Канзас-Сити Чифс
| Канзас-Сити Чифс | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Основан 14 августа 1959 г [ 1 ] [ 2 ] Первый сезон : 1960 год. Игра на стадионе «Эрроухед» Канзас-Сити, Миссури Штаб-квартира находится в системы здравоохранения Канзасского университета. Учебном центре Канзас-Сити, Миссури [ 3 ] | |||||
| |||||
| Принадлежность к лиге / конференции | |||||
Американская футбольная лига (1960–1969)
National Football League (1970–present)
| |||||
Current uniform | |||||
| Team colors | Red, gold, white[4][5][6] | ||||
| Mascot | Warpaint (1963–1988, 2009–2020) K. C. Wolf (1989–present) | ||||
| Website | chiefs.com | ||||
| Personnel | |||||
| Owner(s) | Hunt family[7][8] | ||||
| Chairman | Clark Hunt | ||||
| CEO | Clark Hunt | ||||
| President | Mark Donovan | ||||
| General manager | Brett Veach | ||||
| Head coach | Andy Reid | ||||
| Team history | |||||
| |||||
| Team nicknames | |||||
| Championships | |||||
League championships (6†)
| |||||
| Conference championships (4) | |||||
| Division championships (16) † Does not include AFL Championships won the same season as Super Bowls. | |||||
| Playoff appearances (26) | |||||
| Home fields | |||||
| |||||
| Team owner(s) | |||||
| |||||
« Канзас -Сити Чифс» — профессиональная команда по американскому футболу , базирующаяся в Канзас-Сити, штат Миссури . «Чифс» соревнуются в Национальной футбольной лиге (НФЛ) в качестве клуба-члена дивизиона Конференции американского футбола (AFC) Западного .
Команда была основана в 1959 году под названием « Далласские техасцы» бизнесменом Ламаром Хантом и была членом-учредителем Американской футбольной лиги (AFL). [ 12 ] Весной 1963 года команда переехала в Канзас-Сити. [ 13 ] [ 14 ] и принял свое нынешнее название. [ 15 ] [ 16 ] «Чифс» присоединились к НФЛ в результате слияния в 1970 году , и стоимость команды оценивается более чем в 3,7 миллиарда долларов. [ 17 ] После смерти Ханта в 2006 году его жена Норма и дети стали законными владельцами команды. После смерти Нормы в 2023 году дети Хант унаследовали ее долю во франшизе. Кларк Хант , один из детей Ханта, занимает пост председателя и генерального директора с 2006 года и имеет высшую власть в принятии кадровых решений. Он также является представителем команды на собраниях владельцев лиги.
«Чифс» выиграли три чемпионата AFL в 1962 , 1966 и 1969 годах . [ 18 ] [19] and were the second AFL team (after the New York Jets) to defeat an NFL team in an AFL–NFL World Championship Game, now the Super Bowl, when they defeated the Minnesota Vikings in Super Bowl IV. That victory on January 11, 1970, was the final game before the leagues' merger went into full effect. The Chiefs were also the second team, after the Green Bay Packers (whom they played in Super Bowl I), to appear in more than one Super Bowl (and the first AFL team to do so) as well as the first to appear in the championship game in two different decades. Despite post-season success early in the franchise's history, winning five of their first six postseason games, the team struggled to find success in the playoffs for decades, including losing ten of eleven playoff games from the 1993 AFC Championship Game to 2018, which included an eight-game losing streak. Since then, the Chiefs have risen to dynastic performance under head coach Andy Reid, quarterback Patrick Mahomes, and tight end Travis Kelce, appearing in four Super Bowls since 2019 and winning three, LIV, LVII, and LVIII.[20][21][22]
Franchise history
[edit]American Football League
[edit]In 1959, Lamar Hunt began discussions with other businessmen to establish a professional football league that would rival the National Football League.[18][23][24] Hunt's desire to secure a football team was heightened after watching the 1958 NFL Championship Game between the New York Giants and Baltimore Colts.[23][25] After unsuccessful attempts to purchase and relocate the NFL's Chicago Cardinals to his hometown of Dallas, Texas,[18][26] Hunt went to the NFL and asked to create an expansion franchise in Dallas. The NFL turned him down, so Hunt then established the American Football League and started his own team, the Dallas Texans, to begin play in 1960.
Hunt hired a little-known assistant coach from the University of Miami football team, Hank Stram, to be the team's head coach[23] after the job offer was declined by Bud Wilkinson and Tom Landry.[23] After Stram was hired, Don Klosterman was hired as head scout, and was credited by many for bringing a wealth of talent to the Texans after luring it away from the NFL, often hiding players and using creative means to land them.
The Texans shared the Cotton Bowl with the NFL's Dallas Cowboys for three seasons. The Texans were to have exclusive access to the stadium until the NFL put an expansion team, the Dallas Cowboys, there.[23] While the team averaged a league-best 24,500 at the Cotton Bowl, the Texans gained less attention due to the AFL's relatively lower profile compared to the NFL's.[23] In the franchise's first two seasons, the team managed only an 8–6 and 6–8 record, respectively.[27]
In their third season, the Texans tallied an 11–3 record and a berth in the team's first American Football League Championship Game, against the Houston Oilers.[26][27] The game was broadcast nationally on ABC and the Texans defeated the Oilers 20–17 in double overtime.[26] The game lasted 77 minutes and 54 seconds, which, at the time, was the longest game in the history of professional American Football. It is still the longest championship game in American Football League history.[26]
It turned out to be the last game the team would play as the Dallas Texans. Despite competing against a Cowboys team that managed only a 9–28–3 record in their first three seasons, Hunt decided that the Dallas–Fort Worth media market could not sustain two professional football franchises.[26][28] He considered moving the Texans to either Atlanta or Miami for the 1963 season.[26] He was ultimately swayed by an offer from Kansas City Mayor Harold Roe Bartle.[26][28][29] Bartle promised to triple the franchise's season ticket sales and expand the seating capacity of Municipal Stadium to accommodate the team.[26][28][29]
Hunt agreed to relocate the franchise to Kansas City on May 22, 1963,[13][14] and on May 26, the team was renamed the Kansas City Chiefs.[15][26][28][29] Hunt and head coach Hank Stram initially planned to retain the Texans name, but a fan contest determined the new "Chiefs" name in honor of Mayor Bartle's nickname that he acquired in his professional role as Scout Executive of the St. Joseph and Kansas City Boy Scout Councils, and founder of the Scouting Society, the Tribe of Mic-O-Say.[26][29] Despite the historical use of Native American features, it has been acknowledged that the team's naming was not a direct reference to Native Americans but only to Bartle's nickname "Chief".[30][31] Business Insider journalist Meredith Cash even stated in January 2020 that Bartle "insisted on the team being named after himself" and that "Bartle was known as Chief Lone Bear within Mic-O-Say circles, and eventually the nickname "Chief" caught on among people throughout Kansas City."[32]
The franchise became one of the strongest teams in the now thriving American Football League,[18] with the most playoff appearances for an AFL team (tied with the Oakland Raiders), and the most AFL Championships (three).[26] The team's dominance helped Lamar Hunt become a central figure in negotiations with NFL Commissioner Pete Rozelle to agree on an AFL–NFL merger.[26][33] In the meetings between the two leagues, a merged league championship game was agreed to be played in January 1967 following the conclusion of the leagues' respective 1966 seasons. Hunt insisted on calling the game the "Super Bowl" after seeing his children playing with a popular toy at the time, a Super Ball.[26][33][34] While the first few games were designated the "AFL–NFL World Championship Game", the Super Bowl name became its officially licensed title in years to come.
The Chiefs cruised to an 11–2–1 record in 1966, and defeated the defending AFL Champion Buffalo Bills in the AFL Championship Game.[35] The Chiefs were invited to play the NFL's league champion Green Bay Packers in the first AFL–NFL World Championship Game. Kansas City and Green Bay played a close game for the first half, but Green Bay took control in the final two quarters, winning the game by a score of 35–10.[26] The Chiefs lost the game but gained the respect of several Packers opponents following the game.[36] The Chiefs' inter-league match-up with the Packers was not the last time that they would face an NFL opponent, especially on the championship stage.[26] The following August, Kansas City hosted the NFL's Chicago Bears in the 1967 preseason and won the game 66–24.[26]
Despite losing to the division rival Oakland Raiders twice in the regular season in 1969, the two teams met for a third time in the AFL Championship Game, where Kansas City won 17–7.[27] Backup quarterback Mike Livingston led the team in a six-game winning streak after Len Dawson suffered a leg injury which kept him out of most of the season's games.[26]
While getting plenty of help from the club's defense, Dawson returned from the injury and led the Chiefs to Super Bowl IV.[26] Against the NFL champion Minnesota Vikings,[18] who were favored by 12+1⁄2, the Chiefs dominated the game 23–7 to claim the team's first Super Bowl championship.[26] Dawson was named the game's Most Valuable Player after completing 12-of-17 passes for 142 yards and one touchdown, with 1 interception.[37] The following season, the Chiefs and the rest of the American Football League merged with the National Football League after the AFL–NFL merger became official.[26] The Chiefs were placed in the American Football Conference's West Division.[27]
From 1960 to 1969, the Chiefs/Texans won 87 games, which is the most in the ten-year history of the AFL.[38]
Hank Stram leaves team
[edit]In 1970, the Chiefs won only seven games in their first season in the NFL and missed the playoffs.[27] The following season, the Chiefs tallied a 10–3–1 record and won the AFC West Division.[39] Head coach Hank Stram considered his 1971 Chiefs team as his best, but they failed to capture their championship dominance from 1969.[39] Most of the pieces of the team which won Super Bowl IV two years earlier were still in place for the 1971 season.[39] The Chiefs tied with the Miami Dolphins for the best record in the AFC, and both teams met in a Christmas Day playoff game which the Chiefs lost 27–24 in double overtime.[39] The Dolphins outlasted the Chiefs with a 37-yard field goal.[39] The game surpassed the 1962 AFL Championship Game as the longest ever at 82 minutes and 40 seconds.[39] The game was also the final football game at Kansas City's Municipal Stadium.[39]
In 1972, the Chiefs moved into the newly constructed Arrowhead Stadium at the Truman Sports Complex outside of downtown Kansas City.[39] The team's first game at Arrowhead was against the St. Louis Cardinals, a preseason game that the Chiefs won 24–14.[39] Linebacker Willie Lanier and quarterback Len Dawson won the NFL Man of the Year Award in 1972 and 1973, respectively.
The Chiefs did not return to the post-season for the remainder of the 1970s, and the 1973 season was the team's last winning season for seven years.[39] Hank Stram was fired following a 5–9 season in 1974, and many of the Chiefs' future Hall of Fame players departed by the middle of the decade.[39] From 1975 to 1988, the Chiefs had become a team that rarely won, which provided Chiefs fans with nothing but futility.[40][41] Five head coaches struggled to achieve the same success as Stram, compiling an 81–121–1 record.[40]
In 1980, Coach Marv Levy cut future Hall of Fame Kicker Jan Stenerud for little-known Nick Lowery, who would become the most accurate kicker in NFL history over the next fourteen years. In 1981, running back Joe Delaney rushed for 1,121 yards and was named the AFC Rookie of the Year.[42] The Chiefs finished the season with a 9–7 record and entered the 1982 season with optimism.[42] The NFL Players Association strike curbed the Chiefs' chances of returning to the postseason for the first time in over a decade.[42] The Chiefs tallied a 3–6 record[27] and in the off-season, Joe Delaney died while trying to save several children from drowning in a pond near his home in Louisiana.[43]
The Chiefs drafted quarterback Todd Blackledge over future greats such as Jim Kelly and Dan Marino in the 1983 NFL draft.[44][45] Blackledge never started a full season for Kansas City while Kelly and Marino played Hall of Fame careers.[45] While the Chiefs struggled on offense in the 1980s, they had a strong defensive unit consisting of Pro Bowlers such as Bill Maas, Albert Lewis, Art Still and Deron Cherry.[42]
John Mackovic took over head coaching duties for the 1983 season after Marv Levy was fired.[42] Over the next four seasons, Mackovic coached the Chiefs to a 30–34 record, but took the team to its first postseason appearance in 15 years in the 1986 NFL playoffs.[27] They lost to the New York Jets in the wild-card round.[42] Despite leading the Chiefs to only their third winning season and second playoff appearance since the merger, Mackovic was fired for what Hunt described as a lack of chemistry.[46] Frank Gansz served as head coach for the next two seasons, but won only eight of 31 games.[42]
Marty Schottenheimer era (1989–1998)
[edit]
On December 19, 1988, owner Lamar Hunt hired Carl Peterson as the team's new president, general manager, and chief executive officer. Peterson fired head coach Frank Gansz two weeks after taking over and hired Marty Schottenheimer as the club's seventh head coach.[42] In the 1988 and 1989 NFL Drafts, the Chiefs selected both defensive end Neil Smith and linebacker Derrick Thomas, respectively.[42][48] The defense that Thomas and Smith anchored in their seven seasons together was a big reason why the Chiefs reached the postseason in six straight years.[49]
In Schottenheimer's ten-season tenure as head coach, the Chiefs became a perennial playoff contender, featuring offensive players including Steve DeBerg, Christian Okoye, Stephone Paige and Barry Word, a strong defense, anchored by Thomas, Smith, Albert Lewis and Deron Cherry, and on special teams, Nick Lowery, who was then the most accurate kicker in NFL History.[18] The team recorded a 101–58–1 record, and clinched seven playoff berths.[50] The Chiefs' 1993 season was the franchise's most successful in 22 years.[48] With newly acquired quarterback Joe Montana and running back Marcus Allen, two former Super Bowl champions and Most Valuable Player Award winners, the Chiefs further strengthened their position in the NFL.[48] The 11–5 Chiefs defeated the Pittsburgh Steelers and Houston Oilers on their way to the franchise's first AFC Championship Game appearance against the Buffalo Bills.[48] The Chiefs were overwhelmed by the Bills and lost the game by a score of 30–13.[48] The Chiefs' victory on January 16, 1994, against the Oilers remained the franchise's last post-season victory for 22 years until their 30–0 victory over the Houston Texans on January 9, 2016.
In the 1995 NFL playoffs, the 13–3 Chiefs hosted the Indianapolis Colts in a cold, damp late afternoon game at Arrowhead Stadium.[27][48] Kansas City lost the game 10–7 against the underdog Colts, after kicker Lin Elliot missed three field-goal attempts and quarterback Steve Bono threw three interceptions.[48] The Chiefs selected tight end Tony Gonzalez with the 13th overall selection in the 1997 NFL draft, a move which some considered to be a gamble being that Gonzalez was primarily a basketball player at California. During a 1997 season full of injuries to starting quarterback Elvis Grbac, backup quarterback Rich Gannon took the reins of the Chiefs' offense as the team headed to another 13–3 season.[27][48] Head coach Marty Schottenheimer chose Grbac to start the playoff game against the Denver Broncos despite Gannon's successes in previous weeks.[48] Grbac's production in the game was lacking, and the Chiefs lost to the Broncos 14–10.[48] Denver went on to capture their fifth AFC Championship by defeating Pittsburgh, and then defeated the Green Bay Packers in Super Bowl XXXII. Coach Schottenheimer announced his resignation from the Chiefs following the 1998 season.
Following Schottenheimer's resignation, defensive coordinator Gunther Cunningham took over coaching duties for the next two seasons, compiling a 16–16 record.[48] By the end of the Chiefs' decade of regular-season dominance, Gannon had signed with the Oakland Raiders, Neil Smith signed with the Denver Broncos, and Derrick Thomas was paralyzed in a car accident on January 23, 2000.[48] Thomas died from complications of his injury weeks later.[48] After allegedly reading online that he would be relieved of duties, head coach Gunther Cunningham was fired.[51][52]
Dick Vermeil years (2001–2005)
[edit]Looking to change the Chiefs' game plan which relied on a tough defensive strategy for the past decade, Carl Peterson contacted Dick Vermeil about the Chiefs' head coaching vacancy for the 2001 season.[51] Vermeil previously led the St. Louis Rams to a victory in Super Bowl XXXIV.[52] Vermeil was hired on January 12. The Chiefs then traded a first-round draft pick in the 2001 NFL draft to St. Louis for quarterback Trent Green and signed free agent running back Priest Holmes to be the team's cornerstones on offense.[52]

In 2003, Kansas City began the season with nine consecutive victories, a franchise record.[52] They finished the season with a 13–3 record and the team's offense led the NFL in several categories under the direction of USA Today's Offensive Coach of the Year honoree, Al Saunders.[52] Running back Priest Holmes surpassed Marshall Faulk's single-season touchdown record by scoring his 27th rushing touchdown against the Chicago Bears in the team's regular-season finale.[52][53] The team clinched the second seed in the 2003 NFL playoffs and hosted the Indianapolis Colts in the AFC Divisional Playoffs.[52] In a game where neither team punted, the Chiefs lost the shoot-out 38–31.[52] It was the third time in nine seasons that the Chiefs went 8–0 at home in the regular season, only to lose their post-season opener at Arrowhead.
After a disappointing 7–9 record in 2004, the 2005 Chiefs finished with a 10–6 record but no playoff berth.[52] They were the fourth team since 1990 to miss the playoffs with a 10–6 record.[52] Running back Larry Johnson started in place of the injured Priest Holmes and rushed for 1,750 yards in only nine starts.[52] Prior to the Chiefs' final game of the season, head coach Dick Vermeil announced his retirement.[52] The Chiefs won the game 37–3 over the playoff-bound Cincinnati Bengals.[52]
Decline
[edit]Within two weeks of Vermeil's retirement, the Chiefs returned to their defensive roots with the selection of its next head coach.[52] The team introduced Herm Edwards, a former Chiefs scout and head coach of the New York Jets, as the team's tenth head coach after trading a fourth-round selection in the 2006 NFL draft to the Jets.[52] Quarterback Trent Green suffered a severe concussion in the team's season opener to the Cincinnati Bengals which left him out of play for eight weeks.[52] Backup quarterback Damon Huard took over in Green's absence and led the Chiefs to a 5–3 record.[52]

Kansas City was awarded a Thanksgiving Day game against the Denver Broncos in response to owner Lamar Hunt's lobbying for a third Thanksgiving Day game.[52] The Chiefs defeated the Broncos 19–10 in the first Thanksgiving Day game in Kansas City since 1969.[52] Hunt was hospitalized at the time of the game and died weeks later on December 13 due to complications of prostate cancer.[33][52] The Chiefs honored their owner for the remainder of the season, as did the rest of the league.[52]
Trent Green returned in the middle of the season, but struggled in the final stretch,[52] and running back Larry Johnson set an NFL record with 416 carries in a season.[52] Kansas City managed to clinch their first playoff berth in three seasons with a 9–7 record and a bizarre sequence of six losses from other AFC teams on New Year's Eve, culminating with a Broncos loss to the 49ers.[52] The Indianapolis Colts hosted the Chiefs in the Wild Card playoffs and defeated Kansas City 23–8.
In 2007, Trent Green was traded to the Miami Dolphins[54] leaving the door open for either Damon Huard or Brodie Croyle to become the new starting quarterback.[52] After starting the season with a 4–3 record, the Chiefs lost the remaining nine games when running back Larry Johnson suffered a season-ending foot injury and the quarterback position lacked stability with Huard and Croyle.[52] Despite the team's 4–12 record, tight end Tony Gonzalez broke Shannon Sharpe's NFL record for touchdowns at the position (63) and defensive end Jared Allen led the NFL in quarterback sacks with 15.5.[27]

The Chiefs began their 2008 season with the youngest team in the NFL.[55] The starting lineup had an average of 25.5 years of age.[55] By releasing several veteran players such as cornerback Ty Law and wide receiver Eddie Kennison and trading defensive end Jared Allen,[56] the Chiefs began a youth movement.[55][57] The Chiefs had a league-high thirteen selections in the 2008 NFL draft and chose defensive tackle Glenn Dorsey and offensive lineman Branden Albert in the first round. Analysts quickly called Kansas City's selections as the best of the entire draft.[56][58][59][60] Entering the season, the Chiefs were unsure if injury-prone quarterback Brodie Croyle, who was the incumbent starter, could be their quarterback in the long-term.[60] Croyle was injured in the team's first game of the season and Damon Huard started in Croyle's absence.[61] Tyler Thigpen become the third Chiefs starting quarterback in as many games for a start against the Atlanta Falcons.[62][63] After a poor performance by Thigpen, in which he threw three interceptions against the Falcons defense,[63] Huard was retained as the starting quarterback.[64] The Chiefs struggled off the field as much as on as tight end Tony Gonzalez demanded a trade and running back Larry Johnson was involved in legal trouble.[65][66][67][68]
Croyle returned for the Chiefs' game against the Tennessee Titans, but both he and Damon Huard suffered season-ending injuries in the game.[69] The Chiefs reorganized their offense to a new spread offense game plan focused around Tyler Thigpen.[57][61][70][71] The Chiefs' new offense was implemented to help Thigpen play to the best of his abilities and also following the absence of Larry Johnson, who was suspended for his off-field conduct.[66][70][71][72] The Chiefs made a huge gamble by using the spread offense, as most in the NFL believe that it cannot work in professional football, and also head coach Herm Edwards was traditionally in favor of more conservative, run-oriented game plans.[71]

The 2008 season ended with a franchise worst 2–14 record, where the team suffered historic blowout defeats nearly week-in and week-out,[27][63][73] a 34–0 shut-out to the Carolina Panthers,[74] and allowed a franchise-high 54 points against the Buffalo Bills.[75] The team's general manager, chief executive officer, and team president Carl Peterson resigned at the end of the season,[76] and former New England Patriots vice president of player personnel Scott Pioli was hired as his replacement for 2009.[77]
On January 23, 2009, Herm Edwards was fired as head coach,[78][79] and two weeks later Todd Haley signed a four-year contract to become Edwards' successor.[80][81] Haley had a background with Pioli, which made him an attractive hire for Pioli's first coach in Kansas City.
In April 2009, Tony Gonzalez was traded to the Atlanta Falcons after failed trade attempts over the previous two seasons.[82] Notably, head coach Todd Haley fired offensive coordinator Chan Gailey just weeks before the start of the 2009 season and chose to take on the coordinator duties himself. Throughout 2009 the Chiefs acquired veterans to supplement the Chiefs' young talent including Matt Cassel, Mike Vrabel, Bobby Engram, Mike Brown, Chris Chambers, and Andy Alleman.[83][84][85] The team finished with a 4–12 record, just a two-game improvement upon their record from the 2008 season.
For the 2010 season, the Chiefs made significant hires for their coaching staff, bringing on former Patriots assistant coaches Charlie Weis and Romeo Crennel to coach the offense and defense, respectively. The coaching additions proved to be very successful, as the Chiefs would go on to secure their first AFC West title since 2003. Their ten victories in the 2010 season combined for as many as the team had won in their previous three seasons combined.
On January 9, 2011, the Chiefs lost their home Wild Card playoff game to the Baltimore Ravens 30–7. Six players were chosen for the Pro Bowl: Dwayne Bowe, Jamaal Charles, Brian Waters, Tamba Hali, Matt Cassel, and rookie safety Eric Berry. Jamaal Charles won the FEDEX ground player of the year award and Dwayne Bowe led the NFL in touchdown receptions.[86]
For their first pick in the 2011 NFL draft, the team selected Jon Baldwin.[87] After a poor start, Haley was relieved of duties as head coach on December 12. Clark Hunt made note of "bright spots at different points this season," but felt that overall the Chiefs were not progressing.[88] The highest point of the 2011 season was an upset win against the Packers, who at that time, were undefeated with a 13–0 record. Defensive coordinator Romeo Crennel would be named the team's interim head coach for the remaining three games of the season, including the aforementioned Packers game.[89] On January 9, 2012, Crennel was named the 11th full-time head coach in Chiefs history.[90]
The 2012 Chiefs became the first team since the 1929 Buffalo Bisons to not lead in regulation through any of their first nine games.[91] The Chiefs tied their franchise-worst record of 2–14 and clinched the No. 1 overall pick in the 2013 NFL draft. It is the first time since the merger they have held the first overall pick.[92]
Reemergence and dynasty (2013–present)
[edit]Following the 2012 season, the Chiefs fired head coach Romeo Crennel and general manager Scott Pioli.[93][94] Former Philadelphia Eagles head coach Andy Reid was brought in as head coach to work with new general manager John Dorsey, a former Green Bay Packers head scout.[95][96]

The Chiefs acquired quarterback Alex Smith from the San Francisco 49ers for the Chiefs' second-round pick, 34th overall, in the 2013 draft and a conditional pick in the 2014 draft.[97] Matt Cassel was released shortly after. The Chiefs selected Eric Fisher with the first overall pick of the 2013 NFL draft.[98]
In 2013, the Chiefs started 9–0 for the second time in team history.[99] They led in their wildcard game against the Indianapolis Colts 38–10 shortly after halftime, but collapsed late and lost 45–44.[99]
In 2014, the Chiefs attempted to make the playoffs for the second straight season for the first time since 1995, finishing 9–7 and getting eliminated in Week 17.[100]
After a promising win for the Chiefs against Houston in Week 1, Kansas City went on a five-game losing streak culminating in a 16–10 loss to Minnesota and the loss of Jamaal Charles to a torn ACL.[101] They made one of the most improbable season comebacks in the NFL and won ten straight to improve their record from 1–5 to 11–5. The team clinched a playoff berth after a 17–13 win over Cleveland in Week 16 to become only the second post-merger NFL team to make the playoffs following a 1–5 start.[102]

The streak achieved by the Chiefs broke a franchise record for nine straight (2003, 2013) and second nine plus game win streak under Reid. After a Week 17 win over Oakland 23–17, the Chiefs achieved their longest winning streak in franchise history at ten games. They qualified for the playoffs, playing in the 2015 AFC Wild-Card playoff game, held at NRG Stadium in Houston, Texas on January 9, 2016. The Chiefs defeated the Houston Texans 30–0 to earn their first NFL playoff win in 23 seasons, dating back to the 1993–94 NFL playoffs, a win that also came in Houston. The Chiefs' Wild-Card playoff victory ended what was at the time the third-longest drought in the NFL, and it also ended a then NFL record eight-game playoff losing streak.[103] Riddled with injuries, they were defeated by the New England Patriots 27–20 in the AFC Divisional Round.[104]

The Chiefs first game of the 2016 season was against their division rival, the San Diego Chargers. After facing a 24–3 deficit with six minutes left in the 3rd quarter, the Chiefs engineered a 33–27 comeback win ending with a two-yard touchdown run by Alex Smith in overtime to give the Chiefs their largest regular season comeback to start the season at 1–0.[105] On Christmas Day, the Chiefs defeated the Denver Broncos 33–10 to give Kansas City their tenth straight win against divisional opponents. On January 1, 2017, the Chiefs clinched the AFC West and the second seed going into the playoffs that year, where they fell to the Pittsburgh Steelers 18–16 in the divisional round as Chris Boswell hit six field goals.[106]
The Chiefs finished the 2017 season with a 10–6 record, and won the AFC West.[107] This was the first time in Chiefs history that they won the AFC West in back-to-back years.[108] In the Wild Card round, the Chiefs lost a tight game to the Tennessee Titans 22–21, allowing Derrick Henry to rush for 156 yards. The loss extended their NFL record for most consecutive home playoff losses to six.[109] The game marked the end of Alex Smith's five-year tenure with the Chiefs, as he was traded to the Washington Redskins a few weeks later.[110]

Patrick Mahomes era (2018–present)
[edit]Patrick Mahomes made his NFL debut and first career start in the December 31, 2017, game against the Denver Broncos. The Chiefs won the game 27–24, with Mahomes going 22 for 35 with 284 yards and one interception.[111] The Chiefs began the 2018 season with first-year starter Mahomes as their quarterback and finished the regular season with a record of 12–4, clinching the AFC West for the third year in a row and the AFC's top seed. This included victories over division rivals Los Angeles Chargers, Oakland Raiders and Denver Broncos (twice), along with important conference victories over the Pittsburgh Steelers, Cincinnati Bengals, and Jacksonville Jaguars. Their first loss of the season came at the hands of the New England Patriots with a last-second field goal.[112] Their second loss of the season came against the Los Angeles Rams with a final score of 51–54, in which the Kansas City Chiefs made history by becoming the first NFL team to lose a game after scoring more than 50 points.[113] Mahomes finished the season with 5,097 yards and 50 touchdowns, both team records.[114] He became the 11th quarterback to throw for 5,000 yards and the third to throw for 50 touchdowns.[115] He joined Peyton Manning as only the 2nd player in NFL history to throw for 5,000 yards and 50 touchdowns.[116] For his performance during the season, he was named AP NFL MVP, the first Chief to ever win the award.[117]
In the AFC Divisional round on January 12, 2019, the Chiefs defeated the Indianapolis Colts 31–13 to move on to the AFC Championship Game.[118] This marked the Chiefs' first playoff win in Arrowhead Stadium in 25 years.[119] This also enabled the Chiefs to host the AFC Championship Game for the first time ever.[120] The next week, Kansas City's bid for its first Super Bowl berth in 49 years ended with a 37–31 overtime loss to the New England Patriots.[121]
The Chiefs finished the 2019 regular season with a 12–4 record, winning the AFC West division title for the fourth straight year, and clinched the AFC's second seed behind the Baltimore Ravens.[122] The Chiefs defeated the Houston Texans 51–31 in the AFC Divisional Game after falling behind 24–0 at the start of the second quarter with Mahomes throwing for five touchdowns.[123] The Chiefs hosted their second AFC Championship game in consecutive years facing the sixth-seed Tennessee Titans. The Chiefs then defeated the Titans 35–24 and advanced to Super Bowl LIV.[124] This marked their first Super Bowl appearance in 50 years, since Super Bowl IV.[125]
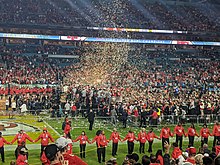
On February 2, 2020, in Hard Rock Stadium in Miami Gardens, Florida, the Chiefs played against the NFC's top seed, the San Francisco 49ers. Following halftime when both teams were tied at ten points, Mahomes threw 2 interceptions in back to back drives in the 3rd and 4th quarters, resulting in the 49ers having a 20–10 lead with under 12 minutes remaining in the game. Sparked by a 44-yard completion to Tyreek Hill on 3rd and 15, the Chiefs scored touchdowns on their next two possessions, with Mahomes throwing touchdowns to Travis Kelce and Damien Williams.[126] With a 24–20 lead with under two minutes remaining, Williams had a 38-yard touchdown run to effectively seal the game for the Chiefs. This marked the first time in NFL postseason history that a team faced ten point deficits in three straight games and won all three by double-digit margins. Mahomes won the Super Bowl Most Valuable Player Award, ending the Chiefs' Super Bowl drought dating back to the AFL-NFL Merger.[127]

On July 6, 2020, Mahomes signed a record ten–year, $503 million contract extension keeping him under contract until the conclusion of the 2031 season. The contract is the largest ever signed in North American sports, more than tripling the value of the previous largest contract signed (although said contract was for a shorter 5 years, signed by Matt Ryan of the Atlanta Falcons).[128] With their week 14 victory over the Miami Dolphins, the Chiefs clinched their fifth consecutive division title. The victory also gave the Chiefs their first 12–1 record in franchise history. They would later win 14 games for the first time in franchise history. In the playoffs they defeated the Cleveland Browns and Buffalo Bills to win the AFC Championship for the second consecutive year.[129][130] The Chiefs would face the Tampa Bay Buccaneers in Super Bowl LV at Raymond James Stadium in Tampa, ultimately losing 9–31, failing to score a touchdown in the game.[131]
In their 2021 season, the Chiefs beat the Pittsburgh Steelers 36–10, earning the team's sixth straight AFC West title on December 26, 2021.[132] The Chiefs began their playoff slate with a win against the Pittsburgh Steelers in the Wild Card round, and advanced to play the Buffalo Bills in the divisional round. Their 42–36 victory over Buffalo came in a game sports commentators and analysts dubbed as one of the greatest modern day NFL playoff games.[133][134][135][136][137][138] Despite being the first team to host the AFC Championship game for four consecutive seasons, the team finished the season losing 24–27 in overtime to the Cincinnati Bengals.
The Chiefs began their 2022 season by trading Tyreek Hill to the Miami Dolphins,[139] and instead opting to stock up on picks in the 2022 NFL draft. They finished the season with a 14–3 regular season record, with losses coming from the Colts, Bills, and Bengals. All three losses were by margins of less than four points. The Chiefs won their seventh consecutive AFC West division championship, and secured the #1 seed in the AFC playoffs.[140] The team hosted their fifth consecutive AFC Championship Game,[141] and second consecutive against the Cincinnati Bengals, winning 23–20 on a game-winning field goal from Harrison Butker.[142] In Super Bowl LVII, the Chiefs defeated the Philadelphia Eagles 38–35 again on a field goal from Butker.[143] With the victory, Mahomes became the first player since Kurt Warner in 1999 to win both the NFL MVP Award and Super Bowl MVP Award in the same season.[144] Head coach Andy Reid won his second Super Bowl championship over the Eagles, the team he had previously led to a Super Bowl appearance.[145]
Entering the 2023 season as defending champions, the Chiefs failed to improve on their 14–3 record from the previous season, despite this they secured their eleventh consecutive winning season and became division champions for the eighth consecutive season.[146][147][148] Their overall record was 11–6, their least successful record under quarterback Patrick Mahomes. In the playoffs, the Chiefs defeated the Miami Dolphins 26–7 in the wildcard round in frigid weather. In the divisional round, the team held on to a narrow 27–24 win over the Buffalo Bills on the road. This was the Chiefs third playoff win in four years over the Bills. They made their sixth consecutive AFC Championship Game appearance, but their first on the road, defeating the Baltimore Ravens 17–10 to advance to their fourth Super Bowl in five years. In a rematch of Super Bowl LIV, the Chiefs overtime defeat of the San Francisco 49ers 25–22 in Super Bowl LVIII moved the franchise to four Super Bowl titles, becoming the seventh franchise to accomplish that number. This was only the second overtime game in Super Bowl history.[149] This marked the first back-to-back Super Bowl wins since Super Bowl XXXIX, making it three Super Bowl wins in five years and cementing them as a dynasty.[150][151]
Championships
[edit]The Chiefs have won four Super Bowl Championships and three AFL Championships – the latter of which were won twice as the Kansas City Chiefs and once under their original name, the Dallas Texans.[152][153]
Super Bowl championships
[edit]| Year | Coach | Super Bowl | Stadium | Location | Opponent | Score | MVP | Record |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1969 | Hank Stram | IV | Tulane Stadium | New Orleans, Louisiana | Minnesota Vikings | 23–7 | QB Len Dawson | 11–3 |
| 2019 | Andy Reid | LIV | Hard Rock Stadium | Miami Gardens, Florida | San Francisco 49ers | 31–20 | QB Patrick Mahomes | 12–4 |
| 2022 | LVII | State Farm Stadium | Glendale, Arizona | Philadelphia Eagles | 38–35 | 14–3 | ||
| 2023 | LVIII | Allegiant Stadium | Paradise, Nevada | San Francisco 49ers | 25–22 | 11–6 | ||
| Total Super Bowl championships won: | 4 | |||||||
American Football League championships
[edit]| Year | Coach | Game | Stadium | Location | Opponent | Score | Record |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1962 | Hank Stram | 1962 AFL Championship Game | Jeppesen Stadium | Houston, Texas | Houston Oilers | 20–17 | 12–3 |
| 1966 | 1966 AFL Championship Game | War Memorial Stadium | Buffalo, New York | Buffalo Bills | 31–7 | 12–2–1 | |
| 1969 | 1969 AFL Championship Game | Oakland-Alameda County Coliseum | Oakland, California | Oakland Raiders | 17–7 | 12–3 | |
| Total AFL championships won: | 3 | ||||||
AFC championships
[edit]| Year | Coach | Stadium | Location | Opponent | Score | Record |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Andy Reid | Arrowhead Stadium | Kansas City, Missouri | Tennessee Titans | 35–24 | 12–4 |
| 2020 | Buffalo Bills | 38–24 | 14–2 | |||
| 2022 | Cincinnati Bengals | 23–20 | 14–3 | |||
| 2023 | M&T Bank Stadium | Baltimore, Maryland | Baltimore Ravens | 17–10 | 11–6 | |
| Total AFC championships won: | 4 | |||||
Logos and uniforms
[edit]When the Texans began playing in 1960, the team's logo consisted of the state of Texas in white with a yellow star marking the location of the city of Dallas. Originally, Hunt chose Columbia blue and orange for the Texans' uniforms, but Bud Adams chose Columbia blue and scarlet for his Houston Oilers franchise.[5] Hunt reverted to red and gold for the Texans' uniforms, which even after the team relocated to Kansas City, remain as the franchise's colors to this day.[5]
The state of Texas on the team's helmet was replaced by an arrowhead design originally sketched by Lamar Hunt on a napkin.[5] Hunt's inspiration for the interlocking "KC" design was the "SF" inside of an oval on the San Francisco 49ers helmets.[5] Unlike the 49ers' logo, Kansas City's overlapping initials appear inside a white arrowhead instead of an oval and are surrounded by a thin black outline.[5] From 1960 to 1973, the Chiefs had grey facemask bars on their helmets, but changed to white facemasks in 1974, making them one of the first teams (alongside the San Diego Chargers, who introduced a yellow facemask that same year) in the NFL to use a non-gray facemask.[5]
The Chiefs' uniform design has essentially remained the same throughout the club's history with only four minor changes occurring.[5] It consists of a red helmet, and either red or white jerseys with the opposite color numbers and names.[5] White pants were used with both jerseys from 1960 to 1967, and 1989 to 1999.[5] Beginning in 2009, during the Pioli/Haley era, the team has alternated between white and red pants for road games during the season. Prior to September 15, 2013, the Chiefs always wore white pants with their red jerseys. The Chiefs do not have an official alternate jersey, although unofficial alternate jerseys are sold for retail.
The Chiefs wore their white jerseys with white pants at home for the 2006 season opener against the Cincinnati Bengals. The logic behind the uniform selection that day was that the Bengals would have to wear their black uniform on a day when hot temperatures were forecast.[154]
In 2007, the Kansas City Chiefs honored Lamar Hunt and the AFL with a special patch.[155] It features the AFL's logo from the 1960s with Hunt's "LH" initials inside the football.[155] In 2008, the patch became permanently affixed to the left chest of both Kansas City's home and away jerseys.[155]
In select games for the 2009 season, the Chiefs, as well as the other founding teams of the American Football League, wore a "throwback" uniform to celebrate the AFL's 50th anniversary.[156]
For the first time in team history, the Chiefs wore red jerseys with red pants, forming an all-red combo in their home opener against the Dallas Cowboys on September 15, 2013.[157] The all-red uniform is now an official uniform combination and has been used multiple times since. It is commonly used for prime-time games at home. The all-red look also served as the basis for the Chiefs' Color Rush design.
Arrowhead Stadium
[edit]
Arrowhead Stadium has been the Chiefs' home field since 1972 and has a capacity of 76,416,[158] which makes it the fifth-largest stadium in the NFL. The stadium underwent a $375 million renovation, completed in mid-2010, which included new luxury boxes, wider concourses and enhanced amenities.[159][77] The stadium renovation was paid for by $250 million in taxpayer money and $125 million from the Hunt Family.[81] The stadium cost $53 million to build in 1972, and an average ticket in 2009 costs $81.[159] Aramark serves as the stadium's concession provider and T-Mobile, Anheuser-Busch and Coca-Cola are major corporate sponsors.[159]
Dating back to the Chiefs' home opener in 1991 to mid-2009, the Chiefs had 155 consecutive sellout games.[159] The streak ended with the final home game of the 2009 season against the Cleveland Browns, resulting in the first local TV blackout in over 19 years.[160] Arrowhead has been called one of the world's finest stadiums[18] and has long held a reputation for being one of the toughest and loudest outdoor stadiums for opposing players to play in.[77][161][162][163] All noise is directly attributed to its fans[164] and was once measured at 116 decibels by the Acoustical Design Group of Mission, Kansas.[165] By way of comparison, take-off of aircraft may lead to a sound level of 106 decibels at the ground.[165] Sports Illustrated named Arrowhead Stadium the "toughest place to play" for opposing teams in 2005.[166] The tailgate party environment outside the stadium on gameday has been compared to a "college football" atmosphere.[167] Arrowhead Stadium features frequent fly-overs from a B-2 Spirit stealth bomber from nearby Whiteman Air Force Base. Since the 1994 NFL season, the stadium has had a natural grass playing surface.[168] From 1972 to 1993, the stadium had an artificial AstroTurf surface.[168]
During the game against the Oakland Raiders on October 13, 2013, Arrowhead Stadium once again became the loudest stadium in the world when the fans set the Guinness Book of World Records record for loudest crowd in an outdoor stadium (137.5 dB), breaking the record set by the Seattle Seahawks just four weeks prior. A few weeks after, Seattle re-gained the record by reaching a noise level of 137.6 decibels.[169][170] Chiefs fans have reclaimed the record once again on September 29, 2014, on ESPN's Monday Night Football against the New England Patriots, the fans recorded a sound reading of 142.2 decibels.[171]
The stadium has been officially named GEHA Field at Arrowhead Stadium (pronounced G.E.H.A.) since 2021. The stadium was renamed after GEHA signed a naming rights deal with the Chiefs.[172]
Training camp and practice facility
[edit]
When the franchise was based in Dallas, the team conducted their inaugural training camp at the New Mexico Military Institute in Roswell, New Mexico.[26] They moved camp to Southern Methodist University, owner Lamar Hunt's alma mater, for 1961 and continued to practice there until 1965.[26] From 1966 to 1971, the Chiefs practiced in Swope Park in Kansas City,[173] and from 1972 to 1991 held camp at William Jewell College in Clay County, Missouri–where Lamar Hunt had extensive business dealings including Worlds of Fun, Oceans of Fun and SubTropolis.[48]

From 1992 to 2009 the Chiefs conducted summer training camp at the University of Wisconsin–River Falls in River Falls, Wisconsin.[174] The Chiefs' 2007 training camp was documented in the HBO/NFL Films documentary reality television series, Hard Knocks.[175] Following the passage of a $25 million state tax credit proposal, the Chiefs moved their training camp to Missouri Western State University in St. Joseph, Missouri, in 2010.[176] The bulk of the tax credits went for improvements to Arrowhead Stadium with $10 million applied to the move to Missouri Western.[177] A climate-controlled, 120-yard NFL regulation grass indoor field, and office space for the Chiefs was constructed at Missouri Western adjacent to the school's Spratt Stadium before the 2010 season.[178]
Outside of training camp and during the regular season, the Chiefs conduct practices at their own training facility nearby Arrowhead Stadium. The facility is located near the Raytown Road entrance to the Truman Sports Complex just east of Interstate 435 and features three outdoor fields (two grass and one artificial turf) as well as an indoor facility with its own full-size field.
Rivalries
[edit]Las Vegas Raiders
[edit]The rivalry between the Chiefs and the Las Vegas Raiders is considered as one of the NFL's most bitter, extending back into the infancy of the AFL.[179] Most notably during the era; both the Chiefs and Raiders appeared in the first two Super Bowl games.[180][181][182] Since the AFL was established in 1960, the Chiefs and Raiders have shared the same division, first being the AFL Western Conference, and since the AFL–NFL merger, the AFC West. The Chiefs lead the regular season series 73–55–2 as of the end of the 2023 season, including a 2–1 playoff record against Las Vegas.[183]
Los Angeles Chargers
[edit]A historic divisional battle for the Chiefs; the rivalry with the Los Angeles Chargers reignited during the 2020s as matchups would feature an offensive battle between Patrick Mahomes and Chargers' pro-bowl quarterback Justin Herbert.[184] The Chiefs lead 69–58–1 as of the end of the 2023 season,[185] but the Chargers won 17–0 in the only playoff meeting between the two teams, a 1992 AFC wild card game.[186]
Denver Broncos
[edit]Chiefs lead 72–56 as of the 2023 season, which included a run of 16 straight wins,[187] but the Broncos won the only playoff game between the two teams, a 1997 AFC Divisional game.[188][189]
Buffalo Bills
[edit]The series originated during the American Football League's inaugural season in 1960, as both the Kansas City Chiefs, then known as the Dallas Texans, and Buffalo Bills were charter teams in the league.[190] Despite being in two different divisions since their founding in 1960, the Bills and Chiefs have had many notable moments in NFL postseason history, most notably the 1966 AFL Championship Game, the 2021 AFC Divisional playoff game (known especially for the infamous '13 Seconds'), and the 2024 AFC Divisional playoff game (known as 'Wide Right II'). Since 2020, the rivalry has redeveloped as both teams consistently contended for the AFC title. A rivalry has also developed between Bills quarterback Josh Allen and Chiefs quarterback Patrick Mahomes, with many comparing it to the former rivalry between Tom Brady and Peyton Manning.[191] As of 2023, Buffalo leads the series 29–25–1, but Kansas City leads the playoff series 4–2. Of the six playoff meetings the teams have contested, three of which were AFL/AFC championship games.[192]
Cincinnati Bengals
[edit]A relatively new rivalry for the Chiefs has formed in the 2020s with the Cincinnati Bengals. Prior to 2021, the rivalry was nonexistent. By 2021 though, the Bengals became a rising team in the AFC with the arrival of a healthy top tier quarterback in Joe Burrow, the #1 pick in the 2020 NFL draft, who could go toe to toe with Patrick Mahomes.[193] The Bengals beat the Chiefs in the 2021 regular season at Arrowhead 34–31, and then followed that up with a victory in that year's AFC Championship Game, a game in which the Cincinnati defense shut the Kansas City offense down in the second half and kicker Evan McPherson hit a game winning field goal in overtime to advance to Super Bowl LVI. In 2022, the Chiefs and Bengals again met in the regular season, with the Bengals prevailing 27–24 and sealing the game off of a rare Travis Kelce fumble. The Chiefs again met the Bengals in the AFC Championship game that season. The Chiefs won the game on a walk off field goal and advanced to Super Bowl LVII thanks to Bengals defensive end Joseph Ossai hitting Patrick Mahomes out of bounds when Mahomes was scrambling for a first down, leading to an unnecessary roughness penalty.[194] The two teams met again in 2023, but did not face Joe Burrow due to Burrow suffering a season ending wrist injury earlier in the season. To date, the Joe Burrow led Bengals are the only AFC team to have a winning record against the Chiefs since Patrick Mahomes became their starting quarterback. As of 2023, the Bengals lead the all-time series 18–16.[195]
Missouri Governor's Cup: St. Louis Cardinals/St. Louis Rams
[edit]When St. Louis, Missouri had NFL teams, namely the Cardinals and later the Rams, a cross-state rivalry existed with the Chiefs; with a trophy being awarded to the winner of each game. The series was active with the Cardinals from 1960 to 1988 prior to their relocation to Arizona. The series found new life from 1995 to 2015 after the Rams played in St. Louis for a 20-year tenure. Despite this, the series ended permanently following the Rams' relocation back to Los Angeles in 2016. Though, following the Rams' return to Los Angeles; the two teams would play each other during the 2018 season in a historic matchup which set the record for the third-highest scoring game of all time,[196] hailed by many as one of the greatest games in league history.[197][198] As of the 2023 season, the Chiefs lead the all-time series 8–5.[199]
Mascots and cheerleaders
[edit]
The Chiefs' first mascot was Warpaint, a nickname given to several breeds of pinto horse. Warpaint served as the team's mascot from 1963 to 1988.[25][200][201] The first Warpaint (born in 1955, died in 1992) was ridden bareback by rider Bob Johnson who wore a full Native American headdress.[25][200] Warpaint circled the field at the beginning of each Chiefs home game and performed victory laps following each Chiefs touchdown.[25][200] On September 20, 2009, a new Warpaint horse was unveiled at the Chiefs' home opener.[202] Warpaint was ridden by a cheerleader in its return.[203] The Chiefs again retired Warpaint in 2021 as a part of their commitment to stop the use of Native American imagery.[204]
In the mid-1980s, the Chiefs featured a short-lived unnamed "Indian man" mascot which was later scrapped in 1988.[200] Since 1989 the cartoon-like K. C. Wolf, portrayed by Dan Meers in a wolf costume, has served as the team's mascot.[25][205] The mascot was named after the Chiefs' "Wolfpack", a group of rabid fans from the team's days at Municipal Stadium.[200] K. C. Wolf is one of the most popular NFL mascots and was the league's first mascot inducted into the Mascot Hall of Fame in 2006.[206]
The Chiefs have employed a cheerleading squad since the team's inception in 1960.[207] In the team's early days, the all-female squad was referred to as the Chiefettes.[208] In addition to the Cheerleaders, in the early 1970s, there was also a dance/drill team that performed for pre-game and halftime. From 1986 to 1992, the cheerleader squad featured a mix of men and women.[207] From 1993 to 2019, the all-female squad has been known as the Chiefs Cheerleaders, and in 2020, one male joined the team.[200][207][208]
Notable players
[edit]Current roster
[edit]Retired numbers
[edit]| Kansas City Chiefs retired numbers | ||||
| No. | Player | Position | Tenure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Jan Stenerud | K | 1967–1979 | |
| 16 | Len Dawson | QB | 1962–1975 | |
| 18 | Emmitt Thomas | CB | 1966–1978 | |
| 28 | Abner Haynes | RB | 1960–1964 | |
| 33 | Stone Johnson 1 2 | RB | 1963 | |
| 36 | Mack Lee Hill 2 | RB | 1964–1965 | |
| 58 | Derrick Thomas 2 | LB | 1989–1999 | |
| 63 | Willie Lanier | LB | 1967–1977 | |
| 78 | Bobby Bell | LB | 1963–1974 | |
| 86 | Buck Buchanan | DT | 1963–1975 | |
| 1 Never on a Chiefs regular season roster. His number was retired after his death after an injury in a preseason game in 1963. 2 Number was posthumously retired. Names in bold spent entire playing career with the Dallas Texans/Kansas City Chiefs. The number 37 has not been worn since the death of Joe Delaney. Number 58 was not issued after the death of Derrick Thomas until it was officially retired in 2009. The numbers 16 and 28 are the only numbers to have been worn by a single player (both Dawson and Haynes respectively). | ||||
Pro Football Hall of Famers
[edit]Twenty-five members of the Pro Football Hall of Fame spent at least some portion of their career with the Chiefs. Thirteen spent the majority of the career with the Chiefs. Ten of the Chiefs in the Hall of Fame were involved with the Chiefs during their Super Bowl Championship season of 1969. The Chiefs have 3 contributors, 3 coaches, and 18 players in the Hall of Fame. Derrick Thomas is the only Chief in the Hall of Fame that was inducted posthumously. Listed below are only people whose tenure with the Chiefs is their reason for induction, not former Chiefs coaches inducted as a player, the only exception being Emmitt Thomas who was inducted as a player for the Chiefs and later become an assistant coach for the team.
| Kansas City Chiefs Hall of Fame enshrinees | ||||
| Players | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Name | Position | Tenure | Inducted |
| 78 | Bobby Bell 1 2 | LB | 1963–1974 | 1983 |
| 63 | Willie Lanier 1 2 | LB | 1967–1977 | 1986 |
| 16 | Len Dawson 2 3 | QB | 1963–1975 | 1987 |
| 86 | Buck Buchanan 1 2 | DT | 1963–1975 | 1990 |
| 3 | Jan Stenerud 1 2 3 | K | 1967–1979 | 1991 |
| 53 | Mike Webster | C | 1989–1990 | 1997 |
| 19 | Joe Montana | QB | 1993–1994 | 2000 |
| 32 | Marcus Allen | RB | 1993–1997 | 2003 |
| 1 | Warren Moon | QB | 1999–2000 | 2006 |
| 18 | Emmitt Thomas 1 2 | CB | 1966–1978 | 2008 |
| 58 | Derrick Thomas | LB | 1989–1999 | 2009 |
| 77 | Willie Roaf | T | 2002–2005 | 2012 |
| 61 | Curley Culp 1 2 3 | DT | 1968–1974 | 2013 |
| 68 | Will Shields | G | 1993–2006 | 2015 |
| 8 | Morten Andersen | K | 2002–2003 | 2017 |
| 88 | Tony Gonzalez 3 | TE | 1997–2008 | 2019 |
| 24 | Ty Law | CB | 2006–2007 | 2019 |
| 42 | Johnny Robinson1 2 | S | 1960–1971 | 2019 |
| 24 | Darrelle Revis | CB | 2017 | 2023 |
| Coaches and contributors | ||||
| Name | Position | Tenure | Inducted | |
| Lamar Hunt | Founder of franchise and American Football League | 1960–2006 | 1972 | |
| Marv Levy | Head coach | 1978–1982 | 2001 | |
| Hank Stram 1 2 3 | Head coach | 1960–1974 | 2003 | |
| Bill Polian | Contributor | 1978–1982 | 2015 | |
| Bobby Beathard | Contributor | 1963, 1966–1967 | 2018 | |
| Dick Vermeil | Head coach | 2001–2005 | 2022 | |
| 1 Began career in the American Football League. 2 Member of 1969 Super Bowl championship team. 3 Spent majority of their career with the Chiefs (names in bold). | ||||
Chiefs Hall of Fame
[edit]Established in 1970, the Chiefs Hall of Fame has inducted a new member, with the exception of the 1983 and 2020 seasons, every year to honor their players, coaches, and contributors in an annual ceremony.[209][210] The requirements for induction are that a player, coach, or contributor must have been with the Chiefs for four seasons and been out of the NFL for four seasons at the time of induction.[209] There are some exceptions, such as Joe Delaney and Derrick Thomas, Delaney was with the team for only two seasons before his death, Thomas was inducted 1 year after his death in January 2000 (2 years after his final season). The Chiefs have the second-most enshrinees of any NFL team in their team Hall of Fame behind the Green Bay Packers, who have enshrined over 100 players and team contributors over the years in the Green Bay Packers Hall of Fame.[209] Nineteen players and the coach of the Super Bowl IV championship team have been inducted into the ring of honor. Three players were posthumously inducted, Derrick Thomas, Joe Delaney, and Mack Lee Hill.
| Chiefs Hall of Fame | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inducted | No. | Player | Position | Tenure |
| 1970 | — | Lamar Hunt | Team founder/Owner | 1960–2006 |
| 1971 | 36 | Mack Lee Hill* | RB | 1964–1965 |
| 1972 | 75 | Jerry Mays | DT | 1961–1970 |
| 1973 | 84 | Fred Arbanas | TE | 1962–1970 |
| 1974 | 42 | Johnny Robinson | S | 1960–1971 |
| 1975 | 88 | Chris Burford | WR | 1960–1967 |
| 1976 | 55 | E. J. Holub | C/LB | 1961–1970 |
| 1977 | 77 | Jim Tyrer | T | 1961–1973 |
| 1978 | 21 | Mike Garrett | RB | 1966–1970 |
| 1979 | 16 | Len Dawson | QB | 1963–1975 |
| 1980 | 78 | Bobby Bell | LB | 1963–1974 |
| 1981 | 86 | Buck Buchanan | DT | 1963–1975 |
| 1982 | 89 | Otis Taylor | WR | 1965–1975 |
| 1983 | No induction | |||
| 1984 | 71 | Ed Budde | G | 1963–1976 |
| 1985 | 63 | Willie Lanier | LB | 1967–1977 |
| 1986 | 18 | Emmitt Thomas | CB | 1966–1978 |
| 1987 | — | Hank Stram | Coach | 1960–1974 |
| 1988 | 44 | Jerrel Wilson | P | 1963–1977 |
| 1989 | 14 | Ed Podolak | RB | 1969–1977 |
| 1990 | 51 | Jim Lynch | LB | 1967–1977 |
| 1991 | 28 | Abner Haynes | RB | 1960–1964 |
| 1992 | 3 | Jan Stenerud | K | 1967–1979 |
| 1993 | 69 | Sherrill Headrick | LB | 1960–1967 |
| 1994 | 58 | Jack Rudnay | C | 1969–1982 |
| 1995 | 32 | Curtis McClinton | RB | 1962–1969 |
| 1996 | 20 | Deron Cherry | S | 1981–1991 |
| 1997 | 73 | Dave Hill | T | 1963–1974 |
| 1998 | 67 | Art Still | DE | 1978–1987 |
| 1999 | 34 | Lloyd Burruss | S | 1981–1991 |
| 2000 | 35 | Christian Okoye | RB | 1987–1992 |
| 2001 | 58 | Derrick Thomas* | LB | 1989–1999 |
| 2002 | 76 | John Alt | T | 1984–1996 |
| 2003 | 59 | Gary Spani | LB | 1978–1986 |
| 2004 | 37 | Joe Delaney* | RB | 1981–1982 |
| 2005 | — | Jack Steadman | President/GM | 1960–1989 |
| 2006 | 90 | Neil Smith | DE | 1988–1996 |
| 2007 | 29 | Albert Lewis | CB | 1983–1993 |
| 2008 | 61 | Curley Culp | DT | 1968–1974 |
| 2009 | 8 | Nick Lowery | K | 1980–1993 |
| 2010 | — | Marty Schottenheimer | Coach | 1989–1998 |
| 2011 | 31 | Kevin Ross | CB | 1984–1993, 1997 |
| 2012 | 68 | Will Shields | G | 1993–2006 |
| 2013 | 26 | Gary Barbaro | S | 1976–1982 |
| 2014 | 31 | Priest Holmes | RB | 2001–2007 |
| 2015 | 24 | Gary Green | CB | 1977–1983 |
| 2016 | 49 | Tony Richardson | FB | 1995–2005 |
| 2017 | 88 | Carlos Carson | WR | 1980–1989 |
| 2018 | 88 | Tony Gonzalez | TE | 1997–2008 |
| 2019 | 54 | Brian Waters | G | 2000–2010 |
| 2020 | No induction | |||
| 2021 | 61 | Tim Grunhard | C | 1990–2000 |
| 2022 | 38 | Kimble Anders | FB | 1991–2000 |
| 2023 | 82 | Dante Hall | WR† | 2000–2006 |
*Posthumous induction
†Hall's primary position was wide receiver and is listed in the Chiefs Hall of Honor as a receiver. However, he was inducted because of his accomplishments as a return specialist.
Records
[edit]Three Chiefs players own major NFL records. Patrick Mahomes owns the record for career quarterback rating with a minimum of 1,500 attempts with 103.9,[211] Derrick Thomas owns the record for sacks in a single game with 7 which he accomplished in 1990,[212] and Travis Kelce owns the record for career receptions in the playoffs.[213] Additionally, Tony Gonzalez, who spent the majority his career with the Chiefs, is the career receiving yards and receptions leader among tight ends. Chiefs players own several less notable records, for example, Mahomes owns the record for fastest quarterback to 100 career passing touchdowns. For a list of franchise records, see List of Kansas City Chiefs records
Head coaches
[edit]Thirteen head coaches have served the Texans/Chiefs franchise since their first season in 1960.[214] Hank Stram, the team's first head coach, led the Chiefs to three AFL championship victories and two appearances in the Super Bowl.[215] Stram was the team's longest-tenured head coach, holding the position from 1960 to 1974.[39] Marty Schottenheimer was hired in 1989 and led Kansas City to seven playoff appearances in his ten seasons as head coach.[42][48] Schottenheimer had the best winning percentage (.634) of all Chiefs coaches.[50] Gunther Cunningham was on the Chiefs' coaching staff in various positions from 1995 to 2008, serving as the team's head coach in between stints as the team's defensive coordinator.[51][52] Dick Vermeil coached the team to a franchise-best 9–0 start in the 2003 season.[216] Of the ten Chiefs coaches, Hank Stram, Marv Levy, and Dick Vermeil have been elected into the Pro Football Hall of Fame, Levy is more well known for his time with the Buffalo Bills.[217] Herm Edwards served as the team's head coach from 2006 to 2008, compiling a 15–33 record and a franchise worst 6–26 record over a two-year span.[78][79][218][219] Todd Haley compiled a 19–26 record with the team from 2009 to 2011, including an AFC West division title in 2010.[80] Haley was fired with three games left in the 2011 season. Romeo Crennel was named interim coach, and was promoted to full-time coach in January 2012. Crennel was fired on Monday, December 31, 2012, after finishing the 2012 season with a 2–14 record. On January 5, 2013, the Chiefs hired Andy Reid to be their next head coach. In Reid's tenure, the Chiefs have never had a sub-.500 season, making the playoffs in 10 of his 11 seasons as head coach, winning the division six times, and twice having two consecutive Super Bowl appearances, and three wins. With a 21–14 victory over the Miami Dolphins, on November 5, 2023, in Frankfurt Germany, Andy Reid tied former Chiefs head coach Hank Stram on the franchise's all-time regular season wins list with 124 victories.[220][221]
Ownership and administration
[edit]
The franchise was founded in 1959 by Lamar Hunt after a failed attempt by Hunt to purchase an NFL franchise and relocate them to Texas.[222] Hunt remained the team's owner until his death in 2006.[222] The Hunt family kept ownership of the team following Lamar's death and Clark Hunt, Lamar's son, represents the family's interests.[159] While Hunt's official title is CEO and Chairman of the Board, he represents the team at all owner meetings.[223][224] In 2010, Hunt assumed role as CEO alongside his role as chairman of the board.[225] According to Forbes, the team entered the 2022 season valued at $3.7 billion ranking them 23rd among the 32 NFL teams.[17]
Owner Lamar Hunt served as the team's president from 1960 to 1976. Because of Lamar Hunt's contributions to the NFL, the AFC Championship trophy is named after him.[226] He promoted general manager Jack Steadman to become the team's president in 1977.[226] Steadman held the job until Carl Peterson was hired by Hunt in 1988 to replace him.[226] Peterson resigned the title as team president in 2008.[227] Denny Thum became the team's interim president following Peterson's departure and was officially given the full position in May 2009.[227][228] Thum resigned from his position on September 14, 2010.[225]
Don Rossi served as the team's general manager for half of the 1960 season, resigning in November 1960.[26] Jack Steadman assumed duties from Rossi and served in the position until 1976.[26][39][226] Steadman was promoted to team president in 1976 and despite being relieved of those duties in 1988,[226] he remained with the franchise until 2006 in various positions.[39][42] Jim Schaaf took over for Steadman as general manager until being fired in December 1988.[42] Carl Peterson was hired in 1988 to serve as the team's general manager, chief executive officer and team president.[42][226] Peterson remained in the position for nineteen years until he announced his resignation from the team in 2008.[227][229] Denny Thum served as interim general manager[227] until January 13, 2009, when the Chiefs named New England Patriots executive Scott Pioli the team's new general manager.[77][230] Pioli was released in early January after the hiring of Andy Reid, and was replaced by John Dorsey. Pioli's record as the Chief's general manager was 23–41.
On June 22, 2017, the Chiefs fired Dorsey.[231] They hired Brett Veach as the new general manager on July 10, 2017.[232]
Staff
[edit]
|
| |||||
Media
[edit]Kansas City radio station WDAF-FM (106.5) is the flagship station for The Chiefs Football Radio Network. The network has affiliates across Missouri, Kansas, Iowa, Nebraska, and Texas, and national reach through desktop and mobile devices. AFC Championship and Super Bowl broadcasts are exclusive to KCSP and WDAF-FM due to NFL rules surrounding the exclusivity of Westwood One's coverage outside of the immediate Kansas City area.
В рамках новейших телевизионных контрактов игры, не относящиеся к прайм-тайму, транслируются на каналах CBS или Fox, причем крупнейшими рынками сбыта являются мегаполисы Канзас-Сити , Уичито и Омаха .
Продюсерская компания, принадлежащая Чифс, называется 65 Toss Power Trap Productions в честь победы на Суперкубке Чифс IV , которая привела к тачдауну на пять ярдов, проведенному Майком Гарреттом . [ 233 ]
Культура
[ редактировать ]Фанатская база
[ редактировать ]

«Чифс» могут похвастаться одной из самых преданных фанатов в НФЛ. [ 160 ] [ 234 ] Канзас-Сити является шестым по величине медиа-рынком, на котором есть команда НФЛ, но у них второй по величине средний показатель посещаемости за последнее десятилетие. [ 164 ] Исследования, проведенные Bizjournals в 2006 году, дали «Чифс» высокие оценки за постоянное привлечение большого количества зрителей как в хорошие, так и в плохие сезоны. [ 235 ] С 1996 по 2006 год «Чифс» собирали в среднем 77 300 болельщиков за игру, занимая второе место в НФЛ после « Вашингтон Редскинз» . [ 235 ] У франшизы есть официальный фан-клуб под названием Chiefs Kingdom , который дает членам возможность пользоваться преимуществами приоритета билетов и VIP-обслуживанием. [ 236 ] [ 237 ]
В конце « Звездного знамени » перед домашними играми многие фанаты «Чифс» намеренно выкрикивают «ЧИФС!» вместо того, чтобы петь «храбрый» в качестве последнего слова. [ 238 ] Это также иногда можно услышать в дорожных играх. [ 239 ] и даже на спортивных мероприятиях близлежащего Университета Канзаса . [ 240 ] В 1996 году генеральный менеджер Карл Петерсон сказал: «Мы все с нетерпением ждем, не только в Arrowhead, но и в дороге, когда мы доберемся до этой строфы государственного гимна ... Нашим игрокам она нравится». [ 238 ] После терактов 11 сентября 2001 года фанаты «Чифс» воздержались от этого в честь тех, кто погиб в результате трагедии, и продолжали делать это до конца сезона 2001 года. [ 241 ] На домашнем матче «Чифс» против «Нью-Йорк Джайентс» 23 сентября 2001 года болельщики аплодировали командам соперников стоя. [ 163 ]
Раньше фанаты скандировали, указывая в сторону команды гостей: «Мы выбьем тебя до чертиков... тебя... тебя, тебя, тебя, тебя!» над песней « Рок-н-ролл. Часть 2 ». [ 242 ] Пение начинается после третьего «эй!» в песне. [ 242 ] Оригинальная версия песни Гэри Глиттера ранее использовалась до тех пор, пока НФЛ не запретила его музыку на своих площадках в 2006 году после того, как британский рокер был осужден по обвинению в сексуальном насилии во Вьетнаме. [ 242 ] Кавер-версия песни в исполнении Tube Tops 2000. [ 242 ] использовался с 2006 по сезон 2015 года. [ 243 ] Позже эта практика была полностью прекращена перед сезоном 2015 года, после того как Глиттер снова арестовали. [ 244 ] В конечном итоге команда приняла песню Beastie Boys « (You Gotta) Fight for Your Right (To Party!) » после того, как Трэвис Келси выкрикнул основной припев, празднуя победы в игре за звание чемпиона AFC и Суперкубке. [ 245 ]
Среди известных поклонников - Брэд Питт , Пол Радд , Джейсон Судейкис , Генри Кавилл , Дэвид Кокнер , Роб Риггл , Хайди Гарднер , Джон Эймос , Мелисса Этеридж и Эрик Стоунстрит . [ 246 ]
Стадион «Эрроухед» также занесен в Книгу рекордов Гиннеса как самый громкий открытый стадион в мире. Это было достигнуто 29 сентября 2014 года во время футбольного матча Monday Night Football против New England Patriots , когда рев толпы достиг 142,2 децибела. [ 247 ] что сравнимо с тем, что вы стоите на расстоянии 100 футов (30 м) от реактивного двигателя, что даже при кратковременном воздействии может привести к необратимому повреждению. [ 248 ]
Международная деятельность
[ редактировать ]НФЛ представила международную программу внутреннего маркетинга лиги в 2021 году. [ 249 ] в рамках которого команды получают права на международный маркетинг в странах за пределами США. «Чифс» были назначены домашней командой в Германию вместе с « Каролина Пантерс» , «Нью-Ингленд Пэтриотс» и «Тампа Бэй Бакканирс» . В 2023 году НФЛ также предоставила Chiefs разрешение расширить маркетинг и работу с болельщиками в Австрии и Швейцарии . [ 250 ] «Чифс» провели игру в Германии В сезоне 2023 года против « Майами Долфинс» . [ 251 ] [ 252 ]
«Чифс» играли международные игры регулярного сезона против «Детройта» в 2015 году в Лондоне и против « Лос-Анджелес Чарджерс» в 2019 году в Мехико . Команда участвовала в предсезонных показательных играх, получивших название American Bowl, в Берлине ( 1990 ), Токио ( 1994 и 1998 ) и Монтеррее , Мексика ( 1996 ). [ 251 ]
Фанатская база «Чифс» расширилась по всему миру, как и у многих других команд НФЛ. Аккаунт в Твиттере предназначен для фанатов Chiefs в Великобритании, признан Kansas City Chiefs и является их официальной фан-страницей в Великобритании. У них много преданных фанатов, которые пишут статьи и берут интервью у игроков команды, таких как Тамба Хали . [ 253 ]
Тони ДиПардо
[ редактировать ]В разные периоды с 1963 по сезон 2008 года трубач Тони ДиПардо и группа The TD Pack Band играли живую музыку на каждой домашней игре Chiefs. [ 254 ] [ 255 ] Группа была известна как The Zing Band, когда команда располагалась на Муниципальном стадионе. В 1969 году главный тренер Хэнк Стрэм наградил ДиПардо кольцом Суперкубка за победу команды в Суперкубке IV. [ 254 ] Когда его здоровье ухудшалось, ДиПардо взял отпуск в группе с 1983 по 1988 год. [ 255 ] Дочь ДиПардо заняла пост руководителя группы в 1989 году, и к этому времени ДиПардо вернулся в группу по многочисленным просьбам. [ 255 ] [ 256 ] В сезоне 2009 года из-за ремонта на стадионе «Эрроухед» группа не вернулась на стадион для выступлений.
ДиПардо умер 27 января 2011 года в возрасте 98 лет. Он находился в больнице с декабря 2010 года из-за аневризмы головного мозга. [ 257 ]
Споры о названии
[ редактировать ]По разным причинам команде были предъявлены обвинения в расизме, присвоении культуры, направленной против коренных народов, а также в неправильном использовании имен, символов и обычаев. [ 258 ] [ 259 ] Название происходит от прозвища бывшего мэра Канзас-Сити Гарольда Роу Бартла , который называл себя « Вождем » в рамках создания « Племя Мик-О-Сэй» , группы, связанной с бойскаутами Америки . [ 260 ] За время существования франшизы также демонстрировалось следующее: логотип в виде наконечника стрелы, жесты фанатов «отбивной томагавком» во время игр, лошадь по кличке Warpaint, использование большого барабана, а также ношение краски на лице, головных уборов и т. д. Символы коренных американцев. [ 261 ] [ 262 ]
Фанаты «Чифс» также продолжают традицию, зародившуюся в Университете штата Флорида в середине 1980-х годов, используя боевое пение семинолов в качестве сплоченного клича в ключевые моменты футбольных игр. [ 263 ] [ 264 ] Перед каждой домашней игрой бывший игрок «Чифс» [ 265 ] или известный фанат Chiefs (например, гонщик NASCAR Клинт Бойер) [ 266 ] или рэпер Tech N9ne [ 267 ] ), называемый почетным барабанщиком, стучит в барабан большой барабанной палкой, чтобы начать отбивную Томагавком .
Использование «Чифс» и их фанатами образов и стереотипов коренных американцев стало источником разногласий, поскольку некоторые осуждают использование таких символов, как «боевой барабан», песен и зрелищ, таких как «Томагавк-Чоп», а также стереотипную одежду фанатов в искусственная боевая раскраска и головные уборы. В 2016 году группы коренных американцев попросили вождей Канзас-Сити прекратить использовать томагавк. [ 268 ] В том же году аналогичный запрос был сделан к «Эксетер Чифс» . [ 269 ] Редакционная коллегия газеты Kansas City Star призвала прекратить практику «отбивки томагавком» в конце 2019 года, отметив противодействие со стороны коренных американцев и племен и заявив, что эта практика формирует стереотипы и дегуманизирует коренных американцев. [ 270 ] Национальный конгресс американских индейцев и Индейский центр Канзас-Сити призвали отправить талисман в отставку. [ 271 ]
«Чифс» избежали более резкой критики со стороны других команд, таких как « Вашингтон Редскинз» и «Кливленд Индианс» , которые изменили свои названия, начиная с сезона 2022 года, за использование индейских названий и логотипов. Внимание возросло в 2020 году перед их появлением в Суперкубке LIV . [ 272 ] Хотя были предприняты усилия по решению других проблем, таких как фанаты, носящие боевую раскраску и головные уборы, отбивная томагавком и сопровождающее ее пение защищаются, в том числе некоторыми местными коренными американцами. По данным общенационального опроса, половина коренных американцев заявила, что «отбивная томагавком» их беспокоит или оскорбляет, а среди тех, кто более привержен традициям коренных народов, эта цифра возрастает до 65%. [ 273 ]
См. также
[ редактировать ]Ссылки
[ редактировать ]- ^ «История вождей» (PDF) . Путеводитель для СМИ Канзас-Сити на 2023 год . НФЛ Предприятия, ООО. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 14 августа 2023 г. Проверено 14 января 2024 г.
- ^ «Факты о команде «Канзас-Сити Чифс»» . ProFootballHOF.com . НФЛ Предприятия, ООО. Архивировано из оригинала 14 января 2024 года . Проверено 14 января 2024 г.
- ^ «Опыт фаната» . Chiefs.com . Архивировано из оригинала 8 февраля 2022 года . Проверено 8 февраля 2022 г.
- ^ «История команды руководителей Канзас-Сити – футбольные операции НФЛ» . Operations.NFL.com . НФЛ Предприятия, ООО. Архивировано из оригинала 21 ноября 2023 года . Проверено 20 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час я дж «История вождей» (PDF) . Путеводитель для СМИ Канзас-Сити на 2023 год (PDF) . НФЛ Предприятия, ООО. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 14 августа 2023 г. Проверено 14 августа 2023 г.
На одном из первых организационных собраний Американской футбольной лиги в конце 1959 года – еще до того, как в командах появились игроки и тренеры – владельцы АФЛ выбрали цвета своей команды. Ламар Хант хочет, чтобы Columbia Blue и Orange были частью его франшизы Dallas Texans. Но прежде чем Хант или любой другой владелец сможет сделать выбор, игрок «Хьюстона» Бад Адамс заявляет, что «Колумбия Блю» является его франшизой «Ойлерз». Хант возвращается к красному и золотому цветам для техасцев, которые по сей день остаются основной цветовой схемой для «Чифс».
- ^ «Капсула команды руководителей Канзас-Сити» (PDF) . Официальная книга рекордов и фактов Национальной футбольной лиги за 2022 год (PDF) . 20 июля 2022 г. Проверено 20 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ «Сотрудники фронт-офиса» . Chiefs.com . Архивировано из оригинала 2 июня 2020 года . Проверено 3 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Эдхольм, Эрик (12 февраля 2024 г.). «Владелец и генеральный директор «Чифс» Кларк Хант ожидает, что ХК Энди Рид вернется в следующем сезоне, чтобы получить шанс на «три-пит» » . НФЛ.com . НФЛ Предприятия, ООО. Архивировано из оригинала 13 февраля 2024 года . Проверено 15 февраля 2024 г.
- ^ Аллен, Скотт (28 января 2020 г.). «Последнее выступление «Чифс» на Суперкубке сопровождалось обвинениями в азартных играх и огромным разочарованием» . Вашингтон Пост . Архивировано из оригинала 13 марта 2020 года . Проверено 22 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Грегори, Шон (3 февраля 2020 г.). «Патрик Магомес привел «Канзас-Сити Чифс» к возвращению на Суперкубок. Он также подтвердил свое величие» . Время . Архивировано из оригинала 7 апреля 2020 года . Проверено 17 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Вагонер, Ник (29 января 2020 г.). «Руководители, 49ers удовлетворяют потребность в скорости в Суперкубке LIV» . ESPN Интернет Венчурс, ООО. Архивировано из оригинала 4 февраля 2020 года . Проверено 4 февраля 2020 г.
- ^ Судья Кларк (30 мая 2020 г.). «Гостевая колонка: Лучшие вожди НЕ в Кантоне и почему они заслуживают быть там» . Иллюстрированный спорт . Архивировано из оригинала 25 марта 2022 года . Проверено 25 марта 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Все готово к переменам техасцев» . Лоуренс Дейли Джорнал-Мир . (Канзас). Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 23 мая 1963 г. с. 10. Архивировано из оригинала 29 апреля 2021 года . Получено 4 марта 2021 г. - из Новостей Google.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Команда AFL переезжает в Канзас-Сити» . Евгений Регистр-охранник . (Орегон). Об этом сообщает AP, сообщает УПИ. 23 мая 1963 г. с. 4Д. Архивировано из оригинала 29 апреля 2021 года . Получено 4 марта 2021 г. - из Новостей Google.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «KC pro Eleven имеет тег «Chiefs»» . Лоуренс Дейли Джорнал-Мир . (Канзас). 27 мая 1963 г. с. 17. Архивировано из оригинала 29 апреля 2021 года . Получено 4 марта 2021 г. - из Новостей Google.
- ^ «Текстовая страница — Имя вождей наследия американских индейцев» . Chiefs.com . 1 января 2020 года. Архивировано из оригинала 14 февраля 2023 года . Проверено 1 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Озанян, Майк (22 августа 2022 г.). «Ценности команды НФЛ на 2022 год: Dallas Cowboys — первая франшиза стоимостью 8 миллиардов долларов» . Форбс . Архивировано из оригинала 14 февраля 2023 года . Проверено 15 февраля 2024 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г «Зал славы профессионального футбола: Руководители Канзас-Сити» . Зал славы профессионального футбола. Архивировано из оригинала 26 января 2016 года . Проверено 22 января 2016 г.
- ^ Шак, Барри (27 мая 2013 г.). «Канзас-Сити Чифс 1969 года: два чемпионата за один сезон» . Отчет отбеливателя . Архивировано из оригинала 25 марта 2022 года . Проверено 25 марта 2022 г.
- ^ Брюэр, Джерри (10 февраля 2023 г.). «Перспектива | Эпоха Патрика Магомеса только начинается. Конец может быть ошеломляющим» . Вашингтон Пост . ISSN 0190-8286 . Архивировано из оригинала 12 февраля 2023 года . Проверено 13 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ Маске, Марк (2 февраля 2020 г.). «Чифс сплотились, чтобы победить команду 49ers со счетом 31–20 и завоевать первый титул Суперкубка за 50 лет» . Вашингтон Пост . ISSN 0190-8286 . Архивировано из оригинала 12 февраля 2023 года . Проверено 13 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ «Канзас-Сити Чифс победили Филадельфию Иглз в Суперкубке LVII» . КМБК . 13 февраля 2023 года. Архивировано из оригинала 12 февраля 2023 года . Проверено 13 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж «История руководителей Канзас-Сити - Истоки АФЛ» . Chiefs.com . Архивировано из оригинала 2 марта 2010 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ НФЛ (3 ноября 2017 г.), На этот раз «Чифс» сражались с «Ковбоями» за сердца Далласа | Основные моменты НФЛ , заархивировано из оригинала 5 июля 2020 г. , получено 4 ноября 2017 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и Альтхаус, с. 35
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час я дж к л м н тот п д р с т в v В х «История вождей Канзас-Сити – 1960-е годы» . Chiefs.com . Архивировано из оригинала 9 июня 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час я дж к «Энциклопедия франчайзинга Kansas City Chiefs» . Справочник по профессиональному футболу. Архивировано из оригинала 19 января 2009 года . Проверено 11 января 2009 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Кухбандер, Брэд (8 февраля 2008 г.). «Кубандер: эта неделя в истории вождей» . Chiefs.com . Архивировано из оригинала 19 февраля 2008 года . Проверено 10 января 2009 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Мины, с. 103
- ^ «Как вожди Канзас-Сити получили свое имя и племя бойскаутов Мик-О-Сэй» . Новости ИКТ . 21 сентября 2019 года. Архивировано из оригинала 4 июля 2020 года . Проверено 3 июля 2020 г.
- ^ «Правдивая история первого вождя Канзас-Сити» . Форбс . Архивировано из оригинала 3 июля 2020 года . Проверено 3 июля 2020 г.
- ^ «Своё спорное название «Чифс» получила от мэра Канзас-Сити, который назывался «Чиф» и настаивал на том, чтобы команда была названа в его честь» . Бизнес-инсайдер . Архивировано из оригинала 1 июля 2020 года . Проверено 4 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Маска, стр. 325.
- ^ Рекс В. Хаппке (30 января 2007 г.). «Легенды Чаши» . Чикаго Трибьюн . Архивировано из оригинала 5 июня 2022 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
Ламар Хант, умерший в декабре, придумал термин «Супербоул» в конце 1960-х годов после того, как увидел, как его дети играют с «Суперболом», надувным детищем культового производителя игрушек Wham-O.
- ^ Мины, стр. 167.
- ^ Мины, стр. 179.
- ^ «Лен Доусон» . Справочник по профессиональному футболу. Архивировано из оригинала 29 августа 2008 года . Проверено 19 июля 2008 г.
- ^ На одну игру больше, чем у « Лос-Анджелес/Сан-Диего Чарджерс» , Справочник по футболу: в нескольких сезонах, с 1960 по 1969 год, в регулярном сезоне, отсортировано по убыванию даты. Архивировано 16 июля 2012 г. на archive.today.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час я дж к л м н «История вождей Канзас-Сити – 1970-е годы» . Chiefs.com . Архивировано из оригинала 9 июня 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Альтхаус, с. 97
- ^ Альтхаус, с. 101
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час я дж к л м «История вождей Канзас-Сити – 1980-е годы» . Chiefs.com . Архивировано из оригинала 1 мая 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ «Джо Делейни отправился на почетный ринг Chiefs в воскресенье» . Chiefs.com . 23 сентября 2004 года. Архивировано из оригинала 13 января 2005 года . Проверено 13 июля 2008 г.
- ^ Альтхаус, с. 167
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Уоррик, Клингер потерпел неудачу в Цинси» . ЭСПН . 16 апреля 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 4 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ↑ Мацкович выпущен. Архивировано 13 декабря 2017 года в Wayback Machine . «Нью-Йорк Таймс» , 9 января 1987 г.
- ^ «Десятилетие, которое стоит запомнить: НФЛ в 90-х» . НФЛ.информация . 20 декабря 1999 года. Архивировано из оригинала 16 февраля 2023 года . Проверено 16 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час я дж к л м н тот «История вождей Канзас-Сити – 1990-е годы» . Chiefs.com . Архивировано из оригинала 9 июля 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ Альтхаус, с. 63
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Рекорд Марти Шоттенхаймера, статистика и рейтинги категорий» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Архивировано из оригинала 9 июля 2008 года . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Такер, Дуг (20 января 2004 г.). «Руководители назначают Гюнтера Каннингема координатором защиты» . США сегодня . Архивировано из оригинала 29 апреля 2021 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час я дж к л м н тот п д р с т в v В х и С аа «История вождей Канзас-Сити – 2000-е» . Chiefs.com . Архивировано из оригинала 9 июня 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ Альтхаус, с. 65
- ^ Паскарелли, Лен (5 июня 2007 г.). «Зеленый переходит к Дельфинам от Шефов в торговле» . Архивировано из оригинала 10 октября 2007 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Клейтон, Джон (6 ноября 2008 г.). «Интересный список женихов Холла» . ЭСПН . Архивировано из оригинала 29 апреля 2021 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «KC обменивает Джареда Аллена в Миннесоту на несколько вариантов драфта» . Chiefs.com . 23 апреля 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 9 июня 2008 года . Проверено 27 ноября 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Chiefs QB Thigpen выйдет на старт против «Фэлконз»» . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 17 сентября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 19 сентября 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «План «День руководителей 1» составлен вместе с Дорси и другими» . ЭСПН . 26 апреля 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 24 октября 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «Для вождей драфт дает количество и много качества» . ЭСПН . 27 апреля 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 22 октября 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Уильямсон, Билл (18 июня 2008 г.). «Несколько выборов 2008 года должны оказать немедленное влияние» . ЭСПН . Архивировано из оригинала 4 августа 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Chiefs QB Croyle отсутствует на этой неделе» . Национальная футбольная лига . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 8 сентября 2008 г. Архивировано из оригинала 10 апреля 2021 г. Проверено 17 сентября 2008 г.
- ^ «Chiefs QB Thigpen выйдет на старт против «Фэлконз»» . ЭСПН . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 17 сентября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 19 сентября 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с «Фэлконз» вернулись в строй после победы над безвыигрышными «Чифс» . Национальная футбольная лига . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 21 сентября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 11 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «Хуард в воскресенье выйдет в стартовом составе на позиции квотербека за Канзас-Сити» . Национальная футбольная лига . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 22 сентября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 7 января 2009 года . Проверено 14 ноября 2008 г.
- ^ «Чифс Джонсон находится под следствием по поводу последнего инцидента с участием женщины» . ЭСПН . 20 октября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 23 октября 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Джонсон из «Чифс», обвиненный в том, что плюнул в лицо женщине, пока не будет играть» . ЭСПН . 28 октября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 30 октября 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Смит, Майкл (12 октября 2008 г.). «Источник: Руководители готовы выслушать предложения по установлению рекорда Т.Э. Гонсалеса» . ЭСПН . Архивировано из оригинала 20 октября 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «Гонсалес говорит товарищам по команде, что он не расстроен из-за неудавшейся заявки на обмен» . ЭСПН . 16 октября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 октября 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «Chiefs QB Кройл вывихнул правое колено, это конец сезона» . ЭСПН . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 19 октября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 22 октября 2008 года . Проверено 19 октября 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Рэнд, Джонатан (13 ноября 2008 г.). «Разрыв шаблона» . Chiefs.com . Архивировано из оригинала 10 января 2009 года . Проверено 14 ноября 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Чадиха, Джеффри (21 ноября 2008 г.). «Распространение вариантов изменений для руководителей» . ЭСПН . Архивировано из оригинала 25 октября 2012 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «Источник: дисциплина Джонсона в ответ на образец поведения» . ЭСПН . 18 октября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 19 октября 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «Титаны» продлевают победную серию, а «Чифс» проигрывают, Кройл» . Национальная футбольная лига . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 19 октября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 23 октября 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «Лучшая игра Уильямса в карьере помогла «Пантерам» победить «Чифс»» . Национальная футбольная лига . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 5 октября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 11 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «Эдвардс, Биллс набрали больше всего очков против «Чифс» в истории» . ЭСПН . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 23 ноября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 6 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «Главный генеральный менеджер Петерсон уйдет в отставку в конце сезона» . ЭСПН . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 15 декабря 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 17 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д «Скотт Пиоли присоединится к «Канзас-Сити Чифс»» . ЭСПН . 13 января 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 20 января 2009 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Руководители увольняют Эдвардса; следующим будет Шанахан?» . ЭСПН . 23 января 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 30 января 2009 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Герм Эдвардс освобожден от обязанностей главного тренера «Чифс» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 23 января 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 26 января 2009 года . Проверено 23 января 2009 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Тодд Хейли назначен главным тренером «Канзас-Сити Чифс»» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 6 февраля 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 9 февраля 2009 года . Проверено 6 февраля 2009 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Чифс нанимают координатора нападения Кардиналов Хейли в качестве тренера» . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 6 февраля 2009 г. Архивировано из оригинала 10 апреля 2021 г. Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «Чифс» обменяли Гонсалеса на выбор на драфте 2010 года» . ЭСПН . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 23 апреля 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 26 апреля 2009 года . Проверено 7 июня 2009 г.
- ^ Кинг, Питер (28 февраля 2009 г.). «Руководители завершили сделку по Касселю» . Иллюстрированный спорт . Архивировано из оригинала 4 марта 2009 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «Chiefs» приобретает QB Мэтта Касселя и LB Майка Врабеля в обмен на «Патриотов» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 28 февраля 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 4 марта 2009 года . Проверено 28 февраля 2009 г.
- ^ «Руководители требуют Чемберса» . ЭСПН . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 3 ноября 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 7 ноября 2009 года . Проверено 3 ноября 2009 г.
- ^ «Прием НФЛ 2010» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Тейчер, Адам (28 апреля 2011 г.). «Канзас-Сити Чифс» выбирает приемника Джонатана Болдуина на драфте НФЛ» . Уичито Игл . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «ХЕЙЛИ ОСВОБОЖДЕНА ОТ ОБЯЗАННОСТЕЙ» . Архивировано из оригинала 7 января 2012 года . Проверено 12 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Ромео Креннел будет тренировать «Чифс» до конца сезона» . Канзас-Сити Чифс . Архивировано из оригинала 7 января 2012 года . Проверено 12 августа 2020 г.
- ^ «Руководители назначат главного тренера Ромео Креннела» . Канзас-Сити Чифс . Архивировано из оригинала 12 января 2012 года . Проверено 12 августа 2020 г.
- ^ «Стилерс 16, Чифс 13 (ОТ)» . Чикаго Трибьюн . 12 ноября 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 24 августа 2022 года . Проверено 24 августа 2022 г.
- ^ «Набор приказов о драфте НФЛ 2013» . CBS Спорт . Архивировано из оригинала 25 мая 2013 года.
- ^ Мортенсен, Крис (31 декабря 2012 г.). «Руководители бросают Креннеля, оставив пока GM Пиоли» . ESPN.com . Ассошиэйтед Пресс . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Гарафоло, Майк (4 января 2013 г.). «Гроссмейстер Скотт Пиоли уволен из «Чифс»» . США СЕГОДНЯ . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Мортенсен, Крис; Шефтер, Адам (4 января 2013 г.). «Рид достиг соглашения о том, чтобы стать следующим тренером «Чифс»» . ESPN.com . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ «Руководители нанимают Джона Дорси из Packers на должность генерального менеджера» . НФЛ.com . 12 января 2013 года . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Уильямсон, Билл (12 марта 2013 г.). «Девятки объявляют об обмене Алекса Смита» . ЭСПН . Архивировано из оригинала 15 марта 2013 года . Проверено 5 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Тейчер, Адам (9 декабря 2020 г.). «Забытый номер 1: Эрик Фишер из «Чифс» оказался достоин выбора?» . ESPN.com . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Бонстил, Мэтт (5 октября 2017 г.). «Чифс» — единственная оставшаяся непобедимая команда, и, вероятно, они обречены» . Вашингтон Пост . ISSN 0190-8286 . Архивировано из оригинала 13 февраля 2023 года . Проверено 24 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Торман, Джоэл (28 декабря 2014 г.). «Чифс» обыграли «Чарджерс», но не попали в плей-офф . Стрелковая гордость . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Тейчер, Адам (12 октября 2015 г.). «Чифс РБ Чарльз вырвал крестообразную связку и выбыл на сезон» . ESPN.com . Ассошиэйтед Пресс . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ «Как команда 1-5 Chiefs начала прямиком в плей-офф» . Фокс Спорт . 8 января 2016 года . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ «Канзас-Сити Чифс» доминируют над техасцами в Хьюстоне . Национальная футбольная лига. Ассошиэйтед Пресс . 9 января 2016. Архивировано из оригинала 19 января 2016 года . Проверено 21 января 2016 г.
- ^ «Патриоты» в пятой игре подряд за титул чемпиона AFC в победе над «Чифс» со счетом 27–20» . Монреальский вестник . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 17 января 2016 года . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Гратхофф, Пит (20 апреля 2021 г.). «Руководители поделились яркими моментами камбэк-победы под руководством Алекса Смита над Чарджерс в 2016 году» . Звезда Канзас-Сити . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «Стилерс» сдержали «Чифс» по шести голам с игры Босуэлла, 18–16» . CBSSports.com . 16 января 2017 г. Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ «Составы руководителей Канзас-Сити на 2017 год, статистика, расписание, призывники команд, отчеты о травмах» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ «Чифс возглавляют «Дельфинов», впервые в истории франшизы завоевывают подряд титулы в дивизионе» . Сеть Миссури. 25 декабря 2017. Архивировано из оригинала 16 октября 2018 года . Проверено 15 октября 2018 г.
- ^ Шваб, Франк (6 января 2018 г.). «Не думали, что печальная история «Чифс» в плей-офф может ухудшиться? Что ж, так оно и было» . Yahoo! Спорт. Архивировано из оригинала 7 января 2018 года . Проверено 6 января 2018 г.
- ^ Тейчер, Адам; Кейм, Джон (31 января 2018 г.). «Источники: «Чифс» обменивают QB Смита на «Редскинз» . ESPN.com . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Гибсон, Брансен (17 июля 2022 г.). «Возвращаясь к первому выходу Патрика Махоумса за команду KC Chiefs» . Наркоман стрелы . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Стайтс, Адам (15 октября 2018 г.). «Победа «Патриотов» над «Чифс» в серии пенальти оправдала шумиху» . SBNation.com . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Гантт, Дарин (20 ноября 2018 г.). «Чифс» становятся первой командой, которая наберет 50 очков и проиграет» . NBC Спорт . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «Журнал игры Патрика Махоумса за 2018 год» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Вайнриб, Бен (31 декабря 2018 г.). «Патрик Махоумс присоединяется к эксклюзивному клубу 50 тачдаунов с пасом на всю карьеру» . Яху Спорт . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «Патрик Магомес из «Чифс» становится вторым в истории, забросившим 50 тачдаунов и 5000 ярдов за сезон» . Сложный . 31 декабря 2018 года . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Розенталь, Грегг (2 февраля 2019 г.). «Chiefs QB Патрик Махоумс назван самым ценным игроком НФЛ 2018 года» . НФЛ.com . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Бакстер, Кевин (13 января 2019 г.). «Патрик Махоумс, Дэмиен Уильямс и защита возглавляют победу в плей-офф над Кольтс» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Шваб, Франк (13 января 2019 г.). «С первой за 25 лет домашней победой в плей-офф «Чифс» одержали еще одну победу в Суперкубке» . Yahoo! Спорт . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Меллинджер, Сэм (18 января 2019 г.). «Баллада о доме «Чифс», стадионе «Эрроухед» и людях, которые его любят» . Звезда Канзас-Сити . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Уилнер, Барри (21 января 2019 г.). «Патриоты» третий раз подряд выходят на Суперкубок, обыгрывая «Чифс» со счетом 37-31 ОТ» . АП Новости . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ «Турнитура НФЛ 2019 и статистика команд» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Макмаллен, Мэтт (13 января 2020 г.). «Чифс» победили техасцев со счетом 51–31 и завершили крупнейшее возвращение в истории франчайзинга . Chiefs.com . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Макмаллен, Мэтт (20 января 2020 г.). «Чифс побеждают Титанов, 35–24, и выходят на Суперкубок» . Chiefs.com . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Палмер, Тод (21 января 2020 г.). «50 лет — это большой срок: переход от Суперкубка IV к LIV» . KSHB 41 Новости Канзас-Сити . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Григорян, Ваге (6 сентября 2020 г.). « Jet Chip Wasp — это момент, который будет длиться вечно, но он также говорит о будущем Chiefs» . Звезда Канзас-Сити . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Макмаллен, Мэтт (3 февраля 2020 г.). «Руководители объединяются, чтобы выиграть Суперкубок LIV, 31–20, и обеспечить безопасность чемпионата мира» . Chiefs.com . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ «Патрик Махоумс обошел Майка Траута по крупнейшему контракту в истории спорта» . ESPN.com . 6 июля 2020 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 августа 2020 года . Проверено 7 июля 2020 г.
- ^ «Чад Хенн заменит травмированного Патрика Махоумса, чтобы помочь «Чифс» победить «Браунс» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 17 января 2021 г. . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Скретта, Дэйв (25 января 2021 г.). «Действующий чемпион Chiefs сбросил счета 38–24 в матче за титул AFC» . АП Новости . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ «Том Брэди выигрывает Суперкубок №7, «Буканьерс» обыграли «Чифс» со счетом 31–9» . АП Новости . 8 февраля 2021 г. . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Тейчер, Адам (27 декабря 2021 г.). «После отсутствия Трэвиса Келси Патрик Махоумс распределяет богатство, поскольку «Канзас-Сити Чифс» выигрывает AFC West» . ЭСПН . Архивировано из оригинала 27 декабря 2021 года . Проверено 27 декабря 2021 г.
- ^ Роджерс, Мартин (24 января 2022 г.). «Лучшая игра плей-офф НФЛ? Чифс и Биллс доказывают это» . Фокс Спорт . Архивировано из оригинала 21 апреля 2022 года . Проверено 24 января 2022 г.
- ^ Морс, Бен (24 января 2022 г.). «Патрик Махоумс становится «Мрачным жнецом», когда «Канзас-Сити Чифс» побеждает «Баффало Биллс» в эпической овертаймовой битве вперед и назад» . CNN . Архивировано из оригинала 30 января 2022 года . Проверено 24 января 2022 г.
- ^ Барнуэлл, Билл (24 января 2022 г.). «Величайший раунд плей-офф НФЛ? 10 выводов от Биллс-Чифс, борьба Тома Брэди и Аарона Роджерса, а также то, как победили «Рэмс», «Форти Найнерс» и «Бенгалс» . ESPN.com . Архивировано из оригинала 25 января 2022 года . Проверено 24 января 2022 г.
- ^ Левин, Джош (24 января 2022 г.). «Как Chiefs-Bills стала одной из величайших игр в истории НФЛ» . Сланец . Архивировано из оригинала 29 июля 2022 года . Проверено 24 января 2022 г.
- ^ Додд, Деннис (24 января 2022 г.). «Эпическая победа «Чифс» над Биллсом заставляет фанатов НФЛ жаждать большего, но лучше этого ничего не может быть» . Национальная футбольная лига . Архивировано из оригинала 31 января 2022 года . Проверено 24 января 2022 г.
- ^ Лей, Том (24 января 2022 г.). «Это был футбольный матч на все времена» . Defector.com . Архивировано из оригинала 28 июля 2022 года . Проверено 24 января 2022 г.
- ^ Шук, Ник (23 марта 2022 г.). «Чифс» обменял WR Тайрика Хилла на «Дельфинс» на несколько вариантов драфта, включая первый раунд драфта 2022 года» . НФЛ.com . Архивировано из оригинала 23 марта 2022 года . Проверено 23 марта 2022 г.
- ^ «Канзас-Сити Чифс» завоевали первое место в АФК, победив «Лас-Вегас Рэйдерс» со счетом 31–13 в финале регулярного сезона» . Скай Спорт . 8 января 2023 г. . Проверено 4 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Эхлин, Грег (27 января 2023 г.). «Чифс» пять раз подряд выигрывали чемпионат AFC дома. «Это безумие» для бизнеса Канзас-Сити» . КСУР . Проверено 4 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Макмаллен, Мэтт (30 января 2023 г.). «Чифс» победили «Бенгалс» со счетом 23–20 и завоевали третий чемпионат АФК за четыре года» . Chiefs.com . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Макмаллен, Мэтт (14 февраля 2023 г.). «Чифс» завершили эпическое возвращение и выиграли Суперкубок LVII, 38-35, над «Филадельфией» . Chiefs.com . Проверено 30 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Чадиха, Джеффри (13 февраля 2023 г.). «Победа в Суперкубке и награда MVP — это лишь часть того, почему сезон 2022 года Патрика Махоумса может оказаться лучшим» . НФЛ.com . Проверено 4 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Гротц, Боб (13 февраля 2023 г.). «Боб Гротц: «Большой красный» Энди Рид отомстил, когда «Чифс» обыграли «Иглз» в Суперкубке LVII» . Делко Таймс . Проверено 4 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Гратофф, Пит (31 декабря 2023 г.). «Восьмой подряд титул «Чифс» в AFC West дает KC историческое преимущество над соперниками в дивизионе» . Звезда Канзас-Сити . Проверено 6 февраля 2024 г.
- ^ Гольдман, Чарльз (31 декабря 2023 г.). «Руководители вошли в историю Западного дивизиона АФК на 17-й неделе против «Бенгалс»» . Спорт от А до Я. Проверено 6 февраля 2024 г.
- ^ «Доминирование руководителей подразделений делает франшизу редкой компанией» . KSHB 41 Новости Канзас-Сити . 1 января 2024 года . Проверено 6 февраля 2024 г.
- ^ Джонс, Джонатан (11 февраля 2024 г.). «Суперкубок 2024 года: правила овертайма после сезона означают, что лучше отдавать, чем получать» . CBS Спорт . Архивировано из оригинала 13 февраля 2024 года . Проверено 13 февраля 2024 г.
- ^ «Патрик Махоумс и «Канзас-Сити Чифс» скрепляют династию повторной победой в Суперкубке» . ТСН.ca. Канадская пресса. 11 февраля 2024 года. Архивировано из оригинала 12 февраля 2024 года . Проверено 12 февраля 2024 г.
- ^ Дэвис, Нейт (12 февраля 2024 г.). «Патрик Махоумс и «Чифс» не оставляют сомнений в Суперкубке: они — династия НФЛ на все времена» . США сегодня . Архивировано из оригинала 12 февраля 2024 года . Проверено 12 февраля 2024 г.
- ^ Черт, Барри. «Канзас-Сити Чифс 1969 года: два чемпионата за один сезон» . Отчет отбеливателя . Архивировано из оригинала 25 марта 2022 года . Проверено 23 августа 2022 г.
- ^ «Сколько Суперкубков выиграли «Чифс»? История выступлений Канзас-Сити в крупных играх» . www.sportingnews.com . 12 августа 2021 года. Архивировано из оригинала 23 августа 2022 года . Проверено 23 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Феррин, Рид. (31 июля 2007 г.) Обертка River Falls: день шестой. Архивировано 20 февраля 2011 г. в Wayback Machine . Руководители Канзас-Сити, дата обращения 29 июля 2013 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с «Нашивка «Ламар Хант» становится постоянной частью униформы «Чифс» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 28 января 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 9 июня 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ «Руководители представят «возвращенную» форму AFL в 2009 году» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 24 марта 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 27 марта 2009 года . Проверено 24 марта 2009 г.
- ^ Торман, Джоэл (15 сентября 2013 г.). «История красного на красном» . Стрелковая гордость . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «Стадион Эрроухед» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. Архивировано из оригинала 30 августа 2009 года . Проверено 14 сентября 2009 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и «Оценки команды НФЛ: 20-е место в Канзас-Сити Чифс» . Форбс . 25 августа 2010 года. Архивировано из оригинала 28 сентября 2010 года . Проверено 15 сентября 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Мосли, Мэтт (29 августа 2008 г.). «Лучшие болельщики НФЛ? Надо отдать должное Стилерс (с трудом)» . ЭСПН . Архивировано из оригинала 31 августа 2008 года . Проверено 14 января 2009 г.
- ^ «Стадионы НФЛ – Стадион Эрроухед» . Архивировано из оригинала 16 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ «Цитаты о стадионе «Эрроухед»» . Архивировано из оригинала 16 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Заметки Питера Кинга - НФЛ» . CNN . 1 октября 2001 года. Архивировано из оригинала 29 марта 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «10 лучших фанатов НФЛ (Фотогалерея)» . FoxSports.com . Архивировано из оригинала 12 сентября 2008 года . Проверено 14 января 2009 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Чифс готовы к заклятому врагу плей-офф Индианаполису» . Топика Капитал-Журнал . 11 января 2004 года. Архивировано из оригинала 5 октября 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ «Опрос Sports Illustrated 2005 года: «Самые трудные места для игры» » . Иллюстрированный спорт . Архивировано из оригинала 16 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ Крампакер, Джон (1 октября 2006 г.). «Компаниям 49 приходится справляться с шумом Arrowhead» . Хроники Сан-Франциско . Архивировано из оригинала 10 октября 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Эта неделя в истории вождей» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 2 февраля 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 7 марта 2008 года . Проверено 9 февраля 2009 г.
- ^ Бенне, Джон (13 октября 2013 г.). «Руководители установили новый мировой рекорд Гиннеса по уровню шума на стадионе» . SBNation.com . Вокс Медиа. Архивировано из оригинала 17 октября 2014 года.
- ^ «Рекорды побиты» . KCCiefs.com . Архивировано из оригинала 15 октября 2013 года . Проверено 13 октября 2013 г.
- ^ «Королевство вождей будет показано на национальном телевидении» . Chiefs.com . 28 сентября 2014 года. Архивировано из оригинала 12 августа 2022 года . Проверено 11 июля 2022 г.
- ^ «Руководители и GEHA объявляют о соглашении о правах на наименование поля GEHA на стадионе «Эрроухед»» . Chiefs.com . 4 марта 2021 г. Архивировано из оригинала 4 марта 2021 г. Проверено 4 марта 2021 г.
- ^ Петерсон, с. 176
- ^ Морис, Пит (21 августа 2009 г.). «До свидания, Ривер Фолс» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. Архивировано из оригинала 26 августа 2009 года . Проверено 6 сентября 2009 г.
- ^ «Чифы будут показаны в сериале HBO «Hard Knocks» этим летом» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 2 июня 2007 года. Архивировано из оригинала 9 июня 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ «Руководители объявляют о планах на тренировочные сборы на 2009 год» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 12 декабря 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 17 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 12 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ «Канзас-Сити Чифс будут тренироваться в Сент-Джозефе» . Джоплин Индепендент . 16 декабря 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 1 апреля 2009 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ «Тренировочный лагерь «Чифс» вернется в Миссури, начиная с 2010 года» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 18 июня 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 22 июня 2009 года . Проверено 19 июня 2009 г.
- ^ Гольдман, Чарльз (15 мая 2024 г.). «НФЛ пытается возродить легендарное соперничество «Чифс» на 13-й неделе» . Спорт от А до Я. Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Макдональд, Джерри (12 сентября 2019 г.). «В последний раз разбрасываем грязью о соперничестве «Рейдеров» и «Чифов» . Новости Меркурия . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2019 года . Проверено 22 сентября 2019 г.
- ^ «10 лучших соперников НФЛ всех времен» . Иллюстрированный спорт . si.com. Архивировано из оригинала 15 октября 2013 года . Проверено 9 марта 2024 г.
- ^ Томас, Майк (23 ноября 2020 г.). «Соперничество ожесточенных вождей и рейдеров вызвало ненависть и изменение правил» . Спортивное вещание | Чистый спорт . Архивировано из оригинала 4 октября 2023 года . Проверено 17 июля 2022 г.
- ^ «Все матчи: Канзас-Сити Чифс против Лас-Вегаса/Лос-Анджелеса/Окленд Рэйдерс» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Проверено 4 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Рид, Джейсон (19 октября 2023 г.). «Краткая история Джастина Герберта против Патрика Махоумса» . Болт Бит . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «Все матчи: Канзас-Сити Чифс против Лос-Анджелеса/Сан-Диего Чарджерс» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «Wild Card — Канзас-Сити Чифс в Сан-Диего Чарджерс — 2 января 1993 года» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Коннер, Мэтт (29 октября 2023 г.). «Победная серия KC Chiefs над «Денвер Бронкос» завершилась на счету 16 подряд» . Наркоман стрелы . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «Вспоминая поражение «Бронкос» от «Стрелы» в плей-офф 1997 года» . DenverBroncos.com . Архивировано из оригинала 11 августа 2022 года . Проверено 9 марта 2024 г.
- ^ «Все матчи: Канзас-Сити Чифс против Денвера Бронкоса» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Проверено 4 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «Кто были первоначальные 8 команд в АФЛ?» . Игра перед деньгами . 28 апреля 2020 г. Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Грэмлинг, Гэри (23 января 2022 г.). «Махоумс-Аллен может достичь уровня соперничества Брейди-Мэннинга» . Иллюстрированный спорт . Архивировано из оригинала 29 июля 2022 года . Проверено 24 января 2022 г.
- ^ «Все матчи: Канзас-Сити Чифс против Баффало Биллс» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Проверено 4 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Мбу, Джошуа (6 августа 2024 г.). «Джо Берроу рассказывает о встрече с Патриком Махоумсом, когда он высказывается о соперничестве в НФЛ» . Зеркало . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Скотт, Джелани (30 января 2023 г.). «Болельщики обсуждают изменивший правила игры Джозеф Оссай против Патрика Магомеса» . Иллюстрированный спорт . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «Все матчи: Канзас-Сити Чифс против Цинциннати Бенгалс» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Проверено 4 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Макмаллен, Мэтт (20 ноября 2018 г.). «Чифс проиграли Рэмс, 54–51, в понедельник вечером по футболу» . Chiefs.com . НФЛ Предприятия, ООО. Архивировано из оригинала 11 сентября 2020 года . Проверено 27 апреля 2019 г.
- ^ Деннис, Кларенс (22 ноября 2018 г.). «Семь статистических данных: Рэмс победили Чифс в триллере вечера понедельника» . TheRams.com . НФЛ Предприятия, ООО. Архивировано из оригинала 11 сентября 2020 года . Проверено 27 апреля 2019 г.
- ^ Вусугян, Фарзин (12 июля 2012 г.). «Канзас-Сити Чифс: 5 лучших соперников вне дивизиона» . Отчет отбеливателя . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2019 года . Проверено 22 сентября 2019 г.
- ^ «Все матчи: Канзас-Сити Чифс против Кливленда/Сент-Луиса/Лос-Анджелес Рэмс» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Проверено 4 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж «Талисманы и чирлидеры «Канзас-Сити Чифс»» . 21 июня 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 10 февраля 2012 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ Маккензи, с. 141
- ^ Эхлин, Грег (21 сентября 2009 г.). «KCUR: Warpaint возвращается на стадион «Эрроухед»» . КСУР. Архивировано из оригинала 5 июня 2011 года . Проверено 21 сентября 2009 г.
- ^ «Боевая раскраска» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. Архивировано из оригинала 14 декабря 2014 года . Проверено 13 ноября 2014 г.
- ^ Макдауэлл, Сэм (27 июля 2021 г.). «Канзас-Сити Чифс не меняет название. Но они оставляют Warpaint на пастбище» . КанзасСити.com . Архивировано из оригинала 28 июля 2021 года . Проверено 28 июля 2021 г.
- ^ «КС Волк» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. Архивировано из оригинала 10 июня 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ «КС Волк» . Талисман Зала славы. Архивировано из оригинала 28 января 2013 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Маккензи, с. 140
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «История вождей Канзас-Сити - болельщики» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. Архивировано из оригинала 22 августа 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Гретц, Боб (11 марта 2009 г.). «Кто следующий в Чифс Холл?» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. Архивировано из оригинала 16 марта 2009 года . Проверено 11 марта 2009 г.
- ^ «Зал славы вождей Канзас-Сити» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. Архивировано из оригинала 9 июня 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ «Карьерные лидеры рейтинга пасовых НФЛ» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Архивировано из оригинала 13 сентября 2019 года . Проверено 14 декабря 2023 г.
- ^ «НФЛ увольняет лидеров одиночных игр» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Архивировано из оригинала 1 ноября 2023 года . Проверено 14 декабря 2023 г.
- ^ Керр, Джефф (7 февраля 2024 г.). «Суперкубок 2024 года: изнутри трансформация Трэвиса Келси в плей-офф; Chiefs TE развеивает все сомнения по поводу регулярного сезона» . CBSSports.com . Архивировано из оригинала 24 февраля 2024 года . Проверено 24 февраля 2024 г.
- ^ «Тренеры «Канзас-Сити Чифс»» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Проверено 4 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «Рекорды Хэнка Стрэма, статистика и рейтинги категорий» . Pro-Football-Reference.com . Проверено 20 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «Вермей и «Чифс» в идеальной гармонии, когда занавес опускается с победой со счетом 37–3» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. Архивировано из оригинала 17 марта 2008 года . Проверено 9 июля 2008 г.
- ^ «Зал славы по франшизе» . Зал славы профессионального футбола. Архивировано из оригинала 7 июля 2008 года . Проверено 9 июля 2008 г.
- ^ «Херм Эдвардс назван 10-м главным тренером в истории «Канзас-Сити Чифс»» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. Архивировано из оригинала 24 мая 2007 года . Проверено 9 июля 2008 г.
- ^ «Руководители получили разрешение поговорить с гермом Эдвардсом» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. Архивировано из оригинала 10 мая 2006 года . Проверено 9 июля 2008 г.
- ^ Диллон, Джон (6 ноября 2023 г.). «ХК «Чифс» Энди Рид сравнял с Хэнком Стрэмом наибольшее количество побед в регулярном сезоне в истории франшизы» . Провод начальников . США сегодня . Проверено 4 августа 2024 г.
- ^ Григорян, Ваге (5 ноября 2023 г.). « Это похоже на сон»: победа «Чифс» над «Дельфинами» завораживает новых немецких фанатов» . Звезда Канзас-Сити . п. 1. Архивировано из оригинала 31 января 2024 года . Проверено 11 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Херб, Кубандер, Луни и Морис, с. 4
- ^ «Кларк Хант, председатель правления» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. Архивировано из оригинала 10 июня 2008 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ Херб, Кубандер, Луни и Морис, с. 6
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Денни Там уходит из состава Chiefs; Кларк Хант становится генеральным директором» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 14 сентября 2010 года. Архивировано из оригинала 17 сентября 2010 года . Проверено 15 сентября 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж Херб, Кубандер, Луни и Морис, с. 411
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д «Карл Петерсон из «Чифс» уходит в отставку; будущее Эдвардса неопределенно» . США сегодня . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 15 декабря 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 17 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 15 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ «Денни Там назначен президентом «Канзас-Сити Чифс»» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 8 мая 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 15 мая 2009 года . Проверено 8 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «Пресс-конференция председателя правления Кларка Ханта по поводу отставки Карла Петерсона» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 15 декабря 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 15 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ «Скотт Пиоли назначен генеральным менеджером «Канзас-Сити Чифс»» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 13 января 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 января 2009 года . Проверено 14 января 2009 г.
- ^ «Руководители, Дорси соглашаются расстаться» . Архивировано из оригинала 10 июля 2017 года . Проверено 11 июля 2017 г.
- ^ «Канзас-Сити Чифс продвигает Бретта Вича на место генерального менеджера» . ЭСПН . 10 июля 2017 года. Архивировано из оригинала 10 июля 2017 года . Проверено 10 июля 2017 г.
- ^ Граверсен, Лайл (15 ноября 2012 г.). «65 Toss Power Trap Productions: что-то, что руководители сделали правильно» . ArrowheadAddict.com . Архивировано из оригинала 20 марта 2023 года . Проверено 20 марта 2023 г.
- ^ Шейн, Адам (2 июня 2009 г.). «Рейтинг НФЛ: инсайдерская оценка каждой франшизы» . Фокс Спорт . Архивировано из оригинала 8 июня 2009 года . Проверено 8 июня 2009 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Томас, Дж. Скотт (4 сентября 2006 г.). «Кливленд занимает первое место в рейтинге лояльности болельщиков НФЛ» . Бизнесжурналы. Архивировано из оригинала 11 октября 2008 года . Проверено 14 января 2009 г.
- ^ «Добро пожаловать в Нацию вождей!» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. Архивировано из оригинала 22 августа 2008 года . Проверено 15 января 2009 г.
- ^ «Ламар Хант объявляет о рождении Нации вождей» . Руководители Канзас-Сити. 16 апреля 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 13 июня 2007 года . Проверено 5 января 2009 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Маккензи, с. 132
- ^ «ВИДЕО: Слушайте Chiefs Kingdom в конце государственного гимна в Аризоне» . KMBC.com . 11 сентября 2022 года. Архивировано из оригинала 13 октября 2022 года . Проверено 13 октября 2022 г.
- ^ Бреннан, Имонн (20 января 2012 г.). «Билл Селф говорит нет «дому вождей» » . ESPN.com . Архивировано из оригинала 13 октября 2022 года . Проверено 13 октября 2022 г.
- ^ «Джайентс обыграли Чифс со счетом 13–3 в оборонительной борьбе» . Иллюстрированный спорт . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 24 сентября 2001 года. Архивировано из оригинала 25 октября 2012 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Пахигян, Джош (3 декабря 2007 г.). «Это праздник: лучшие ритуалы приземления НФЛ» . ЭСПН . Архивировано из оригинала 3 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 16 января 2009 г.
- ^ Гратофф, Пит (21 августа 2015 г.). «The Chiefs меняют песню, посвященную празднованию TD, и фанаты в ярости» . Звезда Канзас-Сити . Архивировано из оригинала 14 августа 2019 года . Проверено 14 августа 2019 г.
- ^ Гратхофф, Пит (3 сентября 2020 г.). «Похоже, что барьер для руководителей, использующих старую песню о приземлении, исчез» . КанзасСити.com . Архивировано из оригинала 12 октября 2023 года . Проверено 13 января 2023 г.
- ^ Гольдман, Чарльз (15 мая 2020 г.). «Напоминание: у Chiefs в 2020 году выйдет новая песня о приземлении» . США сегодня . Архивировано из оригинала 22 января 2021 года . Проверено 4 февраля 2021 г.
- ^ Гарднер, Крис (5 февраля 2021 г.). «Суеверия и барбекю в Канзас-Сити: как фанаты знаменитостей готовятся к Суперкубку» . Голливудский репортер . Архивировано из оригинала 23 августа 2022 года . Проверено 23 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Питерс, Мика (30 сентября 2014 г.). «Руководители побили рекорд Гиннеса по шуму толпы на стадионе «Эрроухед» против Патриотов» . Для победы . США сегодня. Архивировано из оригинала 30 сентября 2014 года . Проверено 4 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «Сравнительная таблица децибел (громкости)» . GCAudio.com . Архивировано из оригинала 1 июля 2016 года . Проверено 2 июля 2016 г.
- ^ «НФЛ объявляет международные команды и рынки в области домашнего маркетинга» . НФЛ.com . 15 декабря 2021 года. Архивировано из оригинала 19 января 2023 года . Проверено 19 января 2023 г.
- ^ Труонг, Уилсон (25 апреля 2023 г.). «НФЛ предоставляет Chiefs расширенное маркетинговое присутствие в Европе, включая Австрию и Швейцарию» . КШБ . Архивировано из оригинала 25 апреля 2023 года . Проверено 25 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Руководители назначены на игру в Германии в 2023 году» . Chiefs.com . 19 января 2023 года. Архивировано из оригинала 19 января 2023 года . Проверено 19 января 2023 г.
- ^ «Руководители сыграют с дельфинами во Франкфурте на игре в Германии в 2023 году» . Chiefs.com . 10 мая 2023 года. Архивировано из оригинала 10 мая 2023 года . Проверено 10 мая 2023 г.
- ^ Arrowheads Abroad (KCCiefsUK) в Твиттере. Архивировано 6 октября 2013 г. в Wayback Machine . Twitter.com. Проверено 29 июля 2013 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Альтхаус, с. 86
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Маккензи, с. 137
- ^ Альтхаус, с. 100
- ^ Унелл, Джастин (27 января 2011 г.). «Умер лидер группы Chiefs Тони ДиПардо» . KSHB 41 News, Канзас-Сити. Архивировано из оригинала 27 сентября 2011 года . Проверено 27 января 2011 г.
- ^ Мойя-Смит, Саймон (20 сентября 2020 г.). «Мнение | Если руководители Канзас-Сити хотят «положить конец расизму», они могут начать со своего имени» . Новости Эн-Би-Си . Архивировано из оригинала 7 февраля 2021 года . Проверено 17 февраля 2021 г.
- ^ Брито, Кристофер (5 февраля 2021 г.). «Протест с призывом к руководителям сменить имя и прекратить использовать отбивные томагавком запланирован перед Суперкубком» . Новости CBS . Архивировано из оригинала 16 февраля 2021 года . Проверено 17 февраля 2021 г.
- ^ Кэш, Мередит (23 января 2020 г.). «Своё спорное название «Чифс» получила от мэра Канзас-Сити, который назывался «Чиф» и настаивал на том, чтобы команда была названа в его честь» . BusinessInsider.com . Архивировано из оригинала 1 июля 2020 года . Проверено 4 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Келли, Александра (5 февраля 2021 г.). «Накануне Суперкубка коренные американцы освистывают команду Канзас-Сити Чифс» . Холм . Архивировано из оригинала 17 февраля 2021 года . Проверено 17 февраля 2021 г.
- ^ Асмелаш, Лия (февраль 2020 г.). «Как команда «Канзас-Сити Чифс» получила свое имя и почему оно так противоречиво» . CNN . Архивировано из оригинала 18 февраля 2021 года . Проверено 17 февраля 2021 г.
- ^ Маккензи, с. 133
- ^ Барнс, Крейг (9 октября 1991 г.). «Томагавк-отбивной – это уже не просто СССР» . Солнечная стража Южной Флориды . Архивировано из оригинала 24 сентября 2013 года . Проверено 29 сентября 2014 г.
- ^ «Мероприятия игрового дня: вожди против гигантов» . Chiefs.com . 28 сентября 2013 г. Архивировано из оригинала 11 июля 2022 г. Проверено 11 июля 2022 г.
- ^ «Клинт Бойер возобновляет предматчевую традицию «Канзас-Сити Чифс»» . NASCAR.com . 9 декабря 2018 года. Архивировано из оригинала 12 января 2020 года . Проверено 8 января 2020 г.
- ^ «Tech N9ne будет приглашенным барабанщиком и духовным лидером на Arrowhead Sunday» . Fox4KC.com . 27 декабря 2019 года. Архивировано из оригинала 27 декабря 2019 года . Проверено 8 января 2020 г.
- ^ Ротфилд, Ариэль (15 января 2016 г.). «Группа коренных народов Канзаса просит фанатов «Канзас-Сити Чифс» прекратить отбивную Томагавком» . КШБ. Архивировано из оригинала 28 декабря 2016 года . Проверено 23 февраля 2017 г.
- ^ Олдфилд, Эд (8 августа 2016 г.). «Послание регбийному клубу Exeter Chiefs от члена племени сиу Дакота Кроу-Крик» . Эксетер Экспресс и Эхо . Архивировано из оригинала 9 августа 2016 года . Проверено 23 февраля 2017 г.
- ^ «Остановите наступление «Удар наконечником стрелы». Пришло время новой традиции вождей» . Звезда Канзас-Сити . 1 ноября 2019 года. Архивировано из оригинала 25 января 2020 года . Проверено 20 января 2020 г.
- ^ Утация Крол, Дебра (10 февраля 2023 г.). «Поскольку «Чифс» участвует в Суперкубке, некоторые коренные жители говорят, что пришло время стереть оскорбительное имя» . США сегодня . Архивировано из оригинала 12 февраля 2023 года . Проверено 12 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ Богаге, Джейкоб (27 января 2020 г.). «Чифс» привносят образы коренных американцев и «отбивную из томагавка» на сцену Суперкубка» . Вашингтон Пост . Архивировано из оригинала 29 января 2020 года . Проверено 29 января 2020 г.
- ^ Элигон, Джон (29 января 2020 г.). «Празднование вождей Канзас-Сити, отбивная разделяет» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 3 июля 2020 года . Проверено 29 января 2020 г.
Дальнейшее чтение
[ редактировать ]- Альтхаус, Билл (2007). Хороший, плохой и злой: вожди Канзас-Сити: душераздирающие, потрясающие и мучительные моменты в истории вождей Канзас-Сити . Книги Триумф. ISBN 978-1-57243-928-3 .
- Грувер, Эд (1997). Лига американского футбола: история из года в год, 1960–1969 гг . МакФарланд Издательство. ISBN 0-7864-0399-3 .
- Херб, Патрик; Кубандер, Брэд; Луни, Джош; и др., ред. (2008). Путеводитель для СМИ Канзас-Сити, 2008 г. Футбольный клуб Канзас-Сити Чифс, Инк.
- Хоскинс, Алан (1999). Тропы войны: иллюстрированная история вождей Канзас-Сити . Издательство Тейлор. ISBN 0-87833-156-5 .
- Маске, Марк (2007). Война без смерти: год экстремальной конкуренции в NFC East профессионального футбола . Группа Пингвин. ISBN 978-1-59420-141-7 .
- Маккензи, Майкл (1997). Arrowhead: Дом вождей . Издательская группа Аддакс. ISBN 1-886110-11-5 .
- Петерсон, Джон Э. (2003). Легкая атлетика Канзас-Сити: история бейсбола, 1954–1967 . МакФарланд. ISBN 0-7864-1610-6 .
- Сталлард, Марк (2004). Энциклопедия вождей Канзас-Сити (2-е изд.). Спортивное Издательство, ООО. ISBN 1-58261-834-8 .





