Владимир Кличко
Владимир Кличко | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Владимир Кличко | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Кличко в 2023 году | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Born | 25 March 1976 Semipalatinsk, Kazakh SSR, Soviet Union | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nationality | Ukrainian | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Partner | Hayden Panettiere (2009–2011; 2013–2018) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Children | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Relatives | Vitali Klitschko (brother) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Military career | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allegiance | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Service/ | Ukrainian Army | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Years of service | 2022–present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Battles/wars | Russian invasion of Ukraine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boxing career | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other names | Dr. Steelhammer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight(s) | Heavyweight | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Height | 1.98 m (6 ft 6 in)[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reach | 206 cm (81 in)[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stance | Orthodox | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boxing record | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total fights | 69 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wins | 64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wins by KO | 53 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Losses | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Medal record
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Website | klitschko | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Владимир Кличко [ а ] (родился 25 марта 1976 года) — бывший украинский боксёр-профессионал, выступавший с 1996 по 2017 год. Дважды становился чемпионом мира в тяжёлом весе , включая объединенные титулы WBA (Super) , IBF , WBO , IBO и Ring журнала . Кличко, стратегический и умный боксер, считается одним из величайших чемпионов в тяжелом весе всех времен. [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 6 ] Он был известен своей исключительной нокаутирующей силой, использованием сильного джеба , прямым правым и левым хуком , быстрой скоростью рук, большой физической силой, которую он использовал при клинчех противников, а также своей спортивной работой ног и подвижностью, необычными для боксеров его размера. [ 7 ] [ 8 ] [ 9 ] [ 10 ]
В качестве любителя Кличко представлял Украину на Олимпийских играх 1996 года , завоевав золотую медаль в супертяжелом весе . Став профессионалом позже в том же году, он победил Криса Берда в 2000 году и завоевал титул WBO в супертяжелом весе. Первое чемпионство Кличко закончилось досадным поражением нокаутом от Корри Сандерс в 2003 году, за которым последовало еще одно досадное поражение нокаутом от Лэймона Брюстера 2004 году в . В частности, Стюарду приписывают переход Кличко от агрессивного панчера к более оборонительно-ориентированному боксёру, так же, как он это сделал с Ленноксом Льюисом с 1995 по 2003 год.
From 2004 to 2015, Wladimir and his brother Vitali Klitschko (himself a multiple-time world champion) dominated heavyweight boxing, a period typically known as the "Klitschko Era" of the division.[11][12] In 2006, Wladimir regained a portion of the world heavyweight championship after defeating Byrd in a rematch to win the IBF and IBO titles. He won his second WBO title by defeating Sultan Ibragimov in 2008. Following his defeat of Ruslan Chagaev in 2009, Klitschko was awarded the Ring title, and lastly he won the WBA title from David Haye in 2011. After defeating Alexander Povetkin in October 2013 and until his loss to Tyson Fury in November 2015, Klitschko was recognised as the lineal champion by the Transnational Boxing Rankings Board.[13] For a period of time in the fall of 2015, Klitschko was ranked as the world's best active boxer, pound for pound, by BoxRec.[14][15] He was also ranked among 10 best pound for pound boxers in the world by The Ring from 17 August 2010 until 23 November 2015, reaching his career peak of No.2 on 25 November 2014.
During Klitschko's reign as world heavyweight champion, his fights would reportedly generate up to 500 million viewers worldwide.[b] Klitschko holds records for the longest cumulative heavyweight title reign of all time, with 4,382 days as world heavyweight champion, and most fighters beaten for the world heavyweight championship, at 23.[c] He also holds records for the most wins and title defences of the unified championship[note 1] in professional boxing history.[33] In 2011, both Wladimir and Vitali entered the Guinness World Records book as brothers with most world heavyweight title fight wins (30 at the time; 40 as of 2020).[34][35][36] Klitschko was inducted into the International Boxing Hall of Fame Class of 2021, having been elected in his first year of eligibility.[37][38]
Early life
[edit]Klitschko was born in Semipalatinsk, Kazakh SSR, Soviet Union (now Semey, Kazakhstan).[39][40][41] He is the son of Nadiia Ulianivna Klychko (née Bulyno) and Volodymyr Rodionovych Klychko (1947–2011), a Soviet Air Force major general and a military attaché of USSR in East Germany. He is the younger brother of former WBC, WBO, and Ring magazine heavyweight champion Vitali Klitschko, the current Mayor of Kyiv.[42] Klitschko's paternal grandmother was Jewish.[43]
The Klitschko brothers lived as children in Czechoslovakia from 1980 to 1985, where their father was stationed with the Soviet occupation forces. They attended a school designated for children of Soviet soldiers in the town of Mimoň in Northern Bohemia.[44]
The Klitschko brothers lived in Pripyat, Ukrainian SSR from 1985 to 1986, when the town was evacuated following the Chernobyl nuclear disaster. The elder Klitschko was also one of the commanders in charge of cleaning up the effects of the Chernobyl nuclear disaster in 1986 and was afterward diagnosed with cancer.[45] He also served as a military attache at the embassy of Ukraine in Germany.[46] His mother is Nadiya Ulyanivna.[47]
Both Wladimir and Vitali hold PhDs[48][49] in sports science,[50] with Wladimir's dissertation discussing how much training to give to young athletes between 14 and 19 based on the development of their bodies.[51] As a reference to their PhDs, Wladimir is announced as "Dr. Steelhammer", a nickname similar to his brother, Vitali, who goes by "Dr. Ironfist".
Amateur career
[edit]Klitschko started training in amateur boxing with Brovary Olympic Reserve School in the late 1980s. In the early 1990s, Klitschko was coached in Poland's Gwardia Warszawa boxing club, where, according to Jerzy Kulej, "He and his brother used to demolish our boys."[52] In 1993, he won the Junior European Championships as a heavyweight. In 1994, he received 2nd place at the Junior World Championships in Istanbul, Turkey, losing to Cuban Michel López Núñez in the finals.[53] In 1995, he won the gold medal at the Military Championships in Ariccia, Italy, defeating Luan Krasniqi, to whom he had lost in the third round of the World Championships in Berlin, Germany earlier that year. In 1996, he captured 2nd place as a Super Heavyweight at the European Championships in Vejle, Denmark losing to Alexei Lezin in the finals. He defeated Lezin later that year in the semi-finals at the 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta.[54] He had an amateur record of 134–6.[55]
He first achieved world attention at the 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta, Georgia. He defeated Paea Wolfgramm to win the Super-Heavyweight gold medal.
Highlights
[edit]Below are the notable achievements of Wladimir Klitschko in amateur boxing:[56]
|
World Championships (91 kg), Berlin, Germany, May 1995:
|
|
Professional career
[edit]"Wladimir hits very hard, harder than (Mike) Tyson. At one point, they ran twelve 800-meter [roughly a half mile] sprints, each under 3 minutes, with a minute rest between each one. I timed every one and every one was under 3 minutes. I never saw a heavyweight do anything even close to that. They work their asses off. To be able to do that, two 250-pound guys – whew. They're two of the best athletes I've ever trained."
—Freddie Roach, who trained both the Klitschko brothers and Mike Tyson, on the athleticism of the brothers.[57]
Early career
[edit]Klitschko turned professional with Universum Box-Promotion in Hamburg under the tutelage of Fritz Sdunek, often being featured on fight cards alongside his elder brother Vitali. After building an undefeated record of 24–0 with 21 KOs, he suffered his first loss to 24–13–1 Ross Puritty, in what was Klitschko's first and only professional fight in Ukraine. Puritty forced Klitschko, who had at that time not gone beyond eight rounds, to punch himself out. Klitschko began to be overwhelmed in the tenth round and went down twice but was allowed to continue. At the start of the eleventh round, with Puritty continuing to land hard punches, Klitschko's trainer, Fritz Sdunek, entered the ring and stopped the fight.[58] Three years later, Klitschko's brother Vitali stopped Puritty in the eleventh round himself. On 18 March 2000, Klitschko fought Paea Wolfgramm, whom he fought previously in the 1996 super-heavyweight Olympic finals. In their professional rematch, Klitschko knocked Wolfgramm out in the first round.
Klitschko vs. Byrd, Jefferson, Shufford
[edit]Wladimir Klitschko got his chance to fight for the world heavyweight championship on 14 October 2000 against WBO champion Chris Byrd. Byrd, considered one of the most avoided fighters in the heavyweight division at the time,[59][60] won the title six months earlier on 1 April from Wladimir's brother Vitali (who had a perfect record of 27 fights, 27 wins, 27 KOs coming into the fight),[59][61] being a late replacement for Donovan Ruddock. In that fight, Byrd was trailing on the scorecards (83–88, 83–88, & 82–89) but was declared the winner after Vitali retired on his stool between 9th and 10th rounds due to shoulder injury.[59] Byrd's title defence against Wladimir was scheduled to take place at Kölnarena in Cologne and was billed as "Revenge Of The Brother".[62] In a fight that was aired on pay-per-view in the United Kingdom,[63] Wladimir won the WBO world heavyweight title from Byrd by a wide unanimous decision (UD) with scores of 120–106, 119–107, and 118–108, flooring his opponent twice.[64]
Klitschko's first defence of the WBO title came on 24 March 2001 against Derrick Jefferson. Jefferson, regarded as a big and athletic brawler and a fan-friendly attraction,[65] was coming into the bout with a record of 23 wins in 26 bouts, with 19 of those wins coming inside the distance (18 of them inside the first three rounds, 11 of them - in the first round).[66][67] Jefferson was mostly known for the sixth-round knockout (KO) of Maurice Harris, which was named The Ring Knockout of the Year in 1999. He was 4–2 in the last six fights, losing by technical knockout (TKO) to David Izon, in a fight he was winning on the scorecards but punched himself out,[68] and Oleg Maskaev in round four after breaking an ankle during the first knockdown in the first round.[69]
For the bout, Jefferson weighed in at 260.25 lbs, the heaviest in his professional career and 20 pounds heavier than in his previous bout.[67] The additional weight appeared to be muscle.[70] The fight lasted only two rounds. In the first round, Klitschko knocked Jefferson down with a short left hook. After the first round Jefferson's left eye was swollen.[70][71] Klitschko knocked him down twice more in round two, once with a straight right hand and again with another left hook, with the fight being stopped after the last knockdown, declaring Klitschko the winner by TKO in the second round. Klitschko earned $1 million for the fight.[71]
Klitschko's next title defence was scheduled less than five months later on 4 August 2001. The fight took place at the Mandalay Bay Events Center in Paradise, Nevada against hometown fighter, Charles Shufford. At the time, Shufford had a 17–1 record, coming off of wins against Jimmy Thunder and Lamon Brewster.[72] Shufford weighed in at 234 lbs., 17 pounds lighter than in his previous bout.[73] Shufford, having played George Foreman opposite Will Smith in the movie Ali, entered the ring with Smith by his side.[74] Klitschko knocked Shufford down three times, once in round two, once in round three (both times with a straight right hand) and in round six with a left hook, with referee stopping the bout after the third knockdown. According to punch stats, Klitschko landed 58 of 262 punches (22%) and Shufford connected on 16 of 190 (8%).[75]
Klitschko vs. Botha, Mercer, McCline
[edit]Klitschko returned to Germany for the next defence of his WBO title against Francois Botha. The fight took place at Hanns-Martin-Schleyer-Halle in Stuttgart, the same venue where Botha had fought Axel Schulz for the IBF title six years earlier, in the most watched boxing match in German TV history.[76][77] According to Botha's coach Abel Sanchez, Botha was in the best shape of his career.[78] The South African contender was game in the opening rounds, trying to catch Klitschko with the right hook, but Klitschko was successfully keeping him at the end of his jab.[78] In the eighth round, Klitschko caught him with a counter right hand and then hit Botha with several shots, knocking him down with a left hook. Botha got up, but was unsteady on his feet and had both eyes swollen, proceeding the referee to stop the bout.[78][79]
Klitschko had his next title defence scheduled three months later, on 29 June 2002 at Etess Arena in Atlantic City, New Jersey, against former WBO heavyweight champion Ray Mercer. It was the first time in his professional career that Klitschko fought an Olympic Gold medalist. 41-year-old Mercer, having fought Lennox Lewis and Evander Holyfield throughout his career, was expected to be a tough challenge for Klitschko that would give him and Lennox Lewis, the WBC and The Ring champion, a second common opponent (along with Francois Botha) and a bout comparable to Lewis vs. Tyson.[80][81] During the build-up to the bout, Mercer referred to Klitschko as "Russian Tommy Morrison".[81] Since his comeback in 2001, Mercer had won four fights over journeymen, three of them inside two rounds, prior to the Klitschko bout.[82]
Klitschko dominated Mercer throughout the entire bout, stopping Mercer in the sixth round. At 2:48 of the first round, Klitschko dropped Mercer with a left hook, becoming only the second man to drop Mercer.[80] Throughout the fight, Klitschko was frequently landing combinations of stiff left jabs, left hooks, and straight right hands. By the fifth round, Mercer's face was swollen and his right eye was cut.[80] In the sixth, Klitschko unleashed a barrage of punches, prompting the referee to stop the bout. Klitschko became the first fighter to defeat Mercer inside the distance.[80] According to CompuBox statistics, Klitschko landed 193 total punches out of 429 thrown (104 power punches out of 167), while Mercer landed 54 shots out of 124 (only 5 power punches landed out of 10 thrown).[80]
Klitschko returned to Mandalay Bay Event Center for his sixth defence on 7 December 2002 against Jameel McCline. McCline, having made his professional boxing debut in 1995, became an established contender after defeating Michael Grant, knocking him down with the first punch thrown and ultimately stopping him in 43 seconds.[83][84] Prior to fighting Klitschko, McCline had defeated two more heavyweight contenders, Lance Whitaker and Shannon Briggs, by wide unanimous decisions.[83] Being 6 ft 6 in tall with an 82 in reach, McCline was of similar height and longer reach than Klitschko,[85] while also being 22 lbs heavier.[83] Many opinion polls gave Klitschko a 60–40 advantage over McCline.[86] The fight was the main event of the card that also featured Floyd Mayweather Jr. defending the WBC lightweight title against Jose Luis Castillo.[87][88]
The fight turned out to be tentative, with Klitschko winning almost every round using his jab and superior footwork. At the end of the tenth round, Klitschko staggered McCline with a barrage of left hooks and overhand rights, and ultimately knocked him down with a left-right combination.[86] Before the start of the eleventh round, McCline's corner threw in the towel, giving Klitschko his 36th career win by stoppage.[86] At the time of the stoppage, the scorecards were 98–91, 99–90 (twice), all in favour of the champion.[86] CompuBox stats showed that Klitschko landed 181 of his 433 punches thrown (42%), and McCline landed 61 of 307 (20%).[88]
The following week after Klitschko's win over McCline, Chris Byrd, whom Klitschko defeated for the WBO world title, beat Evander Holyfield to become IBF world champion.[89]
Klitschko vs. Sanders, Brewster
[edit]
After failing to reach agreements with Kirk Johnson, Fres Oquendo, Lou Savarese and Danny Williams, Universum ultimately signed a 4-fight contract with Corrie Sanders, who was ranked No.9 contender by WBO at the time. According to the agreement, Sanders' first fight was going to be for the WBO world heavyweight title. The fight was scheduled to take place on 8 March 2003 in Hanover, Germany. Klitschko later admitted that he came to the fight unmotivated and was already thinking about the vacation he was going to enjoy after the fight.[90] Klitschko suffered an upset TKO loss to Sanders. With thirty seconds left in the opening round, Wladimir threw a jab but Sanders countered with a big left hook, prompting Klitschko to enter a clinch. While in the clinch, Sanders landed another left hook that send Klitschko to the canvas. Klitschko got up but was dropped again almost immediately. The following round, Sanders continued his assault on a visibly hurt Klitschko, dropping him twice more at the beginning of the round. The referee waived it off after the fourth knockdown. The fight was named Upset of the Year by The Ring for 2003.[91]
After winning two minor bouts in Germany and enlisting the services of legendary boxing trainer Emanuel Steward, Klitschko again fought for the vacant WBO title on 10 April 2004, in Las Vegas, against Lamon Brewster. Klitschko dominated Brewster through the course of the first four rounds, sending him to the canvas in the fourth;[92] however, things turned around in the fifth when Klitschko began tiring and Brewster's punches began backing him up. Not defending himself and leaning into ropes for support, Klitschko took a standing eight count. On unsteady legs, Klitschko fell to the canvas after the bell and the referee stopped the fight for his safety.[93] When talking about the fight, Emmanuel Steward said: "Wladimir was in incredible shape. I've never seen anything like this in my career. I know what it looks like when a boxer is getting hurt from punches. There was definitely something else that caused problems for Wladimir".[94]
Shortly after the fight Klitschko was rushed into hospital. An examination showed Klitschko's blood sugar level almost two times higher than the permissible norm. According to members of Klitschko's team, the doctor told them that Klitschko had been "inches away" from falling into a diabetic coma, and that with blood sugar level that high, Klitschko would've been incapable of handling a single proper training session.[95][96][97][98] After returning from the examination to the hotel, he fell ill with nausea, followed by physical weakness.[99] On 12 April, he arrived in Las Vegas and donated blood and urine samples for an independent examination, which was supposed to be done by Donald Katlin, who specialised in such cases. The examination showed no signs of anabolic steroids in his blood, but Katlin suggested that Klitschko could have been poisoned with Haloperidol. The drug has no taste or smell and causes mental disorders, which are accompanied by impaired coordination, a weakening reaction and overall physical weakness.[100][failed verification][101] Following the results, Klitschko demanded the tests taken by the Medical Center of South Nevada and the Nevada Quest Diagnostics to be passed on to Dr. Robert Wow for further research, but the A sample had already been disposed of, while the B sample, which was supposed to be stored for years, disappeared.[95][99][102] Dr Margaret Goodman, the chairwoman of the Nevada State Athletic Commission's medical advisory board and Nevada's chief ringside physician was in the ring and attending to Klitschko seconds after the referee stopped the fight. Her initial diagnosis of a Grade 3 concussion was confirmed at the hospital after further tests. Goodman was sceptical of the theory that Klitschko had been drugged.[102]
As a result of the circumstances that surrounded the fight, FBI started an investigation.[92] Judd Bernstein, the lawyer representing Klitschko, suggested that he was a victim of an ongoing fight fixing in Las Vegas (which also included fraudulent medical reports), which was investigated by FBI at the time.[103] Bernstein, along with some other journalists, pointed out that in the last 48 hours before the beginning of the fight, the betting odds in favour of Klitschko rapidly dropped from 11-to-1 to 3,5-to-1.[104][105][96][106] According to journalist Keith Teixeira, a group of approximately 40 people associated with Brewster's manager Sam Simon bet from $50,000 to $100,000 on Brewster's victory.[94][92] Members of Klitschko's team also pointed out that shortly before the fight, a security camera recorded a moment when two people entered Klitschko's booth and were there for four minutes. These people had badges, but weren't members of Wladimir's team.[96][107] Wladimir's brother Vitali claimed that during registration of the boxer and his team, the card that belonged to Emmanuel Steward's assistant had already been registered on someone else, and that such card would allow its owner to enter any sporting hall in the building.[104][95]
After the fight, Wladimir's cutman Joe Souza was fired. During the fight, Souza used vaseline on Wladimir's face but also body, which had never been done in any of Klitschko's previous fights. As a replacement, the team hired Jacob "Stitch" Duran.[95][108][97]
Klitschko vs. Williamson, Castillo, Peter
[edit]Following his loss to Brewster, Klitschko began his journey back towards the top of the heavyweight division. First, he faced hard-hitting DaVarryl Williamson.[109] The fight took place at Caesars Palace in Las Vegas, Nevada.[110] Williamson dropped Klitschko forty seconds into the second round, but was outboxed throughout the rest of the bout.[109] An accidental head butt in the closing seconds of the fifth round caused Klitschko bleeding from a cut above his right eye. Due to the cut, the fight was prematurely stopped, with Klitschko being declared the winner by technical decision. Two of the judges scored the fight identically 49–46 in favour of Klitschko, while the third judge had Williamson winning 48–47.[111][112]
After defeating Eliseo Castillo by fourth-round TKO, Klitschko signed to fight Samuel Peter in an IBF and WBO eliminator. Coming into the bout, Klitschko was viewed by many as the underdog[113] against the 7-to-5 favourite Peter who had won all of his 24 fights, with 21 of them having ended inside the distance. At the time, Samuel Peter was considered one of the brightest prospects in the heavyweight division. Distinguished boxing coaches Angelo Dundee and Teddy Atlas expected Peter to win.[114][115] Wladimir's team, including his brother Vitali, were worried about Wladimir, and were against this fight to happen. Wladimir, however, insisted on fighting Peter, claiming that beating a feared, hard-hitting fighter like Samuel Peter would help him to regain his stock and become mandatory challenger for two heavyweight belts.[116][117]
The first four rounds were tentative, with Klitschko working behind the jab, not allowing Peter to close the distance. At the end of the third, Peter staggered Klitschko with a powerful left hook. He hurt Klitschko again in the fifth with another left hook, sending Klitschko to the canvas with the rabbit punch. The referee counted it as the knockdown. Peter immediately went for the attack after Klitschko got up, dropping him again with the rabbit punch. The referee scored it as the second knockdown.[118] Klitschko regained composure and outboxed Peter through sixth to ninth rounds, with Peter frequently trying to hit Klitschko with the rabbit punch whenever escaping from a clinch.[118][119] Near the end of the tenth round Peter staggered Wladimir with a hard right hand, eventually sending Klitschko to the canvas with another right when Wladimir was backing away. In the 11th and 12th rounds, Klitschko was trying to keep Peter at the distance using straight punches. Peter caught him with a left hook in the last round, but was unable to capitalise on it. Instead, Klitschko caught him with a hard counter left hook of his own, staggering Peter for the first time in the fight.[118][119] Eventually the bout went the distance, with Klitschko winning the fight by clear unanimous decision (UD). All the judges scored the bout identically 114–111.[115][120]
Klitschko vs. Byrd II, Brock, Austin
[edit]On 22 April 2006, in Mannheim, Germany, Klitschko faced Chris Byrd for a second time, this time for the IBF heavyweight title. At the time of the bout, Byrd was ranked as the best heavyweight by The Ring, while Klitschko was ranked eighth.[121] Coming into the fight, Klitschko was viewed as the favourite. Many observers expected Klitschko to dominate Byrd similarly to their first bout.[122]
April 22nd, 2006 may be one of the most momentous dates in the history of boxing. On that day, Wladimir Klitschko of Ukraine will most likely easily defeat Chris Byrd of the United States for Byrd's IBF heavyweight title. If that result occurs, it may mark the dawning of a new era in boxing. Three of the four major titlists will be from Eastern Europe. Like the flood waters of Hurricane Katrina that swept away much of New Orleans, a rising tidal wave of Eastern European fighters threatens to sweep away American supremacy in the heavyweight division, putting an end to an era that began with the reign of John L. Sullivan — 124 years ago.
Klitschko defeated Byrd by TKO in the seventh round, becoming a two-time heavyweight world champion in the process. Klitschko dominated the fight using his jab and superior reach, knocking Byrd down twice, once in round five and once in round seven. Byrd beat the count after the second knockdown, but his face was battered and bloody, and the fight was waved off.[124] At the time of the stoppage, judge Roy Francis had the challenger winning every round, while two other judges, Steve Epstein and Robert Hoyle, gave Klitschko all but one round.[125]
In his first title defence, Klitschko agreed to face then-undefeated heavyweight contender Calvin Brock. With a record of 29–0, 22 KOs, Brock was considered one of the most promising and demanded American heavyweight prospects at the time. In an ESPN interview in July 2005, Mike Tyson named him and Samuel Peter as his favourite fighters from the new crop of heavyweights.[126][127][128] In the build-up, Brock expressed confidence in his abilities: "I can adopt to every style. He's big like Jameel McCline, but a better fighter. I will beat him and become the heavyweight champion of the world. Klitschko has a good jab, but they also said Timur's best weapon was his jab. I have a good jab myself. I can adapt to anybody's style, anybody's strength and turn their weapon against them." He also dismissed claims that the division lacks strong competition: "The heavyweight division is stacked with a bunch of talent. It's not weak, definitely not weak. The division is pretty strong and that's why the title keeps changing hands."[126][129]
The fight took place on 11 November 2006 at Madison Square Garden.[130] In the opening rounds, Brock's economical but effective movement made Klitschko reluctant to throw punches, with Wladimir not being able to fully establish his rhythm.[131] In between the third and fourth rounds, Klitschko's trainer Emmanuel Steward urged Wladimir to press the action. Klitschko started fighting more aggressively, hurting Brock several times with the right cross. In the fifth round, Brock opened a cut under Klitschko's left eye that started bleeding heavily in the sixth. In the seventh round, Wladimir caught Brock with a counter right hand before sending him to the canvas with another straight right.[131][132] Brock was able to get up but was unsteady on his feet, prompting the referee to stop the bout.[131][132]
Klitschko then faced mandatory challenger Ray Austin on 10 March 2007, at the SAP Arena in Mannheim, Germany. 36-year-old Austin was mostly known for draws against Sultan Ibragimov, Larry Donald and Lance Whitaker. In preparation for the fight, Austin was trained by a prominent coach Stacey McKinley.[133] Klitschko won by a second-round KO with four consecutive left hooks to Austin's head. Klitschko did not throw a single right hand in that fight.[134]
Klitschko vs. Brewster II, Ibragimov, Thompson
[edit]Klitschko then avenged one of his previous losses as he defeated Lamon Brewster on 7 July 2007, in Cologne, Germany. Brewster's corner asked the referee to stop the fight at the end of the sixth round. It was later revealed that Klitschko fought most of the fight with a broken middle finger on his left hand.[135]
By the end of October 2007, Wladimir Klitschko started negotiations with then-WBO world heavyweight champion Sultan Ibragimov about the unification showdown in the near future. This would be the first heavyweight unification fight since 13 November 1999 when WBC champion Lennox Lewis defeated then-WBA and IBF champion Evander Holyfield.[136][137] On 20 November, Klitschko and Ibragimov officially signed the contract for their unification clash to take place on 23 February 2008 at Madison Square Garden.[138] Two days later in Moscow, a first pre-fight press-conference was held.[139] Klitschko began his preparations for the fight on 18 December. His training camp was located between Santa Monica, Los Angeles and Palm Beach, Florida.[140] Ibragimov began his preparations for the bout on 25 December. Among Ibragimov's sparring partners were Klitschko's former opponent Jameel McCline and Swedish heavyweight prospect Attila Levin.[141][142]
In the pre-fight prediction, a vast majority of Ukrainian, Russian and American observers expected Klitschko to win by either stoppage or unanimous decision. Out of six journalists of the Ukrainian magazine Ring, five predicted Klitschko to stop Ibragimov, with only one expecting Klitschko to win by decision. 24 of 26 members of boxingscene.com expected Klitschko to come out as the winner – 18 of them predicted the win to come by way of KO/TKO, one expert predicted decision, while the remaining five were unsure about either possibility. The remaining two experts predicted Ibragimov to win by decision. 10 of the 12 members of ringsidereport.com picked Klitschko to win, with eight of them expecting the victory to come by way of KO/TKO. The remaining two picked Ibragimov to win by stoppage.[143] In the build-up to the fight, Klitschko's trainer Emmanuel Steward said that Sultan Ibragimov was going to be Wladimir's toughest opponent to date, praising Ibragimov for his hand speed and mobility, while Klitschko complimented Ibragimov on his accomplishments: "Sultan Ibragimov is a boxer that hasn't lost in any of his 23 fights, with the sole draw being against Ray Austin. His amateur career can be described as fantastic, and the fact that he's the heavyweight champion of the world speaks volumes about his professional career as well. I think he's a strong and dangerous opponent that should not be underestimated. His last two fights against Shannon Briggs and Evander Holyfield proved that."[144] Ibragimov's trainer Jeff Mayweather was confident that Ibragimov would be able to establish his rhythm and "press Klitschko to the corner".[145] The pre-fight build-up was marked with controversy after Ibragimov's manager Boris Grinberg insulted Klitschko during one of the interviews: "Sultan Ibragimov knocks out this Ukraine gay, motherf***er!". Grinberg later apologised to Klitschko.[146] The day before the bout, Klitschko weighed in at 238 pounds (108 kg), the lightest since 1999,[147] while Ibragimov's weight was 219 pounds (99 kg), his lightest since 2005.[148]
From the opening bell, both fighters fought tentatively, avoiding risks. Klitschko retreated onto the outside, fighting at a distance and remaining unreachable for Ibragimov who tried to establish his right jab but had his right hand constantly pushed down by Klitschko. By the end of the opening round, Klitschko became more active with his jab, while Ibragimov unsuccessfully tried to catch Wladimir with a series of right and left hooks. By the third round, Klitschko took control of the center of the ring, keeping Ibragimov at the end of his left jab and occasionally throwing right jabs as well.[149] In the fifth round, Klitschko caught Ibragimov with a straight right hand, however Ibragimov appeared to be unhurt. Most of Ibragimov's attempts to close distance ended with Klitschko tying him up. In the second half of the fight, the situation did not change, with Klitschko keeping Ibragimov at distance with straight shots, while Ibragimov was only able to occasionally catch Klitschko with single shots to the body. Ibragimov's corner was almost silent from the sixth round onwards, unable to give their man any meaningful advice.[150] Klitschko's dominance became even more visible after he caught Ibragimov with a straight right in round nine, almost knocking him down. He caught Ibragimov again with a counter left hook at the end of the eleventh. The twelfth round saw Ibragimov unsuccessfully trying to catch Klitschko with overhand shots. Ultimately, the fight went the distance, with Klitschko being declared the winner by unanimous decision. The judges scored the bout 119–110, 117–111 and 118–110.[151][152][153] Klitschko reportedly earned $9 million for the fight.[154][155] He donated $500,000 of his earnings to the Bronx's Laureus Sport for Good Foundation.[156]
The fight was heavily criticised by observers and prominent boxing public figures.[157][158] Boxing promoter Bob Arum called the fight "an absolute shame",[159] while Dan Goossen described it as "awful".[160] Boxing journalist Phil Santos pointed out that Klitschko fought for the majority of the fight "only with his left hand", proving once again that he "is the best heavyweight in the world right now". Santos also noted that such cautious, safety-first style was not going to help Klitschko to increase his popularity in the United States.[161] Some observers were more apologetic of Klitschko's performance: "It's really irritating that so many people, people that know very little about boxing, say that Klitschko's dominance means stagnation for the heavyweight division. There's no denying that once Klitschko collects all the belts, he will go down as one of the all-time greats. Yes, he fights cautiously and isn't willing to exchange shots, but who told us that greatness in boxing is measured with the number of knockdowns? Why the boxer that is able to not get hit with a hard shot over the course of twelve rounds is less great than the champions from the past that sacrificed their health for the sake of success?"[162]
On 12 July 2008, Klitschko faced mandatory challenger Tony Thompson. The fight took place at Color Line Arena in Hamburg, Germany, the same venue where Thompson had defeated then-highly regarded German boxer Luan Krasniqi in a WBO world heavyweight title eliminator almost a year prior.[163][164][165][166][167] In the build-up to the fight, Klitschko praised Thompson for his defensive abilities, while Klitschko's trainer Emmanuel Steward described Thompson as "one of the most difficult fights we will have".[168][169] In the pre-fight interview, Thompson promised that he wouldn't run away from Klitschko, and would stand in front of him and fight toe-to-toe.[170] Being 6 ft 5 in tall with 81½ in reach, Thompson was of similar height and reach as Klitschko.[171] Many observes predicted Thompson to be a tough challenge for Klitschko, expecting Klitschko to ultimately win by TKO in the second half of the fight before the fighters would enter the championship rounds.[172][173] Coming into the fight, Klitschko weighed in at 241 pounds, 6.5 lbs lighter than Thompson.[167]
The opening rounds were tentative, with Klitschko seemingly struggling with Thompson's awkward southpaw style. All three judges gave the first round to Thompson.[170][174] In the second round, both fighters suffered a cut above the right eye after an accidental headbutt.[169] Klitschko's eye began to swell after Thompson caught him with the right hook in the fifth round.[169] After the sixth round, however, Klitschko appeared to have established his dominance in the ring, hurting Thompson with several straight right hands. After the seventh round, both fighter started showing signs of fatigue.[169] In the tenth round, Thompson fell to the canvas during a clinch. It appeared as if Thompson fell down mostly due to being tired rather than being pushed by Klitschko.[170] In the middle of the eleventh, Klitschko caught Thompson with the straight right hand which Thompson did not see coming, falling to the canvas again, with the referee starting the count this time. Thompson beat the count but was unsteady on his feet, prompting the referee to stop the fight.[170][169] At the time of the stoppage, Klitschko was unanimously winning on the scorecards, with scores 98–92 (twice) and 99–91.[171]
In the post-fight interview, Klitschko admitted that the fight turned out to be tougher than expected: "It is not so easy to defend all the titles and it has been a while since I last had a black eye so today I really look like a boxer. I did not expect the victory to come that hard."[169][175] "I was fatigued, I thought he was fatigued too," Tony Thompson said after the fight. "He did what a great champion did, he took advantage when I was vulnerable. The only thing that hurts on me is my heart – for losing."[169] Emmanuel Steward described the knockout sequence as the one that showed the difference between a great heavyweight and the best heavyweight in the world: "They were both tired, but Wladimir has experience now, then he came back with a second wind. The experience is what helped Wladimir to come back with the second wind and find an opportunity to secure the stoppage win."[170][169] Former undisputed world heavyweight champion Lennox Lewis praised Klitschko for his performance: "I've been watching Klitschko for some time, and he's improving with every fight."[170] Meanwhile, unified world cruiserweight champion David Haye criticised the champion for his performance: "If he fights me in the same way he fought that guy he will be knocked out in three rounds. He has got the perfect style for me. I don't want him to have any more fights before me as I don't want someone else to do what I will do against him."[175] Klitschko reportedly earned €8 million (around $12.7 million) for the bout.[176][177]
Klitschko vs. Rahman, Chagaev, Chambers
[edit]
Klitschko was scheduled to defend his titles against Alexander Povetkin later in 2008,[178] but on 25 October, Povetkin withdrew from the fight due to an ankle injury. Instead, Klitschko faced Hasim Rahman on 13 December 2008 and won by TKO. This was the third time Klitschko fought at the SAP Arena in Mannheim, Germany. He dominated the fight, winning every round while making good use of his left jab. Rahman seemed unable to withstand the Klitschko's punch power. In the sixth round, Klitschko knocked Rahman down with a series of left hooks, leaving Rahman visibly disoriented. Between the sixth and seventh rounds, the referee warned Rahman he's going to stop the fight if Rahman continues absorbing punishment without firing back.[179] The referee ultimately called a stop to the contest in the 7th round after Rahman failed to respond to a series of shots.[180][181][182] At the time of the stoppage, Klitschko was leading on all three judges scorecards, respectively 60–53, 60–53, and 60–47.[183] According to CompuBox, Klitschko landed 194 punches (50.4% accuracy) to Rahman's 35 (16.8% accuracy), a nearly six-fold disparity.[184]
Klitschko was scheduled to face David Haye on 20 June 2009, but Haye pulled out within weeks of the fight complaining of a back injury.[185] Immediately after news about Haye's injury broke into public, a handful of heavyweight fighters, such as Alexander Povetkin, Chazz Witherspoon, James Toney, Odlanier Solis, Dominick Guinn and Eddie Chambers, expressed their interest in replacing Haye for the Klitschko showdown.[186] Instead, Klitschko's team started negotiations with Ruslan Chagaev, who was ranked third best heavyweight in the world by The Ring, and WBA world champion Nikolai Valuev, who was regarded as a big draw in Germany at the time. Ultimately, Klitschko reached agreements with Chagaev who agreed to step in for Haye as a last-minute replacement (Valuev's team wanted the fight to be postponed until autumn of that year).[186][187][188] Some observes believed that Chagaev was a better challenege for Klitschko than Haye, given his position in the ranking and the fact that, alongside WBO and IBF world titles, vacant The Ring world heavyweight title was also on the line.[189][190] In the pre-fight comparison, The Ring was giving Klitschko an advantage in power, speed and athletic ability, as well as experience, while also crediting Chagaev for having better defence, praising him for his fundamentals and footwork. In terms of technique, both fighters were described as of equal level.[191]
The fight took place at Veltins Arena in Gelsenkirchen, with over 61,000 fans having attended the fight, the largest audience for a boxing fight in Germany since 1939, when Max Schmeling knocked out Adolf Heuser in front of 70,000 people in Stuttgart.[192][193] Klitschko dominated the fight, keeping Chagaev at the end of his jab and throwing straight right hand whenever necessary. Klitschko dropped Chagaev near the end of the second round, and was gradually fighting more aggressively as the fight progressed. Chagaev's trainer Michael Timm did not allow Chagaev to come out for the tenth round, prompting the referee to wave the bout off, declaring Klitschko the winner by corner retirement (RTD).[194][192] This win had added significance because even though the WBA title was not on the line, many saw Klitschko as the rightful champion.[194][193]
On 9 December 2009, Klitschko's management group, K2 Promotions, confirmed that a bout with Eddie Chambers had been agreed to take place in Germany on 20 March 2010. This mandatory title defence, originally scheduled for December 2009, had to be delayed due to a hand injury that Klitschko sustained in training that required surgery.[195] In the build-up to the fight, Klitschko described Chambers as "the best American heavyweight right now".[196] In the pre-fight comparison of the fighters, The Ring gave Chambers the upper hand in speed and athletic ability, as well as defence, while crediting Klitschko as more powerful and experienced.[197] In the United States, the bout was not televised by any TV station but was aired on the Klitschko's official website for $14.95 instead.[198][196][199] The official venue was the multi-functional football stadium ESPRIT Arena in Düsseldorf, Germany.[196][200]
The bout turned-out to be one-sided, with the champion winning rounds keeping Chambers at the end of his jab and occasionally throwing straight right hands.[201] In the opening rounds, Chambers lifted Klitschko and took him down several times but was not deducted a point nor warned.[201] In between the championship rounds, Klitschko was criticised by his trainer Emmanuel Steward for not fighting aggressively, despite comfortably winning on the scorecards.[201][196] Klitschko picked up his pace during the final round and, with few seconds left, landed a left hook on Chambers' temple. The punch made Chambers fall forwards and lose consciousness for an extended period of time. The referee immediately stepped in and called an end to the contest.[202][203][204][205] It remains the only stoppage loss of Chambers' career.
Klitschko vs. Peter II
[edit]
Following the match with Chambers, a unification fight between Klitschko and David Haye, who, as of November 2009, had held the WBA title, appeared to be in the offing. Klitschko called out the Briton on YouTube in April 2010, stating, "I want to send this message to boxing fans and directly to David Haye. David, you've bitched out on fighting both Klitschko brothers twice already and now's the time to make it happen. On behalf of the boxing fans around the world, I am officially calling you out to fight me. You can't run away from me forever and you need to follow through with this fight if you want to be respected. I'm ready. What're you waiting for?"[206][207]
Haye's trainer, Adam Booth, indicated that Haye would be willing to accept the challenge.[208] Both sides began negotiations for a potential fight and the bout was targeted for September.[209] As the negotiations continued to move forward,[210] the unification fight between Klitschko and Haye was expected to take place in Germany rather than England.[211][212] The IBF set a deadline to end negotiations on 17 May. A few days before the deadline, Haye said he was interested in fighting the older Klitschko, Vitali, rather than Wladimir.[213] The fight did not materialise and Klitschko was set to take on mandatory challenger Alexander Povetkin. On 17 May 2010, the 30-day period of negotiation began for Klitschko to defend his championship against Povetkin.[214] Within this period, discussions to make a fight with Haye were still ongoing.[215]
The bout between Klitschko and Povetkin was initially tentatively scheduled to take place in Frankfurt, Germany, on 11 September 2010. In July 2010, it was confirmed that the bout would be taking place in Frankfurt,[216] with Samuel Peter replacing Povetkin for the scheduled fight as Povetkin failed to show up to the press-conference, deciding to pull out of the fight at the advice of his coach Teddy Atlas who believed Povetkin was not ready to face Klitschko.[217][218] Klitschko faced Peter for the second time, as they had fought in 2005 previously.[219][220] Peter weighed in at 241 pounds, two pounds lighter than their first fight.[221] Klitschko came in at a career heavy of 247 pounds.[221]
Peter started the fight very aggressively and caught Klitschko with a good left hook in the opening minute, although Klitschko ended the round well. Peter was caught with three hard right-hands in the second round, one of which seemed to stun him. Peter tried to duck under the Klitschko jab, but was being tied up on the inside. After four rounds, the fight became one-sided in Klitschko's favour. Peter's right eye was closing and he was taking heavy punishment. After the ninth round, Peter's trainer Abel Sanchez said he would give him one more round.[citation needed] Emmanuel Steward also implored Klitschko to be more aggressive. Peter swung wildly in the tenth and Klitschko put him down with a concussive combination. Referee Robert Byrd did not start a count and waved the fight off, awarding Klitschko the win by KO. Klitschko reportedly earned €5 million ($6.3 million) for the fight.[222] Klitschko was set to fight Derek Chisora on 11 December, but the fight was later called off on 8 December due to Klitschko tearing a muscle in his abdomen.[223][224]
Klitschko vs. Haye
[edit]On 5 January 2011, it was announced that Derek Chisora would get his fight with Klitschko. This enraged David Haye's trainer Adam Booth, who described the move as a "disgrace" on a heated live phone-in with Sky Sports News. Booth alleged Haye had met every single one of Klitschko's demands.[225] The fight against Chisora was rescheduled for 30 April 2011 and was going to take place in SAP Arena, Mannheim.[226] However, on 4 March, it was announced that Klitschko had pulled out of the fight due to not being fully recovered from a torn abdominal muscle. On 5 March, it was instead announced that the highly anticipated fight against Haye would take place on 2 July 2011.[227] The fight was contingent on Klitschko's recovery from a torn abdominal muscle. The contract was written so that if Klitschko was not fully healed, then Haye would fight his brother, Vitali.[228]
Klitschko fought Haye in a heavyweight unification fight for the WBA (Super), IBF, WBO, IBO, and Ring magazine heavyweight titles. The fight took place at the Imtech Arena in Hamburg, Germany on 2 July 2011. Klitschko and Haye agreed to a 50–50 split of the purse and Haye was allotted 7,000 seats at the venue.[229][230][231] Klitschko won by UD, the three judges scored it 117–109, 118–108, and 116–110 all in favour of Klitschko. According to CompuBox, Klitschko landed 134 punches of 509 thrown (26.3% accuracy), while Haye connected on 72 shots out of 290 (24.8%). Klitschko outlanded Haye in every round but fourth.[232] Haye revealed afterwards that he had a broken toe on his right foot, and claimed that it had hindered his game plan for the fight as he felt he was unable to jump out at Klitschko like he had previously in his career. Haye was subject to much derision and ridicule from within the boxing community and fans after citing his toe as part of the reason why he lost.[233] Despite this Klitschko claims that Haye was unable to fight because he was just too good for him.[234][235] [236] Both Klitschko and Haye reportedly earned $32 million each for the fight.[237]
After winning the WBA title, all of the major heavyweight titles were in the hands of the Klitschko family. Wladimir and Vitali became the first and only pair of brothers to hold all of the heavyweight titles simultaneously.[238]
Klitschko vs. Mormeck, Thompson II, Wach
[edit]On 6 October 2011, Klitschko announced his next fight. It was originally to be on 10 December 2011 against the former two time unified cruiserweight world champion, Jean-Marc Mormeck (36–4, 22 KOs). The fight would have taken place at Esprit Arena, Düsseldorf.[239] This was Wladimir's first title defence after his win over David Haye unified all major heavyweight belts in the hands of the Klitschko brothers. The fight was predicted to generate 500 million viewers worldwide, similarly to Wladimir's fight against Haye.[240] On 5 December 2011, the fight was cancelled because Klitschko checked into a hospital to have a kidney stone removed. After the removal operation he suffered from fever and inflammation.[241] The fight was rescheduled for 3 March 2012, with Klitschko dominating and knocking out Mormeck in the fourth round.[242] CompuBox showed that in the 10 minutes and 12 seconds the fight lased, Klitschko landed 39 of 135 punches thrown (29%) and Mormeck landed just 3 of 19 thrown (16%). Mormeck failed to land anything in rounds 1 and 4.[243]
On 4 March 2012, Klitschko stated that he would next fight his mandatory challenger Tony Thompson (36–2, 24 KOs), who had been ranked as the world's eighth best heavyweight by BoxRec at the conclusion of the previous year,[244] in a rematch from their first fight in 2008. At the time, he stated that the newly opened Barclays Arena in New York were interested in showcasing a Klitschko brother. Since they last fought, Thompson recorded five straight wins, all by KO.[245] A purse bid was set by the IBF, where Klitschko, upon request, would receive 85% of the purse split, compared to the usual 75%.[246] The fight was confirmed to take place at the Stade de Suisse in Berne, Switzerland on 7 July.[247] In an interview, Klitschko admitted that Thompson was not his first choice and that he would have rather fought someone he had not fought before.[248] "So far I've always been better in rematches. However, I must not take this lightly as Thompson knows me better than any other fighter", Klitschko said in the build-up to the fight.[249] "I've been waiting for this rematch for so long", Thompson said during one of pre-fight press-conferences, "In Bern, I'm gonna finish what I've started 4 years ago - knock Klitschko out and take the belts back to the United States".[250] Thompson weighed in at 244.75, dropping 10.75 lbs from his last fight, while Klitschko weighed in at 249, the heaviest in his entire career. The additional weight appeared to be muscle.[251]
In the first round, both fighters were cautious, patiently studying each other. Klitschko became more dominant in the second, working mostly with his jab. Thompson unsuccessfully went for the attack and in the process fell to the canvas. The referee did not rule it a knockdown. In the third round, Thompson hurt Klitschko for the first time in the fight with a counter left hand but was still being outboxed by Klitschko. In the fifth round, Klitschko pressed Thompson into a corner and hurt him with a straight right hand, knocking him down. Thompson beat the count but looked hurt, however he was able to survive that round. Klitschko continued his assault in the sixth, sending Thompson down again with a flurry of shots. Thompson got up but had to hold on to the ropes to stand, which prompted the referee to stop the fight, declaring Klitschko the winner by sixth-round TKO.[252] "From the beginning, I had no doubt that I would successfully defend the titles. But it was hard to time an accurate shot. Thompson was elusive, he didn't lose an eye contact at any moment in the fight and was able to see most of my punches", said Klitschko in a post-fight interview.[253] It was his twelfth consecutive title defence, the third-most in heavyweight history.[254][255] CompuBox stats showed Klitschko landed 51 of 121 total punches thrown (42%) and Thompson landed only 25 of 183 thrown (14%).[256]
There was first mention of a potential Klitschko vs. Mariusz Wach (27–0, 15 KOs) fight in August 2011 when Klitschko's team approached Wach's promoters for a fight, however nothing materialised.[257] Wach's promoter Global Boxing stated that it was Klitschko's advisor Shelly Finkel that contacted them. Bernd Boente denied these claims.[258] In August 2012, serious negotiations took place for the fight. A date in November was considered with the venue likely to be in Hamburg, Germany. Terms were fully agreed within days of the negotiations for the fight to take place 10 November.[259][260] Klitschko revealed he would train with Johnathon Banks due to Steward recovering from a bowel operation.[261][262] On 25 October, Steward died at the age of 68.[263] The fight was the first time in his 16-year professional career that he had faced an opponent taller than himself.[264] At 2.02 metres tall, with a reach of 2.08 metres and weighing 251 pounds, Wach was four centimetres taller than Klitschko with a reach two centimetres longer.[265][266] In Poland, the fight was available via pay-per-view platform on Canal+ Sport for 39 zł and Polsat Sport for 40 zł.[267][268][269][270]
On fight night, at the 02 World Arena, Klitschko dominated and retained his titles with a one sided UD. The three judges' scored the fight 120–107, 120–107, and 119–109. The bout opened with a battle between jabs which was won by Klitschko, who was following his jabs with his signature straight right. Wach managed to wobble Klitschko in round five but failed to take advantage. Wach also showed a great chin later in the fight when Klitschko began to let his hands go more landing thunderous shots.[271][272] During the course of twelve rounds, Klitschko landed 274 of 693 punches landed (40%), whilst Wach landed 60 of his 308 thrown (19%).[273] After the fight, there were allegations against Wach that he had used steroids.[274] Klitschko reportedly earned €5.8 million (cca $7.25 million) for the fight.[275][276][277][278]
Days before the Klitschko vs. Wach fight took place, it was revealed that Team Sauerland offered Klitschko €5 million (around $6,5 million) for a possible fight against then-WBO cruiserweight champion Marco Huck in the future. At the time, Huck was preparing for a title defence against Firat Arslan.[279] Klitschko's manager Bernd Boente turned down the offer stating money was not the issue. The reason the fight would never get made was due to the fact that the Klitschko's had a contract with German television network RTL and Huck was signed with their rival network ARD.[280]
Klitschko vs. Pianeta, Povetkin, Leapai
[edit]
At the end of 2012, the WBA ordered Klitschko to fight WBA (Regular) champion Alexander Povetkin of Russia by 24 February 2013,[281] but the two sides couldn't reach an agreement.[282] The WBA let Klitschko have another voluntary title defence before taking on Povetkin, but there should have been a signed contract with Povetkin before 28 February, with a new deadline for their bout no later than 31 July.[283][284]
On 5 March 2013, K2 Promotions announced that Klitschko would fight another undefeated contender, Italian Francesco Pianeta, on 4 May at SAP Arena in Mannheim, Germany.[285] Klitschko had received criticism in regards to past opponents. Pianeta was no different. Speaking to ESPN, he said, "I'm getting always criticised with my opponents, it doesn't matter are they well known or not so much and it's always very difficult to fight against someone that is not known because you are always getting these critics." Pianeta said it was the biggest experience of his life, but not his biggest fight. He went on to say he won his biggest fight against cancer in 2009.[286] From the start, Klitschko systematically broke down the Italian, consistently landing flush straight right hand shots. He dropped Pianeta with a right hand in round four, a left hand put Pianeta down in the fifth; the fight ended at 2:52 in round six when Klitschko put Pianeta down for the third time.[287][288][289] According to CompuBox Stats, Klitschko landed 116 of 277 punches thrown (42%) and Pianeta landed 24 of 104 thrown (23%), an average of 4 punches landed per round.[290]
Promoter Vladimir Hryunov won the right to promote Klitschko vs. Povetkin with a purse bid of $23,333,330 and Russian businessman Andrey Ryabinsky putting up the money. Failed bids made were from K2 Promotions ($7,130,000) and Povetkin's promoter Sauerland Event's ($6,014,444). It allowed Ryabinsky to dictate the location of the fight and guaranteed the fighters the biggest purses of their careers. Based on being entitled to 75 per cent of the winning bid, Klitschko got $17,499,997, while Povetkin received $5,833,333.[291] The Klitschko camp were said to be surprised by the bid.[292] The fight was expected to generate around 100 million viewers in Europe.[293][294][295] It was reported that the president of Russia, Vladimir Putin, was going to attend the fight.[296][297]
The fight took place on 5 October 2013 at the Olympic Stadium in Moscow.[298] The bout was marred with over 160 clinches, most initiated by Klitschko, followed by several repeated roughhouse tactics throughout the match. This included Klitschko's leaning on his opponent and pushing his head down and throwing Povetkin away to prevent Povetkin from clinching, which resulted in the referee scoring some of Povetkin's fallings as knockdowns, as well as Povetkin's punching after the referee's break command and leaning his head too low.[299] Klitschko won by UD, scoring a knockdown in round two from a quick left hook, and three knockdowns in round seven, including one prompted from a straight right hand. All three judges scored it 119–104 on the scorecards.[300][301][302] Klitschko landed 139 of 417 punches (33%) and Povetkin connected on 59 of 283 (21%).[303] After the fight, Klitschko told in the interview that he had little desire to go for the knockout as the Russian crowd would be disappointed, which lead to speculations about the alleged agreement between the champion and organisers to let the bout go the distance,[304][305][306] which Klitschko later denied. With 9.2 rating, the fight became the most popular sporting event on Russian television in 2013, as well as the most watched TV programme of the year in Moscow with 13.9 rating, surpassing the Moscow Victory Day Parade.[307][308] Overall, the fight was watched by 23 million people in Russia.[309] The fight also became the most popular TV programme of the Ukrainian television in 2013 with 19.5 rating (audience 18+)[310][311] and 23 million total viewers[312] and the most watched programme of RTL Television in 2013, averaging 11 million viewers.[313]
In November 2013, Alex Leapai (30–4–3, 24 KOs) caused a huge upset in defeating then-unbeaten Denis Boytsov to become the WBO mandatory challenger.[314] On 5 January 2014 K2 Promotions announced that a deal was close to being reached for the Klitschko vs. Leapai fight to take place in Germany on 26 April.[315][316] Klitschko signed the contract on 3 February.[317] It was revealed that former world title challenger David Tua declined a 'lucrative offer' to spar with Klitschko ahead of the fight. Tua told Australian newspaper The Courier-Mail he "didn't want to help anyone beat a 'Samoan brother'".[318] On fight night, Klitschko knocked Leapai down three times, and referee Eddie Cotton stopped the fight with 55 seconds remaining in the fifth round.[319][320][321] Despite all the pre-fight trash talk done by Leapai, Klitschko told him, "You have truly a lionheart. You never stopped. You were challenging, you were bold. You had great desire to become a champion. Not many of my opponents have that type of attitude, that type of heart." Klitschko landed 147 of 396 punches thrown (37%), while Leapai landed a dire 10 of his 69 (14%). The 10 punches landed were made up of 6 jabs and 4 power punches.[322][323]
Klitschko vs. Pulev, Jennings
[edit]The IBF finally ordered Klitschko vs. Kubrat Pulev on 8 May 2014 and gave a 30-day negotiation period.[324] Klitschko's manager Bernd Boente stated that a potential fight with WBC champion Bermane Stiverne was their main priority, a fight which would see all of the heavyweight belts at stake. Kalle Sauerland stated that he would request to get Klitschko (62–3, 52 KOs) stripped of the IBF title if he didn't fight Pulev. At the same time Deontay Wilder was named as Stiverne's mandatory and the WBC stated he must fight Wilder next.[325] With the IBF purse bid split being 75–25 in favour of the champion, Klitschko requested the split be 80–20 in his favour. The IBF accepted the request.[326] A purse bid took place on 17 June, which was won by K2 Promotions. The winning bid was $7.25 million. Sauerland Event put in a bid for $5.29 million. As per the bid, K2 had the location set as the O2 World Arena in Hamburg, with a possible date being 6 September 2014.[327] In August, Klitschko suffered a bicep injury, thus postponing the fight by at least two months. A new date of 15 November was set.[328] HBO announced that they would air the fight live in the afternoon, making it the 19th Klitschko fight they would show.[329] Two days before the fight, it was revealed only the IBF title would be at stake for Pulev, however if Klitschko loses, the remaining titles would be vacated.[330][331] The fight's worldwide audience was estimated to be 300 million viewers.[332][333][334]
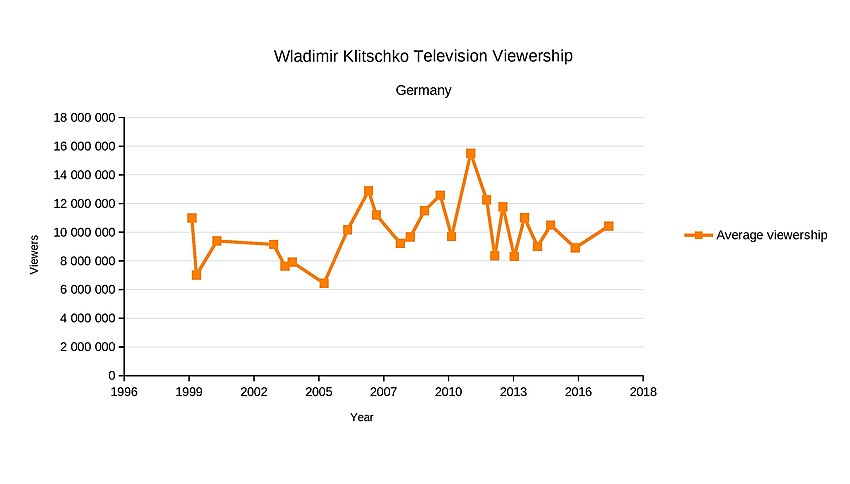
Despite making a spirited effort, Pulev suffered three knockdowns en route to being knocked out in round five by a devastating left hook. The time of stoppage was recorded as 2:11 of round five. In the post-fight interview, Pulev said, "Wladimir is a really good opponent, but he was lucky. I want a rematch". Klitschko praised Pulev, calling him a tough competitor.[335][336] CompuBox stats showed that Klitschko landed 38 of 89 punches thrown (43%), this included 47% of his power punches. Pulev managed to land only 25 of his 110 thrown (23%). This was made up of 10 jabs and 15 power shots landed.[337] The fight drew 10.5 million viewers in Germany[338] and 1.8 million viewers in Bulgaria, becoming the most watched sports event on Bulgarian TV since 2007 and the most watched programme in the history of the television channel Nova TV.[339][340][341][342] The fight also averaged 620,000 viewers on HBO and peaked at 700,000 viewers.[343]
On 20 January 2015 ESPN reported that the potential Klitschko vs. Jennings was confirmed and to take place on 25 April 2015 at Madison Square Garden. Negotiations initially started in November 2014. Klitschko's manager, Bernd Boente finally announced the fight and said all contracts had been signed. The Barclays Center in New York City was originally chosen to stage the fight, but no reason was given for the change of venue.[344]
It would be the fourth time Klitschko would fight at the Garden, his first time at the arena and the United States since 2008, defending his WBA (Super), IBF, WBO, IBO and The Ring heavyweight titles. He defeated Jennings by effective use of his jab and nullifying Jennings' offensive game on the inside, especially by holding Jennings, which resulted in the referee deducting a point in the tenth round for excessive holding, although Klitschko did end up winning via UD with scores of 116–111, 116–111, and 118–109. According to Compubox Stats, Klitschko landed 144 of his 545 punches thrown (26%) whilst Jennings landed 110 of 376 (29 per cent).[345] According to Nielsen Media Research, the fight averaged 1.637 million viewers on HBO, peaking at 1.742 million viewers.[346] With this win, Klitschko defeated 23rd boxer for the world heavyweight championship, beating a record held by Joe Louis for 66 years.[27][28] Klitschko reportedly earned $12.5 million for the fight.[347]
Klitschko vs. Fury
[edit]Klitschko was scheduled to take on undefeated heavyweight contender Tyson Fury, the WBO mandatory challenger, on 24 October 2015. On 25 September 2015, Klitschko postponed the fight, citing a calf injury. It was rescheduled for 28 November 2015.[348] On the night of the fight, there was much controversy, first starting with the gloves, then there was a complaint about the ring canvas. Klitschko reportedly had his hands wrapped without a representative of Fury present, so had to do them again.[349] Klitschko lost the fight by UD, with scores of 115–112, 115–112, and 116–111 all in favour of Fury.[350][351] It was the first defeat Klitschko had suffered in over ten years and marked the end of the 'Klitschko Era', referring to the time period where both Klitschko brothers dominated the division. Klitschko and Fury showed little offence during the twelve rounds, but Fury did enough to take the decision. Klitschko landed 52 of 231 punches thrown (22.5%) and Fury landed 86 of 371 thrown (23.2%).[352]
In the post-fight interview, an emotional Fury said, "This is a dream come true. We worked so hard for this. I've done it. It's hard to come to foreign countries and get decisions. It just means so much to me to come here and get the decision." He then took the microphone to thank Klitschko, "I'd like to say to Wladimir, you're a great champion. And thanks very much for having me. It was all fun and games during the buildup." Klitschko failed to throw his well-known right hand, mostly due to Fury's constant movement and mocking. He said, "Tyson was the faster and better man tonight. I felt quite comfortable in the first six rounds, but I was astonished that Tyson was so fast in the second half as well. I couldn't throw my right hand because the advantage was the longer distance he had." Klitschko had a rematch clause in place.[353][354]
Klitschko was entitled to a rematch with Fury as part of the contract for their first fight. The rematch was eventually announced on 8 April 2016 and set to take place in Fury's home town at the Manchester Arena in Manchester, England on 9 July 2016.[355] However, Tyson Fury announced via a YouTube video that the fight would be postponed due to an ankle sprain he had received during training. He apologised to his fans and confirmed the fight would be rescheduled for a later date. On 7 July, Fury announced via his Twitter account that the rescheduled fight would take place on 29 October at the Manchester Arena. On 23 September, Fury again postponed the fight after being declared "medically unfit",[356] before eventually vacating the WBA (Super), WBO, and IBO titles, citing problems with depression after testing positive for cocaine.[357] The rematch with Klitschko was cancelled as a result.
Klitschko vs. Joshua
[edit]
Days after the Fury rematch was called off, Klitschko was approached by Eddie Hearn, promoter of IBF champion Anthony Joshua, to fight on 28 November date they had set for a second defence. Terms seemed to have been agreed for a £30m fight showdown although an initial contract was yet to be signed.[358] After Fury gave up his world titles, it was said that Klitschko wanted the WBA (Super) title up for grabs in the potential match up against Joshua and waiting for approval, which the WBA kept postponing.[359] A reason as to why the WBA was delaying sanctioning the fight was due them having a legal settlement with Lucas Browne so he could fight for the vacant title next. Klitschko then turned his attention to fighting Browne instead on 10 December, a date his team had an arena set for in Germany.[360] On 24 October, Klitschko suffered a minor calf injury which would rule him out until 2017. Talks between the Klitschko camp and Hearn remained active with a fight set for the first part of 2017.[361][362] On 2 November, the WBA finally agreed to sanction a fight for their super title as long as Joshua defeats Eric Molina in December 2016.[363]
On 10 December, immediately after Joshua had defeated Molina at the Manchester Arena, Klitschko was invited into the ring by Hearn. It was announced that Klitschko and Joshua would face each other for the WBA (Super), IBF and vacant IBO titles at Wembley Stadium, London, on 29 April 2017.[364] WBA president Gilberto Jesus Mendoza confirmed that the winner will have to face mandatory challenger Luis Ortiz next, with deadlines due to be set after the unification fight.[365][366] A day later the IBF announced the winner must fight their mandatory challenger Kubrat Pulev. Because of this clashing with the WBA enforcing their mandatory, it was believed that either Joshua or Klitschko would have to vacate a title.[367] In January 2017, Eddie Hearn announced that over 80,000 tickets had been sold, a new box office record, overtaking Carl Froch vs. George Groves II. He put a request in for 5,000 more tickets to be made available.[368][369] At the weigh in, Klitschko weighed in at 240 and a quarter pounds, the lightest he has weighed since 2009. Joshua came in heavier at 250 pounds.[370]
In front of a post-war record crowd of 90,000 in attendance, Joshua won by TKO in a high-drama contest that saw both men giving their all. They fought a close and cautious first four rounds. In the fifth, Joshua came out and threw a barrage of punches, forcing Klitschko to the canvas. An angry Klitschko rose up and dominated Joshua for the remainder of the round, before landing a clean right hand and scoring his own knockdown in round six. The next few rounds were again cautious, both men wary of each other, until a reinvigorated Joshua attacked Klitschko in round eleven with an upper-cut blow to the right side of Klitschko's face which would be the beginning of the end for the Ukrainian. Joshua then put together a few small but powerful combinations which sent his opponent to the canvas. Klitschko again rose but Joshua knocked him down for a second time in the round by unleashing a seven-punch combination, flooring Klitschko with a left hook. Moments later Joshua tried to end the fight by swinging a few right hooks and managed to back Klitschko into the ropes where he again sent a barrage of punches with no reply. The referee then concluded that Klitschko had taken enough punishment and stopped the fight.[371][372]
At the time of stoppage, Joshua was ahead on two judges' scorecards at 96–93 and 95–93, while the third judge had Klitschko ahead 95–93. CompuBox stats showed that Joshua landed 107 of his 355 punches thrown (30.1%), and Klitschko landed 94 of 256 (36.7%).[373] In the post-fight interviews, Klitschko spoke about the rematch clause, but gave no indication as to whether he would activate it, "Of course we have a rematch in the contract. I need to analyze and see what the heck happened. I wish I could have raised my hands, but congrats to him. He got up, he fought back, and he won the titles."[374] In the press conference after the fight, Joshua said he would have no issues with having another fight with Klitschko, "I don't mind fighting him again, if he wants the rematch. Big respect to Wladimir for challenging the young lions of the division. It's up to him, I don't mind. As long as Rob thinks it's good I'm good to go." Eddie Hearn said Joshua's next fight would likely take place at the end of the year, possibly at the Principality Stadium in Cardiff.[375]
The fight averaged 659,000 viewers on Showtime in the United States. It was shown live and the fight began around 5 pm. ET and 2 pm. PT. Nielsen Media Research revealed the fight peaked at 687,000 viewers which was during rounds five and six.[376] The delayed tape-replay on HBO was watched by an average 738,000 viewers and peaked at 890,000.[377][378] In a press release, German TV channel RTL announced the fight was watched by an average 10.43 million viewers. The whole card averaged 9.59 million viewers. This was higher than the 8.91 million that tuned in to watch Klitschko vs. Fury in 2015. The fight did lower numbers than Klitschko's win over Mariusz Wach in 2012, which was watched by 11 million and Klitschko vs. Haye, which was seen by over 16 million.[379]
On 7 June 2017, the IBF granted Joshua an exception for him to rematch Klitschko instead of fighting mandatory challenger Kubrat Pulev. At this point, it was not said that the rematch would take place. Klitschko said he needed time to review his situation before agreeing to a rematch. It was only weeks after the fight, when Eddie Hearn filed the paperwork to the IBF to request the exception to the mandatory defence. The IBF explained that the rematch must take place no later than 2 December 2017 and the winner must fight Pulev next with no exceptions.[380]
On 11 July 2017, Eddie Hearn travelled to the US to apply for a Nevada boxing licence for promoting and to also scout potential locations in Las Vegas speaking to MGM. He had a tour of the T-Mobile Arena. Although Nigeria, Dubai and China were discussed, Hearn warmed up to the idea of the fight taking place in Las Vegas.[381] Hearn told Sky Sports, "We met with Richard Sturm and the team at MGM in Las Vegas yesterday and had a full tour of the T-Mobile Arena which is very impressive. There is a huge appetite from both sides to hold the rematch there and we will be talking further over the next week or so to see if that can become a reality."[382] Showtime's Stephen Espinoza said a deal could be reached quickly, as he was also eager to get Joshua, who has a contract with Showtime, to fight in US, "It's no secret we've been salivating about getting him over here and certainly that would be a phenomenal fight. It would be the biggest heavyweight Vegas fight in probably a couple of decades, so we would love to host it."[383] On 25 July, Hearn pencilled on 11 November 2017 for the rematch to take place at the T-Mobile Arena.[384] It was reported the fight could be pay-per-view in the US.[385]
Retirement
[edit]On 3 August 2017, Klitschko announced on his official website and social media channels that he was retiring from boxing.[386][387] He ended his professional career with 64 wins in 69 fights, 53 by knockout. He competed in 29 world title fights.[388][389]
Legacy
[edit]
During Klitschko's reign as world heavyweight champion, his fights would reportedly draw up to 500 million viewers worldwide.[b] Klitschko has been named multiple times among the 100 highest paid athletes in the world by Forbes: he was ranked 24th in 2012 (estimated earnings $28 million between June 2011 and June 2012), 41st in 2013 ($24 million), 25th in 2014 ($28 million), 63rd in 2015 ($22.5 million) and 98th in 2017 ($21.5 million).[390][391][392][393][394] Klitschko was unranked by Forbes in 2016, despite the fact that he reportedly earned $22.5 million for the fight against Tyson Fury in November 2015 alone (100th-ranked Buster Posey earned $20.8 million; 85th-ranked Conor McGregor earned $22 million).[395][396] Wladimir Klitschko's total professional career earnings' estimations vary between €150 million and $250 million.[154][155][397][398][399] Known for charity work and philanthropy, Wladimir is one of only 15 current or former alive athletes that have been named UNESCO Champions for Sport.[400][401][402]
Considered national heroes in Ukraine, in 2008 the Klitschko brothers were ranked number 15 in Inter's list of the 100 Greatest Ukrainians following a nation-wide poll that saw around 2.5 million people casting their votes.[403][404][405][406] Boxing fights involving one of the Klitschko brothers regularly attracted between 10 and 20 million viewers in Ukraine; Wladimir's fight against Alexander Povetkin generated even bigger viewership numbers, attracting 23 million viewers.[407][408][409][312] Wladimir has been named multiple times among the 100 most influential people in Ukraine by Korrespondent: he was ranked 95th in 2006, 88th in 2010, 43rd in 2011, 51st in 2012 and 45th in 2013.[410][411][412] Forbes named Klitschko the most popular celebrity in Ukraine in 2015, placing him ahead of a singer Svyatoslav Vakarchuk and Kvartal 95 Studio, and ranked him second and third in 2012 and 2013 respectively (the ranking wasn't conducted in 2014).[413][414][415][416] In 2017, Wladimir was honoured with the Order of Liberty, the highest Ukrainian honour that can be awarded to a person of any nationality, for his achievements in sports and contribution to the economical, scientific and cultural development of Ukraine.[417]
The Klitschkos were also considered big stars in Germany.[418][419][420] A survey carried out by TNS for the Horizont Sport Business in 2003 showed that 91.7% of Germans recognized Wladimir Klitschko while 70.5% celebrated his successes, making him the fourth most recognized and third most beloved athlete in Germany at the time.[421] According to DW, another research conducted no later than 2011 showed that nearly 99% of people in Germany recognized the Klitschko brothers.[422] The CPI Index conducted by the agency Celebrity Performance in 2012 had the Klitschkos ranked second on the list of the most marketable celebrities in Germany,[423][424][425] while in January 2014, based on a survey of 1151 respondents that was conducted by the same agency, the Klitschko brothers were ranked 6th in the "2013 Person of the Year" category.[426] Twelve of his fights generated above 10 million average viewers, and his world heavyweight title defence against Eddie Chambers in March 2010 drew bigger viewership numbers on RTL than the return of the Formula One legend voted the greatest German athlete of the 20th century[427][428] Michael Schumacher.[429][430][431]
Credited for selling out sports stadiums,[432][433][434] Klitschko had eight of his fights take place at sports stadiums in Germany, Switzerland and United Kingdom, with all but one having attendances ranging from 43,000 to 90,000.[435][436][437][438][439][440][441][442][443]
During his career, Wladimir defeated 23 boxers for the world heavyweight championship, the most in boxing history.[29][27][28][444] Klitschko holds several historical records, including the longest combined world championship reign in heavyweight history at 4,382 days (12 years);[24][29][27][28][445] the most beaten opponents and wins in world heavyweight title bouts since the international expansion of boxing governing bodies, at 23 and 25 respectively;[446][447] the most wins in unified title bouts and the longest unified championship reign in professional boxing history at 15 title bouts and 14 consecutive defences respectively. He has the second most total successful title defences of any heavyweight boxer with 23 (including his first reign as WBO champion), behind Joe Louis (25) and ahead of Larry Holmes (20) and Muhammad Ali (19) and the third most consecutive title defenses in heavyweight history. Klitschko fought in 29 world heavyweight title fights, more than any other boxer in history.[448]
As of May 2023, BoxRec ranks Wladimir Klitschko as the 21st greatest European boxer of all time.[449] According to BoxRec, Klitschko has also defeated 12 previously undefeated fighters with a combined record 267–0–5 (174 KOs) – these 12 included Najee Shaheed (professional record 16–0–1, 8 KOs coming into the fight),[450] Zoran Vujicic (14–0, 6 KOs),[451] Eliseo Castillo (18–0–1, 14 KOs),[452] Samuel Peter (24–0, 21 KOs),[453] Calvin Brock (29–0, 22 KOs),[454] Sultan Ibragimov (22–0–1, 17 KOs),[455] Ruslan Chagaev (25–0–1, 17 KOs),[456] Mariusz Wach (27–0, 15 KOs),[457] Francesco Pianeta (28–0–1, 15 KOs),[458] Alexander Povetkin (26–0, 18 KOs),[459] Kubrat Pulev (20–0, 11 KOs)[460] and Bryant Jennings (19–0, 10 KOs).[461] Wladimir has beaten 9 current or former world champions throughout his career. These included heavyweight champions Chris Byrd (twice), Ray Mercer, Lamon Brewster, Samuel Peter (twice), Sultan Ibragimov, Hasim Rahman and Ruslan Chagaev, two-weight world champion David Haye and unified cruiserweight champion Jean-Marc Mormeck.
Known for his punching power, Klitschko defeated his opponent inside the distance 56 times in 69 fights, an 81% knockout-to-win ratio (this includes two DQs and one TD). Of his thirteen remaining bouts, four involved an opponent that Klitschko knocked out in a rematch (Everett Martin, Chris Byrd, Lamon Brewster, and Samuel Peter), three saw him knock his opponent down multiple times on the way to a wide decision victory (David Haye, Alexander Povetkin, and the first fight against Chris Byrd), two saw Klitschko hurt and knock down his opponent before being knocked out himself (Anthony Joshua and the first fight with Lamon Brewster), and three involved fighters who have never been knocked out by anyone before or after in all of their professional careers (Tyson Fury, Sultan Ibragimov, and Ross Puritty).
Analyzing his legacy, Dan Rafael wrote that Klitschko proved himself to be an all-time great heavyweight, and that his legacy will be viewed more favourably as time passes, comparing him to Lennox Lewis in that regard. Rafael believes that Klitschko's 22-fight winning streak from 2004 to 2015, which included unifying three titles, cemented his legacy among the greatest of all time. Klitschko was criticized for his cautious boxing style, but Rafael argues that a lack of exciting fights is not equal to lack of quality. He also believes that the alleged weakness of the era in which Klitschko competed is overexaggerated, arguing that only two eras in heavyweight boxing, the 1970s and 1990s, could be considered great eras, and that Klitschko's era is no weaker than that of Mike Tyson who made only half as many title defenses as Wladimir did. Despite this, Rafael insists that Wladimir still has a lot of quality opponents on his resume, such as Chris Byrd, David Haye, Alexander Povetkin, Calvin Brock, Sultan Ibragimov and Ruslan Chagaev, and that those wins should not be dismissed due to their one-sided nature; in fact, it only emphasizes the quality of Klitschko's boxing skills and in-ring intelligence.[462] Rafael wrote that even though Klitschko suffered some bad losses, the totality of his career must be considered.
In 2021, Klitschko was inducted into the International Boxing Hall of Fame in his first year of eligibility, having been elected over Miguel Cotto and James Toney by a panel of around 200 international boxing historians.[37][38]
Other interests
[edit]Klitschko is also a passionate golfer and was seen playing in the Alfred Dunhill Links Championship in Scotland. The tournament was played over three courses in 2008 including St Andrews, Carnoustie, and Kingsbarns in Fife and Angus. Klitschko was named curator of the Ukrainian pavilion at the 2009 Venice Biennale.[463]
As of October 2015, Klitschko was an adjunct professor at Switzerland's University of St. Gallen, where he taught master's students.[50][464]
Personal life
[edit]
From 2009, Klitschko was in a relationship with American actress Hayden Panettiere. Panettiere has appeared ringside at some of Klitschko's fights, including at Klitschko's 10th-round KO victory over Samuel Peter.[465] The couple had a brief split in 2011, but were together again in 2013.[466] In October 2013, Panettiere confirmed that she and Klitschko were engaged.[467] They have one child together, a daughter, born in December 2014.[468] In August 2018, according to Panettiere's mother, Lesley Vogel, the couple had split for a second time.[469] They were said to be on 'good terms' for the sake of their daughter.[470]
On 6 December 2013, Klitschko and his then-fiancée Hayden Panettiere visited the Euromaidan-protests in Kyiv.[471] His brother Vitali was one of the leading figures of these protests.[472][473] He and Panettiere addressed the crowds.[474]
Wladimir and his brother Vitali have never fought each other in a professional fight as their mother made them promise to never fight each other.[475]
Klitschko speaks four languages: English, German, Russian, and Ukrainian.[476] He was friends with the late German heavyweight legend Max Schmeling.[477]
On 29 March 2012, during a charitable auction in Kyiv, Ukraine, Klitschko auctioned off his 1996 Olympic gold medal to a buyer who bid $1 million. Klitschko said he would use the money to help the dreams of hundreds of thousands of Ukrainian children. After the sale, the buyer immediately returned the medal out of respect for Klitschko and because he wanted it to remain with the Klitschko family.[478][479]
In February 2022, Klitschko joined the Kyiv Territorial Defense Brigade (a military reserve component of the Ukrainian Armed Forces).[480] Both he and his brother Vitali Klitschko, who has been Mayor of Kyiv since 2014, pledged to fight to protect the capital of Ukraine, Kyiv, through armed forces, in response to Russia's invasion of Ukraine that began on 24 February 2022.[481][482] According to The Times, Wladimir and Vitali were on Vladimir Putin's personal hitlist of 24 high-profile Ukrainian figures whom he wanted assassinated.[483][484]
On 10 March 2022, the brothers announced via Telegram that they had raised €100 million of financial support for Ukraine with a fundraising campaign in Germany.[485]
Professional boxing record
[edit]| 69 fights | 64 wins | 5 losses |
|---|---|---|
| By knockout | 53 | 4 |
| By decision | 9 | 1 |
| By disqualification | 2 | 0 |
| No. | Result | Record | Opponent | Type | Round, time | Date | Age | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69 | Loss | 64–5 | Anthony Joshua | TKO | 11 (12), 2:25 | 29 Apr 2017 | 41 years, 35 days | Wembley Stadium, London, England | For IBF, vacant WBA (Super) and IBO heavyweight titles |
| 68 | Loss | 64–4 | Tyson Fury | UD | 12 | 28 Nov 2015 | 39 years, 248 days | Esprit Arena, Düsseldorf, Germany | Lost WBA (Super), IBF, WBO, IBO, and The Ring heavyweight titles |
| 67 | Win | 64–3 | Bryant Jennings | UD | 12 | 25 Apr 2015 | 39 years, 32 days | Madison Square Garden, New York City, New York, US | Retained WBA (Super), IBF, WBO, IBO, and The Ring heavyweight titles |
| 66 | Win | 63–3 | Kubrat Pulev | KO | 5 (12), 2:11 | 15 Nov 2014 | 38 years, 235 days | O2 World, Hamburg, Germany | Retained WBA (Super), IBF, WBO, IBO, and The Ring heavyweight titles |
| 65 | Win | 62–3 | Alex Leapai | TKO | 5 (12), 2:05 | 26 Apr 2014 | 38 years, 32 days | König Pilsener Arena, Oberhausen, Germany | Retained WBA (Super), IBF, WBO, IBO, and The Ring heavyweight titles |
| 64 | Win | 61–3 | Alexander Povetkin | UD | 12 | 5 Oct 2013 | 37 years, 194 days | Olympic Stadium, Moscow, Russia | Retained WBA (Super), IBF, WBO, IBO, and The Ring heavyweight titles |
| 63 | Win | 60–3 | Francesco Pianeta | TKO | 6 (12), 2:52 | 4 May 2013 | 37 years, 40 days | SAP Arena, Mannheim, Germany | Retained WBA (Super), IBF, WBO, IBO, and The Ring heavyweight titles |
| 62 | Win | 59–3 | Mariusz Wach | UD | 12 | 10 Nov 2012 | 36 years, 230 days | O2 World, Hamburg, Germany | Retained WBA (Super), IBF, WBO, IBO, and The Ring heavyweight titles |
| 61 | Win | 58–3 | Tony Thompson | TKO | 6 (12), 1:12 | 7 Jul 2012 | 36 years, 104 days | Stade de Suisse, Bern, Switzerland | Retained WBA (Super), IBF, WBO, IBO, and The Ring heavyweight titles |
| 60 | Win | 57–3 | Jean-Marc Mormeck | KO | 4 (12), 1:12 | 3 Mar 2012 | 35 years, 344 days | Esprit Arena, Düsseldorf, Germany | Retained WBA (Super), IBF, WBO, IBO, and The Ring heavyweight titles |
| 59 | Win | 56–3 | David Haye | UD | 12 | 2 Jul 2011 | 35 years, 99 days | Volksparkstadion, Hamburg, Germany | Retained IBF, WBO, IBO, and The Ring heavyweight titles; Won WBA (Unified) heavyweight title |
| 58 | Win | 55–3 | Samuel Peter | KO | 10 (12), 1:22 | 11 Sep 2010 | 34 years, 170 days | Commerzbank-Arena, Frankfurt, Germany | Retained IBF, WBO, IBO, and The Ring heavyweight titles |
| 57 | Win | 54–3 | Eddie Chambers | KO | 12 (12), 2:55 | 20 Mar 2010 | 33 years, 360 days | Esprit Arena, Düsseldorf, Germany | Retained IBF, WBO, IBO, and The Ring heavyweight titles |
| 56 | Win | 53–3 | Ruslan Chagaev | RTD | 9 (12), 3:00 | 20 Jun 2009 | 33 years, 87 days | Veltins-Arena, Gelsenkirchen, Germany | Retained IBF, WBO, and IBO heavyweight titles; Won vacant The Ring heavyweight title |
| 55 | Win | 52–3 | Hasim Rahman | TKO | 7 (12), 0:44 | 13 Dec 2008 | 32 years, 263 days | SAP Arena, Mannheim, Germany | Retained IBF, WBO, and IBO heavyweight titles |
| 54 | Win | 51–3 | Tony Thompson | KO | 11 (12), 1:38 | 12 Jul 2008 | 32 years, 109 days | Color Line Arena, Hamburg, Germany | Retained IBF, WBO, and IBO heavyweight titles |
| 53 | Win | 50–3 | Sultan Ibragimov | UD | 12 | 23 Feb 2008 | 31 years, 335 days | Madison Square Garden, New York City, New York, US | Retained IBF and IBO heavyweight titles; Won WBO heavyweight title |
| 52 | Win | 49–3 | Lamon Brewster | RTD | 6 (12), 3:00 | 7 Jul 2007 | 31 years, 104 days | Kölnarena, Cologne, Germany | Retained IBF and IBO heavyweight titles |
| 51 | Win | 48–3 | Ray Austin | KO | 2 (12), 1:23 | 10 Mar 2007 | 30 years, 350 days | SAP Arena, Mannheim, Germany | Retained IBF and IBO heavyweight titles |
| 50 | Win | 47–3 | Calvin Brock | TKO | 7 (12), 2:10 | 11 Nov 2006 | 30 years, 231 days | Madison Square Garden, New York City, New York, US | Retained IBF and IBO heavyweight titles |
| 49 | Win | 46–3 | Chris Byrd | TKO | 7 (12), 0:41 | 22 Apr 2006 | 30 years, 28 days | SAP Arena, Mannheim, Germany | Won IBF and vacant IBO heavyweight titles |
| 48 | Win | 45–3 | Samuel Peter | UD | 12 | 24 Sep 2005 | 29 years, 183 days | Boardwalk Hall, Atlantic City, New Jersey, US | Won NABF and vacant NABO heavyweight titles |
| 47 | Win | 44–3 | Eliseo Castillo | TKO | 4 (10), 2:51 | 23 Apr 2005 | 29 years, 29 days | Westfalenhallen, Dortmund, Germany | |
| 46 | Win | 43–3 | DaVarryl Williamson | TD | 5 (10), 3:00 | 2 Oct 2004 | 28 years, 191 days | Caesars Palace, Paradise, Nevada, US | Split TD: Klitschko cut from an accidental head clash |
| 45 | Loss | 42–3 | Lamon Brewster | TKO | 5 (12), 3:00 | 10 Apr 2004 | 28 years, 16 days | Mandalay Bay Events Center, Paradise, Nevada, US | For vacant WBO heavyweight title |
| 44 | Win | 42–2 | Danell Nicholson | TKO | 4 (12), 1:44 | 20 Dec 2003 | 27 years, 270 days | Ostseehalle, Kiel, Germany | Retained WBA Inter-Continental heavyweight title |
| 43 | Win | 41–2 | Fabio Eduardo Moli | KO | 1 (12), 1:49 | 30 Aug 2003 | 27 years, 158 days | Olympiahalle, Munich, Germany | Won vacant WBA Inter-Continental heavyweight title |
| 42 | Loss | 40–2 | Corrie Sanders | TKO | 2 (12), 0:27 | 8 Mar 2003 | 26 years, 348 days | Preussag Arena, Hanover, Germany | Lost WBO heavyweight title |
| 41 | Win | 40–1 | Jameel McCline | RTD | 10 (12), 3:00 | 7 Dec 2002 | 26 years, 257 days | Mandalay Bay Events Center, Paradise, Nevada, US | Retained WBO heavyweight title |
| 40 | Win | 39–1 | Ray Mercer | TKO | 6 (12), 1:08 | 29 Jun 2002 | 26 years, 93 days | Etess Arena, Atlantic City, New Jersey, US | Retained WBO heavyweight title |
| 39 | Win | 38–1 | Francois Botha | TKO | 8 (12), 0:47 | 16 Mar 2002 | 25 years, 356 days | Hanns-Martin-Schleyer-Halle, Stuttgart, Germany | Retained WBO heavyweight title |
| 38 | Win | 37–1 | Charles Shufford | TKO | 6 (12), 2:55 | 4 Aug 2001 | 25 years, 132 days | Mandalay Bay Events Center, Paradise, Nevada, US | Retained WBO heavyweight title |
| 37 | Win | 36–1 | Derrick Jefferson | TKO | 2 (12), 2:09 | 24 Mar 2001 | 24 years, 344 days | Rudi-Sedlmayer-Halle, Munich, Germany | Retained WBO heavyweight title |
| 36 | Win | 35–1 | Chris Byrd | UD | 12 | 14 Oct 2000 | 24 years, 203 days | Kölnarena, Cologne, Germany | Won WBO heavyweight title |
| 35 | Win | 34–1 | Monte Barrett | TKO | 7 (10), 2:40 | 15 Jul 2000 | 24 years, 112 days | London Arena, London, England | |
| 34 | Win | 33–1 | David Bostice | TKO | 2 (12), 1:27 | 29 Apr 2000 | 24 years, 35 days | Madison Square Garden, New York City, New York, US | Retained WBA Inter-Continental heavyweight title |
| 33 | Win | 32–1 | Paea Wolfgramm | KO | 1 (12), 1:30 | 18 Mar 2000 | 23 years, 359 days | Alsterdorfer Sporthalle, Hamburg, Germany | Won vacant WBC International heavyweight title |
| 32 | Win | 31–1 | Lajos Eros | KO | 2 (12), 2:35 | 4 Dec 1999 | 23 years, 254 days | Stadionsporthalle, Hanover, Germany | Retained WBA Inter-Continental and European heavyweight titles |
| 31 | Win | 30–1 | Phil Jackson | KO | 2 (8), 1:59 | 12 Nov 1999 | 23 years, 232 days | The Orleans, Paradise, Nevada, US | |
| 30 | Win | 29–1 | Axel Schulz | TKO | 8 (12), 2:42 | 25 Sep 1999 | 23 years, 184 days | Kölnarena, Cologne, Germany | Retained WBA Inter-Continental heavyweight title; Won vacant European heavyweight title |
| 29 | Win | 28–1 | Joseph Chingangu | RTD | 4 (12), 3:00 | 17 Jul 1999 | 23 years, 114 days | Philips Halle, Düsseldorf, Germany | Won vacant WBA Inter-Continental heavyweight title |
| 28 | Win | 27–1 | Tony LaRosa | TKO | 1 (10), 2:57 | 22 May 1999 | 23 years, 58 days | Sport Palace, Budapest, Hungary | |
| 27 | Win | 26–1 | Everett Martin | TKO | 8 (8) | 24 Apr 1999 | 23 years, 30 days | Circus Krone Building, Munich, Germany | |
| 26 | Win | 25–1 | Zoran Vujicic | KO | 1 (8), 1:02 | 13 Feb 1999 | 22 years, 325 days | Maritim Hotel, Stuttgart, Germany | |
| 25 | Loss | 24–1 | Ross Puritty | TKO | 11 (12), 0:18 | 5 Dec 1998 | 22 years, 255 days | Palace of Sports, Kyiv, Ukraine | Lost WBC International heavyweight title |
| 24 | Win | 24–0 | Donnell Wingfield | KO | 1 (8) | 14 Nov 1998 | 22 years, 234 days | Circus Krone Building, Munich, Germany | |
| 23 | Win | 23–0 | Eli Dixon | KO | 3 (10), 2:26 | 3 Oct 1998 | 22 years, 192 days | Prinz-Garden Halle, Augsburg, Germany | |
| 22 | Win | 22–0 | Steve Pannell | KO | 2 (10) | 19 Sep 1998 | 22 years, 178 days | Arena Oberhausen, Oberhausen, Germany | |
| 21 | Win | 21–0 | Carlos Monroe | TKO | 6 (10), 2:28 | 6 Aug 1998 | 22 years, 134 days | Grand Casino Avoyelles, Marksville, Louisiana, US | |
| 20 | Win | 20–0 | Najee Shaheed | KO | 1 (12) | 10 Jul 1998 | 22 years, 107 days | Circus Krone Building, Munich, Germany | Retained WBC International heavyweight title |
| 19 | Win | 19–0 | Cody Koch | KO | 4 (12) | 23 May 1998 | 22 years, 59 days | Oberrheinhalle, Offenburg, Germany | Retained WBC International heavyweight title |
| 18 | Win | 18–0 | Everett Martin | UD | 8 | 13 Mar 1998 | 21 years, 353 days | Sporthalle Wandsbek, Hamburg, Germany | |
| 17 | Win | 17–0 | Marcus McIntyre | KO | 3 (12) | 14 Feb 1998 | 21 years, 326 days | Maritim Hotel, Stuttgart, Germany | Won vacant WBC International heavyweight title |
| 16 | Win | 16–0 | Derrick Lampkins | TKO | 1 (8) | 20 Dec 1997 | 21 years, 270 days | Oberrheinhalle, Offenburg, Germany | |
| 15 | Win | 15–0 | Ladislav Husarik | TKO | 3 (8) | 13 Dec 1997 | 21 years, 263 days | Alsterdorfer Sporthalle, Hamburg, Germany | |
| 14 | Win | 14–0 | Jerry Halstead | TKO | 2 (8) | 6 Dec 1997 | 21 years, 256 days | Stadthalle, Offenbach am Main, Germany | |
| 13 | Win | 13–0 | Marcos González | KO | 2 (8) | 11 Oct 1997 | 21 years, 200 days | Stadthalle, Cottbus, Germany | |
| 12 | Win | 12–0 | James Pritchard | TKO | 3 (8) | 20 Sep 1997 | 21 years, 179 days | Tivoli Eissporthalle, Aachen, Germany | |
| 11 | Win | 11–0 | Biko Botowamungu | DQ | 5 (6), 0:02 | 23 Aug 1997 | 21 years, 151 days | Maritim Hotel, Stuttgart, Germany | Botowamungu disqualified after his cornermen refused to leave the ring |
| 10 | Win | 10–0 | Gilberto Williamson | TKO | 3 (8) | 12 Jul 1997 | 21 years, 109 days | Berlet-Halle, Hagen, Germany | |
| 9 | Win | 9–0 | Salvador Maciel | KO | 1 (8) | 27 Jun 1997 | 21 years, 94 days | Oberrheinhalle, Offenburg, Germany | |
| 8 | Win | 8–0 | Paul Ashley | KO | 2 (8), 1:25 | 13 Jun 1997 | 21 years, 80 days | Arena Oberhausen, Oberhausen, Germany | |
| 7 | Win | 7–0 | Mark Wills | KO | 1 (8), 2:58 | 10 May 1997 | 21 years, 46 days | Ballsporthalle, Frankfurt, Germany | |
| 6 | Win | 6–0 | Mark Young | RTD | 2 (6), 3:00 | 12 Apr 1997 | 21 years, 18 days | Eurogress, Aachen, Germany | |
| 5 | Win | 5–0 | Carlos Monroe | DQ | 6 (6), 0:34 | 15 Feb 1997 | 20 years, 327 days | Stadthalle, Cottbus, Germany | Monroe disqualified for a headbutt |
| 4 | Win | 4–0 | Troy Weida | TKO | 3 (6), 0:36 | 25 Jan 1997 | 20 years, 306 days | Maritim Hotel, Stuttgart, Germany | |
| 3 | Win | 3–0 | Bill Corrigan | TKO | 1 (4), 1:21 | 21 Dec 1996 | 20 years, 271 days | Zoological Garden, Frankfurt, Germany | |
| 2 | Win | 2–0 | Exum Speight | TKO | 2 (4), 1:54 | 30 Nov 1996 | 20 years, 250 days | Arena Nova, Wiener Neustadt, Austria | |
| 1 | Win | 1–0 | Fabian Meza | KO | 1 (4), 1:35 | 16 Nov 1996 | 20 years, 236 days | Sporthalle Wandsbek, Hamburg, Germany |
Viewership
[edit]| Date | Fight | Billing[62] | Region(s) | Network | Viewership | Source(s) | Note(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
25 September 1999
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Axel Schulz | Klitschko vs. Schulz
|
Germany | RTL Television | 10,530,000
|
[486][487] | [nb 1] |
4 December 1999
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Lajos Eros | Klitschko vs. Eros
|
Germany | Sat.1 | 7,010,000
|
[488] | [nb 1] |
14 October 2000
|
Chris Byrd vs. Wladimir Klitschko | Revenge of the Brother
|
Germany | Sat.1 | 9,390,000
|
[489] | [nb 1] |
8 March 2003
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Corrie Sanders | The Next Big Thing
|
Germany | ZDF | 9,150,000
|
[490] | [nb 1] |
30 August 2003
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Fabio Eduardo Moli | Night of the Giants
|
Germany | ZDF | 7,630,000
|
[491] | [nb 1] |
20 December 2003
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Danell Nicholson | Klitschko vs. Nicholson
|
Germany | ZDF | 7,920,000
|
[492] | [nb 1] |
| Russia | N/A | 16,500,000
|
[493] | [nb 2] | |||
23 April 2005
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Eliseo Castillo | Klitschko vs. Castillo
|
Germany | Das Erste | 6,440,000
|
[494] | [nb 1] |
24 September 2005
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Samuel Peter I | Boardwalk Brawls
|
United States | HBO | 2,036,000
|
[495] | [nb 3][nb 4] |
24 April 2006
|
Chris Byrd vs. Wladimir Klitschko II | Revenge Is The Name of the Game
|
Germany | Das Erste | 10,170,000
|
[496] | [nb 1] |
10 March 2007
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Ray Austin | Danger Zone
|
Germany | RTL Television | 12,890,000
|
[497][498] | [nb 1] |
7 July 2007
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Lamon Brewster II | The Rematch
|
Germany | RTL Television | 11,210,000
|
[499][500] | [nb 1] |
23 February 2008
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Sultan Ibragimov | The Unification
|
Russia | 1 Kanal | 9,500,000
|
[501] | [nb 2] |
| Germany | RTL Television | 2,260,000
|
[502] | [nb 1] | |||
3,790,000
|
[nb 1][nb 5] | ||||||
12 July 2008
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Tony Thompson I | Time To Pick On Someone His Own Size
|
Germany | RTL Television | 9,220,000
|
[503] | [nb 1] |
| Ukraine | Inter | 7,100,000
|
[504] | [nb 2] | |||
13 December 2008
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Hasim Rahman | X-Plosive
|
Germany | RTL Television | 9,670,000
|
[505] | [nb 1] |
| Ukraine | Inter | 5,637,000
|
[506][507] | [nb 1][nb 6] | |||
20 June 2009
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Ruslan Chagaev | Knockout Auf Schalke
|
Germany | RTL Television | 10,390,000
|
[508] | [nb 1] |
| United Kingdom | Sky Sports | 100,000
|
[509] | [nb 1][nb 4] | |||
20 March 2010
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Eddie Chambers | Duell Am Rhein[510]
|
Germany | RTL Television | 12,590,000
|
[511][512] | [nb 1] |
11 September 2010
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Samuel Peter II | Showdown in Frankfurt
|
Germany | RTL Television | 9,700,000
|
[513] | [nb 1] |
| United Kingdom | Sky Sports Main Event | 202,000
|
[514] | [nb 1][nb 4] | |||
2 July 2011
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. David Haye | The Talk Ends Now [citation needed]
|
Worldwide
|
(multiple) | 500,000,000
|
[440][22][17] | [nb 2] |
| Germany | RTL Television | 15,560,000
|
[515][516] | [nb 1] | |||
| Ukraine | Inter | 9,500,000
|
[311] | [nb 1] | |||
| Poland | TVP1 | 3,388,616
|
[517] | [nb 1] | |||
| TVP Sport | |||||||
| TVP HD | 92,000
|
[518] | [nb 1] | ||||
| Hungary | Duna TV | 1,150,000
|
[519] | [nb 2] | |||
588,000
|
[520] | [nb 1] | |||||
| Netherlands | RTL 7 | 507,000
|
[521] | [nb 1] | |||
3 March 2012
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Jean-Marc Mormeck | Alle Gürtel. Ein Champion
|
Germany | RTL Television | 12,260,000
|
[522] | [nb 1] |
| Ukraine | Inter | 9,280,000
|
[523] | [nb 2] | |||
7 July 2012
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Tony Thompson II | Hard Rocks
|
Germany | RTL Television | 8,360,000
|
[524] | [nb 1] |
10 November 2012
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Mariusz Wach | Battle of the Giants
|
Germany | RTL Television | 11,770,000
|
[525] | [nb 1] |
| Ukraine | Inter | 10,600,000
|
[409] | [nb 2] | |||
| Hungary | Sport1 | 500,000
|
[526][527][528] | [nb 2] | |||
4 May 2013
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Francesco Pianeta | Showtime in Mannheim
|
Germany | RTL Television | 8,310,000
|
[525][529] | [nb 1] |
7 October 2013
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Alexander Povetkin | Klitschko vs. Povetkin
|
Germany | RTL Television | 11,020,000
|
[530][531] | [nb 1] |
| Austria | 290,000
|
[532] | [nb 1][nb 7] | ||||
| Ukraine | Inter | 23,000,000
|
[312] | [nb 2] | |||
11,000,000
|
[311] | [nb 1] | |||||
| Russia | 1 Kanal | 23,000,000
|
[309] | [nb 2] | |||
| Czech Republic | Fanda | 255,000
|
[533] | [nb 1][nb 8] | |||
26 April 2014
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Alex Leapai | Can't Stop
|
Germany | RTL Television | 9,000,000
|
[534] | [nb 1] |
15 November 2014
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Kubrat Pulev | Showdown in Hamburg
|
Germany | RTL Television | 10,500,000
|
[338] | [nb 1] |
| Bulgaria | Nova | 1,800,000
|
[339][340][341] | [nb 1] | |||
28 November 2015
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Tyson Fury | Collision Course
|
Germany | RTL Television | 8,910,000
|
[535] | [nb 1] |
| Ukraine | Inter | 9,700,000
|
[536] | [nb 2] | |||
28 April 2017
|
Anthony Joshua vs. Wladimir Klitschko | Joshua vs. Klitschko
|
Germany | RTL Television | 10,430,000
|
[537] | [nb 1] |
| Ukraine | Inter | 4,400,000 | [538] | [nb 1] | |||
| Combined viewership | Worldwide | 1,371,865,000 |
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an Average viewers
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k Total viewers
- ^ Average number of households
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Pay television network
- ^ Same day replay
- ^ Viewers aged 18 and older
- ^ Viewers aged 12 and older
- ^ Viewers aged 15 and older
Pay-per-view bouts
[edit]| Date | Fight | Billing[62] | Pay-per-view buys | Region(s) | Network | Source(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
14 October 2000
|
Chris Byrd vs. Wladimir Klitschko | Revenge of the Brother
|
— | United Kingdom | Sky Box Office | [539] |
20 March 2010
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Eddie Chambers | Duell Am Rhein[510]
|
300,000
|
United States, Canada, Puerto Rico |
klitschko.com | [198][199][540] |
| — | United Kingdom | Primetime | [541] | |||
2 July 2011
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. David Haye | The Talk Ends Now[542]
|
1,197,000
|
United Kingdom | Sky Box Office | [543][544][545] |
10 November 2012
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Mariusz Wach | Battle of the Giants
|
— | Poland | Cyfra+ PPV, Cyfrowy Polsat PPV | [267][268][269] |
26 April 2014
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Alex Leapai | Can't Stop
|
— | Australia | Main Event | [546][547][548] |
| — | New Zealand | Sky Arena | [549][550][551] | |||
28 November 2015
|
Wladimir Klitschko vs. Tyson Fury | Collision Course
|
655,000
|
United Kingdom | Sky Box Office | [552][553] |
28 April 2017
|
Anthony Joshua vs. Wladimir Klitschko | Joshua vs. Klitschko
|
1,631,000
|
United Kingdom | Sky Box Office | [554][555][556][553] |
| Total sales | 3,783,000 |
Notes
[edit]- ^ Wladimir Klitschko is a German transliteration of Russian: Владимир Кличко, IPA: [vɫɐˈdʲimʲɪr klʲɪt͡ɕˈko]; an equivalent English spelling is Vladimir Klichko /ˈklɪtʃkoʊ/. His full name in Ukrainian is: Володимир Володимирович Кличко, romanized: Volodymyr Volodymyrovych Klychko, IPA: [woloˈdɪmɪr woloˈdɪmɪrowɪtʃ klɪtʃˈkɔ].
- ^ Jump up to: a b Attributed to multiple sources: [16][17][18][19][20][21][22][23]
- ^ Attributed to multiple sources: [24][25][26][27][28][29][30][31][32]
- ^ WBA, WBC, IBF and WBO era
References
[edit]- ^ Sky Sports tale of the tape prior to the Anthony Joshua fight.
- ^ HBO World Championship Boxing tale of the tape prior to the Anthony Joshua fight.
- ^ Hauser, Thomas (19 April 2017). "From the Ring: The Greatest Heavyweight of All Time". The Ring. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ^ Iole, Kevin (3 August 2017). "Why Wladimir Klitschko is one of the greatest heavyweights of all time". Yahoo! Sports. Yahoo!. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ^ Rafael, Dan (4 August 2017). "Anthony Joshua ordered to make mandatory defenses of IBF, WBA titles". ESPN. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ^ "Ranking the 15 greatest heavyweight boxers of all time". The Daily Telegraph. Telegraph Media Group. 3 August 2017. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ^ Wladimir Klitschko – An Analysis of the Surgeon at Work. Myboxingcoach.com (21 March 2012). Retrieved 28 November 2015.
- ^ "Klitschko-Haye broken down by expert trainer James Gogue". Archived from the original on 23 April 2019. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ Joshua vs Klitschko: David Haye and Adam Booth reveal the difficulty of facing Wladimir Klitschko
- ^ Fighting Klitschko: What It’s Actually Like To Box Wladimir
- ^ Sherdog.com. "Boxing: Wladimir Klitschko's Loss Signals End of Era". Sherdog.
- ^ "Can Mariusz Wach End The Klitschko Era of Dominance?". 6 November 2012.
- ^ "TBRB: Successions". tbrb.org. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
- ^ "Boxer Lb for Lb Ratings". BoxRec. 15 October 2015. Archived from the original on 15 October 2015. Retrieved 20 January 2024.
- ^ "Boxer Lb for Lb Ratings". BoxRec. 17 November 2015. Archived from the original on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 20 January 2024.
- ^ "Володимира Кличка внесли до Міжнародної зали боксерської слави". obozrevatel.com. Retrieved 12 December 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Zwei Brüder, fünf Titel, 500 Millionen TV-Zuschauer" (in German). Schleswig-Holsteinischer Zeitungsverlag. 4 July 2011. Retrieved 29 March 2023.
- ^ "Провідні країни Європи борються за бій братів Кличків". tsn.ua (in Ukrainian). 31 October 2011. Retrieved 7 May 2021.
- ^ "За право провести бой Кличко соревнуются европейские города" (in Russian). 30 October 2011. Retrieved 5 July 2022.
- ^ "EXCLUSIVE: Boxing legend Wladimir Klitschko admits to 'biggest fight of my life' on war front line". Daily Mirror. 8 March 2022. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ "30 шагов Независимости: история успехов и поражений в ярких фото" (in Russian). 18 August 2021. Retrieved 5 September 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Brüder Gnadenlos". Focus (in German). No. 36. 5 September 2011. p. 130. Retrieved 10 June 2022.
- ^ "Володимиру Кличку – 47: "Помста за брата" та інші видатні перемоги легендарного українця" (in Ukrainian). Channel 24. 25 March 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Most days as a heavyweight boxing champion". Guinness World Records. Retrieved 15 March 2024.
- ^ "Wladimir Klitschko is plotting a spectacular boxing comeback, and he wants to break an old heavyweight record". businessinsider.sg. Business Insider Singapore. Archived from the original on 10 November 2019. Retrieved 26 July 2023.
- ^ "Володимиру Кличку – 44: найкращі нокаути боксера" (in Ukrainian). 25 March 2020. Retrieved 5 February 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Украина сделала свой выбор! Назван лучший боксер в истории страны" (in Russian). Retrieved 28 April 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Władimir Kliczko wróci na ring? "Jeśli wojna się skończy..."" (in Polish). Polsat Sport. 25 April 2022. Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Fury 'mentally happy' to be in ring, eyes Klitschko-like reign". Reuters. 20 May 2020. Retrieved 8 February 2021.
- ^ "Klitschko believes Hrgović will become world boxing champ". croatiaweek.com. 6 April 2019. Retrieved 9 March 2020.
- ^ "Володимир Кличко виступив на Web Summit-2019 в Лісабоні". kreschatic.kiev.ua (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ "Володимир Кличко увійшов до Міжнародного залу боксерської слави". kremenchug.org.ua (in Ukrainian). 15 December 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ "Владимир Кличко" (in Russian). 6 August 2019. Retrieved 12 December 2020.
- ^ "Most boxing heavyweight world title fights won by brothers". Guinness World Records. 2 July 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2024.
- ^ "Boxing legends Oscar De La Hoya Mike Tyson and Floyd Mayweather snag Guinness World Records at WBC convention". Guinness World Records. 12 December 2011.
- ^ "Klitschko brothers included in Guinness World Records". 2 October 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Володимир Кличко включений до Міжнародного залу боксерської слави". sport.ua (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Mayweather, Klitschko, Ward Elected To International Boxing Hall of Fame". boxingscene.com. 15 December 2020. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ Wladimir Klitschko – Boxer. Boxrec.com. Retrieved 19 November 2014.
- ^ Vester, Mark. "Wladimir Klitschko A Fan of Borat", BoxingScene.com, 22 November 2006
- ^ "Vitali & Wladimir Klitschko" (profile) Archived 24 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Tour2Kiev.com, n.d.
- ^ У братьев Кличко умер отец Archived 24 November 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Komsomolskaya Profile, kp.ua, 13 July 2011. (in Russian)
- ^ "Kyiv's mayor learns from the IDF how to defend Ukraine". 10 March 2022.
- ^ Vavrouška, Petr (1 January 2011). Šťastné děti okupantů [Happy children of the occupiers] (in Czech). Retrieved 5 April 2022.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ^ Vladimir Rodionovich Klitschko dies; father of Wladimir and Vitali Klitschko – ESPN . ESPN.go.com (14 July 2011). Retrieved 10 July 2014.
- ^ Помер батько братів Кличків Interfax Ukraine (in Ukrainian) 13 July 2011
- ^ Володимир Кличко. Vesti.ua (in Ukrainian) 9 February 2022
- ^ [1]. Klitschko.com - Wladimir Klitschko Bio. Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ [2]. Klitschko.com - Vitali Klitschko Bio. Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Dwyre, Bill (14 October 2015). "Boxer Wladimir Klitschko is a heavyweight deep thinker". Los Angeles Times. Los Angeles. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- ^ Luscombe, Belinda (14 May 2012). "10 Questions for Wladimir Klitschko". Time. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- ^ "Kliczko już w Polsce nokautował", TVN24, 7 January 2011.
- ^ "World Junior Champs1994". amateur-boxing.strefa.pl.
- ^ "European Championships1996". amateur-boxing.strefa.pl.
- ^ "Wladimir Klitschko - BoxRec". boxrec.com.
- ^ Vladimir Klitschko Amateur Career (in Spanish) compiled by Pedro Cabrera Isidron of the Cuban Olympics Committee. Last updated: 13 August 2006.
- ^ Rosenthal, Michael (19 March 2009). "What are we to make of the Klitschkos?". The Ring. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- ^ "Wladimir Klitschko vs. Ross Puritty - BoxRec". boxrec.com. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Long read: Invisible while standing still: Chris Byrd interview". boxingmonthly.com. 9 February 2018. Archived from the original on 20 March 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ "What I Like About Chris Byrd". boxingscene.com. 7 February 2005. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ "Bout: Chris Byrd v Vitali Klitschko". BoxRec. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Wladimir Klitschko Fights in the Vault". Eye on the Ring. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ "2000-10-14 Wladimir Klitschko vs Chris Byrd I". 5 November 2012. Retrieved 1 November 2020.
- ^ "2000-10-14 Wladimir Klitschko vs Chris Byrd I - Video Dailymotion". Dailymotion. 5 November 2012. Retrieved 30 October 2016.
- ^ "Forgotten Classics: Derrick Jefferson vs Maurice Harris". boxrec.com. Archived from the original on 29 October 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ Wladimir Klitschko v Derrick Jefferson
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Professional boxing record: Derrick Jefferson". Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ David Izon vs. Derrick Jefferson: David Izon 232 lbs beat Derrick Jefferson 243 lbs by TKO at 0:11 in round 9 of 10
- ^ Oleg Maskaev vs. Derrick Jefferson
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Wladimir Klitschko vs Derrick Jefferson - HBO World Championship Boxing March 24 2001". Archived from the original on 29 October 2021. Retrieved 11 March 2020 – via YouTube.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Vladimir Klitschko vs Derrick Jefferson: Klitschko annihilates Jefferson". boxing247.com. Retrieved 30 October 2016.
- ^ "Wladimir Klitschko v Charles Shufford". Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ "Professional boxing record: Charles Shufford". Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ "Photo: Will Smith in the ring cheering on Charles Shufford. The German boxer Wladimir Klitschko won the fight against Shufford. (Photo by Chris Farina/Corbis via Getty Images)". 11 June 2016. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ "Wladimir Klitschko vs. Charles Shufford". Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ "GERMAN BOXING SCENE STRONG — FOR NOW". ringtv.com. 17 June 2009. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Damals: Der Skandalfight Schulz gegen Botha". sport.de. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "WBO HEAVYWEIGHT CHAMPION WLADIMIR KLITSCHKO SCORES IMPRESSIVE EIGHTH-ROUND TKO OVER FRANS BOTHA". boxing247.com. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Wladimir Klitschko Vs Francois Botha 16 03 2002". 9 October 2013. Archived from the original on 29 October 2021. Retrieved 11 March 2020 – via YouTube.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "WLAD IS BAD!!!!!! KLITSCHKO DESTROYS RAY MERCER". Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Geoffrey Ciani: Wladimir Klitschko has a chance to redefine his legacy". 15 May 2016. Archived from the original on 29 October 2021. Retrieved 11 March 2020 – via YouTube.
- ^ "Wladimir Klitschko v Ray Mercer". Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Professional boxing record: Jameel McCline". boxrec.com. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Jameel McCline details overcoming prison bid to have respectable heavyweight career". sportingnews.com. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Wladimir Klitschko vs Jameel McCline". boxrec.com. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Klitschko stops McCline in one-sided affair!". boxing247.com. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Saturday 7, December 2002". Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Wladimir Klitschko vs. Jameel McCline". Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Sharkie's Machine: "The End Of A Legendary Career"". Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Он уничтожил Владимира Кличко за три с половиной минуты. После карьеры хотел стать тренером, но умер от пули" (in Russian). Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ^ "W. Klitschko: Loss to Sanders made me tougher". ESPN. Retrieved 30 October 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c ""В меня не верил даже брат", или Переломный бой в карьере Кличко" (in Russian). 10 April 2020. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- ^ "On This Day: Lamon Brewster bludgeons Vladimir Klitschko to defeat - Boxing News". Boxing News. 10 April 2015. Retrieved 30 October 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Кличко – Брюстер: переломный момент карьеры украинца". ua-football.com (in Russian). 12 April 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Виталий Кличко раскрыл подробности отравления брата Владимира в бою с Брюстером" (in Russian). Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "#Cмотри Владимир Кличко - Лэймон Брюстер" (in Russian). 9 April 2019. Archived from the original on 29 October 2021. Retrieved 27 April 2020 – via YouTube.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Владимира Кличко отравили?" (in Russian). Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- ^ "3 предыдущие поражения Владимира Кличко". Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b The Ring magazine, June 2004. "Poisonous KO?" Author: D. Lederman
- ^ "Haloperidol". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 2 January 2015. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ Product Information [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2013 Sep 29]. Available from: "TGA eBS - Product and Consumer Medicine Information Licence". Archived from the original on 14 March 2017. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Кличко обманывает слащавым алиби» . Ирландские Таймс . 21 марта 2013 года . Проверено 4 марта 2020 г.
- ^ «Федералы предупредили о случае с горизонтальным тяжеловесом» . Хранитель . Проверено 11 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б "Владимира Кличко отравили" (in Russian) . Retrieved 27 April 2020 . [ постоянная мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ "Адвокат Барштейн огласил скандальные подробности боя Владимира Кличко с Брюстером" . sportrbc.ru (in Russian). 8 May 2004 . Retrieved 27 April 2020 .
- ^ "Как отравили Кличко" (in Russian) . Retrieved 27 April 2020 .
- ^ "У команды кличко есть косвенные доказательства, что перед боем за титул чемпиона мира владимира отравили" (in Russian) . Retrieved 27 April 2020 .
- ^ " "Дело об отравлении" Кличко расследует ФБР" . Kp.ru - (in Russian). 20 May 2004 . Retrieved 27 April 2020 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Андрей Соколов (26 October 2013). "Wladimir Klitschko vs DaVarryl Williamson" . YouTube . Archived from the original on 26 June 2019 . Retrieved 30 April 2017 .
- ^ «BoxRec: Даваррил Уильямсон» . Боксрек . Проверено 13 марта 2020 г.
- ^ «BoxRec: Бой: Владимир Кличко против ДаВаррил Уильямсон» . Боксрек . Проверено 13 марта 2020 г.
- ^ «Кличко побеждает раздельным решением судей после удара головой» . Боксрек . Проверено 13 марта 2020 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко против Самуила Петра II» . boxing247.com . 25 июля 2010 года . Проверено 23 марта 2020 г.
- ↑ Владимир Кличко против Сэмюэля Питера, 1-й бой на YouTube . «Большой ринг». (рус.)
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Бой: Владимир Кличко против Самуила Петра I» . boxrec.com . Проверено 23 марта 2020 г.
- ^ «48. Владимир Кличко против Самуэля Петра I. (24 сентября 2005 г.)» . klitschko-brothers.com . 3 ноября 2013 г. Архивировано из оригинала 4 ноября 2018 г. . Проверено 3 ноября 2018 г.
- ^ Документальный фильм «Кличко» на YouTube.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Александр Беленький: Золотой брат Кличко, с. 188–190 (рус.).
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Владимир Кличко против Сэмюэля Питера, 24 сентября 2005 г.» . 9 октября 2013 года. Архивировано из оригинала 29 октября 2021 года . Проверено 23 марта 2020 г. - через YouTube.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко против Сэмюэля Питера» . SecondsOut Новости бокса . Проверено 31 октября 2016 г.
- ^ «Ежегодные рейтинги журнала The Ring: 2005 — BoxRec» . boxrec.com .
- ^ Мощные удары: лучшее в боксе 2006 года . Дж. Э. Грант. 26 ноября 2009 г. ISBN. 9780557002351 . Проверено 24 марта 2020 г.
- ^ «Бёрд-Кличко: исторический поворотный момент в истории супертяжелого веса?» . boxingscene.com . 17 апреля 2006 года . Проверено 24 марта 2020 г.
- ^ «Часть II: Путь братьев Кличко к бесспорному чемпионству» . SecondsOut Новости бокса . Проверено 31 октября 2016 г.
- ^ «Бой: Крис Берд против Владимира Кличко» . boxrec.com . Проверено 24 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Кельвин Брок говорит о Кличко, Ляховиче» . Сентябрь 2006 года . Проверено 24 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ «Блокнот: Брок востребован промоутерами» . 28 июля 2006 г. Проверено 24 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ «Обсуждая свою карьеру, Тайсон затрагивает 20 тем» . ЭСПН. 11 июня 2005 года . Проверено 23 октября 2021 г.
- ^ «ВЛАД ПРИНИМАЕТ ВЫЗОВ БРОКА» . 10 ноября 2006 г. Проверено 24 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ «Бой: Владимир Кличко против Кэлвина Брока» . boxrec.com . Проверено 24 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с «Кличко бросил Брока седьмым, чтобы защитить титул» . 11 ноября 2006 г. Проверено 5 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Владимир Кличко против Кэлвина Брока – Полный бой и нокаут» . Июль 2014. Архивировано из оригинала 29 октября 2021 года . Проверено 5 апреля 2020 г. - через YouTube.
- ^ «Эль ближайший помазанник» . ЭСПН. 9 марта 2007 года . Проверено 12 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко против Рэя Остина: итоги бокса» . boxing247.com . Проверено 31 октября 2016 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко против Леймона Брюстера 2: Результаты бокса» . boxing247.com . Проверено 31 октября 2016 г.
- ^ "Начались переговоры об объединительном бое между Ибрагимовым и Кличко" . sports.ru . 30 October 2007. Archived from the original on 17 July 2019 . Retrieved 17 July 2019 .
- ^ "Бой между Султаном Ибрагимовым и Владимиром Кличко может состояться в феврале" . sports.ru . 30 October 2007. Archived from the original on 17 July 2019 . Retrieved 17 July 2019 .
- ^ "Владимир Кличко и Султан Ибрагимов подписали контракт на проведение объединительного боя" . sports.ru . 20 November 2007. Archived from the original on 17 July 2019 . Retrieved 17 July 2019 .
- ^ "В Москве прошла пресс-конференция Султана Ибрагимова и Владимира Кличко" . sports.ru . 25 November 2007. Archived from the original on 17 July 2019 . Retrieved 17 July 2019 .
- ^ "Владимир Кличко начал подготовку к бою против Ибрагимова" . sports.ru/ . 18 December 2007. Archived from the original on 17 July 2019 . Retrieved 17 July 2019 .
- ^ "Ибрагимов вылетел из Москвы в США" . sports.ru . 25 December 2007. Archived from the original on 17 July 2019 . Retrieved 17 July 2019 .
- ^ "Дорогие билеты на бой Кличко уже распроданы" . Archived from the original on 2 March 2019 . Retrieved 1 March 2019 .
- ^ Ринг (Украинский журнал) №3, 2008, стр.5
- ^ Ринг (Украинский журнал) №2, 2008, стр.2
- ^ Ринг (Украинский журнал) №3, 2008, стр.4
- ^ "Гринберг извинился перед Владимиром Кличко" . sports.ru . 22 February 2008. Archived from the original on 17 July 2019 . Retrieved 17 July 2019 .
- ^ «Рекорд профессионального бокса: Владимир Кличко» . boxrec.com . Проверено 9 июня 2020 г.
- ^ «Рекорд профессионального бокса: Султан Ибрагимов» . boxrec.com . Проверено 9 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Ринг (Украинский журнал) №3, 2008, стр.6-7
- ^ Ринг (Украинский журнал) №3, 2008, стр.7
- ^ "Владимир Кличко - Султан Ибрагимов 23-02-2008" . 3 March 2012. Archived from the original on 29 October 2021 . Retrieved 9 June 2020 – via YouTube.
- ^ Alexander Belenkyi (2011). Властелины ринга. Бокс на въезде и выезде . Astrel. ISBN 978-5-9725-1978-1 . Проверено 9 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Alexander Belenkyi (2011). Властелины ринга. Бокс на въезде и выезде . Astrel. ISBN 978-5-9725-1978-1 . Проверено 9 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б "Умом и кулаками: Владимир Кличко заработал 150 миллионов евро за карьеру" . sportarena.com (in Russian). 11 July 2019 . Retrieved 28 July 2020 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б "Владимир Кличко заработал 150 миллионов евро за карьеру" . sport.24tv.ua (in Russian). 11 July 2019 . Retrieved 28 July 2020 .
- ↑ Кличко жертвует деньги в детский фонд
- ^ «Кличко разгромил Ибрагимова и объединил титулы IBF и WBO» . 24 февраля 2008 года . Проверено 9 июня 2020 г.
- ^ «Кличко победитель, но не воодушевлен» . Хранитель . 24 февраля 2008 года . Проверено 9 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Гуревич В. (25 February 2008). " "Этот бой – позор для бокса". Знаменитый промоутер Боб Арум раскритиковал поединок Владимира Кличко с Султаном Ибрагимовым" . Советский спорт . Archived from the original on 19 July 2019 . Retrieved 19 July 2019 .
- ^ "Дэн Гуссен: "На Кличко с Ибрагимовым было жалко смотреть" " . sports.ru . 15 February 2008. Archived from the original on 19 July 2019 . Retrieved 19 July 2019 .
- ^ Ринг (Украинский журнал) №3, 2008, стр.9
- ^ "КЛИЧКО – ИБРАГИМОВ: КАК СКУЧНО БЫТЬ КОРОЛЕМ… АНАЛИЗ БОЯ" . censor.net.ua (in Russian). 25 February 2008 . Retrieved 9 June 2020 .
- ^ «Красники готовы к Тони Томпсону» . boxing247.com . 5 июня 2007 г. Проверено 23 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Красники избили и выставили напоказ» . Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung (на немецком языке) . Проверено 23 мая 2020 г.
- ^ Глиндмайер, Майк (15 июля 2007 г.). «Заключительный акт канатоходца» . Зеркало (на немецком языке) . Проверено 23 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Конец мечты Шмелинга» . Звезда (на немецком языке). 15 июля 2007 года . Проверено 23 мая 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Рекорд профессионального бокса: Тони Томпсон» . boxrec.com . Проверено 19 мая 2020 г.
- ^ "Кличко: "Томпсон хорошо защищается" " . eurosport.ru (in Russian). 17 June 2008 . Retrieved 1 June 2020 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час «Кличко сохранил титулы в тяжелом весе, нокаутировав Томпсона в 11-м раунде» . ЭСПН. 12 июля 2008 года . Проверено 1 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж "Как Тони Томпсон пытался дважды победить Владимира Кличко" . Коммерсантъ (in Russian). 14 July 2008 . Retrieved 1 June 2020 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Бой: Владимир Кличко против Тони Томпсона» . boxrec.com . Проверено 1 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Лободин К. "Охота на голодного Тигра, p. 42-45". Ring, Ukraine. ISSN 1810-7338 .
- ^ Лободин К. "Ап! И тигры у ног моих сели..., p. 14-19". Ring, Ukraine. ISSN 1810-7338 .
- ^ "Как Тони Томпсон пытался дважды победить Владимира Кличко" . sovsport.ru (in Russian). Archived from the original on 3 December 2020 . Retrieved 1 June 2020 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Боксёр Кличко сохранил титул чемпиона мира после боя в Гамбурге» . Немецкая волна . Проверено 1 июня 2020 г.
- ^ "12 июля: Кличко - Томпсон. На кого ставят букмекеры" . vecherniy.kharkov.ua (in Russian) . Retrieved 27 July 2020 .
- ^ "Кличко получил 8 миллионов евро за бой с Томпсоном" . vesti.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 27 July 2020 .
- ↑ Компания Кличко выиграла гонорар за бой 13 декабря . ESPN.go.com (16 сентября 2008 г.). Проверено 25 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ HBO (17 марта 2016 г.), Владимир Кличко против Хасима Рахмана # 720p , заархивировано из оригинала 29 октября 2021 г. , получено 8 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ HBO (7 января 2009 г.), Владимир Кличко против Хасима Рахмана: лучшие моменты (HBO Boxing) , получено 26 апреля 2017 г.
- ^ Клаудио, Э.Дж. «Мои мысли о матче Владимира Кличко против Хасима Рахмана» . Отчет отбеливателя . Проверено 26 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ агентства, сотрудники телеграфа и. «Владимир Кличко нокаутировал Хасима Рахмана» . «Дейли телеграф» . Архивировано из оригинала 11 января 2022 года . Проверено 26 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ «Бой: Владимир Кличко против Хасима Рахмана» . Проверено 8 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ «Статистика Compubox: Владимир Кличко против Хасима Рахмана» . Проверено 8 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ «Дэвид Хэй ошеломил Владимира Кличко, отказавшись от титульного боя» . Хранитель . 3 июня 2009 года . Проверено 6 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Ринг №6: Цирк тяжеловесных размеров. 2009 год
- ^ «Боэнте: Чагаев заменит обиженного Хэя» . 5 июня 2009 года . Проверено 6 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ «Чагаев заменит Хэя в бою с Кличко» . Радио и телевидение Ирландии . 6 июня 2009 года . Проверено 6 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ «Почему Кличко-Чагаев — самый важный бой в тяжелом весе за последние годы и почему он не принесет никакой пользы» . 17 июня 2009 года . Проверено 6 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ «Чагаев против Кличко: Руслан более сильный противник, чем Хэй?» . 6 июня 2009 года . Проверено 6 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ «ЛИЧ-НА-ЛИЧЬ: КЛИЧКО ПРОТИВ ЧАГАЕВА» . 19 июня 2009 года . Проверено 6 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «КЛИЧКО ОСТАНАВЛИВАЕТ ЧАГАЕВА, ЗАВОЕВЫВАЕТ ТИТУЛ НА РИНГЕ» . 20 июня 2009 года . Проверено 6 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Владимир Кличко нокаутировал Руслана Чагаева» . Хранитель . 20 июня 2009 года . Проверено 6 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Кличко побеждает техническим нокаутом, сохраняет титулы в тяжелом весе» . ЭСПН. 20 июня 2009 года . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ Дж, Кинг. «Владимир Кличко против Эдди Чемберса 20 марта в Германии» . Отчет отбеливателя . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д «Кличко против Чемберса 10 лет назад: как многолетний чемпион разрушил мечты Америки» . Проверено 27 марта 2020 г.
- ^ «НА ГОЛОВУ: В. КЛИЧКО-ЧЕМБЕРС» . 19 марта 2010 года . Проверено 27 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Тот факт, что Кличко-Чемберса нет на американском телевидении, — это новый минимум» . 15 марта 2010 г. Проверено 16 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б "Виталий Кличко: "Уйду, когда с братом соберем все чемпионские пояса" " (in Russian) . Retrieved 1 November 2020 .
- ^ «Бой: Владимир Кличко против Эдди Чемберса» . Проверено 27 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с «Владимир Кличко нокаутирует Эдди Чемберса на последних секундах» . 20 марта 2010 г. Проверено 27 марта 2020 г.
- ^ «Кличко нокаутирует Чемберса, чтобы сохранить титулы» . Си-Эн-Эн. 21 марта 2010 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко нокаутирует Эдди Чемберса на последних секундах» . Плохой левый хук . 20 марта 2010 г. Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ Тилуок, Ник. «Владимир Кличко против Эдди Чемберса: раунд за раундом» . Отчет отбеливателя . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ «Кличко нокаутировал Чемберса, чтобы сохранить корону супертяжеловеса » Немецкая волна . Проверено 27 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Владимир зовет Хэя . Skysports.com. Проверено 19 июня 2011 г.
- ^ Вестер, Марк (14 апреля 2010 г.). «Кличко: «Дэвид «Неудачник» Хэй напуган и лжец» » . BoxingScene.com.
- ↑ Бут: Влад отлично справится . Skysports.com. Проверено 19 июня 2011 г.
- ^ Вестер, Марк (1 мая 2010 г.). «Владимир Кличко – Дэвид Хэй намечены на сентябрь» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 9 мая 2010 г.
- ^ Чиков, Руслан (3 мая 2010 г.). «Переговоры Владимира Кличко и Дэвида Хэя с HBO прошли хорошо» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 9 мая 2010 г.
- ^ Чиков, Руслан (4 мая 2010 г.). «Владимир Кличко-Дэвид Хэй направляются в Германию» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 9 мая 2010 г.
- ^ Саттерфилд, Лем (11 мая 2010 г.). «Представители Владимира Бичко направили предложение о бое Дэвиду Хэю» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 15 мая 2010 г.
- ^ Чиков, Руслан (14 мая 2010 г.). «Хэй хочет видеть Виталия и Владимира-Поветкина по мере приближения крайнего срока» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 15 мая 2010 г.
- ^ Чиков, Руслан (17 мая 2010 г.). «Переговоры Кличко и Хэя продолжаются, несмотря на крайний срок» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 18 мая 2010 г.
- ^ Рино, Рик (28 мая 2010 г.). «Тренер Кличко: Если бы Хэй был мужчиной, он бы откликнулся» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 28 мая 2010 г.
- ^ Ким, Джейсон (4 июля 2010 г.). «Кличко против Поветкина во Франкфурте, Германия» . BoxingNews24.com . Проверено 5 июля 2010 г.
- ^ Дэн Рафаэль (22 июля 2010 г.). «Матч-реванш Кличко-Петр 11 сентября» . ЭСПН . Проверено 2 августа 2020 г.
- ^ Дэн Рафаэль (28 июля 2010 г.). "В.Кличко, Петр соглашаются на условия боя" . ЭСПН . Проверено 2 августа 2020 г.
- ^ «Кличко против Питера Подробности; Боуман против Ацевадо Топс» . BoxingScene.com. 30 июля 2010 г. Проверено 31 июля 2010 г.
- ^ Сукачев, Алексей (11 сентября 2010 г.). «Кличко бьет Питера в десяти раундах, победа нокаутом» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 12 сентября 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «BoxRec: Владимир Кличко» . BoxRec.com. 1 мая 2010 года . Проверено 12 марта 2020 г.
- ^ "Владимир Кличко за бой с Питером заработал 5 миллионов евро" (in Russian). championat.com . Retrieved 31 July 2020 .
- ^ Крис Мэнникс, SI.com (8 декабря 2010 г.). «Кличко порвал брюшную мышцу и отказался от субботней защиты титула» . Иллюстрированный спорт . Проверено 9 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Дэн Рафаэль (9 декабря 2010 г.). «Владимир Кличко снимается с боя» . ЭСПН . Проверено 9 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Персонал (5 января 2011 г.). «Чисора получит свой шанс» . SkySports.com . Проверено 5 января 2011 г.
- ^ Кличко.com . Проверено 19 апреля 2011 г.
- ↑ Бой Кличко-Хэй может состояться за пределами Германии. Архивировано 5 марта 2016 г. на Wayback Machine , Yahoo!.com (12 апреля 2011 г.). Проверено 19 апреля 2011 г.
- ^ «Бойцовский сет Владимир Кличко-Дэвид Хэй» . ЭСПН. 6 марта 2011 года . Проверено 7 марта 2011 г.
- ^ Рекорды бокса BoxRec . Boxrec.com. Проверено 19 июня 2011 г.
- ↑ Бокс – Кличко-Хэй в Гамбурге. Архивировано 24 апреля 2011 года в Wayback Machine . Fightnews.com (20 апреля 2011 г.). Проверено 19 июня 2011 г.
- ^ Профиль , RTL.de. Проверено 19 июня 2011 г.
- ^ «CompuBox: Владимир Кличко против Дэвида Хэя» . Проверено 1 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Джексон, Джейми (18 января 2012 г.). «Дерек Чисора высмеивает предложение Дэвида Хэя драться с Виталием Кличко» . Хранитель . Лондон.
- ^ Баковски, Грегг (2 июля 2011 г.). «Дэвид Хэй против Владимира Кличко – как это было» . Хранитель . Лондон . Проверено 4 июля 2011 г.
- ^ Дэвис, Гарет А. (2 июля 2011 г.). «Владимир Кличко ломает решимость Дэвида Хэя стать абсолютным чемпионом мира в тяжелом весе» . «Дейли телеграф» . Лондон. Архивировано из оригинала 5 июля 2011 года . Проверено 4 июля 2011 г.
- ^ «Кличко окончательно свел счеты с Хэем» . ЭСПН. 2 июля 2011 года . Проверено 2 июля 2011 г.
- ^ "Как боксеры выбивают большие деньги" . klitschko-brothers.com . 7 July 2016. Archived from the original on 27 November 2020 . Retrieved 10 September 2022 .
- ^ Профиль Владимира Кличко , boxrec.com. Проверено 8 июля 2012 г.
- ^ Официальный сайт Виталия и Владимира Кличко , Klitschko.com. Проверено 25 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «СООБЩЕНИЕ/605: Француз Жан-Марк Мормек подтвержден в качестве претендента Владимира Кличко (SB)» . Schattenblick.de (на немецком языке) . Проверено 18 января 2021 г.
- ^ «Кличко снимается с титульного боя» . Новости Би-би-си . 5 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко разгромил Мормека в четырех раундах» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 12 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко против Мормека — статистика CompuBox» . boxingscene.com . Проверено 12 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Годовые рейтинги BoxRec: ежегодные рейтинги тяжеловесов» . Проверено 13 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Владимир признает, что следующим шагом будет матч-реванш с Тони Томпсоном» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 11 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Предложение по гонорару Кличко-Томпсона: 85% доля за Владимира» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 11 декабря 2017 г.
- ↑ Владимир Кличко проведет 12-ю защиту титула в матче-реванше против Тони Томпсона , ESPN, 27 марта 2012 г. Проверено 8 июля 2012 г.
- ^ «Признание Кличко: Томпсон не был моим первым выбором» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 11 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ "Кличко: Томпсон меня знает - Eurosport" . 30 November 2020. Archived from the original on 30 November 2020 . Retrieved 7 November 2021 .
- ^ "Владимир Кличко: Томпсон - сильный и сложный" . korrespondent.net (in Russian) . Retrieved 27 July 2020 .
- ^ "Состоялось взвешивание перед поединком Владимир Кличко – Тони Томпсон" . sports.ru (in Russian). 11 July 2008 . Retrieved 27 July 2020 .
- ^ "Как Тони Томпсон пытался дважды победить Владимира Кличко" (in Russian) . Retrieved 27 July 2020 .
- ^ «Кличко: У меня не было сомнений, но в Томпсона было трудно попасть» . sport.cz (на чешском языке). 8 июля 2012 года . Проверено 27 июля 2020 г.
- ↑ Кличко снова нокаутирует Томпсона. Архивировано 10 июля 2012 года в Wayback Machine . Fightnews.com (7 июля 2012 г.). Проверено 8 июля 2012 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко победил Тони Томпсона техническим нокаутом в шести матчах» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 11 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко против Томпсона — CompuBox» . boxingscene.com . Проверено 11 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко-Вах: Если деньги правильные, они могут подраться» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко-Вах: противоречивые заявления о статусе боя» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Переговоры Кличко-Вах осенью активизируются» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко и Вах достигли соглашения об условиях: бой начался!» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ↑ Бэнкс будет тренировать Владимира Кличко ESPN, 24 октября 2012 г. Дата обращения 28 апреля 2015 г.
- ^ «Кличко-Вах: Джонатон Бэнкс заменит стюарда» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Эмануэль Стюард 1944-2012: Уходит легенда» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Вах подтверждает бой с Кличко» . Boxingnews24.com. Архивировано из оригинала 29 мая 2013 года . Проверено 15 августа 2012 г.
- ↑ Мариуш Вах. Архивировано 17 июня 2015 года на Wayback Machine BoxRec.com. Проверено 28 апреля 2015 г.
- ^ «В. Кличко будет защищать титул против Ваха ростом 6 футов 7 дюймов» . ЭСПН . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «CYFRA+: Кличко - Вах в PPV» (на польском языке) . Проверено 6 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «КЛИЧКО против ВАХ БОЙ: Трансляция за 39 злотых на Canal+» (на польском языке) . Проверено 6 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Бой Кличко против Ваха. Онлайн-трансляция в Интернете и прямой эфир по телевидению» (на польском языке). 9 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 6 июня 2020 г.
- ^ «Событие: Владимир Кличко против Мариуша Ваха» . Проверено 6 июня 2020 г.
- ^ «Кличко легко побеждает Durable Wach за двенадцать» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Доминирующий Кличко нанес удар храброму Ваху» . ЭСПН . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко против Ваха — CompuBox» . boxingscene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Промоутер Ваха взрывается из-за обвинений в стероидах» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ "Кличко заработал 5,3 миллиона евро за бой с Вахом" . lb.ua (in Russian) . Retrieved 12 December 2017 .
- ^ «Исторические курсы конвертации валюты EUR/USD на 12 ноября 2012 года (11.12.2012)» . www.exchangerates.org.uk . Проверено 28 июля 2020 г.
- ^ "Доход Кличко за бой с Вахом составит почти 6 миллионов евро" (in Russian) . Retrieved 1 November 2020 .
- ^ "Кличко заработал за бой с Вахом 5,3 млн. евро" (in Russian). 13 November 2012 . Retrieved 1 November 2020 .
- ^ «Владимир Кличко предложил 5 миллионов евро за бой с Хаком» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 11 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Боэнте: 100 миллионов евро не сделают Кличко против Гека» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 12 декабря 2017 г.
- ↑ Начало переговоров Кличко и Поветкина. Архивировано 6 февраля 2013 года в Wayback Machine . Wbanews.com. Проверено 1 мая 2013 г.
- ^ Кошельковые предложения по поединку Поветкин-Кличко|Boxing/MMA|R-Sport. Все главные новости спорта . ru.rsport.ru (17 января 2013 г.). Проверено 1 мая 2013 г.
- ↑ WBA разрешила Владимиру Кличко отложить бой против Поветкина . Киев Почта . Проверено 1 мая 2013 г.
- ↑ WBA дает Кличко специальное разрешение, но ратифицирует его обязательный бой против Поветкина. Архивировано 3 февраля 2013 года в Wayback Machine . Wbanews.com. Проверено 1 мая 2013 г.
- ^ «Бой Кличко-Пианета завершился 4 мая на SAP Arena» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко не беспокоят критики столкновения Пианеты» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ Христос, Скотт (4 мая 2013 г.). «Результаты: Кличко нокаутирует Пианету в шестом раунде» . Плохой левый хук . Проверено 4 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ «Кличко доминирует и останавливает Пианету в шести раундах» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «60 и 14: Кличко продолжает продлевать свое правление» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко против Планеты — CompuBox» . boxingscene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко поделился долгожданным боем с Александром Поветкиным» . ЭСПН . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ «Лагерь Кличко «удивлен» предложением о гонораре в 23 миллиона долларов» . ЭСПН . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ «Бокс – Владимир Кличко против Александра Поветкина: Как Россия выиграла войну в тяжелом весе» . Проверено 18 мая 2020 г.
- ^ "Кличко – Поветкин: как Россия выиграла войну в тяжелом весе" (in Russian) . Retrieved 3 July 2020 .
- ^ "Ньюсмейкер недели. Ключевые цитаты о бое Кличко – Поветкин" (in Russian) . Retrieved 3 July 2020 .
- ^ "Путин придет на бой Кличко - Поветкин" (in Russian) . Retrieved 21 January 2021 .
- ^ "Владимир Путин посетит бой Кличко и Поветкина" (in Russian) . Retrieved 21 January 2021 .
- ^ «Событие: Владимир Кличко против Александра Поветкина» . Проверено 16 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Поветкин наносил удары после команды "стоп" и слишком низко "нырял" под него
- ^ «Оценочная таблица: Кличко хорош, а Котто сияет» . ЭСПН . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ «Владимир Кличко победил Александра Поветкина в Москве» . Би-би-си Спорт . 5 октября 2013 года . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ «Кличко снова побеждает, затыкая Поветкина» . Плохой левый хук . 5 октября 2013 года . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ «CompuBox – Статистика ThrowdownFantasy.com: Кличко W 12 Поветкин» . www.compuboxonline.com . Архивировано из оригинала 3 октября 2017 года . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ Кличко объяснил, почему не добил Поветкина
- ^ Кличко: не стал расстраивать россиян нокаутом Поветкина
- ^ "Владимир Кличко рассказал, почему не захотел нокаутировать Поветкина" . Archived from the original on 13 December 2017 . Retrieved 12 December 2017 .
- ^ 20 самых рейтинговых трансляций России в 2013 году
- ^ Итоги 2013 года глазами телезрителей 20-ти больших городов страны
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б "Элитный бокс и футбол в лидерах ТВ-проектов РФ" (in Russian). 21 October 2020 . Retrieved 23 October 2020 .
- ^ "Inter Media Group укрепила лидерство на украинском телевидении в 2013 году" . 16 January 2014 . Retrieved 23 January 2023 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с "Сегодня состоится масштабное телешоу, посвященное бою Александра Усика" (in Russian). 27 January 2018 . Retrieved 28 April 2022 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с "Капитуляция российского "витязя": 8 лет назад в Москве Кличко избил Поветкина – видео" (in Russian). Channel 24 . 5 октября 2021 . Retrieved 9 октября 2021 .
- ^ RTL: телевизионный год 2013 (нем.)
- ^ «WBO делает Алекса Леапая обязательным для боя Владимира Кличко» . Новости бокса 24 . Проверено 4 декабря 2013 г. [ постоянная мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ «Кличко и Леапай назначили дату обязательного боя в апреле» . Мировые новости бокса. Архивировано из оригинала 6 января 2014 года . Проверено 5 января 2014 г.
- ^ «Сделка Кличко-Леапай близка к 26 апреля в Германии» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Фото: В. Кличко подписал контракт с Леапаем, 26 апреля» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Дэвид Туа отказывается помогать Кличко в лагере Леапай» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ Латтон, Фил (27 апреля 2014 г.). «Алекс Леапай уничтожен Владимиром Кличко, нанеся всего 10 ударов» . Сидней Морнинг Геральд . Проверено 8 марта 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко финиширует Леапая с результатом в пять» . Плохой левый хук . 26 апреля 2014 года . Проверено 8 марта 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко побеждает превосходящего Леапая в пяти матчах» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко похвалил Leapai за усилия» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко против Леапая — CompuBox» . boxingscene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко против Кубрата Пулева по заказу IBF» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Менеджер Кличко: Целью Влада является Стиверн, а не Пулев» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Запрос Кличко на разделение гонорара 80-20 одобрен IBF» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко-Пулев: К2 превзошла Зауэрланда и выиграла кошелек» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Бой Кличко-Пулев перенесен на 15 ноября в Гамбурге» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «HBO покажет в прямом эфире бой Владимира Кличко – Кубрата Пулева» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко-Пулев: на кону для претендента только пояс IBF» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Пулев может выиграть только один из поясов Кличко» . 14 ноября 2014 г.
- ^ "300 милиона за Кубрат и Кличко!" (in Bulgarian). 15 November 2014 . Retrieved 26 March 2020 .
- ^ "300 милиона зрители на шоуто Пулев - Кличко" (in Bulgarian) . Retrieved 26 March 2020 .
- ^ "300 милиона гледат мегасблъсъка Пулев - Кличко" (in Bulgarian). 15 November 2014 . Retrieved 26 March 2020 .
- ^ «Владимир Кличко тренирует Кубрата Пулева в «Пятом»» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ Владимир Кличко снова сохраняет титул . ESPN.go.com (15 ноября 2014 г.). Проверено 4 декабря 2016 г.
- ^ «Кличко против Пулева — CompuBox » boxingscene.com . Получено 8 декабря.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Кличко-Пулев привлекает 10,5 миллионов зрителей на немецком телевидении» . Новости бокса 24 . 2 декабря 2014 года . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Кличко-Пулев — самая просматриваемая передача в истории Нова ТВ» (на болгарском языке) . Проверено 30 ноября 2020 г. .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «1 миллион смотрел Крисию, Хасана и Ибрагима, 1,8 миллиона отдали предпочтение Пулеву-Кличко» (на болгарском языке) . Проверено 30 ноября 2020 г. .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б "Πĸaepд! 1.8 милиeнo бългopи глĸдoли мoчo Eличae - Xyлĸв пe Beвo тĸлĸвизия" (in Bulgarian). 17 November 2014 . Retrieved 30 November 2020 .
- ^ «Бой Кличко — Пулев взорвал стандарты, собрав 1,8 миллиона зрителей» (на болгарском языке). 17 ноября 2014 года . Проверено 6 июня 2020 г.
- ^ «Возвращение Кличко на HBO — хит на ринге и рейтингах» . BoxingScene.com . Проверено 8 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Бой Кличко-Дженнингс состоится 25 апреля в Гардене» . ЭСПН . Проверено 5 мая 2017 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко решает, что Брайант Дженнингс защитит титул чемпиона в супертяжелом весе» . ЭСПН . 26 апреля 2015 года . Проверено 26 апреля 2015 г.
- ^ «Кличко получил самый высокий рейтинг HBO с 2012 года» . Плохой левый хук . 28 апреля 2015 года . Проверено 5 мая 2017 г.
- ^ "Главные богачи спорта: больше всех зарабатывают Кличко и Ярмоленко, Свитолина – номер один у девушек" . Retrieved 1 December 2020 .
- ^ Владимир Кличко – Тайсон Фьюри отложен из-за травмы чемпиона | Новости бокса . Скай Спорт. Проверено 28 ноября 2015 г.
- ^ «Команда Тайсона Фьюри заставляет Владимира Кличко заново делать бинты» . Ларри Браун Спорт . 28 ноября 2015 года . Проверено 27 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко против Фьюри: Тайсон Фьюри побеждает Владимира Кличко единогласным решением судей» . Скай Спорт . Проверено 27 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ Лутц, Том (28 ноября 2015 г.). «Тайсон Фьюри победил Владимира Кличко: мировой бокс в тяжелом весе – как это было» . Хранитель . ISSN 0261-3077 . Проверено 27 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Фьюри расстраивает Кличко: главная статистика, которую нужно знать» . ЭСПН . Проверено 27 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ Дирс, Бен (2015) « Тайсон Фьюри побеждает Владимира Кличко и становится чемпионом мира », BBC , 29 ноября 2015 г. Проверено 29 ноября 2015 г.
- ^ «Фьюри положил конец правлению Кличко как чемпиона в тяжелом весе» . ЭСПН . Проверено 21 сентября 2017 г.
- ^ «Фьюри и Кличко проведут матч-реванш 9 июля» . Би-би-си Спорт . Проверено 5 июня 2020 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко – Тайсон Фьюри отложен: матч-реванш за звание чемпиона мира в супертяжелом весе отложен» . Би-би-си Спорт . 23 сентября 2016 года . Проверено 26 сентября 2016 г.
- ^ «Тайсон Фьюри написал эмоциональное заявление из 127 слов после освобождения титула чемпиона мира» . GiveMeSport . 13 октября 2016 года. Архивировано из оригинала 13 октября 2016 года . Проверено 13 октября 2016 г.
- ^ «Дата боя Энтони Джошуа и Владимира Кличко будет объявлена позже» . Независимый . 16 октября 2016 г. Проверено 29 октября 2016 г.
- ^ ВБН. «Решение WBA по бою Джошуа против Кличко отложено до понедельника» . WBN — Мировые новости бокса . Архивировано из оригинала 30 октября 2016 года . Проверено 30 октября 2016 г.
- ^ «Кличко-Браун сразятся за титул WBA? | Новости бокса» . Новости бокса . 20 октября 2016 года. Архивировано из оригинала 31 октября 2016 года . Проверено 30 октября 2016 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко отказался от боя с 10 декабря из-за травмы — Новости бокса» . boxingscene.com . 24 октября 2016 г. Проверено 30 октября 2016 г.
- ^ «Энтони Джошуа готовится к весеннему бою с Владимиром Кличко» . BT.com . Проверено 30 октября 2016 г.
- ^ Джей, Фил Д. (2 ноября 2016 г.). «Резолюция WBA: Джошуа против Кличко санкционированы; Ортис исключен; Браун против Бриггса предписано» . WBN — Мировые новости бокса . Проверено 4 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ Эллиотт, Райан (11 декабря 2016 г.). «Бой Энтони Джошуа против Владимира Кличко назначен на 29 апреля» . Телеканал «Новости бокса» . Архивировано из оригинала 14 декабря 2016 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2016 г.
- ^ «Энтони Джошуа или Владимир Кличко выйдут на встречу с Луисом Ортисом, приказывает WBA» . Скай Спорт . 20 декабря 2016 года . Проверено 21 декабря 2016 г.
- ^ «Луис Ортис выстроился в очередь, чтобы встретиться с победителем боя Энтони Джошуа и Владимира Кличко» . 20 декабря 2016 года . Проверено 21 декабря 2016 г. [ постоянная мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ «Победитель боя Джошуа-Кличко столкнется с дилеммой титула чемпиона мира» . ЭСПН . Проверено 26 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ «Джошуа против Кличко: продано более 80 000 билетов» . Сцена бокса . 16 января 2017 года . Проверено 17 января 2017 г.
- ^ «БИТВА ДЖОШУА С КЛИЧКО ПРОДАНО БОЛЕЕ 80 000 TIX» . 16 января 2017 года . Проверено 17 января 2017 г.
- ^ «Джошуа весит 250 фунтов; Кличко весит 240¼ фунтов - Новости бокса» . boxingscene.com . 28 апреля 2017 года . Проверено 28 апреля 2017 г.
- ^ «Джошуа отрывается от пола и нокаутирует Кличко в одиннадцатом раунде — Новости бокса» . boxingscene.com . 29 апреля 2017 года . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ «Би-би-си Спорт» . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ «Джошуа собирается остановить Кличко в 11-м раунде» . ЭСПН . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ «Кличко: Победил лучший мужчина, очень грустно, что я этого не сделал — Новости бокса» . boxingscene.com . 29 апреля 2017 года . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ «Джошуа готов к матчу-реваншу с Кличко, на стадионе «Княжество» - Новости бокса» . boxingscene.com . 30 апреля 2017 года . Проверено 30 апреля 2017 г. .
- ^ «Прямая трансляция боя Джошуа-Кличко привлекла 659 тысяч зрителей на Showtime – Новости бокса» . boxingscene.com . Май 2017 года . Проверено 2 мая 2017 г.
- ^ «Повтор боя Джошуа-Кличко на канале HBO достиг 890 тысяч зрителей – Новости бокса» . boxingscene.com . 2 мая 2017 года . Проверено 3 мая 2017 г.
- ^ «Джошуа-Кличко составляет рейтинги для Showtime и HBO: MMAPayout.com: Бизнес ММА» . mmapayout.com . Проверено 2 мая 2017 г.
- ^ «Рейтинги: Джошуа-Кличко набирает 659 тысяч в США, превышает 10 миллионов в Германии» . Кровавый локоть . 1 мая 2017 года. Архивировано из оригинала 2 мая 2017 года . Проверено 2 мая 2017 г.
- ^ «Джошуа получил исключение из обязательной защиты» . ЭСПН . Проверено 10 июня 2017 г.
- ^ «Джошуа-Кличко II: Херн направляется в Вегас, чтобы поговорить с MGM - Новости бокса» . boxingscene.com . Проверено 29 июля 2017 г. [ постоянная мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ «Матч-реванш Джошуа-Кличко может состояться на T-Mobile Arena - Новости бокса» . boxingscene.com . 13 июля 2017 года . Проверено 29 июля 2017 г.
- ^ «Эспиноза из SHO: Решение Джошуа-Кличко II приближается - Новости бокса» . boxingscene.com . 15 июля 2017 года . Проверено 29 июля 2017 г.
- ^ «Хирн уверен, что матч-реванш Джошуа-Кличко состоится 11 ноября в Вегасе – Новости бокса» . boxingscene.com . 25 июля 2017 года . Проверено 29 июля 2017 г.
- ^ «Матч-реванш Джошуа-Кличко может быть на PPV в США — Новости бокса» . boxingscene.com . 27 июля 2017 года . Проверено 29 июля 2017 г.
- ^ "Решение" . Кличко.com . 3 августа 2017 года . Проверено 3 августа 2017 г.
- ^ «ВЛАДИМИР КЛИЧКО ЗАВЕРШАЕТ БОКСЕРСКУЮ КАРЬЕРУ» . 3 августа 2017 года. Архивировано из оригинала 3 августа 2017 года . Проверено 3 августа 2017 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко завершает карьеру и не будет драться с Энтони Джошуа в реванше» . Би-би-си Спорт . 3 августа 2017 года . Проверено 5 августа 2017 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко уходит из бокса — Новости бокса» . boxingscene.com . 3 августа 2017 года . Проверено 5 августа 2017 г.
- ^ «100 самых высокооплачиваемых спортсменов по версии Forbes: 24-е место Владимир Кличко» . Проверено 2 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «100 самых высокооплачиваемых спортсменов по версии Forbes: № 41 Владимир Кличко» . Проверено 2 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «100 самых высокооплачиваемых спортсменов по версии Forbes: 25-е место Владимир Кличко» . Проверено 2 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «100 самых высокооплачиваемых спортсменов по версии Forbes: Владимир Кличко №63» . Архивировано из оригинала 13 июня 2015 года . Проверено 2 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «100 самых высокооплачиваемых спортсменов по версии Forbes: Владимир Кличко №98» . Проверено 2 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ "Главные богачи спорта: больше всех зарабатывают Кличко и Ярмоленко, Свитолина – номер один у девушек" (in Russian) . Retrieved 2 December 2020 .
- ^ «100 самых высокооплачиваемых спортсменов мира 2016: в цифрах» . Проверено 2 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ "СМИ посчитали, сколько за карьеру боксера заработал Владимир Кличко" . sport.nv.ua (in Russian). 11 июля 2019 . Retrieved 24 мая 2024 года .
- ^ "СМИ: Владимир Кличко заработал 150 миллионов евро за карьеру" . klitschko-brothers.com (in Russian). 11 July 2019. Archived from the original on 28 July 2020 . Retrieved 28 July 2020 .
- ^ «Владимир Кличко: украинский король, который разделял и объединял. Он легенда?» . profiboxing.cz (на чешском языке) . Проверено 23 марта 2021 г.
- ^ «Чемпионы по спорту» . ЮНЕСКО . Проверено 3 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Украинские боксеры Vitality и Владимир Кличко названы чемпионами ЮНЕСКО по спорту» . ЮНЕСКО. 26 февраля 2013 года . Проверено 3 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Виталий и Владимир Кличко признаны чемпионами ЮНЕСКО по спорту» . Архивировано из оригинала 11 ноября 2009 года . Проверено 31 августа 2019 г.
- ^ "Великие Украинцы – сто великих украинцев от 19 до 1" (in Russian). 3 January 2016. Archived from the original on 29 October 2021 . Retrieved 23 ноября 2020 – via YouTube.
- ^ Свобода, Радио (29 May 2008). "В проекте "Великие Украинцы" на телеканале "Интер" победил князь Ярослав Мудрый" . Радио Свобода (in Russian) . Retrieved 23 ноября 2020 .
- ^ "Ярослав Мудрый, Николай Амосов, Степан Бандера – БОЛЬШИЕ УКРАИНЦЫ" . zaxid.net (в Russian). 17 мая 2008 . Retrieved 23 ноября 2020 .
- ^ " Великие Украинцы": Ярослав Мудрый обошел Бандеру" . unian.ua (in Russian) . Retrieved 23 ноября 2020 .
- ^ Линдер, Лео Г. (2013). Кличко . Германия: Neues Leben, Verlag (опубликовано 1 декабря 2013 г.). ISBN 978-33-550-1817-3 .
- ^ «Виталий Кличко в Kiew Geehrt» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 31 октября 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б "Бой Кличко – Вах в России посмотрели 400 тысяч человек" (in Russian). 11 July 2022 . Retrieved 13 January 2023 .
- ^ "ТОП-100 журнала Корреспондент. Полный список самых влиятельных украинцев" (in Russian) . Retrieved 9 November 2020 .
- ^ "ТОП-100 журнала Корреспондент. Полный список самых влиятельных людей Украины" (in Russian) . Retrieved 12 November 2020 .
- ^ "ТОП-100 журнала Корреспондент. Полный список самых влиятельных людей Украины" (in Russian) . Retrieved 9 November 2020 .
- ^ "Forbes назвал Владимира Кличко самым дорогим и популярным украинцем" . capital.ua (in Russian). 24 December 2015 . Retrieved 3 November 2020 .
- ^ "ТОП-10 самых дорогих и самых популярных звезд Украины" . segodnya.ua (in Russian) . Retrieved 3 November 2020 .
- ^ "Forbes назвал самых успешных звезд украинского шоу-бизнеса" . korrespondent.net (in Russian) . Retrieved 3 November 2020 .
- ^ "Рейтинг звезд 2013 - Forbes.ua" . korrespondent.net (in Russian) . Retrieved 3 November 2020 .
- ^ "Указ Президента Украины О награждении государственными наградами Украины по случаю Дня независимости Украины" (in Ukrainian). Verkhovna Rada . Retrieved 1 декабря 2020 .
- ^ «Бокс: Как Кличко стали править немецким боем» . Проверено 6 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ Кулиш, Николай (23 февраля 2008 г.). «В Германии бокс находит признание и центр» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 6 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ " "В Германии братьев Кличко знала каждая бабушка". Истории о раскрутке украинцев для немецкой публики" (in Russian). Archived from the original on 18 August 2020 . Retrieved 6 November 2020 .
- ^ «Свен Ханнавальд — самый популярный немецкий спортсмен» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 7 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ "Кличко в кино: славные парни с железными кулаками" (in Russian) . Retrieved 2 November 2020 .
- ^ «Рейтинг: «Рекламный сварливый» Гюнтер Яух — самый популярный отзыв» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 17 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «Клопп: восходящая звезда отзывов» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 22 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «Повышайте ценность бренда с помощью выдающихся отзывов» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 22 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «Ангела Меркель затмевает всех VIP-персон» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 22 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «Шумахер признан спортсменом века в Германии» . Питпасс . 20 ноября 2004 года . Проверено 27 февраля 2021 г.
- ^ «Шоу ZDF «Спортсмен века» посмотрели 6,11 миллиона зрителей» (на немецком языке). 22 ноября 2004 года . Проверено 23 апреля 2021 г.
- ^ «Более 12 миллионов зрителей: Кличко побеждает всех» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 6 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко лучше Михаэля Шумахера» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 6 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «Рыночные доли в марте: бокс и Формула 1 повышают RTL» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 6 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ Депаоло, Джо (22 апреля 2015 г.). «Владимир Кличко добивается признания себя и Украины» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 23 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко в ударе, и не ждите, что Томпсон его остановит» . Проверено 23 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко объявляет об уходе из бокса» . Проверено 23 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ «Победа Кличко нокаутом: где соперники?» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 23 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко осуществляет избиение» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 23 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ «Стальной молот» ударил снова» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 23 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ «Больше нет сомнений: у бокса есть свой законный чемпион в тяжелом весе» . Проверено 23 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ «Больше нет сомнений: у бокса есть свой законный чемпион в тяжелом весе» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 23 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «От «Битвы в джунглях» до Кардиффа — самая большая посещаемость в истории бокса» . ЭСПН . Проверено 16 июня 2020 г.
- ^ «Кличко защищает титул против «Быстрого Эдди» » (на немецком языке) . Проверено 23 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ «Плотная танцевальная вечеринка с четко распределенными ролями» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 23 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ «Энтони Джошуа нокаутировал Владимира Кличко в 11-м раунде на Уэмбли» . Проверено 23 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ «Большинство противников побеждено за титул чемпиона мира в супертяжелом весе» . Проверено 28 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «Самый продолжительный титул чемпиона мира в супертяжелом весе в объединенном весе » Проверено 28 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «Большинство противников побеждено за титул чемпиона мира в супертяжелом весе - эпоха международной экспансии (1949 – настоящее время)» . Проверено 28 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «Наибольшее количество побед в боях за титул чемпиона мира в супертяжелом весе - эпоха международной экспансии (1949 – настоящее время)» . Проверено 28 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «ВЛАДИМИР КЛИЧКО И БОЙ ЗА ТИТУЛ МИРА, ТИТУЛ-ЦАРСТВУЮЩИЕ КОРОЛИ» . Кольцо. 25 апреля 2017 года . Проверено 13 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Рейтинги BoxRec: Европа, фунты за фунты, активные и неактивные» . Боксрек . Проверено 14 августа 2022 г.
- ^ «Бой: Кличко против Шахида» . Проверено 11 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Бой: Кличко против Вуйчича» . Проверено 11 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Бой: Кличко против Кастильо» . Проверено 11 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Бой: Кличко против Питера» . Проверено 11 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Бой: Кличко против Брока» . Проверено 11 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Бой: Кличко против Ибрагимова» . Проверено 11 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Бой: Кличко против Чагаева» . Проверено 11 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Бой: Бой: Кличко против Ваха» . Проверено 11 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «О теме: Кличко vs Планета» . Проверено 11 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Бой: Кличко против Поветкина» . Проверено 11 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Бой: Кличко против Пулева» . Получено 11 декабря.
- ^ «Бой: Кличко против Дженнингса» . Проверено 11 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Пришло время оценить выдающуюся карьеру Владимира Кличко» . ЭСПН . 15 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Венецианская биеннале: «Олимпийские игры мира искусства» . Edition.cnn.com (9 июня 2009 г.). Проверено 19 июня 2011 г.
- ^ «Управление изменениями и инновациями CAS | Школа руководителей HSG» . www.es.unisg.ch . Проверено 7 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ Эйзингер, Эми (5 января 2010 г.). «Хайден Панеттьери уютно устроилась с чемпионом по боксу Владимиром Кличко в Майами» . Нью-Йорк: nydailynews.comcom.
- ^ «Хайден Панеттьери рассказала о красотке Владимире Кличко» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . 2 апреля 2013 года . Проверено 2 апреля 2013 г.
- ^ Мессер, Лесли (9 октября 2013 г.). «Хайден Панеттьери помолвлена!» . Новости АВС . Проверено 9 октября 2013 г.
- ^ «У Хайден Панеттьери и Владимира Кличко родилась девочка» . Yahoo! . 13 декабря 2014 г.
- ^ «Хайден Панеттьери и Владимир Кличко расстались спустя 9 лет!» . Архивировано из оригинала 17 августа 2018 года . Проверено 4 августа 2018 г.
- ^ Шентон, Зои (4 августа 2018 г.). «Хайден Панеттьери и Владимир Кличко «расстались», как она видела с загадочным мужчиной» . зеркало . Проверено 4 августа 2018 г.
- ↑ Панеттьери о Евромайдане: Я очень уважаю людей, которые отстаивают то, во что верят , Интерфакс-Украина (6 декабря 2013 г.)
- ^ Почему протесты в Украине имеют значение? , BBC News (3 декабря 2013 г.)
- ↑ Активисты разбивают армейские палатки на площади Независимости в Киеве , Интерфакс-Украина (3 декабря 2013 г.)
- ^ (in Russian) Владимир Кличко и Хайден Панеттьери на Евромайдане: видео Wladimir Klitschko and Hayden Panettiere on Euromaidan: video , LIGA.net, 7 December 2013.
- ^ Гэри Морли и Мэтт Виджил (8 апреля 2015 г.). «Владимир Кличко: Железный занавес не является преградой для «Доктора Стилхаммера» » . CNN . Проверено 4 января 2017 г.
- ^ "Пять фактов о боксере Владимире Кличко" . Би-би-си Спорт. 3 августа 2017 г. Проверено 10 августа 2017 г.
- ^ «Кличко против Фьюри: действительно ли Владимир убил бокс в тяжелом весе?» . Би-би-си Спорт . Би-би-си . 23 ноября 2015 г. Проверено 10 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Ruslan Chikov (29 March 2012). W. Klitschko's Gold Medal Grabs $1 Million at Charity Event , Boxingscene.com. Retrieved 8 July 2012.
- ^ Боксер Кличко выставил на аукцион золотую медаль за 1 миллион долларов . Проверено 28 декабря 2014 г.
- ^ (в Russian) The younger Klitschko joined Kyiv's defense , Russian Pravda (2 February 2022)
- ^ «Братья Кличко возьмутся за оружие и будут сражаться за Украину» . Рейтер . 24 февраля 2022 г. Проверено 24 февраля 2022 г.
- ^ «Боксеры ХОФ братья Кличко будут сражаться за Украину» . ЭСПН. 24 февраля 2022 г. Проверено 25 февраля 2022 г.
- ^ "Россия разрушает жизнь миллионов людей": интервью с Виталием и Владимиром Кличко (in Ukrainian). Radio Svoboda . 22 февраля 2023 года . Retrieved 12 апреля 2023 .
- ^ «Виталий Кличко: тяжеловес в списке Путина» . Таймс . 22 февраля 2023 г. Проверено 12 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ "Братья Кличко собирают в Германии 100 миллионов евро для пожертвований Украине" . Редакционная сеть Германия . 10 марта 2022 г. Проверено 26 августа 2023 г.
- ^ «Профиль Владимира Кличко - Бокс в Ист-Сайде» . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Боксеры-тяжеловесы Виталий и Владимир Кличко о ударах, деньгах и поединке в Лас-Вегасе» (на немецком языке). Архивировано из оригинала 31 октября 2020 года . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Виталий Кличко против Криса Берда собрал 9,79 миллиона зрителей, побив рекорд радиостанции Владимира» (на немецком языке). 3 апреля 2000 г. Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко – новый чемпион мира» (на немецком языке). 15 октября 2000 г. Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Бокс возвращается в ZDF спустя девять лет» (на немецком языке). Архивировано из оригинала 27 февраля 2020 года . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Почти восемь миллионов зрителей увидели победу Кличко нокаутом в прямом эфире на ZDF» . Проверено 2 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «Бокс в прямом эфире во втором пресс-релизе ZDF» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 22 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ "ТВ-популярность видов спорта. Итоги-2011" (in Russian) . Retrieved 19 November 2022 .
- ^ «До 8,90 миллиона зрителей увидели победу Владимира Кличко в первом. В среднем 6,44 миллиона зрителей (доля рынка 30,7%) следили за его боем против Элисео Кастильо» . 24 апреля 2005 года . Проверено 17 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ «Свет во тьме: Рейтинги бокса» . Спортивно-деловой журнал . 10 октября 2005 г. Проверено 15 мая 2022 г.
- ^ «Более 10 миллионов зрителей увидели бой Кличко» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Маска становится королем квот» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Почти 13 миллионов зрителей: бой Кличко собрал больше зрителей, чем возвращение Акселя Шульца» (на немецком языке). 11 марта 2007 года . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Более 11 миллионов зрителей увидели победу Кличко» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Около 12,33 миллиона зрителей увидели бой Виталия Кличко с Кевином Джонсоном» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ "Популярность спорта на ТВ. Итоги года" (in Russian) . Retrieved 14 October 2022 .
- ^ «Кличко в тот вечер боксировал с высокими рейтингами» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 17 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ Хармс, Карстен (13 июля 2008 г.). «Кличко не может произвести впечатление, несмотря на победу нокаутом» . Мир (на немецком языке) . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ "Вадим Бухкалов: "Зрители аплодировали Кличко минут сорок" " (in Russian) . Retrieved 15 March 2021 .
- ^ «Только бокс привлекает зрителей» . Гамбургер Абендблатт . 15 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 10 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ "Бой Кличко увидели около шести миллионов украинцев" . Korrespondent . 16 December 2008 . Retrieved 19 November 2022 .
- ^ "Бой Кличко увидели около 6 миллионов украинцев" . news.liga.net . 16 December 2008 . Retrieved 19 November 2022 .
- ^ «Бундеслига, бокс и зимние виды спорта приносят явную победу дня» (на немецком языке). 21 июня 2009 года . Проверено 7 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ «Топ-10 программ недели на телевизорах (июль 1998 г. – сентябрь 2018 г.): с 15 по 21 июня 2009 г.» . Проверено 23 июля 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б "Плакат боя Владимир Кличко - Эдди Чемберс" . klitschko-brothers.com . Retrieved 22 March 2020 .
- ^ «Как Кличко стали править немецким боем» . Независимый . 22 октября 2011 года . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Кличко-Чемберс показывает лучшие цифры для немецкого телевидения со времен Евро-2008» (на немецком языке). Архивировано из оригинала 1 марта 2020 года . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Кличко сносит Сэмюэля Питера: «Следующий, пожалуйста!» » (на немецком языке) . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Топ-10 программ недели на телевизорах (июль 1998 г. – сентябрь 2018 г.): с 6 по 12 сентября 2010 г.» . Проверено 23 июля 2023 г.
- ^ «Высшие рейтинги бокса» (на немецком языке). Архивировано из оригинала 11 сентября 2012 года . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Конец карьеры – RTL прощается с королем рейтингов Кличко» (на немецком языке). 3 августа 2017 г. Архивировано из оригинала 26 ноября 2020 г. . Проверено 7 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Бой Кличко-Хэй: 3,3 миллиона зрителей в Польше» (на польском языке) . Проверено 10 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ «3,5 миллиона зрителей Кличко — Хэй в Польше» (на польском языке). 4 июля 2011 г. Проверено 10 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ «Дуна ТВ побила рекорд матчем Кличко» (на венгерском языке) . Проверено 19 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ «Матч Кличко и Хэя принес пик телерейтингов» (на венгерском языке). 4 июля 2011 года . Проверено 12 мая 2023 г.
- ^ «Полмиллиона зрителей на «боксёрском поединке века» » (на голландском языке). 3 июля 2011 года . Проверено 31 мая 2023 г.
- ^ «Тони Томпсон хочет провести реванш с Владимиром Кличко, но не впечатлен боем с Мормеком» . 5 марта 2012 года . Проверено 23 марта 2021 г.
- ^ "Бой Кличко с Мормеком посмотрело более 9 миллионов украинцев" (in Ukrainian). 10 марта 2012 . Retrieved 21 января 2023 .
- ^ «Победа Кличко обеспечила ему долю рынка в 41,5%» (на немецком языке). 8 июля 2012 г. Архивировано из оригинала 1 марта 2020 г. . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «11,77 миллиона смотрят Кличко и «Рэтсель Вах» » (на немецком языке). 11 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 22 января 2023 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко спрашивает: может ли прийти еще один большой человек?» (на венгерском языке). 12 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 12 мая 2023 г.
- ^ «Кличко добился большого успеха с точки зрения зрительской аудитории» (на венгерском языке) . Проверено 12 мая 2023 г.
- ^ «Полмиллиона венгерских телезрителей смотрели матч Кличко» (на венгерском языке). 12 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 12 мая 2023 г.
- ^ «Кличко теряет более трех миллионов зрителей» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 7 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Кличко против Поветкина: телеаудитория Украины, России и Германии» (на русском языке). Архивировано из оригинала 1 марта 2020 года . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Теленомера: Кличко легко побеждает Маркуса Ланца» (на немецком языке). 6 октября 2013 года . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «290 000 за бокс на RTL, 556 000 за «Wetten, dass..?» на ORF» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 9 июля 2023 г.
- ^ «Талант обыграл CT 1 в воскресенье, но Докторам с начала этого оказалось недостаточно. Нова победила и в субботу» (на чешском языке) . Проверено 10 июля 2021 г.
- ^ «Кличко-Леапай имеет 9 миллионов зрителей на немецкой сети RTL» . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Kampf der Superlative: Кличко против Джошуа» (на немецком языке) . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ "Поединок Кличко-Фьюри на "Интере" посмотрели почти 10 млн. человек" (in Russian) . Retrieved 28 October 2020 .
- ^ «Джошуа-Кличко собрал на Showtime 659 000 зрителей, в Германии число зрителей превысило 10 миллионов» . Май 2017 года . Проверено 16 мая 2020 г.
- ^ "Бой Кличко на "Интере" стал самым рейтинговым спортивным событием года. Что будет дальше?" . Телеканал "Интер" (in Russian). Inter . 3 May 2017. Archived from the original on 24 April 2018 . Retrieved 10 January 2020 .
- ^ «14 октября 2000 г. Владимир Кличко против Криса Берда I» . 5 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 1 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «Кличко рад, что Чемберс сразится на веб-PPV» . 25 февраля 2010 года . Проверено 11 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ «Кличко-Чемберс: Virgin по требованию проводит PPV» . 18 марта 2010 г. Проверено 2 марта 2021 г.
- ^ Кличко против Хэя РЕПРОДУКЦИЯ БОКСА ПРОМО-ФОТО Плакат 40 x 30 см
- ^ «Сводка еженедельных просмотров (продажи на мероприятия Sky Box Office с 13 по 19 июня 2011 г.)» . Совет по исследованию аудитории вещательных компаний . Проверено 19 августа 2023 г.
- ^ «Сводка еженедельных просмотров (покупки на мероприятия Sky Box Office с 20 по 26 июня 2011 г.)» . Совет по исследованию аудитории вещательных компаний . Проверено 8 сентября 2019 г.
- ^ «Сводка еженедельных просмотров (покупки на мероприятия Sky Box Office с 27 июня по 3 июля 2011 г.)» . Совет по исследованию аудитории вещательных компаний . Проверено 8 сентября 2019 г.
- ^ «Владимир Кличко против Алекса Леапая: превью титульного боя» . 24 апреля 2014 года . Проверено 30 ноября 2020 г. .
- ^ «Бокс: Леапай не может сравниться с Кличко; Браун выигрывает титул Содружества» . 27 апреля 2014 года . Проверено 30 ноября 2020 г. .
- ^ «Кличко против Леапая» . Архивировано из оригинала 28 апреля 2014 года . Проверено 30 ноября 2020 г. .
- ^ «Кличко против Леапая: результаты прямых трансляций и обзор раундов» . 26 апреля 2014 года . Проверено 30 ноября 2020 г. .
- ^ «Паркер готовится к бою с Кличко в андеркарте» . Проверено 30 ноября 2020 г. .
- ^ «Джозеф Паркер об андеркарте боя Кличко – Леапай» . Проверено 30 ноября 2020 г. .
- ^ «Сводка еженедельных просмотров (покупки на мероприятия Sky Box Office с 23 по 29 ноября 2015 г.)» . Совет по исследованию аудитории вещательных компаний . Проверено 4 мая 2018 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Джей, Фил (5 января 2020 г.). «Джошуа против Кличко, рекорд Великобритании по PPV» . Мировые новости бокса . Проверено 10 января 2020 г. .
- ^ «Вот сколько Энтони Джошуа заработал за свое потрясающее выступление на Уэмбли» . Джо . 30 апреля 2017 года . Проверено 14 сентября 2018 г.
- ^ «Мероприятия Sky Box Office: ставки покупок с 24 по 30 апреля 2017 г.»
- ^ Маккенна, Крис (31 марта 2018 г.). «Энтони Джошуа получит потрясающий приз за бой с Джозефом Паркером» . Ежедневный экспресс .
Внешние ссылки
[ редактировать ]- Официальный сайт

- Владимир Кличко в BoxRec (требуется регистрация)
- Владимир Кличко на Олимпии
- Профиль CBZ
- ESPN.com
- Владимир Кличко на IMDb
- Реальные истории: Виталий и Владимир Кличко в Грантленде
| Спортивные позиции |
|---|
- 1976 года рождения
- Боксеры на летних Олимпийских играх 1996 года.
- Чемпионы Европейского боксерского союза.
- Чемпионы Международной федерации бокса
- Призывники Международного зала боксерской славы
- Чемпионы Международной боксерской организации
- братья Кличко
- Живые люди
- Медалисты летних Олимпийских игр 1996 года.
- Олимпийские боксеры Украины.
- Олимпийские чемпионы от Украины.
- Олимпийские медалисты по боксу
- Люди Евромайдана
- Проукраинский народ о вторжении России в Украину
- Sportspeople from Semey
- Боксеры супертяжелого веса
- Выпускники Киевского национального университета имени Тараса Шевченко
- Чемпионы журнала «Ринг»
- Украинские спортсмены-эмигранты в Германии
- Украинские спортсмены-эмигранты в США
- Украинские боксеры-мужчины.
- Украинский народ еврейского происхождения
- Украинцы русского происхождения
- Чемпионы Всемирной боксерской организации.
- Чемпионы мира по боксу в тяжелом весе
- Чемпионы Всемирной боксерской ассоциации
- Кавалеры Ордена Свободы (Украина).
- Золотые медалисты Всемирных военных игр от Украины
- Призеры Всемирных военных игр по боксу