Твиттер
 Логотип используется с 2023 года. [а] | |
 Домашнюю страницу X посетили при выходе из системы в августе 2024 г. | |
| Раньше | Твиттер (2006–2023 гг.) |
|---|---|
Тип сайта | Служба социальных сетей |
| Available in | Multilingual |
| Founded | March 21, 2006, in San Francisco, California, U.S. |
| Area served | Worldwide, except blocking countries |
| Owner |
|
| Founder(s) | |
| Chairman | Elon Musk |
| CEO | Linda Yaccarino |
| URL | x.com |
| Registration | Required[b] |
| Launched | July 15, 2006 |
| Current status | Active |
| Native client(s) on | |
| Written in | |
X , обычно называемый прежним названием Twitter , представляет собой службу социальной сети . Это один из крупнейших в мире веб-сайтов социальных сетей и один из самых посещаемых веб-сайтов в мире . [3] [4] Пользователи могут делиться короткими текстовыми сообщениями, изображениями и видео в публикациях (ранее — « твиты »), а также ставить лайки или репостить/ретвитить контент других пользователей. [5] X также включает в себя прямой обмен сообщениями , видео- и аудиозвонки, закладки, списки и сообщества, а также Spaces — функцию социального аудио. Пользователи могут голосовать за контекст, добавленный одобренными пользователями, с помощью функции «Заметки сообщества» .
Twitter был создан в марте 2006 года Джеком Дорси , Ноем Глассом , Бизом Стоуном и Эваном Уильямсом и запущен в июле того же года. Twitter быстро рос; к 2012 году более 100 миллионов пользователей создавали 340 миллионов твитов в день. [6] Twitter, Inc. базировалась в Сан-Франциско , штат Калифорния, и имела более 25 офисов по всему миру. [7] Отличительной особенностью сервиса является то, что сообщения должны быть краткими. Изначально размер сообщений был ограничен 140 символами, но в 2017 году этот лимит был изменен до 280 символов, а в 2023 году он был удален для платных аккаунтов. [8] The majority of tweets are produced by a minority of users.[9][10] In 2020, it was estimated that approximately 48 million accounts (15% of all accounts) were not genuine people.[11]
The service is owned by the American company X Corp., which was established to succeed the prior owner Twitter, Inc. in March 2023 following the October 2022 acquisition of Twitter by Elon Musk for US$44 billion. Musk stated that his goal with the acquisition was to promote free speech on the platform. Since his acquisition, the platform has been criticized for enabling the increased spread of disinformation[12][13][14] and hate speech.[15][16][17] Linda Yaccarino succeeded Musk as CEO on June 5, 2023, with Musk remaining as the chairman and the chief technology officer.[18][19][20] In July 2023, Musk announced that Twitter would be rebranded to X and the bird logo would be retired.[21][22] Branding changes were rolled out over the following year and completed in May 2024. In December 2023, Fidelity estimated the value of the company to be down 71.5% from its purchase price.[23] Since Musk's takeover, data from app-tracking firms has shown that global usage of X has declined by approximately 15%, compared to a decline of 5–10% in some other social media sites.[24][25][26] X has disputed that usage has dropped at all, with Musk claiming that the site had grown to 600 million users as of a May 2024[update] post on X.[27]
History
2006–2007: Creation and initial reaction

Jack Dorsey claims to have introduced the idea of an individual using an SMS service to communicate to a small group during an "all-day brainstorming session" at the podcasting company Odeo in 2006.[28] The original project code name for the service was twttr, an idea that Williams later ascribed to Noah Glass,[29] inspired by Flickr and the five-character length of American SMS short codes. The decision was also partly due to the fact that the domain twitter.com was already in use, and it was six months after the launch of twttr that the crew purchased the domain and changed the name of the service to Twitter.[30] The developers initially considered "10958" as the service's short code for SMS text messaging, but later changed it to "40404" for "ease of use and memorability".[31] Work on the project started in February 2006.[32] Dorsey published the first Twitter message on March 21, 2006:
jack @jack just setting up my twttr
March 21, 2006[33]
Dorsey explained the origin of the "Twitter" title as:[34]
...we came across the word "twitter", and it was just perfect. The definition was "a short burst of inconsequential information", and "chirps from birds". And that's exactly what the product was.
The first Twitter prototype, developed by Dorsey and contractor Florian Weber, was used as an internal service for Odeo employees.[32] The full version was introduced publicly on July 15, 2006.[35] In October 2006, Biz Stone, Evan Williams, Dorsey, and other members of Odeo formed Obvious Corporation and acquired Odeo, together with its assets—including Odeo.com and Twitter.com—from the investors and shareholders.[36] Williams fired Glass, who was silent about his part in Twitter's startup until 2011.[37] Twitter spun off into its own company in April 2007.[38] Williams provided insight into the ambiguity that defined this early period in a 2013 interview:[39]
With Twitter, it wasn't clear what it was. They called it a social network, they called it microblogging, but it was hard to define, because it didn't replace anything. There was this path of discovery with something like that, where over time you figure out what it is. Twitter actually changed from what we thought it was in the beginning, which we described as status updates and a social utility. It is that, in part, but the insight we eventually came to was Twitter was really more of an information network than it is a social network.
2007–2010
The tipping point for Twitter's popularity was the 2007 South by Southwest Interactive (SXSWi) conference. During the event, Twitter usage increased from 20,000 tweets per day to 60,000.[40] "The Twitter people cleverly placed two 60-inch plasma screens in the conference hallways, exclusively streaming Twitter messages," remarked Newsweek's Steven Levy. "Hundreds of conference-goers kept tabs on each other via constant twitters. Panelists and speakers mentioned the service, and the bloggers in attendance touted it."[41] Reaction at the conference was highly positive.[42] Twitter staff received the festival's Web Award prize with the remark "we'd like to thank you in 140 characters or less. And we just did!"[43]
The company experienced rapid initial growth. In 2009, Twitter won the "Breakout of the Year" Webby Award.[44][45] On November 29, 2009, Twitter was named the Word of the Year by the Global Language Monitor, declaring it "a new form of social interaction".[46] In February 2010, Twitter users were sending 50 million tweets per day.[47] By March 2010, the company recorded over 70,000 registered applications.[48] As of June 2010[update], about 65 million tweets were posted each day, equaling about 750 tweets sent each second, according to Twitter.[49] As of March 2011[update], that was about 140 million tweets posted daily.[50] As noted on Compete.com, Twitter moved up to the third-highest-ranking social networking site in January 2009 from its previous rank of twenty-second.[51]

Twitter's usage spikes during prominent events. For example, a record was set during the 2010 FIFA World Cup when fans wrote 2,940 tweets per second in the thirty-second period after Japan scored against Cameroon on June 14, 2010. The record was broken again when 3,085 tweets per second were posted after the Los Angeles Lakers' victory in the 2010 NBA Finals on June 17, 2010,[52] and then again at the close of Japan's victory over Denmark in the World Cup when users published 3,283 tweets per second.[53] The record was set again during the 2011 FIFA Women's World Cup Final between Japan and the United States, when 7,196 tweets per second were published.[54] When American singer Michael Jackson died on June 25, 2009, Twitter servers crashed after users were updating their status to include the words "Michael Jackson" at a rate of 100,000 tweets per hour.[55] The current record as of August 3, 2013[update], was set in Japan, with 143,199 tweets per second during a television screening of the movie Castle in the Sky[56] (beating the previous record of 33,388, also set by Japan for the television screening of the same movie).[57]
The first unassisted off-Earth Twitter message was posted from the International Space Station by NASA astronaut T. J. Creamer on January 22, 2010.[58] By late November 2010, an average of a dozen updates per day were posted on the astronauts' communal account, @NASA_Astronauts. NASA has also hosted over 25 "tweetups", events that provide guests with VIP access to NASA facilities and speakers with the goal of leveraging participants' social networks to further the outreach goals of NASA.
Twitter acquired application developer Atebits on April 11, 2010. Atebits had developed the Apple Design Award-winning Twitter client Tweetie for the Mac and iPhone. The application became the official Twitter client for the iPhone, iPad and Mac.[59]
2010–2014
From September through October 2010, the company began rolling out "New Twitter", an entirely revamped edition of twitter.com. Changes included the ability to see pictures and videos without leaving Twitter itself by clicking on individual tweets which contain links to images and clips from a variety of supported websites, including YouTube and Flickr, and a complete overhaul of the interface, which shifted links such as '@mentions' and 'Retweets' above the Twitter stream, while 'Messages' and 'Log Out' became accessible via a black bar at the very top of twitter.com. As of November 1, 2010[update], the company confirmed that the "New Twitter experience" had been rolled out to all users. In 2019, Twitter was announced to be the 10th most downloaded mobile app of the decade, from 2010 to 2019.[60]
On April 5, 2011, Twitter tested a new homepage and phased out the "Old Twitter".[61] However, a glitch came about after the page was launched, so the previous "retro" homepage was still in use until the issues were resolved; the new homepage was reintroduced on April 20.[62][63] On December 8, 2011, Twitter overhauled its website once more to feature the "Fly" design, which the service says is easier for new users to follow and promotes advertising. In addition to the Home tab, the Connect and Discover tabs were introduced along with a redesigned profile and timeline of Tweets. The site's layout has been compared to that of Facebook.[64][65] On February 21, 2012, it was announced that Twitter and Yandex agreed to a partnership. Yandex, a Russian search engine, finds value within the partnership due to Twitter's real-time news feeds. Twitter's director of business development explained that it is important to have Twitter content where Twitter users go.[66] On March 21, 2012, Twitter celebrated its sixth birthday by announcing that it had 140 million users, a 40% rise from September 2011, who were sending 340 million tweets per day.[67][68]
On June 5, 2012, a modified logo was unveiled through the company blog, removing the text to showcase the slightly redesigned bird as the sole symbol of Twitter.[69][70] On December 18, 2012, Twitter announced it had surpassed 200 million monthly active users.
On January 28, 2013, Twitter acquired Crashlytics in order to build out its mobile developer products.[71] On April 18, 2013, Twitter launched a music app called Twitter Music for the iPhone.[72] On August 28, 2013, Twitter acquired Trendrr,[73] followed by the acquisition of MoPub on September 9, 2013.[74] As of September 2013[update], the company's data showed that 200 million users sent over 400 million tweets daily, with nearly 60% of tweets sent from mobile devices.[75]
During Super Bowl XLVII on February 3, 2013, when the power went out in the Mercedes-Benz Superdome, Mondelez International vice president Lisa Mann was asked to tweet "You can still dunk in the dark", referring to Oreo cookies. She approved and later told Ad Age in 2020, "Literally the world [had] changed when I woke up the next morning." This became a milestone in the development of commenting daily on culture.[76]
2014–2020
In April 2014, Twitter underwent a redesign that made the site resemble Facebook somewhat, with a profile picture and biography in a column left to the timeline, and a full-width header image with parallax scrolling effect.[c][77] That layout was used as the main for the desktop front end until July 2019, undergoing changes over time such as having rounded profile pictures since June 2017.[78]
In April 2015, the Twitter.com desktop homepage changed.[79] Later in the year it became apparent that growth had slowed, according to Fortune,[80] Business Insider,[81] Marketing Land[82] and other news websites including Quartz (in 2016).[83]
On April 29, 2018, the first commercial tweet from space was sent by a private company Solstar utilizing solely commercial infrastructure during the New Shepard flight.[84]
Since May 2018, tweet replies deemed by an algorithm to be detractive from the conversation are initially hidden and only loaded by actuating a "Show more replies" element at the bottom.[85]
In 2019, Twitter released another redesign of its user interface.[86] By the start of 2019[update], Twitter had more than 330 million monthly active users.[87]
2020–2022

Twitter experienced considerable growth during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020.[88] The platform also was increasingly used for misinformation related to the pandemic.[89] Twitter started marking tweets which contained misleading information, and adding links to fact-checks.[90] In May 2020, Twitter moderators marked two tweets from U.S. President Donald Trump as "potentially misleading" and linked to a fact-check.[91] Trump responded by signing an executive order to weaken Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act, which limits social media sites' liability for content moderation decisions.[92][93][94] Twitter later banned Trump, claiming that he violated "the glorification of violence policy".[95] The ban drew criticism from conservatives and European leaders, who saw it as an interference on freedom of speech.[96]
On June 5, 2021, the Nigerian government issued an indefinite ban on Twitter usage in the country, citing "misinformation and fake news spread through it have had real world violent consequences",[97] after the platform removed tweets made by the Nigerian President Muhammadu Buhari.[98] Nigeria's ban was criticized by Amnesty International.[99]
In 2021, Twitter began the research phase of Bluesky, an open source decentralized social media protocol where users can choose which algorithmic curation they want.[100][101] The same year, Twitter also released Twitter Spaces, a social audio feature;[102][103] "super follows", a way to subscribe to creators for exclusive content;[104] and a beta of "ticketed Spaces", which makes access to certain audio rooms paid.[105] Twitter unveiled a redesign in August 2021, with adjusted colors and a new Chirp font, which improves the left-alignment of most Western languages.[106]
In June 2022, Twitter announced a partnership with e-commerce giant Shopify and its plans to launch a sales channel app for U.S. Shopify merchants.[107]
On August 23, 2022, the contents of a whistleblower complaint by former information security head Peiter Zatko to the United States Congress were published. Zatko had been fired by Twitter in January 2022. The complaint alleges that Twitter failed to disclose several data breaches, had negligent security measures, violated United States securities regulations, and broke the terms of a previous settlement with the Federal Trade Commission over the safeguarding of user data. The report also claims that the Indian government forced Twitter to hire one of its agents to gain direct access to user data.[108]
2022–present: Transition to X

Elon Musk entered into a deal to acquire Twitter for US$44 billion on April 25, 2022.[109] The deal formally closed on October 27, 2022, following an attempt by Musk to terminate the deal in July. Immediately following the closure of the deal, Musk ousted existing leadership at Twitter, Inc. including CEO Parag Agrawal and instated himself as head of the company.[110]
Following Twitter's change in ownership, Musk began referring to the platform as "X/Twitter"[111][112][113] and "X (Twitter)",[114] and renamed several features to remove references to bird-oriented terminology, including Birdwatch to Community Notes[115] and Quote Tweets to Quotes.[116] On July 23, 2023, Musk confirmed the rebrand, which started when the X.com domain (formerly associated with PayPal) began redirecting to Twitter;[117] the logo was changed from the bird to the X the next day,[118] and the platform's official main and associated accounts also began using the letter X within their handles.[119] The @x handle was originally owned by photographer Gene X Hwang, who registered it in 2007. Hwang had expressed willingness to sell the handle, but received an email on July 25, 2023, stating that the company was taking it. He was offered some X merchandise and a meeting with the company's leaders, but no financial benefits.[120] The Android app's name and icon were changed to X on Google Play by July 27; the same change went live on the App Store on July 31 after Apple granted an exception to its minimum character length of 2.[121][122][123] Around that time, some more elements of the Twitter branding were removed from the web version, including tweets being renamed to "posts".[124]
The rebrand was described as unusual, given that Twitter's brand was already strong internationally, with words like "tweet" having entered common language.[125] The rebranding has been criticized on the basis that the trademarkability of the name and logo is weak: there are almost 900 companies in the U.S. that own an X trademark,[126] including an existing social media-related logo owned by Meta Platforms.[127] The X logo uses a blackboard bold X, a character that has appeared in mathematical textbooks since the 1970s and that is included in Unicode as U+1D54F 𝕏 MATHEMATICAL DOUBLE-STRUCK CAPITAL X.[128][129]
A few days after the rebrand took effect, an AP Stylebook update recommended that journalists refer to the platform as "X, formerly known as Twitter".[5] In September 2023, Ad Age, citing The Harris Poll, noted that the rebranding had not publicly caught on, with the majority of users as well as notable brands still referring to X as "Twitter".[130] In December 2023, Fidelity estimated the value of the company to be down 71.5% from its purchase price.[23] However, the purchase occurred just before a marketwide price drop and Musk acknowledged that he overpaid for the service.[131][132] Since Musk's takeover, data from app-tracking firms has shown that global usage of X has declined by approximately 15%, compared to a decline of 5–10% in some other social media sites.[24][25][26] This decline in usership has been disputed by Musk, who claimed in May 2024 that there were 600 million monthly active users and 300 million daily active users.[133]
On May 17, 2024, the URL was officially changed from twitter.com to x.com.[134][135]
On July 17, 2024, Musk posted that the headquarters of X would be moved from San Francisco to Austin, Texas. This was in response to the AB 1955 bill signed by California Governor Gavin Newsom which bans school districts from passing policies requiring schools to notify parents if their child asks to change their gender identification.[136][137]
Appearance and features
This section should include only a brief summary of List of Twitter features. (November 2023) |
Tweets
Tweets were publicly visible by default, but senders can restrict message delivery to only their followers. Users can mute users they do not wish to interact with, block accounts from viewing their posts, and remove accounts from their followers list.[138][139][140] Users can post via the Twitter website, compatible external applications (such as for smartphones), or by Short Message Service (SMS) available in certain countries.[141] Users may subscribe to other users' posts—this is known as "following" and subscribers are known as "followers"[142] or "tweeps", a portmanteau of Twitter and peeps.[143] Individual posts can be forwarded by other users to their own feed, a process known as a "repost" or "retweet". In 2015, Twitter launched "quote tweet" (originally called "retweet with comment"),[144] a feature that allows users to add a comment to their post, imbedding one post in the other.[145] Users can also "like" (formerly "favorite") individual tweets.[146]
The counters for "likes", "retweets/reposts", and replies appear next to the respective buttons in timelines such as on profile pages and search results. Counters for likes and reposts exist on a post's standalone page too. Since September 2020, quote tweets, formerly known as "retweet with comment", have their own counter on their post page.[144] Until the legacy desktop front end that was discontinued in 2020, a row with miniature profile pictures of up to ten liking or retweeting users was displayed (earliest documented implementation in December 2011 overhaul), as well as a tweet reply counter next to the according button on a tweet's page.[147][148]
Twitter allows users to update their profile via their mobile phones either by text messaging or by apps released for certain smartphones and tablets.[149] Twitter has been compared to a web-based Internet Relay Chat (IRC) client.[150] Twitter announced in a tweet on September 1, 2022, that the ability to edit a tweet was being tested for select users. The company said the feature was being tested first to determine whether it could be abused. Editing would be allowed for 30 minutes, and previous versions of an edited post would be available. Eventually, all Twitter Blue subscribers would be able to use the feature.[151]
Users can group posts together by topic or type by use of hashtags – words or phrases prefixed with a "#" sign. Similarly, the "@" sign followed by a username is used for mentioning or replying to other users.[152] In 2014, Twitter introduced hashflags, special hashtags that automatically generate a custom emoji next to them for a certain period of time.[153] Hashflags may be generated by Twitter themselves[154] or be purchased by corporations.[155] To repost a message from another X user and share it with one's own followers, a user can click the repost button within the post. Users can reply to other accounts' replies. Users can hide replies to their messages and select who can reply to each of their tweets before sending them: anyone, accounts who follow the poster, specific accounts, or none.[156][157]
The original, strict 140 character limit was gradually relaxed. In 2016, Twitter announced that attachments, links, and media such as photos, videos, and the person's handle, would no longer count; a user photo post used to count for around 24 characters.[158][159] In 2017, Twitter handles were similarly excluded.[160] The same year, Twitter doubled its historical 140-character-limitation to 280.[161] Under the new limit, glyphs are counted as a variable number of characters, depending upon the script they are from.[161] In 2023, Twitter announced that Twitter Blue users could create posts with up to 4,000 characters in length.[162]
t.co is a URL shortening service created by Twitter.[163] It is only available for links posted to Twitter and not available for general use.[163] All links posted to Twitter use a t.co wrapper.[164] Twitter intended the service to protect users from malicious sites,[163] and to use it to track clicks on links within tweets.[163][165] Twitter had previously used the services of third parties TinyURL and bit.ly.[166]
In June 2011, Twitter announced its own integrated photo-sharing service that enables users to upload a photo and attach it to a Tweet right from Twitter.com.[167] Users now also have the ability to add pictures to Twitter's search by adding hashtags to the tweet.[168] Twitter also plans to provide photo galleries designed to gather and syndicate all photos that a user has uploaded on Twitter and third-party services such as TwitPic.[168] On March 29, 2016, Twitter introduced the ability to add a caption of up to 480 characters to each image attached to a tweet,[169][170] accessible via screen reading software or by hovering the mouse above a picture inside TweetDeck. In April 2022, Twitter made the ability to add and view captions globally available. Descriptions can be added to any uploaded image with a limit of 1000 characters. Images that have a description will feature a badge that says ALT in the bottom left corner, which will bring up the description when clicked.[171]
In 2015, Twitter began to roll out the ability to attach poll questions to tweets. Polls are open for up to 7 days, and voters are not personally identified.[172] In Twitter's early years, users could communicate with Twitter using SMS. Twitter discontinued this feature in most countries in April 2023, after hackers had exposed vulnerabilities in the feature.[173][174]
Multimedia content
In 2016, Twitter began to place a larger focus on live streaming video programming, hosting various events including streams of the Republican and Democratic conventions during the U.S. presidential campaign,[175] and winning a bid for non-exclusive streaming rights to ten NFL games in 2016.[176][177] During an event in New York in May 2017, Twitter announced that it planned to construct a 24-hour streaming video channel hosted within the service, featuring content from various partners.[176][178] Twitter announced a number of new and expanded partnerships for its streaming video services at the event, including Bloomberg, BuzzFeed, Cheddar, IMG Fashion, Live Nation Entertainment, Major League Baseball, MTV and BET, NFL Network, the PGA Tour, The Players' Tribune, Ben Silverman and Howard T. Owens' Propagate, The Verge, Stadium and the WNBA.[179] as of the first quarter of 2017[update], Twitter had over 200 content partners, who streamed over 800 hours of video over 450 events.[179]
Twitter Spaces is a social audio feature that enables users to host or participate in a live-audio virtual environment called space for conversation. A maximum of 13 people are allowed onstage. The feature was initially limited to users with at least 600 followers, but since October 2021, any Twitter user can create a Space.[180]
In March 2020, Twitter began to test a stories feature known as "fleets" in some markets,[181][182] which officially launched on November 17, 2020.[183][184] Fleets could contain text and media, are only accessible for 24 hours after they are posted, and are accessed within the Twitter app;[181] Twitter announced it would start implementing advertising into fleets in June 2021.[185] Fleets were removed in August 2021; Twitter had intended for fleets to encourage more users to tweet regularly, but instead they were generally used by already-active users.[186]
Curation
Trending topics

A word, phrase, or topic that is mentioned at a greater rate than others is said to be a "trending topic". A topic can "trend" because of an event that naturally prompts tweets, or through a concerted effort by users.[187] These topics help Twitter and its users understand world events and the public's opinion on them.[188] The Twitter web interface displays a list of trending topics on a sidebar on the home page, along with sponsored content.
Trending topics are sometimes the result of concerted efforts and manipulations by fans of certain celebrities or cultural phenomena, particularly musicians like Lady Gaga, Justin Bieber, Rihanna and One Direction, and novel series Twilight and Harry Potter. Twitter has altered the trend algorithm in the past to prevent manipulation of this type with limited success.[189] Twitter also censors trending hashtags that are claimed to be abusive or offensive. Twitter censored the #thatsafrican[190] and #thingsdarkiessay hashtags after users complained that they found the hashtags offensive.[191]
Lists
In late 2009, the "Twitter Lists" feature was added, making it possible for users to follow a curated list of accounts all at once, rather than following individual users.[142][192] Currently,[when?] lists can be set to either public or private. Public lists may be recommended to users via the general Lists interface and appear in search results.[193] If a users follows a public list, it will appear in the "View Lists" section of their profile, so that other users may quickly find it and follow it as well.[194] Private lists can only be followed if the creator shares a specific link to their list. Lists add a separate tab to the Twitter interface with the title of the list, such as "News" or "Economics".
Moments
In October 2015, Twitter introduced "Moments"—a feature that allows users to curate tweets from other users into a larger collection. Twitter initially intended the feature to be used by its in-house editorial team and other partners; they populated a dedicated tab in Twitter's apps, chronicling news headlines, sporting events, and other content.[195][196] In September 2016, creation of moments became available to all Twitter users.[197]
Algorithm
On October 21, 2021, report based on a "long-running, massive-scale randomized experiment" that analyzed "millions of tweets sent between 1 April and 15 August 2020", found that Twitter's machine learning recommendation algorithm amplified right-leaning politics on personalized user Home timelines.[198]: 1 [199] The report compared seven countries with active Twitter users where data was available—Germany, Canada, the United Kingdom, Japan, France, and Spain—and examined Tweets "from major political groups and politicians".[198]: 4 Researchers used the 2019 Chapel Hill Expert Survey (CHESDATA) to position parties on political ideology within each country.[198]: 4 The "machine learning algorithms"—introduced by Twitter in 2016—personalized 99% of users' feeds by displaying Tweets—even older Tweets and Retweets from accounts the user had not directly followed—but that the algorithm had "deemed relevant" to the users' past preferences.[198]: 4 Twitter randomly chose 1% of users whose Home timelines displayed content in reverse-chronological order from users they directly followed.[198]: 2
Mobile
Twitter had mobile apps for iPhone, iPad, and Android.[200] In April 2017, Twitter introduced Twitter Lite, a progressive web app designed for regions with unreliable and slow Internet connections, with a size of less than one megabyte, designed for devices with limited storage capacity.[201][202]
Twitter Blue
On June 3, 2021, Twitter announced a paid subscription service called Twitter Blue. Following Twitter's ongoing "X" name change, the subscription was rebranded to X Blue (or simply Blue), and, on August 5, 2023, was rebranded to X Premium (or simply Premium).[203][204] The subscription provides additional premium features to the service.[205][206] In November 2023 a "Premium+" subscription was launched, with a higher monthly fee giving benefits such as the omission of adverts on For You and Following feeds.[207]
Verification of paid accounts
In November 2022, Musk announced plans to add account verification and the ability to upload longer audio and video to Twitter Blue. A previous perk offering advertising-free news articles from participating publishers was dropped, but Musk stated that Twitter did want to work with publishers on a similar "paywall bypass" perk.[208][209][210] Musk had pushed for a more expensive version of Twitter Blue following his takeover, arguing that it would be needed to offset a decline in advertising revenue.[211] Twitter states that paid verification is required to help reduce fraudulent accounts.[212]
The verification marker was included in a premium tier of Twitter Blue introduced on November 9, 2022, priced at US$7.99.[213] On November 11, 2022, after the introduction of this feature led to prominent issues involving accounts using the feature to impersonate public figures and companies, Twitter Blue with verification was temporarily suspended.[214][215] After about a month, Twitter Blue was relaunched on December 12, 2022, though for those purchasing the service through the iOS app store, the cost will be $10.99 a month as to offset the 30% revenue split that Apple takes.[216]
Twitter initially grandfathered users and entities that had gained verification due to their status as public figures, referring to them as "legacy verified accounts" that "may or may not be notable".[217] On March 25, 2023, it was announced that "legacy" verification status would be removed; a subscription will be required to retain verified status, costing $1,000 per-month for organizations (which are designated with a gold verified symbol),[212] plus an additional $50 for each "affiliate".[218][219] The change was originally scheduled for April 1, 2023, but was delayed to April 20, 2023, following criticism of the changes.[220] Musk also announced plans for the "For You" timeline to prioritize verified accounts and user followers only beginning April 15, 2023, and threatened to only allow verified users to participate in polls (although the latter change has yet to occur).[221]
Effective April 21, 2023, Twitter requires companies to participate in the verified organizations program in order to purchase advertising on the platform, although companies that spend at least $1,000 on advertising per-month automatically receive membership in the program at no additional cost.[212]
From April 25, 2023, verified users are now prioritized in replies to tweets.[222][223]
User monetization
In June 2021, the company opened applications for its premium subscription options called Super Follows. This lets eligible accounts charge $2.99, $4.99 or $9.99 per month to subscribe to the account.[224] The launch only generated about $6,000 in its first two weeks.[225] In 2023, the Super Follows feature was rebranded as simply "subscriptions", allowing users to publish exclusive long-form posts and videos for their subscribers; the pivot in marketing was reportedly intended to help compete with Substack.[226]
In May 2021, Twitter began testing a Tip Jar feature on its iOS and Android clients. The feature allows users to send monetary tips to certain accounts, providing a financial incentive for content creators on the platform. The Tip Jar is optional and users can choose whether or not to enable tips for their account.[227] On September 23, 2021, Twitter announced that it will allow users to tip users on the social network with bitcoin. The feature will be available for iOS users. Previously, users could tip with fiat currency using services such as Square's Cash App and PayPal's Venmo. Twitter will integrate the Strike bitcoin lightning wallet service. It was noted that at this current time, Twitter will not take a cut of any money sent through the tips feature.[228]
On August 27, 2021, Twitter rolled out Ticketed Spaces, which let Twitter Spaces hosts charge between $1 and $999 for access to their rooms.[229] In April 2022, Twitter announced that it will partner with Stripe, Inc. for piloting cryptocurrency payouts for limited users in the platform. Eligible users of Ticketed Spaces and Super Follows will be able to receive their earnings in the form of USD coin, a stablecoin whose value is that of the U.S. dollar. Users can also hold their earnings in crypto wallets, and then exchange them into other cryptocurrencies.[230]
E-commerce
From 2014 to 2017, Twitter offered a "Buy button" feature, allowing tweets to embed products that could be purchased from within the service. Users could also add their billing and shipping information directly to their accounts. The buy button's platform partners at launch included Stripe, Gumroad, Musictoday, and The Fancy,[231]
In July 2021, Twitter began testing a "Shop module" for iOS users in the United States, allowing accounts associated with brands to display a carousel of cards on their profiles showcasing products. Unlike the Buy button, where order fulfillment was handed from within Twitter, these cards are external links to online storefronts from which the products may be purchased.[232] In March 2022, Twitter expanded the test to allow companies to showcase up to 50 products on their profiles.[233]
In November 2021, Twitter introduced support for "shoppable" live streams, in which brands can hold streaming events that similarly display banners and pages highlighting products that are featured in the presentation.[234]
Usage
Daily user estimates vary as the company does not publish statistics on active accounts. A February 2009 Compete.com blog entry ranked Twitter as the third most used social network based on their count of 6 million unique monthly visitors and 55 million monthly visits.[51] An April 2017 a statista.com blog entry ranked Twitter as the tenth most used social network based on their count of 319 million monthly visitors.[235] Its global user base in 2017 was 328 million.[236] According to Musk, X had 500 million monthly active users in March 2023, 550 million in March 2024, and 600 million in May 2024.[27][237][238]
Demographics
This section needs to be updated. (September 2019) |
In 2009, Twitter was mainly used by older adults who might not have used other social sites before Twitter.[239] According to comScore only 11% of Twitter's users were aged 12 to 17.[239] According to a study by Sysomos in June 2009, women made up a slightly larger Twitter demographic than men—53% over 47%. It also stated that 5% of users accounted for 75% of all activity.[240] According to Quancast, 27 million people in the US used Twitter in September 2009; 63% of Twitter users were under 35 years old; 60% of Twitter users were Caucasian, but a higher than average (compared to other Internet properties) were African American/black (16%) and Hispanic (11%); 58% of Twitter users have a total household income of at least US$60,000.[241] The prevalence of African American Twitter usage and in many popular hashtags has been the subject of research studies.[242][243]
Twitter grew from 100 million monthly active users (MAUs) in September 2011,[244] to 255 million in March 2014,[245] and more than 330 million in early 2019.[246][247][87] In 2013, there were over 100 million users actively using Twitter daily and about 500 million tweets every day.[248] A 2016 Pew research poll found that Twitter is used by 24% of all online US adults. It was equally popular with men and women (24% and 25% of online Americans respectively), but more popular with younger generations (36% of 18–29 year olds).[249] A 2019 survey conducted by the Pew Foundation found that Twitter users are three times as likely to be younger than 50 years old, with the median age of adult U.S. users being 40. The survey found that 10% of users who are most active on Twitter are responsible for 80% of all tweets.[250]
Content
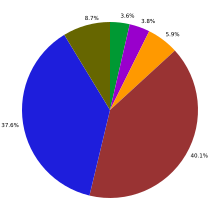
San Antonio-based market-research firm Pear Analytics analyzed 2,000 tweets (originating from the United States and in English) over a two-week period in August 2009 from 11:00 am to 5:00 pm (CST) and separated them into six categories.[251] Pointless babble made up 40%, with 38% being conversational. Pass-along value had 9%, self-promotion 6% with spam and news each making 4%.
Despite Jack Dorsey's own open contention that a message on Twitter is "a short burst of inconsequential information", social networking researcher danah boyd responded to the Pear Analytics survey by arguing that what the Pear researchers labeled "pointless babble" is better characterized as "social grooming" or "peripheral awareness" (which she justifies as persons "want[ing] to know what the people around them are thinking and doing and feeling, even when co-presence isn't viable").[252] Similarly, a survey of Twitter users found that a more specific social role of passing along messages that include a hyperlink is an expectation of reciprocal linking by followers.[253]
Levels of use
According to research published in April 2014, around 44% of user accounts have never tweeted.[254] About 22% of Americans say they have used Twitter, according to a 2019 Pew Research Center survey.[255] In 2009, Nielsen Online reported that Twitter had a user-retention rate of 40%. Many people stop using the service after a month; therefore the site may potentially reach only about 10% of all Internet users.[256] Noting how demographics of Twitter users differ from the average Americans, commentators have cautioned against media narratives that treat Twitter as representative of the population,[257] adding that only 10% of users Tweet actively, and that 90% of Twitter users have Tweeted no more than twice. In 2016, shareholders sued Twitter, alleging it "artificially inflated its stock price by misleading them about user engagement". The company announced on September 20, 2021, that it would pay $809.5 million to settle this class-action lawsuit.[258]
User engagement
User engagement is usually measured by the number of likes, replies and reposts. A 2023 study showed that retweets are more likely to contain positive content and address larger audiences using the first-person pronoun "we". Replies, on the other hand, are more likely to contain negative content and address individuals using the second-person pronoun "you" and the third-person pronouns "he" or "she". While influencers with many followers tend to post positive messages, often using the word "love" when addressing larger audiences, users with less followers tend to engage in interpersonal conversations to provoke user engagement.[259]
Branding

When it was known as Twitter, X was internationally identifiable by its signature bird logo, or the Twitter Bird. The original logo, which was simply the word Twitter, was in use from its launch in March 2006. It was accompanied by an image of a bird which was later discovered to be a piece of clip art created by the British graphic designer Simon Oxley.[260] A new logo had to be redesigned by founder Biz Stone with help from designer Philip Pascuzzo, which resulted in a more cartoon-like bird in 2009. This version had been named "Larry the Bird" after Larry Bird of the NBA's Boston Celtics fame.[260][261]
Within a year, the Larry the Bird logo underwent a redesign by Stone and Pascuzzo to eliminate the cartoon features, leaving a solid silhouette of Larry the Bird that was used from 2010 through 2012.[260] In 2012, Douglas Bowman created a further simplified version of Larry the Bird, keeping the solid silhouette but making it more similar to a mountain bluebird.[262] This logo was simply called the "Twitter Bird" and was used until July 2023.[260][263][264]

On July 22, 2023, Elon Musk announced that the service would be re-branded to "X",[265] in his pursuit of creating an "everything app".[264] Musk's X profile picture, along with the official X accounts, and the icons when browsing/signing up for the platform, were updated to reflect the new logo.[266] The logo (𝕏) is a Unicode mathematical alphanumeric symbol for the letter "X" styled in double-strike bold.
Mike Proulx of The New York Times was critical of this change, saying the brand value has been "wiped out". Mike Carr says the new logo gives a "'Big Brother' tech overlord vibe" in contrast to the "cuddly" nature of the previous bird logo.[267] Users review bombed the newly rebranded "X" app on the iOS App Store on the day it was revealed, and Rolling Stone's Miles Klee said that the rebrand "reeks of desperation".[268][269]
Finances
Revenue sources

On April 13, 2010, Twitter announced plans to offer paid advertising for companies that would be able to purchase "promoted tweets" to appear in selective search results on the Twitter website, similar to Google Adwords' advertising model.[271][272] Users' photos can generate royalty-free revenue for Twitter, and an agreement with World Entertainment News Network (WENN) was announced in May 2011.[273] Twitter generated an estimated US$139.5 million in advertising sales during 2011.[274]
In June 2011, Twitter announced that it would offer small businesses a self-service advertising system.[275] The self-service advertising platform was launched in March 2012 to American Express card members and merchants in the U.S. on an invite-only basis.[276] To continue their advertising campaign, Twitter announced on March 20, 2012, that promoted tweets would be introduced to mobile devices.[277] In April 2013, Twitter announced that its Twitter Ads self-service platform, consisting of promoted tweets and promoted accounts, was available to all U.S. users without an invite.[276]
On August 3, 2016, Twitter launched Instant Unlock Card, a new feature that encourages people to tweet about a brand in order to earn rewards and utilize the social media network's conversational ads. The format itself consists of images or videos with call-to-action buttons and a customizable hashtag.[278]
Advertising bans
In October 2017, Twitter banned the Russian media outlets RT and Sputnik from advertising on their website following the conclusions of the U.S. national intelligence report the previous January that both Sputnik and RT had been used as vehicles for Russia's interference in the 2016 US presidential election.[279] Maria Zakharova for the Russian foreign ministry said the ban was a "gross violation" by the US of free speech.[280]
In October 2019, Twitter announced it would stop running political ads on its ad platform effective November 22. This resulted from several spurious claims made by political ads. Company CEO Dorsey clarified that internet advertising had great power and was extremely effective for commercial advertisers, the power brings significant risks to politics where crucial decisions impact millions of lives.[281] The company reversed the ban in August 2023,[282] publishing criteria governing political advertising which do not allow the promotion of false or misleading content, and requiring advertisers to comply with laws, with compliance being the sole responsibility of the advertiser.[283]
In April 2022, Twitter announced a ban on "misleading" advertisements that go against "the scientific consensus on climate change". While the company did not give full guidelines, it stated that the decisions would be made with the help of "authoritative sources", including the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.[284]
Fines
Twitter had been fined several times for non-compliance with laws and regulations. On May 25, 2022, Twitter was fined $150 million by the Federal Trade Commission and the United States Department of Justice for collecting users' contact details and using them for targeted advertising.[285][286]
Technology
Implementation
Twitter relies on open-source software.[287] The Twitter Web interface uses the Ruby on Rails framework,[288] deployed on a performance enhanced Ruby Enterprise Edition implementation of Ruby.[289][needs update]
In the early days of Twitter, tweets were stored in MySQL databases that were temporally sharded (large databases were split based on time of posting). After the huge volume of tweets coming in caused problems reading from and writing to these databases, the company decided that the system needed re-engineering.[56]
From Spring 2007 to 2008, the messages were handled by a Ruby persistent queue server called Starling.[290] Since 2009, implementation has been gradually replaced with software written in Scala.[291] The switch from Ruby to Scala and the JVM has given Twitter a performance boost from 200 to 300 requests per second per host to around 10,000–20,000 requests per second per host. This boost was greater than the 10x improvement that Twitter's engineers envisioned when starting the switch. The continued development of Twitter has also involved a switch from monolithic development of a single app to an architecture where different services are built independently and joined through remote procedure calls.[56]
As of April 6, 2011, Twitter engineers confirmed that they had switched away from their Ruby on Rails search stack to a Java server they call Blender.[292]
Individual tweets are registered under unique IDs called snowflakes, and geolocation data is added using 'Rockdove'. The URL shortener t.co then checks for a spam link and shortens the URL. Next, the tweets are stored in a MySQL database using Gizzard, and the user receives an acknowledgement that the tweets were sent. Tweets are then sent to search engines via the Firehose API. The process is managed by FlockDB and takes an average of 350 ms.[287]
On August 16, 2013, Raffi Krikorian, Twitter's vice president of platform engineering, shared in a blog post that the company's infrastructure handled almost 143,000 tweets per second during that week, setting a new record. Krikorian explained that Twitter achieved this record by blending its homegrown and open source technologies.[56][293]
API and developer platform
Twitter was recognized for having one of the most open and powerful developer APIs of any major technology company.[294] The service's API allows other web services and applications to integrate with Twitter.[295] Developer interest in Twitter began immediately following its launch, prompting the company to release the first version of its public API in September 2006.[296] The API quickly became iconic as a reference implementation for public REST APIs and is widely cited in programming tutorials.[297]
From 2006 until 2010, Twitter's developer platform experienced strong growth and a highly favorable reputation. Developers built upon the public API to create the first Twitter mobile phone clients as well as the first URL shortener. Between 2010 and 2012, however, Twitter made a number of decisions that were received unfavorably by the developer community.[298] In 2010, Twitter mandated that all developers adopt OAuth authentication with just 9 weeks of notice.[299] Later that year, Twitter launched its own URL shortener, in direct competition with some of its most well-known third-party developers.[300] And in 2012, Twitter introduced stricter usage limits for its API, "completely crippling" some developers.[301][302] While these moves successfully increased the stability and security of the service, they were broadly perceived as hostile to developers, causing them to lose trust in the platform.[303]
In July 2020, Twitter released version 2.0 of the public API[304] and began showcasing Twitter apps made by third-party developers on its Twitter Toolbox section in April 2022.[305]
In January 2023, Twitter ended third-party access to its APIs, forcing all third-party Twitter clients to shut down.[306] This was controversial among the developer community, as many third-party apps predated the company's official apps, and the change was not announced beforehand. Twitterrific's Sean Heber confirmed in a blog post that the 16-year-old app has been discontinued. "We are sorry to say that the app's sudden and undignified demise is due to an unannounced and undocumented policy change by an increasingly capricious Twitter – a Twitter that we no longer recognize as trustworthy nor want to work with any longer."[307]
In February 2023, Twitter announced it would be ending free access to Twitter API, and began offering paid tier plans with a more limited access.[308]
Innovators patent agreement
On April 17, 2012, Twitter announced it would implement an "Innovators Patent Agreement" which would obligate Twitter to only use its patents for defensive purposes.[clarify][309]
Open source
Twitter has a history of both using and releasing open-source software while overcoming technical challenges of their service.[310] A page in their developer documentation thanks dozens of open-source projects which they have used, from revision control software like Git to programming languages such as Ruby and Scala.[311] Software released as open source by the company includes the Gizzard Scala framework for creating distributed datastores, the distributed graph database FlockDB, the Finagle library for building asynchronous RPC servers and clients, the TwUI user interface framework for iOS, and the Bower client-side package manager.[312] The popular Bootstrap frontend framework was also started at Twitter and is 10th most popular repository on GitHub.[313]
On March 31, 2023, Twitter released the source code for Twitter's recommendation algorithm,[314] which determines what tweets show up on the user's personal timeline, to GitHub. According to Twitter's blog post: "We believe that we have a responsibility, as the town square of the internet, to make our platform transparent. So today we are taking the first step in a new era of transparency and opening much of our source code to the global community."[315] Elon Musk, the CEO at the time, had been promising the move for a while — on March 24, 2022, before he owned the site, he polled his followers about whether Twitter's algorithm should be open source, and around 83% of the responses said "yes". In February, he promised it would happen within a week before pushing back the deadline to March 31 earlier this month.[316]
Also in March 2023, Twitter suffered a security attack which resulted in proprietary code being released. Twitter then had the source code removed.[317]
Interface
Twitter introduced the first major redesign of its user interface in September 2010, adopting a dual-pane layout with a navigation bar along the top of the screen, and an increased focus on the inline embedding of multimedia content. Critics considered the redesign an attempt to emulate features and experiences found in mobile apps and third-party Twitter clients.[318][319][320][321]
The new layout was revised in 2011 with a focus on continuity with the web and mobile versions, introducing "Connect" (interactions with other users such as replies) and "Discover" (further information regarding trending topics and news headlines) tabs, an updated profile design, and moving all content to the right pane (leaving the left pane dedicated to functions and the trending topics list).[322] In March 2012, Twitter became available in Arabic, Farsi, Hebrew and Urdu, the first right-to-left language versions of the site.[323] In 2023 the Twitter Web site listed 34 languages supported by Twitter.com.[324]
In September 2012, a new layout for profiles was introduced, with larger "covers" that could be customized with a custom header image, and a display of the user's recent photos posted.[325] The "Discover" tab was discontinued in April 2015,[326] and was succeeded on the mobile app by an "Explore" tab—which features trending topics and moments.[327]
In September 2018, Twitter began to migrate selected web users to its progressive web app (based on its Twitter Lite experience for mobile web), reducing the interface to two columns. Migrations to this iteration of Twitter increased in April 2019, with some users receiving it with a modified layout.[328][329]
In July 2019, Twitter officially released this redesign, with no further option to opt-out while logged in. It is designed to further-unify Twitter's user experience between the web and mobile application versions, adopting a three-column layout with a sidebar containing links to common areas (including "Explore" that has been merged with the search page) which previously appeared in a horizontal top bar, profile elements such as picture and header images and biography texts merged into the same column as the timeline, and features from the mobile version (such as multi-account support, and an opt-out for the "top tweets" mode on the timeline).[330][331]
Security
In response to early Twitter security breaches, the United States Federal Trade Commission (FTC) brought charges against the service; the charges were settled on June 24, 2010. This was the first time the FTC had taken action against a social network for security lapses. The settlement requires Twitter to take a number of steps to secure users' private information, including maintenance of a "comprehensive information security program" to be independently audited biannually.[332]
After a number of high-profile hacks of official accounts, including those of the Associated Press and The Guardian,[333] in April 2013, Twitter announced a two-factor login verification as an added measure against hacking.[334]
On July 15, 2020, a major hack of Twitter affected 130 high-profile accounts, both verified and unverified ones such as Barack Obama, Bill Gates, and Elon Musk; the hack allowed bitcoin scammers to send tweets via the compromised accounts that asked the followers to send bitcoin to a given public address, with the promise to double their money.[335] Within a few hours, Twitter disabled tweeting and reset passwords from all verified accounts.[335] Analysis of the event revealed that the scammers had used social engineering to obtain credentials from Twitter employees to access an administration tool used by Twitter to view and change these accounts' personal details as to gain access as part of a "smash and grab" attempt to make money quickly, with an estimated US$120,000 in bitcoin deposited in various accounts before Twitter intervened.[336] Several law enforcement entities including the FBI launched investigations into the attack.[337]
On August 5, 2022, Twitter disclosed that a bug introduced in a June 2021 update to the service allowed threat actors to link email addresses and phone numbers to twitter user's accounts.[338][339] The bug was reported through Twitter's bug bounty program in January 2022 and subsequently fixed. While Twitter originally believed no one had taken advantage of the vulnerability, it was later revealed that a user on the online hacking forum Breach Forums had used the vulnerability to compile a list of over 5.4 million user profiles, which they offered to sell for $30,000.[340][341] The information compiled by the hacker includes user's screen names, location and email addresses which could be utilized in phishing attacks or used to deanonymize accounts running under pseudonyms.
Outages

During an outage, Twitter users were at one time shown the "fail whale" error message image created by Yiying Lu,[342] illustrating eight orange birds using a net to hoist a whale from the ocean captioned "Too many tweets! Please wait a moment and try again."[343] Web designer and Twitter user Jen Simmons was the first to coin the term "fail whale" in a September 2007 tweet.[344][345] In a November 2013 Wired interview Chris Fry, VP of Engineering at that time, noted that the company had taken the "fail whale" out of use as the platform was now more stable.[346] Twitter had approximately 98% uptime in 2007 (or about six full days of downtime).[347] The downtime was particularly noticeable during events popular with the technology industry such as the 2008 Macworld Conference & Expo keynote address.[348][349]
User accounts
Verified accounts
In June 2009, after being criticized by Kanye West and sued by Tony La Russa over unauthorized accounts run by impersonators, the company launched their "Verified Accounts" program.[350][351] Twitter stated that an account with a "blue tick" verification badge indicates "we've been in contact with the person or entity the account is representing and verified that it is approved".[352] In July 2016, Twitter announced a public application process to grant verified status to an account "if it is determined to be of public interest" and that verification "does not imply an endorsement".[353][354][355] Verified status allows access to some features unavailable to other users, such as only seeing mentions from other verified accounts.[356]
In November 2020, Twitter announced a relaunch of its verification system in 2021. According to the new policy, Twitter verifies six different types of accounts; for three of them (companies, brands, and influential individuals like activists), the existence of a Wikipedia page will be one criterion for showing that the account has "Off Twitter Notability".[357] Twitter states that it will re-open public verification applications at some point in "early 2021".[358]
In October 2022, after the takeover of Twitter by Elon Musk, it was reported that verification would instead be included in the paid Twitter Blue service, and that existing verified accounts would lose their status if they do not subscribe.[359] On November 1, Musk confirmed that verification would be included in Blue in the future, dismissing the existing verification system as a "lords & peasants system".[208][209][210] Following concerns over the possibility of impersonation, Twitter subsequently reimplemented a second "Official" marker, consisting of a grey tick and "Official" text displayed under the username, for high-profile accounts of "government and commercial entities".[360][361]
In December 2022, the "Official" text was replaced by a gold checkmark for organizations, as well as a grey checkmark for government and multilateral accounts.[362][363]
In March 2023, the gold checkmark was made available for organizations to purchase through the Verified Organizations program (formerly called Twitter Blue for Business).[362][363]
Privacy
Tweets are public, but users can also send private "direct messages".[364] Information about who has chosen to follow an account and who a user has chosen to follow is also public, though accounts can be changed to "protected" which limits this information (and all tweets) to approved followers.[365] Twitter collects personally identifiable information about its users and shares it with third parties as specified in its privacy policy. The service also reserves the right to sell this information as an asset if the company changes hands.[366][367] Advertisers can target users based on their history of tweets and may quote tweets in ads[368] directed specifically to the user.
Twitter launched the beta version of their "Verified Accounts" service on June 11, 2009, allowing people with public profiles to announce their account name. The profile pages of these accounts display a badge indicating their status.[369]
On December 14, 2010, the United States Department of Justice issued a subpoena directing Twitter to provide information for accounts registered to or associated with WikiLeaks.[370] Twitter decided to notify its users and said in a statement, "... it's our policy to notify users about law enforcement and governmental requests for their information, unless we are prevented by law from doing so."[364]
In May 2011, a claimant known as "CTB" in the case of CTB v Twitter Inc. took action against Twitter at the High Court of Justice of England and Wales,[371] requesting that the company release details of account holders. This followed gossip posted on Twitter about professional footballer Ryan Giggs's private life. This led to the 2011 British privacy injunctions controversy and the "super-injunction".[372] Tony Wang, the head of Twitter in Europe, said that people who do "bad things" on the site would need to defend themselves under the laws of their own jurisdiction in the event of controversy and that the site would hand over information about users to the authorities when it was legally required to do so.[373] He also suggested that Twitter would accede to a UK court order to divulge names of users responsible for "illegal activity" on the site.[374]
Twitter acquired Dasient, a startup that offers malware protection for businesses, in January 2012. Twitter announced plans to use Dasient to help remove hateful advertisers on the website.[375] Twitter also offered a feature which would allow tweets to be removed selectively by country, before deleted tweets used to be removed in all countries.[376][377] The first use of the policy was to block the account of German neo-Nazi group Besseres Hannover on October 18, 2012.[378] The policy was used again the following day to remove anti-Semitic French tweets with the hashtag #unbonjuif ("a good Jew").[379]
Followed the sharing of images showing the killing of American journalist James Foley in 2014, Twitter said that in certain cases it would delete pictures of people who had died after requests from family members and "authorized individuals".[380][381]
In 2015, following updated terms of service and privacy policy, Twitter users outside the United States were legally served by the Ireland-based Twitter International Company instead of Twitter, Inc. The change made these users subject to Irish and European Union data protection laws.[382]
On April 8, 2020, Twitter announced that users outside of the European Economic Area or United Kingdom (thus subject to GDPR) will no longer be allowed to opt out of sharing "mobile app advertising measurements" to Twitter third-party partners.[383]
On October 9, 2020, Twitter took additional steps to counter misleading campaigns ahead of the 2020 US Election. Twitter's new temporary update encouraged users to "add their own commentary" before retweeting a tweet, by making 'quoting tweet' a mandatory feature instead of optional. The social network giant aimed at generating context and encouraging the circulation of more thoughtful content.[384] After limited results, the company ended this experiment in December 2020.[385]
On May 25, 2022, Twitter was fined $150 million for collecting users' phone numbers and email addresses used for security and using them for targeted advertising, required to notify its users, and banned from profiting from "deceptively collected data".[386] The Federal Trade Commission and the Department of Justice stated that Twitter violated a 2011 agreement not to use personal security data for targeted advertising.
Harassment
In August 2013, Twitter announced plans to introduce a "report abuse" button for all versions of the site following uproar, including a petition with 100,000 signatures, over Tweets that included rape and death threats to historian Mary Beard, feminist campaigner Caroline Criado-Perez and the member of parliament Stella Creasy.[387][388][389] Twitter announced new reporting and blocking policies in December 2014,[390][391][392][393] including a blocking mechanism devised by Randi Harper, a target of GamerGate.[394][395][396] In February 2015, CEO Dick Costolo said he was 'frankly ashamed' at how poorly Twitter handled trolling and abuse, and admitted Twitter had lost users as a result.[397]
As per a research study conducted by IT for Change on abuse and misogynistic trolling on Twitter directed at Indian women in public-political life, women perceived to be ideologically left-leaning, dissenters, Muslim women, political dissenters, and political commentators and women from opposition parties received a disproportionate amount of abusive and hateful messages on Twitter.[398]
In 2016, Twitter announced the creation of the Twitter Trust & Safety Council to help "ensure that people feel safe expressing themselves on Twitter". The council's inaugural members included 50 organizations and individuals.[399] The announcement of Twitter's "Trust & Safety Council" was met with objection from parts of its userbase.[400][401] Critics accused the member organizations of being heavily skewed towards "the restriction of hate speech" and a Reason article expressed concern that "there's not a single uncompromising anti-censorship figure or group on the list".[402][403]
Twitter banned 7,000 accounts and limited 150,000 more that had ties to QAnon on July 21, 2020. The bans and limits came after QAnon-related accounts began harassing other users through practices of swarming or brigading, coordinated attacks on these individuals through multiple accounts in the weeks prior. Those accounts limited by Twitter will not appear in searches nor be promoted in other Twitter functions. Twitter said they will continue to ban or limit accounts as necessary, with their support account stating "We will permanently suspend accounts Tweeting about these topics that we know are engaged in violations of our multi-account policy, coordinating abuse around individual victims, or are attempting to evade a previous suspension".[404]
In September 2021, Twitter began beta testing a feature called Safety Mode.[405] The functionality aims to limit unwelcome interactions through automated detection of negative engagements. If a user has Safety Mode enabled, authors of tweets that are identified by Twitter's technology as being harmful or exercising uninvited behavior will be temporarily unable to follow the account, send direct messages, or see tweets from the user with the enabled functionality during the temporary block period.[406] Jarrod Doherty, senior product manager at Twitter, stated that the technology in place within Safety Mode assesses existing relationships to prevent blocking accounts that the user frequently interacts with.[405]
Suspect and contested accounts
In January 2016, Twitter was sued by the widow of a U.S. man killed in the 2015 Amman shooting attack, claiming that allowing the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) to continually use the platform, including direct messages in particular,[407] constituted the provision of material support to a terrorist organization, which is illegal under U.S. federal law. Twitter disputed the claim, stating that "violent threats and the promotion of terrorism deserve no place on Twitter and, like other social networks, our rules make that clear".[408][409] The lawsuit was dismissed by the United States District Court for the Northern District of California, upholding the Section 230 safe harbor, which dictates that the operators of an interactive computer service are not liable for the content published by its users.[409][410] The lawsuit was revised in August 2016, providing comparisons to other telecommunications devices.[407] The second amended complaint was dismissed by the district court, a decision affirmed on appeal to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit on January 31, 2018.[411]
Twitter suspended multiple parody accounts that satirized Russian politics in May 2016, sparking protests and raising questions about where the company stands on freedom of speech.[412] Following public outcry, Twitter restored the accounts the next day without explaining why the accounts had been suspended.[413] The same day, Twitter, along with Facebook, Google, and Microsoft, jointly agreed to a European Union code of conduct obligating them to review "[the] majority of valid notifications for removal of illegal hate speech" posted on their services within 24 hours.[414] In August 2016, Twitter stated that it had banned 235,000 accounts over the past six months, bringing the overall number of suspended accounts to 360,000 accounts in the past year, for violating policies banning use of the platform to promote extremism.[415]
On May 10, 2019, Twitter announced that they suspended 166,513 accounts for promoting terrorism in the July–December 2018 period, stating there was a steady decrease in terrorist groups trying to use the platform owing to its "zero-tolerance policy enforcement". According to Vijaya Gadde, Legal, Policy and Trust and Safety Lead at Twitter, there was a reduction of 19% terror related tweets from the previous reporting period (January–June 2018).[416][417][418][419][420]
As of July 30, 2020, Twitter will block URLs in tweets that point to external websites that contain malicious content (such as malware and phishing content) as well as hate speech, speech encouraging violence, terrorism, child sexual exploitation, breaches of privacy, and other similar content that is already banned as part of the content of tweets on the site. Users that frequently point to such sites may have their accounts suspended. Twitter said this was to bring their policy in line to prevent users from bypassing their tweet content restrictions by simply linking to the banned content.[421]
Following the onset of protests by Donald Trump's supporters across the US in January 2021, Twitter suspended more than 70,000 accounts, stating that they shared "harmful QAnon-associated content" at a large scale, and were "dedicated to the propagation of this conspiracy theory across the service".[422]
Malicious and fake accounts
Between January and late July 2017, Twitter had identified and shut down over 7,000 fake accounts created by Iranian influence operations.[423]
In May 2018, in response to scrutiny over the misuse of Twitter by those seeking to maliciously influence elections, Twitter announced that it would partner with the nonprofit organization Ballotpedia to add special labels verifying the authenticity of political candidates running for election in the U.S.[424][425]
In December 2019, Twitter removed 5,929 accounts for violating their manipulation policies. The company investigated and attributed these accounts to a single state-run information operation, which originated in Saudi Arabia. The accounts were reported to be a part of a larger group of 88,000 accounts engaged in spammy behavior. However, Twitter did not disclose all of them as some could possibly be legitimate accounts taken over through hacking.[426]
In March 2021, Twitter suspended around 3,500 fake accounts that were running a campaign to influence the American audience, after the US intelligence officials concluded that the assassination of The Washington Post journalist Jamal Khashoggi was "approved" by the Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman. These Saudi accounts were working in two languages, English and Arabic, to influence public opinion around the issue. Many accounts commented directly on the tweets of US-based media houses, including The Post, CNN, CBS News and The Los Angeles Times. Twitter was unable to identify the source of the influence campaign.[427]
As of 2022[update], the top four countries spreading state-linked Twitter misinformation are Russia, China, Iran and Saudi Arabia.[428]
Bot accounts
A bot is a computer program that can automatically post, repost, and follow other accounts. X's open application programming interface and the availability of cloud servers make it possible for X bots to exist within the social networking site.[429] Benign X bots may generate creative content and relevant product updates, whereas malicious bots can make unpopular people seem popular, push irrelevant products on users, and spread misinformation, spam or slander.[430] Bots amass significant influence and have been noted to sway elections, influence the stock market, appeal to the public, and attack governments.[431] As of 2013[update], Twitter said there were 20 million fake accounts on Twitter, representing less than 5% of active users.[432] A 2020 estimate put the figure at 15% of all accounts or around 48 million accounts.[11]
Society
Usage
This section should include only a brief summary of Twitter usage. (November 2023) |

Protesters
Twitter had been used for a variety of purposes in many industries and scenarios. For example, it has been used to organize protests, including the protests over the 2009 Moldovan election, the 2009 student protests in Austria, the 2009 Gaza–Israel conflict, the 2009 Iranian green revolution, the 2010 Toronto G20 protests, the 2010 Bolivarian Revolution, the 2010 Stuttgart21 protests in Germany, the 2011 Egyptian Revolution, 2011 England riots, the 2011 United States Occupy movement, the 2011 anti-austerity movement in Spain, the 2011 Aganaktismenoi movements in Greece, the 2011 demonstration in Rome, the 2011 Wisconsin labor protests, the 2012 Gaza–Israel conflict, the 2013 protests in Brazil, and the 2013 Gezi Park protests in Turkey.[434]
The service was also used as a form of civil disobedience: In 2010, users expressed outrage over the Twitter joke trial by copying a controversial joke about bombing an airport and attaching the hashtag #IAmSpartacus, a reference to the film Spartacus (1960) and a sign of solidarity and support to a man controversially prosecuted after posting a tweet joking about bombing an airport if they canceled his flight. #IAmSpartacus became the number one trending topic on Twitter worldwide.[435] Another case of civil disobedience happened in the 2011 British privacy injunction debate, where several celebrities who had taken out anonymized injunctions were identified by thousands of users in protest to traditional journalism being censored.[436]
During the Arab Spring in early 2011, the number of hashtags mentioning the uprisings in Tunisia and Egypt increased.[437] A study by the Dubai School of Government found that only 0.26% of the Egyptian population, 0.1% of the Tunisian population and 0.04% of the Syrian population are active on Twitter.[438]
Governments
According to documents leaked by Edward Snowden and published in July 2014, the United Kingdom's GCHQ has a tool named BIRDSONG for "automated posting of Twitter updates" and a tool named BIRDSTRIKE for "Twitter monitoring and profile collection".[439][440]
During the 2019–20 Hong Kong protests, Twitter suspended a core group of 1,000 "fake" accounts and an associated network of 200,000 accounts for operating a disinformation campaign that was linked to the Chinese government. In their announcement, Twitter released two data sets detailing the core group's account activity.[441][442][443] Geng Shuang, the spokesperson of the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs, did not comment on the suspensions but suggested that the activity could be attributed to overseas Chinese citizens.[444][445]
On June 12, 2020, Twitter suspended over 7,000 accounts from Turkey because those accounts were fake profiles, designed to support the Turkish president, Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, and were managed by a central authority. Turkey's communication director said that the decision was illogical, biased, and politically motivated.[446] Turkey blocked access to Twitter twice, once after voice recordings appeared on Twitter in which Erdoğan ordered his son to stash away millions of dollars and another time for 12 hours in the aftermath of the earthquake of February 2023, when Erdoğan blamed the people for a disinformation campaign as they criticized the Government for their lack of help.[447]
In May 2021, Twitter labeled one of the tweets by Sambit Patra, a spokesman of the local ruling party BJP in India, as "manipulated media", leading to Twitter's offices in Delhi and Gurgaon being raided by the local police.[448] Twitter issued a statement, calling the police visit "a form of intimidation"..[449] Later, the Indian government released a statement in July 2021 claiming Twitter has lost its liability protection concerning user-generated content. This was brought on by Twitter's failure to comply with the new IT rules introduced in 2021, with a filing stating that the company failed to appoint executives to govern user content on the platform.[450] Twitter stated to India's government in August 2021 that they have appointed permanent executives and staff to provide for compliance to these new IT rules.[451]
According to a report by Reuters, the United States ran a propaganda campaign to spread disinformation about the Sinovac Chinese COVID-19 vaccine, including using fake social media accounts on Twitter to spread the disinformation that the Sinovac vaccine contained pork-derived ingredients and was therefore haram under Islamic law.[452] The campaign primarily targeted people in the Philippines and used a social media hashtag for "China is the virus" in Tagalog.[452] The campaign ran from 2020 to mid-2021.[452] When asked about the accounts by Reuters, Twitter concluded based on activity patterns and internal data that they were a coordinated bot campaign and removed them.[452]
Twitter allows pornographic content as long as it is marked "sensitive" by uploaders, which puts it behind an interstice and hides it from minors.[453] The "super-follow" feature is said to enable competition with the subscription site OnlyFans, used mainly by sex workers.[454] Content filtering services for families and schools have noted that the company makes "it really easy to find" porn and advises blocking the entire domain.[455] Many performers use Twitter's service to market and grow their porn businesses, attracting users to paywalled services like OnlyFans by distributing photos and short video clips as advertisements.[456][457]
In April 2022, Twitter convened a "Red Team" for the project of ACM, "Adult Content Monetization", as it is known internally. Eventually, the project was abandoned, because of the difficulty of implementing Real ID.[458]
Child sexual exploitation
A February 2021 report from the company's Health team begins, "While the amount of CSE (child sexual exploitation) online has grown exponentially, Twitter's investment in technologies to detect and manage the growth has not."[458]
Until February 2022, the only way for users to flag illegal content was to flag it as "sensitive media", a broad category that left much of the worst material unprioritized for moderation. In a February report, employees wrote that Twitter, along with other Tech Companies have "accelerated the pace of CSE content creation and distribution to a breaking point where manual detection, review, and investigations no longer scale" by allowing pornography and failing to invest in systems that could effectively monitor it. The working group made several recommendations, but they were not taken up and the group was disbanded.[458]
As part of its efforts to monetize porn, Twitter held an internal investigation that reported in April 2022, "Twitter cannot accurately detect child sexual exploitation and non-consensual nudity at scale."[458]
John Doe et al. v. Twitter, a civil lawsuit filed in the 9th Circuit Court, alleges that Twitter benefited from sex trafficking and refused to remove the illegal tweets when first informed of them.[459][460] In an amicus brief filed in the case, the NCMEC said, "The children informed the company that they were minors, that they had been 'baited, harassed, and threatened' into making the videos, that they were victims of 'sex abuse' under investigation by law enforcement" but Twitter failed to remove the videos, "allowing them to be viewed by hundreds of thousands of the platform's users".[458]
Some major brands, including Dyson, Mazda, Forbes, and PBS Kids, suspended their marketing campaigns and pulled their ads from the platform, after an investigation into child porn on twitter showed that Twitter failed to suspend 70% of the accounts that shared or solicited the prohibited content. A brand president at Cole Haan said, "We're horrified ... either Twitter is going to fix this, or we'll fix it by any means we can, which includes not buying Twitter ads."[461]
Impact
This section may be too long and excessively detailed. (May 2022) |
On communication
In May 2008, The Wall Street Journal wrote that social networking services such as Twitter "elicit mixed feelings in the technology-savvy people who have been their early adopters. Fans say they are a good way to keep in touch with busy friends. But some users are starting to feel too connected, as they grapple with check-in messages at odd hours, higher cellphone bills and the need to tell acquaintances to stop announcing what they're having for dinner."[462] The following year, John C. Dvorak described Twitter as "the new CB radio".[463]
In April 2023, the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) in New York City announced that it would no longer post real-time service updates on Twitter. The transportation system claimed that the platform cannot be trusted to provide consistent updates that riders need. According to an MTA spokesperson, this decision was made after it experienced two Application Programming Interface (API) interruptions over the previous two weeks. However, only the updates were discontinued and the MTA planned to continue to respond to riders' queries.[464]
In 2023, Twitter introduced a paywall system that required businesses to pay for access to its platform. The payment scheme's upper limit amounts to an annual fee of up to $2.5 million for top-tier access. With the paywall implementation, public agencies issued numerous alerts about potential interruptions to transit and weather. Shanifah Rieara, MTA Acting Chief Customer Officer, revealed that Twitter attempted to demand over $500,000 annually from MTA for platform access, which the latter declined.On May 4, 2023, Twitter backtracked its paywall system, allowing the free posting of automated tweets by verified government profiles. In light of Twitter's decision, MTA announced its resumption of posting automated alerts on the platform.[465]
Emergency use
A practical use for Twitter's real-time functionality is as an effective de facto emergency communication system for breaking news. It was neither intended nor designed for high-performance communication, but the idea that it could be used for emergency communication was not lost on the creators, who knew that the service could have wide-reaching effects early on when the company used it to communicate during earthquakes.[466]
Another practical use that is being studied is Twitter's ability to track epidemics and how they spread.[467] Additionally Twitter serves as a real-time sensor for natural disasters such as bush fires and earthquakes.[468][469]
Education
Twitter has been adopted as a communication and learning tool in educational and research[470] settings mostly in colleges and universities.[471][472] It has been used as a backchannel to promote student interactions, especially in large-lecture courses.[473] Research has found that using Twitter in college courses helps students communicate with each other and faculty, promotes informal learning, allows shy students a forum for increased participation, increases student engagement, and improves overall course grades.[474][475][476]
Twitter has been an increasingly growing in the field of education as an effective tool that can be used to encourage learning and idea, or knowledge sharing, in and outside the classroom.[477] By using or creating hashtags, students and educators are able to communicate under specific categories of their choice to enhance and promote education. A broad example of a hashtag used in education is "edchat", to communicate with other teachers and people using that hashtag. Once teachers find someone they want to talk to, they can either direct message the person or narrow down the hashtag to make the topic of the conversation more specific, using hashtags for scichat (science), engchat (English), sschat (social studies).[477]
In a 2011 study, researchers found that young peoples use of Twitter helped to improve relationships with teachers, encourage interactive learning, and ultimately lead to high grades.[477] In the same study, it was found that out of a group of 158 educators, 92% agreed that the reason they use Twitter is because of how user-friendly it is,[477] another 86% agreed that they started and continue using Twitter because of how easy it is to learn, and finally,[477] 93% said they use Twitter because it is free. People found sifting through large amounts of data to be challenging; however, with the simple nature of Twitter, large amount of information became easily accessible.[478] Much of this simplicity comes from the use of the hashtag and the intuitive nature of how Twitter as a microblogging site operates.[478] These features help to promote education outside the classroom in a global setting where students and educators are easily able to create, connect, and share knowledge. This ultimately promotes growth and learning among students and educators, not just in the classroom, but virtually and around the world.
Public figures
Jonathan Zittrain, professor of Internet law at Harvard Law School, said that "the qualities that make Twitter seem inane and half-baked are what makes it so powerful."[479] In that same vein, and with Sigmund Freud in mind, political communications expert Matthew Auer observed that well-crafted tweets by public figures often deliberately mix trivial and serious information so as to appeal to all three parts of the reader's personality: the id, ego, and superego.[480] The poets Mira Gonzalez and Tao Lin published a book titled Selected Tweets featuring selections of their tweets over some eight years.[481] The novelist Rick Moody wrote a short story for Electric Literature called "Some Contemporary Characters", composed entirely of tweets.[482]
Many commentators have suggested that Twitter radically changed the format of reporting due to instant, short, and frequent communication.[483][484] According to The Atlantic writers Benjamin M. Reilly and Robinson Meyer, Twitter has an outsized impact on the public discourse and media. "Something happens on Twitter; celebrities, politicians and journalists talk about it, and it's circulated to a wider audience by Twitter's algorithms; journalists write about the dustup." This can lead to an argument on a Twitter feed looking like a "debate roiling the country... regular people are left with a confused, agitated view of our current political discourse".[485] In a 2018 article in the Columbia Journalism Review, Matthew Ingram argued much the same about Twitter's "oversized role" and that it promotes immediacy over newsworthiness.[486] In some cases, inauthentic and provocative tweets were taken up as common opinion in mainstream articles. Writers in several outlets unintentionally cited the opinions of Russian Internet Research Agency-affiliated accounts.[486][487]
World leaders

World leaders and their diplomats have taken note of Twitter's rapid expansion and have been increasingly utilizing Twitter diplomacy, the use of Twitter to engage with foreign publics and their own citizens. US Ambassador to Russia, Michael A. McFaul has been attributed as a pioneer of international Twitter diplomacy. He used Twitter after becoming ambassador in 2011, posting in English and Russian.[488] On October 24, 2014, Queen Elizabeth II sent her first tweet to mark the opening of the London Science Museum's Information Age exhibition.[489] A 2013 study by website Twiplomacy found that 153 of the 193 countries represented at the United Nations had established government Twitter accounts.[490] The same study also found that those accounts amounted to 505 Twitter handles used by world leaders and their foreign ministers, with their tweets able to reach a combined audience of over 106 million followers.[490]
According to an analysis of accounts, the heads of state of 125 countries and 139 other leading politicians have Twitter accounts that have between them sent more than 350,000 tweets and have almost 52 million followers. However, only 30 of these do their own tweeting, more than 80 do not subscribe to other politicians and many do not follow any accounts.[491]
Religion
As of October 2015[update], more than twenty Roman Catholic cardinals managed active Twitter accounts,[492] nine of whom were cardinal electors for the 2013 Papal conclave.[493] Pope Benedict XVI's Twitter account was set up in 2012. As of April 2022[update], his successor, Pope Francis, has 18.7 million followers of his Twitter account (@Pontifex).[494][needs update]
Censorship and moderation
Twitter is banned completely in Russia,[495] Iran, China and North Korea[496] and has been intermittently blocked in numerous countries, including Egypt, Iraq, Nigeria, Turkey, Venezuela and Turkmenistan on different bases.[497][498][499][500][501][502] In 2016, Twitter cooperated with the Israeli government to remove certain content originating outside Israel from tweets seen in Israel.[503] In the 11th biannual transparency report published on September 19, 2017, Twitter said that Turkey was the first among countries where about 90% of removal requests came from, followed by Russia, France and Germany.[504] Twitter stated that between July 1 and December 31, 2018, "We received legal demands relating to 27,283 accounts from 47 different countries, including Bulgaria, Kyrgyzstan, Macedonia, and Slovenia for the first time."[505] As part of evidence to a U.S. Senate Enquiry, the company admitted that their systems "detected and hid" several hundred thousand tweets relating to the 2016 Democratic National Committee email leak.[506] During the curfew in Jammu and Kashmir after revocation of its autonomous status on August 5, 2019, the Indian government approached Twitter to block accounts accused of spreading anti-India content;[507] by October 25, nearly one million tweets had been removed as a result.[508]
In March 2022, shortly after Russia's censorship of Twitter, a Tor onion service link was created by the platform to allow people to access the website, even in countries with heavy Internet censorship.[509][510]
Moderation of tweets
Twitter removed more than 88,000 propaganda accounts linked to Saudi Arabia.[511] Twitter removed tweets from accounts associated with the Russian Internet Research Agency that had tried to influence public opinion during and after the 2016 US election.[486][487] In June 2020, Twitter also removed 175,000 propaganda accounts that were spreading biased political narratives for the Chinese Communist Party, the United Russia Party, or Turkey's President Erdogan, identified based on centralized behavior.[512][513] Twitter also removed accounts linked to the governments of Armenia, Egypt, Cuba, Serbia, Honduras, Indonesia and Iran.[514][515][516] Twitter suspended Pakistani accounts tied to government officials for posting tweets about the Kashmir conflict between India and Pakistan.[517] In February 2021, Twitter removed accounts in India that criticized Prime Minister Narendra Modi's government for its conduct during Indian farmers' protests in 2020–2021.[518]
At the start of the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, numerous tweets reported false medical information related to the pandemic. Twitter announced a new policy in which they would label tweets containing misinformation going forward.[90] In April 2020, Twitter removed accounts which defended President Rodrigo Duterte's response to the spread of COVID-19 in the Philippines.[519]
In November 2020, then Chief Technology Officer and future CEO of Twitter Parag Agrawal, when asked by MIT Technology Review about balancing the protection of free speech as a core value and the endeavour to combat misinformation, said: "Our role is not to be bound by the First Amendment, but our role is to serve a healthy public conversation ... focus less on thinking about free speech, but thinking about how the times have changed."[520]
Musk had been critical of Twitter's moderation of misinformation prior to his acquisition of the company.[521] After the transition, Musk eliminated the misinformation moderation team,[522] and stopped enforcing its policy on labeling tweets with misleading information about coronavirus.[523] While Twitter had joined a voluntary program under the European Union's to fight disinformation in June 2022, Musk pulled the company out of the program in May 2023.[524]
Birdwatch

In August 2020, development of Birdwatch was announced, initially described as a moderation tool. Twitter first launched the Birdwatch program in January 2021, intended as a way to debunk misinformation and propaganda, with a pilot program of 1,000 contributors,[525][526] weeks after the January 6 United States Capitol attack.[527] The aim was to "build Birdwatch in the open, and have it shaped by the Twitter community." In November 2021, Twitter updated the Birdwatch moderation tool to limit the visibility of contributors' identities by creating aliases for their accounts, in an attempt to limit bias towards the author of notes.[526][528]
Twitter then expanded access to notes made by the Birdwatch contributors in March 2022, giving a randomized set of US users the ability to view notes attached to tweets and rate them,[529] with a pilot of 10,000 contributors.[530] On average, contributors were noting 43 times a day in 2022 prior to the Russian invasion of Ukraine. This then increased to 156 on the day of the invasion, estimated to be a very small portion of the misleading posts on the platform. By March 1, only 359 of 10,000 contributors had proposed notes in 2022, while a Twitter spokeswoman described plans to scale up the program, with the focus on "ensuring that Birdwatch is something people find helpful and can help inform understanding".[531][532]
By September 2022, the program had expanded to 15,000 users.[533] In October 2022, the most commonly published notes were related to COVID-19 misinformation based on historical usage.[534] In November 2022, at the request of new owner Elon Musk, Birdwatch was rebranded to Community Notes, taking an open-source approach to deal with misinformation,[535] and expanded to Europe and countries outside of the US.[115][536][537]
Court cases and lawsuits
Twitter Inc. v. Taamneh, alongside Gonzalez v. Google, were heard by the United States Supreme Court during its 2022–2023 term. Both cases dealt with Internet content providers and whether they are liable for terrorism-related information posted by their users. In the case of Twitter v. Taamneh, the case asked if Twitter and other social media services are liable for user-generated terrorism content under the Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act of 1996 and are beyond their Section 230 protections. The court ruled in May 2023 that the charges brought against Twitter and other companies were not permissible under the Antiterrorism Act, and did not address the Section 230 question. This decision also supported the Court's per curiam decision in Gonzalez returning that case to the lower court for review in light of the Twitter decision.[538][539]
In 2016, Twitter shareholder Doris Shenwick filed a lawsuit against Twitter, Inc., claiming executives misled investors over the company's growth prospects.[540] In 2021, Twitter agreed to pay $809.5 million to settle.[540]
In May 2022, Twitter agreed to pay $150 million to settle a lawsuit started by the Department of Justice and the Federal Trade Commission. The lawsuit concerned Twitter's use of email addresses and phone numbers of Twitter users to target advertisements at them. The company also agreed to third-party audits of its data privacy program.[541]
On November 3, 2022, on the eve of expected lay-offs, a group of Twitter employees based in San Francisco and Cambridge filed a lawsuit in the U.S. District Court in San Francisco. Naming five current or former workers as plaintiffs, the suit accused the company of violating federal and state laws that govern notice of employment termination.[542] The federal law in question is the Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification (WARN) Act, and the state law in question is California's state WARN Act.[543]
On November 20, 2023, X filed a lawsuit against Media Matters, a media watchdog group. The lawsuit alleges defamation by Media Matters following its publication of a report claiming that advertisements for major brands were displayed alongside posts promoting Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party.[544]
On August 6, 2024, X filed an anti-trust lawsuit in the Northern District of Texas against the World Federation Of Advertisers, Unilever, Mars, CVS and Ørsted, alleging that the advertisers had conspired to withhold “billions of dollars in advertising revenue” from X. The groups ceased advertising on X in response to concerns about "illegal or harmful content on digital media platforms and its monetization via advertising.” The case has been assigned to District Judge Reed O'Connor.[545]
Statistics
User accounts with large follower base
As of 30 March 2023[update], the 11 Twitter accounts with the most followers were:
| Rank | Change (monthly) | Account name | Owner | Followers (millions) | Activity | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | @elonmusk | Elon Musk | 137 | Business magnate | ||
| 2 | @BarackObama | Barack Obama | 133 | 44th U.S. president | ||
| 3 | @justinbieber | Justin Bieber | 113 | Musician | ||
| 4 | @katyperry | Katy Perry | 108 | Musician | ||
| 5 | @rihanna | Rihanna | 108 | Musician and businesswoman | ||
| 6 | @Cristiano | Cristiano Ronaldo | 108 | Footballer | ||
| 7 | @taylorswift13 | Taylor Swift | 92 | Musician | ||
| 8 | @narendramodi | Narendra Modi | 87 | Prime Minister of India | ||
| 9 | @realDonaldTrump | Donald Trump | 87 | 45th U.S. president | ||
| 10 | @ladygaga | Lady Gaga | 85 | Musician and actress | ||
| 11 | @YouTube | YouTube | 79 | Online video platform |
Record tweets
A selfie orchestrated by 86th Academy Awards host Ellen DeGeneres during the March 2, 2014, broadcast was, at the time, the most retweeted image ever.[546] DeGeneres said she wanted to pay homage to Meryl Streep's record 17 Oscar nominations by setting a new record with her and invited other Oscar celebrities to join them. The resulting photo of twelve celebrities broke the previous retweet record within forty minutes and was retweeted over 1.8 million times in the first hour.[547][548][549] By the end of the ceremony it had been retweeted over 2 million times.[547] On May 9, 2017, Ellen's record was broken by Carter Wilkerson (@carterjwm) by collecting nearly 3.5 million retweets in a little over a month.[550] This record was broken when Yusaku Maezawa announced a giveaway on Twitter in January 2019, accumulating 4.4 million retweets. A similar tweet he made in December 2019 was retweeted 3.8 million times.[551]
The most tweeted moment in the history of Twitter occurred on August 2, 2013; during a Japanese television airing of the Studio Ghibli film Castle in the Sky, fans simultaneously tweeted the word balse (バルス)—the incantation for a destruction spell used during its climax, after it was uttered in the film. There was a global peak of 143,199 tweets in one second, beating the previous record of 33,388.[552][553]
The most discussed event in Twitter history occurred on October 24, 2015; the hashtag ("#ALDubEBTamangPanahon") for Tamang Panahon, a live special episode of the Filipino variety show Eat Bulaga! at the Philippine Arena, centering on its popular on-air couple AlDub, attracted 41 million tweets.[554][555] The most-discussed sporting event in Twitter history was the 2014 FIFA World Cup semi-final between Brazil and Germany on July 8, 2014.[556]
According to Guinness World Records, the fastest pace to a million followers was set by actor Robert Downey Jr. in 23 hours and 22 minutes in April 2014.[557] This record was later broken by Caitlyn Jenner, who joined the site on June 1, 2015, and amassed a million followers in just 4 hours and 3 minutes.[558]
See also
Notes
- ^ The logo resembles the mathematical symbol U+1D54F 𝕏 MATHEMATICAL DOUBLE-STRUCK CAPITAL X.[1][2]
- ^ Registration is not required to view individual posts accessed via a direct link (not inclusive of any replies to the post or parent posts to a reply) or to view the top posts of some accounts.
- ^ It is not documented whether the parallax scrolling effect was added with the redesign in April 2014 or subsequently.
References
- ^ Ashworth, Louis (July 24, 2023). "The logo of X, formerly Twitter, wasn't actually stolen". Financial Times. Archived from the original on July 24, 2023. Retrieved July 25, 2023.
- ^ Musk, Elon Reeve [@elonmusk] (July 24, 2023). "𝕏" (Tweet). Retrieved July 30, 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ Kolodny, Lora (September 18, 2023). "Elon Musk says Twitter, now X, is moving to monthly subscription fees and has 550 million users". CNBC. Archived from the original on September 18, 2023. Retrieved September 19, 2023.
- ^ "Top Websites Ranking". Similarweb. Archived from the original on February 10, 2022. Retrieved June 19, 2024.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Conger, Kate (August 3, 2023). "So What Do We Call Twitter Now Anyway?". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on October 12, 2023. Retrieved August 29, 2023.
- ^ "Twitter turns six". Twitter. March 21, 2012. Archived from the original on February 6, 2017. Retrieved August 29, 2014.
- ^ "Company: "About Twitter"". Archived from the original on April 3, 2016. Retrieved April 24, 2014.
- ^ "Twitter Passed 500M Users In June 2012, 140M Of Them In US; Jakarta 'Biggest Tweeting' City". TechCrunch. July 30, 2012.
- ^ Carlson, Nicholas (June 2, 2009). "Stunning New Numbers on Who Uses Twitter". Business Insider. Archived from the original on February 5, 2021. Retrieved January 9, 2021.
- ^ Wojcik, Stefan; Hughes, Adam (April 24, 2019). "Sizing Up Twitter Users". Pew Research Center. Archived from the original on October 29, 2019. Retrieved April 25, 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Rodrıguez-Ruiz, Jorge; Mata-Sanchez, Javier Israel; Monroy, Raul; Loyola-Gonzalez, Octavio; Ĺopez-Cuevas, Armando (April 2020). "A one-class classification approach for bot detection on Twitter". Computers & Security. 91: 101715. doi:10.1016/j.cose.2020.101715. S2CID 212689495. Retrieved June 17, 2022.
- ^ Milmo, Dan (October 9, 2023). "X criticised for enabling spread of Israel-Hamas disinformation". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on October 10, 2023. Retrieved October 10, 2023.
- ^ Goswami, Rohan (October 9, 2023). "X, formerly Twitter, amplifies disinformation amid the Israel-Hamas conflict". CNBC. Archived from the original on October 9, 2023. Retrieved October 10, 2023.
- ^ Lyngaas, Sean; O'Sullivan, Donie; Duffy, Clare (October 9, 2023). "Elon Musk's X adds to fog of war at outset of Israel-Hamas conflict". CNN. Archived from the original on October 10, 2023. Retrieved October 10, 2023.
- ^ Sato, Mia (December 2, 2022). "Hate speech is soaring on Twitter under Elon Musk, report finds". The Verge. Archived from the original on March 19, 2023. Retrieved April 13, 2023.
- ^ "New Data Suggests that Hate Speech is on the Rise on Twitter 2.0". Social Media Today. Archived from the original on September 25, 2023. Retrieved April 13, 2023.
- ^ Frenkel, Sheera; Conger, Kate (December 2, 2022). "Hate Speech's Rise on Twitter Is Unprecedented, Researchers Find". The New York Times. Archived from the original on October 16, 2023. Retrieved September 9, 2023.
- ^ Frier, Sarah (June 5, 2023). "Twitter's New CEO Linda Yaccarino Has First Day in the Role". Bloomberg News. Archived from the original on November 8, 2023. Retrieved June 6, 2023.
- ^ Miller, Monica (December 21, 2022). "Elon Musk to quit as Twitter CEO when replacement found". BBC News. Archived from the original on March 17, 2023. Retrieved December 21, 2022.
- ^ "Twitter's New CEO Linda Yaccarino Has First Day in the Role". Bloomberg.com. June 6, 2023. Archived from the original on June 26, 2023. Retrieved September 9, 2023.
- ^ Valinsky, Jordan (July 24, 2023). "Twitter X logo: Elon Musk rebrands social media platform". CNN Business. Archived from the original on October 3, 2023. Retrieved July 25, 2023.
- ^ "Elon Musk reveals rebranding of Twitter as X - and what he wants us to now call a tweet". Sky News. Archived from the original on August 1, 2023. Retrieved July 25, 2023.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Primack, Dan (December 31, 2023). "Elon Musk's X gets another valuation cut from Fidelity". Axios. Archived from the original on December 31, 2023. Retrieved December 31, 2023.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Hern, Alex (March 26, 2024). "Twitter usage in US 'fallen by a fifth' since Elon Musk's takeover". The Guardian. Archived from the original on March 27, 2024. Retrieved May 6, 2024.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Fischer, Sara (October 26, 2023). "X usage plummets in Musk's first year". Axios. Archived from the original on October 27, 2023. Retrieved May 6, 2024.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Kantrowitz, Alex (October 23, 2023). "The Elon Effect". Slate. Archived from the original on May 6, 2024. Retrieved May 6, 2024.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Elon Musk Says X Now Has 600M Monthly Active Users". Social Media Today. Retrieved June 24, 2024.
- ^ (registration required) Miller, Claire Cain (October 30, 2010). "Why Twitter's C.E.O. Demoted Himself". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 1, 2010. Retrieved October 31, 2010.
- ^ Ev [@ev] (April 13, 2011). "It's true that @Noah never got enough credit for his early role at Twitter. Also, he came up with the name, which was brilliant" (Tweet). Retrieved April 26, 2011 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Buy a vowel? How Twttr became Twitter". CNN Money. November 23, 2010. Archived from the original on April 27, 2019. Retrieved June 9, 2015.
- ^ Sagolla, Dom (January 30, 2009). "How Twitter Was Born". 140 Characters: A Style Guide for the Short Form. Archived from the original on May 8, 2019. Retrieved February 4, 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Carlson, Nicholas (April 13, 2011). "How Twitter Was Founded". Business Insider. Archived from the original on July 14, 2018. Retrieved September 4, 2013.
- ^ jack [@jack] (March 21, 2006). "just setting up my twttr" (Tweet). Retrieved February 4, 2011 – via Twitter.
- ^ Sano, David (February 18, 2009). "Twitter Creator Jack Dorsey Illuminates the Site's Founding Document". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on May 2, 2019. Retrieved June 18, 2009.
- ^ Arrington, Michael (July 15, 2006). "Odeo Releases Twttr". TechCrunch. AOL. Archived from the original on May 1, 2019. Retrieved September 18, 2010.
- ^ Malik, Om (October 25, 2006). "Odeo RIP, Hello Obvious Corp". GigaOM. Archived from the original on May 2, 2019. Retrieved June 20, 2009.
- ^ Madrigal, Alexis (April 14, 2011). "Twitter's Fifth Beatle Tells His Side of the Story". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on May 23, 2019. Retrieved April 26, 2011.
- ^ Lennon, Andrew. "A Conversation with Twitter Co-Founder Jack Dorsey". The Daily Anchor. Archived from the original on July 27, 2009. Retrieved February 12, 2009.
- ^ Lapowsky, Issie (October 4, 2013). "Ev Williams on Twitter's Early Years". Inc. Archived from the original on April 10, 2019. Retrieved October 5, 2013.
- ^ Meyers, Courtney Boyd (July 15, 2011). "5 years ago today Twitter launched to the public". The Next Web. Archived from the original on April 27, 2019. Retrieved May 5, 2017.
- ^ Levy, Steven (April 30, 2007). "Twitter: Is Brevity The Next Big Thing?". Newsweek. Archived from the original on April 12, 2010. Retrieved February 4, 2011.
- ^ Terdiman, Daniel (March 10, 2007). "To Twitter or Dodgeball at SXSW?". CNET. Archived from the original on December 3, 2013. Retrieved February 4, 2011.
- ^ Stone, Biz (February 4, 2011). "We Won!". Twitter Blog. Archived from the original on February 24, 2008. Retrieved May 7, 2008 – via Twitter.
- ^ "13th Annual Webby Special Achievement Award Winners". The Webby Awards. Archived from the original on February 20, 2011. Retrieved February 22, 2011.
- ^ Paul, Ian (May 5, 2009). "Jimmy Fallon Wins Top Webby: And the Winners Are..." PC World. Archived from the original on February 25, 2021. Retrieved February 22, 2011.
- ^ "Top Word of 2009: Twitter". Languagemonitor.com. November 29, 2009. Archived from the original on May 14, 2012. Retrieved July 28, 2014.
- ^ Beaumont, Claudine (February 23, 2010). "Twitter Users Send 50 Million Tweets Per Day – Almost 600 Tweets Are Sent Every Second Through the Microblogging Site, According to Its Own Metrics". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on January 10, 2022. Retrieved February 7, 2011.
- ^ "Twitter Registers 1,500 Per Cent Growth in Users". New Statesman. March 4, 2010. Archived from the original on May 3, 2019. Retrieved February 7, 2011.
- ^ Garrett, Sean (June 18, 2010). "Big Goals, Big Game, Big Records". Twitter Blog (blog of Twitter). Archived from the original on February 13, 2011. Retrieved February 7, 2011.
- ^ "Twitter Blog: #numbers". March 14, 2011. Archived from the original on March 25, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2012 – via Twitter.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Kazeniac, Andy (February 9, 2009). "Social Networks: Facebook Takes Over Top Spot, Twitter Climbs". Compete.com. Archived from the original on July 21, 2011. Retrieved February 17, 2009.
- ^ Miller, Claire Cain (June 18, 2010). "Sports Fans Break Records on Twitter". Bits (blog of The New York Times). Archived from the original on January 12, 2011. Retrieved February 7, 2011.
- ^ Van Grove, Jennifer (June 25, 2010). "Twitter Sets New Record: 3,283 Tweets Per Second". Mashable. Archived from the original on September 20, 2018. Retrieved February 7, 2011.
- ^ "Women's World Cup Final breaks Twitter record". ESPN. July 18, 2011. Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved July 31, 2011.
- ^ Shiels, Maggie (June 26, 2009). "Web Slows After Jackson's Death". BBC News. Archived from the original on October 26, 2009. Retrieved February 7, 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Krikorian, Raffi (August 16, 2013). "New Tweets per second record, and how!". Twitter Blogs. Archived from the original on August 22, 2013. Retrieved November 22, 2021.
- ^ Kanalley, Craig (January 2, 2013). "Tweets-Per-Second Record Set By Japan, Korea On New Year's Day 2013". HuffPost. Archived from the original on October 19, 2017. Retrieved January 3, 2013.
- ^ Press release (January 22, 2010). "Media Advisory M10-012 – NASA Extends the World Wide Web Out into Space" Archived December 13, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. NASA. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- ^ Miller, Claire Cain (April 11, 2010). "Twitter Acquires Atebits, Maker of Tweetie". Bits (blog of The New York Times). Archived from the original on December 18, 2010. Retrieved February 7, 2011.
- ^ Rayome, Alison DeNisco. "Facebook was the most-downloaded app of the decade". CNET. Archived from the original on December 18, 2019. Retrieved December 18, 2019.
- ^ Praetorius, Dean (May 4, 2011). "Twitter Users Report Twitter.com Has A New Homepage (SCREENSHOTS)". HuffPost. Archived from the original on October 27, 2017. Retrieved May 22, 2011.
- ^ Dunn, John E (April 6, 2011). "Twitter Delays Homepage Revamp After Service Glitch". PC World. Archived from the original on May 10, 2011. Retrieved May 22, 2011.
- ^ Crum, Chris (April 20, 2011). "New Twitter Homepage Launched". Archived from the original on April 24, 2011. Retrieved April 25, 2011.
- ^ "Twitter: Yours to discover". Archived from the original on January 18, 2012. Retrieved January 20, 2012 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Twitter 2.0: Everything You Need to Know About the New Changes". Fox News. April 7, 2010. Archived from the original on April 15, 2012. Retrieved January 20, 2012.
- ^ "Twitter partners with Yandex for real-time search". Reuters. February 21, 2012. Archived from the original on September 24, 2015. Retrieved July 2, 2017.
- ^ "Twitter Says It Has 140 Million Users". Mashable. March 21, 2012. Archived from the original on May 2, 2019. Retrieved March 21, 2012.
- ^ "Twitter Now Has More Than 200 Million Monthly Active Users". Mashable. December 18, 2012. Archived from the original on July 14, 2018. Retrieved December 18, 2012.
- ^ Rodriguez, Salvador (June 6, 2012). "Twitter flips the bird, adopts new logo". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on July 12, 2012. Retrieved May 5, 2017.
- ^ Gilbertson, Scott (June 8, 2012). "Twitter's New Logo Inspires Parodies, CSS Greatness". Wired. Archived from the original on November 6, 2018. Retrieved May 5, 2017.
- ^ T. Huang, Gregory (February 5, 2013). "Twitter's Boston Acquisitions: Crashlytics Tops $100M, Bluefin Labs Close Behind". Xconomy. Archived from the original on April 27, 2019. Retrieved November 22, 2021.
- ^ Ulanoff, Lance (April 18, 2013). "Twitter Launches Twitter #music App and Service". Mashable. Archived from the original on September 21, 2018. Retrieved April 28, 2013.
- ^ "Twitter acquires real-time social data company Trendrr to help it better tap into TV and media". The Next web. August 28, 2013. Archived from the original on April 27, 2019. Retrieved August 29, 2013.
- ^ Isidore, Chris (September 10, 2013). "Twitter makes another acquisition". CNN Money. Archived from the original on April 24, 2019. Retrieved September 10, 2013.
- ^ Moore, Heidi (September 12, 2013). "Twitter files for IPO in first stage of stock market launch". The Guardian. Archived from the original on August 1, 2019. Retrieved September 13, 2013.
- ^ Schultz, E.J. (October 5, 2020). "Q&AA: The CMO Fixer: After working for major marketers, Lisa Mann now places CMOs and other executives. She gives her take on what's ailing top brands and what companies are looking for in top execs". Advertising Age. 91 (19): 6.
- ^ Savov, Vlad (April 8, 2014). "Twitter redesign looks a lot like Facebook". The Verge. Archived from the original on March 10, 2021. Retrieved March 1, 2021.
- ^ "Check out our new look!". Archived from the original on January 23, 2024. Retrieved January 23, 2024 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Twitter.com gets a refresh". Archived from the original on July 30, 2019. Retrieved July 30, 2019 – via Twitter.
- ^ Ingram, Matthew (October 25, 2015). "What if the Twitter growth everyone is hoping for never comes?". Fortune. Archived from the original on November 6, 2019. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ Beaver, Laurie; Boland, Margaret (October 28, 2015). "Twitter user growth continues to stall". Business Insider. Archived from the original on November 6, 2019. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ Beck, Martin (October 27, 2015). "Revenue Is Up, But Twitter Is Still Struggling In Slow Growth Mode". Marketing Land. Archived from the original on July 30, 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ Truong, Alice (February 10, 2016). "Twitter now has a problem that's way worse than slow user growth". Quartz. Archived from the original on November 6, 2019. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ Bogan, Ray (May 4, 2018). "Commercial space travelers will soon be able to send a tweet from space". Fox News. Archived from the original on March 5, 2023. Retrieved February 24, 2023.
- ^ Oremus, Will (May 15, 2018). "Twitter Will Start Hiding Tweets That 'Detract From the Conversation'". Slate. Archived from the original on June 8, 2023. Retrieved April 11, 2021.
- ^ "Like It or Not, You're Getting Twitter's Redesigned Website Soon". PC Magazine. Archived from the original on March 17, 2021. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Molina, Brett (October 26, 2017). "Twitter overcounted active users since 2014, shares surge on profit hopes". USA Today. Archived from the original on January 1, 2020. Retrieved December 2, 2017.
- ^ "Q2 2020 Letter to Shareholders, July 23, 2020, @TwitterIR" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on October 22, 2021. Retrieved March 14, 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Full Page Reload". IEEE Spectrum: Technology, Engineering, and Science News. July 29, 2020. Archived from the original on January 3, 2021. Retrieved August 26, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Roth, Yoel; Pickles, Nick (May 11, 2020). "Updating our Approach to Misleading Information". Archived from the original on February 28, 2021. Retrieved May 28, 2020 – via Twitter.
- ^ Lybrand, Holmes; Subramaniam, Tara (May 27, 2020). "Fact-checking Trump's recent claims that mail-in voting is rife with fraud". CNN. Archived from the original on February 28, 2021. Retrieved May 28, 2020.
- ^ Allyn, Bobby (May 28, 2020). "Stung By Twitter, Trump Signs Executive Order To Weaken Social Media Companies". NPR. Archived from the original on June 28, 2020. Retrieved May 29, 2020.
- ^ "Trump signs executive order targeting social media companies". CNN. May 28, 2020. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved May 29, 2020.
- ^ Conger, Kate; Isaac, Mike (May 28, 2020). "Defying Trump, Twitter Doubles Down on Labeling Tweets". The New York Times. Archived from the original on May 28, 2020. Retrieved May 29, 2020.
- ^ "Twitter 'permanently suspends' Trump's account". BBC News. January 8, 2021. Archived from the original on June 8, 2021. Retrieved November 6, 2022.
- ^ "Germany and France Oppose Trump's Twitter Exile". Bloomberg.com. January 11, 2021. Archived from the original on March 26, 2021. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
'The chancellor sees the complete closing down of the account of an elected president as problematic,' Steffen Seibert, her chief spokesman, said at a regular news conference in Berlin. Rights like the freedom of speech 'can be interfered with, but by law and within the framework defined by the legislature – not according to a corporate decision.'
- ^ "Nigeria's Twitter ban: Government orders prosecution of violators". BBC News. June 6, 2021. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022. Retrieved June 20, 2021.
- ^ "Nigeria suspends Twitter after the social media platform freezes president's account". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Archived from the original on December 5, 2021. Retrieved June 20, 2021.
- ^ Ohuocha, Chijioke (June 5, 2021). "Nigerian telecoms firms suspend access to Twitter". Reuters. Archived from the original on June 11, 2021. Retrieved June 20, 2021.
- ^ Goldsmith, Jill (February 10, 2021). "Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey On Section 230, Transparency, Appeals And Twitter Turning 15". Deadline. Archived from the original on March 6, 2021. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ^ Matney, Lucas (January 15, 2021). "Twitter's decentralized future". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on June 29, 2023. Retrieved November 6, 2022.
- ^ Rodriguez, Salvador (May 3, 2021). "Twitter launches Spaces live-audio rooms to all users with more than 600 followers". CNBC. Archived from the original on July 23, 2021. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ Lyons, Kim (May 3, 2021). "Twitter will now let anyone with 600 or more followers host its audio Spaces on mobile". The Verge. Archived from the original on August 10, 2021. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ "Twitter launches subscription-based feature "super follows"". Reuters. September 1, 2021. Archived from the original on March 5, 2023. Retrieved November 6, 2022.
- ^ Robertson, Adi (June 22, 2021). "Twitter is opening applications to test Ticketed Spaces and Super Follows". The Verge. Archived from the original on July 1, 2021. Retrieved June 23, 2021.
- ^ Bonifac, Igor (August 11, 2021). "Twitter rolls out redesign with proprietary Chirp font". Engadget. Archived from the original on August 13, 2021. Retrieved August 11, 2021.
- ^ "Twitter partners with Shopify to bring merchants' products to Twitter Shopping". TechCrunch. June 22, 2022. Archived from the original on June 29, 2022. Retrieved June 23, 2022.
- ^ Vincent, James (August 23, 2022). "Twitter's former security chief says company lied about bots and safety". The Verge. Archived from the original on August 25, 2022. Retrieved August 23, 2022.
- ^ Feiner, Lauren (April 25, 2022). "Twitter accepts Elon Musk's buyout deal". CNBC. Archived from the original on April 26, 2022. Retrieved April 25, 2022.
- ^ Kay, Grace; Hays, Kali. "Elon Musk is officially Twitter's new owner, and he's firing executives already". Business Insider. Archived from the original on October 28, 2022. Retrieved October 28, 2022.
- ^ Musk, Elon Reeve [@elonmusk] (July 19, 2023). "Great work by the X/Twitter team" (Tweet). Retrieved July 30, 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ Musk, Elon Reeve [@elonmusk] (July 18, 2023). "Using your own inline ads is fine for now, until X/Twitter can offer this" (Tweet). Retrieved July 30, 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ Musk, Elon Reeve [@elonmusk] (June 30, 2023). "Subscribe to X/Twitter Blue" (Tweet). Retrieved July 30, 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ "xAI: Understand the Universe". x.ai. Archived from the original on July 30, 2023. Retrieved July 30, 2023.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Biron, Bethany. "Elon Musk said Twitter's Birdwatch feature will be renamed 'Community Notes' and is aimed at 'improving information accuracy' amid growing content-moderation concerns". Business Insider. Archived from the original on November 15, 2022. Retrieved November 15, 2022.
- ^ @PopCrave (January 10, 2023). "Twitter's latest UI change has renamed 'Quote Tweets' to 'Quotes,' and moved tweet views to a different row. The device a user is tweeting from is also visible again" (Tweet). Retrieved July 30, 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ Davis, Wes (July 23, 2023). "Twitter's rebrand to X may actually be happening soon". The Verge. Archived from the original on October 13, 2023. Retrieved July 23, 2023.
- ^ "Twitter changes logo to 'X', replacing blue bird symbol". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on July 24, 2023. Retrieved July 24, 2023.
- ^ Roth, Emma (July 25, 2023). "Elon Musk just changed Twitter's logo again — sort of". The Verge. Archived from the original on July 25, 2023. Retrieved July 25, 2023.
- ^ Titcomb, James (July 26, 2023). "'They just took it': Elon Musk takes over @x Twitter account without paying owner". The Daily Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Archived from the original on July 26, 2023. Retrieved July 26, 2023.
- ^ "X (Previously Twitter) 10.0.0-beta.0 (Arm64-v8a) (480-640dpi) (Android 6.0+) APK Download by X Corp". Archived from the original on July 30, 2023. Retrieved August 9, 2023.
- ^ "X (Previously Twitter) 10.0.0-release.0 (Nodpi) (Android 6.0+) APK Download by X Corp". Archived from the original on July 30, 2023. Retrieved August 9, 2023.
- ^ "Twitter gets special permission to be 'X' in the iOS App Store". July 31, 2023. Archived from the original on July 31, 2023. Retrieved July 31, 2023.
- ^ "As Musk renames Twitter to X; 'Tweets' now 'posts', 'retweets' become 'reposts': Report". Hindustan Times. July 29, 2023. Archived from the original on August 13, 2023. Retrieved August 14, 2023.
- ^ "Twitter was the Holy Grail of branding. Then Elon Musk ditched it. Experts question why". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. July 26, 2023. Archived from the original on August 10, 2023. Retrieved August 9, 2023.
- ^ "Why Twitter's rebrand to X could be legally challenging". CBS News. July 25, 2023. Archived from the original on August 4, 2023. Retrieved August 4, 2023.
- ^ Sheth, Sonam; Sundar, Sindhu. "Meta already appears to hold the rights to 'X.' It could make Twitter's rebrand complicated". Business Insider. Archived from the original on August 4, 2023. Retrieved August 4, 2023.
- ^ "Twitter's new 'X' logo looks suspiciously like a Unicode character - Business Insider". Business Insider. Archived from the original on November 10, 2023. Retrieved November 9, 2023.
- ^ Brodkin, Jon (July 24, 2023). "Musk rushes out new Twitter logo—it's just an X that someone tweeted at him". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on July 30, 2023. Retrieved August 4, 2023.
- ^ Nudd, Tim (September 15, 2023). "Twitter users don't want to call it X — Inside the platform's marketing challenge". Advertising Age. Archived from the original on September 15, 2023. Retrieved September 16, 2023.
- ^ Smith, Connor. "Musk Is Overpaying for Twitter—by a Lot. Here's the Math". www.barrons.com. Retrieved July 6, 2024.
- ^ Spangler, Todd (October 20, 2022). "Elon Musk Says He's 'Obviously Overpaying' for Twitter in $44 Billion Deal but Sees Huge Upside Long-Term". Variety. Retrieved July 6, 2024.
- ^ Perez, Sarah (June 3, 2024). "You can now customize your For You feed on Threads using swipes". TechCrunch. Retrieved June 20, 2024.
- ^ Cartwright, Jason (May 15, 2024). "Goodbye Twitter.com, Welcome to X.com". techAU. Archived from the original on May 15, 2024. Retrieved May 15, 2024.
- ^ "Twitter's domain is now officially x.com, Elon Musk 'tweets'". The Economic Times. May 17, 2024. ISSN 0013-0389. Archived from the original on May 17, 2024. Retrieved May 17, 2024.
- ^ Pehling, Dave; Ramirez, Len (July 16, 2024). "Elon Musk says X, SpaceX headquarters will relocate to Texas from California - CBS San Francisco". www.cbsnews.com. Retrieved July 17, 2024.
- ^ "Elon Musk to move SpaceX and X HQ over gender identity law". www.bbc.com. Retrieved July 17, 2024.
- ^ "Know Your Twitter Terms: 'Block' vs. 'Mute'". Wired. Archived from the original on August 9, 2020. Retrieved July 20, 2020.
- ^ Gibbs, Samuel (May 13, 2014). "13 reasons to mute people on Twitter". The Guardian. Archived from the original on January 19, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2020.
- ^ "Now every Twitter web user can 'soft block' annoying followers". The Verge. October 11, 2021. Archived from the original on October 14, 2021. Retrieved October 12, 2021.
- ^ "Using Twitter with Your Phone". Twitter Support. Archived from the original on March 15, 2010. Retrieved June 1, 2010.
We currently support 2-way (sending and receiving) Twitter SMS via short codes and one-way (sending only) via long codes.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Stone, Biz (October 30, 2009). "There's a List for That". Archived from the original on April 29, 2013. Retrieved February 1, 2010 – via Twitter.
- ^ Brown, Amanda (March 2, 2011). "The tricky business of business tweeting". The Irish Times. Archived from the original on October 23, 2012. Retrieved April 28, 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Porter, Jon (September 1, 2020). "Twitter quote tweets are now easier to find". The Verge. Archived from the original on February 28, 2021. Retrieved May 23, 2021.
- ^ Shu, Catherine (April 7, 2015). "Twitter Officially Launches Its 'Retweet With Comment' Feature". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on May 22, 2021. Retrieved May 22, 2021.
- ^ "Twitter officially kills off favorites and replaces them with likes". The Verge. Archived from the original on October 9, 2017. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ Smith, Catharine (December 8, 2011). "9 Things You Need To Know About Twitter's Massive Redesign". HuffPost. Archived from the original on August 17, 2021. Retrieved August 16, 2021.
- ^ "Diese Tweets wurden am häufigsten geteilt". Capital.de (in German). May 27, 2020. Archived from the original on August 16, 2021. Retrieved August 16, 2021.
- ^ "Download the free Twitter app | Twitter". Archived from the original on May 25, 2019. Retrieved July 30, 2019 – via Twitter.
- ^ Stutzman, Fred (April 11, 2007). "The 12-Minute Definitive Guide to Twitter". AOL Developer Network. Archived from the original on July 4, 2008. Retrieved November 12, 2008.
- ^ Santiago, Evan (September 3, 2022). "The edit button may finally be coming to Twitter. Here's when you'll be able to use it". The Charlotte Observer. Archived from the original on September 1, 2022. Retrieved September 4, 2022.
- ^ Strachan, Donald (February 19, 2009). "Twitter: How To Set Up Your Account". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on January 10, 2022. Retrieved February 13, 2011.
- ^ Magdaleno, Alex (June 11, 2014). "Raise Your 'Hashflags': Twitter Reintroduces World Cup Hashtags". Mashable. Archived from the original on May 16, 2021. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ "Twitter hashflags call out support for the Asian American community: Thursday Wake-Up Call". Advertising Age. March 18, 2021. Archived from the original on May 16, 2021. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ Johnson, Lauren (February 2, 2016). "Twitter's Branded Emojis Come With a Million-Dollar Commitment". Archived from the original on May 16, 2021. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ Peters, Jay (May 20, 2020). "Twitter is testing a way to let you limit replies to your tweets". Archived from the original on November 9, 2020. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Peters, Jay (July 13, 2021). "Twitter will let you change who can reply to a tweet after you post it". The Verge. Archived from the original on July 16, 2021. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ "Coming soon to Twitter: More room to tweet". Associated Press. May 24, 2016. Archived from the original on February 6, 2017. Retrieved May 24, 2016.
- ^ Lever, Rob (May 24, 2016). "Twitter eases 140 character limit". Yahoo Tech. Archived from the original on May 9, 2017. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ Newton, Casey (March 30, 2017). "Twitter redesigns replies so usernames don't count against the 140-character limit". The Verge. Archived from the original on March 8, 2021. Retrieved August 24, 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Giving you more characters to express yourself". Archived from the original on September 27, 2017. Retrieved September 27, 2017.
- ^ Fingas, John (February 8, 2023). "Twitter Blue users can now post tweets with up to 4,000 characters". Engadget. Archived from the original on February 8, 2023. Retrieved February 8, 2023.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "About Twitter's Link Service". Twitter Help Center (module of Twitter). Archived from the original on February 25, 2011. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
- ^ Garrett, Sean (June 8, 2010). "Links and Twitter: Length Shouldn't Matter". Twitter Blog (blog of Twitter). Archived from the original on February 23, 2011. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
- ^ Metz, Cade (September 2, 2010). "Twitter Tightens Grip on Own Firehose". The Register. Archived from the original on May 28, 2020. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
- ^ Weisenthal, Joe (May 6, 2009). "Twitter Switches from TinyURL to Bit.ly". Business Insider. Archived from the original on March 8, 2013. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
- ^ "Twitter now with integrated photo-sharing service and completely new twitter search". Techshrimp. June 1, 2011. Archived from the original on June 30, 2011. Retrieved June 1, 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Mike Flacy "Twitter photo sharing goes live for all users" Archived March 14, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Digital Trends. August 9, 2011. Retrieved August 10, 2011.
- ^ Twitter Help center: Picture Descriptions – How to make images accessible for people Archived March 27, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Accessible images for everyone". Archived from the original on January 24, 2021. Retrieved August 31, 2019 – via Twitter.
- ^ Lyons, Kim (April 7, 2022). "Twitter rolls out its ALT badge and improved image descriptions". The Verge. Archived from the original on April 8, 2022. Retrieved April 7, 2022.
- ^ "Your Twitter Feed Is About to Be Flooded With Polls". Wired. October 21, 2015. Archived from the original on October 19, 2017. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- ^ Binder, Matt (April 28, 2020). "Twitter quietly deletes millions of accounts from the old text message days". Mashable. Archived from the original on March 8, 2021. Retrieved January 6, 2021.
- ^ Kastrenakes, Jacob (April 27, 2020). "Twitter turns off its original SMS service in most countries". The Verge. Archived from the original on November 21, 2020. Retrieved January 6, 2021.
- ^ "Twitter and CBS News to partner for live stream of Republican and Democratic National Conventions". CBS News. July 11, 2016. Archived from the original on April 27, 2019. Retrieved July 11, 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Twitter plans to broadcast live video 24 hours a day". The Verge. April 26, 2017. Archived from the original on April 27, 2019. Retrieved May 12, 2017.
- ^ Brodkin, Jon (April 5, 2016). "Twitter buys NFL streaming rights for 10 Thursday Night Football games". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on April 5, 2016. Retrieved April 5, 2016.
- ^ "Twitter still thinks it's a TV platform — and here are its dozen new shows". Re/code. May 2, 2017. Archived from the original on April 27, 2019. Retrieved May 12, 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Twitter Pushes Live-Video Deals With MLB, National Football League, Viacom, BuzzFeed, Live Nation, WNBA and More". Variety. May 2017. Archived from the original on April 27, 2019. Retrieved May 12, 2017.
- ^ Roth, Emma (October 21, 2021). "Twitter is finally letting everyone create Spaces". The Verge. Archived from the original on October 28, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Twitter starts testing its own version of Stories, called 'Fleets,' which disappear after 24 hours". TechCrunch. March 4, 2020. Archived from the original on March 5, 2020. Retrieved September 27, 2020.
- ^ "Twitter brings Fleets to India, for 'those uncomfortable with public tweets'". The Indian Express. June 10, 2020. Archived from the original on November 28, 2020. Retrieved September 27, 2020.
- ^ Hayes, Dade (November 17, 2020). "Twitter Launches Disappearing 'Fleets' Globally After Tests In Select Markets". Deadline. Archived from the original on November 28, 2020. Retrieved January 6, 2021.
- ^ Newton, Casey (November 18, 2020). "What Twitter Fleets signals about the future of the company". The Verge. Archived from the original on March 11, 2021. Retrieved November 18, 2020.
- ^ Lyons, Kim (June 1, 2021). "Twitter's Fleets are getting Stories-like ads". The Verge. Archived from the original on June 6, 2021. Retrieved June 6, 2021.
- ^ Heath, Alex (July 14, 2021). "Twitter is shutting down Fleets, its expiring tweets feature". The Verge. Archived from the original on August 3, 2021. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ "Bloggers back media against youth league". Archived from the original on July 18, 2011. Retrieved April 3, 2010.
- ^ "Top Twitter Trends of 2009". Archived from the original on April 29, 2013. Retrieved April 3, 2010.
- ^ Woollaston, Vicky. "Justin Bieber fans beat Twitter 'block'". Web User. Archived from the original on November 22, 2012. Retrieved January 20, 2012.
- ^ Weiner, David (June 21, 2009). "#Thatsafrican – When Twitter Went Racist?". HuffPost. Archived from the original on October 19, 2017. Retrieved April 3, 2010.
- ^ "Thingsdarkiessay causes a Twitter storm". Independent Online. South Africa. November 5, 2009. Archived from the original on January 30, 2016. Retrieved January 11, 2012.
- ^ "Twitter Lists!". Support forum at help.twitter.com. n.d. Archived from the original on December 22, 2009. Retrieved February 13, 2011.
- ^ "Twitter gets a new 'List Search' feature; Know what it is all about". HT Tech. May 26, 2023. Archived from the original on May 29, 2023. Retrieved May 29, 2023.
- ^ Chin, Monica (March 5, 2020). "How to create a Twitter List (and join others)". The Verge. Archived from the original on May 29, 2023. Retrieved May 29, 2023.
- ^ Pierce, David (October 6, 2015). "Meet Moments, Twitter's Most Important New Feature Ever". Wired. ISSN 1059-1028. Archived from the original on March 8, 2021. Retrieved July 17, 2019.
- ^ Newton, Casey (October 6, 2015). "Twitter launches Moments, its dead-simple tab for browsing the best tweets". The Verge. Archived from the original on March 8, 2021. Retrieved July 17, 2019.
- ^ Kastrenakes, Jacob (September 28, 2016). "Twitter opens its Moments feature up to everyone". The Verge. Archived from the original on March 8, 2021. Retrieved July 17, 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Huszár, Ferenc; Ktena, Sofia Ira; O'Brien, Conor; Belli, Luca; Schlaikjer, Andrew; Hardt, Moritz (October 21, 2021). "Algorithmic Amplification of Politics on Twitter" (PDF). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 119 (1): 27. arXiv:2110.11010. doi:10.1073/pnas.2025334119. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 8740571. PMID 34934011. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 22, 2021. Retrieved October 23, 2021.
- ^ "Twitter's algorithm favours right-leaning politics, research finds". BBC News. October 22, 2021. Archived from the original on October 29, 2021. Retrieved October 23, 2021.
- ^ "Twitter apps for phones, tablets and computers". Archived from the original on April 2, 2017. Retrieved April 6, 2017 – via Twitter.
- ^ Byford, Sam (April 6, 2017). "Twitter Lite is a faster, leaner mobile web version of Twitter". The Verge. Archived from the original on April 27, 2019. Retrieved April 6, 2017.
- ^ Russell, Jon (April 6, 2016). "Twitter launches a 'lite' mobile web app that's optimized for emerging markets". TechCrunch. AOL. Archived from the original on April 27, 2019. Retrieved April 6, 2017.
- ^ "Twitter Blue Seemingly Getting X Rebranding". ComicBook.com. Archived from the original on August 6, 2023. Retrieved August 6, 2023.
- ^ "X (Twitter) Blue is Dead, Welcome X Premium • iPhone in Canada Blog". iPhone in Canada. August 5, 2023. Archived from the original on August 6, 2023. Retrieved August 6, 2023.
- ^ Perez, Sarah (June 3, 2021). "Twitter launches its premium subscription, Twitter Blue, initially in Canada and Australia". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on August 3, 2021. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Peters, Jay (November 9, 2021). "Twitter will now let you pay to undo tweets and read ad-free news in the US". The Verge. Archived from the original on November 10, 2021. Retrieved April 24, 2022.
- ^ Sankaran, Vishwam (November 6, 2023). "Elon Musk unveils new sarcasm-loving AI chatbot for premium X subscribers". The Independent. Archived from the original on November 6, 2023. Retrieved December 7, 2023.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Roth, Emma (November 1, 2022). "Twitter discontinues ad-free articles for Blue subscribers". The Verge. Archived from the original on November 6, 2022. Retrieved November 6, 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Peters, Jay (November 1, 2022). "Elon Musk will let you pay $8 to be a verified 'lord' on Twitter". The Verge. Archived from the original on April 21, 2023. Retrieved November 6, 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Roth, Emma (November 5, 2022). "Elon Musk's $7.99 Twitter Blue with verification is 'coming soon' on iOS". The Verge. Archived from the original on November 6, 2022. Retrieved November 6, 2022.
- ^ Binder, Matt (November 8, 2022). "Can an $8 Twitter subscription bail out Elon Musk? Let's look at the numbers". Mashable. Archived from the original on November 18, 2022. Retrieved November 18, 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Сойерс, Пол (21 апреля 2023 г.). «Похоже, что Twitter теперь требует, чтобы все рекламодатели имели подтвержденную галочку» . ТехКранч . Архивировано из оригинала 22 апреля 2023 года . Проверено 26 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ О'Салливан, Дони; Корн, Дженнифер (6 ноября 2022 г.). «Илон Маск откладывает план проверки Твиттера по «голубому чеку» на 8 долларов до окончания промежуточных выборов» . Си-Эн-Эн. Архивировано из оригинала 8 ноября 2022 года . Проверено 9 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ Беланджер, Эшли (11 ноября 2022 г.). «Twitter незаметно отказывается от платной проверки за 8 долларов; «обманывать людей недопустимо», — говорит Маск» . Арс Техника . Архивировано из оригинала 11 ноября 2022 года . Проверено 12 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ Лерман, Рэйчел; Закшевский, Кот (11 ноября 2022 г.). «Первый крупный продукт Илона Маска в Твиттере был приостановлен из-за распространения фейковых аккаунтов» . Вашингтон Пост . Архивировано из оригинала 16 ноября 2022 года . Проверено 17 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ Аллин, Бобби (12 декабря 2022 г.). «Илон Маск перезапускает Twitter Blue с более высокой ценой для пользователей iPhone» . ЭНЕРГЕТИЧЕСКИЙ ЯДЕРНЫЙ РЕАКТОР . Архивировано из оригинала 12 декабря 2022 года . Проверено 12 декабря 2022 г.
- ^ Силберлинг, Аманда (8 декабря 2022 г.). «Синяя клетка Шредингера: согласно Твиттеру, я могу быть заметным, а может и не быть» . ТехКранч . Архивировано из оригинала 28 марта 2023 года . Проверено 28 марта 2023 г.
- ^ Ганс, Джаред (25 марта 2023 г.). «Twitter начнет поэтапный отказ от устаревшей системы проверки с 1 апреля, но не все потеряют синие чеки» . Холм . Nexstar Media, Inc. Архивировано из оригинала 28 марта 2023 года . Проверено 28 марта 2023 г.
- ^ Спенглер, Тодд (23 марта 2023 г.). «Twitter в апреле отзовет значки «устаревшего» проверенного аккаунта, оставив синие галочки только платным подписчикам» . Разнообразие . Архивировано из оригинала 30 марта 2023 года . Проверено 24 марта 2023 г.
- ^ Госвами, Рохан (20 апреля 2023 г.). «Twitter наконец-то убрал устаревшие галочки проверки» . CNBC. Архивировано из оригинала 25 апреля 2023 года . Проверено 25 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ Шредер, Стэн (25 апреля 2023 г.). «Илон Маск говорит, что проверенные аккаунты в Твиттере теперь имеют приоритет, что бы это ни значило» . Машаемый . Архивировано из оригинала 25 апреля 2023 года . Проверено 25 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ Шредер, Стэн (25 апреля 2023 г.). «Илон Маск говорит, что проверенные аккаунты в Твиттере теперь имеют приоритет, что бы это ни значило» . Машаемый . Архивировано из оригинала 25 апреля 2023 года . Проверено 30 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ «Twitter для приоритета ответов от отслеживаемых и проверенных пользователей» . Таймс оф Индия . 20 марта 2023 г. ISSN 0971-8257 . Архивировано из оригинала 21 июля 2023 года . Проверено 21 июля 2023 г.
- ^ Шляпник, Тейлор (1 сентября 2021 г.). «Twitter запускает платную подписку «Super Follows», чтобы вы могли зарабатывать на своих твитах» . Технический кризис. Архивировано из оригинала 9 сентября 2021 года . Проверено 28 сентября 2021 г.
- ^ Перес, Сара (12 сентября 2021 г.). «Twitter Super Follows заработал всего около 6 тысяч долларов за первые две недели» . Технический кризис. Архивировано из оригинала 28 сентября 2021 года . Проверено 28 сентября 2021 г.
- ^ «Twitter заменяет «Суперподписки» на «Подписки » . Engadget . 14 апреля 2023 года. Архивировано из оригинала 25 апреля 2023 года . Проверено 25 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ Гартенберг, Хаим (6 марта 2021 г.). «Twitter тестирует новую функцию Tip Jar для отправки денег на ваши любимые счета» . Грань . Архивировано из оригинала 6 мая 2021 года . Проверено 7 мая 2021 г.
- ^ Родригес, Сальвадор (23 сентября 2021 г.). «Теперь вы можете получать оплату в биткойнах за использование Twitter» . CNBC. Архивировано из оригинала 24 сентября 2021 года . Проверено 23 сентября 2021 г.
- ^ Карман, Эшли (27 августа 2021 г.). «Twitter начинает запускать Ticketed Spaces для некоторых пользователей iOS» . Грань. Архивировано из оригинала 29 сентября 2021 года . Проверено 28 сентября 2021 г.
- ^ Маттакал, Лиза Полин (22 апреля 2022 г.). «Twitter и Stripe пилотируют платежи в криптовалюте для авторов» . Рейтер . Архивировано из оригинала 26 апреля 2022 года . Проверено 24 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ Поппер, Бен (8 сентября 2014 г.). «Теперь вы можете покупать вещи прямо в Твиттере» . Грань . Архивировано из оригинала 6 ноября 2022 года . Проверено 6 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ Портер, Джон (28 июля 2021 г.). «Твиттер запускает новый раздел покупок для брендов» . Грань . Архивировано из оригинала 31 июля 2021 года . Проверено 28 июля 2021 г.
- ^ «Twitter начинает тестирование функции «Магазины» для развития электронной коммерции» . «Экспресс Трибьюн» . 10 марта 2022 года. Архивировано из оригинала 10 марта 2022 года . Проверено 10 марта 2022 г.
- ^ «Walmart станет первым ритейлером, который протестирует новую платформу покупок в прямом эфире Twitter» . ТехКранч . 22 ноября 2021 года. Архивировано из оригинала 3 декабря 2021 года . Проверено 2 декабря 2021 г.
- ^ «Глобальные социальные сети, ранжированные по количеству пользователей» . Статистика . Архивировано из оригинала 29 января 2022 года . Проверено 18 июня 2017 г.
- ^ Фигерман, Сет. «Twitter сейчас теряет пользователей в США» CNNMoney . Архивировано из оригинала 27 апреля 2019 года . Проверено 23 марта 2018 г.
- ^ «Маск говорит, что у X 600 миллионов активных пользователей в месяц» . news.bloomberglaw.com . Проверено 24 июня 2024 г.
- ^ Перес, Сара (3 июня 2024 г.). «Теперь вы можете настроить ленту «Для вас» в темах с помощью пролистывания» . ТехКранч . Проверено 24 июня 2024 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Миллер, Клэр Кейн (25 августа 2009 г.). «Кто движет популярностью Twitter? Не подростки» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 27 апреля 2019 года . Проверено 18 сентября 2009 г.
- ^ Ченг, Алекс; Эванс, Марк (июнь 2009 г.). «Внутри Твиттера – углубленный взгляд на мир Твиттера» . Сисомос . Архивировано из оригинала 3 апреля 2023 года . Проверено 23 февраля 2011 г.
- ^ Блафф, Брайан (май 2010 г.). «Кто пользуется Твиттером?» . сайт-искатель.com. Архивировано из оригинала 31 мая 2010 года . Проверено 22 сентября 2010 г.
- ^ Чен, Адриан (17 мая 2011 г.). «Почему так много чернокожих в Твиттере» . Зевака . Юнивизион Коммуникейшнс . Архивировано из оригинала 11 мая 2019 года . Проверено 5 мая 2017 г.
- ^ Сэйнт, Ник (30 апреля 2010 г.). «Почему Twitter более популярен среди чернокожих, чем среди белых?» . Бизнес-инсайдер . Аксель Спрингер SE . Архивировано из оригинала 10 апреля 2019 года . Проверено 5 мая 2017 г.
- ^ Тейлор, Крис (8 сентября 2011 г.). «У Twitter 100 миллионов активных пользователей» . Машаемый . Архивировано из оригинала 20 апреля 2012 года . Проверено 16 сентября 2011 г.
- ^ «Twitter сообщает о результатах за первый квартал 2014 года» . Архивировано из оригинала 9 июня 2014 года . Проверено 9 июня 2014 г.
- ^ Иветт Александер, Поляризация в Твиттерсфере: Что 86 миллионов твитов говорят о политическом составе американских пользователей Твиттера и о том, как они взаимодействуют с новостями. Архивировано 7 июня 2021 года в Wayback Machine Knight Foundation/
- ^ Дин Фрилон, доцент Школы журналистики и СМИ Хассмана, Твиты слева, справа и в центре: как пользователи и внимание распределяются в Твиттере. Архивировано 1 августа 2021 года в Wayback Machine , Knight Foundation.
- ^ «Обыкновенные акции Twitter, Inc» . Архивировано из оригинала 7 ноября 2019 года . Проверено 9 июня 2014 г.
- ^ «Обновление социальных сетей 2016» . Исследовательский центр Пью: Интернет, наука и технологии . 11 ноября 2016 года. Архивировано из оригинала 29 октября 2019 года . Проверено 23 марта 2018 г.
- ^ Войчик, Стефан; Хьюз, Адам (24 апреля 2019 г.). «Оценка пользователей Twitter» . Исследовательский центр Пью. Архивировано из оригинала 29 октября 2019 года . Проверено 9 января 2021 г.
- ^ Келли, Райан, изд. (12 августа 2009 г.). «Исследование Твиттера – август 2009 г.». Исследование Twitter показывает интересные результаты об использовании (PDF) . Сан-Антонио, Техас: Pear Analytics. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 15 июля 2011 года.
- ^ Бойд, Дана (16 августа 2009 г.). «Твиттер: «бессмысленная болтовня» или периферийная осведомленность + социальный уход?» . Архивировано из оригинала 7 марта 2012 года . Проверено 19 сентября 2009 г.
- ^ Эйвери Холтон; Кан Бэк; Марк Коддингтон; Яшур; Кэролайн (2014). «Поиск и обмен: мотивы для размещения ссылок в Твиттере». Отчеты о коммуникационных исследованиях . 31 (1): 33–40. дои : 10.1080/08824096.2013.843165 . S2CID 143390964 .
- ^ Мерфи, Дэвид (13 апреля 2014 г.). «44 процента аккаунтов в Твиттере никогда не писали в Твиттере» . Журнал ПК . Архивировано из оригинала 21 сентября 2018 года . Проверено 17 сентября 2017 г.
- ^ «Доля взрослых американцев, использующих социальные сети, включая Facebook, практически не изменилась с 2018 года» . Исследовательский центр Пью . 10 апреля 2019 года. Архивировано из оригинала 31 марта 2021 года . Проверено 11 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Голдсмит, Белинда (29 апреля 2009 г.). «Многие пользователи Твиттера быстро уходят: исследование» . Рейтер . Архивировано из оригинала 8 марта 2021 года . Проверено 22 февраля 2011 г.
- ^ Мадригал, Алексис К. (24 апреля 2019 г.). «Твиттер — это не Америка» . Атлантика . Архивировано из оригинала 20 марта 2021 года . Проверено 11 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Хальс, Том; Балу, Ниведита (20 сентября 2021 г.). «Twitter пытается урегулировать коллективный иск 2016 года на 800 миллионов долларов» . Денверская газета . Архивировано из оригинала 21 сентября 2021 года . Проверено 20 сентября 2021 г.
- ^ Сегев, Элад (апрель 2023 г.). «Обмен чувствами и взаимодействие с пользователями в Твиттере: все дело во мне и тебе» . Социальные сети + Общество . 9 (2). дои : 10.1177/20563051231183430 . S2CID 259304684 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Рехак, Мелани (8 августа 2014 г.). «Кто сделал эту птицу в Твиттере?» . Журнал «Нью-Йорк Таймс» . Архивировано из оригинала 9 августа 2014 года . Проверено 22 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ Фриман, Эрик (август 2011 г.). «Логотип Twitter назван в честь Ларри Берда» . Yahoo!Спорт . Архивировано из оригинала 19 октября 2017 года . Проверено 1 марта 2012 г.
- ^ Холлидей, Джош (7 июня 2012 г.). «Не подбрасывайте птицу! Twitter представляет строгие правила использования нового логотипа» . Хранитель . Архивировано из оригинала 27 апреля 2019 года . Проверено 11 октября 2014 г.
- ^ Григгс, Брэндон (7 июня 2012 г.). «Логотип птицы Твиттера претерпевает изменения» . CNN . Архивировано из оригинала 27 апреля 2019 года . Проверено 7 июня 2012 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Катбертсон, Энтони (24 июля 2023 г.). «Twitter переименовывается в X в рамках плана Илона Маска по созданию «приложения для всего» » . Независимый . Архивировано из оригинала 24 июля 2023 года . Проверено 24 июля 2023 г.
- ^ «Смена логотипа Твиттера: пять фактов о ныне мертвой синей птице Твиттера» . Раскадровка18 . 24 июля 2023 года. Архивировано из оригинала 23 июля 2023 года . Проверено 24 июля 2023 г.
- ^ Савов Влад (24 июля 2023 г.). «Маск объявляет, что фанаты представили новый логотип «X» в Твиттере в резком изменении» . Новости Блумберга . Архивировано из оригинала 24 июля 2023 года . Проверено 24 июля 2023 г.
- ^ Мак, Райан; Сюй, Тиффани (24 июля 2023 г.). «От Twitter до X: Илон Маск начинает стирать культовый интернет-бренд» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . ISSN 0362-4331 . Архивировано из оригинала 31 июля 2023 года . Проверено 1 августа 2023 г.
- ^ Перес, Сара (2 августа 2023 г.). «Пользователи App Store понижают оценку ребрендинга Twitter до X из-за отзывов с 1 звездой» . ТехКранч . Архивировано из оригинала 3 октября 2023 года . Проверено 18 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ Кли, Майлз (24 июля 2023 г.). «Ребрендинг Twitter «X» — это самый отчаянный трюк Илона Маска» . Роллинг Стоун . Архивировано из оригинала 3 октября 2023 года . Проверено 18 сентября 2023 г.
- ^ МакШейн, Джулианна (25 июля 2023 г.). «Полиция остановила удаление вывески Twitter в штаб-квартире компании, поскольку Илон Маск меняет бренд на «X» » . Новости Эн-Би-Си . Проверено 1 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Артур, Чарльз (13 апреля 2010 г.). «Twitter представляет рекламный план «продвигаемых твитов» – Twitter позволит рекламодателям платить за появление твитов в результатах поиска» . Хранитель . Лондон. Архивировано из оригинала 27 апреля 2019 года . Проверено 23 февраля 2011 г.
- ^ Кимберли, Сара (13 апреля 2010 г.). «Twitter представляет рекламную платформу для продвигаемых твитов» . MediaWeek (издание для Великобритании). Архивировано из оригинала 20 января 2013 года . Проверено 5 февраля 2011 г.
- ^ Лоран, Оливье (11 мая 2011 г.). «Генеральный директор фотоагентства рассматривает споры на TwitPic» . Британский журнал фотографии . Лондон. Архивировано из оригинала 3 августа 2011 года . Проверено 17 августа 2011 г.
Сделка предоставит WENN эксклюзивные права на продажу изображений, размещенных на сервисе TwitPic.
- ^ «Доходы от рекламы в Твиттере вырастут на 210% до $139,5 млн в 2011 году» . Архивировано из оригинала 9 мая 2022 года . Проверено 9 мая 2022 г.
- ^ Вассерман, Тодд (9 июня 2011 г.). «Twitter автоматизирует покупку рекламы к концу года» . Mashable.com. Архивировано из оригинала 3 мая 2019 года . Проверено 14 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Майнерс, Зак (30 апреля 2013 г.). «Twitter открывает рекламу самообслуживания для всех» . СМО . ИДГ Коммуникации. Архивировано из оригинала 19 августа 2014 года . Проверено 18 августа 2014 г.
- ^ «Twitter выпускает продвигаемые твиты для мобильных устройств». Архивировано 23 декабря 2017 г., в Wayback Machine ; Вассерман, Тодд. 20 марта 2012 г. mashable.com.
- ^ Свант, Мэри. «Twitter помогает брендам стимулировать общение с помощью карт мгновенной разблокировки» . Рекламная неделя . Архивировано из оригинала 4 декабря 2016 года . Проверено 4 августа 2016 г.
- ^ Двоскин, Элизабет (26 октября 2017 г.). «Твиттер запрещает российским государственным новостным сайтам RT и Sputnik покупать рекламу» . Вашингтон Пост . Архивировано из оригинала 30 октября 2020 года . Проверено 25 февраля 2020 г.
- ^ «Твиттер запрещает рекламу Russia Today и сети Sputnik, ссылаясь на вмешательство в выборы» . Время . 27 октября 2017 года. Архивировано из оригинала 27 октября 2017 года . Проверено 26 июля 2018 г.
- ^ «Twitter запрещает политическую рекламу на своей платформе, оказывая давление на непокорный Facebook» . Новости18 . 31 октября 2019 года. Архивировано из оригинала 8 марта 2021 года . Проверено 31 октября 2019 г.
- ^ Пол, Кари (30 августа 2023 г.). «Twitter позволяет политическим кандидатам и партиям США размещать рекламу при смене политики» . Хранитель . Архивировано из оригинала 17 ноября 2023 года . Проверено 17 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ «Политический контент» . Х для бизнеса. Архивировано из оригинала 17 ноября 2023 года . Проверено 17 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Кальма, Жюстин (22 апреля 2022 г.). «Твиттер запрещает «вводящую в заблуждение» рекламу об изменении климата» . Грань . Архивировано из оригинала 25 апреля 2022 года . Проверено 23 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ Милмо, Дэн (26 мая 2022 г.). «Twitter оштрафован на 150 миллионов долларов за передачу контактных данных пользователей рекламодателям » Хранитель . Архивировано из оригинала 11 июля 2022 года . Проверено 27 мая 2022 г.
- ^ Закшевский, Кот (25 мая 2022 г.). «Twitter заплатит штраф в 150 миллионов долларов за обманным образом собранные данные» . Вашингтон Пост . Архивировано из оригинала 21 ноября 2023 года . Проверено 17 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Воан-Николс, Стивен (30 августа 2012 г.). «Как Twitter публикует ваши твиты с открытым исходным кодом» . ЗДНет . Архивировано из оригинала 5 октября 2014 года . Проверено 10 сентября 2012 г.
- ^ Гомес, Ли (22 июня 2009 г.). «Крысолов из зарплаты» . Форбс . Архивировано из оригинала 11 марта 2021 года . Проверено 16 июня 2009 г.
- ^ Кинг, Райан (25 сентября 2009 г.). «Твиттер на Рубине» . Архивировано из оригинала 27 сентября 2009 года . Проверено 31 октября 2009 г.
Недавно мы перенесли Twitter из специальной сборки Ruby 1.8.6 в версию-кандидат Ruby Enterprise Edition, любезно предоставленную Phusion. Нашей основной мотивацией была интеграция патчей MBARI от Brent, которые повышают стабильность памяти.
- ^ Пейн (16 января 2008 г.). «Анонсируем Старлинг» . Архивировано из оригинала 20 января 2008 года . Проверено 11 января 2009 г. - через Twitter.
- ^ Веннерс, Билл (3 апреля 2009 г.). «Твиттер на Scala» . Разработчик Артима. Архивировано из оригинала 19 июня 2009 года . Проверено 17 июня 2009 г.
- ^ «Поиск в Твиттере теперь в 3 раза быстрее» . 6 апреля 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 6 февраля 2017 года . Проверено 4 января 2016 г.
- ^ Малик, Ом (17 августа 2013 г.). «Как Twitter масштабировал свою инфраструктуру, чтобы обеспечить рекордное количество твитов в секунду» . ГИГАОМ . Архивировано из оригинала 24 февраля 2021 года . Проверено 17 августа 2013 г.
- ^ «10 лучших веб-API – соединение современных технологий» . ВебДАМ . 11 января 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 1 апреля 2021 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2016 г.
- ^ «Twitter API Wiki/FrontPage» . Архивировано из оригинала 3 ноября 2010 года . Проверено 18 сентября 2010 г. - через Twitter.
- ^ «Представляем API Twitter | Блоги Twitter» . Архивировано из оригинала 23 декабря 2016 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2016 г. - через Twitter.
- ^ «Учебное пособие по Ruby on Rails (Rails 5)» . Мягкая обложка.io . Архивировано из оригинала 25 декабря 2021 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2016 г.
- ^ «10-летняя борьба Twitter с отношениями с разработчиками | Северные API |» . Скандинавские API . 23 марта 2016. Архивировано из оригинала 20 декабря 2016 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2016 г.
- ^ Парр, Бен (25 апреля 2010 г.). «Твиттер запускает обратный отсчет до OAuthcalypse» . Машаемый . Архивировано из оригинала 16 августа 2019 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2016 г.
- ^ «Twitter запустит программу сокращения URL-адресов и может заблокировать TinyURL и bit.ly» . Компьютерный еженедельник . Архивировано из оригинала 25 февраля 2021 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2016 г.
- ^ Стримс, Кимбер (11 ноября 2012 г.). «Tweetro говорит, что он «полностью парализован» строгим ограничением Twitter в 100 000 пользовательских токенов» . Грань . Архивировано из оригинала 2 февраля 2021 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2016 г.
- ^ Воутерс, Робин (17 августа 2012 г.). «Изменения API Twitter устанавливают максимальное количество пользователей для третьих лиц» . Thenextweb.com. Архивировано из оригинала 2 мая 2019 года . Проверено 9 мая 2013 г.
- ^ Ха, Энтони (16 августа 2012 г.). «Twitter сковывает клиентские приложения наручниками новыми изменениями API» . ТехКранч . Архивировано из оригинала 24 февраля 2021 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2016 г.
- ^ «Twitter представляет новый, полностью переработанный API для разработчиков, который выйдет на следующей неделе» . ТехКранч . 16 июля 2020 года. Архивировано из оригинала 27 апреля 2022 года . Проверено 28 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «Twitter хочет вернуть доверие разработчиков» . ТехКранч . 21 апреля 2022 года. Архивировано из оригинала 27 апреля 2022 года . Проверено 28 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «RIP Сторонние клиенты Twitter» . Журнал ПК . Проверено 5 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ «Твиттеррифик: Конец эпохи» . Iconfactory: Комната отдыха . Проверено 5 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ «Twitter закрывает свой бесплатный API, вот что сломается» . Engadget . 8 февраля 2023 г. . Проверено 5 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ О'Брайен, Терренс (17 апреля 2012 г.). «Twitter представляет патентное соглашение новаторов и клянется не злоупотреблять патентной системой» . Engadget . АОЛ . Проверено 11 августа 2012 г.
- ^ «Твиттер/Открытый исходный код» . Архивировано из оригинала 15 апреля 2013 года . Проверено 18 апреля 2013 г. - через Twitter.
- ^ «Спасибо за открытый исходный код» . Архивировано из оригинала 15 апреля 2013 года . Проверено 18 апреля 2013 г. - через Twitter.
- ^ «Открытый исходный код» . Проверено 4 января 2017 г. - через Twitter.
- ^ «Поиск: Звезды>1» . Гитхаб . Проверено 27 февраля 2020 г.
- ^ «Исходный код алгоритма рекомендаций Twitter» . Гитхаб . 31 марта 2023 г. . Проверено 1 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ «Новая эра прозрачности Twitter» . Блог в Твиттере . 31 марта 2023 г. . Проверено 1 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ Кастро, Алекс (31 марта 2023 г.). «Twitter делает свой алгоритм «открытым», как и обещал Илон Маск» . Грань . Проверено 1 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ «Твиттер сообщает, что части исходного кода просочились в сеть | CNN Business» . 27 марта 2023 г.
- ^ «Краткая история многочисленных редизайнов Твиттера» . Рекламная неделя . 26 апреля 2014 года . Проверено 17 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Калор, Майкл (16 сентября 2010 г.). «Совершите экскурсию по новому Твиттеру» . Проводной . ISSN 1059-1028 . Проверено 17 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Остроу, Адам. «А вот и новый Twitter.com» . Машаемый . Проверено 17 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Гроув, Дженнифер Ван (15 сентября 2010 г.). «Новый Twitter — это атака на все настольные приложения» . Машаемый . Проверено 17 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Хьюстон, Томас (8 декабря 2011 г.). «Редизайн приложения и веб-сайта Twitter: практические фотографии и видео» . Грань . Проверено 17 июля 2019 г.
- ^ «Запуск версий Twitter на арабском, фарси, иврите и урду» . Новости Би-би-си . 7 марта 2012 года . Проверено 7 марта 2012 г.
- ^ «Поддерживаемые языки и браузеры» . Платформа разработчиков Twitter . 30 июня 2020 г. Проверено 17 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ О'Кэрролл, Лиза (18 сентября 2012 г.). «Редизайн Твиттера делает больше фотографий» . Хранитель . ISSN 0261-3077 . Проверено 17 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Поппер, Бен (8 апреля 2015 г.). «Twitter убирает вкладку Discover » Грань . Проверено 17 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Ньютон, Кейси (26 января 2017 г.). «Twitter заменяет вкладку «Моменты» на «Обзор» . Грань . Проверено 17 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Музил, Стивен. «Twitter тестирует новые макеты рабочего стола» . CNET . Проверено 17 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Брайт, Питер (6 сентября 2018 г.). «Прогрессивные веб-приложения становятся мейнстримом, поскольку Twitter делает свой мобильный сайт основным» . Арс Техника . Проверено 17 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Галлахер, Шон (15 июля 2019 г.). «Twitter меняет Twitter.com, чтобы он стал больше похож на мобильное приложение» . Арс Техника . Проверено 17 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Ли, Дами (15 июля 2019 г.). «В обновленном дизайне Twitter для настольных компьютеров использованы некоторые из лучших функций мобильного приложения» . Грань . Проверено 17 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Гонсалвес, Антоне (25 июня 2010 г.). «Twitter и федеральные органы урегулируют расходы на безопасность – Twitter должен создать и поддерживать «комплексную программу информационной безопасности» и разрешить проверку программы третьей стороной два раза в год в течение 10 лет» . Информационная неделя . Архивировано из оригинала 23 октября 2010 года . Проверено 23 февраля 2011 г.
- ^ «Twitter предупреждает новостные организации о возможной хакерской атаке в Сирии» . Дескриер. 30 апреля 2013 года . Проверено 30 апреля 2013 г.
- ^ Родригес, Сальвадор (23 мая 2013 г.). «Twitter добавляет возможность двухэтапной аутентификации, чтобы помочь защититься от хакеров» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Проверено 10 июня 2013 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Статт, Ник (15 июля 2020 г.). «Барак Обама, Джо Байден, Илон Маск, Apple и другие подверглись беспрецедентной атаке в Твиттере» . Грань . Проверено 15 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Конгер, Кейт; Поппер, Натаниэль (17 июля 2020 г.). «Хакеры рассказывают историю атаки на Твиттер изнутри» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 17 июля 2020 года . Проверено 17 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Макмиллан, Роберт; Волц, Дастин (19 июля 2020 г.). «ФБР расследует взлом Твиттера на фоне более широкой обеспокоенности по поводу безопасности платформы» . Уолл Стрит Джорнал . Проверено 7 июля 2020 г.
- ^ «Twitter подтверждает, что нулевой день использовался для раскрытия данных 5,4 миллиона аккаунтов» . Мигающий компьютер . Проверено 11 августа 2022 г.
- ^ «Twitter подтверждает утечку данных, в результате которой были раскрыты данные 5,4 миллиона пользователей; у злоумышленников все еще могут быть данные» . Новости18 . 8 августа 2022 г. . Проверено 11 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Паганини, Пьерлуиджи (5 августа 2022 г.). «Twitter подтверждает, что нулевой день использовался для доступа к данным 5,4 миллиона аккаунтов» . Дела безопасности . Проверено 11 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Картер, Дилан. «Twitter признался в утечке данных, в результате которой были раскрыты контактные данные 5,4 миллиона аккаунтов» . Брюссель Таймс . Проверено 11 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Уокер, Роб (15 февраля 2009 г.). «Неудачный кит» . Поглощено. Журнал «Нью-Йорк Таймс» . п. 17 . Проверено 15 февраля 2009 г.
- ^ Уайт, Мюррей (1 июня 2008 г.). «Твит, Твит – произошло землетрясение» . Торонто Стар . Проверено 23 февраля 2011 г.
- ^ «La vera storia della balena di Twitter» [Настоящая история Твиттер-кита]. Ла Стампа (на итальянском языке). 24 января 2015 года. Архивировано из оригинала 8 марта 2021 года . Проверено 30 августа 2019 г.
- ^ Симмонс, Джен [@jensimmons] (2 сентября 2007 г.). «О, неудачник, из-за тебя мой сайт проваливается. Больше никакого кросспостинга WordPress-twitter» ( Твит ) – через Twitter .
- ^ Хонан, Мат (25 ноября 2013 г.). «Убивая кита-неудачника с Кристофером Фраем из Твиттера» . Проводной . Проверено 4 мая 2018 г.
- ^ «Болезни роста Twitter стали причиной большого количества простоев в 2007 году» . Royal Pingdom ( Pingdom ) блог . 19 декабря 2007. Архивировано из оригинала 29 декабря 2010 года . Проверено 23 февраля 2011 г.
- ^ Дорси, Джек (15 января 2008 г.). «МакВорлд» . Twitter Blog ( блог Twitter) . Проверено 23 февраля 2011 г.
- ^ Курамото, Джейк (15 января 2008 г.). «MacWorld ставит Twitter на колени» . Oracle AppsLab. Архивировано из оригинала 16 июля 2011 года . Проверено 7 мая 2008 г.
- ^ Стоун, Биз (6 июня 2009 г.). «Не играю в мяч» – через Твиттер.
- ^ Канэлли, Крейг (12 марта 2013 г.). «Почему Twitter проверяет пользователей: история синей галочки» . ХаффПост . Проверено 9 июня 2014 г.
- ^ Кэшмор, Пит (11 июня 2009 г.). «Twitter запускает проверенные аккаунты» . Машаемый . Проверено 9 июня 2014 г.
- ^ «О верифицированных аккаунтах» . Архивировано из оригинала 20 июля 2016 года.
- ^ «Объявление о процессе подачи заявок на подтвержденные учетные записи» . 19 июля 2016 г. – через Twitter.
- ^ Берджесс, Мэтт (20 июля 2016 г.). «Твиттер открывает проверку для всех» . Проводной . Проверено 16 сентября 2016 г.
- ^ Вагнер, Курт (12 сентября 2013 г.). «Twitter представляет эксклюзивную функцию для проверенных пользователей» . Машаемый . Проверено 9 июня 2014 г.
- ^ Харрисон, Стивен (4 декабря 2020 г.). «Twitter хочет использовать Википедию, чтобы определить, кто получит синюю галочку» . Сланец . Проверено 4 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ Статт, Ник (17 декабря 2020 г.). «Twitter запускает новую политику проверки 20 января» . Грань . Проверено 19 февраля 2021 г.
- ^ Хит, Алекс (31 октября 2022 г.). «Twitter планирует начать взимать за проверку 20 долларов в месяц» . Грань . Проверено 6 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ Сато, Миа (9 ноября 2022 г.). «Новые серые «официальные» проверки Twitter распространяются на некоторые громкие аккаунты» . Грань . Проверено 9 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ Лопатто, Элизабет (11 ноября 2022 г.). «Серая галочка Twitter «Официальный» возвращается, теперь, когда «Проверено» бессмысленно» . Грань . Проверено 18 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Теперь Twitter позволяет предприятиям управлять синими галочками своих сотрудников за огромную цену» . Машаемый . 31 марта 2023 г. . Проверено 24 июля 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Виггерс, Кайл (12 декабря 2022 г.). «Twitter запускает Blue for Business и награждает золотыми галочками «юридические лица» » . ТехКранч . Проверено 24 июля 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Раше, Доминик (8 января 2011 г.). «Депутат Исландии борется с требованием США предоставить данные ее аккаунта в Твиттере» . Хранитель . Лондон . Проверено 10 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Как скрыть своих подписчиков и тех, на кого вы подписаны в Твиттере | Класс | Синоним» . Класс.synonym.com. 9 ноября 2015 года . Проверено 7 декабря 2015 г.
- ^ «Политика конфиденциальности Твиттера» . 14 мая 2007 года. Архивировано из оригинала 25 июня 2009 года . Проверено 11 марта 2009 г. - через Twitter.
- ^ Валлийский, Кейтлин; Шредер, Стэн (31 августа 2023 г.). «Мы ознакомились с новой политикой конфиденциальности X, поэтому вам не придется это делать» . Машаемый . Проверено 3 июня 2024 г.
- ^ Ханселл, Сол (16 июля 2009 г.). «Рекламодатели следят за каждым вашим твитом» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 17 июля 2009 г.
- ^ Маккарти, Кэролайн (12 июня 2009 г.). «Сильные игроки Твиттера получают блестящие значки «Проверено»» . CNET . Архивировано из оригинала 3 мая 2012 года . Проверено 23 февраля 2011 г.
- ^ «Повестка в суд в Твиттере» (PDF) . Салон.com . 17 января 2009 года . Проверено 10 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Twitter Inc., Неизвестные плакаты, поданные в суд Великобритании на спортсмена, известного как «CTB»» Bloomberg LP.com, 20 мая 2011 г.
- ^ «Пользователи Твиттера получили судебный запрет на конфиденциальность» . Politics.co.uk. Архивировано из оригинала 23 мая 2011 года . Проверено 22 мая 2011 г.
- ^ «Европейский руководитель Twitter Тони Ван вынес юридическое предупреждение» . Новости Би-би-си . Великобритания. 25 мая 2011 года . Проверено 25 мая 2011 г.
- ^ Смит, Льюис (26 мая 2011 г.). «Руководитель Twitter намекает, что ему, возможно, придется раскрыть имена пользователей» . Независимый . Великобритания . Проверено 13 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Twitter покупает стартап Dasient Security для борьбы со спамом» . ХаффПост . 24 января 2012 г.
- ^ «Twitter для выборочной «цензуры» твитов по странам» . Новости Би-би-си . 27 января 2012 г.
- ^ «Блог Twitter - Твиты все еще должны идти» 26 января 2012 г. Проверено 27 января 2012 г.
- ^ Кулиш, Николай (18 октября 2012 г.). «Твиттер блокирует доступ немцев к неонацистской группе» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 октября 2012 года . Проверено 5 мая 2017 г.
- ^ «Твиттер удаляет французские антисемитские твиты» . Новости Би-би-си . Би-би-си. 19 октября 2012 года . Проверено 5 мая 2017 г.
- ^ «Твиттер пытается заблокировать изображения смерти Джеймса Фоули» . Yahoo! Тех. 20 августа 2014 года . Проверено 6 сентября 2014 г.
- ^ Векслер, Ню [@wexler] (19 августа 2014 г.). «Политика Твиттера в отношении СМИ в отношении умершего пользователя» ( Твит ) – через Твиттер .
- ^ «Ирландия станет регулятором конфиденциальности для 300 миллионов пользователей Twitter» . Ирландские Таймс . Проверено 12 мая 2015 г.
- ^ Кастренакес, Якоб (8 апреля 2020 г.). «Twitter уведомляет пользователей о том, что теперь он передает больше данных рекламодателям» . Грань . Проверено 9 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ «Twitter борется с хаосом на выборах, призывая пользователей цитировать твиты, а не ретвитить» . Грань . 9 октября 2020 г. Проверено 9 октября 2020 г.
- ^ Белл, К. (17 декабря 2020 г.). «Ретвиты вернулись в норму, поскольку Twitter завершает эксперимент с цитатами» . Engadget . Проверено 20 марта 2022 г.
- ^ Милмо, Дэн (26 мая 2022 г.). «Twitter оштрафован на 150 миллионов долларов за передачу контактных данных пользователей рекламодателям » Хранитель . Проверено 27 мая 2022 г.
- ^ «Тони Ван из Twitter приносит извинения жертвам насилия» , BBC News, 3 августа 2013 г. Проверено 3 августа 2013 г.
- ^ «О гордости, предубеждениях и преследованиях в Твиттере», The New York Times , 3 августа 2013 г. Проверено 3 августа 2013 г.
- ^ «Twitter обновляет свои правила для пользователей после волнений по поводу изнасилований и угроз о взрыве» , CNET, 3 августа 2013 г. Проверено 3 августа 2013 г.
- ^ «Twitter объявляет о радикальном обновлении инструментов отчетности и блокировки» . Арс Техника . 2 декабря 2014 г.
- ^ «Создание более безопасного Твиттера» . Получено 30 июля 2019 г. - через Twitter.
- ^ «Твиттер представляет новые инструменты для борьбы с преследованиями» . Новости CBS.
- ^ «Твиттер дает преследуемым пользователям немного боеприпасов» . technewsworld.com . 4 декабря 2014 года . Проверено 30 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Салим, Фахад (4 декабря 2014 г.). «Twitter Inc (TWTR) может использовать модель автоблокировки Gamergate для блокировки миллионов фейковых аккаунтов?» . ТехИнсайдер .
- ^ «Заблокировано в Твиттере: ограничения программного обеспечения в борьбе с ненавистью в Интернете» . Глобус и почта . Торонто. 4 декабря 2014 г.
- ^ Уоффорд, Тейлор (29 ноября 2014 г.). «Новый инструмент одной женщины, позволяющий остановить преследования Gamergate в Твиттере» . Newsweek . Проверено 6 декабря 2014 г.
- ^ Тику, Ниташа (5 февраля 2015 г.). «Генеральный директор Twitter: «Мы плохо справляемся со злоупотреблениями» » . Грань . Проверено 5 февраля 2015 г.
- ^ «Выгодные провокации» (PDF) . ИТ для перемен . июль 2022 года . Проверено 4 июля 2023 г.
- ^ Корпоративный блог Twitter «Объявление о создании Совета по доверию и безопасности Twitter»
- ^ Зигфрид, Эван (23 августа 2016 г.). Республиканская партия GPS . Небесный конек. ISBN 9781510717336 . Проверено 12 ноября 2017 г.
- ^ Олбрайт, Данн (29 февраля 2016 г.). «Является ли Совет доверия и безопасности Twitter фронтом цензуры?» . Используйте . Проверено 12 ноября 2017 г.
- ^ Паддефатт, Эндрю (11 февраля 2016 г.). «Просто еще один «черный ящик»? Первые мысли о Совете по доверию и безопасности Twitter» . ID круга . Проверено 12 ноября 2017 г.
- ^ Соаве, Робби (20 февраля 2016 г.). «Забанил ли оруэлловский совет Твиттера «Доверие и безопасность» Роберта Стейси Маккейна?» . Причина (журнал) . Проверено 12 ноября 2017 г.
- ^ Коллинз, Бен; Задрожный, Бренди (21 июля 2020 г.). «Twitter блокирует 7000 аккаунтов QAnon и ограничивает 150 000 других в рамках масштабных репрессий» . Новости Эн-Би-Си . Проверено 21 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Питерс, Джей (1 сентября 2021 г.). «Новый безопасный режим Twitter автоматически блокирует оскорбительные аккаунты» . Грань . Проверено 23 сентября 2021 г.
- ^ Василе, Космин (2 сентября 2021 г.). «Twitter запускает Super Follows и безопасный режим» . Телефонная арена . Проверено 18 мая 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «В возобновленном иске говорится, что личные сообщения в Твиттере — это все равно, что передать ИГИЛ спутниковый телефон» . Грань . 30 августа 2016 г. Проверено 31 августа 2016 г.
- ^ «Иск обвиняет Twitter в террористической атаке ИГИЛ» . Уолл Стрит Джорнал . Проверено 16 января 2016 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Может ли Twitter нести ответственность за твиты ИГИЛ?» . Уолл Стрит Джорнал . Проверено 20 января 2016 г.
- ^ «Twitter не несет юридической ответственности за рост ИГИЛ, постановил окружной суд Калифорнии» . Грань . 10 августа 2016 г. Проверено 11 августа 2016 г.
- ^ Смит, Милан Д. младший (31 января 2018 г.). «Филдс против Twitter, Inc» . Апелляционный суд США девятого округа . Проверено 24 мая 2024 г.
- ^ «Twitter приостанавливает работу русских сатирических аккаунтов, поднимая вопросы о свободе слова | Новости» . Московская Таймс . Июнь 2016 года . Проверено 2 июня 2016 г.
- ^ Таймс, Москва; сеть, часть Нового Востока (2 июня 2016 г.). «Твиттер разблокировал поддельный аккаунт Путина после широкой критики» . Хранитель . Проверено 2 июня 2016 г.
- ^ Херн, Алекс (31 мая 2016 г.). «Facebook, YouTube, Twitter и Microsoft подписывают Кодекс ЕС о разжигании ненависти» . Хранитель . Проверено 7 июня 2016 г.
- ^ Вайзе, Элизабет (18 августа 2016 г.). «Twitter заблокировал 235 000 аккаунтов за экстремизм» . США сегодня . Проверено 20 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ «За шесть месяцев Twitter заблокировал более 1,6 миллиона аккаунтов, пропагандирующих терроризм» . Экономические времена . 10 мая 2019 года. Архивировано из оригинала 31 мая 2019 года . Проверено 22 февраля 2021 г.
- ^ Холт, Крис (10 мая 2019 г.). «Блокировки Твиттера за пропаганду терроризма снова сократились» . Engadget . Проверено 10 мая 2019 г.
- ^ Абриль, Даниэль (10 мая 2019 г.). «Количество нарушений, о которых сообщили пользователи Twitter, выросло на 19%, но количество наказанных аккаунтов сократилось» . Удача .
- ^ «Сообщения в Твиттере бывают крайне содержательными» . Новости СБС . 10 мая 2019 г. Проверено 10 мая 2019 г.
- ^ «Twitter заблокировал более 166 000 аккаунтов, связанных с пропагандой терроризма» . Тех2 . Первый пост. 10 мая 2019 г. Проверено 10 мая 2019 г.
- ^ Белл, Карисса (28 июля 2020 г.). «Твиттер заблокирует ссылки, пропагандирующие разжигание ненависти и насилия» . Engadget . Проверено 28 июля 2020 г.
- ^ «Twitter заблокировал 70 000 аккаунтов QAnon, поскольку консерваторы сообщают о потере подписчиков» . Грань . Проверено 12 января 2020 г.
- ^ Тимберг, Крейг; Ромм, Тони (25 июля 2019 г.). «Это уже не только русские, поскольку иранцы и другие страны активизируют усилия по дезинформации в преддверии выборов 2020 года» . Вашингтон Пост .
- ^ «Твиттер навешивает ярлыки на политических кандидатов в США» . ЦБС. 23 мая 2018 года . Проверено 23 мая 2018 г.
- ^ Скола, Нэнси (23 мая 2018 г.). «Твиттер для проверки кандидатов на выборах на промежуточных выборах» . Политик . Проверено 23 мая 2018 г.
- ^ «Twitter и Facebook удаляют аккаунты в целях подавления вмешательства» . Йорк Пресс . 20 декабря 2019 года . Проверено 20 декабря 2019 г.
- ^ «Когда США обвинили наследного принца Саудовской Аравии в причастности к убийству Хашогги, фейковые аккаунты в Твиттере развязали войну» . Вашингтон Пост . Проверено 7 марта 2021 г.
- ^ «Понимание глобальной дезинформации и информационных операций: выводы нового аналитического веб-сайта ASPI» . Австралийский институт стратегической политики . 30 марта 2022 г. Архивировано из оригинала 29 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ Дуббин, Роб. «Восстание ботов в Твиттере» . Житель Нью-Йорка . Проверено 15 мая 2014 г.
- ^ Майнерс, Зак (6 мая 2014 г.). «Бот или нет? Исследователи создают приложение для обнаружения ботов в Твиттере» . Мир ПК . Проверено 15 мая 2014 г.
- ^ Урбина, Ян (10 августа 2013 г.). «Я флиртую и пишу в Твиттере. Следуйте за мной в No. Socialbot» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 15 мая 2014 г.
- ^ Д'Онфро, Джиллиан (4 октября 2013 г.). «Twitter признал, что 5% его «пользователей» — фейки» . Бизнес-инсайдер . Проверено 15 мая 2014 г.
- ^ Джек Дорси (8 июля 2011 г.). Впечатления от Твиттера Белого дома . Белый дом . Проверено 10 июля 2011 г. - из Национального архива .
- ^ Бюттнер, Рикардо и Бюттнер, Катарина (2016). Систематический обзор литературы по исследованиям Твиттера с точки зрения социально-политической революции . 49-я ежегодная Гавайская международная конференция по системным наукам . Кауаи, Гавайи: IEEE. дои : 10.13140/RG.2.1.4239.9442 .
- ^ Сиддик, Харун (12 ноября 2010 г.). «Кампания #IAmSpartacus взрывается в Твиттере в поддержку шутника из аэропорта» . Хранитель . Проверено 20 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ Габбат, Адам; Тейлор, Мэтью (22 мая 2011 г.). "Шотландская газета выявила судебный запрет на футболиста" . Хранитель . Проверено 22 мая 2011 г.
- ^ «Влияние Твиттера на арабскую весну» . Глобус и почта . 19 августа 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 7 июля 2017 года . Проверено 20 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ Фокс, Зоя (8 июня 2012 г.). «Как арабский мир использует Facebook и Twitter» . Машаемый . Проверено 20 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ «Утечка GCHQ содержит список хакерских инструментов британских кибершпионов» . Новости Би-би-си . 15 июля 2014 года . Проверено 16 июля 2014 г.
- ^ «Инструменты и методы JTRIG» . Проверено 16 июля 2014 г.
- ^ Келли, Макена (19 августа 2019 г.). «Facebook и Twitter раскрывают китайских троллей, распространяющих сомнения по поводу протестов в Гонконге» . Грань . Проверено 28 августа 2019 г.
- ^ Иносенсио, Рами (20 августа 2019 г.). «Протесты в Гонконге: Twitter и Facebook расправляются с «ложными» аккаунтами, связанными с Китаем» . Новости CBS . Проверено 28 августа 2019 г.
- ^ «Информационные операции, направленные на Гонконг» . Блог в Твиттере . 19 августа 2019 г.
- ^ «Китай критикует Facebook и блокировку фейковых аккаунтов в Twitter» . Рейтер . 20 августа 2019 года . Проверено 28 августа 2019 г.
- ^ «Китай сопротивляется обвинениям Twitter и Facebook в дезинформации» . Уолл Стрит Джорнал . 20 августа 2019 года . Проверено 28 августа 2019 г.
- ^ «Анкара реагирует на решение Twitter приостановить действие аккаунтов» . Хюрриет Дейли Ньюс . 13 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Бурга, Солкир (15 февраля 2023 г.). «Как реакция Турции на землетрясение подвела ее народ» . Время . Проверено 17 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ Сингх, Маниш (24 мая 2021 г.). «Полиция в Индии посетила офис Twitter из-за ярлыка «манипулирование СМИ»» . ТехКранч . Проверено 27 мая 2021 г.
- ^ Сингх, Маниш (27 мая 2021 г.). «Twitter заявляет, что обеспокоен запугиванием Индии и требует еще 3 месяца для соблюдения новых ИТ-правил» . ТехКранч . Проверено 27 мая 2021 г.
- ^ «Twitter теряет иммунитет в отношении пользовательского контента в Индии» . Рейтер . 6 июля 2021 г. . Проверено 6 июля 2021 г.
- ^ Триведи, Упманью (6 августа 2021 г.). «Твиттер сообщает, что назначил чиновников для соблюдения правил Индии» . Новости Блумберга . Проверено 6 августа 2021 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Бинг, Крис; Шехтман, Джоэл (14 июня 2024 г.). «Пентагон провел секретную кампанию против вакцинации, чтобы подорвать позиции Китая во время пандемии» . Рейтер .
- ^ «Конфиденциальная политика Twitter в отношении СМИ | Помощь Twitter» . Получено 14 апреля 2022 г. - через Twitter.
- ^ «Как Twitter становится все более похожим на OnlyFans — и что это значит для пользователей» . Независимый . 4 марта 2021 г. . Проверено 14 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ Запал, Хейли (16 марта 2021 г.). «Порно в Твиттере: вот что должен знать каждый родитель» . Лаять . Проверено 14 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ Ньютон, Кейси (30 августа 2022 г.). «Как проблема Twitter с детской порнографией разрушила планы компании в отношении конкурента OnlyFans» . Грань . Проверено 3 июня 2024 г.
- ^ Диксон, Эй Джей (2 февраля 2021 г.). «Секс-работники обеспокоены тем, что их удалят из Твиттера» . Роллинг Стоун . Проверено 3 июня 2024 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и Ньютон, Кейси (30 августа 2022 г.). «Как проблема Twitter с детской порнографией разрушила планы компании в отношении конкурента OnlyFans» . Грань . Проверено 30 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ «Лица в Твиттере утверждают, что получили выгоду от торговли детьми в целях сексуальной эксплуатации» . news.bloomberglaw.com . Проверено 30 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ «Доу против Twitter, Inc., 555 F. Supp. 3d 889 (ND Cal. 2021), Мнение суда» . Bloomberglaw.com . Проверено 30 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ Черт, Шейла; Пол, Кэти (29 сентября 2022 г.). «Эксклюзив: бренды взрывают Twitter из-за рекламы рядом с аккаунтами с детской порнографией» . Рейтер . Проверено 30 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ Лавалле, Эндрю (16 марта 2007 г.). «Друзья обмениваются твиттерами, и разочарование: новые службы обмена сообщениями в реальном времени переполняют некоторых пользователей обыденными обновлениями от друзей» . Уолл Стрит Джорнал . Архивировано из оригинала 14 марта 2015 года . Проверено 22 февраля 2011 г.
- ^ Дворжак, Джон К. (25 августа 2009 г.). «Твиттер — новое CB-радио» . Журнал ПК .
- ^ «Транспортная система Нью-Йорка прекращает обновления в Твиттере и сообщает, что платформа «больше не надежна» » . Фокс Ньюс.
- ^ «MTA Нью-Йорка возобновляет оповещения о транзите в Твиттере» . Си-Эн-Эн.
- ^ Миллс, Александр; Чен, Руи; Ли, ДжинКю; Рао, Х. Рагхав (2009). «Приложения Web 2.0 для экстренных случаев: насколько полезным может быть Twitter для экстренного реагирования?» (PDF) . Twitter для управления чрезвычайными ситуациями и смягчения их последствий : 3. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 6 февраля 2017 г. Проверено 20 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ Джарвис, Брук (4 марта 2013 г.). «Twitter становится инструментом для отслеживания эпидемий гриппа и других проблем общественного здравоохранения» . Вашингтон Пост . Проверено 21 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ Пауэр, Роберт; Робинсон, Белла; Рэтклифф, Дэвид (2013). «В поисках пожаров с помощью Твиттера» (PDF) . Материалы семинара Австралазийской ассоциации языковых технологий . Проверено 21 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ Эрл, Пол; Боуден, Дэниел; Гай, Мишель (2011). «Обнаружение землетрясений в Твиттере: мониторинг землетрясений в социальном мире» . Анналы геофизики . 54 (6) . Проверено 21 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ Гранжан, Мартин (2016). «Анализ социальной сети Twitter: составление карты сообщества цифровых гуманитарных наук» . Cogent Искусства и Гуманитарные науки . 3 (1): 1171458. doi : 10.1080/23311983.2016.1171458 . S2CID 114999767 .
- ^ Рэнкин, М. (2010). «Некоторые общие комментарии по поводу «эксперимента в Твиттере»»
- ^ Гроссек и Холотеску (2008). «Можем ли мы использовать Twitter для образовательных мероприятий?» Архивировано 18 мая 2012 года в Wayback Machine : электронное обучение и программное обеспечение для образования, Бухарест, Румыния. материалах 4-й Международной научной конференции
- ^ Елавский, К. Майкл; Мислан, Кристина; Елавский, Стериани (2011). «Когда меньше говоришь, значит больше: изучаем результаты использования Твиттера в большом лекционном зале». Обучение, СМИ и технологии . 36 (3): 215–233. дои : 10.1080/17439884.2010.549828 . ISSN 1743-9884 .
- ^ Юнко, Р.; Хейбергер, Г.; Локен, Э. (2011). «Влияние Твиттера на вовлеченность и оценки студентов колледжей: Твиттер и вовлеченность студентов» . Журнал компьютерного обучения . 27 (2): 119–132. дои : 10.1111/j.1365-2729.2010.00387.x .
- ^ Юнко, Рейнол; Елавский, К. Майкл; Хейбергер, Грег (2013). «Испытание Твиттера: оценка результатов студенческого сотрудничества, вовлеченности и успеха» . Британский журнал образовательных технологий . 44 (2): 273–287. дои : 10.1111/j.1467-8535.2012.01284.x . ISSN 0007-1013 .
- ^ Эбнер, Мартин; Линхардт, Конрад; Рос, Матиас; Мейер, Ирис (2010). «Микроблоги в высшем образовании – шанс облегчить неформальное и процессно-ориентированное обучение?» . Компьютеры и образование . 55 (1). Эльзевир Б.В.: 92–100. дои : 10.1016/j.compedu.2009.12.006 . ISSN 0360-1315 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и Кэрри, Росс; Манингер, Роберт; ЛаПрери, Кимберли; Салливан, Сэм (весна 2015 г.). «Использование Twitter в создании возможностей профессионального обучения» . Журнал административных вопросов: соединение образования, практики и исследований . 5 : 55–76. дои : 10.5929/2015.5.1.7 . ISSN 2153-7615 . ЭРИК EJ1062476 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Гринхау, Кристина; Глисон, Бенджамин (3 октября 2012 г.). «Twitteracy: Twitter как новая практика грамотности». Образовательный форум . 76 (4): 464–478. дои : 10.1080/00131725.2012.709032 . S2CID 145800002 .
- ^ ( требуется регистрация ) Коэн, Ноам (20 июня 2009 г.). «Твиттер на баррикадах: шесть извлеченных уроков» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 21 июня 2009 г.
- ^ Ауэр, Мэтью (2011). «Политические науки социальных сетей». Журнал политических исследований . 39 (4): 709–736. дои : 10.1111/j.1541-0072.2011.00428.x . S2CID 153590593 .
- ^ Эскория, Юлия (8 июня 2015 г.). «Избранные твиты Миры Гонсалес и Тао Линя глубже, чем кажется» . Фейдер . Проверено 6 января 2021 г.
- ^ Куруц, Стивен (1 декабря 2009 г.). «Рассказ Рика Муди в Твиттере вызвал длинный список жалоб» . Уолл Стрит Джорнал . Проверено 19 мая 2012 г.
- ^ «Влияние Твиттера на журналистику | Офф-книга» . PBS LearningMedia . Проверено 31 января 2021 г.
- ^ Чемберлен, Крейг. «Как Twitter изменил освещение новостей?» . news.illinois.edu . Проверено 31 января 2021 г.
- ^ «Твиттер не так важен, как кажется журналистам» . Атлантика . 12 февраля 2020 г. . Проверено 31 января 2021 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с «Журналисты уделяют слишком много внимания Твиттеру?» . Обзор журналистики Колумбии . Проверено 31 января 2021 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Большинство крупных СМИ использовали российские твиты в качестве источников партийных мнений: исследование» . Обзор журналистики Колумбии . Проверено 31 января 2021 г.
- ^ Лендлер, Марк (4 февраля 2014 г.). «В сценарном мире дипломатии всплеск твитов» . Международная Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 28 апреля 2014 г.
- ^ Селлан-Джонс, Рори (24 октября 2014 г.). «Первый твит королевы» . Новости Би-би-си .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Исследование твипломатии 2013 – Международные организации» . Twiplomacy.com . Проверено 27 апреля 2014 г.
- ^ Джон Хейлприн Все лидеры имеют твиттер, но лишь немногие имеют твиты. Рекламодатель, 28 июля 2012 г., стр. 64.
- ^ «Список кардиналов в Твиттере (октябрь 2015 г.)» . Sixfortyone.co.uk. Архивировано из оригинала 19 января 2016 года . Проверено 12 октября 2015 г.
- ^ Ньюкомб, Алисса (6 марта 2013 г.). «Кардиналы в Твиттере делятся мыслями перед конклавом» . Новости АВС . Проверено 24 сентября 2013 г.
- ^ Шарки, Линда (23 мая 2014 г.). «Причина, по которой у Папы есть Twitter, а не аккаунт в Facebook» . Независимый . Проверено 11 апреля 2016 г.
- ^ Сганга, Николь (4 марта 2022 г.). «Россия блокирует доступ к Facebook и Twitter» . Новости CBS . Проверено 14 марта 2022 г.
- ^ «Религия, Твиттер и свобода: мирный взрыв» . Экономист . 27 мая 2015 года . Проверено 2 июня 2015 г.
- ^ Браниган, Таня. «Китай блокирует Twitter, Flickr, YouTube и Hotmail накануне годовщины Тяньаньмэнь» . Хранитель . Лондон.
- ^ «Иракский кризис: Twitter, Google, YouTube и Facebook заблокированы правительством, чтобы остановить заговор ИГИЛ» . Интернэшнл Бизнес Таймс, Великобритания . 13 июня 2014 г.
- ^ «Нигерия приостанавливает работу Twitter после того, как твит президента был удален» . Хранитель . Рейтер . 4 июня 2021 г. . Проверено 4 июня 2021 г.
- ^ «Оспаривание запрета на доступ в Турции» – через Twitter.
- ^ Лайя, Патрисия (15 февраля 2014 г.). «Венесуэльцы заблокированы в Твиттере из-за нарастания протестов оппозиции» . Bloomberg.com .
- ^ «Профиль страны Туркменистана» . Мониторинг BBC . 26 февраля 2018 г.
- ^ Майкл Шеффер Омер-Ман (9 августа 2016 г.). «Как Израиль пытается обеспечить соблюдение приказов о неразглашении информации за пределами своих границ» . 972 Маг . Проверено 23 сентября 2016 г.
- ^ «Турция — первая страна, добивающаяся удаления контента в Твиттере: отчет» . Хюрриет Дейли Ньюс . 20 сентября 2017 г. Проверено 20 сентября 2017 г.
- ^ «Турция получила наибольшее количество запросов на удаление контента в Твиттере» . Новости ИПА . 11 мая 2019 года. Архивировано из оригинала 8 марта 2021 года . Проверено 14 сентября 2019 г.
- ^ «Комитет Сената США по судебной власти, Подкомитет по преступности и терроризму: показания Шона Дж. Эджетта, исполняющего обязанности главного юрисконсульта, Twitter Inc» (PDF) . 31 октября 2017 года . Проверено 6 ноября 2017 г.
- ^ «Правительство просит Twitter заблокировать аккаунты, пропагандирующие антииндийский контент с использованием Кашмира» . Индостан Таймс . 12 августа 2019 г.
- ^ «Твиттер удаляет почти 1 миллион твитов в Кашмире, обвиняемых в подчинении индийской цензуре» . Newsweek . 25 октября 2019 г. . Проверено 5 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «Twitter запускает сервис Tor Onion, упрощающий доступ к сайту в России» . Вице (журнал) . 8 марта 2022 г. . Проверено 26 мая 2022 г.
- ^ Робертсон, Ади (8 марта 2022 г.). «Twitter запускает сервис Tor для более безопасного и конфиденциального обмена сообщениями» . Грань . Проверено 26 мая 2022 г.
- ^ «Твиттер только что заблокировал более 88 000 аккаунтов, связанных с кампанией по дезинформации в Саудовской Аравии» . Бизнес-инсайдер . 20 декабря 2019 г.
- ^ Уиндер, Дэйви. «Мощный шаг Твиттера заставил замолчать 175 000 китайских и российских аккаунтов с фейковыми новостями» . Форбс . Проверено 31 января 2021 г.
- ^ «Раскрытие сетей государственных информационных операций, которые мы удалили» . Получено 31 января 2021 г. - через Twitter.
- ^ «Twitter приостанавливает работу аккаунтов, управляемых правительством на Кубе» . Новости Би-би-си . 12 сентября 2019 г.
- ^ «Твиттер удаляет аккаунты, связанные с Египтом, Саудовской Аравией и другими странами» . Рейтер . 2 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ «Твиттер удаляет сотни аккаунтов, которые, по его словам, связаны с Ираном, Россией и Арменией» . Рейтер . 23 февраля 2021 г.
- ^ «В Твиттере сообщили о блокировке 200 аккаунтов из-за Кашмира» . Рассвет . 20 августа 2019 г.
- ^ «Twitter блокирует аккаунты в Индии, поскольку Моди оказывает давление на социальные сети» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 10 февраля 2021 г. Архивировано из оригинала 28 декабря 2021 г.
- ^ «Twitter приостанавливает учетные записи, защищающие ответ Дутерте на COVID-19 – отчет» . Филиппинский Daily Inquirer . 10 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ «EmTech Stage: технический директор Twitter о дезинформации» . Technologyreview.com . 18 ноября 2020 г. . Проверено 30 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ Бергенгрюен, Вера (27 апреля 2022 г.). « Мы вернулись». Крайне правые группы празднуют захват Твиттера Илоном Маском» . Время . Проверено 27 мая 2023 г.
- ^ Коллинз, Бен; Задрожный, Бренди; Ингрэм, Дэвид (4 ноября 2023 г.). «За несколько дней до промежуточных выборов Twitter увольняет сотрудников, которые борются с дезинформацией» . Новости Эн-Би-Си . Проверено 27 мая 2023 г.
- ^ «Twitter положил конец политике Маска по дезинформации о Covid» . Новости Би-би-си . 30 ноября 2022 г. . Проверено 30 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ Джиллетт, Франческа (27 мая 2023 г.). «Твиттер выходит из добровольного кодекса ЕС по дезинформации» . Новости Би-би-си . Проверено 27 мая 2023 г.
- ^ Холлистер, Шон (4 октября 2020 г.). «Birdwatch» в Твиттере выглядит как новая попытка искоренить пропаганду и дезинформацию» . Грань . Архивировано из оригинала 19 ноября 2023 года . Проверено 19 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Лайонс, Ким (25 января 2021 г.). «Twitter запускает Birdwatch — программу проверки фактов, предназначенную для борьбы с дезинформацией» . Грань . Архивировано из оригинала 24 марта 2021 года . Проверено 25 января 2021 г.
- ^ Эллиотт, Виттория (17 октября 2023 г.). «Основной инструмент Илона Маска для борьбы с дезинформацией о X усугубляет проблему, утверждают инсайдеры» . Проводной . ISSN 1059-1028 . Архивировано из оригинала 17 октября 2023 года . Проверено 17 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Лайонс, Ким (22 ноября 2021 г.). «Twitter вводит псевдонимы для участников своей программы модерации Birdwatch» . Грань . Архивировано из оригинала 22 ноября 2021 года . Проверено 22 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ Перес, Сара (3 марта 2022 г.). «Twitter будет показывать проверки фактов сообщества Birdwatch большему количеству пользователей после критики» . Технический кризис . Архивировано из оригинала 3 марта 2022 года . Проверено 3 марта 2022 г.
- ^ Сато, Миа (3 марта 2022 г.). «Twitter начнет показывать некоторым пользователям краудсорсинговые проверки фактов» . Грань . Проверено 28 февраля 2024 г.
- ^ Оремус, Уилл; Меррилл, Джереми Б. (2 марта 2022 г.). «Поскольку в Украине бушует дезинформация, инструмент проверки фактов Twitter не появляется» . Вашингтон Пост . Архивировано из оригинала 4 июня 2023 года . Проверено 3 марта 2022 г.
- ^ Гёдель, Уильям; Сандерсон, Зеве; Аслетт, Кевин; Наглер, Джонатан; Бонно, Ричард; Персили, Натаниэль; Такер, Джошуа А. (28 октября 2021 г.). «Модерирование с мафией: оценка эффективности краудсорсинговой проверки фактов в реальном времени» . Журнал онлайн-доверия и безопасности . 1 (1). дои : 10.54501/jots.v1i1.15 . ISSN 2770-3142 . Архивировано из оригинала 24 ноября 2023 года . Проверено 25 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Келли, Макена (7 сентября 2022 г.). «Twitter расширяет свою экспериментальную систему модерации сообщества» . Грань . Архивировано из оригинала 19 ноября 2023 года . Проверено 19 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Фейфе, Корин (10 октября 2022 г.). «Как показывают данные, дезинформация о COVID-19 является самой большой проблемой для программы Twitter Birdwatch» . Грань . Архивировано из оригинала 19 ноября 2023 года . Проверено 19 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Шанкаран, Вишвам (12 декабря 2022 г.). «Новая функция заметок сообщества Twitter позволяет людям добавлять контекст к твитам» . Независимый . Архивировано из оригинала 18 ноября 2023 года . Проверено 18 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Бальдаккино, Жюльен (10 августа 2023 г.). «С «заметками сообщества» Twitter (X) следует по стопам Википедии» . Франция Интер (на французском языке). Архивировано из оригинала 2 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 21 октября 2023 г.
- ^ Лелуп, Дэмиен (3 июля 2023 г.). «Я провел неделю в качестве «арбитра истины» в сервисе «Заметки сообщества» Твиттера» . Le Monde.fr . Архивировано из оригинала 22 октября 2023 года . Проверено 21 октября 2023 г.
- ^ Херли, Лоуренс (18 мая 2023 г.). «Верховный суд обходит решение об объеме иммунитета интернет-компаний от исков по поводу пользовательского контента» . Новости Эн-Би-Си . Проверено 18 мая 2023 г.
- ^ Масник, Майк (18 мая 2023 г.). «Верховный суд пока оставляет в покое 230 человек, но судья Томас дает довольно хорошее объяснение, почему они вообще существуют» . Техдирт . Проверено 4 августа 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Twitter согласен выплатить компенсацию в размере 809,5 миллионов долларов по иску о росте акционеров» . Время . Проверено 6 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ Робертсон, Ади (25 мая 2022 г.). «Twitter заплатит 150 миллионов долларов за использование телефонных номеров безопасности людей для таргетинга рекламы» . Грань . Проверено 26 мая 2022 г.
- ^ «Twitter подал в суд из-за непредвиденных увольнений, поскольку поглощение Илона Маска потрясло компанию» . Новости Эн-Би-Си. 4 ноября 2022 г. . Проверено 6 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ «Работники подали в суд на Twitter из-за предстоящих увольнений, которые, по их словам, являются незаконными» . Yahoo! Финансы. 4 ноября 2022 г. . Проверено 6 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ «X Илона Маска подает в суд на Media Matters из-за анализа антисемитизма» . 21 ноября 2023 г. . Проверено 21 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Скарселла, Майк (6 августа 2024 г.). «X Маска обвиняет рекламодателей в бойкоте платформы в новом иске» . Рейтер . Проверено 6 августа 2024 г.
- ^ «Селфи на церемонии вручения «Оскара» побило рекорд ретвитов» . Новости Би-би-си . 3 марта 2014 года . Проверено 3 марта 2014 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «#BBCtrending: Селфи на церемонии вручения «Оскара» побило рекорд ретвитов» . Тренд BBC . Би-би-си. 3 марта 2014 года . Проверено 28 июля 2014 г.
- ^ «Селфи Эллен ДеДженерес на церемонии вручения «Оскара» установило рекорд ретвитов и обрушило Twitter» . Леджер . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 3 марта 2014 года. Архивировано из оригинала 3 марта 2014 года . Проверено 3 марта 2014 г.
- ^ Хаббард, Эми (2 марта 2014 г.). «Оскар-2014, год селфи: твит Эллен стал рекордсменом по ретвитам» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Проверено 7 октября 2014 г.
- ^ @Твиттер (10 мая 2017 г.). «@carterjwm 👆 Это официально. Картер, твой твит пользуется наибольшим количеством ретвитов за всю историю. #NuggsForCarter» ( твит ) . Проверено 9 мая 2017 г. — через Twitter .
- ^ «20 самых ретвитируемых твитов» . 30 июля 2020 г. Проверено 15 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ Оремус, Уилл (19 августа 2013 г.). «Фестиваль Бальсе: трансляция «Небесного замка» в Японии побила рекорд Твиттера по количеству твитов в секунду» . Сланец . Проверено 26 июня 2014 г.
- ^ Эшкрафт, Брайан. «Как старое японское аниме побило рекорд Твиттера» . Котаку . Проверено 31 августа 2018 г.
- ^ «Фанаты на Филиппинах и по всему миру отправили 41 миллион твитов с упоминанием #ALDubEBTAmangPanahon» . Аккаунт с подтвержденными данными в Твиттере . 27 октября 2015 года . Проверено 30 октября 2015 г.
- ^ Мендоса, Арвин (25 октября 2015 г.). « АлДуб» побил рекорд чемпионата мира по футболу в Твиттере» . Филиппинский Daily Inquirer . Проверено 25 октября 2015 г.
- ^ Томчак, Анн-Мари (9 июля 2014 г.). «#BBCtrending: разгром чемпионата мира по футболу в Бразилии бьет рекорды Твиттера» . Би-би-си . Проверено 9 июля 2014 г.
- ^ «Самое быстрое время для достижения миллиона подписчиков в Твиттере» . Книги рекордов Гиннесса . 12 апреля 2014 года . Проверено 19 мая 2015 г.
- ^ Паркинсон, Ханна Джейн (2 июня 2015 г.). «Кейтлин Дженнер побила мировой рекорд Твиттера, набрав миллион подписчиков» . Хранитель . Проверено 20 мая 2022 г.
Дальнейшее чтение
- Фиттон, Лаура; Грюн, Майкл Э.; Постон, Лесли; предисловие Джека Дорси (2009). Твиттер для чайников . Хобокен, Нью-Джерси: Wiley Publishing. ISBN 9780470479919 .
- Туфекчи, Зейнеп. 2017. Твиттер и слезоточивый газ: сила и хрупкость сетевого протеста . Издательство Йельского университета .
Внешние ссылки
- Твиттер
- 2006 заведения в Калифорнии
- 2006 год в Сан-Франциско
- Мобильные приложения американских социальных сетей
- Американские социальные сети
- Программное обеспечение Android (операционная система)
- Илон Маск
- Интернет-ресурсы, основанные в 2006 году.
- программное обеспечение iOS
- Программное обеспечение MacOS
- Услуги микроблогов
- Многоязычные веб-сайты
- Собственное кроссплатформенное программное обеспечение.
- Интернет в режиме реального времени
- Текстовые сообщения
- Сервисы Tor Onion
- Приложения универсальной платформы Windows
- Программное обеспечение WatchOS
- Сайты с крайне правыми материалами
