Legitimacy (family law)
The examples and perspective in this article deal primarily with Europe and North America and do not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (April 2023) |
| Family law |
|---|
| Family |
Legitimacy, in traditional Western common law, is the status of a child born to parents who are legally married to each other, and of a child conceived before the parents obtain a legal divorce. Conversely, illegitimacy, also known as bastardy, has been the status of a child born outside marriage, such a child being known as a bastard, a love child, a natural child, or illegitimate. In Scots law, the terms natural son and natural daughter carry the same implications.
The importance of legitimacy has decreased substantially in Western developed countries since the sexual revolution of the 1960s and 1970s and the declining influence of Christian churches, especially Catholic, Anglican, and Lutherans, in family and social life.
Births outside marriage now represent majorities in multiple countries in Western Europe, the Americas, and many former European colonies.[citation needed]
Law
[edit]England's Statute of Merton (1235) stated, regarding illegitimacy: "He is a bastard that is born before the marriage of his parents."[1] This definition also applied to situations when a child's parents could not marry, as when one or both were already married or when the relationship was incestuous.
The Poor Act 1575 formed the basis of English bastardy law. Its purpose was to punish a bastard child's mother and putative father, and to relieve the parish from the cost of supporting mother and child. "By an act of 1576 (18 Elizabeth C. 3), it was ordered that bastards should be supported by their putative fathers, though bastardy orders in the quarter sessions date from before this date. If the genitor could be found, then he was put under very great pressure to accept responsibility and to maintain the child."[2]
Under English law, a bastard could not inherit real property and could not be legitimized by the subsequent marriage of father to mother. There was one exception: when his father subsequently married his mother, and an older illegitimate son (a "bastard eignè") took possession of his father's lands after his death, he would pass the land on to his own heirs on his death, as if his possession of the land had been retroactively converted into true ownership. A younger non-bastard brother (a "mulier puisnè") would have no claim to the land.[3]
There were many "natural children" of Scotland's monarchy granted positions which founded prominent families. In the 14th century, Robert II of Scotland gifted one of his illegitimate sons estates in Bute, founding the Stewarts of Bute, and similarly a natural son of Robert III of Scotland was ancestral to the Shaw Stewarts of Greenock.[4]
In Scots law an illegitimate child, a "natural son" or "natural daughter", would be legitimated by the subsequent marriage of his parents, provided they had been free to marry at the date of the conception.[5][6] The Legitimation (Scotland) Act 1968 extended legitimation by the subsequent marriage of the parents to children conceived when their parents were not free to marry, but this was repealed in 2006 by the amendment of section 1 of the Law Reform (Parent and Child) (Scotland) Act 1986 (as amended in 2006) which abolished the status of illegitimacy stating that "(1) No person whose status is governed by Scots law shall be illegitimate ...".
The Legitimacy Act 1926[7] of England and Wales legitimised the birth of a child if the parents subsequently married each other, provided that they had not been married to someone else in the meantime. The Legitimacy Act 1959 extended the legitimisation even if the parents had married others in the meantime and applied it to putative marriages which the parents incorrectly believed were valid. Neither the 1926 nor 1959 Acts changed the laws of succession to the British throne and succession to peerage and baronetcy titles. In Scotland children legitimated by the subsequent marriage of their parents have always been entitled to succeed to peerages and baronetcies and the Legitimation (Scotland) Act 1968 extended this right to children conceived when their parents were not free to marry.[8] The Family Law Reform Act 1969 (c. 46) allowed a bastard to inherit on the intestacy of his parents. In canon and in civil law, the offspring of putative marriages have also been considered legitimate.[9]
Since December 2003 in England and Wales, April 2002 in Northern Ireland and May 2006 in Scotland, an unmarried father has parental responsibility if he is listed on the birth certificate.[10]
In the United States, in the early 1970s a series of Supreme Court decisions held that most common-law disabilities imposed upon illegitimacy were invalid as violations of the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution.[11] Still, children born out of wedlock may not be eligible for certain federal benefits (e.g., automatic naturalization when the father becomes a US citizen) unless the child has been legitimized in the appropriate jurisdiction.[12][13]
Many other countries have legislatively abolished any legal disabilities of a child born out of wedlock.[14][citation needed]
In France, legal reforms regarding illegitimacy began in the 1970s, but it was only in the 21st century that the principle of equality was fully upheld (through Act no. 2002-305 of 4 March 2002, removing mention of "illegitimacy" — filiation légitime and filiation naturelle; and through law no. 2009-61 of 16 January 2009).[15][16][17] In 2001, France was forced by the European Court of Human Rights to change several laws that were deemed discriminatory, and in 2013 the Court ruled that these changes must also be applied to children born before 2001.[18]
In some countries, the family law itself explicitly states that there must be equality between the children born outside and inside marriage: in Bulgaria, for example, the new 2009 Family Code lists "equality of the born during the matrimony, out of matrimony and of the adopted children" as one of the principles of family law.[19]
The European Convention on the Legal Status of Children Born out of Wedlock[20] came into force in 1978. Countries which ratify it must ensure that children born outside marriage are provided with legal rights as stipulated in the text of this convention. The convention was ratified by the UK in 1981 and by Ireland in 1988.[21]
In later years, the inheritance rights of many illegitimate children have improved, and changes of laws have allowed them to inherit properties.[22] More recently, the laws of England have been changed to allow illegitimate children to inherit entailed property, over their legitimate brothers and sisters.[citation needed]
Contemporary situation
[edit]Despite the decreasing legal relevance of illegitimacy, an important exception may be found in the nationality laws of many countries, which do not apply jus sanguinis (nationality by citizenship of a parent) to children born out of wedlock, particularly in cases where the child's connection to the country lies only through the father. This is true, for example, of the United States,[23] and its constitutionality was upheld in 2001 by the Supreme Court in Nguyen v. INS.[24] In the UK, the policy was changed so that children born after 1 July 2006 could receive British citizenship from their father if their parents were unmarried at the time of the child's birth; illegitimate children born before this date cannot receive British citizenship through their father.[25]

Legitimacy also continues to be relevant to hereditary titles, with only legitimate children being admitted to the line of succession. Some monarchs, however, have succeeded to the throne despite the controversial status of their legitimacy. For example, Elizabeth I succeeded to the throne though she was legally held illegitimate as a result of her parents' marriage having been annulled after her birth.[26] Her older half-sister Mary I had acceded to the throne before her in a similar circumstance: her parents' marriage had been annulled in order to allow her father to marry Elizabeth's mother.
Annulment of marriage does not currently change the status of legitimacy of children born to the couple during their putative marriage, i.e., between their marriage ceremony and the legal annulment of their marriage. For example, canon 1137 of the Roman Catholic Church's Code of Canon Law specifically affirms the legitimacy of a child born to a marriage that is declared null following the child's birth.[27]
The Catholic Church is also changing its attitude toward unwed mothers and baptism of the children. In criticizing the priests who refused to baptize out-of-wedlock children, Pope Francis argued that the mothers had done the right thing by giving life to the child and should not be shunned by the church:[28][29][30]
In our ecclesiastical region there are priests who don't baptise the children of single mothers because they weren't conceived in the sanctity of marriage. These are today's hypocrites. Those who clericalise the church. Those who separate the people of God from salvation. And this poor girl who, rather than returning the child to sender, had the courage to carry it into the world, must wander from parish to parish so that it's baptised!
Nonmarital births
[edit]
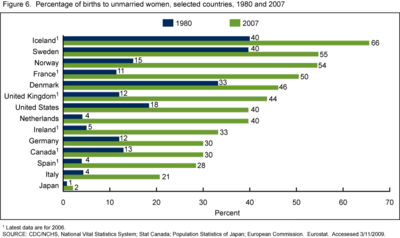

The proportion of children born outside marriage has been rising since the turn of the 21st century in most European Union countries,[49][50] North America, and Australia.[51] In Europe, besides the low levels of fertility rates and the delay of motherhood, another factor that now characterizes fertility is the growing percentage of births outside marriage. In the EU, this phenomenon has been on the rise in recent years in almost every country; and in eight EU countries, mostly in northern Europe, as well as in Iceland outside of the EU, it already accounts for the majority of births.[50]
In 2009, 41% of children born in the United States were born to unmarried mothers, a significant increase from the 5% of half a century earlier. That includes 73% of non-Hispanic black children, 53% of Hispanic children (of all races), and 29% of non-Hispanic white children.[52][53] In 2020, the proportion was almost similar, with 40.5% of children born in the United States being born to unmarried mothers.[54]
In April 2009, the National Center for Health Statistics announced that nearly 40 percent of American infants born in 2007 were born to an unwed mother; that of 4.3 million children, 1.7 million were born to unmarried parents, a 25 percent increase from 2002.[55] Most births to teenagers in the United States (86% in 2007) are nonmarital; in 2007, 60% of births to women 20–24, and nearly one-third of births to women 25–29, were nonmarital.[31] In 2007, teenagers accounted for just 23% of non-marital births, down steeply from 50% in 1970.[31]
In 2014, 42% of all births in the 28 EU countries were nonmarital.[56] The percentage was also 42% in 2018.[50] In 2018, births outside of marriage represented the majority of births in eight EU member states: France (60%), Bulgaria (59%), Slovenia (58%), Portugal (56%), Sweden (55%), Denmark and Estonia (both 54%), and the Netherlands (52%). The lowest percentage were in Greece, Cyprus, Croatia, Poland and Lithuania, with a percentage of under 30%.[50]
To a certain degree, religion (the religiosity of the population - see religion in Europe) correlates with the proportion of non-marital births (e.g., Greece, Cyprus, Croatia have a low percentage of births outside marriage), but this is not always the case: Portugal (56% in 2018[50]) is among the most religious countries in Europe.
The proportion of non-marital births is also approaching half in the Czech Republic (48.5%. in 2021[57]), the United Kingdom (48.2% as of 2017[56]) and Hungary (46.7% as of 2016[56]).
The prevalence of births to unmarried women varies not only between different countries, but also between different geographical areas of the same country: for example, in Germany, there are very strong differences between the regions of former West Germany and East Germany with a non-religious majority. Significantly more children are born out of wedlock in eastern Germany than in western Germany. In 2012, in eastern Germany 61.6% of births were to unmarried women, while in western Germany only 28.4% were.[58] In the UK, in 2014, 59.4% of births were non-marital in North East of England, 58.9% in Wales, 54.2% in North West England, 52.4% in Yorkshire and the Humber, 52% in East Midlands, 50.8% in Scotland, 50.4% in West Midlands, 48.5% in South West England, 45.5% in East of England, 43.2% in Northern Ireland, 42.9% in South East England, and 35.7% in London.[59]
In France, in 2012, 66.9% of births were non-marital in Poitou-Charentes,[60] while only 46.6% were in Ile-de-France (which contains Paris).[61] One of the reasons for the lower prevalence of non-marital births in the metropolis is the high number of immigrants from conservative world regions.[62] In Canada, in Quebec, the majority of births since 1995 onwards have been outside marriage.[63] As of 2015, 63% of births were outside marriage in Quebec.[64]
Traditionally conservative Catholic countries in the EU now also have substantial proportions of non-marital births, as of 2016 (except where otherwise stated):[56] Portugal (52.8% [65]), Spain (45.9%), Austria (41.7%[66]), Luxembourg (40.7%[56]) Slovakia (40.2%[67]), Ireland (36.5%),[68] Malta (31.8%[67])
The percentage of first-born children born out of wedlock is considerably higher (by roughly 10%, for the EU), as marriage often takes place after the first baby has arrived. For example, for the Czech Republic, whereas the total nonmarital births are less than half, 47.7%, (third quarter of 2015) the percentage of first-born outside marriage is more than half, 58.2%.[69]
In Australia, in 1971, only 7% of births were outside of marriage, compared to 36% in 2020.[70] The proportion of births outside of marriage was the highest in the Northern Territory (59%) and the lowest in the ACT (28%).[70]
Latin America has the highest rates of non-marital childbearing in the world (55–74% of all children in this region are born to unmarried parents).[71] In most countries in this traditionally Catholic region, children born outside marriage are now the norm. Recent figures from Latin America show non-marital births to be 74% in Colombia, 70% in Paraguay, 69% in Peru, 63% in the Dominican Republic, 58% in Argentina, 55% in Mexico.[72][73][74] In Brazil, non-marital births increased to 65.8% in 2009, up from 56.2% in 2000.[75] In Chile, non-marital births increased to 70.7% in 2013, up from 48.3% in 2000.[76]
Even in the early 1990s, the phenomenon was very common in Latin America. For example, in 1993, out-of-wedlock births in Mexico were 41.5%, in Chile 43.6%, in Puerto Rico 45.8%, in Costa Rica 48.2%, in Argentina 52.7%, in Belize 58.1%, in El Salvador 73%, in Suriname 66%, and in Panama 80%.[77]
Out-of-wedlock births are less common in Asia: in 1993 the rate in Japan was 1.4%; in Israel, 3.1%; in China, 5.6%; in Uzbekistan, 6.4%; in Kazakhstan, 21%; and in Kyrgyzstan, 24%.[77] However, in the Philippines, the out-of-wedlock birth rate was 37% in 2008–2009,[73] which skyrocketed to 52.1% by 2015.[78]
Covert illegitimacy
[edit]Covert illegitimacy is a situation which arises when someone who is presumed to be a child's father (or mother) is in fact not the biological father (or mother). Frequencies as high as 30% are sometimes assumed in the media, but research[79][80] by sociologist Michael Gilding traced these overestimates back to an informal remark at a 1972 conference.[81]
The detection of unsuspected illegitimacy can occur in the context of medical genetic screening,[82] in genetic family name research,[83][84] and in immigration testing.[85] Such studies show that covert illegitimacy is in fact less than 10% among the sampled African populations, less than 5% among the sampled Native American and Polynesian populations, less than 2% of the sampled Middle Eastern population, and generally 1%–2% among European samples.[82]
Causes for rise in nonmarital births
[edit]The rise in illegitimacy noted in Britain throughout the eighteenth century has been associated with the rise of new employment opportunities for women, making them less dependent upon a husband's earnings.[86] However, the Marriage Act 1753 sought to curb this practice, by combining the spousals and nuptials; and by the start of the 19th century, social convention prescribed that brides be virgins at marriage, and illegitimacy became more socially discouraged, especially during the Victorian era.[87] Later in the 20th century, the social changes of the 1960s and 1970s started to reverse this trend, with an increase in cohabitation and alternative family formation. Elsewhere in Europe and Latin America, the increase in nonmarital births from the late 20th century on has been linked to secularization, enhanced women's rights and standing in society, and the fall of authoritarian dictatorships.[88][89][90]
Before the dissolution of Marxist–Leninist regimes in Europe, women's participation in the workforce was actively encouraged by most governments, but socially conservative regimes such as that of Nicolae Ceausescu practiced restrictive and natalist policies regarding family reproduction, such as total bans on contraception and abortion, and birth rates were tightly controlled by the state. After the dissolution of those regimes, the population was given more choices on how to organize their personal lives, and in regions such as former East Germany, the rate of births outside marriage increased dramatically: as of 2012, 61.6% of births there were outside marriage.[58] Far-right regimes such as those of Francoist Spain and Portugal's Estado Novo also fell, leading to the democratization and liberalization of society. In Spain and Portugal, important legal changes throughout the 1970s and 1980s included legalization of divorce, decriminalization of adultery, introduction of gender equality in family law, and removal of the ban on contraception.[91]
In many countries there has been a dissociation between marriage and fertility, with the two no longer being closely associated—with births to unmarried couples, as well as childless married couples, becoming more common and more socially acceptable. Contributions to these societal changes have been made by the weakening of social and legal norms that regulate peoples' personal lives and relations, especially in regard to marriage, secularization and decreased church control of reproduction, increased participation of women in the labor force, changes in the meaning of marriage, risk reduction, individualism, changing views on female sexuality, and availability of contraception.[88][92][93] New concepts have emerged, such as that of reproductive rights, though these concepts have not been accepted by all cultures. Under the notions of reproductive and sexual rights, individuals—not the state, church, community, etc.—shall decide whether and when individuals shall have children, their number and spacing, the circumstances under which individuals will or will not be sexually active, and their choice of intimate partners and type of relationship.
It is argued that in some places where the control of the church (especially the Roman Catholic Church) was traditionally very strong, the social changes of the 1960s and 1970s have led to a negative reaction of the population against the lifestyles promoted by the church. One of the explanations of the current high rates of unmarried cohabitation in Quebec is that the traditionally strong social control of the church and the Catholic doctrine over people's private relations and sexual morality has led the population to rebel against traditional and conservative social values;[94] since 1995 the majority of births in this province are outside marriage, and as of 2015, in Quebec, 63% of children were born to unmarried women.[64] The past few decades have seen decreased marriage rates in most Western countries, and this decrease has been accompanied by increased emergence of non-traditional family forms. Average marriage rates across OECD countries have fallen from 8.1 marriages per 1,000 people in 1970 to 5.0 in 2009.[95]
Research on the situation in Bulgaria[89] has concluded that:
[The rise in unmarried cohabitation] shows that for many people it is not of great importance [whether] their union is a legal marriage or [a] consensual union. This [indicates] clear changes in [people's] value orientations [...] and less social pressure for marriage.
History
[edit]

Certainty of paternity has been considered important in a wide range of eras and cultures, especially when inheritance and citizenship were at stake, making the tracking of a man's estate and genealogy a central part of what defined a "legitimate" birth. The ancient Latin dictum, "Mater semper certa est" ("The [identity of the] mother is always certain", while the father is not), emphasized the dilemma.
In English common law, Justice Edward Coke in 1626 promulgated the "Four Seas Rule" (extra quatuor maria) asserting that, absent impossibility of the father being fertile, there was a presumption of paternity that a married woman's child was her husband's child. That presumption could be questioned, though courts generally sided with the presumption, thus expanding the range of the presumption to a "Seven Seas Rule". But it was only with the Marriage Act 1753 that a formal and public marriage ceremony at civil law was required, whereas previously marriage had a safe haven if celebrated in an Anglican church. Still, many "clandestine" marriages occurred.
In many societies, people born out of wedlock did not have the same rights of inheritance as those within it, and in some societies, even the same civil rights. [which?] In the United Kingdom and the United States, as late as the 1960s and in certain social strata even up to today, nonmarital birth has carried a social stigma.[97][98] In previous centuries unwed mothers were forced by social pressure to give their children up for adoption. In other cases nonmarital children have been reared by grandparents or married relatives as the "sisters", "brothers" or "cousins" of the unwed mothers.[99]
In most national jurisdictions, the status of a child as a legitimate or illegitimate heir could be changed—in either direction—under the civil law: A legislative act could deprive a child of legitimacy; conversely, a marriage between the previously unmarried parents, usually within a specified time, such as a year, could retroactively legitimate a child's birth.
Fathers of illegitimate children often did not incur comparable censure or legal responsibility, due to social attitudes about sex, the nature of sexual reproduction, and the difficulty of determining paternity with certainty.
By the final third of the 20th century, in the United States, all the states had adopted uniform laws that codified the responsibility of both parents to provide support and care for a child, regardless of the parents' marital status, and gave non-marital as well as adopted persons equal rights to inherit their parents' property. In the early 1970s, a series of Supreme Court decisions abolished most, if not all, of the common-law disabilities of non-marital birth, as being violations of the equal-protection clause of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution.[100] Generally speaking, in the United States, "illegitimate" has been supplanted by the phrase "born out of wedlock."
In contrast, other jurisdictions (particularly western continental European countries) tend to favour social parentage over the biological parentage. Here a man (not necessarily the biological father) may voluntarily recognise the child to be identified as the father, thus giving legitimacy to the child; the biological father does not have any special rights in this area. In France, a mother may refuse to recognize her own child (see anonymous birth).
A contribution to the decline of the concept of illegitimacy had been made by increased ease of obtaining divorce. Before this, the mother and father of many children had been unable to marry each other because one or the other was already legally bound, by civil or canon law, in a non-viable earlier marriage that did not permit divorce. Their only recourse, often, had been to wait for the death of the earlier spouse(s). Thus Polish political and military leader Józef Piłsudski (1867–1935) was unable to marry his second wife, Aleksandra, until his first wife, Maria, died in 1921; by this time, Piłsudski and Aleksandra had two out-of-wedlock daughters.[101]
Social implications
[edit]
Nonmarital birth has affected not only the individuals themselves. The stress that such circumstances of birth once regularly visited upon families is illustrated in the case of Albert Einstein and his wife-to-be, Mileva Marić, who—when she became pregnant with the first of their three children, Lieserl—felt compelled to maintain separate domiciles in different cities.[102][103]

Some persons born outside of marriage have been driven to excel in their endeavors, for good or ill, by a desire to overcome the social stigma and disadvantage that attached to it. Nora Titone, in her book My Thoughts Be Bloody, recounts how the shame and ambition of actor Junius Brutus Booth's two actor sons born outside of marriage, Edwin Booth and John Wilkes Booth, spurred them to strive, as rivals, for achievement and acclaim—John Wilkes, the assassin of Abraham Lincoln, and Edwin, a Unionist who a year earlier had saved the life of Lincoln's son, Robert Todd Lincoln, in a railroad accident.[104]

Historian John Ferling, in his book Jefferson and Hamilton: The Rivalry That Forged a Nation, makes the same point: that Alexander Hamilton's non-marital birth spurred him to seek accomplishment and distinction.[105] The Swedish artist Anders Zorn (1860–1920) was similarly motivated by his non-marital birth to prove himself and excel in his métier.[106]

Similarly, T. E. Lawrence's biographer Flora Armitage writes about being born outside of marriage: "The effect on [T. E.] Lawrence of this discovery was profound; it added to the romantic urge for heroic conduct—the dream of the Sangreal—the seed of ambition, the desire for honor and distinction: the redemption of the blood from its taint."[97]
Another biographer, John E. Mack, writes in a similar vein: "[H]is mother required of him that he redeem her fallen state by his own special achievements, by being a person of unusual value who accomplishes great deeds, preferably religious and ideally on an heroic scale. Lawrence did his best to fulfill heroic deeds. But he was plagued, especially after the events of the war activated his inner conflicts, by a deep sense of failure. Having been deceived as a child he was later to feel that he himself was a deceiver—that he had deceived the Arabs..."[107] "Mrs. Lawrence's original hope that her sons would provide her personal redemption by becoming Christian missionaries was fulfilled only by [Lawrence's brother] Robert."[108]
Mack elaborates further: "Part of his creativity and originality lies in his 'irregularity,' in his capacity to remain outside conventional ways of thinking, a tendency which... derives, at least in part, from his illegitimacy. Lawrence's capacity for invention and his ability to see unusual or humorous relationships in familiar situations come also... from his illegitimacy. He was not limited to established or 'legitimate' solutions or ways of doing things, and thus his mind was open to a wider range of possibilities and opportunities. [At the same time] Lawrence's illegitimacy had important social consequences and placed limitations upon him, which rankled him deeply... At times he felt socially isolated when erstwhile friends shunned him upon learning of his background. Lawrence's delight in making fun of regular officers and other segments of 'regular' society... derived... at least in part from his inner view of his own irregular situation. His fickleness about names for himself [he changed his name twice to distance himself from his "Lawrence of Arabia" persona] is directly related... to his view of his parents and to his identification with them [his father had changed his name after running off with T. E. Lawrence's future mother]."[109]

Christopher Columbus' first son, Diego Columbus (born between 1474 and 1480; died 1526), by Columbus' wife, Filipa Moniz Perestrelo, followed in his father's footsteps to become the 2nd Admiral of the Indies, 2nd Viceroy of the Indies, and 4th Governor of the Indies.[110] Columbus' second son, Fernando Columbus (also known as Hernando; 1488–1539), was his out-of-wedlock son by Beatriz Enríquez de Arana and—while he grew up with a fair amount of power and privilege—due to the circumstances of his birth he never quite gained the prominence his father did. Hernando Columbus' biographer Edward Wilson-Lee[111] says Hernando "always wanted to prove himself his father's son in spirit. [S]o he undertook th[e] extraordinary project [of] building a universal library that would [hold] every book in the world... [H]e very much saw this as a counterpart to his father's desire to circumnavigate the world.... Hernando was going to build a universal library that would circumnavigate the world of knowledge."[112]
However, realizing that such a large collection of books would not be very useful without a way of organizing and distilling them, he employed an army of readers to read every book and distill it down to a short summary, or "epitome". The result was the Libro de los Epitomes (Book of Epitomes). Soon after Hernando's death in 1539 at age 50, this volume went missing for nearly 500 years—until in 2019 it was serendipitously discovered in a University of Copenhagen special collection. Many of the early printed publications that the Book of Epitomes summarizes are now lost; but thanks to the out-of-wedlock bibliophile Hernando Columbus, eager to emulate in his own way his father and "legitimate" half-brother, invaluable insights are becoming available into the knowledge and thought of the early Modern Period.[112]

In more recent times, Steve Jobs' adoption due to the nonmarried status of his biological parents influenced his life and career.[113] He confided to close friends that he was driven by the pain he felt about having been put up for adoption and not having known who his birth parents were.[114]
Violence and honor killings
[edit]While births outside marriage are considered acceptable in many world regions, in some parts of the world they remain highly stigmatized. Women who have given birth under such circumstances are often subjected to violence at the hands of their families; and may even become victims of so-called honor killings.[115][116][117] These women may also be prosecuted under laws forbidding sexual relations outside marriage and may face consequent punishments, including stoning.[118]
In fiction
[edit]Illegitimacy has for centuries provided a motif and plot element to works of fiction by prominent authors, including William Shakespeare, Benjamin Franklin, Henry Fielding, Voltaire, Jane Austen, Alexandre Dumas, père, Charles Dickens, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Wilkie Collins, Anthony Trollope, Alexandre Dumas, fils, George Eliot, Victor Hugo, Leo Tolstoy, Ivan Turgenev, Fyodor Dostoyevsky, Thomas Hardy, Alphonse Daudet, Bolesław Prus, Henry James, Joseph Conrad, E. M. Forster, C. S. Forester, Marcel Pagnol, Grace Metalious, John Irving, and George R. R. Martin.
Notables
[edit]Some pre-20th-century modern individuals whose unconventional "illegitimate" origins did not prevent them from making (and in some cases helped inspire them to make) notable contributions to humanity's art or learning have included Leone Battista Alberti[119] (1404–1472), Leonardo da Vinci[120] (1452–1519), Erasmus of Rotterdam[121] 1466–1536), Jean le Rond d'Alembert[122] (1717–1783), Alexander Hamilton (1755 or 1757–1804), James Smithson[123] (1764–1829), John James Audubon[124] (1785–1851), Alexander Herzen[125] (1812—1870), Jenny Lind[126] (1820–1887), and Alexandre Dumas, fils[127] (1824–1895).
See also
[edit]- Abortion in the United States
- Affiliation (family law)
- Anne Orthwood's bastard trial
- Bastard (Jewish law)
- Bastard (law of England and Wales)
- Childwite
- Colonial American bastardy laws
- Defect of birth
- Filiation
- Hague Adoption Convention
- Illegitimacy in fiction
- Legitimacy law in England and Wales
- Legitime
- Marks of distinction
- Nonmarital birth rates by country
- Non-paternity event
- Orphan
- Unintended pregnancy
References
[edit]- ^ "1788 - Before European Settlement". Archived from the original on 2012-02-05. Retrieved 2012-03-20.
- ^ Macfarlane, Alan (1980). "Illegitimacy and illegitimates in English history" (PDF). In Laslett, Peter; et al. (eds.). Bastardy and its comparative history. Arnold – via Alanmacfarlane.com.
- ^ William Blackstone (1753), Commentaries on the Laws of England, Book II, Chapter XV "Of Title by Purchase and I. Escheat", Section 5.
- ^ Smibert, Thomas (1850). The clans of the Highlands of Scotland: an account of their annals, with delineations of their tartans, and family arms. pp. 3 et seq.
- ^ AB Wilkinson and KMcK Norrie, The Law Relating to Parent and Child in Scotland, W.Green, Edinburgh 2nd Ed 1999 para 1.54
- ^ "Category: Baptisms". Genealogy and Family History in Scotland. 12 April 2017. Retrieved 9 July 2018.
- ^ Legitimacy Act 1926 (16 & 17 Geo. 5 c. 60)
- ^ Viscount of Drumlanrig's Tutor 1977 SLT (Lyon Ct) 16
- ^ "Defect of Birth (Illegitimacy)". Catholic Encyclopedia. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ "Parental rights and responsibilities". UK Government. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ "US Supreme Court Cases from Justia & Oyez". Retrieved 19 July 2011.
- ^ "§ 320.2: Who is eligible for citizenship?" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-04-14. Retrieved 2015-04-07.
- ^ Watson vs. the United States, specifically the USCIS denial letter in Exhibit S, Hklaw.com
- ^ e.g. section 1 of the Law Reform (Parent and Child) (Scotland) Act 1986 (as amended in 2006) which abolished the status of illegitimacy.
- ^ Serge BRAUDO. "Autorité parentale - Définition". Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ "National Report: France" (PDF). Ceflonline.net. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ "LOI n° 2009-61 du 16 janvier 2009 ratifiant l'ordonnance n° 2005-759 du 4 juillet 2005 portant réforme de la filiation et modifiant ou abrogeant diverses dispositions relatives à la filiation - Legifrance". Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ "European Court of Human Rights". HUDOC. Retrieved 2023-02-11.
- ^ "FAMILY CODE: In force from 01.10.2009: Chapter one: GENERAL PROVISIONS" (PDF). Kenarova.com. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ "Liste complète". Bureau des Traités. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ "Liste complète". Bureau des Traités. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ "Make a claim to a deceased person's estate". GOV.UK. 5 February 2020. Retrieved 2023-04-06.
- ^ "Instructions for N-600, Application for Certificate of Citizenship" (PDF). U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 October 2010. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ^ Tuan Anh Nguyen et al. v. Immigration and Naturalization Service, 533 U.S. 53 (2001).
- ^ "Nationality policy: children of unmarried parents" (PDF). Home Office. v2.0. 6 November 2018. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-11-24.
- ^ "Elizabeth I". The Stuart Successions Project.
- ^ "Canon 1137". Code of Canon Law. Libreria Editrice Vaticana. Retrieved 2021-12-15.
The children conceived or born of a valid or putative marriage are legitimate.
- ^ The Guardian (13 March 2013). "Pope Francis on gay marriage, unmarried mothers … and journalists". London.
- ^ Fox (13 March 2013). "Francis is first pope from the Americas". Fox News.
- ^ ABC News. "Francis Becomes First Latin American Pope". Abcnews.go.com. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ a b c "Changing Patterns of Nonmarital Childbearing in the United States". CDC/National Center for Health Statistics. May 13, 2009. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ Grove, Robert D.; Hetzel, Alice M. (1968). Vital Statistics Rates in the United States 1940-1960 (PDF) (Report). Public Health Service Publication. Vol. 1677. U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, U.S. Public Health Service, National Center for Health Statistics. p. 185.
- ^ Ventura, Stephanie J.; Bachrach, Christine A. (October 18, 2000). Nonmarital Childbearing in the United States, 1940-99 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 48. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. pp. 28–31.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Ventura, Stephanie J.; Menacker, Fay; Park, Melissa M. (February 12, 2002). Births: Final Data for 2000 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 50. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 46.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Ventura, Stephanie J.; Menacker, Fay; Park, Melissa M.; Sutton, Paul D. (December 18, 2002). Births: Final Data for 2001 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 51. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 47.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Sutton, Paul D.; Ventura, Stephanie J.; Menacker, Fay; Munson, Martha L. (December 17, 2003). Births: Final Data for 2002 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 52. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 57.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Sutton, Paul D.; Ventura, Stephanie J.; Menacker, Fay; Munson, Martha L. (September 8, 2005). Births: Final Data for 2003 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 54. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 52.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Sutton, Paul D.; Ventura, Stephanie J.; Menacker, Fay; Kirmeyer, Sharon (September 29, 2006). Births: Final Data for 2004 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 55. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 57.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Sutton, Paul D.; Ventura, Stephanie J.; Menacker, Fay; Kirmeyer, Sharon; Munson, Martha L. (December 5, 2007). Births: Final Data for 2005 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 56. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 57.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Sutton, Paul D.; Ventura, Stephanie J.; Menacker, Fay; Kirmeyer, Sharon; Mathews, T.J. (January 7, 2009). Births: Final Data for 2006 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 57. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 54.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Sutton, Paul D.; Ventura, Stephanie J.; Mathews, T.J.; Kirmeyer, Sharon; Osterman, Michelle J.K. (August 9, 2010). Births: Final Data for 2007 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 58. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 46.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Sutton, Paul D.; Ventura, Stephanie J.; Mathews, T.J.; Osterman, Michelle J.K. (December 8, 2010). Births: Final Data for 2008 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 59. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 46.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Ventura, Stephanie J.; Osterman, Michelle J.K.; Kirmeyer, Sharon; Mathews, T.J.; Wilson, Elizabeth C. (November 3, 2011). Births: Final Data for 2009 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 60. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 46.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Ventura, Stephanie J.; Osterman, Michelle J.K.; Wilson, Elizabeth C.; Mathews, T.J. (August 28, 2012). Births: Final Data for 2010 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 61. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 45.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Ventura, Stephanie J.; Osterman, Michelle J.K.; Mathews, T.J. (June 28, 2013). Births: Final Data for 2011 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 62. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 43.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Osterman, Michelle J.K.; Curtin, Sally C. (December 30, 2013). Births: Final Data for 2012 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 62. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 41.
- ^ Martin, Joyce A.; Hamilton, Brady E.; Osterman, Michelle J.K.; Curtin, Sally C.; Mathews, T.J. (January 15, 2015). Births: Final Data for 2013 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 64. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. p. 40.
- ^ Hamilton, Brady E.; Martin, Joyce A.; Osterman, Michelle J.K.; Curtin, Sally C.; Mathews, T.J. (December 23, 2015). Births: Final Data for 2014 (PDF) (Report). National Vital Statistics Reports. Vol. 64. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. pp. 7 & 41.
- ^ "MPIDR - Spatial aspects of the rise of nonmarital fertility across Europe since 1960: the role of states and regions in shaping patterns of change". Demogr.mpg.de. Archived from the original on 2015-09-23. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ a b c d e "42% of births in the EU are outside marriage".
- ^ "Share of births outside marriage and teenage births" (PDF). OECD Directorate for Employment, Labour, and Social Affairs. Retrieved Oct 19, 2009.
- ^ "National Vital Statistics Reports, Volume 59, Number 3, December 21, 2010" (PDF).
- ^ "Our view on kids: When unwed births hit 41%, it's just not right". USA Today. 25 January 2011.
- ^ "FastStats". 17 May 2022.
- ^ Ravitz, Jessica (April 8, 2009). "Out-of-wedlock births hit record high". CNN. Retrieved Oct 19, 2009.
- ^ a b c d e "Eurostat - Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". Ec.europa.eu. 2016-08-11. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ "Population change - year 2021". Czech Statistical Office (CZCO). 21 March 2022.
- ^ a b "The low importance of marriage in eastern Germany – social norms and the role of peoples' perceptions of the past" (PDF). Demographic-research.org. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ "[ARCHIVED CONTENT] Release Edition Reference Tables". Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 22 December 2015. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ "Résultats de la recherche | Insee". Insee.fr (in French). Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ "Résultats de la recherche | Insee". Insee.fr (in French). Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ "Tony Travers: Thanks to immigrants we're the capital for marriage". Evening Standard. 24 September 2013. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ "Proportion de naissances hors mariage1 selon le rang de naissance, Québec, 1976-2014". Institut de la Statistique du Québec. Archived from the original on 5 December 2018. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ a b "Proportion de naissances hors mariage selon le rang de naissance, Québec, 1976-2015". Stat.gouv.qc.ca. Archived from the original on 2018-12-05. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ "PORDATA - Live births outside of marriage, with parents co-habiting or not (%) in Portugal". Pordata.pt. 2016-04-28. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ "Births". STATISTIK AUSTRIA. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ a b "Eurostat - Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". ec.europa.eu.
- ^ "Eurostat - Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". ec.europa.eu.
- ^ "Population change - 1st - 3rd quarter of 2015 | CZSO". Czso.cz. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ a b "Births in Australia | Australian Institute of Family Studies".
- ^ "Global Children's Trends | The Sustainable Demographic Dividend". Sustaindemographicdividend.org. Retrieved 2013-02-11.
- ^ "Births outside marriage". Childtrends.org. Archived from the original on 2015-02-06. Retrieved 2014-12-06.
- ^ a b "Global Children's Trends - The Sustainable Demographic Dividend". Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ "Illegitimate Nation: An Examination of Out-of-Wedlock Births Among Immigrants and Natives". June 2007.
- ^ "The Evolution of Births Outside of Marriage, Paternal Recognition and Children's Rights in Brazil". Paa2013.princeton.edu. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ Grupo Copesa (13 July 2014). "Alza de hijos fuera del matrimonio muestra evolución de la familia en Chile". Archived from the original on 15 July 2014. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ a b UN. "Live births by legitimacy status, and percent illegitimate: 1990 - 1998" (PDF).
- ^ "2015 PSA data on live births by legitimacy by regions" (PDF).
- ^ Gilding, Michael (2005). "Rampant misattributed paternity: the creation of an urban myth". People and Place. 13 (12): 1–11.
- ^ Gilding, M. (2009). "Paternity Uncertainty and Evolutionary Psychology: How a Seemingly Capricious Occurrence Fails to Follow Laws of Greater Generality". Sociology. 43: 140–691. doi:10.1177/0038038508099102. S2CID 145367552.
- ^ Philipp EE (1973) "Discussion: moral, social and ethical issues". In: Wolstenholme GEW, Fitzsimons DW, eds. Law and ethics of AID and embryo transfer. Ciba Foundation symposium. Vol 17. London: Associated Scientific 63–66
- ^ a b Bellis MA, Hughes K, Hughes S, Ashton JR (September 2005). "Measuring paternal discrepancy and its public health consequences". J Epidemiol Community Health. 59 (9): 749–54. doi:10.1136/jech.2005.036517. PMC 1733152. PMID 16100312.
- ^ Sykes, B; Irven, C (2000). "Surnames and the Y chromosome". Am J Hum Genet. 66 (4): 1417–1419. doi:10.1086/302850. PMC 1288207. PMID 10739766.
- ^ King, Turi E.; Jobling, Mark A. (2009), "Founders, Drift, and Infidelity: The Relationship between Y Chromosome Diversity and Patrilineal Surnames", Molecular Biology and Evolution, 26 (5): 1093–102, doi:10.1093/molbev/msp022, PMC 2668828, PMID 19204044
- ^ Forster, P; Hohoff, C; Dunkelmann, B; Schürenkamp, M; Pfeiffer, H; Neuhuber, F; Brinkmann, B (2015). "Elevated germline mutation rate in teenage fathers". Proc Biol Sci. 282 (1803): 20142898. doi:10.1098/rspb.2014.2898. PMC 4345458. PMID 25694621.
- ^ Griffin, Emma (2013). "Sex, illegitimacy and social change in industrializing Britain'". Social History. 38 (2): 139–161. doi:10.1080/03071022.2013.790236. S2CID 143607918.
- ^ "UK | The no-sex 'myth'". BBC News. 2002-10-03. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ a b "Currently cohabiting: relationship expectations and outcomes in the British Household Panel Survey (BHPS): Ernestina Coast" (PDF). Epc2008.princeton.edu. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ a b Elena von der Lippe (Koytcheva). "Contemporary union formation in Bulgaria: the emergence of cohabitation". ResearchGate. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ "Why are cohabitation and extra-marital births so few in Japan?" (PDF). Demogr.mpg.de. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ "Spain - SOCIAL VALUES AND ATTITUDES". Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ Cherlin, Andrew J. (1 January 2004). "The Deinstitutionalization of American Marriage". Journal of Marriage and Family. 66 (4): 848–861. doi:10.1111/j.0022-2445.2004.00058.x. JSTOR 3600162.
- ^ "The reproductive context of cohabitation in comparative perspective: Contraceptive use in the United States, Spain, and France" (PDF). Demographic-research.org. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ Laplante, Benoît (1 January 2006). "The Rise of Cohabitation in Quebec: Power of Religion and Power over Religion". The Canadian Journal of Sociology. 31 (1): 1–24. doi:10.2307/20058678. JSTOR 20058678.
- ^ "Doing Better for Families: Chapter 1: Families are changing" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-12-22. Retrieved 2014-05-06.
- ^ Figure 9, Frances Finnegan, Do Penance or Perish, Congrave Press, 2001.
- ^ a b Flora Armitage, The Desert and the Stars: A Biography of Lawrence of Arabia, p. 42.
- ^ John E. Mack, A Prince of Our Disorder: The Life of T.E. Lawrence, pp. 28–29, 32.
- ^ On the 4 March 2011 Charlie Rose TV interview program, British Nobel laureate Paul Nurse told such a story of "shame": he was reared by his grandparents as the supposed younger brother of his now-deceased biological mother, and has never learned who his biological father was.
- ^ "Illegitimacy". Justia. Retrieved 2009-10-19.
- ^ Andrzej Garlicki, "Piłsudski, Józef Klemens," Polski słownik biograficzny, vol. XXVI, 1981, pp. 320, 323.
- ^ J. Renn and R. Schulmann, Albert Einstein / Mileva Marić: The Love Letters, 1992, pp. 73–74, 78.
- ^ Alice Calaprice and Trevor Lipscombe, Albert Einstein: A Biography, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2005, ISBN 978-0-313-33080-3, pp. 22–23.
- ^ Nora Titone. My Thoughts Be Bloody: The Bitter Rivalry Between Edwin and John Wilkes Booth That Led to an American Tragedy. New York: Simon and Schuster; 2010 [cited September 24, 2011]. ISBN 978-1-4165-8605-0.
- ^ Discussed by Ferling in a 9 October 2013 lecture on C-SPAN2 Book TV.
- ^ "Anders Zorn in the Gilded Age", PBS biography (Colorado Public Television), one hour, 2013.
- ^ John E. Mack, A Prince of Our Disorder: The Life of T. E. Lawrence, 1976, p. 28.
- ^ John E. Mack, A Prince of Our Disorder: The Life of T. E. Lawrence, 1976, p. 32.
- ^ John E. Mack, A Prince of Our Disorder: The Life of T. E. Lawrence, 1976, pp. 28–29.
- ^ "Diego Columbus". Encyclopedia Britannica. 23 February 2024.
- ^ Edward Wilson-Lee, The Catalogue of Shipwrecked Books: Young Columbus and the Quest for a Universal Library, William Collins, 2018.
- ^ a b Ari Shapiro, "Christopher Columbus' Son Had an Enormous Library. Its Catalog Was Just Found", All Things Considered, NPR newscast, 24 April 2019 [1]
- ^ Bradford, Krista (2023-09-14). "The Good Search | National Retained Executive Search Firm". The Good Search. Retrieved 2023-12-15.
- ^ Batura, Paul, with Jim Daly (2017-03-20). "The Improbable Adoption Story of Steve Jobs". Jim Daly. Retrieved 2023-12-15.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "BBC - Ethics: Honour Crimes". Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ "Refugee Review Tribunal, Australia: RRT Research Response". Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-05-01. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- ^ "Turkey condemns 'honour killings'". BBC News. 1 March 2004.
- ^ "Nigeria stoning appeal adjourned". CNN. 3 June 2003.
- ^ Joan Kelly-Gadol, "Leon Battista Alberti" (last updated 21 April 2021), Encyclopaedia Britannica [2]
- ^ "Leonardo da Vinci", The Encyclopedia Americana, vol. 17, pp. 228-236, Danbury, CT, Grolier Incorporated, 1986, ISBN 0-7172-0117-1, p. 228.
- ^ "Erasmus", The Encyclopedia Americana, vol. 10, pp. 541–542, Danbury, CT, Grolier Incorporated, 1986, ISBN 0-7172-0117-1, p. 541.
- ^ "Alembert, Jean le Rond d'", The Encyclopedia Americana, vol. 1, Danbury, CT, Grolier Incorporated, 1986, ISBN 0-7172-0117-1, p. 526.
- ^ "Smithson, James", The Encyclopedia Americana, vol. 25, Danbury, CT, Grolier Incorporated, 1986, ISBN 0-7172-0117-1, p. 65.
- ^ "Audubon, John James", The Encyclopedia Americana, vol. 2, Danbury, CT, Grolier Incorporated, 1986, ISBN 0-7172-0117-1, p. 677.
- ^ "Herzen, Aleksandr Ivanovich", The Encyclopedia Americana, vol. 14, Danbury, CT, Grolier Incorporated, 1986, ISBN 0-7172-0117-1, pp. 161-162.
- ^ Carole Rosen (2004), "Lind (married name Lind-Goldschmidt), Jenny (Johanna Maria)", doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/16671, in Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (subscription required).
- ^ "Dumas, Alexandre", The Encyclopedia Americana, vol. 9, Danbury, CT, Grolier Incorporated, 1986, ISBN 0-7172-0117-1, pp. 466-467.
Bibliography
[edit]- Flora Armitage, The Desert and the Stars: a Biography of Lawrence of Arabia, illustrated with photographs, New York, Henry Holt and Company, 1955.
- Andrzej Garlicki, "Piłsudski, Józef Klemens," Polski słownik biograficzny, vol. XXVI, Wrocław, Polska Akademia Nauk, 1981, pp. 311–24.
- Shirley Foster Hartley, Illegitimacy, University of California Press, 1975.
- Alysa Levene, Thomas Nutt & Samantha Williams, eds. Illegitimacy in Britain, 1700–1920. Palgrave Macmillan; 2005 [cited 24 September 2011]. ISBN 978-1-4039-9065-5.
- John E. Mack. A Prince of Our Disorder: The Life of T. E. Lawrence. Harvard University Press; 1998 [cited September 24, 2011]. ISBN 978-0-674-70494-7.
- Charles Simic, "You Laugh Uncontrollably" (review of Bohumil Hrabal, Mr. Kafka and Other Tales from the Time of the Cult, translated from the Czech by Paul Wilson, New Directions, 142 pp., $14.95 [paper]), The New York Review of Books, vol. LXIII, no. 8 (May 12, 2016), pp. 58–60.
- Jenny Teichman. Illegitimacy: an examination of bastardy. Cornell University Press; 1982 [cited September 24, 2011]. ISBN 978-0-8014-1491-6.
- Nora Titone, My Thoughts Be Bloody: The Bitter Rivalry between Edwin and John Wilkes Booth that Led to an American Tragedy, New York, Simon and Schuster, 2010 [cited September 24, 2011], ISBN 978-1-4165-8605-0.
External links
[edit]- Percentage of Births to Unmarried Mothers by State: 2014 (distribution of births outside marriage across the United States)
- Cuckolded fathers rare in human populations
- Ari Shapiro, "Christopher Columbus' Son Had an Enormous Library. Its Catalog Was Just Found", All Things Considered, NPR newscast, 24 April 2019 [3]
- The Psychological Effects of Being an Illegitimate Child - Low self-esteem, trust issues, and identity problems
