Банейт Северина
| Банейт Северина | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Банейт Королевства Венгрия | |||||||||
| 1228–1526 | |||||||||
 Карта Северинской Бановины в 13 -м веке | |||||||||
| История | |||||||||
• Established | 1228 | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 1526 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Romania | ||||||||
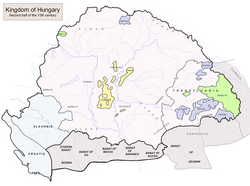

The Banate of Severin or Banate of Szörény ( Hungarian : Szörényi bánság ; Romanian : Banatul Severinului ; Latin : Banatus Zewrinensis ; Bulgarian : Северинско банство , Severinsko banstvo ; Serbian : Северинска бановина , Severinska banovina ) was a Hungarian political, military and administrative unit with a special role in the initially anti- Bulgarian , latterly anti- Ottoman defensive system of the medieval Kingdom of Hungary . It was founded by Prince Béla in 1228.
Территория
[ редактировать ]Банат Северина был маршем (или пограничной провинцией) средневекового королевства Венгрии между Нижним Дунаем и рекой Олт (в современной Оления в Румынии). [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] Хартия гранта, выпущенная 2 июня 1247 года для рыцарских госпиталеров , упомянул OLT как его восточную границу. [ 1 ] Рыцари получили «землю Северина» (Terra de Zeurino) , [ 4 ] наряду с близлежащими горами, от Белы IV Венгрии . [ 1 ] [ 5 ] Король описал тот же регион, что и «пустынная и депопулированная» земля в письме к папе Григорию IX 7 июня 1238 года. [6] Modern scholars assume that either the Hungarian conquest of the territory or confrontations between Bulgaria and Hungary had forced the local population to flee[clarification needed].[6] Historian László Makkai says, the population began to increase by the end of the 1230s, because Béla requested the pope to appoint a bishop for Severin.[7]
The 1247 charter of grant also mentioned that "Cumania" bordered the Land of Severin from the east.[8] The same diploma listed two Vlach (or Romanian) political units—the kenezatus of John and Farcaș—which were subjected to the Hospitallers on this occasion.[9][1][2] A third kenezatus, which was ruled by Voivode Litovoi, was not included in the grant, but it was left to the Vlachs "as they had held it".[8][2][10] However, Béla gave the Hospitallers half of the royal revenues collected in Litovoi's land, with the exception of the revenues from the "Land of Hátszeg" (now Țara Hațegului in Romania).[11][12] Alexandru Madgearu says, the diploma shows that Litovoi's kenezatus bordered the Land of Severin to the north, thus the banate must have only included southern Oltenia in the middle of the 13th century.[3] The kenezatus of Voivode Seneslau, which was located to the east of the Olt, was fully excluded from the grant.[9]
The bans initially had their seat at the fortress of Szörény (now Drobeta-Turnu Severin in Romania).[13][14] After Szörény was lost in the late 13th century, the fort of Miháld (now Mehadia in Romania) was the center of the province.[14] In addition to Miháld, the banate included Orsova (now Orșova in Romania) and the Romanian districts along the upper course of the Temes (Timiș) river.[13][14]
History
[edit]Kaloyan of Bulgaria occupied the region between the rivers Cerna and the Olt around 1199.[3] The Kingdom of Hungary was also expanding southwards over the Carpathian Mountains in the early 13th century, which gave rise to conflicts between the two countries.[14][15] The Cuman tribes dwelling to the east of the Olt as far as the river Siret agreed to pay a yearly tribute to the kings of Hungary in early 1227.[13] The Hungarians captured the Bulgarian fortress of Severin during a military campaign against Bulgaria in 1231.[16]
In 1330 the Banate was roughly conquered by Basarab the First, and most of it remained in the jurisdiction of Wallachia for the next centuries.
After the 1526 Battle of Mohács, the Banate of Severin was divided. The south-eastern part (eastwards from Varcsaró - Vârciorova, today part of Bolvașnița) came under the jurisdiction of Wallachian princes and in the north-western part (westwards from Orsova - present-day Orșova - inclusive) was gradually reorganized into the Banate of Lugos and Karánsebes.
Bans of Severin
[edit]This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (January 2018) |
List of bans
[edit]Thirteenth century
[edit]| Term | Incumbent | Monarch | Notes | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 1226–c. 1232 | Buzád Hahót | Andrew II | He styled himself "former ban" in 1233. His close relationship with Andrew II's son, Béla, Duke of Transylvania, suggests that he was the ban of Severin (instead of being the ban of Slavonia). | [17] |
| c. 1233 | Lucas | Andrew II | [18] | |
| 1235 | Pous Csák | Béla IV | Also Master of the treasury and ispán (or head) of Bács County | [18] |
| c. 1240 | Osl Osl | Béla IV | [18] | |
| c. 1243 | Stephen Csák | Béla IV | [18] | |
| c. 1260 | Lawrence, son of Kemény | Béla IV | First rule. | [18] |
| c. 1262 | Stephen | Béla IV | He is only mentioned in a non-authentic charter. | [18] |
| c. 1263 | Lawrence | Stephen V (king junior) | Also Master of the treasury of Stephen V. | [18] |
| c. 1268 | Alexander, son of Drugh | Stephen V (king junior) | [18] | |
| c. 1268 | Ugrin Csák | Stephen V (king junior) | First rule. | [18] |
| c. 1270 | Lawrence, son of Kemény | Stephen V | Second rule. Also ispán of Doboka County. | [19] |
| c. 1270 | Panyit Miskolc | Stephen V | [19] | |
| 1271–1272 | Lawrence, son of Kemény | Stephen V | Third rule. Also ispán of Doboka County. | [19] |
| 1272 | Albert Ákos | Stephen V | [19] | |
| 1272–1274 | Paul Gutkeled | Ladislaus IV | First rule. Also ispán of Valkó and Doboka Counties. | [20] |
| 1274–1275 | Ugrin Csák | Ladislaus IV | Second rule. | [19] |
| 1275 | Paul Gutkeled | Ladislaus IV | Second rule. | [20] |
| 1275–1276 | Mikod Kökényesradnót | Ladislaus IV | [19] | |
| 1276 | Ugrin Csák | Ladislaus IV | Third rule. | [19] |
| 1277–1278 | Paul Gutkeled (?) | Ladislaus IV | He is only mentioned in non-authentic charters. Third rule. | [20] |
| 1279 | Lawrence, son of Lawrence | Ladislaus IV | First rule. | [19] |
| 1291 | Lawrence, son of Lawrence | Andrew III | Second rule, but he may have continuously held the office from 1279 to 1291 | [19] |
Fourteenth century
[edit]| Term | Incumbent | Monarch | Notes | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1335–1341 | Denis Szécsi | Charles I | Also master of the stewards. | [21] |
| 1342–1349 | Stephen Losonci | Charles I, Louis I | [21] | |
| 1350–1355 | Nicholas Szécsi | Louis I | Also ispán of Keve and Krassó Counties. | [21] |
| 1355–1359 | Denis Lackfi | Louis I | Also master of the horse, and ispán of Keve and Krassó Counties. | [21] |
| 1359–1379 | Vacant. | [21] | ||
| 1375–1376 | John Treutel | Louis I | [21] | |
| 1376–1387 | Vacant. | [21] |
- 1299–1307 András Tárnok
- 1308–1313 András Tárnok and Márton Tárnok
- 1314–1318 Domokos Csornai
- 1319–1323 László Rátholti
- 1323–1329 Dénes Szécsi
- 1324 Pál
- 1330–1341 Dénes Szécsi
- 1342–1349 István Losonci
- 1350–1355 Miklós Szécsi
- 1355–1359 Dénes Lackfi
- 1359–1375 vacant
- 1376 János Treutel
- 1376–1387 vacant
- 1387 László Losonci Jr.
- 1387–1388 István Losonci
- 1388–1390 János Kaplai-Serkei
- 1390–1391 Miklós Perényi
- 1392 Szemere Gerebenci
- 1392–1393 Bebek Detre
- 1393 Frank Szécsi
- 1393–1397 vacant
- 1397 Lukács of Oszkola
- 1393–1408 vacant
- 1408–1409 Pipo of Ozora
- 1409 vacant
- 1410 Lőrinc, son of Majos
- 1410–1428 vacant
- 1428 Imre Marcali
- 1430–1435 Miklós Redwitz
- 1429–1435 vacant
- 1435 László Hagymás of Beregszó and János Dancs of Macedonia
- 1436–1439 Franko Talovac
- 1439–1446 John Hunyadi, Ban of Severin
- 1445–1446 Miklós Újlaki
- 1447–1454 Mihály Csornai
- 1449 Balázs Csornai
- 1452–1454 Péter Dancs of Sebes
- 1455-57 vacant
- 1458 Vlad and Gergely Bethlen
- 1459–1460 vacant
- 1460 László Dóczi
- 1462–1463 Nicholas of Ilok
- 1464–1466 vacant
- 1466 János Pongrácz of Dengeleg
- 1467 vacant
- 1467 István and Mihály de Muthnoki
- 1468–1471 vacant
- 1471–1478 Imre Hédervári
- 1478 János Erdő and Domokos Bethlen
- 1478 vacant
- 1479 Ambrus Török and György Szenthelsebethi
- 1479 Bertalan Pathócsy
- 1480–1483 Bertalan Pathócsy and Ferenc Haraszti
- 1483–1489 Ferenc Haraszti and András Szokoly
- 1490 Imre Ozorai
- 1491 Imre Ozorai and Dánfy András of Doboz
- 1491–1492 Ferenc Haraszti and Dánfy András of Doboz
- 1492 Móré Fülöp Csulai
- 1492–1494 Móré György Csulai and Ferenc Balassa
- 1495–1501 Tárnok Péter Macskási and Jakab Gerlisthey
- 1501 Jakab Gerlisthey and Bélai Barnabás
- 1502 Jakab Gerlisthey and Tárnok Péter Macskási
- 1503 Bélai Barnabás
- 1503 Jakab Gerlisthey
- 1504–1508 Jakab Gerlisthey and Barnabás Bélai
- 1508–1513 Mihály Paksi and Barnabás Bélai
- 1514 Barnabás Bélai and János Szapolyai
- 1515–1516 Miklós Hagymási of Berekszó
- 1517–1518 vacant
- 1519 Bélai Barnabás
- 1520–1521 Miklós Gerlisthey
- 1522–1523 János Vitéz Kállay
- 1524–1526 János Vitéz Kállay and János Szapolyai
- 1526–1540 Under the rule of Lugos and Karánsebes Bans
- 1526–1860 Under Ottoman occupation
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Papacostea 1998, p. 230.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Curta 2006, p. 407.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Madgearu 2017, p. 207.
- ^ Pop 2013, p. 338.
- ^ Makkai 1994b, pp. 196–197.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Madgearu 2017, p. 208.
- ^ Makkai, László (2001–2002), The Cumanian Country and the Province of Severin, Institute of History of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Hungarian Research Institute of Canada, Atlantic Research and Publications, retrieved 12 April 2017
- ^ Jump up to: a b Vásáry 2005, p. 146.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Makkai 1994b, p. 197.
- ^ Papacostea 1998, p. 231.
- ^ Curta 2006, pp. 407–408.
- ^ Pop 2013, p. 337.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Engel 2001, p. 95.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Makkai 1994a, p. 657.
- ^ Curta 2006, pp. 405–406.
- ^ Madgearu 2017, p. 206.
- ^ Zsoldos 2011, pp. 49, 291–292.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i Zsoldos 2011, p. 49.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i Zsoldos 2011, p. 50.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в Msoldos 2011 , с. 50, 342.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в дюймовый и фон глин Engel 1996 , p. 32
Библиография
[ редактировать ]- Керта, Флорин (2006). Юго-восточная Европа в средневековье, 500-1250 . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-0-521-89452-4 .
- Энгель, Пал (1996). Светская архонтология Венгрии, 1301-1457, И. [светская архонтология Венгрии, 1301-1457, том I] (у Венгрии). История, Институт истории венгерской академии наук. ISBN 963-8312-44-0 .
- Энгель, Пал (2001). Царство Святого Стефана: история средневековой Венгрии, 895–1526 . IB Tauris Publishers. ISBN 1-86064-061-3 .
- Madgearu, Александру (2017). Асаниды: политическая и военная история второй болгарской империи, 1185–1280 . Брилль ISBN 978-9-004-32501-2 .
- Makkai, László (1994a). «Szörényi Banat [Banate of Severin]». В Кристо, Джула; Энгель, Павел; Makk, Ferenc (Eds.). Ранняя венгерская историческая лексика (9-14 века) [Энциклопедия ранней венгерской истории (9-14 веков)] (у венгерских). Академический издатель. п. 657. ISBN 963-05-6722-9 .
- Makkai, László (1994b). «Появление поместья (1172-1526)». В Кёпечи, Бела; Барта, Габор; Bóna, István; Маккай, Ласло; Szász, Zoltán; Борус, Джудит (ред.). История Трансильвании . Академический издатель. стр. 178-243. ISBN 963-05-6703-2 .
- Papacostea, șerban (1998). Между крестовым походом и монгольской империей . Центр транссильванских исследований, Румынский культурный фонд. ISBN 973-577-186-1 .
- Поп, Иоан-Авел (2013). «De Manibus valachorum scismaticorum ...»: румын и власть в средневековом царстве Венгрии, тринадцатый и четырнадцатый века . Питер Лэнд издание. ISBN 978-3-631-64866-7 .
- Vásáry, István (2005). Cumans and Tatars: восточные военные в дотоманских Балканах, 1185-1365 . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 0-521-83756-1 .
- Zsoldos, Attila (2011). Светская архонтология Венгрии, 1000-1301 [Светская архонтология Венгрии, 1000-1301] (на Венгрии). История, Институт истории венгерской академии наук. ISBN 978-963-9627-38-3 .
Дальнейшее чтение
[ редактировать ]- Hațegan I., Тевтонские рыцари в Банате Северина (1429-1435), «Тибискус-гистори», Музей Баната, Тимияра, 1978, с. 191-196.
- http://mek.niif.hu/02100/02114/html/316.html История Трансильвании
Внешние ссылки
[ редактировать ]