Международное признание Абхазии и Южной Осетии
| Рус-георгическая война |
|---|
 |
| Основные темы |
| Связанные темы |
|
|
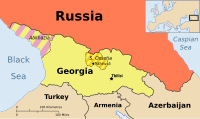
Абхазия и Южная Осетия являются сепаратистскими районами Грузии в Кавказе . [ 1 ] Большинство стран признают их частью Грузии, в то время как Россия, Венесуэла, Никарагуа, Науру и Сирия считают их независимыми. Первоначальное признание России независимости Абхазии и Южной Осетии произошло после после Русесооргианской войны в 2008 году. Правительство Грузии считает республики, занятые Россией, территории .
Абхазия и Южная Осетия были когда -то признаны до семи государств -членов ООН , пока Тувалу не отказался от признания обоих в 2014 году, [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] и Вануату уточнил статус их признания. Вануату подтвержден в 2019 году, он поддерживает грузинскую территориальную целостность, включая две спорные территории. [ 5 ] [ 6 ] Абхазия и Южная Осетия признают друг друга, а также имеют некоторое признание со стороны государств-членов.
История
[ редактировать ]Южная Осетия объявила независимость от Грузии во время войны в Южной Осетии в 1991–1992 годах 29 мая 1992 года, причем ее конституция относилась к «Республике Южной Осетии». [ 7 ] [ 8 ] [ 9 ] Абхазия объявила о своей независимости после своей войны с Грузией в 1992–1993 годах. [ 10 ] Его конституция была принята 26 ноября 1994 года. [ 11 ] [ 12 ]
В августе 2008 года война в Южной Осетии в 2008 году между Грузией с одной стороны и Южной Осетии, Абхазией и Россией и России, с другой стороны, с одной стороны и южной осетии, Абхазией и России и изгнанию грузинских военных с обеих территорий.
Признание России
[ редактировать ]Услышав вышеупомянутые апелляции как Абхазского, так и Южно -Осетианского руководства, 25 августа 2008 года Совет Федерации и штат Дюма принял ходатайства, призывающие президента Дмитрия Медведева признать независимость обоих штатов и установить дипломатические отношения . 26 августа 2008 года президент Медведев подписал указы, признавая независимость Абхазии и Южной Осетии как суверенные государства. [ 13 ]
В Совете Безопасности ООН Соединенные Штаты в значительной степени критиковали Российскую поддержку правительств сепаратистов, обвиняя правительство в нарушении территориальной целостности Грузии . В ответ Виталия Чуркин , постоянный представитель России в ООН, напал на утверждение США на моральный высокий язык, вспомнив его вторжение в Ирак в 2003 году. [ 14 ] Другие обвинили Соединенные Штаты в лицемерии, сославшись на его поддержку нарушения сербской территориальной целостности, когда они признали независимость Косово в 2008 году. [ 15 ]
Российское правительство также приветствовало признание Никарагуа двух штатов и призвало другие страны «признать реальность» и следовать примеру Никарагуа. Президент Даниэль Ортега объявил, что его правительство «признает независимость Южной Осетии и Абхазии и полностью поддерживает позицию правительства России». [ 16 ] Медведев также подписал закон федеральных законопроектов, ратифицирующих дружбу, сотрудничество и пакты об взаимной помощи между его правительством и Абхазией и Южной Осетии. Законы предусматривали обязательства каждого штата оказать помощь друг другу, если кто -либо из них подвергается нападению, совместную защиту границ Абхазии и Южной Осетии, а также сотрудничество по широкому кругу экономических, социальных и гуманитарных проблем. Государства также будут совместно противостоять организованию преступности, международного терроризма и незаконного оборота наркотиков, документы на этот счет были подписаны в течение 10 лет с возможностью автоматического продления сделки. [ 17 ]
Ответ Грузии
[ редактировать ]Президент Грузии Михайл Саакашвили считал движение России попыткой изменить границы Европы силой. Ниже приведены некоторые выдержки из его заявления: [ 18 ]
Это первая попытка на европейской территории ... Со времен режима Гитлера и Советского Союза Сталина, где крупное государство пытается в одностороннем порядке, с применением силы, чтобы полностью сокрушить соседнюю страну и открыто аннексирует свою территорию.
Это немыслие беззаконие и наглость ... Россия нанесла немыслимый ущерб своему месту в международном сообществе.
Вопрос о восстановлении территориальной целостности Грузии и защиты ее свободы-это не внутренняя грузинская проблема или вопрос Грузии и России. Сейчас это вопрос России и остальной части цивилизованного мира. Будущее Грузии, это не только будущее Грузии, это будущее всего цивилизованного мира ...
Заместитель министра иностранных дел Гига Бокерия сказал: «Это неуверенная аннексия этих территорий, которые являются частью Грузии». [ 19 ]
28 августа парламент Грузии принял резолюцию, объявляющую об Абхазии и Южной Осетии « территории, занятые Россией », и дал указание правительству аннулировать все предыдущие договоры о российском миротворческом языке. [ 20 ] На следующий день правительство объявило, что оно разорвало дипломатические связи с Россией, поскольку посольство Грузии в Москве и российское посольство в Тбилиси в результате закрылось . Грузия вспомнила своего посла из России и приказала всем российским дипломатам покинуть Грузию, заявив, что будут сохранены только консульские отношения. Российское министерство иностранных дел прокомментировало это решение, заявив, что от 600 000 до 1 миллиона грузин в России останутся на «милосердие судьбы». [ 21 ] [ 22 ]
Позже Грузия также разорвала дипломатические отношения с Никарагуа. [ 23 ] Грузия переехала на экономическую изоляцию регионов. Был издан запрет на экономическую деятельность в регионах без грузинского разрешения, и любой, кто пойман, нарушив этот запрет грузинскими властями, столкнулся с судебным преследованием. Грузинский военно -морской флот блокировал побережье Абхазии и захватил 23 грузовых корабля, пытаясь принести припасы в Абхазию, в частности, топливные принадлежности. Абхазия зависит от импорта топлива и в результате столкнулась с серьезной нехваткой. Россия начала развертывать лодки из своего собственного черного морского флота 21 сентября 2009 года, в ответ. [24] In August 2009, Russia and South Ossetia accused Georgia of shelling Ossetian villages and kidnapping four South Ossetian citizens. Russia threatened to use force unless the shelling stopped, and put its troops stationed in South Ossetia on high alert.[25]
In January 2010, Georgia adopted a strategy regarding the reintegration of Abkhazia and South Ossetia.[26] The strategy is called Involvement through Cooperation and it was presented to the international organisations as well as to Abkhazia and South Ossetia. The document says Georgia views peaceful methods as the only way for conflict solution and that there won't be a war with these regions. It envisions engagement of people of these two regions through education as well as social, economic and business projects, instead of isolation.[27][28]
It is officially illegal under Georgian law to enter South Ossetia or Abkhazia through Russia, without permission from Georgia; it is possible to travel through Georgian territory to Abkhazia, though as Georgia cannot assure the safety inside the disputed territories, going to either Abkhazia or South Ossetia is not recommended by the Georgian government.[29][30][31] It is not possible for foreigners to enter South Ossetia from Georgian controlled territory, as the South Ossetian de facto authorities do not facilitate nor allow this.[32]
Western response
[edit]The European Union, NATO,[33] the OSCE,[34] and the United States[35] immediately voiced displeasure with Russia's decision.
Developments since 2008
[edit]After the Russian recognition, Nicaragua, Venezuela, Nauru, Vanuatu and Tuvalu soon followed suit and recognized Abkhazia and South Ossetia as independent states. However, in 2013 and 2014, Vanuatu and Tuvalu have scrapped their recognition. Russia has invested a significant money in diplomatic strategy to promote recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia and display its soft power.[36] However, Russia seems to have stopped investing in the recognition project after 2014. One of the possible reasons might be worsening of the financial situation in Russia following the Russo-Ukrainian War and international sanctions on Russia. Abkhazia has started a new campaign to strengthen the relations with the foreign countries and present itself as an independent actor. Abkhaz officials have visited a number of countries, including China, Italy, Turkey and Israel. They have also met with the officials from South Africa, Jordan and El Salvador, and sent diplomatic notes to other countries, such as Egypt, France, Guatemala and Sri Lanka. This campaign reached its peak in 2017, but subsequently decreased and largely halted with the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.[37] Syria remains the only country which has recognized Abkhazia and South Ossetia since 2009.[38]
States formally recognising Abkhazia or South Ossetia as independent
[edit]UN members
[edit]| State | Date of recognition | Diplomatic relations established | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26 August 2008[39][40][41] | 9 September 2008[42] | Ambassadors Semyon Grigoriyev and Elbrus Kargiyev presented their credentials to Abkhaz President Sergey Bagapsh and South Ossetian President Eduard Kokoity on 16 December 2008.[43] An Embassy of Russia to South Ossetia was opened in February 2009.[44] An Embassy of South Ossetia to the Russian Federation was opened in 2009. An Embassy of Russia to Abkhazia was opened on 1 May 2009.[45] An Embassy of Abkhazia to Russia was opened on 18 May 2010.[46] | |
| 2 | 5 September 2008[47][48][49] | 10 September 2009 (Abkhazia)[50] 14 April 2010 (South Ossetia)[citation needed] |
The Ambassador of Nicaragua to Abkhazia resides in Moscow.[51] The South Ossetian Embassy in Managua was opened on 30 August 2011.[52] In 2022, an Abkhaz Embassy in Nicaragua was established. Until then, Abkhazia was represented in Nicaragua via its Ambassador in Caracas.[53] | |
| 3 | 10 September 2009[54] | 9 July 2010 (South Ossetia) 12 July 2010 (Abkhazia)[55][56] |
President Hugo Chávez met the leaders of both states in Caracas and said "I'm sure we, together with Abkhazia and South Ossetia, will be able to build strong relations with Latin American nations such as Paraguay, Uruguay, Cuba, Bolivia, Ecuador, Brazil and Argentina."[57] Ambassador of Venezuela Hugo José García Hernández presented his credentials to Abkhaz President Sergey Bagapsh on 12 July 2010."[58] An Embassy of Abkhazia to Venezuela was opened on 12 July 2010.[59] | |
| 4 | 15 December 2009 (Abkhazia) 16 December 2009 (South Ossetia)[60] |
15 December 2009 (Abkhazia) 16 December 2009 (South Ossetia)[61] |
Representatives of Nauru were present as observers for the presidential elections in Abkhazia on 26 August 2011.[62] In 2018, the president of South Ossetia appointed a representative for Nauru.[63] | |
| 5 | 29 May 2018 | 22 July 2018[64] | In May 2018, the Syrian government recognized the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia.[65][66] In October 2020, the Abkhazia government inaugurated Embassy chancery to the Damascus, Syria.[citation needed] |
Partially recognized states
[edit]| State | Date of recognition | Diplomatic relations established | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19 September 2005 or before[note 1] | 26 September 2007[67] | Abkhazia and South Ossetia mutually recognise each other.[68] Embassy of South Ossetia to Abkhazia was opened on 15 April 2008.[citation needed] Ambassador of Abkhazia Nodar Pliev presented his credentials to South Ossetian President Eduard Kokoity on 10 December 2010.[69] | |
| 2 | 22 January 1993 or before (Abkhazia)[note 1] 12 October 1994 or before (South Ossetia)[note 1] |
— | Transnistria, Abkhazia and South Ossetia mutually recognise each other.[68] Representative offices of Transnistria in Abkhazia and South Ossetia have been opened.[70] Representative offices of Abkhazia and South Ossetia in Tiraspol have been opened. | |
| 3 | 30 September 2010 (South Ossetia)[71][72][73][74][75][76] | — | De facto recognition.
On 29 September 2010 the SADR Minister for African Issues Mohamed Yeslem Beyssat said referring to South Ossetia: “Western Sahara de facto recognizes the independence of South Ossetia. Now we have to formalise relations de jure, including the establishment of diplomatic relations".[72] The two states have had various formal and informal contacts.[77] In 2019, the Abkhaz Ambassador in Venezuela met with the Ambassador of the SADR in the same country.[78] |
Former partially recognized states
[edit]| Entity | Date of recognition | Diplomatic relations established | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 27 June 2014 (South Ossetia)
25 February 2022 (from Abkhazia) and 9 March 2022 (reciprocal recognition from DPR) |
12 May 2015 (South Ossetia)
9 March 2022 (Abkhazia) |
After receiving South Ossetian recognition in 2014, the Donetsk People's Republic reciprocated recognition and additionally recognized Abkhazia on 11 May 2015.[79]
On 22 February 2022, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs published a statement welcoming the recognition of independence of the Donetsk and Luhansk People's Republics by Russian President Vladimir Putin. On 25 February 2022 President Aslan Bzhania announced the recognition of the Donetsk People's Republic and Luhansk People's Republic. Russia annexed the DPR on 30 September 2022. The annexation is internationally unrecognised. | |
| 2 | 18 June 2014 (South Ossetia) 25 February 2022 (from Abkhazia) and 10 March 2022 (reciprocal recognition from LPR)[80] |
28 January 2015 (South Ossetia)[81] 10 March 2022 (Abkhazia)[82] |
After receiving diplomatic recognition from South Ossetia in 2014, the Luhansk People's Republic (LPR) reciprocated recognition on 28 January 2015.[83] In April 2015, South Ossetia opened the first foreign embassy in Luhansk.[84] On 22 February 2022, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs published a statement welcoming the recognition of independence of the Donetsk and Luhansk People's Republics by Russian President Vladimir Putin. On 25 February 2022 President Aslan Bzhania announced the recognition of the Donetsk People's Republic and Luhansk People's Republic. On 10 March 2022 the LPR recognized Abkhazia's independence.[85][86] Russia annexed the LPR on 30 September 2022. The annexation is internationally unrecognised. | |
| 3 | 17 November 2006[87] | — | Republic of Artsakh, Abkhazia and South Ossetia mutually recognise each other.[88]
On 12 February 2010 it was announced that it is expected to establish diplomatic relations with Abkhazia.[89] Artsakh had ceased to exist on 1 January 2024. |
States that recognised Abkhazia or South Ossetia as independent, but subsequently withdrew recognition
[edit]UN member states
[edit]| State | Date of recognition | Diplomatic relations established | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18 September 2011 (Abkhazia)[90] 19 September 2011 (South Ossetia)[citation needed] |
On 31 March 2014 Georgia and Tuvalu signed an agreement on establishing diplomatic and consular relations. The agreement was signed by Tuvalu's Minister of Environmental Protection, Foreign Affairs, Labour and Trade, and Georgian Foreign Minister Maya Panjikidze during the visit of Tuvalu's governmental delegation to Georgia. The agreement stipulates that both sides agreed to develop relations on the grounds of the principles of sovereign equality, friendly relations and cooperation, territorial integrity, non-violation of borders and non-interference in homeland affairs. It emphasises that Tuvalu recognises the territorial integrity of Georgia within its international recognised borders, including its regions – Abkhazia's autonomous republic and Tskhinvali region.[2][3][91] In April 2014, it was suggested that Russia was more embarrassed by Tuvalu's withdrawal of recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia, than by international sanctions for Crimea, since this "decision could spell the end of a years-long diplomatic strategy that has cost Russia millions."[92] | ||
| 2 | 23 May 2011 (Abkhazia)[93] | 23 May 2011 (Abkhazia)[94] |
On 23 May 2011 Vanuatu recognised Abkhazia's independence and established diplomatic relations, according to the Abkhazian Ministry of Foreign Affairs,[95] while Vanuatu initially remained silent on the issue.[96] Confusion arose about the actual status of the recognition after a change of Vanuatuan government in June 2011 when officials denied and others reconfirmed the recognition.[97] Russian newspaper Kommersant claimed to have laid their hands on a facsimile of a signed agreement between both countries.[93] However, the issue dragged on for months within Vanuatu's governing ranks,[98] according to some related to domestic power politics and personal feuds. In 2012 Vanuatu's UN envoy maintained the country does not recognize Abkhazia, while a senior official of Vanuatu's Ministry of Foreign Affairs confirmed this by saying "the country has definitely not recognized Abkhazia", adding "the government had expressed the intention to maintain dialogue with Abkhazia".[99] In corroboration of that, Vanuatu maintained throughout the years its support for Georgia's annually submitted United Nations resolution regarding the return of internally displaced persons to Abkhazia, generally seen as an expression of support for the territorial integrity of Georgia.[100] On 18 March 2013, Johnny Koanapo, Vanuatu Director-General of Foreign Affairs, stated that diplomatic relations had never been established with Abkhazia. He said that "There's been a confusion over what the government had intended to do which was just simply a letter stating that there might be an intention to establish relations with Abkhazia. But at this point in time, there's no action on that and there's no decision".[101][102] On 20 May 2013, the Georgian president Saakashvili said at an Asian summit Vanuatu "changed their mind" and does not recognize Abkhazia,[103] which Vanuatu's new Prime Minister Moana Carcasses Kalosil confirmed.[104] On 12 July 2013 Georgia and Vanuatu signed an agreement on establishing diplomatic and consular relations, which stated that "the Republic of Vanuatu recognises territorial integrity of Georgia within its internationally recognised borders, including its regions – the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia and the Tskhinvali Region/South Ossetia."[105] Abkhazia's Foreign Minister Viacheslav Chirikba responded by claiming that Vanuatu had not officially withdrawn its recognition of Abkhazia.[106] On 30 March 2015, Vanuatu Foreign Minister Sato Kilman met with Chirikba in Moscow, the two officials expressing their desire to strengthen bilateral relations.[107] The following day, Kilman declared in an interview with RIA Novosti that "nothing had changed" in respect to Vanuatu's 2011 recognition of Abkhazia, but that the Carcasses government had merely decided to pursue diplomatic relations with Georgia rather than Abkhazia, that he didn't consider diplomatic relations with Abkhazia and Georgia to be incompatible, and that he hoped diplomatic relations with Abkhazia would soon be formalised.[108] In June 2015, Kilman was sacked as Foreign Minister, partly as a result of this meeting, with Prime Minister Joe Natuman again clarifying the government's position that "Abkhazia is part of Georgia".[109][110] However, the following week Kilman replaced Natuman as Prime Minister.[111] On 14 March 2019 Vanuatu Foreign Minister Ralph Regenvanu met with his Georgian counterpart David Zalkaliani in Tbilisi.[112] While both sides committed to deepen bilateral ties, Regenvanu "confirmed Vanuatu's support of Georgia's sovereignty and territorial integrity", according to the Georgian Ministry of Foreign Affairs.[5] Zalkaliani commented "We are grateful that the Republic of Vanuatu is consistent in pursuing the non-recognition policy of the so-called independence of Georgia's occupied regions, in full compliance with fundamental norms and principles of international law". The following day Regenvanu visited the conflict line[113] and a Memorandum of Co-operation was signed between the two sides. While at the conflict line, Regenvanu said: "Vanuatu has always recognized the territorial integrity of Georgia. In 2011 we had a minister who expressed a different position. In my opinion, he was influenced by certain individuals and recognized the independence of South Ossetia and Abkhazia. His decision was not an official position of the state".[6] | |
States that do not recognise Abkhazia or South Ossetia as independent
[edit]UN member states
[edit]| State | Position |
|---|---|
| Neither the Islamic Republic nor the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan has recognized Abkhazia or South Ossetia. Nevertheless, a delegation of the Islamic Emirate visited Abkhazia in February 2023 and met with the foreign minister.[114] | |
| The Albanian Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a statement condemning Russia's decision to recognise Abkhazia and South Ossetia, calling the move "totally unacceptable" and "contrary to UN Security Council resolutions". The Ministry denied any parallels to its own recognition of Kosovo, claiming Kosovo to be a special case.[115] | |
| The Prime Minister of Antigua and Barbuda Baldwin Spencer held talks in May 2012 with Irakli Khintba, Deputy Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Abkhazia, regarding that country's desire to obtain official recognition from Antigua and Barbuda. Baldwin Spencer pledged to continue dialogue on the issue with Abkhazian officials.[116] In 2022, the Abkhaz foreign minister had a telephone conversation with Paul Chet Greene, the Minister of Foreign Affairs, International Trade and Immigration of Antigua and Barbuda.[117] | |
| In 2008, Argentinian Foreign Minister Jorge Taiana ruled out that Argentina would recognize Abkhazia's and South Ossetia's independence.[118] Nevertheless, the Abkhaz foreign minister Maxim Gvinjia said in 2010 that Abkhazia hoped to establish diplomatic relations with Argentina. Abkhazia even planned to open an embassy in Buenos Aires.[119] Even without recognition, South Ossetia has an unofficial representative in Argentina.[120] | |
| In 2008, President Serzh Sargsyan (in office 2008–2018) stated that Armenia will not formally recognise Abkhazia and South Ossetia as independent states any time soon but reiterated his support for their residents’ right to self-determination. He also said that Armenia will not recognise them for the same reason that it did not recognise Kosovo's independence and that Armenia can not recognise another entity in the same situation as long as it has not recognised the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic.[121] Tigran Balayan, Head of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs Press Office said, "Armenia has always favoured and continues to believe that any attempt for military solution to conflicts is futile. Such conflicts should be resolved on the basis of free expression of the will of the people".[122] In 2016, Sargsyan met with then Vice-Foreign Minister of Abkhazia Kan Tania.[123]
In 2023, President Nikol Pashinyan stated that Armenia fully respects and acknowledges Georgia's territorial integrity and considers Abkhazia and South Ossetia as Georgian territories.[124] For the first time, in 2024, Armenia voted in favor of the Georgia resolution at the United Nations which would United Nations General Assembly adopted a resolution to reiterate the right of return of all displaced persons and refugees to Georgia's Abkhazia and Tskhinvali Region/South Ossetia and support Georgia's territorial integrity.[125] | |
| Foreign Minister Stephen Smith said that "the declaration overnight by Russian President Medvedev I don't believe is a helpful contribution. Indeed some may regard that as provocative. I don't think it helps circumstances in Georgia and I don't think it helps relationships generally between Russia and the rest of the world. Australia respects the territorial integrity of Georgia and our ongoing position is that we believe that Russia should abide by the ceasefire effected through the European Union and President Sarkozy and return its forces to the positions they occupied on August 6 and 7".[126][127] | |
| Foreign Minister Ursula Plassnik said that "this step goes against all the principles of Georgian sovereignty, independence and territorial integrity, which Russia has repeatedly accepted in the UN Security Council. The Georgian conflict must be solved through dialogue and international mediation, not through unilateral measures".[128] | |
| On 9 December 1994, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Azerbaijan announced that the unilateral decision of sovereignty by the Abkhazian Supreme Soviet was "a flagrant violation" and that "it is in contrast with the peace negotiations and creates new serious threats in the region".[129]
On 27 August 2008, Azerbaijani Foreign Ministry spokesman Khazar Ibrahim stated, "Azerbaijan's position remains unchanged. We recognise Georgia's territorial integrity".[130] | |
| On 28 August 2008, Vasily Dolgolyov, the Belarusian Ambassador to Russia, said that Belarus would in the next day or two recognise the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. President Alexander Lukashenko had also expressed support for Russia, saying "Under the circumstances Russia had no other moral choice but to support appeals of South Ossetian and Abkhazian peoples on the recognition of their right for self-determination in line with fundamental international documents."[131][132] Lukashenko then suggested considering this issue at the CSTO Collective Security Council Summit on 5 September 2008. However, Lukashenko later reaffirmed Belarus' intentions to recognise the breakaway republics, stating that the issue would be addressed after the parliamentary election on 28 September 2008.[133] On 25 September, President of Abkhazia Sergei Bagapsh and President of South Ossetia Eduard Kokoity officially requested that Lukashenko recognise the independence of their republics.[134] In September 2008 it was announced that the Belarusian parliament would debate on the recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia "soon".[135] However, Belarus decided not to recognise the two regions as independent states.
According to Peter Rutland, the EU has rewarded the Belarusian President Lukashenko for not recognising the republics by suspending the travel ban for top Belarusian officials that had been imposed in 2004.[136] Karel Schwarzenberg has stated publicly, that if Belarus recognises Abkhazia and South Ossetia, it can forget about the Eastern Partnership. "If they would recognize South Ossetia and Abkhazia it would create a very, very difficult situation for Belarus," Schwarzenberg has said.[137] Sweden, co-author of the Eastern Partnership program, rejected Lavrov's position as "completely unacceptable". The EU's position on Georgia is not 'blackmail' but "is about upholding the principles of the EU and international law, which Russia should also be respecting", stated Swedish foreign minister Carl Bildt[138] According to Eurasianet.org, which cites Russian media reports, Belarus is under Kremlin pressure to recognise South Ossetia and Abkhazia. There have been suppositions Russia has offered Belarus a $500 million credit on condition that Belarus recognises the two regions as independent.[139] In June 2009, President Alexander Lukashenko of Belarus said Moscow had made recognition of South Ossetia and Abkhazia a condition for Belarus to receive the last $500 million of a $2 billion loan, but added that Belarus’ position was not for sale. Russian officials have denied any such link.[140][141] The dispute over the loan led to the June 2009 Milk War between Belarus and Russia. The government of Belarus has informed its citizens to abide by Georgian laws when travelling to the regions. The Foreign Ministry of Belarus stated that Belarusians should only use entrance points on the Georgian side.[citation needed] Belarusian lawmakers visited Abkhazia and South Ossetia in late 2009 to study the situation and decide to postpone decision to spring 2010.[142] South Ossetia asked for a symmetrical approach between them and Abkhazia.[143] In 2021, an OSCE expert estimated that Belarus might be one of the next countries to recognize Abkhazia.[144] In November 2021, South Ossetian president Anatoly Bibilov said that he expects a diplomatic recognition from Belarus soon.[145][146] In 2022, Alexander Lukashenko visited Abkhazia for the first time and met with the Abkhaz president Bzhania and proclaimed "We want to build not just a bridge of friendship, but very serious relations." However, Belarus still did not recognize Abkhazia's independence.[147] | |
| Belgian foreign minister Karel De Gucht called the recognition of South Ossetia and Abkhazia unacceptable and a violation of the territorial integrity of Georgia. He added that Russia has created a dangerous precedent that threatens the stability of Europe. Nevertheless, South Ossetia named a representative for the Benelux countries.[148] | |
| In 2008, Foreign Ministry spokesperson Dimitar Tsanchev said, "The decision of Russian authorities to recognise the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia is causing serious worry. Bulgaria once again re-iterates its unconditional support for the independence, sovereignty and internationally recognised borders".[149] Despite this official stance, Bulgarian trade with Abkhazia surged in the end of the 2010s.[150] In 2018, a Bulgarian business delegation had visited Abkhazia and met with Abkhaz prime minister Gennadi Gagulia.[151] Abkhazia has an unofficial representative in Bulgaria.[152] | |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina has not officially recognized the independence of Abkhazia or South Ossetia. In June 2017, Milorad Dodik, the President of the Republika Srpska, has met with the then newly elected South Ossetian President Anatoliy Bibilov. Dodik expressed his readiness for cooperation with South Ossetia. According to the South Ossetian press service, the two agreed tentatively that Dodik would visit Tskhinvali on 20 September 2017.[153] In January 2018, the South Ossetian president Bibilov attended the Republika Srpska's "Statehood Day" and representatives of South Ossetia and Republika Srpska signed a memorandum of cooperation in Banja Luka.[154] Additionally, Bibilov opened a representation office in Banja Luka.[155]
Georgia sent a protest note to Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Bosnian Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a statement, saying that Bosnia and Herzegovina has "good and friendly relations with Georgia based on mutual respect of territorial integrity and sovereignty".[156] The ministry also noted that it was unaware of the visit of Bibilov. However, President of President of Republika Srpska Milorad Dodik said that Bibilov was visiting "the Serb entity, not the Bosnian state". He also stated that "Georgia does not have a friendly attitude towards the RS [Republika Srpska], we know that, and neither do we have one towards it".[157] | |
| Bolivia has not officially recognized the independence of Abkhazia or South Ossetia. In April 2009, the Abkhaz foreign ministry announced that it expects a recognition of Bolivia soon. Then-foreign minister Viacheslav Chirikba later said that his announcement was a mistake and the recognition never materialized.[158] In 2018, a member of the Bolivian embassy in Venezuela attended a celebration at the Abkhaz embassy in Caracas.[159] In 2021, the Abkhaz Ambassador in Venezuela met with the Bolivian Ambassador in the same country. During the meeting, both discussed the establishment of humanitarian, trade and economic ties between both countries.[160] | |
| Brazil has not recognised the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. Immediately after the war in 2008, Brazilian foreign minister Celso Amorim said that his country "defends in a very strong way the principle of territorial integrity" and does not plan to recognize any new state anytime soon.[161] Nevertheless, South Ossetia named a representative for Brazil who works on "connecting with economic and political circles in the country" in 2013.[162] | |
| In 2024, Burundi voted against the Georgia resolution at the United Nations which would United Nations General Assembly adopted a resolution to reiterate the right of return of all displaced persons and refugees to Georgia's Abkhazia and Tskhinvali Region/South Ossetia and support Georgia's territorial integrity.[125] | |
| Minister of Foreign Affairs, David Emerson, issued the statement on the situation in Georgia saying that "Canada is gravely concerned about Russia's recognition of the independence of South Ossetia and Abkhazia. This recognition violates Georgia's territorial integrity and sovereignty and is contrary to UN Security Council resolutions supported by Russia, as well as to the six-point peace plan brokered by President Nicolas Sarkozy on behalf of the EU".[163] | |
| On 27 August 2008 Foreign Ministry spokesman Qin Gang said that China is "concerned of the latest development in South Ossetia and Abkhazia". He also said "We have a knowledge of the complicated history and reality of the South Ossetia and Abkhazia issues. In accordance with China's consistent and principled stance on issues of this kind, we hope the relevant parties can resolve the issue through dialogue and consultation".[164] At the first SCO summit after the Russian recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia, Chinese President Hu Jintao played a pivotal role in resisting Russian lobbying for the recognition of independence for Abkhazia and South Ossetia.[165] Since 2015, Chinese firms have started commercial relations with Abkhazia.[166] In 2019, Abkhazia participated in the International Exhibition for Food, Beverages, Hotel/Restaurant equipment, Foodservice, Catering, Bakery and Retail Industries in Shanghai and a Chinese business delegation visited Abkhazia.[167] The delegation even met with the Abkhaz foreign minister Daur Kove.[168] In 2021, the Chinese Ambassador in Syria met with the Abkhaz Ambassador in Syria.[169] | |
| Former President Stjepan Mesić stated that he is worried over the Russian decision and said that "such a decision makes the complex situation in the region even more complex". He also said that "fait accompli policy could create an impression that the move was aimed at avoiding talks on the future status of South Ossetia and Abkhazia".[170] Neven Jurica, former Croatian Permanent Representative to the United Nations, called the Russian Federation's action regrettable and illegitimate.[171] | |
| At a UN Security Council meeting regarding the Georgia situation, Jorge Urbina, the Permanent Representative to the UN for Costa Rica, referred to the Russian actions as the dismemberment of a UN member state by force. "We cannot, and the international community should not, reward this approach, which is counter in all aspects to international law.... Such a settlement could not be based on 'might is right' and must include respect for the territorial integrity of Georgia, the rights of the peoples of Abkhazia and South Ossetia, and the integrity of international law and the principles of peaceful coexistence as enshrined in the United Nations Charter."[172] | |
| In 2024, Cuba voted against the Georgia resolution at the United Nations which would United Nations General Assembly adopted a resolution to reiterate the right of return of all displaced persons and refugees to Georgia's Abkhazia and Tskhinvali Region/South Ossetia and support Georgia's territorial integrity.[125] | |
| Foreign Minister Markos Kyprianou has said that relations of Russia and Cyprus are very close but on the other hand Cyprus supports "the respect and protection of the territorial integrity of states, and this is a principle which the Republic of Cyprus supports and supported in the case of Kosovo, so developments of the past few days in Georgia have worried us".[173] The government has issued a statement saying that "Cyprus expresses its deep concern over developments in Georgia. The Republic of Cyprus supports the respect of the rules of international law including the respect of the territorial integrity of states, of the UN Charter and of the principles of the Helsinki Final Act. Moreover, the Cyprus Government supports peaceful resolution of international disputes by political means through negotiations, avoiding unilateral actions that could aggravate the situation in this sensitive region".[174] | |
| The Czech Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a statement calling Russia's action "an attack on the independence, sovereignty and territorial integrity of Georgia".[175] | |
| Foreign Minister Per Stig Møller declared "unconditional support for Georgia's territorial integrity".[175] | |
| Dominican Republic MPs Francisco Matos and Ramon Fernandez travelled to Abkhazia in December 2010 and met with Abkhaz officials, including Sergey Shamba, Maxim Gvindzhia and Nugzar Ashuba. The Dominican Republic politicians voiced their support for the establishment of friendly ties with Abkhazia, and invited their Abkhazian counterparts to visit their country to establish inter-parliamentary ties.[176] Dominican Republic Deputy Prime Minister José Miguel Abreu visited Abkhazia in May 2011 and met with senior Abkhaz government officials. Sergey Bagapsh stated in Moscow that recognition from a Latin American nation could be expected in May.[177] Philip H. Gordon, the American Assistant Secretary of State for European and Eurasian Affairs, then warned the Dominican Republic against recognising the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia.[178] The United States government invited President Leonel Fernández to New York City for a conference and sent a private plane for that purpose. After his visit, the Dominican government did not communicate anymore with the Abkhaz government.[158] | |
| Ecuador's President Rafael Correa promised to consider recognition if Abkhazia and South Ossetia requested it. Leaders from Abkhazia and South Ossetia responded saying they would send official requests for recognition.[citation needed] Abkhazia submitted such a request in December 2009.[179] However, according to one confidential US diplomatic cable released by WikiLeaks, possibility of Ecuador's recognition of Abkhazia or South Ossetia "was played up" in the press and Correa made no such commitments to Russia. To this day, Ecuador has not recognized Abkhazia or South Ossetia.[180] | |
| Foreign Minister Urmas Paet stated "Russia's move is a deliberate breach of international law and the principles of stability in Europe. Estonia, like all European Union and NATO member states, adheres firmly to the principles of Georgia's territorial integrity".[181] | |
| Eritrea has not recognized Abkhazia and South Ossetia. Nevertheless, there were official meetings between Eritrean and Abkhazian and South Ossetian officials. On 10 June 2014, Abkhaz Foreign Minister Viacheslav Chirikba held a meeting with the delegation of the State of Eritrea consisting of the Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary of the State of Eritrea in the Russian Federation Teklay Minassie Asgedom and Head of the Department of Asia and the Pacific of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the State of Eritrea Kalekristos Zariseney Gebreyezus in the MFA of Abkhazia.[182] On 19 April 2018, South Ossetian Foreign Minister Dmitry Medoev met with the Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary of the State of Eritrea to the Russian Federation, Petros Tseggay Asged, in Yalta.[183] | |
| Finnish Foreign Minister Alexander Stubb said that "the recognition of independence for South Ossetia and Abkhazia violates fundamental OSCE principles. As all OSCE participating States, Russia is committed to respecting the sovereignty and territorial integrity of others. Russia should follow OSCE principles by respecting the territorial integrity and sovereignty of Georgia. Russia should immediately withdraw all troops from Georgia and implement the ceasefire agreement, including the modalities defined in the 16 August 2008 letter of French President Nicolas Sarkozy. The international community cannot accept unilaterally established buffer zones".[184] | |
| The French Foreign Ministry spokesman said, "We consider this is a regrettable decision and I recall our attachment to the territorial integrity of Georgia".[185] French Foreign Minister Bernard Kouchner said that "in a certain way, yes, ethnic cleansing is taking place" in villages previously controlled by the Georgian side. "We cannot accept these violations of international law, of accords for security and cooperation in Europe, of United Nations resolutions, and the taking ... of a territory by the army of a neighbouring country."[186] | |
| Chancellor Angela Merkel said, "this contradicts the principle of territorial integrity, a principle based on the international law of nations and for this reason it is unacceptable".[187] | |
| Minister of Foreign Affairs Dora Bakoyannis stated that among the principles of Greek foreign policy is "respect for the independence and territorial integrity of states". Furthermore, she expressed dismay at the developments and stated that they subscribed to the French Presidency's statement condemning the decision to recognise the regions of South Ossetia and Abkhazia.[188] | |
| Haiti does not recognize the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. In 2022, the Haitian Ambassador in Venezuela met the Abkhaz Ambassador in that country and they exchanged views on a wide range of issues of interstate cooperation and discussed the prospects for establishing bilateral cooperation.[189] | |
| The Hungarian Foreign Ministry issued a statement, regretting the decision of the Russian government and stating that "these decisions do not serve the stability of the Caucasus region and do not advance negotiations over a settlement of the very conflict which has produced severe humanitarian and material consequences".[190] | |
| Sturla Böðvarsson, Speaker of Althing, condemned Russia for recognising the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia in a joint declaration with speakers of Norway, Sweden, Finland, Denmark, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. Statement said that the recognition violates United Nations Security Council resolutions and contradicts principles of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe. Speakers also called on Russia to reverse its decision.[191] | |
| Marty Natalegawa, Indonesian Permanent Representative to the United Nations, said that he had been watching the situation apprehensively and that the developments were of deep concern and did not speak well for the Security Council. He said that his country had spoken in favour of diplomacy and the power of argument over force and that the Sarkozy six-point document had been a welcome development that should have ensured that the principle of the inviolability of a State's sovereignty and territorial integrity remained intact. He expressed disappointment that the Security Council had instead remained silent in the face of the violation. He also said that the principles of the peaceful resolution of differences and of territorial integrity were fundamental.[171] In 2018, the South Ossetian foreign minister met with a special representative of the Government of Indonesia, Nicolas Messet, in Nauru.[192] | |
| The Ambassador of Iran to Russia, Mahmoud Reza Sajjadi, said in February 2009 that his nation will not recognise Abkhazia and South Ossetia's independence in the near future, "as it can cause war in many areas," but on the other hand he did not rule out eventual Iranian recognition of the independence of the two areas. Sajjadi defended Russia's measures in the 2008 South Ossetia war and its decision to recognise Abkhazia and South Ossetia as independent nations. Sajjadi also said he sympathised with the people of Abkhazia and South Ossetia and that Tehran will work with Moscow to develop the two areas' economy.[193] In July 2019, the South Ossetian Minister of Foreign Affairs Dmitry Medoyev said that his country is willing to expand its cooperation with Iran. There are "deep-rooted economic, scientific and cultural ties between Iran and South Ossetian", he added.[194] In December 2019, Sergey Shakaryants, an Armenian specialist on the South Caucasus, wrote that the Iranians "have convinced the leaders of South Ossetia that Iran may soon recognize their republic diplomatically".[195] | |
| Minister for Foreign Affairs, Micheál Martin stated in a statement that "This deeply regrettable decision is contrary to the principles of Georgia's sovereignty, independence and territorial integrity. Moreover, it can only complicate the urgent task of finding political solutions to the acute difficulties in the region and to the wider international tensions which have developed over the past weeks".[196] | |
| The Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs stated on 10 August 2008 that "Israel is following with great concern the developments in South Ossetia and Abkhazia and hopes the violence will end. Israel recognises the territorial integrity of Georgia and calls for a peaceful solution."[197] | |
| Foreign Minister Franco Frattini said "The move does not apply in an international legal framework. An ethnic-based balkanisation of the Caucasus is a serious danger for all".[198] Nevertheless, Italy has relatively close relations with Abkhazia. In 2016, an Abkhaz cultural institute and in 2017, an unofficial Abkhaz diplomatic mission opened in Rome.[199][200][201][202] Additionally, South Ossetia opened an unofficial mission in Rome in 2016. The Italian authorities do not recognize it.[203][204] | |
| Yasuaki Tanizaki, director general of the Japanese Foreign Ministry's European bureau, said "Our country is gravely concerned about the move. Our country hopes that Russia [...] will take responsible actions for the region's stability".[205] | |
| Jordan has not recognized the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. Nevertheless, a high-ranking delegation of the country visited Abkhazia in 2018. The members of the delegations included the vice-president of the Senate of Jordan and other prominent politicians.[206][207][208] Abkhazia has a representative in Jordan.[209] | |
| In 2008, Kazakhstan's President Nursultan Nazarbayev said he understood the measures taken by Russia and urged the international community against raising the prospect of a new Cold War,[210] while also saying he considers that "Russia's actions were directed to protect the residents of long-suffering regions. In response Russia could either ignore or prevent the bloodshed".[211] In October 2008, Foreign Minister Marat Tazhin said that "the principle of territorial integrity is key in international law" and that for this reason Kazakhstan did not recognise Abkhazia and South Ossetia or Kosovo.[212] In December 2008, Prime Minister Karim Masimov stated that "We have an official position. Kazakhstan did not recognise Kosovo and does not recognise Abkhazia and South Ossetia. We consider that borders are defined and Kazakhstan will not recognise any new states."[213] Kazakhstan also send humanitarian aid to the conflict zone and offered help with peace talks.[214][215] In 2019, South Ossetia began exporting goods to Kazakhstan.[216] In 2022, the Abkhaz and the South Ossetian government supported the CSTO intervention in the country during the 2022 Kazakh unrest.[217][218] | |
| At a Minsk press conference on 27 August 2008, Kyrgyzstan's Ambassador to Belarus said regarding South Ossetian and Abkhazian independence that "(a)ll legal aspects should be measured as the situation is unusual. It is unusual in view of the recognition of separate states in the CIS and Georgia's withdrawal from the CIS. These issues allow us to approach the topic with due consideration, allow us to study and listen to analysts, observers, counsellors of state. As the issue is being studied I cannot express an opinion because the issue is too fresh".[219] | |
| Foreign Minister Māris Riekstiņš condemned Russia's recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. Stating that such "a decision is contrary to the principles of Georgia's independence, sovereignty and territorial integrity, which are recognised by the United Nation's Charter, the Final Act of the Helsinki Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe and the UN Security Council resolutions".[220] In December 2009, President of Latvia Valdis Zatlers, said that Latvia will never recognise the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia.[221] | |
| The leader of Lebanon's parliamentary majority Saad Hariri statement states, "The recognition issue will be solved at the highest state level. But we will fine-tune contacts with South Ossetia and Abkhazia now. For example, delegations of our businessmen will leave for there soon; Lebanon feels what situation South Ossetia was stuck in; Lebanon is also a small state which comes under threats. On one side there is Israel, which has attacked us many times. On the other side there is Syria which threatens Lebanon from time to time; Russians were taking measures to protect their citizens and local residents in South Ossetia; Russia is one of the states which in no way wants to get involved in military conflicts; Moscow's negative attitude to the beginning of the war in Iraq and efforts made to prevent military scenario in Iran's situation are examples for this. Russia advocates peaceful resolution everywhere".[222][223] | |
| Lithuania's Prime Minister Gediminas Kirkilas said that Russia's decision to recognise Abkhazia and South Ossetia was a violation of the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Georgia.[224] | |
| A joint Ministry of State and Ministry of Foreign Affairs statement states "We noted with regret the decision taken by the Russian authorities to recognise the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia, a decision contrary to the basic principles of the UN Charter and the OSCE. It is contrary with the obligations which Russia took on several occasions at the time of Security Council resolution votes, in particular Resolution 1808".[225] Nevertheless, South Ossetia named a representative for the Benelux countries.[148] | |
| In 2024, Mali voted against the Georgia resolution at the United Nations which would United Nations General Assembly adopted a resolution to reiterate the right of return of all displaced persons and refugees to Georgia's Abkhazia and Tskhinvali Region/South Ossetia and support Georgia's territorial integrity.[125] | |
| The government of Mexico expressed concern for stability, peace and international security following the Russian recognition and urged all parties to achieve a peaceful solution and lasting peace in the Caucasus region through dialogue. It also called on those involved to respect the principles of the Charter of the United Nations and international law.[226] | |
| In 2011, the government of the Federated States of Micronesia established diplomatic relations with Georgia.[227] Nevertheless, the then-President of Micronesia, Peter M. Christian, met the South Ossetian foreign minister in 2018.[228][192] | |
| Faced with its own breakaway region, Transnistria, the government of Moldova released a statement saying it would not recognise the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia.[229]
Gagauzia, an autonomous region of Moldova, passed a resolution, recognising independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia, backing Russia's actions in the regions, and asking central Moldova's government to recognise these states.[230] | |
| Montenegro does not recognize the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. In 2016, Abkhazia participated in an international tourism fair called the International Tourism Exchange, Tourism Fair, Equipment for Hotels and Catering (METUBES 2016) in Budva. After Georgian protests, the Abkhaz exhibition pavillon was closed.[231][232][192] | |
| Dutch Foreign Minister Maxime Verhagen expressed on behalf of the cabinet his "great concern" about the Russian position and said that "for the Netherlands, the territorial integrity of Georgia within the internationally recognised borders, also earlier recognised by Russia, remains the basis for a solution to this crisis. The one-sided recognition of South Ossetia and Abkhazia by Russia does not bring this solution nearer".[233] Nevertheless, South Ossetia named a representative for the Benelux countries.[148] | |
| In 2024, North Korea voted against the Georgia resolution at the United Nations which would United Nations General Assembly adopted a resolution to reiterate the right of return of all displaced persons and refugees to Georgia's Abkhazia and Tskhinvali Region/South Ossetia and support Georgia's territorial integrity.[125] | |
| Minister of Foreign Affairs Jonas Gahr Støre said that "Norway emphasises the use of peaceful means in the efforts to settle conflicts in Europe, based on the UN's assumption of respect for territorial integrity. A recognition of the breakaway Georgian regions are in breach of these assumptions. And it is not a constructive contribution to a long range and peaceful solution to the conflict".[234] | |
| Oman has not recognized the independence of either Abkhazia or South Ossetia. Nevertheless, the Ambassador of Oman in Damascus met with the Abkhaz Ambassador in 2021.[235] | |
| Pakistan does not recognize the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. In January 2021, the President of the Association of Pakistanis in Russia met with Abkhaz foreign minister Daur Kove. They discussed the establishment of Abkhaz-Pakistani business relations.[236] In March 2021, the Ambassador of Pakistan in Syria met with the Abkhaz Ambassador in the same country.[237] | |
| Ricardo Alberto Arias, Panama's UN Ambassador stated his nation's continuing support for the territorial integrity of Georgia in a Security Council meeting on 28 August 2008.[172] | |
| Ollanta Humala, leader of the Peruvian Nationalist Party, said his party had submitted a proposal to the Peruvian Congress for recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. He cited Peru's recognition of Kosovo as a justification.[238] The issue was ultimately not discussed,[citation needed] with the territorial integrity of Georgia (with whom relations had not yet been established) being implicitly recognised by Peru instead, as the country has consistenly abstained to vote on the issue at the United Nations General Assembly[239] except for one case where a vote in favour was cast regarding cooperation with Georgia regarding the humanitarian situation in both regions.[240] | |
| Foreign Minister Radosław Sikorski called for respect for Georgia's territorial integrity.[241] The President of Poland Lech Kaczyński said that the Russian decision violates international law and is an attempt to sanction the consequences of an "unprecedented aggression" by Russia against an independent Georgian state. Kaczyński urged Russian President Dmitry Medvedev to "immediately withdraw all Russian troops from Georgia" and pledged his country's "unwavering support" for the Georgian people.[242] | |
| The Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a statement saying that "The respect for the sovereignty of the Georgia inside of its internationally recognised borders has been permanently underlined for United Nations, the European Union and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe".[243] | |
| The Foreign Ministry issued a statement saying that "This unilateral, regrettable and legally unfounded act can affect the situation in the area, as well as the perspectives of solving the region's conflicts. As an EU and NATO member, Romania will plead inside the international organisations it belongs to, as well as in bilateral relationships with the countries in the region for a solution that will respect the territorial integrity of Georgia".[244] | |
| In 2011, the San Marino authorities declared, that they are planning to establish political, cultural and scientific contacts with Abkhazia.[245] The same year, a delegation of the Abkhaz foreign ministry was the first time in San Marino.[246] In April 2012, the Secretary of State for Foreign and Political Affairs, Antonella Mularoni, said that the San Marino government will continue to respect Georgia's territorial boundaries and will not recognize Abkhazia.[247] In 2013, the governments of Abkhazia and South Ossetia asked San Marino for a recognition of their independence.[248] The same year, Abkhazia appointed a representative for San Marino.[249] Even though San Marino does not recognize the independence of South Ossetia, the South Ossetian foreign minister Dmitry Medoyev visited the country in 2017. He met the chairman of the Committee on Foreign Affairs of the Grand and General Council and a group of the then-governing party Democratic Socialist Left.[250] Despite the lack of diplomatic relations, South Ossetia regularly sends diplomatic notes to San Marino.[251] In 2021, South Ossetia appointed a representative for San Marino who resides in the small republic.[252] | |
| During a meeting with Prime Minister Vladimir Putin, the Secretary of the Saudi National Security Council, Bandar bin Sultan, told that King Abdullah and the whole leadership of the country had full understanding for the actions of the Russian side in South Ossetia.[253]
Saudi Arabia does not recognizes Abkhazia or South Ossetia. In May 2012, during the visit to Georgia, Abdullah bin Zamil Al-Drees, a head of the delegation of Majlis al-Shura of Saudi Arabia, said that the kingdom's position was based on its foreign policy in support of the territorial integrity of countries.[254] | |
| The Serbian Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a statement saying that they respected the "territorial integrity of internationally recognized states" but that the declaration of independence by the Republic of Kosovo and its subsequent international recognition has had a destabilising effect by setting a precedent for similar declarations by other regions.[255] On 3 September 2008, President Boris Tadić stated the position of Serbia as "Serbia is not going to recognise these so-called new countries."[256] In May 2012, the Serbian Parliament was to consider formal recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia.[257] | |
| The Foreign Ministry of Sierra Leone has never published any statement regarding the territorial integrity of Georgia or the recognition of Abkhazia or South Ossetia. In 2019, a representative of the Parliament of Sierra Leone met with a delegation of the Parliament of South Ossetia.[258] | |
| A statement issued by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs said that Slovakia "disapproves of these steps and confirms the main principles, based on the long-standing position of the Slovak Republic regarding Georgia and the solution of conflicts on its territory. These principles are: sovereignty and territorial integrity of Georgia within its internationally recognised borders and solution of the conflicts exclusively by peaceful means and talks in compliance with the international law". The statement also said that "the Slovak government, as one of few EU member states, can insist on the principle of the territorial integrity of Georgia, as it has done also in the case of Serbia and Kosovo".[259] | |
| Prime Minister Janez Janša said "We are united on the need to ensure peace, stability, territorial integrity in Georgia and the broader region and to give the region a European perspective" after a meeting with Czech and Latvian counterparts Mirek Topolánek and Ivars Godmanis.[260] | |
| Somalia's External Affairs and International Co-operation ministry said on 5 October 2008 in Mogadishu that Somalia recognises the territorial integrity of Georgia.[261] Somalia's Ambassador to Russia Mohammed Mahmud Handule on 1 October 2008 was reported as saying Somalia's Transitional Federal Government would recognise the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia.[262] This stance was rebuffed by Mohamed Jama Ali, the General Director of the External Affairs and International Co-operation ministry (Somali Ministry of Foreign Affairs) as "an irregular statement"," which does not represent our government's foreign policy".[261][263] | |
| In 2008, Dumisani Kumalo, the Permanent Representative of South Africa to the United Nations, said that his country "had repeatedly stressed the need for countries to resolve differences through negotiations. A resort to the use of force diminished the chance for a lasting solution to a situation and it increased the suffering of all the people involved".[172] Nevertheless, the South African Ambassador to Venezuela met the Abkhaz Ambassador in the same country in 2018.[264] | |
| Aligning itself with Russia, South Korea's President Lee Myung-bak signed a joint declaration with Russia which stated that the two countries shared "a common assessment of Georgia's invasion of South Ossetia." South Korea also coincided with Russia in expressing "concern over the recent situation in Georgia" and support for "using peaceful means and dialogue to settle the problem."[265] In 2018, a South Ossetian delegation – including foreign minister Dmitry Medoev – visited South Korea.[266] | |
| Foreign Minister Miguel Ángel Moratinos said that the government of Spain regrets the decision of Russia. He also said that this decision by Moscow is "unacceptable" and "not conducive to creating the conditions necessary for settlement of the conflict between Russia and Georgia". Moratinos reiterated the "need to fully respect the principles of international law, in particular the territorial integrity of states, in this case, of Georgia." In addition, he recalled that this is the stance that "Spain has always maintained", an allusion to the opposition of the Spanish government to recognition of the Kosovo independence.[267] | |
| On 28 August 2008, Sudan's envoy to the UN, Abdel-Haleem Abdel-Mahmood, stated that Sudan's recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia is contingent upon developments on the issue of Kosovo's declaration of independence in the International Court of Justice. As Sudan remains opposed to Kosovo's independence, their negative view about such declarations may change only if it is declared legal by the ICJ.[268] | |
| Swedish Minister of Foreign Affairs Carl Bildt condemned Russia's recognition, saying that "the Russian government leadership now has chosen this route means they have chosen a policy of confrontation, not only with the rest of Europe, but also with the international community in general".[269][270] Carl Bildt predicted that the recognition of the independence of South Ossetia and Abkhazia is likely to be followed by only a "miserable" lot of other countries, such as Belarus, Syria, Cuba and Venezuela. Bildt also said that "South Ossetian independence is a joke. We are talking about a smugglers' paradise of 60,000 people financed by the Russian security services. No one can seriously consider that as an independent state".[271] In December 2009, Carl Bildt said that "this idea of South Ossetia's independence is increasingly seen as bad joke in Moscow, which it obviously is."[272] | |
| The government of Switzerland called for a political solution to the conflict in Georgia in accord with international principles: Both Georgia's right to sovereignty and the democratic will of the people in South Ossetia and Abkhazia have to be respected. A government spokesman also stated "Switzerland regrets that a solution has not yet been found that meets the United Nations Charter, the Helsinki Accords and the Charter of Paris. The Swiss government has not yet discussed the issue of independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. It also did not mention the territorial integrity in the context of Georgia.[273][274][275] | |
| The Moscow Times reports that the President of Tajikistan, Emomalii Rahmon, expressed his support for Russia's recognition of South Ossetia and Abkhazia, stating, "Our countries are natural strategic partners... which envisions... support for each other's actions."[276] He also stated, that Russia and Georgia should solve their conflict through political and diplomatic means.[277] | |
| A Foreign Ministry statement on 26 August 2008 declared that "Turkey attaches importance to the independence, sovereignty and territorial integrity of Georgia and is highly concerned about the recent developments. Turkey is of the opinion that this conflict should be resolved through peaceful means".[278] On 26 May 2018, The Turkish National Defense Minister Nurettin Canikli stated that Turkey is supporting Georgia's territorial integrity. | |
| In 2008, Ukrainian Deputy Prime Minister Grigoriy Nemirya stated that Kyiv took an unchangeable and principal position to support Georgia's territorial integrity and sovereignty.[279] The Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a statement calling the recognition a "gross violation of norms and principles of the international law, bilateral and multilateral agreements, in particular the United Nations Charter and Helsinki Accords. Actual annexation of part of Georgian territory through creation and support of the puppet regimes certifies a reanimation of doctrine of 'right of force' in the Russian Federation for solving of international problems. Ukraine categorically reprobates an adventurous decision of Russia to recognise the self-declared independence and calls for international community to combine efforts in relation to absolute confirmation and observance of territorial integrity of Georgia and implementation of the undertaken international obligations of Russia". It also said that the Commonwealth of Independent States are bound to respect the territorial integrity of other CIS states, in this case Georgia.[280] The Chairman of the Verkhovna Rada Arseniy Yatsenyuk said "only the United Nations can rule on this question. This is factually a violation of international law". President Viktor Yushchenko stressed that Ukraine does not support the decision of Russia to recognise the independence of South Ossetia and Abkhazia. "We are sorry about [the] adoption of such a decision. For Ukraine it is unacceptable therefore we cannot support the position."[281] However, the parliament of Ukraine's Autonomous Republic of Crimea passed a resolution, supporting independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia, backing Russia's actions in the regions, and urging the Ukrainian parliament to "accept" the independence of these states.[282][283][284] A similar Party of Regions resolution in the Ukrainian parliament denouncing Georgia and calling upon Ukraine to recognize the independence of both territories failed.[285] In October 2009, Ukrainian Ambassador to Russia Kostyantyn Gryshchenko said that "We must not recognize neither Kosovo nor Abkhazia, nor South Ossetia in no case".[286] After the 2014 Ukrainian revolution, the new Ukrainian government toughened its stance towards Abkhazia and South Ossetia (like Transnistria). In 2018, Ukrainian ships forcefully intercepted Abkhaz ships in the Black Sea.[290] | |
| Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs David Miliband accused Russian President Dmitry Medvedev of "inflaming" the crisis. He said that "the announcement by President Medvedev that Russia will recognise South Ossetia and Abkhazia is unjustifiable and unacceptable. It will also not work. It is contrary to the principles of the peace agreement, which Russia recently agreed, and to recent Russian statements. It takes no account of the views of the hundreds of thousands of Georgians and others who have been forced to abandon their homes in the two territories. We fully support Georgia's independence and territorial integrity, which cannot be changed by decree from Moscow." He called on Russia to "abide by international law as the basis for resolving this crisis" and stated that he will assemble the "widest possible coalition against Russian aggression".[291] British Prime Minister Gordon Brown urged the EU to review ties with Russia and that the group must intensify its support for Georgia and others who may face Russian aggression. Brown said the G7 should consider meeting more regularly, thus excluding Russia, which belongs to the G8. Brown commenting on the conflict in Georgia and Russia's recognition of the two breakaway regions said "My message to Russia is simple: if you want to be welcome at the top table of organisations such as the G8, OECD and WTO, you must accept that with rights and responsibilities". Brown said that Russia "cannot pick and choose which rules to adhere to."[292] | |
| President George W. Bush condemned the actions taken by Russia and called on them to "reconsider this irresponsible decision." Bush then stated that in "accordance with United Nations Security Council Resolutions that remain in force, Abkhazia and South Ossetia are within the internationally recognised borders of Georgia, and they must remain so."[293] Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice also said the decision made by Russia was "regrettable" and further stated that since "the United States is a permanent member of the Security Council this simply will be dead on arrival in the Security Council."[294] United States President George W. Bush acknowledged the ceasefire accord brokered by the French President and President of the European Council, Nicolas Sarkozy. The accord was signed by Russian President Dmitry Medvedev on 12 August 2008[295] and by Georgian President Mikheil Saakashvili on 15 August 2008.[296] President Bush stated that he would send Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice to Tbilisi to "convey America's unwavering support for Georgia's democratic government."[297] He also called upon Russia to respect the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Georgia.[297] The Russian government welcomed the support expressed by President Bush for the ceasefire accords but stated "[i]t is regrettable, however, that the American side continues to refuse to recognise the real cause of what happened, consisting in that the regime of Mikhail Saakashvili had in violation of all its international commitments unleashed the war against the South Ossetian people."[298] United States Vice President Dick Cheney traveled to Georgia on 4 September 2008 to reassure Georgia's President Mikheil Saakashvili of the United States' "commitment to Georgia’s territorial integrity."[299] Vice President Dick Cheney went on to denounce Russia's actions calling them "an illegitimate, unilateral attempt to change [Georgia's] borders by force that has been universally condemned by the free world"[299] and pledged that Georgia would become a member of NATO.[300] United States Secretary of Defense Robert Gates said that "Russia’s behavior over the past week has called into question the entire premise of that dialogue and has profound implications for our security relationship going forward, both bilaterally and with NATO."[301] He further went on to say that if "Russia does not step back from its aggressive posture and actions in Georgia, the U.S.-Russian relationship could be adversely affected for years to come."[301] In October 2009, State Secretary Hillary Clinton said that the United States would not recognise the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia.[302] To help the conflict resolution in the Caucasus, the Cultural Affairs Officer at the U.S. Embassy in Tbilisi started an exchange program for Abkhaz university employees in 2018. The professors from Abkhazian State University visited the United States. They visited the Arizona State University, San Diego State University, Rutgers University, Virginia Tech, Pennsylvania State University, University of Maryland, College Park and the United States Department of Agriculture.[303] | |
| In 2008, Vladimir Norov, the foreign minister of Uzbekistan, said following a regular session of the Uzbekistan-EU Cooperation Council in Brussels that his country has not reached a decision on recognition.[citation needed] As of 2020, Uzbekistan had not recognized Abkhazia. During the summer of 2020, due to the COVID-19 pandemic in Abkhazia, the Uzbek government wanted to evacuate several hundred guest workers from Abkhazia. Because the Uzbek government did not recognize Abkhazia, they negotiated with the Russian government to organize the evacuation.[304] | |
| In 2008, Ministry of Foreign Affairs Spokesman Le Dung publicly reiterated that Vietnam's "consistent policy is to promote peaceful resolution of international disputes in accordance with basic principles of international law and the United Nations Charter".[305] In a non-public conversation, Phạm Bình Minh, then the Deputy Minister of Foreign Affairs, told Michael W. Michalak, the Ambassador of the United States to Vietnam, that Georgian President Saakashvili's decision to invade South Ossetia was the reason for the crisis and added that Russia's decision was "a direct consequence of the US-led movement to recognize Kosovo", which Vietnam had opposed.[158] In 2022, the Vietnamese Ambassador in Venezuela established a first official contact with the Abkhaz Ambassador in that country.[306] | |
| In 2024, Zimbabwe voted against the Georgia resolution at the United Nations which would United Nations General Assembly adopted a resolution to reiterate the right of return of all displaced persons and refugees to Georgia's Abkhazia and Tskhinvali Region/South Ossetia and support Georgia's territorial integrity.[125] |
Other states
[edit]| State | Position |
|---|---|
| President of Kosovo Fatmir Sejdiu said that Kosovo cannot serve as an example for Russia to recognise South Ossetia or Abkhazia. He said, "We have always stressed that Kosovo has special characteristics; that it is sui generis and it cannot be used as a precedent for other conflict zones, areas or regions". He did not comment on Russia's recognition of South Ossetia and Abkhazia, but said that Kosovo was "on the side of great world powers" on that issue.[307] | |
| President of Northern Cyprus Mehmet Ali Talat said he respected the will of the people in South Ossetia and Abkhazia. A spokesman for Talat called for Moscow to review its policy on Cyprus and said there were lessons in the developments for the Greek Cypriots.[308] | |
| Palestine has so far not recognized the independence of Abkhazia or South Ossetia. In 2015, Abdel Hafiz Nofal, the Ambassador of the State of Palestine to the Russian Federation, met with Abkhaz foreign minister Viacheslav Chirikba and Igor Ahba, the Abkhaz Ambassador to Russia.[309] In 2022, Nofal met with Inal Ardzinba, who had become Abkhaz foreign minister in late 2021.[310] | |
| The head of Republic of China's representative office in Russia Antonio Chen said on 10 November 2011 in an interview published in the Kommersant newspaper: "Taiwan is ready for trade-economic and cultural cooperation with Abkhazia and South Ossetia. But as far as their political recognition is concerned, a mutual exchange of opinions on this issue has not been held yet".[311] |
Former partially recognized states
[edit]| State | Position |
|---|---|
| On 20 February 1992, Georgian President Zviad Gamsakhurdia and Chechen President Dzokhar Dudayev signed a joint communique, which, among other things, recognized the "inviolability of historical borders" and that therefore "South Ossetia must remain a part of Georgia".[312]
On 10 December 1997, President of Chechnya Aslan Maskhadov appointed Ruslan Tuntaev as a "plenipotentiary representative of the Chechen republic-Ichkeria" to Abkhazia. The envoy was appointed with a mandate of handling "economic and cultural-humanitarian affairs", with nothing being stated about political relations.[313] On 19 December 1997, Tuntaev was removed from his post by Maskhadov following Tuntaev's statement that the Chechen republic of Ichkeria "might recognize the Abkhazia's independence soon". Maskhadov's administration described this statement as an "illegal and uncoordinated action". Kazbek Khajiev, Maskhadov's press secretary, said that Chechnya would not endanger its friendly relations with Georgia to "promote somebody's ambitions".[314] |
Positions taken by intergovernmental organisations
[edit]Under international law, intergovernmental organisations do not themselves possess the legal capacity to recognise any state diplomatically; their member states do so individually. However, depending on the intergovernmental organisation's rules of internal governance and the positions of their member states, they may express positive or negative opinions as to declarations of independence, or choose to offer or withhold membership to a newly declared state.
| International organisation | Position |
|---|---|
| In April 2008, the United Nations Security Council unanimously passed Resolution 1808 that reaffirmed "the commitment of all Member States to the sovereignty, independence and territorial integrity of Georgia within its internationally recognised borders and supports all efforts by the United Nations and the Group of Friends of the Secretary-General, which are guided by their determination to promote a settlement of the Abkhaz–Georgian conflict only by peaceful means and within the framework of the Security Council resolutions."[315][316]
In August 2008, UN Secretary General Ban Ki-moon stated that "the question of recognition of states is a matter for sovereign states to decide. Today's developments may have wider implications for security and stability in the Caucasus. The secretary-general regrets that ongoing efforts to find a common solution on the way forward in the crisis in Georgia within the Security Council may be complicated".[317] Michele Montas, a spokesperson for UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon, denied comparisons of Kosovo with the two regions and said, "I think that you should compare the two situations. The history of the two situations is different and this has been stressed several times".[318] The President of the UN General Assembly, Miguel d'Escoto Brockmann of Nicaragua, sided with Russia in the course of this war, which led to criticism by Western diplomats.[319] | |
| On 3 September, The CSTO member countries supported Russia's stance on the events in the Caucasus in a collective statement. The member states also backed a Russian proposal to impose an arms embargo on Georgia.[citation needed]
| |
| Former Secretary General Terry Davis said "The unilateral recognition of the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia by the Russian Federation violates the territorial integrity of a fellow Council of Europe member state. It jeopardises prospects for a negotiated settlement of the dispute about the future status of these two regions. Russia cannot have it both ways. In the past, Russia has strongly supported the principle of territorial integrity. The decision to recognise Abkhazia and South Ossetia must strike any objective observer as being inconsistent with this principle. The ultimate victim of this decision is the international credibility of the Russian Federation. The Russians cannot invoke international law only when they feel like it".[185] | |
| The EU leaders held an emergency summit on 1 September 2008, "strongly condemned" Russia's unilateral decision and recalled "that a peaceful and lasting solution to the conflict in Georgia must be based on full respect for the principles of independence, sovereignty and territorial integrity recognised by international law, the Final Act of the Helsinki Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe and United Nations Security Council resolutions." They also called on other states not to recognise this proclaimed independence and asked the European Commission to examine the practical consequences to be drawn.[323] Swedish Foreign Secretary and Chairman of the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe, Carl Bildt, said that the Russian position is "certainly just as unacceptable" as Nazi Germany "defending its rights" in Sudetenland in 1938. Minister-Counsellor and Acting Head of Mission of the Russian embassy in Stockholm, Mikhail Skupov, condemned this statement as "not objective and unfortunate" and wished Sweden had a more objective and "constructive" stance, since Russia "has not annexed anything".[324][325][326]
The EU's executive arm, the European Commission, issued a statement stating it "fully shares and supports" the EU French presidency's statement on the Russian act on Tuesday (26 August 2012).[327] French and UK foreign ministers have voiced fears that Russia may be planning scenarios similar to those that occurred in Georgia in countries traditionally regarded by Russia as being in its sphere of influence,[328] directly bordering the EU, such as Moldova and Ukraine. Their fears are prompted by rising tension between Ukraine and Russia, and fresh calls for independence from Moldova by separatists in the breakaway region of Transnistria.[329] Sergei Lavrov stated "I think it's a manifestation of the complete embarrassment at the fact that the favourite pet of Western capitals... didn't justify their hopes" and said that comments from Bernard Kouchner suggesting Russia has plans for Moldova and Ukraine, is a "sick fantasy".[330] Lavrov is under sanctions from the US, UK, EU, Canada, and Australia for his role in the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[331][332] | |
| G7 | On 27 August 2008, the seven foreign ministers of the G7 member states – Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United States and the United Kingdom – issued a Joint Statement on Georgia, condemning the action of a fellow G8 member. The statement said, "Russia's decision has called into question its commitment to peace and security in the Caucasus."[333] The Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs responded stating that the statement justified Georgia's aggression and dismissed claims that Russia violated the territorial integrity of Georgia. Furthermore, the Ministry stated that Russia has complied with the Sarkozy-Medvedev peace plan and that Russian actions have prevented further destabilisation in the Caucasus region.[334][335] |
| Secretary General Jaap de Hoop Scheffer said "this is in direct violation of numerous UN Security Council resolutions regarding Georgia's territorial integrity, resolutions that Russia itself has endorsed. Russia's actions in recent weeks call into question Russia's commitment to peace and security in the Caucasus. NATO firmly supports the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Georgia and calls on Russia to respect these principles".[187] In December 2009, following NATO summit it was announced that NATO member states will not recognise Abkhazia and South Ossetia and called on Russia to reverse its decision.[336] | |
| Organisation for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) | OSCE chairman-in-Office, Finnish Foreign Minister Alexander Stubb said "the recognition of independence for South Ossetia and Abkhazia violates fundamental OSCE principles. As all OSCE participating States, Russia is committed to respecting the sovereignty and territorial integrity of others".[337]
On 9 July 2012, the OSCE Parliamentary Assembly passed a resolution at its annual session in Monaco, underlining Georgia's territorial integrity and referring to breakaway Abkhazia and South Ossetia as "occupied territories". The resolution "urges the Government and the Parliament of the Russian Federation, as well as the de facto authorities of Abkhazia, Georgia and South Ossetia, Georgia, to allow the European Union Monitoring Mission unimpeded access to the occupied territories." It also says that the OSCE Parliamentary Assembly is "concerned about the humanitarian situation of the displaced persons both in Georgia and in the occupied territories of Abkhazia, Georgia and South Ossetia, Georgia, as well as the denial of the right of return to their places of living." The Assembly is the parliamentary dimension of the OSCE with 320 lawmakers from the organization's 56 participating states, including Russia.[338] |
| Shanghai Cooperation Organisation | According to different sources it seems disputed that Russia has gained global support from the member states in the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO).[original research?] The Hindu reported that Russia has gained crucial support from the People's Republic of China and other member states in the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation.[339] Xinhua News Agency reported that a joint declaration was issued at 28 August 2008 SCO Dushanbe summit and signed by the leaders of all six full members, most notably Russian President Dmitry Medvedev. The communique denounces force as a means to solve international problems, expressed concern over the tense situation, and called upon all parties to solve the ongoing South Ossetia conflict through peaceful dialogue. The heads have agreed to the six-point plan which was established in Moscow (12 August) and have expressed support to Russia.[340] Western sources added that the SCO called for respect for every country's territorial integrity,[341] stating, "The participants [of the SCO summit] underscore the need for respect of the historical and cultural traditions of each country and each people, for efforts aimed at the preservation, under international law, of the unity of a state and its territorial integrity".[342] On 29 August 2008, Western and some Russian sources confirmed that the SCO Group "refused to back Moscow in its conflict with Georgia, and to support Moscow's recognition of South Ossetia and Abkhazia".[343][344][345][346] |
| Union of Russia and Belarus | On 4 August 2008, Pavel Borodin, then State Secretary of the Union of Russia and Belarus, told the radio station Ekho Moskvy that he supported Russia and that South Ossetia and Abkhazia could be accepted into the Union before the end of 2008.[citation needed] On 10 February 2022, the new Abkhaz foreign minister Inal Ardzinba met with State Secretary of the Union State of Russia and Belarus Dmitry Mezentsev. They both discussed integration processes in the post-Soviet space.[347] In March 2022, they met again.[348] In October 2022, according to the online publication Abkhazia Post, the foreign ministries of Abkhazia, Belarus and Russia established a trilateral forum of consultations on questions about the Union State.[349] |
Positions taken by non-state actors
[edit]Regions with independent governments
[edit]| Entity | Position |
|---|---|
| On 26 August 2008 a spokesman for the Palestinian group Hamas, which governs the Gaza Strip, welcomed the diplomatic recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. He said that there were similarities between the situations of the Abkhazian, South Ossetian peoples, and the Palestinian people. The spokesman said, "We, Palestinians, also struggle to attain recognition for our rights, the main of which is the right to be an independent state. We hope that the decision of Moscow becomes the beginning of recognition of peoples which combat for freedom and justice".[350][351][352] | |
| Международное признанное правительство Йемена не признало ни Абхазию, ни Южной Осетии. Тем не менее, Абдулла Али Сабри, чрезвычайный посол и пособие правительства Верховного политического совета, доминированного в Хути , в Дамаске , встретился с послом Абхаз в Сирии в 2021 году. Оба представителя обменивались мнениями на возможные области двустороннего сотрудничества между двусторонним сотрудничество Республика Абхазия и Исламская Республика Йемена, а также укрепление отношений между обеими сторонами. [ 353 ] |
Международные неправительственные организации
[ редактировать ]| Международная организация | Позиция |
|---|---|
| Организация непредставленных наций и народов (UPO) | Организации непредставленных наций и народов, основанной на Гааге , членами которых являются 69 организаций, ищущих самоопределение и представительство, из которых Абхазия (но не Южная Осетия) является одним из заявлений 29 августа 2008 Призывы к самоопределению были официально приняты во внимание. [ 354 ] |
| Международная организация по стандартизации (ISO) | Ни Абхазия, ни Южная Осетия в настоящее время не являются членом руководящей структуры Международной организации по стандартизации (ISO).
Независимо от их статуса членства ISO, ISO также потенциально выпустит стандартизированный код страны для каждого. Согласно правилам процедуры, за которым следует Агентство по техническому обслуживанию ISO 3166, базирующееся в Женеве, новый код ISO 3166-1 для Абхазии и/или Южной Осетии будет выпущен только после того, как он появится в именах странологий Организации Объединенных Наций или в статистике ООН. Список отделов страны и региона для статистического использования. [ 355 ] Чтобы появиться в терминологическом бюллетене, он должен (а) быть допущенным в Организацию Объединенных Наций, (б) присоединиться к специализированному агентству ООН , либо (в) стать государственной партией в Статут Международного суда . [ 356 ] Ни один из этих критериев не был соблюден. |
| Интернет -корпорация для назначенных имен и номеров (ICANN) | ICANN , благодаря своей поддержке кодовых имен страны , отвечает за добавление новых доменов кода страны (CCTLDS) для использования в адресации Интернета. Правила процедуры диктуют Абхазию и/или Южную Осецию, должны сначала получить код ISO 3166-1 (обсуждается выше), прежде чем CCTLD может быть введено. [ 357 ] |
Смотрите также
[ редактировать ]- Международное признание чеченской Республики Ичкерия
- Международная реакция на русесуоргианскую войну
- Международная реакция на аннексию Крыма Российской Федерацией
- Международное признание Донецской Народной Республики и Народной Республики Луганской
- Список государств с ограниченным признанием
- 2006 г. Референдум по независимости Южного Осетиана
- Предложенная русская аннексия Южной Осетии
 Абхазия Портал
Абхазия Портал
Примечания
[ редактировать ]- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в Неясно, существует ли дата, когда Абхазия, Южная Осетия и Транснестрия официально признали друг друга или они всегда делали это, и когда они установили дипломатические отношения. Abhazia и Transnistria подписали договор о дружбе и сотрудничестве 22 января 1993 года , Южной Осетии и Transnistria по договору о дружбе и сотрудничестве 12 октября 1994 года, а также Абхазии и Южной Осетии о дружбе и сотрудничестве 19 сентября 2005 года.
Ссылки
[ редактировать ]- ^ «Грузия: Абхазия и Южная Осетия» . Принстонская энциклопедия самоопределения . Получено 11 апреля 2024 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Гражданская Грузия (31 марта 2014 г.). «Тувалу втягивает Абхазию, признание S.Ossetia» . Получено 28 января 2022 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный «Заявление Министерства иностранных дел Грузии относительно установления дипломатических и консульских отношений» . Архивировано с оригинала 6 октября 2014 года . Получено 30 сентября 2014 года .
- ^ «Сирия признает независимость оккупированной Абхазии и Южной Осетии в Грузии» . Повестка дня . Архивировано из оригинала 29 мая 2018 года . Получено 29 мая 2018 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный «Министры иностранных дел Грузии, Вануату, обещают углубить связи» . Гражданская Грузия . 14 марта 2019 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный «Министр иностранных дел Вануату, международное сотрудничество и визиты на внешнюю торговлю, возле оккупационной линии» . Министерство иностранных дел Грузия (на Грузии). 15 марта 2019 года. Архивировано с оригинала 16 августа 2022 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Конституция Южной Осетии» . Архивировано из оригинала 15 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ "Абхазия и Южная Осетия требуют независимости" . Archived from the original on 1 September 2008 . Retrieved 18 November 2008 .
- ^ Внешняя политика России: изменение систем, устойчивые интересы . Роберт Х. Дональдсон, Джозеф Л. Ноги. Я Шарп. 2005. с. 199. ISBN 978-0-7656-1568-8 .
{{cite book}}: Cs1 maint: другие ( ссылка ) - ^ «Профиль Абхазии» . BBC News . 23 мая 2012 года . Получено 22 марта 2024 года .
- ^ Конституция Абхазии Архивирована 18 января 2009 года на машине Wayback (на русском языке)
- ^ "Абгихия " Архивировано из оригинала декабря 8 Получено 18 ноября
- ^ The New York Times , 26 августа 2008 года: « Россия поддерживает независимость грузинских анклавов » Клиффорда Дж. Леви.
- ^ Совета Безопасности Организации Объединенных Наций Отчет 5969 . S/PV/5969 Page 16. Г -н Чуркин Россия 28 августа 2008 года. Получено 3 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ Рединг, Эндрю (28 августа 2008 г.). «Это лицемерие кавказа» . Глобус и почта . Получено 29 августа 2008 года .
- ^ «Неупо: Абхазия: Россия приветствует признание Никарагуа Южной Осетии и Абхазией» . Архивировано с оригинала 19 апреля 2016 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ RBC News .
- ^ (in Russian) Михаил Саакашвили назвал действия России в отношении Грузии "силовой попыткой изменить границы внутри Европы Archived 12 September 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Россия признает грузинских повстанцев BBC 26 августа 2008 года.
- ^ Гражданская Грузия (28 августа 2008 г.). «Абхазия, S.Ossetia официально объявлена оккупированной территорией» . Получено 28 января 2022 года .
- ^ "В Петербурге президенты России и Украины открыли памятник Тарасу Шевченко как символ культурных связей" . 22 December 2000 . Retrieved 5 April 2016 .
- ^ Российско-георгианская виза Связи остаются архивными 8 сентября 2008 года на машине Wayback Kommersant 4 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ Гражданская Грузия (29 ноября 2008 г.). «Грузия сокращает галстуки с Никарагуа над S.Ossetia, признанием абхазии» . Получено 22 января 2022 года .
- ^ «Россия предупреждает Грузию от захвата кораблей, связанных с Абхазией» . Rt. 3 сентября 2009 г. Архивировано с оригинала 19 июля 2012 года . Получено 7 июня 2010 года .
- ^ «Южная Осетия обвиняет Грузию в сборе заложников-новости-информирование о бизнес-портале» . Архивировано из оригинала 6 июня 2014 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Грузия раскрывает стратегию на оккупированных территориях » . Радио Свободная Европа/Радио Свобода . 31 января 2010 . Получено 22 марта 2024 года .
- ^ «Георгиандэсти форум» . georgiandaily.com . Архивировано из оригинала 11 июля 2011 года.
- ^ "Geotimes - дом" . Архивировано с оригинала 24 сентября 2015 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Другой гражданин Джорджии, похищенный вблизи оккупации Чинвали - тревожная статистика 2018 года» . Георгианджурнал . Получено 22 июня 2019 года .
- ^ «Архил Татунашвили Архив» . Гражданский . Получено 22 июня 2019 года .
- ^ «Один год с момента жестокого убийства Грузинского гражданина Арчила Татунашвили, занимающими силы» . Повестка дня . Получено 22 июня 2019 года .
- ^ «Процедуры входа для иностранных граждан, прибывающих в Южную Республику Осетии» . Министерство иностранных дел Южной Осетии . Получено 28 января 2022 года .
- ^ Отношения НАТО с Грузией Архивировали 5 сентября 2008 года на машине Wayback NATO 2 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ Гражданская Грузия (26 августа 2008 г.). «Председатель ОБСЕ осуждает признание России Абхазией, S.Ossetia» . Получено 22 января 2022 года .
- ^ США осуждает Россию по поводу Грузии BBC 4 сентября 2008 г.
- ^ Оливер Булло (2 апреля 2014 г.). «Эта крошечная островная нация Тихого океана только что дала России большой синяк» . Новая республика .
- ^ «Холодные отношения Абхазии с Центральной Азией» . Новая Европа . 29 августа 2022 года.
- ^ «Сирия признает Абхазию, Южная Осетия» . Гражданская Грузия . 29 мая 2018 года.
- ^ Медведев, Дмитрия (26 августа 2008 г.). «Заявление президента России Дмитрий Медведев, 26 августа 2008 года» . Москва: федеральное правительство России. Архивировано из оригинала 2 сентября 2008 года . Получено 4 сентября 2008 года .
- ^ "Указ Президента Российской Федерации от 26.08.2008 г. № 1261" . Президент России .
- ^ "Указ Президента Российской Федерации от 26.08.2008 г. № 1260" . Президент России .
- ^ «Trend News: Россия официально установила дипломатические отношения с Абхазией и Южной Осетии» . News.trendaz.com. Архивировано из оригинала 17 сентября 2008 года . Получено 3 октября 2008 года .
- ^ «Послы в Абхазии и Южной Осетии представляют свои полномочия« Itar-Tass »16.12.2008, 18:43» . Архивировано из оригинала 20 декабря 2008 года.
- ^ «Грузия устанавливает условия для восстановления дипломатических связей с Россией» . Georgiatimes.info . Архивировано из оригинала 21 июля 2011 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ Посольство России в Абхазии начало работу на постоянной основе. « Интерфакс » 01 мая 2009 года 23:26
- ^ «Посольство Абхазии в Россию открылось в Москве» . Archive.is . 29 мая 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 29 мая 2012 года.
- ^ Президент Республики Никарагуа Указ № 47-2008 webcitation.org/5ajfhstly Arucked Webcite .
- ^ Президент Республики Никарагуа Указ № 46-2008 webcitation.org/5ajftb665, а также продуманные веб -сайты .
- ^ "Новости NEWSru.com: Южную Осетию и Абхазию в Никарагуа признали официально: подписаны все документы" . 5 September 2008 . Retrieved 5 April 2016 .
- ^ Никарагуа, Абхазия устанавливает дипломатические отношения, архивные 14 сентября 2009 года на машине Wayback , «Itar-Tass», 11 сентября 2009 г., 07.37
- ^ «Посольства в Абхазии» . www.mfaabkhazia.net . Архивировано из оригинала 9 января 2011 года.
- ^ «Южная Осетия открывает посольство Home Office-Канал Пик TV» . Архивировано из оригинала 21 января 2012 года . Получено 19 сентября 2011 года .
- ^ «Инар Ладария представил копии своих полномочий Денису Монкаде, министру иностранных дел Никарагуа» . Министерство иностранных дел Абхазии . 17 февраля 2022 года . Получено 17 марта 2022 года .
- ^ "Венесуэла признает Южную Осетию и Абхазию – Чавес" . РИА Новости . 10 September 2009 . Retrieved 5 April 2016 .
- ^ Mprr [1] (pdf)
- ^ Mprr: Посол Абьясии представил стиль копии перед венесуэльскими властями [2]
- ^ [3] [ мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ "Архививая копия" . Архивировано из оригинала 11 февраля 2012 года . Получено 4 августа 2010 года .
{{cite web}}: CS1 Maint: архивная копия как заголовок ( ссылка ) - ^ «Официальная служба Амбийской Республики в Венесуэле » Получено 8 октября
- ^ «Тихоокеанский остров признает грузинский регион повстанцев» . Рейтер . 15 декабря 2009 г. Архивировано с оригинала 13 июля 2019 года . Получено 15 декабря 2009 года .
- ^ Науру признало Южную Осетию . – Грани.ру, 16 December 2009
- ^ «Представители Науру будут наблюдателями на президентских выборах в Абхазии» . Архивировано с оригинала 25 марта 2012 года . Получено 19 сентября 2011 года .
- ^ «Новозеландец, чтобы представлять Южную Осетии в Науру» . Радио Новая Зеландия . 25 января 2018 года . Получено 25 января 2018 года .
- ^ «Сирия, Южная Осетия Соглашение о том, чтобы установить дипломатические связи» . Сирия Таймс . 22 июля 2018 года. Архивировано с оригинала 25 июля 2018 года . Получено 22 июля 2018 года .
- ^ Повестка дня (29 мая 2018 г.). «Сирия признает независимость отколовшегося Грузии Абхазии и Южной Осетии» . Архивировано из оригинала 29 мая 2018 года . Получено 29 мая 2018 года .
- ^ Сана (29 мая 2018 г.). «Сирия, Абхазия, Осетия согласна обмениваться признанием, установить дипломатические отношения на уровне посольства» . Сирийское арабское информационное агентство . Получено 29 мая 2018 года .
- ^ "Страница не найдена" . Archived from the original on 27 April 2015 . Retrieved 5 April 2016 .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный "Абхазия, Южная Осетия и Приднестровье признали независимость друг друга и призвали всех к этому же" . Newsru . 17 November 2006 . Retrieved 26 August 2008 .
- ^ «Эдуард Кокотити принял посла Абхаза в полномочия С. Осетия Нодар Плайв» . Архивировано с оригинала 27 марта 2012 года . Получено 19 апреля 2012 года .
- ^ Представительство Приднестровской Молдавской Республики в Республике Южная Осетия Полем Представительская канцелярия Transnistria в Южной Осетии (на русском языке) . Получено 13 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ Полу признанного Западной Сахары, чтобы распознать Южную Осетия // Грузинская ежедневная газету, 29 сентября 2010 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный «Полу признанного Западной Сахары, чтобы распознать Южную Осетии» . Евразия . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ ПОЛИСАРИО: "Западная Сахара признает независимость и суверенитет Южной Осетии" // Regnum, 29 September 2010
- ^ Константин Кочиев: независимость Южной Осетии признает Западная Сахара // Кавказский Узел, 30 September 2010
- ^ Независимость Южной Осетии признала непризнанная Западная Сахара, на очереди – Алжир // NEWSru.com, 30 September 2010
- ^ Грузия: Непризнанная Западная Сахара признала Цхинвал // Росбалт, 30 September 2010
- ^ «Приветствия Министерства иностранных дел в Осетии в Южной Осетии в Арабскую Демократическую Республику Сахара по случаю 35 -летия Декларации Дня независимости содержания | Министерство иностранных дел» . mfa.rsogov.org . Получено 19 января 2023 года .
- ^ "Заур Гваджава принял участие в церемонии празднования Дня Африки" . mfaapsny.org (in Russian) . Retrieved 31 January 2022 .
- ^ «Украинские сепаратисты признают Абхазию, Южную Осетии, 13 мая 2015 года» . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2015 года . Получено 13 мая 2015 года .
- ^ "Апсныпресс – Луганская Народная Республика Признала Суверенитет И Независимость Республики Абхазия" . Apsnypress.info . Retrieved 16 March 2022 .
- ^ «Народная Республика Луганск признает Южную Осетия | Новости | Москва времена» . www.themoscowtimes.com . Архивировано из оригинала 15 июля 2015 года . Получено 19 апреля 2022 года .
- ^ "Апсныпресс – Абхазия И Луганская Народная Республика Установили Дипломатические Отношения" . Apsnypress.info . Retrieved 16 March 2022 .
- ^ «Народная Республика Луганской республики признает Южную Осетии - новости» . Москва времена . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ Вадим Дьяконов. «Посольство Южной Осетии открылось в LNR» . «15-я регион» . Архивировано с оригинала 23 марта 2016 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Луганск признает Абхазию» . Гражданская Грузия . 10 марта 2022 года . Получено 10 марта 2022 года .
- ^ "Заявление главы ЛНР Леонида Пасечника (Statement by head of the LPR Leonid Pasechnik)" . Lugansk Information Center . 10 March 2022 . Retrieved 10 March 2022 .
- ^ "Cтраны, признавшие независимость Республики Абхазия" . Archived from the original on 18 February 2013 . Retrieved 5 April 2016 .
- ^ Вице-спикер парламента Абхазии: Выборы в НКР соответствуют всем международным стандартам : "Абхазия, Южная Осетия, НКР и Приднестровье уже давно признали независимость друг друга и очень тесно сотрудничают между собой", – сказал вице-спикер парламента Абхазии. ... "...Абхазия признала независимость Нагорно-Карабахской Республики..." – сказал он."
- ^ "Кавказский Узел – Атанесян: Нагорный Карабах фактически признал независимость Абхазии" . Кавказский Узел . Retrieved 5 April 2016 .
- ^ «О установлении дипломатических отношений между Республикой Абхазия и Тувалу . Архивировано из оригинала 11 ноября 2011 года . Получено 24 сентября 2011 года .
- ^ «Тувалу возвращает признание независимости Абхазии и так называемой Южной Осетии» . 31 марта 2014 года. Архивировано с оригинала 31 марта 2014 года . Получено 31 марта 2014 года .
- ^ Оливер Булло (2 апреля 2014 г.). «Эта крошечная островная нация Тихого океана только что дала России большой синяк» . Новая республика .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный «Факсимильные полномочия» Верительное факсимиле Полем Kommersant (на русском языке). 7 июня 2011 года. Архивировано с оригинала 8 июня 2011 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Абхазия и Тихоокеан» . Министерство иностранных дел (Абхазия) . Архивировано из оригинала 16 апреля 2012 года . Получено 8 августа 2013 года .
- ^ «О установлении дипломатических отношений между Республикой Абхазия и Республикой Вануату» . Абхаз Мир. 27 мая 2011 г. Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Приключения в дипломатии пальмы: Вануату признает Абхазию» . Евразия . 1 июня 2011 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Правительство Вануату подтверждает признание Абхазии» . Radio New Zealand International . 7 июня 2011 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Прозрачность международного пресс -релиза Vanuatu по признанию Абхазии» . Transparency International Georgia. 8 августа 2011 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Признать или не распознать Абхазию? Это вопрос Вануату» . Радио Свободная Европа. 26 августа 2012 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Статус внутренне перемещенных лиц и беженцев из Абхазии, Джорджия и региона Чинвали / Южная Осетия, Грузия: Резолюция / принята Генеральной Ассамблеей» . Объединенные Нации. 3 июля 2012 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Вануату признает путаницу из -за Абхазии ссылки» . Radio New Zealand International . 18 марта 2013 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Путаница задерживается из -за связей Вануату с Абхазией» . Radio New Zealand International . 18 марта 2013 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Саакашвили говорит, что остров Тихого океана больше не признает Абхазию» . Радио Свободная Европа. 26 августа 2012 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Премьер -министр Вануату рассказывает о сильной оппозиции Абхазийским связям» . Radio New Zealand International . 21 мая 2013 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ Гражданская Грузия (15 июля 2013 г.). «Грузия, Вануату устанавливает дипломатические связи» . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Вануату не отменяет свое признание Абхазии - Абхаз Министерство иностранных дел» . Interfax. 17 июля 2013 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Заседание министра иностранных дел Республики Абхазия Виачеслав Чирикба с министром иностранных дел, международным сотрудничеством и внешней торговлей Республики Вануату Г -н Сато Мельтек Килман Ливтувану» . Министерство иностранных дел Абхазии. 31 марта 2015 года. Архивировано с оригинала 2 апреля 2015 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ "Глава МИД Вануату: мы нуждаемся в крове, еде, воде и медикаментах" . RIA Novosti. 31 March 2015 . Retrieved 5 September 2022 .
- ^ «Натуман объясняет причины прекращения Килмана» . Vanuatu Daily Post . 10 июня 2015 года . Получено 10 июня 2015 года .
- ^ «Vanuatu PM излагает обеспокоенность с Килманом» . Radio New Zealand International . 10 июня 2015 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Джо Натуман убрал премьер-министр Вануату в беспрепятственном голосовании; Сато Килман восстанавливает высшую работу» . ABC News . 12 июня 2015 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Давит Залкали: Мы очень ценим сильную поддержку правительства Вануату для суверенитета и территориальной целостности Грузии в его международно признанных границах» . Министерство иностранных дел Грузия (на Грузии). 14 марта 2019 года. Архивировано с оригинала 9 апреля 2022 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Министры иностранных дел Грузии, Вануату, обещают углубить связи» . Грузия сегодня . 15 марта 2019 года . Получено 5 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «Министр иностранных дел #abkazia inal Ardzinba провел встречу с делегацией посольства #afghanistan в #Russia» . Получено 13 февраля 2023 года .
- ^ «Албания осуждает признание России грузинскими отколочными регионами_англиша_ксинхуа» . Архивировано с оригинала 4 марта 2016 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Премьер -министр Спенсер в переговорах с чиновниками Республики Абхазия» . Правительство Антигуа и Барбуда . 28 мая 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 14 мая 2013 года . Получено 27 марта 2013 года .
- ^ «Инал Ардзинба, министр иностранных дел Абхазии, поговорил с Полом Чет Грин, министром иностранных дел, международной торговли и иммиграции Антигуа и Барбуды» . Абхаз Министерство иностранных дел. 30 июня 2022 года . Получено 6 июля 2022 года .
- ^ «Аргентина исключает признание» . Буэнос -Айрес : B92 . 29 февраля 2008 года. Архивировано с оригинала 15 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ «Абхазия заинтересована в установлении дипломатических отношений с Аргентиной» . Абхаз Мир. 27 февраля 2010 года.
- ^ "Окончательная экспансия Грузии со стороны Турции – вопрос времени. Дмитрий Медоев" . 24news.am. 31 August 2020.
- ^ «Армения исключает Абхазию, Южная Оссетия признание» . Радиостанция "Free Europe / Freedom" . Архивировано из оригинала 9 ноября 2008 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ Ответ Тиграна Балаяна, руководителя пресс -службы MFA на вопросы агентства новостей Regnum Archived 13 февраля 2012 года на Machine Wayback , Regnum News, 27 августа 2008 г.
- ^ "Президент Армении встретился с представителями абхазского режима" . Наша Абхазия . Retrieved 28 July 2022 .
- ^ "Армения полноценно признает территориальную целостность Грузии – Пашинян" . Эхо Кавказа . 24 November 2023.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в дюймовый и фон «Генеральная Ассамблея ООН проходит к резолюции об IDP Грузии - Гражданская Грузия» . 4 июня 2024 года.
- ^ «Смит не впечатлен русской позицией» . Архивировано из оригинала 16 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ «Смит, чтобы вести переговоры с Россией по провинциям повстанцев» . ABC News . 27 августа 2008 г. Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Георгиандэсти форум» . georgiandaily.com . Архивировано из оригинала 27 августа 2008 года.
- ^ Zbigniew Brzezinski; Пейдж Брайан Салливан; Пейдж Салливан (1997). Россия и Содружество независимых государств: документы, данные и анализ . Я Шарп. п. 592. ISBN 9780585027005 .
- ^ « Сегодня . Архивировано из оригинала 18 января 2012 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Дипломат: Беларусь, чтобы узнать Абхазию, Южную Осетии Скоро_ENGILSH_XINHUA» . Архивировано из оригинала 31 августа 2008 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ (по исландскому) Беларусь признает регионы разделения, архивные 2 сентября 2008 года в Wayback Maachine в Visir.is newportal
- ^ (in Russian) Белоруссия скоро признает независимость Абхазии и Южной Осетии
- ^ Президенты Абхазии и Южной Осетии обращаются к письмам президенту Александру Лукашенко с просьбой признать их независимость, архивируя 16 октября 2008 года на машине Wayback
- ^ Николоз Самхарадзе: Признание России независимости Абхазии и Южной Осетии , Нью -Йорк (Нью -Йорк): издательство Колумбийского университета 2021, с. 228
- ^ Ратленд, Питер (31 октября 2008 г.). «Грузия: дорогостоящие иллюзии» . Переходы онлайн . Получено 23 марта 2009 года . [ Постоянная мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ «Министры иностранных дел ЕС обсуждают восточное партнерство» . Radiofreeeurope/Radioliberty . Архивировано из оригинала 21 января 2014 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «ЕС расширяет свою« сферу влияния », - говорит Россия» . Euobserver . 21 марта 2009 г. Получено 24 марта 2009 г.
- ^ «Россия предлагает Беларусь 500 миллионов долларов за признание Абхазии» . Евразия . 24 марта 2009 г. Архивировано с оригинала 11 августа 2009 года . Получено 26 января 2008 года .
- ^ Лукашенко обвиняет Россию в шантажировании Беларуси в распознавании грузинских регионов . Los Angeles Times . 5 июня 2009 г.
- ^ Беларусный лидер отвергает условия по российскому займу . Рейтер . 5 июня 2009 г.
- ^ "Парламент Белоруссии в этом году не будет рассматривать вопрос признания Абхазии и Южной Осетии" . Archived from the original on 22 November 2009.
- ^ "Южная Осетия попросила Минск поступить с ней как с Абхазией" . Rosbalt. Archived from the original on 2 December 2009.
- ^ «Отношения между Абхазией и Сирией: к воздействию домино с Беларусью и Северной Кореей?» Полем Российский совет по международным делам . 23 июня 2021 года . Получено 2 июля 2021 года .
- ^ «Отношения между Абхазией и Сирией: к воздействию домино с Беларусью и Северной Кореей?» Полем Гражданский . 16 ноября 2021 года . Получено 1 января 2022 года .
- ^ "Южная Осетия ждет признания независимости со стороны Белоруссии и других стран" . TASS . 15 November 2021 . Retrieved 1 January 2022 .
- ^ «Беларусь в Лукашенко посещает Абхазию» . Евразия . 28 сентября 2022 года . Получено 1 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в "Anatoly Bibilov met with representatives of South Ossetia in Transnistria and Benelux countries" . Государственное Информационное Агентство "Рес" . RES Agency. 1 November 2019 . Retrieved 15 May 2020 .
- ^ «Болгария» обеспокоена признанием России Южной Осетии, независимости Абхазии » . София Эхо . 26 августа 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 31 августа 2008 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Сложная смесь» . Молодой мир . 12 октября 2019 года . Получено 29 ноября 2020 года .
- ^ "Болгарские предприниматели готовы инвестировать в Абхазию" (in Russian). Aiaaira. 4 July 2018. Archived from the original on 11 December 2020 . Retrieved 29 November 2020 .
- ^ «Абхазия в системе международных отношений» . MFA Apsny . Получено 13 июля 2022 года .
- ^ «Президент Republika Srpska встречает южного лидера Осетиан» . Гражданская Грузия . 2 июня 2017 года . Получено 28 января 2022 года .
- ^ «Грузия протестует в Боснии по поводу визита лидера Осетиана» . Балканское понимание.
- ^ «Южный лидер Осетиан встречается с боснийским сербским коллегой» . OC Media .
- ^ «Сараево: Мы уважаем территориальную целостность Грузии» . Гражданская Грузия .
- ^ «Грузия протестует в Боснии по поводу визита лидера Осетиана» . Балканское понимание. 11 января 2018 года.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в Donnacha - Beacháin (31 июля 2019 г.). «Cheque Mates? Стремление Абхазии к международному признанию» . Исследования переходных государств и обществ . 11 (1).
- ^ «Заур Гваджава сделал прием по случаю 25-го годовщины Дня победы и 10-летичной годовщины признания Абхазии Российской Федерацией» . Абхаз Министерство иностранных дел. 22 октября 2018 года . Получено 25 декабря 2021 года .
- ^ "Комментарий Министра иностранных дел Республики Абхазия Инала Ардзинба в связи со встречей Посла Абхазии и Посла Боливии в Венесуэле" (in Russian). Abkhaz foreign ministry. 24 December 2021 . Retrieved 25 December 2021 .
- ^ «Интервью министра Чельсо Аморима газете Кларин, 9/9/2008» (на португальском). Министерство иностранных дел (Бразилия) . 8 сентября 2008 г. Получено 9 октября 2019 года .
- ^ «Южная Осетия ищет контакт с Бразилией» (на немецком языке). Америка21. 23 августа 2019 года . Получено 9 октября 2019 года .
- ^ «Заявление министра Эмерсона о ситуации в Грузии - канадском мофе», архивировав 1 сентября 2008 года в The Wayback Machine International.gc.CA 26 августа 2008 г.
- ^ «Пресс -секретарь FM: Китай», связанный с ситуацией в Южной Осетии, Абхазия » . Люди ежедневно онлайн. Архивировано с оригинала 16 ноября 2018 года . Получено 24 июня 2017 года .
- ^ «Россия, Китай и измерение Грузии» . Чистка Получено 24 июня 2017 года .
- ^ «Китай, чтобы инвестировать в электромобили, мобильные телефоны и дороги в Абхазии?» Полем Евразия . Получено 6 октября 2020 года .
- ^ «CCI RA представлял продукты производителей Abkhaz на международной выставке в Шанхае» . Торговая палата Республики Абхазия . Получено 22 января 2021 года .
- ^ «На встрече с делегацией из Китая» . Министерство иностранных дел Республики Абхазия . Получено 6 октября 2020 года .
- ^ «Заявление Министерства иностранных дел Республики Абхазия в отношении давления грузинской стороны на посла Китайской Народной Республики на Сирию» . Абхаз Министерство иностранных дел. 9 ноября 2021 года . Получено 16 января 2022 года .
- ^ «Мезик обеспокоен признанием России Южная Осетия и Абхазия » . Получено 5 2016 года апреля
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный «Георгиандэсти форум» . georgiandaily.com . Архивировано из оригинала 30 августа 2008 года.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в «Совет Безопасности, проинформированный по политическим делам, миротворчеством в области развития Грузии, в том числе 26 августа Указы о признании на Абхазии, Южная Оссетия» . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Главная - Famagusta Gazette Online - Последние новости, проблемы на Кипре, погода» . Архивировано из оригинала 12 сентября 2008 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Министерство иностранных дел - новости - Кипр, обеспокоенный событиями в Грузии» . Архивировано с оригинала 3 марта 2016 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный «Лидеры ЕС осуждают Россию в тени Косово» . 26 августа 2008 г. Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Депутаты Доминиканской Республики поддерживают установление дружеских отношений с Абхазией» . Сухум : правительство Абхазии . 10 декабря 2010 года. Архивировано с оригинала 2 марта 2011 года . Получено 1 июня 2011 года .
- ^ Вице-премьер Доминиканской республики встретится с руководством Абхазии (на русском языке). Sukhum : Interfax . 13 мая 2011 года . Получено 1 июня 2011 года .
- ^ «США предупреждают Доминиканскую Республику против признания Южной Осетии, Абхазии» . Тбилиси : Итар-Тасс . 21 мая 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 25 мая 2011 года . Получено 1 июня 2011 года .
- ^ «Абхазия просит Эквадора признать ее независимость» . Итар Тасс . 3 декабря 2009 г. Архивировано с оригинала 16 марта 2010 года . Получено 3 декабря 2009 года .
- ^ «Дни культуры Эквадора в Грузии» . Гражданская Грузия . 1 июня 2011 года.
- ^ «Эстония не одобряет решение России признать независимость сепаратистских регионов Грузии» . Архивировано из оригинала 3 сентября 2012 года.
- ^ Мир, Абхаз (10 июня 2014 г.). «Первое визит эритрейской делегации в Абхазию» . Абхаз Мир - История, Культура и Политика Абхазии .
- ^ «Пресс -релиз Министерства иностранных дел в Республике Южная Осетия» . Министерство иностранных дел Южной Осетии .
- ^ «Председатель ОБСЕ осуждает признание России Южной Осетии, Абхазия Независимость» Формин. Finland.fi 26 августа 2008 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Реакция на признание России повстанцев , Би -би -си , 26 августа 2008 года.
- ^ Гражданская Грузия (27 августа 2008 г.). «Отчеты: Кушнер говорит о этнической чистке» . Получено 28 января 2022 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный «BBC News - Европа - Реакция на признание России повстанцев» . 26 августа 2008 г. Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Греческое министерство иностранных дел: официальный сайт» . Архивировано из оригинала 1 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ «Заур Гваджава встретился с послом Республики Гаити в Венесуэлу Дэвид Лесли» . 21 июня 2022 года . Получено 8 июля 2022 года .
- ^ Министерство иностранных дел Венгрии сожалеет, что президент России подписал постановление о признании Южной Осетии и Абхазии - заявление министерства, архивное 30 августа 2008 года на машине Wayback . Министерство иностранных дел Венгрии. Получено 26 августа 2008 года.
- ^ «Последние новости, World News & Multimedia» . www.nytimes.com .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в "Dmitry Medoev held meetings with the President of Micronesia and the Special Representative of Indonesia" . Государственное информационное агентство "Рес" . 2 February 2018.
- ^ «Иран не признает Абхазию, в ближайшее время независимость С. Осетии» . Фарс -агентство. 7 февраля 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 13 августа 2009 года . Получено 10 февраля 2009 года .
- ^ «Южная Осетия желает стимулировать сотрудничество с Ираном - политические новости» . Агентство TASNIM .
- ^ «Тегеран расширяет усилия по борьбе с нас, Израилем и Турцией по всему южному Кавказа» . Джеймстаун .
- ^ «Заявление министра иностранных дел о российском признании Абхазии и Южной Осетии» . Архивировано из оригинала 30 августа 2008 года.
- ^ «Заявление MFA о ситуации в Грузии» . GXMSDEV . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Георгиандэсти форум» . georgiandaily.com . Архивировано из оригинала 28 августа 2008 года.
- ^ «Открытие Абхазского института культуры, названного в честь Дмитрия Гулия в Италии» . Министерство иностранных дел Республики Абхазия . 17 июня 2016 года . Получено 31 июля 2020 года .
- ^ «Абхазский институт культуры открылся в Италии» . Apsnypress . 17 июня 2016 года. Архивировано с оригинала 14 февраля 2022 года . Получено 31 июля 2020 года .
- ^ "В ИТАЛИИ ЗАРЕГИСТРИРОВАНО ДИПЛОМАТИЧЕСКОЕ ПРЕДСТАВИТЕЛЬСТВО РЕСПУБЛИКИ АБХАЗИЯ" . Abkhazinform . 29 November 2017 . Retrieved 29 September 2020 .
- ^ «Абхаз Аджека представлен на популярном фестивале перца в Италии» . Мировой конгресс Абаза . 12 сентября 2019 года . Получено 29 сентября 2020 года .
- ^ «Южная Осетия открывает миссию в Риме, министерство иностранных дел Италии, чтобы не признавать ее» . Тасс 1 апреля 2016 года . Получено 31 августа 2020 года .
- ^ «Италия не признает де -факто Южную Осетии« посольство »в Риме» . Повестка дня . 2 апреля 2016 года . Получено 31 августа 2020 года .
- ^ «Георгиандэсти форум» . georgiandaily.com . Архивировано из оригинала 28 августа 2008 года.
- ^ «У президента была встреча с делегацией из Хасемитского королевства Иордании» . Президент ofabkhazia.org . 5 июля 2018 года . Получено 8 марта 2021 года .
- ^ "О встрече с делегацией из Иордании" . mfaapsny.org . 5 July 2018 . Retrieved 8 March 2021 .
- ^ «На встрече с делегацией из Иордании» . mfaapsny.org . 6 июля 2018 года . Получено 28 июня 2021 года .
- ^ «Абхазия в системе международных отношений» . mfaapsny.org . Получено 28 июня 2021 года .
- ^ «Казахстан понимает действия России» . Грузинский ежедневно. 28 августа 2008 г. Получено 28 августа 2008 года .
- ^ «Новости тенденции: Казахстан заботы о негативном влиянии конфликтов на региональную безопасность: посл» . News.trendaz.com. Архивировано из оригинала 7 сентября 2008 года . Получено 3 октября 2008 года .
- ^ АО ИД «Комсомольская правда». "Казахстан не станет признавать Южную Осетию" . АО ИД «Комсомольская правда» . Archived from the original on 25 January 2016 . Retrieved 5 April 2016 .
- ^ "Руководство Казахстана не будет признавать независимость Абхазии и Южной Осетии" . Retrieved 5 April 2016 .
- ^ «Анализ: Казахстан и Южная Осетия - нефтяная связь» . УПИ . Получено 21 апреля 2019 года .
- ^ «Kazakhstan предлагает помощь с Ossetian, Abhaz Talks» . Radiofreeeurope/Radioliberty . Получено 21 апреля 2019 года .
- ^ "В Казахстане появятся вина из Южной Осетии" . Retrieved 21 April 2019 .
- ^ «Заявление президента Аг Бжании, президента Республики Абхазия в связи с ситуацией в Республике Казахстан» . Абхаз Министерство иностранных дел. 8 января 2022 года . Получено 25 января 2022 года .
- ^ "Ответ Министра иностранных дел Республики Южная Осетия Д.Н. Медоева на вопрос корреспондента ИА "Рес" о событиях в Казахстане" (in Russian). South Ossetian foreign ministry. 7 January 2022 . Retrieved 25 January 2022 .
- ^ Независимость Южной Осетии, Абхазия нуждается в размышлениях, посол Кыргызстана говорит, что архивировал 31 августа 2008 года на машине Wayback , Национальный юридический интернет -портал Республики Беларусь, 27 августа 2008 г.
- ^ «Министр иностранных дел Рикстиш осуждает решение России признать независимость Абхазии и Южной Осетии» . Архивировано из оригинала 30 августа 2008 года.
- ^ "Президент Латвии заявляет, что его страна никогда не признает независимость Абхазии и Южной Осети" . Retrieved 10 December 2009 .
- ^ «Я аналитик по акциям - журнал 2020» . Я акции аналитика .
- ^ Мир, Абхаз. «Ливан мог признать S.Ossetia, Abhazia» . Абхаз Мир | История, культура и политика Абхазии .
- ^ «Times Times: Show/228122, Балтийские государства-концпенд-россияна-распознавание-георгиан-регионы .html» . Архивировано из оригинала 17 июня 2018 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Объединенная декларация Жан-Клода Юнкера и Жана Ассельборна после признания Россией о независимости Абхазии и южной Осетии» . Архивировано из оригинала 1 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ «Работает Мексика в Южной Осетии и Абьясии » . Арчндд из оригинала 1 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ « Протокол по созданию дипломатических и консульских отношений между федеративными государствами Микронезии и Грузии , fsmgov.org 12 августа 2011 года» (PDF) .
- ^ "Press release of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of South Ossetia | Министерство иностранных дел" . mfa.rsogov.org .
- ^ «Молдова отвергает признание грузинских регионов» . Рейтер . 29 августа 2008 г. Получено 30 августа 2008 года .
- ^ Текст обращения Народного собрания Гагаузии к руководству Молдавии о признании Абхазии и Южной Осетии (на русском языке). Регновое информационное агентство . 19 сентября 2008 г. Получено 8 августа 2013 года .
- ^ « Абхазская выставка в Черногории закрыла по просьбе Грузии , dfwatch.net 25 апреля 2016 года» . 25 апреля 2016 года.
- ^ «Черногория продолжил Грузию» . www.tppra.org .
- ^ «Нидерланды боятся за отношения ЕС с Россией» . Архивировано из оригинала 31 августа 2008 года.
- ^ «Пост в Норвегии - ваши последние новости из Норвегии, Норвегия Новости на английском языке» . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года . [ Постоянная мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ "Баграт Хутаба провел встречу с Послом Султаната Оман в Сирии" . mfaapsny.org . Retrieved 26 April 2021 .
- ^ "Даур Кове принял Президента ассоциации содействия по установлению деловых связей с Пакистаном «BACP" Джавада Рахмана Шехрия" . mfaapsny.org . Retrieved 26 April 2021 .
- ^ "Баграт Хутаба встретился с Чрезвычайным и Полномочным Послом Исламской Республики Пакистан" . mfaapsny.org . Retrieved 26 April 2021 .
- ^ «Перу не может отрицать Южную Осетии и признание Абьясии за ее независимость» (PDF) . Риа Новости . 19 ноября 2009 г.
- ^ Рамирес-Гастон 2018 , с. 79
- ^ Рамирес-Гастон 2018 , с. 80
- ^ «Польша поддерживает Грузию по поводу кризиса по признанию россии» . Архивировано из оригинала 31 августа 2008 года.
- ^ «Польша осуждает российское признание Южной Осетии, Абхазию» . Архивировано с оригинала 9 марта 2016 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ Кавказа Португальское правительство следует за «С беспокойством» кризис в архивировании 1 сентября 2008 года на машине Wayback , Public , 26 августа 2008 г.
- ^ Румынское министерство иностранных дел Официальное заявление , 26 августа 2008 года.
- ^ «Сан -Марино для установления отношений с Абхазией: голос России» . Архивировано из оригинала 3 июня 2013 года.
- ^ "Посольство Республики Абхазия в Российской Федерации – Делегация МИД Абхазии прибыла в Республику Сан-Марино" . embabhazia.ru .
- ^ «Относительно признания Абхазии - Секретариат государственного государства по иностранным делам - Республика Сан -Марино» . www.esteri.sm .
- ^ "Южная Осетия и Абхазия попросили признать их независмость Италию и Сан-Марино" . ИА REGNUM .
- ^ "Mauro Murgia Appointed Representative of the Foreign Ministry of the Republic of Abkhazia for San Marino"Полем mfaapsy.org
- ^ "Сообщение пресс-службы Министерства иностранных дел Республики Южная Осетия | Министерство иностранных дел" . www.mfa-rso.su .
- ^ "Послание Председателя Парламента Республики Южная Осетия А. Тадтаева | Министерство иностранных дел" . www.mfa-rso.su .
- ^ "Сообщение пресс-службы Министерства иностранных дел Республики Южная Осетия" . www.mfa-rso.su .
- ^ "Саудовская Аравия с пониманием отнеслась к действиям России в Южной Осетии" . Gazeta.Ru . 4 September 2008 . Retrieved 4 September 2008 .
- ^ «Грузинская оценка позиции королевства о независимости Абхазии и Осетии» (на арабском языке). Аль-Джазира. 24 мая 2012 года.
{{cite news}}: Cs1 maint: нераспознанный язык ( ссылка ) - ^ «MFA выражает« беспокойство »по поводу Кавказа» . Архивировано из оригинала 30 августа 2008 года.
- ^ «Сербия не узнает регионы Грузии» . 3 сентября 2008 г. Получено 12 апреля 2021 года .
- ^ Сербия Маллс признание Абхазии, С. Асетия Архивирована 30 мая 2012 года на машине Wayback , голос России, 27 мая 2012 г.
- ^ Диалог, который состоялся в рамках Форума, будет способствовать решению наиболее актуальных международных и региональных проблем, – Алан Тадтаев , parliamentrso.org 06.07.2019. .
- ^ «Словацкая республика не одобряет признание Абхазии и Южной Осетии Российской Федерацией» . Архивировано из оригинала 26 августа 2008 года.
- ^ «Три премьер -министра ЕС призывают к Caucasus Peace, stability_english_xinhua» . Архивировано с оригинала 4 марта 2016 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный «Африканское пресс -агентство, 5 октября 2008 года» . 13 сентября 2023 года.
- ^ «Сомали приветствует российские корабли в пиратской борьбе: посол» . Agence France-Presse . 1 октября 2008 года. Архивировано с оригинала 5 октября 2008 года . Получено 1 октября 2008 года .
- ^ [4] Мариг онлайн, Сомали: Сомалийское правительство отрицает признание Абхазии .
- ^ «Заур Гваджава провел встречу с Джозефом Нокси, послом Южной Африки в Венесуэле» . mfaapsny.org .
- ^ «Внешний взгляд: российское партнерство Сеула» . United Press International. 7 октября 2008 года. Архивировано с оригинала 15 января 2009 года . Получено 30 октября 2012 года .
- ^ «Дмитрий Медоев провел ряд встреч в Республике Корея и России Дальний Восток» . Res. 12 февраля 2018 года . Получено 25 декабря 2018 года .
- ^ «Antena 3 TV. Онлайн -сериал, новости, видео, телевизионные программы (Испания, ЕС)» . Antena3.com . 4 мая 2016 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года . [ Постоянная мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ «Sudan Un Andervoy говорит, что война в Грузии ослабила международное давление на свою страну» . 3 сентября 2008 года. Архивировано с оригинала 16 апреля 2016 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ Москва признает грузинские регионы повстанцев , архивные 31 августа 2008 года в The Wayback Machine , Warsaw Business Journal, 26 августа 2008 г.
- ^ BILDT: Россия «нарушает международное право», архивировав 27 августа 2008 года на машине Wayback , местный, 26 августа 2008 года.
- ^ Кремль говорит, что шаг может иметь неприятные последствия , Financial Times, 27 августа 2008 года.
- ^ «Швеция: признание Южной Осетии и Абхазии Россией -« плохая шутка » » . Архивировано из оригинала 13 декабря 2009 года . Получено 10 декабря 2009 года .
- ^ «Кабинет кабинета высказывается в конфликте Грузии» . SWI SWISSINFO.CH . Архивировано из оригинала 19 сентября 2012 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Швейцария призывает к политическому решению конфликта Грузии - Daily's Daily Online» . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ Xuequan, MU (4 сентября 2008 г.). «Швейцария призывает к политическому решению конфликта Грузии» . Женева : Синьхуа . Архивировано из оригинала 3 сентября 2008 года . Получено 1 декабря 2020 года .
- ^ Крайнова, Наталья (1 сентября 2008 г.). «С. Осетия говорит о присоединении к России» . Москва времена . Архивировано из оригинала 2 сентября 2008 года . Получено 1 сентября 2008 года .
- ^ «Таджикистан призывает Россию, Грузию, решить конфликт с помощью политических, дипломатических средств» . Синьхуа . 30 августа 2008 года. Архивировано с оригинала 1 сентября 2008 года . Получено 30 августа 2008 года .
- ^ «№: 158 - 26 августа 2008 года, пресс -релиз, касающийся независимости Грузии (неофициальный перевод)» . Республика Турция Министерство иностранных дел . Архивировано с оригинала 19 апреля 2016 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ Несколько стран более осуждают Указ президента России, архивные 24 ноября 2011 года на машине Wayback
- ^ «Министерство иностранных дел Украины» . Архивировано с оригинала 29 сентября 2012 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ «Украина не будет поддерживать независимость Южной Осетии, Абхазии-президента-официального веб-сайта президента Украины» . www.president.gov.ua. Архивировано из оригинала 31 августа 2008 года . Получено 27 августа 2008 года .
- ^ «Крым призывает к признанию сепаратистов Грузии» . Финансовые времена . 17 сентября 2008 года. Архивировано с оригинала 15 августа 2009 года . Получено 20 сентября 2008 года .
- ^ Парламент Крыма поддержал независимость Южной Осетии и Абхазии (на русском языке). allcrimea.net. 17 сентября 2008 г. Получено 8 августа 2013 года .
- ^ «Признание грузинских регионов говорит Крым Украины» . Рейтер . 17 сентября 2008 года. Архивировано с оригинала 12 января 2009 года . Получено 20 сентября 2008 года .
- ^ «Выборы Януковича открывают крымскую сепаратистскую угрозу» . Джеймстаун . Фонд Джеймстауна . 2 марта 2010 г. Получено 14 декабря 2020 года .
- ^ Грищенко считает правильным непризнание Косово, Абхазии и Южной Осетии (на русском языке). liga.net. 11 октября 2010 года. Архивировано с оригинала 2 октября 2011 года . Получено 7 июня 2010 года .
- ^ «Янукович сигнализирует Украина, возможно, не распознавать Южную Оссетии, Абхазию» . Апа 3 марта 2010 г. Архивировано с оригинала 25 марта 2012 года . Получено 8 августа 2013 года .
- ^ «Украина не признавать независимость Абхазии и Южной Осетии - Гришченко» . Unian. 14 мая 2010 г. Получено 7 июня 2010 года .
- ^ «Янукович: признание независимости Абхазии, Южной Осетии и Косово нарушает международное право» . Kyiv Post. 4 июня 2010 г. Получено 7 июня 2010 года .
- ^ «Украина сдерживает судно, несущие сигареты из Абхазии» . Свобода и демократия часы. 5 января 2018 года . Получено 2 января 2019 года .
- ^ «Милибэнд взрывает Россию двигаться» . Архивировано из оригинала 2 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ "Медведев говорит ЕС России нанести удар по враждебным действиям" Bloomberg.com 31 августа 2008 г.
- ^ Президент Буш осуждает действия, предпринятые президентом России в отношении Грузии . Управление пресс -секретаря. 26 августа 2008 г.
- ^ Россия признает грузинских повстанцев BBC News 26 августа 2008 года.
- ^ «Пресс -заявление после переговоров с президентом Франции Николасом Саркози» (пресс -релиз). Москва: президент России . 12 августа 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 23 августа 2008 года . Получено 30 августа 2008 года .
- ^ Буш критикует действия Москвы в Грузии Рейтер 15 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный «Президент Буш обсуждает ситуацию в Грузии, призывает Россию прекратить военные операции» (пресс -релиз). Белый дом . 13 августа 2008 г. Получено 30 августа 2008 года .
- ^ «Российский представитель MFA Андреи Нестеренко Комментарий в связи с заявлением президента США Джорджа Буша о Южной Осетии» (пресс -релиз). Министерство иностранных дел (Россия) . 14 августа 2008 г. Получено 30 августа 2008 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Чейни поддерживает членство в НАТО в Джорджии Нью -Йорк Таймс 4 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ Deciant Cheney Conse Georgia присоединится к Nato Guardian 5 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Стивен Ли Майерс/Том Шанкер: Помощники Буша говорят, что действия России в Грузии ставят под угрозу связи , Нью -Йорк Таймс 14 августа 2008 года.
- ^ "KM.RU – новости, экономика, автомобили, наука и техника, кино, музыка, спорт, игры, анекдоты, курсы валют | KM.RU" . www.km.ru . Archived from the original on 26 November 2009.
- ^ «Достижение занятых территорий Грузии через обмены» . Совет американских послов .
- ^ "Сообщение Оперативного штаба МИД Узбекистана" . Uzbek Ministry of Foreign Affairs . 29 October 2020 . Retrieved 30 October 2020 .
- ^ «Вьетнам поддерживает мирные решения в области споров» . Архивировано из оригинала 7 сентября 2008 года . Получено 7 сентября 2008 года .
- ^ «Заур Гваджава участвовал в праздновании по случаю 77 -й годовщины Вьетнама» . Получено 26 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ «B92 - Новости -« Косово - это не Осетия и Абхазия » - Интернет, радио и телевизионная станция; последние новости от Сербии» . B92.net. 27 августа 2008 г. Получено 3 октября 2008 года .
- ^ «Голоса талата уважения к воле народов С. Осетии и Абхазии» . Сегодняшний Заман . 28 августа 2008 года. Архивировано с оригинала 1 сентября 2008 года . Получено 28 августа 2008 года .
- ^ «Информация о встрече В. Чирикбы с послами Сирии и Палестины» . Абхаз Министерство иностранных дел. 2 декабря 2015 года . Получено 8 ноября 2020 года .
- ^ «Инал Ардзинба встретился с Абделем Хафизом Нофалом, необыкновенным послом и полейпотендартом Палестины в Российскую федерацию» . Абхаз Министерство иностранных дел. 30 мая 2022 года . Получено 1 июня 2022 года .
- ^ "Interfax" . Архивировано из оригинала 9 мая 2013 года . Получено 12 января 2012 года .
- ^ Али, Хазиханов (1992). «Gamsakhurdia и Dudayev принимают совместное коммюнике». Ежедневный отчет: Центральная Евразия . Сервис. п. 55
- ^ «Чеченский представитель Абхазии назначен» . Джеймстаун . 12 декабря 1997 года.
- ^ «Центральная Азия и Кавказ» . Центральная Азия и Кавказ (1–3). Центральная Азия и Кавказ, Информационный и аналитический центр: 155. 2000.
- ^ «Резолюция 1808: ситуация в Грузии» . Совет Безопасности Организации Объединенных Наций . 15 апреля 2008 г. Получено 12 мая 2021 года .
- ^ «Совет Безопасности расширяет мандат миссии наблюдателя Грузии до 15 октября, единогласно приняв резолюцию 1808 (2008)» . Объединенные Нации. 15 апреля 2008 г. Получено 22 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ «Главные голоса ООН о российском переезде по Южной Осетии, Абхазия» . Синьхуанет. 27 августа 2008 года. Архивировано с оригинала 11 октября 2009 года . Получено 29 июня 2010 года .
- ^ не сравнивайте косо в чем . -либо » «ООН :
- ^ Барбара Старк: Международное право и его недовольство: противодействие кризисам , Нью -Йорк (Нью -Йорк): издательство Кембриджского университета 2015, с. 243.
- ^ «Российские союзники не могут поддержать Москву на анклавах» . Рейтер. 4 сентября 2008 года. Архивировано с оригинала 15 сентября 2008 года . Получено 25 августа 2021 года .
- ^ Нынешняя ситуация толкает Абхазию и ЮО в систему коллективной безопасности – Бордюжа (на русском языке). Ереван : Новости Армения. 2 сентября 2008 года. Архивировано с оригинала 15 сентября 2008 года . Получено 3 сентября 2008 года .
- ^ Данилиан, Эмиль (2 сентября 2008 г.). «Саркисиан обсуждает кризис в Грузии с российским лидером» . Радио Свободная Европа/Радио Свобода . Получено 3 сентября 2008 года .
- ^ Выводы президентства необычайного Европейского совета, состоявшегося в Брюсселе (1 сентября 2008 г.). Полем BBC News . 1 сентября 2008 г.
- ^ «Русское раздражение по поводу позиции Швеции» (пресс -релиз). Посольство России в Стокгольме . 27 августа 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 20 мая 2007 года . Получено 29 августа 2008 года .
- ^ Русское раздражение по поводу шведского отношения архивировано 23 августа 2011 года в The Wayback Machine , Dagens Nyheter, 28 августа 2008 года.
- ^ Среда в европейском кризисе , Карл Билдт - все эти дни, 27 августа 2008 года.
- ^ «ЕС осуждает решение России признать независимость Абхазии» . Архивировано из оригинала 16 сентября 2008 года.
- ^ Лухтерхандт, Отто (29 августа 2008 г.). «Бывшие советские государства боятся российской агрессии» . Шпигель . Получено 1 сентября 2008 года .
- ^ Европа говорит о «санкциях» против Москвы, заархивированной 31 августа 2008 года в The Wayback Machine , Europe 1 Radio, 28 августа 2008 года.
- ^ Уокер, Маркус; Галлони, Алессандра ; Чазан, парень; Миллер, Джон У. (28 августа 2008 г.). «ЕС остается разделенным на наказание России» . Wall Street Journal . Берлин , Париж, Лондон и Брюссель . Получено 2 сентября 2008 года .
- ^ «Вторжение Украины: Запад вводит санкции в отношении России Путина и Лавров» . BBC News . 26 февраля 2022 года. Архивировано из оригинала 28 февраля 2022 года . Получено 8 июня 2022 года .
- ^ «Австралия планирует ввести санкции непосредственно на президента России Владимира Путина» . ABC News . 25 февраля 2022 года . Получено 8 июня 2022 года .
- ^ Совместное заявление министров иностранных министров о Грузии Архивировало 31 августа 2008 года на машине Wayback . America.gov. 27 августа 2008 г.
- ^ «Российская информация о МИД и комментарии отдела прессы в связи с заявлением G7, касающимися признания России за независимость Южной Осетии и Абхазии» (пресс -релиз). Министерство иностранных дел (Россия) . 29 августа 2008 г. Получено 29 августа 2008 года .
- ^ «G7 оправдал грузинскую агрессию» . Kommersant . 29 августа 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 31 августа 2008 года . Получено 29 августа 2008 года .
- ^ "НАТО ОТКАЗАЛОСЬ ПРИЗНАТЬ ЮЖНУЮ ОСЕТИЮ" . Retrieved 10 December 2009 .
- ^ «Председатель ОБСЕ осуждает признание России Южной Осетии, независимости Абхазии» . Получено 24 апреля 2021 года .
- ^ Администратор «Соаре, чтобы посетить Кавказ на следующей неделе» . Архивировано из оригинала 14 июля 2012 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ Поддержка России на SCO Summit The Hindu : Vladimir Radyuhin, Москва .
- ^ «Лидеры ШОС говорят, что не могут быть решены, просто используя force_english_xinhua» . Архивировано с оригинала 3 марта 2016 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ Марк Тран, Джулиан Боргер из Киева и Ян Трейнор в Брюсселе (28 августа 2008 г.). «ЕС угрожает санкциям против России | World News | Guardian.co.uk» . Лондон: Guardian.co.uk . Получено 3 октября 2008 года .
- ^ «Россия: Кремль пытается надеть смелое лицо после дипломатической пощечины по Грузии» . Eurasianet.org . Архивировано из оригинала 5 сентября 2008 года . Получено 5 апреля 2016 года .
- ^ Kommersant: «Союзники подвели его», архивировали 6 сентября 2008 года на машине Wayback , 29-2008 августа.
- ^ Официальное объявление организации Архивировало 14 сентября 2008 года на машине Wayback на саммите Душанбе 28 августа 2008 года (на китайском языке) .
- ^ Официальное объявление организации Архивировало 14 сентября 2008 года на машине Wayback на саммите Душанбе 28 августа 2008 года (на русском языке) .
- ^ «Декларация на главе штата Шанхайская организация сотрудничества (полный текст . » )
- ^ «Инал Ардзинба встретился с государственным секретарем профсоюзного штата Россия и Беларуси» . mfaapsny.org . Получено 2 марта 2022 года .
- ^ "В Москве состоялась встреча Инала Ардзинба с Госсекретарем Союзного государства России и Белоруссии Дмитрием Мезенцевым" . mfaapsny.org . Retrieved 23 March 2022 .
- ^ «О взаимодействии между Республикой #abkazia и #UnionState и трехсторонним форматом с #Russia 🇷🇺 и #belarus 🇧🇾 MFA объявили, что соглашение было достигнуто на регулярных консультациях» . Twitter.com . Получено 19 октября 2022 года .
- ^ ХАМАС приветствует признание независимости Абхазии и Южной Осетии (на русском языке). Gazeta.ru. 26 августа 2008 г. Получено 26 августа 2008 года .
- ^ «Только Хамас Палестины поддерживает признание Кремля Абхазией, Южная Осетия» . Грузинский ежедневно. 27 августа 2008 г. Получено 27 августа 2008 года .
- ^ Coughlin, Con; Бломфилд, Адриан (27 августа 2008 г.). «Грузия: Европа объединяется, чтобы осудить Кремля» . Ежедневный телеграф . Лондон Архивировано из оригинала 12 января 2022 года . Получено 27 августа 2008 года .
- ^ «Баграт Хутаба встретился с послом Йемена в Сирию» . MFA Apsny . Получено 19 марта 2021 года .
- ^ «Заявление Генерального секретаря об Абхазии» . Неспособный 29 августа 2008 г. Получено 13 сентября 2009 года .
- ^ «Общие вопросы» . ISO - Агентство по техническому обслуживанию для ISO 1366 кодов страны . Получено 28 марта 2009 года .
- ^ «ISO 3166-1 и Country Coded Top Level Domains (CCTLDS)» . ISO - Агентство по техническому обслуживанию для кодов страны ISO 3166 . Получено 29 июня 2009 года .
- ^ «Косово, Траннистрия, Абхазия домены высшего уровня» . Dnxpert. 4 сентября 2008 года. Архивировано с оригинала 6 декабря 2008 года . Получено 28 марта 2009 года .
Источники
[ редактировать ]- Рамирес-Гастон Лекка, Фернандо (6 ноября 2018 года). Решение -принятие Перу в Организации Объединенных Наций перед лицом вооруженных вмешательств России в Абьясии (методы). Дипломатическая академия Перу Хавьер Перес де Куэллар.
- 2008 в Грузии (страна)
- Рус-георгическая война
- Политика Грузии (страна)
- Абхазия -Руссия Отношения
- Россия -юг Осетия Отношения
- Грузия (страна) –russia отношения
- Иностранные отношения Абхазии
- Иностранные отношения Южной Осетии
- 2008 в Абхазии
- 2008 в Южной Осетии
- Дипломатическое признание
- Абхазия - Юг Осетия Отношения

