Жан-Джозеф Транши
Жан-Джозеф Транши | |
|---|---|
| Рожденный | 2 января 1752 г. |
| Умер | 30 апреля 1815 года (в возрасте 63 лет) |
| Национальность | Французский |
| Занятие | Картограф |
Жан-Джозеф Транчо (2 января 1752 года-30 апреля 1815 года) был французским военным картографом . Он наиболее хорошо известен своим топографическим обзором Рейнландии при Наполеоне , и его помощь в измерении меридианской дуги Франции с астрономом Пьером Метханом, чтобы определить длину метра .
Биография
[ редактировать ]Transnchot родился 2 января 1752 года в Kœur-La Petite , Фрэнсис . [ 1 ] Его родителями были Ремигюс Транчо, плотник и Мария Мори. [ 2 ]
Транчо впервые использовался в качестве картографа в 1774 году в триангуляции Корсики, который был заказан указанием Французской короны в 1770 году. [ 3 ] После завершения этой задачи Транчо изучал астрономию с Пьером Мечейном , прежде чем ему было дано приказ о триангуляции и связывал свою карту Корсики с соседней Сардинией и прибрежной Тосканой. Эта задача была завершена с использованием нового изобретения, повторного круга , [ 4 ] С 1788 по 1791 год, и впоследствии он был признан Мечейном и Французской академией наук за его работу. [ 3 ]
Following the cartography of these Mediterranean islands, Tranchot was approached by the French Academy of Sciences to accompany Méchain as his primary adjutant in measuring the southern part of meridian arc of France. This project, spanning 1791 to 1799, started in Barcelona and ended at Rodez, and the resulting measurement became the basis for the metric system's unit of length, the meter.[4] Alongside working with Méchain, Tranchot assisted Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre in measuring the baseline at Perpignan to assist in the meridian survey.[4]
In 1794, Tranchot was appointed to the scientific staff of the Dépôt de la Guerre.[1] By 1801, the French government under Napoleon promoted him to the rank of Colonel and tasked him with mapping the Rhineland's topography.[5] This final work lasted from 1801 until 1814. In this time, Tranchot completed 167 maps of the area, now known as the "Tranchot Maps". The project was finished in 1828 by Karl Freiherr von Müffling.[1]
Tranchot died in 1815 from a stroke.
Tranchot Maps
[edit]-
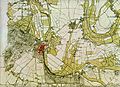
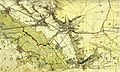
Rhineland quadrants surveyed by Tranchot
-
Survey of Kleve, Germany
-
Survey of Bergheim, Germany
References
[edit]- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Saarland Biografien". www.saarland-biografien.de (in German). Retrieved 31 August 2021.
- ^ Willems, Bernhard (1955). Colonel Tranchot and the Tranchot Stone on the High Fens. Eupen. p. 3.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Augoyat, Antoine-Marie (1822). Notice sur M. Maissiat, chef d'escadron au Corps royal des ingénieurs-géographes militaires, suivie de notices sur la carte des ex-quatre départemens réunis de la rive gauche du Rhin, et sur M. Tranchot, colonel au Corps royal des ingénieurs-géographes militaires (in French). Paris: Anselin er Pochard. Retrieved 31 August 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Alder, Ken (2002). The Measure of All Things : The Seven-Year Odyssey and Hidden Error that Transformed the World. New York: Free Press. ISBN 978-0743216760.
- ^ Antologia Militare (PDF). 1 February 2020. pp. 21–22. Retrieved 31 August 2021.