Ordnance Survey National Grid
This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2008) |
| Geodesy |
|---|
 |
The Ordnance Survey National Grid reference system (OSGB), also known as British National Grid (BNG),[1][2] is a system of geographic grid references, distinct from latitude and longitude, whereby any location in Great Britain can be described in terms of its distance from the origin (0, 0), which lies to the west of the Isles of Scilly.[3]
The Ordnance Survey (OS) devised the national grid reference system, and it is heavily used in its survey data, and in maps based on those surveys, whether published by the Ordnance Survey or by commercial map producers. Grid references are also commonly quoted in other publications and data sources, such as guide books and government planning documents.
A number of different systems exist that can provide grid references for locations within the British Isles: this article describes the system created solely for Great Britain and its outlying islands (including the Isle of Man). The Irish grid reference system is a similar system created by the Ordnance Survey of Ireland and the Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland for the island of Ireland. The Irish Transverse Mercator (ITM) coordinate reference system was adopted in 2001 and is now the preferred coordinate reference system across Ireland. ITM is based on the Universal Transverse Mercator coordinate system (UTM), used to provide grid references for worldwide locations, and this is the system commonly used for the Channel Islands. European-wide agencies also use UTM when mapping locations, or may use the Military Grid Reference System (MGRS), or variants of it.
Grid letters
[edit]

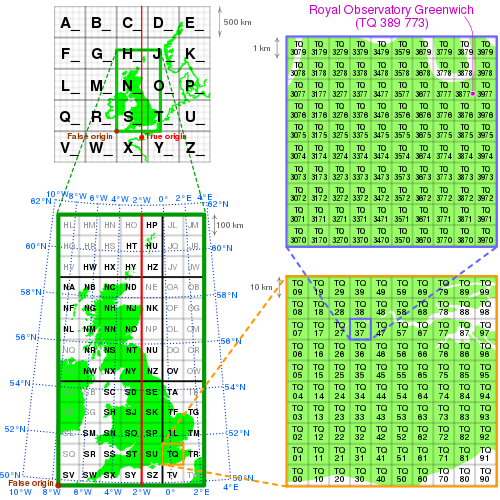
The first letter of the British National Grid is derived from a larger set of 25 squares of size 500 km by 500 km, labelled A to Z, omitting one letter (I) (refer diagram below), previously used as a military grid.[4] Four of these largest squares contain significant land area within Great Britain: S, T, N and H. The O square contains a tiny area of North Yorkshire, Beast Cliff at OV 0000, almost all of which lies below mean high tide.[5] For the second letter, each 500 km square is subdivided into 25 squares of size 100 km by 100 km, each with a letter code from A to Z (again omitting I) starting with A in the north-west corner to Z in the south-east corner. These squares are outlined in light grey on the "100km squares" map, with those containing land lettered. The central (2° W) meridian is shown in red.
Grid digits
[edit]Within each square, eastings and northings from the south west corner of the square are given numerically. For example, NH0325 means a 1 km square whose south-west corner is 3 km east and 25 km north from the south-west corner of square NH. A location can be indicated to varying resolutions numerically, usually from two digits in each coordinate (for a 1 km square) through to five (for a 1 m square); in each case the first half of the digits is for the first coordinate and the second half for the other. The most common usage is the six figure grid reference, employing three digits in each coordinate to determine a 100 m square. For example, the grid reference of the 100 m square containing the summit of Ben Nevis is NN 166 712. (Grid references may be written with or without spaces; e.g., also NN166712.) NN has an easting of 200 km and northing of 700 km, so the OSGB36 National Grid location for Ben Nevis is at 216600, 771200.
All-numeric grid references
[edit]Grid references may also be quoted as a pair of numbers: eastings then northings in metres, measured from the southwest corner of the SV square. 13 digits may be required for locations in Orkney and further north. For example, the grid reference for Sullom Voe Oil Terminal in the Shetland Islands may be given as HU396753 or 439668,1175316.
Another, distinct, form of all-numeric grid reference is an abbreviated alphanumeric reference where the letters are simply omitted, e.g. 166712 for the summit of Ben Nevis. Unlike the numeric references described above, this abbreviated grid reference is incomplete; it gives the location relative to an OS 100×100 km square, but does not specify which square. It is often used informally when the context identifies the OS 2-letter square. For example, within the context of a location known to be on OS Landranger sheet 41 (which extends from NN000500 in the south-west to NN400900 in the north-east) the abbreviated grid reference 166712 is equivalent to NN166712. If working with more than one Landranger sheet, this may also be given as 41/166712.
Alternatively, sometimes numbers instead of the two-letter combinations are used for the 100×100 km squares. The numbering follows a grid index where the tens denote the progress from West to East and the units from South to North. In the north of Scotland, the numbering is modified: the 100 km square to the north of 39 is numbered N30; the square to the north of 49 is N40, etc.
Compatibility with related systems
[edit]The grid is based on the OSGB36 datum (Ordnance Survey Great Britain 1936, based on the Airy 1830 ellipsoid), and was introduced after the retriangulation of 1936–1962.[citation needed] It replaced the Cassini Grid which had previously been the standard projection for Ordnance Survey maps.[6][7]
The Airy ellipsoid is a regional best fit for Britain; more modern mapping tends to use the GRS80 ellipsoid used by the Global Positioning System (the Airy ellipsoid assumes the Earth to be about 1 km smaller in diameter than the GRS80 ellipsoid, and to be slightly less flattened). The British maps adopt a transverse Mercator projection with an origin (the "true" origin) at 49° N, 2° W (an offshore point in the English Channel which lies between the island of Jersey and the French port of St. Malo).[8] Over the Airy ellipsoid a straight line grid, the National Grid, is placed with a new false origin to eliminate negative numbers, creating a 700 km by 1300 km grid. This false origin is located south-west of the Isles of Scilly.
In order to minimize the overall scale error, a factor of 2499/2500 is applied. This creates two lines of longitude about 180 km east and west of the central meridian along which the local scale factor equals 1, i.e. map scale is correct. Inside these lines the local scale factor is less than 1, with a minimum of 0.04% too small at the central meridian.[9] Outside these lines the local scale factor is greater than 1, and is about 0.04% too large near the east and west coasts. Grid north and true north are only aligned on the central meridian (400 km easting) of the grid which is 2° W (OSGB36) and approx. 2° 0′ 5″ W (WGS 84).
OSGB 36 was also used by Admiralty nautical charts until 2000[citation needed] after which WGS 84 has been used.
A geodetic transformation between OSGB 36 and other terrestrial reference systems (like ITRF2000, ETRS89, or WGS 84) can become quite tedious if attempted manually. The most common transformation is called the Helmert datum transformation, which results in a typical 7 m error from true. The definitive transformation from ETRS89 that is published by the Ordnance Survey is called the National Grid Transformation OSTN15.[10][11] This models the detailed distortions in the 1936–1962 retriangulation, and achieves backwards compatibility in grid coordinates to sub-metre accuracy.
Datum shift between OSGB 36 and WGS 84
[edit]The difference between the coordinates on different datums varies from place to place. The longitude and latitude positions on OSGB 36 are the same as for WGS 84 at a point in the Atlantic Ocean well to the west of Great Britain. In Cornwall, the WGS 84 longitude lines are about 70 metres east of their OSGB 36 equivalents, this value rising gradually to about 120 m east on the east coast of East Anglia. The WGS 84 latitude lines are about 70 m south of the OSGB 36 lines in South Cornwall, the difference diminishing to zero in the Scottish Borders, and then increasing to about 50 m north on the north coast of Scotland. (If the lines are further east, then the longitude value of any given point is further west. Similarly, if the lines are further south, the values will give the point a more northerly latitude.) The smallest datum shift is on the west coast of Scotland and the greatest in Kent.
Datum shift between OSGB 36 and ED 50
[edit]These two datums are not both in general use in any one place, but for a point in the English Channel halfway between Dover and Calais, the ED50 longitude lines are about 20 m east of the OSGB36 equivalents, and the ED50 latitude lines are about 150 m south of the OSGB36 ones.[citation needed]
Summary parameters of the coordinate system
[edit]- Datum: OSGB36
- Map projection: Transverse Mercator projection using Redfearn series
- True origin: 49°N, 2°W
- False origin: 400 km west, 100 km north of True Origin
- Scale factor: 0.9996012717[a]
- EPSG Code: EPSG:27700
- Ellipsoid: Airy 1830[b]
- Semi-major axis a: 6377563.396 m
- Semi-minor axis b: 6356256.909 m
- Flattening (derived constant): 1/299.3249646
See also
[edit]- Ordnance Datum Newlyn
- International Map of the World § Map Indexing System
- Irish grid reference system
- Maidenhead Locator System
- United States National Grid
- World Geodetic System
Notes
[edit]- ^ Scale factor is defined by its base-10 logarithm of (0.9998268 − 1) exactly.[12]
- ^ The defining Airy dimensions are a 20923713 feet, b 20853810 feet. In the Retriangulation the base-10 logarithm of the number of metres in a foot was set at (0.48401603 − 1)[13] exactly and the Airy metric dimensions are calculated from that. The flattening is exactly 69903 divided by 20923713.
References
[edit]- ^ "OSGB 1936 / British National Grid: EPSG Projection — Spatial Reference". spatialreference.org. Archived from the original on 10 March 2016. Retrieved 9 March 2016.
- ^ "Coordinate systems and projections for beginners". 26 March 2012. Archived from the original on 26 October 2021. Retrieved 19 September 2021.
- ^ "A Beginners Guide to UK Geography (2023)". Open Geography Portal. Office for National Statistics. 24 August 2023. Retrieved 9 December 2023.
- ^ http://www.ordnancesurvey.co.uk: Guide to the National Grid, page 9 (archived version, May 2006)
- ^ Standing, Peter (2006). "OV0000 a unique grid square at Beast Cliff". Geograph Project. Archived from the original on 1 November 2017. Retrieved 11 June 2007.
- ^ Winterbotham, Harold St. John Loyd (1925). "Ordnance Survey of Scotland "Popular" Edition. One-inch map". The Geographical Journal. 65 (2): 160–162. doi:10.2307/1782246. JSTOR 1782246.
- ^ Steers, James Alfred (1965). An Introduction to the Study of Map Projections (15 ed.). University of London Press. p. 229.
- ^ OS Net, The true origin
- ^ Ordnance Survey (1946). "A brief description of the National Grid and reference system". London: His Majesty's Stationery Office. p. 4.
- ^ Greaves, Mark (2016). "OSGM15 and OSTN15: Updated transformations for UK and Ireland" (PDF). Geomatics World. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 August 2022. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- ^ "Surveying guidelines". Ordnance Survey. Archived from the original on 18 July 2017.
- ^ Mugnier, Clifford (October 2003). "Grids and Datums, United Kingdom" (PDF). p. 1095. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 October 2022. Retrieved 19 February 2022.
- ^ A guide to coordinate systems in Great Britain (see External links), footnote 10 on page 44
External links
[edit]- Ordnance Survey A guide to coordinate systems in Great Britain: An introduction to mapping coordinate systems and the use of GPS datasets with Ordnance Survey mapping; Version 3.6, 2020 [Retrieved 19 February 2022].
- Ordnance Survey's Grid script: a brief introduction to the National Grid Reference; Version November 2011 [Retrieved 13 February 2014].
- "The National Grid FAQs". Ordnance Survey. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- "Ordnance Survey Guide to the National Grid" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 August 2019. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- "Ordnance Survey Guide to coordinate systems" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 April 2019. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- "Interactive Ordnance Survey Mapping showing grid references". Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- "Co-ordinate Converter". Retrieved 20 February 2021. - Multiple-format co-ordinate transformer for Great Britain & Channel Islands
- "Programs to convert Ordnance Survey grid references". Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- "Open Source Javascript Conversion Library". Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- "GPL Java Conversion Library". Archived from the original on 18 January 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- "Perl Conversion Library". Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- "The sole part of Great Britain that lies in the OV square". Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- "Convert between Latitude/Longitude & OS National Grid References". Retrieved 20 February 2021. (JavaScript source code)
- ".Net library to convert between lat/lon in various coordinate systems and grid reference". Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- "UK Grid Reference". Retrieved 20 February 2021. Web utility to find a UK grid reference
- LatLong <> OS Grid Ref converts & presents in many formats, generates specific links to that location for several useful map web pages - 1840–present. LatLong WSG84 <> GB, Ireland (inc NI) and Chanel Islands (30U) GR formats recognised. Distance measure for dog-leg routes & area calculations.
- "OS British National Grids". GitHub. Retrieved 15 August 2021. Open source dataset (in GeoPackage format) of the British National Grids at various resolutions, available for download from Ordnance Survey's GitHub.
