Line Melampsora
| Line Melampsora | |
|---|---|
| |
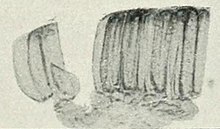
| Телетоспоры мелампсоры Лини, тесно связанные друг с другом, на лене usitatissimum | |
| Научная классификация | |
| Домен: | Эукариота |
| Королевство: | Грибы |
| Разделение: | Basidiomycota |
| Сорт: | Pucciniomycetes |
| Заказ: | Pucciniales |
| Семья: | Melampsoraceae |
| Genus: | Melampsora |
| Species: | M. lini
|
| Binomial name | |
| Melampsora lini | |
| Synonyms | |
Melampsora Lini - это вид гриба и патогена растений , обнаруженный в Ирландии и обычно известный как лена . [ 1 ]
Жизненный цикл
[ редактировать ]Патоген является обязательным биотрофом, что означает, что каждая стадия его цикла зависит от наличия живого хозяина . Направление между воспроизведением сексуально или асексально зависит от доступности хозяина.
В сексуальном отношении жизненный цикл начинается, когда базидиоспоры приземляются на льняных листьях и образуют пикнию в течение декабря и до января. [ 2 ] Затем AECIUM образуются из пикния после оплодотворения с пикниоспорой, которая имеет другой тип спаривания. Затем Urediniospores и Aeciospores образуют пустулы на листьях, которые высвобождают больше споров, приводящих к дальнейшей инфекции на соседних листьях. Затем телиоспоры образуются на стволе растений и подвергаются мейозу . После этого телиоспоры пробирают гаплоидные базидиоспоры, повторяющие цикл.
Asexually, the pathogen cycles between forming pustules and infecting surrounding leaves and plants. The pathogen is autoecious, meaning it completes its life cycle on a single plant. This is done purely through mitosis and produces genetically identical cells within the pustules.[3]
Hosts
[edit]Radiola linoides has been recorded as a host for Melampsora lini in the UK.[4]
The pathogen prefers an environment in the temperate plains or hills of the United Kingdom rather than in high altitude and cold conditions. Due to this, there is a higher prevalence of resistance seen in hosts in these more favorable environment compared to hosts seen in mountainous ranges.[5] This is primarily due to the fact that there is a higher evolutionary pressure placed on these plants. Those that can defend against the pathogen go on to reproduce and pass on the genes responsible for their immunity.
Symptoms and signs
[edit]Signs and symptoms of flax rust include:[6]
Signs
[edit]All signs are uniform for the hosts of the pathogen stated before. The only difference is the amount of signs seen due to the varying leaf shapes of the plants.
Symptoms
[edit]- Yellowing of leaves
- Necrotic leaf spots
Symptoms are uniform for the hosts of the stated above. There is some variation in the amount of symptoms seen because of the amount of available host area infected by the pathogen.
Research
[edit]The pathogen itself is not known for being detrimental to farmers since it does not take away from the total yield. During the 1990s, the pathogen was used as a role model for the molecular basis of plant immunity. The majority of research worked on observing the pathogenicity of a variety of physiological races of the pathogen and the resistance and susceptibility of the "gene-for-gene" relationship and understanding the breakdown of resistance when using a single gene.[1] This led to the use of incorporating multiple resistance genes to ensure resistance persisted.
From the late 1980s to present, the focus of research shifted to more specific molecular studies. One major discovery included the cytoplasmic nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat proteins. These proteins help provide resistance against fungi, oomycetes, bacteria, viruses, nematodes, insects, and parasitic plants. This was found through observing point mutations, re-assortment of mutation, and duplication and deletion of LRR units done by intragenic recombination in Australia in 2007.[3][1]
References
[edit]- ^ Jump up to: a b c Nemri, Adnane; Saunders, Diane G. O.; Anderson, Claire; Upadhyaya, Narayana M.; Win, Joe; Lawrence, Gregory J.; Jones, David A.; Kamoun, Sophien; Ellis, Jeffrey G.; Dodds, Peter N. (2014). "The genome sequence and effector complement of the flax rust pathogen Melampsora lini". Frontiers in Plant Science. 5: 98. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00098. PMC 3970004. PMID 24715894.
- ^ "Life Cycle of Melampsora (With Diagram) | Fungi". Biology Discussion. 2016-11-28. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Dean, Ralph; Van Kan, JAN A. L.; Pretorius, Zacharias A.; Hammond-Kosack, KIM E.; Di Pietro, Antonio; Spanu, Pietro D.; Rudd, Jason J.; Dickman, Marty; Kahmann, Regine; Ellis, Jeff; Foster, Gary D. (2012). "The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology". Molecular Plant Pathology. 13 (4): 414–430. doi:10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00783.x. PMC 6638784. PMID 22471698.
- ^ Lawrence, G.J.; Dodds, P.N.; Ellis, J.G. (2007). "Rust of flax and linseed caused by Melampsora lini". Molecular Plant Pathology. 8: 349–364.
- ^ Barrett, Luke G.; Thrall, Peter H.; Burdon, Jeremy J.; Nicotra, Adrienne B.; Linde, Celeste C. (2008). "Population structure and diversity in sexual and asexual populations of the pathogenic fungus Melampsora lini". Molecular Ecology. 17 (14): 3401–15. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294x.2008.03843.x. PMC 2653454. PMID 18573166.
- ^ "flax rust (Melampsora lini)". www.plantwise.org. Retrieved 2018-10-31.