Solar eclipse of January 15, 2010
| Solar eclipse of January 15, 2010 | |
|---|---|
 Annularity from Jinan, China | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | 0.4002 |
| Magnitude | 0.919 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 668 s (11 min 8 s) |
| Coordinates | 1°36′N 69°18′E / 1.6°N 69.3°E |
| Max. width of band | 333 km (207 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| (P1) Partial begin | 4:05:28 |
| (U1) Total begin | 5:13:55 |
| Greatest eclipse | 7:07:39 |
| (U4) Total end | 8:59:04 |
| (P4) Partial end | 10:07:35 |
| References | |
| Saros | 141 (23 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9529 |
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Friday, January 15, 2010,[1][2] with a magnitude of 0.919. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. It was the longest annular solar eclipse of the millennium,[3] and the longest until December 23, 3043, with the length of maximum eclipse of 11 minutes, 7.8 seconds, and the longest duration of 11 minutes, 10.7 seconds.[4] This is about 4 minutes longer than total solar eclipses could ever get. (The solar eclipse of January 4, 1992, was longer, at 11 minutes, 40.9 seconds, occurring in the middle of the Pacific Ocean.)[5]
Lasting 11 minutes and 7.8 seconds, and eclipse magnitude of only 0.91903, this was the longest and smallest annular solar eclipse of the 21st century. The eclipse was visible as only a partial eclipse in much of Africa, Eastern Europe, the Middle East and Asia. It was seen as an annular eclipse within a narrow stretch of 300 km (190 mi) width across Central Africa, Maldives, South Kerala (India), South Tamil Nadu (India), Sri Lanka and parts of Bangladesh, Burma and China.
Eclipse details
[edit]- Eclipse Magnitude: 0.91903
- Eclipse Obscuration: 0.84462
- Gamma: 0.40016
- Saros Series: 141st (23 of 70)
- Sun Right Ascension: 19.8
- Moon Right Ascension: 19.79
- Sun Declination: -21.1
- Moon Declination: -20.8
- Sun Diameter: 1951.0 arcseconds
- Moon Diameter: 1768.6 arcseconds
- Radius of the Penumbral Shadow: 7,322.7 km (4,550.1 mi)
- Radius of the Antumbral Shadow: 361.7 km (224.8 mi)
- Path Width: 333.1 km (207 mi)
- Greatest Eclipse: 2010 January 15 at 07:06:33.2 UTC
- Apogee at 2010 January 17 at 01:41 UTC (406,433 km (252,546 mi))
| Event | UTC time |
| First Penumbral External Contact | 2010 Jan 15 at 04:05:27.6 UTC |
| First Umbral External Contact | 2010 Jan 15 at 05:13:55.0 UTC |
| First Central Line | 2010 Jan 15 at 05:17:34.8 UTC |
| First Umbral Internal Contact | 2010 Jan 15 at 05:21:15.9 UTC |
| First Penumbral Internal Contact | 2010 Jan 15 at 06:50:06.9 UTC |
| Greatest Eclipse | 2010 Jan 15 at 07:06:33.2 UTC |
| Last Penumbral Internal Contact | 2010 Jan 15 at 07:22:37.8 UTC |
| Last Umbral Internal Contact | 2010 Jan 15 at 08:51:40.5 UTC |
| Last Central Line | 2010 Jan 15 at 08:55:22.8 UTC |
| Last Umbral External Contact | 2010 Jan 15 at 08:59:03.9 UTC |
| Last Penumbral External Contact | 2010 Jan 15 at 10:07:35.3 UTC |
Visibility of the eclipse
[edit]
The eclipse started in the Central African Republic near the border with Chad, traversed DR Congo, Uganda, Kenya, passed through the northern tip of Tanzania, southwestern Somalia and three islands of Seychelles (Bird, Denis and Aride), before it entered the Indian Ocean, where it reached its greatest visibility. It then passed through Maldives. The annular eclipse at Malé, the capital city of the country, started at 12:20:17 and ended at 12:31:02 local time (UTC+5), lasting for 10 minutes and 45 seconds (645 seconds). This was also the longest duration of any eclipse with an international airport in its track.[6]
At approximately 13:20 IST, the annular solar eclipse entered India at Thiruvananthapuram (Trivandrum), the capital of Kerala and exited India at Rameswaram, Tamil Nadu.
The eclipse was viewable for 10 minutes in India. After Rameswaram, it entered Sri Lanka at Delft Island, exited at Jaffna in Sri Lanka, crossed the Bay of Bengal and re-entered India in Mizoram.

Thiruvananthapuram, which was the entry point of the eclipse in India, was equipped with telescopes and announced facilities for the public to view the eclipse.[7] Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre, situated in Trivandrum, analysed the atmospheric-ionospheric parameters during the eclipse.[8] Many scientists camped in the city to witness and study the eclipse.[9]
At Rameswaram, the sunrise was not visible due to thick clouds, but it started getting clear at around 9 am local time and became almost totally clear by the time the eclipse began. The sky had a thin layer of cirrus clouds till 2:30 pm. Among the eclipse-watchers was Sky Watchers' Association of North Bengal (SWAN) from Siliguri at the foothills of West Bengal and Tamil Nadu Astronomical Association.
Dhanushkodi, which falls on the central line of the eclipse, was a good place to view the eclipse. The northernmost limit of shadow in India was Cuddalore, Neyveli, Erode, Kodaikanal, and Madurai. Other prime viewing locations in Tamil Nadu include Thoothukudi and Cape Comorin, 22 km north of the center line. The exact location of the line is between the NH end and the Dhanushkodi ruins. Dhanushkodi is about 2 km east of the central line. The degree difference is about 0.2 between the central line – with Kodandaramar Temple and Dhanushkodi ruins vice versa. Dhanushkodi is about 5 km from the Kodandaramar Temple.
After South Asia, the antumbra passed through the southern tip of Bangladesh, Myanmar and China before leaving the Earth.
Gallery
[edit]-
Animation of path
-
Degania A, Israel, 5:41 UTC
-
Bangalore, India, 7:20 UTC
-
Jaffna, Sri Lanka, 7:56 UTC
-
Sanda, Hyogo, 7:59 UTC
-
Bandar Pusat Jengka, Malaysia, 8:05 UTC
-
Akashi, Hyogo, 8:05 UTC
-
Chennai, India, 8:10 UTC
-
Reflection of the eclipse from Pallipalayam, India
-
Stages of annular eclipse from Thiruvananthapuram, India
-
Batticaloa, Sri Lanka, 8:28 UTC
-
Hanoi, Vietnam, 8:36 UTC
-
Central, Hong Kong, 8:40 UTC
-
Taichung, Taiwan, 9:19 UTC
Related eclipses
[edit]Eclipses in 2010
[edit]- An annular solar eclipse on January 15.
- A partial lunar eclipse on June 26.
- A total solar eclipse on July 11.
- A total lunar eclipse on December 21.
Metonic
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of March 29, 2006
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of November 3, 2013
Tzolkinex
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of December 4, 2002
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of February 26, 2017
Half-Saros
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of January 9, 2001
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of January 21, 2019
Tritos
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of February 16, 1999
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of December 14, 2020
Solar Saros 141
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of January 4, 1992
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of January 26, 2028
Inex
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of February 4, 1981
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of December 26, 2038
Triad
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of March 17, 1923
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of November 15, 2096
Solar eclipses of 2008–2011
[edit]This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[10]
The partial solar eclipses on June 1, 2011 and November 25, 2011 occur in the next lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2008 to 2011 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
121 Partial in Christchurch, New Zealand |
February 7, 2008 Annular |
−0.95701 | 126 Totality in Kumul, Xinjiang, China |
August 1, 2008 Total |
0.83070 | |
131 Annularity in Palangka Raya, Indonesia |
January 26, 2009 Annular |
−0.28197 | 136 Totality in Kurigram District, Bangladesh |
July 22, 2009 Total |
0.06977 | |
141 Annularity in Jinan, Shandong, China |
January 15, 2010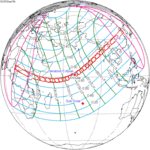 Annular |
0.40016 | 146 Totality in Hao, French Polynesia |
July 11, 2010 Total |
−0.67877 | |
151 Partial in Poland |
January 4, 2011 Partial |
1.06265 | 156 | July 1, 2001 Partial |
−1.49171 | |
Saros 141
[edit]This eclipse is a part of Saros series 141, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 70 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on May 19, 1613. It contains annular eclipses from August 4, 1739 through October 14, 2640. There are no hybrid or total eclipses in this set. The series ends at member 70 as a partial eclipse on June 13, 2857. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of annularity was produced by member 20 at 12 minutes, 9 seconds on December 14, 1955. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit.[11]
| Series members 12–33 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 12 | 13 | 14 |
 September 17, 1811 |
 September 28, 1829 |
 October 9, 1847 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 |
 October 19, 1865 |
 October 30, 1883 |
 November 11, 1901 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 |
 November 22, 1919 |
 December 2, 1937 |
 December 14, 1955 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 |
 December 24, 1973 |
 January 4, 1992 |
 January 15, 2010 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 |
 January 26, 2028 |
 February 5, 2046 |
 February 17, 2064 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 |
 February 27, 2082 |
 March 10, 2100 |
 March 22, 2118 |
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
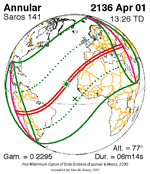 April 1, 2136 |
 April 12, 2154 |
 April 23, 2172 |
| 33 | ||
 May 4, 2190 | ||
Metonic series
[edit]The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 20 eclipse events between June 10, 1964 and August 21, 2036 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June 10–11 | March 28–29 | January 14–16 | November 3 | August 21–22 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
 June 10, 1964 |
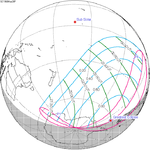 March 28, 1968 |
 January 16, 1972 |
 November 3, 1975 |
 August 22, 1979 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
 June 11, 1983 |
 March 29, 1987 |
 January 15, 1991 |
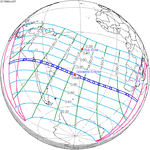 November 3, 1994 |
 August 22, 1998 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
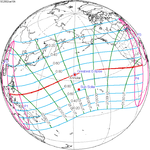 June 10, 2002 |
 March 29, 2006 |
 January 15, 2010 |
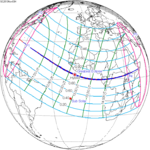 November 3, 2013 |
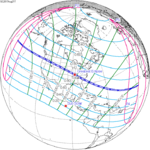 August 21, 2017 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
 June 10, 2021 |
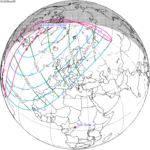 March 29, 2025 |
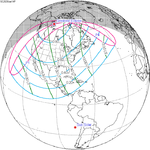 January 14, 2029 |
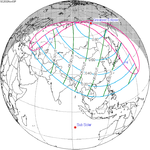 November 3, 2032 |
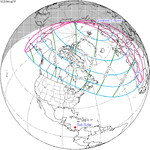 August 21, 2036 |
Tritos series
[edit]This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1801 and 2200 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 August 28, 1802 (Saros 122) |
 July 27, 1813 (Saros 123) |
 June 26, 1824 (Saros 124) |
 May 27, 1835 (Saros 125) |
 April 25, 1846 (Saros 126) |
 March 25, 1857 (Saros 127) |
 February 23, 1868 (Saros 128) |
 January 22, 1879 (Saros 129) |
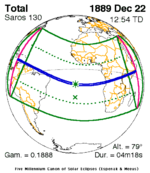 December 22, 1889 (Saros 130) |
 November 22, 1900 (Saros 131) |
 October 22, 1911 (Saros 132) |
 September 21, 1922 (Saros 133) |
 August 21, 1933 (Saros 134) |
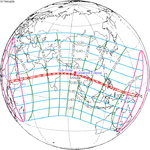 July 20, 1944 (Saros 135) |
 June 20, 1955 (Saros 136) |
 May 20, 1966 (Saros 137) |
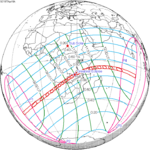 April 18, 1977 (Saros 138) |
 March 18, 1988 (Saros 139) |
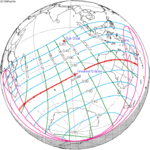 February 16, 1999 (Saros 140) |
 January 15, 2010 (Saros 141) |
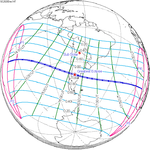 December 14, 2020 (Saros 142) |
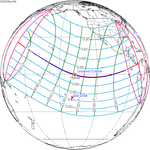 November 14, 2031 (Saros 143) |
 October 14, 2042 (Saros 144) |
 September 12, 2053 (Saros 145) |
 August 12, 2064 (Saros 146) |
 July 13, 2075 (Saros 147) |
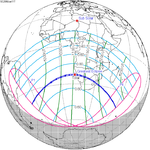 June 11, 2086 (Saros 148) |
 May 11, 2097 (Saros 149) |
 April 11, 2108 (Saros 150) |
 March 11, 2119 (Saros 151) |
 February 8, 2130 (Saros 152) |
 January 8, 2141 (Saros 153) |
 December 8, 2151 (Saros 154) |
 November 7, 2162 (Saros 155) |
 October 7, 2173 (Saros 156) |
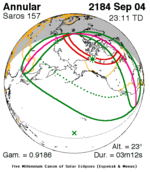 September 4, 2184 (Saros 157) |
 August 5, 2195 (Saros 158) | |||
Inex series
[edit]This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1801 and 2200 | ||
|---|---|---|
 June 6, 1807 (Saros 134) |
 May 15, 1836 (Saros 135) |
 April 25, 1865 (Saros 136) |
 April 6, 1894 (Saros 137) |
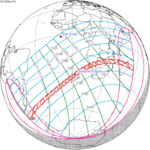 March 17, 1923 (Saros 138) |
 February 25, 1952 (Saros 139) |
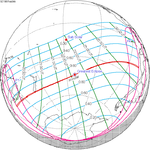 February 4, 1981 (Saros 140) |
 January 15, 2010 (Saros 141) |
 December 26, 2038 (Saros 142) |
 December 6, 2067 (Saros 143) |
 November 15, 2096 (Saros 144) |
 October 26, 2125 (Saros 145) |
 October 7, 2154 (Saros 146) |
 September 16, 2183 (Saros 147) |
|
Notes
[edit]- ^ "Solar eclipse dazzles Africa and Asia". Intelligencer Journal/Lancaster New Era. 2010-01-16. p. 32. Retrieved 2023-10-25 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Thousands view solar eclipse in Africa, Asia". Tri-City Herald. 2010-01-16. p. 6. Retrieved 2023-10-25 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ NASA – Solar Eclipse Search Engine
- ^ Espenak, Fred. "Besselian Elements for Annular Solar Eclipse of 2010 Jan 15". NASA Eclipse Web Site.
- ^ Annular Solar Eclipse Occurs on January 15, 2010
- ^ NASA: Eclipses During 2010: Annular Solar Eclipse of January 15
- ^ Facilities to view the solar eclipse in Trivandrum
- ^ VSSC expects insights from eclipse
- ^ City Bureau (January 15, 2010). "Celestial treat, a day away". The Hindu. Archived from the original on January 17, 2010.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 141". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
References
[edit]- NASA: Annular Solar Eclipse of 2010 January 15
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- NASA: Eclipses During 2010: Annular Solar Eclipse of January 15
- Eclipse.org.uk: Annular eclipse of the Sun: 2010 January 15 Archived 2010-11-11 at the Wayback Machine
- www.sciencemaldives.org: January 15th 2010 Solar Eclipse, Maldives Archived 2010-01-18 at the Wayback Machine
- Hermit.org Visibility graphics
- www.eclipser.ca: Jay Anderson 2010 January 15 Annular Solar Eclipse Archived 2009-01-27 at the Wayback Machine
External links
[edit]- Annular Solar Eclipse of Dali, Yunnan, China
- SpaceWeather.com: January 15, 2010 solar eclipse
- Eclipse over the Temple of Poseidon, APOD 1/18/2010, partial eclipse of Sounion, Greece
- Millennium Annular Solar Eclipse, APOD 1/22/2010, annularity of Kanyakumari, India, the same picture chosen as APOD again on 5/19/2012, Annular Solar Eclipse
- Eclipses in the Shade, APOD 1/23/2010, from Alif Alif Atoll, Maldives
- Annular Eclipse Over Myanmar, APOD 1/26/2010, annularity of Ananda Temple, Bagan, Myanmar
- 2010 Annular Eclipse January 15, 2010, from India by Jay Pasachoff
- Solar Eclipse animation of January 15, 2010
- ShadowAndSubstance.com: January 15, 2010, solar eclipse animations for geographical locations Archived January 19, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- Eclipse photography taken from Rameswaram, Tamil Nadu, India
- Eclipse-Chasers: January 15, 2010 annular solar eclipse
- SWAN Website




















