БДСМ
| Аспекты | |
|---|---|
| Б&Д, Б/Д или BD | Бондаж и дисциплина |
| Д&с, Д/с или Дс | Доминирование и подчинение |
| S&M, S/M или SM | Садизм и мазохизм |
| Роли | |
| Топ/доминантный | Партнер, который выполняет или контролирует деятельность |
| Нижний/покорный | Партнер, который получает или контролируется |
| Выключатель | Переключается между ролями |
БДСМ — это разновидность часто эротических практик или ролевых игр, включающих связывание , дисциплину , доминирование и подчинение , садомазохизм и другие связанные с этим межличностные динамики. Учитывая широкий спектр практик, некоторыми из которых могут заниматься люди, не считающие себя практикующими БДСМ, включение в БДСМ-сообщество или субкультуру часто говорят, что зависит от самоидентификации и совместного опыта.
Инициализм от 1991 БДСМ впервые упоминается в сообщении Usenet года. [ 1 ] и интерпретируется как комбинация сокращений B/D (Бондаж и Дисциплина), D/s (Доминирование и подчинение) и S/M (Садизм и Мазохизм). БДСМ сейчас используется как универсальное словосочетание, охватывающее широкий спектр видов деятельности, форм межличностных отношений и отдельных субкультур. Сообщества БДСМ обычно приветствуют всех, кто ненормативен и идентифицирует себя с сообществом; это могут быть трансвеститы , энтузиасты модификации тела , любители ролевых игр с животными , резиновые фетишисты и другие.
Activities and relationships in BDSM are often characterized by the participants' taking on roles that are complementary and involve inequality of power; thus, the idea of informed consent of both the partners is essential. The terms submissive and dominant are often used to distinguish these roles: the dominant partner ("dom") takes psychological control over the submissive ("sub"). The terms top and bottom are also used; the top is the instigator of an action while the bottom is the receiver of the action. The two sets of terms are subtly different: for example, someone may choose to act as bottom to another person, for example, by being whipped, purely recreationally, without any implication of being psychologically dominated, and submissives may be ordered to massage their dominant partners. Although the bottom carries out the action and the top receives it, they have not necessarily switched roles.
The abbreviations sub and dom are frequently used instead of submissive and dominant. Sometimes the female-specific terms mistress, domme, and dominatrix are used to describe a dominant woman, instead of the sometimes gender-neutral term dom. Individuals who change between top/dominant and bottom/submissive roles—whether from relationship to relationship or within a given relationship—are called switches. The precise definition of roles and self-identification is a common subject of debate among BDSM participants.[2]
Fundamentals
BDSM is an umbrella term for certain kinds of erotic behaviour between consenting adults, encompassing various subcultures. Terms for roles vary widely among the subcultures. Top and dominant are widely used for those partner(s) in the relationship or activity who are, respectively, the physically active or controlling participants. Bottom and submissive are widely used for those partner(s) in the relationship or activity who are, respectively, the physically receptive or controlled participants. The interaction between tops and bottoms—where physical or mental control of the bottom is surrendered to the top—is sometimes known as "power exchange", whether in the context of an encounter or a relationship.[3]
BDSM actions can often take place during a specific period of time agreed to by both parties, referred to as "play", a "scene", or a "session". Participants usually derive pleasure from this, even though many of the practices—such as inflicting pain or humiliation or being restrained—would be unpleasant under other circumstances. Explicit sexual activity, such as sexual penetration, may occur within a session, but is not essential.[4] For legal reasons, such explicit sexual interaction is seen only rarely in public play spaces and is sometimes banned by the rules of a party or playspace. Whether it is a public "playspace"—ranging from a party at an established community dungeon to a hosted play "zone" at a nightclub or social event—the parameters of allowance can vary. Some have a policy of panties/nipple sticker for women (underwear for men) and some allow full nudity with explicit sexual acts.[3]
The fundamental principles for the exercise of BDSM require that it be performed with the informed consent of all parties. Since the 1980s, many practitioners and organizations have adopted the motto (originally from the statement of purpose of GMSMA—a gay SM activist organization) safe, sane and consensual (SSC), which means that everything is based on safe activities, that all participants are of sufficiently sound mind to consent, and that all participants do consent.[5] Mutual consent makes a clear legal and ethical distinction between BDSM and such crimes as sexual assault and domestic violence.[6]

Some BDSM practitioners prefer a code of behaviour that differs from SSC. Described as "risk-aware consensual kink" (RACK), this code shows a preference for a style in which the individual responsibility of the involved parties is emphasized more strongly, with each participant being responsible for their own well-being. Advocates of RACK argue that SSC can hamper discussion of risk because no activity is truly "safe", and that discussion of even low-risk possibilities is necessary for truly informed consent. They further argue that setting a discrete line between "safe" and "not-safe" activities ideologically denies consenting adults the right to evaluate risks versus rewards for themselves; that some adults will be drawn to certain activities regardless of the risk; and that BDSM play—particularly higher-risk play or edgeplay—should be treated with the same regard as extreme sports, with both respect and the demand that practitioners educate themselves and practice the higher-risk activities to decrease risk. RACK may be seen as focusing primarily upon awareness and informed consent, rather than accepted safe practices.[7]
Consent is the most important criterion. The consent and compliance for a sadomasochistic situation can be granted only by people who can judge the potential results. For their consent, they must have relevant information (the extent to which the scene will go, potential risks, if a safeword will be used, what that is, and so on) at hand and the necessary mental capacity to judge. The resulting consent and understanding is occasionally summarized in a written "contract", which is an agreement of what can and cannot take place.[8]
BDSM play is usually structured such that it is possible for the consenting partner to withdraw their consent at any point during a scene;[9] for example, by using a safeword that was agreed on in advance.[10][11] Use of the agreed safeword (or occasionally a "safe symbol" such as dropping a ball or ringing a bell, especially when speech is restricted) is seen by some as an explicit withdrawal of consent. Failure to honor a safeword is considered serious misconduct and could constitute a crime, depending on the relevant law,[10] since the bottom or top has explicitly revoked their consent to any actions that follow the use of the safeword. For other scenes, particularly in established relationships, a safeword may be agreed to signify a warning ("this is getting too intense") rather than explicit withdrawal of consent; and a few choose not to use a safeword at all.
Terminology and subtypes

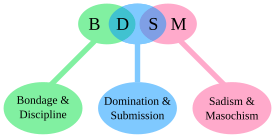
The initialism BDSM stands for:[13]
- Bondage and discipline (B&D)
- Dominance and submission (D&s)
- Sadomasochism (or S&M)
These terms replaced sadomasochism, as they more broadly cover BDSM activities and focus on the submissive roles instead of psychological pain.[13] The model is only an attempt at phenomenological differentiation. Individual tastes and preferences in the area of human sexuality may overlap among these areas.
Under the initialism BDSM, these psychological and physiological facets are also included:
The term bondage describes the practice of physical restraint. Bondage is usually, but not always, a sexual practice.[14] While bondage is a very popular variation within the larger field of BDSM, it is nevertheless sometimes differentiated from the rest of this field.[15] A 2015 study of over 1,000 Canadians showed that about half of all men held fantasies of bondage, and almost half of all women did as well.[16] In a strict sense, bondage means binding the partner by tying their appendages together; for example, by the use of handcuffs or ropes, or by lashing their arms to an object. Bondage can also be achieved by spreading the appendages and fastening them with chains or ropes to a St. Andrew's cross or spreader bars.[17]
The term discipline describes psychological restraining, with the use of rules and punishment to control overt behaviour.[citation needed] Punishment can be pain caused physically (such as caning), humiliation caused psychologically (such as a public flagellation) or loss of freedom caused physically (for example, chaining the submissive partner to the foot of a bed). Another aspect is the structured training of the bottom.[18]
Dominance and submission (also known as D&s, Ds or D/s) is a set of behaviours, customs and rituals relating to the giving and accepting of control of one individual over another in an erotic or lifestyle context. It explores the more mental aspect of BDSM. This is also the case in many relationships not considering themselves as sadomasochistic; it is considered to be a part of BDSM if it is practiced purposefully. The range of its individual characteristics is thereby wide.[19]

Often, BDSM contracts are set out in writing to record the formal consent of the parties to the power exchange, stating their common vision of the relationship dynamic.[3] The purpose of this kind of agreement is primarily to encourage discussion and negotiation in advance and then to document that understanding for the benefit of all parties. Such documents have not been recognized as being legally binding, nor are they intended to be. These agreements are binding in the sense that the parties have the expectation that the negotiated rules will be followed. Often other friends and community members may witness the signing of such a document in a ceremony, and so parties violating their agreement can result in loss of face, respect or status with their friends in the community.
In general, as compared to conventional relationships, BDSM participants go to greater lengths to negotiate the important aspects of their relationships in advance, and to contribute significant effort toward learning about and following safe practices.[20]
In D/s, the dominant is the top and the submissive is the bottom. In S/M, the sadist is usually the top and the masochist the bottom, but these roles are frequently more complicated or jumbled (as in the case of being dominant, masochists who may arrange for their submissive to carry out S/M activities on them). As in B/D, the declaration of the top/bottom may be required, though sadomasochists may also play without any power exchange at all, with both partners equally in control of the play.[citation needed]
Etymology
The term sadomasochism is derived from the words sadism and masochism. These terms differ somewhat from the same terms used in psychology since those require that the sadism or masochism cause significant distress or involve non-consenting partners.[21] Sadomasochism refers to the aspects of BDSM surrounding the exchange of physical or emotional pain. Sadism describes sexual pleasure derived by inflicting pain, degradation, humiliation on another person or causing another person to suffer. On the other hand, the masochist enjoys being hurt, humiliated, or suffering within the consensual scenario.[3] Sadomasochistic scenes sometimes reach a level that appears more extreme or cruel than other forms of BDSM—for example, when a masochist is brought to tears or is severely bruised—and is occasionally unwelcome at BDSM events or parties.[citation needed] Sadomasochism does not imply enjoyment through causing or receiving pain in other situations (for example, accidental injury, medical procedures).[citation needed]


The terms sadism and masochism are derived from the names of the Marquis de Sade and Leopold von Sacher-Masoch, based on the content of the authors' works. Although the names of de Sade and Sacher-Masoch are attached to the terms sadism and masochism respectively, the scenes described in de Sade's works do not meet modern BDSM standards of informed consent.[22] BDSM is solely based on consensual activities, and based on its system and laws. The concepts presented by de Sade are not in accordance with the BDSM culture, even though they are sadistic in nature.[citation needed] In 1843, the Ruthenian physician Heinrich Kaan published Psychopathia Sexualis (Psychopathy of Sex), a writing in which he converts the sin conceptions of Christianity into medical diagnoses. With his work, the originally theological terms perversion, aberration and deviation became part of the scientific terminology for the first time.[dubious – discuss] The German psychiatrist Richard von Krafft-Ebing introduced the terms sadism and masochism to the medical community in his work Neue Forschungen auf dem Gebiet der Psychopathia sexualis (New research in the area of Psychopathy of Sex) in 1890.[23]
In 1905, Sigmund Freud described sadism and masochism in his Three Essays on the Theory of Sexuality as diseases developing from an incorrect development of the child psyche and laid the groundwork for the scientific perspective on the subject in the following decades. This led to the first time use of the compound term sado-masochism (German sado-masochismus) by the Viennese psychoanalytic Isidor Isaak Sadger in their work, "Über den sado-masochistischen Komplex" ("Regarding the sadomasochistic complex") in 1913.[24]
In the later 20th century, BDSM activists have protested against these conceptual models, as they were derived from the philosophies of two singular historical figures. Both Freud and Krafft-Ebing were psychiatrists; their observations on sadism and masochism were dependent on psychiatric patients, and their models were built on the assumption of psychopathology.[25] BDSM activists[who?] argue that it is illogical to attribute human behavioural phenomena as complex as sadism and masochism to the "inventions" of two historic individuals. Advocates of BDSM[who?] have sought to distinguish themselves from widely held notions of antiquated psychiatric theory by the adoption of the term BDSM as a distinction from the now common usage of those psychological terms, abbreviated as S&M.[citation needed]
Behavioural and physiological aspects

BDSM is commonly mistaken as being "all about pain".[26] Freud was confounded by the complexity and counterintuitiveness of practitioners' doing things that are self-destructive and painful.[27] Rather than pain, BDSM practitioners are primarily concerned with power, humiliation, and pleasure.[26] The aspects of D/s and B/D may not include physical suffering at all, but include the sensations experienced by different emotions of the mind.[26]
Of the three categories of BDSM, only sadomasochism specifically requires pain, but this is typically a means to an end, as a vehicle for feelings of humiliation, dominance, etc.[28] In psychology, this aspect becomes a deviant behaviour once the act of inflicting or experiencing pain becomes a substitute for or the main source of sexual pleasure.[29] In its most extreme, the preoccupation on this kind of pleasure can lead participants to view humans as insensate means of sexual gratification.[30]
Dominance and submission of power are an entirely different experience, and are not always psychologically associated with physical pain. Many BDSM activities involve no pain or humiliation, but just the exchange of power and control.[26] During the activities, the participants may feel endorphin effects comparable to "runner's high" and to the afterglow of orgasm.[31] The corresponding trance-like mental state is also called subspace, for the submissive, and domspace, for the dominant. Some use body stress to describe this physiological sensation.[32] The experience of algolagnia is important, but is not the only motivation for many BDSM practitioners. The philosopher Edmund Burke called the sensation of pleasure derived from pain "sublime".[33] Couples engaging in consensual BDSM tend to show hormonal changes that indicate decreases in stress and increases in emotional bonding.[34]
There is an array of BDSM practitioners who take part in sessions in which they do not receive any personal gratification. They enter such situations solely with the intention to allow their partners to indulge their own needs or fetishes. Professional dominants do this in exchange for money, but non-professionals do it for the sake of their partners.[citation needed]
In some BDSM sessions, the top exposes the bottom to a range of sensual experiences, such as pinching; biting; scratching with fingernails; erotic spanking; erotic electrostimulation; and the use of crops, whips, liquid wax, ice cubes, and Wartenberg wheels.[35] Fixation by handcuffs, ropes, or chains may occur. The repertoire of possible "toys" is limited only by the imagination of both partners. To some extent, everyday items, such as clothespins, wooden spoons, and plastic wrap, are used in sex play.[36] It is commonly considered that a pleasurable BDSM experience during a session depends strongly on the top's competence and experience and the bottom's physical and mental state. Trust and sexual arousal help the partners enter a shared mindset.[37][38]
Types of play

Following are some of the types of BDSM play:
- Animal roleplay
- Bondage (BDSM)
- Breast torture
- Cock and ball torture
- Diaper play
- Edgeplay
- Erotic electrostimulation
- Erotic sexual denial
- Spanking
- Flogging
- Human furniture
- Japanese bondage
- Medical play
- Omorashi and bathroom use control
- Paraphilic infantilism
- Play piercing
- Predicament bondage
- Pussy torture
- Salirophilia
- Sexual roleplay
- Suspension
- Tickle torture
- Urolagnia
- Wax play
Safety

Besides safe sex, BDSM sessions often require a wider array of safety precautions than vanilla sex (sexual behaviour without BDSM elements).[10] To ensure consent related to BDSM activity, pre-play negotiations are commonplace, especially among partners who do not know each other very well. In practice, pick-up scenes at clubs or parties may sometimes be low in negotiation (much as pick-up sex from singles bars may not involve much negotiation or disclosure). These negotiations concern the interests and fantasies of each partner and establish a framework of both acceptable and unacceptable activities.[39] This kind of discussion is a typical "unique selling proposition" of BDSM sessions and quite commonplace.[40] Additionally, safewords are often arranged to provide for an immediate stop of any activity if any participant should so desire.[41]
Safewords are words or phrases that are called out when things are either not going as planned or have crossed a threshold one cannot handle. They are something both parties can remember and recognize and are, by definition, not words commonly used playfully during any kind of scene. Words such as no, stop, and don't, are often inappropriate as a safeword if the roleplaying aspect includes the illusion of non-consent.
The traffic light system (TLS) is the most commonly used set of safewords.
- Red – meaning: stop immediately and check the status of your partner
- Yellow – meaning: slow down, be careful[42]
- Green – meaning: I'm all good, we can start. If used it's normally uttered by everyone involved before the scene can start.[43][44]
At most clubs and group-organized BDSM parties and events, dungeon monitors (DMs) provide an additional safety net for the people playing there, ensuring that house rules are followed and safewords respected.
BDSM participants are expected to understand practical safety aspects, such as the potential for harm to body parts. Contusion or scarring of the skin can be a concern. Using crops, whips, or floggers, the top's fine motor skills and anatomical knowledge can make the difference between a satisfying session for the bottom and a highly unpleasant experience that may even entail severe physical harm.[45] The very broad range of BDSM "toys" and physical and psychological control techniques often requires a far-reaching knowledge of details related to the requirements of the individual session, such as anatomy, physics, and psychology.[46][47][48] Despite these risks, BDSM activities usually result in far less severe injuries than sports like boxing and football, and BDSM practitioners do not visit emergency rooms any more often than the general population.[49]
It is necessary to be able to identify each person's psychological "squicks" or triggers in advance to avoid them. Such losses of emotional balance due to sensory or emotional overload are a fairly commonly discussed issue. It is important to follow participants' reactions empathetically and continue or stop accordingly.[10][50] For some players, sparking "freakouts" or deliberately using triggers may be the desired outcome. Safewords are one way for BDSM practices to protect both parties. However, partners should be aware of each other's psychological states and behaviours to prevent instances where the "freakouts" prevent the use of safewords.
After any BDSM activities, it is important that the participants go through sexual aftercare, to process and calm down from the activity. After the sessions, participants can need aftercare because their bodies have experienced trauma and they need to mentally come out of the role play.[51]
Social aspects
Types of relationships
- Long term
A 2003 study, the first to look at these relationships, fully demonstrated that "quality long-term functioning relationships" exist among practitioners of BDSM, with either sex being the top or bottom (the study was based on 17 heterosexual couples).[52] Respondents in the study expressed their BDSM orientation to be built into who they are, but considered exploring their BDSM interests an ongoing task, and showed flexibility and adaptability in order to match their interests with their partners.[53] The "perfect match" where both in the relationship shared the same tastes and desires was rare, and most relationships required both partners to take up or put away some of their desires.[53] The BDSM activities that the couples partook in varied in sexual to nonsexual significance for the partners who reported doing certain BDSM activities for "couple bonding, stress release, and spiritual quests".[54] The most reported issue amongst respondents was not finding enough time to be in role with most adopting a lifestyle wherein both partners maintain their dominant or submissive role throughout the day.[55]
Amongst the respondents, it was typically the bottoms who wanted to play harder, and be more restricted into their roles when there was a difference in desire to play in the relationship.[55][56] The author of the study, Bert Cutler, speculated that tops may be less often in the mood to play due to the increased demand for responsibility on their part: being aware of the safety of the situation and prepared to remove the bottom from a dangerous scenario, being conscious of the desires and limits of the bottom, and so on.[56] The author of the study stressed that successful long-term BDSM relationships came after "early and thorough disclosure" from both parties of their BDSM interests.[56]
Many of those engaged in long-term BDSM relationships learned their skills from larger BDSM organizations and communities.[57] There was a lot of discussion by the respondents on the amount of control the top possessed in the relationships but "no discussion of being better, or smarter, or of more value" than the bottom.[58] Couples were generally of the same mind of whether or not they were in an ongoing relationship, but in such cases, the bottom was not locked up constantly, but that their role in the context of the relationship was always present, even when the top was doing non-dominant activities such as household chores, or the bottom being in a more dominant position.[58] In its conclusion the study states:
The respondents valued themselves, their partners, and their relationships. All couples expressed considerable goodwill toward their partners. The power exchange between the cohorts appears to be serving purposes beyond any sexual satisfaction, including experiencing a sense of being taken care of and bonding with a partner.[59]
The study further goes on to list three aspects that made the successful relationships work: early disclosure of interests and continued transparency, a commitment to personal growth, and the use of the dominant/submissive roles as a tool to maintain the relationship.[60] In closing remarks, the author of the study theorizes that due to the serious potential for harm, couples in BDSM relationships develop increased communication that may be higher than in mainstream relationships.[61]
- Professional services
A professional dominatrix or professional dominant, often referred to within the culture as a pro-dom(me), offers services encompassing the range of bondage, discipline, and dominance in exchange for money. The term dominatrix is little-used within the non-professional BDSM scene. A non-professional dominant woman is more commonly referred to simply as a domme, dominant, or femdom (short for female dominance). Professional submissives ("pro-subs"), although far more rare, do exist.[62]
Scenes
In BDSM, a "scene" is the stage or setting where BDSM activity takes place, as well as the activity itself.[63][64][65][66] The physical place where a BDSM activity takes place is usually called a dungeon, though some prefer less dramatic terms, including playspace or club. A BDSM activity can, but need not, involve sexual activity or sexual roleplay. A characteristic of many BDSM relationships is the power exchange from the bottom to the dominant partner, and bondage features prominently in BDSM scenes and sexual roleplay.
"The Scene" (including use of the definite article the) is also used in the BDSM community to refer to the BDSM community as a whole. Thus someone who is on "the Scene", and prepared to play in public, might take part in "a scene" at a public play party.[67]
A scene can take place in private between two or more people and can involve a domestic arrangement, such as servitude or a casual or committed lifestyle master/slave relationship. BDSM elements may involve settings of slave training or punishment for breaches of instructions.
A scene can also take place in a club, where the play can be viewed by others. When a scene takes place in a public setting, it may be because the participants enjoy being watched by others, or because of the equipment available, or because having third parties present adds safety for play partners who have only recently met.[68]
Etiquette
Most standard social etiquette rules still apply when at a BDSM event, such as not intimately touching someone you do not know, not touching someone else's belongings (including toys), and abiding by dress codes.[69] Many events open to the public also have rules addressing alcohol consumption, recreational drugs, cell phones, and photography.[70]
A specific scene takes place within the general conventions and etiquette of BDSM, such as requirements for mutual consent and agreement as to the limits of any BDSM activity. This agreement can be incorporated into a formal contract. In addition, most clubs have additional rules which regulate how onlookers may interact with the actual participants in a scene.[71] As is common in BDSM, these are founded on the catchphrase "safe, sane, and consensual".
Parties and clubs
BDSM play parties are events in which BDSM practitioners and other similarly interested people meet in order to communicate, share experiences and knowledge, and to "play" in an erotic atmosphere. BDSM parties show similarities to ones in the dark culture, being based on a more or less strictly enforced dress code; often clothing made of latex, leather or vinyl/PVC, lycra and so on, emphasizing the body's shape and the primary and secondary sexual characteristics. The requirement for such dress codes differ. While some events have none, others have a policy in order to create a more coherent atmosphere and to prevent outsiders from taking part.[72]
At these parties, BDSM can be publicly performed on a stage, or more privately in separate "dungeons".[73] A reason for the relatively fast spread of this kind of event is the opportunity to use a wide range of "playing equipment", which in most apartments or houses is unavailable. Slings, St. Andrew's crosses (or similar restraining constructs), spanking benches, and punishing supports or cages are often made available. The problem of noise disturbance is also lessened at these events, while in the home setting many BDSM activities can be limited by this factor. In addition, such parties offer both exhibitionists and voyeurs a forum to indulge their inclinations without social criticism. Sexual intercourse is not permitted within most public BDSM play spaces or not often seen in others, because it is not the emphasis of this kind of play. In order to ensure the maximum safety and comfort for the participants, certain standards of behaviour have evolved; these include aspects of courtesy, privacy, respect and safewords.[10] Today BDSM parties are taking place in most of the larger cities in the Western world.
This scene appears particularly on the Internet, in publications, and in meetings such as at fetish clubs (like Torture Garden), SM parties, gatherings called munches, and erotic fairs like Venus Berlin. The annual Folsom Street Fair held in San Francisco is the world's largest BDSM event.[74] It has its roots in the gay leather movement. The weekend-long festivities include a wide range of sadomasochistic erotica in a public clothing optional space between 8th and 13th streets with nightly parties associated with the organization.[75]
There are also conventions such as Living in Leather and Black Rose.
Psychology
Research indicates that there is no evidence that a preference for BDSM is a consequence of childhood abuse.[76] Some reports suggest that people abused as children may have more BDSM injuries and have difficulty with safe words being recognized as meaning stop the previously consensual behaviour;[77] thus, it is possible that people choosing BDSM as part of their lifestyle, who also were previously abused, may have had more police or hospital reports of injuries. There is also a link between transgender individuals who have been abused and violence occurring in BDSM activities.[78]
Joseph Merlino, author and psychiatry adviser to the New York Daily News, said in an interview that a sadomasochistic relationship, as long as it is consensual, is not a psychological problem:
It's a problem only if it is getting that individual into difficulties, if he or she is not happy with it, or it's causing problems in their personal or professional lives. If it's not, I'm not seeing that as a problem. But assuming that it did, what I would wonder about is what is his or her biology that would cause a tendency toward a problem, and dynamically, what were the experiences this individual had that led him or her toward one of the ends of the spectrum.[79]
Some psychologists agree that experiences during early sexual development can have a profound effect on the character of sexuality later in life. Sadomasochistic desires, however, seem to form at a variety of ages. Some individuals report having had them before puberty, while others do not discover them until well into adulthood. According to one study, the majority of male sadomasochists (53%) developed their interest before the age of 15, while the majority of females (78%) developed their interest afterward (Breslow, Evans, and Langley 1985). The prevalence of sadomasochism within the general population is unknown. Despite female sadists being less visible than males, some surveys have resulted in comparable amounts of sadistic fantasies between females and males.[80] The results of such studies demonstrate that one's sex does not determine preference for sadism.[81]
Following a phenomenological study of nine individuals involved in sexual masochistic sessions who regarded pain as central to their experience,[82] sexual masochism was described as an addiction-like tendency, with several features resembling that of drug addiction: craving, intoxication, tolerance and withdrawal. It was also demonstrated how the first masochistic experience is placed on a pedestal, with subsequent use aiming at retrieving this lost sensation, much as described in the descriptive literature on addiction.
Prevalence

BDSM occurs among people of all genders and sexual orientations, and in varied occurrences and intensities.[84][85][86] The spectrum ranges from couples with no connections to the subculture outside of their bedrooms or homes, without any awareness of the concept of BDSM, playing "tie-me-up-games", to public scenes on St. Andrew's crosses at large events such as the Folsom Street Fair in San Francisco. Estimation on the overall percentage of BDSM-related sexual behaviour varies.[87]
Alfred Kinsey stated in his 1953 nonfiction book Sexual Behavior in the Human Female that 12% of females and 22% of males reported having an erotic response to a sadomasochistic story.[88] In that book erotic responses to being bitten were given as:[88]
| Erotic responses | By females | By males |
|---|---|---|
| Definite and/or frequent | 26% | 26% |
| Some response | 29% | 24% |
| Never | 45% | 50% |
| Number of cases | 2200 | 567 |
A non-representative survey on the sexual behaviour of American students published in 1997 and based on questionnaires had a response rate of about 8–9%. Its results showed 15% of homosexual and bisexual males, 21% of lesbian and female bisexual students, 11% of heterosexual males and 9% of female heterosexual students committed to BDSM related fantasies.[89] In all groups the level of practical BDSM experiences were around 6%. Within the group of openly lesbian and bisexual females, the quote was significantly higher, at 21%. Independent of their sexual orientation, about 12% of all questioned students, 16% of lesbians and female bisexuals and 8% of heterosexual males articulated an interest in spanking. Experience with this sexual behaviour was indicated by 30% of male heterosexuals, 33% of female bisexuals and lesbians, and 24% of the male gay and bisexual men and female heterosexual women.[89] Even though this study was not considered representative, other surveys indicate similar dimensions in differing target groups.[90][91][92]
A representative study done from 2001 to 2002 in Australia found that 1.8% of sexually active people (2.2% men, 1.3% women but no significant sex difference) had engaged in BDSM activity in the previous year. Of the entire sample, 1.8% of men and 1.3% of women had been involved in BDSM. BDSM activity was significantly more likely among bisexuals and homosexuals of both sexes. But among men in general, there was no relationship effect of age, education, language spoken at home or relationship status. Among women, in this study, activity was most common for those between 16 and 19 years of age and least likely for females over 50 years. Activity was also significantly more likely for women who had a regular partner they did not live with, but was not significantly related with speaking a language other than English or education.[76]
Another representative study, published in 1999 by the German Institut für rationale Psychologie, found that about 2/3 of the interviewed women stated a desire to be at the mercy of their sexual partners from time to time. 69% admitted to fantasies dealing with sexual submissiveness, 42% stated interest in explicit BDSM techniques, 25% in bondage.[93] A 1976 study in the general US population suggests three per cent have had positive experiences with Bondage or master-slave roleplaying. Overall 12% of the interviewed females and 18% of the males were willing to try it.[94][95] A 1990 Kinsey Institute report stated that 5% to 10% of Americans occasionally engage in sexual activities related to BDSM, 11% of men and 17% of women reported trying bondage.[96][97] Some elements of BDSM have been popularized through increased media coverage since the middle 1990s. Thus both black leather clothing, sexual jewelry such as chains and dominance roleplay appear increasingly outside of BDSM contexts.
According to yet another survey of 317,000 people in 41 countries, about 20% of the surveyed have at least used masks, blindfolds or other bondage utilities once, and 5% explicitly connected themselves with BDSM.[98] In 2004, 19% mentioned spanking as one of their practices and 22% confirmed the use of blindfolds or handcuffs.[98]
A 1985 study found 52 out of 182 female respondents (28%) were involved in sadomasochistic activities.[99]
- Recent surveys
A 2009 study on two separate samples of male undergraduate students in Canada found that 62 to 65%, depending on the sample, had entertained sadistic fantasies, and 22 to 39% engaged in sadistic behaviours during sex. The figures were 62 and 52% for bondage fantasies, and 14 to 23% for bondage behaviours.[100] A 2014 study involving a mixed sample of Canadian college students and online volunteers, both male and female, reported that 19% of male samples and 10% of female samples rated the sadistic scenarios described in a questionnaire as being at least "slightly arousing" on a scale that ranged from "very repulsive" to "very arousing";[101] the difference was statistically significant.[101] The corresponding figures for the masochistic scenarios were 15% for male students and 17% for female students, a non-significant difference.[101] In a 2011 study on 367 middle-aged and elderly men recruited from the broader community in Berlin, 21.8% of the men self-reported sadistic fantasies and 15.5% sadistic behaviors;[102] 24.8% self-reported any such fantasy and/or behavior.[102] The corresponding figures for self-reported masochism were 15.8% for fantasy, 12.3% for behaviour, and 18.5% for fantasy and/or behaviour.[102] In a 2008 study on gay men in Puerto Rico, 14.8% of the over 425 community volunteers reported any sadistic fantasy, desire or behaviour in their lifetime; the corresponding figure for masochism was 15.7%.[103] A 2017 cross-sectional representative survey among the general Belgian population demonstrated a substantial prevalence of BDSM fantasies and activities; 12.5% of the population performed one of more BDSM-practices on a regular basis.[104]
| Lifetime BDSM behaviors among North American medical students[105] | Straight men | Gay men | Bisexual men | Straight women | Gay women | Bisexual women |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Has been restrained for pleasure | 12% | 20% | 13% | 19% | 38% | 55% |
| Has restrained someone else for pleasure | 17.5% | 17% | 13% | 13% | 36% | 51% |
| Has received pain for pleasure | 4% | 6.5% | 18% | 8% | 10% | 36% |
| Has inflicted pain for pleasure | 5% | 6% | 9% | 4% | 6.5% | 26% |
Medical categorization
Reflecting changes in social norms, modern medical opinion is now moving away from regarding BDSM activities as medical disorders, unless they are nonconsensual or involve significant distress or harm.
DSM
In the past, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), the American Psychiatric Association's manual, defined some BDSM activities as sexual disorders.[106] Following campaigns from advocacy organizations including the National Coalition for Sexual Freedom,[106] the current version of the DSM, DSM-5, excludes consensual BDSM from diagnosis when the sexual interests cause no harm or distress.[107]
ICD
The World Health Organization's International Classification of Diseases (ICD) has made similar moves in recent years.
Section F65 of the current revision, ICD-10, indicates that "mild degrees of sadomasochistic stimulation are commonly used to enhance otherwise normal sexual activity". The diagnostic guidelines for the ICD-10 state that this class of diagnosis should only be made "if sadomasochistic activity is the most important source of stimulation or necessary for sexual gratification".[108]
In Europe, an organization called ReviseF65 has worked to remove sadomasochism from the ICD.[109] In 1995, Denmark became the first European Union country to have completely removed sadomasochism from its national classification of diseases. This was followed by Sweden in 2009, Norway in 2010 and Finland 2011.[110][111][112] Recent surveys on the spread of BDSM fantasies and practices show strong variations in the range of their results.[113] Nonetheless, researchers assume that 5 to 25 per cent of the population practices sexual behaviour related to pain or dominance and submission. The population with related fantasies is believed to be even larger.[113]
The ICD is in the process of revision, and recent drafts have reflected these changes in social norms.[114] As of July 2018[update], the final advance preview of the ICD-11 has de-pathologised most things listed in ICD-10 section F65, characterizing as pathological only those activities which are either coercive, or involving significant risk of injury or death, or distressing to the individual committing them, and specifically excluding consensual sexual sadism and masochism from being regarded as pathological.[115][116][117] The ICD-11 classification consider sadomasochism as a variant in sexual arousal and private behaviour without appreciable public health impact and for which treatment is neither indicated nor sought."[118]
According to the WHO ICD-11 Working Group on Sexual Disorders and Sexual Health, stigmatization and discrimination of fetish- and BDSM individuals are inconsistent with human rights principles endorsed by the United Nations and the World Health Organization.[118]
The final advance text is to be officially presented to the members of the WHO in 2019, ready to come into effect in 2022.[119]
Coming out



Some people who are interested in or curious about BDSM decide to come out of the closet, although many sadomasochists remain closeted. Depending upon a survey's participants, about 5 to 25 per cent of the US population show affinity to the subject.[89][120] Other than a few artists and writers,[121] practically no celebrities are publicly known as sadomasochists.
Public knowledge of one's BDSM lifestyle can have detrimental vocational and social effects for sadomasochists. Many face severe professional consequences[122] or social rejection if they are exposed, either voluntarily or involuntarily, as sadomasochists.
Within feminist circles, the discussion is split roughly into two camps: some who see BDSM as an aspect or reflection of oppression (for example, Alice Schwarzer) and, on the other side, pro-BDSM feminists, often grouped under the banner of sex-positive feminism (see Samois); both of them can be traced back to the 1970s.[123] Some feminists have criticized BDSM for eroticizing power and violence and reinforcing misogyny. They argue that women who engage in BDSM are making a choice that is ultimately bad for women.[124] Feminist defenders of BDSM argue that consensual BDSM activities are enjoyed by many women and validate the sexual inclinations of these women.[125] They argue that there is no connection between consensual kinky activities and sex crimes, and that feminists should not attack other women's sexual desires as being "anti-feminist". They also state that the main point of feminism is to give an individual woman free choices in her life; which includes her sexual desire. While some feminists suggest connections between consensual BDSM scenes and non-consensual rape and sexual assault, other sex-positive ones find the notion insulting to women.[126][127]
Roles are not fixed to gender, but personal preferences. The dominant partner in a heterosexual relationship may be the woman rather than the man, or BDSM may be part of male/male or female/female sexual relationships. Finally, some people switch, taking either a dominant or submissive role on different occasions. Several studies investigating the possibility of a correlation between BDSM pornography and the violence against women also indicate a lack of correlation. In 1991, a lateral survey came to the conclusion that between 1964 and 1984, despite the increase in amount and availability of sadomasochistic pornography in the U.S., Germany, Denmark and Sweden, there is no correlation with the national number of rapes to be found.[128]
Operation Spanner in the U.K. proves that BDSM practitioners still run the risk of being stigmatized as criminals. In 2003, the media coverage of Jack McGeorge showed that simply participating and working in BDSM support groups poses risks to one's job, even in countries where no law restricts it.[129] Here a clear difference can be seen to the situation of homosexuality.[clarification needed] The psychological strain appearing in some individual cases is normally neither articulated nor acknowledged in public. Nevertheless, it leads to a difficult psychological situation in which the person concerned can be exposed to high levels of emotional stress.[130]
In the stages of "self-awareness", he or she realizes their desires related to BDSM scenarios or decides to be open for such. Some authors call this internal coming-out. Two separate surveys on this topic independently came to the conclusion that 58 per cent and 67 per cent of the sample respectively, had realized their disposition before their 19th birthday. Other surveys on this topic show comparable results.[131][132] Independent of age, coming-out can potentially result in a difficult life crisis, sometimes leading to thoughts or acts of suicide. While homosexuals have created support networks in the last decades, sadomasochistic support networks are just starting to develop in most countries. In German-speaking countries they are only moderately more developed.[133] The Internet is the prime contact point for support groups today, allowing for local and international networking. In the U.S., Kink Aware Professionals (KAP) a privately funded, non-profit service provides the community with referrals to psychotherapeutic, medical, and legal professionals who are knowledgeable about and sensitive to the BDSM, fetish, and leather community.[134] In the U.S. and the U.K., the Woodhull Freedom Foundation & Federation, National Coalition for Sexual Freedom (NCSF) and Sexual Freedom Coalition (SFC) have emerged to represent the interests of sadomasochists. The German Bundesvereinigung Sadomasochismus is committed to the same aim of providing information and driving press relations. In 1996, the website and mailing list Datenschlag went online in German and English providing the largest bibliography, as well as one of the most extensive historical collections of sources related to BDSM.
Social (non-medical) research
Richters et al. (2008) found that people who engaged in BDSM were more likely to have experienced a wider range of sexual practices (e.g., oral or anal sex, more than one partner, group sex, phone sex, viewed pornography, used a sex toy, fisting, etc.). They were, however, not any more likely to have been coerced, unhappy, anxious, or experiencing sexual difficulties. On the contrary, men who had engaged in BDSM scored lower on a psychological distress scale than men who did not.[76]
There have been few studies on the psychological aspects of BDSM using modern scientific standards. Psychotherapist Charles Moser has said there is no evidence for the theory that BDSM has common symptoms or any common psychopathology, emphasizing that there is no evidence that BDSM practitioners have any special psychiatric other problems based on their sexual preferences.[130]
Problems sometimes occur with self-classification. During the phase of the "coming-out", self-questioning related to one's own "normality" is common. According to Moser, the discovery of BDSM preferences can result in fear of the current non-BDSM relationship's destruction. This, combined with the fear of discrimination in everyday life, leads in some cases to a double life which can be highly burdensome. At the same time, the denial of BDSM preferences can induce stress and dissatisfaction with one's own "vanilla"-lifestyle, feeding the apprehension of finding no partner. Moser states that BDSM practitioners having problems finding BDSM partners would probably have problems in finding a non-BDSM partner as well. The wish to remove BDSM preferences is another possible reason for psychological problems since it is not possible in most cases. Finally, the scientist states that BDSM practitioners seldom commit violent crimes. From his point of view, crimes of BDSM practitioners usually have no connection with the BDSM components existing in their life. Moser's study comes to the conclusion that there is no scientific evidence, which could give reason to refuse members of this group work- or safety certificates, adoption possibilities, custody or other social rights or privileges. The Swiss psychoanalyst Fritz Morgenthaler shares a similar perspective in his book, Homosexuality, Heterosexuality, Perversion (1988). He states that possible problems result not necessarily from the non-normative behavior, but in most cases primarily from the real or feared reactions of the social environment towards their own preferences.[135] In 1940 psychoanalyst Theodor Reik reached implicitly the same conclusion in his standard work Aus Leiden Freuden. Masochismus und Gesellschaft.[136]
Moser's results are further supported by a 2008 Australian study by Richters et al. on the demographic and psychosocial features of BDSM participants. The study found that BDSM practitioners were no more likely to have experienced sexual assault than the control group, and were not more likely to feel unhappy or anxious. The BDSM males reported higher levels of psychological well-being than the controls. It was concluded that "BDSM is simply a sexual interest or subculture attractive to a minority, not a pathological symptom of past abuse or difficulty with 'normal' sex."[137]
Gender differences in research
Several recent studies have been conducted on the gender differences and personality traits of BDSM practitioners. Wismeijer and van Assen (2013) found that "the association of BDSM role and gender was strong and significant" with only 8% of women in the study being dominant compared to 75% being submissive.;[138] Hébert and Weaver (2014) found that 9% of women in their study were dominant compared to 88% submissive;[139] Weierstall1 and Giebel (2017) likewise found a significant difference, with 19% of women in the study as dominant compared to 74% as submissive, and a study from Andrea Duarte Silva (2015) indicated that 61.7% of females who are active in BDSM expressed a preference for a submissive role, 25.7% consider themselves a switch, while 12.6% prefer the dominant role. In contrast, 46.6% of men prefer the submissive role, 24% consider themselves to be switches and 29.5% prefer the dominant role.[140] They concluded that "men more often display an engagement in dominant practices, whereas females take on the submissive part. This result is inline with a recent study about mate preferences that has shown that women have a generally higher preference for a dominant partner than men do (Giebel, Moran, Schawohl, & Weierstall, 2015). Women also prefer dominant men, and even men who are aggressive, for a short-term relationship and for the purpose of sexual intercourse (Giebel, Weierstall, Schauer, & Elbert, 2013)".[141] Similarly, studies on sexual fantasy differences between men and women show the latter prefer submissive and passive fantasies over dominant and active ones, with rape and force being common.[142]
Gender differences in masochistic scripts

One common belief of BDSM and kink is that women are more likely to take on masochistic roles than men. Roy Baumeister (2010) actually had more male masochists in his study than female, and fewer male dominants than female. The lack of statistical significance in these gender differences suggests that no assumptions should be made regarding gender and masochistic roles in BDSM. One explanation why we might think otherwise lies in our social and cultural ideals about femininity; masochism may emphasize certain stereotypically feminine elements through activities like feminization of men and ultra-feminine clothing for women. But such tendencies of the submissive masochistic role should not be interpreted as a connection between it and the stereotypical female role—many masochistic scripts do not include any of these tendencies.[143]
Baumeister found that masochistic males experienced greater: severity of pain, frequency of humiliation (status-loss, degrading, oral), partner infidelity, active participation by other persons, and cross-dressing. Trends also suggested that male masochism included more bondage and oral sex than female (though the data was not significant). Female masochists, on the other hand, experienced greater: frequency in pain, pain as punishment for 'misdeeds' in the relationship context, display humiliation, genital intercourse, and presence of non-participating audiences. The exclusiveness of dominant males in a heterosexual relationship happens because, historically, men in power preferred multiple partners. Finally, Baumeister observes a contrast between the 'intense sensation' focus of male masochism to a more 'meaning and emotion' centred female masochistic script.[143]
Prior argues that although some of these women may appear to be engaging in traditional subordinate or submissive roles, BDSM allows women in both dominant and submissive roles to express and experience personal power through their sexual identities. In a study that she conducted in 2013, she found that the majority of the women she interviewed identified as bottom, submissive, captive, or slave/sex slave. In turn, Prior was able to answer whether or not these women found an incongruity between their sexual identities and feminist identity. Her research found that these women saw little to no incongruity, and in fact felt that their feminist identity supported identities of submissive and slave. For them, these are sexually and emotionally fulfilling roles and identities that, in some cases, feed other aspects of their lives. Prior contends that third wave feminism provides a space for women in BDSM communities to express their sexual identities fully, even when those identities seem counter-intuitive to the ideals of feminism. Furthermore, women who do identify as submissive, sexually or otherwise, find a space within BDSM where they can fully express themselves as integrated, well-balanced, and powerful women.[144]
Women in S/M culture
Levitt, Moser, and Jamison's 1994 study provides a general, if outdated, description of characteristics of women in the sadomasochistic (S/M) subculture. They state that women in S/M tend to have higher education, become more aware of their desires as young adults, are less likely to be married than the general population. The researchers found the majority of females identified as heterosexual and submissive, a substantial minority were versatile—able to switch between dominant and submissive roles—and a smaller minority identified with the dominant role exclusively. Oral sex, bondage and master-slave script were among the most popular activities, while feces/watersports were the least popular.[145]
Orientation observances in research
BDSM is considered by some of its practitioners to be a sexual orientation.[146] The BDSM and kink scene is more often seen as a diverse pansexual community. Often this is a non-judgmental community where gender, sexuality, orientation, preferences are accepted as is or worked at to become something a person can be happy with.[147] In research, studies have focused on bisexuality and its parallels with BDSM, as well as gay-straight differences between practitioners.
Comparison between gay and straight men in S/M
Demographically, Nordling et al.'s (2006) study found no differences in age, but 43% of gay male respondents compared to 29% of straight males had university-level education. The gay men also had higher incomes than the general population and tended to work in white-collar jobs while straight men tended toward blue-collar ones. Because there were not enough female respondents (22), no conclusions could be drawn from them.
Sexually speaking, the same 2006 study by Nordling et al. found that gay males were aware of their S/M preferences and took part in them at an earlier age, preferring leather, anal sex, rimming, dildos and special equipment or uniform scenes. In contrast, straight men preferred verbal humiliation, mask and blindfolds, gags, rubber/latex outfits, caning, vaginal sex, straitjackets, and cross-dressing among other activities. From the questionnaire, researchers were able to identify four separate sexual themes: hyper-masculinity, giving and receiving pain, physical restriction (i.e. bondage), and psychological humiliation. Gay men preferred activities that tended towards hyper-masculinity while straight men showed greater preference for humiliation, significantly higher master/madame-slave role play at ≈84%. Though there were not enough female respondents to draw a similar conclusion with, the fact that there is a difference in gay and straight men suggests strongly that S/M (and BDSM in general) can not be considered a homogenous phenomenon. As Nordling et al. (2006) puts it, "People who identify as sadomasochists mean different things by these identifications." (54)[148]
Bisexuality
In Steve Lenius' original 2001 paper, he explored the acceptance of bisexuality in a supposedly pansexual BDSM community. The reasoning behind this is that 'coming-out' had become primarily the territory of the gay and lesbian, with bisexuals feeling the push to be one or the other (and being right only half the time either way). What he found in 2001, was that people in BDSM were open to discussion about the topic of bisexuality and pansexuality and all controversies they bring to the table, but personal biases and issues stood in the way of actively using such labels. A decade later, Lenius (2011) looks back on his study and considers if anything has changed. He concluded that the standing of bisexuals in the BDSM and kink community was unchanged, and believed that positive shifts in attitude were moderated by society's changing views towards different sexualities and orientations. But Lenius (2011) does emphasize that the pansexual promoting BDSM community helped advance greater acceptance of alternative sexualities.[149][150]
Brandy Lin Simula (2012), on the other hand, argues that BDSM actively resists gender-conforming and identified three different types of BDSM bisexuality: gender-switching, gender-based styles (taking on a different gendered style depending on the gender of partner when playing), and rejection of gender (resisting the idea that gender matters in their play partners). Simula (2012) explains that practitioners of BDSM routinely challenge our concepts of sexuality by pushing the limits on pre-existing ideas of sexual orientation and gender norms. For some, BDSM and kink provides a platform in creating identities that are fluid, ever-changing.[151]
History of psychotherapy and current recommendations
Psychiatry has an insensitive history in the area of BDSM. There have been many involvements by institutions of political power to marginalize subgroups and sexual minorities.[87] Mental health professionals have a long history of holding negative assumptions and stereotypes about the BDSM community. Beginning with the DSM-II, Sexual Sadism and Sexual Masochism have been listed as sexually deviant behaviours. Sadism and masochism were also found in the personality disorder section.[152] This negative assumption has not changed significantly which is evident in the continued inclusion of Sexual Sadism and Sexual Masochism as paraphilias in the DSM-IV-TR.[153] The DSM-V, however, has depathologized the language around paraphilias in a way that signifies "the APA's intent to not demand treatment for healthy consenting adult sexual expression".[154] These biases and misinformation can result in pathologizing and unintentional harm to clients who identify as sadists and/or masochists and medical professionals who have been trained under older editions of the DSM can be slow to change in their ways of clinical practice.
According to Kolmes et al. (2006), major themes of biased and inadequate care to BDSM clients are:
- Considering BDSM to be unhealthy
- Requiring a client to give up BDSM activities in order to continue in treatment
- Confusing BDSM with abuse
- Having to educate the therapist about BDSM
- Assuming that BDSM interests are indicative of past family/spousal abuse
- Therapists misrepresenting their expertise by stating that they are BDSM-positive when they are not actually knowledgeable about BDSM practices
These same researchers suggested that therapists should be open to learning more about BDSM, to show comfort in talking about BDSM issues, and to understand and promote "safe, sane, consensual" BDSM.[87]
There has also been research which suggests BDSM can be a beneficial way for victims of sexual assault to deal with their trauma, most notably by Corie Hammers, but this work is limited in scope and, to date, has not undergone empirical testing as a treatment.[citation needed]
Clinical issues
Nichols (2006) compiled some common clinical issues: countertransference, non-disclosure, coming out, partner/families, and bleed-through.[155]
Countertransference is a common problem in clinical settings. Despite having no evidence, therapists may find themselves believing that their client's pathology is "self-evident". Therapists may feel intense disgust and aversive reactions. Feelings of countertransference can interfere with therapy. Another common problem is when clients conceal their sexual preferences from their therapists. This can compromise any therapy. To avoid non-disclosure, therapists are encouraged to communicate their openness in indirect ways with literature and artworks in the waiting room. Therapists can also deliberately bring up BDSM topics during the course of therapy. With less informed therapists, sometimes they over-focus on clients' sexuality which detracts from original issues such as family relationships, depression, etc. A special subgroup that needs counselling is the "newbie". Individuals just coming out might have internalized shame, fear, and self-hatred about their sexual preferences. Therapists need to provide acceptance, care, and model positive attitude; providing reassurance, psychoeducation, and bibliotherapy for these clients is crucial. The average age when BDSM individuals realize their sexual preference is around 26 years.[87] Many people hide their sexuality until they can no longer contain their desires. However, they may have married or had children by this point.[citation needed]
History
Origins



Practices of BDSM survive from some of the oldest textual records in the world, associated with rituals to the goddess Inanna (Ishtar in Akkadian). Cuneiform texts dedicated to Inanna which incorporate domination rituals. In particular, she points to ancient writings such as Inanna and Ebih (in which the goddess dominates Ebih), and Hymn to Inanna describing cross-dressing transformations and rituals "imbued with pain and ecstasy, bringing about initation [sic?] and journeys of altered states of consciousness; punishment, moaning, ecstasy, lament and song, participants exhausting themselves in weeping and grief."[156][157]
During the 9th century BC, ritual flagellations were performed in Artemis Orthia, one of the most important religious areas of ancient Sparta, where the Cult of Orthia, a pre-Olympic religion, was practiced. Here, ritual flagellation called diamastigosis took place, in which young adolescent men were whipped in a ceremony overseen by the priestess.[158] These are referred to by a number of ancient authors, including Pausanius (III, 16: 10–11).[159]
One of the oldest graphical proofs of sadomasochistic activities is found in the Etruscan Tomb of the Whipping near Tarquinia, which dates to the 5th century BC. Inside the tomb, there is a fresco which portrays two men who flagellate a woman with a cane and a hand during an erotic situation.[160] Another reference related to flagellation is to be found in the sixth book of the Satires of the ancient Roman Poet Juvenal (1st–2nd century A.D.),[161] further reference can be found in Petronius's Satyricon where a delinquent is whipped for sexual arousal.[162] Anecdotal narratives related to humans who have had themselves voluntary bound, flagellated or whipped as a substitute for sex or as part of foreplay reach back to the 3rd and 4th century BC.[citation needed]
In Pompeii, a whip-mistress figure with wings is depicted on the wall of the Villa of Mysteries, as part of an initiation of a young woman into the Mysteries. The whip-mistress role drove the sacred initiation of ceremonial death and rebirth.[163] The archaic Greek Aphrodite may too once have been armed with an implement, with archaeological evidence of armed Aphrodites known from a number of locations in Cythera, Acrocorinth and Sparta,[164] and which may have been a whip.[163]
The Kama Sutra of India describes four different kinds of hitting during lovemaking, the allowed regions of the human body to target and different kinds of joyful "cries of pain" practiced by bottoms. The collection of historic texts related to sensuous experiences explicitly emphasizes that impact play, biting and pinching during sexual activities should only be performed consensually since only some women consider such behavior to be joyful. From this perspective, the Kama Sutra can be considered one of the first written resources dealing with sadomasochistic activities and safety rules. Further texts with sadomasochistic connotation appear worldwide during the following centuries on a regular basis.[165]
There are anecdotal reports of people willingly being bound or whipped, as a prelude to or substitute for sex, during the 14th century. The medieval phenomenon of courtly love in all of its slavish devotion and ambivalence has been suggested by some writers to be a precursor of BDSM.[166][167] Some sources[who?] claim that BDSM as a distinct form of sexual behavior originated at the beginning of the 18th century when Western civilization began medically and legally categorizing sexual behavior (see Etymology).
Flagellation practiced within an erotic setting has been recorded from at least the 1590s evidenced by a John Davies epigram,[168][169] and references to "flogging schools" in Thomas Shadwell's The Virtuoso (1676) and Tim Tell-Troth's Knavery of Astrology (1680).[170][171] Visual evidence such as mezzotints and print media is also identified revealing scenes of flagellation, such as "The Cully Flaug'd" from the British Museum collection.[172]
John Cleland's novel Fanny Hill, published in 1749, incorporates a flagellation scene between the character's protagonist Fanny Hill and Mr Barville.[173] A large number of flagellation publications followed, including Fashionable Lectures: Composed and Delivered with Birch Discipline (c. 1761), promoting the names of women offering the service in a lecture room with rods and cat o' nine tails.[174]

Other sources give a broader definition, citing BDSM-like behavior in earlier times and other cultures, such as the medieval flagellates and the physical ordeal rituals of some Native American societies.[175]
BDSM ideas and imagery have existed on the fringes of Western culture throughout the 20th century.[176] Robert Bienvenu attributes the origins of modern BDSM to three sources, which he names as "European Fetish" (from 1928), "American Fetish" (from 1934), and "Gay Leather" (from 1950).[177] Another source are the sexual games played in brothels, which go back to the 19th century, if not earlier. Charles Guyette was the first American to produce and distribute fetish related material (costumes, footwear, photography, props and accessories) in the U.S. His successor, Irving Klaw, produced commercial sexploitation film and photography with a BDSM theme (most notably with Bettie Page) and issued fetish comics (known then as "chapter serials") by the now-iconic artists John Willie, Gene Bilbrew, and Eric Stanton.
Stanton's model Bettie Page became at the same time one of the first successful models in the area of fetish photography and one of the most famous pin-up girls of American mainstream culture. Italian author and designer Guido Crepax was deeply influenced by him, coining the style and development of European adult comics in the second half of the 20th century. The artists Helmut Newton and Robert Mapplethorpe are the most prominent examples of the increasing use of BDSM-related motives in modern photography and the public discussions still resulting from this.[178]
Alfred Binet first coined the term erotic fetishism in his 1887 book, Du fétichisme dans l'amour[179] Richard von Krafft-Ebing saw BDSM interests as the end of a continuum.[180]
Leather movement

Leather has been a predominantly gay male term to refer to one fetish, but it can stand for many more. Members of the gay male leather community may wear leathers such as motorcycle leathers, or may be attracted to men wearing leather. Leather and BDSM are seen as two parts of one whole. Much of the BDSM culture can be traced back to the gay male leather culture, which formalized itself out of the group of men who were soldiers returning home after World War II (1939–1945).[181] World War II was the setting where countless homosexual men and women tasted the life among homosexual peers. Post-war, homosexual individuals congregated in larger cities such as New York, Chicago, San Francisco, and Los Angeles. They formed leather clubs and bike clubs; some were fraternal services. The establishment of Mr. Leather Contest and Mr. Drummer Contest were made around this time. This was the genesis of the gay male leather community. Many of the members were attracted to extreme forms of sexuality, for which peak expression was in the pre-AIDS 1970s.[182] This subculture is epitomized by the Leatherman's Handbook by Larry Townsend, published in 1972, which describes in detail the practices and culture of gay male sadomasochists in the late 1960s and early 1970s.[183][184] In the early 1980s, lesbians also joined the leathermen as a recognizable element of the gay leather community. They also formed leather clubs, but there were some gender differences, such as the absence of leatherwomen's bars. In 1981, the publication of Coming to Power by lesbian-feminist group Samois led to a greater knowledge and acceptance of BDSM in the lesbian community.[185] By the 1990s, the gay men's and women's leather communities were no longer underground and played an important role in the kink community.[182]
Today, the leather movement is generally seen as a part of the BDSM-culture instead of as a development deriving from gay subculture, even if a huge part of the BDSM-subculture was gay in the past. In the 1990s, the so-called New Guard leather subculture evolved. This new orientation started to integrate psychological aspects into their play.[citation needed]
The Leather Archives and Museum (LA&M) in Chicago was founded in 1991 by Chuck Renslow and Tony DeBlase as a “community archives, library, and museum of leather, kink, fetish, and BDSM history and culture.”[186] The LA&M has an extensive collection of leather- and BDSM-related artifacts, including one of three original leather pride flags.[187]
The San Francisco South of Market Leather History Alley consists of four works of art along Ringold Alley honoring leather culture; it opened in 2017.[188][189] One of the works of art is metal bootprints along the curb which honor 28 people (including Steve McEachern, owner of the Catacombs, a gay and lesbian S/M fisting club, and Cynthia Slater, a founder of the Society of Janus, the second oldest BDSM organization in the United States) who were an important part of the leather communities of San Francisco.[189][188]
Internet
In the late 1980s, the Internet provided a way of finding people with specialized interests around the world as well as on a local level, and communicating with them anonymously.[10][190] This brought about an explosion of interest and knowledge of BDSM, particularly on the usenet group alt.sex.bondage. When that group became too cluttered with spam, the focus moved to soc.subculture.bondage-bdsm. With an increased focus on forms of social media, FetLife was formed, which advertises itself as "a social network for the BDSM and fetish community". It operates similarly to other social media sites, with the ability to make friends with other users, events, and pages of shared interests.
In addition to traditional sex shops, which sell sex paraphernalia, there has also been an explosive growth of online adult toy companies that specialize in leather/latex gear and BDSM toys. Once a very niche market, there are now very few sex toy companies that do not offer some sort of BDSM or fetish gear in their catalog. Kinky elements seem to have worked their way into "vanilla" markets. The former niche expanded to an important pillar of the business with adult accessories.[191] Today practically all suppliers of sex toys do offer items which originally found usage in the BDSM subculture. Padded handcuffs, latex and leather garments, as well as more exotic items like soft whips for fondling and TENS for erotic electro stimulation, can be found in catalogs aiming at classical vanilla target groups, indicating that former boundaries increasingly seem to shift.
During the last years, the Internet also provides a central platform for networking among individuals who are interested in the subject. Besides countless private and commercial choices, there is an increasing number of local networks and support groups emerging. These groups often offer comprehensive background and health-related information for people who have been unwillingly outed as well as contact lists with information on psychologists, physicians and lawyers who are familiar with BDSM-related topics.[192]
University clubs
Increasingly, American universities are witnessing BDSM and kink education by providing student clubs, such as Columbia University's Conversio Virium[193][194] and Iowa State University's Cuffs.[195] University BDSM clubs are also found in the U.K.,[196][197][198][199] Canada,[200][201] Belgium,[202] and Taiwan.[203]
Some American universities—such as Indiana University and Michigan State University—have professors who research and teach classes on BDSM.[204][205][206][207][208][209]
Legal status
Austria

Section 90 of the Austrian criminal code declares bodily injury (Sections 83–84) or the endangerment of physical security (Section 89) to not be subject to penalty in cases in which the victim has consented and the injury or endangerment does not offend moral sensibilities. Case law from the Austrian Supreme Court has consistently shown that bodily injury is only offensive to moral sensibilities, thus it is only punishable when a "serious injury" (damage to health or an employment disability lasting more than 24 days) or the death of the "victim" results. A light injury is generally considered permissible when the "victim" has consented to it. In cases of threats to bodily well being the standard depends on the probability that an injury will actually occur. If serious injury or even death would be a likely result of a threat being carried out, then even the threat itself is considered punishable.[210]
Canada
In 2004, a judge in Canada ruled that videos seized by the police featuring BDSM activities were not obscene and did not constitute violence, but a "normal and acceptable" sexual activity between two consenting adults.[211]
In 2011, the Supreme Court of Canada ruled in R. v. J.A. that a person must have an active mind during the specific sexual activity in order to legally consent. The Court ruled that it is a criminal offence to perform a sexual act on an unconscious person—whether or not that person consented in advance.[212]
Germany

According to Section 194 of the German criminal code, the charge of insult (slander) can only be prosecuted if the defamed person chooses to press charges. False imprisonment can be charged if the victim—when applying an objective view—can be considered to be impaired in their rights of free movement. According to Section 228, a person inflicting a bodily injury on another person with that person's permission violates the law only in cases where the act can be considered to have violated good morals in spite of permission having been given. On 26 May 2004, the Criminal Panel No. 2 of the Bundesgerichtshof (German Federal Court) ruled that sado-masochistically motivated physical injuries are not per se indecent and thus subject to Section 228.[213]
Following cases in which sado-masochistic practices had been repeatedly used as pressure tactics against former partners in custody cases, the Appeals Court of Hamm ruled in February 2006 that sexual inclinations toward sado-masochism are no indication of a lack of capabilities for successful child-raising.[214]
Italy
In Italian law, BDSM is right on the border between crime and legality, and everything lies in the interpretation of the legal code by the judge. This concept is that anyone willingly causing "injury" to another person is to be punished. In this context, though, "injury" is legally defined as "anything causing a condition of illness", and "illness" is ill-defined itself in two different legal ways. The first is "any anatomical or functional alteration of the organism" (thus technically including little scratches and bruises too); the second is "a significant worsening of a previous condition relevant to organic and relational processes, requiring any kind of therapy". This could make it somewhat risky to play with someone, as later the "victim" may call foul play citing even an insignificant mark as evidence against the partner. Also, any injury requiring over 20 days of medical care must be denounced by the professional medic who discovers it, leading to automatic indictment of the person who caused it.[215]
Nordic countries
In September 2010, a Swedish court acquitted a 32-year-old man of assault for engaging in consensual BDSM play with a 16-year-old girl (the age of consent in Sweden is 15).[216] Norway's legal system has likewise taken a similar position,[217] that safe and consensual BDSM play should not be subject to criminal prosecution. This parallels the stance of the mental health professions in the Nordic countries which have removed sadomasochism from their respective lists of psychiatric illnesses.
Switzerland
The age of consent in Switzerland is 16 years, which also applies to BDSM play. Minors (i.e., those under 16) are not subject to punishment for BDSM play as long as the age difference between them is less than three years. Certain practices, however, require granting consent for light injuries, with only those over 18 permitted to give consent. On 1 April 2002, Articles 135 and 197 of the Swiss Criminal Code were tightened to make ownership of "objects or demonstrations [...] which depict sexual acts with violent content" a punishable offense. This law amounts to a general criminalization of sado-masochism since nearly every sado-masochist will have some kind of media that fulfills this criterion. Critics also object to the wording of the law which puts sado-masochists in the same category as pedophiles and pederasts.[218]
United Kingdom
In British law, consent is an absolute defense to common assault, but not necessarily to actual bodily harm, where courts may decide that consent is not valid, as occurred in the case of R v Brown.[219] Accordingly, consensual activities in the U.K. may not constitute "assault occasioning actual or grievous bodily harm" in law. The Spanner Trust states that this is defined as activities which have caused injury "of a lasting nature" but that only a slight duration or injury might be considered "lasting" in law.[220] The decision contrasts with the later case of R v Wilson in which conviction for non-sexual consensual branding within a marriage was overturned, the appeal court ruling that R v Brown was not an authority in all cases of consensual injury and criticizing the decision to prosecute.[221]
Following Operation Spanner, the European Court of Human Rights ruled in January 1999 in Laskey, Jaggard and Brown v. United Kingdom that no violation of Article 8 occurred because the amount of physical or psychological harm that the law allows between any two people, even consenting adults, is to be determined by the jurisdiction the individuals live in, as it is the State's responsibility to balance the concerns of public health and well-being with the amount of control a State should be allowed to exercise over its citizens. In the Criminal Justice and Immigration Bill 2007, the British Government cited the Spanner case as justification for criminalizing images of consensual acts, as part of its proposed criminalization of possession of "extreme pornography".[222] Another contrasting case was that of Stephen Lock in 2013, who was cleared of actual bodily harm on the grounds that the woman consented. In this case, the act was deemed to be sexual.[223]
United States

The United States Federal law does not list a specific criminal determination for consensual BDSM acts. Many BDSM practitioners cite the legal decision of People v. Jovanovic, 95 N.Y.2d 846 (2000), or the "Cybersex Torture Case",[224] which was the first U.S. appellate decision to hold (in effect) that one does not commit assault if the victim consents. However, many individual states do criminalize specific BDSM actions within their state borders. Some states specifically address the idea of "consent to BDSM acts" within their assault laws, such as the state of New Jersey, which defines "simple assault" to be "a disorderly persons offense unless committed in a fight or scuffle entered into by mutual consent, in which case it is a petty disorderly persons offense".[225]
Oregon Ballot Measure 9 was a ballot measure in the U.S. state of Oregon in 1992, concerning sadism, masochism, gay rights, pedophilia, and public education, that drew widespread national attention. It would have added the following text to the Oregon Constitution:
All governments in Oregon may not use their monies or properties to promote, encourage or facilitate homosexuality, pedophilia, sadism or masochism. All levels of government, including public education systems, must assist in setting a standard for Oregon's youth which recognizes that these behaviors are abnormal, wrong, unnatural and perverse and they are to be discouraged and avoided.
It was defeated in the 3 November 1992 general election with 638,527 votes in favor, 828,290 votes against.[226]
Национальная коалиция за сексуальную свободу собирает отчеты о наказаниях за сексуальные действия, совершенные по согласию взрослых , и об их использовании в делах об опеке над детьми . [ 227 ]
Культурные аспекты
Сегодня культура БДСМ существует в большинстве западных стран. [ 228 ] Это дает практикующим БДСМ возможность обсудить актуальные темы и проблемы БДСМ с единомышленниками. Эту культуру часто рассматривают как субкультуру , главным образом потому, что часть общественности до сих пор часто считает БДСМ «необычным». Многие люди скрывают свою принадлежность к обществу, поскольку боятся непонимания и социальной изоляции. [ 229 ]
В отличие от подходов, пытающихся объяснить садомазохизм с помощью психологических, психоаналитических, медицинских или судебно-медицинских подходов, которые стремятся классифицировать поведение и желания и найти первопричину, Романа Бирн предполагает, что такие практики можно рассматривать как примеры «эстетической сексуальности». в котором основополагающий физиологический или психологический импульс не имеет значения. Скорее, садизм и мазохизм могут практиковаться путем выбора и обдумывания, движимых определенными эстетическими целями, связанными со стилем, удовольствием и идентичностью. Эти практики при определенных обстоятельствах и контекстах можно сравнить с созданием искусства. [ 230 ]
Символы
Одним из наиболее часто используемых символов БДСМ-сообщества является форма трискелиона внутри круга. [ 231 ] Различные формы трискеле имели множество применений и значений во многих культурах; его использование в БДСМ происходит от « Кольца О» в классической книге « История О» . Проект эмблемы БДСМ заявляет об авторских правах на одну конкретную форму символа трискелиона; другие варианты трискелиона свободны от подобных претензий по авторским правам. [ 232 ]
Трискелион как символ БДСМ можно легко воспринимать как три отдельные части аббревиатуры БДСМ; это BD, DS и SM (связывание и дисциплина, доминирование и подчинение, садизм и мазохизм). Это три отдельных элемента, которые обычно связаны друг с другом.

Кожаный флаг гордости , показанный справа, является символом кожаной субкультуры и также широко используется в БДСМ. В континентальной Европе « Кольцо О» широко распространено среди практикующих БДСМ. [ 233 ]

Флаг прав БДСМ, показанный справа, был разработан Таносом, Мастером из Великобритании . Он частично основан на дизайне кожаного флага гордости , а также включает версию эмблемы БДСМ (но не настолько похожую, чтобы подпадать под конкретные претензии Стива Куагмира по авторским правам на эмблему). Флаг прав БДСМ призван отражать веру в то, что люди, чьи сексуальные предпочтения или предпочтения в отношениях включают практику БДСМ, заслуживают тех же прав человека, что и все остальные, и не должны подвергаться дискриминации за занятие БДСМ с согласия взрослых. [ 234 ]
Флаг вдохновлен кожаным флагом гордости и эмблемой БДСМ, но специально предназначен для представления концепции прав БДСМ и отсутствия ограничений на коммерческое использование других символов. Он разработан так, чтобы люди, знакомые либо с кожаным флагом гордости, либо с БДСМ-трискелионом (или трискеле), были узнаваемы как «что-то связанное с БДСМ»; и быть отличительным независимо от того, воспроизведено ли оно в полноцветном или черно-белом режиме (или в другой паре цветов). [ 235 ]
БДСМ и фетиш-предметы и стили широко распространились в повседневной жизни западных обществ благодаря различным факторам, таким как авангардная мода, хэви-метал , готическая субкультура и научно-фантастические сериалы. [ 236 ] и многие люди часто не осознают своих корней в БДСМ. Хотя в 1990-х годах оно в основном ограничивалось субкультурами панка и БДСМ, с тех пор оно распространилось на более широкие части западного общества.
Кино и музыка
- В музыке: румынская певица и автор песен Нави включила сцены БДСМ и шибари в свой клип "Picture Perfect" (2014). [ 237 ] Видео было запрещено в Румынии из-за его откровенного содержания. [ 238 ] В 2010 году Рианны появились песня « S&M » и Кристины Агилеры сингл « Not Myself Tonight », полные образов БДСМ.
- В кино: Хотя БДСМ-деятельность изначально проявлялась в скрытой форме, в 1960-х годах такие известные литературные произведения, как «История О» и «Венера в мехах», были экранизированы явно. С выходом в 1986 году фильма «9½ недель» тема БДСМ была перенесена в массовое кино. С 1990-х годов кинематографическое представление альтернативной сексуальности, включая БДСМ, резко возросло, о чем свидетельствуют такие документальные постановки, как Graphic Sexual Horror (фильм 2009 года, основанный на веб-сайте Insex ), Kink (фильм 2013 года, основанный на веб-сайте Kink.com ). и такие фильмы, как «Пятьдесят оттенков серого» (2015) и два его продолжения «На пятьдесят оттенков темнее» (2017) и «Пятьдесят оттенков свободы» (2018).
- БДСМ-деятельностью, которая скорее является оскорбительной . Однако в обществе ошибочно считают фильмы «Пятьдесят оттенков серого» (2015) и два их продолжения «Пятьдесят оттенков темнее» (2017) и «Пятьдесят оттенков свободы» (2018) [ 239 ] «Многое из того, что происходит в главных отношениях «Пятидесяти оттенков серого», является домашним насилием, как физическим, так и эмоциональным, и для людей, чье понимание БДСМ теперь основано на покачивающихся шариках и комнатах боли, это опасное заблуждение, которое следует поощрять». [ 240 ]
Театр
Хотя можно было бы установить определенные элементы, связанные с БДСМ, в классическом театре, только после появления современного театра БДСМ стал основной темой некоторых пьес. Примером этого являются две работы: одна австрийская и одна немецкая, в которых БДСМ не только включен, но и является неотъемлемой частью сюжетной линии пьесы.
- Worauf sich Körper kaprizieren , Австрия. Питер Керн поставил и написал сценарий этой комедии, которая представляет собой современную адаптацию фильма Жана Жене 1950 года «Песнь любви» . Речь идет о браке, в котором жена (ветеран кино Мириам Гольдшмидт) подвергает своего мужа (Генрих Херки) и дворецкого (Гюнтер Буббник) садистскому обращению, пока их места не займут два новых персонажа. [ 241 ]
- Ах, Хильда ( О, Хильда ), Германия. Премьера пьесы Анны Швеммер состоялась в Берлине. Юная Хильда беременеет и после того, как ее бросил парень, решает стать профессиональной доминатрикс, чтобы зарабатывать деньги. В пьесе тщательно вырисовывается игривая и легкомысленная картина мира профессиональных доминатриц. [ 242 ]
Литература

Хотя примеры литературы, ориентированной на БДСМ и фетишистские вкусы, были созданы и в более ранние периоды, литературу БДСМ в том виде, в котором она существует сегодня, невозможно найти намного раньше, чем Вторая мировая война .
Слово «садизм» происходит от произведений Донатьена Альфонса Франсуа, маркиза де Сада , а слово «мазохизм» происходит от Леопольда фон Захер-Мазоха , автора «Венеры в мехах» . Однако стоит отметить, что маркиз де Сад описывает насилие без согласия в своих произведениях, например, в «Жюстине» . Венера в мехах описывает отношения «дом-суб» по обоюдному согласию.
Центральным произведением в современной литературе о БДСМ, несомненно, является «История О » (1954) Анны Дескло под псевдонимом Полин Реаж .
Другие известные работы включают «9½ недель » (1978) Элизабет Макнил , некоторые произведения писательницы Энн Райс ( «Выход в Эдем » и ее Утверждение Спящей красавицы» серию книг « ), Жанны де Берг ( «L'Image» (1956), посвященный Полине Реаж ). ), «Гор» серию Джона Нормана и, естественно, все произведения Патрика Калифии , Глории Брейм , группы Samois и многих писателей Жоржа Батая ( «Histoire de l’oeil-Story of the Eye» , «Мадам Эдварда», 1937), как а также Боба Фланагана ( «Сонеты рабов» (1986), «Журнал траха» (1987), «Вкус меда» (1990)). Общей частью многих стихотворений Пабло Неруды является размышление о чувствах и ощущениях, возникающих в результате отношений ЭПЭ или эротического обмена властью. Трилогия «Пятьдесят оттенков» — это серия очень популярных эротических любовных романов Э. Л. Джеймс , в которых присутствует БДСМ; однако романы подверглись критике за неточное и вредное изображение БДСМ. [ 243 ]
В 21 веке ряд престижных университетских издательств, таких как Университет Дьюка , Университет Индианы и Чикагский университет , опубликовали книги о БДСМ, написанные профессорами, тем самым придавая академическую легитимность этой когда-то табуированной теме. [ 244 ]
Искусство
- В фотографии: Эрик Кролл и Ирвинг Клоу (с Бетти Пейдж , первой известной моделью бондажа), а также японский фотограф Араки Нобуёси , чьи работы выставлены в нескольких крупных художественных музеях, галереях и частных коллекциях, таких как баронесса Мэрион Ламберт, крупнейший в мире держатель современного фотографического искусства. Также Роберт Мэпплторп , чья самая противоречивая работа связана с андерграундной БДСМ-сценой конца 1960-х и начала 1970-х годов в Нью-Йорке. Гомоэротизм этой работы вызвал общенациональные дебаты по поводу государственного финансирования спорных произведений искусства.
- Рисунки из комиксов: Гвидо Крепакс с Histoire d'O (1975), Жюстин (1979) и Венера в Пелличче (1984); вдохновлен творчеством Полины Реаж , маркиза де Сада и Леопольда фон Захер-Мазоха . «Джон Вилли и Приключения милой Гвендолин» (1984), легший в основу фильма «Опасности Гвендолин в стране йик-яков» . «Солнечный камень/Милосердие» (с 2011 г. по настоящее время) Книги Степана Сеича стали очень популярными и их можно найти во многих обычных книжных магазинах по всему миру.
- В графическом дизайне: Эрик Стэнтон и его работа о доминировании и женском рабстве, а также Хадзиме Сораяма и Роберт Бишоп.
- В скульптуре в стиле ар-деко : Бруно Зак создал, пожалуй, свою самую известную скульптуру под названием «Ездовой урожай» ( ок. 1925 г. ), на которой изображена скудно одетая госпожа, владеющая хлыстом . [ 245 ]
См. также
Ссылки
- ^ «БДСМ н. (в записи Б, н. )» . Оксфордский онлайн-словарь английского языка (проект). Издательство Оксфордского университета. Июнь 2013. Архивировано из оригинала 31 декабря 2015 года . Проверено 29 ноября 2015 г.
- ^ Грау, Джонсон (1995). «Что означают B&D, S&M, D&S, «верх», «низ» . Кожаные розы. Архивировано из оригинала 11 января 2008 года . Проверено 27 января 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д «Словарь БДСМ-терминов» . Архивировано из оригинала 2 декабря 2014 года . Проверено 26 ноября 2014 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Миллер, Филипп; Девон, Молли; Гранциг, Уильям А. (1995). К черту розы, пошли мне шипы: Романтика и сексуальное колдовство садомазохизма . Книги о мистических розах. п. 55 . ISBN 978-0-9645960-0-9 .
- ^ Билл Хенкин, Сибил Холидей: Садомазохизм по обоюдному согласию: как говорить об этом и как делать это безопасно , стр. 64, Издатель: Daedalus Publishing Company 2006, ISBN 978-1-881943-12-9
- ^ «VICSS / Разница между злоупотреблениями и обменом властью со стороны NLA, Голландского информационного центра СМИ SM и Powerrotics» . Архивировано из оригинала 16 декабря 2007 года . Проверено 10 декабря 2007 г.
- ^ «Стойка против SSC» . Внутри Реальности . 2003. Архивировано из оригинала 8 января 2007 года . Проверено 13 ноября 2006 г.
- ^ Досси Истон, Джанет В. Харди: Новая книга топпингов , Greenery Press (Калифорния) 2002, ISBN 978-1-890159-36-8
- ^ Досси Истон, Джанет В. Харди: Новая книга топпингов , стр. 72, Greenery Press (Калифорния) 2002, ISBN 978-1-890159-36-8
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж Уайзман, Джей (1998). SM 101: Реалистическое введение . Калифорния: Greenery Press. ISBN 978-0-9639763-8-3 .
- ^ Досси Истон, Джанет В. Харди: Новая книга топпингов , стр. 71, Greenery Press (Калифорния), 2002 г.
- ^ «Словарь сдержанной элегантности поз и позиций рабыни в бондаже» . www.restrainedelegance.com . Архивировано из оригинала 23 августа 2017 года . Проверено 8 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Философствуя о сексе. Архивировано 5 июня 2021 года в Wayback Machine , PT 244.
- ^ Маттиас Т. Дж. Гримме: Справочник по бондажу. Инструкция по эротическому бондажу . Харон Верлаг, Гамбург, 1999 г., ISBN 978-3-931406-16-5 . (Немецкий)
- ^ Ли «Бриджитт» Харрингтон: Шибари, которые вы можете использовать: японское веревочное бондаж и эротическое макраме , Mystic Productions 2007, ISBN 978-0-615-14490-0 .
- ^ Джойал, Кристиан К.; Коссетта, Амели; Лапьер, Ванесса (февраль 2015 г.). «Что такое необычная сексуальная фантазия?». Журнал сексуальной медицины . 12 (№ 2): 328–340. дои : 10.1111/jsm.12734 . ISSN 1743-6095 . ПМИД 25359122 . S2CID 33785479 .
- ^ Уайзман, Джей (2000). Справочник Джея Уайзмана по эротическому бондажу . КА: Гринери Пресс. ISBN 978-1-890159-13-9 .
- ^ Билл Хенкин, Сибил Холидей: Садомазохизм по обоюдному согласию: как говорить об этом и как делать это безопасно , стр. 71, Daedalus Publishing Company, 1996, ISBN 978-1-881943-12-9 .
- ^ «Лицом к лицу: Госпожа и покорная» . Новости Би-би-си . 22 сентября 2005 г. Архивировано из оригинала 26 декабря 2007 г. Проверено 22 октября 2009 г.
- ^ Уайзман, Джей. «Переговоры и формы переговоров» . Архивировано из оригинала 2 декабря 2014 года . Проверено 26 ноября 2014 г.
- ^ МакГрил, Скотт А. (25 июля 2013 г.). «БДСМ, личность и психическое здоровье» . Психология сегодня . Архивировано из оригинала 3 декабря 2019 года . Проверено 26 ноября 2014 г.
- ^ cp: Маркиз де Сад: 120 дней Содома , Пбл. ReadHowYouWant (1 декабря 2006 г.), ISBN 978-1-4250-3448-1 , страницы 407–409 «Они вам больше не понадобятся», - пробормотал он, бросая каждую вещь в большую решетку. «Нет больше необходимости в этой мантии, этом платье, эти чулки, этот лиф, нет, — сказал он, когда все было израсходовано, — теперь тебе нужен только гроб».
- ^ Подробности, описывающие развитие теоретической конструкции «извращение» Краффта-Эбинга и его отношение к этому термину, см. Андреа Бекманн, Журнал уголовного правосудия и популярной культуры , 2001; 8 (№ 2) 66–95 онлайн на сайте Deconstructing Myths. Архивировано 3 марта 2016 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ^ Исидор Исаак Садгер: «О садомазохистском комплексе» в: Ежегодник психоаналитических и психопатологических исследований , том 5, 1913, стр. 157–232 (немецкий).
- ^ Крюгер и Каплан 2001, с. 393: «Номенклатура DSM, относящаяся к сексуальной психопатологии, подверглась критике как расплывчатая и не прошедшая полевых испытаний DSM». ( Примечание: здесь «DSM» не имеет отношения к «BDSM». Это стандартная аббревиатура для « Руководства по диагностике и статистике психических расстройств » .)
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и Баркер, Иантафи и Гупта 2007 , с. 13
- ^ Вайнер, Ирвинг Б.; Крейгхед, В. Эдвард (2010). Психологическая энциклопедия Корсини, четвертое издание, том 4 . Хобокен, Нью-Джерси: John Wiley & Sons. п. 1488. ИСБН 9780470170243 .
- ^ «Садомазохизм | Определение, поведение, патологизация и факты | Британника» . www.britanica.com . Проверено 5 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ Дэвис, Джанет Л.; Яношик, Эллен Гастингс (1991). Психическое здоровье и уход за психиатрами: заботливый подход . Бостон, Массачусетс: Jones & Bartlett Learning. стр. 390 . ISBN 0867204427 .
- ^ Крейгхед, В. Эдвард; Немерофф, Чарльз Б. (2004). Краткая энциклопедия психологии и поведенческих наук Корсини . Хобокен, Нью-Джерси: John Wiley & Sons. п. 562. ИСБН 0471220361 .
- ^ Голдберг, Джефф (1988). Анатомия научного открытия . Бантамские книги, 1988. ISBN 978-0-553-34631-2 ; ISBN 978-0-553-17616-2 (британское издание); ISBN 978-0-553-05261-9
- ^ Фрис, DS (2002). «Опиоидные анальгетики». В Уильямс Д.А., Лемке ТЛ. Принципы медицинской химии Фоя (5-е изд.). Филадельфия: Липпинкотт Уильямс и Уилкинс. ISBN 978-0-683-30737-5
- ^ Берк, Эдмунд (1909). О вкусе: О возвышенном и прекрасном; Размышления о Французской революции; Письмо благородному лорду; с введением, примечаниями и иллюстрациями . ПФ Коллиер и сын. OCLC 16729697 . Архивировано из оригинала 13 апреля 2021 года . Проверено 13 апреля 2021 г.
- ^ Сагарин, Брэд Дж.; Катлер, Берт; Катлер, Надин; Лоулер-Сагарин, Кимберли А.; Матушевич, Лесли (1 апреля 2009 г.). «Гормональные изменения и связь между парами при садомазохистской деятельности по обоюдному согласию». Архив сексуального поведения . 38 (№ 2): 186–200. дои : 10.1007/s10508-008-9374-5 . ISSN 0004-0002 . ПМИД 18563549 . S2CID 15989116 .
- ^ Уильям Брэйм, Глория Брэйм: Другая любовь: мир сексуального доминирования и подчинения (мягкая обложка), Виллард, 1996, ISBN 978-0-679-76956-9
- ^ Клаудия Варрин: Искусство чувственного женского доминирования: Руководство для женщин , Цитадель, 2000, ISBN 978-0-8065-2089-6
- ^ Джон Уоррен, доктор философии: Любящий доминант , Greenery Press (Калифорния), 2-е изд. ред., ISBN 978-1-890159-20-7
- ^ Билл Хенкин, Сибил Холидей: Садомазохизм по обоюдному согласию: как говорить об этом и как делать это безопасно , Daedalus Publishing Company 1996, ISBN 978-1-881943-12-9
- ^ Дэвид Стейн: Коперниканская революция С/М: от закрытого мира к бесконечной Вселенной и безопасное разумное согласие: эволюция шибболета, доступно на сайте s/m-leather History.
- ^ Билл Хенкин, Сибил Холидей: Садомазохизм по обоюдному согласию: как говорить об этом и как делать это безопасно , страницы 80–94, Daedalus Publishing Company 1996, ISBN 978-1-881943-12-9
- ^ Дебора Кэмерон, Дон Кулик: язык и сексуальность , стр. 24, Cambridge University Press, 2003, ISBN 978-0-521-00969-0
- ^ Тристан Таормино (ред.): Полное руководство по извращениям: БДСМ, ролевые игры и эротика , стр. 26, Cleis Press 2012, ISBN 978-1573447799
- ^ Гилмор, Пейсли (25 января 2018 г.). «Найдены самые популярные в мире «безопасные слова», и вот это да! » Космополитен . Архивировано из оригинала 13 января 2019 года . Проверено 12 января 2019 г. .
- ^ «Что такое стоп-слово и нужно ли оно вам?» . Метро . 22 февраля 2018 года. Архивировано из оригинала 13 января 2019 года . Проверено 12 января 2019 г. .
- ^ Джозеф В. Бин: Порка , Greenery Press (Калифорния), 2000, ISBN 978-1-890159-27-6
- ^ Джек Ринелла: Серия «Руководство по сумкам с игрушками», Greenery Press (Калифорния), например, «Руководство по играм с горячим воском и температурам» по мешкам с игрушками , ISBN 978-1-890159-57-3
- ^ Арне Хоффманн, Лексикон садомазохизма. Внутреннее руководство по темному эротизму: практики и инструменты, люди и институты, литература и кино, политика и философия , стр. 42, Schwarzkopf & Schwarzkopf 2000, ISBN 978-3-89602-290-5 (немецкий)
- ^ Филип Миллер, Молли Девон, Уильям А. Гранциг: К черту розы, пошли мне шипы: Романтика и сексуальное колдовство садомазохизма , стр. 95, Mystic Rose Books 1995, ISBN 978-0-9645960-0-9
- ^ Баркер, Иантафи и Гупта 2007 , стр. 6
- ^ Досси Истон, Джанет В. Харди: Новая книга топпингов , стр. 111
- ^ Зейн, Закари (4 октября 2019 г.). «Что такое послеполовой уход и почему это так важно?» . Мужское здоровье . Архивировано из оригинала 20 июля 2020 года . Проверено 20 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Катлер 2003 , с. 99
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Катлер 2003 , с. 102
- ^ Катлер 2003 , с. 103
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Катлер 2003 , с. 104
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Катлер 2003 , с. 107
- ^ Катлер 2003 , с. 108
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Катлер 2003 , с. 109
- ^ Катлер 2003 , с. 110
- ^ Катлер 2003 , с. 111
- ^ Катлер 2003 , с. 112
- ^ «Справочник профессиональных сабвуферов» . Архивировано из оригинала 9 февраля 2009 года . Проверено 6 октября 2014 г.
- ^ «БДСМ-словарь» . Ксеромаг . Архивировано из оригинала 31 декабря 2018 года . Проверено 5 октября 2018 г.
- ^ «Что такое Д/с» . Архивировано из оригинала 4 февраля 2012 года . Проверено 29 января 2012 г. Глоссарий Dom Sub
- ^ Обер, Лорен. «Кинк 101» . Семь дней . Архивировано из оригинала 6 октября 2018 года . Проверено 5 октября 2018 г.
- ^ «ОПРЕДЕЛЕНИЯ ТЕРМИНОВ БДСМ» . Архивировано из оригинала 24 февраля 2012 года . Проверено 29 января 2012 г. Условия «Хозяйка Скай»
- ^ * Аггравал, Анил (2008). Судебно-медицинские и судебно-медицинские аспекты сексуальных преступлений и необычных сексуальных практик . ЦРК Пресс. ISBN 978-1-4200-4308-2 . Архивировано из оригинала 26 июля 2020 года . Проверено 5 июля 2010 г. С.147-148, 154, 172, 174
- ^ «Определение терминов» . Архивировано из оригинала 1 января 2012 года . Проверено 29 января 2012 г. Определения праймера Novad
- ^ Преподобный (29 апреля 2013 г.). «Основы этикета подземелий» . Доминирующее руководство . Архивировано из оригинала 31 августа 2016 года . Проверено 5 декабря 2016 г.
- ^ «Правила клуба мошенников» . Клуб негодяев . Архивировано из оригинала 29 сентября 2014 года . Проверено 25 мая 2018 г.
- ^ «Общий клубный этикет для ЛЮБОГО фетиш-клуба» . странное игровое пространство. Архивировано из оригинала 26 апреля 2018 года . Проверено 25 апреля 2018 г.
- ^ datenschlag.org. Архивировано 30 ноября 2007 г. в Wayback Machine (немецкий).
- ^ Досси Истон, Джанет В. Харди: Новая книга о топпинге . Страница 163
- ^ «Ярмарка на Фолсом-стрит» . Архивировано из оригинала 15 декабря 2007 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2007 г.
- ^ Фимрите, Питер (22 сентября 2014 г.). «Фантазия становится реальностью на ярмарке на Фолсом-стрит» . Сфгейт . Архивировано из оригинала 14 февраля 2017 года . Проверено 13 февраля 2017 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Рихтерс, Джульетта; Де Виссер, Ричард О.; Риссел, Крис Э.; Грулич, Андрей Э.; Смит, Энтони Массачусетс (1 июля 2008 г.). «Демографические и психосоциальные особенности участников рабства и дисциплины, «садомазохизма» или доминирования и подчинения (БДСМ): данные национального опроса» (PDF) . Журнал сексуальной медицины . 5 (№ 7): 1660–1668. дои : 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2008.00795.x . ISSN 1743-6109 . ПМИД 18331257 . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 20 октября 2016 года.
- ^ Йозифкова, Ева (11 августа 2013 г.). «Садомазохистский секс по обоюдному согласию (БДСМ): корни, риски и различия между БДСМ и насилием». Текущие отчеты психиатрии . 15 (#9): 392. doi : 10.1007/s11920-013-0392-1 . ISSN 1523-3812 . ПМИД 23933978 . S2CID 29054687 .
- ^ Кук-Дэниэлс, Лори; Мансон, Майкл (5 мая 2010 г.). «Сексуальное насилие, жестокое обращение с пожилыми людьми и сексуальность взрослых трансгендеров в возрасте 50 лет и старше: результаты трех опросов». Журнал семейных исследований ЛГБТ . 6 (№ 2): 142–177. дои : 10.1080/15504281003705238 . ISSN 1550-428X . S2CID 57665777 .
- ↑ Интервью с доктором Джозефом Мерлино и Дэвидом Шенкбоуном, Wikinews , 5 октября 2007 г.
- ^ Федоров 2008 , с. 640: «...опросы не обнаружили различий в частоте садистских фантазий у мужчин и женщин».
- ^ Федоров 2008 , с. 644: «Этот обзор показывает, что сексуальный садизм в его нынешнем понимании является неоднородным явлением».
- ^ Курт Х. и Ронель Н. (в печати). Пристрастие к боли. Международный журнал терапии правонарушителей и сравнительной криминологии.
- ^ n: БДСМ как бизнес: Интервью с доминатриксами - полная стенограмма.
- ^ Браун, Эшли; Баркер, Эдвард Д.; Рахман, Кази (2020). «Систематический обзор распространенности, этиологических, психологических и межличностных факторов, связанных с БДСМ» . Журнал сексуальных исследований . 57 (6): 781–811. дои : 10.1080/00224499.2019.1665619 . ПМИД 31617765 . S2CID 204740964 .
- ^ Бреслоу и др. О распространенности и роли женщин в садомазохистской субкультуре: отчет об эмпирическом исследовании . Архив сексуального поведения, 14/1985, стр. 303–17. В книге Томаса С. Вайнберга: S&M: Исследования доминирования и подчинения (ред.), Prometheus Books, Нью-Йорк, 1995. ISBN 978-0-87975-978-0
- ^ Глория Г. Брэйм , БДСМ/фетиш-секс: обзор и исследование. Архивировано 21 декабря 2007 г. в Wayback Machine . Проверено 9 ноября 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Колмс, К.; Сток, В.; Мозер, К. (2006). «Исследование предвзятости в психотерапии с клиентами БДСМ». Журнал гомосексуализма . 50 (№ 2–3): 301–324. дои : 10.1300/j082v50n02_15 . ПМИД 16803769 . S2CID 21097726 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Сексуальное поведение самки человека , стр. 677-678.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Эллиот, Лиланд / Брантли, Синтия, Секс в кампусе , 1997, Random House, Нью-Йорк
- ^ Брокманн, Анджела: Сила и эротизм , 1996, Сексологический институт e. В. Гамбург, Гамбург (немецкий)
- ^ Персон, Этель С. / Терестман, Нетти / Майерс, Уэйн А. / Голдберг, Юджин Л. / Сальвадори, Кэрол: «Гендерные различия в сексуальном поведении и фантазиях среди студентов колледжей», 1989, в: Журнал «Секс и брак» Терапия , к.д. 15, № 3, 1989, С. 187–198.
- ^ Бреслоу, Норман: Отчет SM Research, v1.1 , 1999 г.
- ^ Арне Хоффманн, Лексикон нарушения табу , Schwarzkopf & Schwarzkopf, 2003, ISBN 978-3-89602-517-3 (немецкий)
- ^ «Что на самом деле происходит в кампусе», Playboy, октябрь 1976 г., S. 128–131, 160–164, 169. (см. Чарльз Мозер / Юджин Э. Левитт: «Исследовательско-дескриптивное исследование садомазохистски ориентированного образца», в журнале). секс-исследований , том 23, 1987, с. 322-337.)
- ^ Томас С. Вайнберг (ред.): S&M: Исследования доминирования и подчинения , Prometheus Books, Нью-Йорк, 1995, ISBN 978-0-87975-978-0
- ^ Уолтер Лоу: Секс-опрос читателей Playboy . 1983.
- ↑ На основе «Секс-опроса читателей Playboy» 1983 года, проведенного Уолтером Лоу. kinseyinstitute.org. Архивировано 20 апреля 2012 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Глобальный секс-опрос Durex, 2005 г., стр. 15. Онлайн- опрос Durex Global Sex Survey, 2005 г. Архивировано 15 марта 2009 г. на Wayback Machine.
- ^ Бреслоу, Н., Эванс, Л. и Лэнгли, Дж. (1985). «О распространенности и роли женщин в садомазохистской субкультуре: отчет об эмпирическом исследовании». Арх. Секс. Поведение. 14: 303-317.
- ^ Кевин М. Уильямс; Барри С. Купер; Тереза М. Хауэлл; Джон К. Юлль; Делрой Л. Паулхус (2009). «Вывод о сексуально девиантном поведении на основе соответствующих фантазий». Уголовное правосудие и поведение . 36 (№ 2): 198–222. дои : 10.1177/0093854808327277 . S2CID 33364099 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Саманта Дж. Доусон; Бриттани А. Баннерман и Мартин Л. Лалюмьер (2014). «Парафилические интересы: исследование половых различий в доклинической выборке». Сексуальное насилие: журнал исследований и лечения . 28 (№1): 1–26. дои : 10.1177/1079063214525645 . ПМИД 24633420 . S2CID 541989 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Алерс С.Дж., Шефер Г.А., Мундт И.А., Ролл С., Энглерт Х., Виллих С.Н., Бейер К.М. (2011). «Насколько необычно содержание парафилий? Связанные с парафилией модели сексуального возбуждения в выборке мужчин из местного сообщества». Журнал сексуальной медицины . 8 (№ 5): 1362–70. дои : 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2009.01597.x . ПМИД 19929918 .
- ^ Эдвард Х. Фанкханель (2008). Докторская диссертация: Парафилии среди геев в Пуэрто-Рико (PDF) (Отчет). Американская академия клинических сексологов. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 22 марта 2015 года . Проверено 13 апреля 2015 г.
- ^ Лиен Холвоет; Вим Хейс; Виолетт Коппенс; Жантьен Сеувс; Крис Геталс; Мануэль Морренс (2017). «Пятьдесят оттенков бельгийского серого: распространенность фантазий и действий, связанных с БДСМ, среди населения в целом». Журнал сексуальной медицины . 9 (№ 14): 1152–1159. дои : 10.1016/j.jsxm.2017.07.003 . HDL : 10067/1450920151162165141 . ПМИД 28781214 .
- ^ Брейер, Бенджамин Н.; Смит, Джеймс Ф.; Айзенберг, Майкл Л.; Андо, Кэтрин А.; Роуэн, Тами С.; Шиндел, Алан В. (2010). «Влияние сексуальной ориентации на сексуальность и сексуальную практику североамериканских студентов-медиков» . Журнал сексуальной медицины . 7 (7): 2391–2400. дои : 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2010.01794.x . ПМЦ 3607668 . ПМИД 20384941 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Герсон, Мерисса Натан (13 января 2015 г.). «БДСМ против DSM» . Атлантика . Архивировано из оригинала 13 июля 2018 года . Проверено 13 июля 2018 г.
- ^ «Парафилические расстройства» (PDF) . dsm5.org . Американская психиатрическая ассоциация. 2013. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 24 июля 2016 года . Проверено 26 августа 2016 г.
- ^ «Садомазохизм, F65.5» (PDF) . Классификация психических и поведенческих расстройств МКБ-10: Клинические описания и диагностические рекомендации . Всемирная организация здравоохранения. п. 172. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 23 марта 2014 года . Проверено 8 марта 2014 г.
- ^ Рейерсол О, Скейд С (2006). «МКД диагностирует фетишизм и садомазохизм». Журнал гомосексуализма . 50 (№ 2–3): 243–62. дои : 10.1300/J082v50n02_12 . ПМИД 16803767 . S2CID 7120928 .
- ^ «Диагнозы фетиша и СМ удалены в Швеции» . Пересмотреть F65. 17 ноября 2008 г. Архивировано из оригинала 27 декабря 2009 г. Проверено 4 марта 2010 г.
- ^ «СМ и фетиш исключены из норвежского больничного списка» . ПересмотретьF65 . 6 февраля 2010 года. Архивировано из оригинала 6 февраля 2010 года . Проверено 4 марта 2010 г.
- ^ «Финляндия присоединяется к сексуальной реформе Северных стран» . ПересмотретьF65 . 13 мая 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 21 июня 2011 года . Проверено 7 июня 2011 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Голые факты – статистика числовых фетишистов» (на немецком языке). Архивировано из оригинала 8 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 9 ноября 2008 г.
- ^ Джиами, Ален (2 мая 2015 г.). «Между DSM и МКБ: парафилии и трансформация сексуальных норм» (PDF) . Архив сексуального поведения . 44 (№ 5): 1127–1138. дои : 10.1007/s10508-015-0549-6 . ISSN 0004-0002 . ПМИД 25933671 . S2CID 21614140 . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 20 сентября 2016 года . Проверено 13 августа 2016 г.
- ^ «МКБ-11 — Статистика смертности и заболеваемости — Парафилические расстройства» . icd.who.int . Архивировано из оригинала 1 августа 2018 года . Проверено 2 июля 2018 г.
- ^ «МКБ-11 — Статистика смертности и заболеваемости — 6D33 Принудительный сексуальный садизм» . icd.who.int . Архивировано из оригинала 1 августа 2018 года . Проверено 13 июля 2018 г.
- ^ «КТО снимает бдсм и фетишизм с больничного» . revisef65.net . Архивировано из оригинала 2 июля 2018 года . Проверено 2 июля 2018 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Крюгер, Ричард Б.; Рид, Джеффри М.; Во-первых, Майкл Б.; Марэ, Адель; Кисмоди, Эстер; Брикен, Пер (2017). «Предложения по парафильным расстройствам в Международной классификации болезней и проблем, связанных со здоровьем, одиннадцатый пересмотр (МКБ-11)» . Архив сексуального поведения . 46 (№ 5): 1529–1545. дои : 10.1007/s10508-017-0944-2 . ISSN 0004-0002 . ПМЦ 5487931 . ПМИД 28210933 .
- ^ «ВОЗ публикует новую Международную классификацию болезней (МКБ 11)» . Всемирная организация здравоохранения . Архивировано из оригинала 4 июля 2018 года . Проверено 2 июля 2018 г.
- ^ Янус, Сэмюэл С. / Янус, Синтия Л., 1994. Отчет Януса о сексуальном поведении , Уайли, Нью-Йорк, ISBN 978-0-471-01614-4
- ^ Кинан, Джиллиан (9 ноября 2012 г.). «Найти в себе смелость раскрыть фетиш» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 23 июня 2016 года . Проверено 13 августа 2016 г.
- ^ Кинан, Джиллиан (28 октября 2014 г.). «Могут ли вас действительно уволить за извращение? Абсолютно» . Сланец . Архивировано из оригинала 13 августа 2016 года . Проверено 13 августа 2016 г.
- ^ Алиса Шварцер: «Женский мазохизм — это сотрудничество!» из выпуска 2 EMMA , 1991 г.
- ^ Элис Шварцер, выпуск 2 EMMA , 1991 г.
- ↑ БДСМ и феминизм: взгляд изнутри, Тэмми Джо Экхарт. Архивировано 29 мая 2015 г. в Wayback Machine , май 2011 г.
- ^ Гейл Рубин : Думая о сексе: Заметки по радикальной теории политики сексуальности . В книге Кэрол С. Вэнс (ред.), « Удовольствие и опасность: исследование женской сексуальности» , стр. 267–319. Рутледж и Кеган Пол, Бостон, 1984. ISBN 978-0-04-440867-3
- ^ Венди МакЭлрой : Право женщины на порнографию . Пресса Сен-Мартена 1997, ISBN 978-0-312-15245-1
- ^ Берл Катчински , «Порнография и изнасилование: теория и практика?» в: Международный журнал права и психиатрии , Vol. 14, 1991, стр. 47–66.
- ^ Ной, Тимоти (3 декабря 2002 г.). «Удовольствие, боль и Саддам Хусейн» . Slate.com . Архивировано из оригинала 23 ноября 2008 года . Проверено 9 ноября 2008 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Чарльз Мозер , в Журнале социальной работы и человеческой сексуальности , 1988 г., (7;1, S.43–56).
- ^ Шпенглер, Андреас : Садомазохисты и их субкультуры , Campus Verlag, 1979, Франкфурт-на-Майне / Нью-Йорк (немецкий)
- ^ «Данные попали в смущающий опрос I — результаты повторных ответов на старые вопросы» . Обследование данных (на немецком языке). Архивировано из оригинала 25 июля 2016 года . Проверено 28 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ Ева Дашек и Аксель Конрад: Эмпирическое исследование связи между избранными факторами и инклюзивным сексуальным садомазохизмом , онлайн -см-исследование. Архивировано 22 ноября 2007 г. в Wayback Machine (немецкий).
- ^ «ncsfreedom.org» . Архивировано из оригинала 11 июня 2010 года . Проверено 6 октября 2014 г.
- ^ Фриц Моргенталер: Гомосексуализм, Гетеросексуальность, Извращение , Аналитика, апрель 1988 г., ISBN 978-0-88163-060-2
- ^ Теодор Рейк: От страдания к радости. Мазохизм и общество , Фишер, 1983, ISBN 978-3-596-26768-2 (немецкий)
- ^ Рихтерс, Дж.; Де Виссер, Р.О.; Риссель, CE; Грулич А.Е.; Смит, А. (2008). «Демографические и психосоциальные особенности участников рабства и дисциплины, «садомазохизма» или доминирования и подчинения (БДСМ): данные национального опроса». Журнал сексуальной медицины . 5 (№ 7): 1660–1668. дои : 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2008.00795.x . ПМИД 18331257 .
- ^ Висмейер, Андреас; ван Ассен, Марсель (2013). «Психологические характеристики практикующих БДСМ». Журнал сексуальной медицины . 10 (№ 8): 1943–1952. дои : 10.1111/jsm.12192 . ПМИД 23679066 .
- ^ Эбер, Али; Уивер, Анджела (2014). «Исследование особенностей личности, связанных с БДСМ-ориентациями». Канадский журнал человеческой сексуальности . 24 (№ 1): 49–62. дои : 10.3138/cjhs.2467 . S2CID 143570286 .
- ^ Сильва, Андреа Дуарте (2015). Через боль – больше выгоды? - Исследование психосоциальных преимуществ садомазохизма (Диссертация). п. 41. Архивировано из оригинала 3 марта 2021 года . Проверено 26 февраля 2021 г.
- ^ Вейершталь, Роланд; Гибель, Гильда (2017). «Контрольный список садомазохизма: инструмент для оценки садомазохистского поведения» . Архив сексуального поведения . 46 (№ 3): 735–745. дои : 10.1007/s10508-016-0789-0 . ПМИД 27488306 .
- ^ Уилсон, Гленн (2010). «Анкета о секс-фантазиях: обновление». Сексуальная терапия и терапия отношений . 25 (№ 1): 68–72. дои : 10.1080/14681990903505799 . S2CID 144679434 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Баумайстер, РФ (1988). «Гендерные различия в мазохистских сценариях». Журнал сексуальных исследований . 25 (№ 4): 478–499. дои : 10.1080/00224498809551477 .
- ^ Прайор, Эмили (2013). «Женские перспективы обмена властью БДСМ» . Электронный журнал человеческой сексуальности . 16 . Архивировано из оригинала 25 января 2022 года . Проверено 4 марта 2015 г.
- ^ Левитт, Э.Э.; Мозер, К.; Джеймисон, КВ (1994). «Распространенность и некоторые атрибуты женщин в садомазохистской субкультуре: второй отчет». Архив сексуального поведения . 23 (№ 4): 465–473. дои : 10.1007/bf01541410 . ПМИД 7993186 . S2CID 28743901 .
- ↑ Джиллиан Кинан, [1] Архивировано 11 ноября 2014 г. в Wayback Machine , Slate , 18 августа 2014 г.
- ^ Вайс, доктор медицины (2006). Работа в игре: сексуальность БДСМ в районе залива Сан-Франциско. Антропология, 229–245.
- ^ Нордлинг, Н.; Санднабба, Северная Каролина; Санттила, П.; Элисон, Л. (2006). «Различия и сходства между геями и натуралами, вовлеченными в садомазохистскую субкультуру». Журнал гомосексуализма . 50 (№ 2–3): 41–57. дои : 10.1300/j082v50n02_03 . ПМИД 16803758 . S2CID 25370996 .
- ^ Лениус, С (2001). «Бисексуалы и БДСМ». Журнал бисексуальности . 1 (№ 4): 69–78. дои : 10.1300/j159v01n04_06 . S2CID 142599575 .
- ^ Лениус, С (2011). «Размышление о «Бисексуалах и БДСМ: бисексуальные люди в пансексуальном сообществе» - десять лет спустя (и обзор следующей сексуальной революции)». Журнал бисексуальности . 11 (№ 4): 420–425. дои : 10.1080/15299716.2011.620466 . S2CID 143156292 .
- ^ Симула, БЛ (2012). «Отменяет ли бисексуальность гендер? Гендер, сексуальность и бисексуальное поведение среди участников БДСМ». Журнал бисексуальности . 12 (№ 4): 484–506. дои : 10.1080/15299716.2012.729430 . S2CID 144476771 .
- ^ Американская психиатрическая ассоциация. (1968). Диагностическое и статистическое руководство по психическим расстройствам (2-е изд.). Вашингтон, округ Колумбия: Американская психиатрическая ассоциация.
- ^ Американская психиатрическая ассоциация. (2000). Диагностическое и статистическое руководство по психическим расстройствам (4-е изд., перераб.). Вашингтон, округ Колумбия: Американская психиатрическая ассоциация.
- ^ Админ, Блог. «Блог NCSF» . ncsfreedom.org . Архивировано из оригинала 22 апреля 2016 года . Проверено 5 апреля 2016 г.
- ^ Николс, М (2006). «Психотерапевтические проблемы с «странными» клиентами: клинические проблемы, ваши и их». Журнал гомосексуализма . 50 (№ 2–3): 281–300. дои : 10.1300/j082v50n02_14 . ПМИД 16803768 . S2CID 37706751 .
- ^ Номис, Энн О. (2013) История и искусство доминатрисы Мэри Иган Паблишинг и Анна Номис Ltd ISBN 978-0-9927010-0-0 стр. 59-60
- ^ «Леди самого большого сердца» или «Гимн Инане С» доступно в Электронном текстовом корпусе шумерской литературы Оксфордского университета http://etcsl.orinst.ox.ac.uk/section4/tr4073.htm . Архивировано 5 апреля. 2014 г. на Wayback Machine. линиях 80-90
- ^ Номис, Энн О. (2013) «Древняя богиня-доминанта и ее посвященные жрицы» в книге «История и искусство доминанты» Мэри Иган Паблишинг и Анна Номис Ltd, стр. 61-62
- ^ Павсаний III, 16: 10-11, можно посмотреть по адресу: http://www.theoi.com/Text/Pausanias3B.html#16. Архивировано 22 декабря 2013 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ^ Марио Моретти/Леонард фон Мэтт: Этрусская живопись в Тарквинии . Кельн, 1974 г., стр. 90, рис. 762-63, ISBN 978-3-7701-0541-0
- ↑ Ювенал : Сатиры 6, строки 474–511. Архивировано 11 мая 2008 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Петроний: Сатирикон. Архивировано 30 января 2008 г. в Wayback Machine (лат.).
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Номис, Энн О. (2013) «Кнут и тайны» в книге «История и искусство доминатрисы» Mary Egan Publishing & Anna Nomis Ltd, Великобритания ISBN 978-0-9927010-0-0 стр.62-64
- ^ Павсаний называет их святилищем Афродиты Урании на Кифере, храмом Афродиты на вершине Акрокоринфа и древним храмом Афродиты с верхним этажом в Спарте. См. Павсаний III, 23:1, II, 5:1, III, 15:10.
- ^ Камасутра Малланаги Ватсияяна, перевод Венди Донигер, Oxford University Press 2003, ISBN 978-0-19-283982-4 Книга II: главы 4, 5, 7, 8, страницы 45–64.
- ^ Дени де Ружмон (1956), Любовь в западном мире: описание идеала целомудренной любви под влиянием катаров доктрин
- ↑ Арне Хоффманн: В кожаном переплете. Садомазохизм в мировой литературе , стр. 11, Ubooks 2007, ISBN 978-3-86608-078-2 (немецкий)
- ^ Эпиграмма 33: «Откровенно»
- ^ Бромли, Джеймс М. (1 мая 2010 г.). «Социальные отношения и мазохистская сексуальная практика в «Хорошей доблести». Современная филология . 107 (№ 4): 556–587. дои : 10.1086/652428 . ISSN 0026-8232 . S2CID 144194164 .
- ^ Джонс, М. (2007) «Печать месяца: Калли Флауг» в британских печатных изображениях (BPI) до 1700 года , доступно по адресу: http://www.bpi1700.org.uk/research/printOfTheMonth/december2007. html. Архивировано 24 декабря 2013 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ^ Номис, Энн О. (2013) «Школы порки и их хулиганы» в книге «История и искусство доминатрисы» Мэри Иган Паблишинг и Анна Номис Ltd, 2013. ISBN 978-0-9927010-0-0 стр.80-81
- ^ Джонс, М. (2007) «Печать месяца: Калли Флауг» в британских печатных изображениях (BPI) до 1700 года, можно посмотреть по адресу: http://www.bpi1700.org.uk/research/printOfTheMonth/december2007 . .html Архивировано 24 декабря 2013 г. в Wayback Machine и там же.
- ↑ Джон Клеланд: Фанни Хилл: Мемуары женщины, доставляющей удовольствие , Penguin Classics, (7 января 1986 г.), ISBN 978-0-14-043249-7, стр. 180 и далее.
- ^ Модные лекции, прочитанные с использованием березовой дисциплины (ок. 1761 г.), Редкие книги Британской библиотеки, цит. по Nomis (2013), op cit.
- ^ «Европейские средневековые испытания» . Архивировано из оригинала 14 августа 2014 года . Проверено 6 октября 2014 г.
- ^ Томазос, Костас; О'Горман, Кевин; Макларен, Эндрю С. (июнь 2017 г.). «От отдыха к туризму: Как БДСМ демонстрирует переход девиантных занятий в массовые продукты» (PDF) . Управление туризмом . 60 : 30–41. дои : 10.1016/j.tourman.2016.10.018 . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 15 июля 2019 года . Проверено 15 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Роберт Бьенвеню: Докторская диссертация «Развитие садомазохизма как культурного стиля в Соединенных Штатах двадцатого века». Архивировано 16 марта 2010 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ^ Университет Центральной Англии в Бирмингеме : Книга «Попытка конфискации Мэпплторна» официальными лицами в 1997 году за непристойность.
- ^ Бине, А. (1887). «Du fetishisme dans l’amour» [=Фетишизм в любви] в: Revue Philosophique , 24, стр. 143–167
- ^ фон Краффт-Эбинг, Р. Сексуальная психопатия с особым упором на антипатический сексуальный инстинкт: судебно-медицинское исследование . Транс Ребман FJ из 12-го немецкого изд. Нью-Йорк: Специальные книги; 1965: 129–218, 533–543.
- ^ Роберт Бьенвеню, Развитие садомазохизма как культурного стиля в Соединенных Штатах двадцатого века , 2003, докторская диссертация, онлайн в формате PDF о садомазохизме как культурном стиле. Архивировано 16 ноября 2007 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Лениус, С (2001). «Бисексуалы и БДСМ». Журнал бисексуальности . 1 (№ 4): 69–78. дои : 10.1300/j159v01n04_06 . S2CID 142599575 .
- ^ Таунсенд, Ларри, Справочник Лезермана , Olympia Press, 1972 г., седьмое издание, 2004 г., доступно в LT Publications, почтовый ящик 302, Беверли-Хиллз, Калифорния, 90213-0302.
- ^ сравните Патрика Калифию (ред.), Робина Суини (ред.): Второе пришествие: читатель из Лезердайка . Элисон Пабнс., 1996, ISBN 978-1-55583-281-0
- ↑ Гейл Рубин : «Самой», Leather Times , 21:3–7, 2004, доступно на сайте: Leatherarchives.org. Архивировано 27 марта 2009 г. на Wayback Machine.
- ^ «О ЛА&М» . Leatherarchives.org . Архивировано из оригинала 3 июля 2023 года . Проверено 12 декабря 2023 г.
- ^ «Кожаный флаг гордости» . Leatherarchives.org . Архивировано из оригинала 28 ноября 2023 года . Проверено 12 декабря 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Кожаные мемуары Ринголд Элли - Паблик-арт и архитектура со всего мира» . www.artandarchitecture-sf.com . Архивировано из оригинала 23 июня 2018 года . Проверено 23 июня 2018 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Полл, Лаура (21 июня 2018 г.). «В честь гей-кожаной культуры арт-инсталляцией в переулке СоМа – J» . Дж . Jweekly.com. Архивировано из оригинала 23 июня 2018 года . Проверено 23 июня 2018 г.
- ^ «Альтернативный образ жизни: что им пришлось делать с чатом MSN» . 10 января 2013 г. Архивировано из оригинала 10 января 2013 г.
- ^ Берч, доктор Роберт В. «Секс-игрушки для взрослых» . Кожаные розы. Архивировано из оригинала 23 февраля 2008 года . Проверено 27 января 2008 г.
- ^ «Инвентарь/Игрушки» . Кожаные розы. Архивировано из оригинала 29 января 2008 года . Проверено 27 января 2008 г.
- ^ «Колумбийский университет» . Архивировано из оригинала 21 декабря 2016 года . Проверено 7 ноября 2017 г.
- ^ «Конверсио Вириум» . www.conversiovirium.com . Архивировано из оригинала 29 сентября 2018 года . Проверено 9 января 2020 г.
- ^ «Главная — Университет штата Айова — Студенческие организации» . www.stuorg.iastate.edu . Архивировано из оригинала 7 июля 2018 года . Проверено 14 апреля 2018 г.
- ^ «Fetsoc @ Союз студентов Йоркского университета» . www.yusu.org . Архивировано из оригинала 24 июля 2018 года . Проверено 2 ноября 2017 г.
- ^ «Фетиш» . УЭА СУ . Норидж, Великобритания: Союз студентов Университета Восточной Англии. Архивировано из оригинала 7 ноября 2017 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2023 г.
- ^ «Фетиш» . www.guildofstudents.com . Архивировано из оригинала 24 июля 2018 года . Проверено 2 ноября 2017 г.
- ^ «Имперский колледж Лондона» . Архивировано из оригинала 30 октября 2018 года . Проверено 5 апреля 2018 г.
- ^ «Kinky @ York – Leatherati Online» . 12 января 2010 г. Архивировано из оригинала 25 января 2022 г. . Проверено 7 ноября 2017 г.
- ^ «БДСМ 101 — Студенческие мероприятия — Студенческий союз Университета Калифорнии» . Архивировано из оригинала 17 июня 2018 года . Проверено 14 апреля 2018 г.
- ^ «Каджира Гент — Домашняя страница» . kajira.ugent.be . Архивировано из оригинала 11 августа 2018 года . Проверено 13 августа 2018 г.
- ^ «Отдел студенческой деятельности Национального Тайваньского университета» . Activity.osa.ntu.edu.tw . Архивировано из оригинала 13 августа 2018 года . Проверено 13 августа 2018 г.
- ^ «Программа бакалавриата – факультет антропологии – Университет Индианы в Блумингтоне» . www.indiana.edu . Архивировано из оригинала 5 апреля 2018 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Излом, острые ощущения и согласие: познакомьтесь с профессором, ведущим двойную жизнь эксперта по БДСМ» . 7 октября 2016 г. Архивировано из оригинала 14 августа 2018 г. Проверено 11 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Джули Феннелл — мой.Галлоде» . my.gallaudet.edu . Архивировано из оригинала 13 августа 2018 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Люди — наука БДСМ» . www.scienceofbdsm.com . Архивировано из оригинала 13 августа 2018 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Марго Вайс – доцент кафедры американских исследований и антропологии» . mdweiss.faculty.wesleyan.edu . Архивировано из оригинала 14 августа 2018 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ Холт, Карен (7 апреля 2016 г.). «В черном списке: границы, нарушения и ответное поведение в БДСМ-сообществе» . Девиантное поведение . 37 (8): 917–930. дои : 10.1080/01639625.2016.1156982 . S2CID 147465698 – через Тейлора и Фрэнсиса.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Strafgesetzbuch (StGB)» (PDF) . Законодательство онлайн (на немецком языке). Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 19 апреля 2019 г. Проверено 25 мая 2018 г.
- ^ Баркер, Иантафи и Гупта 2007 .
- ^ Майк Бланчфилд (27 мая 2011 г.). «Женщина не может дать согласие на секс, находясь без сознания, постановил Верховный суд» . Торонто Стар . Архивировано из оригинала 30 мая 2011 года . Проверено 27 мая 2011 г.
- ↑ Решение Bundesgerichtshof от 26 мая 2004 г., 2 StR 505/03, которое можно найти по адресу: BGHSt 49, 166 ( Bundesgerichtshof.de Архивировано 18 ноября 2018 г. в Wayback Machine )
- ↑ Апелляционный суд Хамма в своем решении от 1 февраля 2006 г., дело номер 10 UF 147/04, доступно онлайн на портале Министерства юстиции земли Северный Рейн-Вестфалия. Архивировано 17 декабря 2004 г. на Wayback Machine (немецкий язык).
- ^ Айзад. Архивировано 14 декабря 2007 г. в Wayback Machine , БДСМ - Руководство для исследователей крайнего эротизма , Кастельвекки, 2004 г. ISBN 978-88-7615-025-8
- ^ «Человек освобожден по знаковому делу S&M» . 28 сентября 2010 г. Архивировано из оригинала 21 сентября 2013 г. Проверено 6 октября 2014 г.
- ↑ SM og loven . Архивировано 25 июня 2010 г. в Wayback Machine (норвежский).
- ↑ Группа по интересам БДСМ в Швейцарии. Архивировано 28 декабря 2007 г. в Wayback Machine (немецкий).
- ^ «Представление Spanner Trust в Наблюдательный совет Министерства внутренних дел по вопросам сексуальных преступлений» . Спэннер Траст. Архивировано из оригинала 14 декабря 2007 года . Проверено 27 января 2008 г.
- ^ «История гаечного футляра» . Спаннер Траст . Архивировано из оригинала 17 мая 2011 года . Проверено 8 февраля 2011 г.
- ^ Р против Уилсона (1996). Текст постановления на сайте: «Р против Уилсона (1996) 2 Cr App Rep 241» . LawTeacher.com. Архивировано из оригинала 28 декабря 2010 года . Проверено 8 февраля 2011 г.
- ↑ Палата общин: Законопроект об уголовном правосудии и иммиграции. Архивировано 6 июля 2017 года в Wayback Machine.
- ^ Кендалл, Бен (22 января 2013 г.). «Садовник оправдан в нападении после садомазохистского секс-сеанса по мотивам «Пятидесяти оттенков серого»» . Независимый . Лондон. Архивировано из оригинала 25 сентября 2015 года . Проверено 24 августа 2017 г.
- ^ «ЛЮДИ штата Нью-Йорк, истец, против Оливера ЙОВАНОВИЧА, ответчика» . НайтиПРАВО . 25 сентября 1997 года. Архивировано из оригинала 13 апреля 2021 года . Проверено 13 апреля 2021 г.
- ^ «Уголовные преступления Нью-Джерси» . njlawman.com . Архивировано из оригинала 4 ноября 2016 года . Проверено 28 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ «Синяя книга штата Орегон: инициатива, референдум и отзыв: 1988–1995 годы» (PDF) . штат.или.нас . Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 8 ноября 2018 года . Проверено 28 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ «Реагирование на инцидент» . Национальная коалиция за сексуальную свободу. Архивировано из оригинала 11 октября 2019 года . Проверено 11 октября 2019 г.
- ^ «Всемирный каталог клубов и Мунка» . Worldbdsm.com . Архивировано из оригинала 27 декабря 2007 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2007 г.
- ^ Безре, Таня; Вайнберг, Томас С.; Эдгар, Тимоти (январь 2012 г.). «Раскрытие информации о БДСМ и борьба со стигмой: определение возможностей для полового воспитания» . Американский журнал сексуального образования . 7 (1): 37–61. дои : 10.1080/15546128.2012.650984 . ISSN 1554-6128 . ПМЦ 3382736 . ПМИД 22754406 .
- ^ Романа Бирн (2013) Эстетическая сексуальность: литературная история садомазохизма. Архивировано 22 сентября 2015 года в Wayback Machine , Нью-Йорк: Bloomsbury, стр. 1-4.
- ^ Люминаис, Мисти (май 2012 г.). Привычка быть извращенным: практика и сопротивление в БДСМ-сообществе, Техас (PDF) . Университет штата Вашингтон. п. 121. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 10 ноября 2014 года . Проверено 10 ноября 2014 г.
- ^ «Главная страница эмблемы» . Архивировано из оригинала 24 сентября 2014 года . Проверено 6 октября 2014 г.
- ^ Пионтек, Вольф. «О «Кольце О»: Кольцо О как фетиш и символ БДСМ» . Фетиш-драгоценности . Архивировано из оригинала 12 сентября 2017 года . Проверено 8 августа 2017 г.
- ^ «Информированное согласие: флаг прав БДСМ» . Архивировано из оригинала 2 мая 2013 года.
- ^ «BDSMrights.com» . Архивировано из оригинала 10 мая 2011 года . Проверено 30 марта 2011 г.
- ^ Фуэнтес Родригес, Сезар: Готический мир . (Quarentena Ediciones, 2007, ISBN 978-84-933891-6-1 )
- ^ «Видео, которое не может оставить равнодушным! Нави тащили по полу, тянули за волосы, реально били и пороли в жестоких БДСМ-сценах» . libertatea.ro (на румынском языке). 22 октября 2014 года . Проверено 28 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ «Нави — Picture Perfect — Видео» . shibaridojo.blogspot.ro . 29 апреля 2015 года. Архивировано из оригинала 28 ноября 2016 года . Проверено 28 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ Фальк, Г.; Вайнберг, Т.С. (1983). Садомазохизм и популярная западная культура . Амхерст, Нью-Йорк: Книги Прометея Нью-Йорка. стр. 137–144.
- ^ «Мне нравится покорный секс, но «Пятьдесят оттенков» — это не развлечение, а насилие» . Сексуальность . Хранитель . 25 августа 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 14 сентября 2021 года . Проверено 24 июня 2021 г.
- ↑ Der Standard , издание от 3 сентября 2006 г.
- ↑ BILD -Zeitung, Берлин, 15 марта 1998 г.
- ^ Грин, Эмма (10 февраля 2015 г.). «Согласия недостаточно: тревожный секс пятидесяти оттенков» . Атлантика . Архивировано из оригинала 13 апреля 2021 года . Проверено 13 апреля 2021 г.
- ^ Палья, Камилла (20 мая 2013 г.). «Ученые в рабстве» . Хроника высшего образования . Архивировано из оригинала 26 августа 2018 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2017 г.
- ^ «Работа Бруно Зака «Riding Crop Girl» побила мировой рекорд за 150 602 доллара на арт-аукционе Bonhams» . Просто собираю . 26 июня 2015 года. Архивировано из оригинала 30 июня 2015 года . Проверено 13 апреля 2021 г.
Дальнейшее чтение
- Рехор, Дженнифер Ева (2015). «Чувственное, эротическое и сексуальное поведение женщин из сообщества «кинк»» . Архив сексуального поведения . 44 (№ 4): 825–836. дои : 10.1007/s10508-015-0524-2 . ПМК 4379392 . ПМИД 25795531 .
- Болдуин, Гай . Связывающие узы: SM/Кожа/Фетиш Эротический стиль: проблемы, общение и советы , Daedalus Publishing, 1993. ISBN 978-1-881943-09-9 .
- Баркер, Мэг; Янтафи, А.; Гупта, К. (2007). «Извращенные клиенты, странные консультации? Проблемы и потенциал БДСМ» (PDF) . Открытое онлайн-исследование . Рутледж. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 14 марта 2011 года . Проверено 12 января 2011 г.
- Брэйм, Глория Г. , Брэйм, Уильям Д. и Джейкобс, Джон. Другая любовь: исследование мира сексуального доминирования и подчинения. Villard Books, Нью-Йорк, 1993. ISBN 978-0-679-40873-4
- Брейм, Глория . Приходите сюда: здравое руководство по извращенному сексу , Fireside, 2000. ISBN 978-0-684-85462-5 .
- Калифорния, Пэт . Чувственная магия . Нью-Йорк, Книги Маскарада, 1993. ISBN 978-1-56333-131-2
- Катлер, Берт (февраль 2003 г.). Выбор партнера, динамика власти и сексуальный торг в самоопределяющихся БДСМ-парах (Диссертация). Сан-Франциско: Институт перспективных исследований человеческой сексуальности.
- Федоров, Пол Дж. (2008). «Садизм, садомазохизм, секс и насилие» . Канадский журнал психиатрии . 53 (№ 10): 637–646. дои : 10.1177/070674370805301003 . ПМИД 18940032 .
- Долли Лама. Дневник садомазохистского романа ., ПИП! Пресс (Калифорния), 2006 г., ISBN 978-0-9705392-5-0
- Хенкин, Уильям А., Сибил Холидей. Согласованный садомазохизм: как говорить об этом и как делать это безопасно , Daedalus Publishing, 1996. ISBN 978-1-881943-12-9 .
- Янус, Сэмюэл С. и Янус, Синтия Л. Отчет Януса о сексуальном поведении , John Wiley & Sons, 1994. ISBN 978-0-471-01614-4
- Мастерс, Питер. Этот любопытный человеческий феномен: исследование некоторых необычно изученных аспектов БДСМ . Корпорация Наска-Плейнс, 2008 г. ISBN 978-1-934625-68-2
- Филлипс, Анита . Защита мазохизма , Фабер и Фабер, новое издание 1999 г. ISBN 978-0-571-19697-5
- Ньюмар, Стейси (2011). Игра на грани: садомазохизм, риск и близость . Блумингтон: Издательство Университета Индианы. ISBN 0-253-22285-0 .
- Номис, Энн О. (2013) История и искусство домина Мэри Иган Паблишинг и Анна Номис Ltd, Великобритания ISBN 978-0-9927010-0-0
- Ринелла, Джек. Полный раб: создание и ведение эротического доминантно-покорного образа жизни , Daedalus Publishing, 2002. ISBN 978-1-881943-13-6 .
- Саес, Фернандо и Виньуалес, Ольга, Кожаные шкафы , Изд. Беллатерра, 2007. ISBN 978-84-7290-345-6
- Ларри Таунсенд . «Справочник Лезермана» , первое издание 1972 года (это была первая книга, популяризировавшая БДСМ для широкой публики — это была книга в мягкой обложке, широко доступная в газетных киосках и книжных магазинах по всей территории Соединенных Штатов)
- Уайзман, Джей . SM 101: Реалистическое введение (1-е изд., 1992 г.); 2-е изд. Гринери Пресс , 2000. ISBN 978-0-9639763-8-3
- Бирн, Романа (2013) Эстетическая сексуальность: литературная история садомазохизма. Архивировано 22 сентября 2015 года в Wayback Machine , Нью-Йорк: Блумсбери. ISBN 978-1-4411-0081-8
- Доминари, Раджан (2019). Добро пожаловать в Darkside: Учебник по БДСМ . Издательская компания АКО. ISBN 978-1734527100 .
Внешние ссылки
- «Боль и эротика» Лесли Холл (архивировано 17 декабря 2008 г.)
- Митчелл, Тони (2018). «Эрик Стэнтон и история причудливого подполья» . Фетишисты. Архивировано из оригинала 5 декабря 2018 года . Проверено 4 декабря 2018 г.

