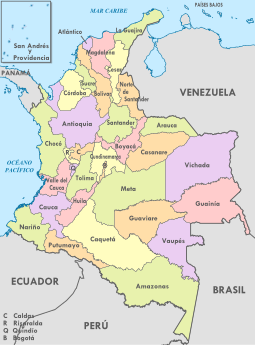
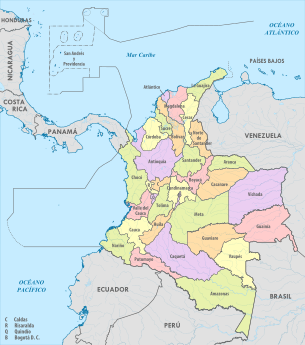
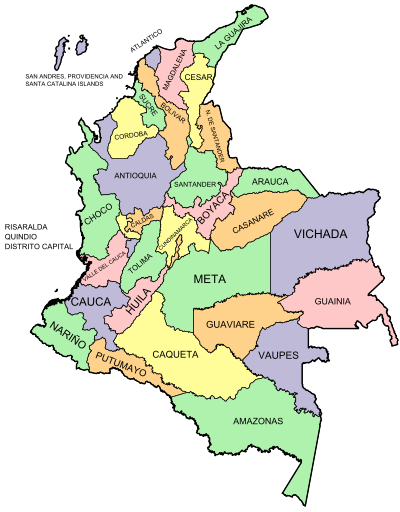
Departments of Colombia
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (March 2009) |
| Capital district and Colombian regions Distrito Capital y los Departamentos de Colombia (Spanish) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary state |
| Location | Republic of Colombia |
| Number | 32 Departments 1 Capital District |
| Populations | 48,932 (Vaupés) – 8,906,342 (Capital District) |
| Areas | 50 km2 (19.3 sq mi) (San Andrés) – 109,665.0 km2 (42,341.89 sq mi) (Amazonas) |
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions | |
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of Colombia |
|---|
 |
Departments of Colombia refer to the administrative divisions of Colombia. As of 2024[update], the unitary republic is made up of thirty-two departments. Each department has a governor and an assembly, elected by popular vote for a four-year period.
Current departments
[edit]Colombia is a unitary republic made up of thirty-two administrative divisions referred to as departments (Spanish: departamentos, sing. departamento) and one Capital District (Distrito Capital).[1] Each department has a governor (gobernador) and an Assembly (Asamblea Departamental), elected by popular vote for a four-year period. The governor cannot be re-elected in consecutive periods. Departments are country subdivisions and are granted a certain degree of autonomy.
Departments are formed by a grouping of municipalities (municipios, sing. municipio). Municipal government is headed by mayor (alcalde) and administered by a municipal council (concejo municipal), both of which are elected by popular vote for four-year periods.
Some departments have subdivisions above the level of municipalities, commonly known as provinces.
| ID | Region | Governor | Party or Coalition | Capital | Area (km2) | Population (December 2022)[3] | Density per km2 | Established as a department | Flag | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | Capital District | Carlos Fernando Galán | New Liberalism | Bogotá | 1,587 | 8,906,342 | 4670.80 | 1861 | DC | |
| 01 | Amazonas | Óscar Enrique Sánchez Guerrero | Historic Pact for Colombia | Leticia | 109,665 | 82,068 | 0.7 | 1991 | AM | |
| 02 | Antioquia | Andrés Julián Rendón Cardona | Por Antioquia Firme | Medellín | 63,612 | 6,887,306 | 100.72 | 1886 | AN | |
| 03 | Arauca | Manuel Alexander Pérez Rueda | Democratic Center | Arauca | 23,818 | 304,978 | 11.01 | 1991 | AR | |
| 04 | Atlántico | Eduardo Verano de la Rosa | Colombian Liberal Party | Barranquilla | 3,388 | 2,804,025 | 748.38 | 1910 | AT | |
| 05 | Bolívar | Yamil Hernando Arana Padaui | Bolivar Mejor | Cartagena | 25,978 | 2,236,603 | 79.69 | 1886 | BL | |
| 06 | Boyacá | Carlos Andrés Amaya Rodriguez | Boyacá Grande | Tunja | 23,189 | 1,259,601 | 52.50 | 1824 | BY | |
| 07 | Caldas | Henry Gutiérrez Angel | Por El Caldas Que Quiere La Gente | Manizales | 7,888 | 1,036,455 | 126.55 | 1905 | CL | |
| 08 | Caquetá | Luis Francisco Ruiz Aguilar | Coalición Revive Caqueta | Florencia | 88,965 | 419,275 | 4.52 | 1981 | CQ | |
| 09 | Casanare | César Augusto Ortiz Zorro | Coalición Por Casanare | Yopal | 44,640 | 442,068 | 9.42 | 1991 | CS | |
| 10 | Cauca | Jorge Octavio Guzmán Gutiérrez | La Fuerza Del Pueblo | Popayán | 29,308 | 1,516,018 | 49.97 | 1824 | CA | |
| 11 | Cesar | Elvia Milena Sanjuán Dávila | El Cesar En Marcha | Valledupar | 22,905 | 1,341,697 | 52.42 | 1967 | CE | |
| 12 | Chocó | Nubia Carolina Córdoba Curi | Colombian Liberal Party | Quibdó | 46,530 | 553,519 | 11.49 | 1947 | CH | |
| 13 | Córdoba | Erasmo Elías Zuleta Bechara | Cordoba Pr1mero | Montería | 25,020 | 1,856,496 | 71.33 | 1951 | CO | |
| 14 | Cundinamarca | Jorge Emilio Rey Ángel | Caminando, Escuchando, Gobernando | Bogotá | 24,210 | 2,473,634 | 120.57 | 1824 | CU | |
| 15 | Guainía | Arnulfo Rivera Naranjo | Coalición Trabajemos Guainía | Inirida | 72,238 | 52,061 | 0.67 | 1991 | GN | |
| 16 | Guaviare | Yeison Ferney Rojas Martínez | Guaviare Seguimos Avanzando | San José del Guaviare | 53,460 | 90,357 | 1.55 | 1991 | GV | |
| 17 | Huila | Rodrigo Villaba Mosquera | Por Un Huila Grande | Neiva | 19,890 | 1,140,932 | 55.32 | 1910 | HU | |
| 18 | La Guajira | Jairo Alfonso Aguilar Deluque | Union Party for the People, Radical Change, Independent Social Alliance, La Fuerza de la Paz and Partido Demócrata | Riohacha | 20,848 | 1,002,394 | 42.24 | 1965 | LG | |
| 19 | Magdalena | Rafael Alejandro Martínez | Fuerza Ciudadana | Santa Marta | 23,188 | 1,463,427 | 57.86 | 1824 | MA | |
| 20 | Meta | Rafaela Cortés Zambrano | Coalición Fe y Firmeza | Villavicencio | 82,805 | 1,080,706 | 12.14 | 1959 | ME | |
| 21 | Nariño | Luis Alfonso Escobar Jaramillo | Historic Pact for Colombia | Pasto | 33,268 | 1,629,181 | 49.01 | 1910 | NA | |
| 22 | Norte de Santander | William Villamizar Laguado | Coalición Por Amor A Nuestra Gente Del Norte | Cúcuta | 21,658 | 1,651,278 | 68.87 | 1910 | NS | |
| 23 | Putumayo | Carlos Andrés Marroquín Luna | Coalición Somos La Fuerza De La Gente | Mocoa | 24,885 | 369,064 | 13.99 | 1991 | PU | |
| 24 | Quindío | Juan Miguel Galvis Bedoya | Creemos Colombia | Armenia | 1,845 | 569,569 | 292.63 | 1966 | QD | |
| 25 | Risaralda | Juan Diego Patiño Ochoa | Colombian Liberal Party | Pereira | 4,140 | 977,829 | 227.87 | 1966 | RI | |
| 26 | San Andrés y Providencia | Nicolas Iván Gallardo Vásquez | Coalición Avanzar es Posible | San Andrés | 52 | 65,228 | 1178.46 | 1991 | SA | |
| 27 | Santander | Juvenal Díaz Mateus | Coalición Es Tiempo Juvenal Gobernador | Bucaramanga | 30,537 | 2,324,090 | 71.55 | 1886 | ST | |
| 28 | Sucre | Lucy Inés García Montes | Coalición Mujer de Resultados | Sincelejo | 10,917 | 972,350 | 82.89 | 1966 | SU | |
| 29 | Tolima | Adriana Magali Matiz Vargas | Coalición Con Seguridad en el Territorio | Ibagué | 23,562 | 1,346,935 | 56.45 | 1886 | TO | |
| 30 | Valle del Cauca | Dilian Francisca Toro Torres | Coalición Unidos por el Valle | Cali | 22,140 | 4,589,278 | 202.16 | 1910 | VC | |
| 31 | Vaupés | Luis Alfredo Gutiérrez García | Gente en Movimiento | Mitú | 54,135 | 48,932 | 0.75 | 1991 | VP | |
| 32 | Vichada | Hecson Alexys Benito Castro | Union Party for the People | Puerto Carreño | 100,242 | 115,778 | 1.08 | 1991 | VD |
Indigenous territories
[edit]The indigenous territories are at the third level of administrative division in Colombia, as are the municipalities. Indigenous territories are created by agreement between the government and indigenous communities. In cases where indigenous territories cover more than one department or municipality, local governments jointly administer them with the indigenous councils, as set out in Articles 329 and 330 of the Colombian Constitution of 1991. Also indigenous territories may achieve local autonomy if they meet the requirements of the law.
Article 329 of the 1991 constitution recognizes the collective indigenous ownership of indigenous territories and repeats that are inalienable. Law 160 of 1994 created the National System of Agrarian Reform and Rural Development Campesino, and replaced Law 135 of 1961 on Agrarian Social Reform; it establishes and sets out the functions of INCORA, one of the most important being to declare which territories will acquire the status of indigenous protection and what extension of existing ones will be allowed. Decree 2164 of 1995 interprets Law 160 of 1994, providing, among other things, a legal definition of indigenous territories.[4]
Indigenous territories in Colombia are mostly in the departments of Amazonas, Cauca, La Guajira, Guaviare, and Vaupés.[1]
History
[edit]Historical predecessors of current departments
[edit]| Evolution of Colombian departments | |||||
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
| Current name and flag | Established as a department | First established under the following name | Establishment of earliest territorial predecessor | Sovereign State that established the earliest territorial predecessor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1991 | Intendancy of Amazonas | 1931 | ||
| 1886 | Province of Antioquia | 1576 | ||
| 1991 | Commissary of Arauca | 1911 | ||
| 1910 | Province of Sabanilla | 1852 | ||
| 1861 | Federal District of Bogotá | 1861 | ||
| 1886 | Province of Cartagena | 1533 | ||
| 1824 | Province of Tunja | 1539 | ||
| 1908 | Department of Caldas | 1908 | ||
| 1981 | Intendancy of Caquetá | 1905 | ||
| 1991 | Province of Casanare | 1660 | ||
| 1824 | Province of Popayán | 1537 | ||
| 1967 | Department of Cesar | 1967 | ||
| 1947 | Province of Chocó | 1726 | ||
| 1951 | Department of Córdoba | 1951 | ||
| 1824 | Province of Santafé de Bogotá | 1550 | ||
| 1991 | Commissary of Guainía | 1963 | ||
| 1991 | Commissary of Guaviare | 1977 | ||
| 1910 | Province of Neiva | 1610 | ||
| 1965 | Province of Riohacha | 1789 | ||
| 1824 | Province of Santa Marta | 1533 | ||
| 1959 | Intendancy of Meta | 1905 | ||
| 1910 | Province of Pasto | 1823 | ||
| 1910 | Province of Pamplona | 1555 | ||
| 1991 | Commissary of Putumayo | 1912 | ||
| 1966 | Department of Quindío | 1966 | ||
| 1966 | Department of Risaralda | 1966 | ||
| 1991 | Providence Island Colony | 1630 | ||
| 1886 | Province of Socorro | 1795 | ||
| 1966 | Department of Sucre | 1966 | ||
| 1886 | Province of Mariquita | 1550 | ||
| 1910 | Province of Cauca | 1835 | ||
| 1991 | Commissary of Vaupés | 1910 | ||
| 1991 | Commissary of Vichada | 1913 |
The Republic of Gran Colombia
[edit]When it was first established in 1819, The Republic of Gran Colombia had three departments. Venezuela, Cundinamarca (now Colombia) and Quito (now Ecuador).[5] In 1824, the Distrito del Centro (which became Colombia) was divided into five departments and further divided into seventeen provinces. One department, Isthmus Department, consisting of two provinces, later became the sovereign country of Panama.[6]
Republic of New Granada
[edit]With the dissolution of Gran Colombia in 1826 by the Revolution of the Morrocoyes (La Cosiata), New Granada kept its 17 provinces. In 1832 the provinces of Vélez and Barbacoas were created, and in 1835 those of Buenaventura and Pasto were added. In 1843 those of Cauca, Mompós and Túquerres were created. At this time the cantons (cantones) and parish districts were created, which provided the basis for the present-day municipalities.[6][7]
By 1853 the number of provinces had increased to thirty-six, namely:Antioquia, Azuero, Barbacoas, Bogotá, Buenaventura, Cartagena, Casanare, Cauca, Chiriquí, Chocó, Córdova, Cundinamarca, García Rovira, Mariquita, Medellín, Mompós, Neiva, Ocaña, Pamplona, Panamá, Pasto, Popayán, Riohacha, Sabanilla, Santa Marta, Santander, Socorro, Soto, Tequendama, Tunja, Tundama, Túquerres, Valle de Upar, Veraguas, Vélez and Zipaquirá.[7] However, the new constitution of 1853 introduced federalism, which lead to the consolidation of provinces into states. By 1858 this process was complete, with a resulting eight federal states: Panamá was formed in 1855, Antioquia in 1856, Santander in May 1857, and Bolívar, Boyacá, Cauca, Cundinamarca and Magdalena were formed in June 1858. 1861 saw the creation of the final federal state of Tolima.[8]
Republic of Colombia
[edit]The Colombian Constitution of 1886 converted the states of Colombia into departments, with the state presidents renamed as governors. The states formed the following original departments:
- Antioquia Department
- Bolívar Department
- Boyacá Department
- Cauca Department
- Cundinamarca Department
- Magdalena Department
- Panamá Department
- Santander Department
- Tolima Department
Maps gallery
[edit]- Departments of Colombia with municipalities
- Map with numbered departments
- Departments of Colombia with names
- Political map of Colombia
- Topography of Colombia, highly variable per department
See also
[edit]- ISO 3166-2:CO
- List of Colombian flags
- List of political and geographic subdivisions by total area
- States of Colombia
- List of Colombian departments by Human Development Index
References
[edit]- ^ Jump up to: a b "Division Política de Colombia" (in Spanish). Portal ColombiaYA.com. Archived from the original on 10 March 2009.
- ^ "Elecciones Territoriales 2023 - Resultados Electorales". La República (in Spanish). Retrieved 2024-01-15.
- ^ "Archive copy". Archived from the original on 2011-05-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Decree 2164 of 1995 provides "Reserva Indígena. Es un globo de terreno baldío ocupado por una o varias comunidades indígenas que fué delimitado y legalmente asignado por el INCORA a aquellas para que ejerzan en él los derechos de uso y usufructo con exclusión de terceros. Las reservas indígenas constituyen tierras comunales de grupos étnicos, para los fines previstos en el artículo 63 de la Constitución Política y la ley 21 de 1991. [...] Territorios Indígenas. Son las áreas poseidas en forma regular y permanente por una comunidad, parcialidad o grupo indígena y aquellas que, aunque no se encuentren poseidas en esa forma, constituyen el ámbito tradicional de sus actividades sociales, económicas y culturales. " Art. 21: "Los resguardos son una institución legal y sociopolítica de carácter especial, conformada por una o más comunidades indígenas, que con un título de propiedad colectiva que goza de las garantías de la propiedad privada, poseen su territorio y se rigen para el manejo de éste y su vida interna por una organización autónoma amparada por el fuero indígena y su sistema normativo propio."
- ^ Guhl Nannetti, Ernesto (1991). "Capítulo XII: División Política de la Gran Colombia". Las fronteras políticas y los límites naturales: escritos geograficos [Political Boundaries and Their Natural Limits: Geographic writings] (in Spanish). Bogotá: Fondo FEN. ISBN 978-958-9129-22-7.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Aguilera Peña, Mario (January 2002). "División política administrativa de Colombia". Credential Historia (in Spanish). Bogotá: Banco de la República. Archived from the original on 16 February 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Oficina Nacional de Estadística (Office of National Statistics) (1876). "Estadística de Colombia" [Colombian Statistics] (PDF) (in Spanish). Bogotá: Oficina Nacional de Estadística. Retrieved 23 November 2016.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Domínguez, Camilo; Chaparro, Jeffer; Gómez, Carla (2006). "Construcción y deconstrucción territorial del Caribe Colombiano durante el siglo XIX". Scripta Nova (Revista Electrónica de Geografía y Ciencias Sociales). 10 (218 (75)).
External links
[edit]- "Departments of Colombia". Statoids.