDF). American University. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 4, 2016. Retrieved February 7, 2016.
- ^ a b Bowler, Shaun; Donovan, Todd (January 11, 2016). "A Partisan Model of Electoral Reform Voter Identification Laws and Confidence in State Elections". State Politics & Policy Quarterly. 16 (3): 340–361. doi:10.1177/1532440015624102. ISSN 1532-4400. S2CID 156332614.
- ^ Bowler, Shaun; Brunell, Thomas; Donovan, Todd; Gronke, Paul (June 2015). "Election administration and perceptions of fair elections". Electoral Studies. 38: 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.electstud.2015.01.004.
- ^ Stewart, Charles; Ansolabehere, Stephen; Persily, Nathaniel (2016). "Revisiting Public Opinion on Voter Identification and Voter Fraud in an Era of Increasing Partisan Polarization". Stanford Law Review. 68 (6): 1455.
- ^ King, Bridgett A. (June 1, 2017). "Policy and Precinct: Citizen Evaluations and Electoral Confidence". Social Science Quarterly. 98 (2): 672–689. doi:10.1111/ssqu.12303. ISSN 1540-6237.
- ^ Muhlhausen, David B.; Weber Sikich, Keri (September 10, 2007). "New Analysis Shows Voter Identification Laws Do Not Reduce Turnout" (PDF). The Heritage Foundation.
- ^ a b "A Dead-Simple Algorithm Reveals the True Toll of Voter ID Laws". Wired. Retrieved January 4, 2018.
- ^ a b Ansolabehere, Stephen; Hersh, Eitan D. (January 1, 2017). "ADGN: An Algorithm for Record Linkage Using Address, Date of Birth, Gender, and Name". Statistics and Public Policy. 4 (1): 1–10. doi:10.1080/2330443X.2017.1389620.
- ^ Weiser, Wendy; et al. (September 8, 2011). "Citizens Without Proof Stands Strong". Brennan Center. Archived from the original on October 23, 2012. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
- ^ "Not a Race Card". Bernardgoldberg.com. August 29, 2011. Archived from the original on September 21, 2011. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ Sobel, Richard; Smith, Robert Ellis (January 1, 2009). "Voter-ID Laws Discourage Participation, Particularly among Minorities, and Trigger a Constitutional Remedy in Lost Representation". PS: Political Science & Politics. 42 (1): 107–10. doi:10.1017/S1049096509090271. ISSN 1537-5935. S2CID 155018528.
- ^ Atkeson, Lonna Rae; Kerevel, Yann P.; Alvarez, R. Michael; Hall, Thad E. (October 2014). "Who Asks For Voter Identification? Explaining Poll-Worker Discretion" (PDF). The Journal of Politics. 76 (4): 944–57. doi:10.1017/S0022381614000528.
- ^ a b Hood, M. V.; Bullock, C. S. (October 15, 2012). "Much Ado About Nothing? An Empirical Assessment of the Georgia Voter Identification Statute". State Politics & Policy Quarterly. 12 (4): 394–414. doi:10.1177/1532440012452279. S2CID 154528911.
- ^ Vercellotti, Timothy (2006). "Protecting The Franchise, or Restricting It? The Effects of Voter Identification Requirements on Turnout" (PDF). American Political Science Association Conference. Retrieved October 20, 2016.
- ^ Mycoff, Jason D.; Wagner, Michael W.; Wilson, David C. (January 1, 2009). "The Empirical Effects of Voter-ID Laws: Present or Absent?". PS: Political Science & Politics. 42 (1): 121–26. doi:10.1017/S1049096509090301. ISSN 1537-5935. S2CID 54631.
- ^ Pastor, R. A.; Santos, R.; Prevost, A.; Stoilov, V. (September 16, 2009). "Voting and ID Requirements: A Survey of Registered Voters in Three States". The American Review of Public Administration. 40 (4): 461–81. doi:10.1177/0275074009342892. S2CID 153640870.
- ^ Olver, Christopher (September 28, 2011). "ID at the polls: Assessing the impact of recent state voter ID laws on voter turnout". Journalist's Resource. Retrieved May 27, 2017.
- ^ a b "Elections: Issues Related to State Voter Identification Laws". Government Accountability Office. February 27, 2015. Retrieved April 3, 2016.
- ^ Bill, Hobby; Jones, Mark P.; Jim, Granato; Renée, Cross; Cong, Huang; David, Llanos; Chris, Mainka; Kwok-Wai, Wan; Ching-Hsing, Wang (2015). "The Texas Voter ID Law and the 2014 Election: A Study of Texas's 23rd Congressional District". Rice Digital Scholarship Archive. hdl:1911/92679.
- ^ a b Valentino, Nicholas A.; Neuner, Fabian G. (February 1, 2016). "Why the Sky Didn't Fall: Mobilizing Anger in Reaction to Voter ID Laws". Political Psychology. 38 (2): 331–350. doi:10.1111/pops.12332. hdl:2027.42/136349. ISSN 1467-9221.
- ^ "The Effects of Photographic Identification on Voter Turnout in Indiana: A County-Level Analysis" (PDF). in.gov.
- ^ Hopkins, Daniel J.; Meredith, Marc; Morse, Michael; Smith, Sarah; Yoder, Jesse (March 2017). "Voting But for the Law: Evidence from Virginia on Photo Identification Requirements". Journal of Empirical Legal Studies. 14 (1): 79–128. doi:10.1111/jels.12142. S2CID 2009591.
- ^ Esposito, Francesco Maria; Focanti, Diego; Hastings, Justine S (2019). "Effects of Photo ID Laws on Registration and Turnout: Evidence from Rhode Island". National Bureau of Economic Research. Working Paper Series. doi:10.3386/w25503. S2CID 35326396.
- ^ Primus, Richard (June 2010). "The Future of Disparate Impact". Michigan Law Review. 108 (8): 1341–1387. JSTOR 20775015.
- ^ Newkirk, Vann (February 18, 2017). "How Voter ID Laws Discriminate". The Atlantic. Retrieved May 28, 2017.
- ^ Barreto, Matt A.; Nuño, Stephen; Sanchez, Gabriel R.; Walker, Hannah L. (November 9, 2018). "The Racial Implications of Voter Identification Laws in America". American Politics Research. 47 (2): 238–249. doi:10.1177/1532673x18810012. ISSN 1532-673X. S2CID 158689870.
- ^ Barnes, Robert; Marimow, Ann E. (July 29, 2016). "Appeals court strikes down North Carolina's voter-ID law". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 29, 2016.
- ^ a b Domonoske, Camila (July 29, 2016). "U.S. Appeals Court Strikes Down North Carolina's Voter ID Law". NPR. Retrieved July 29, 2016.
- ^ Alvarez, R. Michael Michael; Bailey, Delia; Katz, Jonathan N. (2008). "The Effect of Voter Identification Laws on Turnout". California Institute of Technology Social Science Working Paper. doi:10.2139/ssrn.1084598. hdl:1721.1/96594.
- ^ Barreto, Matt A.; Nuño, Stephen A.; Sanchez, Gabriel R. (January 8, 2009). "The Disproportionate Impact of Voter-ID Requirements on the Electorate – New Evidence from Indiana" (PDF). PS: Political Science & Politics. 42 (1): 111. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.518.553. doi:10.1017/S1049096509090283. S2CID 12494324.
- ^ Hood, M.V.; Bullock, C. S. (July 1, 2008). "Worth a Thousand Words?: An Analysis of Georgia's Voter Identification Statute". American Politics Research. 36 (4): 555–79. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.594.7618. doi:10.1177/1532673X08316608. S2CID 144237016.
- ^ Silver, Nate (July 15, 2012). "Measuring the Effects of Voter Identification Laws". FiveThirtyEight. Retrieved December 2, 2016.
- ^ Jenkins, Colleen (November 2, 2012). "Insight: Scant evidence of voter suppression, fraud in states with ID laws". Reuters. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
- ^ Bump, Philip (October 9, 2014). "Voter ID laws in Kansas and Tennessee dropped 2012 turnout by over 100,000 votes". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 7, 2016.
- ^ Rocha, Rene R.; Matsubayashi, Tetsuya (September 1, 2014). "The Politics of Race and Voter ID Laws in the States The Return of Jim Crow?". Political Research Quarterly. 67 (3): 666–79. doi:10.1177/1065912913514854. ISSN 1065-9129. S2CID 2130153.
- ^ White, Ariel R.; Nathan, Noah L.; Faller, Julie K. (February 1, 2015). "What Do I Need to Vote? Bureaucratic Discretion and Discrimination by Local Election Officials". American Political Science Review. 109 (1): 129–42. doi:10.1017/S0003055414000562. ISSN 1537-5943. S2CID 145471717.
- ^ Cobb, Rachael V.; Greiner; James, D.; Quinn, Kevin M. (June 14, 2010). "Can Voter ID Laws Be Administered in a Race-Neutral Manner? Evidence from the City of Boston in 2008". Quarterly Journal of Political Science. Rochester, NY: Social Science Research Network. SSRN 1625041.
- ^ Atkeson, Lonna Rae; Bryant, Lisa Ann; Hall, Thad E.; Saunders, Kyle; Alvarez, Michael (March 1, 2010). "A new barrier to participation: Heterogeneous application of voter identification policies". Electoral Studies. 29 (1): 66–73. doi:10.1016/j.electstud.2009.08.001.
- ^ Gillespie, June Andra (2015). "Voter Identification and Black Voter Turnout An Examination of Black Voter Turnout Patterns in Georgia, 2000–2014". Phylon. 52 (2): 43–67. JSTOR 43681953.
- ^ Hajnal, Zoltan; Lajevardi, Nazita; Nielson, Lindsay (January 5, 2017). "Voter Identification Laws and the Suppression of Minority Votes". The Journal of Politics. 79 (2): 363–379. doi:10.1086/688343. ISSN 0022-3816. S2CID 20943777.
- ^ a b Grimmer, Justin; Hersh, Eitan; Meredith, Marc; Mummolo, Jonathan; Nall, Clayton (April 18, 2018). "Obstacles to Estimating Voter ID Laws' Effect on Turnout". The Journal of Politics. 80 (3): 1045–1051. doi:10.1086/696618. ISSN 0022-3816. S2CID 158764888.
- ^ Hajnal, Zoltan; Kuk, John; Lajevardi, Nazita (April 18, 2018). "We All Agree: Strict Voter ID Laws Disproportionately Burden Minorities". The Journal of Politics. 80 (3): 1052–1059. doi:10.1086/696617. ISSN 0022-3816. S2CID 158480092.
- ^ Gelman, Andrew (June 11, 2018). "A new controversy erupts over whether voter identification laws suppress minority turnout". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 11, 2018.
- ^ a b Kertscher, Tom (May 24, 2017). "Did first-time use of photo ID cause 200,000 drop in Wisconsin voter turnout in presidential race?". PolitiFact. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ Koerth-Baker, Maggie (December 19, 2017). "Politics Moves Fast. Peer Review Moves Slow. What's A Political Scientist To Do?". FiveThirtyEight. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ Hood, M. V.; Buchanan, Scott E. (April 2, 2019). "Palmetto Postmortem: Examining the Effects of the South Carolina Voter Identification Statute". Political Research Quarterly. 73 (2): 492–505. doi:10.1177/1065912919837663. ISSN 1065-9129. S2CID 159341383.
- ^ "Political Science Quarterly: Spring 2019: Voter ID Laws: The Disenfranchisement of Minority Voters?". www.psqonline.org. Retrieved June 3, 2019.
- ^ Heller, Lauren R.; Miller, Jocelyne; Stephenson, E. Frank (June 1, 2019). "Voter ID Laws and Voter Turnout". Atlantic Economic Journal. 47 (2): 147–157. doi:10.1007/s11293-019-09623-8. ISSN 1573-9678. S2CID 189875682.
- ^ Fraga, Bernard L.; Miller, Michael G. (2022). "Who Do Voter ID Laws Keep from Voting?". The Journal of Politics. 84 (2): 1091–1105. doi:10.1086/716282. ISSN 0022-3816. S2CID 238773001.
- ^ a b c d e f Schaffer, Frederic Charles; Wang, Tova Andrea (2009). "Is Everyone Else Doing It? Indiana's Voter Identification Law in International Perspective" (PDF). Harvard Law and Policy Review. Retrieved February 15, 2016.
- ^ "Voting at a polling place". Australian Electoral Commission. Retrieved August 14, 2018.
- ^ a b c "Foreign election officials amazed by trust-based U.S. voting system". Foreign Policy. November 6, 2012. Retrieved February 15, 2016.
- ^ Roff, Peter (June 10, 2011). "Poll: Democrats and Republicans Support a Voter ID-Check Law". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved May 16, 2012.
- ^ Blanton, Dana (April 18, 2012). "Fox News Poll: Most think voter ID laws are necessary". Fox News. Retrieved May 16, 2012.
- ^ "Republicans and Democrats Move Further Apart in Views of Voting Access". Pew Research Center. April 22, 2021.
- ^ Wilson, David C.; Brewer, Paul R. (January 2016). "Do Frames Emphasizing Harm to Age and Racial-Ethnic Groups Reduce Support for Voter ID Laws?". Social Science Quarterly. 97 (2): 391–406. doi:10.1111/ssqu.12234.
- ^ Banks, Antoine J.; Hicks, Heather M. (August 2015). "Fear and Implicit Racism: Whites' Support for Voter ID laws". Political Psychology. 37 (5): 641–658. doi:10.1111/pops.12292.
- ^ Atkeson, Lonna Rae; Alvarez, R. Michael; Hall, Thad E.; Sinclair, J. Andrew (December 2014). "Balancing Fraud Prevention and Electoral Participation: Attitudes Toward Voter Identification". Social Science Quarterly. 95 (5): 1381–98. doi:10.1111/ssqu.12110.
- ^ "Who believes in voter fraud? Americans who are hostile to immigrants". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 1, 2017.
- ^ Russell, Berman (August 30, 2021). "The Obvious Voting-Rights Solution That No Democrat Will Propose". The Atlantic, Atlantic Media Company.
- ^ Coleman, K.J. et al. (November 3, 2014) Voter Identification Requirements: Background and Legal Issues Washington, D.C.
- ^ Fogarty, Brian J.; Curtis, Jessica; Gouzien, Patricia Frances; Kimball, David C.; Vorst, Eric C. (April 1, 2015). "News attention to voter fraud in the 2008 and 2012 US elections". Research & Politics. 2 (2): 205316801558715. doi:10.1177/2053168015587156. ISSN 2053-1680.
- ^ Hicks, William D.; McKee, Seth C.; Sellers, Mitchell D.; Smith, Daniel A. (March 1, 2015). "A Principle or a Strategy? Voter Identification Laws and Partisan Competition in the American States". Political Research Quarterly. 68 (1): 18–33. doi:10.1177/1065912914554039. ISSN 1065-9129. S2CID 154205969.
- ^ a b c d e Hicks, William D.; McKee, Seth C.; Smith, Daniel A. (February 21, 2016). "The Determinants of State Legislator Support for Restrictive Voter ID Laws". State Politics & Policy Quarterly. 16 (4): 411–431. doi:10.1177/1532440016630752. ISSN 1532-4400. S2CID 27742794.
- ^ Mendez, Matthew S.; Grose, Christian R. (June 12, 2018). "Doubling Down: Inequality in Responsiveness and the Policy Preferences of Elected Officials". Legislative Studies Quarterly. 43 (3): 457–491. doi:10.1111/lsq.12204. ISSN 0362-9805. S2CID 158018434.
- ^ Biggers, Daniel R.; Hanmer, Michael J. (January 16, 2017). "Understanding the Adoption of Voter Identification Laws in the American States". American Politics Research. 45 (4): 560–588. doi:10.1177/1532673x16687266. S2CID 157200254.
- ^ Bright, Chelsie L. M.; Lynch, Michael S. (February 2017). "Kansas Voter ID Laws". Political Research Quarterly. 70 (2): 340–347. doi:10.1177/1065912917691638. S2CID 157372093.
- ^ Herman, Jody L.; Brown, Taylor N.T. (August 2018). "Impact of Strict Voter ID Laws on Transgender Voters in 2018 General Election". Williams Institute. Retrieved August 25, 2018.
- ^ a b "Hawaii Voter ID Law No Big Deal". Honolulu Magazine. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ Louis Jacobson (July 28, 2011). "Rhode Island's Voter ID Law: Oddity or Game-Changer". governing.com. Archived from the original on January 31, 2016. Retrieved January 18, 2016.
- ^ Blake, Aaron (June 21, 2021). "Stacey Abrams and the Democrats' evolution on voter ID". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 29, 2021.
- ^ Bernstein, Brittany (June 17, 2021). "Stacey Abrams Endorses Manchin's Election Law Compromise". National Review. Retrieved June 29, 2021.
- ^ a b c d Jennie Bowser, Bev DePriest. "Voter ID: State Requirements". Ncsl.org. Retrieved November 12, 2011.
- ^ "Voter ID is a hot topic but will Alabama's ID law stop election fraud". Anniston Star. July 15, 2012. Archived from the original on January 11, 2014. Retrieved February 22, 2013.
- ^ "Voter ID law not yet submitted to feds". All Alabama. June 12, 2013. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ "Alabama photo voter ID law". AllAlabama.com. June 26, 2013. Retrieved June 28, 2013.
- ^ "Alabama Photo Voter Identification". Alabamavoterid.com. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ Charles M. Blow, "Trump's Troubles in the Black Belt", New York Times, August 8, 2016; accessed August 8, 2016
- ^ "Alabama Photo Voter Identification - Alabama Secretary of State" (PDF). www.alabamavoterid.com. Retrieved August 14, 2018.
- ^ "Lynn Revisits Law". Anchorage Daily News. Archived from the original on March 18, 2013. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ "House Journal". Alaska State Legislature. January 16, 2013.
- ^ "Proof of Identification at the Polls". Archived from the original on May 4, 2014. Retrieved May 4, 2014.
- ^ "Arkansas Judge Finds State Voter-ID Law Unconstitutional". The Wall Street Journal. May 2, 2014. Archived from the original on May 11, 2014. Retrieved May 8, 2014.
- ^ "Martin, et al. v. Kohls et al., 2014 Ark. 427, 444 S.W.3d 496 (Ark. 2014)". Archived from the original on February 16, 2016. Retrieved February 12, 2016.
- ^ "Where and How to Vote". California Secretary of State. Retrieved July 3, 2022.
- ^ California Standards for Proof of Residency or Identity When Proof Is Required by Help America Vote Act , February 10, 2006
- ^ "List of Acceptable Forms of ID". Colorado Secretary of State. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ "Norwalk, CT – Official Website – Voter ID Requirements". Norwalkct.org. Retrieved December 4, 2014.
- ^ "Long Distance Voter". Long Distance Voter. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ "General Voting Information". Florida Division of Elections. Archived from the original on March 17, 2010. Retrieved August 18, 2013.
- ^ "Complicated History of Georgia Voting". The GRIO MSNBC. April 3, 2012. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ Scanlan, Quinn (April 8, 2021). "Civic groups file lawsuit challenging absentee ballot provisions in Georgia's election law". ABC News. Retrieved April 8, 2021.
- ^ "Voting in Hawaii". Office of Elections. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "Idaho voting". IdahoVotes.com. Archived from the original on July 18, 2013. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "Illinois Voter ID Bill". Huff Post Chicago. February 29, 2012. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "Photo ID Law". Indiana Secretary of State. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ "Voter ID FAQ". Iowa Secretary of State. Retrieved June 26, 2021.
- ^ Carpenter, Tim. "Voter ID Now Kansas Law". The Topeka Capital-Journal. Archived from the original on January 14, 2014. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ Williams, Pete (April 29, 2020). "Appeals court, in blow to Kobach, strikes down Kansas law requiring proof of citizenship to vote". NBC News. Retrieved April 29, 2020.
- ^ "Voter Information". Kentucky State Board of Elections. Archived from the original on June 4, 2013. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "State by State Voter ID..." Ballotpedia. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "Maine Election Information". Rock the Vote. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "Proposed Voter ID ..." MarylandReporter.com. February 11, 2013. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "Voter checklist". Boston.com. November 6, 2012. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "Secretary of State outlines voter identification policies". Michigan Secretary of State. September 5, 2007. Retrieved January 11, 2014.
- ^ Star Tribune: Congrats, Minnesotans: You made the state No. 1 in voter participation[permanent dead link] November 22, 2016, reprinted on MN Secretary of State website.
- ^ "Registering to Vote". Minnesota Secretary of State. Retrieved July 3, 2022.
- ^ Minnesota Elections Facts: Fact and Fiction, Voter Registration, Before Election Day, After Election Day... 'FACT: Every ballot cast in Minnesota is associated with a registered, eligible voter', Office of Minnesota Secretary of State, Retrieved July 3, 2022
- ^ "Voter ID Laws". National Conference of State Legislatures.
- ^ Wing, Nicholas (July 6, 2012). "Mississippi Voter ID Law..." The Huffington Post. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "Voter rights act ruling clears..." gulflive.com. June 25, 2013. Retrieved June 30, 2013.
- ^ EL. "Mississippi Voter ID". State of Mississippi. Retrieved November 20, 2018.
- ^ "Missouri House Passes Voter ID". St. Louis Post-Dispatch. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ IT, Missouri Secretary of State -. "State of Missouri - Election Night Results". enrarchives.sos.mo.gov. Retrieved August 14, 2018.
- ^ Celock, John (January 25, 2013). "Montana Voter ID Bill Tabled..." The Huffington Post. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ Registering to Vote, Nebraska Secretary of State
- ^ "Miller Calls for Voter ID". Las Vegas Review Journal. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "Voting Requirements". NJ Department of State. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "New York Voting Registration". Project Vote Smart. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "North Carolina legislators..." FayObserver. Archived from the original on June 24, 2013. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ Ann E. Marimow (July 29, 2016). "Appeals court strikes down North Carolina's voter-ID law". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 29, 2016.
- ^ Julia Harte; Andy Sullivan (July 29, 2016). "North Carolina Voter ID Law Targeted African-Americans, Appeals Court Rules". Huffington Post. Retrieved July 30, 2016.
- ^ Michael Wines; Alan Blinder (July 30, 2016). "Federal Appeals Court Strikes Down North Carolina Voter ID Requirement". The New York Times. p. A1. Retrieved May 16, 2017.
- ^ "Recent Case: Fourth Circuit Strikes Down Provisions of Election Law Enacted with Racially Discriminatory Intent" (PDF). Harvard Law Review. 130: 1752. 2017. Retrieved May 16, 2017.
- ^ "U.S. Supreme Court Refuses to Revive North Carolina Voter-ID Law". Bloomberg News. May 15, 2017. Retrieved May 15, 2017.
- ^ Adam Liptak; Michael Wines (May 16, 2017). "Strict North Carolina Voter ID Law Thwarted After Supreme Court Rejects Case". The New York Times. p. A1. Retrieved May 16, 2017.
- ^ "North Carolina v. North Carolina State Conference of the NAACP". SCOTUSblog. Retrieved May 16, 2017.
- ^ "Voter ID". North Carolina Board of Elections. Retrieved September 26, 2019.
Beginning in 2020, North Carolina voters will be asked to provide photo identification when voting in-person or absentee-by-mail....
- ^ Frazin, Rachel (December 27, 2019). "Judge halts North Carolina voter ID law". The Hill.
- ^ "N. Carolina Attorneys File Appeal Plans of Voter ID Ruling". Spectrum News. Associated Press. January 24, 2020. Retrieved January 25, 2020.
- ^ a b Dunphy, Peter (July 31, 2019). "The State of Voting Rights Litigation (July 2019)". Brennan Center for Justice. Retrieved January 9, 2020.
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions About Voter Identification". Ohio Secretary of State. 2011. Archived from the original on October 22, 2014. Retrieved October 22, 2014.
- ^ Higgs, Robert (January 31, 2013). "Ohio House may again..." Cleveland.com. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "Ohio's New Voter Suppression Law Unpacked". Democracy Docket. January 18, 2023. Retrieved January 23, 2023.
- ^ "Oklahoma Voter ID Law Not Like..." Tulsa World. Archived from the original on June 24, 2013. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ Camhi, Tiffany (June 6, 2020). "How Oregon became the first state to vote by mail in a presidential election". OPB. Retrieved September 17, 2020. (audio)
- ^ "Determination on Declaratory Relief and Permanent Injunction" (PDF). Pennsylvania Commonwealth Courts. Retrieved January 21, 2014.
- ^ Bidgood, Jess (September 11, 2012). "Rhode Island Primary Tests..." The New York Times. Retrieved June 30, 2013.
- ^ Standera, Renee. "US District Court upholds South Carolina Voter ID law". WMBF-TV. Retrieved October 11, 2012.
- ^ "UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA SC vs. US Ruling" (PDF). UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA. Retrieved October 11, 2012.
- ^ Underhill, Wendy (January 4, 2016). "Voter Identification Requirements; Voter ID Laws". National Conference of State Legislatures. Retrieved January 21, 2016.
- ^ "Voter ID Laws Haven't Changed". American News. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ "Voter ID". TN Dept. of Safety and Homeland Security. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ "Texas Takes Aim At Blocked Voter ID Law". Fox News. March 15, 2012.
- ^ "Texas AG Greg Abbot..." Dallas News. Retrieved June 30, 2013.
- ^ "Courts reject Texas and Wisconsin voter ID laws". BBC News. October 10, 2014. Retrieved October 10, 2014.
- ^ "Supreme Court allows Texas voter ID law for now". CNN. October 18, 2014. Retrieved October 19, 2014.
- ^ "Court Strikes Down Texas Voter ID Law". KHOU Houston. Archived from the original on August 8, 2015. Retrieved August 5, 2015.
- ^ Robert Barnes, "Appeals court says Texas voter-ID law discriminates against minorities", Washington Post, July 20, 2016; accessed August 4, 2016
- ^ Tesfaye, Sophia (February 27, 2017). "Jeff Sessions drops DOJ lawsuit against discriminatory Texas voter ID case, reverses 6 years of litigation: The Department of Justice plans to abandon its claim that Texas GOP lawmakers targeted voters of color". Salon. Retrieved July 9, 2017.
- ^ "Voter ID Laws". Vote Utah 2012. Archived from the original on April 25, 2013. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ Vermont Statutes Annotated, Title 17, Chapter 51, "Conduct of Elections", §2563, retrieved March 30, 2015.
- ^ Nolan, Jim; Schmidt, Markus (February 5, 2013). "Senate, House pass bills to limit forms of acceptable voter ID". The News & Advance. Retrieved April 6, 2020.
- ^ "Supreme Court Will..." The Roanoke Star. June 18, 2013. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ "With Voting Rights Act..." PBS Frontline. Retrieved July 1, 2013.
- ^ "Gov. Northam signs legislation that repeals Virginia vote ID law, makes Election Day state holiday". WVEC. April 12, 2020. Retrieved April 18, 2020.
- ^ Millhiser, Ian (April 15, 2020). "Kentucky just made it harder to vote during a pandemic". Vox. Retrieved April 18, 2020.
- ^ "New Washington Resident - Elections & Voting - WA Secretary of State". n.d. Retrieved September 9, 2020.
- ^ McNulty, Timothy (January 7, 2013). "West Virginia GOP..." Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "Voter ID law takes effect". Charleston Gazette-Mail. December 31, 2017. Retrieved November 20, 2018.
- ^ "Divided court upholds Wisconsin's voter ID law". Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. Retrieved September 16, 2014.
- ^ Davey, Monica (September 13, 2014). "Federal Appeals Court Permits Wisconsin Voter ID Law". The New York Times. Retrieved September 16, 2014.
- ^ Liptak, Adam (October 9, 2014) – "Courts Strike Down Voter ID Laws in Wisconsin and Texas". The New York Times. Retrieved December 26, 2014.
- ^ Barnes, Robert (October 9, 2014) – "Supreme Court Blocks Wisconsin Voter ID Law". The Washington Post. Retrieved December 26, 2014.
- ^ "WMTV Channel 15". Retrieved February 16, 2016.
- ^ "Frank v. Walker - Preliminary Injunction Motion Granted". American Civil Liberties Union. Retrieved January 9, 2020.
- ^ Marley, Patrick (May 31, 2018). "Appeals court yet to rule on Wisconsin voter ID and other election laws after 16 months". Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. Retrieved January 9, 2020.
- ^ Jenkins, Cameron (April 8, 2021). "Wyoming governor signs voter ID bill". The Hill. Retrieved January 25, 2023.
- ^ Downey, Sarah (April 15, 2021). "Wyoming approves Voter ID bill". The Center Square. Retrieved January 25, 2023.
- ^ "Voter Identification Requirements". October 31, 2014.
Further reading
[edit]- "Who Lacks ID in America Today? An Exploration of Voter ID Access, Barriers, and Knowledge" (June 2024 study by Center for Democracy and Civic Engagement at the University of Maryland)
- Compilation of research on voter ID by Brennan Center (April 11, 2017)
- State Voter Identification Requirements: Analysis, Legal Issues, and Policy Considerations. Washington, DC: Congressional Research Service, October 21, 2016.
- The Right to Vote: The Contested History of Democracy in the United States. Basic Books. by Alexander Keyssar (2009)
- Historical account suggesting photo identification for voting: Scientific American, "A Suggestion In Photography", 27 November 1880, p. 337

