Czech–Slovak languages
| Czech–Slovak | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Central Europe |
| Linguistic classification | Indo-European
|
Early forms | |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Glottolog | czec1260 |
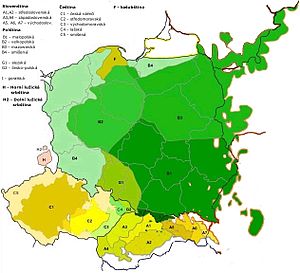 Czech–Slovak dialects in yellow and gold (A/C), within West Slavic | |
The Czech–Slovak languages (or Czecho-Slovak) are a subgroup within the West Slavic languages comprising the Czech and Slovak languages.
Most varieties of Czech and Slovak are mutually intelligible, forming a dialect continuum (spanning the intermediate Moravian dialects) rather than being two clearly distinct languages; standardised forms of these two languages are, however, easily distinguishable and recognizable because of disparate vocabulary, orthography, pronunciation, phonology, suffixes and prefixes. The eastern Slovak dialects are more divergent and form a broader dialect continuum with the Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic, most notably Polish.
The name "Czechoslovak language" is mostly reserved for an official written standard devised in the 19th century that was intended to unify Czech and Slovak. It was proclaimed an official language of Czechoslovakia and functioned de facto as Czech with slight Slovak input.
History
[edit]The early Slavic expansion reached Central Europe in the 7th century, and the West Slavic dialects diverged from common Slavic over the following centuries. The West Slavic tribes settled on the eastern fringes of the Carolingian Empire, along the Limes Saxoniae. Prior to the Magyar invasion of Pannonia in the 890s, the West Slavic polity of Great Moravia spanned much of Central Europe between what is now Eastern Germany and Western Romania. In the high medieval period, the West Slavic tribes were again pushed to the east by the incipient German Ostsiedlung, decisively so following the Wendish Crusade in the 11th century.
West Slavic as a group distinct from common Slavic thus emerges during the 7th to 9th centuries. The Czech-Slovak in turn develops as a separate dialect continuum within West Slavic during roughly the 10th to 12th centuries, just predating the first written attestation of the language in the 13th to 14th centuries. The diversification of West Slavic had the characteristic of a dialect continuum. For example, the spirantisation of Slavic /g/ to /h/ is an areal feature shared by the Czech-Slovak group with both Ukrainian and Sorbian (but not with Polish). This innovation appears to have traveled from east to west, and is sometimes attributed to contact with Scytho-Sarmatian.[2] It is approximately dated to the 12th century in Slovak, the 12th to 13th century in Czech and the 14th century in Upper Sorbian.[3]
The Bohemian state was incorporated as the Kingdom of Bohemia in the 13th century. The Slovaks, on the other hand, never became part of the Holy Roman Empire in the medieval period, being incorporated into the Kingdom of Hungary. For this reason, the history of the closely related Czech and Slovak peoples took a significantly different course during the later medieval period, the Czechs being associated with the Holy Roman Empire and the Slovaks being affected by the history of Eastern Europe (the history of Hungary and the Mongol invasion). In the 16th century, however, they were once again united under Habsburg rule, and after the fall of the Habsburg monarchy sharing their own country of Czechoslovakia during 1918–1992.
In the modern period, the spoken language of Bohemia became influenced by the written standard and developed into Common Czech, largely effacing dialectal variation within Bohemia. By contrast, Moravia remained dialectally diverse, with a series of variants intermediate between Czech and Slovak,[4] and are thus sometimes viewed as dialects of Slovak rather than Czech. The Czech–Slovak group was summarized under the term "Bohemian–Moravian–Slovak" (Böhmisch-Mährisch-Slowakisch) in the Austrian census of Cisleithania beginning in the 1880s.[5]
The Czechoslovak language was an attempt to create a single written standard, first proposed during the national revival in the 1830s and the official language of the First Czechoslovak Republic from 1920 to 1938.
In television and radio, Czech and Slovak were used in equal ratios. Since the dissolution of Czechoslovakia in 1993, the Czech and Slovak written standards have been the official languages of the Czech Republic and Slovakia, respectively.
Beginning in the 1990s, a political movement of Moravian linguistic separatism has developed. [6] On the occasion of 2011 Census of the Czech Republic, several Moravian organizations (Moravané and Moravian National Community among others) led a campaign to promote the Moravian nationality and language. The 2011 census recorded 62,908 native speakers of Moravian.[7]
Varieties
[edit]The Czech-Slovak dialect continuum historically blended into Silesian in the west and Old Ruthenian (also known as Chancery Slavonic) in the east. With the development of the written standards in the 19th century, it has become less diversified, but there remains a pronounced dialectal division in Moravia. The southeastern Moravian dialects, in particular, are sometimes considered dialects of Slovak rather than Czech, e.g. using the same declension patterns for nouns and pronouns and the same verb conjugations as Slovak.[8]
- Czech language: since the later 20th century largely standardised, dialectal use is now mostly restricted to older speakers)[9] Common Czech (obecná čeština) is the main vernacular based on the dialect of the Prague region.[10]
- Nářečí středočeská (Central Bohemian dialects)
- Nářečí jihozápadočeská (Southwestern Bohemian dialects)
- Nářečí severovýchodočeská (Northeastern Bohemian dialects)
- Moravian dialects (moravština)[11]
- Bohemian-Moravian (Nářečí českomoravská, transitional to Bohemian Czech)
- Central Moravian (Hanakian, Nářečí středomoravská)
- Podskupina tišnovská (Tišnov subgroup)
- Lach/Silesian (Nářečí slezská, transitional Silesian)
- Eastern Moravian (Moravian-Slovak, Nářečí východomoravská, transitional to Slovak)
- Podskupina slovácká (Moravian Slovak subgroup)
- Podskupina valašská (Moravian Wallachian subgroup)
- Knaanic language (Judeo-Czech) †
- Slovak language
- Western Slovak dialects (in Kysuce, Trenčín, Trnava, Nitra, Záhorie)
- Central Slovak dialects (in Liptov, Orava, Turiec, Tekov, Hont, Novohrad, Gemer and the historic Zvolen county)
- Lowland (dolnozemské) Slovak dialects (outside Slovakia in the Pannonian Plain in Serbian Vojvodina, and in southeastern Hungary, western Romania, and the Croatian part of Syrmia)
- Eastern Slovak dialects (in Spiš, Šariš, Zemplín and Abov, transitional to Ruthenian)
In a 1964 textbook on Czech dialectology, Břetislav Koudela used the sentence put the flour from the mill in the cart to highlight phonetic differences between dialects:[12]
Standard Czech: Dej mouku ze mlýna na vozík. Standard Slovak: Daj múku z mlyna na vozík.
Comparison of written standards
[edit]
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2009) |
The following comparison concerns the contemporary written standards:
- Orthography
Slovak graphemes that do not exist in Czech are: ä, ľ, ĺ, ŕ, ô. Czech graphemes that do not exist in Slovak are: ě, ř and ů (see Pronunciation for Czech language and Pronunciation for Slovak language).
- Phonology
Slovak has the following phonemes which Czech does not have: /ʎ/, /rː/, /lː/, and the diphthongs /ɪɐ/, /ɪe/, /ɪʊ/, /ʊo/ (also /ɛɐ/ in higher-style standard Slovak, or some dialects); and on the contrary, Czech has /r̝/. Slovak, unlike Czech, uses palatal consonants more frequently (that is, is phonetically "softer"), but there are some exceptions. Slovak de, te, ne are usually pronounced as the Czech dě, tě, ně. The "rhythmic law" in Slovak prohibits two adjacent long syllables.[13][14]
- Grammar
Slovak grammar is somewhat more regular than the grammar of literary Czech, since present-day standard Slovak was not codified until the 19th century. The two languages have differences in declension and conjugation endings and paradigms (e.g. Slovak -cia, -ej, -dlo, -ť, -ov, -om, -mi – Czech -c(i)e, -é, -tko, -t, -ů, -em, y). Slovak does not commonly use the vocative case, while the Czech vocative is still very much alive.[15] Slovak uses the passive voice formed as in English less than Czech, and prefers the passive voice formed using the reflexive pronoun sa (as in East Slavic languages) instead.
- Lexicon
Lexical differences are mostly of simple historical origin. As for professional terminology, except for biology (esp. all names of animals and plants), the Czech terminology was mostly taken over (in Slovakised form) for practical reasons. The Czech-Slovak Dictionary of Different Terms (1989, Prague) contains some 11,000 entries (without professional terminology):
| English | Slovak | Czech |
|---|---|---|
| yeah | hej | jo |
| if | ak | jestli, jestliže, -li |
| really, actually | naozaj | opravdu |
| just, only | iba, len | pouze, jenom, jen |
| to like | páčiť sa | líbit se |
| as well | tiež | také, taky, (less commonly) též |
| but | veď | vždyť |
| hot | horúci | horký |
| let, may | nech | ať, nechť |
| to wish | želať | přát |
| to see | zbadať | spatřit |
| next to | pri, popri, vedľa | vedle |
| cemetery | cintorín | hřbitov |
| especially | najmä | především, obzvlášť, zejména |
| to forgive, to excuse | prepáčiť | prominout |
| apart from, besides | okrem | kromě, mimo, vyjma |
| operation (of machine) | prevádzka | provoz, chod |
| traffic | premávka | provoz |
| war | vojna | válka, (less commonly) vojna |
| current | terajší | stávající |
| bad | zlý | špatný |
| worse (adv.) | horšie | hůř |
| to go | ísť | jet, jít |
| as soon as | len čo | jakmile |
| to forget | zabudnúť | zapomenout |
| once | raz | jednou |
| next | budúci | příští |
| ball | lopta | míč |
| button | gombík | knoflík |
| pub | krčma | hospoda |
| stamp | pečiatka | razítko |
| room | izba | pokoj |
| to acquire | nadobudnúť | nabýt |
| behaviour | správanie | chování |
| to listen | počuť | slyšet |
| to watch (TV) | pozerať (televíziu) | dívat se na (televizi) |
| to look | pozerať | koukat |
| to look like | vyzerať | vypadat |
| to say, to speak | povedať, vravieť | říct, mluvit |
| vrecko | kapsa | |
| to clean up | upratovať | uklízet |
| because | keďže | jelikož |
| surname | priezvisko | příjmení |
| cellar | pivnica | sklep |
| including | vrátane | včetně |
| autumn | jeseň | podzim |
| be called (as in name), | volať sa | jmenovat se |
| boy | chalan | kluk |
| girl | dievča | holka, děvče |
| breakfast | raňajky | snídaně |
| to count | rátať, počítať | počítat |
| snack | olovrant | svačina |
| to clug, to stuff | pchať | cpát |
| laundry | bielizeň | prádlo |
| press, newspaper | tlač | tisk |
| although | hoci | ačkoliv |
| pillow | vankúš | polštář |
| that is | čiže | čili |
| thirst | smäd | žízeň |
| strike (of employees) | štrajk | stávka |
| bet, wager, stake | stávka | sázka |
| race | preteky | závod |
| Good bye | dovidenia | na shledanou |
| cat | mačka | kočka |
| blackbird | drozd | kos |
| to kiss | bozkať | líbat |
| now | teraz | teď, nyní |
| goods | tovar | zboží |
| potatoes | zemiaky | brambory |
| trap | klepec, pasca | past, léčka |
| the same, equal | rovnaký | stejný |
| dishes | riad | nádobí |
| tissue, handkerchief | vreckovka | kapesník |
| be surprised, wonder | čudovať sa | divit se |
| pencil | ceruzka | tužka |
| perhaps | azda, vari, snáď | snad |
| easy | ľahký | snadný, lehký |
| trouble | ťažkosť | potíž, nesnáz |
| baggage | batožina | zavazadlo |
| branch | konár | větev |
| to meet | stretnúť sa | setkat se, potkat |
| spine | chrbtica | páteř |
| he/she/it is not | nie je | není |
| to do, to make | robiť, spraviť | dělat, udělat |
| to apologize, to excuse | ospravedlniť sa | omluvit se |
| to smoke | fajčiť | kouřit |
| whatever | hocičo, voľačo | leccos, cokoliv |
| blueberry | čučoriedka | borůvka |
| apricot | marhuľa | meruňka |
| cabbage | kapusta | zelí |
| Savoy cabbage | kel | kapusta |
| legume, pulses | strukoviny | luštěniny |
| chickpeas | cícer | cizrna |
| lentils | šošovica | čočka |
| rye | raž | žito |
| demand | dopyt | poptávka |
| offer; supply | ponuka | nabídka |
| early, soon | skoro, čoskoro | brzy |
| earlier, sooner | skôr | dřív |
| late | neskorý, neskoro | pozdní, opožděný, pozdě |
| later | neskôr | později |
| suddenly | zrazu | najednou |
| fairy tale | rozprávka | pohádka |
| tramway | električka | tramvaj |
| pork | bravčové | vepřové |
| mutton | baranina | skopové |
| breastfeed | dojčiť | kojit |
| infant | dojča | kojenec |
| baby | bábätko | miminko |
| (the) rest (of a group) | zvyšok | zbytek |
| lips | pery | rty |
| lipstick | rúž | rtěnka |
| flock | kŕdeľ | hejno |
| railway station | (železničná) stanica | nádraží |
| despite | napriek | navzdory |
| when | keď | když |
| glass (of water) | pohár | sklenice, sklenička |
| pepper | čierne korenie | pepř |
| ill | chorý | nemocný |
| illness | choroba | nemoc, (less commonly) choroba |
| dot | bodka | tečka |
| wall | múr | zeď |
| bricklayer | murár | zedník |
| shoulder | plece | rameno |
| to heat | kúriť | topit |
| turtle | korytnačka | želva |
| camel | ťava | velbloud |
| even (number) | párny | sudý |
| odd (number) | nepárny | lichý |
| finally | napokon, nakoniec | nakonec |
| butcher | mäsiar | řezník |
| slim, thin | chudý | hubený |
| poor | chudobný | chudý |
Examples of words with different meanings: SK topiť (to melt/to drown) (could be same meanings, depends on region) – CZ topit (to heat/to drown), SK kúriť (to heat) – CZ kouřit (to smoke), SK horký (bitter) – CZ horký (hot) but hořký (bitter), SK stávka (stake, bet) – CZ stávka (strike), SK chudý (slim, skinny) – CZ chudý (poor; metaphorically also slim), SK kapusta (cabbage) – CZ kapusta (Savoy cabbage), SK pivnica (cellar) – CZ pivnice (pub), SK syrový (cheesy, of cheese) – CZ syrový (raw, uncooked) but sýrový (of cheese), SK spraviť (to make, to create) – CZ spravit (to repair, to fix). Czech months are of Slavic origin (e.g. říjen), whereas the Slovak months are of Latin origin (e.g. október).
Although most words are in fact different, they are largely similar, being cognates, which makes both languages mutually intelligible to a significant extent; e.g. foreign (SK cudzí – CZ cizí), reason (SK dôvod – CZ důvod), to want (SK chcieť – CZ chtít), to promise (SK sľubovať – CZ slibovat), if (SK keby – CZ kdyby), river (SK rieka – CZ řeka), church (SK kostol – CZ kostel), wedding (SK svadobný – CZ svatební), who (SK kto – CZ kdo), to ask (SK spýtať sa – CZ zeptat se), to fail (SK zlyhať – CZ selhat), almost (SK takmer – CZ téměř), thanks (SK ďakujem, vďaka – CZ děkuju, díky).
Example text
[edit]Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in Slovak:
- Všetci ľudia sa rodia slobodní a rovní v dôstojnosti aj právach. Sú obdarení rozumom a svedomím a majú sa k sebe správať v duchu bratstva.
Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in Czech (adjusted to Slovak translation):
- Všichni lidé se rodí svobodní a rovní v důstojnosti i právech. Jsou obdařeni rozumem a svědomím a mají se k sobě chovat v duchu bratrství.
Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in English:
- All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
See also
[edit]- West Slavic languages
- History of the Czech language
- History of the Slovak language
- Czechoslovak language
References
[edit]- ^ Habijanec, Siniša (2020). "Pannonian Rusyn". In Greenberg, Marc; Grenoble, Lenore (eds.). Brill Encyclopedia of Slavic Languages and Linguistics. Brill Publishers. ISBN 978900437500. ISSN 2589-6229. Retrieved 2024-04-01.
The third theory defines Pannonian Rusyn as a West Slavic language originating in the East Slovak Zemplín and Šariš dialects and being a mixture of the two. It fits the linguistic data in the most consistent manner and has been accepted by an overwhelming majority of scholars in the field (Bidwell 1966; Švagrovský 1984; Witkowski 1984; Lunt 1998; Čarskij 2011) and verified by several comprehensive analyses of Pannonian Rusyn language data (Bidwell 1966; Lunt 1998; Čarskij 2011).
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: length (help) - ^ Абаев В. И. О происхождении фонемы g (h) в славянском языке // Проблемы индоевропейского языкознания. М., 1964, 115—121. Эдельман Д. И. К происхождению ирано-славянских диахронических паралелей // Славянская языковая и этноязыковая системы в контакте с неславянским окружением. М., 2002, 76—77.
- ^ Pronk-Tiethoff, The Germanic loanwords in Proto-Slavic, 2013, p. 71 (fn 26))
- ^ Kortmann & van der Auwera 2011, p. 516).
- ^ Kortmann & van der Auwera 2011, p. 714.
- ^ BLÁHA, Ondřej. Moravský jazykový separatismus: zdroje, cíle, slovanský kontext. In Studia Moravica. Acta Universitatis Palackianae Olomucensis Facultas Philosophica – Moravica. Olomouc : UP v Olomouci, 2005. ISSN 1801-7061. Svazek III.
- ^ Tab. 153 Obyvatelstvo podle národnosti, mateřského jazyka a podle pohlaví (czso.cz)
- ^ Šustek, Zbyšek (1998). "Otázka kodifikace spisovného moravského jazyka (The question of codifying a written Moravian language)" (in Czech). University of Tartu. Retrieved July 21, 2014.
- ^ Eckert 1993, pp. 143–144
- ^ Wilson 2010, p. 21. Compared to standard Czech, Common Czech is characterized by simpler inflection patterns and some phonological differences. Daneš, František (2003). "The present-day situation of Czech". Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic. Retrieved August 10, 2014.
- ^ Wilson 2010, pp. 49f..
- ^ Koudela, Břetislav (1964). Vývoj českého jazyka a dialektologie. Československé státní pedagogické nakladatelství. p. 173.
- ^ Christina Y. Bethin, Slavic Prosody: Language Change and Phonological Theory (1998), p. 217.
- ^ Scheer, Tobias (2001). "The Rhythmic Law in Czech: Vowel-final Prefixes" (PDF). Current Issues in Formal Slavic Linguistics: 37–48. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- ^ Sussex, Rolan; Cubberley, Paul (2011). The Slavic Languages. Cambridge Language Surveys. pp. 57–58. ISBN 978-0-521-29448-5.
Bibliography
[edit]- Eckert, Eva (1993). Varieties of Czech: Studies in Czech Sociolinguistics. Editions Rodopi. ISBN 978-90-5183-490-1.
- Kortmann, Bernd; van der Auwera, Johan (2011). The Languages and Linguistics of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide. Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3110220261.
- Wilson, James (2010). Moravians in Prague: A Sociolinguistic Study of Dialect Contact in the Czech Republic. Peter Lang. pp. 49–50.
External links
[edit]- "Map of Czech Dialects". Český statistický úřad (Czech Statistical Office). 2003. Archived from the original on 1 December 2012. Retrieved 26 July 2014.
