Острова Бату
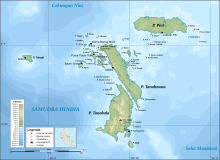
Острова Бату представляют собой архипелаг Индонезии , расположенный в Индийском океане , у западного побережья Суматры , между Ниасом и Сибетом . Три основных острова, приблизительно одинакового размера, - это Pini , Tanahmasa и Tanahbala . Есть семьдесят пять небольших островов, из которых самые большие-Сипика, Телло и Сигата (все у западного побережья Танахмаса), Симук (значительно дальше к западу) и Божо (к югу от Танахбалы); Менее половины населены. Общая площадь земли семи административных районов составляет 1 201,1 км 2 Полем Острова регулируются как часть регентства Южной Ниас в провинции Северная Суматра . На индонезийском и малайском , Бату означает скала или камень .
Экватор проходит через архипелаг , к северу от Танамаса и к югу от Пини. Административно, PINI (с оффшорными островками) образует район Пулау Пулау Бату Тимр (Ист -Острова Бату) Южного Ниас Ридженси . Остальная часть архипелага на переписи 2010 года ранее включала в районы Пулау Пулау Бату (острова Бату) и Хибала того же регентства; Тем не менее, оба были впоследствии разделены на новые районы - район Танахмаса был сформирован из части района Хибала, и из районов района Пулау Пулау Бату были образованы три новых района ( Остров Западных Бату), Пулау Пулау Бату . Пулау Бату Утара (острова Северного Бату, которые лежат к северу от Танамаса) и Симук районы . Первоначальные районы остаются с уменьшенными областями и населением, и, таким образом, острова теперь образуют семь отдельных районов.
| Name | Area in km2 |
Population Census 2010[1] |
Population Census 2020[2] |
Administrative centre (with location) |
Number of villages |
Post code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tanahmasa | 451.43 | (b) | 4,807 | Baluta (on Tanamasa Island) | 12 | 22887 |
| Pulau Pulau Batu Timur (East Batu Islands) |
372.05 | 2,483 | 3,091 | Labuhan Hiu (on Pini Island) | 10 | 22884 |
| Hibala (a) | 225.75 | 9,620 | 7,716 | Eho (on Tanabala Island) | 17 | 22881 |
| Pulau Pulau Batu (c) (Batu Islands) |
105.09 | 16,365 | 9,731 | Pasar Pulau Tello (on Tello Island) | 22 | 22882 |
| Pulau Pulau Batu Barat (e) (West Batu Islands) |
21.06 | (d) | 2,320 | Bawositora (on Sigata Island) | 9 | 22883 |
| Simuk (island) | 20.42 | (d) | 1,934 | Gobo (on Simuk Island) | 6 | 22886 |
| Pulau Pulau Batu Utara (f) (North Batu Islands) |
6.30 | (d) | 3,894 | Silima Banua Marit (on Marit Island) | 12 | 22885 |
| Totals for Kepulauan Batu | 1,201.10 | 28,468 | 33,493 | 88 |
Notes: (a) Hibala District now comprises 42 islands, chiefly Tanahbala Island but including Bojo Island to its south.
(b) The 2010 population of Tanah Masa District (comprising that part of Tanahmasa Island previously part of Hibala District) is included in the 2010 population of Hibala District.
(c) Pulau Pulau Batu District now includes various small islands, including Tello, Batumakele and Sibele.
(d) The 2010 populations of Simuk District (Simuk Island), Pulau Pulau Batu Barat District and Pulau Pulau Batu Utara District are included in the 2010 population of Pulau Pulau Batu District.
(e) comprises numerous small islands including Sigata, Sipika, Pono, Sibaranu, Hayo and Bintuang.
(f) comprises numerous small islands including Marit, Lorang, Memong and Lorang.
The four new districts in the Batu Islands are Pulau Pulau Batu Barat (West Batu Islands), Pulau Pulau Batu Utara (North Batu Islands), Simuk (Simuk Island) and Tanah Masa (that part of Tanahmasa Island previously part of Hibala District).
People
[edit]The people of the Batu Islands have had substantial interaction with the populations of Nias, to the north, whose language they share. The islands have occasionally been a destination for slaves who escaped from Nias, and in the past decade have become a destination for surfing boat charters from Padang, on the Sumatran mainland. The population at the 2010 Census was 28,468.[3]
The islands were visited by Simon Reeve during Equator, a 2006 BBC TV Series.
Wildlife
[edit]A population of the Sunda clouded leopard had been recorded here.[4]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- ^ Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021.
- ^ Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- ^ Wilting A.; Christiansen P.; Kitchener A. C.; Kemp Y. J. M.; Ambu L.; Fickel, J. (2010). "Geographical variation in and evolutionary history of the Sunda clouded leopard (Neofelis diardi) (Mammalia: Carnivora: Felidae) with the description of a new subspecies from Borneo". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 58 (2): 317–28. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2010.11.007. PMID 21074625.



