Чандигарх столичный регион
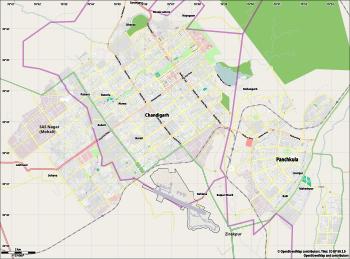
Столичный регион Чандигарх (CCR) или Метрополитен Чандигарх (CMR) - это район, который включает в себя Союза город Чандигарх и его соседние города Мохали , Харар , Зиракпур , Нью -Чандигарх (в Пенджабе) и Панчкула , Пинджор , Калк , Барвала (в Харине). Администрация Чандигарха, Управление по развитию районов Мохали (GMADA) и Управление городского развития Haryana (HUDA) являются различными властями, ответственными за развитие этого региона. [ 1 ] Бадди , промышленный город в соседнем Химачал -Прадеш, также рядом.
Экономика региона взаимозависима, поскольку область непрерывно населена, хотя и падает под разными государствами. Существует много движения людей и товаров ежедневно в пригороды и обратно, как большинство людей, работающих в Чандигархе, живут в пригороде, как Зиракпур . Местная индустрия находится на окраине, таких как Дерабасси, Лалру и Бадди. Подавляющее большинство квалифицированных работников в частном секторе поступают из соседних штатов, таких как Химачал -Прадеш, Пенджаб и Харьяна.
History
[edit]The Indian Ministry of Home Affairs asked the Chandigarh Administration in October 2011 to "coordinate with the Punjab and Haryana governments for working out the modalities" of a Regional Planning Board (RPB) for the Chandigarh Capital Region (CCR). The intention was to harmonize and improve facilities across the region and coordinate local administrations. Responsibilities of the RPB would include disaster management, health planning, biomedical waste and traffic management.[2][3]
The 'Master Plan 2031' submitted to the UT administrator in January 2013 included a proposal for a "inter-state regional plan for the Chandigarh Capital Region".[4] However the final plan confined itself to the UT boundary, and did not mention the proposed "Chandigarh Capital Region".[5] Instead, the plan expected responsibilities for the region to be coordinated between Punjab, Haryana and Chandigarh UT, and that the Chandigarh plan "with the GMADA Plan 2056 and the Haryana Development Plan should together arrive at a metropolitan plan".[6]
As of May 2019[update] the Chandigarh capital region along the lines of the National Capital Region remains an un-implemented concept.[7]
Definition
[edit]The cities, towns and areas that would be part of the Chandigarh Capital region have a total population of 3,358,653 and their city-wise populations are:
| Rank | City | Union territory / State | Population (2011)[8] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chandigarh | Chandigarh | 1,055,450 |
| 2 | Mohali | Punjab | 176,152 |
| 3 | Panchkula | Haryana | 211,175 |
| 4 | Kharar | Punjab | 109,323 |
| 5 | Zirakpur | Punjab | 95,553 |
Mohali District (Punjab) and Panchkula District ( Haryana ) are part of the CCR.Derabassi, Lalru, Banur and Kurali in Mohali district. Kalka, Pinjore, Barwala and Raipur Rani in the Panchkula district can be considered another town in Chandigarh Capital Region
Industry
[edit]Chandigarh IT Park is a technology park located within Chandigarh, with presence of companies like Airtel, Tech Mahindra and Infosys.
Mohali IT City is the infrastructure to facilitate information technology in the city. It spreads over 1700 acres developed by GMADA situated near Chandigarh International Airport. Infosys is given 50 Acres of land to develop state of art campus.
Quark has 40 Acres campus in Mohali for Quark software Inc. and other IT Companies like Emerson and Infosys.
Swaraj Tractors has Three Assembly Plants , one Engine Plant and one Foundry shop in Mohali District. CLAAS, German MNC has its Plant near Morinda in Mohali District. SML ISUZU has truck Plant near Ropar. Verka and Sun Pharma also have Plants in Mohali.
Dera Bassi - Lalru is another belt with mostly medium industry, this place has many spinning mills including the Nahar group. Bhushan Steel also has a presence here.
Panchkula IT Park is the state of art infrastructure to facilitate information technology in the city. It spreads over 74 acres developed by HSIIDC situated in sector 22. Bharat Electronics has a factory in Panchkula.
Hindustan Machine Tools has a tractor factory in Pinjore, while Associated Cement Companies has a cement factory in Pinjore.
The metropolitan areas of Chandigarh, Mohali, and Panchkula collectively form a tri-city.
This region is the zonal headquarters for a large number of banks, their offices are mainly in the "Bank Square" in sector 17 Chandigarh. This area also houses the regional office (usually covering Punjab, Northern Haryana, Himachal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir) for a lot of FMCG companies.
Healthcare infrastructure
[edit]The prominent hospitals in the region are
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar State Institute of Medical Sciences, Sector 56, Mohali
- Fortis Hospital, Sector 62, Mohali
- Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research PGIMER, Sector 12, Chandigarh
- Alchemist Hospital, Sector 21, Panchkula
- Command Hospital, Chandigarh, Chandimandir Cantonment
- General Hospital, Chandigarh, Sector 6, Panchkula
- Govt Medical College and Hospital (GMCH), Sector 32, Chandigarh
- Govt Medical Superspeciality Hospital (GMSH), Sector 16, Chandigarh
- Max Hospital, Sector 56, Mohali
- Ojas Hospital, Sector 26, Panchkula
- Paras Hospital, HSIIDC Park, Sector 22, Panchkula
Educational institutes
[edit]Schools
[edit]- Carmel Convent School
- Government Model Senior Secondary School, Sector-16, Chandigarh
- St. John's High School, Chandigarh
- Bhavan Vidyalaya, Chandigarh
- Shivalik Public School, Chandigarh
- St Soldier’s School, Panchkula
- Strawberry Fields School
- Vivek High School, Chandigarh
- Yadavindra Public School, Mohali
Colleges and universities
[edit]- Chandigarh
- Central Scientific Instruments Organisation (CSIO)
- Chandigarh College of Architecture (CCA)
- Chandigarh College of Engineering and Technology (CCET)
- Government Medical College and Hospital, Chandigarh (GMCH)
- Institute of Microbial Technology (IMTECH)
- National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology (NIEIT) Chandigarh campus
- Panjab University, government university
- Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER)
- Punjab Engineering College (PEC)
- Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory (|TBRL-DRDO Chandigarh)
- Mohali
- Army Institute of Law
- C-DAC Mohali campus
- Chandigarh University, private university
- Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Mohali (IISER Mohali)
- Indian School of Business (ISB) Mohali campus
- Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST)
- National Institutes of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER)
- Northern India Institute of Fashion Technology (NIIFT Mohali)
- Plaksha University, private university
- New Chandigarh
- Homi Bhabha Cancer Hospital & Research Centre (Tata Memorial Center) New Chandigarh campur
- Panchkula
- AIIMS AYUSH Panchkula campus
- National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) Panchkula campus
- Ropar
- Indian Institute of Technology Ropar (IIT, Ropar Indian)
- National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology (NIEIT) Ropar campus
Sports
[edit]- Inderjit Singh Bindra Stadium, Mohali
- Maharaja Yadavindra Singh International Cricket Stadium, New Chandigarh
- Mohali International Hockey Stadium Mohali
- Chandigarh Hockey Stadium Sec42 Chandigarh
- Tau Devi Lal Cricket Stadium, Sector 3 Panchkula
Transport
[edit]- Air transport
- Shaheed Bhagat Singh International Airport, near Aerocity in Mohali, has both domestic and international flights.
- Pinjore Aerodrome, no scheduled commercial flights as of July 2023.
- Железнодорожный транспорт - Метро в пригороде:
- Железнодорожный транспорт - поезда на дальние расстояния:
- Железнодорожный вокзал Чандигарх
- Железнодорожный вокзал Чанди Мандир , в городе Панчкула
- Железнодорожный вокзал Калка , отправная точка Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО Калка -Шимла Железнодорожная и северная термин линии Дели -Калка .
- Железнодорожный вокзал Мохали
- Дорожный транспорт: для автобусных терминалов (ISBT) следовало за межстатровыми автобусами:
Ссылки
[ редактировать ]- ^ «Остерегайтесь! Изменение в статусе города разрушит его уникальность» . Трибуна . 23 июля 2018 года . Получено 3 января 2019 года .
- ^ «Палубы очищены для региона Капитала Чандигарх» . The Times of India . Архивировано из оригинала 7 октября 2011 года.
- ^ «Регион Чандигарх получает кивок» . Daily Post India . Чандигарх. 24 января 2012 года. Архивировано с оригинала 8 апреля 2013 года.
- ^ «Регион Чандигарх Столица включен в генеральный план '31» . The Times of India . Архивировано из оригинала 11 апреля 2013 года.
- ^ «Генеральный план Чандигарх 2031, преамбула» (PDF) . Администрация Чандигарха. п. 9
- ^ «Генеральный план Чандигарх 2031, региональный контекст» (PDF) . Администрация Чандигарха. п. 23
- ^ Ядав, Дипак (5 мая 2015 г.). «Первые шаги, чтобы сделать Тричитин одним» . The Times of India .
- ^ «Индия: крупные агломерации» . .citypopulation.de . Получено 14 декабря 2014 года .
Внешние ссылки
[ редактировать ]30 ° 38′52 ″ N 76 ° 27′14 ″ E / 30,6476695 ° N 76,4539836 ° E
