Сакия


Сакия арабский или сакия ( ) : ساقية , также пишется сакия или сакья ) - это механическое устройство жизни. называется колесом , таблевой , резат также персидским Это [ 1 ] Он похож на функцию совка , в котором используются ведра, банки или сочки, прикрепленные либо непосредственно к вертикальному колесу, либо к бесконечному ремню, активируемому таким колесом. Вертикальное колесо само по себе прикреплено приводным валом к горизонтальному колесу, которое традиционно приводится в движение мощностью животных ( волы , ослы и т. Д.), Поскольку оно не использует силу проточной воды , сакия отличается от нории. и любой другой тип водяного колеса.
Сакия все еще используется в Индии , Египте и других частях Ближнего Востока , а также на полуостровах иберийском полуострове и на Балеарских островах . Возможно, это было изобретено в Птолемейском королевстве Египта, Ирана , Куша или Индии . Сакия в основном использовался для орошения, но не исключительно, как показывает пример Qusayr 'Amra , где он использовался, по крайней мере, частично для обеспечения воды для королевской бани. [ 2 ]
Name and meaning
[ редактировать ]Etymology and related meanings
[edit]The Arabic word saqiya (Arabic: ساقية) is derived from the root verb saqa (Arabic: سقى), meaning to "give to drink" or "make (someone/something) drink".[3] From this, the word saqiya (often transliterated as seguia in Morocco or the Maghreb[4][5][6]) has the sense of "one that gives water" or "irrigator". Its general meaning is to denote a water channel for irrigation or for city water supplies, but by extension it applies to a device which provides water for such irrigation.[3][7] Likewise, Spanish acequia, derived from the same word, is used to denote an irrigation canal or water channel in Spain.[8][9] In the Maghreb and Morocco, the related word saqqaya (Arabic: سقاية) also denotes a public fountain where residents could take water (similar in function to a sabil).[10][11] The English term Persian wheel is first attested in the 17th century (but in the earliest case for a water-driven wheel).[12]
Saqiya versus noria
[edit]The term saqiyah or saqiya is the usual term for water-raising devices powered by animals.[13] The term noria is commonly used for devices which use the power of moving water to turn the wheel instead.[14] Other types of similar devices are grouped under the name of chain pumps. A noria in contrast uses the water power obtained from the flow of a river. The noria consists of a large undershot water-wheel whose rim is made up of a series of containers which lift water from the river to an aqueduct at the top of the wheel.[14][15] Some famous examples are the norias of Hama in Syria or the Albolafia noria in Cordoba, Spain.[16]
However, the names of traditional water-raising devices used in the Middle East, India, Spain and other areas are often used loosely and overlappingly, or vary depending on region. Al-Jazari's famous book on mechanical devices, for example, groups the water-driven wheel and several other types of water-lifting devices under the general term saqiya.[17][18] In Spain, by contrast, the term noria is used for both types of wheels, whether powered by animals or water current.[14]
Description
[edit]With buckets directly on the wheel
[edit]The saqiya is a large hollow wheel, traditionally made of wood. One type has its clay pots or buckets attached directly to the periphery of the wheel, which limits the depth it can scoop water from to less than half its diameter. The modern version is normally made of galvanized sheet steel and consists of a series of scoops. The modern type dispenses the water near the hub rather than from the top, the opposite of the traditional types. It is a method of irrigation frequently met within various parts of the Indian subcontinent.
Saqiya wheels range in diameter from two to five metres. Though traditionally driven by draught animals, they are now increasingly attached to an engine. While animal-driven saqiyas can rotate at 2–4 rpm, motorised ones can make as much as 8–15 rpm. The improved modern versions are also known as zawaffa and jhallan.

With buckets attached to endless belt
[edit]The historical Middle-Eastern device known in Arabic as saqiya usually had its buckets attached to a double chain, creating a so-called "pot garland". This allowed scooping water out of a much deeper well.
An animal-driven saqiya can raise water from 10 to 20 metres depth, and is thus considerably more efficient than a swape[clarification needed] or shadoof, as it is known in Arabic, which can only pump water from 3 metres.
Types
[edit]There are two main types of saqiya. One type consists of a vertical wheel which is slung with an endless belt or chain of buckets. The buckets hang down into a well which may be up to 8 m (26 ft) deep. The second type has the buckets or other water containers attached directly to the vertical wheel.
The most primitive saqiyas are driven by donkeys, mules, or oxen. The animal turns a horizontal wheel, which is engaged with the vertical wheel and so causes it to turn. This causes the buckets of the first type to circulate and lift up water from a deeper well, or with the second type, it causes the vertical wheel to rotate and scoop up water from a less deep well.
In terms of propulsion, there is a different, much rarer type of saqiya which uses the same general technique, but it is driven by wind. In Spanish an animal-driven saqiya is named aceña, with the exception of the Cartagena area, where it is called a noria de sangre, or "waterwheel of blood". The wind-driven saqiyas there, are virtually identical in appearance with the local grinding mills.
History
[edit]Kingdom of Kush
[edit]
The saqiya was known in the Kingdom of Kush as Kolē.[19] The Ancient Nubians developed the saqiya to improve irrigation during the Meroitic period. The introduction of this machine had a decisive influence on agriculture as this wheel lifted water 3 to 8 metres with much less labour force and time than the Shaduf, which was the previous irrigation device in the Kingdom. The Shaduf relied on human energy while the saqiya was driven by buffalos or other animals.[19]
India
[edit]
The sāqiyah might, according to Ananda Coomaraswamy, have been invented in India, where the earliest reference to it is found in the Panchatantra (c. 3rd century BCE), where it was known as an araghaṭṭa;[20] which is a combination or the words ara (speedy or a spoked[wheel]) and ghaṭṭa "pot"[21] in Sanskrit. That device was either used like a sāqiyah, to lift water from a well while being powered by oxen or people, or it was used to irrigate fields when it was powered in the manner of a water-wheel by being placed in a stream or large irrigation channel. In the latter case we usually speak of a noria as opposed to a sāqiyah.[22]
Egypt
[edit]Paddle-driven water-lifting wheels had appeared in ancient Egypt by the 4th century BCE.[23] According to John Peter Oleson, both the compartmented wheel and the hydraulic noria appeared in Egypt by the 4th century BCE, with the saqiya being invented there a century later. This is supported by archeological finds at Faiyum, where the oldest archeological evidence of a water wheel has been found, in the form of a saqiya dating back to the 3rd century BCE. A papyrus dating to the 2nd century BCE also found in Faiyum mentions a water wheel used for irrigation, a 2nd-century BC fresco found at Alexandria depicts a compartmented saqiya, and the writings of Callixenus of Rhodes mention the use of a saqiya in the Ptolemaic Kingdom during the reign of Ptolemy IV Philopator in the late 3rd century BCE.[24]
Early Mediterranean evidence of a saqiya is from a tomb painting in Ptolemaic Egypt that dates to the 2nd century BCE. It shows a pair of yoked oxen driving a compartmented waterwheel. The saqiya gear system is already shown fully developed to the point that "modern Egyptian devices are virtually identical".[25] It is assumed that the scientists of the Musaeum, at the time the most active Greek research center, may have been involved in its implementation.[26] An episode from Caesar's Civil War in 48 BC tells of how Caesar's enemies employed geared waterwheels to pour sea water from elevated places on the position of the trapped Romans.[27]
Roman Empire
[edit]Philo of Byzantium wrote of such a device in the 2nd century B.C.;[28] the historian Vitruvius mentioned them around 30 B.C.; remains of tread wheel driven, bucket chains, dating from the 2nd century B.C., have been found in baths at Pompeii,[29] and Costa, Italy; fragments of the buckets and a lead pipe, from a crank handle operated, chain driven, bilge pump, were found one of the 1st century A.D. Nemi ships, of Lake Nemi;[30][31][32] and a preserved 2nd century A.D. example, used to raise water from a well, to an aquifer in London, has also been unearthed.[33]
Talmudic sources
[edit]The term used by Talmudic sources for a saqiya is 'antelayyā-wheel.[34]
Medieval Islamic realm
[edit]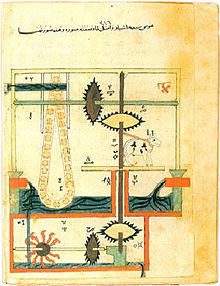
A manuscript by Ismail al-Jazari featured an intricate device based on a saqiya, powered in part by the pull of an ox walking on the roof of an upper-level reservoir, but also by water falling onto the spoon-shaped pallets of a water wheel placed in a lower-level reservoir.[35]
Complex saqiyas consisting of more than 200 separate components were used extensively by Muslim inventors and engineers in the medieval Islamic world.[36] The mechanical flywheel, used to smooth out the delivery of power from a driving device to a driven machine and, essentially, to allow lifting water from far greater depths (up to 200 metres), was employed by ibn Bassal (fl. 1038–1075), of al-Andalus.[37]
The first known use of a crank in a saqiya was featured in another one of al-Jazari's machines.[38][verification needed] The concept of minimising the intermittence is also first implied in one of al-Jazari's saqiya devices, which was to maximise the efficiency of the saqiya.[38] Al-Jazari also constructed a water-raising device that was run by hydropower, though the Chinese had been using hydropower for the same purpose before him. Animal-powered saqiyas and water-powered norias similar to the ones he described have been supplying water in Damascus since the 13th century,[39] and were in everyday use throughout the medieval Islamic world.[38]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ "Water lifting devices". Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ "Qusayr 'Amra : Site Management Plan" (PDF). Whc.unesco.org. January 2014. Retrieved 2016-05-28.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Wehr, Hans (1979). A Dictionary of Modern Written Arabic. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. p. 485. ISBN 9783447020022.
- ^ El Faiz, Mohammed; Ruf, Thierry (2010). "An Introduction to the Khettara in Morocco: Two Contrasting Cases". Water and Sustainability in Arid Regions: Bridging the Gap Between Physical and Social Sciences. Springer. pp. 151–163. ISBN 978-90-481-2776-4.
- ^ Ait Khandouch, Mohamed (2000). "L'eau, facteur limitant de l'espace oasien. Le cas des oasis de Skoura et Amkchoud au sud du Maroc". Bulletin de l'Association de géographes français. 77 (1): 69–77.
- ^ Madani, Tariq (1999). "Le réseau hydraulique de la ville de Fès". Archéologie islamique. 8–9: 119–142.
- ^ Декер, Майкл (2008). «Вода в вино: торговля и технологии в поздней древности» . Технология в переходе AD 300-650 . Брилль п. 87. ISBN 9789047433040 .
- ^ Блум, Джонатан М. (2020). Архитектура Исламского Запада: Северная Африка и Иберийский полуостров, 700-1800 . Издательство Йельского университета. п. 164. ISBN 9780300218701 .
- ^ «Определение ацекии» . www.merriam-webster.com . Получено 2021-03-03 .
- ^ Эль Хаммар, Abdeltif (2005). «Мечети и ораторские острова Мекны (девятый-18 век): религиозная география, архитектура и проблема Qibla». Докторская диссертация. Lumière-Lyon University 2.
- ^ Ферхат, Халима (2008). «Маринид Фес: Зенит и признаки упадка» . Город в исламском мире . Брилль С. 247–267. ISBN 9789004162402 .
- ^ Блит, Уолтер (1653). Английский показатель улучшился, или, Svrvey of Hvsbandry Svrveyed, обнаружив необычность всех земель, которые могут быть под двойной и высокой, ... Глава XIX и т. Д.
- ^ Глик, Томас Ф. (2010). "Сакия". В Бьорке Роберт Э. (ред.). Оксфордский словарь средневековья . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 9780198662624 .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в Глик, Томас Ф. (2010). "Нория". В Бьорке Роберт Э. (ред.). Оксфордский словарь средневековья . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 9780198662624 .
- ^ Burke III, Edmund (2009). «Ислам в центре: технологические комплексы и корни современности». Журнал мировой истории . 20 (2): 165–186. doi : 10.1353/jwh.0.0045 . S2CID 143484233 .
- ^ Миранда, Адриана (2007). Архитектура воды в землях Сирии: водные колеса . L'Erma di Bot Cutters. ISBN 978-88-8265-433-7 .
- ^ Casulleras, Josep (2014). «Механика и инженерия». В Калине, Ибрагим (ред.). Оксфордская энциклопедия философии, науки и технологий в исламе . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 9780199812578 .
- ^ Даллал, Ахмад; Шефер-Моссенсон, Мири (2003). «Наука, медицина и технология». В Эспозито, Джон Л. (ред.). Оксфордская история ислама . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 9780195125580 .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Г. Мохтар (1981-01-01). Древние цивилизации Африки . ЮНЕСКО. Международный научный комитет по разработке общей истории Африки. п. 309. ISBN 9780435948054 Полем Получено 2012-06-19 -через books.google.com.
- ^ «Персидское колесо в Индии» . Base.dph.info . Получено 2016-05-28 .
- ^ Клаус Глашофф. «Санскритский словарь для разговорного санскрита» . Spokensanskrit.de . Получено 2016-05-28 .
- ^ «Персидское колесо пересмотрено- Арагатта | Сбор дождевой воды» . Rainwaterharvesting.wordpress.com. 23 февраля 2008 года . Получено 2016-05-28 .
- ^ Орджан Викандер (2008). «Глава 6: Источники энергии и эксплуатации власти». В Джоне Питере Олесон (ред.). Оксфордский справочник по технике и технологии в классическом мире . Издательство Оксфордского университета . С. 141–2. ISBN 978-0-19-518731-1 .
- ^ Адриана де Миранда (2007). Архитектура воды в землях Сирии: водные колеса . L'erma di Bretschneider. С. 38–9. ISBN 978-88-8265-433-7 .
- ^ Butson : стр. 234, 270
- ^ Butson : стр. 271f.
- ^ Butson 2000 , 271
- ^ «Цепный насос Филона ( Мангани )» . Kotsanas.com . Получено 2021-11-03 .
- ^ Развитие гимназии и грако-римских городских пейзажей . Ульрих Мания, Моника Трюмпер. Берлин. 2018. ISBN 978-3-9819685-0-7 Полем OCLC 1100399313 .
{{cite book}}: CS1 Maint: местоположение отсутствует издатель ( ссылка ) CS1 Maint: Другие ( ссылка ) - ^ Робинсон, Дамиан. Морская археология и древняя атмосфера в Средиземноморье . Оксфордский центр морской археологии монографии. С. 43–44.
- ^ Олесон, Джон Петр (1984-06-30). Греческие и римские механические устройства, подтягивающие воды: история технологии . Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-90-277-1693-4 .
- ^ Нидхэм, том 4, часть 2, с. 109
- ^ Блэр, Ян; Испания, Роберт; Тейлор, Тони (2019-04-08), Bouet, Alain (ed.), «Технология римских цепочек ковша 1-го и 2 века из Лондона: от раскопок до реконструкции» , Aquam in Altum Expres Élévatrices d'aeau dans the antiquité , antiqua scripta, pessac: ausonius édizions, pp. 85–114, ISBN 978-2-35613-295-6 Получено 2021-11-03
- ^ Роберт Р. Стиглиц (2006). "Тел Таниним" . Библия и интерпретация . Получено 16 сентября 2015 года .
- ^ Нидхэм, том 4, часть 2, с. 353.
- ^ Дональд Хилл (1996), «Инжиниринг», в Рошди Раш, Энциклопедия истории арабской науки , том. 3, с. 751–795 [771].
- ^ «Маховик» (PDF) . themechanic.weebly.com .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в Дональд Хилл , «Инжиниринг», с. 776, в Roshdi Rashed, ed., Энциклопедия истории арабской науки , Vol. 2, с. 751–795, Routledge , London и New York
- ^ «История науки и техники в исламе» . Архивировано из оригинала 8 февраля 2014 года . Получено 16 февраля 2015 года .
Ссылки
[ редактировать ]- Oleson, John Peter (2000), «Вода, в Wikander, örjan (ed.), Справочник по древней водной технологии , технологии и изменениям в истории, вып. 2, Лейден: Брилл, с. 217–302, ISBN 90-04-11123-9
Дальнейшее чтение
[ редактировать ]- Fraenkel, P., (1990) «Устройства для накатывания воды: справочник для пользователей и выборов» промежуточных технологических публикаций .
- Моленаар А., (1956) «Устройства для подъема воды для орошения . »