Хорватская война за независимость
| Хорватская война за независимость | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Часть югославских войн | |||||||||
центральная улица Дубровника , Страдун , в руинах во время осады Дубровника ; поврежденная Вуковарская водонапорная башня , символ раннего конфликта, под флагом Хорватии ; Вуковар ; Мемориальное кладбище сербский танк Т-55, уничтоженный по дороге на Дрниш ; солдаты хорватской армии готовятся уничтожить сербский танк; Подбитый Югославской народной армии танк | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
1994–95:
|
1992–95:
| ||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| Units involved | |||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
300,000 displaced[21] |
300,000 displaced[24] | ||||||||
Хорватская война за независимость — вооруженный конфликт , который велся с 1991 по 1995 год между хорватскими силами, лояльными правительству Хорватии , провозгласившей независимость от Социалистической Федеративной Республики Югославии (СФРЮ), и сербами контролируемой Югославской народной армией (ЮНА). и местные сербские силы, при этом ЮНА прекратила свои боевые операции в Хорватии к 1992 году. [ я ]
Большинство хорватов поддержали независимость Хорватии от Югославии, в то время как многие этнические сербы, живущие в Хорватии, поддержанные Сербией , [ 28 ] [ 29 ] выступал против отделения и выступал за то, чтобы земли, на которые претендуют сербы, находились в общем государстве с Сербией. Большинство сербов стремились к созданию нового сербского государства в составе югославской федерации, включая территории Хорватии и Боснии и Герцеговины с этническим сербским большинством или значительными меньшинствами. [ 30 ] [ 31 ] и попытался завоевать как можно большую часть Хорватии. [ 32 ] [ 33 ] [ 34 ] Хорватия провозгласила независимость 25 июня 1991 года, но согласилась отложить ее с помощью Соглашения Бриони и разорвать все оставшиеся связи с Югославией 8 октября 1991 года.
The JNA initially tried to keep Croatia within Yugoslavia by occupying all of Croatia.[35][36] After this failed, Serb forces established the self-proclaimed proto-state Republic of Serbian Krajina (RSK) within Croatia which began with the Log Revolution. After the ceasefire of January 1992 and international recognition of the Republic of Croatia as a sovereign state,[37][38] the front lines were entrenched, the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) was deployed,[39] and combat became largely intermittent in the following three years. During that time, the RSK encompassed 13,913 square kilometers (5,372 sq mi), more than a quarter of Croatia.[40] In 1995, Croatia launched two major offensives known as Operation Flash and Operation Storm;[12][41] these offensives effectively ended the war in its favor. The remaining United Nations Transitional Authority for Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Sirmium (UNTAES) zone was peacefully reintegrated into Croatia by 1998.[13][17]
The war ended with Croatian victory, as it achieved the goals it had declared at the beginning of the war: independence and preservation of its borders.[12][13] Approximately 21–25% of Croatia's economy was ruined, with an estimated US$37 billion in damaged infrastructure, lost output, and refugee-related costs.[42] Over 20,000 people were killed in the war,[43] and refugees were displaced on both sides. The Serbian and Croatian governments began to progressively cooperate with each other, but tensions remain, in part due to verdicts by the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY) and lawsuits filed by each country against the other.[44][45]
In 2007, the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY) returned a guilty verdict against Milan Martić, one of the Serb leaders in Croatia, for having colluded with Slobodan Milošević and others to create a "unified Serbian state".[46] Between 2008 and 2012, the ICTY had prosecuted Croatian generals Ante Gotovina, Mladen Markač and Ivan Čermak for alleged involvement in the crimes related to Operation Storm. Čermak was acquitted outright, and the convictions of Gotovina and Markač were later overturned by an ICTY Appeals Panel.[47][48] The International Court of Justice dismissed mutual claims of genocide by Croatia and Serbia in 2015. The Court reaffirmed that, to an extent, crimes against civilians had taken place, but it ruled that specific genocidal intent was not present.[49]
Background
[edit]Political changes in Yugoslavia
[edit]
In the 1970s, Yugoslavia's socialist regime became severely splintered into a liberal-decentralist nationalist faction led by Croatia and Slovenia that supported a decentralized federation to give greater autonomy to Croatia and Slovenia, versus a conservative-centralist nationalist faction led by Serbia that supported a centralized federation to secure Serbia's and the Serbs' interests across Yugoslavia—as they were the largest ethnic group in the country as a whole.[50] From 1967 to 1972 in Croatia and 1968 and 1981 protests in Kosovo, nationalist doctrines and actions caused ethnic tensions that destabilized Yugoslavia.[51] The suppression by the state of nationalists is believed to have had the effect of identifying Croat nationalism as the primary alternative to communism itself and made it a strong underground movement.[52]
A crisis emerged in Yugoslavia with the weakening of the communist states in Eastern Europe towards the end of the Cold War, as symbolized by the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989. In Croatia, the regional branch of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia, the League of Communists of Croatia, had lost its ideological potency.[53][54] Slovenia and Croatia advocated decentralization.[55] SR Serbia, headed by Slobodan Milošević, adhered to centralism and single-party rule, and in turn effectively ended the autonomy of the autonomous provinces of Kosovo and Vojvodina by March 1989, taking command of their votes in the Yugoslav federal presidency.[29][54][56][57] Nationalist ideas started to gain influence within the ranks of the still-ruling League of Communists, while Milošević's speeches, notably the 1989 Gazimestan speech in which he talked of "battles and quarrels", favored continuation of a unified Yugoslav state — one in which all power would continue to be centralized in Belgrade.[29][58][59]
In the autumn of 1989, the Serbian government pressured the Croatian government to allow a series of Serb nationalist rallies in the country, and the Serbian media and various Serbian intellectuals had already begun to refer to the Croatian leadership as "Ustaše", and began to make reference to genocide and other crimes committed by the Ustaše between 1941 and 1945. The Serbian political leadership approved of the rhetoric and accused the Croatian leadership of being "blindly nationalistic" when it objected.[60]
Having completed the anti-bureaucratic revolution in Vojvodina, Kosovo, and Montenegro, Serbia secured four out of eight federal presidency votes in 1991,[58] which rendered the governing body ineffective as other republics objected and called for reform of the Federation.[61] In 1989, political parties were allowed and a number of them had been founded, including the Croatian Democratic Union (Croatian: Hrvatska demokratska zajednica) (HDZ), led by Franjo Tuđman, who later became the first president of Croatia.[62] Tuđman ran on a nationalist platform[63] with a program of "national reconciliation" between Croatian communists and former Ustašes (fascists) being a key component of his party's political program.[64] Accordingly, he also integrated former Ustaše members into the party and state's apparatus.[65]

In January 1990, the League of Communists broke up on ethnic lines, with the Croatian and Slovene factions demanding a looser federation at the 14th Extraordinary Congress. At the congress, Serbian delegates accused the Croatian and Slovene delegates of "supporting separatism, terrorism and genocide in Kosovo".[66] The Croatian and Slovene delegations, including most of their ethnic Serb members, eventually left in protest, after Serbian delegates rejected every proposed amendment.[58][67]
January 1990 also marked the beginning of court cases being brought to Yugoslavia's Constitutional Court on the matter of secession.[68] The first was the Slovenian Constitutional Amendments case after Slovenia claimed the right to unilateral secession pursuant to the right of self-determination.[69] The Constitutional Court ruled that secession from the federation was only permitted if there was the unanimous agreement of Yugoslavia's republics and autonomous provinces.[68] The Constitutional Court noted that 1974 Constitution's Section I of the Basic Principles of the Constitution identified that self-determination including secession "belonged to the peoples of Yugoslavia and their socialist republics".[68] The matter of Kosovo secession was addressed in May 1991 with the court claiming that "only the peoples of Yugoslavia" had the right to secession, Albanians were considered a minority and not a people of Yugoslavia.[68]
The 1990 survey conducted among Yugoslav citizens showed that ethnic animosity existed on a small scale.[70] Compared to the results from 25 years before, Croatia was the republic with the highest increase in ethnic distance. Furthermore, there was significant increase of ethnic distance among Serbs and Montenegrins toward Croats and Slovenes and vice versa.[70] Of all respondents, 48% of Croats said that their affiliation with Yugoslavia is very important to them.[70]
In February 1990, Jovan Rašković founded the Serb Democratic Party (SDS) in Knin, whose program aimed to change the regional division of Croatia to be aligned with ethnic Serb interests.[71] Prominent members of the RSK government, including Milan Babić and Milan Martić, later testified that Belgrade directed a propaganda campaign portraying the Serbs in Croatia as being threatened with genocide by the Croat majority.[72] On 4 March 1990, 50,000 Serbs rallied at Petrova Gora and shouted negative remarks aimed at Tuđman,[71] chanted "This is Serbia",[71] and expressed support for Milošević.[73][74]
The first free elections in Croatia and Slovenia were scheduled for a few months later.[75] The first round of elections in Croatia was held on 22 April, and the second round on 6 May.[76] The HDZ based its campaign on greater sovereignty (eventually outright independence) for Croatia, fueling a sentiment among Croats that "only the HDZ could protect Croatia from the aspirations of Milošević towards a Greater Serbia". It topped the poll in the elections (followed by Ivica Račan's reformed communists, Social Democratic Party of Croatia) and was set to form a new Croatian Government.[76]
A tense atmosphere prevailed on May 13, 1990, when a football game was held at Zagreb in Maksimir Stadium between Zagreb's Dinamo team and Belgrade's Red Star. The game erupted into violence between the Croatian and Serbian fans and with the police.[77]
On 30 May 1990, the new Croatian Parliament held its first session. President Tuđman announced his manifesto for a new Constitution (ratified at the end of the year) and a multitude of political, economic, and social changes, notably to what extent minority rights (mainly for Serbs) would be guaranteed. Local Serb politicians opposed the new constitution. In 1991, Croats represented 78.1% and Serbs 12.2% of the total population of Croatia,[78] but the latter held a disproportionate number of official posts: 17.7% of appointed officials in Croatia, including police, were Serbs. An even greater proportion of those posts had been held by Serbs in Croatia earlier, which created a perception that the Serbs were guardians of the communist regime.[79] Serbian politician and sociologist Vesna Pešić states that this caused discontent among the Croats but that it never actually undermined their own dominance in SR Croatia.[53] After the HDZ came to power, many Serbs employed in the public sector, especially the police, were fired and replaced by Croats.[80] This, combined with Tuđman's remarks, i.e. "Thank God my wife is not a Jew or a Serb",[81] were distorted by Milošević's media to spark fear that any form of an independent Croatia would be a new "Ustashe state". In one instance, TV Belgrade showed Tuđman shaking hands with German Chancellor Helmut Kohl (who would be the first government leader in the world to recognise independent Croatia and Slovenia) accusing the two of plotting "a Fourth Reich".[82][83] Aside from the firing of many Serbs from public sector positions, another concern among Serbs living in Croatia was the HDZ's public display of the šahovnica (Croatian checkerboard) in the Croatian coat of arms, which was associated with the fascist Ustaše regime.[84] This was a misconception as the checkerboard had a history going back to the fifteenth century and was not identical to the one that was used in the WW2-era Independent State of Croatia.[85] However, Tuđman's xenophobic rhetoric and attitude towards Croatian Serbs as well as his support for former Ustaše leaders did little to ease Serb fears.[86][87][88]
Civil unrest and demands for autonomy
[edit]Immediately after the Slovenian parliamentary election and the Croatian parliamentary election in April and May 1990, the JNA announced that the Tito-era doctrine of "general people's defense", in which each republic maintained a Territorial defense force (Serbo-Croatian: Teritorijalna obrana) (TO), would henceforth be replaced by a centrally directed system of defense. The republics would lose their role in defense matters, and their TOs would be disarmed and subordinated to JNA headquarters in Belgrade, but the new Slovenian government acted quickly to retain control over their TO.[89] On 14 May 1990, the weapons of the TO of Croatia, in Croat-majority regions, were taken away by the JNA,[90] preventing the possibility of Croatia having its own weapons as was done in Slovenia.[91][92] Borisav Jović, Serbia's representative in the Federal Presidency and a close ally of Slobodan Milošević, claimed that this action came at the behest of Serbia.[93]
According to Jović, on 27 June 1990 he and Veljko Kadijević, the Yugoslav Defence Minister, met and agreed that they should, regarding Croatia and Slovenia, "expel them forcibly from Yugoslavia, by simply drawing borders and declaring that they have brought this upon themselves through their decisions". According to Jović, the next day he obtained the agreement of Milošević.[94] However, Kadijević, of mixed Serb-Croat heritage and a Yugoslav Partisan in World War II, was loyal to Yugoslavia and not a Greater Serbia; Kadijević believed that if Slovenia left Yugoslavia the state would collapse and thus he discussed with Jović about possibly using the JNA to impose martial law in Slovenia to prevent this potential collapse and was willing to wage war with the secessionist republics to prevent their secession.[95] Kadijević considered the political crisis and ethnic conflict to have been caused by the actions of foreign governments, particularly Germany, which he accused of seeking to break up Yugoslavia to allow Germany to exercise a sphere of influence in the Balkans.[96] Kadijević regarded the Croatian government of Tuđman to be a fascist-inspired and that Serbs had the right to be protected from Croatian "armed formations".[96]
After the election of Tuđman and the HDZ, a Serb Assembly was established in Srb, north of Knin, on 25 July 1990 as the political representation of the Serb people in Croatia. The Serb Assembly declared "sovereignty and autonomy of the Serb people in Croatia".[97]
The new Croatian government implemented policies that were seen as openly nationalistic and anti-Serbian in nature, such as the removal of the Serbian Cyrillic script from correspondence in public offices.[98][99]
Greater Serbian circles have no interest in protecting the Serbian people living in either Croatia or Bosnia or anywhere else. If that were the case, then we could look and see what it is in the Croatian constitution, see what is in the declaration on minorities, on the Serbs in Croatia and on minorities, because the Serbs are treated separately there. Let us see if the Serbs have less rights than the Croats in Croatia. That would be protecting the Serbs in Croatia. But that is not what is sought. Gentlemen, what they want is territory.
— Stjepan Mesić on Belgrade's intentions in the war[100]
In August 1990, an unrecognized mono-ethnic referendum was held in regions with a substantial Serb population which would later become known as the Republic of Serbian Krajina (RSK) (bordering western Bosnia and Herzegovina) on the question of Serb "sovereignty and autonomy" in Croatia.[101] This was an attempt to counter changes made to the constitution. The Croatian government sent police forces to police stations in Serb-populated areas to seize their weapons. Among other incidents, local Serbs from the southern hinterlands of Croatia, mostly around the city of Knin, blocked roads to tourist destinations in Dalmatia. This incident is known as the "Log Revolution".[102][103] Years later, during Martić's trial, Babić claimed he was tricked by Martić into agreeing to the Log Revolution, and that it and the entire war in Croatia was Martić's responsibility, and had been orchestrated by Belgrade.[104] The statement was corroborated by Martić in an interview published in 1991.[105] Babić confirmed that by July 1991 Milošević had taken over control of the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA).[106] The Croatian government responded to the blockade of roads by sending special police teams in helicopters to the scene, but were intercepted by SFR Yugoslav Air Force fighter jets and forced to turn back to Zagreb. The Serbs felled pine trees or used bulldozers to block roads to seal off towns like Knin and Benkovac near the Adriatic coast. On 18 August 1990, the Serbian newspaper Večernje novosti claimed "almost two million Serbs were ready to go to Croatia to fight".[102]
On 21 December 1990, the SAO Krajina was proclaimed by the municipalities of the regions of Northern Dalmatia and Lika, in south-western Croatia. Article 1 of the Statute of the SAO Krajina defined the SAO Krajina as "a form of territorial autonomy within the Republic of Croatia" in which the Constitution of the Republic of Croatia, state laws, and the Statute of the SAO Krajina were applied.[97][107]
On 22 December 1990, the Parliament of Croatia ratified the new constitution,[108] which was seen by Serbs as taking away rights that had been granted by the Socialist constitution.[109] The constitution did define Croatia as "the national state of the Croatian nation and a state of members of other nations and minorities who are its citizens: Serbs ... who are guaranteed equality with citizens of Croatian nationality ..."[97]
Following Tuđman's election and the perceived threat from the new constitution,[108] Serb nationalists in the Kninska Krajina region began taking armed action against Croatian government officials. Croatian government property throughout the region was increasingly controlled by local Serb municipalities or the newly established "Serbian National Council". This would later become the government of the breakaway Republic of Serbian Krajina (RSK).[97]
After it was discovered that Martin Špegelj had pursued a campaign to acquire arms through the black market in January 1991 an ultimatum was issued requesting disarming and disbanding of Croatian military forces considered illegal by the Yugoslav authorities.[110][111] Croatian authorities refused to comply, and the Yugoslav army withdrew the ultimatum six days after it was issued.[112][113]
On 12 March 1991, the leadership of the Army met with the Presidency of the SFRY in an attempt to convince them to declare a state of emergency which would allow for the army to take control of the country. Yugoslav army chief Veljko Kadijević declared that there was a conspiracy to destroy the country, saying:
An insidious plan has been drawn up to destroy Yugoslavia. Stage one is civil war. Stage two is foreign intervention. Then puppet regimes will be set up throughout Yugoslavia.
— Veljko Kadijević, 12 March 1991.[114]
Jović claims that Kadijević and the Army in March 1991 supported a coup d'état as a way out of the crisis but then changed their minds four days later.[115] Kadijević's response to this was that "Jović is lying".[115] Kadijević claims he was invited to a meeting in March 1991 in Jović's office, two days after huge protests organized by Vuk Drašković on the streets of Belgrade, where Milošević, according to Kadijević, requested that the army take control of the country through a military coup.[115] Kadijević's apparent response was to inform Milošević that he could not make such a decision by himself, and that he'd discuss the request with army leaders and later inform Jović's office about their decision.[115] Kadijević then said that their decision was against the putsch and that he informed Jović's office in written form about it.[115] Jović claims that such document doesn't exist.[115]
Ante Marković has described that after the Presidency meeting failed to achieve the results the Army wanted that Kadijević met with him with the proposed coup d'état against the secessionist republics.[116] During the meeting Marković responded to Kadijević by saying that the plan failed to arrest Milošević.[116] Kadijević replied "He is only one fighting for Yugoslavia. Without him, we could not be proposing this." Marković rejected the plan and afterwards communication between Kadijević and Marković broke down.[116]
Military forces
[edit]Serb and Yugoslav People's Army forces
[edit]
The JNA was initially formed during World War II to carry out guerrilla warfare against occupying Axis forces. The success of the Partisan movement led to the JNA basing much of its operational strategy on guerrilla warfare, as its plans normally entailed defending against NATO or Warsaw Pact attacks, where other types of warfare would put the JNA in a comparatively poor position. That approach led to maintenance of a Territorial Defense system.[117]
On paper, the JNA seemed a powerful force, with 2,000 tanks and 300 jet aircraft (mainly Soviet or locally produced). However, by 1991, the majority of this equipment was 30 years old, as the force consisted primarily of T-54/55 tanks and MiG-21 aircraft.[118] Still, the JNA operated around 300 M-84 tanks (a Yugoslav version of the Soviet T-72) and a sizable fleet of ground-attack aircraft, such as the Soko G-4 Super Galeb and the Soko J-22 Orao, whose armament included AGM-65 Maverick guided missiles.[119] By contrast, more modern cheap anti-tank missiles (like the AT-5) and anti-aircraft missiles (like the SA-14) were abundant and were designed to destroy much more advanced weaponry. Before the war the JNA had 169,000 regular troops, including 70,000 professional officers. The fighting in Slovenia brought about a great number of desertions, and the army responded by mobilizing Serbian reserve troops. Approximately 100,000 evaded the draft, and the new conscripts proved an ineffective fighting force. The JNA resorted to reliance on irregular militias.[120] Paramilitary units like the White Eagles, Serbian Guard, Dušan Silni, and Serb Volunteer Guard, which committed a number of massacres against Croat and other non-Serbs civilians, were increasingly used by the Yugoslav and Serb forces.[121][122] There were also foreign fighters supporting the RSK, mostly from Russia.[123] With the retreat of the JNA forces in 1992, JNA units were reorganized as the Army of Serb Krajina, which was a direct heir to the JNA organization, with little improvement.[6][124]
By 1991, the JNA officer corps was dominated by Serbs and Montenegrins; they were overrepresented in Yugoslav federal institutions, especially the army. 57.1% of JNA officers were Serbs, while Serbs formed 36.3% of the population of Yugoslavia.[79] A similar structure was observed as early as 1981.[125] Even though the two peoples combined comprised 38.8% of the population of Yugoslavia, 70% of all JNA officers and non-commissioned officers were either Serbs or Montenegrins.[126] In July 1991, the JNA was instructed to "completely eliminate Croats and Slovenes from the army", most of whom had already begun to desert en masse.[why?][127]
Croatian forces
[edit]
The Croatian military was in a much worse state than that of the Serbs. In the early stages of the war, lack of military units meant that the Croatian Police force would take the brunt of the fighting. The Croatian National Guard (Croatian: Zbor narodne garde), the new Croatian military, was formed on 11 April 1991, and gradually developed into the Croatian Army (Croatian: Hrvatska vojska) by 1993. Weaponry was in short supply, and many units were either unarmed or were equipped with obsolete World War II-era rifles. The Croatian Army had only a handful of tanks, including World War II-surplus vehicles such as the T-34, and its Air Force was in an even worse state, consisting of only a few Antonov An-2 biplane crop-dusters that had been converted to drop makeshift bombs.[128][129]
In August 1991, the Croatian Army had fewer than 20 brigades. After general mobilization was instituted in October, the size of the army grew to 60 brigades and 37 independent battalions by the end of the year.[130][131] In 1991 and 1992, Croatia was also supported by 456 foreign fighters, including British (139), French (69), and German (55).[132] The seizure of the JNA's barracks between September and December helped to alleviate the Croatians' equipment shortage.[133][134] By 1995, the balance of power had shifted significantly. Serb forces in Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina were capable of fielding an estimated 130,000 troops; the Croatian Army, Croatian Defence Council (Croatian: Hrvatsko vijeće obrane) (HVO), and the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina could field a combined force of 250,000 soldiers and 570 tanks.[135][136]
Course of the war
[edit]1991: Open hostilities begin
[edit]First armed incidents
[edit]
Ethnic hatred grew as various incidents fueled the propaganda machines on both sides. During his testimony before the ICTY, one of the top Krajina leaders, Milan Martić, stated that the Serb side started using force first.[137]
The conflict escalated into armed incidents in the majority-Serb populated areas. The Serbs attacked Croatian police units in Pakrac in early March,[10][138] while one Josip Jović is widely reported as the first police officer killed by Serb forces as part of the war, during the Plitvice Lakes incident in late March 1991.[11][139]
In March and April 1991, Serbs in Croatia began to make moves to secede from that territory. It is a matter of debate to what extent this move was locally motivated and to what degree the Milošević-led Serbian government was involved. In any event, the SAO Krajina was declared, which consisted of any Croatian territory with a substantial Serb population. The Croatian government viewed this move as a rebellion.[97][140][141]
From the beginning of the Log Revolution and the end of April 1991, nearly 200 incidents involving the use of explosive devices and 89 attacks on the Croatian police were recorded.[29] The Croatian Ministry of the Interior started arming an increasing number of special police forces, and this led to the building of a real army. On 9 April 1991, Croatian President Tuđman ordered the special police forces to be renamed Zbor Narodne Garde ("National Guard"); this marks the creation of a separate military of Croatia.[142]
Significant clashes from this period included the siege of Kijevo, where over a thousand people were besieged in the inner Dalmatian village of Kijevo, and the Borovo Selo killings, where Croatian policemen engaged Serb paramilitaries in the eastern Slavonian village of Borovo and suffered twelve casualties.[143] Violence gripped eastern Slavonian villages: in Tovarnik, a Croat policeman was killed by Serb paramilitaries on 2 May, while in Sotin, a Serb civilian was killed on 5 May when he was caught in a crossfire between Serb and Croat paramilitaries.[143] On 6 May, the 1991 protest in Split against the siege of Kijevo at the Navy Command in Split resulted in the death of a Yugoslav People's Army soldier.
On 15 May, Stjepan Mesić, a Croat, was scheduled to be the chairman of the rotating presidency of Yugoslavia. Serbia, aided by Kosovo, Montenegro, and Vojvodina, whose presidency votes were at that time under Serbian control, blocked the appointment, which was otherwise seen as largely ceremonial. This maneuver technically left Yugoslavia without a head of state and without a commander-in-chief.[144] Two days later, a repeated attempt to vote on the issue failed. Ante Marković, prime minister of Yugoslavia at the time, proposed appointing a panel which would wield presidential powers.[145] It was not immediately clear who the panel members would be, apart from defense minister Veljko Kadijević, nor who would fill position of JNA commander-in-chief. The move was quickly rejected by Croatia as unconstitutional.[146] The crisis was resolved after a six-week stalemate, and Mesić was elected president — the first non-communist to become Yugoslav head of state in decades.[147]
Throughout this period, the federal army, the JNA, and the local Territorial Defense Forces continued to be led by federal authorities controlled by Milošević. Helsinki Watch reported that Serb Krajina authorities executed Serbs who were willing to reach an accommodation with Croat officials.[29]
Declaration of independence
[edit]On 19 May 1991, the Croatian authorities held a referendum on independence with the option of remaining in Yugoslavia as a looser union.[148] Serb local authorities issued calls for a boycott, which were largely followed by Croatian Serbs. The referendum passed with 94% in favor.[149]
The newly constituted Croatian military units held a military parade and review at Stadion Kranjčevićeva in Zagreb on 28 May 1991.[150]
The parliament of Croatia declared Croatia's independence and dissolved its association with Yugoslavia on 25 June 1991.[2][151] The Croatian parliament's decision was partially boycotted by left-wing parliament deputies.[152] The European Community and the Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe urged Croatian authorities to place a three-month moratorium on the decision.[153]
The government of Yugoslavia responded to the declarations of independence of Croatia and Slovenia with Yugoslav Prime Minister Ante Marković declaring the secessions to be illegal and contrary to the Constitution of Yugoslavia, and supported the JNA taking action to secure the integral unity of Yugoslavia.[154]
In June and July 1991, the short armed conflict in Slovenia came to a speedy end, partly because of the ethnic homogeneity of the population of Slovenia.[151] It was later revealed that a military strike against Slovenia, followed by a planned withdrawal, was conceived by Slobodan Milošević and Borisav Jović, then president of the SFR Yugoslavia presidency. Jović published his diary containing the information and repeated it in his testimony at the Milošević trial at the ICTY.[127]
Croatia agreed to the Brioni Agreement that involved freezing its independence declaration for three months, which eased tensions a little.[3]
Escalation of the conflict
[edit]In July, in an attempt to salvage what remained of Yugoslavia, JNA forces were involved in operations against predominantly Croat areas. In July the Serb-led Territorial Defence Forces started their advance on Dalmatian coastal areas in Operation Coast-91.[155] By early August, large areas of Banovina were overrun by Serb forces.[156]
With the start of military operations in Croatia, Croats and a number of Serbian conscripts started to desert the JNA en masse, similar to what had happened in Slovenia.[155][157] Albanians and Macedonians started to search for a way to legally leave the JNA or serve their conscription term in Macedonia; these moves further homogenized the ethnic composition of JNA troops in or near Croatia.[158]
One month after Croatia declared its independence, the Yugoslav army and other Serb forces held something less than one-third of the Croatian territory,[156] mostly in areas with a predominantly ethnic Serb population.[159][160] The JNA military strategy partly consisted of extensive shelling, at times irrespective of the presence of civilians.[161] As the war progressed, the cities of Dubrovnik, Gospić, Šibenik, Zadar, Karlovac, Sisak, Slavonski Brod, Osijek, Vinkovci, and Vukovar all came under attack by Yugoslav forces.[162][163][164][165] The United Nations (UN) imposed a weapons embargo; this did not affect JNA-backed Serb forces significantly, as they had the JNA arsenal at their disposal, but it caused serious trouble for the newly formed Croatian army. The Croatian government started smuggling weapons over its borders.[166][167]
We will soon gain control of Petrinja, Karlovac and Zadar because it has been shown that it is in our interest and the interest of the army to have a large port.
— Milan Martić, August 19, 1991, on the expansion of Republic of Serbian Krajina at Croatia's expense[105]
In August 1991, the Battle of Vukovar began.[168][169] Eastern Slavonia was gravely impacted throughout this period, starting with the Dalj massacre,[170] and fronts developed around Osijek and Vinkovci in parallel to the encirclement of Vukovar.[171][172][173][174] In September, Serbian troops completely surrounded the city of Vukovar. Croatian troops, including the 204th Vukovar Brigade, entrenched themselves within the city and held their ground against elite armored and mechanized brigades of the JNA, as well as Serb paramilitary units.[175][176] Vukovar was almost completely devastated; 15,000 houses were destroyed.[177] Some ethnic Croatian civilians had taken shelter inside the city. Other members of the civilian population fled the area en masse. Death toll estimates for Vukovar as a result of the siege range from 1,798 to 5,000.[122] A further 22,000 were exiled from Vukovar immediately after the town was captured.[177][178]
Some estimates include 220,000 Croats and 300,000 Serbs internally displaced for the duration of the war in Croatia.[24] In many areas, large numbers of civilians were forced out by the military. It was at this time that the term ethnic cleansing—the meaning of which ranged from eviction to murder—first entered the English lexicon.[179]
On October 3, the Yugoslav Navy renewed its blockade of the main ports of Croatia. This move followed months of standoff for JNA positions in Dalmatia and elsewhere now known as the Battle of the Barracks. It also coincided with the end of Operation Coast-91, in which the JNA failed to occupy the coastline in an attempt to cut off Dalmatia's access to the rest of Croatia.[180]
On October 5, President Tuđman made a speech in which he called upon the whole population to mobilize and defend against "Greater Serbian imperialism" pursued by the Serb-led JNA, Serbian paramilitary formations, and rebel Serb forces.[131] On 7 October, the Yugoslav air force attacked the main government building in Zagreb, an incident referred to as the bombing of the Banski Dvori.[181][182] The next day, as a previously agreed three-month moratorium on implementation of the declaration of independence expired, the Croatian Parliament severed all remaining ties with Yugoslavia. 8 October is now celebrated as Independence Day in Croatia.[4] The bombing of the government offices and the Siege of Dubrovnik that started in October[183] were contributing factors that led to European Union (EU) sanctions against Serbia.[184][185] On 15 October after the capture of Cavtat by the JNA, local Serbs led by Aco Apolonio proclaimed the Dubrovnik Republic.[186] The international media focused on the damage to Dubrovnik's cultural heritage; concerns about civilian casualties and pivotal battles such as the one in Vukovar were pushed out of public view. Nonetheless, artillery attacks on Dubrovnik damaged 56% of its buildings to some degree, as the historic walled city, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, sustained 650 hits by artillery rounds.[187]
Peak of the war
[edit]
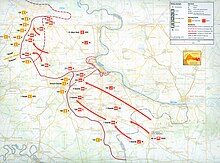
In response to the 5th JNA Corps advance across the Sava River towards Pakrac and further north into western Slavonia,[188] the Croatian army began a successful counterattack in early November 1991, its first major offensive operation of the war. Operation Otkos 10 (31 October to 4 November) resulted in Croatia recapturing an area between the Bilogora and Papuk mountains.[189][190] The Croatian Army recaptured approximately 270 square kilometers (100 sq mi) of territory in this operation.[190]
The Vukovar massacre took place in November;[191][192] the survivors were transported to prison camps such as Ovčara and Velepromet, with the majority ending up in Sremska Mitrovica prison camp.[193] The sustained siege of Vukovar attracted heavy international media attention. Many international journalists were in or near Vukovar, as was UN peace mediator Cyrus Vance, who had been Secretary of State to former US President Carter.[194]
Also in eastern Slavonia, the Lovas massacre occurred in October[121][195] and the Erdut massacre in November 1991, before and after the fall of Vukovar.[196] At the same time, the Škabrnja massacre and Gospić massacre occurred in the Dalmatian hinterland.[197]
Croats became refugees in their own country.
— Mirko Kovač on the 10th anniversary of the end of the Croatian War[198]
On 14 November, the Navy blockade of Dalmatian ports was challenged by civilian ships. The confrontation culminated in the Battle of the Dalmatian channels, when Croatian coastal and island based artillery damaged, sank, or captured a number of Yugoslav navy vessels, including Mukos PČ 176, later rechristened PB 62 Šolta.[199] After the battle, the Yugoslav naval operations were effectively limited to the southern Adriatic.[200]
Croatian forces made further advances in the second half of December, including Operation Orkan 91. In the course of Orkan '91, the Croatian army recaptured approximately 1,440 square kilometers (560 sq mi) of territory.[190] The end of the operation marked the end of a six-month-long phase of intense fighting: 10,000 people had died; hundreds of thousands had fled and tens of thousands of homes had been destroyed.[201]

On December 19, as the intensity of the fighting increased, Croatia won its first diplomatic recognition by a western nation—Iceland—while the Serbian Autonomous Oblasts in Krajina and western Slavonia officially declared themselves the Republic of Serbian Krajina.[32] Four days later, Germany recognized Croatian independence.[37] On December 26, 1991, the Serb-dominated federal presidency announced plans for a smaller Yugoslavia that could include the territory captured from Croatia during the war.[33]
However, on December 21, 1991 for the first time in the war Istria was under attack.[202] The Serbian Forces attacked the airport near the city of Vrsar, situated in the south-western of the peninsula between the city of Poreč and Rovinj, with two MiG-21 and two Galeb G-2.[203] Afterwards, Yugoslav airplanes carpet bombed Vrsar's Crljenka airport, resulting in two deaths.[204] Mediated by foreign diplomats, ceasefires were frequently signed and frequently broken. Croatia lost much territory, but expanded the Croatian Army from the seven brigades it had at the time of the first ceasefire to 60 brigades and 37 independent battalions by December 31, 1991.[130]

The Arbitration Commission of the Peace Conference on Yugoslavia, also referred to as Badinter Arbitration Committee, was set up by the Council of Ministers of the European Economic Community (EEC) on August 27, 1991, to provide the Conference on Yugoslavia with legal advice. The five-member Commission consisted of presidents of Constitutional Courts in the EEC. Starting in late November 1991, the committee rendered ten opinions. The Commission stated, among other things, that SFR Yugoslavia was in the process of dissolution and that the internal boundaries of Yugoslav republics may not be altered unless freely agreed upon.[1]
Factors in favour of Croatia's preservation of its pre-war borders were the Yugoslav Federal Constitution Amendments of 1971, and the Yugoslav Federal Constitution of 1974. The 1971 amendments introduced a concept that sovereign rights were exercised by the federal units, and that the federation had only the authority specifically transferred to it by the constitution. The 1974 Constitution confirmed and strengthened the principles introduced in 1971.[205][206] The borders had been defined by demarcation commissions in 1947, pursuant to decisions of AVNOJ in 1943 and 1945 regarding the federal organization of Yugoslavia.[207]
1992: Ceasefire
[edit]A new UN-sponsored ceasefire, the fifteenth in just six months, was agreed on January 2, 1992, and came into force the next day.[6] This so-called Sarajevo Agreement became a lasting ceasefire. Croatia was officially recognized by the European Community on January 15, 1992.[37] Even though the JNA began to withdraw from Croatia, including Krajina, the RSK clearly retained the upper hand in the occupied territories due to support from Serbia.[124] By that time, the RSK encompassed 13,913 square kilometers (5,372 sq mi) of territory.[40] The area size did not encompass another 680 square kilometers (260 sq mi) of occupied territory near Dubrovnik, as that area was not considered part of the RSK.[208]
Ending the series of unsuccessful ceasefires, the UN deployed a protection force in Serbian-held Croatia—the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR)—to supervise and maintain the agreement.[209] The UNPROFOR was officially created by UN Security Council Resolution 743 on February 21, 1992.[39] The warring parties mostly moved to entrenched positions, and the JNA soon retreated from Croatia into Bosnia and Herzegovina, where a new conflict was anticipated.[6] Croatia became a member of the UN on May 22, 1992, which was conditional upon Croatia amending its constitution to protect the human rights of minority groups and dissidents.[38] Expulsions of the non-Serb civilian population remaining in the occupied territories continued despite the presence of the UNPROFOR peacekeeping troops, and in some cases, with UN troops being virtually enlisted as accomplices.[210]
The Yugoslav People's Army took thousands of prisoners during the war in Croatia, and interned them in camps in Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. The Croatian forces also captured some Serbian prisoners, and the two sides agreed to several prisoner exchanges; most prisoners were freed by the end of 1992. Some infamous prisons included the Sremska Mitrovica camp, the Stajićevo camp, and the Begejci camp in Serbia, and the Morinj camp in Montenegro.[211] The Croatian Army also established detention camps, such as the Lora prison camp in Split.[211]

Armed conflict in Croatia continued intermittently on a smaller scale. There were several smaller operations undertaken by Croatian forces to relieve the siege of Dubrovnik, and other Croatian cities (Šibenik, Zadar and Gospić) from Krajina forces. Battles included the Miljevci plateau incident (between Krka and Drniš), on June 21–22, 1992,[212] Operation Jaguar at Križ Hill near Bibinje and Zadar, on May 22, 1992, and a series of military actions in the Dubrovnik hinterland: Operation Tigar, on 1–13 July 1992,[213] in Konavle, on 20–24 September 1992, and at Vlaštica on September 22–25, 1992. Combat near Dubrovnik was followed by the withdrawal of JNA from Konavle, between September 30 and October 20, 1992.[214] The Prevlaka peninsula guarding entrance to the Bay of Kotor was demilitarized and turned over to the UNPROFOR, while the remainder of Konavle was restored to the Croatian authorities.[215]
1993: Croatian military advances
[edit]Fighting was renewed at the beginning of 1993, as the Croatian army launched Operation Maslenica, an offensive operation in the Zadar area on January 22. The objective of the attack was to improve the strategic situation in that area, as it targeted the city airport and the Maslenica Bridge,[216] the last entirely overland link between Zagreb and the city of Zadar until the bridge area was captured in September 1991.[217] The attack proved successful as it met its declared objectives,[218] but at a high cost, as 114 Croat and 490 Serb soldiers were killed in a relatively limited theater of operations.[219]

While Operation Maslenica was in progress, Croatian forces attacked Serb positions 130 kilometers (81 mi) to the east. They advanced towards the Peruća Hydroelectric Dam and captured it by January 28, 1993, shortly after Serb militiamen chased away the UN peacekeepers protecting the dam.[220] UN forces had been present at the site since the summer of 1992. They discovered that the Serbs had planted 35 to 37 tons of explosives spread over seven different sites on the dam in a way that prevented the explosives' removal; the charges were left in place.[220][221] Retreating Serb forces detonated three of explosive charges totaling 5 tons within the 65-meter (213 ft) high dam in an attempt to cause it to fail and flood the area downstream.[221][222] The disaster was prevented by Mark Nicholas Gray, a colonel in the British Royal Marines, a lieutenant at the time, who was a UN military observer at the site. He risked being disciplined for acting beyond his authority by lowering the reservoir level, which held 0.54 cubic kilometers (0.13 cu mi) of water, before the dam was blown up. His action saved the lives of 20,000 people who would otherwise have drowned or become homeless.[223]
Operation Medak Pocket took place in a salient south of Gospić, from September 9–17. The offensive was undertaken by the Croatian army to stop Serbian artillery in the area from shelling nearby Gospić.[224] The operation met its stated objective of removing the artillery threat, as Croatian troops overran the salient, but it was marred by war crimes. The ICTY later indicted Croatian officers for war crimes. The operation was halted amid international pressure, and an agreement was reached that the Croatian troops were to withdraw to positions held prior to September 9, while UN troops were to occupy the salient alone. The events that followed remain controversial, as Canadian authorities reported that the Croatian army intermittently fought against the advancing Canadian Princess Patricia's Canadian Light Infantry before finally retreating after sustaining 27 fatalities.[225] The Croatian ministry of defense and UN officer's testimonies given during the Ademi-Norac trial deny that the battle occurred.[226][227][228][229]
| Ethnic group | 1991[230] | 1993[231] |
|---|---|---|
| Serbs | 245,800 (52.3%) | 398,900 (92%) |
| Croats | 168,026 (35.8%) | 30,300 (7%) |
| Others | 55,895 (11.9%) | 4,395 (1%) |
| Total | 469,721 | 433,595 |
On February 18, 1993, Croatian authorities signed the Daruvar Agreement with local Serb leaders in Western Slavonia. The aim of the secret agreement was normalizing life for local populations near the frontline. However, authorities in Knin learned of this and arrested the Serb leaders responsible.[232] In June 1993, Serbs began voting in a referendum on merging Krajina territory with Republika Srpska.[201] Milan Martić, acting as the RSK interior minister, advocated a merger of the "two Serbian states as the first stage in the establishment of a state of all Serbs" in his April 3 letter to the Assembly of the Republika Srpska. On January 21, 1994, Martić stated that he would "speed up the process of unification and pass on the baton to all Serbian leader Slobodan Milošević" if elected president of the RSK".[233] These intentions were countered by the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) Resolution 871 in October 1993, when the UNSC affirmed for the first time that the United Nations Protected Areas, i.e. the RSK held areas, were an integral part of the Republic of Croatia.[234]
During 1992 and 1993, an estimated 225,000 Croats, as well as refugees from Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia, settled in Croatia. Croatian volunteers and some conscripted soldiers participated in the war in Bosnia and Herzegovina.[235] In September 1992, Croatia had accepted 335,985 refugees from Bosnia and Herzegovina, most of whom were Bosniak civilians (excluding men of drafting age).[236] The large number of refugees significantly strained the Croatian economy and infrastructure.[237] The American Ambassador to Croatia, Peter Galbraith, tried to put the number of Muslim refugees in Croatia into a proper perspective in an interview on 8 November 1993. He said the situation would be the equivalent of the United States taking in 30,000,000 refugees.[238]
1994: Erosion of support for Krajina
[edit]
In 1992, the Croat-Bosniak conflict erupted in Bosnia and Herzegovina, just as each was fighting with the Bosnian Serbs. The war was originally fought between the Croatian Defence Council and Croatian volunteer troops on one side and the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) on the other, but by 1994, the Croatian Army had an estimated 3,000 to 5,000 troops involved in the fighting.[239] Under pressure from the United States,[240] the belligerents agreed on a truce in late February,[241] followed by a meeting of Croatian, Bosnian, and Bosnian Croat representatives with US Secretary of State Warren Christopher in Washington, D.C., on February 26, 1994. On March 4, Franjo Tuđman endorsed the agreement providing for the creation of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and an alliance between Bosnian and Croatian armies against the Serb forces.[7][242] This led to the dismantling of Herzeg-Bosnia and reduced the number of warring factions in Bosnia and Herzegovina from three to two.[243]
In late 1994, the Croatian Army intervened in Bosnia from November 1–3, in Operation Cincar near Kupres,[14] and from November 29 – December 24 in the Winter '94 operation near Dinara and Livno.[15][16] These operations were undertaken to detract from the siege of the Bihać region and to approach the RSK capital of Knin from the north, isolating it on three sides.[135]
During this time, unsuccessful negotiations mediated by the UN were under way between the Croatian and RSK governments. The matters under discussion included opening the Serb-occupied part of the Zagreb–Slavonski Brod motorway near Okučani to transit traffic, as well as the putative status of Serbian-majority areas within Croatia. The motorway initially reopened at the end of 1994, but it was soon closed again due to security issues. Repeated failures to resolve the two disputes would serve as triggers for major Croatian offensives in 1995.[244]

At the same time, the Krajina army continued the Siege of Bihać, together with the Army of Republika Srpska from Bosnia.[245] Michael Williams, an official of the UN peacekeeping force, said that when the village of Vedro Polje west of Bihać had fallen to a RSK unit in late November 1994, the siege entered the final stage. He added that heavy tank and artillery fire against the town of Velika Kladuša in the north of the Bihać enclave was coming from the RSK. Western military analysts said that among the array of Serbian surface-to-air missile systems that surrounded the Bihać pocket on Croatian territory, there was a modern SAM-2 system probably brought there from Belgrade.[246] In response to the situation, the Security Council passed Resolution 958, which allowed NATO aircraft deployed as a part of the Operation Deny Flight to operate in Croatia. On November 21, NATO attacked the Udbina airfield controlled by the RSK, temporarily disabling runways. Following the Udbina strike, NATO continued to launch strikes in the area, and on November 23, after a NATO reconnaissance plane was illuminated by the radar of a surface-to-air missile (SAM) system, NATO planes attacked a SAM site near Dvor with AGM-88 HARM anti-radiation missiles.[247]
In later campaigns, the Croatian army would pursue a variant of blitzkrieg tactics, with the Guard brigades punching through the enemy lines while the other units simply held the lines at other points and completed an encirclement of the enemy units.[130][135] In a further attempt to bolster its armed forces, Croatia hired Military Professional Resources Inc. (MPRI) in September 1994 to train some of its officers and NCOs.[citation needed] Begun in January 1995, MPRI's assignment involved fifteen advisors who taught basic officer leadership skills and training management. MPRI activities were reviewed in advance by the US State Department to ensure they did not involve tactical training or violate the UN arms embargo still in place.[248]
1995: End of the war
[edit]Tensions were renewed at the beginning of 1995 as Croatia sought to put increasing pressure on the RSK. In a five-page letter on 12 January Franjo Tuđman formally told the UN Secretary General Boutros Boutros-Ghali that Croatia was ending the agreement permitting the stationing of UNPROFOR in Croatia, effective 31 March. The move was purportedly motivated by actions by Serbia and the Serb-dominated Federal Republic of Yugoslavia to provide assistance to the Serb occupation of Croatia and allegedly integrate the occupied areas into Yugoslav territory. The situation was noted and addressed by the UN General Assembly:[249]
... regarding the situation in Croatia, and to respect strictly its territorial integrity, and in this regard concludes that their activities aimed at achieving the integration of the occupied territories of Croatia into the administrative, military, educational, transportation and communication systems of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (Serbia and Montenegro) are illegal, null and void, and must cease immediately.[250]
— The United Nations General Assembly resolution 1994/43, regarding to the occupied territories of Croatia

International peacemaking efforts continued, and a new peace plan called the Z-4 plan was presented to Croatian and Krajina authorities. There was no initial Croatian response, and the Serbs flatly refused the proposal.[251] As the deadline for UNPROFOR to pull out neared, a new UN peacekeeping mission was proposed with an increased mandate to patrol Croatia's internationally recognized borders. Initially the Serbs opposed the move, and tanks were moved from Serbia into eastern Croatia.[252] A settlement was finally reached, and the new UN peacekeeping mission was approved by United Nations Security Council Resolution 981 on March 31. The name of the mission was the subject of a last-minute dispute, as Croatian Foreign Minister Mate Granić insisted that the word Croatia be added to the force's name. The name United Nations Confidence Restoration Operation in Croatia (UNCRO) was approved.[253]
Violence erupted again in early May 1995. The RSK lost support from the Serbian government in Belgrade, partly as a result of international pressure. At the same time, the Croatian Operation Flash reclaimed all of the previously occupied territory in Western Slavonia.[41] In retaliation, Serb forces attacked Zagreb with rockets, killing 7 and wounding over 200 civilians.[254] The Yugoslav army responded to the offensive with a show of force, moving tanks towards the Croatian border, in an apparent effort to stave off a possible attack on the occupied area in Eastern Slavonia.[255]
During the following months, international efforts mainly concerned the largely unsuccessful United Nations Safe Areas set up in Bosnia and Herzegovina and trying to set up a more lasting ceasefire in Croatia. The two issues virtually merged by July 1995 when a number of the safe areas in eastern Bosnia and Herzegovina were overrun and one in Bihać was threatened.[256] In 1994, Croatia had already signaled that it would not allow Bihać to be captured,[135] and a new confidence in the Croatian military's ability to recapture occupied areas brought about a demand from Croatian authorities that no further ceasefires were to be negotiated; the occupied territories would be re-integrated into Croatia.[257] These developments and the Washington Agreement, a ceasefire signed in the Bosnian theater, led to another meeting of presidents of Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina on 22 July, when the Split Agreement was adopted. In it, Bosnia and Herzegovina invited Croatia to provide military and other assistance, particularly in the Bihać area. Croatia accepted, committing itself to an armed intervention.[258]

From 25 to 30 July, the Croatian Army and Croatian Defence Council (HVO) troops attacked Serb-held territory north of Mount Dinara, capturing Bosansko Grahovo and Glamoč during Operation Summer '95. That offensive paved the way for the military recapture of occupied territory around Knin, as it severed the last efficient resupply route between Banja Luka and Knin.[259] On 4 August, Croatia started Operation Storm, with the aim of recapturing almost all of the occupied territory in Croatia, except for a comparatively small strip of land, located along the Danube, at a considerable distance from the bulk of the contested land. The offensive, involving 100,000 Croatian soldiers, was the largest single land battle fought in Europe since World War II.[260] Operation Storm achieved its goals and was declared completed on 8 August.[12]
The Croatian human rights organization Hrvatski helsinški odbor, counted 677 Serb civilians killed by Croatian forces after Operation Storm, mostly old people who remained, while other Serb civilians fled.[261] An additional 837 Serb civilians are listed as missing following Operation Storm.[262] Other sources indicate a 181 more victims were killed by Croatian forces and buried in a mass grave in Mrkonjić Grad, following a continuation of the Operation Storm offensive into Bosnia.[263][264]
Many of the civilian population of the occupied areas fled during the offensive or immediately after its completion, in what was later described in various terms ranging from expulsion to planned evacuation.[12] Krajina Serb sources (Documents of HQ of Civilian Protection of RSK, Supreme Council of Defense published by Kovačević,[265] Sekulić,[266] and Vrcelj[267]) say that the evacuation of Serbs was organized and planned beforehand.[268][better source needed] According to Amnesty International, "some 200,000 Croatian Serbs, including the entire Croatian Serb Army, fled to the neighbouring Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and areas of Bosnia and Herzegovina under Bosnian Serb control. In the aftermath of the operations members of the Croatian Army and police murdered, tortured, and forcibly expelled Croatian Serb civilians who had remained in the area as well as members of the withdrawing Croatian Serb armed forces".[269] The ICTY, on the other hand, concluded that only about 20,000 people were deported.[47] The BBC noted 200,000 Serb refugees at one point.[270][271] Croatian refugees exiled in 1991 were finally allowed to return to their homes. In 1996 alone, about 85,000 displaced Croats returned to the former Krajina and western Slavonia, according to the estimates of the U.S. Committee for Refugees and Immigrants.[272]
In the months that followed, there were still some intermittent, mainly artillery, attacks from Serb-held areas in Bosnia and Herzegovina on the Dubrovnik area and elsewhere.[9] The remaining Serb-held area in Croatia, in Eastern Slavonia, was faced with the possibility of military confrontation with Croatia. Such a possibility was repeatedly stated by Tuđman after Storm.[273] The threat was underlined by the movement of troops to the region in mid-October,[274] as well as a repeat of an earlier threat to intervene militarily—specifically saying that the Croatian Army could intervene if no peace agreement was reached by the end of the month.[275]
Reintegration of Eastern Slavonia
[edit]Further combat was averted on 12 November when the Erdut Agreement was signed by the RSK acting defense minister Milan Milanović,[13][276] on instructions received from Slobodan Milošević and Federal Republic of Yugoslavia officials.[277][278] The agreement stated that the remaining occupied area was to be returned to Croatia, with a two-year transitional period.[13] The new UN transitional administration was established as the United Nations Transitional Authority for Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Sirmium (UNTAES) by United Nations Security Council Resolution 1037 of 15 January 1996.[279] The agreement also guarantees the right of establishment of a Joint Council of Municipalities for the local Serbian community.
The transitional period was subsequently extended by a year. On 15 January 1998, the UNTAES mandate ended and Croatia regained full control of the area.[17] As the UNTAES replaced the UNCRO mission, the Prevlaka peninsula, previously under UNCRO control, was put under the control of United Nations Mission of Observers in Prevlaka (UNMOP). The UNMOP was established by United Nations Security Council Resolution 1038 of 15 January 1996, and terminated on 15 December 2002.[215]
Notable defections
[edit]On 25 October 1991, Yugoslav Air Force pilot Rudolf Perešin flew his MiG-21R to Austria and defected.[280][281] He later fought on behalf of Croatian forces in the war, ultimately dying after being shot down in 1995.[280]
On 4 February 1992, air force pilot Danijel Borović flew his MiG-21bis to Croatia and defected.[281] He later fought on behalf of Croatian forces in the war. The MiG-21bis itself was later shot down on 24 June 1992, killing pilot Anto Radoš.
On 15 May 1992, air force pilots Ivica Ivandić and Ivan Selak flew their MiG-21bis to Croatia and defected.[282] Both later fought on behalf of Croatian forces in the war and survived. Ivandić's MiG-21bis was shot down on 14 September 1993, killing pilot Miroslav Peris.
Impact and aftermath
[edit]Assessment of type and name of the war
[edit]
The standard term applied to the war as directly translated from Croatian is Homeland war (Croatian: Domovinski rat),[283] while the term Croatian War of Independence is also used.[284][285][286][287] Early English sources also called it the War in Croatia, the Serbo-Croatian War,[citation needed] and the Conflict in Yugoslavia.[3][27]
Different translations of the Croatian name for the war are also sometimes used, such as Patriotic War, although such use by native speakers of English is rare.[288] The official term used in Croatian is the most widespread name used in Croatia but other terms are also used. Another is Greater-Serbian Aggression (Croatian: Velikosrpska agresija). The term was widely used by the media during the war, and is still sometimes used by the Croatian media, politicians and others.[26][289][290]
Two views exist as to whether the war was a civil or an international war. The government of Serbia often states that it was entirely a "civil war".[291][292] The prevailing view in Croatia and of most international law experts, including the ICTY, is that the war was an international conflict, between the rump Yugoslavia and Serbia against Croatia, supported by Serbs in Croatia.[293][294][295] The Croatian international legal scholar and Yale University professor, Mirjan Damaška, said that the question of aggression was not one for the ICJ to decide as at the time of the verdict, the international crime of aggression had not yet been defined.[296] Neither Croatia nor Yugoslavia ever formally declared war on each other.[297] Unlike the Serbian position that the conflict need not be declared as it was a civil war,[291] the Croatian motivation for not declaring war was that Tuđman believed that Croatia could not confront the JNA directly and did everything to avoid an all-out war.[298]
All acts and omissions charged as Grave Breaches of the Geneva Conventions of 1949 occurred during the international armed conflict and partial occupation of Croatia. ... Displaced persons were not allowed to return to their homes and those few Croats and other non-Serbs who had remained in the Serb-occupied areas were expelled in the following months. The territory of the RSK remained under Serb occupation until large portions of it were retaken by Croatian forces in two operations in 1995. The remaining area of Serb control in Eastern Slavonia was peacefully re-integrated into Croatia in 1998.[299]
— ICTY's indictment against Milošević
Casualties and refugees
[edit]

Most sources place the total number of deaths from the war at around 20,000.[43][300][301] According to the head of the Croatian Commission for Missing Persons, Colonel Ivan Grujić, Croatia suffered 12,000 killed or missing, including 6,788 soldiers and 4,508 civilians.[302] Another source gives a figure of 14,000 killed on the Croatian side, of whom 43.4% were civilians.[303] Official figures from 1996 also list 35,000 wounded.[25] Ivo Goldstein mentions 13,583 killed or missing,[304] while Anglo-Croatian historian Marko Attila Hoare reports the number to be 15,970[305] (citing figures from January 2003 presented by scientific researcher Dražen Živić).[306] Close to 2,400 persons were reported missing during the war.[307] In 2018, the Croatian Memorial-Documentation Center of Homeland War published new figures, indicating 22,211 killed or missing in the war: 15,007 killed or missing on the Croatian side and 7,204 killed or missing on the Serb side. 1,077 of those killed on the territories of the Republic of Serbian Krajina were non-Serbs.[20] However, on Croatian government-controlled territory, the Center did not break-out the ethnic structure of the total number of 5,657 civilians killed, due to missing data.[308]
As of 2016, the Croatian government listed 1,993 missing persons from the war, of whom 1093 were Croats (428 soldiers and 665 civilians), while the remaining 900 were Serbs (5 soldiers and 895 civilians).[309][310] As of 2009, there were more than 52,000 persons in Croatia registered as disabled due to their participation in the war.[311] This figure includes not only those disabled physically due to wounds or injuries sustained, but also persons whose health deteriorated due to their involvement in the war, including diagnoses of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, as well as posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).[312] In 2010, the number of war-related PTSD-diagnosed persons was 32,000.[313]
In total, the war caused 500,000 refugees and displaced persons.[314] Around 196,000[315] to 247,000 (in 1993)[316] Croats and other non-Serbs were displaced during the war from or around the RSK. The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) said that 221,000 were displaced in 2006, of which 218,000 had returned.[317] Up to 300,000 Croats were displaced, according to other sources.[21] The majority were displaced during the initial fighting and during the JNA offensives of 1991 and 1992.[210][318] On 16 March 1994, Croatia registered 492,636 displaced or refugees on its territory (241,014 persons from Croatia itself and 251,622 from Bosnia and Herzegovina), an estimated 10% of the country's population.[319] Some 150,000 Croats from Republika Srpska and Serbia have obtained Croatian citizenship since 1991,[320] many due to incidents like the expulsions in Hrtkovci.[321]

The Belgrade-based non-government organization Veritas lists 7,134 killed and missing from the Republic of Serbian Krajina, including 4,484 combatants and 2,650 civilians, and 307 JNA members who were not born or lived in Croatia. Most of them were killed or went missing in 1991 (2,729) and 1995 (2,348). The most deaths occurred in Northern Dalmatia (1,605).[22] The JNA has officially acknowledged 1,279 killed in action. The actual number was probably considerably greater, since casualties were consistently underreported. In one example, official reports spoke of two slightly wounded soldiers after an engagement, however, according to the unit's intelligence officer, the actual number was 50 killed and 150 wounded.[23][322]
According to Serbian sources, some 120,000 Serbs were displaced from 1991 to 1993, and 250,000 were displaced after Operation Storm.[323] The number of displaced Serbs was 254,000 in 1993,[316] dropping to 97,000 in the early 1995[315] and then increasing again to 200,000 by the end of the year. Most international sources place the total number of Serbs displaced at around 300,000. According to Amnesty International 300,000 were displaced from 1991 to 1995, of which 117,000 were officially registered as having returned as of 2005.[269] According to the OSCE, 300,000 were displaced during the war, of which 120,000 were officially registered as having returned as of 2006. However, it is believed the number does not accurately reflect the number of returnees, because many returned to Serbia, Montenegro, or Bosnia and Herzegovina after officially registering in Croatia.[317] According to the UNHCR in 2008, 125,000 were registered as having returned to Croatia, of whom 55,000 remained permanently.[324]
While the prewar 1991 Croatian census counted 581,663 Serbs, or 12.2% of the population in Croatia,[325] the first postwar 2001 census showed only 201,631 Serbs remaining in Croatia, or just 4.5% of the population.
The Croatian Association of Prisoners in Serbian Concentration Camps and Croatian Disabled Homeland War Veterans Association were founded to help victims of prison abuse.[326][327]
A 2013 report by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Croatia entitled 'Assessment of the Number of Sexual Violence Victims during the Homeland War on the Territory of the Republic of Croatia and Optimal Forms of Compensation and Support of Victims', determined the estimated victims (male and female) of rape and other forms of sexual assault on both sides to number between approximately 1,470 and 2,205 or 1,501 and 2,437 victims.[328] Most victims were non-Serbs assaulted by Serbs.[328] By region, the largest number of rapes and acts of sexual violence occurred in Eastern Slavonia, with an estimated 380-570 victims.[328] According to the UNDP report, between 300 and 600 men (4.4%-6.6% of those imprisoned) and between 279 and 466 women (or 30%-50% of those imprisoned) suffered from various forms of sexual abuse while being held in Serbian detention camps and prisons (including those in Serbia proper).[328] Between 412 and 611 Croat women were raped in the Serb-occupied territories, outside of detention camps, from 1991 to 1995.[328] Croat forces were also known to have committed rapes and acts of sexual violence against Serb women during Operations Flash and Storm, with an estimated 94-140 victims.[328] Sexual abuse of Serb prisoners also occurred in the Croat-run Lora and Kerestinec camps.[328]
On May 29, 2015, the Croatian parliament passed the first law in the country that recognises rape as a war crime – the Law on the Rights of Victims of Sexual Violence during the Military Aggression against the Republic of Croatia in the Homeland War.[329] The legislation, which is overseen by the Croatian War Veterans’ Ministry, provides victims with medical and legal aid as well as financial compensation from the state – up to 20,000 euros. These benefits do not depend on a court verdict.[329]
As of May 2019, Željka Žokalj from the War Veterans’ Ministry, said that around 25 million kunas (3.37 million euros) have already been awarded to victims. Since 2015, 249 compensation requests have been filed and 156 of them approved.[329]
Wartime damage and minefields
[edit]

Official figures on wartime damage published in Croatia in 1996 specify 180,000 destroyed housing units, 25% of the Croatian economy destroyed, and US$27 billion of material damage.[25] Europe Review 2003/04 estimated the war damage at US$37 billion in damaged infrastructure, lost economic output, and refugee-related costs, while GDP dropped 21% in the period.[42] 15 percent of housing units and 2,423 cultural heritage structures, including 495 sacral structures, were destroyed or damaged.[330] The war imposed an additional economic burden of very high military expenditures. By 1994, as Croatia rapidly developed into a de facto war economy, the military consumed as much as 60 percent of total government spending.[331]
Yugoslav and Serbian expenditures during the war were even more disproportionate. The federal budget proposal for 1992 earmarked 81 percent of funds to be diverted into the Serbian war effort.[332] Since a substantial part of the federal budgets prior to 1992 was provided by Slovenia and Croatia, the most developed republics of Yugoslavia, a lack of federal income quickly led to desperate printing of money to finance government operations. That in turn produced the worst episode of hyperinflation in history: Between October 1993 and January 1995, Yugoslavia, which then consisted of Serbia and Montenegro, suffered through a hyperinflation of five quadrillion percent.[333][334]
Many Croatian cities were attacked by artillery, missiles, and aircraft bombs by RSK or JNA forces from RSK or Serb-controlled areas in Bosnia and Herzegovina, as well as Montenegro and Serbia. The most shelled cities were Vukovar, Slavonski Brod (from the mountain of Vučjak),[335] and Županja (for more than 1,000 days),[336] Vinkovci, Osijek, Nova Gradiška, Novska, Daruvar, Pakrac, Šibenik, Sisak, Dubrovnik, Zadar, Gospić, Karlovac, Biograd na moru, Slavonski Šamac, Ogulin, Duga Resa, Otočac, Ilok, Beli Manastir, Lučko, Zagreb, and others[337][338][339] Slavonski Brod was never directly attacked by tanks or infantry, but the city and its surrounding villages were hit by more than 11,600 artillery shells and 130 aircraft bombs in 1991 and 1992.[340]
Approximately 2 million mines were laid in various areas of Croatia during the war. Most of the minefields were laid with no pattern or any type of record being made of the position of the mines.[341] A decade after the war, in 2005, there were still about 250,000 mines buried along the former front lines, along some segments of the international borders, especially near Bihać, and around some former JNA facilities.[342] As of 2007, the area still containing or suspected of containing mines encompassed approximately 1,000 square kilometers (390 sq mi).[343] More than 1,900 people were killed or injured by land mines in Croatia since the beginning of the war, including more than 500 killed or injured by mines after the end of the war.[344] Between 1998 and 2005, Croatia spent €214 million on various mine action programs.[345] As of 2009, all remaining minefields are clearly marked.[346] During the 2015 European migrant crisis, there existed concerns over areas where mines could affect the flow of refugees coming from Serbia to Croatia.[347]
War crimes and the ICTY
[edit]The International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY) was established by UN Security Council Resolution 827, which was passed on 25 May 1993. The court has power to prosecute persons responsible for serious violations of international humanitarian law, breaches of the Geneva Conventions, violating the laws or customs of war, committing genocide, and crimes against humanity committed in the territory of the former SFR Yugoslavia since 1 January 1991.[348]
The indictees by ICTY ranged from common soldiers to Prime Ministers and Presidents. Some high-level indictees included Slobodan Milošević (President of Serbia), Milan Babić (president of the RSK), and Ante Gotovina (general of the Croatian Army).[349] Franjo Tuđman (President of Croatia) died in 1999 of cancer while the ICTY's prosecutors were still investigating him.[350] According to Marko Attila Hoare, a former employee at the ICTY, an investigative team worked on indictments of senior members of the "joint criminal enterprise", including not only Milošević, but Veljko Kadijević, Blagoje Adžić, Borisav Jović, Branko Kostić, Momir Bulatović and others. These drafts were rejected, reportedly upon the intervention of Carla del Ponte and the indictment limited to Milošević.[351]
Between 1991 and 1995, Martić held positions of minister of interior, minister of defense and president of the self-proclaimed "Serbian Autonomous Region of Krajina" (SAO Krajina), which was later renamed "Republic of Serbian Krajina" (RSK). He was found to have participated during this period in a joint criminal enterprise which included Slobodan Milošević, whose aim was to create a unified Serbian state through commission of a widespread and systematic campaign of crimes against non-Serbs inhabiting areas in Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina envisaged to become parts of such a state.[46]
— International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia, in its verdict against Milan Martić


By the time of the last verdict delivered in 2023, the ICTY has convicted nine officials from the Serb/Montenegrin side and nobody from the Croatian side. Milan Martić received the largest sentence: 35 years in prison.[352] Milan Babić received 13 years. He expressed remorse for his role in the war, asking his "Croat brothers to forgive him".[353] In 2007, two former Yugoslav army officers were sentenced for the Vukovar massacre at the ICTY in The Hague. Veselin Šljivančanin was sentenced to 10 years and Mile Mrkšić to 20 years in prison.[354] Prosecutors stated that following the capture of Vukovar, the JNA handed over several hundred Croats to Serbian forces. Of these, at least 264 (mostly injured soldiers, but also two women and a 16-year-old child)[355] were murdered and buried in mass graves in the neighborhood of Ovčara, on the outskirts of Vukovar.[356] The city's mayor, Slavko Dokmanović, was brought to trial at the ICTY, but committed suicide in 1998 in captivity before proceedings began.[357]
Generals Pavle Strugar and Miodrag Jokić were sentenced by the ICTY to eight and seven years, respectively, for shelling Dubrovnik.[358] A third indictee, Vladimir Kovačević, was declared mentally unfit to stand trial.[359] The Yugoslav Army's Chief of the General Staff, Momčilo Perišić, was charged with aiding and abetting war crimes but eventually acquitted on all charges.[360] Ex-RSK President Goran Hadžić died during the trial. In 2018, Vojislav Šešelj was sentenced to 10 years for crimes against humanity perpetrated through persecution and deportation of Croats from Vojvodina in 1992,[361] while he was also given an additional cumulative sentence of 4 years and 9 months for contempt of court.[362]
In 2023, the follow-up International Residual Mechanism for Criminal Tribunals sentenced State Security Service (SDB) officers within the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Serbia Jovica Stanišić and Franko Simatović for aiding and abetting a murder in Daljska Planina in June 1992 through their control of Serb paramilitary, as well as other crimes in Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia, included them in a joint criminal enterprise, and sentenced them each to 15 years in prison.[363][364] The Tribunal concluded:
...The Trial Chamber found proven beyond reasonable doubt that, from at least August 1991 and at all times relevant to the crimes charged in the Indictment, a common criminal purpose existed to forcibly and permanently remove the majority of non-Serbs from large areas of Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina, through the commission of the crimes of persecution, murder, deportation, and inhumane acts (forcible transfer) charged in the Indictment. It further found that a joint criminal enterprise existed, in which the common criminal purpose was shared by senior political, military, and police leadership in Serbia, SAO Krajina, SAO SBWS, and Republika Srpska, with core members being Slobodan Milošević, Radmilo Bogdanović, Radovan Stojičić (Badža), Mihalj Kertes, Milan Martić, Milan Babić, Goran Hadžić, Radovan Karadžić, Ratko Mladić, Momčilo Krajišnik, Biljana Plavšić, and Željko Ražnatović (Arkan).... The Appeals Chamber has further concluded that all reasonable doubt has been eliminated that Stanišić and Simatović possessed the requisite mens rea for joint criminal enterprise liability.[365]
A number of Croat civilians in hospitals and shelters marked with a red cross were targeted by Serb forces.[366] There were numerous well-documented war crimes against civilians and prisoners of war perpetrated by Serb and Yugoslav forces in Croatia: the Dalj killings,[367] the Lovas massacre,[121][195] the Široka Kula massacre,[368] the Baćin massacre,[367] the Saborsko massacre,[369] the Škabrnja massacre,[197] the Voćin massacre,[367][370] and the Zagreb rocket attacks.
There were a number of prison camps where Croatian POWs and civilians were detained, including the Sremska Mitrovica camp, the Stajićevo camp, and the Begejci camp in Serbia, and the Morinj camp in Montenegro.[211] The Croatian Association of Prisoners in Serbian Concentration Camps was later founded in order to help the victims of prison abuse. The Croatian Army established detention camps, like Lora prison camp in Split.[211]
Croatian war crimes included the Gospić massacre, the Sisak killings in 1991 and 1992,[372] and others,[373][374] which were likewise prosecuted by Croatian courts or the ICTY. Another infamous instance of war crimes, in what would later become known as the "Pakračka Poljana" case, committed by a reserve police unit commanded by Tomislav Merčep, involved the killing of prisoners, mostly ethnic Serbs, near Pakrac in late 1991 and early 1992.[375] The events were initially investigated by the ICTY, but the case was eventually transferred to the Croatian judiciary.[376] More than a decade later, five members of this unit, although not its commander, were indicted on criminal charges related to these events, and convicted.[377] Merčep was arrested for crimes in Pakrac, as well as crimes in central Croatia and Zagreb in December 2010 and sentenced in 2016 to five and a half years.[378][379] Merčep, who died in 2020,[380] had also been implicated with his units in the kidnappings and executions of Serb civilians in Vukovar prior to the town's fall to the JNA in 1991 but never charged for those crimes.[381] In 2009, Branimir Glavaš, a Croatian incumbent MP at the time, was convicted of war crimes committed in Osijek in 1991 and sentenced to jail by a Croatian court.[382]
The ICTY indicted Croatian officers Janko Bobetko, Rahim Ademi, and Mirko Norac, for crimes committed during Operation Medak Pocket, but that case was also transferred to Croatian courts. Norac was found guilty and jailed for 7 years; Ademi was acquitted.[383] Bobetko was declared unfit to stand trial due to poor health.[384][385] The ICTY's indictment against General Ante Gotovina cited at least 150 Serb civilians killed in the aftermath of Operation Storm.[386] The Croatian Helsinki Committee registered 677 Serb civilians killed in the operation.[387] Louise Arbour, a prosecutor of the ICTY, stated that the legality and legitimacy of the Operation itself was not the issue, but that the ICTY was required to investigate whether crimes were committed during the campaign.[388] The Trial Chamber reiterated that the legality of Operation Storm is "irrelevant" for the case at hand, since the ICTY's remit is processing war crimes.[389] In 2011, Gotovina was sentenced to 24 and Markač to 18 years in prison. In 2012, their convictions were overturned and both were immediately released. Čermak was acquitted of all charges.[47] Recorded war crimes that were committed against ethnic Serbs, particularly the elderly, during or in the aftermath of Operation Storm include the Golubić killings, Grubori massacre, and Varivode massacre.
In the first-degree verdict, the trial chamber found that "certain members of the Croatian political and military leadership shared the common objective of the permanent removal of the Serb civilian population from the Krajina by force or threat of force", implicating Franjo Tuđman, Gojko Šušak, who was the Minister of Defence and a close associate of Tuđman's, and Zvonimir Červenko, the Chief of the Croatian army Main Staff.[47] Nevertheless, in the second-degree verdict, the appeals chamber dismissed the notion of such a joint criminal enterprise. The verdict meant the ICTY convicted no Croats for their role in the Croatian War of Independence.[48]
Serbia's role
[edit]During the war
[edit]
While Serbia and Croatia never declared war on each other, Serbia was directly and indirectly involved in the war through a number of activities.[297] Its foremost involvement entailed material support of the JNA. Following the independence of various republics from SFR Yugoslavia, Serbia provided the bulk of manpower and funding that was channeled to the war effort through Serbian control of the Yugoslav presidency and the federal defense ministry.[127] Serbia actively supported various paramilitary volunteer units from Serbia that were fighting in Croatia.[121][122] Even though no actual fighting occurred on Serbian or Montenegrin soil, involvement of the two was evident through the maintenance of prison camps in Serbia and Montenegro, which became places where a number of war crimes were committed.[211]
Borders are always dictated by the strong, never by the weak ... We simply consider it as a legitimate right and interest of the Serb nation to live in one state.
Slobodan Milošević, 16 March 1991, on the breakup of Yugoslavia.[393]
Milošević's trial at the ICTY revealed numerous declassified documents of Belgrade's involvement in the wars in Croatia and Bosnia.[124][160] Evidence introduced at trial showed exactly how Serbia and the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia financed the war, that they provided weapons and material support to Bosnian and Croatian Serbs, and demonstrated the administrative and personnel structures set up to support the Bosnian Serb and Croatian Serb armies.[124][394] It was established that Belgrade, through the federal government, financed more than 90 percent of the Krajina budget in 1993; that the Supreme Defense Council decided to hide aid to Republika Srpska and Krajina from the public; that the National Bank of Krajina operated as a branch office of the National Bank of Yugoslavia; and that by March 1994 FR Yugoslavia, Krajina, and Republika Srpska used a single currency. Numerous documents demonstrated that branches of the Krajina Public Accountancy Service were incorporated into Serbia's accountancy system in May 1991, and that the financing of Krajina and Republika Srpska caused hyperinflation in FR Yugoslavia.[124] The trial revealed that the JNA, the Serbian Ministry of Interior, and other entities (including Serb civilian groups and police) armed Serb civilians and local territorial defense groups in the RSK before the conflict escalated.[124]
In 1993, the US State Department reported that right after the Maslenica and Medak pocket operations, authorities in Serbia dispatched substantial numbers of "volunteers" to Serb-held territories in Croatia to fight.[316] A former secretary of the Serbian paramilitary leader Željko Ražnatović testified at the Hague, confirming that Ražnatović took his orders, and his money, directly from the secret police run by Milošević.[395]
This degree of control was reflected in negotiations held at various times between Croatian authorities and the RSK, as the Serbian leadership under Milošević was regularly consulted and frequently made decisions on behalf of the RSK.[6] The Erdut Agreement that ended the war was signed by a RSK minister on instructions from Milošević.[13][277][278] The degree of control Serbia held over SFR Yugoslavia and later the RSK was evidenced through testimonies during the Milošević trial at the ICTY.[127][277][278]
Serbia's state-run media were reportedly used to incite the conflict and further inflame the situation,[396][397] and also to broadcast false information about the war and the state of the Serbian economy.[398]
Following the rise of nationalism and political tensions after Slobodan Milošević came to power, as well as the outbreaks of the Yugoslav Wars, numerous anti-war movements developed in Serbia.[399][400][401] The anti-war protests in Belgrade were held mostly because of opposition to the Battle of Vukovar and Siege of Dubrovnik,[399][401] while protesters demanded the referendum on a declaration of war and disruption of military conscription.[402][403][404] It is estimated that between 50,000 and 200,000 people deserted from the Milošević-controlled Yugoslav Army during the wars, while between 100,000 and 150,000 people emigrated from Serbia refusing to participate in the war.[402][401] According to professor Renaud De la Brosse, senior lecturer at the University of Reims and a witness called by the ICTY, it is surprising how great the resistance to Milošević's propaganda was among Serbs, given that and the lack of access to alternative news.[405] By late December 1991, just over a month after victory had been proclaimed in Vukovar, opinion polls found that 64% of Serbian people wanted to end the war immediately and only 27% were willing for it to continue.[406]
After the war
[edit]
After the successful implementation of the Erdut Agreement which ended armed conflict in 1995, the relations between Croatia and Serbia gradually improved and the two countries established diplomatic relations following an agreement in early August 1996.[408]
In a case before the International Court of Justice, Croatia filed a suit against the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia on 2 July 1999, citing Article IX of the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide.[409] With the transformation of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia into Serbia and Montenegro and the dissolution of that country in 2006, Serbia is considered its legal successor.[409] The application was filed for Croatia by a U.S. lawyer, David B. Rivkin.[410] Serbia reciprocated with the genocide lawsuit against the Republic of Croatia on 4 January 2010.[411] The Serbian application covers missing people, killed people, refugees, expelled people, and all military actions and concentration camps with a historical account of genocide committed by the Independent State of Croatia during World War II.[412]
In 2003, Stjepan Mesić became the first Croatian head of state to visit Belgrade since 1991. Both Mesić and the President of Serbia and Montenegro, Svetozar Marović, issued mutual apologies to Croat and Serb victims of the war.[413]
By 2010, Croatia and Serbia further improved their relations through an agreement to resolve remaining refugee issues,[44] and visits of Croatian President Ivo Josipović to Belgrade,[45] and of the Serbian President Boris Tadić to Zagreb and Vukovar. During their meeting in Vukovar, President Tadić gave a statement expressing his "apology and regret", while President Josipović said "that no crimes committed at the time would go unpunished." The statements were made during a joint visit to the Ovčara memorial center, site of the Vukovar massacre.[407]
Role of the international community
[edit]The war developed at a time when the attention of the United States and the world was on Iraq, and the Gulf War in 1991, along with a sharp rise in oil prices and a slowdown in the growth of the world economy.[414]
Between 19 and 23 December 1991, several other European countries, beginning with Germany and the Vatican City, followed by Sweden and Italy, announced their recognition of Croatia's (and Slovenia's) independence.[37] The European Union as a whole recognized the independence of the two republics on 15 January 1992.
Each of the major foreign governments acted somewhat differently:
- Germany – up until 1991, Germany supported a 'status quo'.[415] According to diplomat Gerhard Almer, the Yugoslav disintegration was feared as "a bad example for the dissolution of the Soviet Union", sparking fears that violence could also be used against the nations that were about to declare independence from the Soviet Union.[416] During the war, this policy changed, when Helmut Kohl announced that Germany recognized Slovenia and Croatia as independent countries.
- United Kingdom – John Major's government favored neutrality.
- United States – The United States, under George H. W. Bush, tended to favour non-intervention at first,[417] just like the United Kingdom. In contrast, from 1993, the administration led by Bill Clinton tended to engage itself in order to end the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia. Cyrus Vance supported the 'integrity of Yugoslavia'.[418]
- Russia – The Russian government under Boris Yeltsin tended to oppose recognition of Croatia although Russia recognized Croatia on 17 February 1992, while the United States did the same on 7 April 1992.[419]
Notable people
[edit]- Roza Miletić (born 1934), Croatian war veteran
See also
[edit]| History of Croatia |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
|
|
Annotations
[edit]- ^ As determined by the Badinter Arbitration Committee, SFR Yugoslavia dissolved during the war.[1] On 25 June 1991, the Croatian parliament declared the independence of Croatia, following a referendum held in May.[2] The decision was suspended for three months;[3] the declaration became effective on 8 October 1991, and Croatia was no longer part of Yugoslavia.[4]
- ^ After all former Yugoslav federal republics except Serbia and Montenegro declared independence, the two declared the creation of a new country – the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia – on 27 April 1992, disbanding the JNA soon afterwards.[5] Serb-controlled units of the JNA participated in combat operations throughout 1991 and up to May 1992 in support of the Republic of Serbian Krajina.[6]
- ^ Bosnia and Herzegovina was particularly significant for the war in late 1994 and in 1995. Pursuant to the Washington Agreement, the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina was formed as a subunit of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (RBiH) representing both Bosnian Croat and Bosniak (Bosnian Muslim) ethnic groups. Most significantly, the Washington Agreement specifically permitted Croatian Army to enter Bosnia and Herzegovina, thereby allowing operations Cincar and Winter '94 against the army of Republika Srpska, outflanking the RSK capital at Knin and creating a new strategic situation before the decisive battles of the war.[7]
- ^ Initially, SAO Krajina, SAO Western Slavonia, and SAO Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia were separate entities and fought individually against the Croatian government. As of December 19, 1991, the SAOs became part of the RSK.
- ^ In 1992–94, Republika Srpska was intermittently involved in Croatian military operations, mostly through provision of military and other aid to the RSK, occasional air raids launched from Mahovljani airbase near Banja Luka, and most significantly through artillery attacks against a number of cities in Croatia, especially Slavonski Brod, Županja, and Dubrovnik.[8][9]
- ^ There was no formal declaration of war. The first armed clash of the war was the Pakrac clash on 1 March 1991,[10] followed by the Plitvice Lakes incident on 31 March 1991, when the first fatalities occurred.[11] The last major combat operation was Operation Storm, from 5–8 August 1995.[12] Formally, hostilities ceased when the Erdut Agreement was signed on 12 November 1995.[13]
- ^ There were also some conflicts in Bosnia and Herzegovina, particularly in late 1994 and early 1995. Among those, the most significant to the course of the war were Cincar,[14] and Operation Winter '94.[15][16]
- ^ Three months after the military defeat of the RSK in Operation Storm,[12] the UN-sponsored Erdut Agreement between the Croatian and RSK authorities was signed on 12 November 1995.[13] The agreement provided for a two-year transitional period, later extended by a year, during which the remaining occupied territory of Croatia was to be transferred to control of the Croatian government. The agreement was implemented by UNTAES and successfully completed by 1998.[17]
- ^ In Croatia, the war is primarily referred to as the "Homeland War" (Croatian: Domovinski rat) and also as the "Greater-Serbian Aggression" (Croatian: Velikosrpska agresija).[25][26] In Serbian sources, "War in Croatia" (Serbian: Рат у Хрватској, Rat u Hrvatskoj) and (rarely) "War in Krajina" (Serbian: Рат у Крајини, Rat u Krajini) are used.[27]
Notes
[edit]- ^ Jump up to: a b Allain Pellet (1992). "The Opinions of the Badinter Arbitration Committee: A Second Breath for the Self-Determination of Peoples" (PDF). European Journal of International Law. 3 (1): 178–185. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.ejil.a035802. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 29, 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Chuck Sudetic (June 26, 1991). "2 Yugoslav States Vote Independence To Press Demands". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 10, 2012. Retrieved 12 December 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Chuck Sudetic (June 29, 1991). "Conflict in Yugoslavia; 2 Yugoslav States Agree to Suspend Secession Process". The New York Times. Archived from the original on May 18, 2013. Retrieved December 12, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Ceremonial session of the Croatian Parliament on the occasion of the Day of Independence of the Republic of Croatia". Official web site of the Parliament of Croatia. Sabor. October 7, 2004. Archived from the original on March 14, 2012. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
- ^ "Two Republics Transform Selves Into a New, Smaller Yugoslavia". The Los Angeles Times. Associated Press. April 28, 1992. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved January 7, 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Chuck Sudetic (January 3, 1992). "Yugoslav Factions Agree to U.N. Plan to Halt Civil War". The New York Times. Archived from the original on May 18, 2013. Retrieved December 16, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Steven Greenhouse (March 18, 1994). "Muslims and Bosnian Croats Give Birth to a New Federation". The New York Times. Archived from the original on May 18, 2013. Retrieved December 17, 2010.
- ^ Peter Maass (July 16, 1992). "Serb Artillery Hits Refugees – At Least 8 Die As Shells Hit Packed Stadium". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on November 5, 2013. Retrieved December 23, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Raymond Bonner (August 17, 1995). "Dubrovnik Finds Hint of Deja Vu in Serbian Artillery". The New York Times. Archived from the original on May 18, 2013. Retrieved December 18, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Stephen Engelberg (March 3, 1991). "Belgrade Sends Troops to Croatia Town". The New York Times. Archived from the original on May 18, 2013. Retrieved December 11, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Chuck Sudetic (April 1, 1991). "Deadly Clash in a Yugoslav Republic". The New York Times. Archived from the original on May 18, 2013. Retrieved December 11, 2010.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж Дин Э. Мерфи (8 августа 1995 г.). «Хорваты объявляют победу, конец блиц» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 12 октября 2012 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г Крис Хеджес (12 ноября 1995 г.). «Сербы в Хорватии решают ключевую проблему, отказываясь от земли» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Чак Судетич (4 ноября 1994 г.). «Боснийская армия и хорваты изгоняют сербов из города» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Роджер Коэн (12 января 1995 г.). «Хорватия намерена отменить мандат сил ООН на своей территории» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 11 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Бург и Шуп (2000) , с. 331
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Крис Хеджес (16 января 1998 г.). «Этническое болото возвращается в Хорватию» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Тус: В октябре 1991 года. У HV было 70 000 солдат. [ мертвая ссылка ] Родина война.hr
- ^ «Центр домовинского рата – 1995» . Архивировано из оригинала 19 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 17 июля 2012 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Зебич, Энис (15 января 2018 г.). «Человеческие потери в хорватской войне: 22 211 человек». Радио Свободная Европа (на хорватском языке). Архивировано из оригинала 17 декабря 2019 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2019 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Фуонг 2005 , с. 157.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Сербские жертвы войны и разрушений на территории Хорватии и бывшего РСК в 1990-1998 годах» . Веритас . Архивировано из оригинала 24 ноября 2020 года . Проверено 16 июня 2015 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Мештрович (1996) , стр. 77–78
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Занотти (2011) , стр. 111
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Дарко Зубринич. «Хорватия в составе бывшей Югославии» . Хорватская история.нет. Архивировано из оригинала 29 июля 2012 года . Проверено 7 февраля 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Мирко Биланджич (июль 2008 г.). « Хорватская армия в международных отношениях (краткое содержание на английском языке)». Полемос: Журнал междисциплинарных исследований войны и мира (на хорватском языке). 11 (22). Хорватская социологическая ассоциация и издательство Jesenski & Turk. ISSN 1331-5595 . Архивировано из оригинала 16 октября 2013 года . Проверено 21 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Србия-Хрватска, темель стабильности» [Сербия-Хорватия, основа стабильности] (на сербском языке). Б92 . 4 ноября 2010 года. Архивировано из оригинала 8 ноября 2010 года . Проверено 22 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Вердикт Мартича , стр. 122–123
«Судебная палата установила, что доказательства свидетельствуют о том, что президент Сербии Слободан Милошевич открыто поддерживал сохранение Югославии как федерации, частью которой станет САО Краина. Однако доказательства установили, что Милошевич тайно намеревался создать сербскую Государство должно было быть создано путем создания военизированных формирований и провоцирования инцидентов, чтобы создать ситуацию, в которой ЮНА могла бы вмешаться. Первоначально ЮНА вмешалась, чтобы разделить стороны, но впоследствии ЮНА вмешалась, чтобы обеспечить безопасность территорий, которые, как предполагалось, станут частью будущего сербского государства». - ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж «Итоговый отчет Комиссии экспертов Организации Объединенных Наций, созданной в соответствии с резолюцией 780 (1992) Совета Безопасности, Приложение IV – Политика этнической чистки. Подготовил: М. Шериф Бассиуни» . Объединенные Нации. 28 декабря 1994 года. Архивировано из оригинала 4 мая 2012 года . Проверено 19 марта 2011 г.
- ^ Вердикт Бабича , стр. 6.
«В период действия Обвинительного заключения, примерно с 1 августа 1991 года по 15 февраля 1992 года, сербские силы, состоящие из подразделений ЮНА, местных сербских подразделений ТО, подразделений ТО из Сербии и Черногории, местных полицейских подразделений МВД, полицейских подразделений МВД из Сербии и военизированных формирований подразделения атаковали и взяли под свой контроль города, деревни и поселения ... Эти действия были направлены на окончательное и насильственное изгнание большей части хорватского и другого несербского населения примерно с одной трети Хорватии, чтобы превратить эту территорию в Государство с преобладанием сербов». - ^ Чак Судетич (5 августа 1991 г.). «Сербы отказываются вести переговоры в Хорватии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 11 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 24 января 2011 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Столкновения в Хорватии растут; посредники пессимистичны» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 19 декабря 1991 года. Архивировано из оригинала 15 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 29 июля 2012 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Президентство под руководством сербов разрабатывает план для Новой и Малой Югославии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 27 декабря 1991 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Браун и Карим (1995) , с. 120
- ^ Кадиевич (1993) , стр. 134–135
- ^ Бьелажак и др. 2009 , с. 241
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Стивен Кинзер (24 декабря 1991 г.). «Словения и Хорватия получили одобрение Бонна» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 20 июня 2012 года . Проверено 29 июля 2012 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Пол Л. Монтгомери (23 мая 1992 г.). «Три бывшие югославские республики приняты в ООН» The New York Times . Архивировано из оригинала 11 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 29 июля 2012 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Совета Безопасности ООН Резолюция 743 . S/RES/743(1992) 21 февраля 1992 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б "Republika Hrvatska i Domovinski rat 1990. – 1995. dokumenti" [Республика Хорватия и хорватская война за независимость 1990–1995 годов, документы] (на хорватском языке). Профиль. Архивировано из оригинала 22 мая 2011 года . Проверено 20 января 2011 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Роджер Коэн (2 мая 1995 г.). «Хорватия нанесла удар по району удержания повстанческих сербов, пересекая линии ООН» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Обзор Европы (2003) , с. 75
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Президенты извиняются за войну в Хорватии» . Новости Би-би-си . Би-би-си. 10 сентября 2003 года. Архивировано из оригинала 31 марта 2012 года . Проверено 7 февраля 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Агентство ООН приветствует сербско-хорватское соглашение по вопросам беженцев и возвращения» . Объединенные Нации. 26 ноября 2010 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Сербия и Хорватия налаживают связи благодаря переговорам в Белграде» . Новости Би-би-си . Би-би-си. 18 июля 2010 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Милан Мартич приговорен к 35 годам заключения за преступления против человечности и военные преступления» . Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 12 июня 2007 года. Архивировано из оригинала 4 августа 2012 года . Проверено 24 августа 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д «Резюме решения по делу Готовиной и др.» (PDF) . Гаага: Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 15 апреля 2011 г. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 4 августа 2012 г. . Проверено 15 апреля 2011 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Гаагский военный суд оправдал хорватских генералов Готовину и Маркача» . Новости Би-би-си . 16 ноября 2012. Архивировано из оригинала 16 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 16 ноября 2012 г.
- ^ Международный Суд и 3 февраля 2015 г.
- ^ Энциклопедия народов Worldmark: Европа. Гейл Групп, 2001. Стр. 73.
- ^ Йович 2009 , с. 19.
- ^ Йович 2009 , с. 21.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Пешич 1996 , с. 12.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Косово» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 23 июля 2010. Архивировано из оригинала 23 октября 2012 года . Проверено 10 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Генри Камм (8 декабря 1985 г.). «Югославская республика ревностно охраняет свои завоевания» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 15 мая 2013 года . Проверено 10 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Сербская Воеводина восстанавливает автономию» . Радио Свободная Европа/Радио Свобода . 15 декабря 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 14 декабря 2010 года . Проверено 10 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Страновое исследование: Югославия (бывшая): политические инновации и Конституция 1974 года (глава 4)» . Библиотека Конгресса. Архивировано из оригинала 30 июня 2015 года . Проверено 27 января 2011 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Браун и Карим (1995) , с. 116
- ^ Тим Джуда (1 июля 2001 г.). «Поражение тирана знаменует собой судьбоносный день сербов» . Хранитель . Архивировано из оригинала 9 июня 2021 года . Проверено 19 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Глаурдич, Йосип (2011). Час Европы: западные державы и распад Югославии . Издательство Йельского университета. стр. 52–53. ISBN 978-0-300-16645-3 .
- ^ Фрукты (2005) , с. 433
- ^ Бранка Магас (13 декабря 1999 г.). «Некролог: Франьо Туджман» . Независимый . Архивировано из оригинала 10 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 17 октября 2011 .
- ^ Гловер, Джонатан (2001). Человечество: моральная история двадцатого века . Издательство Йельского университета. п. 125. ИСБН 978-0-30008-715-4 . Архивировано из оригинала 28 октября 2023 года . Проверено 15 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Хокенос, Пол (2018). Призвание к Родине: Патриотизм изгнания и Балканские войны . Издательство Корнельского университета. п. 20. ISBN 978-1-50172-565-4 . Архивировано из оригинала 28 октября 2023 года . Проверено 15 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Фишер 2006 , с. 70.
- ^ Глаурдич, Йосип (2011). Час Европы: западные державы и распад Югославии . Издательство Йельского университета. п. 71. ИСБН 978-0-300-16645-3 .
- ^ «Рачанский некролог» . Таймс . 30 апреля 2007 г. Архивировано из оригинала 28 октября 2023 г. Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Игорь Приморац, Александр Павкович. Идентичность, самоопределение и отделение . Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2006. стр. 158.
- ^ Игорь Приморац, Александр Павкович. Идентичность, самоопределение и отделение . Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2006. стр. 158.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Перунович 2015
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Гольдштейн (1999) , с. 214
- ^ Вердикт Бабича , стр. 9.
- ^ Рамет 2006 , с. 382
- ^ «Югославия: Демонстрации в Хорватии и Воеводине» . УВКБ ООН . 1 мая 1990 года. Архивировано из оригинала 24 марта 2012 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Эволюция в Европе; Югославия надеется на свободное голосование в 90-х» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 23 апреля 1990 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Эволюция в Европе; консерваторы побеждают в Хорватии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 9 мая 1990 года. Архивировано из оригинала 10 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «День, когда загорелся стадион Максимир» . Далье.com. 13 мая 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 8 мая 2011 года . Проверено 19 января 2011 г.
- ↑ Обвинительное заключение Милошевича , стр. 29.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Белаяц и др. 2009 , с. 239.
- ^ «Хорватия в Югославии, 1945–91» . Британская энциклопедия . Британская энциклопедия, Inc. Архивировано из оригинала 15 марта 2012 года . Проверено 18 ноября 2010 г.
- ^ «Всемирный справочник меньшинств и коренных народов – Хорватия: обзор» . Международная группа по правам меньшинств . УВКБ ООН . 2008. Архивировано из оригинала 16 апреля 2013 года . Проверено 29 июня 2012 г.
- ^ Стивен Энгельберг (1 сентября 1991 г.). «Создание Великой Сербии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 12 февраля 2022 года . Проверено 29 июня 2012 г.
- ^ Браун и Карим (1995) , с. 119
- ^ Фишер 2006 , с. 57.
- ^ Рамет, Сабрина П. (2010). Политика Центральной и Юго-Восточной Европы с 1989 года . Издательство Кембриджского университета. стр. 261–262. ISBN 978-1-13948-750-4 . Архивировано из оригинала 28 октября 2023 года . Проверено 15 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Макдональд, Дэвид Брюс (2002). Балканские Холокосты?: Сербская и хорватская пропаганда, ориентированная на жертв, и война в Югославии . Издательство Манчестерского университета. стр. 262–263. ISBN 978-0-71906-467-8 . Архивировано из оригинала 28 октября 2023 года . Проверено 15 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Сайдеман, Стивен М.; Эйрес, Р. Уильям (2008). Для родственников или страны: ксенофобия, национализм и война . Издательство Колумбийского университета. п. 74. ИСБН 978-0-23151-449-1 . Архивировано из оригинала 28 октября 2023 года . Проверено 15 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Саймент, Джеймс; Хилл, Кеннет (2012). Энциклопедия конфликтов со времен Второй мировой войны . Рутледж. п. 492. ИСБН 978-1-13659-621-6 . Архивировано из оригинала 28 октября 2023 года . Проверено 15 июня 2020 г.
- ^ «История — Территориальная оборона» . Словенские вооруженные силы . Архивировано из оригинала 14 апреля 2019 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Креш 2010 , с. 54.
- ^ Креш 2010 , с. 6.
- ^ Бьелажак и др. 2009 , стр. 237, 240
- ^ Глаурдич, Йосип (2011). Час Европы: западные державы и распад Югославии . Издательство Йельского университета. п. 57. ИСБН 978-0-300-16645-3 .
- ^ Йович, Борисав (1995). Последние дни СФРЮ . Белград: Политика. стр. 160–161.
- ^ Адам ЛеБор. Милошевич: Биография. Лондон, Великобритания: Bloomsbury Publishing, 2003 г. [ нужна страница ]
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Сабрина П. Рамет. Размышляя о Югославии: научные дебаты о распаде Югославии и войнах в Боснии и Косово. Издательство Кембриджского университета, 2005. P117.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и Приговор Мартича , стр. 44–49.
- ^ Гуськова, Елена (2001). История югославского кризиса (1990-2000 гг.) . Москва. п. 147. ИСБН 5941910037 .
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: отсутствует местоположение издателя ( ссылка ) - ^ в Никифоров, К. (2011). Yugoslavia in the 20th century: Sketches of Political History . Индрик. pp. 780–781. ISBN 9785916741216 .
- ^ «Стенограммы Милошевича» . Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 1 октября 2002 г. с. 10528. Архивировано из оригинала 5 марта 2011 года . Проверено 5 марта 2011 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (7 августа 1990 г.). «Сербское меньшинство ищет роль в отдельной Хорватии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Дороги перекрыты из-за нарастания волнений в Югославии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Рейтер . 19 августа 1990 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Вооруженные сербы охраняют дороги в Хорватии во время референдума» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 20 августа 1990 года. Архивировано из оригинала 3 января 2023 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Новостной репортаж IWPR: Мартич «спровоцировал» хорватский конфликт» . iwpr.net . Институт освещения войны и мира . 17 февраля 2006 года. Архивировано из оригинала 29 сентября 2007 года . Проверено 7 февраля 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Чак Судетич (19 августа 1991 г.). «Перемирие в Хорватии на грани краха» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 3 мая 2017 года . Проверено 15 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Стенограмма Милана Бабича» . МТБЮ . 17 февраля 2006 г., стр. 1504–1510. Архивировано из оригинала 13 января 2011 года . Проверено 10 января 2011 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (2 октября 1990 г.). «Хорватские сербы заявляют о своей автономии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 12 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Кризис в Кремле; Хорватия получает право на отделение» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Ассошиэйтед Пресс . 22 декабря 1990 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 10 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Пешич 1996 , с. 10–11 Права [наций] быть «конституционными» были признаны не только в пределах их соответствующих государств, но и среди соотечественников, населяющих территорию других югославских республик. В некоторых случаях эти этнические диаспоры рассматривали конститутивную природу югославской государственности как дающую им право распространить суверенитет своей национальной «родины» на территории, которые они населяли. Так было с сербами в Хорватии, которые в 1991 году составляли 12% населения. Позже этот статус породил огромные проблемы, дав хорватским сербам «право» на отделение от Хорватии и дав Хорватии право отказать им в этом статусе. назвав их «меньшинством» в своей новой конституции.
- ^ «Непокорные югославские республики готовятся к нападению» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Ассошиэйтед Пресс. 20 января 1991 года. Архивировано из оригинала 4 мая 2017 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (22 января 1991 г.). «Югославия предупреждает Хорватию о необходимости разоружить свои войска» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 3 мая 2017 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (25 января 1991 г.). «Непокорная Хорватская Республика отказывается разоружить военизированную полицию» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 4 мая 2017 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (27 января 1991 г.). «Противостояние в Югославии началось» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 4 мая 2017 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Смерть Югославии. Британская радиовещательная корпорация (Би-би-си). 1995.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж Интервью RTS с Велько Кадиевичем, ноябрь 2007 г., на YouTube
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Ленард Дж. Коэн, Ясна Драгович-Сосо. Государственный крах в Юго-Восточной Европе: новые перспективы распада Югославии . Издательство Университета Пердью, 2008. P323.
- ^ Итоговый отчет Комиссии экспертов ООН, созданной в соответствии с резолюцией Совета Безопасности 780 (1992) (28 декабря 1994 г.). «Военная структура, стратегия и тактика враждующих группировок» . Университет Западной Англии. Архивировано из оригинала 7 февраля 2011 года . Проверено 20 января 2011 г.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: числовые имена: список авторов ( ссылка ) - ^ Западноевропейский Союз (1986) , с. 107
- ^ Финляндия (2004) , стр. 20–21
- ^ Стивен Энгельберг (23 декабря 1991 г.). «Югославская этническая ненависть вызывает страх перед бесконечной войной» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д «69 хорватских гражданских лиц убито у Ловасу у октября 1991 года» [69 хорватских гражданских лиц, убитых в Ловасе в октябре 1991 года] (на сербском языке). Б92. 20 октября 2010. Архивировано из оригинала 4 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 22 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с «Итоговый отчет Комиссии экспертов Организации Объединенных Наций, созданной в соответствии с резолюцией 780 (1992) Совета Безопасности ООН, Приложение III.A Специальные силы; под руководством: М. Шерифа Бассиуни; S/1994/674/Add.2 ( Том IV)» . Школа гуманитарных, языковых и социальных наук (UWE) . 27 мая 1994 года. Архивировано из оригинала 20 октября 2010 года . Проверено 20 октября 2010 г.
- ^ «Использование наемников как средство нарушения прав человека и противодействия осуществлению права народов на самоопределение – Записка Генерального секретаря» . Объединенные Нации. 29 августа 1995 года. Архивировано из оригинала 17 января 2022 года . Проверено 23 января 2011 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж «Взвешивание доказательств – уроки процесса над Слободаном Милошевичем» . Хьюман Райтс Вотч . 13 декабря 2006 года . Проверено 18 ноября 2010 г.
- ^ Манн (1996) , стр. 363.
- ^ Итоговый отчет Комиссии экспертов ООН, созданной в соответствии с резолюцией Совета Безопасности 780 (1992) (28 декабря 1994 г.). «Военная структура, стратегия и тактика враждующих группировок» . Университет Западной Англии . Архивировано из оригинала 7 февраля 2011 года . Проверено 20 января 2011 г.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: числовые имена: список авторов ( ссылка ) - ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д «Изьява на основу правила 89 (F)» [Заявление в соответствии с правилом 89 (F)] (на сербском языке). Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 16 ноября 2003. Архивировано из оригинала 14 июня 2012 года . Проверено 18 января 2011 г.
Милошевич и я решительно потребовали от Кадиевича следующего: 1. Ответить словенцам энергично, используя все средства, включая военно-воздушные силы. Им больше нельзя позволять проявлять неуважение к Югославской народной армии. Затем уйти из Словении. Мы примем своевременное решение по этому вопросу. Таким образом, моральный дух армии улучшится, Хорватия испугается, а сербский народ успокоится. 2. Основные силы YPA должны быть сгруппированы на линии Карловац-Плитвицкие [озёра] на западе; Баранья, Осиек, Винковцы – Сава [река] на востоке и Неретва [река] на юге. Таким образом, все территории, населенные сербами, будут охвачены до окончательного решения, то есть до тех пор, пока народ не примет свободное решение на референдуме. 3. Полностью исключить хорватов и словенцев из армии.
- ^ Георг Мадер (2006). «ВВС Хорватии, на которые наложено эмбарго». Мировой журнал авиации . 24 (Весна). Лондон, Великобритания: Aerospace Publishing: 145. ISBN. 1-874023-66-2 .
- ^ Фрукты (2005) , с. 562
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Томас, (2006) , стр. 21–25.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Чак Судетич (6 октября 1991 г.). «Несмотря на перемирие, снаряды все еще падают на хорватские города» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Берислав Елинич (24 ноября 2009 г.). «Жизнь после войны за чужую родину» [Жизнь после войны за чужую родину]. Национальный (на хорватском языке). NCL Media Grupa doo Архивировано из оригинала 27 мая 2012 года . Проверено 23 января 2011 г.
- ^ Алан Коуэлл (24 сентября 1991 г.). «Сербы и хорваты: взгляд на войну в разных призмах» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 29 июля 2018 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Душан Стоянович (19 марта 2010 г.). «Бывший сербский генерал: герой или предатель?» . Бостон Глобус . Архивировано из оригинала 24 сентября 2015 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Рамет (2006) , с. 452
- ^ Роджер Коэн (5 ноября 1994 г.). «Торговля оружием в Боснию продолжается, несмотря на эмбарго» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Миланские стенограммы Мартича» . Гаага: Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 15 февраля 2006 г. с. 1360. Архивировано из оригинала 5 августа 2011 года . Проверено 12 мая 2011 г.
Скажите, пожалуйста, была ли одна из сторон ответственна за эскалацию насилия и демонстрации силы? Ответ. Ответственность несут обе стороны, но, насколько мне известно, сербская сторона первой начала применять силу.
- ^ Стивен Энгельберг (4 марта 1991 г.). «Сербско-хорватская разборка на одной деревенской площади» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Отмечено 19-летие Плитвицкой акции» . морх.час . Министерство обороны Республики Хорватия . 31 марта 2010. Архивировано из оригинала 17 июля 2011 года . Проверено 11 сентября 2010 г.
- ^ Дэвид Биндер (18 марта 1991 г.). «Сербский чиновник объявляет часть Хорватии отдельной» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (2 апреля 1991 г.). «Повстанцы-сербы усложняют раскол в единстве Югославии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Содружество , стр. 272–278.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Стивен Энгельберг (5 мая 1991 г.). «Еще один погибший, поскольку столкновения в Югославии продолжаются» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 3 мая 2017 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Селестин Болен (16 мая 1991 г.). «Новый кризис охватил Югославию из-за ротации руководства» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 3 мая 2017 года . Проверено 12 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Селестин Болен (18 мая 1991 г.). «Югославия не может занять пост президента» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 4 мая 2017 года . Проверено 12 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (19 мая 1991 г.). «Хорватия отвергает югославскую комиссию» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 4 мая 2017 года . Проверено 12 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (1 июля 1991 г.). «Белград приказывает армии вернуться в казармы» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 4 мая 2017 года . Проверено 12 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Хорватия призывает к созданию Югославии в стиле ЕС» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . 16 июля 1991 года. Архивировано из оригинала 5 марта 2016 года . Проверено 20 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (20 мая 1991 г.). «Хорватия голосует за суверенитет и конфедерацию» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 11 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 12 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Хронология Отечественной войны» . osrh.hr . Военные Хорватии . Архивировано из оригинала 22 октября 2010 года . Проверено 11 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Браун и Карим (1995) , стр. 117.
- ^ «Секс: Часть левого блока отказалась голосовать за независимость» . Новый список (на хорватском языке). КИТАЙ . 25 июня 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 24 марта 2019 года . Проверено 29 ноября 2012 г.
- ^ Алан Райдинг (26 июня 1991 г.). «Европейцы предупреждают о расколе Югославии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 12 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Ленард Дж. Коэн, Ясна Драгович-Сосо. Государственный крах в Юго-Восточной Европе: новые перспективы распада Югославии. Издательство Университета Пердью, 2008. Стр. 323.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Армия покидает больше городов в Хорватии» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . 29 сентября 1991 года. Архивировано из оригинала 4 декабря 2013 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Чарльз Т. Пауэрс (1 августа 1991 г.). «Сербские силы ведут борьбу за крупный участок Хорватии» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 16 мая 2012 года . Проверено 29 июля 2012 г.
- ^ Стивен Энгельберг (16 июля 1991 г.). «Югославская армия обновляется после неудач» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Хорватия и Союзная Республика Югославия (СРЮ): Военная служба» . Верховный комиссар ООН по делам беженцев – Refworld . Совет по иммиграции и беженцам Канады . 1 сентября 1993 года. Архивировано из оригинала 24 марта 2012 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (24 июля 1991 г.). «Хорваты отвергают новый мирный пакт» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 4 мая 2017 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Стивен Энгельберг (27 июля 1991 г.). «Сербия отправляет припасы соотечественникам в Хорватии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Стивен Энгельберг (12 декабря 1991 г.). «Германия возлагает надежды на Хорватию» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 3 мая 2017 года . Проверено 27 сентября 2010 г.
Перед войной югославская армия призывала своих солдат во всех югославских республиках. Теперь ему приходится полагаться на сербских резервистов и сербских нерегулярных формирований, которые плохо обучены. В недавнем отчете миссии наблюдателей сделан вывод о том, что армия регулярно обстреливала гражданские районы.
- ^ «Югославская армия движется к Дубровнику и еще двум городам» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Ассошиэйтед Пресс . 3 октября 1991 года. Архивировано из оригинала 6 марта 2011 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Кэрол Дж. Уильямс (4 ноября 1991 г.). «Белград получил последнее предупреждение от ЕС» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 4 марта 2016 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Чарльз Т. Пауэрс (28 июля 1991 г.). «30 человек убиты в ходе неослабевающей ярости сражений в Хорватии» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 3 марта 2016 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Хорватия заявляет, что по ее истребителям нацелены ракеты» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Рейтер . 29 декабря 1991 года. Архивировано из оригинала 4 марта 2016 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Кристофер Беллами (10 октября 1992 г.). «Хорватия создала «сеть контактов», чтобы избежать эмбарго на поставки оружия» . Независимый . Архивировано из оригинала 10 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Натаниэль К. Нэш (11 января 1992 г.). «Поставка чилийского оружия в Хорватию усиливает напряженность» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 3 мая 2017 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (24 августа 1991 г.). «Боевые действия могут разрушить югославское перемирие» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 15 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (26 августа 1991 г.). «Новая борьба в Хорватии после Боннского предупреждения» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 15 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Стивен Энгельберг (3 августа 1991 г.). «Сообщается, что в ходе беспорядков в Хорватии погибло до 80 человек» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 4 мая 2017 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (23 августа 1991 г.). «Хорватия гневно устанавливает крайний срок для перемирия» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ Джон Тальябу (2 сентября 1991 г.). «Европейцы прибывают в Югославию, чтобы продвигать мирный план» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ Джон Тальябу (11 сентября 1991 г.). «Европейцы не могут умиротворить хорватский город» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ Алан Коуэлл (22 сентября 1991 г.). «Хорваты подвергаются ожесточенному нападению; призывы к реальному перемирию игнорируются» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 4 мая 2017 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ Габриэль Партос (13 июня 2003 г.). «Вуковарская резня: Что произошло» . Новости Би-би-си . Би-би-си. Архивировано из оригинала 9 августа 2012 года . Проверено 15 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Эндрю В. Маки (10 июля 2009 г.). «Свидетель утверждает, что Станишич снабжал хорватских сербов оружием» . Верховный комиссар ООН по делам беженцев – Refworld . Институт освещения войны и мира . Архивировано из оригинала 17 октября 2012 года . Проверено 15 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Хелен Сини (22 августа 2006 г.). «Хорватия: Вуковар все еще преследуется тенью своего прошлого» . Немецкая волна . АРД (телерадиокомпания) . Архивировано из оригинала 24 октября 2012 года . Проверено 15 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «15 000 вспоминают осаду Вуковара в 1991 году» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 19 ноября 2001 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 15 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Уильям Сэфайр (14 марта 1993 г.). «О языке. Этническая чистка» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 27 сентября 2010 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (3 октября 1991 г.). «Военно-морская блокада Хорватии возобновляется» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Югославские самолеты атаковали президентский дворец Хорватии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 8 октября 1991 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Кэрол Дж. Уильямс (8 октября 1991 г.). «Атака на дворец лидера Хорватии» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 22 октября 2013 года . Проверено 23 января 2011 г.
- ^ Бьелажак и др. 2009 , стр. 249–250.
- ^ Дэвид Биндер (9 ноября 1991 г.). «Бродяги Старого города в югославской осаде» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Алан Райдинг (9 ноября 1991 г.). «Европейские страны объявляют санкции против Белграда» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 3 мая 2017 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ↑ Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии (МТБЮ) во время суда над президентом Сербии Слободаном Милошевичем определил, что Республика Дубровник является частью нескольких регионов Хорватии, которые Милошевич стремился включить в «государство с доминированием сербов». ( http://www.icty.org/x/cases/slobodan_milosevic/ind/en/040727.pdf Архивировано 20 мая 2013 г., в Wayback Machine ) (страницы 2–3 оригинального факса). МТБЮ заявил, что кампания ЮНА в районе Дубровника была направлена на обеспечение территории Республики Дубровник. ( http://www.icty.org/sid/7948. Архивировано 8 апреля 2011 г., в Wayback Machine )
- ^ «Хронология сербов в Хорватии - 6 декабря 1991 г.» . Верховный комиссар ООН по делам беженцев – Refworld . Меньшинства в опасности . 2004. Архивировано из оригинала 24 марта 2012 года . Проверено 5 января 2011 г.
- ^ Бьелажак и др. 2009 , с. 245
- ^ Чак Судетич (4 ноября 1991 г.). «Армия бросается на захват хорватского города» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 29 июля 2012 года . Проверено 29 июля 2012 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Желько Крушель (24 декабря 2005 г.). « Оркан» и «Откос» разгоняют планы Великой Сербии» [«Оркан» и «Откос» разгоняют планы Великой Сербии]. Весник (на хорватском языке). Народное Новине д.д.
- ^ Чак Судетич (18 ноября 1991 г.). «Хорваты признали потерю Дунайского города» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 28 января 2023 года . Проверено 15 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Евгений Брчич (29 июня 1998 г.). «Хорваты хоронят жертв Вуковарской резни» . Независимый . Архивировано из оригинала 3 ноября 2020 года . Проверено 15 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Югославия – новые сообщения о пытках» . Международная амнистия . Март 1992 г. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 2 ноября 2010 г. Проверено 15 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Балканы: В Гааге начинается судебный процесс по делу о резне в Вуковаре» . Радио Свободная Европа/Радио Свобода . Совет управляющих телерадиокомпанией . 11 октября 2005 года. Архивировано из оригинала 14 сентября 2010 года . Проверено 11 сентября 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Прокурор Сербии по военным преступлениям расследует 12 массовых убийств хорватов в 1991 году» . jurist.law.pitt.edu . Jurist Legal News & Research Services, Inc., 30 мая 2007 г. Архивировано из оригинала 13 января 2011 г. . Проверено 19 декабря 2010 г.
- ↑ Обвинительное заключение Милошевича , стр. 17.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Подозреваемый в военных преступлениях в Хорватии экстрадирован» . Си-Эн-Эн Интернэшнл . Радиовещательная система Тернера . 16 ноября 2001 года. Архивировано из оригинала 2 октября 2012 года . Проверено 19 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Мирко Ковач (9 октября 2005 г.). «Геноцида сербов не было» . Список черногорской литературы (на сербском языке). Доклинская академия наук и искусств . Архивировано из оригинала 27 февраля 2021 года . Проверено 27 января 2011 г.
- ^ Эдуард Шоштарич (8 июля 2008 г.). «Битва за парусник «Ядран »» . Национальный (на хорватском языке). NCL Media Grupa doo Архивировано из оригинала 16 июля 2012 года . Проверено 25 января 2011 г.
- ^ Вертхайм (2007) , стр. 145–146.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Чак Судетич (20 июня 1993 г.). «Боевые действия в Боснии облегчаются благодаря перемирию» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 14 декабря 2010 г. [ постоянная мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ «Бомбе суль'Истрия» (PDF) . ла Република . Декабрь 1991 года. Архивировано из оригинала 16 октября 2013 года . Проверено 6 марта 2013 г.
- ^ «L'Istria e la terza guerra balcanica - Истрия в Третьей Балканской войне» (PDF) . Фучине Мьют. Октябрь 1999 года. Архивировано из оригинала 14 октября 2013 года . Проверено 6 марта 2013 г.
- ^ «Врсарские волонтеры посетили - во Врсаре поклоняются глухим - веб-сайт на хорватском языке» (PDF) . УХДДР. Апрель 2011. Архивировано из оригинала 21 сентября 2013 года . Проверено 6 марта 2013 г.
- ^ Чобанов, Саша; Рудольф, Даворин (2009). «Югославия: унитарное государство или федерация исторических усилий сербских и хорватских народов — одна из причин распада Югославии» . Труды юридического факультета в Сплите (на хорватском языке). 46 (2). Университет Сплита, юридический факультет . ISSN 1847-0459 . Архивировано из оригинала 24 сентября 2015 года . Проверено 10 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Роланд Рич (1993). «Признание государств: Распад Югославии и Советского Союза» . Европейский журнал международного права . 4 (1): 36–65. doi : 10.1093/oxfordjournals.ejil.a035834 . Архивировано из оригинала 19 июля 2021 года . Проверено 20 января 2011 г.
- ^ Эгон Кралевич (ноябрь 2007 г.). «Вклад в историю государственного управления: комиссия по демаркации границы при президенте правительства Народной Республики Хорватия, 1945–1946 (английский язык) краткое название)] (PDF) . Архив журнала (на хорватском языке). 50 (50). Государственный архив Хорватии . ISSN 0570-9008 . Архивировано из оригинала 27 ноября 2019 года . Проверено 10 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Дубровницкая епархия» [Дубровницкая епархия] (на хорватском языке). Конференция хорватских епископов . Архивировано из оригинала 3 марта 2021 года . Проверено 20 января 2011 г.
Сегодня площадь епархии составляет 1368 км. 2 . ... Половина епархии была оккупирована. [Сегодня епархия охватывает 1368 км². 2 . ... Половина епархии была оккупирована.]
- ^ Кэрол Дж. Уильямс (29 января 1992 г.). «Блок-блок тормозит развертывание ООН в Югославии» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 14 июня 2013 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Кэрол Дж. Уильямс (9 мая 1992 г.). «Несербы в хорватской зоне вынуждены покинуть страну» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 4 марта 2016 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и «Итоговый отчет Комиссии экспертов Организации Объединенных Наций, созданной в соответствии с резолюцией 780 (1992) Совета Безопасности ООН, Приложение VIII — Тюремные лагеря; под руководством: М. Шерифа Бассиуни; S/1994/674/Add.2 ( Том IV)» . Школа гуманитарных, языковых и социальных наук (UWE) . 27 мая 1994 года. Архивировано из оригинала 22 октября 2010 года . Проверено 20 октября 2010 г.
- ^ Майкл Т. Кауфман (24 июня 1992 г.). «Хорватские войска напали на территорию Сербии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Майкл Т. Кауфман (15 июля 1992 г.). «Стены и воля Дубровника» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Последние войска югославской армии выводятся из Хорватии» .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Превлаский полуостров — МНООНПП — Справочная информация» . Объединенные Нации. Архивировано из оригинала 28 февраля 2010 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (24 января 1993 г.). «Хорваты сражаются с сербами за ключевой мост у Адриатики» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 21 января 2011 г.
- ^ Бьелажак и др. 2009 , с. 242.
- ^ Чак Судетич (25 января 1992 г.). «Югославский лидер угрожает хорватам» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 29 июля 2018 года . Проверено 21 января 2011 г.
- ^ « Масленица отмечает свое 14-летие». dnevnik.hr (на хорватском языке). Новое ТВ (Хорватия) . 20 января 2007. Архивировано из оригинала 9 марта 2012 года . Проверено 21 января 2011 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Джон Дарнтон (29 января 1992 г.). «Битва за плотину в Хорватии нарастает, вытесняя силы ООН» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 29 июля 2018 года . Проверено 21 января 2011 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Джон Дарнтон (29 января 1992 г.). «Хорваты спешно работают на разрушающейся плотине» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 29 июля 2018 года . Проверено 21 января 2011 г.
- ^ Кэрол Дж. Уильямс (30 января 1993 г.). «Хорваты спешат осушить огромное озеро за плотиной» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 11 января 2012 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Том Уилки (16 сентября 1995 г.). «Невоспетый армейский офицер спас 20 000 жизней» . Независимый . Архивировано из оригинала 23 декабря 2014 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Дэниел Симпсон (3 декабря 2002 г.). «Хорватия защищает генерала, обвиняемого в военных преступлениях» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 21 января 2011 г.
- ^ Ли Виндзор (2001). «Профессионализм под огнем» (PDF) . Бюллетень армейской доктрины и подготовки . 4 (3). Командование сухопутных войск канадских вооруженных сил : 20–27. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 10 июня 2011 года.
- ^ «Канадцы награждены за фиктивный бой» (на хорватском языке). Национальный. 11 декабря 2002. Архивировано из оригинала 27 мая . Получено 25 , января
- ^ «Карманная битва Медака — миф » . Канада.com . Новости постмедиа . 20 сентября 2007 года. Архивировано из оригинала 9 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 25 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Офицер полиции ООН: Весь карман Медака был уничтожен намеренно» [Офицер полиции ООН: Весь карман Медака был уничтожен намеренно]. dnevnik.hr (на хорватском языке). Новый телевизор . 21 февраля 2008. Архивировано из оригинала 22 мая 2011 года . Проверено 25 января 2011 г.
Отвечая на вопрос о предполагаемом конфликте между хорватской армией и канадским батальоном, МакГиннес сказал, что один или два раза произошла перестрелка, но пострадавших нет. [Отвечая на вопрос о предполагаемом столкновении хорватской армии и канадского батальона, МакГиннес сказал, что один или два раза произошла перестрелка, но ранений не было]
- ^ «Пуковник СООНО-а: HV se nije sukobio s plavim kacigama» [Полковник СООНО: Хорватская армия не столкнулась с голубыми касками]. dnevnik.hr (на хорватском языке). Нова ТВ. 20 февраля 2008. Архивировано из оригинала 14 октября 2013 года . Проверено 25 января 2011 г.
- ^ Обвинительное заключение Милошевича , стр. 22.
- ^ Вердикт Мартича , с. 112
- ^ «Мартич обязан своей славой блокпостам в Книне» . Смысл-Агентство. 16 января 2006 года. Архивировано из оригинала 24 июня 2017 года . Проверено 11 сентября 2010 г.
- ^ Вердикт Мартича , с. 125
Усилия по объединению Хорватской Краины и Боснийской Краины продолжались с 1992 по 1995 год. Факты показывают, что руководство RSK стремилось к союзу и, в конечном итоге, к объединению с РС в БиГ, и что Милан Мартич был за такое объединение. В письме от 3 апреля 1993 года, среди прочего, Милана Мартича как министра внутренних дел Ассамблее РС, написанного от имени «сербов из РСК», пропагандируется объединение «двух сербских государств в качестве первого этап создания государства всех сербов». Более того, в этой связи Судебная палата ссылается на доказательства, касающиеся операции «Коридор 92». 21 января 1994 года во время предвыборной кампании по выборам президента РСК Милан Мартич заявил, что он «ускорит процесс объединения» и «передаст эстафету нашему общесербскому лидеру Слободану Милошевичу». - ^ «Резолюция 871 (1993) Совета Безопасности ООН о ситуации в бывшей Югославии» . 3 октября 1993 года. Архивировано из оригинала 21 сентября 2004 года . Проверено 11 сентября 2010 г.
7. Подчеркивает важность, которую он придает в качестве первого шага на пути к осуществлению плана Организации Объединенных Наций по поддержанию мира для Республики Хорватии процессу восстановления власти Республики Хорватии в розовых зонах , и в этом контекст требует возрождения Совместной комиссии, созданной под председательством СООНО; 8. Настоятельно призывает все стороны и других, кого это касается, сотрудничать с СООНО в достижении и осуществлении соглашения о мерах укрепления доверия, включая восстановление электро-, водоснабжения и связи во всех регионах Республики Хорватия, и подчеркивает в этом контексте важность этого соглашения. касается открытия железной дороги между Загребом и Сплитом, автомагистрали между Загребом и Жупанией и Адриатического нефтепровода, обеспечения бесперебойного движения через пролив Масленица и восстановления подачи электроэнергии и воды во все регионы Республики Хорватия. включая территории, охраняемые Организацией Объединенных Наций.
- ^ Джон Ф. Бернс (6 июля 1992 г.). «Хорваты претендуют на свой кусок Боснии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Мезнарич, Сильва; Златкович Зима, Елена (февраль 1993 г.). «Вынужденная миграция и потоки беженцев в Хорватии, Словении и Боснии и Герцеговине: раннее предупреждение, начало и текущее состояние потоков» . Убежище . 12 (7): 3–4. дои : 10.25071/1920-7336.21183 . Архивировано из оригинала 31 декабря 2014 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2014 г.
- ^ Йиган Чазан (9 июня 1992 г.). «Хорватское побережье испытывает трудности с 200 000 беженцев: Йиган Чазан в Сплите находит место для многих, спасающихся от войны в Боснии» . Хранитель . Архивировано из оригинала 6 апреля 2020 года . Проверено 31 декабря 2014 г.
- ^ Бласкович (1997) , с. 103.
- ^ Пол Льюис (4 февраля 1994 г.). «Совет Безопасности ООН предупреждает Хорватию о вводе войск в Боснию» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Дойл Макманус (25 февраля 1994 г.). «Хорваты и мусульмане вызваны в США для переговоров» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 5 марта 2016 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Уильям Э. Шмидт (24 февраля 1994 г.). «Хорваты и мусульмане заключили перемирие, чтобы положить конец другому конфликту в Боснии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Стивен Кинзер (4 марта 1994 г.). «Хорватский лидер поддерживает пакт боснийских мусульман и хорватов» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Босния и Герцеговина — Справочная информация» . Всемирная книга фактов . Центральное разведывательное управление . Архивировано из оригинала 24 января 2021 года . Проверено 11 сентября 2010 г.
За декларацией суверенитета Боснии и Герцеговины в октябре 1991 года последовала декларация независимости от бывшей Югославии 3 марта 1992 года после референдума, бойкотированного этническими сербами. Боснийские сербы, поддерживаемые соседними Сербией и Черногорией, ответили вооруженным сопротивлением, направленным на разделение республики по этническому признаку и объединение территорий, контролируемых сербами, для формирования «Великой Сербии». В марте 1994 года боснийцы и хорваты сократили количество враждующих группировок с трех до двух, подписав соглашение о создании совместной боснийско-хорватской федерации Боснии и Герцеговины.
- ^ Стивен Кинзер (4 января 1995 г.). «Открытая дорога в Хорватии: путь к миру?» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 11 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Роджер Коэн (12 декабря 1994 г.). «Конфликт на Балканах: в Хорватии; Балканская война может распространиться на Хорватию» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 12 мая 2023 года . Проверено 13 октября 2010 г.
- ^ Роджер Коэн (28 октября 1994 г.). «Трудная земля» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 20 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Бакнэм (2003) , стр. 182–83
- ^ Дэвид Айзенберг (19 августа 2010 г.). «MPRI не может читать мысли: давайте подадим на них в суд» . Хаффингтон Пост . Архивировано из оригинала 2 сентября 2010 года . Проверено 17 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Хорватия сообщает ООН о прекращении действия соглашения о войсках» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 13 января 1995 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Ситуация на оккупированных территориях Хорватии» . Генеральная Ассамблея ООН. 9 февраля 1995 года. Архивировано из оригинала 29 июня 2011 года . Проверено 14 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Вердикт Мартича , стр. 58.
- ^ Раймонд Боннер (14 марта 1995 г.). «Хорватские сербы сопротивляются новой роли ООН» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Кристофер С. Рен (1 апреля 1995 г.). «ООН голосует за сохранение своих войск на Балканах еще на 8 месяцев» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Вердикт Мартича , стр. 114–117
- ^ Роджер Коэн (7 мая 1995 г.). «Сербия перебрасывает танки к границе с Хорватией» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Тони Барбер (28 октября 1995 г.). «Хорваты готовы бросить войска в битву при Бихаче» . Независимый . Великобритания. Архивировано из оригинала 19 июня 2011 года . Проверено 13 октября 2010 г.
- ^ Уильям Д. Монтальбано (1 августа 1995 г.). «Балканская война надвигается, поскольку Хорватия расширяет свое влияние» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 5 марта 2016 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Хорватия поможет Боснии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 23 июля 1995 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 2 января 2011 г.
- ^ Алан Коуэлл (30 июля 1995 г.). «Хорватия переходит в наступление на сербов» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 6 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 30 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Хорватское наступление» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 8 августа 1995 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «ХХО: После Шторма никто не был осужден за военные преступления!» . www.vecernji.hr (на хорватском языке). Архивировано из оригинала 1 октября 2022 года . Проверено 1 октября 2022 г.
- ^ «О преступлениях в Олудже молчат. «Он убил брата и сестру, поджег мать и коров в коровнике» » . www.index.hr (на хорватском языке). Архивировано из оригинала 28 октября 2023 года . Проверено 1 октября 2022 г.
- ^ «В Мрконич Граде ищут правду о погибших на войне» . balkans.aljazeera.net (на боснийском языке). Архивировано из оригинала 1 октября 2022 года . Проверено 1 октября 2022 г.
- ^ «Список Ютарни – ХРОНОЛОГИЯ ДЕЛА ГОРОДА МРКОНИЧ Что на самом деле произошло в 1995 и 1996 годах, кто участвовал в боевых действиях, чьи имена оказались в уголовных обвинениях...» www.jutarnji.hr (на хорватском языке). 13 ноября 2016 г. Архивировано из оригинала 1 октября 2022 г. Проверено 1 октября 2022 г.
- ^ Ковачевич и Линта (2003) , стр. 93–94
- ^ Секулич (2000) , стр. 171–246
- ^ Врцель (2002) , стр. 212–222
- ^ Марко Аттила Хоаре (14 марта 2008 г.). «Как Хорватия и США предотвратили геноцид с помощью операции «Шторм» » . Общество Генри Джексона . Архивировано из оригинала 17 марта 2011 года . Проверено 20 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Хорватия: «Операция «Шторм»» – справедливости по-прежнему нет десять лет спустя» . Международная амнистия . 26 августа 2005 года. Архивировано из оригинала 19 января 2011 года . Проверено 27 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Хорватия отмечает годовщину Шторма» . Новости Би-би-си . 5 августа 2005 г. Архивировано из оригинала 16 июля 2022 г. Проверено 23 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Мэтт Проджер (5 августа 2005 г.). «Выселенные сербы помнят Шторм» . Новости Би-би-си . Би-би-си. Архивировано из оригинала 19 февраля 2009 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Всемирное обследование беженцев — Хорватия» . Комитет США по делам беженцев и иммигрантов . Архивировано из оригинала 15 марта 2008 года . Проверено 19 ноября 2010 г.
- ^ «Президент Хорватии обещает вернуть себе анклав, удерживаемый сербами» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 27 августа 1995 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Крис Хеджес (15 октября 1995 г.). «Хорватия сообщила о переброске войск в спорный сербский регион» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Президент Хорватии снова угрожает нападением» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Рейтер . 5 ноября 1995 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Эрдутское соглашение» (PDF) . Институт мира США . 12 ноября 1995 г. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 1 февраля 2013 г. . Проверено 17 января 2011 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Рене ван дер Линден (29 марта 1996 г.). «Запрос Хорватии на членство в Совете Европы – Отчет» . Совет Европы . Архивировано из оригинала 11 января 2012 года . Проверено 17 января 2011 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с «Суд над Слободаном Милошевичем - Стенограмма» . Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 15 октября 2003 г., стр. 27555–27556. Архивировано из оригинала 17 мая 2013 года . Проверено 17 января 2011 г.
- ^ Совета Безопасности ООН Резолюция 1037 . S/RES/1037(1996) (1996)
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «МиГ-21 Рудольфа Пересина выставлен на обозрение у здания Минобороны» . Н1 . 12 мая 2019. с. 1. Архивировано из оригинала 30 октября 2022 года . Проверено 30 октября 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Президент наградил пилота за полет первого МиГа на хорватскую сторону» . Всего новостей Хорватии . 3 февраля 2021. с. 1. Архивировано из оригинала 30 октября 2022 года . Проверено 30 октября 2022 г.
- ^ «Иван Селак рассказал, как он и Ивица Ивандич 30 лет назад бежали из ЮНА на МИГах: «Мы вернули украденное» » . Истра21 . 15 мая 2022. с. 1. Архивировано из оригинала 30 октября 2022 года . Проверено 30 октября 2022 г.
- ^ Йосип Черина (июль 2008 г.). «Защитники района Бенковац в хорватской войне за независимость» [Ветераны хорватской войны в районе Бенковаца в хорватской войне за независимость (краткое содержание на английском языке)]. Социальные исследования (на хорватском языке). 17 (3). Институт социальных наук Иво Пилара. ISSN 1330-0288 . Архивировано из оригинала 16 октября 2013 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Эми Фэллон (2 апреля 2010 г.). «Подозреваемый в совершении сербских военных преступлений Майл Босник арестован в Глостере» . Хранитель . Архивировано из оригинала 5 марта 2017 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Роджер Коэн (12 января 1995 г.). «Хорватия намерена отменить мандат сил ООН на своей территории» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 11 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Хорватия отмечает резню в Вуковаре» . Новости Би-би-си . Би-би-си. 18 ноября 2006. Архивировано из оригинала 4 апреля 2012 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Тревор Борман (28 сентября 2010 г.). «Настоящий капитан Драган» . ABC News (Австралия) . Архивировано из оригинала 3 декабря 2010 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Славко Галужан (декабрь 1999 г.). «Боевая эффективность противопехотных мин: опыт Хорватской отечественной войны (резюме на английском языке)». Полемос: Журнал междисциплинарных исследований войны и мира (на хорватском языке). 2 (3–4). Хорватская социологическая ассоциация и издательство Jesenski & Turk. ISSN 1331-5595 . Архивировано из оригинала 15 января 2013 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Марио Драгун (27 мая 2008 г.). «Пресс-релиз 155/08» . Министерство иностранных дел и европейской интеграции (Хорватия) . Архивировано из оригинала 17 февраля 2013 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Хорватское руководство комментирует Еремича» . Б92 . 28 мая 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 4 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Белаяц и др. 2009 , стр. 238–239.
- ^ Даниэль Бёмер (17 октября 2009 г.). «Почему Сербия должна защищать Младича?» [Почему Сербия должна защищать Младича?]. Мир онлайн (на немецком языке). Мир . Архивировано из оригинала 20 октября 2012 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
Борис Тадич: « Я должен отказаться от роли преступника для Сербии. Это была гражданская война, и все были вовлечены в нее. Мы все должны нести свою ответственность ». (Перевод: «Я должен отказаться от роли преступника для Сербии»). . Это была гражданская война, и в ней участвовали все. Мы должны взять на себя всю свою ответственность».)
- ^ Бьелажак и др. 2009 , стр. 238–241.
- ^ «Прокурор против Душко Тадича по прозвищу «Дуле» » . Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 5 октября 1995 года. Архивировано из оригинала 17 мая 2013 года . Проверено 19 января 2011 г.
Вооруженный конфликт в бывшей Югославии начался вскоре после того, как Словения и Хорватия провозгласили свою независимость 25 июня 1991 года между вооруженными силами СФРЮ и Словении и Хорватии. Такой вооруженный конфликт, конечно, следует характеризовать как внутренний, поскольку действие деклараций независимости было приостановлено по предложению ЕС на три месяца. По истечении трехмесячного периода, 7 октября 1991 г., Словения провозгласила свою независимость с этой даты, а Хорватия - с 8 октября 1991 г. Таким образом, вооруженный конфликт в бывшей Югославии следует считать международным, поскольку 8 октября 1991 г., поскольку в этот день была определена независимость этих двух государств. - ^ «Заключительный отчет Комиссии экспертов, созданной в соответствии с резолюцией 780 (1992) Совета Безопасности – Общие выводы и рекомендации» . Объединенные Нации. 27 мая 1994 года. Архивировано из оригинала 21 октября 2012 года . Проверено 7 сентября 2011 г.
- ^ «Мирьян Дамашка: «В юриспруденции я добился гораздо большего в Америке, чем добился бы, если бы остался на родине, но я был бы счастливее, если бы остался в Хорватии » . Информатор. 10 января 2020 года. Архивировано из оригинала 22 января 2021 года . Проверено 17 января 2021 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Дэвид Биндер (8 января 1992 г.). «Посланник ООН в Югославии говорит, что растущая усталость от войны привела к прекращению огня» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 11 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 18 января 2011 г.
- ^ Зильбер и Литтл (1996) , с. 170
- ↑ Обвинительное заключение Милошевича , стр. 28, 32.
- ^ «Сербия ответит на обвинения Хорватии в геноциде встречным иском в Международном Суде» . SETimes.com . Юго-Восточная Европа Таймс . 20 ноября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 2 августа 2012 года . Проверено 7 февраля 2010 г.
- ^ «ООН рассмотрит заявление Хорватии о геноциде против Сербии» . Тегеран Таймс . 19 ноября 2008 года. Архивировано из оригинала 14 июня 2011 года . Проверено 7 февраля 2010 г.
- ^ «Свидетель Мартич подробно описывает жертвы войны в Хорватии» . Global Voices БАЛКАНЫ. Архивировано из оригинала 3 марта 2016 года . Проверено 13 апреля 2006 г.
- ^ Финк 2010 , с. 469.
- ^ Гольдштейн (1999) , с. 256
- ^ Марко Аттила Хоаре (апрель 2008 г.). «Геноцид в Боснии и провал международного правосудия» (PDF) . Кингстонский университет. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 12 марта 2012 года . Проверено 22 января 2020 г.
- ^ «Воздействие сербской агрессии на население Хорватии» . Архивировано из оригинала 30 августа 2018 года . Проверено 12 октября 2018 г.
- ^ «Хорватия/Сербия: необходимы дополнительные действия для поиска пропавших без вести» . Международный комитет Красного Креста (МККК). 4 ноября 2010 года. Архивировано из оригинала 19 ноября 2010 года . Проверено 23 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Глобус – ХОРВАТСКАЯ КНИГА МЕРТВЫХ Последняя правда обо всех жертвах войны» . www.jutarnji.hr (на хорватском языке). 9 января 2018 года. Архивировано из оригинала 28 октября 2020 года . Проверено 27 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ «Глобус – ХОРВАТСКАЯ КНИГА МЕРТВЫХ Последняя правда обо всех жертвах войны» . www.jutarnji.hr (на хорватском языке). 9 января 2018 года. Архивировано из оригинала 28 октября 2020 года . Проверено 30 августа 2020 г.
- ^ «Книга пропавших без вести на территории Республики Хорватия» . Международный комитет Красного Креста (МККК). 1 января 2010 года. Архивировано из оригинала 5 августа 2011 года . Проверено 23 января 2011 г.
- ^ Весна Роллер (7 ноября 2009 г.). «HZMO: Справку об инвалидности получили 45 703 человека, ранее служившие в хорватской армии» [Хорватский институт пенсионного страхования: Справку об инвалидности получили 45 703 человека, ранее служившие в хорватской армии]. Голос Славонии (на хорватском языке). Glas Славонидже д.д. Архивировано из оригинала 19 июля 2011 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ С. Дукич (23 июня 2009 г.). « Дополнительно 8000 человек стали инвалидами из-за Отечественной войны за последние три года». Свободная Далмация (на хорватском языке). Европапресс Холдинг . Архивировано из оригинала 19 октября 2012 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ Станислав Сольдо (30 октября 2010 г.). «Пациенты с посттравматическим стрессовым расстройством: мы заблокируем все учреждения первичной медико-санитарной помощи». Свободная Далмация (на хорватском языке). Европапресс Холдинг. Архивировано из оригинала 11 января 2012 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ Фрукты (2005) , с. 439
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Гражданские и политические права в Хорватии» . Хьюман Райтс Вотч. 1 октября 1995 г. с. 62. Архивировано из оригинала 11 октября 2012 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с «Практика прав человека в Хорватии, 1993 г.» . Госдепартамент США. 31 января 1994 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Хорватия: Отдельные события в области правосудия переходного периода» (PDF) . Международный центр правосудия переходного периода. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 18 июня 2013 года . Проверено 5 сентября 2009 г.
- ^ Кэрол Дж. Уильямс (14 декабря 1991 г.). «Сербским беженцам не по себе в роли оккупантов» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 8 марта 2011 года . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Шаллер 1996 , с. 894.
- ^ Доминелли (2007) , с. 163
- ^ Маркус Таннер (24 августа 1992 г.). « Ссора из-за «чистки» привела к кризису в Воеводине» . Независимый . Архивировано из оригинала 10 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 19 января 2011 г.
- ^ Мештрович, Степан Габриэль (1996). Мештрович.С. (1996), Геноцид после эмоций: Постэмоциональная Балканская война, Taylor & Francisco Ltd, стр.77 . Психология Пресс. ISBN 9780415122948 . Проверено 28 апреля 2010 г.
- ^ Штрбац, Саво (декабрь 1999 г.). «Преступления против сербов на территории Хорватии в период 90–99 годов» [Преступления против сербов на территории Хорватии в период 1990–1999 годов] (PDF) . Veritas - Бюллетень (на сербском языке). Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 25 марта 2009 г. Проверено 5 сентября 2009 г.
- ^ Хорватия – События 2008 года . Хьюман Райтс Вотч . 14 января 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 12 октября 2012 года . Проверено 5 сентября 2009 г.
- ^ «Федеральный институт статистики и учета ФНРЮ и СФРЮ, переписи населения 1948, 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981 и 1991 годов по территориальной организации, муниципалитетам и связанным с ними поселениям в 1991 году» (PDF) . Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 20 июня 2022 г. Проверено 1 октября 2022 г.
- ^ «Шимонович подтверждает Йосипович: Лагеря включены в иск против Сербии» [Шимонович подтверждает Йосипович: Лагеря включены в иск против Сербии]. Business.hr (на хорватском языке). Business.hr doo, 8 января 2010 г. Архивировано из оригинала 13 февраля 2010 г. . Проверено 17 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Всемирная федерация ветеранов - Алфавитный список по странам» . Всемирная федерация ветеранов (WVF) . Архивировано из оригинала 7 сентября 2011 года . Проверено 17 января 2011 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г «Оценка количества жертв сексуального насилия во время Отечественной войны Республики Хорватия и оптимальные формы компенсации и поддержки жертв» (PDF) . ПРООН. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 20 января 2022 года . Проверено 22 января 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Владисавлевич, Аня; Лакич, Младен; Бегишолли, Блерта (19 июня 2019 г.). «Компенсация приходит с опозданием для жертв изнасилования во время Балканских войн» . БалканИнсайт . РОЖДЕНИЕ . Проверено 22 января 2020 г.
- ^ Майя Сайлер Гармаз (21 декабря 1991 г.). «Бесконечная реконструкция после войны». Весник (на хорватском языке). Народне Новине д.д. Архивировано из оригинала 18 декабря 2014 года . Проверено 20 января 2011 г.
- ^ Содружество (1999), с. 280
- ^ Чак Судетич (21 декабря 1991 г.). «Распад Югославии набирает обороты» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 20 января 2011 г.
- ^ Боб Дэвис (8 мая 2009 г.). «Гипер-гиперинфляция» . Уолл Стрит Джорнал . Проверено 20 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Худший эпизод гиперинфляции в истории: Югославия 1993–94» . Государственный университет Сан-Хосе . Архивировано из оригинала 7 декабря 2012 года . Проверено 20 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Произошло 31 августа». Хорватский альбом для вырезок (на хорватском языке). Хорватский информационный центр. Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 27 января 2011 г.
Сербы с горы Вучак в Боснии и Герцеговине непрерывно обстреливают Славонски-Брод
- ^ «Произошло 26 октября». Хорватский альбом для вырезок (на хорватском языке). Хорватский информационный центр. Архивировано из оригинала 18 мая 2013 года . Проверено 27 января 2011 г.
Постоянная общая опасность в округе продолжается с апреля 1992 года... Сербы из Боснии обстреливают город около 12-ти часов дня, когда на улицах больше всего людей.
- ^ Чак Судетич (20 октября 1991 г.). «Конвой с гуманитарной помощью стал жертвой в Хорватии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Боевые действия в Хорватии ухудшаются из-за удара по пригороду Загреба» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 11 сентября 1993 года . Проверено 7 октября 2010 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (5 ноября 1991 г.). «Югославские бои бушуют накануне переговоров» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Елич А. (декабрь 1994 г.). «Детские жертвы в хорватской общине во время войны 1991–1992 годов» . Архив болезней в детстве . 71 (6): 540–2. дои : 10.1136/adc.71.6.540 . ПМК 1030096 . ПМИД 7726618 .
- ^ Сольдо С., Пунтарич Д., Петровицки З., Пргомет Д. (февраль 1999 г.). «Травмы, нанесенные противопехотными минами солдатам хорватской армии на фронте в Восточной Славонии во время войны 1991–1992 годов в Хорватии» . Военная медицина . 164 (2): 141–4. дои : 10.1093/milmed/164.2.141 . ПМИД 10050574 .
- ^ Хэнсон (2000) , с. 96.
- ^ Николас Уолтон (30 мая 2007 г.). «Хорватские пчелы вынюхивают мины» . Новости Би-би-си . Би-би-си . Проверено 17 января 2010 г.
- ^ «Помощь минным жертвам (МПА)» . Хорватский центр противоминной деятельности. 2010. Архивировано из оригинала 11 марта 2012 года . Проверено 17 января 2010 г.
- ^ Марцин Монко (30 сентября 2005 г.). «Хорватия: безопасные игровые площадки в опасных зонах» . Международный комитет Красного Креста. Архивировано из оригинала 1 октября 2012 года . Проверено 17 января 2010 г.
- ^ Валентина Поп (10 августа 2009 г.). «Хорватский регион требует помощи ЕС по противопехотным минам» . EUobserver . Проверено 17 января 2010 г.
- ^ «Кризис мигрантов: предупреждение о минах в Хорватии после пересечения границы – BBC News» , BBC.com , 16 сентября 2015 г. , получено 16 сентября 2015 г.
- ^ «Устав Трибунала» . Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии . Сентябрь 2009 года . Проверено 19 января 2011 г.
- ^ «О МТБЮ» . Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. Архивировано из оригинала 31 января 2011 года . Проверено 19 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Саймонс, Марлиз (15 апреля 2011 г.). «Суд ООН признал двух хорватских генералов виновными в военных преступлениях и освободил третьего» . Нью-Йорк Таймс .
- ^ Аттила Хоар, Марко (июнь 2005 г.). «Капитуляция Гаагского трибунала» . Хельсинкский комитет по правам человека в Сербии . Проверено 9 апреля 2011 г.
- ^ «Сербский лидер заключен в тюрьму за военные преступления» . Новости Би-би-си . Би-би-си. 10 марта 2006 года . Проверено 20 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Милан Бабич — бывший дантист, основавший обреченную Сербскую Республику Краина и инициировавший «этническую чистку» » . Таймс . 10 марта 2006 года . Проверено 20 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Гаага утроит срок тюремного заключения в Вуковаре» . Новости Би-би-си . Би-би-си. 5 мая 2009 года . Проверено 15 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Арматта, Джудит (2010). Сумерки безнаказанности: Суд над Слободаном Милошевичем за военные преступления . Дарем, Северная Каролина: Издательство Университета Дьюка . п. 190. ИСБН 978-0-8223-4746-0 .
- ^ «Трибунал ООН вынесет решение по делу о резне в Вуковаре» . Рейтер . 25 сентября 2007 года . Проверено 11 сентября 2010 г.
- ^ Марлиз Саймонс (30 июня 1998 г.). «Серб, обвиненный в массовом убийстве, покончил жизнь самоубийством» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Генерал виновен в нападении на Дубровник» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 1 февраля 2005 года . Проверено 11 апреля 2011 г.
- ^ «Владимира Ковачевича признали неспособным предстать перед судом» . Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 12 апреля 2006 года . Проверено 12 июня 2012 г.
- ^ «Момчило Перишич: приговор главнокомандующему югославской армии отменен» . Би-би-си. 28 февраля 2013 г.
- ^ «Суд ООН отменил оправдательный приговор сербскому политику за военные преступления» . Айриш Таймс . 11 апреля 2018 г.
- ^ «Первое неуважение к суду: Воислав Шешель» (PDF) . МТБЮ. «2-е неуважение к суду: Воислав Шешель» (PDF) . МТБЮ. «Третье неуважение к суду: Воислав Шешель» (PDF) . МТБЮ.
- ^ «ООН высоко оценивает вынесение окончательного решения Уголовному трибуналу по бывшей Югославии» . Новости ООН . 31 мая 2023 г. . Проверено 17 августа 2023 г.
- ^ «СТАНИШИЧ и СИМАТОВИЧ (МИКТ-15-96-А)» . Гаага: Международный остаточный механизм для уголовных трибуналов. 31 мая 2023 г. . Проверено 17 августа 2023 г.
- ^ «Прокурор против Йовицы Станишича и Франко Симатовича — решение Апелляционной палаты» (PDF) . Гаага: Международный остаточный механизм для уголовных трибуналов. 31 мая 2023 г. с. 142, 256 . Проверено 17 августа 2023 г.
- ^ Рой В. Гутман (31 декабря 1998 г.). «В центре внимания нарушения международного гуманитарного права: роль СМИ» . Международное обозрение Красного Креста (325). Международный комитет Красного Креста . Архивировано из оригинала 17 сентября 2011 года . Проверено 15 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с «Обвинительное заключение Милошевича (текст)» . Новости Би-би-си . Би-би-си. 29 октября 2001 года . Проверено 19 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Хорватия: Информация о злоупотреблениях, совершенных в период с апреля 1992 г. по сентябрь 1992 г. сербскими военными и военизированными формированиями в Краине в целом и в частности в местах, указанных в ответе HRV16050.E» . Верховный комиссар ООН по делам беженцев – Refworld . Совет по иммиграции и беженцам Канады . 1 февраля 1994 года. Архивировано из оригинала 17 октября 2012 года . Проверено 20 декабря 2010 г.
- ↑ Вердикт Мартича , стр. 79–85.
- ^ Стивен Энгельберг (19 декабря 1991 г.). «Жители хорватских деревень рассказывают о резне, устроенной сербскими войсками» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 16 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Милошевич презирает суд» . Новости Би-би-си . 3 июля 2001 года . Проверено 4 февраля 2011 г.
- ^ « Отчет Amnesty International за 2010 год – Хорватия » . УВКБ ООН — Refworld . Международная амнистия . 28 мая 2010. Архивировано из оригинала 17 октября 2012 года . Проверено 13 января 2011 г.
- ^ Чак Судетич (25 января 1992 г.). «Доказательства резни указывают на хорватов» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 19 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Хорватия признала, что сербские мирные жители были убиты» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Ассошиэйтед Пресс . 3 октября 1995 года . Проверено 19 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Мерсепа подозревают в убийстве или исчезновении 43 человек» . Т-портал . Т-Ком Хрватска. 12 декабря 2010. Архивировано из оригинала 17 июля 2011 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ Берислав Елинич (31 июля 2006 г.). «Сулджик умирает, заявление против Мерсепа невозможно» . Насьональ . NCL Media Grupa doo Архивировано из оригинала 27 мая 2012 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Presuda i rješenje broj: I Kž 81/06-7» [Номер постановления и решения: I Kž 81/06-7] (на хорватском языке). Верховный суд Республики Хорватия . 10 мая 2006 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Хорватия задерживает бывшего чиновника за военные преступления» . Новости ЦБК . Канадская радиовещательная корпорация . 10 декабря 2010 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ Милекич, Свен (12 мая 2016 г.). «Сотрудник хорватской полиции Мерсеп заключен в тюрьму за военные преступления» . Балканский взгляд .
- ^ Владисавлевич, Аня (17 ноября 2020 г.). «Умер хорватский военный преступник Томислав Мерсеп» . Балканский взгляд .
- ^ Хеддл, Драго (7 мая 2012 г.). «Мерсеп и Вуковар» . Балканский взгляд .
- ^ «Босния арестовывает хорватского депутата, осужденного за военные преступления» . Радио Свободная Европа/Радио Свобода . Совет управляющих телерадиокомпанией . 13 мая 2009 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Рахим Адеми оправдан» (PDF) . Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Досье: Генерал Янко Бобетко» . Новости Би-би-си . Би-би-си. 29 апреля 2003 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ «Умер Янко Бобетко, 84 года, Герой независимости Хорватии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Ассошиэйтед Пресс . 30 апреля 2003 года . Проверено 22 января 2011 г.
- ^ Весна Перич Зимонич (12 марта 2008 г.). «Хорватский генерал, обвиняемый в этнических чистках против сербов, предстанет перед судом» . Независимый . Проверено 13 октября 2010 г.
- ^ Марина Карлович-Саболич (15 сентября 2001 г.). «Унесенные бурей» . Свободная Далмация . Европапресс Холдинг . Проверено 13 октября 2010 г.
- ^ «Заявление судьи Луизы Арбур, прокурора МТБЮ во время ее визита в Загреб, Хорватия» . Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 20 июля 1999 года . Проверено 19 ноября 2010 г.
- ^ «Судьи разрешают внести поправки в обвинительный акт по операции «Шторм»» . Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 21 октября 2005 г. Архивировано из оригинала 26 мая 2024 г. Проверено 19 ноября 2010 г.
- ^ Николас Вуд (18 марта 2006 г.). «Конец Великой Сербии» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 12 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Некролог: Слободан Милошевич» . Новости Би-би-си . Би-би-си. 11 марта 2006 года . Проверено 12 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Решение Апелляционной палаты МТБЮ; 18 апреля 2002 г.; Причины решения по промежуточной апелляции обвинения в отказе в объединении постановлений; Параграф 8
- ^ Додер и Брэнсон 1999 , с. 81.
- ^ Вердикт Перишича , стр. 3, 8
- ^ Марлиз Саймонс (24 апреля 2003 г.). «Таинственный свидетель сталкивается с Милошевичем» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 21 июля 2012 года . Проверено 29 октября 2010 г.
- ^ Милош Васич (23 января 1999 г.). «Политика фальсификата». Време (на сербском языке). ООО НП "ВРЕМЕ" Архивировано из оригинала 22 октября 2012 года . Проверено 23 января 2011 г.
- ^ Кристофер Беннетт. «Как разрушители Югославии использовали средства массовой информации» . Служба общественного вещания . Проверено 23 января 2011 г.
- ^ Джейн Перлез (10 августа 1997 г.). «Сербские СМИ — это шоу одного актера» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 23 января 2011 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Удовицки и Риджуэй, 2000 , стр. 255–266.
- ^ Fridman 2010
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с «Антивоенные и мирные идеи в истории Сербии и антивоенных движений до 2000 года» . republika.co.rs . 2011 . Проверено 4 мая 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Памятник Неизвестному дезертиру» . Погода . 2008 год . Проверено 4 мая 2020 г.
- ^ Удовицки и Риджуэй 2000 , с. 258
- ^ Пауэрс 1997 , с. 467
- ^ «Комментарий: Пропагандистская война Милошевича» . Институт освещения войны и мира . Проверено 5 мая 2020 г.
- ^ Сигара 1996 , стр. 40–42.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Сербский лидер Тадич приносит извинения за резню в Вуковаре в 1991 году» . Новости Би-би-си . Би-би-си. 4 ноября 2010 г. Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Сербия и Хорватия соглашаются на дипломатические отношения» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 8 августа 1996 года . Проверено 18 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Предварительные возражения (Хорватия против Сербии)» (PDF) . Международный Суд . 18 ноября 2008 г. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 17 октября 2013 г. . Проверено 19 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Заявление о возбуждении производства (Хорватия и Югославия)» (PDF) . Международный Суд . 2 июля 2008 г. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 26 июля 2011 г. . Проверено 19 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Сербия подала иск против Хорватии о геноциде» . Б92. 4 января 2010 года. Архивировано из оригинала 8 июня 2011 года . Проверено 19 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Никакое судебное разбирательство не было бы лучше для Загреба» . Блич. 4 января 2010 года. Архивировано из оригинала 22 декабря 2010 года . Проверено 19 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ «Президенты извиняются за войну в Хорватии» . 10 сентября 2003 года . Проверено 15 января 2022 г.
- ^ Обзор и перспективы сырьевых товаров на 1991–92 годы, Продовольственная и сельскохозяйственная организация ФАО.
- ^ Глаурдик (2011) , стр. 59, 124-125.
- ^ Глаурдик (2011) , с. 160
- ^ Глаурдик (2011) , с. 110
- ^ Глаурдик (2011) , стр. 264–265.
- ^ Азраил, Джереми Р. и Эмиль А. Пайин. Разработка политики США и России в отношении применения силы. Санта-Моника, Калифорния: RAND Corporation, 1996. Глава 11: Югославия: 1989–1996 годы , автор Уоррен Циммерманн.
Ссылки
[ редактировать ]Книги
[ редактировать ]- Белаяц, Миля; Жунец, Озрен; Мечислав Бодушинский; Рафаэль Дращак; Игорь Граовац; Салли Кент; Рюдигер Малли; Срджа Павлович; Джейсон Вуич (2009). «Война в Хорватии, 1991–1995» (PDF) . В Инграо, Чарльз В.; Эммерт, Томас Аллан (ред.). Противостояние югославским противоречиям: инициатива ученых (PDF) . Издательство Университета Пердью . ISBN 978-1-55753-533-7 .
- Бласкович, Джерри (1997). Анатомия обмана: личный опыт американского врача с реалиями войны в Хорватии . Нью-Йорк: Издательство Dunhill. ISBN 0-935016-24-4 .
- Браун, Синтия; Карим, Фархад (1995). Разыгрывание «коммунальной карты»: общинное насилие и права человека . Нью-Йорк: Хьюман Райтс Вотч . ISBN 978-1-56432-152-7 .
- Бакнэм, Марк (2003). Ответственность командования . База ВВС Максвелл: Издательство Air University Press. ISBN 1-58566-115-5 . OCLC 52199670 .
- Бург, Стивен Л.; Шуп, Пол С. (2000). Война в Боснии и Герцеговине: этнический конфликт и международное вмешательство . Нью-Йорк: М.Э. Шарп . ISBN 1-56324-309-1 .
- Джокич, Деян (2003). Югославизм: истории неудачной идеи, 1918–1992 гг . Издательство C. Hurst & Co. ISBN 978-1-85065-663-0 .
- Доминелли, Лена (2007). Оживление сообществ в глобализирующемся мире . Хэмпшир: Издательство Ashgate . ISBN 978-0-7546-4498-9 .
- Додер, Душко; Брэнсон, Луиза (1999). Милошевич: Портрет тирана . Саймон и Шустер . ISBN 0-684-84308-0 .
- Финк, Джордж (2010). Стресс войны, конфликта и катастрофы . Академическая пресса. ISBN 978-0123813824 .
- Финлан, Аластер (2004). Распад Югославии, 1991–1999 гг . Оксфорд: Издательство Osprey . ISBN 1-84176-805-7 .
- Фрухт, Ричард К. (2005). Восточная Европа: введение в людей, земли и культуру . Санта-Барбара, Калифорния: ABC-CLIO. ISBN 1-57607-800-0 .
- Фишер, Шэрон (2006). Политические изменения в посткоммунистической Словакии и Хорватии: от националистического к европеистическому . Спрингер. ISBN 978-0-23060-088-1 .
- Глаурдич, Йосип (2011). Час Европы: западные державы и распад Югославии . Издательство Йельского университета. ISBN 978-0-300-16645-3 .
- Гольдштейн, Иво (1999). Хорватия: История . Лондон: Издательство C. Hurst & Co. ISBN 1-85065-525-1 .
- Хэнсон, Алан (2000). «Независимость Хорватии от Югославии, 1991–1992» (PDF) . В Гринберге, Мелани К.; Бартон, Джон Х.; МакГиннесс, Маргарет Э. (ред.). Слова о войне, посредничестве и арбитраже для предотвращения смертельных конфликтов (PDF) . Роуман и Литтлфилд . ISBN 0-8476-9892-0 . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 20 июля 2006 г.
- Йович, Деян (2009). Югославия: государство, которое отмерло . Издательство Университета Пердью. ISBN 978-1-55753-495-8 .
- Кадиевич, Велько (1993). ( государства Мой взгляд на роспуск: армия без на сербском языке). Белград: Политика. ISBN 86-7607-047-4 .
- Ковачевич, Драго; Линта, Миодраг (2003). Клетка: Краина в организованной войне [ Клетка: Краина в организованной войне ] (на сербском языке). Белград: Сербский демократический форум. ISBN 86-83759-04-0 .
- Манн, Майкл (2005). Темная сторона демократии: объяснение этнической чистки . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 0-521-53854-8 .
- Месич, Степан (2004). Распад Югославии: политические мемуары . Издательство Центральноевропейского университета. ISBN 963-9241-81-4 .
- Мештрович, Степан Габриэль (1996). Геноцид после эмоций: постэмоциональная Балканская война . Рутледж. ISBN 0-415-12294-5 .
- Фуонг, Кэтрин (2005). Международная защита внутренне перемещенных лиц . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-1139442268 .
- Рамет, Сабрина П. (2006). Три Югославии: государственное строительство и легитимация, 1918–2005 гг . Блумингтон: Издательство Университета Индианы . ISBN 0-253-34656-8 .
- Шаллер, Джейн Грин (1996). «Защита детей и их здоровья во время войны» . В Верхеллене, Юджин (ред.). Мониторинг прав детей . Гаага: Издательство Мартинуса Нийхоффа. ISBN 978-9041101617 .
- Секулич, Милисав (2000). Книн Фелл в Белграде [ Книн Фелл в Белграде ] (на сербском языке). Нидда Верлаг. УДК: 3 355,45 (497,5-074) «1991/1995».
- Зильбер, Лаура ; Литтл, Аллан (1996). Гибель Югославии . Книги о пингвинах . ISBN 0-14-026168-0 .
- Зильбер, Лаура ; Литтл, Аллан (1997). Югославия: Смерть нации . Лондон: Книги Пингвинов . ISBN 0-14-026263-6 .
- Томас, Найджел (2006). Югославские войны: Словения и Хорватия, 1991–95 гг . Оксфорд: Издательство Osprey . ISBN 1-84176-963-0 .
- Врцель, Марко (2002). Война за Сербскую Краину: 1991–1995 [ Война за Сербскую Краину: 1991–1995 ] (на сербском языке). Белград: Сербское культурное общество «Зора». ISBN 978-86-83809-06-6 .
- Вертхайм, Эрик (2007). Руководство Военно-морского института по боевым флотам мира: их корабли, самолеты и системы . Издательство Военно-морского института. ISBN 978-1-59114-955-2 .
- Западноевропейский союз (1986). Материалы – Ассамблея Западноевропейского Союза: Официальные акты – Ассамблея Европейского Союза . Университет Вирджинии .
- Занотти, Лаура (2011). Управляющий беспорядок: миротворческие операции ООН, международная безопасность и демократизация в эпоху после холодной войны . Пенн Стейт Пресс. ISBN 978-0-271-03761-5 .
- Пауэрс, Роджер С. (1997). Протест, власть и перемены: энциклопедия ненасильственных действий от ACT-UP до избирательного права женщин . Рутледж . ISBN 978-1136764820 .
- Удовицкий, Ясминка; Риджуэй, Джеймс (2000). Сожгите этот дом: создание и разрушение Югославии . Дарем, Северная Каролина: Издательство Университета Дьюка . ISBN 978-1136764820 .
- Сигара, Норман (1996). «Сербо-хорватская война, 1991 год». В Мештровиче, Степан Габриэль (ред.). Геноцид после эмоций: постэмоциональная Балканская война . Лондон: Рутледж. ISBN 978-0-415-12293-1 .
Другие источники
[ редактировать ]- «Прокурор против Милана Бабича - Решение» (PDF) . Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 26 июня 2009 года . Проверено 11 сентября 2010 г.
- Восточная Европа и Содружество Независимых Государств . Рутледж. 1999. ISBN 978-1-85743-058-5 .
- Мир информации (2003). Обзор Европы . Коган Пейдж . ISBN 0-7494-4067-8 .
- «Прокурор против Милана Мартича – Решение» (PDF) . Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 12 июня 2007 года . Проверено 11 августа 2010 г.
- «Прокурор Трибунала против Слободана Милошевича (IT-02-54) – Обвинительное заключение» (PDF) . Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 22 октября 2002 года . Проверено 18 октября 2010 г.
- «Краткое содержание решения по делу Прокурора против Момчило Перишича» (PDF) . Гаага: Международный уголовный трибунал по бывшей Югославии. 6 сентября 2011 года . Проверено 7 сентября 2011 г.
- Пешич, Весна (апрель 1996 г.). «Сербский национализм и истоки югославского кризиса» . Миротворчество (8). Институт мира США . Проверено 29 ноября 2012 г.
- Креш, Мария, изд. (сентябрь 2010 г.). «Прилог «Полиция в Домовинском рату 1990–1991 гг.» » (PDF) . Глазило «Мир, Углед, Повьеренье» (на хорватском языке) (42). Министерство внутренних дел Республики Хорватия . ISSN 1846-3444 . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 3 июля 2017 года . Проверено 30 сентября 2011 г.
- «Применение Конвенции о предупреждении преступления геноцида и наказании за него (Хорватия против Сербии)» (PDF) . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 13 декабря 2016 г.
- Перунович, Срека (2015). «Враждебность в Югославии перед ее распадом: открытия опроса общественного мнения». Этносы . 16 (6): 819–841. дои : 10.1177/1468796815576059 . S2CID 147068505 .
- Фридман, Орли (2010). « Это было похоже на войну с собственным народом: антивоенный активизм в Сербии в 1990-е годы». Журнал национализма и этнической принадлежности . 39 (4): 507–522. дои : 10.1080/00905992.2011.579953 . S2CID 153467930 .
Внешние ссылки
[ редактировать ]- Освещение Sense Tribunal разбирательств МТБЮ и Международного Суда
- War Photo Limited - Изображения войны
- Еще изображения войны
- «Югославия: пытки, умышленные и произвольные убийства в зонах боевых действий» . Международная амнистия . Ноябрь 1991 года.
- «Злоупотребление психиатрией» [Злоупотребление психиатрией]. НИН (на сербском языке). Рингьер Аксель Спрингер. 14 октября 1999 года . Проверено 30 января 2011 г.
- Хорватский мемориально-документационный центр Отечественной войны (на хорватском языке)
- Хорватская война за независимость
- Конфликты 1990-х годов
- 1990-е в Хорватии
- Отношения Хорватии и Сербии
- Политическая история Сербии
- Декоммунизация
- Сепаратизм в Хорватии
- Войны с участием Хорватии
- Войны с участием Боснии и Герцеговины
- Войны с участием Сербии
- Войны с участием Балкан
- Войны за независимость
- Югославские войны