Тип II Supernova

типа II Supernova или Snii [ 1 ] (множественное число: сверхновые ) возникает в результате быстрого коллапса и насильственного взрыва массивной звезды . Звезда должна иметь как минимум восемь раз, но не более 40-50 раз, масса солнца ( M ☉ ) для этого типа взрыва. [ 2 ] Сверхновые типа II отличаются от других типов сверхновых с присутствием водорода в их спектрах . Они обычно наблюдаются в спиральных руках галактик , и в областях H II но не в эллиптических галактиках ; Они, как правило, состоят из старых звезд с низкой массой, с немногими молодыми, очень массивными звездами, необходимыми для выздоровления сверхновой.
Звезды генерируют энергию путем ядерного слияния элементов. В отличие от солнца, массивные звезды обладают массой, необходимой для объединения элементов, которые имеют атомную массу, превышающую водород и гелий, хотя и при все более высоких температурах и давления , вызывая соответствующий более короткий звездный срок службы. Давление дегенерации электронов и энергия, генерируемая этими реакциями слияния, достаточны, чтобы противостоять силе тяжести и предотвратить разрушение звезды, сохраняя звездное равновесие. Звездные слияния все более высокие элементы массы, начиная с водорода , а затем гелия , продвигаясь через периодическую таблицу, пока ядро железа и никеля не будет произведено . Слияние железа или никеля не дает чистой выходной энергии, поэтому дальнейшее слияние не может произойти, оставляя инерцию никеля -железа. Из -за отсутствия выходной энергии, создающего внешнее тепловое давление, ядро сжимается из -за силы тяжести до тех пор, пока не может быть в значительной степени поддержать давление вырождения электронов.
When the compacted mass of the inert core exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit of about 1.4 M☉, electron degeneracy is no longer sufficient to counter the gravitational compression. A cataclysmic implosion of the core takes place within seconds. Without the support of the now-imploded inner core, the outer core collapses inwards under gravity and reaches a velocity of up to 23% of the speed of light, and the sudden compression increases the temperature of the inner core to up to 100 billion kelvins. Neutrons and neutrinos are formed via reversed beta-decay, releasing about 1046 joules (100 foe) in a ten-second burst. The collapse of the inner core is halted by the repulsive nuclear force and neutron degeneracy, causing the implosion to rebound and bounce outward. The energy of this expanding shock wave is sufficient to disrupt the overlying stellar material and accelerate it to escape velocity, forming a supernova explosion. The shock wave and extremely high temperature and pressure rapidly dissipate but are present for long enough to allow for a brief period during which the production of elements heavier than iron occurs.[3] Depending on initial mass of the star, the remnants of the core form a neutron star or a black hole. Because of the underlying mechanism, the resulting supernova is also described as a core-collapse supernova.
There exist several categories of Type II supernova explosions, which are categorized based on the resulting light curve—a graph of luminosity versus time—following the explosion. Type II-L supernovae show a steady (linear) decline of the light curve following the explosion, whereas Type II-P display a period of slower decline (a plateau) in their light curve followed by a normal decay. Type Ib and Ic supernovae are a type of core-collapse supernova for a massive star that has shed its outer envelope of hydrogen and (for Type Ic) helium. As a result, they appear to be lacking in these elements.
Formation
[edit]
Stars far more massive than the sun evolve in complex ways. In the core of the star, hydrogen is fused into helium, releasing thermal energy that heats the star's core and provides outward pressure that supports the star's layers against collapse – a situation known as stellar or hydrostatic equilibrium. The helium produced in the core accumulates there. Temperatures in the core are not yet high enough to cause it to fuse. Eventually, as the hydrogen at the core is exhausted, fusion starts to slow down, and gravity causes the core to contract. This contraction raises the temperature high enough to allow a shorter phase of helium fusion, which produces carbon and oxygen, and accounts for less than 10% of the star's total lifetime.
In stars of less than eight solar masses, the carbon produced by helium fusion does not fuse, and the star gradually cools to become a white dwarf.[4][5] If they accumulate more mass from another star, or some other source, they may become Type Ia supernovae. But a much larger star is massive enough to continue fusion beyond this point.
The cores of these massive stars directly create temperatures and pressures needed to cause the carbon in the core to begin to fuse when the star contracts at the end of the helium-burning stage. The core gradually becomes layered like an onion, as progressively heavier atomic nuclei build up at the center, with an outermost layer of hydrogen gas, surrounding a layer of hydrogen fusing into helium, surrounding a layer of helium fusing into carbon via the triple-alpha process, surrounding layers that fuse to progressively heavier elements. As a star this massive evolves, it undergoes repeated stages where fusion in the core stops, and the core collapses until the pressure and temperature are sufficient to begin the next stage of fusion, reigniting to halt collapse.[4][5]
Core-burning nuclear fusion stages for a 25-solar mass star Process Main fuel Main products 25 M☉ star[6] Temperature
(K)Density
(g/cm3)Duration hydrogen burning hydrogen helium 7×107 10 107 years triple-alpha process helium carbon, oxygen 2×108 2000 106 years carbon-burning process carbon Ne, Na, Mg, Al 8×108 106 1000 years neon-burning process neon O, Mg 1.6×109 107 3 years oxygen-burning process oxygen Si, S, Ar, Ca 1.8×109 107 0.3 years silicon-burning process silicon nickel (decays into iron) 2.5×109 108 5 days
Core collapse
[edit]The factor limiting this process is the amount of energy that is released through fusion, which is dependent on the binding energy that holds together these atomic nuclei. Each additional step produces progressively heavier nuclei, which release progressively less energy when fusing. In addition, from carbon-burning onwards, energy loss via neutrino production becomes significant, leading to a higher rate of reaction than would otherwise take place.[7] This continues until nickel-56 is produced, which decays radioactively into cobalt-56 and then iron-56 over the course of a few months. As iron and nickel have the highest binding energy per nucleon of all the elements,[8] energy cannot be produced at the core by fusion, and a nickel-iron core grows.[5][9] This core is under huge gravitational pressure. As there is no fusion to further raise the star's temperature to support it against collapse, it is supported only by degeneracy pressure of electrons. In this state, matter is so dense that further compaction would require electrons to occupy the same energy states. However, this is forbidden for identical fermion particles, such as the electron – a phenomenon called the Pauli exclusion principle.
When the core's mass exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit of about 1.4 M☉, degeneracy pressure can no longer support it, and catastrophic collapse ensues.[10] The outer part of the core reaches velocities of up to 70000 km/s (23% of the speed of light) as it collapses toward the center of the star.[11] The rapidly shrinking core heats up, producing high-energy gamma rays that decompose iron nuclei into helium nuclei and free neutrons via photodisintegration. As the core's density increases, it becomes energetically favorable for electrons and protons to merge via inverse beta decay, producing neutrons and elementary particles called neutrinos. Because neutrinos rarely interact with normal matter, they can escape from the core, carrying away energy and further accelerating the collapse, which proceeds over a timescale of milliseconds. As the core detaches from the outer layers of the star, some of these neutrinos are absorbed by the star's outer layers, beginning the supernova explosion.[12]
For Type II supernovae, the collapse is eventually halted by short-range repulsive neutron-neutron interactions, mediated by the strong force, as well as by degeneracy pressure of neutrons, at a density comparable to that of an atomic nucleus. When the collapse stops, the infalling matter rebounds, producing a shock wave that propagates outward. The energy from this shock dissociates heavy elements within the core. This reduces the energy of the shock, which can stall the explosion within the outer core.[13]
The core collapse phase is so dense and energetic that only neutrinos are able to escape. As the protons and electrons combine to form neutrons by means of electron capture, an electron neutrino is produced. In a typical Type II supernova, the newly formed neutron core has an initial temperature of about 100 billion kelvins, 104 times the temperature of the Sun's core. Much of this thermal energy must be shed for a stable neutron star to form, otherwise the neutrons would "boil away". This is accomplished by a further release of neutrinos.[14] These 'thermal' neutrinos form as neutrino-antineutrino pairs of all flavors, and total several times the number of electron-capture neutrinos.[15] The two neutrino production mechanisms convert the gravitational potential energy of the collapse into a ten-second neutrino burst, releasing about 1046 joules (100 foe).[16]
Through a process that is not clearly understood, about 1%, or 1044 joules (1 foe), of the energy released (in the form of neutrinos) is reabsorbed by the stalled shock, producing the supernova explosion.[13] Neutrinos generated by a supernova were observed in the case of Supernova 1987A, leading astrophysicists to conclude that the core collapse picture is basically correct. The water-based Kamiokande II and IMB instruments detected antineutrinos of thermal origin,[14] while the gallium-71-based Baksan instrument detected neutrinos (lepton number = 1) of either thermal or electron-capture origin.
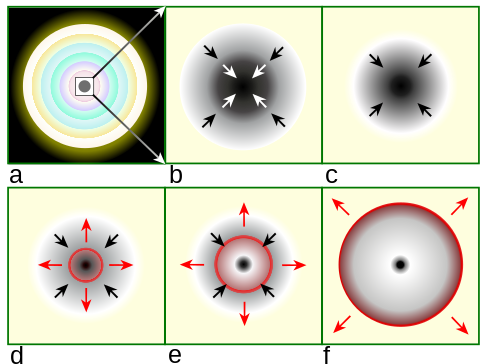
When the progenitor star is below about 20 M☉ – depending on the strength of the explosion and the amount of material that falls back – the degenerate remnant of a core collapse is a neutron star.[11] Above this mass, the remnant collapses to form a black hole.[5][17] The theoretical limiting mass for this type of core collapse scenario is about 40–50 M☉. Above that mass, a star is believed to collapse directly into a black hole without forming a supernova explosion,[18] although uncertainties in models of supernova collapse make calculation of these limits uncertain.
Theoretical models
[edit]The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory which describes three of the four known fundamental interactions between the elementary particles that make up all matter. This theory allows predictions to be made about how particles will interact under many conditions. The energy per particle in a supernova is typically 1–150 picojoules (tens to hundreds of MeV).[19][failed verification] The per-particle energy involved in a supernova is small enough that the predictions gained from the Standard Model of particle physics are likely to be basically correct. But the high densities may require corrections to the Standard Model.[20] In particular, Earth-based particle accelerators can produce particle interactions which are of much higher energy than are found in supernovae,[21] but these experiments involve individual particles interacting with individual particles, and it is likely that the high densities within the supernova will produce novel effects. The interactions between neutrinos and the other particles in the supernova take place with the weak nuclear force, which is believed to be well understood. However, the interactions between the protons and neutrons involve the strong nuclear force, which is much less well understood.[22]
The major unsolved problem with Type II supernovae is that it is not understood how the burst of neutrinos transfers its energy to the rest of the star producing the shock wave which causes the star to explode. From the above discussion, only one percent of the energy needs to be transferred to produce an explosion, but explaining how that one percent of transfer occurs has proven extremely difficult, even though the particle interactions involved are believed to be well understood. In the 1990s, one model for doing this involved convective overturn, which suggests that convection, either from neutrinos from below, or infalling matter from above, completes the process of destroying the progenitor star. Heavier elements than iron are formed during this explosion by neutron capture, and from the pressure of the neutrinos pressing into the boundary of the "neutrinosphere", seeding the surrounding space with a cloud of gas and dust which is richer in heavy elements than the material from which the star originally formed.[23]
Neutrino physics, which is modeled by the Standard Model, is crucial to the understanding of this process.[20] The other crucial area of investigation is the hydrodynamics of the plasma that makes up the dying star; how it behaves during the core collapse determines when and how the shockwave forms and when and how it stalls and is reenergized.[24]
In fact, some theoretical models incorporate a hydrodynamical instability in the stalled shock known as the "Standing Accretion Shock Instability" (SASI). This instability comes about as a consequence of non-spherical perturbations oscillating the stalled shock thereby deforming it. The SASI is often used in tandem with neutrino theories in computer simulations for re-energizing the stalled shock.[25]
Computer models have been very successful at calculating the behavior of Type II supernovae when the shock has been formed. By ignoring the first second of the explosion, and assuming that an explosion is started, astrophysicists have been able to make detailed predictions about the elements produced by the supernova and of the expected light curve from the supernova.[26][27][28]
Light curves for Type II-L and Type II-P supernovae
[edit]
When the spectrum of a Type II supernova is examined, it normally displays Balmer absorption lines – reduced flux at the characteristic frequencies where hydrogen atoms absorb energy. The presence of these lines is used to distinguish this category of supernova from a Type I supernova.
When the luminosity of a Type II supernova is plotted over a period of time, it shows a characteristic rise to a peak brightness followed by a decline. These light curves have an average decay rate of 0.008 magnitudes per day; much lower than the decay rate for Type Ia supernovae. Type II is subdivided into two classes, depending on the shape of the light curve. The light curve for a Type II-L supernova shows a steady (linear) decline following the peak brightness. By contrast, the light curve of a Type II-P supernova has a distinctive flat stretch (called a plateau) during the decline; representing a period where the luminosity decays at a slower rate. The net luminosity decay rate is lower, at 0.0075 magnitudes per day for Type II-P, compared to 0.012 magnitudes per day for Type II-L.[29]
The difference in the shape of the light curves is believed to be caused, in the case of Type II-L supernovae, by the expulsion of most of the hydrogen envelope of the progenitor star.[29] The plateau phase in Type II-P supernovae is due to a change in the opacity of the exterior layer. The shock wave ionizes the hydrogen in the outer envelope – stripping the electron from the hydrogen atom – resulting in a significant increase in the opacity. This prevents photons from the inner parts of the explosion from escaping. When the hydrogen cools sufficiently to recombine, the outer layer becomes transparent.[30]
Type IIn supernovae
[edit]The "n" denotes narrow, which indicates the presence of narrow or intermediate width hydrogen emission lines in the spectra. In the intermediate width case, the ejecta from the explosion may be interacting strongly with gas around the star – the circumstellar medium.[31][32] The estimated circumstellar density required to explain the observational properties is much higher than that expected from the standard stellar evolution theory.[33] It is generally assumed that the high circumstellar density is due to the high mass-loss rates of the Type IIn progenitors. The estimated mass-loss rates are typically higher than 10−3 M☉ per year. There are indications that they originate as stars similar to luminous blue variables with large mass losses before exploding.[34] SN 1998S and SN 2005gl are examples of Type IIn supernovae; SN 2006gy, an extremely energetic supernova, may be another example.[35]
Some supernovae of type IIn show interactions with the circumstellar medium, which leads to an increased temperature of the cirumstellar dust. This warm dust can be observed as a brightening in the mid-infrared light. If the circumstellar medium extends further from the supernova, the mid-infrared brightening can cause an infrared echo, causing the brightening to last more than 1000 days. These kind of supernovae belong to the rare 2010jl-like supernovae, named after the archetypal SN 2010jl. Most 2010jl-like supernovae were discovered with the decommissioned Spitzer Space Telescope and the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer (e.g. SN 2014ab, SN 2017hcc).[36][37][38][39]
Type IIb supernovae
[edit]A Type IIb supernova has a weak hydrogen line in its initial spectrum, which is why it is classified as a Type II. However, later on the H emission becomes undetectable, and there is also a second peak in the light curve that has a spectrum which more closely resembles a Type Ib supernova. The progenitor could have been a massive star that expelled most of its outer layers, or one which lost most of its hydrogen envelope due to interactions with a companion in a binary system, leaving behind the core that consisted almost entirely of helium.[40] As the ejecta of a Type IIb expands, the hydrogen layer quickly becomes more transparent and reveals the deeper layers.[40] The classic example of a Type IIb supernova is SN 1993J,[41][42] while another example is Cassiopeia A.[43] The IIb class was first introduced (as a theoretical concept) by Woosley et al. in 1987,[44] and the class was soon applied to SN 1987K[45] and SN 1993J.[46]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Prantzos, N (1996). "Stellar nucleosynthesis and γ-ray line astronomy". Astronomy & Astrophysics Supplement Series. 120: 330–310. Bibcode:1996A&AS..120C.303P – via SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System (ADS).
- ^ Gilmore, Gerry (2004). "The Short Spectacular Life of a Superstar". Science. 304 (5697): 1915–1916. doi:10.1126/science.1100370. PMID 15218132. S2CID 116987470.
- ^ "Introduction to Supernova Remnants". NASA Goddard/SAO. 2006-09-07. Archived from the original on 2020-05-28. Retrieved 2007-05-01.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Richmond, Michael. "Late stages of evolution for low-mass stars". Rochester Institute of Technology. Archived from the original on 2020-06-11. Retrieved 2006-08-04.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Hinshaw, Gary (2006-08-23). "The Life and Death of Stars". NASA Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Mission. Archived from the original on 2013-06-03. Retrieved 2006-09-01.
- ^ Woosley, S.; Janka, H.-T. (December 2005). "The Physics of Core-Collapse Supernovae". Nature Physics. 1 (3): 147–154. arXiv:astro-ph/0601261. Bibcode:2005NatPh...1..147W. doi:10.1038/nphys172. S2CID 118974639.
- ^ Clayton, Donald (1983). Principles of Stellar Evolution and Nucleosynthesis. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-10953-4.
- ^ Fewell, M. P. (1995). "The atomic nuclide with the highest mean binding energy". American Journal of Physics. 63 (7): 653–658. Bibcode:1995AmJPh..63..653F. doi:10.1119/1.17828.
- ^ Fleurot, Fabrice. "Evolution of Massive Stars". Laurentian University. Archived from the original on 2017-05-21. Retrieved 2007-08-13.
- ^ Lieb, E. H.; Yau, H.-T. (1987). "A rigorous examination of the Chandrasekhar theory of stellar collapse". Astrophysical Journal. 323 (1): 140–144. Bibcode:1987ApJ...323..140L. doi:10.1086/165813. Archived from the original on 2022-01-25. Retrieved 2020-03-18.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Fryer, C. L.; New, K. C. B. (2006-01-24). "Gravitational Waves from Gravitational Collapse". Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics. Archived from the original on 2006-12-13. Retrieved 2006-12-14.
- ^ Hayakawa, T.; Iwamoto, N.; Kajino, T.; Shizuma, T.; Umeda, H.; Nomoto, K. (2006). "Principle of Universality of Gamma-Process Nucleosynthesis in Core-Collapse Supernova Explosions". The Astrophysical Journal. 648 (1): L47–L50. Bibcode:2006ApJ...648L..47H. doi:10.1086/507703.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Fryer, C.L.; New, K.B.C. (2006-01-24). "Gravitational Waves from Gravitational Collapse, section 3.1". Los Alamos National Laboratory. Archived from the original on 2006-10-13. Retrieved 2006-12-09.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Mann, Alfred K. (1997). Shadow of a star: The neutrino story of Supernova 1987A. New York: W. H. Freeman. p. 122. ISBN 978-0-7167-3097-2. Archived from the original on 2008-05-05. Retrieved 2007-11-19.
- ^ Гриббин, Джон Р .; Гриббин, Мэри (2000). Stardust: Supernovae и жизнь - космическая связь . Нью -Хейвен: издательство Йельского университета . п. 173. ISBN 978-0-300-09097-0 Полем Архивировано из оригинала 2014-12-10 . Получено 2007-11-19 .
- ^ Barwick, S.; Beacom, J.; и др. (2004-10-29). «APS Neutrino исследование: отчет о рабочей группе нейтрино астрофизики и космологии» (PDF) . Американское физическое общество . Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 2018-12-16 . Получено 2006-12-12 .
- ^ Фрайер, Крис Л. (2003). «Формирование черной дыры из звездного коллапса» . Классическая и квантовая гравитация . 20 (10): S73 - S80. Bibcode : 2003cqgra..20s..73f . doi : 10.1088/0264-9381/20/10/309 . S2CID 122297043 . Архивировано из оригинала 2020-10-31 . Получено 2019-11-29 .
- ^ Фрайер, Крис Л. (1999). «Ограничения массы для формирования черной дыры». Астрофизический журнал . 522 (1): 413–418. Arxiv : Astro-ph/9902315 . Bibcode : 1999Apj ... 522..413f . doi : 10.1086/307647 . S2CID 14227409 .
- ^ Иззард, RG; Рамирес Руис, E.; Tout, CA (2004). «Скорость образования сверхновых и гамма-всплесков гамма-луча» . Ежемесячные уведомления Королевского астрономического общества . 348 (4): 1215. Arxiv : Astro-ph/0311463 . Bibcode : 2004mnras.348.1215i . doi : 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07436.x . S2CID 119447717 .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Rampp, M.; Buras, R.; Янка, Х.-Т.; Раффелт, Г. (11–16 февраля 2002 г.). «Моделирование суперновой основной коллапса: вариации физики ввода». Труды 11 -го семинара по «Ядерной астрофизике» . Замок Рингберг, Тегернзее, Германия. С. 119–125. Arxiv : Astro-ph/0203493 . Bibcode : 2002nuas.conf..119r .
- ^ Ackerstaff, K.; и др. (Opal Collaboration) (1998). «Тесты стандартной модели и ограничения на новую физику из-за измерения производства Fermion-Pair в 189 GV в LEP» . Европейский физический журнал c . 2 (3): 441–472. arxiv : hep-ex/9708024 . doi : 10.1007/s100529800851 . S2CID 195313000 . Архивировано из оригинала 2007-03-21 . Получено 2007-03-18 .
- ^ «Нобелевская премия по физике 2004 года» . Нобелевский фонд. 2004-10-05. Архивировано из оригинала на 2007-05-03 . Получено 2007-05-30 .
- ^ Стовер, Дон (2006). «Жизнь в пузыре». Популярная наука . 269 (6): 16.
- ^ Янка, Х.-Т.; Langanke, K.; Марек, А.; Martínez Pinedo, G.; Мюллер, Б. (2007). «Теория суперновах ядра Колопса». Столетний объем физических сообщений . 142 (1–4): 38–74. Arxiv : Astro-ph/0612072 . Bibcode : 1993JHYD..142..229H . doi : 10.1016/0022-1694 (93) 90012-х .
- ^ Ивакам, Вакана; Kotake, Kei; Ohnishi, Naofumi; Ямада, Шоичи; Савада, Кейсуке (10–15 марта 2008 г.). «3D-моделирование нестабильности аккреционного шока в суперновах основной коллеги» (PDF) . 14 -й семинар по ядерной астрофизике. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 15 марта 2011 года . Получено 30 января 2013 года .
- ^ Blinnikov, Si; Röpke, FK; Сорокина, EI; Gieseler, M.; Рейнек, М.; Travaglio, C.; Hillebrandt, W.; Stritzinger, M. (2006). «Теоретические кривые света для моделей дефляции типа IA Supernova». Астрономия и астрофизика . 453 (1): 229–240. Arxiv : Astro-ph/0603036 . Bibcode : 2006a & A ... 453..229b . doi : 10.1051/0004-6361: 20054594 . S2CID 15493284 .
- ^ Young, Timothy R. (2004). "A Parameter Study of Type II Supernova Light Curves Using 6 M He Cores". The Astrophysical Journal. 617 (2): 1233–1250. arXiv:astro-ph/0409284. Bibcode:2004ApJ...617.1233Y. doi:10.1086/425675. S2CID 16722121.
- ^ Rauscher, T.; Heger, A.; Hoffman, R. D.; Woosley, S. E. (2002). "Nucleosynthesis in Massive Stars With Improved Nuclear and Stellar Physics". The Astrophysical Journal. 576 (1): 323–348. arXiv:astro-ph/0112478. Bibcode:2002ApJ...576..323R. doi:10.1086/341728. S2CID 59039933.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Doggett, J. B.; Branch, D. (1985). "A Comparative Study of Supernova Light Curves". Astronomical Journal. 90: 2303–2311. Bibcode:1985AJ.....90.2303D. doi:10.1086/113934.
- ^ "Type II Supernova Light Curves". Swinburne University of Technology. Archived from the original on 2019-10-17. Retrieved 2007-03-17.
- ^ Filippenko, A. V. (1997). "Optical Spectra of Supernovae". Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics. 35: 309–330. Bibcode:1997ARA&A..35..309F. doi:10.1146/annurev.astro.35.1.309. S2CID 25194088.
- ^ Pastorello, A.; Turatto, M.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Danziger, I. J.; Mazzali, P. A.; Patat, F.; Filippenko, A. V.; Schlegel, D. J.; Matheson, T. (2002). "The type IIn supernova 1995G: interaction with the circumstellar medium". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 333 (1): 27–38. arXiv:astro-ph/0201483. Bibcode:2002MNRAS.333...27P. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2002.05366.x. S2CID 119347211.
- ^ Langer, N. (22 September 2012). "Presupernova Evolution of Massive Single and Binary Stars". Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics. 50 (1): 107–164. arXiv:1206.5443. Bibcode:2012ARA&A..50..107L. doi:10.1146/annurev-astro-081811-125534. S2CID 119288581.
- ^ Kiewe, Michael; Gal-Yam, Avishay; Arcavi, Iair; Leonard, Douglas C.; Enríquez, J. Emilio; Cenko, S. Bradley; Fox4, Derek B.; Moon, Dae-Sik; Sand, David J.; Soderberg, Alicia M. (2011). "Caltech Core-Collapse Project (CCCP) observations of type IIn supernovae: typical properties and implications for their progenitor stars". The Astrophysical Journal. 744 (10): 10. arXiv:1010.2689. Bibcode:2012ApJ...744...10K. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/744/1/10. S2CID 119267259.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Smith, N.; Chornock, R.; Silverman, J. M.; Filippenko, A. V.; Foley, R. J. (2010). "Spectral Evolution of the Extraordinary Type IIn Supernova 2006gy". The Astrophysical Journal. 709 (2): 856–883. arXiv:0906.2200. Bibcode:2010ApJ...709..856S. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/709/2/856. S2CID 16959330.
- ^ Bevan, A. M.; Krafton, K.; Wesson, R.; Andrews, J. E.; Montiel, E.; Niculescu-Duvaz, M.; Barlow, M. J.; De Looze, I.; Clayton, G. C. (2020-05-01). "Disentangling Dust Components in SN 2010jl: The First 1400 Days". The Astrophysical Journal. 894 (2): 111. arXiv:2004.01503. Bibcode:2020ApJ...894..111B. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab86a2. ISSN 0004-637X.
- ^ Мория, TJ; Stritzinger, MD; Taddia, F.; Моррелл, Н.; Suntzeff, NB; Contreras, C.; Галл, C.; Hjorth, J.; Ashall, C.; Ожоги, кр; Busta, L.; Campillay, A.; Castellón, S.; Corco, C.; Дэвис С. (2020-09-01). «Проект Carnegie Supernova II. Наблюдения за SN 2014AB, возможно, выявляя SN IIN 2010JL с ранее существовавшей пылью» . Астрономия и астрофизика . 641 : A148. Arxiv : 2006.10198 . Bibcode : 2020a & a ... 641a.148m . doi : 10.1051/0004-6361/2020388118 . ISSN 0004-6361 . S2CID 237554659 .
- ^ Тевено, Мелина (2020-12-01). «Средние инфракрасные обнаружения SNE II с Neowise» . Исследовательские заметки Американского астрономического общества . 4 (12): 243. Bibcode : 2020rnaas ... 4..243t . doi : 10.3847/2515-5172/abd415 . ISSN 2515-5172 .
2017HCC впервые упоминается в этой исследовательской записке как 2010JL-подобный, но, к сожалению, Moran et al. Пропустил эту исследовательскую записку.
- ^ Моран, с.; Fraser, M.; Kotak, R.; Pastorello, A.; Бенетти, с.; Бреннан, SJ; Gutiérrez, CP; Kankare, E.; Kuncarayakti, H.; Mattila, S.; Рейнольдс, ТМ; Андерсон, JP; Браун, PJ; Campana, S.; Chambers, KC (2023-01-01). «Долгая жизнь избытка: взаимодействующий переходный SN 2017HCC» . Астрономия и астрофизика . 669 : A51. Arxiv : 2210.14076 . Bibcode : 2023a & A ... 669a..51m . doi : 10.1051/0004-6361/202244565 . ISSN 0004-6361 . S2CID 253107572 .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Утробин, вице -президент (1996). «Неремальная ионизация и возбуждение в Supernova 1993J типа IIB 1993J». Астрономия и астрофизика . 306 (5940): 219–231. Bibcode : 1996a & A ... 306..219U .
- ^ Nomoto, K.; Suzuki, T.; Shigeyama, T.; Kumagai, S.; Yamaoka, H.; Saio, H. (1993). «Модель типа IIB для SuperNova 1993J». Природа . 364 (6437): 507. Bibcode : 1993nater.364..507n . doi : 10.1038/364507a0 . S2CID 4363061 .
- ^ Chevalier, RA; Содерберг, AM (2010). «Сверхновые типа IIB с компактными и расширенными предшественниками». Астрофизический журнал . 711 (1): L40 - L43. Arxiv : 0911.3408 . Bibcode : 2010Apj ... 711L..40c . doi : 10.1088/2041-8205/711/1/L40 . S2CID 118321359 .
- ^ Краузе, О.; Birkmann, S.; USUDA, T.; Хаттори, Т.; Goto, M.; Rieke, G.; Миссильт, К. (2008). «Кассиопея, а сверхновая была IIB типа». Наука . 320 (5880): 1195–1197. Arxiv : 0805.4557 . Bibcode : 2008Sci ... 320.1195K . doi : 10.1126/science.1155788 . PMID 18511684 . S2CID 40884513 .
- ^ Woosley, SE; Пинто, Пенсильвания; Мартин, PG; Уивер, Томас А. (1987). «Supernova 1987a в большом магеллановом облаке - взрыв приблизительно 20 солнечной массовой звезды, которая испытала потерю массы?». Астрофизический журнал . 318 : 664. Bibcode : 1987Apj ... 318..664W . doi : 10.1086/165402 .
- ^ Филиппенко, Алексей В. (1988). «Supernova 1987K - тип II в молодости, тип IB в старости». Астрономический журнал . 96 : 1941. Bibcode : 1988aj ..... 96.1941f . doi : 10.1086/114940 .
- ^ Филиппенко, Алексей В.; Мэтисон, Томас; Хо, Луис С. (1993). «The Type IIB Supernova 1993J в M81: близкий родственник сверхновых типа IB» . Астрофизические журнальные буквы . 415 : L103. Bibcode : 1993Apj ... 415L.103f . doi : 10.1086/187043 .
Внешние ссылки
[ редактировать ]- «Список всех известных сверхновых типа II» . Открытый каталог сверхновой . Архивировано из оригинала 2017-01-10 . Получено 2017-01-09 .
- Меррифилд, Майкл. Харан, Б. (ред.). Тип II Supernovae . Шестьдесят символов (видео лекция). Ноттингем, Великобритания: Университет Ноттингема .
- Гибни, Элизабет (2018-04-18). «Как взорвать звезду» . Природа . 556 (7701): 287–289. Bibcode : 2018natur.556..287g . doi : 10.1038/d41586-018-04601-7 . PMID 29670276 . S2CID 4956943 .
