Symphyotrichum стабильная
| Symphyotrichum стабильная | |
|---|---|

| |
| Св. Стабиль , Онтарио , Канада | |
| Научная классификация | |
| Королевство: | Plantae |
| Клада : | Трахеофиты |
| Клада : | Покрытосеменные |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Tribe: | Astereae |
| Subtribe: | Symphyotrichinae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Subgenus: | Symphyotrichum subg. Symphyotrichum |
| Section: | Symphyotrichum sect. Symphyotrichum |
| Species: | S. firmum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum firmum | |
| |
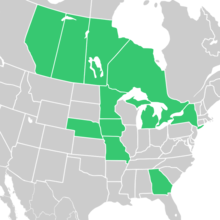
| Native distribution[2] | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
Basionym
Alphabetical list | |
Symphyotrichum firmum (ранее Aster Firmus ), широко известный как сияющая астр , блестящая астр [ 3 ] гладкий болотный астер , [ 4 ] и глянцевая астер , [ 5 ] является видом цветущего растения в семействе астерасей, уроженцев Канады и Соединенных Штатов.
Описание
[ редактировать ]Symphyotrichum firmum - это многолетнее травянистое растение , которое может достигать высоты 2 meters (6+1⁄2 feet). It forms large colonies with long, creeping rhizomes. The stem is hairless or it may have stiff, short hairs, often formed in vertical lines. It is sometimes dark red or purple at the nodes (where the leaf connects to the stem). The leaves are alternate, up to 15 cm (6 in) long and 3 см ( 1 + 1 ~ 5 дюймов) шириной и застегивается стебель. Основная вена на нижней поверхности листья безволосая или слегка волосатая возле кончика. [ 5 ] [ 6 ]
It flowers August through October. The flower heads are От 1,5 до 3,5 см ( от 5 ⁄ 8 до 1 + 3 ~ 8 дюймов) с помощью до 40 лучевых цветов и 50 цветов диска . Рэй -цветочки варьируются от белого до бледно -голубых или лаванды. Дисковые цветочки от желтого до сливочного цвета, становясь розовыми или фиолетовыми со зрелостью. [ 5 ] [ 6 ]
S. firmum has a diploid chromosome count with a base number of x = 8 (2n = 16).[5]
Compared to the closely related Symphyotrichum puniceum, S. firmum is less hairy overall, has denser inflorescences of smaller, whiter flowers, and grows in larger, denser patches.[4][6]
-
Symphyotrichum puniceum on left and S. firmum on right
-
Involucre showing phyllaries and bracts
-
Flower heads close-up
Taxonomy
[edit]Symphyotrichum firmum is closely related and morphologically very similar to Symphyotrichum puniceum (purple-stemmed aster), and is not always treated as a separate species. However, there is little evidence of intergrades between the two taxa, and most sources now treat them as distinct.[5][6]
Distribution and habitat
[edit]Its range is poorly known due to confusion with the closely related Symphyotrichum puniceum.[5] In Canada it has been recorded from Alberta to Quebec.[3] In the United States, it occurs in the Midwest, some parts of the Northeast, and in the Appalachian Mountains south to Georgia.[5][6][2] It is more common in the western part of its range.[6]
Symphyotrichum firmum grows in moist and sunny areas such as fens and wet prairies.[4][7] It is often found growing with S. puniceum.[6] Unlike S. puniceum, it sometimes spreads into drier areas.[4]
Ecology
[edit]Bees that have been observed visiting the flowers include the bicolored striped-sweat bee (Agapostemon virescens), various bumble bees (Bombus species), small carpenter bees (Ceratina species), the sweat bee named Halictus ligatus, and Drury's long-horned bee (Melissodes druriellus).[a][7]
Conservation
[edit]As of December 2021[update], NatureServe listed Symphyotrichum firmum as Secure (G5) worldwide, Vulnerable (S3) in Quebec, and Presumed Extirpated (SX) in New Jersey.[1]
Notes
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ Jump up to: a b NatureServe 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d POWO 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Brouillet et al. 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Reznicek, Voss & Walters 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Brouillet et al. 2006.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Warners & Laughlin 1999.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Wilhelm & Rericha 2017, p. 1100.
References
[edit]- Brouillet, L.; Desmet, P.; Coursol, F.; Meades, S.J.; Favreau, M.; Anions, M.; Bélisle, P.; Gendreau, C.; Shorthouse, D. (2019). "Symphyotrichum firmum (Nees) G.L. Nesom". data.canadensys.net. Database of Vascular Plants of Canada (VASCAN). Retrieved 7 January 2020.
- Brouillet, L.; Semple, J.C.; Allen, G.A.; Chambers, K.L.; Sundberg, S.D. (2006). "Symphyotrichum firmum". In Flora of North America Editorial Committee (ed.). Flora of North America North of Mexico (FNA). Vol. 20. New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press. Retrieved 5 July 2021 – via eFloras.org, Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, MO & Harvard University Herbaria, Cambridge, MA.
- NatureServe (6 December 2021). "Symphyotrichum firmum - Swamp Aster". NatureServe Explorer (explorer.natureserve.org). NatureServe. Retrieved 12 December 2021.
- POWO (2019). "Symphyotrichum firmum (Nees) G.L.Nesom". Plants of the World Online (www.plantsoftheworldonline.org). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 4 July 2021.
- Reznicek, A.A.; Voss, E.G.; Walters, B.S., eds. (February 2011). "Symphyotrichum firmum". Michigan Flora Online. University of Michigan Herbarium. Retrieved 7 January 2020.
- Warners, D.P.; Laughlin, D.C. (1999). "Evidence for a species-level distinction of two co-occurring asters: Aster puniceus L. and Aster firmus Nees" (PDF). Great Lakes Botanist. 38 (2). Retrieved 8 January 2020.
- Вильгельм, Г .; Rericha, L. (2017). Флора Чикагского региона: флористический и экологический синтез . Иллюстрирован Лоуэром, М.М. Индианаполис, Индиана : Академия науки Индианы . ISBN 978-1883362157 Полем OCLC 983207050 .
- Natureserve безопасные виды
- Symphyotrichum
- Флора Западной Канады
- Флора Восточной Канады
- Флора северо-центральных Соединенных Штатов
- Флора северо -восточных Соединенных Штатов
- Флора юго -восточных Соединенных Штатов
- Растения, описанные в 1818 году
- Таксоны, названные Кристианом Готфридом Даниэлем Нис фон Эсенбек



