Мьянма - Тайландская граница

Граница Мьянма -Таиланда является международной границей между территорией Мьянмы (ранее Бирма ) и Таиландом . Граница составляет 2416 км (1501 миль) в длину и проходит от севере на Лаоса до побережья Андаманского моря на юге. [ 1 ]
Описание
[ редактировать ]Граница начинается на севере у Лаоса с Лаосом в слиянии рек Кок и Меконга и после короткого следования кока, а затем в Саи , затем продолжается по суше на запад через серию нерегулярных линий через диапазон Ден Лаос , Прежде чем повернуться на юго-запад и присоединиться к реке Салэйн . Граница следует за рекой Салэйн, а затем в реке Моэй на юг, перед тем, как покинуть ее, и пройдет на юг по суше через хребет Dawna и линейку Билауктаунг (в совокупности эти горы образуют холмы Тенассерима ). Граница продолжается на юг вниз по Малайскому полуострове , почти прорезая Таиланд в двух в Прачуап Хири -хана , прежде чем добраться до перешейка Кра и реки Крабури , который затем следует через широкий устье к Андаманскому морю. Морская граница затем следует координатам, отмеченным соглашением о континентальном понижении стран о континентальном шельфе по отношению к Индии с Индией, которая контролирует Андаманские и Никобарские острова .
History
[edit]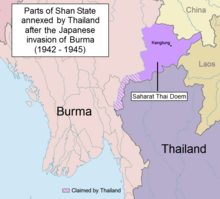
The border regions have historically been contested between the various Thai and Burmese states.[2] Fighting between Burma and the Siamese Ayutthaya Kingdom over control of what is now Myanmar's Tanintharyi Region dominated the area in the 16th century, before Burma destroyed Ayutthaya and took control of the region in 1767.[2] Soon after, Siam extended suzerainty over the Lanna Kingdom (now Northern Thailand), which had previously been under Burmese control. Burmese expansion in the 19th century brought it into conflict with the British in India, sparking a series of conflicts which ended with Burma being occupied and incorporated into British India.[2] With France occupying French Indochina in the same period, the two European states allowed the Kingdom of Siam (the old name for Thailand) to retains its independence as a buffer state.[3][4]

In 1868 Britain and Siam signed a treaty delimiting the Burma-Thai border from the Salween south to the Andaman Sea.[2] Following some confusion as to the border's location, on the ground demarcation of the border commenced from 1889 to 1892.[2] In 1892 the northern section of the border delimited and then demarcated on the ground from 1893 to 1894, with a final boundary treaty with maps signed on 17 October 1894.[2] The northern terminus of the border was fixed in 1896 when the British and French agreed that the Mekong would serve as the Burma-Laos border.[2] Some minor boundary adjustments occurred in 1929 and 1934.[2] In 1941, following Japan's invasion of Burma, parts of Burma were ceded to Siam as the Saharat Thai Doem territory, however these areas were returned to Burma in 1946 following Japan's defeat and since then the border has remained in place.[2][5][6] In 1937 Burma was separated from India and became a separate colony, gaining full independence in 1948, at which point the border became an international frontier between two sovereign states.[2]
At present there is an outstanding dispute over the ownership of some small islands in the Andaman Sea.[7]
From 2010 to 2012 there were clashes along the border between the Myanmar army and the Karen National Liberation Army.[8][9]
In 2021, the Myanmar military clashed with civilians in the border areas. Many of them fled and ended up in Thailand. [10]
In 2023 there were more clashes and the governments of both countries have decided to form a humanitarian task force. [11][12]
Border crossings
[edit]As of 2019[update], there were 6 permanent border crossings, 1 temporary border crossing, 13 checkpoints for border trade and 1 special checkpoint for border trade.[13]
Permanent border crossings
[edit]| No | Myanmar | Thailand | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Border post | Road | Border post | Opening hours | ||
| 1 | Tachileik, Shan State | 1 | Mae Sai 1, Mae Sai District, Chiang Rai | 0630 - 2100 | The border crossing is via the First Bridge over the Sai River. |
| 2 | 1041 | Mae Sai 2, Mae Sai District, Chiang Rai | 0630 -1830 | The border crossing is via the Second Bridge over the Sai River. | |
| 3 | Myawaddy, Kayin State | 12 | Mae Sot 1, Mae Sot District, Tak | 0530 - 2030 | The border crossing is via the First Thai-Myanmar Friendship Bridge over the Moei River. |
| 4 | 130 | Mae Sot 2, Mae Sot District, Tak | 0630 - 1830 | The border crossing is via the Second Thai-Myanmar Friendship Bridge over the Moei River. | |
| 5 | Htee Kee, Dawei, Tanintharyi Region | 3229 | Ban Phu Nam Ron, Mueang Kanchanaburi District, Kanchanaburi | 0600 - 2000 | |
| 6 | Kawthaung, Tanintharyi Region | - | Bang Rin Fisheries Pier, Mueang Ranong District, Ranong | 0630 - 0000 | Ferry Border Crossing. Consists of checkpoints located adjacent to 4 separate piers on the Thai side. |
| Pak Nam Ranong, Mueang Ranong District, Ranong | |||||
| Ranong Customs Pier, Mueang Ranong District, Ranong | |||||
| Andaman Club Pier, Mueang Ranong District, Ranong | |||||

Temporary border crossings
[edit]These border crossings are open for foreigners for travel purposes only.
| No | Myanmar | Thailand | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Border post | Road | Border post | Opening hours | ||
| 1 | Payathonzu, Kayin State | 323 | Dan Phra Chedi Sam Ong (Three Pagodas Pass), Sangkhla Buri District, Kanchanaburi | 0830 - 1800 | |
Checkpoints for border trade
[edit]These border crossings are open for cross-border local trade only. There are 13 checkpoints for border trade officially recognized by the Ministry of Interior, located in Chiang Rai, Chiang Mai, Mae Hong Son and Ranong provinces. Entering the opposite country beyond these checkpoints and their associated markets is illegal.
Special checkpoint for border trade
[edit]One special checkpoint for border trade is planned as a future permanent crossing. Entering the opposite country beyond these checkpoints and their associated markets is currently[may be outdated] illegal.
| No | Myanmar | Thailand | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Border post | Road | Border post | Opening hours | ||
| 1 | Mawdaung, Tanintharyi Region | 1039 | Dan Singkhon (Singkhon Pass), Mueang Prachuap Khiri Khan District, Prachuap Khiri Khan | 0630 - 1800 | |
Gallery
[edit]-
A scenic viewpoint of the border along the Daen Lao Range from Thailand's Mae Sai District
-
Pier at Kawthaung
-
The border along the Moei river, with Myanmar on the opposite bank
-
Border gate at Mae Sai
-
The border bridge at Tachilek
-
Mae Sot border crossing
-
Border control gate at Dan Sing Khon
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Burma". CIA World Factbook. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j "International Boundary Study No. 63 – Burma – Thailand Boundary" (PDF). US Department of State. 1 February 1966. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ Pholsena, Vatthana (2007). LAOS, From Buffer State to Crossroads. Silkworm Books. ISBN 978-9749480502.
- ^ Macgregor, John (1994). Through the Buffer State : Travels in Borneo, Siam, Cambodia, Malaya and Burma. White Lotus Co Ltd; 2 edition. ISBN 978-9748496252.
- ^ Donald M. Seekins, Historical Dictionary of Burma (Myanmar), p. 251
- ^ "A Forgotten Invasion: Thailand in Shan State, 1941–45"
- ^ Sophal, Sek (13 January 2020). "New subs sign of troubles to come?" (Opinion). Bangkok Post. Retrieved 13 January 2020.
- ^ «Тысячи бегут в столкновениях Мьянмы» . Аль Джазира . 8 ноября 2010 г. Получено 9 ноября 2010 года .
- ^ «Гражданская война угрожает после избрания Бирмы» . ABC News . 9 ноября 2010 г. Получено 9 ноября 2010 года .
- ^ «Воздушные налеты в армии Мьянмы отправляют сотни людей, бегущих в Таиланд» .
- ^ «Таиланд, пытаясь спасти 162 граждан, поскольку десятки тысяч бегут в борьбе с Мьянмой» . Получено 2024-02-08 .
- ^ «Таиланд, Мьянма, чтобы сформировать целевую группу по оказанию помощи в качестве пограничных беспорядков» . Получено 2024-02-08 .
- ^ соглашение о пересечении» . Крестное «Информация через






