Пеннакук
| Общая численность населения | |
|---|---|
| вымирать как племя | |
| Регионы со значительным населением | |
| Южный Мэн Северо -Восточный Массачусетс Южный Нью -Гемпшир | |
| Языки | |
| Незабежный алгонкский язык | |
| Религия | |
| Религия коренных народов |
Пеннакук , , также известный под именами Penacook и Pennacock , были алгонкинскими коренными народами которые жили в штате Массачусетс , Нью -Гемпшир и Южный Мэн . Они были не объединенным племенем, а сетью политических и культурных союзных сообществ. [ 1 ] Пенакук также был названием конкретной местной деревни в том, что сейчас является Конкордом, Нью -Гемпшир . [ 2 ]
Пеннакук был связан, но не была частью оригинальной конфедерации Вабанаки , которая включает в себя народы Miꞌkmaq , Maliseet , Passamaquoddy и Penobscot .
Имя
[ редактировать ]Pennacook также написан как Penacook и Pennacock. Название Пеннакук примерно переводится (на основе родственников Абенаки ) как «в нижней части холма». [ 3 ]
Территория
[ редактировать ]Historian David Stewart-Smith suggests that the Penacook were Central Abenaki people.[4] Their southern neighbors were the Massachusett and Wampanoag.[5]
Pennacook territory bordered the Connecticut River in the West, Lake Winnipesauke in the north, the Piscataqua to the east, and the villages of the closely allied Pawtucket confederation along the southern Merrimack River to the south. The Pennacook homeland was built around the upper Merrimack and the major towns at Amoskeag Falls (now Manchester) and Pennacook (now Concord), which served as major population hubs and later fallback centers for people across the region during the colonial period.[5]
Confederacy
[edit]The Pennacook were a loose and fluid confederacy of village communities.[2] Pennacook was a specific community within this confederacy that also included Accominta,[7] Agawam, Amoskeag, Coosuc, Cowasack, Nashua, Naumkeag, Newickawanoc, Ossipee, Piscataway, Piscatequa, Souhegan, Squamscot, Wambesit, Washacum, Winnepesaukee, Wachusett, and other villages.[2]
The children of Pennacook Sachem Passaconaway intermarried with the children of Pawtucket Bashaba Nanepashemet in the 17th century.[citation needed] Because decisions to ally and become a part of such alliances were largely in the hands of the leaders of individual bands, the membership of these confederations and alliances fluctuated regularly.
Subsistence
[edit]Pennacook people were semi-sedentary.[5] Families and bands had permanent claims to territory, and their hierarchical political structure from locally representative sagamores to more regionally representative sachems was fundamentally democratic and designed to reduce conflict and provide social stability. Leaders and sachems like Passaconaway played important roles in organizing long-distance kin and trade networks with allied neighbors (his own children were all married to the children of allied political leaders).[8] Before the major epidemics of the 16th and 17th century would kill 90% of the Pennacook population, the Merrimack Valley and its tributaries like the Souhegan, Piscataquog, and Suncook, would have been densely populated, the environment carefully maintained. David Stewart-Smith (1998:19) estimated that the Merrimack Valley had 8,000–25,000 people before the epidemics, with a median of around 16,500 for the central area around Pennacook.[5]
The major and permanent Pennacook towns and villages were built along the major rivers, and many were on the east side of the Merrimack, ostensibly for protection from the west. Life revolved around the seasons, and spring would begin with women collecting maple sap to make maple sugar. Men would return to hunting grounds and burn their grounds to turn over nutrients in the soils for later cultivation. In late spring the rivers and creeks would swell as the great fish like salmon and shad made their way up the Merrimack. Many Pennacook villages were built just above natural waterfalls that trapped fish and made it easier to catch them in the late spring. Fiddlehead season would be followed by others still known today, like blueberry and raspberry seasons. During the summers, families would disperse to summer villages and hunting camps. Women did most of the work of building and maintaining homes as well as farming. Their main crops were varieties of maize/corn and squash, which they planted along rivers and in meadows. While they found it difficult to clear the massive old-growth trees, the Pennacook were experts at manipulating beavers to move their dams and ponds up and down creeks and brooks, thereby clearing and opening up land for farms that would be essential to the first Europeans who arrived and found cleared fields ready for cultivation. Many of these fields were scattered with the bones of the Pennacook who had recently died of smallpox or other diseases. The fall was an important hunting and nut harvesting season (butternuts, hickory nuts, black walnuts, and beech nuts were all tasty, and several southern, fire-resistant species were propagated farther north when possible). The presence of southern, fire-resistant species of nut trees like hickories and black walnuts in New Hampshire today is thanks to the Pennacook. The forests would generally be burned again in the late fall before families returned to the more permanent winter camps to wait out the long winter. In addition to being farmers, hunters, and foragers, it is important to remember that the Pennacook and the peoples of the Merrimack River Valley were also long-distance traders, and their major towns of Pennacook and Amoskeag drew people from around the region in the late spring and summers. For more, see Michael Caduto's 2004 book, A Time Before New Hampshire and the work of David Stewart-Smith.[9][5]
History
[edit]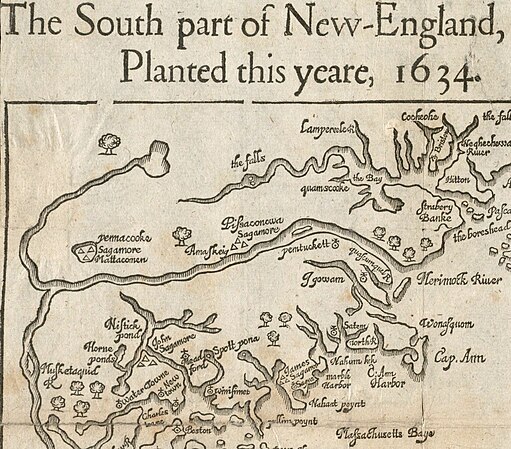
One of the first Indian tribes to encounter European colonists, the Pennacook were devastated by infectious diseases carried by the newcomers. Suffering high mortality, they were in a weakened state and subject to raids by Mohawk of the Iroquois Confederacy from the west, and Micmac (Mi'kmaq) tribes from the north, who also took a toll of lives. Chief Passaconaway had a military advantage over English colonists from New England, but he decided to make peace with them rather than lose more of his people through warfare. They were caught up in King Philip's War, however, and lost more members. Although Wonalancet, the chief who succeeded Passaconaway, tried to maintain neutrality in the war, bands of Pennacook in western Massachusetts did not.
After King Philip's War, the colonists of New England enslaved some Pennacook captives. Some joined the Schaghticoke.[12] Other Pennacooks fled to the Hudson Valley and on to Quebec.[2] North-bound refugees eventually merged with other member tribes of the Wabanaki Confederacy. In the north, some Pennacook merged into the Pigwacket people, an Abenaki group.[5] Gordon M. Day suggested that Pennacook moved north to Odanak Reserve in Quebec, and their descendants belong to the Odanak First Nation, an Abenaki government in Canada.[13]
Cultural heritage groups
[edit]Several groups in present-day Vermont claim to be Pennacook bands. The Odanak Abenaki Band Council has denounced them.[14][15] Contemporary scholarship indicates that most members of such groups have a single Indigenous ancestor many generations removed or no Indigenous ancestry at all.[16][17] Indigenous activists and their allies strongly critique this phenomenon, sometimes called race-shifting, as a threat to the sovereignty of Indigenous nations and part of a larger pattern of settler self-indigenization.[citation needed]
Legacy
[edit]William James Sidis hypothesized in his book The Tribes and the States (1935) that the Pennacook tribes greatly influenced the democratic ideals which European settlers instituted in New England.
The Boy Scouts of America's Boston-based Spirit of Adventure Council adopted the name "Pennacook" for its Order of the Arrow lodge.[18]
Notable Pennacook
[edit]- George Tahanto, sachem, land proprietor, participant in Deerfield Raid
- Passaconaway, 17th-century sachem, or leader, of the Pennacook proper in New Hampshire
- Plausawa (c. 1700–1754), a veteran of King George's War and last known Native American living in the town of Suncook, New Hampshire
- Wonalancet (c. 1619–1697), 17th-century sachem and son of Passconaway
See also
[edit]- Lake Winnipesaukee, named after a subtribe of the Pennacook
- Native American tribes in Massachusetts
- Penacook, New Hampshire
- Plausawa
- New Hampshire Historical Marker No. 238: The Pennacook
Notes
[edit]- ^ David Stewart-Smith, "The Pennacook Indians and the New England frontier," p. 6.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Sherburn Friend Cook, The Indian Population of New England in the Seventeenth Century, p. 13
- ^ Waldman 2006, pp. 220–21.
- ^ David Stewart-Smith, "The Pennacook Indians and the New England frontier," p. 1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Stewart-Smith 1998.
- ^ Clark, Patricia Roberts (21 October 2009). Tribal Names of the Americas: Spelling Variants and Alternative Forms, Cross-Referenced. McFarland. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-7864-5169-2.
- ^ Or Accomentas, Accominticus, Accomintycus, Accomynticus.[6]
- ^ Stewart-Smith, David (1994). "Pennacook-Pawtucket Relations: The Cycles of Family Alliance on the Merrimack River in the 17th Century". Actes du Congres des Algonquinistes. 25. ISSN 0831-5671.
- ^ Caduto, Michael J. (2003). A Time Before New Hampshire: The Story of A Land and Native Peoples. Illustrated by Adelaide Tyrol. Hanover: University of New Hampshire. ISBN 1-58465-185-7. OCLC 50285128.
- ^ Вуд, Уильям. Южная часть Новой Англии, которая посадила в этом году, 1634 (карта) . Получено 2021-11-02 -через цифровое Содружество.
- ^ Перли, Сидни (1912). Индийская земля титулов округа Эссекс, штат Массачусетс . Салем, Массачусетс: Книжный и печатный клуб Essex - через интернет -архив.
- ^ Мерфри, Даниэль С. (2012). Коренная Америка: государственная историческая энциклопедия Санта-Барбара, Калифорния: ABC-Clio. П. 736. ISBN 9780313381270 .
- ^ День, Гордон (1981). Личность индейцев святого Франциска . Оттава: Национальные музеи Канады.
- ^ «Даррил Леру перевод утверждения Оданака» .
- ^ «Объединение самопровозглашенных групп Абенаки» .
- ^ "Раковина" . 9 июня 2019 года.
- ^ Леру, Дэррил (2019). Искаженное происхождение: белые претендуют на идентичность коренных народов . Виннипег, Манитоба: Университет Манитобы Пресс.
- ^ «Пеннакук Лодж, Орден Стрелы - Дух приключенческого совета» . Oapennacook.org . Получено 2016-01-12 .
Ссылки
[ редактировать ]- Кук, друг Шербурн (1976). Индийское население Новой Англии в семнадцатом веке . Беркли: Университет Калифорнийской прессы. ISBN 0-520-09553-7 .
- Джонсон, М. и Хук, Р. Родные племена Северной Америки , Compendium Publishing, 1992. ISBN 1-872004-03-2
- Стюарт-Смит, Дэвид (1998). Индейцы Пеннакук и граница Новой Англии, около 1604–1733 гг . Институт Союза - через ProQuest.
- Waldman, Carl (2006). Энциклопедия племен коренных американцев . Нью -Йорк: Книги по гамму. ISBN 978-1-43811010-3 .
Внешние ссылки
[ редактировать ]- История Пеннакук
- Сидис, Уильям. Племена и штаты , 1935