1948 United States Senate elections
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
33 of the 96 seats in the United States Senate 49 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
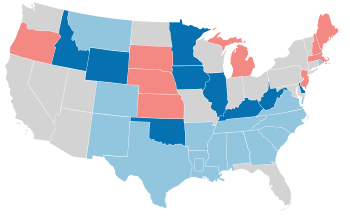 Results of the elections: Democratic gain Democratic hold Republican hold No election Rectangular inset (Louisiana): both seats up for election | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1948 United States Senate elections were held concurrently with the election of Democratic President Harry S. Truman for a full term. The 32 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and one special election was held to fill a vacancy. Truman campaigned against an "obstructionist" Congress that had blocked many of his initiatives, and additionally, the U.S. economy recovered from the postwar recession of 1946–1947 by election day. Thus, Truman was rewarded with a Democratic gain of nine seats in the Senate, enough to give them control of the chamber.[1][2] This was the last time until 2020 that Democrats flipped a chamber of Congress in a presidential election cycle.
Results summary
[edit]| 54 | 42 |
| Democratic | Republican |
Colored shading indicates party with largest share of that row.
| Parties | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Republican | Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last elections (1946) Before these elections |
45 | 51 | 0 | 96 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not up | 30 | 33 | 0 | 63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up | 15 | 18 | 0 | 33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class 2 (1942→1948) | 14 | 18 | 0 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special: Class 3 | 1 | 0 | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incumbent retired | 3 | 5 | — | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Held by same party | 3 | 4 | — | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Replaced by other party | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result | 4 | 4 | 0 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incumbent ran | 12 | 13 | — | 25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Won re-election | 10 | 5 | — | 17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lost re-election | — | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lost renomination but held by same party |
2 | 0 | — | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result | 20 | 5 | 0 | 25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total elected | 24 | 9 | 0 | 33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net change | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nationwide vote | 13,056,944 | 9,764,384 | 269,669 | 23,090,997 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share | 56.55% | 42.29% | 1.17% | 100% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result | 54 | 42 | 0 | 96 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Clerk of the U.S. House of Representatives[3]
Gains, losses, and holds
[edit]Retirements
[edit]Five Republicans and three Democrats retired instead of seeking re-election.
Defeats
[edit]Eight Republicans and two Democrats sought re-election but lost in the primary or general election.
Post election changes
[edit]Change in composition
[edit]Before the elections
[edit]| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | ||
| D18 | D17 | D16 | D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 |
| D19 | D20 | D21 | D22 | D23 | D24 | D25 | D26 | D27 | D28 |
| D38 Mont. Ran |
D37 Miss. Ran |
D36 La. (sp) Retired |
D35 La. (reg) Ran |
D34 Ga. Ran |
D33 Colo. Ran |
D32 Ark. Ran |
D31 Ala. Ran |
D30 | D29 |
| D39 N.M. Retired |
D40 N.C. (sp) N.C. (reg) Ran |
D41 R.I. Ran |
D42 S.C. Ran |
D43 Tenn. Ran |
D44 Texas Retired |
D45 Va. Ran |
R51 Wyo. Ran |
R50 W.Va. Ran |
R49 S.D. Retired |
| Majority → | |||||||||
| R39 Ky. Ran |
R40 Maine Retired |
R41 Mass. Ran |
R42 Mich. Ran |
R43 Minn. Ran |
R44 Neb. Ran |
R45 N.H. Ran |
R46 N.J. Retired |
R47 Okla. Retired |
R48 Ore. Ran |
| R38 Kan. Retired |
R37 Iowa Ran |
R36 Ill. Ran |
R35 Idaho Ran |
R34 Del. Ran |
R33 | R32 | R31 | R30 | R29 |
| R19 | R20 | R21 | R22 | R23 | R24 | R25 | R26 | R27 | R28 |
| R18 | R17 | R16 | R15 | R14 | R13 | R12 | R11 | R10 | R9 |
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | ||
Election results
[edit]| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | ||
| D18 | D17 | D16 | D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 |
| D19 | D20 | D21 | D22 | D23 | D24 | D25 | D26 | D27 | D28 |
| D38 Mont. Re-elected |
D37 Miss. Re-elected |
D36 La. (sp) Hold |
D35 La. (reg) Re-elected |
D34 Ga. Re-elected |
D33 Colo. Re-elected |
D32 Ark. Re-elected |
D31 Ala. Re-elected |
D30 | D29 |
| D39 N.M. Hold |
D40 N.C. (sp) N.C. (reg) Hold |
D41 R.I. Re-elected |
D42 S.C. Re-elected |
D43 Tenn. Hold |
D44 Texas Hold |
D45 Va. Re-elected |
D46 Del. Gain |
D47 Idaho Gain |
D48 Ill. Gain |
| Majority → | D49 Iowa Gain | ||||||||
| R39 N.H. Re-elected |
R40 N.J. Hold |
R41 Ore. Re-elected |
R42 S.D. Hold |
D54 Wyo. Gain |
D53 W.Va. Gain |
D52 Okla. Gain |
D51 Minn. Gain |
D50 Ky. Gain | |
| R38 Neb. Re-elected |
R37 Mich. Re-elected |
R36 Mass. Re-elected |
R35 Maine Hold |
R34 Kan. Hold |
R33 | R32 | R31 | R30 | R29 |
| R19 | R20 | R21 | R22 | R23 | R24 | R25 | R26 | R27 | R28 |
| R18 | R17 | R16 | R15 | R14 | R13 | R12 | R11 | R10 | R9 |
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | ||
| Key: |
|
|---|
Race summaries
[edit]Special elections during the 80th Congress
[edit]In these special elections, the winner was seated during 1948 or before January 3, 1949; ordered by election date.
| State | Incumbent | Results | Candidates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Party | Electoral history | |||
| Louisiana (Class 3) |
William C. Feazel | Democratic | 1948 (Appointed) | Interim appointee retired. Winner elected November 2, 1948. Democratic hold. |
|
| North Carolina (Class 2) |
William B. Umstead | Democratic | 1946 (Appointed) | Interim appointee lost nomination. Winner elected November 2, 1948. Democratic hold. Winner also elected to the next full term. |
|
Elections leading to the next Congress
[edit]In these general elections, the winners were elected for the term beginning January 3, 1949; ordered by state.
All of the elections involved the Class 2 seats.
| State | Incumbent | Results | Candidates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Party | Electoral history | |||
| Alabama | John Sparkman | Democratic | 1946 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Arkansas | John L. McClellan | Democratic | 1942 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Colorado | Edwin C. Johnson | Democratic | 1936 1942 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Delaware | C. Douglass Buck | Republican | 1942 | Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Democratic gain. |
|
| Georgia | Richard Russell Jr. | Democratic | 1932 (special) 1936 1942 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Idaho | Henry Dworshak | Republican | 1946 (special) | Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Democratic gain. |
|
| Illinois | C. Wayland Brooks | Republican | 1940 (special) 1942 |
Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Democratic gain. |
|
| Iowa | George A. Wilson | Republican | 1942 | Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Democratic gain. |
|
| Kansas | Arthur Capper | Republican | 1918 1924 1930 1936 1942 |
Incumbent retired. New senator elected. Republican hold. |
|
| Kentucky | John Sherman Cooper | Republican | 1946 (special) | Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Democratic gain. |
|
| Louisiana | Allen J. Ellender | Democratic | 1936 1942 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Maine | Wallace H. White | Republican | 1930 1936 1942 |
Incumbent retired. New senator elected. Republican hold. |
|
| Massachusetts | Leverett Saltonstall | Republican | 1944 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Michigan | Homer S. Ferguson | Republican | 1942 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Minnesota | Joseph H. Ball | Republican | 1940 (Appointed) 1942 (Retired) 1942 |
Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Democratic–Farmer–Labor gain. |
|
| Mississippi | James Eastland | Democratic | 1941 (Appointed) 1941 (Retired) 1942 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Montana | James E. Murray | Democratic | 1934 (special) 1936 1942 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Nebraska | Kenneth S. Wherry | Republican | 1942 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New Hampshire | Styles Bridges | Republican | 1936 1942 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New Jersey | Albert W. Hawkes | Republican | 1942 | Incumbent retired. New senator elected. Republican hold. |
|
| New Mexico | Carl Hatch | Democratic | 1933 (Appointed) 1934 (special) 1936 1942 |
Incumbent retired. New senator elected. Democratic hold. |
|
| North Carolina | William B. Umstead | Democratic | 1946 (Appointed) | Interim appointee lost nomination. New senator elected. Democratic hold. Winner also elected to finish the term, see above. |
|
| Oklahoma | Edward H. Moore | Republican | 1942 | Incumbent retired. New senator elected. Democratic gain. |
|
| Oregon | Guy Cordon | Republican | 1944 (Appointed) 1944 (special) |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Rhode Island | Theodore F. Green | Democratic | 1936 1942 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| South Carolina | Burnet R. Maybank | Democratic | 1941 (special) 1942 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| South Dakota | Vera C. Bushfield | Republican | 1948 (Appointed) | Interim appointee retired. New senator elected. Republican hold. Incumbent resigned December 26, 1948 and winner appointed December 31, 1948 to finish the term. |
|
| Tennessee | Tom Stewart | Democratic | 1938 (special) | Incumbent lost re-nomination. New senator elected. Democratic hold. |
|
| Texas | W. Lee O'Daniel | Democratic | 1941 (special) 1942 |
Incumbent retired. New senator elected. Democratic hold. |
|
| Virginia | A. Willis Robertson | Democratic | 1946 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| West Virginia | Chapman Revercomb | Republican | 1942 | Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Democratic gain. |
|
| Wyoming | Edward V. Robertson | Republican | 1942 | Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Democratic gain. |
|
Closest races
[edit]Six races had a margin of victory under 10%:
| State | Party of winner | Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Idaho | Democratic (flip) | 1.5% |
| Michigan | Republican | 2.2% |
| Delaware | Democratic (flip) | 2.6% |
| New Jersey | Republican | 2.7% |
| Kentucky | Democratic (flip) | 3.1% |
| Massachusetts | Republican | 6.6% |
Wyoming is the tipping point state with a margin of 14.2%.
Alabama
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Sparkman: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% 90–100% Parsons: 50-60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | John Sparkman (Incumbent) | 185,534 | 84.00% | |
| Republican | Paul G. Parsons | 35,341 | 16.00% | |
| Majority | 150,193 | 68.00% | ||
| Turnout | 220,875 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Arkansas
[edit]
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | John L. McClellan (Incumbent) | 216,401 | 100.00% | |
| Democratic hold | ||||
Colorado
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Johnson: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Edwin C. Johnson (Incumbent) | 340,719 | 66.79% | |
| Republican | Will Nicholson | 165,069 | 32.36% | |
| Progressive | Joe Gurule | 2,981 | 0.58% | |
| Socialist | Carle Whithead | 1,352 | 0.27% | |
| Majority | 175,650 | 34.43% | ||
| Turnout | 510,121 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Delaware
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County Results Frear: 50–60% Buck: 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | J. Allen Frear Jr. | 71,888 | 50.85% | |
| Republican | C. Douglass Buck (incumbent) | 68,246 | 48.28% | |
| Majority | 3,642 | 2.57% | ||
| Turnout | 141,362 | |||
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
Georgia
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
 County results Russell: >90% | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Richard Russell Jr. (Incumbent) | 362,104 | 99.89% | |
| Write-In | Larkin Marshall | 388 | 0.11% | |
| Write-In | Ellis Arnall | 9 | 0.00% | |
| Write-In | Roy Harris | 2 | 0.00% | |
| Write-In | Harry Sommers | 1 | 0.00% | |
| Majority | 361,716 | 99.78% | ||
| Turnout | 362,504 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Idaho
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Miller: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Dworshak: 40-50% 50-60% 60-70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
Democrat Bert H. Miller defeated incumbent Republican Henry Dworshak. As of 2024, this remains the only time that a Democrat would win Idaho's Class 2 Senate seat. Dworshak was appointed back to this seat in October 1949 after Miller died earlier that month and served until he himself died in 1962.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Bert H. Miller | 107,000 | 49.96% | |
| Republican | Henry Dworshak (Incumbent) | 103,868 | 48.49% | |
| Progressive | John Derr | 3,154 | 1.47% | |
| Socialist | Paul Wengert | 166 | 0.08% | |
| Majority | 3,132 | 1.47% | ||
| Turnout | 214,188 | |||
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
Illinois
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Douglas: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% Tie: 40–50% Brooks: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Paul Douglas | 2,147,754 | 55.07% | |
| Republican | Charles W. Brooks (Incumbent) | 1,740,026 | 44.61% | |
| Prohibition | Enoch A. Holtwick | 9,784 | 0.25% | |
| Socialist Labor | Frank Schnur | 2,693 | 0.07% | |
| None | Write-In | 28 | 0.00% | |
| Majority | 407,728 | 10.46% | ||
| Turnout | 3,900,285 | |||
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
Iowa
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Gillette: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% Wilson: 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Guy Gillette | 578,226 | 57.80% | |
| Republican | George A. Wilson (Incumbent) | 415,778 | 41.56% | |
| Progressive | Seymour Pitcher | 3,387 | 0.34% | |
| Prohibition | Z. Everett Kellum | 2,580 | 0.26% | |
| Socialist | Hugo Bockewitz | 441 | 0.04% | |
| Majority | 162,448 | 16.24% | ||
| Turnout | 1,000,412 | |||
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
Kansas
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Schoeppel: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% McGill: 40–50% 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Andrew Frank Schoeppel | 393,412 | 54.92% | |
| Democratic | George McGill | 305,987 | 42.72% | |
| Prohibition | C. Floyd Hester | 16,943 | 2.37% | |
| Majority | 87,425 | 12.20% | ||
| Turnout | 716,342 | |||
| Republican hold | ||||
Kentucky
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Chapman: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% Cooper: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Virgil Chapman | 408,256 | 51.39% | |
| Republican | John Sherman Cooper (Incumbent) | 383,776 | 48.31% | |
| Socialist | W. A. Standefur | 1,232 | 0.16% | |
| Progressive | H. G. Stanfield | 924 | 0.12% | |
| Socialist Labor | David R. Cox | 254 | 0.03% | |
| Write-In | John Y. Brown | 26 | 0.00% | |
| Write-In | O. G. Gaines | 1 | 0.00% | |
| Majority | 24,480 | 3.08% | ||
| Turnout | 794,469 | |||
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
Louisiana
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
Louisiana (regular)
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Parish results Ellender: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% >90% | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Allen J. Ellender (Incumbent) | 330,115 | 100.00% | |
| Independent | Maurice Eugene Clark | 9 | 0.00% | |
| Majority | 330,106 | 100.00% | ||
| Turnout | 330,124 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Louisiana (special)
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 Parish results Long: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% 90–100% Jenkins: 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Russell B. Long | 306,336 | 74.96% | |
| Republican | Clem S. Clarke | 102,331 | 25.04% | |
| Majority | 204,005 | 49.92% | ||
| Turnout | 408,667 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Maine
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County Results Smith: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% >90% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Margaret Chase Smith | 159,182 | 71.30% | |
| Democratic | Adrian H. Scolten | 64,074 | 28.70% | |
| Majority | 95,108 | 42.60% | ||
| Turnout | 223,256 | |||
| Republican hold | ||||
Massachusetts
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Saltonstall: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% 90–100% Fitzgerald: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Leverett Saltonstall (Incumbent) | 1,088,475 | 52.95% | |
| Democratic | John I. Fitzgerald | 954,398 | 46.42% | |
| Socialist Labor | Henning A. Blomen | 9,266 | 0.45% | |
| Prohibition | E. Tallmadge Root | 3,652 | 0.18% | |
| None | Scattering | 7 | 0.00% | |
| Majority | 134,077 | 6.53% | ||
| Turnout | 2,055,798 | |||
| Republican hold | ||||
Michigan
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Ferguson: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% Hook: 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Homer S. Ferguson (Incumbent) | 1,045,156 | 50.68% | |
| Democratic | Frank E. Hook | 1,000,329 | 48.51% | |
| Prohibition | Harold A. Lindahl | 12,146 | 0.59% | |
| Socialist | Michael Magee | 2,160 | 0.10% | |
| Socialist Labor | Theos S. Grove | 1,418 | 0.07% | |
| Socialist Workers | Genora Dollinger | 882 | 0.04% | |
| None | Scattering | 2.57% | 0.00% | |
| Majority | 44,827 | 2.17% | ||
| Turnout | 2,062,093 | |||
| Republican hold | ||||
Minnesota
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Humphrey: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Ball: 50-60% 60-70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic (DFL) | Hubert Humphrey | 729,494 | 59.78% | |
| Republican | Joseph H. Ball (Incumbent) | 485,801 | 39.81% | |
| Socialist Workers | Vincent R. Dunne | 4,951 | 0.41% | |
| None | Scattering | 41.56% | 0.00% | |
| Majority | 243,693 | 19.97% | ||
| Turnout | 1,220,250 | |||
| Democratic (DFL) gain from Republican | ||||
Mississippi
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | James Eastland (Incumbent) | 151,478 | 100.00% | |
| Democratic hold | ||||
Montana
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Murray: 50–60% 60–70% Davis: 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Incumbent United States Senator James E. Murray, who was first elected to the Senate in a special election in 1934 and was re-elected in 1936 and 1942, ran for re-election. After winning the Democratic primary, he faced Tom J. Davis, an attorney and the Republican nominee, in the general election. Following a narrow re-election in 1936, Murray significantly expanded his margin of victory and comfortably won re-election over Davis, winning his fourth term and his third full term in the Senate.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | James E. Murray (Incumbent) | 125,193 | 56.65% | |
| Republican | Tom J. Davis | 94,458 | 42.74% | |
| Prohibition | C. S. Hanna | 1,352 | 0.61% | |
| Majority | 30,735 | 13.91% | ||
| Turnout | 221,003 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Nebraska
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Wherry: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Carpenter: 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Kenneth S. Wherry (Incumbent) | 267,575 | 56.67% | |
| Democratic | Terry Carpenter | 204,320 | 43.27% | |
| N/A | Scattering | 261 | 0.06% | |
| Majority | 63,255 | 13.40% | ||
| Turnout | 472,156 | |||
| Republican hold | ||||
New Hampshire
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Bridges: 50–60% 60–70% 80–90% Fortin: 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Styles Bridges (Incumbent) | 129,600 | 58.14% | |
| Democratic | Alfred E. Fortin | 91,760 | 41.17% | |
| Progressive | John G. Rideout | 1,538 | 0.69% | |
| Majority | 37,840 | 16.97% | ||
| Turnout | 222,898 | |||
| Republican hold | ||||
New Jersey
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County Results Hendrickson: 40–50% 50-60% 60-70% 70-80% Alexander: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Robert C. Hendrickson | 934,720 | 49.99% | |
| Democratic | Archibald S. Alexander | 884,414 | 47.30% | |
| Progressive | James Imbrie | 22,658 | 1.21% | |
| Socialist | Rubye Smith | 11,450 | 0.61% | |
| Socialist Workers | George Breitman | 8,076 | 0.43% | |
| Prohibition | George W. Rideout | 4,656 | 0.25% | |
| Socialist Labor | George E. Bopp | 3,908 | 0.21% | |
| Majority | 50,306 | 2.69% | ||
| Turnout | 1,869,882 | |||
| Republican hold | ||||
New Mexico
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Anderson: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% Hurley: 40–50% 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Clinton Anderson | 108,269 | 57.44% | |
| Republican | Patrick J. Hurley | 80,226 | 42.40% | |
| Progressive | Brígido Provencio | 705 | 0.37% | |
| Majority | 28,043 | 14.04% | ||
| Turnout | 188,202 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
North Carolina
[edit]There were 2 elections to the same seat, due to the December 15, 1946 death of three-term Democrat Josiah Bailey. Democratic former congressman William B. Umstead was appointed December 18, 1946 to continue Bailey's term, pending a special election.
Umstead supported the conservative Taft–Hartley Act. The Democratic former Governor of North Carolina J. Melville Broughton was seen as a "rather liberal alternative" to Umstead. Broughton beat Umstead in the Democratic primaries and then won the general elections.
North Carolina (special)
[edit]| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | J. Melville Broughton | 206,605 | 52.30% | |
| Democratic | William B. Umstead (Incumbent) | 188,420 | 47.70% | |
| Majority | 18,196 | 4.60% | ||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | J. Melville Broughton | 534,917 | 100.00% | |
| Democratic hold | ||||
North Carolina (regular)
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Scott: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% 90-100% West: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | J. Melville Broughton | 207,981 | 53.10% | |
| Democratic | William B. Umstead (Incumbent) | 183,865 | 46.90% | |
| Majority | 23,894 | 6.10% | ||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | J. Melville Broughton | 540,762 | 70.70% | |
| Republican | John A. Wilkinson | 220,307 | 28.80% | |
| Majority | 320,455 | 41.91% | ||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Broughton was seated December 31, 1948 to finish the current term but died March 6, 1949, just after the new term began. His death lead to another appointment (Democrat Frank Graham) in 1949 and another special election in 1950 of Democrat Willis Smith. Smith also died during the term, leading to yet another appointment (Democrat Alton A. Lennon) and 1954 special election (of Democrat W. Kerr Scott). In all, five senators held the seat during the 1949–1955 term.
Oklahoma
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Kerr: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% >90% Rizley: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Robert S. Kerr | 441,654 | 62.30% | |
| Republican | Ross Rizley | 265,169 | 37.40% | |
| Independent | W. O. Pratt | 2,108 | 0.30% | |
| Majority | 176,485 | 24.90% | ||
| Turnout | 708,931 | |||
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
Oregon
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Cordon: 50-60% 60-70% 70-80% Wilson: 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Guy Cordon (Incumbent) | 299,295 | 60.03% | |
| Democratic | Manley J. Wilson | 199,275 | 39.97% | |
| Majority | 100,020 | 20.06% | ||
| Turnout | 498,570 | |||
| Republican hold | ||||
Rhode Island
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Theodore F. Green (Incumbent) | 190,158 | 59.35% | |
| Republican | Thomas P. Hazard | 130,262 | 40.65% | |
| Majority | 59,896 | 18.70% | ||
| Turnout | 320,420 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
South Carolina
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Results by county Maybank: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% Dorn: 30–40% 40–50% 50-60% 60–70% Bennett: 80-90% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Senator Burnet R. Maybank was opposed in the Democratic primary by U.S. Representative William Jennings Bryan Dorn and three other candidates. Maybank obtained over 50% in the primary election on August 10 to avoid a runoff election.
| Democratic Primary | ||
|---|---|---|
| Candidate | Votes | % |
| Burnet R. Maybank | 161,608 | 51.5 |
| W.J. Bryan Dorn | 76,749 | 24.4 |
| Neville Bennett | 43,068 | 13.7 |
| Alan Johnstone | 17,689 | 5.6 |
| Marcus A. Stone | 14,904 | 4.8 |
Since the end of Reconstruction in 1877, the Democratic Party dominated the politics of South Carolina and its statewide candidates were never seriously challenged. Maybank did not campaign for the general election as there was no chance of defeat.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Burnet R. Maybank (Incumbent) | 135,998 | 96.45% | |
| Republican | J. Bates Gerald | 5,008 | 3.55% | |
| Majority | 130,990 | 92.90 | ||
| Turnout | 141,006 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
South Dakota
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Mundt: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% Engel: 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Karl E. Mundt | 144,084 | 59.33% | |
| Democratic | John A. Engel | 98,749 | 40.67% | |
| Majority | 45,335 | 18.66% | ||
| Turnout | 242,833 | |||
| Republican hold | ||||
Tennessee
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 Results by county Kefauver: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% 90–100% Reece: 40–50% 50-60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Estes Kefauver | 326,142 | 65.33% | |
| Republican | B. Carroll Reece | 166,947 | 33.44% | |
| Independent | John Randolph Neal Jr. | 6,103 | 1.22% | |
| None | Scattering | 26 | 0.01% | |
| Majority | 159,195 | 31.89% | ||
| Turnout | 499,218 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Texas
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County Results[6] Johnson: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% >90% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Incumbent Democrat W. Lee O'Daniel decided to retire rather than seek a second full term. Congressman Lyndon Johnson won the highly contested Democratic primary against former governor Coke Stevenson. Johnson went on to win the general election against Republican Jack Porter, but by a closer margin than usual for Texas Democrats.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Lyndon Johnson | 702,985 | 66.22% | |
| Republican | Jack Porter | 349,665 | 32.94% | |
| Prohibition | Samuel N. Morris | 8,913 | 0.84% | |
| Majority | 353,320 | 33.28% | ||
| Turnout | 1,061,563 | |||
| Democratic hold | ||||
Virginia
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Incumbent Democrat A. Willis Robertson defeated Republican Robert H. Woods and was re-elected to his first full term in office.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | A. Willis Robertson (Incumbent) | 253,865 | 65.74% | −2.41% | |
| Republican | Robert H. Woods | 118,546 | 30.70% | +1.68% | |
| Independent | Howard Carwile | 6,788 | 1.76% | ||
| Progressive | Virginia Foster Durr | 5,347 | 1.38% | +1.38% | |
| Socialist | Clarke T. Robb | 1,627 | 0.42% | −2.40% | |
| Write-ins | 5 | <0.01% | |||
| Majority | 135,319 | 35.04% | −4.09% | ||
| Turnout | 386,168 | ||||
| Democratic hold | Swing | ||||
West Virginia
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Neely: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Revercomb: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Matthew M. Neely | 435,354 | 56.99% | |
| Republican | Chapman Revercomb (Incumbent) | 328,534 | 43.01% | |
| Majority | 106,810 | 13.98% | ||
| Turnout | 763,888 | |||
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
Wyoming
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 County results Hunt: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Robertson: 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2020) |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Lester C. Hunt | 57,953 | 57.11% | |
| Republican | Edward V. Robertson (Incumbent) | 43,527 | 42.89% | |
| Majority | 14,426 | 14.22% | ||
| Turnout | 101,480 | |||
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
|}
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ William S. White (November 4, 1948). "SWEEP IN CONGRESS – Democrats Obtain 54-42 Margin in Senate by Winning 9 G.O.P. Seats". New York Times. Retrieved April 8, 2014.
- ^ "Truman Sweep". New York Times. November 7, 1948. Retrieved April 8, 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad Clerk of the U.S. House of Representatives (1949-03-01). "Statistics of the Presidential and Congressional Election of November 2, 1948" (PDF). U.S. Government Printing Office. pp. 14–15, 50.
- ^ a b Kalb, Deborah, ed. (2010). Guide to U.S. Elections. Washington, DC: CQ Press. p. 1524. ISBN 978-1-60426-536-1.
- ^ a b Kalb, Deborah, ed. (2010). Guide to U.S. Elections. Washington, DC: CQ Press. p. 1458. ISBN 978-1-60426-536-1.
- ^ Heard, Alexander; Strong, Donald (1950). Southern Primaries and Elections 1920-1949. University of Alabama Press. pp. 184–186. ISBN 9780836955248.
Further reading
[edit]- Hartley, Robert E. Battleground 1948: Truman, Stevenson, Douglas, and the Most Surprising Election in Illinois History (Southern Illinois University Press; 2013)
























































