Крупнейшие доисторические животные

К крупнейшим доисторическим животным относятся как позвоночные , так и беспозвоночные виды. Многие из них описаны ниже вместе с типичным диапазоном их размеров (общие даты исчезновения см. по ссылке на каждый из них). Многие упомянутые виды на самом деле могут не быть крупнейшими представителями своей клады из-за неполноты летописи окаменелостей , а многие из приведенных размеров являются лишь приблизительными, поскольку ни один полный экземпляр не был найден. Масса их тела, в частности, во многом является лишь предположением, поскольку мягкие ткани редко окаменели. В целом размер вымерших видов подвергался энергетическому влиянию. [1] и биомеханические ограничения. [2]
Синапсиды немлекопитающих (Synapsida)
[ редактировать ]Caseasaurs (Caseasauria)
[ редактировать ]The herbivorous Alierasaurus was the largest caseid and the largest amniote to have lived at the time, with an estimated length around 6–7 m (20–23 ft).[3] Cotylorhynchus hancocki is also large, with an estimated length and weight of at least 6 m (20 ft)[4] and more than 500 kg (1,100 lb).[5]
Edaphosaurids (Edaphosauridae)
[edit]
The largest edaphosaurids were Lupeosaurus at 3 m (9.8 ft) long[6] and Edaphosaurus, which could reach even more than 3 m (9.8 ft) in length.[7]
Sphenacodontids (Sphenacodontidae)
[edit]The biggest carnivorous synapsid of Early Permian was Dimetrodon, which could reach 4.6 m (15 ft) and 250 kg (550 lb).[8] The largest members of the genus Dimetrodon were also the world's first fully terrestrial apex predators.[9]
Tappenosauridae
[edit]The Middle Permian Tappenosaurus was estimated at 5.5 m (18 ft) in length, nearly as large as the largest dinocephalians.[10]
Therapsids (Therapsida)
[edit]Anomodonts (Anomodontia)
[edit]
The plant-eating dicynodont Lisowicia bojani is the largest-known of all non-mammalian synapsids, at about 4.5 m (15 ft) long, 2.6 m (8 ft 6 in) tall, and 9,000 kg (20,000 lb) in body mass.[11][12][13]
Dinocephalians (Dinocephalia)
[edit]
Among the largest carnivorous non-mammalian synapsids was the dinocephalian Anteosaurus, which was 5–6 m (16–20 ft) long, and weighed 500–600 kg (1,100–1,300 lb).[14][15] Fully grown Titanophoneus from the same family Anteosauridae likely had a skull of 1 m (3.3 ft) long.[15] Another enormous dinocephalian was the Late Permian Eotitanosuchus (a possible synonym to Biarmosuchus[16]). Adult specimens could reach 6 m (20 ft) in length and over 600 kg (1,300 lb) in weight.[16]
Gorgonopsians (Gorgonopsia)
[edit]
Inostrancevia latifrons is the largest known gorgonopsian, with a skull length of more than 60 cm (24 in), a total length approaching 3.5 m (11 ft) and a mass of 300 kg (660 lb).[17] Rubidgea atrox is the largest African gorgonopsian, with skull of nearly 45 cm (18 in) long.[18] Other large gorgonopsians include Dinogorgon with skull of ~40 cm (16 in) long,[19] Leontosaurus with skull of almost 40 cm (16 in) long,[18] and Sycosaurus with skull of ~38 cm (15 in) long.[18]
Therocephalians (Therocephalia)
[edit]The largest of therocephalians is Scymnosaurus,[20][21] which reached a size of the modern hyena.[22]
Non-mammalian cynodonts (Cynodontia)
[edit]- The largest known non-mammalian cynodont is Scalenodontoides, a traversodontid, which had a maximum skull length of approximately 61.7 centimetres (24.3 in) based on a fragmentary specimen.[23]
- Paceyodon davidi was the largest of morganucodontans, cynodonts close to mammals. It is known by a right lower molariform 3.3 mm (0.13 in) in length, which is bigger than molariforms of all other morganucodontans.[24]
- The largest known docodont was Castorocauda, almost 50 cm (20 in) in length.[25]
Mammals (Mammalia)
[edit]Non-therian mammals
[edit]Gobiconodonts (Gobiconodonta)
[edit]
The largest gobiconodont and the largest well-known Mesozoic mammal was Repenomamus.[26][27][28][29][30][31] The known adult of Repenomamus giganticus reached a total length of around 1 m (3 ft 3 in) and an estimated mass of 12–14 kg (26–31 lb).[28] With such parameters it surpassed in size several small theropod dinosaurs of the Early Cretaceous.[32] Gobiconodon was also a large mammal,[30][31] it weighed 5.4 kilograms (12 lb),[28] had a skull of 10 cm (3.9 in) in length, and had 35 cm (14 in) in presacral body length.[33]
Multituberculates (Multituberculata)
[edit]The largest multituberculate[34] Taeniolabis taoensis is the largest non-therian mammal known, at a weight possibly exceeding 100 kg (220 lb).[35]
Monotremes (Monotremata)
[edit]
- The largest known monotreme (egg-laying mammal) ever was the extinct long-beaked echidna species known as Murrayglossus, known from a couple of bones found in Western Australia. It was the size of a sheep, weighing probably up to 30 kg (66 lb).[36]
- The largest known ornithorhynchid is Obdurodon tharalkooschild, it was even larger than 70 cm (28 in)-long Monotrematum sudamericanum.[37]
- Kollikodon was likely the largest monotreme in the Mesozoic. Its body length could be up to a 1 m (3 ft 3 in).[38]
Metatherians (Metatheria)
[edit]
- The largest non-marsupial metatherian was Thylacosmilus, weigh 80 to 120 kilograms (180 to 260 lb),[39][40] one estimate suggesting even 150 kg (330 lb).[41] Proborhyaenid Proborhyaena gigantea is estimated to weigh over 50 kg (110 lb) and possibly reached 150 kg (330 lb).[42] Australohyaena is another large metatherian, weighing up to 70 kilograms (150 lb).[43]
- Stagodontid mammal Didelphodon was one of the largest Mesozoic metatherians and all Cretaceous mammals.[44] Its skull could reach over 10 centimetres (3.9 in) in length[45] and a weight of complete animal was 5.2 kilograms (11 lb).[46]
Marsupials (Marsupialia)
[edit]- The largest known marsupial, and the largest metatherian, is the extinct Diprotodon, about 3 m (9.8 ft) long, standing 2 m (6 ft 7 in) tall and weighing up to 2,786 kg (6,142 lb).[47] Fellow vombatiform Palorchestes azael was similar in length being around 2.5 m (8.2 ft), with body mass estimates indicating it could exceed 1,000 kg (2,200 lb).[48]
- The largest known carnivorous marsupial was Thylacoleo carnifex. Measurements taken from a number of specimens show they averaged 101 to 164 kg (223 to 362 lb) in weight.[49][50]
- The largest known kangaroo was an as yet unnamed species of Macropus, estimated to weigh 274 kg (604 lb),[51] larger than the largest known specimen of Procoptodon, which could grow up to 2 m (6 ft 7 in) and weigh 230 kg (510 lb).[52] Some species from the genus Sthenurus were similar in size or a bit larger than the extant grey kangaroo (Macropus giganteus).[53]
- The largest potoroid ever recorded was Borungaboodie, which was nearly 30% bigger than the largest living species and weighted up to 10 kg (22 lb).[54]
Non-placental eutherians
[edit]
Cimolestans (Cimolesta)
[edit]The largest known cimolestan is Coryphodon, 1 m (3 ft 3 in) high at the shoulder, 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) long[55][56] and up to 700 kg (1,500 lb) of mass.[57] Barylambda was also a huge mammal, at 650 kg (1,430 lb).[58] Wortmania and Psittacotherium from the group Taeniodonta were among the largest mammals of the Early Paleocene.[59] Lived as soon as half a million years after K–Pg boundary, Wortmania reached 20 kg (44 lb) in body mass. Psittacotherium, which appeared two million years later, reached 50 kg (110 lb).[59]
Leptictids (Leptictida)
[edit]The largest leptictid ever discovered is Leptictidium tobieni from the Middle Eocene of Germany. It had a skull 101 mm (4.0 in) long, head with trunk 375 mm (14.8 in) long, and tail 500 mm (20 in) long.[60] Close European relatives from the same family Pseudorhyncocyonidae had skulls of 67–101 mm (2.6–4.0 in) in length.[60]
Tenrecs and allies (Afroscida)
[edit]The larger of the two species of bibymalagasy (Plesiorycteropus madagascariensis), extinct tenrec relatives from Madagascar, is estimated to have weighed from 10 to 18 kilograms (21 to 40 lb).[61]
Even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla)
[edit]
- The largest known land-dwelling artiodactyl was Hippopotamus gorgops with a length of 4.3 m (14 ft), a height of 2.1 m (6 ft 11 in), and a weight of 5 t (11,000 lb).[62]
- Daeodon and similar in size and morphology Paraentelodon[63] were the largest-known entelodonts that ever lived, at 3.7 m (12 ft) long and 1.77 m (5.8 ft) high at the shoulder.[64] The huge Andrewsarchus from the Eocene of Inner Mongolia had skull 83.4 cm (32.8 in) long[65] though the taxonomy of this genus is disputed.[66][67]

- The largest of Bovinae as well as the largest bovid was Bison latifrons. It reached a weight from 1,250 kg (2,760 lb)[68][69] to 2,000 kg (4,400 lb),[70] 4.75 m (15.6 ft) in length, shoulder height of 2.31 m (7.6 ft),[71] and had horns that spanned 2.13 m (7 ft 0 in).[72] The North American Bison antiquus reached up to 4.6 m (15 ft) long, 2.27 m (7.4 ft) tall, weight of 1,588 kg (3,501 lb),[73] and horn span of 1 m (3.3 ft).[71] The African Pelorovis reached 2 t (2.2 short tons) in weight and had bony cores of the horns about 1 m (3 ft 3 in) long.[74] Another enormous bovid, the african giant buffalo (Syncerus antiquus) reached 3 m (9.8 ft) in length from muzzle to the end of the tail, 1.85 m (6.1 ft) in height at the withers, 1.7 m (5.6 ft) in height at the hindquarters,[75][76] and the distance between the tips of its horns was as large as 2.4 m (7 ft 10 in).[75] Aside from local populations and subspecies of extant species, such as the gaur population in Sri Lanka, European bison in British Isles, Caucasian wisent and Carpathian wisent, the largest modern extinct bovid is aurochs (Bos primigenius) with an average height at the shoulders of 155–180 cm (61–71 in) in bulls and 135–155 cm (53–61 in) in cows, while aurochs populations in Hungary had bulls reaching 155–160 cm (61–63 in).[77] The kouprey (Bos sauveli), reaching 1.7–1.9 m (5 ft 7 in – 6 ft 3 in) in shoulder height,[78][79] has existed since the Middle Pleistocene[80] and is also considered to be possibly extinct.[81][82]
- The long-legged Megalotragus is possibly the largest known alcelaphine bovid,[83] bigger than the extant wildebeest.[84] The tips of horns of M. priscus were located at a distance of about 1.2 m (3 ft 11 in) from each other.[85]

- The extinct cervid Irish elk (Megaloceros giganteus) reached over 2.1 m (7 ft) in height, 680 kg (1,500 lb) in mass and could have antlers spanning up to 4.3 m (14 ft) across, about twice the maximum span for a moose's antlers.[86][87] The giant moose (Cervalces latifrons) reached 2.1 to 2.4 m (6.9 to 7.9 ft) high[88] and was twice as heavy as the Irish elk but its antler span at 2.5 m (8.2 ft) was smaller than that of Megaloceros.[89][90] North American stag-moose (Cervalces scotti) reached 2.5 metres (8.2 ft) in length and a weight of 708.5 kilograms (1,562 lb).[91][92]
- The largest known giraffid, aside from the extant giraffe, is Sivatherium, with a body weight of 1,250 kg (2,760 lb).[93]
- The largest protoceratid was Synthetoceras, it reached 2 m (6 ft 7 in) long and 150–200 kg (330–440 lb) in mass.[94][95]
- The largest known wild suid to ever exist was Kubanochoerus gigas, having measured up to 500 kg (1,100 lb) and stood around 1 m (3 ft 3 in) tall at the shoulder.[96] Megalochoerus could be similar in size, possibly weighing 303 kg (668 lb) or 526 kg (1,160 lb).[97]
- The largest tayassuid extinct Platygonus species were similar in size to modern peccaries especially giant peccary, at around 1 m (3.3 ft) in body length, and had long legs, allowing them to run well. They also had a pig-like snout and long tusks which were probably used to fend off predators.[98]
- The largest camelid was Titanotylopus from the Miocene of North America. It possibly reached 2,485.6 kg (5,480 lb) and a shoulder height of over 3.4 m (11 ft).[99][100] The Syrian camel (Camelus moreli) was twice as big as the modern camels.[101] It was 3 m (9.8 ft) at the shoulder[102] and 4 m (13 ft) tall.[101] Camelops had legs to be 20% longer than that of Dromedary, and was about 2.3 m (7 ft 7 in) tall at the shoulder and weighed about 1,000 kg (2,200 lb).[103]
Cetaceans (Cetacea)
[edit]
- The heaviest archeocete, and possibly the heaviest known mammal was Perucetus, with weight estimated at 85–340 t (84–335 long tons; 94–375 short tons), while length is estimated at 17.0–20.1 meters (55.8–65.9 ft).[104] The longest of known Eocene archeocete whales was Basilosaurus at 17–20 m (56–66 ft) in length.[105][106][107]
- The largest squalodelphinid was Macrosqualodelphis at 3.5 m (11 ft) in length.[108]
- Some Neogene rorquals were comparable in size to modern huge relatives. Parabalaenoptera was estimated to be about the size of the modern gray whale,[109] about 16 m (52 ft) long. Some balaenopterids perhaps rivaled the blue whale in terms of size,[109] though other studies disagree that any baleen whale grew that large in the Miocene.[110]
Odd-toed ungulates (Perissodactyla)
[edit]

- The largest known perissodactyl, and the second largest land mammal (see Palaeoloxodon namadicus) of all time was the hornless rhino Paraceratherium. The largest individual known was estimated at 4.8 m (15.7 ft) tall at the shoulders, 7.4 m (24.3 ft) in length from nose to rump, and 17 t (18.7 short tons) in weight.[111][112]
- Some prehistoric horned rhinos also grew to large sizes. The biggest Elasmotherium reached up to 5–5.2 m (16–17 ft) long,[113] 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) high[114] and weighed 3.5–5 t (3.9–5.5 short tons).[115][113][114] Such parameters make it the largest rhino of the Quaternary.[115] Woolly rhinoceros (Coelodonta antiquitatis) of the same time reached 1,100–1,500 kg (2,400–3,300 lb)[116] or 2,000 kg (4,400 lb),[117][118] 1.93 m (6 ft 4 in) at the shoulder height and 4.6 m (15 ft) in length.[119]
- Metamynodon, an amynodontid, reached 4 m (13 ft) in length, comparable to Hippopotamus in measurement and shape.[120]
- The giant tapir (Tapirus augustus) was the largest tapir ever, at about 623 kg (1,373 lb)[121] and 1 m (3.3 ft) tall at the shoulders.[122] Earlier, this mammal was estimated even bigger, at 1.5 m (4.9 ft) tall, and assigned to the separate genus Megatapirus.[122]
- One of the biggest chalicotheres was Moropus.[123] It stood about 2.4 metres (8 ft) tall at the shoulder.[124]
- Late Eocene perissodactyls from the family Brontotheriidae attained huge sizes. The North American Megacerops (also known as Brontotherium[125]) reached 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) tall at the shoulders,[126] 5 m (16 ft) in length,[125] and 3 t (6,600 lb) in weight.[127] Embolotherium from Asia was equal in size.[128]
- The largest prehistoric horse was Equus giganteus of North America. It was estimated to grow to more than 1,250 kg (1.38 short tons) and 2 m (6 ft 7 in) at the shoulders.[129] The largest anchitherine equid was Hypohippus at 403 to 600 kg (888 to 1,323 lb), comparable to large modern domestic horses.[130][131] Megahippus is another large anchitheriine. With the body mass of 266.2 kg (587 lb) it was much heavier than most of its close relatives.[130]
Phenacodontids (Phenacodontidae)
[edit]The largest known phenacodontid is Phenacodus. It was 1.5 m (4 ft 11 in) long[132] and weighed up to 56 kg (123 lb).[133]
Dinoceratans (Dinocerata)
[edit]The largest known dinoceratan was Eobasileus with skull length of 102 cm (40 in), 2.1 m (6 ft 11 in) tall at the back and 1.5 m (4 ft 11 in) tall at the shoulder.[134] Another huge animal of this group was Uintatherium, with skull length of 76 cm (30 in), 1.5 m (4 ft 11 in) tall at the shoulder,[134] 4 m (13 ft) in length and 2.25 t (2.48 short tons), the size of a rhinoceros.[135] Despite their large size, Eobasileus as well as Uintatherium had a very small brain.[134][135]
Carnivores (Carnivora)
[edit]Caniformia
[edit]


- The largest terrestrial mammalian carnivore and the largest known bear, as well as the largest known mammalian land predator of all time, was Arctotherium angustidens, the South American short-faced bear. A humerus of A. angustidens from Buenos Aires indicates that the males of the species could have weighed 1,588–1,749 kg (3,501–3,856 lb) and stood at least 3.4 m (11 ft) tall on their hind-limbs.[136][137] Another huge bear was the giant short-faced bear (Arctodus simus), with the average weight of 625 kg (1,378 lb) and the maximum estimated at 957 kg (2,110 lb).[138] There is a guess that the largest individuals of this species could reached even larger mass, up to 1,200 kg (2,600 lb).[139] The extinct cave bear (Ursus spelaeus) was also heavier than many recent bears. Largest males weighed as much as 1,000 kg (2,200 lb).[140] Ailuropoda baconi from the Pleistocene was larger than the modern giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca).[141]
- The biggest odobenid and one of the biggest pinnipeds to have ever existed is Pontolis magnus, with a skull length of 60 cm (24 in) (twice as large as the skulls of modern male walruses)[142] and having a total body length of more than 4 m (13 ft).[143][144] Only the modern male elephant seals (Mirounga) reach similar sizes.[143] The second largest prehistoric pinniped is Gomphotaria pugnax with a skull length of nearly 47 cm (19 in).[142]
- One of the largest of prehistoric otariids is Thalassoleon, comparable in size to the biggest extant fur seals. An estimated weight of T. mexicanus is no less than 295–318 kg (650–701 lb).[145]
- The biggest known mustelid to ever exist was likely the giant otter, Enhydriodon. It exceeded 3 m (9.8 ft) in length, and would have weighed in at around 200 kg (440 lb), much larger than any other known mustelid, living or extinct.[146][147][148] There were other giant otters, like Siamogale, at around 50 kg (110 lb)[149] and Megalenhydris, which was larger than a modern-day giant river otter.[150] Megalictis was the largest purely terrestrial mustelid[151] (although Enhydriodon had recently been mentioned as the largest mustelid that also happens to be a terrestrial predator[146]). Similar in size to the jaguar, Megalictis ferox had even wider skull, almost as wide as of the black bear.[151] Megalictis had a powerful bite force, allowing it to eat large prey and crush bones, as modern hyenas and jaguars can.[151] Another large-bodied mustelid was the superficially cat-like Ekorus from the Miocene of Africa. At almost 44 kg (97 lb), the long-legged Ekorus was about the size of a wolf[152] and filling a similar to leopards ecological niche before big cats came to the continent.[153] Other huge mustelids include Perunium[154] and hypercarnivorous Eomellivora, both from the Late Miocene.[155]
- The heaviest procyonid was possibly South American Chapalmalania. It reached 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) in body length with a short tail and 150 kilograms (330 lb), comparable in size to an American black bear (Ursus americanus).[156] Another huge procyonid was Cyonasua, which weighted about 15–25 kg (33–55 lb), about the same size as a medium-sized dog.[157]
- The largest canid of all time was Epicyon haydeni, which stood 90 cm (35 in) tall at the shoulder, had a body length of 2.4 m (7.9 ft) and weighed 100–125 kg (220–276 lb),[158][159][160] with the heaviest known specimen weighing up to 170 kg (370 lb).[41] The extinct dire wolf (Aenocyon dirus) reached 1.5 m (4 ft 11 in) in length and weighed between 50 and 110 kg (110 and 243 lb).[41][161] The largest wolf (Canis lupus) subspecies ever existed in Europe is the Canis lupus maximus from the Late Pleistocene of France. Its long bones are 10% larger than those of extant European wolves and 20% longer than those of C. l. lunellensis.[162] The Late Pleistocene Italian wolf was morphometrically close to C. l. maximus.[163]
- The largest bear-dog was a species of Pseudocyon weighing around 773 kg (1,704 lb), representing a very large individual.[164]
Feliformia
[edit]

- The largest nimravid was probably Quercylurus major as its fossils suggest it was similar in size to the modern-day brown bear and was scansorial.[165] In 2021, Eusmilus was declared as the largest of the holplophonine nimravids, reaching the weight of nearly 111 kg (245 lb), comparable to a small African lion.[166] However, the largest Hoplophoneus was estimated at 160 kg (350 lb).[41]
- The biggest saber-toothed cats are Amphimachairodus kabir and Smilodon populator, with the males possibly reaching 350–490 kg (770–1,080 lb) and 220–450 kg (490–990 lb) respectively.[41][167][168] Another contender for the largest felid of all time is Machairodus. M. horribilis from China was estimated at 405 kg (893 lb)[169] while the North American M. lahayishupup weighed up to 410 kg (900 lb).[170][171][172] Xenosmilus was also a huge cat. It reached around 2 m (6.6 ft) long[173] and weighed around 300–350 kg (660–770 lb).[169]
- The heaviest known pantherine felids are the Ngangdong tiger (Panthera tigris soloensis), which are estimated to have weighed up to 486 kg (1,071 lb),[168] the American lion (Panthera atrox), weighing up to 363 kg (800 lb),[174][175] the Eurasian cave lion (Panthera spelaea), weighing up to 339 kg (747 lb),[168] and the Natodomeri lion of eastern Africa, which was comparable in size to large members of P. atrox.[176] Being the ancestor of the modern jaguar,[177] Panthera gombaszoegensis was much larger, up to 150 kg (330 lb) in maximum weight.[177]
- Some extinct feline felids also surpassed their modern relatives in size. The Eurasian giant cheetah (Acinonyx pardinensis) reached 60–121 kg (132–267 lb), approximately twice as large as the modern cheetah.[178] The North American Pratifelis was larger than the extant cougar.[179]
- The largest barbourofelid was Barbourofelis fricki, with the shoulder height of 90 cm (35 in).[180]
- The largest viverrid known to have existed is Viverra leakeyi, which was around the size of a wolf or small leopard at 41 kg (90 lb).[181]
- The largest known fossil hyena is Pachycrocuta, estimated at 90–100 cm (35–39 in) at the shoulder[182] and 190 kg (420 lb) weight.[41] Another huge hyena with mass over 100 kg (220 lb) is the cave hyena. It is actually a subspecies of the African spotted hyena, which is at 10% smaller than the extinct cave hyena.[183]
- The percrocutid feliform, Dinocrocuta, was two or even three times as large as the extant spotted hyena, 160 or 240 kg (350 or 530 lb).[184]
- The extinct giant fossa (Cryptoprocta spelea) had a body mass in range from 17 kg (37 lb)[185] to 20 kg (44 lb),[186] much larger than the modern fossa weighs (up to 8.6 kg (19 lb) for adult males[187]).
Hyaenodonts (Hyaenodonta)
[edit]The largest hyaenodont was Simbakubwa at 1,500 kg (3,300 lb).[188] Another giant hyaenodont, Megistotherium reached 500 kg (1,100 lb)[41] and had a skull of 66.4 cm (26.1 in) in length.[189]
Oxyaenids (Oxyaenidae)
[edit]
The largest known oxyaenid was Sarkastodon weighing in at 800 kg (1,800 lb).[41]
Mesonychians (Mesonychia)
[edit]Some mesonychians reached a size of a bear. Such large were Mongolonyx from Asia[190] and Ankalagon from North America.[191][192] Another large mesonychian is Harpagolestes with a skull length of a half a meter in some species.[190]
Bats (Chiroptera)
[edit]Found in Quaternary deposits of South and Central Americas, Desmodus draculae had a wingspan of 0.5 m (20 in) and a body mass of up to 60 g (2.1 oz). Such proportions make it the largest vampire bat that ever evolved.[193]
Hedgehogs, gymnures, shrews, and moles (Eulipotyphla)
[edit]
The largest known animal of the group Eulipotyphla was Deinogalerix,[194] measuring up to 60 cm (24 in) in total length, with a skull up to 21 cm (8.3 in) long.[195]
Rodents (Rodentia)
[edit]
- Several of the extinct South American dinomyids were much bigger than the modern rodents. Josephoartigasia monesi was the largest-known rodent of all time, approximately weighing an estimated 480–500 kg (1,060–1,100 lb).[196] Phoberomys pattersoni weighed 125–150 kg (276–331 lb).[196] Both Josephoartigasia and Phoberomys reached about 1.5 m (4 ft 11 in) tall at the shoulder.[197] Another huge dinomyid, Telicomys gigantissimus had a minimal weight of 200 kg (440 lb).[197]
- Amblyrhiza inundata from the family Heptaxodontidae was a massive animal, it weighed 50–200 kg (110–440 lb).[198][197]
- The largest beaver was the giant beaver (Castoroides) of North America. It grew over 2 m in length and weighed roughly 90 to 125 kg (198 to 276 lb), also making it one of the largest rodents to ever exist.[199]
- The largest old world porcupine are the Hystrix refossa was larger than living porcupines. It was approximately 20% larger than its closest relative, the living Indian porcupine (H. indica), reaching lengths of over 115 cm (45 in).
Rabbits, hares, and pikas (Lagomorpha)
[edit]The biggest known prehistoric lagomorph is Minorcan giant lagomorph Nuralagus rex at 12 kg (26 lb).[200]
Pangolins (Pholidota)
[edit]The largest pangolin was the extinct Manis palaeojavanica [201] Its total length is measured up to 2.5 m (8.2 ft).[202]
Primates (Primates)
[edit]
- The largest known primate as well as the largest hominid of all time was Gigantopithecus blackii, standing 3 m (9.8 ft) tall and weighing 540 kg (1,200 lb).[203][204] However In 2017, new studies suggested a body mass of 200–300 kg (440–660 lb) for this primate.[205] Another giant hominid was Meganthropus palaeojavanicus at 2.4 m (7 ft 10 in) in body height,[206] although it is known from very poor remains.[207]
- During the Pleistocene, some archaic humans were close in sizes or even larger than early modern humans. Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis) reached 77.6 kg (171 lb) and 66.4 kg (146 lb) in average weight for males and females, respectively, larger than the parameters of modern humans (Homo sapiens) (68.5 kg (151 lb) and 59.2 kg (131 lb) for males and females, respectively).[208] A tibia from Kabwe (Zambia) indicates an indeterminate Homo individual of possibly 181.2 cm (71.3 in) in height. It was one of the tallest humans of the Middle Pleistocene and noticeably large even compared to recent humans.[209] The tallest Homo sapiens individuals from the Middle Pleistocene of Spain reached 194 cm (76 in) and 174 cm (69 in) for males and females, respectively.[209] Some Homo erectus could be as large as 185 cm (73 in) tall and 68 kg (150 lb) in weight.[210][211]
- The largest known Old World monkey is the prehistoric baboon, with a male specimen of Dinopithecus projected to weigh an average of 46 kg (101 lb) and up to 57 kg (126 lb).[212] It exceeds the maximum weight record of the chacma baboon, the largest extant baboon. One source projects a specimen of Theropithecus oswaldi to have weighed 72 kg (159 lb).[213]
- The largest known New World monkey was Cartelles, which is studied as specimen of Protopithecus, weighing up to 34.27 kg (75.6 lb). Caipora bambuiorum is another large species, weighing up to 27.74 kg (61.2 lb).[214]
- The largest omomyids were Macrotarsius and Ourayia from the Middle Eocene. Both reached 1.5–2 kg (3.3–4.4 lb) in weight.[215]
- Some prehistoric lemuriform primates grew to huge sizes as well. Archaeoindris was a 1.5-metre-long (4.9 ft) sloth lemur that lived in Madagascar and weighed 150–187.8 kg (331–414 lb),[216] as large as an adult male gorilla.[217] Palaeopropithecus from the same family was also heavier than most modern lemurs, at 25.8–45.8 kg (57–101 lb).[218] Megaladapis is another large extinct lemur at 1.3 to 1.5 m (4 ft 3 in to 4 ft 11 in) in length[citation needed] and an average body mass of around 140 kg (310 lb).[219] Other estimates suggest 46.5–85.1 kg (103–188 lb) but its still much larger than any extant lemur.[218]
Elephants, mammoths, and mastodons (Proboscidea)
[edit]

- The largest known land mammal ever was a proboscidean called Palaeoloxodon namadicus which weighed about 22 t (24.3 short tons) and measured about 5.2 m (17.1 ft) tall at the shoulder.[111] The largest individuals of the steppe mammoth of Eurasia (Mammuthus trogontherii) estimated to reach 4.5 m (14.8 ft) at the shoulders and 14.3 t (15.8 short tons) in weight.[111][220] Stegodon zdanskyi, the biggest species of Stegodon, was 13 t (14.3 short tons) in body mass.[111] Another enormous proboscidean is Stegotetrabelodon syrticus, over 4 m (13 ft) in height and 11 to 12 t (12.1 to 13.2 short tons) in weight.[111] The Columbian mammoth (Mammuthus columbi) was about 4 m (13.1 ft) tall at the shoulder but didn't weigh as much as other huge mammoths. Its average mass was 9.5 t (10.5 short tons) with one unusually large specimen about 12.5 t (13.8 short tons).[111] Columbian mammoths had very long tusks. The largest known mammoth tusk, 4.9 m (16 ft) long, belonged to this species.[221]
- The largest mammutid was the Neogene Mammut borsoni. The biggest specimen reached 4.1 m (13 ft) tall and weighed about 16 t (17.6 short tons).[111] This species also had the longest tusks, 5.02 m (16.5 ft) long from basis to tip along the curve.[222]
- Deinotherium was the largest proboscidean in Deinotheriidae family. Bones retrieved in Crete confirm the existence of specimen 4.1 m (13 ft) tall at the shoulders and more than 14 t (15.4 short tons) in weight.[111]
Sea cows (Sirenia)
[edit]According to reports, Steller's sea cows have grown to 8 to 9 m (26 to 30 ft) long as adults, much larger than any extant sirenians.[223] The weight of Steller's sea cows is estimated to be 8–10 t (8.8–11.0 short tons).[224]
Arsinoitheres (Arsinoitheriidae)
[edit]
The largest known arsinoitheriid was Arsinoitherium. A. zitteli would have been 1.75 m (5 ft 9 in) tall at the shoulders, and 3 m (9.8 ft) long.[225][226] A. giganteum reached even larger size than A. zitteli.[227]
Hyraxes (Hyracoidea)
[edit]Some of the prehistoric hyraxes were extremely large compared to modern small relatives. The largest hyracoid ever evolved is Titanohyrax ultimus.[228] With the mass estimation in rage of 600 kg (1,300 lb) to over 1,300 kg (2,900 lb) it was close in size to Sumatran rhinoceros.[229] Another enormous hyrax is Megalohyrax which had skull of 391 mm (15.4 in) in length[230] and reached the size of tapir.[231][228] More recent Gigantohyrax was three times as large as the extant relative Procavia capensis,[232] although it is noticeably smaller than earlier Megalohyrax and Titanohyrax.[233]
Desmostylians (Desmostylia)
[edit]
The largest known desmostylian was a species of Desmostylus, with skull length of 81.8 cm (32.2 in) and comparable in size to the Steller's sea cow.[234]
Paleoparadoxia is also known as one of the largest desmostylians, with body length of 3.03 m (9.9 ft).[235]
Armadillos, glyptodonts and pampatheres (Cingulata)
[edit]The largest cingulate known is Doedicurus, at 4 m (13 ft) long, 1.5 m (4 ft 11 in) high[135] and reaching a mass of approximately 1,910 to 2,370 kg (2.11 to 2.61 short tons).[citation needed] The largest species of Glyptodon, Glyptodon clavipes, reached 3–3.3 m (9.8–10.8 ft) in length[236][135] and 2 t (2.2 short tons) in weight.[citation needed]
Anteaters and sloths (Pilosa)
[edit]The largest known pilosan is Eremotherium, a ground sloth with an estimated weight of up to 6.55 t (7.22 short tons) and a length of up to 6 m (20 ft),[237] which is as big as a bull African bush elephant. The closely related ground sloth Megatherium attained similarly large dimensions.[238]
Astrapotherians (Astrapotheria)
[edit]Some of the largest known astrapotherians weighed about 3–4 t (3.3–4.4 short tons), including the genus Granastrapotherium[239] and some species of Parastrapotherium (P. martiale).[240] The skeleton remains suggests that the species Hilarcotherium miyou was even larger, with a weight of 6.456 t (7.117 short tons).[241]
Litopterns (Litopterna)
[edit]The largest known litoptern was Macrauchenia, which had three hoofs per foot. It was a relatively large animal, with a body length of around 3 m (9.8 ft).[242]
Notoungulates (Notoungulata)
[edit]The largest notoungulate known of complete remains is Toxodon. It was about 2.7 m (8 ft 10 in) in body length, and about 1.5 m (4 ft 11 in) high at the shoulder and resembled a heavy rhinoceros. Although incomplete, the preserved fossils suggests that Mixotoxodon were the most massive member of the group, with a weight about 3.8 t (4.2 short tons).[243]
Pyrotherians (Pyrotheria)
[edit]The largest mammal of the South American order Pyrotheria was Pyrotherium at 2.9–3.6 m (9 ft 6 in – 11 ft 10 in) in length and 1.8–3.5 t (4,000–7,700 lb) in weight.[244]
Reptiles (Reptilia)
[edit]Lizards and snakes (Squamata)
[edit]
- Mosasaurs are the largest-known squamates. The largest-known mosasaur is likely Mosasaurus hoffmanni, estimated at more than 17 m (56 ft) in length,[245][246] however these estimations are based on heads and total body length ratio 1:10, which is unlikely for Mosasaurus, and probably that ratio is about 1:7.[247] Another giant mosasaur is Tylosaurus, estimated at 10–14 m (33–46 ft) in length.[248][249] Another mosasaur, Prognathodon can reach similar size.
- The largest known prehistoric snake is Titanoboa cerrejonensis, estimated at 12.8 m (42 ft) or even 14.3 m (47 ft)[250] in length and 1,135 kg (2,502 lb) in weight,[251] and madtsoiid Vasuki indicus which is estimated to reach between 11–15 m (36–49 ft).[252] A close rival in size to those snakes is palaeophiid marine snake Palaeophis colossaeus, which may have been around 9 m (30 ft) in length[251][253][254] or even up to 12.3 m (40 ft).[255] Another known very large fossil snake is Gigantophis garstini, estimated at 9.3–10.7 m (31–35 ft) in length,[256][257] although later study shows smaller estimation about 6.6–7.2 m (22–24 ft).[258] The largest fossil python is Liasis dubudingala with length roughly 9 m (30 ft).[259] The largest viper as well as the largest venomous snake ever recorded is Laophis crotaloides from the Early Pliocene of Greece. This snake reached over 3 m (9.8 ft) in length and 26 kg (57 lb) in weight.[260][261] Another huge fossil viper is indeterminate species of Vipera. With a length of around 2 m (6 ft 7 in) it was one of the biggest predators of Mallorca during the Early Pliocene.[262] The largest known blind snake is Boipeba tayasuensis with estimated total length of 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in).[263]
- The largest known land lizard is probably megalania (Varanus priscus) at 7 m (23 ft) in length.[264] As extant relatives, megalania could have been venomous and in that case this lizard was also the largest venomous vertebrate ever evolved.[265] However, maximum size of this animal is subject to debate.[266]
Turtles, tortoises and close relatives (Pantestudines)
[edit]Cryptodira
[edit]- The largest known turtle ever was Archelon ischyros at 5 m (16 ft) long and 2,200 kg (4,900 lb).[267] Possible second-largest sea turtle was Protostega at 3.9 m (13 ft) in total body length.[268][269] There is even a larger specimen of this genus from Texas estimated at 4.2 m (14 ft) in total length.[270][268] Partially known Cratochelone is estimated to reach 4 m (13 ft) in total length.[271] Another huge prehistoric sea turtle is the Late Cretaceous Gigantatypus, estimated at over 3.5 m (11 ft) in length.[272] Psephophorus terrypratchetti from the Eocene attained 2.3–2.5 m (7.5–8.2 ft) in body length.[273]
- The largest tortoise was Megalochelys atlas at up to 2 m (6.6 ft) in shell length[274] and weighing 0.8–1.0 t (1,800–2,200 lb).[127] M. margae had carapace of 1.4–2 m (4.6–6.6 ft) long; an unnamed species from Java reached at least 1.75 m (5.7 ft) in carapace length.[275] The Cenozoic Titanochelon were also larger than extant giant tortoises, with a shell length of up to 2 m (6 ft 7 in).[276][277] Other giant tortoises include Centrochelys marocana at 1.8–2 m (5.9–6.6 ft) in carapace length and Mesoamerican Hesperotestudo sp. at 1.5 m (4.9 ft) in carapace length.[275]
- The largest trionychid ever recorded is indeterminate specimen GSP-UM 3019 from the Middle Eocene of Pakistan. Bony carapace of GSP-UM 3019 is 120 cm (3.9 ft) long and 110 cm (3.6 ft) wide indicates the total carapace diameter (with soft margin) about 2 m (6.6 ft).[278] Drazinderetes tethyensis from the same formation had a bony carapace 80 cm (2.6 ft) long and 70 cm (2.3 ft) wide.[278] Another huge trionychid is North American Axestemys byssinus at over 2 m (6.6 ft) in total length.[279]
Side-necked turtles (Pleurodira)
[edit]
The largest freshwater turtle of all time was the Miocene podocnemid Stupendemys, with an estimated parasagittal carapace length of 2.86 m (9 ft 5 in) and weight of up to 1,145 kg (2,524 lb).[280] Carbonemys cofrinii from the same family had a shell that measured about 1.72 m (5 ft 8 in),[281][282][283] complete shell was estimated at 1.8 m (5.9 ft).[284]
Macrobaenids (Macrobaenidae)
[edit]The largest macrobaenids were the Early Cretaceous Yakemys, Late Cretaceous Anatolemys, and Paleocene Judithemys. All reached 70 cm (2.3 ft) in carapace length.[285]
Meiolaniformes
[edit]
The largest meiolaniid was Meiolania. Meiolania platyceps had a carapace 100 cm (3.3 ft) long[275] and probably reached over 3 m (9.8 ft) in total body length.[286] An unnamed Late Pleistocene species from Queensland was even larger, up to 200 cm (6.6 ft) in carapace length.[275] Ninjemys oweni reached 100 cm (3.3 ft) in carapace length[275] and 200 kg (440 lb) in weight.[287]
Sauropterygians (Sauropterygia)
[edit]Placodonts and close relatives (Placodontiformes)
[edit]Placodus was among the largest placodonts, with a length of up to 3 m (9.8 ft).[288]
Nothosaurs and close relatives (Nothosauroidea)
[edit]The largest nothosaur as well as the largest Triassic sauropterygian was Nothosaurus giganteus at 7 m (23 ft) in length.[289]
Plesiosaurs (Plesiosauria)
[edit]- The largest known plesiosauroid was an indeterminate specimen possibly belonging to Aristonectes (identified as cf. Aristonectes sp.), with a body length of 11–11.9 metres (36–39 ft) and body mass of 10.7–13.5 metric tons (11.8–14.9 short tons).[290] Another long plesiosauroid was Albertonectes at 11.2–11.6 metres (37–38 ft).[291] Thalassomedon rivaled it in size, with its length at 10.86–11.6 m (35.6–38.1 ft).[292] Other large plesiosauroids are Styxosaurus and Elasmosaurus. Both reached some more than 10 m (33 ft) in length.[293][294] Hydralmosaurus (previously synonymized with Elasmosaurus and Styxosaurus) reached 9.44 m (31.0 ft) in total body length.[294] In past, Mauisaurus was considered to be more than 8 m (26 ft) in length,[295][294] but later it was determined as nomen dubium.[296]

- There is much controversy over the largest-known of the Pliosauroidea. Pliosaurus funkei (also known as "Predator X") is a species of large pliosaur, known from remains discovered in Norway in 2008. This pliosaur has been estimated at 10–13 m (33–43 ft) in length.[297] However, in 2002, a team of paleontologists in Mexico discovered the remains of a pliosaur nicknamed as "Monster of Aramberri", which is also estimated at 15 m (49 ft) in length,[298] with shorter estimation about 11.5 m (38 ft).[299] This species is, however, claimed to be a juvenile and has been attacked by a larger pliosaur.[300] Some media sources claimed that Monster of Aramberri was a Liopleurodon but its species is unconfirmed thus far.[298] Another very large pliosaur was Pliosaurus macromerus, known from a single 2.8-metre-long (9.2 ft) incomplete mandible.[301] The Early Cretaceous Kronosaurus queenslandicus is estimated at 9–10.9 m (30–36 ft) in length and 10.6–12.1 t (11.7–13.3 short tons) in weight.[302][303] The Late Jurassic Megalneusaurus rex could reach lengths of 7.6–9.1 metres (25–30 ft).[304][305] Close contender in size was the Late Cretaceous Megacephalosaurus eulerti with a length in range of 6–9 m (20–30 ft).[306]
Proterosuchids (Proterosuchidae)
[edit]Proterosuchus fergusi is the largest known proterosuchid with a skull length of 47.7 cm (18.8 in) and a possible body length of 3.5–4 m (11–13 ft).[307]
Erythrosuchids (Erythrosuchidae)
[edit]
The largest erythrosuchid was Erythrosuchus africanus with a maximum length of 4.75–5 m (15.6–16.4 ft).[308]
Phytosaurs (Phytosauria)
[edit]Some of the largest known phytosaurs include Redondasaurus with a length of 6.4 m (21 ft)[309] and Smilosuchus with a length of more than 7 m (23 ft).[310]
Non-crocodylomorph pseudosuchians (Pseudosuchia)
[edit]
- The largest shuvosaurid and one of the largest pseudosuchian from the Triassic period was Sillosuchus. Biggest specimens could have reached 9–10 m (30–33 ft) in length.[311][312]
- The largest known carnivorous pseudosuchian of the Triassic is loricatan Fasolasuchus tenax, which measured an estimated of 8 to 10 m (26 to 33 ft).[313][311][312] It is both the largest "rauisuchian" known to science, and the largest non-dinosaurian terrestrial predator ever discovered.[citation needed] Biggest individuals of Postosuchus[314] and Saurosuchus[315] had a body length of around 7 m (23 ft). A specimen of Prestosuchus discovered in 2010 suggest that this animal also reached lengths of nearly 7 m (23 ft) making it one of the largest Triassic pseudosuchians.[316]
- Desmatosuchus was likely one of the largest known aetosaurs, about 4–6 m (13–20 ft) in length and 280 kg (620 lb) in weight.[317][318][319]
Crocodiles and close relatives (Crocodylomorpha)
[edit]

Aegyptosuchids (Aegyptosuchidae)
[edit]The Late Cretaceous Aegisuchus is the main contender for the title of the largest crocodylomorph ever recorded. It reached 15 m (49 ft) in length by the lower estimate and as much as 22 m (72 ft) by the upper estimate,[320] although a length of over 15 m is likely an overestimate.[320]
Crocodylians (Crocodylia)
[edit]- The largest caiman and likely the largest crocodylian was Purussaurus brasiliensis estimated at 11–13 m (36–43 ft).[321] According to another information, maximum estimate measure 11.4 m (37 ft) and almost 7.8 t (8.6 short tons) in length and in weight respectively.[322] Another giant caiman was Mourasuchus. Various estimates suggest the biggest specimens reached 9.47 m (31.1 ft) in length and 8.5 t (9.4 short tons) in weight[323] or 4.7–5.98 m (15.4–19.6 ft) in body length.[324]
- The largest alligatoroid is likely Deinosuchus riograndensis at 12 m (39 ft) long and weighing 8.5 t (9.4 short tons).[325][326]
- The largest extinct species of the genus Alligator was the Haile alligator (Alligator hailensis), which had a skull 52.5 cm (20.7 in) long and was similar in size to the extant American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis).[327]
- The largest gavialids were Asian Rhamphosuchus at 8–11 m (26–36 ft)[328][329][322] and South American Gryposuchus at 10.15 m (33.3 ft) in length.[330][329]
- The basal crocodyloidean Astorgosuchus bugtiensis from the Oligocene was large. It estimated at 8 m (26 ft) in length.[329]
- The largest known true crocodile was Euthecodon which estimated to have reached 6.4–8.6 m (21–28 ft) or even 10 m (33 ft) long.[331][322] The largest species of the modern Crocodylus were Kenyan Crocodylus thorbjarnarsoni at 7.56 m (24.8 ft) in length,[332][322] Tanzanian Crocodylus anthropophagus at 7.5 m (25 ft) in length[333][334] and indeterminate species from Kali Gedeh (Java) at 6–7 m (20–23 ft) in length.[335]
- The largest known mekosuchian is Paludirex vincenti, which is estimated to reach up to 5 m (16 ft).[336][337][264] Partial jaw specimen from Pliocene that is attributed to Quinkana suggest an individual about 6–7 m (20–23 ft) in length,[264] although other species (known from Oligocene to Pleistocene) are smaller with length around 1.5–3 m (4 ft 11 in – 9 ft 10 in).[338][339][340]
Paralligatorids (Paralligatoridae)
[edit]The largest paralligatorid was likely Kansajsuchus estimated at up to 8 m (26 ft) long.[341]
Tethysuchians (Tethysuchia)
[edit]- Some extinct pholidosaurids reached giant sizes. In the past, the Sarcosuchus imperator was believed to be the largest crocodylomorph, with initial estimates proposing a length of 12 m (39 ft) and a weight of 8 t (8.8 short tons).[342] However, recent estimates have now shrunk to a length of 9 to 9.5 m (29.5 to 31.2 ft) and a weight of 3.5 to 4.3 metric tons (3.9 to 4.7 short tons).[343] Related to Sarcosuchus, Chalawan thailandicus could reached more than 10 m (33 ft) in length,[344] although other estimates suggest 7–8 m (23–26 ft).[329]
- The largest dyrosaurid was Phosphatosaurus gavialoides estimated at 9 m (30 ft) in length.[345][329]
Stomatosuchids (Stomatosuchidae)
[edit]Stomatosuchus, a stomatosuchid, estimated at 10 m (33 ft) in length.[346]
Notosuchians (Notosuchia)
[edit]- Some of largest terrestrial notosuchian crocodylomorphs were the Miocene sebecid Barinasuchus, with a skull of 95–110 cm (37–43 in) long, and Eocene sebecid Dentaneosuchus with estimated mandible length of 1 m (3.3 ft).[347][348] Various estimates suggest a possible length of these animals between 3–10 m (9.8–32.8 ft). Using proportion of Stratiotosuchus which is also large to have 47 cm (19 in) long skull,[349] Barinasuchus is estimated to have length at least 6.3 m (21 ft).[347][348]
- Other huge notosuchian, although only known from fragmentary material, is an early member Razanandrongobe, which skull size may exceeded that of Barinasuchus and overall length may be around 7 m (23 ft).[350][351]
Thalattosuchians (Thalattosuchia)
[edit]
- The largest thalattosuchian as well as the largest teleosauroid was unnamed fossil remain from Paja Formation, which may belongs to animal with length of 9.6 m (31 ft),[352] which is as large as outdated length estimate of the Early Cretaceous Machimosaurus rex, more recently estimated at 7.15 m (23.5 ft) in length.[353] Neosteneosaurus edwardsi (previously known as Steneosaurus edwardsi[354]) was the biggest Middle Jurassic crocodylomorph, it reached 6.6 m (22 ft) long.[353]
- Plesiosuchus was very large metriorhynchid. With the length of 6.83 m (22.4 ft) it exceeded even some pliosaurids of the same time and locality such as Liopleurodon.[355] Other huge metriorhynchids include Tyrannoneustes at 5 m (16 ft) in length[356] and Torvoneustes at 4.7 m (15 ft) in length.[357]
Basal crocodylomorphs
[edit]Redondavenator was the largest Triassic crocodylomorph ever recorded,[358] with a skull of at least 60 cm (2.0 ft) in length.[359][360] Another huge basal crocodylomorph was Carnufex[358] at 3 m (9.8 ft) long even through that is immature.[361]
Pterosaurs (Pterosauria)
[edit]
- The largest known pterosaur was Quetzalcoatlus northropi, at 127 kg (280 lb) and with a wingspan of 10–12 m (33–39 ft).[362] Another close contender is Hatzegopteryx, also with a wingspan of 12 m (39 ft) or more.[362] This estimate is based on a skull 3 m (9.8 ft) long.[363] Yet another possible contender for the title is Cryodrakon which had a 10-metre (33 ft) wingspan.[364] An unnamed pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Nemegt Formation could reach a wingspan of nearly 10 m (33 ft).[365][366] According to various assumptions, the wingspan of Arambourgiania philadelphiae reached from 8 m (26 ft) to more than 10 m (33 ft).[365][364] South American Tropeognathus reached the maximum wingspan of 8.7 m (29 ft).[367][368]
- The largest of non-pterodactyloid pterosaurs as well as the largest Jurassic pterosaur[369] was Dearc, with an estimated wingspan between 2.2 m (7 ft 3 in) and 3.8 m (12 ft).[370] Only a fragmentary rhamphorhynchid specimen from Germany could be larger (184% the size of the biggest Rhamphorhynchus).[371] Other large non-pterodactyloid pterosaurs were Sericipterus, Campylognathoides and Harpactognathus, with the wingspan of 1.73 m (5 ft 8 in),[372] 1.75 m (5 ft 9 in),[372] and 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in),[371] respectively.
Choristoderes (Choristodera)
[edit]The largest known choristoderan, Kosmodraco dakotensis (previously known as Simoedosaurus dakotensis[373]) is estimated to have had a total length of around 5 m (16 ft).[374][373]
Tanystropheids (Tanystropheidae)
[edit]
Tanystropheus, the largest of all tanystropheids, reached up to 5 m (16 ft) in length.[375]
Thalattosaurs (Thalattosauria)
[edit]The largest species of thalattosaur, Miodentosaurus brevis grew to more than 4 m (13 ft) in length.[376] The second largest member of this group is Concavispina with a length of 3.64 m (11.9 ft).[377]
Ichthyosaurs (Ichthyosauria)
[edit]
In April 2018, paleontologists announced the discovery of a previously unknown ichthyosaur that may have reached lengths of 26 m (85 ft) making it one of the largest animals known, rivaling some blue whales in size.[378][379] These remains were later named Ichthyotitan and it has been estimated to reach up to 25 m (82 ft), which makes it the largest ichthyosaur and the largest marine reptile ever.[380] Another large ichthyosaur was the Late Triassic Shastasaurus sikanniensis at 21 m (69 ft) in length[381][382] and 81.5 t (180,000 lb) in weight.[383] Another, larger ichthyosaur was found in 1850 in Aust.[384] Its remains seemed to surpass the measurements of the other ichthyosaur, but the researchers commented that the remains were too fragmentary for a size estimate to be made.[384] Another huge ichthyosaur was Shonisaurus popularis at 15 m (49 ft) in length and 29.7 t (65,000 lb) in weight.[382] The largest Middle Triassic ichthyosaur as well as the largest animal of that time was Cymbospondylus youngorum at 17.65 m (57.9 ft) in length[383] and 44.7 t (99,000 lb) in weight.[383]
Tangasaurids (Tangasauridae)
[edit]The largest tangasaurid was Hovasaurus with an estimated snout-vent length of 30–35 cm (12–14 in) and a tail of 60 cm (24 in).[385]
Pareiasaurs (Pareiasauria)
[edit]Largest pareiasaurs reached up to 3 m (9.8 ft) in length. Such sizes had Middle Permian Bradysaurus, Embrithosaurus, and Nochelesaurus from South Africa,[386] and the Late Permian Scutosaurus from Russia.[386] The most robust Scutosaurus had 1.16 t (2,600 lb) in body mass.[386]
Captorhinids (Captorhinidae)
[edit]The heavy built Moradisaurus grandis, with a length of 2 m (6 ft 7 in),[387] is the largest known captorhinid.[388] The second largest captorhinid was Labidosaurikos with the largest adult skull specimen 28 cm (11 in) long.[389]
Non-avian dinosaurs (Dinosauria)
[edit]Sauropodomorphs (Sauropodomorpha)
[edit]The largest of non-sauropod sauropodomorphs ("prosauropod") was Euskelosaurus. It reached 12.2 m (40 ft) in length and 2 t (2.2 short tons) in weight.[390] Another huge sauropodomorph Yunnanosaurus youngi reached 13 m (43 ft) long.[391]
Sauropods (Sauropoda)
[edit]
- A mega-sauropod, Maraapunisaurus fragillimus (previously known as Amphicoelias fragillimus), is a contender for the largest-known dinosaur in history. It has been estimated at 58–60 m (190–197 ft) in maximum length and 122,400 kg (269,800 lb) in weight.[392] Unfortunately, the fossil remains of this dinosaur have been lost.[392] More recently, it was estimated at 35–40 m (115–131 ft) in length and 80–120 t (180,000–260,000 lb) in weight.[393]
- Known from the incomplete and now disintegrated remains, the Late Cretaceous Bruhathkayosaurus matleyi was an anomalously large sauropod.[394] Informal estimations suggested as huge parameters as 45 m (148 ft) in length and 139–220 t (306,000–485,000 lb) in weight.[395] Some estimation however, suggests 37 m (121 ft) and 95 t (209,000 lb) but it still much heavier than most other sauropods.[395] More recent estimations by Gregory Paul in 2023 has placed its weight range around 110 t (240,000 lb) to a 170 t (370,000 lb). If true, it would make Bruhathkayosaurus the single largest terrestrial animal to have walked the earth and would have rivalled the largest blue whale recorded.[396]
- BYU 9024, a massive cervical vertebra found in Utah,[397] may belong to Barosaurus lentus[398][399] or Supersaurus vivianae[400] of a huge size, possibly 45–48 m (148–157 ft) in length and 60–66 t (132,000–146,000 lb) in body mass.[401][399] Supersaurus vivianae itself may have been the longest dinosaur yet discovered as a study of 3 specimens suggested length of 39 m (128 ft) or over 40 m (130 ft).[400]

- Mamenchisaurus sinocanadorum was likely the largest mamenchisaurid, reaching nearly 35 m (115 ft) in length and 60–80 t (130,000–180,000 lb) in weight.[393] Xinjiangtitan shanshanesis from the same family had 15 m (49 ft)-long neck, about 55% of its total length that could be at least 27 m (89 ft).[402]
- The Middle Jurassic Breviparopus taghbaloutensis was mentioned in The Guinness Book of Records as the longest dinosaur at 48 m (157 ft) although this animal is known only from fossil tracks.[403][404] Originally thought to be a brachiosaurid, it was later identified as a huge diplodocoid, possibly 33.5 m (110 ft) in length and 62 t (137,000 lb) in weight.[405]

- The tallest sauropod was Sauroposeidon proteles with estimated height at 16.5–18 m (54–59 ft).[406][407][408] Asiatosaurus could reach 17.5 m (57 ft) in height but this animal is known only from teeth.[408] Giraffatitan was estimated at 16 m (52 ft) in height.[409]
Other huge sauropods include Argentinosaurus, Alamosaurus, and Puertasaurus with estimated lengths of 30–33 m (98–108 ft) and weights of 50–80 t (55–88 short tons).[410] Patagotitan was estimated at 37 m (121 ft) in length[411] and 57 t (63 short tons) in average weight,[412] and was similar in size to Argentinosaurus and Puertasaurus.[413] Giant sauropods like Supersaurus, Sauroposeidon, and Diplodocus probably rivaled them in length but not in weight.[392] Dreadnoughtus was estimated at 49 t (108,000 lb) in weight[412] and 26 m (85 ft) in length but the most complete individual was immature when it died.[414] Turiasaurus is considered of being the largest dinosaur from Europe,[415][416] with an estimated length of 30 m (98 ft) and a weight of 50 t (55 short tons).[410][416] However, with lower estimate at 21 m (69 ft) and 30 t (66,000 lb) it was smaller than Portuguese Lusotitan that reached 24 m (79 ft) in length and 34 t (75,000 lb) in weight.[417]
Many large sauropods are still unnamed and may rival the current record holders:
- The "Archbishop", a large brachiosaur that was discovered in 1930. As of October 2023[update], a scientific paper on the specimen is still in progress.[418]
- Brachiosaurus nougaredi is yet another large brachiosaur from Early Cretaceous North Africa. The remains have been lost, but the sacrum drawing remains. It suggests a sacrum of almost 1.3 m (4.3 ft) long,[419] making it the largest dinosaur sacrum discovered so far, except those of Argentinosaurus and Apatosaurus.[420]
- In 2010, the femur of a large sauropod was discovered in France. The femur suggests an animal that grew to immense sizes.[421]
Non-avian theropods (Theropoda)
[edit]
- The largest theropod as well as the largest terrestrial (or possibly semi-aquatic)[422] predator yet known is Spinosaurus aegyptiacus, with the largest specimen known estimated at 12.6–18 m (41–59 ft) in length and around 7–20.9 t (8–23 short tons) in weight.[423][424] New estimates published in 2014 and 2018, based on a more complete specimen supported that Spinosaurus could reach lengths of 15 to 16 meters (49 to 52 ft).[425][426][427] The latest estimates suggest a weight of 6.4 to 7.5 metric tons (7.1 to 8.3 short tons).[426][427] The White Rock spinosaurid had vertebrae comparable in dimensions to Spinosaurus, it was likely a huge theropod with a length over 10 m (33 ft).[428]
- Other large theropods were Giganotosaurus carolinii, and Tyrannosaurus rex, whose largest specimens known estimated at 13.2 m (43 ft)[429] and 12.3 m (40 ft)[430] in length, and weigh between 4.2 to 13.8 t (4.6 to 15.2 short tons)[431][432][433][423] and 4.5 metric tons (5.0 short tons)[434][435] to over 7.2 metric tons (7.9 short tons),[430] respectively. Some other notable giant theropods (e.g. Carcharodontosaurus, Acrocanthosaurus, and Mapusaurus) may also have rivaled them in size.
- Macroelongatoolithus, ranging from 34–61 cm (1.12–2.00 ft) in length,[436] is the largest known type of dinosaur egg.[437] It is assigned to oviraptorosaurs like Beibeilong.[437]
Armoured dinosaurs (Thyreophora)
[edit]The largest-known thyreophoran was Ankylosaurus at 9 m (30 ft) in length and 6 tonnes (6.6 short tons) in weight.[438][439] Stegosaurus was also 9 m (30 ft) long[416] but around 5 tonnes (5.5 short tons) tonnes in weight.[citation needed]
Pachycephalosaurs (Pachycephalosauria)
[edit]The largest pachycephalosaur was the eponymous Pachycephalosaurus. Previously claimed to be at 7 m (23 ft) in length,[416] it was later estimated about 4.5 metres (14.8 ft) long and a weight of about 450 kilograms (990 lb).[440]
Ceratopsians (Ceratopsia)
[edit]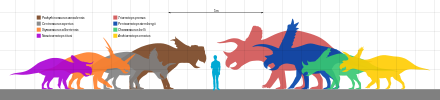
The largest ceratopsian known is Triceratops horridus, along with the closely related Eotriceratops xerinsularis both with estimated lengths of 9 m (30 ft). Pentaceratops and several other ceratopsians rival them in size.[441] Titanoceratops had one of the longest skull of any land animal, at 2.65 m (8.7 ft) long.[442]
Ornithopods (Ornithopoda)
[edit]
- The very largest known ornithopods, like Shantungosaurus were as heavy as medium-sized sauropods at up to 23 t (25 short tons),[443][444] and 16.6 m (54 ft) in length.[443] Magnapaulia reached 12.5 m (41 ft) in length,[445] or, according to original description, even 15 m (49 ft).[446][416] The Mongolian Saurolophus, S. angustirostris, reached 13 m (43 ft) long and possibly more.[447] Such animal could weighed up to 11 t (12 short tons).[447] The largest Edmontosaurus reached 12 m (39 ft) in length and around 6 t (6.6 short tons) in body mass.[448] An estimated maximum length of Brachylophosaurus is 11 m (36 ft) resulting in weight of 7 t (7.7 short tons).[449] PASAC-1, informally named "Sabinosaurus", is the largest well-known North American saurolophine,[450] around 11 m (36 ft) long, that is about 20% larger than other known specimens.[451] Hypsibema missouriensis was up to 10.7 m (35 ft) long.[452][453] The Late Cretaceous Charonosaurus was estimated around 10 m (33 ft) in length and 5 t (5.5 short tons) in weight.[416][454]
- The largest ornithopod outside of Hadrosauroidea was likely the Iguanodon. Biggest specimens reached 11 m (36 ft) in length[455][456] and weighed around 4.5 t (5.0 short tons).[457] Another large ornithopod is Iguanacolossus, with 9 m (30 ft) in length and 5 t (5.5 short tons) in weight.[458][459]
- The largest rhabdodontid was Matheronodon, estimated at 4.8 m (16 ft) in length.[460] Rhabdodon reached approximately 4 m (13 ft) and 250 kg (550 lb) according to 2016 estimates.[461]
Birds (Aves)
[edit]
The largest bird in the fossil record may be the extinct elephant bird species Aepyornis maximus of Madagascar, whose closest living relative is the kiwi. Giant elephant birds exceeded 2.3 metres (7.5 ft) in height, and average a mass of 850 kg (1,870 lb)[462]
The largest fowl was the mihirung Dromornis stirtoniof Australia. It exceeded 2.7 m (8.9 ft) in height, and average a mass of 500 kilograms (1,100 lb)[463]
Another contender is Brontornis burmeisteri, an extinct flightless bird from South America which reached a weight of 319 kg (703 lb) and a height of approximately 2.8 metres (9.2 ft).[464]
The tallest recorded bird was Pachystruthio dmanisensis, a relative of the ostrich. This particular species of bird stood at 3.5 metres (11.5 ft) tall and average a mass of 450 kg (990 lb)[465]
The largest known flightless neoave was the terror bird Paraphysornis brasiliensis of South America,the Brazilian terror bird exceeded 240 kg (530 lb) in mass,[466]
Table of heaviest extinct bird species
[edit]Enantiornitheans (Enantiornithes)
[edit]One of the largest enantiornitheans was Enantiornis,[487] with a length in life of around 78.5 cm (30.9 in), hip height of 34 cm (13 in), weight of 6.75 kg (14.9 lb),[488] and wingspan comparable to some of the modern gulls, around 1.2 m (3 ft 11 in).[487] Gurilynia was the largest Mesozoic bird from Mongolia, with a length of 53 cm (21 in), hip height of 23.2 cm (9.1 in), and weight of 2.1 kg (4.6 lb).[488]
Avisauridae
[edit]
The Late Cretaceous Avisaurus was almost as large as Enantiornis. It had a wingspan around 1.2 m (3 ft 11 in),[487] a length of 72 cm (28 in), hip height of 31.5 cm (12.4 in), and weight of 5.1 kg (11 lb).[488] Even larger could be the Soroavisaurus. One tibiotarsus (PVL-4033) indicates an animal with a length of 80 cm (31 in), hip height of 35 cm (14 in), and weight of 7.25 kg (16.0 lb).[488] However, according to Walker and Dyke (2009) which considered PVL-4033 as Martinavis sp., its tibiotarsus length is 85.6 mm (3.37 in),[489] much shorter than that of Lectavis (156 mm (6.1 in) tibiotarsus)[490] which the same book estimated a length of 41 cm (16 in), hip height of 30 cm (12 in), and weight of 1.15 kg (2.5 lb).[488] Mirarce was comparable in size to a turkey, much larger than most of other enantiornitheans.[491]
Pengornithidae
[edit]One of the biggest Early Cretaceous enantiornithine bird was Pengornis at 50 cm (1.6 ft) in length[416] and skull length of 54.7 mm (2.15 in).[492]
Gargantuaviidae
[edit]Gargantuavis is the largest known bird of the Mesozoic, a size ranging between the cassowary and the ostrich, and a mass of 140 kg (310 lb) like modern ostriches.[493] In 2019 specimens MDE A-08 and IVPP-V12325 were measured at 1.8 m (5 ft 11 in) in length, 1.3 m (4 ft 3 in) in hip height, and 120 kg (260 lb) in weight.[473]
Dromornithiformes
[edit]
The largest dromornithid was Dromornis stirtoni over 3 m (9.8 ft) tall[494] and 528–584 kg (1,164–1,287 lb) in mass for males.[495]
Gastornid (Gastornithiformes)
[edit]Large individuals of Gastornis reached up to 2 m (6 ft 7 in) in height.[496] Weight of Gastornis ranges from 100 kg (220 lb) to 156 kg (344 lb) and sometimes to 180 kg (400 lb) for European specimens and from 160 kg (350 lb) to 229 kg (505 lb) for North American.[497][471][498]
Waterfowl (Anseriformes)
[edit]
Possibly flightless, the Miocene Garganornis ballmanni was larger than any extant members of Anseriformes, with 15.3–22.3 kg (34–49 lb) in body mass.[499] Another huge anseriform was the flightless New Zealand goose (Cnemiornis). It reached 15–18 kg (33–40 lb), approaching in size to small species of moa.[500]
Swans (Cygnini)
[edit]The largest known swan was the Pleistocene giant swan (Cygnus falconeri), which reached a bill-to-tail length of about 190–210 cm (75–83 in),[501] a weight of around 16 kg (35 lb), and a wingspan of 3 m (9.8 ft).[502][503][504] The New Zealand swan (Cygnus sumnerensis) weighed up to 10 kg (22 lb), compared to the related extant black swan at only 6 kg (13 lb).[505] The large marine swan Annakacygna yoshiiensis from the Miocene of Japan far exceeded the extant mute swan in both size and weight.[506]
Anatinae
[edit]Finsch's duck (Chenonetta finschi) reached 1–2 kg (2.2–4.4 lb) in weight, surpassing related modern Australian wood duck (800 g (1.8 lb)).[507]
Pelicans, ibises and allies (Pelecaniformes)
[edit]- The Early Pliocene Pelecanus schreiberi was larger than most extant pelicans. Pelecanus odessanus from the Late Miocene was probably the same size as P. schreiberi, its tarsometatarsus is 150 mm (5.9 in) long.[508]
- The largest herons Bennu heron (Ardea bennuides) Based on remains discovered, it was approximately 2 m (6.6 ft) tall and had a wingspan up to 2.7 m (8.9 ft), thus surpassing the size of the largest living species in the heron family, the goliath heron.[509]
- The ever largest ibis Jamaican ibis (Xenicibis xympithecus) as a large ibis, weighing about 2 kg (70 oz).
Storks and allies (Ciconiiformes)
[edit]
The largest known of Ciconiiformes was Leptoptilos robustus, standing 1.8 m (5 ft 11 in) tall and weighing an estimated 16 kg (35 lb).[510][483] Ciconia maltha is a relatively large species of Ciconia, with a height of over 5 feet (1.5 meters) and a wingspan up to 10 feet (3.0 meters) across.[511]
Cranes (Gruiformes)
[edit]A large true crane (Gruinae) from the late Miocene (Tortonian) of Germany was equal in size to the biggest extant cranes and resembled the long-beaked Siberian crane (Leucogeranus leucogeranus).[512]
Shorebirds (Charadriiformes)
[edit]Miomancalla howardi was the largest known charadriiform of all time, weighing approximately 0.6 kg (1.3 lb) more than the second-largest member, the great auk (Pinguinus impennis).[513]
Hesperornithines (Hesperornithes)
[edit]The largest known of the hesperornithines was Canadaga arctica at 2.2 m (7 ft 3 in) long.[514]
New World vultures (Cathartiformes)
[edit]
One of the heaviest flying birds of all time was Argentavis, a Miocene teratornithid. The immense bird had a wingspan estimated up to 5.09–6.5 m (16.7–21.3 ft)[475][515] and a weight up to 70 to 72 kg (154 to 159 lb).[516][475] Argentavis's humerus was only slightly shorter than an entire human arm.[517] Another huge teratorn was Aiolornis, with a wingspan of around 5 m (16 ft).[518] The Pleistocene Teratornis merriami reached 13.7 kg (30 lb) and 2.94–3.38 m (9.6–11.1 ft) in wingspan, with lower size estimates still exceeding the largest specimens of California condor (Gymnogyps californianus).[519]
Seriemas and allies (Cariamiformes)
[edit]
The largest known-ever Cariamiforme and largest phorusrhacid or "terror bird" (highly predatory, flightless birds of America) was Brontornis, which was about 175 cm (69 in) tall at the shoulder, could raise its head 2.8 m (9 ft 2 in) above the ground and could have weighed as much as 400 kg (880 lb).[520] The immense phorusrhacid Kelenken stood 3 m (9.8 ft) tall[521][522] with a skull 716 mm (28.2 in) long (460 mm (18 in) of which was beak), had the largest head of any known bird.[521] South American Phorusrhacos stood 2.4-2.7 m (7.9-8.8 ft) tall, and weighed nearly 130 kilograms (290 lb), as much as a male ostrich.[523][524] The largest North American phorusrhacid was Titanis, which reached a height of approximately 2.5 m (8.2 ft),[525] slightly taller than an African forest elephant.
Accipitriforms (Accipitriformes)
[edit]
The largest known bird of prey ever was the enormous Haast's eagle (Hieraaetus moorei), with a wingspan of 2.6 to 3 m (8 ft 6 in to 9 ft 10 in), relatively short for their size.[526][527] Total length was probably up to 1.4 m (4 ft 7 in) in female[528] and they weighed about 10 to 15 kg (22 to 33 lb).[529] Another giant extinct hawk was Titanohierax about 7.3 kg (16 lb) that lived in the Antilles and The Bahamas, where it was among the top predators.[530] An unnamed late Quaternary eagle from Hispaniola could be 15–30% larger than the modern golden eagle (Aquila chrysaetos).[531] Some extinct species of Buteogallus surpassed their extant relatives in size. Buteogallus borrasi was about 33% larger than the modern great black hawk (B. urubitinga).[532] B. daggetti, also known as "walking eagle", was around 40% larger than the savanna hawk (B. meridionalis).[533] Eyles's harrier (Circus eylesi) from the Pleistocene-Holocene of New Zealand was more than twice heavier than the extant C. approximans.[534]
Moa (Dinornithiformes)
[edit]The tallest known bird was the South Island giant moa (Dinornis robustus), part of the moa family of New Zealand that went extinct about 500 years ago. It stood up to 3.7 m (12 ft) tall,[535] and weighed approximately half as much as a large elephant bird due to its comparatively slender frame.[536]
Tinamous (Tinamiformes)
[edit]MPLK-03, a tinamou specimen that existed during the Late Pleistocene in Argentina, possibly belongs to the modern genus Eudromia and surpacces extant E. elegans and E. formosa in size by 2.2–8% and 6–14%, respectively.[537]
Elephant birds (Aepyornithiformes)
[edit]The largest bird in the fossil record may be the extinct elephant birds (Vorombe, Aepyornis) of Madagascar, which were related to the ostrich. They exceeded 3 m (9.8 ft) in height and 500 kilograms (1,100 lb) in weight.[536]
Ostriches (Struthioniformes)
[edit]With 450 kg (990 lb) in body mass, Pachystruthio dmanisensis from the lower Pleistocene of Crimea was the largest bird ever recorded in Europe. Despite its giant size, it was a good runner.[538] A possible specimen of Pachystruthio from the lower Pleistocene of Hebei Province (China) was about 300 kg (660 lb) in weight, twice heavier than the common ostrich (Struthio camelus).[539] Remains of the massive Asian ostrich (Struthio asiaticus) from the Pliocene[540] indicate a size 20% bigger than adult male of the extant Struthio camelus.[541]
Pigeons and doves (Columbiformes)
[edit]
The largest pigeon relative known was the dodo (Raphus cucullatus), possibly exceeding 1 m (3.3 ft) in height and weighing as much as 28 kg (62 lb), although recent estimates have indicated that an average wild dodo weighed much less at approximately 10.2 kg (22 lb).[542][543]
Pheasants, turkeys, gamebirds and allies (Galliformes)
[edit]The largest known of the Galliformes was likely the giant malleefowl, which could reach 7 kg (15 lb) in weight.[544]
Songbirds (Passeriformes)
[edit]The largest known songbird is the extinct giant grosbeak (Chloridops regiskongi) at 280 mm (11 in) long.[citation needed]
Cormorants and allies (Suliformes)
[edit]
- The largest known cormorant was the spectacled cormorant of the North Pacific (Phalacrocorax perspicillatus), which became extinct around 1850 and averaged around 6.4 kg (14 lb) and 1.15 m (3 ft 9 in).[486]
- The largest known darter was Giganhinga with estimated weight about 17.7 kg (39 lb),[481] earlier study even claims 25.7 kg (57 lb).[545]
- The largest known plotopterid, penguin-like flightless bird was Copepteryx titan that is known from 22 cm (8.7 in) long femur, almost twice as long as that of emperor penguin.[546]
Grebes (Podicipediformes)
[edit]The largest known grebe, the Atitlán grebe (Podylimbus gigas), reached a length of about 46–50 centimetres (18–20 in).[547]
Bony-toothed birds (Odontopterygiformes)
[edit]The largest known of the Odontopterygiformes— a group which has been variously allied with Procellariiformes, Pelecaniformes and Anseriformes and the largest flying birds of all time other than Argentavis were the huge Pelagornis, Cyphornis, Dasornis, Gigantornis and Osteodontornis.[citation needed] They had a wingspan of 5.5–6 m (18–20 ft) and stood about 1.2 m (3 ft 11 in) tall.[citation needed] Exact size estimates and judging which one was largest are not yet possible for these birds, as their bones were extremely thin-walled, light and fragile, and thus most are only known from very incomplete remains.[citation needed]
Woodpeckers and allies (Piciformes)
[edit]The largest known woodpecker is the possibly extinct imperial woodpecker (Campephilus imperialis) with a total length of about 56–60 cm (22–24 in).[548]
Parrots (Psittaciformes)
[edit]The largest known parrot is the extinct Heracles inexpectatus with a length of about 1 meter (3.3 feet).[549]
Penguins (Sphenisciformes)
[edit]
One of the heaviest penguins ever known is Kumimanu fordycei, with a body mass estimate of 148 to 159.7 kg (326 to 352 lb), dervied from humerus measurments.[550] Another example is Palaeeudyptes klekowskii of Antarctica, with a bill-to-tail length estimated at 2.02 m (6 ft 8 in) and an estimated body weight of 84.2 kg (186 lb), slightly smaller than previous estimates.[550][551] The Eocene Anthropornis nordenskjoeldi is comparable in size, and was once estimated to reach lengths of 2.05 m (6 ft 9 in) and a weight of 108 kg (238 lb).[552] However, recent estimation from humerus measurements put A. nordenskjoeldi more in the range of 67 kg (148 lb) in weight.[550] Other large penguins include the New Zealand giant penguin (Pachydyptes pondeorsus) weighing around 65.4 to 94.6 kg (144 to 209 lb), and Icadyptes salasi at 52.8 to 73.0 kg (116.4 to 160.9 lb).[553][550]
Owls (Strigiformes)
[edit]The largest known owl of all time was the Cuban Ornimegalonyx at 1,100 mm (43.3 in) tall probably exceeding 9 kg (20 lb).[554]
Amphibians (Amphibia)
[edit]The largest known amphibian of all time was the 9.1 m (30 ft) long temnospondyl Prionosuchus.[555]
Lissamphibians (Lissamphibia)
[edit]Frogs and toads (Anura)
[edit]
The largest known frog ever was an as yet unnamed Eocene species that was about 58–59.1-centimetre-long (22.8–23.3 in).[556] The Late Cretaceous Beelzebufo grew to at least 23.2 cm (9.1 in) (snout-vent length), which is around the size of a modern African bullfrog.[557]
Salamanders, newts and allies (Urodela)
[edit]
- Andrias matthewi was the largest lissamphibian ever known, with total length up to 2.3 m (7 ft 7 in).[558]
- Habrosaurus was the largest sirenid. It reached 1.6 m (5 ft 3 in) long.[559]
Diadectomorphs (Diadectomorpha)
[edit]
The largest known diacectid, herbivorous Diadectes, was a heavily built animal, up to 3 m (9.8 ft) long, with thick vertebrae and ribs.[560][561]
Anthracosauria
[edit]The largest known anthracosaur was Anthracosaurus, with skull about 40 cm (16 in) in length.[562]
Embolomeri
[edit]
The longest member of this group was Eogyrinus attheyi, species sometimes placed under genus Pholiderpeton.[563] Its skull had length about 41 cm (16 in).[564]
Temnospondyls (Temnospondyli)
[edit]
The largest known temnospondyl amphibian is Prionosuchus, which grew to lengths of 9 m (30 ft).[555] Another huge temnospondyl was Mastodonsaurus giganteus at 6 m (20 ft) long.[565] Unnamed species of temnospondyl from Lesotho is partial, but possible body length estimation is 7 m (23 ft).[566]
Fishes (Pisces)
[edit]Fishes are a paraphyletic group of non-tetrapod vertebrates.
Jawless fish (Agnatha)
[edit]Conodonts (Conodonta)
[edit]Iowagnathus grandis is estimated to have length over 50 cm (1.6 ft).[567]
Heterostracans (Heterostraci)
[edit]Some members of Psammosteidae such as Obruchevia and Tartuosteus are estimated to reached up to 2 m (6.6 ft).[568]
Thelodonts (Thelodonti)
[edit]Although known from partial materials, Thelodus parvidens (=T. macintoshi) is estimated to reached up to 1 m (3.3 ft).[569]
Cephalaspidomorphs (Cephalaspidomorphi)
[edit]A species of Parameteoraspis reached up to 1 m (3.3 ft).[570]
Spiny sharks (Acanthodii)
[edit]The largest of the now-extinct Acanthodii was Xylacanthus grandis, an ischnacanthiform based on a ~35 cm (14 in) long jaw bone. Based on the proportions of its relative Ischnacanthus, X. grandis had an estimated total length of 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in).[571]
Placoderms (Placodermi)
[edit]
The largest known placoderm was the giant predatory Dunkleosteus. The largest and most well known species was D. terrelli, various estimate put its length around 4.1–10 m (13.5–32.8 ft) in length and 1–4 t (1.1–4.4 short tons) in weight.[572] Another large placoderm, Titanichthys, may have rivaled it in size.[573] Titanichthys is estimated to have a length around 4.1–7.5 m (13–25 ft)[574][575][576][572]
Cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes)
[edit]Mackerel sharks (Lamniformes)
[edit]
- Species in the extinct genus Otodus were huge. A giant shark, Otodus megalodon[577][578][579] is by far the biggest mackerel shark ever known.[580] Most estimates of megalodon's size extrapolate from teeth, with maximum length estimates up to 10.6–20 m (35–66 ft)[578][579][581] and average length estimates of 10.5 m (34 ft).[582][583] Due to fragmentary remains, there have been many contradictory size estimates for megalodon, as they can only be drawn from fossil teeth and vertebrae.[584]: 87 [585] Mature male megalodon may have had a body mass of 12.6 to 33.9 metric tons (13.9 to 37.4 short tons), and mature females may have been 27.4 to 59.4 metric tons (30.2 to 65.5 short tons), assuming that males could range in length from 10.5 to 14.3 m (34 to 47 ft) and females 13.3 to 17 m (44 to 56 ft).[586] Related to megalodon, Otodus angustidens and O. chubutensis reached the large sizes too. Each was estimated at 9.3 m (31 ft)[587] and 12.2 m (40 ft),[588] respectively.
- Other giant mackerel sharks were Pseudoscapanorhynchidae from the Cretaceous period. Cretodus had a size range of 9–11 m (30–36 ft) (for C. crassidens),[589] Leptostyrax reached lengths of 6.3–8.3 m (21–27 ft).[590]
- The Cenozoic Parotodus reached up to 7.6 m (25 ft) in length.[591]
- The heaviest thresher shark was likely Alopias grandis. It was similar in size or even larger than the extant great white shark and probably did not have an elongated dorsal tail, characteristic of modern relatives.[592]
Ground sharks (Carcharhiniformes)
[edit]The Cenozoic Hemipristis serra was considerably larger than its modern-day relatives and had much larger teeth. Its total length is estimated to be at 6 metres (20 ft) long.[593]
Hybodonts (Hybodontiformes)
[edit]One of the largest hybodontiforms was the Jurassic Asteracanthus with body length of up to 3 m (9.8 ft).[594] Crassodus reifi is known from less materials, however it is estimated that reached over 3 m (9.8 ft).[595]
Ctenacanthiformes
[edit]The largest member of ctenacanthiformes is Saivodus striatus with estimated length around 6–9 m (20–30 ft).[596][572]
Skates and allies (Rajiformes)
[edit]The giant sclerorhynchid Onchopristis reached about 4.25 m (13.9 ft) in length.[597]
Eugeneodont (Eugeneodontida)
[edit]
The largest known eugeneodont is an as-yet unnamed species of Helicoprion discovered in Idaho. The specimens suggest an animal that possibly exceeded 12 m (39 ft) in length.[598] Another fairly large eugeneodont is Parahelicoprion. Being more slimmer than Helicoprion, it reached nearly the same size,[598] possibly up to 12 m (39 ft) in length.[599] Both had the largest sizes among the animals of Paleozoic era.[600][599]
Lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii)
[edit]Coelacanths (Actinistia)
[edit]
The largest coelacanth is Cretaceous Mawsonia gigas with estimated total length up to 5.3 m (17 ft). Jurassic Trachymetopon may have reached size close to that, about 5 m (16 ft).[601] An undetermined mawsoniid from the Maastrichtian deposits of Morocco probably reached 3.65–5.52 m (12.0–18.1 ft) in length.[602][601]
Lungfish (Dipnoi)
[edit]Cretaceous Ceratodus sp. from Western Interior is estimated to had a length around 4 m (13 ft).[603]
Stem-tetrapods (Tetrapodomorpha)
[edit]

- Not only the largest known rhizodont, but also the largest lobe-finned fish was the 5.63–7 m (18.5–23.0 ft) long Rhizodus.[604][572] Another large rhizodonts were Strepsodus with estimated length around 3–5 m (9.8–16.4 ft) and Barameda estimated at 3–4 m (9.8–13.1 ft) in length.[605][606]
- Tristichopterid Hyneria reached length up to 3.5 m (11 ft).[572]
Ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii)
[edit]Acipenseriformes
[edit]- Gyrosteus, which belongs to extinct acipenseriform family Chondrosteidae, is estimated to have standard length about 6–7 m (20–23 ft).[607]
- The largest known fossil sturgeon is "Acipenser" gigantissimus known from fragmentary remains, which is estimated to reach up to 5.8 m (19 ft).[608]
- The largest known fossil paddlefish is unnamed remain from Judith River Formation, it may exceeded 2 m (6 ft 7 in), known remains exceeded size of recently extinct Chinese paddlefish, which scientifically reported to exceed 3 m (9.8 ft).[609]
Pachycormiformes
[edit]
The largest known ray-finned fish and largest bony fish of all time was the pachycormid, Leedsichthys problematicus, at around 16.5 m (54 ft) long.[610] Earlier estimates have had claims of larger individuals with lengths over 27 m (89 ft).[611][612]
Ichthyodectiformes
[edit]
The largest known of ichthyodectiform fish was Xiphactinus, which measured up to 6.1 m (20 ft) long.[613] Ichthyodectes reached 3 m (9.8 ft) long, twice lesser than Xiphactinus.[614]
Pycnodontiformes
[edit]The largest known pycnodontiform was Gyrodus circularis, with length up to 2 m (6 ft 7 in).[615]
Bichirs (Polypteriformes)
[edit]The Late Cretaceous Bawitius was likely the largest bichir of all time. It reached up to 3 m (9.8 ft) in length.[616]
Opahes, ribbonfishes, oarfishes and allies (Lampriformes)
[edit]Megalampris was likely the largest fossil opah. This fish was around 4 m (13 ft) in length when alive, which is twice the length of the largest living opah species, Lampris guttatus.[617]
Salmon and trout (Salmoniformes)
[edit]The largest salmon was Oncorhynchus rastrosus, varying in size from 1.9 m (6 ft 3 in) and 177 kg (390 lb)[618] to 2.4 m (7 ft 10 in) and 200 kg (440 lb).[619][618]
Pufferfishes, boxfishes, triggerfishes, ocean sunfishes and allies (Tetraodontiformes)
[edit]- Austromola angerhoferi had total body length about 3.2 m (10 ft), and total height 4 m (13 ft), comparable with largest ocean sunfish.[620][621]
- Some extinct species of Balistes like B. vegai and B. crassidens are estimated to have total length up to 1.8 m (5 ft 11 in).[622]
Lizardfishes (Aulopiformes)
[edit]The largest lizardfish was Stratodus which could reach length of 5 m (16 ft).[623]
Echinoderms (Echinodermata)
[edit]Crinozoa
[edit]
Sea lilies (Crinoidea)
[edit]Longest stem of Seirocrinus subangularis reached over 26 m (85 ft).[624]
Asterozoa
[edit]Starfish (Asteroidea)
[edit]Helianthaster from Hunsrück Slate had radius about 25 cm (9.8 in).[625]
Graptolites (Graptolithina)
[edit]The longest known graptoloid graptolite is Stimulograptus halli at 1.45 m (4.8 ft). It found in Silurian deposits of the United Kingdom.[626]
Kinorhynchs (Kinorhyncha)
[edit]Cambrian kinorhynchs from Qingjiang biota, also known as "mud dragons", reached 4 cm (1.6 in) in length, much larger than extant relatives that grow only a few millimeters in length.[627][628]
Arthropods (Arthropoda)
[edit]Dinocaridida
[edit]Gilled lobopodians
[edit]
Based on the findings of mouthparts, the Cambrian gilled lobopodian Omnidens amplus is estimated to have been 1.5 metres (4.9 ft).[629] It is also known as the largest Cambrian animal known to exist.[629]
Radiodont (Radiodonta)
[edit]
The largest known radiodont is Aegirocassis benmoulai, estimated to have been at least 2 m (6 ft 7 in) long.[630][631]
Chelicerata
[edit]Sea spiders (Pycnogonida)
[edit]The largest fossil sea spider is Palaeoisopus problematicus with legspan about 32 cm (13 in).[632]
Horseshoe crabs and allies (Xiphosura)
[edit]- Willwerathia reached 9 cm (3.5 in) in carapace width and was the largest species of basal ("synziphosurine") xiphosurans.[633][634] However, the Devonian Maldybulakia reached nearly 11.5 cm (4.5 in)[635] and was assigned to xiphosurans in 2013.[634]
- Horseshoe crab trackway icnofossil Kouphichnium lithographicum from Cerin in Ain indicates length of animal 77.4–85.1 cm (30.5–33.5 in).[636]
Chasmataspidids (Chasmataspidida)
[edit]
The largest chasmataspidids were the Ordovician Hoplitaspis at 29 cm (11 in) in length and similar in size range Chasmataspis.[637]
Eurypterids (Eurypterida)
[edit]
- The largest known eurypterid was Jaekelopterus rhenaniae at 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) in length, which is also the largest arthropod known to exist.[638] Erettopterus grandis possibly reached this same length but this is based on an incomplete telson only. A close contender was Acutiramus bohemicus at 2.1 m (6 ft 11 in) in length.[639] The largest megalograptid as well as the largest Ordovician eurypterid was Pentecopterus. It reached up to 1.7 m (5 ft 7 in) in length.[640] All these were eurypterine eurypterids.[639][640]
- The largest stylonurine eurypterid was Hibbertopterus, with 1.8 m (5 ft 11 in) in length.[639]
Arachnids (Arachnida)
[edit]- There are three contenders for largest-known arachnid as well as the largest scorpions of all time: Pulmonoscorpius kirktonensis, Brontoscorpio anglicus and Praearcturus gigas. Each was estimated to have been 70 cm (28 in),[641] 90 cm (35 in)[642] and up to 100 cm (39 in),[643] respectively.
- Mongolarachne jurassica is the largest described fossil spider, with the total body length of female is approximately 24.6 mm (0.97 in) while the front legs reach about 56.5 mm (2.22 in) in length.[644] Dinodiplura ambulacra had larger body length, combined length of carapace and opisthosoma reaches 26.15 mm (1.030 in).[645]
- The largest of prehistoric whipscorpions and possibly the largest-known whipscorpion ever discovered[646] was Mesoproctus rayoli. Type species had body length reaching 66.9 mm (2.63 in) with a carapace of 25.7 mm (1.01 in) in length, while another specimen have a carapace of 32.5 mm (1.28 in) in length and 16 mm (0.63 in) in width, comparable or even larger than the extant Mastigoproctus have.[647][648]
- The largest Ricinulei to ever exist was Curculioides bohemondi with a body length of 21.77 mm (0.857 in).[649]
- The largest fossil acariform mite and also the largest erythraeoid mite ever recorded was Immensmaris chewbaccei with idiosoma of more than 8 mm (0.31 in) in length.[650]
- The largest known trigonotarbid was Kreischeria with a minimal length of 51 mm (2.0 in).[651] The second largest was Pleophrynus at 36 mm (1.4 in) in length.[651]
Artiopods (Artiopoda)
[edit]Retifacies probably reached up to 55 cm (22 in).[652] Tegopelte is another one example of large non-trilobite artiopod, reached 280 mm (11 in) long[653] and was the largest of the Burgess Shale bilaterians, surpassing all other benthic organisms by at least twice.[653]
Trilobites (Trilobita)
[edit]Some of trilobites exceeded 60 cm (24 in) in length. A nearly complete specimen of Isotelus rex from Manitoba attained a length over 70 cm (28 in), and an Ogyginus forteyi from Portugal was almost as long. Fragments of trilobites suggest even larger record sizes. An isolated pygidium of Hungioides bohemicus implies that the full animal was 90 cm (35 in) long.[654]
Myriapods (Myriapoda)
[edit]
The largest known myriapod by far was Arthropleura. Measuring 2.5 metres (8 ft 2 in) long[655] and 50 centimetres (20 in) wide.[656] Some specimens could have been even larger, up to 2.63 metres (8 ft 8 in) in length and 50 kilograms (110 lb) in weight.[657][658]
Non-hexapod crustaceans (Crustacea)
[edit]Cycloids (Cyclida)
[edit]The largest cyclid was Opolanka decorosa, the Late Triassic Halicyne-like cycloid which reached over 6 cm (2.4 in) across the carapace.[659]
Remipedes (Remipedia)
[edit]Tesnusocaris had body length at least 9.5 cm (3.7 in),[660] larger than every living remipedes which could reach up to 4.5 cm (1.8 in).[661]
Insects (Insecta)
[edit]Sawflies, wasps, bees, ants and allies (Hymenoptera)
[edit]
- The largest known of this group was the giant ant Titanomyrma giganteum with queens growing to 6 cm (2.4 in). It had a wingspan of 15 cm (5.9 in).[662]
- Apis lithohermaea is one of the largest honey bees ever found, comparable in size to the modern Apis dorsata.[663]
- The giant horntail Ypresiosirex orthosemos reached 67.9 mm (2.67 in) in length including the incomplete ovipositor.[664] Another example of giant sawfly is Hoplitolyda duolunica, with wingspan over 92 mm (3.6 in).[665]
Fleas (Siphonaptera)
[edit]The largest known in Siphonaptera was probably Pseudopulex magnus, growing to 0.90 in (22.8 mm) in length.[666]
Earwigs (Dermaptera)
[edit]
Extinct as recently as after 1967[667][668] and also submitted as the Holocene subfossils,[669] the Saint Helena giant earwig (Labidura herculeana, with synonym Labidura loveridgei) reached 84 mm (3.3 in) in length including forceps 34 mm (1.3 in) long.[667]
Chresmodidae
[edit]Chresmodidae had long specialized legs like of the modern Gerridae family. One of the Chresmodidae, Chresmoda obscura, could have reached a size of about 19 centimetres (7.5 in).[670]
Beetles (Coleoptera)
[edit]One of the largest known fossil beetles in the superfamily Scarabaeoidea is Protognathinus spielbergi. It had total length including mandibles about 5.5 centimetres (2.2 in).[671] The largest fossil scarabaeid was Oryctoantiquus borealis with an estimated body length of 5 centimetres (2.0 in).[672]
Titanopterans (Titanoptera)
[edit]
Related to modern orthopterans, titanopterans from the Triassic period were much larger. The wingspan of Gigatitan vulgaris was up to 40 centimetres (16 in).[673] Clatrotitan andersoni also reached a huge size, having a forewing of 13.8 centimetres (5.4 in) long.[674]
Antlions and related net-winged insects (Neuroptera)
[edit]Makarkinia adamsi from the Crato Formation is estimated to have the longest forewings of any neuropteran species, estimated at 160 mm (6.3 in).[675]
Cockroaches, termites, mantises and allies (Dictyoptera)
[edit]- Some Carboniferous cockroach-like insects grouping in Blattoptera like Archoblattina beecheri[676] and Necymylacris (Xenoblatta) scudderi[677][678] could reach around 9 centimetres in total length, which is comparable to a modern Megaloblatta longipennis.
- Cretaceous cockroach Ptiloteuthis foliatus had 7.9 cm (3.1 in) long wing.[679]
- Found in the Miocene of Austria, the giant termite Gyatermes styriensis reached 25 mm (0.98 in) in body length and had a wingspan of 76 mm (3.0 in).[680]
Dragonflies, damselflies and griffinflies (Odonatoptera)
[edit]
- The largest known odonatopteran insect was Meganeuropsis permiana with single wing of 33 cm (13 in). Meganeura had a 32 cm (13 in) long wing.[681]
- Triadotypid odonatan Reisia gelasii (=Triadotypus guillaumei) from Triassic had 136 millimetres (5.4 in) long wing, and wingspan can be 280 millimetres (11 in).[682][683]
Mayflies (Ephemeroptera)
[edit]- The largest known mayfly is Permian Ponalex maximus, with 55 mm (2 in) long hindwing.[684] Cretaceous Epicharmeropsis quadrivenulosus had 37 mm (1 in) long forewing.[685]
- Although Bojophlebia prokopi from the Upper Carboniferous of Moravia (Czech Republic) with a wingspan of 45 cm (18 in) is described as the largest mayfly,[686] later study shows that this insect is not related to mayflies.[687]
Palaeodictyoptera
[edit]The largest known palaeodictyopteran was Mazothairos, with an estimated wingspan of up to 560 mm (22 in).[688] If subcircular wing known from Piesberg Quarry belongs to palaeodictyopteran, it possibly had single wing length at least 30 cm (12 in).[689]
Archaeognatha (jumping bristletails) and other wingless primitive insects
[edit]- The largest known machilid is Triassic Gigamachilis, with 40 millimetres (1.6 in) body length not counting the length of the filament, and estimated total length about 80 millimetres (3.1 in).[690]
- The largest specimens of the extinct suborder Monura reached 30 millimetres (1.2 in) or more, not counting the length of the filament.[691]
- Although Ramsdelepidion was once considered as 60 millimetres (2.4 in)-long silverfish,[692] it was later considered that classification is uncertain and just treated as stem group insect.[693]
- Wingless early insect Carbotriplura had body length about 103 millimetres (4.1 in) without tail filaments.[694]
Chaetognatha
[edit]The Cambrian Timorebestia koprii lived 518 million years ago and was a relative of the extant arrow worms living in today's oceans. Growing to lengths of 30 cm, including the antennae, they were much larger and massive than modern forms. Before the evolution of nektonic panarthropods, jawed vertebrates and cephalopods, this group of large predatory gnathiferans dominated the top of the food chain.[695][696]
Ringed worms (Annelida)
[edit]Websteroprion is the largest known fossil eunicidan annelid, with estimated length ranges 0.42–8.3 m (1 ft 5 in – 27 ft 3 in), however comparison with closely related extant taxa indicates length around 1–2 m (3 ft 3 in – 6 ft 7 in).[697] It also had the biggest scolecodonts of any prehistoric polychaete, up to 13.2 mm (0.52 in) in length and possibly larger.[697]
Molluscs (Mollusca)
[edit]Snails and slugs (Gastropoda)
[edit]
- The largest known gastropods were in the genus Campanile, with the extinct Campanile giganteum having shell lengths up to 90 cm (35 in)[698] or even more than 120 cm (47 in).[699]
- The largest known cowrie is Vicetia bizzottoi, with shell length of 33.5 cm (13.2 in).[700]
- Pebasiconcha immanis is the largest land snail ever known, shell height is 25.6 cm (10.1 in) with a partial specimen that may exceed 30 cm (12 in) in height.[701]
Bivalves (Bivalvia)
[edit]- The largest known bivalve ever as well as the largest inoceramid was Platyceramus platinus, a giant that usually had an axial length of 1 m (3 ft 3 in), but some individuals could reach an axial length of up to 3 m (9.8 ft).[702] Another large prehistoric bivalve was Inoceramus. In 1952, 187 cm (6.14 ft)-long specimen of Inoceramus steenstrupi was found in the Late Cretaceous deposits of Greenland.[703]
- Some Permian alatoconchid genus like Shikamaia had shell length about 1 m (3 ft 3 in).[704] Previous estimation reconstructed length of Shikamaia around 1.6 m (5 ft 3 in).[705]
- The longest ostreid is Konbostrea, with shell height reaching up to 1.2 m (3 ft 11 in).[706]
- Rudist Titanosarcolites had overall size around 2 m (6 ft 7 in).[707]
Tusk shells (Scaphopoda)
[edit]- Complete shell length of tusk shell Prodentalium onoi is estimated to be over 30 cm (12 in).[708]
Cephalopods (Cephalopoda)
[edit]
Nautiloids (Nautiloidea)
[edit]The largest and longest known of nautiloids was Endoceras giganteum with a shell length of 5.73 m (18.8 ft). There is a record of individual whose shell length had reached 9.14 m (30.0 ft), but it is doubtful.[709]
Ammonites (Ammonoidea)
[edit]The largest known ammonite was Parapuzosia seppenradensis.[710] A partial fossil specimen found in Germany had a shell diameter of 1.95 m (6 ft 5 in), but the living chamber was incomplete, so the estimated shell diameter was probably about 3.5 m (11 ft) and weighed about 705 kg (1,554 lb) when it was alive.[711] However, later study estimates shell diameter up to around 2 m (6 ft 7 in).[712]
Belemnites (Belemnoidea)
[edit]The largest known belemnite was Megateuthis gigantea, reaching about 50 and 700 mm (2.0 and 27.6 in) in maximum diameter and length of rostrum, respectively.[713]
Squids, octopuses, cuttlefishes and allies (Neocoleoidea)
[edit]- Octopod Enchoteuthis melanae (considered as specimen of Tusoteuthis longa) had mantle length up to 2 metres (6 ft 7 in), comparable to the modern-day giant squid. Previously, this taxon is considered as animal like giant squid, with total length including arms over 10 metres (33 ft). However, considering other fossil relatives, total length including arms is estimated to be around 3 metres (9.8 ft).[714]
- Both non-octopod Yezoteuthis and teuthid Haboroteuthis are estimated to be similar in size to the modern-day giant squid.[715][716]
Brachiopods (Brachiopoda)
[edit]
The largest brachiopod ever evolved was Striatifera striata from Akkermanovka Quarry, Russia, with height up to 0.5 metres (1 ft 8 in).[717] Another huge brachiopod was the Carboniferous Gigantoproductus giganteus, with shell width from 30 cm (12 in)[718] to over 35 centimetres (14 in).[707][719] Titanaria costellata had large and long shell 35–36 cm (14–14 in) in width, nearly as large as Gigantoproductus.[720]
Hyoliths (Hyolitha)
[edit]The largest hyolith is Macrotheca almgreeni, with length about 50 centimetres (20 in).[707][721]
Cnidarians (Cnidaria)
[edit]Jellyfishes and allies (Medusozoa)
[edit]The largest fossil jellyfish is Cambrian Cordubia gigantea, with diameter of 88 centimetres (35 in).[722] Specimens from the Cambrian of Wisconsin reached 70 cm (28 in) in length.[723]
Vendobionts (Vendobionta)
[edit]Petalonamids (Petalonamae)
[edit]
Longest specimens of Trepassia wardae (also known as Charnia wardi) reached 185 cm (73 in) in length.[724] Charnia masoni is known from specimens as small as only 1 cm (0.39 in), up to the largest specimens of 66 cm (26 in) in length.[725]
Proarticulata
[edit]Dickinsonia tenuis reached 1.4 m (4.6 ft) in length, that makes it one of the largest precambrian organisms.[726][727]
Sponges (Porifera)
[edit]The largest known Permian sponge Gigantospongia had diameter up to 2.5 metres (8 ft 2 in).[728]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Carbone, Chris; Teacher, Amber; Rowcliffe, J (2007). "The Costs of Carnivory". PLOS Biology. 5 (2): e22. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050022. PMC 1769424. PMID 17227145.
- ^ Hokkanen, J.E.I. (21 February 1986). "The size of the largest land animal". Journal of Theoretical Biology. 118 (4): 491–499. Bibcode:1986JThBi.118..491H. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.63.3969. doi:10.1016/S0022-5193(86)80167-9. PMID 3713220.
- ^ Romano, Marco; Citton, Paolo; Maganuco, Simone; Sacchi, Eva; Caratelli, Martina; Ronchi, Ausonio; Nicosia, Umberto (2019). Somerville, I. D. (ed.). "New basal synapsid discovery at the Permian outcrop of Torre del Porticciolo (Alghero, Italy)". Geological Journal. 54 (3): 1554–1566. Bibcode:2019GeolJ..54.1554R. doi:10.1002/gj.3250. ISSN 0072-1050. S2CID 133755506.
- ^ "Permian Stratigraphy – International Commission on Stratigraphy International Union of Geological Sciences" (PDF). permian.stratigraphy.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 December 2018. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ Reisz, Robert R.; Fröbisch, Jörg (16 April 2014). "The Oldest Caseid Synapsid from the Late Pennsylvanian of Kansas, and the Evolution of Herbivory in Terrestrial Vertebrates". PLOS ONE. 9 (4): e94518. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...994518R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0094518. PMC 3989228. PMID 24739998.
- ^ Romer, A.S.; Price, L.W. (1940). "Review of the Pelycosauria". Geological Society of America Special Papers (28): 400, 403. ISBN 978-0-8137-2028-9.
- ^ "Edaphosaurus". Palaeos. Archived from the original on 20 February 2022. Retrieved 9 September 2022.
- ^ Berman, D.S.; Reisz, R.R.; Martens, T.; Henrici, A.C. (2001). "A new species of Dimetrodon (Synapsida: Sphenacodontidae) from the Lower Permian of Germany records first occurrence of genus outside of North America" (PDF). Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 38 (5): 803–812. Bibcode:2001CaJES..38..803B. doi:10.1139/cjes-38-5-803.
- ^ Brink, Kirstin S.; Reisz, Robert R. (16 October 2014). "Hidden dental diversity in the oldest terrestrial apex predator Dimetrodon". Nature Communications. 5: 3269. Bibcode:2014NatCo...5.3269B. doi:10.1038/ncomms4269. PMID 24509889.
- ^ Olson, E.C. (1955). "Parallelism in the evolution of the Permian reptilian faunas of the Old and New Worlds". Fieldiana. 37 (13): 395. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ St. Fleur, Nicholas (4 January 2019). "An Elephant-Size Relative of Mammals That Grazed Alongside Dinosaurs". The New York Times. Retrieved 9 September 2022.
- ^ Sulej, Tomasz; Niedzwiedzki, Grzegorz (4 January 2019). "An elephant-sized Late Triassic synapsid with erect limbs". Science. 363 (6422): 78–80. Bibcode:2019Sci...363...78S. doi:10.1126/science.aal4853. PMID 30467179.
- ^ "Gigantic mammal "cousin" discovered". Science Daily. 23 November 2018. Archived from the original on 22 August 2022. Retrieved 10 September 2022.
- ^ van Valkenburgh, Blaire; Jenkins, Ian (2002). "Evolutionary Patterns in the History of Permo-Triassic and Cenozoic synapsid predators". Paleontological Society Papers 8: 267–288.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Brithopodidae / Anteosauridae". Kheper. M.Alan Kazlev. Archived from the original on 12 August 2019. Retrieved 9 September 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Eotitanosuchidae". Kheper. M.Alan Kazlev. Archived from the original on 6 August 2019. Retrieved 9 September 2022.
- ^ Prothero, Donald R. (18 April 2022). "20. Synapsids: The Origin of Mammals". Vertebrate Evolution: From Origins to Dinosaurs and Beyond. Boca Raton: CRC Press. doi:10.1201/9781003128205-4. ISBN 978-0-367-47316-7. S2CID 246318785.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Kammerer, Christian F. (2016). "Systematics of the Rubidgeinae (Therapsida: Gorgonopsia)". PeerJ. 4: e1608. doi:10.7717/peerj.1608. PMC 4730894. PMID 26823998.
- ^ Frank Zachos, Robert Asher (22 October 2018). Mammalian Evolution, Diversity and Systematics. De Gruyter. pp. 158–159. ISBN 978-3-11-034155-3. Retrieved 9 September 2022.
- ^ J. Van Den Heever (1987), Dissertation Presented for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy at the University of Stellenbosch
- ^ LYDEKKER, R. (1908). "The Year's Vertebrate Palæontology". Science Progress in the Twentieth Century (1906–1916). 2 (7): 501–524. JSTOR 43776634.
- ^ Broom, Robert (1903). "On Some New Primitive Theriodonts". Annals of the South African Museum. 4.
- ^ Tolchard, Frederick; Kammerer, Christian F.; Butler, Richard J.; Hendrickx, Christophe; Benoit, Julien; Abdala, Fernando; Choiniere, Jonah N. (26 July 2021). "A new large gomphodont from the Triassic of South Africa and its implications for Gondwanan biostratigraphy" (PDF). Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 41 (2): e1929265. Bibcode:2021JVPal..41E9265T. doi:10.1080/02724634.2021.1929265. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 237517965.
- ^ William A. Clemens (2011). "New morganucodontans from an Early Jurassic fissure filling in Wales (United Kingdom)". Palaeontology. 54 (5): 1139–1156. Bibcode:2011Palgy..54.1139C. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2011.01094.x.
- ^ Rose 2006, p. 56
- ^ Paul Selden; John Nudds (19 September 2012). Evolution of Fossil Ecosystems. Second edition. Academic Press. p. 178. ISBN 978-0-12-404629-0. Retrieved 25 August 2022.
- ^ Zofia Kielan-Jaworowska; Richard L. Cifelli; Zhe-Xi Luo (2004). "Chapter 12: Metatherians". Mammals from the Age of Dinosaurs: origins, evolution, and structure. New York: Columbia University Press. p. 243. ISBN 978-0-231-11918-4.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Prothero, Donald R. (15 November 2016). The Princeton Field Guide to Prehistoric Mammals. Princeton University Press. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-691-15682-8. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Frank Zachos, Robert Asher (22 October 2018). Mammalian Evolution, Diversity and Systematics. De Gruyter. p. 224. ISBN 978-3-11-034155-3. Retrieved 25 August 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Rose 2006, p. 62.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Kielan-Jaworowska, Zofia (2013). In Pursuit of Early Mammals. Indiana University Press. p. 115. ISBN 978-0-253-00824-4. Retrieved 25 August 2022.
- ^ Hu; et al. (2005). "Large Mesozoic mammals fed on young dinosaurs" (PDF). Nature. 433 (7022): 149–152. Bibcode:2005Natur.433..149H. doi:10.1038/nature03102. PMID 15650737. S2CID 2306428.
- ^ T. S. Kemp (2005). The Origin and Evolution of Mammals. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 183. ISBN 978-0-19-850761-1. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Rose 2006, p. 60
- ^ Thomas E. Williamson, Stephen L. Brusatte, Ross Secord, Sarah Shelley, A new taeniolabidoid multituberculate (Mammalia) from the middle Puercan of the Nacimiento Formation, New Mexico, and a revision of taeniolabidoid systematics and phylogeny, 5 October 2015, doi: 10.1111/zoj.12336: "Taeniolabidoids underwent a modest taxonomic radiation during the early Palaeocene of North America and underwent a dramatic increase in body size, with Taeniolabis taoensis possibly exceeding 100 kg"
- ^ "Zaglossus hacketti – extinct giant echidna". Tourism Western Australia. Archived from the original on 26 January 2014. Retrieved 28 April 2014.
- ^ Pian, Rebecca; Archer, Michael; Hand, Suzanne J. (1 November 2013). "A new, giant platypus, Obdurodon tharalkooschild, sp. nov. (Monotremata, Ornithorhynchidae), from the Riversleigh World Heritage Area, Australia". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (6): 1255–1259. Bibcode:2013JVPal..33.1255P. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.782876. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 85776473.
- ^ Weil, Anne (2005). "Mammalian palaeobiology: Living large in the Cretaceous". Nature. 433 (7022) (published 12 January 2005): 116–117. Bibcode:2005Natur.433..116W. doi:10.1038/433116b. PMID 15650725. S2CID 52869101.
- ^ Prevosti, Francisco J.; Forasiepi, Analía; Zimicz, Natalia (5 November 2011). "The Evolution of the Cenozoic Terrestrial Mammalian Predator Guild in South America: Competition or Replacement?". Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 20 (1): 3–21. doi:10.1007/s10914-011-9175-9. hdl:11336/2663. S2CID 15751319.
- ^ Ercoli, Marcos Darío; Prevosti, Francisco Juan (1 December 2011). "Estimación de Masa de las Especies de Sparassodonta (Mammalia, Metatheria) de Edad Santacrucense (Mioceno Temprano) a Partir del Tamaño del Centroide de los Elementos Apendiculares: Inferencias Paleoecológicas" [Mass Estimation of the Holy Cross (Early Miocene) Sparassodonta (Mammalia, Metatheria) Species from the Centroid Size of the Appendicular Elements: Paleoecological Inferences]. Ameghiniana (in Spanish). 48 (4): 462–479. doi:10.5710/amgh.v48i4(347). S2CID 129838311.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h Sorkin, Boris (December 2008). "A biomechanical constraint on body mass in terrestrial mammalian predators". Lethaia. 41 (4): 333–347. Bibcode:2008Letha..41..333S. doi:10.1111/j.1502-3931.2007.00091.x.
- ^ Engelman, Russell K.; Flynn, John J. (John Joseph); Wyss, André R.; Croft, Darin A. (17 July 2020). Eomakhaira molossus, a new saber-toothed sparassodont (Metatheria: Thylacosmilinae) from the early Oligocene (?Tinguirirican) Cachapoal locality, Andean Main Range, Chile. (American Museum novitates, no. 3957) (Report). American Museum of Natural History. hdl:2246/7235.
- ^ A. M. Forasiepi, M. Judith Babot, and N. Zimicz. 2014. Australohyaena antiqua (Mammalia, Metatheria, Sparassodonta), a large predator from the Late Oligocene of Patagonia. Journal of Systematic Palaeontology 13(6):503–525 DOI: 10.1080/14772019.2014.926403
- ^ Rose 2006, p. 78
- ^ Zofia Kielan-Jaworowska; Richard L. Cifelli; Zhe-Xi Luo (2004). "Chapter 12: Metatherians". Mammals from the Age of Dinosaurs: origins, evolution, and structure. New York: Columbia University Press. p. 428. ISBN 978-0-231-11918-4.
- ^ Wilson, G.P.; Ekdale, E.G.; Hoganson, J.W.; Calede, J.J.; Linden, A.V. (2016). "A large carnivorous mammal from the Late Cretaceous and the North American origin of marsupials". Nature Communications. 7: 13734. Bibcode:2016NatCo...713734W. doi:10.1038/ncomms13734. PMC 5155139. PMID 27929063.
- ^ "Ice Age Marsupial Topped Three Tons, Scientists Say". Archived from the original on 13 April 2010.
- ^ Richards, Hazel L.; Wells, Rod T.; Evans, Alistair R.; Fitzgerald, Erich M. G.; Adams, Justin W. (13 September 2019). "The extraordinary osteology and functional morphology of the limbs in Palorchestidae, a family of strange extinct marsupial giants". PLOS ONE. 14 (9): e0221824. Bibcode:2019PLoSO..1421824R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0221824. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 6744111. PMID 31518353.
- ^ Alloing-Séguier, Léanie; Sánchez-Villagra, Marcelo R.; Lee, Michael S. Y.; Lebrun, Renaud (2013). "The Bony Labyrinth in Diprotodontian Marsupial Mammals: Diversity in Extant and Extinct Forms and Relationships with Size and Phylogeny". Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 20 (3): 191–198. doi:10.1007/s10914-013-9228-3. S2CID 16385939.
- ^ Wroe, S.; Myers, T. J.; Wells, R. T.; Gillespie, A. (1999). "Estimating the weight of the Pleistocene marsupial lion, Thylacoleo carnifex (Thylacoleonidae:Marsupialia): implications for the ecomorphology of a marsupial super-predator and hypotheses of impoverishment of Australian marsupial carnivore faunas". Australian Journal of Zoology. 47 (5): 489. doi:10.1071/ZO99006. ISSN 0004-959X.
- ^ Hocknull, Scott A.; Lewis, Richard; Arnold, Lee J.; Pietsch, Tim; Joannes-Boyau, Renaud; Price, Gilbert J.; Moss, Patrick; Wood, Rachel; Dosseto, Anthony; Louys, Julien; Olley, Jon; Lawrence, Rochelle A. (18 May 2020). "Extinction of eastern Sahul megafauna coincides with sustained environmental deterioration". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 2250. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.2250H. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-15785-w. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7231803. PMID 32418985.
- ^ Helgen, K. M.; Wells, R. T.; Kear, B. P.; Gerdtz, W. R.; Flannery, T. F. (2006). "Ecological and evolutionary significance of sizes of giant extinct kangaroos". Australian Journal of Zoology. 54 (4): 293–303. doi:10.1071/ZO05077.
- ^ Janis, CM; Buttrill, K; Figueirido, B (2014). "Locomotion in Extinct Giant Kangaroos: Were Sthenurines Hop-Less Monsters?". PLOS ONE. 9 (10): e109888. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9j9888J. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109888. PMC 4198187. PMID 25333823.
- ^ Long, John A. (2002). Prehistoric Mammals of Australia and New Guinea: One Hundred Million Years of Evolution. Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 174. ISBN 978-0-8018-7223-5.
- ^ Kazimierz Kowalski (1976). Mammals. An Outline of Theriology. Polish Scientific Publishers. p. 442. Retrieved 17 September 2022.
- ^ John W. Hoganson (2007). Dinosaurs, Sharks, and Woolly Mammoths. State Historical Society of North Dakota. p. 36. ISBN 978-1-891419-33-1. Retrieved 17 September 2022.
- ^ Uhen, Mark D.; Gingerich, Philip D. (1995). "Evolution of Coryphodon (Mammalia, Pantodonta) in the Late Paleocene and Early Eocene of Northwestern Wyoming" (PDF). Contributions from the Museum of Paleontology, University of Michigan. 29 (10): 264. OCLC 742731820. Retrieved 17 September 2022.
- ^ "Paleocene mammals of the world". Archived from the original on 11 September 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Paleocene mammals of the world". www.paleocene-mammals.de. Archived from the original on 3 August 2022. Retrieved 17 September 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b TJ Meehan, Larry D. Martin (1 September 2012). "New Large Leptictid Insectivore from the Late Paleogene of South Dakota, USA". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 57 (3): 509–518. doi:10.4202/app.2011.0035. S2CID 129358395.
- ^ MacPhee, Ross (January 1994). "Morphology, adaptations, and relationships of Plesiorycteropus, and a diagnosis of a new order of eutherian Mammals". Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History (220): 148 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ "Hippopotamus - paleofiles.com". Archived from the original on 31 October 2020.
- ^ Donald R. Prothero, Scott E. Foss (2007). The Evolution of Artiodactyls. The Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 128–129. ISBN 978-0-8018-8735-2. Retrieved 26 September 2020.
- ^ Peterson, O. A. (1909). "A revision of the Entelodontidae". Memoirs of the Carnegie Museum. 4 (3): 41–158. doi:10.5962/p.234831. hdl:2027/mdp.39015017493571. S2CID 247000277.
- ^ Osborn, H. F. (11 November 1924). "Andrewsarchus, giant mesonychid of Mongolia" (PDF). American Museum Novitates (146). American Museum of Natural History. Archived from the original on 2 November 2020.
- ^ Thewissen, J. G. M.; Cooper, Lisa Noelle; Clementz, Mark T.; Bajpai, Sunil; Tiwari, B. N. (2009). "Thewissen et al. Reply". Nature. 458 (7236): E5. Bibcode:2009Natur.458....5T. doi:10.1038/nature07775. S2CID 4431497.
- ^ R. Tabuce, J. Clavel, and M. T. Antunes. 2011. A structural intermediate between triisodontids and mesonychians (Mammalia, Acreodi) from the earliest Eocene of Portugal. Naturwissenschaften 98:145–155
- ^ East, Shirley G. (29 December 2011). The Dream Hunters Epoch: The Paleo Indians Series. Xlibris Corporation. ISBN 978-1-4653-9694-5.
- ^ Fariña, Richard A.; Vizcaíno, Sergio F.; Iuliis, Gerry De (22 May 2013). Megafauna: Giant Beasts of Pleistocene South America. Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-0-253-00719-3.
- ^ "Bison Latifrons – Characteristics, Behavior and Habitat of Bison Latifrons, the Giant Bison". Archived from the original on 10 November 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Extinct Long-horned Bison & Ancient Bison (Bison latifrons and B. antiquus) Fact Sheet: Summary. San Diego Zoo Global Library". Archived from the original on 15 January 2021.
- ^ Kurten, B; Anderson, E (1980). "Order Artiodactyla". Pleistocene mammals of North America (1st ed.). New York: Columbia University Press. pp. 295–339. ISBN 0-231-03733-3.
- ^ "Warkworth Western Weekend Rodeo | Competitors". Archived from the original on 21 August 2011. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- ^ Palmer, Douglas, ed. (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. p. 281. ISBN 978-1-84028-152-1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Camps, Gabriel (1992). "Bubalus antiquus". In Camps, Gabriel (ed.). Encyclopédie Berbère (in French). Aix-en-Provence: Edisud. pp. 1642–1647. doi:10.4000/encyclopedieberbere.1875. Archived from the original on 18 July 2020. Retrieved 31 August 2022.
- ^ Pomel, Auguste (1893). Bubalus antiquus. Carte de Géologie de l'Algérie – Paléontologie Monographies de Vertébrés (in French). Algiers: imprimerie P. Fontana. pp. 1–94, pl.1–10. doi:10.5962/bhl.title.13867.
- ^ Kysely, René. "Aurochs and potential crossbreeding with domestic cattle in Central Europe in the Eneolithic period. A metric analysis of bones from the archaeological site of Kutná Hora-Denemark (Czech Republic)". Anthropozoologica. 43 (2): 2008.
- ^ "Kouprey (Bos sauveli)". Archived from the original on 10 August 2011.
- ^ Burnie D and Wilson DE (Eds.), Animal: The Definitive Visual Guide to the World's Wildlife. DK Adult (2005), ISBN 0-7894-7764-5
- ^ K. Suraprasit; J.-J. Jaegar; Y. Chaimanee; O. Chavasseau; C. Yamee; P. Tian; S. Panha (2016). "The Middle Pleistocene vertebrate fauna from Khok Sung (Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand): biochronological and paleobiogeographical implications". ZooKeys (613): 1–157. Bibcode:2016ZooK..613....1S. doi:10.3897/zookeys.613.8309. PMC 5027644. PMID 27667928.
- ^ Douglas M. Considine, Glenn D. Considine (2013). Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia. Springer US. p. 446. ISBN 978-1-4757-6918-0. Retrieved 28 August 2022.
- ^ Herring, Andy D. (2014). Beef Cattle Production Systems. CABI. p. 22. ISBN 978-1-78064-507-0. Retrieved 28 August 2022.
- ^ Terry Harrison (27 January 2011). Paleontology and Geology of Laetoli: Human Evolution in Context. Volume 2: Fossil Hominins and the Associated Fauna. Springer Netherlands. p. 404. ISBN 978-90-481-9962-4. Retrieved 17 September 2022.
- ^ Discovery. Magazine of the Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University. Volumes 13–16. Peabody Museum of Natural History. 1978. p. 9. Retrieved 17 September 2022.
- ^ Report of the South African Association for the Advancement of Science. Volume 96. South African Association for the Advancement of Science. 2000. p. 163. Retrieved 17 September 2022.
- ^ David Petersen (1989). "Of Moose, Megaloceros and Miracles". Motherearthnews.com. Archived from the original on 4 May 2017.
- ^ Moen, Ron A.; Pastor, John; Cohen, Yosef (1999). "Antler growth and extinction of Irish elk" (PDF). Evolutionary Ecology Research: 235–249. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 August 2022.
- ^ Charalampos Kevrekidis; Dimitris S. Kostopoulos (March 2017). "The southernmost occurrence of Cervalces latifrons (Johnson, 1874) (Artiodactyla: Cervidae) in Europe". ResearchGate. doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.24751.53928.
- ^ Geist, Valerius (1998). Deer of the world: their evolution, behaviour, and ecology. Stackpole Books. ISBN 978-0-8117-0496-0.Oxworth Books. pp. 111, 126, 247–250. (1998) ISBN 0-8117-0496-3
- ^ Breda, Marzia (2010). "Cervalces latifrons". Natural History Museum. Archived from the original on 4 January 2014.
- ^ Strauss, Bob. "Stag Moose – Facts and Figures". Thoughtco.com. Archived from the original on 4 November 2021. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ^ "(in Spanish)". Laignoranciadelconocimiento.blogspot.com.es. 23 December 2011. Archived from the original on 27 January 2022. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ^ Basu, Christopher; Falkingham, Peter L.; Hutchinson, John R. (January 2016). "The extinct, giant giraffid Sivatherium giganteum: skeletal reconstruction and body mass estimation". Biology Letters. 12 (1): 20150940. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2015.0940. PMC 4785933. PMID 26763212.
- ^ Palmer, D., ed. (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. p. 273. ISBN 1-84028-152-9.
- ^ Janis, C. M., Theodor, J. M., & Boisvert, B. (2002). Locomotor evolution in camels revisited: a quantitative analysis of pedal anatomy and the acquisition of the pacing gait. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, 22(1), 110–121.
- ^ Teeth: Kubanochoerus gigas lii (GUAN). tesorosnaturales.es
- ^ Pickford, M. (2006). "New suoid specimens from Gebel Zelten, Libya". Estudios Geológicos. 62 (1). doi:10.3989/egeol.0662147.
- ^ Palmer 1999, p. 269
- ^ Giant Camel Disappeared Species Archived 10 November 2013 at the Wayback Machine. Intechinc.com (5 July 2011)
- ^ Mendoza, M.; Janis, C. M.; Palmqvist, P. (2006). "Estimating the body mass of extinct ungulates: a study on the use of multiple regression". Journal of Zoology. 270 (1): 90–101. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.541.9021. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2006.00094.x.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Giant camel fossil found in Syria". BBC News. 10 October 2006. Archived from the original on 27 September 2019. Retrieved 17 April 2013.
- ^ Rebecca Wragg Sykes (17 June 2022). Néandertal, un parent: À la découverte de nos origines. Delachaux et Niestlé. ISBN 978-2-603-02968-8. Retrieved 28 August 2022.
- ^ Anthony J. Stuart, 2021, Vanished Giants: The Lost World of the Ice Age, "6.17 Yesterday's Camel: Camelops Hesternus", p.99, University of Chicago Press
- ^ Bianucci, G.; Lambert, O.; Urbina, M.; Merella, M.; Collareta, A.; Bennion, R.; Salas-Gismondi, R.; Benites-Palomino, A.; Post, K.; de Muizon, C.; Bosio, G.; Di Celma, C.; Malinverno, E.; Pierantoni, P.P.; Villa, I.M.; Amson, E. (2023). "A heavyweight early whale pushes the boundaries of vertebrate morphology". Nature. 620 (7975): 824–829. Bibcode:2023Natur.620..824B. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06381-1. PMID 37532931. S2CID 260433513.
- ^ Gingerich, P. D.; Arif, M; Bhatti, M Akram; Anwar, M; Sanders, William J (1997). "Basilosaurus drazindai and Basiloterus hussaini, New Archaeoceti (Mammalia, Cetacea) from the Middle Eocene Drazinda Formation, with a Revised Interpretation of Ages of Whale-Bearing Strata in the Kirthar Group of the Sulaiman Range, Punjab (Pakistan)". Contributions from the Museum of Paleontology, University of Michigan. 30 (2): 55–81. hdl:2027.42/48652. OCLC 742731913.
- ^ Kellogg R. A review of the Archaeoceti. Carnegie Institution of Washington Publications. 1936; 482: 1–366.
- ^ Voss, Manja; Antar, Mohammed Sameh M.; Zalmout, Iyad S.; Gingerich, Philip D. (2019). "Stomach contents of the archaeocete Basilosaurus isis: Apex predator in oceans of the late Eocene". PLOS ONE. 14 (1). e0209021. Bibcode:2019PLoSO..1409021V. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0209021. PMC 6326415. PMID 30625131.
- ^ Giovanni Bianucci; Giulia Bosio; Elisa Malinverno; Christian De Muizon; Igor Villa; Mario Urbina; Olivier Lambert (2018). "A new large squalodelphinid (Cetacea, Odontoceti) from Peru sheds light on the Early Miocene platanistoid disparity and ecology". Royal Society Open Science. 5 (4): 172–302. Bibcode:2018RSOS....572302B. doi:10.1098/rsos.172302. PMC 5936943. PMID 29765678. S2CID 21680097. Archived from the original on 13 August 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Deméré, T.A.; Berta, A.; McGowen, M.R. (2005). "The taxonomic and evolutionary history of fossil and modern balaenopteroid mysticetes". Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 12 (1/2): 99–143. doi:10.1007/s10914-005-6944-3. S2CID 90231.
- ^ Slater, Graham J.; Goldbogen, Jeremy A.; Pyenson, Nicholas D. (31 May 2017). "Independent evolution of baleen whale gigantism linked to Plio-Pleistocene ocean dynamics". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 284 (1855): 20170546. doi:10.1098/rspb.2017.0546. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 5454272. PMID 28539520.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h Larramendi, A. (2016). "Shoulder height, body mass and shape of proboscideans" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 61. doi:10.4202/app.00136.2014. S2CID 2092950.
- ^ Fortelius, M.; Kappelman, J. (1993). "The largest land mammal ever imagined". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 108: 85–101. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1993.tb02560.x.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Zhegallo, V.; Kalandadze, N.; Shapovalov, A.; Bessudnova, Z.; Noskova, N.; Tesakova, E. (2005). "On the fossil rhinoceros Elasmotherium (including the collections of the Russian Academy of Sciences)" (PDF). Cranium. 22 (1): 17–40.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Schvyreva, A.K. (2016). Эласмотерии плейстоцена Евразии (PDF) (in Russian). pp. 103–105.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Kosintsev, P.; Mitchell, K. J.; Devièse, T.; van der Plicht, J.; Kuitems, M.; Petrova, E.; Tikhonov, A.; Higham, T.; Comeskey, D.; Turney, C.; Cooper, A.; van Kolfschoten, T.; Stuart, A. J.; Lister, A. M. (2019). "Evolution and extinction of the giant rhinoceros Elasmotherium sibiricum sheds light on late Quaternary megafaunal extinctions". Nature Ecology & Evolution. 3 (1): 31–38. doi:10.1038/s41559-018-0722-0. hdl:11370/78889dd1-9d08-40f1-99a4-0e93c72fccf3. PMID 30478308. S2CID 53726338.
- ^ Krause, Hans (2011). "Hkhpe 07 02". hanskrause.de. Archived from the original on 28 August 2022. Retrieved 10 September 2022.
- ^ Hans-Dieter Sues, Ross D.E. MacPhee (30 June 1999). Extinctions in Near Time. Causes, Contexts, and Consequences. Springer US. p. 262. ISBN 978-0-306-46092-0. Retrieved 17 September 2022.
- ^ Boeskorov, G. G. (2012). "Some specific morphological and ecological features of the fossil woolly rhinoceros (Coelodonta antiquitatis Blumenbach 1799)". Biology Bulletin. 39 (8): 692–707. Bibcode:2012BioBu..39..692B. doi:10.1134/S106235901208002X. S2CID 24868968.
- ^ "Coelodonta antiquitatis (Mammal)". Triebold Paleontology, Inc. Archived from the original on 2 June 2012. Retrieved 28 August 2022.
- ^ "Amynodonts". Archived from the original on 8 September 2006.
- ^ Maclaren, Jamie A; Hulbert, Richard C; Wallace, Steven C; Nauwelaerts, Sandra (5 October 2018). "A morphometric analysis of the forelimb in the genus Tapirus (Perissodactyla: Tapiridae) reveals influences of habitat, phylogeny and size through time and across geographical space". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 184 (2): 499–515. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zly019. ISSN 0024-4082.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Stanislav Drobyshevsky (2021). Палеонтология антрополога. Том 3. Кайнозой (Paleontology of anthropologist. Volume 3. Cenozoic). LitRes. ISBN 978-5-04-380567-6. Retrieved 19 September 2022.
- ^ Patricia Vickers Rich; Thomas Hewitt Rich; Mildred Adams Fenton; Carroll Lane (15 January 2020). The Fossil Book: A Record of Prehistoric Life. Dover Publications. p. 573. ISBN 978-0-486-83855-7. Retrieved 25 August 2022.
- ^ Agate Fossils National Monument NPS Natural Resource Report NPS/NRPC/GRD/NRR-2009/080 (J. Graham, March 2009)
- ^ Jump up to: a b Bob Strauss. "Overview of Brontotherium (Megacerops)". About. Archived from the original on 21 November 2021.
- ^ "Brontotherium – Titanothere – Oligocene epoch". Archived from the original on 26 May 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gregory S. Paul; Guy D. Leahy (1994). "Terramegathermy in the time of the titans: Restoring the metabolics of colossal dinosaurs" (PDF). The Paleontological Society Special Publications. 7: Dino Fest: 177–198. doi:10.1017/S2475262200009515. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2022.
- ^ "Brontotheriidae. American Museum of Natural History". Archived from the original on 20 November 2021.
- ^ Eisenmann, Vera (2003). "Gigantic horses" (PDF). Advances in Vertebrate Paleontology.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Bruce J. MacFadden (1992). Fossil Horses: Systematics, Paleobiology, and Evolution of the Family Equidae. Cambridge University Press. p. 284. ISBN 0-521-47708-5. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ^ Kathleen M. Janis (1998). Evolution of Tertiary Mammals of North America: Volume 1, Terrestrial, Carnivores, Ungulates and Ungulatel-like mammals. Cambridge University Press. p. 545. ISBN 978-0-521-35519-3. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ^ T. S. Kemp (4 November 2004). The Origin and Evolution of Mammals. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 237. ISBN 978-0-19-154517-7. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ^ Jerison, Harry J (December 2007). "What Fossils Tell Us about the Evolution of the Neocortex" (PDF). Evolution of Nervous Systems: 1–12. doi:10.1016/B0-12-370878-8/00065-3. ISBN 978-0-12-370878-6.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Patricia Vickers Rich; Thomas Hewitt Rich; Mildred Adams Fenton; Carroll Lane Fenton (15 January 2020). The Fossil Book: A Record of Prehistoric Life. Dover Publications. p. 555. ISBN 978-0-486-83855-7. Retrieved 4 September 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Ice Age Mammals - EnchantedLearning.com".
- ^ Soibelzon, L. H.; Schubert, B. W. (January 2011). "The Largest Known Bear, Arctotherium angustidens, from the Early Pleistocene Pampean Region of Argentina: With a Discussion of Size and Diet Trends in Bears". Journal of Paleontology. 85 (1): 69–75. doi:10.1666/10-037.1. hdl:11336/104215. S2CID 129585554. Retrieved 1 June 2011.
- ^ Dell'Amore, C. (2011): Biggest Bear Ever Found, National Geographic News, Published 3 February 2011
- ^ Figueirido; et al. (2010). "Demythologizing Arctodus simus, the "short-faced" long-legged and predaceous bear that never was". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 30 (1): 262–275. Bibcode:2010JVPal..30..262F. doi:10.1080/02724630903416027. S2CID 85649497.
- ^ SOIBELZON, LEOPOLDO H.; SCHUBERT, BLAINE W. (2011). "The Largest Known Bear, Arctotherium Angustidens, from the Early Pleistocene Pampean Region of Argentina: With a Discussion of Size and Diet Trends in Bears". Journal of Paleontology. 85 (1): 69–75. doi:10.1666/10-037.1. hdl:11336/104215. JSTOR 23019499. S2CID 129585554.
- ^ Live Science Staff (25 November 2008). "Huge Cave Bears: When and Why They Disappeared". Live Science.
- ^ C. Jin, R. L. Ciochon, W. Dong, R. M. Hunt, Jr., J. Liu, M. Jaeger, and Q. Zhu. 2007. "The first skull of the earliest giant panda". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 104:10932-10937
- ^ Jump up to: a b Berta, Annalisa (2017). The Rise of Marine Mammals: 50 Million Years of Evolution. Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 110. ISBN 978-1-4214-2325-8. Retrieved 21 August 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Xénia Keighley; Morten Tange Olsen; Peter Jordan; Sean P.A. Desjardins (2021). The Atlantic Walrus: Multidisciplinary Insights into Human-Animal Interactions. Charlotte Cockle. p. 17. ISBN 978-0-12-817431-9. Retrieved 21 August 2022.
- ^ Morgan Churchill, Mark T. Clementz, Naoki Kohno. "Cope's rule and the evolution of body sizein Pinnipedimorpha (Mammalia: Carnivora)". Evolution. 2015 Jan;69(1):201-15. doi:10.1111/evo.12560
- ^ István Fozy; István Szente; Gareth Dyke (1977). Otarioid seals of the Neogene. Geological Survey Professional Paper, Volume 992. Geological Survey (U.S.). pp. 61–62. Retrieved 21 August 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Grohe, Camille; Uno, Kevin; Boisserie, Jean-Renaud (2022). "Lutrinae Bonaparte, 1838 (Carnivora, Mustelidae) from the Plio-Pleistocene of the Lower Omo Valley, southwestern Ethiopia: systematics and new insights into the paleoecology and paleobiogeography of the Turkana otters". Comptes Rendus Palevol (in French). 30 (30): 684–693. doi:10.5852/cr-palevol2022v21a30. S2CID 252106648.
- ^ Geraads, Denis; Alemseged, Zeresenay; Bobe, René; Reed, Denné (2011). "Enhydriodon dikikae, sp. nov. (Carnivora: Mammalia), a gigantic otter from the Pliocene of Dikika, Lower Awash, Ethiopia". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 31 (2): 447–453. Bibcode:2011JVPal..31..447G. doi:10.1080/02724634.2011.550356. S2CID 84797296.
- ^ "The Bear Otter". Wired. 26 March 2011.
- ^ "Siamogale melilutra: Giant Otter Fossils Reveal New Species – Paleontology – Sci-News.com". sci-news.com.
- ^ "Islands of otters and strange foxes". scienceblogs.com.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Valenciano, Alberto; Baskin, Jon A.; Abella, Juan; Pérez-Ramos, Alejandro; Álvarez-Sierra, M. Ángeles; Morales, Jorge; Hartstone-Rose, Adam (7 April 2016). "Megalictis, the Bone-Crushing Giant Mustelid (Carnivora, Mustelidae, Oligobuninae) from the Early Miocene of North America". PLOS ONE. 11 (4): e0152430. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1152430V. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0152430. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4824437. PMID 27054570.
- ^ Prothero, Donald R. (2016). The Princeton Field Guide to Prehistoric Mammals. Princeton University Press. p. 144. ISBN 978-1-4008-8445-2. Retrieved 28 August 2022.
- ^ Turner, Alan (2004). Evolving eden: an illustrated guide to the evolution of the African large-mammal fauna. Mauricio Antón. New York: Columbia University Press. pp. 106–107. ISBN 0-231-11944-5. OCLC 53900492.
- ^ Orlov, Y. U. 1948. Perunium ursogulo Orlov, a new gigantic extinct mustelid (a contribution to the morphology of the skull and brain and to the phylogeny of Mustelidae). Acta Zoologica 29:63–105.
- ^ Valenciano, Alberto; Abella, Juan; Sanisidro, Oscar; Hartstone-Rose, Adam; Álvarez-Sierra, María Ángeles; Morales, Jorge (27 May 2015). "Complete description of the skull and mandible of the giant mustelid Eomellivora piveteaui Ozansoy, 1965 (Mammalia, Carnivora, Mustelidae), from Batallones (MN10), late Miocene (Madrid, Spain)". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (4): e934570. Bibcode:2015JVPal..35E4570V. doi:10.1080/02724634.2014.934570. S2CID 86216613.
- ^ Forasiepi, Analía M.; Prevosti, Francisco J. (2018). Evolution of South American mammalian predators during the Cenozoic: paleobiogeographic and paleoenvironmental contingencies. Cham: Springer. pp. 124–125. ISBN 978-3-319-03701-1.
- ^ Tarquini, Juliana; Toledo, Néstor; Soibelzon, Leopoldo H.; Morgan, Cecilia C. (March 2017). "Body mass estimation for †Cyonasua (Procyonidae, Carnivora) and related taxa based on postcranial skeleton". Historical Biology. 30 (4): 496–506. doi:10.1080/08912963.2017.1295042. hdl:11336/49670. S2CID 90408657.
- ^ Díaz-Sibaja, R. (2010). "Titanes Vol. 1 Mamíferos." Fósil Revista de Paleontología. ISSN 0717-9235
- ^ Andersson, Ki (2005). "Were there pack-hunting canids in the Tertiary, and how can we know?". Paleobiology. 41 (4): 333–347. Bibcode:2005Pbio...31...56A. doi:10.1666/0094-8373(2005)031<0056:WTPCIT>2.0.CO;2. S2CID 85306826.
- ^ Wang, Xiaoming; Tedford, Richard H. (2008). Dogs: Their Fossil Relatives & Evolutionary History.
- ^ "Wolves, Coyotes, and Dogs (Genus Canis)". Museum.state.il.us. Retrieved 23 October 2011.
- ^ Boudadi-Maligne, Myriam (2012). "Une nouvelle sous-espèce de loup (Canis lupus maximus nov. Subsp.) dans le Pléistocène supérieur d'Europe occidentale [A new subspecies of wolf (Canis lupus maximus nov. subsp.) from the upper Pleistocene of Western Europe]". Comptes Rendus Palevol. 11 (7): 475. doi:10.1016/j.crpv.2012.04.003.
- ^ Berte, E.; Pandolfi, L. (2014). "Canis lupus (Mammalia, Canidae) from the Late Pleistocene deposit of Avetrana (Taranto, Southern Italy)". Rivista Italiana di Paleontoligia e Stratigrafia. 120 (3): 367–379.
- ^ Figueirido, Borja; Pérez−Claros, Juan A.; Hunt, Robert M. Jr.; Palmqvist, Paul. "Body mass estimation in amphicyonid carnivoran mammals: A multiple regression approach from the skull and skeleton – Acta Palaeontologica Polonica" (PDF). www.app.pan.pl. doi:10.4202/app.2010.0005. S2CID 56051166.
- ^ Jordi Agusti and Mauricio Anton: Mammoths, Sabertooths, and Hominids 65 million years of Mammalian Evolution in Europe, Columbia University Press, 2002, pp.81–83
- ^ Barrett, Paul Zachary (26 October 2021). "The largest hoplophonine and a complex new hypothesis of nimravid evolution". Scientific Reports. 11 (1): 21078. Bibcode:2021NatSR..1121078B. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-00521-1. PMC 8548586. PMID 34702935. S2CID 240000358.
- ^ Peigné, S.; de Bonis, L.; Likius, A.; Mackaye, H. T.; Vignaud, P.; Brunet, M. (2005). "A new machairodontine (Carnivora, Felidae) from the Late Miocene hominid locality of TM 266, Toros-Menalla, Chad". Comptes Rendus Palevol. 4 (3): 243–253. Bibcode:2005CRPal...4..243P. doi:10.1016/j.crpv.2004.10.002.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Sherani, Shaheer (2016). "A new specimen-dependent method of estimating felid body mass" (PDF). PeerJ Preprints: 16. doi:10.7287/peerj.preprints.2327v2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2022. Retrieved 25 August 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Giovanni G. Bellani (2019). Felines of the World. Discoveries in Taxonomic Classification and History. Elsevier Science. pp. 30–31. ISBN 978-0-12-817277-3. Retrieved 19 September 2022.
- ^ "Newly identified saber-toothed cat is one of largest in history".
- ^ Orcutt, John D.; Calede, Jonathan J.M. (2021). "Quantitative Analyses of Feliform Humeri Reveal the Existence of a Very Large Cat in North America During the Miocene". Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 28 (3): 729–751. doi:10.1007/s10914-021-09540-1. S2CID 235541255.
- ^ "Giant Saber-Toothed Cat Roamed North America during Miocene | Paleontology". Sci-News.com. 4 May 2021. Retrieved 19 September 2022.
- ^ "Xenosmilus". ucmp.berkeley.edu. Retrieved 4 September 2022.
- ^ Merriam, J. C. & Stock, C. 1932: The Felidae of Rancho La Brea. Carnegie Institution of Washington Publications 442, 1–231.
- ^ DeSantis, L. R.; Schubert, B. W.; Scott, J. R.; Ungar, P. S. (2012). "Implications of diet for the extinction of saber-toothed cats and American lions". PLOS ONE. 7 (12): e52453. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...752453D. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052453. PMC 3530457. PMID 23300674.
- ^ Manthi, Fredrick K.; Brown, Francis H.; Plavcan, Michael J.; Werdelin, Lars (March 2018). "Gigantic lion, Panthera leo, from the Pleistocene of Natodomeri, eastern Africa". Journal of Paleontology. 92 (2): 305–312. Bibcode:2018JPal...92..305M. doi:10.1017/jpa.2017.68. ISSN 0022-3360.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Argant, Alain; Argant, Jacqueline (2011). "The Panthera gombaszogensis story: the contribution of the Château Breccia (Saône-et-Loire, Burgundy, France)". Quaternaire (Hors-serie 4): 247–269.
- ^ Anne Schmidt-Kuentzel; Laurie Marker; Lorraine K. Boast (2017). Cheetahs: Biology and Conservation. Elsevier Science. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-12-804120-8. Retrieved 4 September 2022.
- ^ Lane, H.H. (1947). "Survey of the Fossil Vertebrates of Kansas: Part V: The Mammals (Continued)" (PDF). Transactions of the Kansas Academy of Science (1903–). 50 (3/4). Kansas Academy of Science (published December 1947): 273–314. doi:10.2307/3625600. JSTOR 3625600.
- ^ Antón, Mauricio (22 November 2013). Sabertooth. Indiana University Press. pp. 104–107. ISBN 978-0-253-01049-0. Retrieved 26 August 2022.
- ^ Alan Turner, National Geographic Prehistoric Mammals National Geographic, 2004, ISBN 0-7922-7134-3
- ^ Turner, Alan; Antón, Mauricio (1996). "The giant hyaena Pachycrocuta brevirostris (Mammalia, Carnivora, Hyaenidae)". Geobios. 29 (#4): 455–468. Bibcode:1996Geobi..29..455T. doi:10.1016/S0016-6995(96)80005-2.
- ^ Flannery, Tim (2018). Europe. The First 100 Million Years. Penguin Books Limited. p. 29: Other temperate giants. ISBN 978-0-14-198903-7. Retrieved 21 August 2022.
- ^ "Sabertooth's Bane: Introducing Dinocrocuta". wordpress.com. 12 January 2016. Archived from the original on 12 November 2020.
- ^ Personal communication from R. Dewer in Burness et al., 2001, table 1
- ^ Wroe et al., 2004, p. 297
- ^ Goodman, S. (2009). "Family Eupleridae (Madagascar Carnivores)". In Wilson, D.; Mittermeier, R. (eds.). Handbook of the Mammals of the World. Volume 1: Carnivores. Lynx Edicions. ISBN 978-84-96553-49-1. Archived from the original on 25 July 2011. Retrieved 31 May 2010.
- ^ Borths, M. R.; Stevens, N. J. (2019). "Simbakubwa kutokaafrika, gen. et sp. nov. (Hyainailourinae, Hyaenodonta, "Creodonta," Mammalia), a gigantic carnivore from the earliest Miocene of Kenya". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 39 (1): e1570222. Bibcode:2019JVPal..39E0222B. doi:10.1080/02724634.2019.1570222. S2CID 145972918.
- ^ Savage, R. J. G. (1973). "Megistotherium, gigantic hyaenodont from Miocene of Gebel Zelten, Libya". Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), Geology. 22 (7): 483–511. doi:10.5962/p.150151.
- ^ Jump up to: a b N. N. Kramarenko (1974). Зоогеография палеогена Азии (Zoogeography of Paleogene of Asia). Publishing office "Nauka". pp. 113–114. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^ O'Leary, Maureen A.; Lucas, Spencer G.; Williamson, Thomas E. (2000). "A new specimen of Ankalagon (Mammalia, Mesonychia) and evidence of sexual dimorphism in mesonychians". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 20 (2): 387–93. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2000)020[0387:ANSOAM]2.0.CO;2. JSTOR 4524103. S2CID 86542114.
- ^ Paleocene mammals of the world "Carnivores, creodonts and carnivorous ungulates: Mammals become predators"
- ^ "100,000-Year-Old Fossil of Giant Vampire Bat Found in Argentina – Paleontology – Sci-News.com". sci-news.com. 26 July 2021.
- ^ Villier, Boris (2010). "Deinogalerix: a giant hedgehog from the Miocene". Annali dell'Università di Ferrara. 6: 93–102. ISSN 1824-2707.
- ^ Freudenthal, M. (1972). "Deinogalerix koenigswaldi nov. gen., nov. spec., a giant insectivore from the Neogene of Italy". Scripta Geologica. 14: 1–19.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Engelman, Russell K. (June 2022). "Resizing the largest known extinct rodents (Caviomorpha: Dinomyidae, Neoepiblemidae) using occipital condyle width". Royal Society Open Science. 9 (6): 220370. Bibcode:2022RSOS....920370E. doi:10.1098/rsos.220370. PMC 9198521. PMID 35719882.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Defler, Thomas (2018). History of Terrestrial Mammals in South America. Springer International Publishing. pp. 151–154. ISBN 978-3-319-98449-0. Retrieved 27 August 2022.
- ^ Biknevicus, A. R.; McFarlane, D. A.; MacPhee, R. D. E. (1993). "Body size in Amblyrhiza inundata (Rodentia: Caviomorpha), an extinct megafaunal rodent from the Anguilla Bank, West Indies: Estimates and implications". American Museum Novitates (3079). New York: American Museum of Natural History: 1–25. hdl:2246/4976.
- ^ Swinehart, Anthony L.; Richards, Ronald L. (2001). "Paleoecology of Northeast Indiana Wetland Harboring Remains of the Pleistocene Giant Beaver (Castoroides Ohioensis)". Proceedings of the Indiana Academy of Science. 110: 151. Retrieved 18 August 2022.
- ^ Milius, Susan (2011). "The Bunny That Ruled Minorca". Science News. 179 (9): 18. doi:10.1002/scin.5591790921.
- ^ Gaudin, Timothy J.; Emry, Robert J.; Wible, John R. (December 2009). "The Phylogeny of Living and Extinct Pangolins (Mammalia, Pholidota) and Associated Taxa: A Morphology Based Analysis". Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 16 (4): 235–305. doi:10.1007/s10914-009-9119-9. ISSN 1064-7554. S2CID 1773698.
- ^ Hooijer, D.A., 1947 - A femur of Manis palaeojavanica Dubois from Western Java - Proceedings of the Koninklijke Nederlandsche Akademie van Wetenschappen 50 (4): 423–418
- ^ Ciochon, Russell L. "The Ape that Was – Asian fossils reveal humanity's giant cousin". University of Iowa. Archived from the original on 25 May 2015. Retrieved 7 September 2022.
- ^ Pettifor, Eric (2000) [1995]. "From the Teeth of the Dragon: Gigantopithecus Blacki". Selected Readings in Physical Anthropology. Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company. pp. 143–149. ISBN 978-0-7872-7155-8. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 7 September 2022.
- ^ Zhang, Yingqi; Harrison, Terry (January 2017). "Gigantopithecus blacki: a giant ape from the Pleistocene of Asia revisited". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 162 (S63): 153–177. doi:10.1002/ajpa.23150. ISSN 0002-9483. PMID 28105715. S2CID 46838584.
- ^ Wibowo, A. "Steps of The Asian Giants: Modeling the Body Size Related Foraging Ecology of Meganthropus palaeojavanicus, a 8 Feet Hominid in Central Java". Preprints 2020, 2020110504 (doi: 10.20944/preprints202011.0504.v1).
- ^ Zanolli, Clément; Kullmer, Ottmar; Kelley, Jay; Bacon, Anne-Marie; Demeter, Fabrice; Dumoncel, Jean; Fiorenza, Luca; Grine, Frederick E.; Hublin, Jean-Jacques; Nguyen, Anh Tuan; Nguyen, Thi Mai Huong (May 2019). "Evidence for increased hominid diversity in the Early to Middle Pleistocene of Indonesia". Nature Ecology & Evolution. 3 (5): 755–764. Bibcode:2019NatEE...3..755Z. doi:10.1038/s41559-019-0860-z. ISSN 2397-334X. PMID 30962558. S2CID 102353734.
- ^ Froehle AW, Churchill SE (2009). "Energetic Competition Between Neandertals and Anatomically Modern Humans" (PDF). PaleoAnthropology: 96–116. Retrieved 12 September 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Carretero, José-Miguel; Rodríguez, Laura; García-González, Rebeca; Arsuaga, Juan-Luis; Gómez-Olivencia, Asier; Lorenzo, Carlos; Bonmatí, Alejandro; Gracia, Ana; Martínez, Ignacio (2012). "Stature estimation from complete long bones in the Middle Pleistocene humans from the Sima de los Huesos, Sierra de Atapuerca (Spain)" (PDF). Journal of Human Evolution. 62 (2): 242–255. Bibcode:2012JHumE..62..242C. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2011.11.004. PMID 22196156.
- ^ Alan Walker, Richard Leakey (1993). The Nariokotome Homo erectus skeleton. Harvard University Press. p. 412. ISBN 978-0-674-60075-1. Retrieved 2 October 2022.
- ^ Migliano AB, Guillon M (2012). "The Effects of Mortality, Subsistence, and Ecology on Human Adult Height and Implications for Homo Evolution". Current Anthropology. 53 (S6): 359–368. doi:10.1086/667694. S2CID 84442763.
- ^ Delson, Eric; Terranova, Carl J.; Jungers, William J; Sargis, Sargis; Jablonski, Nina G.; Dechow, Paul C. (2000). "Body mass in Cercopithecidae (Primates, Mammalia): estimation and scaling in extinct and extant taxa". Anthropological Papers of the American Museum of Natural History. 83: 1–159.
- ^ Jablonski, Nina; Leakey, Meave; Anton, Mauricio (1 January 2008), Jablonski, N.G. Leakey, M.G. and Anton, M. (2008) Systematic Paleontology of the Cercopithecines. In: Jablonski, N.G. and Leakey, M.G. (eds.) Koobi Fora Research Project. Volume 6. The Fossil Monkeys. California Academy of Sciences, San Francisco, pp. 103–300., pp. 103–300, retrieved 10 September 2022
- ^ Perry, Jonathan M. G.; Cooke, Siobhán B.; Runestad Connour, Jacqueline A.; Burgess, M. Loring; Ruff, Christopher B. (2018). "Articular scaling and body mass estimation in platyrrhines and catarrhines: Modern variation and application to fossil anthropoids". Journal of Human Evolution. 115: 20–35. Bibcode:2018JHumE.115...20P. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2017.10.008. ISSN 1095-8606. PMID 29150186.
- ^ Rachel H. Dunn. "Additional postcranial remains of omomyid primates from the Uinta Formation, Utah and implications for the locomotor behavior of large-bodied omomyids". Journal of Human EvolutionVolume 58, Issue 5, May 2010, pp. 406–417
- ^ Jungers, W. L.; Demes, B.; Godfrey, L. R. (2008). "How Big were the "Giant" Extinct Lemurs of Madagascar?". In Fleagle, J. G.; Gilbert, C. C. (eds.). Elwyn Simons: A Search for Origins. Developments in Primatology: Progress and Prospects. p. 350. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-73896-3_23. ISBN 978-0-387-73895-6.
- ^ Godfrey, L. R.; Jungers, W. L. (2002). "Quaternary fossil lemurs". In Hartwig, W. C (ed.). The Primate Fossil Record. Cambridge University Press. p. 101. ISBN 978-0-521-66315-1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Crowley, B.E., & Godfrey, L.R. (2019). "Strontium Isotopes Support Small Home Ranges for Extinct Lemurs". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 490. doi: 10.1002/ajp.20817
- ^ Megaladapis edwardsi: Scientific information. Archived copy from 20 January 2021.
- ^ Osborn, H. F. (1942). Proboscidea, Vol. II. New York: The American Museum Press.
- ^ Lister, A.; Bahn, P. (2007). Mammoths – Giants of the Ice Age (3 ed.). London: Frances Lincoln. ISBN 978-0-520-26160-0.
- ^ Mol, D. and van Logchem, W. 2009. The mastodon of Milia: the longest tusks in the world. Deposits 19: 28–32.
- ^ Marsh, Helene; O'Shea, Thomas J.; Reynolds III, John E. (2011). "Steller's sea cow: discovery, biology and exploitation of a relict giant sirenian". Ecology and Conservation of the Sirenia: Dugongs and Manatees. New York, New York: Cambridge University Press. pp. 18–35. ISBN 978-0-521-88828-8. OCLC 778803577.
- ^ Scheffer, Victor B. (November 1972). "The Weight of the Steller Sea Cow". Journal of Mammalogy. 53 (4): 912–914. doi:10.2307/1379236. JSTOR 1379236.
- ^ Andrews, C.W. (1906). A descriptive catalogue of the Tertiary Vertebrata of the Fayûm. British Museum, London. Taylor and Francis. p. 324.
- ^ Mondéjar-Fernández; et al. (2008). "El género Arsinoitherium: catálogo de la colección inédita del Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle de París y el problema del número de especies". Palaeontologica Nova (in Spanish). SEPAZ (8): 292–304.
- ^ Sanders, W.J., Kappelman, J., and Rasmussen, D.T. 2004. New large−bodied mammals from the late Oligocene site of Chilga, Ethiopia. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 49 (3): 365–392.[1].
- ^ Jump up to: a b Rose 2006, p. 260
- ^ Rodolphe Tabuce (2016). "A mandible of the hyracoid mammal Titanohyrax andrewsi in the collections of the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, Paris (France) with a reassessment of the species". Palaeovertebrata. 40 (1): e4. doi:10.18563/pv.40.1.e4.
- ^ J. G. M. Thewissen; E. L. Simons (2001). "Skull of Megalohyrax eocaenus (Hyracoidea, Mammalia) from the Oligocene of Egypt". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 21 (1): 98–106. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2001)021[0098:SOMEHM]2.0.CO;2. JSTOR 4524175. S2CID 86063305.
- ^ Donald R. Prothero; Robert M. Schoch (1989). The Evolution of Perissodactyls. Oxford University Press. p. 65. ISBN 978-0-19-506039-3. Retrieved 20 September 2022.
- ^ Skinner, J. D.; Chimimba, Christian T. (2005). The Mammals of the Southern African Sub-region. Cambridge University Press. p. 41. ISBN 978-1-107-39405-6. Retrieved 20 September 2022.
- ^ Werdelin, Lars; Sanders, William Joseph (2010). Cenozoic Mammals of Africa. University of California Press. p. 143. ISBN 978-0-520-25721-4. Retrieved 20 September 2022.
- ^ Pyenson, Nicholas D.; Vermeij, Geerat J. (2016). "The rise of ocean giants: Maximum body size in Cenozoic marine mammals as an indicator for productivity in the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans". Biology Letters. 12 (7). doi:10.1098/rsbl.2016.0186. PMC 4971165. PMID 27381883. S2CID 1652462.
- ^ Hayashi, Shoji; Houssaye, Alexandra; Nakajima, Yasuhisa; Chiba, Kentaro; Ando, Tatsuro; Sawamura, Hiroshi; Inuzuka, Norihisa; Kaneko, Naotomo; Osaki, Tomohiro (2 April 2013). "Bone Inner Structure Suggests Increasing Aquatic Adaptations in Desmostylia (Mammalia, Afrotheria)". PLOS ONE. 8 (4): e59146. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...859146H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059146. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3615000. PMID 23565143.
- ^ Lister, Adrian (24 April 2018). Darwin's Fossils. The Collection That Shaped the Theory of Evolution. Smithsonian. p. 57. ISBN 978-1-58834-617-9. Retrieved 4 September 2022.
- ^ Larmon, Jean T.; McDonald, H. Gregory; Ambrose, Stanley; DeSantis, Larisa R. G.; Lucero, Lisa J. (27 February 2019). "A year in the life of a giant ground sloth during the Last Glacial Maximum in Belize". Science Advances. 5 (2): eaau1200. Bibcode:2019SciA....5.1200L. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aau1200. PMC 6392778. PMID 30820449.
- ^ "BBC – Science & Nature – Wildfacts – Megatherium". 1 February 2014. Archived from the original on 1 February 2014. Retrieved 29 June 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Johnson, Steven C. and Madden, Richard H.. Uruguaytheriinae Astrapotheres of Tropical South America. Chapter 22 in "Vertebrate Paleontology in the Neotropics. The Miocene Fauna of La Venta, Colombia". Edited by Richard F. Kay, Richard H. Madden, Richard L. Cifelli, and John J. Flynn. Smithsonian Institution Press. Washington and London.
- ^ Kramarz, Alejandro G.; Bond, Mariano (2008). "Revision of Parastrapotherium (Mammalia, Astrapotheria) and other Deseadan astrapotheres of Patagonia". Ameghiniana. 45 (3). Retrieved 1 March 2013.
- ^ Carrillo, Juan D.; Amson, Eli; Jaramillo, Carlos; Sánchez, Rodolfo; Quiroz, Luis; Cuartas, Carlos; Rincón, Aldo F.; Sánchez-Villagra, Marcelo R. (2018). "The Neogene record of northern South American native ungulates". Smithsonian Contributions to Paleobiology. 101 (101): iv-67. doi:10.5479/si.1943-6688.101. S2CID 135113342.
- ^ Gingerich, Philip D. (1998). "Paleobiological Perspectives on Mesonychia, Archaeoceti, and the Origin of Whales". In Thewissen, J.G.M. (ed.). The emergence of whales: evolutionary patterns in the origin of Cetacea. New York: Plenum Press. pp. 423–450. ISBN 978-0-306-45853-8.
- ^ Elissamburu, A (2012). "Estimación de la masa corporal en géneros del Orden Notoungulata". Estudios Geológicos. 68 (1): 91–111. doi:10.3989/egeol.40336.133. hdl:11336/197170.
- ^ Croft, D. A.; Gelfo, J. N.; López, G. M. (2020). "Splendid Innovation: The Extinct South American Native Ungulates". Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences. 48: 259–290. Bibcode:2020AREPS..48..259C. doi:10.1146/annurev-earth-072619-060126. S2CID 213737574.
- ^ Dortangs, Rudi W.; Schulp, Anne S.; Eric W. A. Mulder; John W.M. Jagt (2002). "A large new mosasaur from the Upper Cretaceous of The Netherlands". Netherlands Journal of Geosciences. 81 (1): 1–8. Bibcode:2002NJGeo..81....1D. doi:10.1017/S0016774600020515.
- ^ Grigoriev, Dimitry V. (2014). "Giant Mosasaurus hoffmanni (Squamata, Mosasauridae) from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of Penza, Russia" (PDF). Proceedings of the Zoological Institute RAS. 318 (2): 148–167. doi:10.31610/trudyzin/2014.318.2.148. S2CID 53574339.
- ^ Fanti, Federico; Cau, Andrea; Negri, Alessandra (1 May 2014). "A giant mosasaur (Reptilia, Squamata) with an unusually twisted dentition from the Argille Scagliose Complex (late Campanian) of Northern Italy". Cretaceous Research. 49: 91–104. Bibcode:2014CrRes..49...91F. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2014.01.003. ISSN 0195-6671.
- ^ Everhart, Mike. "Research: Tylosaurus proriger – A new record of a large mosasaur from the Smoky Hill Chalk". Oceans of Kansas. Retrieved 12 May 2010.
- ^ "Fact File: Tylosaurus Proriger from National Geographic". Archived from the original on 7 February 2010. Retrieved 12 May 2010.
- ^ Head, Jason; Bloch, Jonathan; Moreno Bernal, Jorge; Rincón Burbano, Aldo Fernando; Bourque, Jason (2013), Cranial osteology, body size, systematics, and ecology of the giant Paleocene snake Titanoboa cerrejonensis, Society of Vertebrate Paleontology, pp. 140–141, retrieved 22 May 2017
- ^ Jump up to: a b Head, Jason J.; et al. (5 February 2009). "Giant boid snake from the Palaeocene neotropics reveals hotter past equatorial temperatures" (PDF). Nature. 457 (7230): 715–717. Bibcode:2009Natur.457..715H. doi:10.1038/nature07671. PMID 19194448. S2CID 4381423. Retrieved 12 May 2010.
- ^ Datta, Debajit; Bajpai, Sunil (18 April 2024). "Largest known madtsoiid snake from warm Eocene period of India suggests intercontinental Gondwana dispersal". Scientific Reports. 14 (1): 8054. Bibcode:2024NatSR..14.8054D. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-58377-0. ISSN 2045-2322. PMID 38637509.
- ^ Rage, Jean-Claude; Bajpai, Sunil; Johannes G. M. Thewissen; Tiwari, Brahma N. (2003). "Early Eocene snakes from Kutch, Western India, with a review of the Palaeophiidae" (PDF). Geodiversitas. 25 (4): 695–716. ISSN 1280-9659. Retrieved 12 May 2010.
- ^ Rage, J.-C. (1983). "Palaeophis colossaeus nov. sp. (le plus grand Seprent connu?) de l'Eocène du Mali et le problème du genre chez les Palaeopheinae". Comptes Rendus des Séances de l'Académie des Sciences. 3 (296): 1741–1744.
- ^ "Large palaeophiid and nigerophiid snakes from Paleogene Trans-Saharan Seaway deposits of Mali – Acta Palaeontologica Polonica". www.app.pan.pl. Retrieved 8 January 2021.
- ^ Head, J. & Polly, D. 2004. They might be giants: morphometric methods for reconstructing body size in the world's largest snakes. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 24 (Supp. 3), 68A-69A.
- ^ "A giant among snakes". newscientist.com.
- ^ Rio, Jonathan P.; Mannion, Philip D. (4 July 2017). "The osteology of the giant snake Gigantophis garstini from the upper Eocene of North Africa and its bearing on the phylogenetic relationships and biogeography of Madtsoiidae". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 37 (4): e1347179. Bibcode:2017JVPal..37E7179R. doi:10.1080/02724634.2017.1347179. hdl:10044/1/48946. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 90335531.
- ^ Scanlon, John D.; Mackness, Brian S. (1 January 2001). "A new giant python from the Pliocene Bluff Downs Local Fauna of northeastern Queensland". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 25 (4): 425–437. Bibcode:2001Alch...25..425S. doi:10.1080/03115510108619232. ISSN 0311-5518. S2CID 85185368.
- ^ Owen, R. (1857). "On the Fossil Vertebrae of a Serpent (Laophis crotaloides, Ow.) discovered by Capt. Spratt, R.N., in a Tertiary Formation at Salonica". Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society. 13 (1–2): 196–199. doi:10.1144/GSL.JGS.1857.013.01-02.28. S2CID 131142130.
- ^ Benjamin P. Kear (2014). "Rediscovery of Laophis crotaloides – the worlds largest viper?". researchgate.net. Retrieved 14 September 2022.
- ^ Bailon, S., Bover, P., Quintana, J., & Alcover, J. A. (2010). First fossil record of Vipera Laurenti 1768 "Oriental vipers complex" (Serpentes: Viperidae) from the Early Pliocene of the western Mediterranean islands. Comptes Rendus Palevol, 9, 147–154.
- ^ Fachini, Thiago Schineider; Onary, Silvio; Palci, Alessandro; Lee, Michael S. Y.; Bronzati, Mario; Hsiou, Annie Schmaltz (18 December 2020). "Cretaceous Blind Snake from Brazil Fills Major Gap in Snake Evolution". iScience. 23 (12): 101834. Bibcode:2020iSci...23j1834F. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2020.101834. ISSN 2589-0042. PMC 7718481. PMID 33305189.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Molnar, R. E. (2004). Dragons in the Dust: The Paleobiology of the Giant Monitor Lizard Megalania. Indiana University Press. pp. 174–175. ISBN 0-253-34374-7. OCLC 52775128.
- ^ Fry, B.; Wroe, S.; Teeuwisse, W.; Van Osch, M. J. P.; Moreno, K.; Ingle, J.; McHenry, C.; Ferrara, T.; Clausen, P.; Scheib, H.; Winter, K. L.; Greisman, L.; Roelants, K.; Van Der Weerd, L.; Clemente, C. J.; Giannakis, E.; Hodgson, W. C.; Luz, S.; Martelli, P.; Krishnasamy, K.; Kochva, E.; Kwok, H. F.; Scanlon, D.; Karas, J.; Citron, D. M.; Goldstein, E. J. C.; McNaughtan, J. E.; Norman, J. A.; et al. (2009). "A central role for venom in predation by Varanus komodoensis (Komodo Dragon) and the extinct giant Varanus (Megalania) priscus". PNAS. 106 (22): 8969–74. Bibcode:2009PNAS..106.8969F. doi:10.1073/pnas.0810883106. PMC 2690028. PMID 19451641.
- ^ "Review of Dragons in the Dust: The Paleobiology of the Giant Monitor Lizard Megalania, by Ralph E. Molnar, 2004 in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 25(2):479, June 2005" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 January 2016. Retrieved 16 September 2022.
- ^ Colston, T. J.; Kulkarni, P.; Jetz, W.; Pyron, R. A. (2020). "Phylogenetic and spatial distribution of evolutionary diversification, isolation, and threat in turtles and crocodilians (non-avian archosauromorphs)". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 20 (1): 81. Bibcode:2020BMCEE..20...81C. doi:10.1186/s12862-020-01642-3. PMC 7350713. PMID 32650718.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Mike Everhart. "Marine turtles from the Western Interior Sea". Oceans of Kansas. Archived from the original on 7 April 2022.
- ^ Igor Gennadievich Danilov; Ekaterina M. Obraztsova; Maxim Savvich Arkhangelsky; Alexey V. Ivanov; Alexander Averianov (2022). "Protostega gigas and other sea turtles from the Campanian of Eastern Europe, Russia". Cretaceous Research. 135: 105196. Bibcode:2022CrRes.13505196D. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2022.105196. S2CID 247431641.
- ^ Derstler, K.; Leitch, A. D.; Larson, P. L.; Finsley, C.; Hill, L. (1993). "The World's Largest Turtles – The Vienna Archelon (4.6 m) and the Dallas Protostega (4.2 m), Upper Cretaceous of South Dakota and Texas". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 13 (suppl. to no. 3) (33A).
- ^ Kear, Benjamin P. (11 September 2006). "Reassessment of Cratochelone Berneyi Longman, 1915, a giant sea turtle from the Early Cretaceous of Australia". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 26 (3): 779–783. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2006)26[779:ROCBLA]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 140149175.
- ^ H. F. Kaddumi (2006). "A new genus and species of gigantic marine turtles (Chelonioidea: Cheloniidae) from the Maastrichtian of the Harrana Fauna-Jordan" (PDF). PalArch's Journal of Vertebrate Palaeontology. 3 (1): 1–14. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 February 2012. Retrieved 4 February 2010.
- ^ R. Kohler (1995). "A new species of the fossil turtle Psephophorus (Order Testudines) from the Eocene of the South Island, New Zealand". Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand. 25 (3): 371–384. Bibcode:1995JRSNZ..25..371K. doi:10.1080/03014223.1995.9517495. Archived from the original on 4 October 2021.
- ^ Naish, Darren (31 January 2024). "Megalochelys, Truly a Giant Tortoise". Tetrapod Zoology. Retrieved 30 May 2024.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Rhodin, Anders G. J.; Thomson, Scott; Georgalis, Georgios L.; Karl, Hans Volker; Danilov, Igor G.; Takahashi, Akio; de la Fuente, Marcelo SaulIcon; Bourque, Jason; Delfino, Massimo; Bour, Roger; Iverson, John B.; Shaffer, Bradley H.; van Dijk, Peter Paul (2015). "Turtles and Tortoises of the World During the Rise and Global Spread of Humanity: First Checklist and Review of Extinct Pleistocene and Holocene Chelonians" (PDF). Chelonian Research Monographs. 5: 1–66. doi:10.3854/crm.5.000e.fossil.checklist.v1.2015. ISBN 978-0-9653540-9-7. ISSN 1088-7105. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 September 2022.
- ^ Pérez-García, Adán; Vlachos, Evangelos (1 November 2014). "New generic proposal for the European Neogene large testudinids (Cryptodira) and the first phylogenetic hypothesis for the medium and large representatives of the European Cenozoic record". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 172 (3): 653–719. doi:10.1111/zoj12183. ISSN 0024-4082.
- ^ Pérez-García, Adán; Vlachos, Evangelos; Arribas, Alfonso (March 2017). "The last giant continental tortoise of Europe: A survivor in the Spanish Pleistocene site of Fonelas P-1" (PDF). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 470: 30–39. Bibcode:2017PPP...470...30P. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.01.011. hdl:10261/277114. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 January 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Jason J Head; Philip D. Gingerich; S. Mahmood Raza (1999). "Drazinderetes tethyensis, a new large trionychid (Reptilia: Testudines) from the marine Eocene Drazinda Formation of the Sulaiman Range, Punjab (Pakistan)" (PDF). Museum of Paleontology, The University of Michigan. pp. 199–214. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 October 2022.
- ^ Grande, Lance (14 June 2013). The Lost World of Fossil Lake: Snapshots from Deep Time. University of Chicago Press. p. 200. ISBN 978-0-226-92296-6.
- ^ Cadena, E.-A.; Scheyer, T.M.; Carrillo-Briceño, J.D.; Sánchez, R.; Aguilera-Socorro, O.A.; Vanegas, A.; Pardo, M.; Hansen, D.M.; Sánchez-Villagra, M.R. (12 February 2020). "The anatomy, paleobiology, and evolutionary relationships of the largest extinct side-necked turtle". Science Advances. 6 (7): eaay4593. Bibcode:2020SciA....6.4593C. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aay4593. PMC 7015691. PMID 32095528.
- ^ "Researchers reveal ancient giant turtle fossil". Phys.org. 17 May 2012. Archived from the original on 22 September 2022. Retrieved 13 October 2022.
- ^ Maugh II, Thomas H. (18 May 2012). "Researchers find fossil of a turtle that was size of a Smart car". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 23 September 2022. Retrieved 13 October 2022.
- ^ Freeman, David (17 May 2012). "Car-Sized Reptile Lived Alongside Titanoboa, Scientists Say". Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 23 September 2022. Retrieved 13 October 2022.
- ^ Edwin A. Cadena; Daniel T. Ksepka; Carlos A. Jaramillo; Jonathan I. Bloch (2012). "New pelomedusoid turtles from the late Palaeocene Cerrejón Formation of Colombia and their implications for phylogeny and body size evolution". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 10 (2): 313–331. Bibcode:2012JSPal..10..313C. doi:10.1080/14772019.2011.569031. S2CID 59406495.
- ^ Tong, Haiyan; Chanthasit, Phornphen; Naksri, Wilailuck; Ditbanjong, Pitaksit; Suteethorn, Suravech; Buffetaut, Eric; Suteethorn, Varavudh; Wongko, Kamonlak; Deesri, Uthumporn; Claude, Julien (November 2021). "Yakemys multiporcata n. g. n. sp., a Large Macrobaenid Turtle from the Basal Cretaceous of Thailand, with a Review of the Turtle Fauna from the Phu Kradung Formation and Its Stratigraphical Implications". Diversity. 13 (12): 630. doi:10.3390/d13120630.
- ^ Lauren E. Brown, Don Moll (October 2019). "The enigmatic palaeoecology and palaeobiogeography of the giant, horned, fossil turtles of Australasia: a review and reanalysis of the data". Herpetological Journal. 29 (4): 252–263. doi:10.33256/hj29.4.252263. ISSN 0268-0130. Archived from the original on 18 June 2022.
- ^ Ross D.E. MacPhee, Hans-Dieter Sues (1999). Extinctions in near time: causes, contexts, and consequences. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers. p. 251. ISBN 978-0-306-46092-0.
- ^ "PLACODONTS: The bizarre "walrus-turtles" of the Triassic". Oceans of Kansas. Archived from the original on 30 January 2022.
- ^ Liu, Jun (27 November 2014). "A gigantic nothosaur (Reptilia: Sauropterygia) from the Middle Triassic of SW China and its implications for the Triassic biotic recovery". Scientific Reports. 4: 7142. Bibcode:2014NatSR...4E7142L. doi:10.1038/srep07142. PMC 4245812. PMID 25429609.
- ^ O'Gorman, J.P.; Santillana, S.; Otero, R.; Reguero, M. (1 October 2019). "A giant elasmosaurid (Sauropterygia; Plesiosauria) from Antarctica: New information on elasmosaurid body size diversity and aristonectine evolutionary scenarios". Cretaceous Research. 102: 37–58. Bibcode:2019CrRes.102...37O. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2019.05.004. ISSN 0195-6671. S2CID 181725020.
- ^ Kubo, T.; Mitchell, M. T.; Henderson, D. M. (2012). "Albertonectes vanderveldei, a new elasmosaur (Reptilia, Sauropterygia) from the Upper Cretaceous of Alberta". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 32 (3): 557–572. Bibcode:2012JVPal..32..557K. doi:10.1080/02724634.2012.658124. S2CID 129500470.
- ^ Smith, Elliott (1 January 2020). "Revision of the Genus Styxosaurus and Relationships of the Late Cretaceous Elasmosaurids (Sauropterygia: Plesiosauria) of the Western Interior Seaway". Theses, Dissertations and Capstones.
- ^ Mike Everhart (2005). "Bite marks on an elasmosaur (Sauropterygia; Plesiosauria) paddle from the Niobrara Chalk (Upper Cretaceous) as probable evidence of feeding by the lamniform shark, Cretoxyrhina mantelli" (PDF). PalArch's Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 2 (2). Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 2 October 2009.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c O'Gorman, J. P. (2016). "A Small Body Sized Non-Aristonectine Elasmosaurid (Sauropterygia, Plesiosauria) from the Late Cretaceous of Patagonia with Comments on the Relationships of the Patagonian and Antarctic Elasmosaurids". Ameghiniana. 53 (3): 245–268. doi:10.5710/AMGH.29.11.2015.2928. S2CID 133139689.
- ^ Hiller, Norton; Mannering, A.A.; Jones, C.M.; Cruickshank, A.R.I. (2005). "The nature of Mauisaurus haasti Hector, 1874 (Reptilia: Plesiosauria)". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 25 (3): 588–601. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2005)025[0588:TNOMHH]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 130607702.
- ^ Hiller, Norton; O'Gorman, José P.; Otero, Rodrigo A.; Mannering, Al A. (2017). "A reappraisal of the Late Cretaceous Weddellian plesiosaur genus Mauisaurus Hector, 1874". New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics. 60 (2): 112–128. Bibcode:2017NZJGG..60..112H. doi:10.1080/00288306.2017.1281317. S2CID 132037930.
- ^ Knutsen, Espen M.; Druckenmiller, Patric S.; Hurum, Jørn H. (2012). "A new species of Pliosaurus (Sauropterygia: Plesiosauria) from the Middle Volgian of central Spitsbergen, Norway" (PDF). Norwegian Journal of Geology. 92: 235–258. ISSN 1502-5322. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 March 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Buchy, M.-C.; Frey, E.; Stinnesbeck, W.; López-Oliva, J.G. (2003). "First occurrence of a gigantic pliosaurid plesiosaur in the late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian) of Mexico" (PDF). Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France. 174 (3): 271–278. doi:10.2113/174.3.271. hdl:2042/260.
- ^ McHenry, Colin Richard (2009). Devourer of Gods: the palaeoecology of the Cretaceous pliosaur Kronosaurus queenslandicus (PDF) (PhD). pp. 1–460.
- ^ "Monster von Arramberri". Archived from the original on 3 March 2012. Retrieved 10 September 2022.
- ^ "The Cumnor monster mandible". Archived from the original on 11 October 2011. Retrieved 10 September 2022.
- ^ Benjamin P. Kear (8 April 2003). "Cretaceous marine reptiles of Australia: a review of taxonomy and distribution". Cretaceous Research. 24 (3): 277–303. Bibcode:2003CrRes..24..277K. doi:10.1016/S0195-6671(03)00046-6.
- ^ McHenry, Colin R. 2009. Devourer of Gods: The palaeoecology of the Cretaceous pliosaur Kronosaurus queenslandicus. The University of Newcastle, N.S.W. Australia, Web. [2]
- ^ "The Largest Pliosaurid from North America". Archived from the original on 1 August 2016.
- ^ Judy Massare, William R Wahl, Melissa Connely, Mike Ross (2014). Palaeoecology of the marine reptiles of the Redwater Shale Member of the Sundance Formation (Jurassic) of central Wyoming, USA. Geological Magazine 151(01):167–182 DOI:10.1017/S0016756813000472
- ^ Schumacher, B. A.; Carpenter, K.; Everhart, M. J. (2013). "A new Cretaceous Pliosaurid (Reptilia, Plesiosauria) from the Carlile Shale (middle Turonian) of Russell County, Kansas". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (3): 613–628. Bibcode:2013JVPal..33..613S. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.722576. S2CID 130165209.
- ^ Desojo 2013, p. 20
- ^ Desojo 2013, p. 22
- ^ "Redondasaurus". New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science. Archived from the original on 20 December 2015. Retrieved 15 October 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Hans-Dieter Sues (2019). The Rise of Reptiles: 320 Million Years of Evolution. Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 176. ISBN 978-1-4214-2867-3. Retrieved 28 August 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Sterling J. Nesbitt (2011). "The Early Evolution of Archosaurs: Relationships and the Origin of Major Clades". Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 352: 1–292. doi:10.1206/352.1. hdl:2246/6112. S2CID 83493714.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Desojo 2013, p. 260
- ^ Nesbitt, S. J., Brusatte, S. L., Desojo, J. B., Liparini, A., França, M. A. G. D., Weinbaum, J. C., & Gower, D. J. (2013). Rauisuchia. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 379(1), 241–274. https://doi.org/10.1144/SP379.1
- ^ Desojo 2013, p. 527
- ^ Michael J. Benton (2015). Vertebrate Palaeontology. Wiley Blackwell. p. 158. ISBN 978-1-118-40755-4. Retrieved 15 September 2022.
- ^ Liparini, A.; Schultz, C. L. (2013). "A reconstruction of the thigh musculature of the extinct pseudosuchian Prestosuchus chiniquensis from the Dinodontosaurus Assemblage Zone (Middle Triassic Epoch), Santa Maria 1 Sequence, southern Brazil". Geological Society, London, Special Publications. 379 (1): 441–468. Bibcode:2013GSLSP.379..441L. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.985.9550. doi:10.1144/SP379.20. S2CID 130984792.
- ^ Parker, W.G. (2005). "A new species of the Late Triassic aetosaur Desmatosuchus (Archosauria: Pseudosuchia)". Comptes Rendus Palevol. 4 (4): 327–340. Bibcode:2005CRPal...4..327P. doi:10.1016/j.crpv.2005.03.002.
- ^ Desojo, J. B.; Heckert, A. B.; Martz, J. W.; Parker, W. G.; Schoch, R. R.; Small, B. J.; Sulej, T. (2013). "Aetosauria: A clade of armoured pseudosuchians from the Upper Triassic continental beds". Geological Society, London, Special Publications. 379 (1): 203–239. Bibcode:2013GSLSP.379..203D. doi:10.1144/SP379.17. S2CID 129267515.
- ^ von Baczko, M. B., Desojo, J. B., Gower, D. J., Ridgely, R., Bona, P., &Witmer, L. M. (2021). New digital braincase endocasts of two species of Desmatosuchus and neurocranial diversity within Aetosauria (Archosauria: Pseudosuchia). The Anatomical Record, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.24798
- ^ Jump up to: a b Casey M. Holliday and Nicholas M. Gardner (2012). "A New Eusuchian Crocodyliform with Novel Cranial Integument and Its Significance for the Origin and Evolution of Crocodylia". PLOS ONE. 7 (1): e30471. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...730471H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030471. PMC 3269432. PMID 22303441.
- ^ Bocquentin, Jean; Melo, Janira (2006). "Stupendemys souzai sp. nov (Pleurodira, Podocnemididae) from the Miocene-Pliocene of the Solimões Formation, Brazil". Revista Brasileira de Paleontologia. 9 (2): 187–192. doi:10.4072/rbp.2006.2.02.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Крупнейшие крокодиломорфы". vk.com (in Russian). Retrieved 6 September 2022.
- ^ Cidade, Giovanne M.; Rincón, Ascanio D.; Solórzano, Andrés (2020). "New cranial and postcranial elements of Mourasuchus (Alligatoroidea: Caimaninae) from the late Miocene of Venezuela and their palaeobiological implications". Historical Biology. 33 (10): 2387–2399. doi:10.1080/08912963.2020.1795844. S2CID 225395230.
- ^ Paiva, Ana Laura S.; Godoy, Pedro L.; Souza, Ray B. B.; Klein, Wilfried; Hsiou, Annie S. (13 August 2022). "Body size estimation of Caimaninae specimens from the miocene of South America". Journal of South American Earth Sciences. 118: 103970. Bibcode:2022JSAES.11803970P. doi:10.1016/j.jsames.2022.103970. ISSN 0895-9811. S2CID 251560425.
- ^ Schwimmer, David R. (2002). "The Size of Deinosuchus". King of the Crocodylians: The Paleobiology of Deinosuchus. Indiana University Press. pp. 42–63. ISBN 978-0-253-34087-0.
- ^ Lucas, Spencer G.; Sullivan, Robert M.; Spielmann, Justin A. (2006). "The Giant Crocodylian Deinosuchus from the Upper Cretaceous of the San Juan Basin, New Mexico" (PDF). New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin. 35. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 June 2009. Retrieved 11 May 2010.
- ^ Stout, J.B. (2020). "New early Pleistocene Alligator (Eusuchia: Crocodylia) from Florida bridges a Gap in Alligator evolution". Zootaxa. 4868 (1): 41–60. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4868.1.3. PMID 33311408. S2CID 226337860.
- ^ Head, J. J. (2001). "Systematics and body size of the gigantic, enigmatic crocodyloid Rhamphosuchus crassidens, and the faunal history of Siwalik Group (Miocene) crocodylians". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 21 (Supplement to No. 3): 1–117. doi:10.1080/02724634.2001.10010852. S2CID 220414868.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Martin, Jeremy E.; Antoine, Pierre-Olivier; Perrier, Vincent; Welcomme, Jean-Loup; Metais, Gregoire; Marivaux, Laurent (4 July 2019). "A large crocodyloid from the Oligocene of the Bugti Hills, Pakistan" (PDF). Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 39 (4): e1671427. Bibcode:2019JVPal..39E1427M. doi:10.1080/02724634.2019.1671427. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 209439989. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 September 2022.
- ^ Riff, D.; Aguilera, O. A. (2008). "The world's largest gharials Gryposuchus: description of G. croizati n. sp. (Crocodylia, Gavialidae) from the Upper Miocene Urumaco Formation, Venezuela". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 82 (2): 178–195. Bibcode:2008PalZ...82..178R. doi:10.1007/bf02988408. S2CID 85172486.
- ^ Storrs, G. W. (2003). Late Miocene-Early Pliocene crocodilian fauna of Lothagam, southwest Turkana Basin, Kenya. In: Lothagam: The Dawn of Humanity in Eastern Africa pp. 137–159. New York. Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-11870-8.
- ^ Brochu, C. A.; Storrs, G. W. (2012). "A giant crocodile from the Plio-Pleistocene of Kenya, the phylogenetic relationships of Neogene African crocodylines, and the antiquity of Crocodylus in Africa". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 32 (3): 587. Bibcode:2012JVPal..32..587B. doi:10.1080/02724634.2012.652324. S2CID 85103427.
- ^ "Crocodylus anthropophagus". Palaeocritti.com. Archived from the original on 14 June 2016.
- ^ Ewen Callaway (24 February 2010). "Monster crocodile was ancient human nightmare". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 7 December 2021.
- ^ Delfino, Massimo; De Vos, John (March 2014). "A giant crocodile in the Dubois Collection from the Pleistocene of Kali Gedeh (Java)". Integrative Zoology. 9 (2): 141–147. doi:10.1111/1749-4877.12065. hdl:2318/141647. PMID 24673759.
- ^ "Crikey! Massive prehistoric croc emerges from South East Queensland". ScienceDaily. Retrieved 9 January 2021.
- ^ Wroe, S.; Field, J.H.; Archer, M.; Grayson, D.K.; Price, G.J.; Louys, J.; Faith, T.; Webb, G.E.; Davidson, I.; Mooney, S.D. (2013). "Climate change frames debate over the extinction of megafauna in Sahul (Pleistocene Australia-New Guinea)". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110 (22): 8777–8781. Bibcode:2013PNAS..110.8777W. doi:10.1073/pnas.1302698110. PMC 3670326. PMID 23650401.
- ^ Wroe, Stephen (2002). "A review of terrestrial mammalian and reptilian carnivore ecology in Australian fossil faunas, and factors influencing their diversity: the myth of reptilian domination and its broader ramifications". Australian Journal of Zoology. 50 (1): 1. doi:10.1071/zo01053. ISSN 0004-959X.
- ^ Flannery, T. F. (1990). "Pleistocene faunal loss: implications of the aftershock for Australia's past and future". Archaeology in Oceania. 25 (2): 45–55. doi:10.1002/j.1834-4453.1990.tb00232.x.
- ^ Sobbe, Ian H.; Price, Gilbert J.; Knezour, Robert A. (2013). "A ziphodont crocodile from the late Pleistocene King Creek catchment, Darling Downs, Queensland". Memoirs of the Queensland Museum. 52 (2): 601–606.
- ^ Storrs, G. W.; Efimov, M. B. (2000). "Mesozoic crocodyliforms of north-central Eurasia". In Michael J. Benton; Mikhail A. Shishkin; David M. Unwin; Evgenii N. Kurochkin (eds.). The Age of Dinosaurs in Russia and Mongolia. Cambridge University Press. pp. 402–419.
- ^ Lyon, Gabrielle (9 December 2001). "Fact Sheet". SuperCroc. Project Exploration. Retrieved 22 September 2007.
- ^ Haley D O'Brien, Leigha M Lynch; Kent A Vliet; Brueggen, John; Gregory M Erickson; Paul M Gignac (2019). "Crocodylian Head Width Allometry and Phylogenetic Prediction of Body Size in Extinct Crocodyliforms". Integrative Organismal Biology. 1 (1): obz006. doi:10.1093/iob/obz006. PMC 7671145. PMID 33791523.
- ^ Martin, J. E.; Lauprasert, K.; Buffetaut, E.; Liard, R. & Suteethorn, V. (2013). "A large pholidosaurid in the Phu Kradung Formation of north-eastern Thailand". Palaeontology. 57 (4): 757–769. doi:10.1111/pala.12086. S2CID 128482290.
- ^ Buffetaut, E. (1978). "Les Dyrosauridae (Crocodylia, Mesosuchia) des phosphates de l'Eocène inférieur de Tunisie: Dyrosaurus, Rhabdognathus, Phosphatosaurus". Géologie Méditerranéenne. 5 (2): 237–256. doi:10.3406/geolm.1978.1046.
- ^ Naish, D. 2002. Fossils explained 34: Crocodilians. Geology Today 2: 71–77. Archived copy from 24 January 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Molnar RE, de Vasconcellos FM (2016). "Cenozoic dinosaurs in South America – revisited". Memoirs of Museum Victoria. 74: 363–377. doi:10.24199/j.mmv.2016.74.25.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Martin, Jeremy E.; Pochat-Cottilloux, Yohan; Laurent, Yves; Perrier, Vincent; Robert, Emmanuel; Antoine, Pierre-Olivier (28 October 2022). "Anatomy and phylogeny of an exceptionally large sebecid (Crocodylomorpha) from the middle Eocene of southern France". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 42 (4). Bibcode:2022JVPal..42E3828M. doi:10.1080/02724634.2023.2193828. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 258361595.
- ^ Riff, D.; Kellner, A.W.A. (2011). "Baurusuchid crocodyliforms as theropod mimics: clues from the skull and appendicular morphology of Stratiotosuchus maxhechti (Upper Cretaceous of Brazil)". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 163 (s1): s37–s56. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2011.00713.x.
- ^ Dal Sasso, C.; Pasini, G.; Fleury, G.; Maganuco, S. (2017). "Razanandrongobe sakalavae, a gigantic mesoeucrocodylian from the Middle Jurassic of Madagascar, is the oldest known notosuchian". PeerJ. 5: e3481. doi:10.7717/peerj.3481. PMC 5499610. PMID 28690926.
- ^ "Giant croc had teeth like a T. rex". BBC News. BBC. 4 July 2017. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ Cortés, Dirley; Larsson, Hans C.E.; Maxwell, Erin E.; Parra Ruge, Mary Luz; Patarroyo, Pedro; Wilson, Jeffrey A. (6 October 2019). "An Early Cretaceous Teleosauroid (Crocodylomorpha: Thalattosuchia) from Colombia". Ameghiniana. 56 (5): 365. doi:10.5710/amgh.26.09.2019.3269. ISSN 0002-7014. S2CID 210110716.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Young, MT; Rabi, M.; Bell, MA; Foffa, D.; Steel, L.; Sachs, S.; Peyer, K. (2016). "Big-headed marine crocodyliforms and why we must be cautious when using extant species as body length proxies for long-extinct relatives". Palaeontologia Electronica. 19 (3): 1–14. doi:10.26879/648.
- ^ Johnson, Michela M.; Young, Mark T.; Brusatte, Stephen L. (2020). "The phylogenetics of Teleosauroidea (Crocodylomorpha, Thalattosuchia) and implications for their ecology and evolution". PeerJ. 8: e9808. doi:10.7717/peerj.9808. PMC 7548081. PMID 33083104.
- ^ Young, M. T.; Brusatte, S. L.; De Andrade, M. B.; Desojo, J. B.; Beatty, B. L.; Steel, L.; Fernández, M. S.; Sakamoto, M.; Ruiz-Omeñaca, J. I.; Schoch, R. R. (2012). Butler, Richard J (ed.). "The Cranial Osteology and Feeding Ecology of the Metriorhynchid Crocodylomorph Genera Dakosaurus and Plesiosuchus from the Late Jurassic of Europe". PLOS ONE. 7 (9): e44985. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...744985Y. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044985. PMC 3445579. PMID 23028723.
- ^ Young, M. T.; De Andrade, M. B.; Brusatte, S. L.; Sakamoto, M.; Liston, J. (2013). "The oldest known metriorhynchid super-predator: A new genus and species from the Middle Jurassic of England, with implications for serration and mandibular evolution in predacious clades". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 11 (4): 475–513. Bibcode:2013JSPal..11..475Y. doi:10.1080/14772019.2012.704948. S2CID 85276836.
- ^ Young, Mark T.; Brusatte, Stephen L.; De Andrade, Marco Brandalise; Desojo, Julia B.; Beatty, Brian L.; Steel, Lorna; Fernández, Marta S.; Sakamoto, Manabu; Ruiz-Omeñaca, José Ignacio; Schoch, Rainer R.; (2012) "The Cranial Osteology and Feeding Ecology of the Metriorhynchid Crocodylomorph Genera Dakosaurus and Plesiosuchus from the Late Jurassic of Europe", in Butler, Richard J. (ed.), PLoS ONE, vol. 7, no. 9, p. e44985, pmid 23028723, pmc 3445579, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044985
- ^ Jump up to: a b Lindsay E. Zanno, Susan Drymala, Sterling J. Nesbitt, Vincent P. Schneider (2015) Early crocodylomorph increases top tier predator diversity during rise of dinosaurs. Scientific Reports volume 5, Article number: 9276
- ^ Nesbitt, Sterling J.; Irmis, Randall B.; Lucas, Spencer G.; Hunt, Adrian P. (2005). "A giant crocodylomorph from the Upper Triassic of New Mexico". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 79 (4): 471–478. Bibcode:2005PalZ...79..471N. doi:10.1007/bf02988373. S2CID 128541365.
- ^ Crocodylomorpha. Crocodiles and their relatives, archive copy from 20 June 2022.
- ^ Zanno, Lindsay E.; Drymala, Susan; Nesbitt, Sterling J.; Schneider, Vincent P. (19 March 2015). "Early crocodylomorph increases top tier predator diversity during rise of dinosaurs". Scientific Reports. 5: 9276. Bibcode:2015NatSR...5E9276Z. doi:10.1038/srep09276. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 4365386. PMID 25787306.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Witton, M. P.; Naish, D. (2008). McClain, Craig R (ed.). "A Reappraisal of Azhdarchid Pterosaur Functional Morphology and Paleoecology". PLOS ONE. 3 (5): e2271. Bibcode:2008PLoSO...3.2271W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002271. PMC 2386974. PMID 18509539.
- ^ Buffetaut, E.; Grigorescu, D.; Csiki, Z. (2002). "A new giant pterosaur with a robust skull from the latest Cretaceous of Romania" (PDF). Naturwissenschaften. 89 (4): 180–184. Bibcode:2002NW.....89..180B. doi:10.1007/s00114-002-0307-1. PMID 12061403. S2CID 15423666.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Paul, Gregory S. (2022). The Princeton Field Guide to Pterosaurs. Princeton University Press. pp. 155–172. doi:10.1515/9780691232218. ISBN 978-0-691-23221-8. S2CID 249332375.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Takanobu Tsuihiji; Brian Andres; Patrick M O'Connor; Mahito Watabe; Khishigjav Tsogtbaatar; Mainbayar Buuvei (2017). "Gigantic pterosaurian remains from the Upper Cretaceous of Mongolia". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 37 (5): e1361431. Bibcode:2017JVPal..37E1431T. doi:10.1080/02724634.2017.1361431. S2CID 134424023.
- ^ "Ancient Winged Terror Was One of the Largest Animals to Fly". 31 October 2017. Archived from the original on 30 March 2019.
- ^ Kellner, A. W. A.; Campos, D. A.; Sayão, J. M.; Saraiva, A. N. A. F.; Rodrigues, T.; Oliveira, G.; Cruz, L. A.; Costa, F. R.; Silva, H. P.; Ferreira, J. S. (2013). "The largest flying reptile from Gondwana: A new specimen of Tropeognathus cf. T. Mesembrinus Wellnhofer, 1987 (Pterodactyloidea, Anhangueridae) and other large pterosaurs from the Romualdo Formation, Lower Cretaceous, Brazil". Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências. 85 (1): 113–135. doi:10.1590/S0001-37652013000100009. PMID 23538956.
- ^ Rodrigues, T.; Kellner, A. (2013). "Taxonomic review of the Ornithocheirus complex (Pterosauria) from the Cretaceous of England". ZooKeys (308): 1–112. Bibcode:2013ZooK..308....1R. doi:10.3897/zookeys.308.5559. PMC 3689139. PMID 23794925.
- ^ "Fossil of largest Jurassic pterosaur found on Skye". BBC News. 22 February 2022. Retrieved 22 February 2022.
- ^ Natalia Jagielska; Michael O’Sullivan; Gregory F. Funston; et al. (February 2022). "A skeleton from the Middle Jurassic of Scotland illuminates an earlier origin of large pterosaurs". Current Biology. 32: 1–8. doi:10.1016/J.CUB.2022.01.073. ISSN 0960-9822. Wikidata Q110984418.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Spindler, Frederik; Ifrim, Christina (2021). "Die Spur einer Spur – ein möglicher erster Flugsaurier aus Ettling Trace of a trace – a putative first pterosaur from the Ettling locality". Archaeopteryx. 37: 75–83.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Andres, B.; Clark, J. M.; Xing, X. (2010). "A new rhamphorhynchid pterosaur from the Upper Jurassic of Xinjiang, China, and the phylogenetic relationships of basal pterosaurs" (PDF). Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 30 (1): 163–187. Bibcode:2010JVPal..30..163A. doi:10.1080/02724630903409220. S2CID 53688256. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 July 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Brownstein, C.D. (2022). "High morphological disparity in a bizarre Paleocene fauna of predatory freshwater reptiles". BMC Ecol Evol. 22 (34): 34. doi:10.1186/s12862-022-01985-z. PMC 8935759. PMID 35313822.
- ^ Matsumoto, R.; Evans, S. E. (10 December 2010). "Choristoderes and the freshwater assemblages of Laurasia". Journal of Iberian Geology. 36 (2): 253–274. Bibcode:2010JIbG...36..253M. doi:10.5209/rev_JIGE.2010.v36.n2.11. ISSN 1886-7995. Archived from the original on 18 August 2020.
- ^ Tiane M. De-Oliveira, Felipe L. Pinheiro,Átila Augusto Stock Da-Rosa, Sérgio Dias-Da-Silva, Leonardo Kerber. 2018. "A new archosauromorph from South America provides insights on the early diversification of tanystropheids". PLOS ONE 15(5): e0233216. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230890
- ^ Zhao, Li-Jun; Sato, Tamaki; Liu, Jun; Li, Chun; Wu, Xiao-Chun (2010). "A new skeleton of Miodentosaurus brevis (Diapsida: Thallatosauria) with a further study of the taxon" (PDF). Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 48 (1): 1–10.
- ^ Liu, J.; Zhao, L. J.; Li, C.; He, T. (2013). "Osteology of Concavispina biseridens (Reptilia, Thalattosauria) from the Xiaowa Formation (Carnian), Guanling, Guizhou, China". Journal of Paleontology. 87 (2): 341–350. Bibcode:2013JPal...87..341L. doi:10.1666/12-059R1.1. S2CID 83684967.
- ^ De la Salle P, R Lomax D, A Massare J, Gallois R (2018). "A giant Late Triassic ichthyosaur from the UK and a reinterpretation of the Aust Cliff "dinosaurian" bones". PLOS ONE. 13 (4). doi:10.6084/m9.figshare.5975440. Archived from the original on 27 February 2022.
- ^ Pickrell, John (2018). "Prehistoric "Sea Monster" May Be Largest That Ever Lived". Archived from the original on 31 May 2022.
- ^ Lomax, Dean R.; Salle, Paul de la; Perillo, Marcello; Reynolds, Justin; Reynolds, Ruby; Waldron, James F. (17 April 2024). "The last giants: New evidence for giant Late Triassic (Rhaetian) ichthyosaurs from the UK". PLOS ONE. 19 (4): e0300289. Bibcode:2024PLoSO..1900289L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0300289. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 11023487. PMID 38630678.
- ^ "Triassic Giant". Archived from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 13 October 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Sander, P.M.; Romero Pérez de Villar, P.; Furrer, H.; Wintrich, T. (2022). "Giant Late Triassic Ichthyosaurs from the Kössen Formation of the Swiss Alps and Their Paleobiological Implications" (PDF). Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 41 (6): e2046017. doi:10.1080/02724634.2021.2046017. S2CID 248444094. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 September 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Sander, P.M.; Griebeler, E.M.; Klein, N.; Juarbe, J.V.; Wintrich, T.; Revell, L.J.; Schmitz, L. (2021). "Early giant reveals faster evolution of large body size in ichthyosaurs than in cetaceans" (PDF). Science. 374 (6575): eabf5787. doi:10.1126/science.abf5787. PMID 34941418. S2CID 245444783. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 October 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Researchers have found a 205-million-year-old jawbone from one of the largest animals that ever lived". Newsweek. 9 April 2018. Archived from the original on 21 September 2022.
- ^ P.J. Currie. "Hovasaurus boulei, an aquatic eosuchian from the Upper Permian of Madagascar". Palaeont. afr., 24 (1981), p. 112.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Marco Romano; Fabio Manucci; Bruce Rubidge; Marc J. Van den Brandt (17 June 2021). "Volumetric Body Mass Estimate and in vivo Reconstruction of the Russian Pareiasaur Scutosaurus karpinskii". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 9. doi:10.3389/fevo.2021.692035. hdl:11573/1634310.
- ^ McGhee, George R. Jr. (7 August 2018). Carboniferous Giants and Mass Extinction: The Late Paleozoic Ice Age World. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-54338-5. Retrieved 16 October 2019 – via Google Books.
- ^ Piñeiro, Graciela; Núñez Demarco, Pablo; Meneghel, Melitta D. (17 May 2016). "The ontogenetic transformation of the mesosaurid tarsus: a contribution to the origin of the primitive amniotic astragalus". PeerJ. 4: e2036. doi:10.7717/peerj.2036. PMC 4878385. PMID 27231658.
- ^ Dodick, J.T. and Modesto, S.P., 1995. The cranial anatomy of the captorhinid reptile Labidosaurikos meachami from the Lower Permian of Oklahoma. Palaeontology, 38(3), p.687.
- ^ Patricia Vickers Rich; Thomas Hewitt Rich; Mildred Adams Fenton; Carroll Lane (15 January 2020). The Fossil Book: A Record of Prehistoric Life. Dover Publications. p. 444. ISBN 978-0-486-83855-7. Retrieved 13 October 2022.
- ^ Lu, J., Li, T., Zhong, S., Azuma, Y., Fujita, M., Dong, Z., and Ji, Q. (2007). "New yunnanosaurid dinosaur (Dinosauria, Prosauropoda) from the Middle Jurassic Zhanghe Formation of Yuanmou, Yunnan Province of China". Memoir of the Fukui Prefectural Dinosaur Museum, 6: 1–15.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Kenneth Carpenter (2006). "Biggest of the big: a critical re-evaluation of the mega-sauropod Amphicoelias fragillimus". In "Paleontology and Geology of the Upper Jurassic Morrison Formation". New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin. 36: 131–138.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Paul, Gregory S. (2019). "Determining the largest known land animal: A critical comparison of differing methods for restoring the volume and mass of extinct animals" (PDF). Annals of the Carnegie Museum. 85 (4): 335–358. doi:10.2992/007.085.0403. S2CID 210840060. Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 September 2022.
- ^ Galton, Peter M.; Ayyasami, Krishnan (1 July 2017). "Purported latest bone of a plated dinosaur (Ornithischia: Stegosauria), a "dermal plate" from the Maastrichtian (Upper Cretaceous) of southern India". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie – Abhandlungen. 285 (1): 91–96. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2017/0671. ISSN 0077-7749.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Molina-Perez & Larramendi (2020). Dinosaur Facts and Figures: The Sauropods and Other Sauropodomorphs. New Jersey: Princeton University Press. p. 46. ISBN 978-0-691-19069-3.
- ^ Paul, Gregory S.; Larramendi, Asier (11 April 2023). "Body mass estimate of Bruhathkayosaurus and other fragmentary sauropod remains suggest the largest land animals were about as big as the greatest whales". Lethaia. 56 (2): 1–11. Bibcode:2023Letha..56..2.5P. doi:10.18261/let.56.2.5. ISSN 0024-1164. S2CID 259782734.
- ^ Mike Taylor (2019). "Supersaurus, Ultrasaurus and Dystylosaurus in 2019, part 2: what we found in Utah". svpow.com. Archived from the original on 21 September 2022.
- ^ Mike Taylor (16 September 2016). "How horrifying was the neck of Barosaurus?". svpow.com. Archived from the original on 22 September 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Molina-Perez & Larramendi (2020). Dinosaur Facts and Figures: The Sauropods and Other Sauropodomorphs. New Jersey: Princeton University Press. p. 36. ISBN 9780691190693.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Curtice, Brian (2021). "New Dry Mesa Dinosaur Quarry Supersaurus vivianae (Jensen 1985) axial elements provide additional insight into its phylogenetic relationships and size, suggesting an animal that exceeded 39 meters in length" (PDF). p. 92. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 October 2022.
- ^ Mike Taylor (16 June 2019). "The size of the BYU 9024 animal". svpow.com. Archived from the original on 16 April 2022.
- ^ Molina-Perez & Larramendi (2020). Dinosaur Facts and Figures: The Sauropods and Other Sauropodomorphs. New Jersey: Princeton University Press. p. 156. ISBN 978-0-691-19069-3.
- ^ Peter Matthews (1992). The Guinness Book of Records. Guinness Publishing. p. 42. ISBN 9780851129785.
- ^ Tim Footman, Mark C. Young (May 2001). Guinness World Records 2001. Bantam Books. p. 276. ISBN 978-0-553-58375-5.
- ^ Molina-Pérez & Larramendi (2020). Dinosaur Facts and Figures: The Sauropods and Other Sauropodomorphs. New Jersey: Princeton University Press. p. 32. ISBN 9780691202976.
- ^ Wedel, Mathew J.; Cifelli, R. L.; Sanders, R.. K. (2000). "Osteology, paleobiology, and relationships of the sauropod dinosaur Sauroposeidon" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 45: 343–388. S2CID 59141243. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 June 2020.
- ^ Guinness World Records. Bantam Books. 2004. p. 110. ISBN 9780553587128.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Molina-Pérez, Rubén; Larramendi, Asier (29 September 2020). Dinosaur Facts and Figures: The Sauropods and Other Sauropodomorphs. Princeton University Press. p. 55. ISBN 978-0-691-19069-3.
- ^ Paul, G.S. (1988). "The brachiosaur giants of the Morrison and Tendaguru with a description of a new subgenus, Giraffatitan, and a comparison of the world's largest dinosaurs" (PDF). Hunteria. 2 (3): 1–14. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 June 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Paul, G.S., 2010, The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs, Princeton University Press.
- ^ "Giant dinosaur slims down... a bit". BBC News. 10 August 2017. Archived from the original on 21 September 2022. Retrieved 17 October 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Otero, Alejandro; Carballido, José L.; Pérez Moreno, Agustín (2020). "The appendicular osteology of Patagotitan mayorum (Dinosauria, Sauropoda)". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 40 (4): e1793158. Bibcode:2020JVPal..40E3158O. doi:10.1080/02724634.2020.1793158. S2CID 225012747.
- ^ "Don't believe the hype: Patagotitan was not bigger than Argentinosaurus". Sauropod Vertebra Picture of the Week. 9 August 2017. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
- ^ Lacovara, Kenneth J.; Lamanna, M. C.; Ibiricu, L. M.; Poole, J. C.; Schroeter, E. R.; Ullmann, P. V.; Voegele, K. K.; Boles, Z. M.; Carter, A. M.; Fowler, E. K.; Egerton, V. M.; Moyer, A. E.; Coughenour, C. L.; Schein, J. P.; Harris, J. D.; Martínez, R. D.; Novas, F. E. (4 September 2014). "A Gigantic, Exceptionally Complete Titanosaurian Sauropod Dinosaur from Southern Patagonia, Argentina". Scientific Reports. 4 (1): 6196. Bibcode:2014NatSR...4E6196L. doi:10.1038/srep06196. PMC 5385829. PMID 25186586.
- ^ Rafael Royo-Torres; Alberto Cobos; Luis Alcalá (2006). "A Giant European Dinosaur and a New Sauropod Clade" (PDF). Science. 314 (5807): 1925–1927. Bibcode:2006Sci...314.1925R. doi:10.1126/science.1132885. PMID 17185599. S2CID 9343711.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Holtz, Thomas R. Jr. (2012). Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 October 2022.
Winter 2011 Appendix
- ^ Molina-Pérez, Rubén; Larramendi, Asier (29 September 2020). Dinosaur Facts and Figures: The Sauropods and Other Sauropodomorphs. Princeton University Press. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-691-19069-3.
- ^ "Paper describing NHMUK PV R5937, a Tendaguru brachiosaurid known as "The Archbishop"". GitHub. 25 August 2022.
- ^ de Lapparent, A. F. (1960). "Les dinosauriens du "continental intercalaire" du Sahara central"" [The dinosaurs of the "continental intercalaire" of the central Sahara] (PDF). Mémoires de la Société Géologique de France. Nouvelle Séries (in French). 39 (1–6). Translated by Carrano, Matthew: 1–57.
- ^ Mannion, P. D.; Upchurch, Paul; Barnes, Rosie N.; Mateus, Octávio (2013). "Osteology of the Late Jurassic Portuguese sauropod dinosaur Lusotitan atalaiensis (Macronaria) and the evolutionary history of basal titanosauriforms" (PDF). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 168: 98–206. doi:10.1111/zoj.12029.
- ^ Nima. "Is the French Monster a Euhelopodid?". paleoking.blogspot.com.
- ^ Thompson, Helen. "Meet the Mighty Spinosaurus, the First Dinosaur Adapted for Swimming". Smithsonian. Retrieved 22 November 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Therrien, F.; Henderson, D.M. (2007). "My theropod is bigger than yours...or not: estimating body size from skull length in theropods". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 27 (1): 108–115. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2007)27[108:MTIBTY]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 86025320.
- ^ dal Sasso, C.; Maganuco, S.; Buffetaut, E.; Mendez, M.A. (2005). "New information on the skull of the enigmatic theropod Spinosaurus, with remarks on its sizes and affinities". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 25 (4): 888–896. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2005)025[0888:NIOTSO]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 85702490.
- ^ Ibrahim, Nizar; Sereno, Paul C.; Dal Sasso, Cristiano; Maganuco, Simone; Fabri, Matteo; Martill, David M.; Zouhri, Samir; Myhrvold, Nathan; Lurino, Dawid A. (2014). "Semiaquatic adaptations in a giant predatory dinosaur". Science. 345 (6204): 1613–6. Bibcode:2014Sci...345.1613I. doi:10.1126/science.1258750. PMID 25213375. S2CID 34421257. Supplementary Information
- ^ Jump up to: a b Henderson, D.M. (2018). "A buoyancy, balance and stability challenge to the hypothesis of a semi-aquatic Spinosaurus Stromer, 1915 (Dinosauria: Theropoda)". PeerJ. 6: e5409. doi:10.7717/peerj.5409. PMC 6098948. PMID 30128195.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Molina-Pérez & Larramendi 2016. Récords y curiosidades de los dinosaurios Terópodos y otros dinosauromorfos, Larousse. Barcelona, Spain p. 259
- ^ Naish, Darren (9 June 2022). "A Giant Spinosaurid Dinosaur from the Cretaceous of the Isle of Wight". Tetrapod Zoology. Retrieved 29 August 2022.
- ^ Calvo, Jorge O.; Coria, Rodolfo (1998). "New specimen of Giganotosaurus Carolinii" (PDF). GAIA: 117–122. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 February 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Henderson DM (1 January 1999). "Estimating the masses and centers of mass of extinct animals by 3-D mathematical slicing". Paleobiology. 25 (1): 88–106.
- ^ Coria, R. A.; Currie, P. J. (2002). "The braincase of Giganotosaurus carolinii (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Upper Cretaceous of Argentina". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 22 (4): 802–811. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2002)022[0802:TBOGCD]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 85678725.
- ^ Coria, R. A.; Salgado, L. (1995). "A new giant carnivorous dinosaur from the Cretaceous of Patagonia". Nature. 377 (6546): 225–226. Bibcode:1995Natur.377..224C. doi:10.1038/377224a0. S2CID 30701725.
- ^ Calvo, J.O.; Coria, R.A. (1998). "New specimen of Giganotosaurus carolinii (CORIA & SALGADO, 1995), supports it as the largest theropod ever found" (PDF). Gaia. 15: 117–122. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 February 2008.
- ^ Anderson, J. F.; Hall-Martin, A. J.; Russell, D. (1985). "Long bone circumference and weight in mammals, birds and dinosaurs". Journal of Zoology. 207 (1): 53–61. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1985.tb04915.x.
- ^ Bakker, R. T. (1986). The Dinosaur Heresies. New York: Kensington Publishing. p. 241. ISBN 978-0-688-04287-5. OCLC 13699558.
- ^ Simon, D. J. (2014). "Giant Dinosaur (theropod) Eggs of the Oogenus Macroelongatoolithus (Elongatoolithidae) from Southeastern Idaho: Taxonomic, Paleobiogeographic, and Reproductive Implications" (PDF). Doctoral Dissertation, Montana State University. Bozeman. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 August 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Pu, H.; Zelenitsky, D.K.; Lü, J.; Currie, P.J.; Carpenter, K.; Xu, L.; Koppelhus, E.B.; Jia, S.; Xiao, L.; Chuang, H.; Li, T.; Kundrát, M.; Shen, C. (2017). "Perinate and eggs of a giant caenagnathid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of central China". Nature Communications. 8: 14952. Bibcode:2017NatCo...814952P. doi:10.1038/ncomms14952. PMC 5477524. PMID 28486442.
- ^ Vickaryous, M.K., Maryanska, T., & Weishampel, D.B. 2004. Ankylosauria. In: Weishampel, D.B., Dodson, P., & Osmólska, H. (Eds.). The Dinosauria (2nd edition). Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 363–392.
- ^ Coombs, Walter P. (December 1978). "Theoretical Aspects of Cursorial Adaptations in Dinosaurs". The Quarterly Review of Biology. 53 (4): 393–418. doi:10.1086/410790. S2CID 84505681.
- ^ Paul, Gregory S. (2010). The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. p. 244. ISBN 978-0-691-13720-9.
- ^ Holtz, Thomas R. Jr. (2008). Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages (PDF). New York: Random House. pp. updated appendix. ISBN 978-0-375-82419-7.
- ^ Longrich, N.R. (2011). "Titanoceratops ouranos, a giant horned dinosaur from the Late Campanian of New Mexico". Cretaceous Research. 32 (3): 264–276. Bibcode:2011CrRes..32..264L. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2010.12.007.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Zhao, X.; Li, D.; Han, G.; Hao, H.; Liu, F.; Li, L.; Fang, X. (2007). "Zhuchengosaurus maximus from Shandong Province". Acta Geoscientia Sinica. 28 (2): 111–122. doi:10.1007/s10114-005-0808-x. S2CID 119700784.
- ^ Morris, William J. (1981). "A new species of hadrosaurian dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous of Baja California: ?Lambeosaurus laticaudus". Journal of Paleontology. 55 (2): 453–462.
- ^ Prieto-Márquez, A.; Chiappe, L. M.; Joshi, S. H. (2012). Dodson, Peter (ed.). "The lambeosaurine dinosaur Magnapaulia laticaudus from the Late Cretaceous of Baja California, Northwestern Mexico". PLOS ONE. 7 (6): e38207. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...738207P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0038207. PMC 3373519. PMID 22719869.
- ^ Morris, William J. (1981). "A new species of hadrosaurian dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous of Baja California: ?Lambeosaurus laticaudus". Journal of Paleontology. 55 (2): 453–462.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Paul, Greg (2010). "The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs". New Jersey: Princeton University Press. p. 335.
- ^ Wosik, M.; Evans, D.C. (2022). "Osteohistological and taphonomic life-history assessment of Edmontosaurus annectens (Ornithischia: Hadrosauridae) from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Ruth Mason dinosaur quarry, South Dakota, United States, with implication for ontogenetic segregation between juvenile and adult hadrosaurids". Journal of Anatomy. 241 (2): 272–296. doi:10.1111/joa.13679. PMC 9296034. PMID 35801524.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: PMC embargo expired (link) - ^ Paul, G.S., 2010, The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs, Princeton University Press p. 304
- ^ Conti, S.; Vila, B.; Sellés, A. G.; Galobart, À.; Benton, M. J.; Prieto- Márquez, A. (2020). "The oldest lambeosaurine dinosaur from Europe: Insights into the arrival of Tsintaosaurini" (PDF). Cretaceous Research. 107: 40. Bibcode:2020CrRes.10704286C. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2019.104286. hdl:1983/be876efb-979c-4237-94f9-5f8d80121f7e. S2CID 208195457. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 April 2021.
- ^ Kirkland, J.I.; Hernández-Rivera, R.; Gates, T.; Paul, G.S.; Nesbitt, S.; Serrano-Brañas, C.I.; Garcia-de la Garza, J.P. (2006). "Large hadrosaurine dinosaurs from the latest Campanian of Coahuila, Mexico". In Lucas, S.G.; Sullivan, R.M. (eds.). Late Cretaceous Vertebrates from the Western Interior (PDF). New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin. Vol. 35. Albuquerque: New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science. pp. 299–315. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 July 2019.
- ^ Powers, Marc (11 July 2004). "Holden signs state dinosaur bill". The Daily Dunkin Democrat. Daily Dunklin Democrat. Archived from the original on 4 February 2011. Retrieved 29 August 2022.
- ^ Powers, Marc (19 February 2004). "A bone to pick for Missouri". Southeast Missourian. Archived from the original on 18 November 2015. Retrieved 29 August 2022.
- ^ Paul, Gregory S. (2016). The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs. Princeton University Press. p. 342. ISBN 978-1-78684-190-2. OCLC 985402380.
- ^ Verdú, F.J.; Godefroit, P.; Royo-Torres, R.; Cobos, A.; Alcalá, L. (2017). "Individual variation in the postcranial skeleton of the Early Cretaceous Iguanodon bernissartensis (Dinosauria: Ornithopoda)". Cretaceous Research. 74: 65–86. Bibcode:2017CrRes..74...65V. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2017.02.006.
- ^ Gasulla, J.M.; Escaso, F.; Narváez, I.; Sanz, J.L.; Ortega, F. (2022). "New Iguanodon bernissartensis Axial Bones (Dinosauria, Ornithopoda) from the Early Cretaceous of Morella, Spain". Diversity. 14 (2): 63. doi:10.3390/d14020063.
- ^ Nye, E.; Feist-Burkhardt, S.; Horne, D.J.; Ross, A.J.; Whittaker, J.E. (2008). "The palaeoenvironment associated with a partial Iguanodon skeleton from the Upper Weald Clay (Barremian, Early Cretaceous) at Smokejacks Brickworks (Ockley, Surrey, UK), based on palynomorphs and ostracods". Cretaceous Research. 29 (3): 417–444. Bibcode:2008CrRes..29..417N. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2008.01.004.
- ^ McDonald, A. T.; Kirkland, J. I.; DeBlieux, D. D.; Madsen, S. K.; Cavin, J.; Milner, A. R. C.; Panzarin, L. (2010). "New Basal Iguanodonts from the Cedar Mountain Formation of Utah and the Evolution of Thumb-Spiked Dinosaurs". PLOS ONE. 5 (11): e14075. Bibcode:2010PLoSO...514075M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014075. PMC 2989904. PMID 21124919.
- ^ Paul, Gregory S. (2016). The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs 2nd edition. New Jersey: Princeton University Press. p. 319.
- ^ Beall, A. (2017). "This "ugly" dinosaur had giant scissor-like teeth". Alphr. Dennis Publishing.
It was around five metres long, I guess.
- ^ Paul, Gregory S. (2016). The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs. Princeton University Press. p. 312. ISBN 978-1-78684-190-2. OCLC 985402380.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i Murray, P. F. & Vickers-Rich, P. (2004)
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Degrange, F. J., Noriega, J. I., & Areta, J. I. (2012). Diversity and paleobiology of the Santacrucian birds. Early Miocene paleobiology in Patagonia: high-latitude paleocommunities of the Santa Cruz Formation, 138–155.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Lazaro, Enrico de (28 June 2019). "Giant Birds Roamed Europe Two Million Years Ago | Paleontology | Sci-News.com". Sci.News: Breaking Science News. Retrieved 3 March 2023.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Molina-Pérez, Rubén; Larramendi, Asier (2019). Dinosaurs Facts and Figures: The Theropods. Princeton University Press. p. 179. ISBN 978-0-691-18031-1.
- ^ Buffetaut1, Eric; Angst, Delphine (2017). "How Large was the Giant Ostrich of China?". EVOLUÇÃO – Revista de Geistória e Pré-História. 2 (1): 6–8. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Brennan, Imogen (19 February 2016). "Bones from ancestor of 'giant duck' discovered in Australia". PM. www.abc.net.au.
- ^ Tambussi, C. P., & Degrange, F. J. (2013). The dominance of zoophagous birds: just a cliché?. In South American and Antarctic Continental Cenozoic Birds (pp. 87–102). Springer, Dordrecht.
- ^ Gould, G. C.; Quitmyer, I. R. (2005). "Titanis walleri: Bones of Contention" (PDF). Bulletin of the Florida Museum of Natural History. 45 (4): 201–229. doi:10.58782/flmnh.xumx1681.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Eric Buffetaut und Delphine Angst: Stratigraphic distribution of large flightless birds in the Palaeogene of Europe and its palaeobiological and palaeogeographical implications. Earth-Science Reviews 32 (2), 2014, S. 394–408.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Meat Weights and Nutritional Yield Values for New Zealand Archaeofauna
- ^ Jump up to: a b Рубен Молина-Перес; Асьер Ларраменди; Дэвид Коннолли; Гонсало Анхель Рамирес Крус; Андрей Атучин (25 июня 2019 г.). Факты и цифры о динозаврах: тероподы и другие динозаврообразные Издательство Принстонского университета. п. 282. ИСБН 978-0-691-19059-4 . Проверено 30 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Госпиталече, Каролина А. (2014). «Новые кости гигантских пингвинов из Антарктиды: систематическое и палеобиологическое значение» . Comptes Рендус Палевол . 13 (7): 555–560. Бибкод : 2014CRPal..13..555A . дои : 10.1016/j.crpv.2014.03.008 . hdl : 11336/32571 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Александр, Дэвид Э. (24 июля 2007 г.). «Древний Аргентавис снова парит» . Труды Национальной академии наук Соединенных Штатов Америки . 104 (30): 12233–12234. Бибкод : 2007PNAS..10412233A . дои : 10.1073/pnas.0705515104 . ЧВК 1941455 . ПМИД 17640902 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Палеобиология раннего миоцена в Патагонии: высокоширотные палеосообщества Патагонии»
- ^ Амадон (1947), Расмуссен и др. (1987, 2001)
- ^ Фишер, Харви И. (1945). «Передвижение ископаемых грифов Teratornis». Американский натуралист из Мидленда . 33 (3): 725–742. дои : 10.2307/2421186 . ISSN 0003-0031 . JSTOR 2421186 .
- ^ Ксепка, Дэниел Т. (7 июля 2014 г.). «Летные качества самой крупной летучей птицы» . ПНАС . 111 (29): 10624–10629. Бибкод : 2014PNAS..11110624K . дои : 10.1073/pnas.1320297111 . ПМЦ 4115518 . ПМИД 25002475 .
- ^ Перкинс, Сид (9 апреля 2015 г.). «Обнаружен новый вид «птицы ужаса»» . Наука . дои : 10.1126/science.aab2465 . Проверено 14 апреля 2015 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Арета, Дж.И.; Норьега, Дж.И.; Агнолин, Ф. (2007). «Гигантский дротик (Pelecaniformes: Anhingidae) из верхнего миоцена Аргентины и расчет веса ископаемых Anhingidae». Новогодний ежегодник по геологии и палеонтологии-трактаты . 243 (3): 343–350. дои : 10.1127/0077-7749/2007/0243-0343 . ЛПВП : 11336/80812 .
- ^ НОРТКОТ, EM (2008). РАЗМЕР, ФОРМА И ПРИВИТИКА ВЫМЕРШЕГО МАЛЬТИЙСКОГО ЛЕБЕДЯ CYGNUS FALCONERI. Ибис, 124 (2), 148–158. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-919x.1982.tb03753.x
- ^ Jump up to: а б Мейер Х.Дж., Р.А.Дью (2010). «Новый вид гигантского аиста марабу (Aves: Ciconiiformes) из плейстоцена Лян Буа, Флорес (Индонезия)» . Зоологический журнал Линнеевского общества . 160 (4): 707–724. дои : 10.1111/j.1096-3642.2010.00616.x .
- ^ Ангст, Д.; Бюффето, Э.; Абурашид, А. (март 2011 г.). «Конец толстого дронта? Новая оценка массы Raphus cucullatus ». Naturwissenschaften . 98 (3): 233–236. Бибкод : 2011NW.....98..233A . дои : 10.1007/s00114-010-0759-7 . ПМИД 21240603 . S2CID 29215473 .
- ^ Достойно, Тревор Х.; Хэнд, Сюзанна Дж.; Арчер, Майкл; Скофилд, Р. Пол; Де Пьетри, Ванеса Л. (август 2019 г.). «Свидетельства существования гигантского попугая из раннего миоцена Новой Зеландии» . Письма по биологии . 15 (8): 20190467. doi : 10.1098/rsbl.2019.0467 . ISSN 1744-9561 . ПМК 6731479 . ПМИД 31387471 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Калифорнийская академия наук - Наука под парусом. Архивировано 7 июня 2012 года в Wayback Machine . Calacademy.org
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Колин Тадж (20 октября 2009 г.). Птица: естественная история того, кто такие птицы, откуда они пришли и как они живут . Корона. п. 64. ИСБН 978-0-307-45976-3 . Проверено 29 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д и Рубен Молина-Перес; Асьер Ларраменди; Дэвид Коннолли; Гонсало Анхель Рамирес Крус; Андрей Атучин (25 июня 2019 г.). Факты и цифры о динозаврах: тероподы и другие динозаврообразные Издательство Принстонского университета. п. 281. ИСБН 978-0-691-19059-4 . Проверено 29 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Уокер, Сирил А.; Дайк, Гарет Дж. (2009). «Эуэнантиорнитиновые птицы из позднего мела Эль-Брете (Аргентина)» . Ирландский журнал наук о Земле . 27 :15–62. дои : 10.1353/ijes.2009.a810006 . ISSN 0790-1763 . JSTOR 25780698 .
- ^ Чьяппе, Луис М. «Энантиорнитин (Aves) tarsometatarsi из меловой формации Лечо на северо-западе Аргентины. Американский музей новитирует; № 3083» . Библиотека наследия биоразнообразия . Проверено 20 декабря 2023 г.
- ^ Аттерхольт, Джесси; Хатчисон, Дж. Ховард; О'Коннор, Цзинмай К. (13 ноября 2018 г.). «Наиболее полный энантиорнитин из Северной Америки и филогенетический анализ Avisauridae» . ПерДж . 6 : е5910. дои : 10.7717/peerj.5910 . ПМК 6238772 . ПМИД 30479894 .
- ^ Чжоу, Чжунхэ; Кларк, Джулия; Чжан, Фучэн (май 2008 г.). «Понимание разнообразия, размера тела и морфологической эволюции крупнейшей энантиорнитиновой птицы раннего мела» . Журнал анатомии . 212 (5): 565–77. дои : 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2008.00880.x . ПМК 2409080 . ПМИД 18397240 .
- ^ Бюффето, Э.; Ле Лефф, Ж. (1998). «Новая гигантская наземная птица из верхнего мела на юге Франции». Журнал Геологического общества, Лондон . 155 (155): 1–4. Бибкод : 1998JGSoc.155....1B . дои : 10.1144/gsjgs.155.1.0001 . S2CID 128496095 .
- ^ Мюссер, Энн. «Громовая птица Стиртона» . Австралийский музей . Архивировано из оригинала 31 августа 2022 года . Проверено 10 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ Чинсами, А., Хэндли, В.Д., Йейтс. AM, Уорти, TH (2016). Половой диморфизм позднемиоценового mihirung Dromornis stirtoni (Aves: Dromornithidae) из местной фауны Алкуты центральной Австралии. Журнал палеонтологии позвоночных, 36:5, DOI: 10.1080/02724634.2016.1180298.
- ^ Уитмер, Лоуренс; Роуз, Кеннет (1991). «Биомеханика челюстного аппарата гигантской эоценовой птицы Diatryma : Значение для диеты и образа жизни» (PDF) . Палеобиология . 17 (2): 95–120. Бибкод : 1991Pbio...17...95W . дои : 10.1017/S0094837300010435 . S2CID 18212799 . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 28 июля 2010 года.
- ^ Джеральд Майр: Gastornithidae. В: Джеральд Майр: Ископаемые птицы палеогена. Springer-Verlag, Берлин и Гейдельберг, 2009 г., стр. 44–47.
- ^ Дельфина Ангст и Эрик Баффето: Палеобиология гигантских нелетающих птиц. Оксфорд, 2017, С. 1–282 (С. 173–214).
- ^ Мейер, HJM (2014). «Своеобразный гусеобразный (Aves: Anseriformes) из миоцена Гаргано (Италия)» . Comptes Рендус Палевол . 13 (1): 19–26. Бибкод : 2014CRPal..13...19M . дои : 10.1016/j.crpv.2013.08.001 .
- ^ TH Worthy , Ричард Н. Холдэуэй (2002). Затерянный мир Моа. Доисторическая жизнь Новой Зеландии . Издательство Университета Индианы. п. 232. ИСБН 978-0-253-34034-4 . Проверено 1 октября 2022 г.
- ^ Сноу, Д.В.; Перринс, CM (1998). Птицы Западной Палеарктики (Краткое изд.). ОУП. ISBN 0-19-854099-Х .
- ^ НОРТКОТ, EM (2008). Размер, форма и облик вымершего мальтийского лебедя Cygnus falconeri. Ибис, 124 (2), 148–158. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-919x.1982.tb03753.x
- ^ Ватанабэ Дж. и Мацуока Х. (2015). Нелетающая ныряющая утка (Aves, Anatidae) из плейстоцена Ширии, северо-восток Японии. Журнал палеонтологии позвоночных, 35 (6), e994745. https://doi.org/10.1080/02724634.2014.994745
- ^ Ватанабэ, Дж. (2017). Количественное распознавание нелетания у ископаемых Anatidae по пропорциям скелета. Аук, 134 (3), 672–695. https://doi.org/10.1642/auk-17-23.1
- ^ Гибб, Джон (27 июля 2017 г.). «Наконец-то собственный лебедь Новой Зеландии» . Отаго Дейли Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 17 августа 2017 года . Проверено 1 октября 2022 г.
- ^ Мацуока Х, Хасегава Ю (2022). « Annakacygna , новый род двух замечательных нелетающих лебедей (Aves, Anatidae, Cygnini) из миоцена Гуммы, центральная Япония: с примечанием о сдвиге пищевой ниши птиц и специализации крыльев для родительской заботы» (PDF) . Вестник Музея естественной истории Гумма . 26 : 1–30.
- ^ Достойно, Тревор Х.; Олсон, Сторрс Л. (2002). «Отношения, адаптации и повадки вымершей утки «Euryanas» finschi» (PDF) . Ноторнис . 49 (1): 1–17. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 19 октября 2007 года.
- ^ Олсон, Сторрс Л. (1999). «Новый вид пеликана (Aves: Pelecanidae) из нижнего плиоцена Северной Каролины и Флориды» (PDF) . Труды Биологического общества Вашингтона . 112 (3): 503–509. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 10 октября 2022 года.
- ^ Каллахан, Д. (2014). История наблюдения за птицами в 100 объектах . Блумсбери Паблишинг Plc. п. 15. ISBN 978-1408-1-8618-3 .
- ^ «На острове хоббитов найдена гигантская птица» . 7 декабря 2010 г. - через BBC News.
- ^ Халберт-младший, Ричард К. и Вальдес, Натали (2013). «Окаменелости позвоночных Флориды: Ciconia Maltha » . Флоридский музей естественной истории . Проверено 30 сентября 2015 г.
- ^ Г. Майр; Томас Лехнер; М. Бёме (14 июля 2020 г.). «Череп очень крупного журавля из позднего миоцена Южной Германии с заметками о филогенетических взаимоотношениях современных Gruinae» . Журнал орнитологии . 161 (4): 923–933. дои : 10.1007/s10336-020-01799-0 . S2CID 220505689 .
- ^ Смит, Н. 2015. Эволюция массы тела у Pan-Alcidae (Aves, Charadriiformes): эффекты объединения неонтологических и палеонтологических данных. Палеобиология. дои: 10.1017/pab.2015.24
- ^ Уилсон, Лаура; Чин, Карен; Камба, Стивен; Дайк, Гарет (1 марта 2011 г.). «Высокоширотная гесперорнитиформа (Aves) с острова Девон: палеобиогеография и размерное распределение гесперорнитиформ Северной Америки» . Журнал систематической палеонтологии . 9 (1): 9–23. Бибкод : 2011JSPal...9....9W . дои : 10.1080/14772019.2010.502910 . S2CID 83749554 .
- ^ Ксепка, Дэниел Т. (22 июля 2014 г.). «Летные качества самой крупной летучей птицы» . Труды Национальной академии наук Соединенных Штатов Америки . 111 (29): 10624–10629. Бибкод : 2014PNAS..11110624K . дои : 10.1073/pnas.1320297111 . ПМК 4115518 . ПМИД 25002475 .
- ^ Чаттерджи, С.; Темплин, Р.Дж.; Кэмпбелл, Кентукки (24 июля 2007 г.). «Аэродинамика Аргентависа , крупнейшей в мире летающей птицы из миоцена Аргентины» . Труды Национальной академии наук Соединенных Штатов Америки . 104 (30): 12398–12403. Бибкод : 2007PNAS..10412398C . дои : 10.1073/pnas.0702040104 . ЧВК 1906724 . ПМИД 17609382 .
- ^ Кэмпбелл, Кеннет Э. младший; Тонни, EP (1983). «Размер и передвижение тераторнов» (PDF) . Аук . 100 (2): 390–403. дои : 10.1093/аук/100.2.390 .
- ^ Кэмпбелл, Кеннет; Скотт, Эрик; Спрингер, Кэтлин (1999). «Новый род невероятного тераторна» . Смитсоновский вклад в палеобиологию . 89 : 169–175 – через Researchgate.
- ^ Кеннет Э. Кэмпбелл-младший, Эдуардо П. Тонни. « Размер и передвижение тераторнов (Aves: Teratornithidae) ». The Auk, том 100, выпуск 2, апрель 1983 г., стр. 390–403, https://doi.org/10.1093/auk/100.2.390.
- ^ Альваренга, Эркулано МФ; Хёфлинг, Элизабет (2003). «Систематический пересмотр Phorusrhacidae (Aves: Ralliformes)» . Отдельные статьи по зоологии . 43 (4). дои : 10.1590/S0031-10492003000400001 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Ксепка, Дэниел Т. (2014). «Полёты фантазии в эволюции птиц». Американский учёный . 102 (1): 39. дои : 10.1511/2014.106.36 . ISSN 0003-0996 . JSTOR 43707746 .
- ^ Тамбусси, Клаудия П.; Дегранж, Федерико Дж. (2013). «Неогеновые птицы Южной Америки». Южноамериканские и антарктические континентальные кайнозойские птицы . Springer Briefs по наукам о системе Земли. Спрингер. стр. 59–86. дои : 10.1007/978-94-007-5467-6_7 . ISBN 978-94-007-5466-9 .
- ^ Крофт, Дарин А. (2016). Рогатые броненосцы и рафтинговые обезьяны: удивительные ископаемые млекопитающие Южной Америки . Издательство Университета Индианы. п. 120. ИСБН 978-0-253-02084-0 . Проверено 30 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Альваренга, Эркулано МФ; Хёфлинг, Элизабет (2003). «Систематический пересмотр Phorusrhacidae (Aves: Ralliformes)» . Отдельные статьи по зоологии . 43 (4): 55–91. дои : 10.1590/S0031-10492003000400001 .
- ^ Рид Викандер, Джеймс С. Монро (2015). Историческая геология . Cengage Обучение. п. 368. ИСБН 9781305480766 . Проверено 27 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Маас, П. «Недавно вымершие животные – Информация о видах – Орел Хааста» . Шестое вымирание. Архивировано из оригинала 20 января 2013 года . Проверено 19 апреля 2013 г.
- ^ «Орел Хааста» . Группа исследований палеобиологии и биоразнообразия. Архивировано из оригинала 5 мая 2014 года . Проверено 19 апреля 2013 г.
- ^ Уорти, Т. и Холдэуэй, Р., Затерянный мир Моа: доисторическая жизнь Новой Зеландии . Издательство Университета Индианы (2003), ISBN 978-0-253-34034-4
- ^ Брэтуэйт, Д.Х. (декабрь 1992 г.). «Заметки о весе, летных способностях, среде обитания и добыче орла Хааста ( Harpagornis moorei )» (PDF) . Ноторнис . 39 (4). Орнитологическое общество Новой Зеландии : 239–247. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 19 января 2012 года . Проверено 26 января 2014 г.
- ^ Даррен Нэйш (27 января 2008 г.). «Титаны-ястребы и другие суперхищники» . Научные блоги. Архивировано из оригинала 25 сентября 2022 года . Проверено 30 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ Дэвид В. Стедман, Хуан Н. Альмонте Милан и Алексис М. Мичайлив « Вымерший орел (Aves: Accipitridae) из четвертичного периода Эспаньолы ». Журнал исследований хищников 53 (3), 319–333, (13 августа 2019 г.). https://doi.org/10.3356/JRR-18-769
- ^ Олсон, Сторрс Л.; Суарес, Уильям (20 апреля 2007 г.). «Кубинский ископаемый орел Aquila borrasi Arredondo: увеличенная версия большого черного ястреба Buteogallus urubitinga (Gmelin)» (PDF) . Журнал исследований хищников . 41 (4). Фонд исследования хищников : 288. doi : 10.3356/0892-1016(2007)41[288:TCFEAB]2.0.CO;2 . S2CID 55380044 .
- ^ Олсон, Сторрс Л. (2007). «Ходячий орел» Wetmoregyps daggetti Miller: увеличенная версия саванного ястреба ( Buteogallus meridionalis )» (PDF) . Орнитологические монографии (63): 110–114. дои : 10.2307/40166902 . JSTOR 40166902 . Проверено 30 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ Холдэуэй, Ричард Н.; Достойно, Тревор Х. (март 1997 г.). «Переоценка ископаемых позвоночных позднечетвертичного периода болота Пирамидальной долины, Северный Кентербери, Новая Зеландия» . Новозеландский журнал зоологии . 24 (1): 69–121. дои : 10.1080/03014223.1997.9518107 .
- ^ Рахаман, Садекур (8 ноября 2014 г.). «10 крупнейших птиц в мире (живые)» AllTopTens.com» .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Вуд, Джеральд Книга рекордов Гиннеса по фактам и подвигам животных (1983) ISBN 978-0-85112-235-9
- ^ Марк Эш; Хорхе Норьега; Джон Дидерле; Стивен Сойбельзон; Леопольд Сойбельзон; Серхио Родригес; Элиша Бейлинсон (2018). «Неожиданный крупный хохлатый тинаму (Eudromia, Tinamidae, Birds) вблизи последнего ледникового максимума (MIS 2, поздний плейстоцен) в аргентинских пампасах » Историческая биология 32 (3): 330–338. дои : 10.1080/08912963.2018.1491568 . hdl : 11336/84901 . S2CID 91851921 .
- ^ Зеленков, Н.В.; Лавров А.В.; Старцев Д.Б.; Вислобокова И.А.; Лопатин, А.В. (2019). «Гигантская птица раннего плейстоцена из Восточной Европы: неожиданный компонент наземной фауны во время прибытия раннего человека». Журнал палеонтологии позвоночных . 39 (2): e1605521. Бибкод : 2019JVPal..39E5521Z . дои : 10.1080/02724634.2019.1605521 . S2CID 198384367 .
- ^ Эрик Баффето, Дельфин Ангст. «Гигантский страус из формации Нихэван нижнего плейстоцена в Северном Китае, с обзором ископаемых страусов Китая». Разнообразие 2021, 13, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13020047 .
- ^ Джеральд Майр (31 октября 2016 г.). Птичья эволюция. Ископаемая летопись птиц и ее палеобиологическое значение . Уайли. п. 98. ИСБН 978-1-119-02076-9 . Проверено 30 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ Сесиль Мурер-Шовир, Денис Гераадс (январь 2008 г.). «Struthionidae и Pelagornithidae (Aves: Struthioniformes, Odontopterygiformes) из позднего плиоцена Ахл-эль-Углама, Марокко» . Ориктос . 7 : 169–194.
- ^ Вермей, Гират Дж. (2004). Природа: экономическая история . Издательство Принстонского университета, ISBN 0-691-11527-3
- ^ Ангст, Д.; Бюффето, Э.; Абурашид, А. (2011). «Конец толстого дронта? Новая оценка массы Raphus cucullatus». Naturwissenschaften . 98 (3): 233–236. Бибкод : 2011NW.....98..233A . дои : 10.1007/s00114-010-0759-7 . ПМИД 21240603 . S2CID 29215473 .
- ^ Викерс-Рич, Патрисия; Найт, Фрэнк (1985). Кадимакара – вымершие позвоночные Австралии . Издательство Принстонского университета. ISBN 978-0-909674-26-7 .
- ^ Риндеркнехт, А.; Норьега, Дж.И. (2002). «Новый род Anhingidae (Aves: Pelecaniformes) из плиоцена-плейстоцена Уругвая (формация Сан-Хосе)» . Амегиниана . 39 (2): 183–191. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 9 мая 2022 года . Проверено 5 мая 2022 г.
- ^ Мори, Хироцугу; Мията, Казунори (2021). «Особи ранних Plotopteridae (Aves) из формаций Итанура и Какиноура (последний эоцен — ранний олигоцен), Сайкай, префектура Нагасаки, Западная Япония» . Палеонтологические исследования . 25 (2): 145–159. дои : 10.2517/2020PR018 . ISSN 1342-8144 . S2CID 233029559 .
- ^ Гриском, Ладлоу (1929). «Исследования птиц Гватемалы из коллекции Дуайта. 1». Американский музей послушников (379). hdl : 2246/5418 .
- ^ «Императорский дятел Campephilus Imperialis » . БердЛайф Интернэшнл. Архивировано из оригинала 4 марта 2016 года . Проверено 28 февраля 2011 г.
- ^ Достойно, Тревор Х.; Хэнд, Сюзанна Дж.; Арчер, Майкл; Скофилд, Р. Пол; Де Пьетри, Ванеса Л. (2019). «Свидетельства существования гигантского попугая из раннего миоцена Новой Зеландии» . Письма по биологии . 15 (8). дои : 10.1098/rsbl.2019.0467 . ПМК 6731479 . ПМИД 31387471 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д Ксепка, Дэниел Т.; Филд, Дэниел Дж.; Хит, Трейси А.; Петт, Уокер; Томас, Дэниел Б.; Джованарди, Симоне; Теннисон, Алан Джей Ди (8 февраля 2023 г.). «Самый крупный из известных ископаемых пингвинов дает представление о ранней эволюции размеров клиновидного тела и анатомии ласт» . Журнал палеонтологии . 97 (2): 434–453. Бибкод : 2023JPal...97..434K . дои : 10.1017/jpa.2022.88 . ISSN 0022-3360 . S2CID 256709376 .
- ^ Акоста Госпиталече, Каролина (1 октября 2014 г.). «Новые кости гигантских пингвинов из Антарктиды: систематическое и палеобиологическое значение» . Comptes Рендус Палевол . 13 (7): 555–560. Бибкод : 2014CRPal..13..555A . дои : 10.1016/j.crpv.2014.03.008 . hdl : 11336/32571 . ISSN 1631-0683 .
- ^ «Размеры тела эоценовых антарктических пингвинов» . Польские полярные исследования .
- ^ Шмид, Рэндольф Э. (25 июня 2007 г.). «Гигантские пингвины, возможно, бродили по Перу» . Associated Press через Washington Post . Проверено 29 июня 2007 г.
- ^ Арредондо, Оскар (1976) перевел Олсона, Сторрса Л. Великие хищные птицы плейстоцена Кубы, стр. 169–187 в «Смитсоновский вклад в палеобиологию, номер 27; Сборник статей по палеонтологии птиц в честь 90-летия со дня рождения Александра Ветмора»
- ^ Jump up to: а б Дэниел Л. Леви, Ребекка Хилд (август 2015 г.). «Проблемы биологического масштабирования и решения у амфибий» . Перспективы Колд-Спринг-Харбор в биологии . 8 (1): а019166. doi : 10.1101/cshperspect.a019166 . ПМЦ 4691792 . ПМИД 26261280 .
- ^ Родриго А. Отеро; Паулина Хименес-Уидоброб; Серджио Сото-Акуна; Роберто Э. Юрий-Янес (2014). «Свидетельства существования гигантской шлемованной лягушки (Australobatrachia, Calyptocephalellidae) с эоценовых уровней бассейна Магальянес, на самом юге Чили» . Журнал южноамериканских наук о Земле . 55 : 133–140. Бибкод : 2014JSAES..55..133O . дои : 10.1016/j.jsames.2014.06.010 .
- ^ Эванс, Сьюзен Э.; Гроенке, Джозеф Р.; Джонс, Марк Э.Х.; Тернер, Алан Х.; Краузе, Дэвид В. (2014). «Новый материал о Beelzebufo , гипероссифицированной лягушке (амфибия: Anura) из позднего мела Мадагаскара» . ПЛОС ОДИН . 9 (1): e87236. Бибкод : 2014PLoSO...987236E . дои : 10.1371/journal.pone.0087236 . ПМК 3905036 . ПМИД 24489877 .
- ^ Нейлор, Брюс Г. (1981). «Криптожаберные саламандры из палеоцена и миоцена Саскачевана». Копейя . 1981 (1): 76–86. дои : 10.2307/1444042 . ISSN 0045-8511 . JSTOR 1444042 .
- ^ Уилсон, Грегори П.; Клеменс, Уильям А.; Хорнер, Джон Р.; Хартман, Джозеф Х. (21 января 2014 г.). В конце мелового периода в типовом местонахождении формации Хелл-Крик в Монтане и прилегающих районах . Геологическое общество Америки. ISBN 978-0-8137-2503-1 .
- ^ Лори Дж. Витт, Джанали П. Колдуэлл (25 марта 2013 г.). Герпетология. Вводная биология амфибий и рептилий . Эльзевир Наука. п. 96. ИСБН 978-0-12-386920-3 . Проверено 25 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ Георг Ф. Стридтер , Р. Гленн Норткатт (2020). Мозг сквозь время. Естественная история позвоночных . Издательство Оксфордского университета. п. 276. ИСБН 978-0-19-512568-9 . Проверено 25 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ Панчен, Ал. (1977). «Об Anthracosaurus russelli Huxley (амфибия: Labyrinthodontia) и семействе Anthracosauridae». Философские труды Лондонского королевского общества. Серия Б, Биологические науки . 279 (968): 447–512. Бибкод : 1977РСТБ.279..447П . дои : 10.1098/rstb.1977.0096 . ISSN 0080-4622 . JSTOR 2417840 .
- ^ Марьянович, Давид; Лорен, Мишель (4 января 2019 г.). «Филогения палеозойских конечностей позвоночных, заново оцененная посредством пересмотра и расширения крупнейшей опубликованной матрицы соответствующих данных» . ПерДж . 6 : е5565. дои : 10.7717/peerj.5565 . ISSN 2167-8359 . ПМК 6322490 . ПМИД 30631641 .
- ^ Панчен, Ал. (1972). «Череп и скелет Eogyrinus attheyi Watson (амфибия: Labyrinthodontia)». Философские труды Лондонского королевского общества. Серия Б, Биологические науки . 263 (851): 279–326. Бибкод : 1972РСТБ.263..279П . дои : 10.1098/rstb.1972.0002 . ISSN 0080-4622 . JSTOR 2417176 .
- ^ Шох, Р.Р. (1999). «Сравнительная остеология Mastodonsaurus giganteus (Jaeger, 1828) из среднего триаса (Lettenkeuper: Longobardian) Германии (Баден-Вюртемберг, Бавария, Тюрингия)» (PDF) . Вклад Штутгарта в серию по естествознанию B. 278 : 1–175.
- ^ Штайер, Ж. Себастьян; Дамиани, Росс (1 мая 2005 г.). «Гигантский брахиопоидный темноспондил из верхнего триаса или нижней юры Лесото». Бюллетень геологического общества Франции . 176 (3): 243–248. дои : 10.2113/176.3.243 . ISSN 0037-9409 .
- ^ Лю, Хуайбао П.; Бергстрем, Стиг М.; Витцке, Брайан Дж.; Бриггс, Дерек Э.Г.; Маккей, Роберт М.; Ферретти, Анналиса (2017). «Исключительно сохранившиеся аппараты конодонтов с гигантскими элементами из среднего ордовика Виннешик Консерват-Лагерштетте, Айова, США» . Журнал палеонтологии . 91 (3): 493–511. Бибкод : 2017JPal...91..493L . дои : 10.1017/jpa.2016.155 . ISSN 0022-3360 . S2CID 132698401 .
- ^ «Систематика, филогенетика и макроэволюция гетеростраков: исследование закономерностей эволюции вымерших бесчелюстных позвоночных | Research Explorer | Манчестерский университет» . www.research.manchester.ac.uk . Проверено 24 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Тернер, Сьюзен (1986). «Thelodus macintoshi Stetson 1928, самый крупный из известных телодонтов (Agnatha: Thelodonti)» . Бревиора . 486 : 1–18. ISSN 0006-9698 .
- ^ Альберт, Джеймс С.; Джонсон, Дерек М.; Кнауфт, Джейсон Х. (2009). «Окаменелости позволяют лучше оценить размеры тела предков, чем существующие таксоны рыб» . Акта Зоология . 90 : 357–384. дои : 10.1111/j.1463-6395.2008.00364.x .
- ^ Орвиг, Тор (1967). «Некоторые новые акантодические материалы из нижнего девона Европы» . Журнал Лондонского Линнеевского общества, Зоология . 47 (311): 131–153. дои : 10.1111/j.1096-3642.1967.tb01400.x .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д и Энгельман, Рассел К. (2023). «Сказка о девонских рыбах: новый метод оценки длины тела предполагает гораздо меньшие размеры Dunkleosteus terrelli (Placodermi: Arthrodira)» . Разнообразие . 15 (3): 318. дои : 10.3390/d15030318 . ISSN 1424-2818 .
- ^ Гилберт Пауэлл Ларвуд, Пол Д. Тейлор (1990). Основные эволюционные излучения . Ассоциация систематиков. п. 310. ИСБН 978-0-19-857718-8 . Проверено 28 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Бюллетень 70 . Огайо. Отдел геологической разведки. 1996. с. 290. ИСБН 9780931079054 . Проверено 28 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Чарли Андервуд; Марта Рихтер; Зерина Йохансон (2019). Эволюция и развитие рыб . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 13. ISBN 978-1-107-17944-8 . Проверено 31 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Башфорд Дин (1895). Рыбы, живые и ископаемые: очерк их форм и вероятных взаимоотношений . Макмиллан и компания. п. 130 . Проверено 28 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Шимада, К.; Чендлер, RE; Лам, ОЛТ; Танака, Т.; Уорд, диджей (2016). «Новая неуловимая отодонтидная акула (Lamniformes: Otodontidae) из нижнего миоцена и комментарии к таксономии родов отодонтид, включая кладу «мегатубатых». Историческая биология . 29 (5): 1–11. дои : 10.1080/08912963.2016.1236795 . S2CID 89080495 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Симада, Кенсю (2019). «Возвращение к размеру большезубой акулы Otodus megalodon (Lamniformes: Otodontidae)». Историческая биология . 33 (7): 1–8. дои : 10.1080/08912963.2019.1666840 . ISSN 0891-2963 . S2CID 208570844 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Купер, Дж.А.; Пимьенто, К.; Феррон, ХГ; Бентон, MJ (2020). «Размеры тела вымершей гигантской акулы Otodus megalodon : 2D-реконструкция» . Научные отчеты . 10 (14596): 14596. Бибкод : 2020NatSR..1014596C . дои : 10.1038/s41598-020-71387-y . ПМЦ 7471939 . ПМИД 32883981 .
- ^ деГрюи, Майкл (2006). Идеальная акула (сериал). Би-би-си (Великобритания).
- ^ Перес, Виктор; Ледер, Ронни; Бадо, Тедди (2021). «Оценка длины тела неогеновых макрофагов пластинчатообразных акул (Carcharodon и Otodus), полученная на основе связанных с ними ископаемых зубных рядов» . Электронная палеонтология . 24 (1): 1–28. дои : 10.26879/1140 .
- ^ Пимьенто, К.; Макфадден, Би Джей; Клементс, CF; Варела, С.; Харамильо, К.; Велес-Хуарбе, Дж.; Силлиман, БР (2016). «Географические закономерности распространения Carcharocles megalodon с течением времени открывают подсказки о механизмах вымирания». Журнал биогеографии . 43 (8): 1645–1655. Бибкод : 2016JBiog..43.1645P . дои : 10.1111/jbi.12754 . S2CID 55776834 .
- ^ Пимьенто, К.; Балк, Массачусетс (2015). «Тенденции размеров тела вымершей гигантской акулы Carcharocles megalodon : глубокий взгляд на морских хищников» . Палеобиология . 41 (3): 479–490. Бибкод : 2015Pbio...41..479P . дои : 10.1017/pab.2015.16 . ПМЦ 4541548 . ПМИД 26321775 .
- ^ Ренц, Марк (2002). Мегалодон: Охота на охотника . Лихай-Эйкерс, Флорида: PaleoPress. стр. 100-1 1–159. ISBN 978-0-9719477-0-2 . OCLC 52125833 .
- ^ Портелл, Роджер; Хьюбелл, Гордон; Донован, Стивен; Грин, Джереми; Харпер, Дэвид ; Пикерилл, Рон (2008). «Миоценовые акулы в формациях Кендис и Гранд-Бэй на Карриаку, Гренадины, Малые Антильские острова» (PDF) . Карибский научный журнал . 44 (3): 279–286. дои : 10.18475/cjos.v44i3.a2 . S2CID 87154947 . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 20 июля 2011 года.
- ^ Готфрид, доктор медицины; Компаньо, LJV; Боуман, Южная Каролина (1996). «Размер и анатомия скелета гигантской большезубой акулы Carcharodon megalodon ». В Климли; Эйнли (ред.). Большие белые акулы: биология Carcharodon carcharias . Сан-Диего, Калифорния: Academic Press. стр. 55–89. ISBN 978-0-12-415031-7 .
- ^ Готфрид, доктор медицинских наук, Фордайс Р.Э. (2001). «Связанный экземпляр Carcharodon angustidens (Chondrichthyes, Lamnidae) из позднего олигоцена Новой Зеландии с комментариями о взаимоотношениях Carcharodon ». Журнал палеонтологии позвоночных . 21 (4): 730–739. doi : 10.1671/0272-4634(2001)021[0730:AASOCA]2.0.CO;2 . S2CID 86092645 .
- ^ Андрес, Лутц. «Окаменелости мегазубов, найденные в скалах Калверт в Мэриленде» . Архивировано из оригинала 26 августа 2022 года . Проверено 10 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ Амальфитано, Якопо; Далла Веккья, Фабио Марко; Карнавал, Джорджио; Форначари, Элиана; Роги, Гвидо; Джусберти, Лука (10 мая 2022 г.). «Морфология и палеобиология позднемеловой крупной акулы Cretodus crassidens (Dixon, 1850) (Neoselachii; Lamniformes)» (PDF) . Журнал палеонтологии . 96 (5): 1166–1188. Бибкод : 2022JPal...96.1166A . дои : 10.1017/jpa.2022.23 . ISSN 0022-3360 . S2CID 248702856 .
- ^ Фредериксон, Дж.А.; Шефер, С.Н.; Дусетт-Фредериксон, JA (2015). «Гигантская акула из нижнемеловой формации Дак-Крик в Техасе» . ПЛОС ОДИН . 10 (6): e0127162. Бибкод : 2015PLoSO..1027162F . дои : 10.1371/journal.pone.0127162 . ПМЦ 4454486 . ПМИД 26039066 .
- ^ Кент, BW (1999). «Предположения о размере и морфологии вымершей ламноидной акулы Parotodus benedeni (le Hon)» (PDF) . Мозазавр . 6 :11–15.
- ^ Уорд, диджей; Кент, BW (2015). Новый гигантский вид акулы-молотилки из миоцена США (Отчет). Музей естественной истории. дои : 10.13140/RG.2.1.1723.0969 .
- ^ Пимьенто, Каталина; Канталапьедра, Хуан Л.; Симада, Кенсю; Филд, Дэниел Дж.; Смаерс, Йерун Б. (2019). «Эволюционные пути к гигантизму акул и скатов» . Эволюция . 73 (3): 588–599. дои : 10.1111/evo.13680 . ISSN 1558-5646 . ПМИД 30675721 . S2CID 59224442 .
- ^ Себастьян Штумпф, Фавиэль А. Лопес-Ромеро, Рене Киндлиманн, Фредерик Лакомба, Буркхард Пол, Юрген Кривет. Уникальный гибодонтиформный скелет дает новое представление о мезозойской жизни хондрихтиев. 2021. https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.fqz612jr5
- ^ Майш, Майкл В.; Мацке, Андреас Т. (1 июня 2016 г.). «Новая акула-гибодонтид (Chondrichthyes, Hybodontiformes) из нижнеюрской формации Posidonienschiefer в Доттернхаузене, юго-запад Германии» . Новогодний ежегодник по геологии и палеонтологии-трактаты . 280 (3): 241–257. дои : 10.1127/njgpa/2016/0577 .
- ^ Кац, Б. (4 февраля 2020 г.). «Челюсть акулы возрастом 330 миллионов лет обнаружена в пещере Кентукки» .
- ^ Вильялобос-Сегура, Э.; Кривет, Дж.; Вулло, Р.; Штумпф, С.; Уорд, диджей; Андервуд, CJ (2021). «Скелетные останки эвригалинного склероринхоида † Onchopristis (Elasmobranchii) из среднего мела и их палеонтологическое значение». Зоологический журнал Линнеевского общества . 193 (2): 746–771. doi : 10.1093/zoolinnean/zlaa166 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Пилозубые левиафаны курсировали по древним морям» . Eartharchives.org . Архивировано из оригинала 22 августа 2021 года.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Stanislav Drobyshevsky (2022). Палеонтология антрополога. Книга 1. Докембрий и палеозой (Paleontology of anthropologist. Volume 1. Precambrian and Paleozoic) . Eksmo . ISBN 978-5-04-209523-8 . Проверено 31 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Тапанила, Л.; Прюитт, Дж.; Вилга, CD; Прадел, А. (2020). «Пилы, ножницы и акулы: позднепалеозойские эксперименты с симфизарным зубным рядом» . Анатомическая запись . 303 (2): 363–376. дои : 10.1002/ar.24046 . ПМИД 30536888 . S2CID 54478736 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Кавин, Лайонел; Пьюз, Андре; Ферранте, Кристоф; Гино, Гийом (3 июня 2021 г.). «Гигантские мезозойские целаканты (Osteichthyes, Actinistia) демонстрируют значительную разницу в размерах тела, не связанную с таксическим разнообразием» . Научные отчеты . 11 (1): 11812. Бибкод : 2021NatSR..1111812C . дои : 10.1038/s41598-021-90962-5 . ISSN 2045-2322 . ПМЦ 8175595 . ПМИД 34083600 .
- ^ Пауло М. Брито; Дэйвид. М. Мартилль; Ян Ивз; Рой Э. Смит; Сэмюэл Э.А. Купер (июнь 2021 г.). «Морской целакант позднемелового (маастрихтского) периода из Северной Африки» . Меловые исследования . 122 : 104768. Бибкод : 2021CrRes.12204768B . дои : 10.1016/j.cretres.2021.104768 . S2CID 233551515 .
- ^ Симада, Кенсю; Киркланд, Джеймс И. (2011). «Загадочная мезозойская двоякодышащая рыба королевских размеров из Северной Америки». Труды Канзасской академии наук . 114 (1/2): 135–141. дои : 10.1660/062.114.0114 . ISSN 0022-8443 . JSTOR 41309634 . S2CID 84698238 .
- ^ Джеффри, Дж. Э. (2003). «Нижние челюсти ризодонтид: анатомия, функции и эволюция внутри стеблевой группы четвероногих» . Труды Королевского общества Эдинбурга: Науки о Земле . 93 (3): 255–276. дои : 10.1017/S0263593300000432 . S2CID 129517553 .
- ^ Джеффри, Джонатан Э. (1 сентября 2012 г.). «Краниальная морфология каменноугольного ризодонтида Screbinodus ornatus (Osteichthyes: Sarcopterygii)». Журнал систематической палеонтологии . 10 (3): 475–519. Бибкод : 2012JSPal..10..475J . дои : 10.1080/14772019.2011.595961 . ISSN 1477-2019 . S2CID 84810001 .
- ^ Холланд, Тимоти (14 декабря 2010 г.). «Останки остихтиана верхнего девона из реки Генуя, Виктория, Австралия» . Мемуары музея Виктории . 67 : 35–44. дои : 10.24199/j.mmv.2010.67.04 .
- ^ Хорнунг, Ян Дж.; Сакс, Свен (22 января 2020 г.). «Первая находка Gyrosteus mirabilis (Actinopterygii, Chondrosteidae) из тоара (нижняя юра) Балтийского региона» . ПерДж . 8 : е8400. дои : 10.7717/peerj.8400 . ISSN 2167-8359 . ПМК 6982408 . ПМИД 32002331 .
- ^ Несов, Л.А. (1997). Меловые неморские позвоночные Северной Евразии. СПб.: Институт земной коры СПбГУ, 218 с.
- ^ Гранде, Лэнс; Бемис, Уильям Э. (1991). «Остеология и филогенетические взаимоотношения ископаемых и современных веслоносов (Polyodontidae) с комментариями о взаимоотношениях Acipenseriformes» . Мемуары (Общество палеонтологии позвоночных) . 1 : II–121. дои : 10.2307/3889328 . ISSN 1062-161X . JSTOR 3889328 .
- ^ Листон Дж., Ньюбри М., Чалландс Т. и Адамс К., 2013, «Рост, возраст и размер юрской пахикормиды Leedsichthyspromaticus (Osteichthyes: Actinopterygii) в: Arratia, G., Schultze, Х. и Уилсон, М. (ред.) Мезозойские рыбы 5 – Глобальное разнообразие и эволюция . Верлаг, д-р Фридрих Пфайль, Мюнхен, Германия, стр. 145–175.
- ^ Мартилл, Д.М., 1988, « Leedsichthyspromaticus , гигантская костистая рыба-фильтратор из юрского периода Англии и Франции», Новогоднего справочника по геологии и палеонтологии Ежемесячные выпуски , 1988 (11): 670–680.
- ^ [Ред.] «Поймай 100-футовую рыбу», The Mirror , Лондон, Англия, 18 сентября 2003 г.
- ^ «В Мордене происходит крупное открытие окаменелостей» (PDF) . Канадский центр открытия ископаемых. 16 июля 2010 г. Пресс-релиз.
- ^ Эверхарт, Майкл Дж. (11 сентября 2017 г.). Океаны Канзаса: естественная история западного внутреннего моря . Издательство Университета Индианы. п. 110. ИСБН 978-0-253-02715-3 . Проверено 26 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Кривет, Юрген (2008). «Зубной ряд загадочной рыбы-пикнодонта Athrodon wittei (Fricke, 1876) (Neopterygii, Pycnodontiformes; поздняя юра; северо-запад Германии)» (PDF) . Ископаемый рекорд . 11 (2): 61–66. Бибкод : 2008FossR..11...61K . дои : 10.1002/mmng.200800002 .
- ^ Грандстафф, бакалавр наук; Смит, Дж. Б.; Ламанна, MC; Лаковара, К.Дж.; Абдель-Гани, MS (2012). « Bawitius , gen. nov., гигантский полиптерид (Osteichthyes, Actinopterygii) из верхнемеловой формации Бахария в Египте». Журнал палеонтологии позвоночных . 32 (1): 17–26. Бибкод : 2012JVPal..32...17G . дои : 10.1080/02724634.2012.626823 . S2CID 140547157 .
- ^ Готфрид, Майкл Д.; Фордайс, Р. Юэн; Раст, Сиборн (2006). « Megalampris keyesi , гигантская рыба-луна (Teleostei, Lampridiformes) из позднего олигоцена Новой Зеландии». Журнал палеонтологии позвоночных . 6 (3): 544–551. doi : 10.1671/0272-4634(2006)26[544:MKAGMT]2.0.CO;2 . S2CID 85849900 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Санки, Джулия; Бивер, Джейкоб; Басуга, Янис; Паласиос, Франциско; Вагнер, Хью (2016). «Гигантский лосось с шипами, Oncorhynchus rastrosus и «река Прото-Туолумн» (ранний плиоцен) Центральной Калифорнии» . ПалеоБиос . 33 : 1–16. дои : 10.5070/P9331033123 .
- ^ Стирли, РФ и Г.Р. Смит. 2016. Лососевые рыбы из мио-плиоценовых озерных отложений на равнине Западной Снейк-Ривер и Большой Бассейн. в У. Л. Финке и Н. Карпентере (ред.). Рыбы мио-плиоценовой равнины и окрестностей Западной реки Снейк . Разное. Паб. Музейная зоология, Мичиганский университет 204:1–45.
- ^ Грегорова, Рузена; Шульц, Ортвин; Харцхаузер, Матиас; Кро, Андреас; Чорич, Степан (12 июня 2009 г.). «Гигантская солнечная рыба раннего миоцена из Северо-Альпийского предгорья (Австрия) и ее значение для филогении молд». Журнал палеонтологии позвоночных . 29 (2): 359–371. Бибкод : 2009JVPal..29..359G . дои : 10.1671/039.029.0201 . ISSN 0272-4634 . S2CID 54774567 .
- ^ Тройер, Эмили М.; Бетанкур-Р, Рикардо; Хьюз, Лили С.; Вестнит, Марк; Карневале, Джорджо; Уайт, Уильям Т.; Погоноски, Джон Дж.; Тайлер, Джеймс С.; Болдуин, Кэрол С.; Орти, Гильермо; Бринкворт, Эндрю; Клавель, Жюльен; Арсила, Дахиана (11 июля 2022 г.). «Влияние палеоклиматических изменений на эволюцию размеров тела морских рыб» . Труды Национальной академии наук . 119 (29): e2122486119. Бибкод : 2022PNAS..11922486T . дои : 10.1073/pnas.2122486119 . ISSN 0027-8424 . ПМЦ 9308125 . ПМИД 35858316 .
- ^ Виньола Лопес, Лазаро В.; Карр, Ричард; Лоренцо, Логель (20 октября 2020 г.). «Первое появление ископаемых балистов (Tetradontiformes: Balistidae) из миоцена Кубы с описанием нового вида и пересмотром ископаемых балистов». Историческая биология . 32 (9): 1290–1299. Бибкод : 2020HBio...32.1290V . дои : 10.1080/08912963.2019.1580278 . ISSN 0891-2963 . S2CID 92003143 .
- ^ Мишо, Марк (2012). «Stratodontidae, Маастрихтен-дю-Нигер, часть 1» . HAL Открытая наука . Архивировано из оригинала 27 мая 2022 года.
- ^ Гесс, Ганс (2010). «Онлайн-трактат, № 16, Часть T, переработанный, Том 1, Глава 19: Палеоэкология пелагических криноидей» . Трактат онлайн . дои : 10.17161/to.v0i0.4086 . ISSN 2153-4012 .
- ^ Блейк, Дэниел Б. (1 июня 2009 г.). «Переоценка девонского семейства Helianthasteridae Gregory, 1899 (Asteroidea: Echinodermata)». Палеонтологический журнал . 83 (2): 293–308. Бибкод : 2009PalZ...83..293B . дои : 10.1007/s12542-009-0020-x . ISSN 1867-6812 . S2CID 131480746 .
- ^ Дэвид К. Лойделл, Роберт Ф. Ловеридж (23 апреля 2001 г.). «Самый длинный граптолит в мире?». Геологический журнал . 36 (1): 55–57. Бибкод : 2001GeolJ..36...55L . дои : 10.1002/gj.875 . S2CID 129566263 .
- ^ Фу, Дунцзин, Дай, Лю, Юнин, Цуй, Линьхао; Юн, Хао, Юй; Сунь, Ао, Цун; Вэньруй; Роберт Р.; Чжан, Синлян (22 марта 2019 г.). — ископаемое Лагерштетте типа сланцев Берджесс из раннего кембрия» . Science «Биота Цинцзян 363 (6433): 1338–1342 . : 363.1338F . doi : 10.1126 . ISSN 0036-8075 . PMID 30898931 . / science.aau8800 2019Sci ...
- ^ « В Китае обнаружена «умопомрачительная» партия окаменелостей возрастом более 500 миллионов лет» . Хранитель . 21 марта 2019 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Винтер, Якоб; Поррас, Луис; Янг, Флетчер Дж.; Бадд, Грэм Э.; Эджкомб, Грегори Д. (2016). «Ротовой аппарат кембрийского жаберного лобопода Pambdelurion Whittingtoni» . Палеонтология . 59 (6): 841–849. Бибкод : 2016Palgy..59..841V . дои : 10.1111/пала.12256 . hdl : 1983/16da11f1-5231-4d6c-9968-69ddc5633a8a . ISSN 1475-4983 . S2CID 88758267 .
- ^ Ван Рой, Питер; Дейли, Эллисон С.; Бриггс, Дерек Э.Г. (2015). «Гомология конечностей туловища аномалокаридид, выявленная гигантским фильтратором с парными створками» . Природа . 522 (7554): 77–80. Бибкод : 2015Natur.522...77V . дои : 10.1038/nature14256 . ISSN 1476-4687 . ПМИД 25762145 . S2CID 205242881 .
- ^ Лерози-Обрил, Руди; Пейтс, Стивен (14 сентября 2018 г.). «Новый радиодонт, питающийся взвесью, предполагает эволюцию микропланктивных животных в кембрийском макронектоне» . Природные коммуникации . 9 (1): 3774. Бибкод : 2018NatCo...9.3774L . дои : 10.1038/s41467-018-06229-7 . ISSN 2041-1723 . ПМК 6138677 . ПМИД 30218075 .
- ^ Бергстрем, Ян; Штюрмер, Вильгельм; Винтер, Герхард (1 июня 1980 г.). «Palaeoisopus, Palaeopantopus и Palaeothea, членистоногие-пикногониды из нижнедевонского сланца Хунсрюк, Западная Германия» . Палеонтологический журнал . 54 (1–2): 7–54. Бибкод : 1980PalZ...54....7B . дои : 10.1007/BF02985882 . S2CID 86746066 .
- ^ Андерсон, Лайалл И.; Пошманн, Маркус; Браукманн, Карстен (1998). «Об эмсских (нижнедевонских) членистоногих Рейнских Сланцевых гор: 2. Синзифосуриновая Willwerathia » . Палеонтологическая газета . 72 (3–4): 325–336. Бибкод : 1998PalZ...72..325A . дои : 10.1007/BF02988363 . ISSN 0031-0220 . S2CID 128464147 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Ламсделл, Джеймс К. (1 января 2013 г.). «Пересмотренная систематика палеозойских «мечехвостов» и миф о монофилетической меченосце» . Зоологический журнал Линнеевского общества . 167 (1): 1–27. дои : 10.1111/j.1096-3642.2012.00874.x . ISSN 0024-4082 .
- ^ Эджкомб, Грегори Д. (25 ноября 1998 г.). «Ранние многоногие членистоногие из Австралии: Мальдибулакия из девона Нового Южного Уэльса» . Записи Австралийского музея . 50 (3): 293–313. дои : 10.3853/j.0067-1975.50.1998.1288 .
- ^ Гайяр, Кристиан (1 декабря 2011 г.). «Гигантская тропа лимулидов (Kouphichnium Lithographicum) из литографических известняков Серина (поздний кимеридж, Франция): этологическое и экологическое значение» . Швейцарский журнал геонаук . 104 (1): 57–72. дои : 10.1007/s00015-010-0032-2 . ISSN 1661-8734 . S2CID 140543244 .
- ^ Ламсделл, Джеймс К.; Гандерсон, Джеральд О.; Мейер, Рональд К. (8 января 2019 г.). «Обыкновенное членистоногие из позднеордовикского периода Big Hill Lagerstätte (Мичиган) обнаруживает неожиданное экологическое разнообразие внутри Chasmataspidida» . Эволюционная биология BMC . 19 (1): 8. Бибкод : 2019BMCEE..19....8L . дои : 10.1186/s12862-018-1329-4 . ISSN 1471-2148 . ПМК 6325806 . ПМИД 30621579 .
- ^ Брэдди, Саймон Дж; Пошманн, Маркус; Тетли, О. Эрик (23 февраля 2008 г.). «Гигантский коготь обнаружил самое большое членистоногое в истории » Письма по биологии . 4 (1): 106–109. дои : 10.1098/rsbl.2007.0491 . ПМЦ 2412931 . ПМИД 18029297 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Ламсделл, Джеймс К.; Брэдди, Саймон Дж. (2009). «Правило Коупа и теория Ромера: закономерности разнообразия и гигантизма у эвриптерид и палеозойских позвоночных» . Письма по биологии . 6 (2): 265–9. дои : 10.1098/rsbl.2009.0700 . ПМК 2865068 . ПМИД 19828493 . Дополнительная информация . Архивировано из оригинала 28 февраля 2018 года . Проверено 5 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Ламсделл, Джеймс К.; Бриггс, Дерек Э.Г.; Лю, Хуайбао; Витцке, Брайан Дж.; Маккей, Роберт М. (1 сентября 2015 г.). «Самый старый описанный эвриптерид: гигантский мегалограптид среднего ордовика (дарривилиана) из Виннешик-Лагерштетте в Айове» . Эволюционная биология BMC . 15 (1): 169. Бибкод : 2015BMCEE..15..169L . дои : 10.1186/s12862-015-0443-9 . ПМК 4556007 . ПМИД 26324341 .
- ^ Джерам, Эндрю Дж. (1993). «Скорпионы из Визеа Восточного Кирктона, Западный Лотиан, Шотландия, с ревизией инфраотряда Mesoscorpionina» . Труды Королевского общества Эдинбурга по наукам о Земле и окружающей среде . 84 (3–4): 283–299. Бибкод : 1993EETR..84..283J . дои : 10.1017/S0263593300006106 . ISSN 1755-6929 . S2CID 131416804 .
- ^ Кьеллесвиг-Варинг, Эрик Н. (1972). «Brontoscorpio anglicus: гигантский нижнепалеозойский скорпион из Центральной Англии». Журнал палеонтологии . 46 (1): 39–42. ISSN 0022-3360 . JSTOR 1302906 .
- ^ Кьеллесвиг-Варинг, EN (1986). «Повторное исследование ископаемых скорпионов мира» . Палеонтография Американа . 55 : 1–287.
- ^ Селден, Пенсильвания; Ши, СК; Рен, Д. (2011). «Золотой паук-круготкач (Araneae: Nephilidae: Nephila ) из средней юры Китая» . Письма по биологии . 7 (5): 775–8. дои : 10.1098/rsbl.2011.0228 . ПМК 3169061 . ПМИД 21508021 .
- ^ Селден, Пол А.; Да Коста Касадо, Фабио; Вианна Мескита, Мариса (2006). «Пауки-мигаломорфы (Araneae: Dipluridae) из нижнего мела Crato lagerstätte, бассейн Арарипе, северо-восток Бразилии: МЕЛОВЫЕ ПАУКИ ИЗ КРАТО, БРАЗИЛИЯ» . Палеонтология . 49 (4): 817–826. дои : 10.1111/j.1475-4983.2006.00561.x . hdl : 1808/8355 . S2CID 3845623 .
- ^ Дэвид М. Мартилл; Гюнтер Бехли; Роберт Ф. Ловеридж (2007). Ископаемые пласты Крато в Бразилии: окно в древний мир . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 124. ИСБН 978-1-139-46776-6 . Проверено 22 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Сантана, Уильям; Пиньейру, Эллиссон П.; Сильва, Тьяго Андраде; Лима, Дэниел (3 января 2024 г.). «Описание новой окаменелости Thelyphonida (Arachnida, Uropygi) и дальнейшая запись Cratosolpuga wunderlichi Selden, в Селдене и Шире, 1996 г. (Arachnida, Solifugae) из формации Крато (апт/альб), бассейн Арарипе, Бразилия» . ПерДж . 12 : е16670. дои : 10.7717/peerj.16670 . ISSN 2167-8359 . ПМЦ 10771091 . ПМИД 38188171 .
- ^ Джейсон А. Данлоп, Дэвид М. Мартилл. Первый паук-кнут (Arachnida: Amblypygi) и три новых паука-хлыста (Arachnida: Thelyphonida) из нижнемеловой формации Крато в Бразилии . Труды Королевского общества Эдинбурга: Науки о Земле, 92, 325–334, 2002.
- ^ Уэлен, Найл; Селден, Пол (2021). «Новый гигантский рицинулеид (Arachnida, Ricinulei) из Пенсильвании штата Иллинойс и идентификация нового, онтогенетически стабильного, диагностического признака» . Журнал палеонтологии . 95 (3): 601–612. Бибкод : 2021JPal...95..601W . дои : 10.1017/jpa.2020.104 .
- ^ Дж. А. Данлоп, К. Франерт и Дж. Макол. 2018. Гигантский клещ в меловом бирманском янтаре . Ископаемая запись 21: 285–290
- ^ Jump up to: а б Росслер, Ронни и Данлоп, Джейсон А. (1997). «Переописание крупнейшего паукообразного тригонотарбида - Kreischeria wiedei Geinitz 1882 из верхнего карбона Цвиккау, Германия». Палеонтологический журнал . 71 (3–4): 237–245. Бибкод : 1997PalZ...71..237R . дои : 10.1007/BF02988493 . S2CID 129447249 .
- ^ Чжан, Маоинь; Лю, Ю; Хоу, Сянгуан; Ортега-Эрнандес, Хавьер; Май, Хуэйцзюань; Шмидт, Мишель; Мельцер, Роланд Р.; Го, Цзинь (2022). «Вентральная морфология нетрилобитных парнокопытных Retifacies ненормальной Hou, Chen & Lu, 1989, из раннекембрийской биоты Чэнцзян, Китай» . Биология . 11 (8): 1235. doi : 10.3390/biology11081235 . ISSN 2079-7737 . ПМК 9405172 . ПМИД 36009864 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Николас Дж. Минтер, М. Габриэла Мангано и Жан-Бернар Карон (2011). «Скольжение по поверхности с помощью движения членистоногих Берджесс Шейл» . Труды Королевского общества B: Биологические науки . 279 (1733): 1613–1620. дои : 10.1098/рспб.2011.1986 . ПМЦ 3282348 . ПМИД 22072605 .
- ^ Гутьеррес-Марко, Хуан К.; Са, Артур А.; Гарсия-Беллидо, Диего К.; Рабано, Изабель; Валерио, Мануэль (2009). «Гигантские трилобиты и скопления трилобитов из ордовика Португалии». Геология . 37 (5): 443–446. Бибкод : 2009Geo....37..443G . дои : 10.1130/G25513A.1 .
- ^ Джордж Р. Макги-младший (12 ноября 2013 г.). Когда вторжение на сушу провалилось: наследие девонского вымирания . Издательство Колумбийского университета. ISBN 978-0-231-16057-5 .
- ^ «Волнение открытия» . Виртуальный музей Канады . Архивировано из оригинала 4 февраля 2012 года . Проверено 17 апреля 2006 г.
- ^ «На пляже Нортумберленда найдена самая крупная ископаемая многоножка в истории» . Новости Би-би-си . 21 декабря 2021 г. Проверено 21 декабря 2021 г.
- ^ Нил Дэвис; и др. (21 декабря 2021 г.). «Самое большое членистоногое в истории Земли: данные по недавно обнаруженным останкам артроплевры (серпуховская формация Стейнмор, Нортумберленд, Англия)» . Журнал Геологического общества . 179 (3). дои : 10.1144/jgs2021-115 . S2CID 245401499 .
- ^ Дзик, Ежи (2008). «Строение жабр и взаимоотношения триасовых циклоидных ракообразных» (PDF) . Журнал морфологии . 269 (12): 1501–1519. дои : 10.1002/jmor.10663 . ПМИД 18690662 . S2CID 17617567 .
- ^ Эмерсон, MJ; Шрам, Франция (1991). «Ремипедия, часть 2: палеонтология» . Труды Общества естественной истории Сан-Диего . 7 :1–52.
- ^ Ремипедия: Виды — робустус, Годзиллиус . Crustacea.net (2 октября 2002 г.)
- ^ Шааль, Стефан (27 января 2006 г.). «Мессель». ЭЛС . дои : 10.1038/npg.els.0004143 . ISBN 978-0-470-01617-6 .
- ^ Энгель, М.С. (2006). «Гигантская медоносная пчела Apislithohermaea Engel из миоцена Японии и геологическая история Apis (Hymenoptera: Apidae)» . Наука о медоносных пчелах – Университет Тамагава (Япония) (на японском языке). ISSN 0388-2217 .
- ^ Арчибальд, С.Б.; Расницын, АП (2015). «Новые раннеэоценовые Siricomorpha (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Pamphiliidae, Siricidae, Cephidae) из высокогорья Оканаган, западная часть Северной Америки». Канадский энтомолог . 148 (2): 209–228. дои : 10.4039/tce.2015.55 . S2CID 85743832 .
- ^ Гао, Тайпин; Ши, Чунгкун; Расницын Александр П.; Рен, Донг (3 мая 2013 г.). «Hoplitolyda duolunica gen. et sp. nov. (Insecta, Hymenoptera, Praesiricidae), крупнейший на сегодняшний день пилильщик из мезозоя Китая» . ПЛОС ОДИН . 8 (5): е62420. Бибкод : 2013PLoSO...862420G . дои : 10.1371/journal.pone.0062420 . ISSN 1932-6203 . ПМЦ 3643952 . ПМИД 23671596 .
- ^ Чжан, Яньцзе; Ши, Чунгкун; Расницын, Александр; Рен, Донг; Гао, Тайпин (2020). «Новая блоха из раннего мела Китая» . Acta Palaeontologica Polonica . 65 . дои : 10.4202/app.00680.2019 . ISSN 0567-7920 . S2CID 213622677 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Лабидура» . Естественная история острова Святой Елены и Вознесения . Архивировано из оригинала 17 июля 2011 года . Проверено 13 октября 2022 г.
- ^ Уокер, Мэтт (17 ноября 2014 г.). «Самая большая в мире уховертка объявлена вымершей» . BBC Земля . Архивировано из оригинала 1 мая 2017 года . Проверено 13 октября 2022 г.
- ^ Ф. Э. Цойнер. 1962. Субфоссильный гигантский дермаптерон с острова Святой Елены. Труды Лондонского зоологического общества 138: 651–653.
- ^ «Ископаемое с идентификационным номером: 1780 – Chresmoda obscura ГЕРМАР, 1839 – Окаменелости Зольнхофена» . Solnhofen-fossilienatlas.de . Архивировано из оригинала 20 августа 2022 года . Проверено 13 октября 2022 г.
- ^ Шалюмо, Ф.; Брошье, Б. (2001). «Une forme ископаемое nouvelle de Chiasognathinae: Protognathinus spielbergi (Coleoptera, Lucanidae)» (PDF) . Ламбиллионея . 101 : 593–595. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 20 сентября 2022 года.
- ^ Бретт Рэтклифф; Дена М. Смит; Дайан Мари Эрвин (2005). «Oryctoantiquus borealis, новый род и вид из эоцена Орегона, США, старейшая в мире ископаемая династия и крупнейший ископаемый скарабеид (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Dynastinae)» . Бюллетень колеоптерологов . 59 : 127–135. doi : 10.1649/0010-065X(2005)059[0127:OBNGAS]2.0.CO;2 . S2CID 18230496 .
- ^ Пак Тэ-Юн С.; Ким, До Юн; Нам, Ги-Су; Ли, Миринаэ (6 мая 2022 г.). «Новый титаноптеран Magnatitan jongheoni n. gen. n. sp. с юго-запада Корейского полуострова» . Журнал палеонтологии . 96 (5): 1111–1118. Бибкод : 2022JPal...96.1111P . дои : 10.1017/jpa.2022.30 . ISSN 0022-3360 . S2CID 248592776 .
- ^ Маккеун, Кейт К. (15 мая 1937 г.). «Новые крылья ископаемых насекомых (Protohemiptera, семейство Mesotitanidae)» . Записи Австралийского музея . 20 (1): 31–37. дои : 10.3853/j.0067-1975.20.1937.565 . ISSN 0067-1975 . [ постоянная мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ Бечли, Г.; Макаркин В.Н. (2016). «Новый гигантский вид златоглазки (Insecta: Neuroptera) из нижнего мела Бразилии подтверждает появление Kalligrammatidae в Америке». Меловые исследования . 58 : 135–140. Бибкод : 2016CrRes..58..135B . дои : 10.1016/j.cretres.2015.10.014 .
- ^ Селлардс, Элиас Ховард (1 апреля 1903 г.). «Некоторые новые особенности строения палеозойских тараканов» . Американский научный журнал . с4-15 (88): 307–315. Бибкод : 1903AmJS...15..307S . дои : 10.2475/ajs.s4-15.88.307 . ISSN 0002-9599 .
- ^ Пасхальный день, Кэри Рэй (2004). Стратиграфия и палеонтология Кладбищенского холма (десмуанский-миссурийский период: верхний карбон), округ Колумбия, восточный Огайо (Диссертация). Университет штата Огайо. Архивировано из оригинала 20 сентября 2022 года . Проверено 20 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Шнайдер, Йорг; Шольце, Франк; Германн, Себастьян; Лукас, Спенсер (16 апреля 2021 г.). «ПОЗДНЕПЕНСИЛЬВАНСКАЯ ПРИБРЕЖНАЯ ФАУНА НАСЕКОМЫХ КАРЬЕРА КИННИ-БРИК, ИСКОПАЕМЫЕ БЕСПОЗВОНОЧНЫЕ И ПОЗВОНОЧНЫЕ, ЛАГЕРШТЕТ, НЬЮ-МЕКСИКО» . Бюллетень Американского музея естественной истории . 84 .
- ^ Род Ptiloteuthis Gabb: Notulae Naturae Академии естественных наук Филадельфии, вып. 9 . Академия естественных наук. ISBN 978-1-60483-009-5 .
- ^ Энгель, М.С.; Гросс, М. (2008). «Гигантский термит из позднего миоцена Штирии, Австрия (Isoptera)». Naturwissenschaften . 96 (2): 289–295. Бибкод : 2009NW.....96..289E . дои : 10.1007/s00114-008-0480-y . ПМИД 19052720 . S2CID 21795900 .
- ^ Ганд, Г.; Нел, АН; Флек, Г.; Гарруст, Р. (1 января 2008 г.). «Odonatoptera позднепермского бассейна Лодев (Insecta)» . Журнал иберийской геологии (на испанском языке). 34 (1): 115–122. ISSN 1886-7995 .
- ^ Чжан, Хайчунь; Чжэн, ДаРань; Ван, Бо; Фанг, Ян; Яржембовский, Эдмунд А. (1 мая 2013 г.). «Самый крупный из известных стрекоз в Китае: Сюфуа чаой Чжан и Ван, род. и пр. нояб. из средней юры Внутренней Монголии» . Китайский научный бюллетень . 58 (13): 1579–1584. Бибкод : 2013ЧСБу..58.1579З . дои : 10.1007/s11434-012-5567-3 . ISSN 1861-9541 . S2CID 95712438 .
- ^ Дереньокур, Изабель; Вапплер, Торстен; Андерсон, Джон; Бету, Оливье (2017). «Новое триадотипидное насекомое из позднего триаса Южной Африки» . Acta Palaeontologica Polonica . 62 . дои : 10.4202/app.00345.2017 . ISSN 0567-7920 . S2CID 115149987 .
- ^ Синищенкова, Нина (2012). «Самая большая ископаемая подёнка (Insecta: Ephemerida = Ephemeroptera) из верхнепермского местонахождения Исады, Север Европейской России» . Дальневосточный энтомолог .
- ^ Хуан, Цзяндун; Рен, Донг; Синищенкова Нина Д.; Ши, Чунгкун (2 ноября 2007 г.). «Новый род и вид Hexagenitidae (Insecta: Ephemeroptera) из формации Исянь, Китай» . Зоотакса . 1629 (1): 39–50. дои : 10.11646/zootaxa.1629.1.3 . ISSN 1175-5334 .
- ^ Дж. Кукалова-Пек. 1985. Эфемероидное жилкование крыльев на основе новых гигантских каменноугольных подёнок и основные морфологии, филогения и метаморфоз крыловидных насекомых (Insecta, Ephemerida) . Канадский журнал зоологии 63 (4): 933–955.
- ^ Срок, Павел; Станичек, Арнольд Х.; Бехли, Гюнтер (2 ноября 2015 г.). «Ревизия гигантского крыловидного насекомого Bojophlebia prokopi Kukalová-Peck, 1985 (Hydropaeoptera: Bojophlebiidae) из каменноугольного периода Чешской Республики, с первым кладистическим анализом ископаемых палеоптерообразных насекомых». Журнал систематической палеонтологии . 13 (11): 963–982. Бибкод : 2015JSPal..13..963S . дои : 10.1080/14772019.2014.987958 . ISSN 1477-2019 . S2CID 84037275 .
- ^ Кукалова-Пек, Ярмила; Ричардсон, Юджин С. (1983). «Новые Homoiopteridae (Insecta: Paleodictyoptera) с сочленениями крыльев из слоев верхнего карбона Мейзон-Крик, штат Иллинойс». Канадский журнал зоологии . 61 (7): 1670–1687. дои : 10.1139/z83-218 .
- ^ Браукманн, Карстен; СТАБО, КАРЛ (2007). «Подкруглое крыло насекомого из позднего карбона из Оснабрюка, Германия» . Клаусталер Геовиссеншафтен . 6 : 79–85.
- ^ Монтанья, Маттео; Хауг, Иоахим Т.; Страда, Лаура; Хауг, Кэролин; Фельбер, Маркус; Тинтори, Андреа (7 апреля 2017 г.). «Центральная нервная система и мышечные пучки сохранились у гигантского щетинистого хвоста возрастом 240 миллионов лет (Archaeognatha: Machilidae)» . Научные отчеты . 7 (1): 46016. Бибкод : 2017НатСР...746016М . дои : 10.1038/srep46016 . ISSN 2045-2322 . ПМК 5384076 . ПМИД 28387236 .
- ^ Хоэлл, Х.В.; Дойен, Дж. Т. и Перселл, А. Х. (1998). Введение в биологию и разнообразие насекомых (2-е изд.). Издательство Оксфордского университета. п. 321. ИСБН 0-19-510033-6 .
- ^ Шир, Уильям А.; Кукалова-Пек, Ярмила (15 февраля 2011 г.). «Экология палеозойских наземных членистоногих: ископаемые свидетельства» . Канадский журнал зоологии . 68 (9): 1807–1834. дои : 10.1139/z90-262 .
- ^ Стокар, Рудольф. «Первая мезозойская запись о вымерших аптериготных насекомых рода Dasyleptus (Insecta: Archaeognatha: Monura: Dasyleptidae) из триаса Монте-Сан-Джорджио (Швейцария)» . Палеразнообразие . 4 .
- ^ Станичек, Арнольд Х.; Срок, Павел; Бехли, Гюнтер (2014). «Ни чешуйница, ни домашняя птица: загадочная каменноугольная карботриплура kukalovae Kluge, 1996 (Insecta: Carbotriplurida) — предполагаемая ископаемая сестринская группа крылатых насекомых (Insecta: Pterygota)» . Систематическая энтомология . 39 (4): 619–632. Бибкод : 2014SysEn..39..619S . дои : 10.1111/syen.12076 . S2CID 83792881 .
- ^ Пак Тэ-Юн С.; Нильсен, Мортен Лунде; Парри, Люк А.; Соренсен, Мартин Винтер; Ли, Миринаэ; Ким, Джи-Хун; Ан, Инхе; Парк, Чанкунь; де Виво, Джачинто; Смит, М. Пол; Харпер, Дэвид А.Т.; Нильсен, Арне Т.; Винтер, Якоб (2024). «Гигантский хетогнат стеблевой группы» . Достижения науки . 10 (1): eadi6678. Бибкод : 2024SciA...10I6678P . дои : 10.1126/sciadv.adi6678 . ISSN 2375-2548 . ПМЦ 10796117 . ПМИД 38170772 .
- ^ « Гигантские» черви-хищники возрастом более полумиллиарда лет обнаружены в Северной Гренландии . Бристольский университет . 3 января 2024 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Эрикссон, Матс Э.; Парри, Люк А.; Рудкин, Дэвид М. (февраль 2017 г.). «Старейший на Земле «червь Боббит» - гигантизм у девонской полихеты-евницида» . Научные отчеты . 7 (2): 239–260. Бибкод : 2017NatSR...743061E . дои : 10.1038/srep43061 . ПМК 5318920 . ПМИД 28220886 .
- ^ Цюрих, ETH-Библиотека. «Гигантские брюхоногие моллюски рода Campanile из карибского эоцена» . Электронная периодика (на немецком языке). Архивировано из оригинала 15 июня 2022 года.
- ^ Церитий гигантский или колокольчик гигантский . Архивная копия от 28 июля 2016 г.
- ^ Доминичи, Стефано; Форнасьеро, Мариагабриелла; Джусберти, Лука (14 декабря 2020 г.). «Самый крупный из известных каури и итеративная эволюция гигантских брюхоногих моллюсков» . Научные отчеты . 10 (1): 21893. Бибкод : 2020NatSR..1021893D . дои : 10.1038/s41598-020-78940-9 . ISSN 2045-2322 . ПМЦ 7736312 . ПМИД 33318588 .
- ^ Весселинг Ф.П. (2006). «Моллюски из миоценовой формации Пебас Перуанской и Колумбийской Амазонии». Scripta Geologica 133 : 19–290. Рисунок 274. аннотация , PDF
- ^ Журнал палеонтологии, январь 2007 г., Том. 81, № 1 (январь 2007 г.), стр. 64–81.
- ^ "Verdens største musling" . Архивировано из оригинала 18 августа 2022 года.
- ^ Асато, Кайто; Касе, Томоки; Оно, Теруо; Сашида, Кацуо; Агемацу, Сатико (2017). «Морфология, систематика и палеоэкология шикамайских, аберрантных пермских двустворчатых моллюсков (Alatoconchidae: Ambonychioidea) из Японии» . Палеонтологические исследования . 21 (4): 358–379. дои : 10.2517/2017PR002 . ISSN 1342-8144 . S2CID 135126528 .
- ^ «Информационный бюллетень Музея окаменелостей может опубликовать № 25, посвященный окаменелостям крупных ракушек с горы Киншо» (PDF) . Музей окаменелостей Кинсёяма .
- ^ ЧИНЗЕЙ, К. (1986). «Строение раковины, рост и функциональная морфология удлиненной меловой устрицы» . Палеонтология . 29 (1): 139–154.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Вермей, Гират Дж. (15 января 2016 г.). «Гигантизм и его последствия для истории жизни» . ПЛОС ОДИН . 11 (1): e0146092. Бибкод : 2016PLoSO..1146092V . дои : 10.1371/journal.pone.0146092 . ISSN 1932-6203 . ПМЦ 4714876 . ПМИД 26771527 .
- ^ Асато, Кайто; Касе, Томоки (2021). «Гигантские ладьевидные моллюски (Mollusca) из пермского известняка Акасака, центральная Япония» . Журнал палеонтологии . 95 (4): 748–762. Бибкод : 2021JPal...95..748A . дои : 10.1017/jpa.2021.3 . ISSN 0022-3360 . S2CID 233649005 .
- ^ Клюг, Кристиан; Баетс, Кеннет Де; Крёгер, Бьёрн; Белл, Марк А.; Корн, Дитер; Пейн, Джонатан Л. (2015). «Нормальные гиганты? Временные и широтные сдвиги палеозойского гигантизма морских беспозвоночных и глобальные изменения» . Летайя . 48 (2): 267–288. Бибкод : 2015Лета..48..267К . дои : 10.1111/лет.12104 . ISSN 1502-3931 .
- ^ Пейн, Джонатан Л.; Бойер, Элисон Г.; Браун, Джеймс Х.; Финнеган, Сет; Ковалевский, Михал; Краузе, Ричард А.; Лайонс, С. Кэтлин; Макклейн, Крейг Р.; Макши, Дэниел В.; Новак-Готтшалл, Филип М.; Смит, Фелиса А.; Стемпьен, Дженнифер А.; Ван, Стив С. (6 января 2009 г.). «Двухфазное увеличение максимального размера жизни на протяжении 3,5 миллиардов лет отражает биологические инновации и экологические возможности» . Труды Национальной академии наук . 106 (1): 24–27. Бибкод : 2009PNAS..106...24P . дои : 10.1073/pnas.0806314106 . ISSN 0027-8424 . ПМК 2607246 . ПМИД 19106296 .
- ^ Тейхерт, К. и Б. Куммель 1960. Размер эндоцероидных головоногих моллюсков . Музей сравнительной зоологии Бревиоры 128 : 1–7.
- ^ Ифрим, Кристина; Стиннесбек, Вольфганг; Гонсалес, Артуро Х. Гонсалес; Шорндорф, Нильс; Гейл, Эндрю С. (10 ноября 2021 г.). «Онтогенез, эволюция и палеогеографическое распространение крупнейшего в мире аммонита Parapuzosia (P.) seppenradensis (Landois, 1895)» . ПЛОС ОДИН . 16 (11): e0258510. Бибкод : 2021PLoSO..1658510I . дои : 10.1371/journal.pone.0258510 . ISSN 1932-6203 . ПМЦ 8580234 . ПМИД 34758037 .
- ^ Иба, Ясухиро; Сано, Син-Ичи; Гото, Мичихару (январь 2015 г.). «Крупные белемниты уже были распространены в ранней юре — новые данные из Центральной Японии». Палеонтологические исследования . 19 (1): 21–25. дои : 10.2517/2014PR025 . S2CID 55001872 .
- ^ Фукс, Дирк; Иба, Ясухиро; Хейнг, Александр; Иидзима, Масая; Клюг, Кристиан; Ларсон, Нил Л.; Швайгерт, Гюнтер (2020). Брайард, Арно (ред.). «Muensterelloidea: филогения и эволюция характера мезозойских стволовых осьминогов» . Статьи по палеонтологии . 6 (1): 31–92. Бибкод : 2020PPal....6...31F . дои : 10.1002/spp2.1254 . ISSN 2056-2802 . S2CID 198256507 .
- ^ Танабэ, Казусигэ; Хикида, Ёсинори; Иба, Ясухиро (2006). «Две колеоидные челюсти из верхнего мела Хоккайдо, Япония» . Журнал палеонтологии . 80 (1): 138–145. doi : 10.1666/0022-3360(2006)080[0138:TCJFTU]2.0.CO;2 . ISSN 0022-3360 . S2CID 130583140 .
- ^ Танабэ, Казусигэ; Мисаки, Акихиро; Убуката, Такао (2014). «Позднемеловые находки крупных мягкотелых колеоидов на основе остатков нижней челюсти с Хоккайдо, Япония» . Acta Palaeontologica Polonica . дои : 10.4202/app.00052.2013 . ISSN 0567-7920 .
- ^ Мычко, Эдуард Васильевич; Фельдман, Родни М.; Швейцер, Кэрри Э.; Алексеев Александр Сергеевич (25 октября 2019 г.). «Новый род Cyclida (Crustacea) из нижнего карбона (Миссисипи, Визе) России и Англии и новые виды из Визеа России» . Новогодний ежегодник по геологии и палеонтологии-трактаты . 294 : 81–90. дои : 10.1127/njgpa/2019/0847 . S2CID 210640676 .
- ^ Джордж Р. МакГи-младший (2019). Конвергентная эволюция на Земле. Уроки поиска внеземной жизни . МТИ Пресс. п. 47. ИСБН 9780262354189 . Проверено 23 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Войтех Турек; Дж. Марек; Йозеф Бенеш (1989). Окаменелости мира. Комплексное практическое руководство по сбору и изучению окаменелостей . Арч Кейп Пресс. п. 146. ИСБН 9780517679043 . Проверено 23 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Хелен Маргерит Мьюир-Вуд, Густав Артур Купер (1960). Морфология, классификация и образ жизни Productoidea (Brachiopoda) . Геологическое общество Америки. п. 334. ИСБН 9780813710815 . Проверено 23 августа 2022 г.
- ^ Пил, Джон С.; Йохельсон, Эллис Л. (1984). «Пермские Toxeumorphorida из Гренландии: оценка класса моллюсков Xenoconchia» . Летайя . 17 (3): 211–221. Бибкод : 1984Лета..17..211П . дои : 10.1111/j.1502-3931.1984.tb01619.x . ISSN 0024-1164 .
- ^ Майор, Эдвард; Линан, Эладиус; Винтанед, Хосе Антонио Гамес; Мунис, Фернандо; Гозало, Родольфо (3 марта 2021 г.). «Выброшенная на мель медуза в самом нижнем кембрии (Кордубане) Испании » Испанский журнал палеонтологии . 19 (2): 191–198. дои : 10.7203/sjp.19.2.20531 . ISSN 2660-9568 . S2CID 126508499 .
- ^ Том Кларк. Желе откатывают время вспять . Природа (2002).
- ^ М. ЛАФЛАММ, ГМ НАРБОННА, К. ГРИНТРИ И ММ АНДЕРСОН. 2016. Морфология и тафономия эдиакарской ветви: Чарния с полуострова Авалон в Ньюфаундленде . Департамент геологических наук и геологической инженерии, Королевский университет, Кингстон, Онтарио, Канада K7L 3N6. Архивная копия от 18 августа 2022 года.
- ^ Данн, Фрэнсис С.; Уилби, Филип Р.; Кенчингтон, Шарлотта Г.; Гражданкин Дмитрий В.; Донохью, Филип CJ; Лю, Александр Г. (2019). «Анатомия эдиакарского рангеоморфа Charnia masoni » . Статьи по палеонтологии . 5 (1): 157–176. Бибкод : 2019PPal....5..157D . дои : 10.1002/spp2.1234 . ПМК 6472560 . ПМИД 31007942 .
- ^ Дженкинс, RJF (1992). «Функциональные и экологические аспекты эдиакарских комплексов» . В Липпсе, Дж.; Синьор, PW (ред.). Происхождение и ранняя эволюция Metazoa . Нью-Йорк, штат Нью-Йорк: Спрингер. стр. 131–176. ISBN 978-0-306-44067-0 . OCLC 231467647 .
- ^ Федонкин М.А.; Гелинг Дж.Г.; Грей К.; Нарбонн ГМ; Викерс-Рич П. (2007). Восстание животных. Эволюция и разнообразие царства животных . Издательство Университета Джонса Хопкинса. п. 326. ИСБН 978-0-8018-8679-9 .
- ^ Ригби, Дж. Кейт; Сеновбари-Дарьян, Баба (1996). «Gigantospongia, новый род, самая крупная известная пермская губка, Капитанский известняк, горы Гуадалупе, Нью-Мексико». Журнал палеонтологии . 70 (3): 347–355. Бибкод : 1996JPal...70..347R . дои : 10.1017/S0022336000038294 . ISSN 0022-3360 . JSTOR 1306431 . S2CID 130222477 .
Источники
[ редактировать ]- Роуз, Кеннет Дэвид (2006). Начало эпохи млекопитающих . Балтимор: JHU Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-8472-6 .
- Дезохо, Джулия Бренда (2013). Анатомия, филогения и палеобиология ранних архозавров и их родственников . Лондон: Геологическое общество. ISBN 978-1-86239-361-5 .

