OODA loop
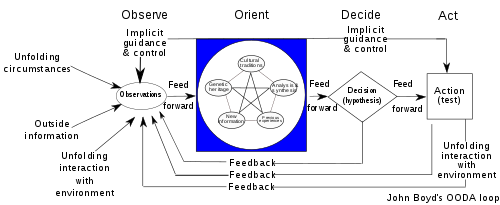
The OODA loop (observe, orient, decide, act) is a decision-making model developed by military strategist and United States Air Force Colonel John Boyd. He applied the concept to the combat operations process, often at the operational level during military campaigns. It is often applied to understand commercial operations and learning processes. The approach explains how agility can overcome raw power in dealing with human opponents. It is especially applicable to cyber security and cyberwarfare.[1]
The OODA loop has become an important concept in litigation,[2] business,[3] law enforcement,[4] management education,[5] and military strategy. According to Boyd, decision-making occurs in a recurring cycle of "observe, orient, decide, act". An entity (whether an individual or an organization) that can process this cycle quickly, observing and reacting to unfolding events more rapidly than an opponent, can thereby get inside the opponent's decision cycle and gain the advantage.
Dominic Cummings, Chief Advisor to the UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson, credited the success of the Vote Leave campaign in the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum to its faster processing of OODA loops, along with the focus of Vote Leave on disrupting the OODA loops of the opposing Britain Stronger in Europe campaign team.[6]
Some scholars are critical of the concept. Aviation historian Michael Hankins, for example, writes that "the OODA loop is vague enough that its defenders and attackers can each see what they want to see in it. For some, the OODA concept’s flexibility is its strength, but for others it becomes so generalized as to lose its usefulness." He concludes that "The OODA loop is merely one way among a myriad of ways of describing intuitive processes of learning and decision making that most people experience daily. It is not incorrect, but neither is it unique or especially profound."[7]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Clarke, Richard (2019). The Fifth Domain:Defending Our Country, Our Companies, and Ourselves in the Age of Cyber Threats. Penguin Press. p. 81. ISBN 978-0525561965.
- ^ Dreier pp. 20–85.
- ^ Richards pp. 162–171.
- ^ Papenfuhs, Steve (Pappy). "The OODA loop, reaction time, and decision making". PoliceOne.com. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
- ^ Ryder, Mike; Downs, Carolyn (November 2022). "Rethinking reflective practice: John Boyd's OODA loop as an alternative to Kolb". The International Journal of Management Education. 20 (3): 100703. doi:10.1016/j.ijme.2022.100703.
- ^ "On the referendum #27: Banks, Russia, conspiracies and Vote Leave". 11 June 2018.
- ^ Michael W. Hankins, Flying Camelot: The F-15, the F-16, and the Weaponization of Fighter Pilot Nostalgia (Cornell University Press, 2021), 134-135.
Bibliography[edit]
- Boyd, John R. (3 September 1976). Destruction and Creation (PDF). U.S. Army Command and General Staff College.
- Boyd, John, R., The Essence of Winning and Losing, 28 June 1995 a five slide set by Boyd.
- Dreier, A.S. (2012). Strategy, Planning & Litigating to Win. Boston, MA: Conatus Press. ISBN 978-0615676951. OCLC 917563752.
- Greene, Robert, OODA and You
- Hillaker, Harry, Code one magazine, "John Boyd, United States Air Force Retired, Father of the F16", July 1997.
- Linger, Henry, Constructing The Infrastructure for the Knowledge Economy: Methods and Tools, Theory and Practice, p. 449
- Metayer, Estelle, Decision making: It's all about taking off – and landing safely…, Competia, December 2011
- Osinga, Frans, "Science, Strategy and War The Strategic Theory of John Boyd"
- Richards, Chet, Certain to Win: the Strategy of John Boyd, Applied to Business (2004) ISBN 1413453775
- Ullman, David G., [1]"OO–OO–OO!” The Sound of a Broken OODA Loop], Crosstalk, April 2007
External links[edit]
- Archived documents
- Video: The OODA Loop and Clausewitzian "Friction"
- Bazin, A. (2005). "Boyd's OODA Loop and the Infantry Company Commander". Infantry Magazine.
- OODA Loop 2.0: Information, Not Agility, Is Life OODA Loop 2.0: Information, Not Agility, Is Life
- OODA Loop in Emergency Preparedness OODA Loop in Emergency Preparedness
