испанский грипп
| испанский грипп | |
|---|---|
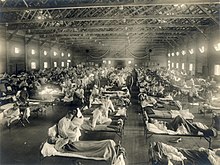 | |
| Болезнь | Грипп |
| Штамм вируса | Штаммы A/H1N1 |
| Расположение | По всему миру |
| Дата | February 1918 – April 1920[1] |
| Suspected cases‡ | 500 million (estimated)[2] |
Deaths | 25–50 million (generally accepted), other estimates range from 17 to 100 million[3][4][5] |
| ‡Suspected cases have not been confirmed by laboratory tests as being due to this strain, although some other strains may have been ruled out. | |
| Influenza (flu) |
|---|
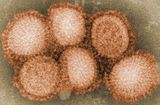 |
Пандемия гриппа 1918–1920 годов , также известная как Великая эпидемия гриппа или распространенное неправильное название «испанский грипп» , была исключительно смертоносной глобальной пандемией гриппа, вызванной подтипом H1N1 вируса А. гриппа Самый ранний зарегистрированный случай произошел в марте 1918 года в штате Канзас в США, а в апреле новые случаи были зарегистрированы во Франции, Германии и Великобритании. Два года спустя почти треть мирового населения, или, по оценкам, 500 миллионов человек, были инфицированы в четырех последовательных волнах. Оценки смертности варьируются от 17 до 50 миллионов человек. [ 6 ] и, возможно, до 100 миллионов, [ 7 ] что делает эту пандемию одной из самых смертоносных в истории .
The pandemic broke out near the end of World War I, when wartime censors in the belligerent countries suppressed bad news to maintain morale, but newspapers freely reported the outbreak in neutral Spain, creating a false impression of Spain as the epicenter and leading to the "Spanish flu" misnomer.[8] Limited historical epidemiological data make the pandemic's geographic origin indeterminate, with competing hypotheses on the initial spread.[2]
Most influenza outbreaks disproportionately kill the young and old, with a higher survival rate in-between, but this pandemic had unusually high mortality for young adults.[9] Scientists offer several explanations for the high mortality, including a six-year climate anomaly affecting migration of disease vectors with increased likelihood of spread through bodies of water.[10] However, the claim that young adults had a high mortality during the pandemic has been contested.[11] Malnourishment, overcrowded medical camps and hospitals, and poor hygiene, exacerbated by the war, promoted bacterial superinfection, killing most of the victims after a typically prolonged death bed.[12][13]
The 1918 Spanish flu was the first of three flu pandemics caused by H1N1 influenza A virus; the others being the 1977 Russian flu and the 2009 Swine flu pandemics.[14][15][16]
Etymologies

This pandemic was known by many different names—some old, some new—depending on place, time, and context. The etymology of alternative names historicises the scourge and its effects on people who would only learn years later that invisible viruses caused influenza.[17] The lack of scientific answers led the Sierra Leone Weekly News (Freetown) to suggest a biblical framing in July 1918, using an interrogative from Exodus 16 in ancient Hebrew:[a] "One thing is for certain—the doctors are at present flabbergasted; and we suggest that rather than calling the disease influenza they should for the present until they have it in hand, say Man hu—'What is it?'"[19][20][21]
Descriptive names
Outbreaks of influenza-like illness were documented in 1916–17 at British military hospitals in Étaples, France,[22] and just across the English Channel at Aldershot, England. Clinical indications in common with the 1918 pandemic included rapid symptom progression to a "dusky" heliotrope cyanosis of the face. This characteristic blue-violet cyanosis in expiring patients led to the name 'purple death'.[23][24][25]
The Aldershot physicians later wrote in The Lancet, "the influenza pneumococcal purulent bronchitis we and others described in 1916 and 1917 is fundamentally the same condition as the influenza of this present pandemic."[26] This "purulent bronchitis" is not yet linked to the same A/H1N1 virus,[27] but it may be a precursor.[26][28][29]
In 1918, 'epidemic influenza' (Italian: influenza, influence),[30] also known at the time as 'the grip' (French: la grippe, grasp),[31] appeared in Kansas in the U.S. during late spring, and early reports from Spain began appearing on 21 May.[32][33] Reports from both places called it 'three-day fever' (fiebre de los tres días).[34][35][36]
Associative names

Many alternative names are exonyms in the practice of making new infectious diseases seem foreign.[37][38][39] This pattern was observed even before the 1889–1890 pandemic, also known as the 'Russian flu', when the Russians already called epidemic influenza the 'Chinese catarrh', the Germans called it the 'Russian pest', while the Italians in turn called it the 'German disease'.[40][41] These epithets were re-used in the 1918 pandemic, along with new ones.[42]
'Spanish' influenza

Outside Spain, the disease was soon misnamed 'Spanish influenza'.[43][44] In a 2 June 1918 The Times of London dispatch titled, "The Spanish Epidemic," a correspondent in Madrid reported over 100,000 victims of, "The unknown disease…clearly of a gripal character," without referring to "Spanish influenza" directly.[45] Three weeks later The Times reported that, "Everybody thinks of it as the 'Spanish' influenza to-day."[46] Three days after that an advertisement appeared in The Times for Formamint tablets to prevent "Spanish influenza".[47][48] When it reached Moscow, Pravda announced, "Ispánka (the Spanish lady) is in town," making 'the Spanish lady' another common name.[49]
The outbreak did not originate in Spain (see below),[50] but reporting did, due to wartime censorship in belligerent nations. Spain was a neutral country unconcerned with appearances of combat readiness, and without a wartime propaganda machine to prop up morale;[51][52] so its newspapers freely reported epidemic effects, including King Alfonso XIII's illness, making Spain the apparent locus of the epidemic.[53] The censorship was so effective that Spain's health officials were unaware its neighboring countries were similarly affected.[54]
In an October 1918 "Madrid Letter" to the Journal of the American Medical Association, a Spanish official protested, "we were surprised to learn that the disease was making ravages in other countries, and that people there were calling it the 'Spanish grip'. And wherefore Spanish? …this epidemic was not born in Spain, and this should be recorded as a historic vindication."[55] But before this letter could be published, The Serbian Newspaper (Corfu) said, "Various countries have been assigning the origin of this imposing guest to each other for quite some time, and at one point in time they agreed to assign its origin to the kind and neutral Spain…"[56]

Other exonyms
French press initially used 'American flu', but adopted 'Spanish flu' in lieu of antagonizing an ally.[57] In the spring of 1918, British soldiers called it 'Flanders flu', while German soldiers used 'Flandern-Fieber' (Flemish fever), both after a famous battlefield in Belgium where many soldiers on both sides fell ill.[42][39][58][59] In Senegal it was named 'Brazilian flu', and in Brazil, 'German flu'.[60] In Spain it was also known as the 'French flu' (gripe francesa),[50][8] or the 'Naples Soldier' (Soldado de Nápoles), after a popular song from a zarzuela.[b][57] Spanish flu (gripe española) is now a common name in Spain,[62] but remains controversial there.[63][64]
Other names derived from geopolitical borders and social boundaries. In Poland it was the 'Bolshevik disease',[60][65] while the Bolsheviks referred to it as the 'Kirghiz disease'.[59] Some Africans called it a 'white man's sickness', but in South Africa, white men also used the ethnophaulism 'kaffersiekte' (lit. negro disease).[42][66] Japan blamed sumo wrestlers for bringing the disease home from a match in Taiwan by calling it 'sumo flu' (Sumo Kaze), even though three top wrestlers died there.[67][68]
World Health Organization 'best practices' first published in 2015 now aim to prevent social stigma by no longer associating culturally significant names with new diseases, listing "Spanish flu" under "examples to be avoided".[69][38][70] Many authors now eschew calling this the Spanish flu,[57] instead using variations of '1918–19/20 flu/influenza pandemic'.[71][72][73]
Local names
Some language endonyms did not name specific regions or groups of people. Examples specific to this pandemic include: Northern Ndebele: 'Malibuzwe' (let enquiries be made concerning it), Swahili: 'Ugonjo huo kichwa na kukohoa na kiuno' (the disease of head and coughing and spine),[74] Yao: 'chipindupindu' (disease from seeking to make a profit in wartime), Otjiherero: 'kaapitohanga' (disease which passes through like a bullet),[75] and Persian: 'nakhushi-yi bad' (disease of the wind).[76][77]
Other names
This outbreak was also commonly known as the 'great influenza epidemic',[78][79] after the 'great war', a common name for World War I before World War II.[80] French military doctors originally called it 'disease 11' (maladie onze).[39] German doctors downplayed the severity by calling it 'pseudo influenza' (Latin: pseudo, false), while in Africa, doctors tried to get patients to take it more seriously by calling it 'influenza vera' (Latin: vera, true).[81]
A children's song from the 1889–90 flu pandemic[82] was shortened and adapted into a skipping-rope rhyme popular in 1918.[83][84] It is a metaphor for the transmissibility of 'Influenza', where that name was clipped to the apheresis 'Enza':[85][86][87]
I had a little bird,
its name was Enza.
I opened the window,
and in-flu-enza.
History
Timeline
First wave of early 1918

The pandemic is conventionally marked as having begun on 4 March 1918 with the recording of the case of Albert Gitchell, an army cook at Camp Funston in Kansas, United States, despite there having been cases before him.[88] The disease had already been observed 200 miles (320 km) away in Haskell County as early as January 1918, prompting local doctor Loring Miner to warn the editors of the U.S. Public Health Service's academic journal Public Health Reports.[80] Within days of the 4 March first case at Camp Funston, 522 men at the camp had reported sick.[89] By 11 March 1918, the virus had reached Queens, New York.[90] Failure to take preventive measures in March/April was later criticized.[91]
As the U.S. had entered World War I, the disease quickly spread from Camp Funston, a major training ground for troops of the American Expeditionary Forces, to other U.S. Army camps and Europe, becoming an epidemic in the Midwest, East Coast, and French ports by April 1918, and reaching the Western Front by the middle of the month.[88] It then quickly spread to the rest of France, Great Britain, Italy, and Spain and in May reached Wrocław and Odessa.[88] After the signing of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (March 1918), Germany started releasing Russian prisoners of war, who then brought the disease to their country.[92] It reached North Africa, India, and Japan in May, and soon after had likely gone around the world as there had been recorded cases in Southeast Asia in April.[93] In June an outbreak was reported in China.[94] After reaching Australia in July, the wave started to recede.[93]
The first wave of the flu lasted from the first quarter of 1918 and was relatively mild.[95] Mortality rates were not appreciably above normal;[2] in the United States ~75,000 flu-related deaths were reported in the first six months of 1918, compared to ~63,000 deaths during the same time period in 1915.[96] In Madrid, Spain, fewer than 1,000 people died from influenza between May and June 1918.[97] There were no reported quarantines during the first quarter of 1918. However, the first wave caused a significant disruption in the military operations of World War I, with three-quarters of French troops, half the British forces, and over 900,000 German soldiers sick.[98]
Deadly second wave of late 1918


The second wave began in the second half of August 1918, probably spreading to Boston, Massachusetts and Freetown, Sierra Leone, by ships from Brest, where it had likely arrived with American troops or French recruits for naval training.[98] From the Boston Navy Yard and Camp Devens (later renamed Fort Devens), about 30 miles west of Boston, other U.S. military sites were soon afflicted, as were troops being transported to Europe.[99] Helped by troop movements, it spread over the next two months to all of North America, and then to Central and South America, also reaching Brazil and the Caribbean on ships.[100] In July 1918, the Ottoman Empire saw its first cases in some soldiers.[101] From Freetown, the pandemic continued to spread through West Africa along the coast, rivers, and the colonial railways, and from railheads to more remote communities, while South Africa received it in September on ships bringing back members of the South African Native Labour Corps returning from France.[100] From there it spread around southern Africa and beyond the Zambezi, reaching Ethiopia in November.[102] On 15 September, New York City saw its first fatality from influenza.[103] The Philadelphia Liberty Loans Parade, held in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, on 28 September 1918 to promote government bonds for World War I, resulted in 12,000 deaths after a major outbreak of the illness spread among people who had attended the parade.[104]
From Europe, the second wave swept through Russia in a southwest–northeast diagonal front, as well as being brought to Arkhangelsk by the North Russia intervention, and then spread throughout Asia following the Russian Civil War and the Trans-Siberian railway, reaching Iran (where it spread through the holy city of Mashhad), and then later India in September, as well as China and Japan in October.[105] The celebrations of the Armistice of 11 November 1918 also caused outbreaks in Lima and Nairobi, but by December the wave was mostly over.[106]
The second wave of the 1918 pandemic was much more deadly than the first. The first wave had resembled typical flu epidemics; those most at risk were the sick and elderly, while younger, healthier people recovered easily. October 1918 was the month with the highest fatality rate of the whole pandemic.[107] In the United States, ~292,000 deaths were reported between September–December 1918, compared to ~26,000 during the same time period in 1915.[96] The Netherlands reported over 40,000 deaths from influenza and acute respiratory disease. Bombay reported ~15,000 deaths in a population of 1.1 million.[108] The 1918 flu pandemic in India was especially deadly, with an estimated 12.5–20 million deaths in the last quarter of 1918 alone.[95][page needed]
Third wave of 1919

Pandemic activity persisted, in general, into 1919 in many places. This persistence in activity is possibly attributable to climate, specifically in the Northern Hemisphere, where it was winter and thus the usual time for influenza activity.[109][110] The pandemic nonetheless continued into 1919 largely independent of region and climate.[109]
Cases began to rise again in some parts of the United States as early as late November 1918,[111] with the Public Health Service issuing its first report of a "recrudescence of the disease" being felt in "widely scattered localities" in early December.[112] This resurgent activity varied across the country, however, possibly on account of differing restrictions.[110] Michigan, for example, experienced a swift resurgence of influenza that reached its peak in December, possibly as a result of the lifting of the ban on public gatherings.[113] Pandemic interventions, such as bans on public gatherings and the closing of schools, were reimposed in many places in an attempt to suppress the spread.[112]
There was "a very sudden and very marked rise in general death rate" in most cities in January 1919; nearly all experienced "some degree of recrudescence" of the flu in January and February.[114]: 153–154 Significant outbreaks occurred in cities including Los Angeles,[115] New York City,[1] Memphis, Nashville, San Francisco, and St. Louis.[116] By 21 February, with some local variation, influenza activity was reported to have been declining since mid-January in all parts of the country.[117] Following this "first great epidemic period" that had commenced in October 1918, deaths from pneumonia and influenza were "somewhat below average" in the large cities of the United States between May 1919 and January 1920.[114]: 158 Nonetheless, nearly 160,000 deaths were attributed to these causes in the first six months of 1919.[118]
It was not until later in the winter and into the spring that a clearer resurgence appeared in Europe. A significant third wave had developed in England and Wales by mid-February, peaking in early March, though it did not fully subside until May.[119] France also experienced a significant wave that peaked in February, alongside the Netherlands. Norway, Finland, and Switzerland saw recrudescences of pandemic activity in March, and Sweden in April.[120]
Much of Spain was affected by "a substantial recrudescent wave" of influenza between January and April 1919.[121] Portugal experienced a resurgence in pandemic activity that lasted from March to September 1919, with the greatest impact being felt on the west coast and in the north of the country; all districts were affected between April and May specifically.[122]
Influenza entered Australia for the first time in January 1919 after a strict maritime quarantine had shielded the country through the latter part of 1918.[123] It assumed epidemic proportions first in Melbourne, peaking in mid-February.[124] The flu soon appeared in neighboring New South Wales and South Australia and then spread across the country throughout the year.[123] New South Wales experienced its first wave of infection between mid-March and late May,[125] while a second, more severe wave occurred in Victoria between April and June.[124]
Land quarantine measures hindered the spread of the disease, resulting in varied experiences of exposures and outbreaks among the various states. Queensland was not infected until late April; Western Australia avoided the disease until early June, and Tasmania remained free from it until mid-August.[123] Out of the six states, Victoria and New South Wales experienced generally more extensive epidemics. Each experienced another significant wave of illness over the winter. The second epidemic in New South Wales was more severe than the first,[125] while Victoria saw a third wave that was somewhat less extensive than its second, more akin to its first.[124]
The disease also reached other parts of the world for the first time in 1919, such as Madagascar, which saw its first cases in April; the outbreak had spread to practically all sections of the island by June.[126] In other parts, influenza recurred in the form of a true "third wave". Hong Kong experienced another outbreak in June,[127] as did South Africa during its fall and winter months in the Southern Hemisphere.[128][129][130] New Zealand also experienced some cases in May.[131]
Parts of South America experienced a resurgence of pandemic activity throughout 1919. A third wave hit Brazil between January and June.[109] Between July 1919 and February 1920, Chile, which had been affected for the first time just in October 1918, experienced a severe second wave, with mortality peaking in August 1919.[132] Montevideo similarly experienced a second outbreak between July and September.[133]
The third wave particularly affected Spain, Serbia, Mexico and Great Britain, resulting in hundreds of thousands of deaths.[134] It was in general less severe than the second wave but still much more deadly than the initial first wave.
Fourth wave of 1920

In the Northern Hemisphere, fears of a "recurrence" of the flu grew as fall approached. Experts cited the history of past flu epidemics, such as that of 1889–1890, to predict that such a recurrence a year later was not unlikely,[135][136] though not all agreed.[137] In September 1919, U.S. Surgeon General Rupert Blue said a return of the flu later in the year would "probably, but by no means certainly," occur.[138] France had readied a public information campaign before the end of the summer,[139] and Britain began preparations in the fall with the manufacture of vaccine.[140]
In Japan, the flu broke out again in December and spread rapidly throughout the country, a fact attributed at the time to the coming of cold weather.[141][142] Pandemic-related measures were renewed to check the spread of the outbreak, and health authorities recommended the use of masks.[142] The epidemic intensified in the latter part of December before swiftly peaking in January.[143]
Between October 1919 and 23 January 1920, 780,000 cases were reported across the country, with at least 20,000 deaths recorded by that date. This apparently reflected "a condition of severity three times greater than for the corresponding period of" 1918–1919, during Japan's first epidemic.[143] Nonetheless, the disease was regarded as being milder than it had been the year before, albeit more infectious.[144] Despite its rapid peak at the beginning of the year, the outbreak persisted throughout the winter, before subsiding in the spring.[145]
In the United States, there were "almost continuously isolated or solitary cases" of flu throughout the spring and summer months of 1919.[146] An increase in scattered cases became apparent as early as September,[147] but Chicago experienced one of the first major outbreaks of the flu beginning in the middle of January.[148] The Public Health Service announced it would take steps to "localize the epidemic",[149] but the disease was already causing a simultaneous outbreak in Kansas City and quickly spread outward from the center of the country in no clear direction.[146] A few days after its first announcement, PHS issued another assuring that the disease was under the control of state health authorities and that an outbreak of epidemic proportions was not expected.[150]
It became apparent within days of the start of Chicago's explosive growth in cases that the flu was spreading in the city at an even faster rate than in winter 1919, though fewer were dying.[151] Within a week, new cases in the city had surpassed its peak during the 1919 wave.[152] Around the same time, New York City began to see its own sudden increase in cases,[153] and other cities around the country were soon to follow.[154] Certain pandemic restrictions, such as the closing of schools and theaters and the staggering of business hours to avoid congestion, were reimposed in cities like Chicago,[155] Memphis,[156] and New York City.[157] As they had during the epidemic in fall 1918, schools in New York City remained open,[157] while those in Memphis were shuttered as part of more general restrictions on public gatherings.[156]

The fourth wave in the United States subsided as swiftly as it had appeared, reaching a peak in early February.[158] "An epidemic of considerable proportions marked the early months of 1920", the U.S. Mortality Statistics would later note; according to data at this time, the epidemic resulted in one third as many deaths as the 1918–1919 experience.[159] New York City alone reported 6,374 deaths between December 1919 and April 1920, almost twice the number of the first wave in spring 1918.[1] Other U.S. cities including Detroit, Milwaukee, Kansas City, Minneapolis, and St. Louis were hit particularly hard, with death rates higher than all of 1918.[116] The Territory of Hawaii experienced its peak of the pandemic in early 1920, recording 1,489 deaths from flu-related causes, compared with 615 in 1918 and 796 in 1919.[160]
Poland experienced a devastating outbreak during the winter months, with its capital Warsaw reaching a peak of 158 deaths in a single week, compared to the peak of 92 reached in December 1918; however, the 1920 epidemic passed in a matter of weeks, while the 1918–1919 wave had developed over the entire second half of 1918.[161] By contrast, the outbreak in western Europe was considered "benign", with the age distribution of deaths beginning to take on that of seasonal flu.[162] Five countries in Europe (Spain, Denmark, Finland, Germany and Switzerland) recorded a late peak between January–April 1920.[120]
Mexico experienced a fourth wave between February and March. In South America, Peru experienced "asynchronous recrudescent waves" throughout the year. A severe third wave hit Lima, the capital city, between January and March, resulting in an all-cause excess mortality rate approximately four times greater than that of the 1918–1919 wave. Ica similarly experienced another severe pandemic wave in 1920, between July and October.[163] A fourth wave also occurred in Brazil, in February.[109]
Korea and Taiwan, both colonies of Japan at this time, also experienced pronounced outbreaks in late 1919 and early 1920.[164][165]
Post-pandemic
By mid-1920, the pandemic was largely considered to be "over" by the public as well as governments.[166] Though parts of Chile experienced a third, milder wave between November 1920 and March 1921,[132] the flu seemed to be mostly absent through the winter of 1920–1921.[114]: 167 In the United States, for example, deaths from pneumonia and influenza were "very much lower than for many years".[114]: 167
Influenza began to be reported again from many places in 1921.[114]: 168 The pandemic continued to be felt in Chile, where a fourth wave affected seven of its 24 provinces between June and December 1921.[132] The winter of 1921–1922 was the first major reappearance of seasonal influenza in the Northern Hemisphere after the pandemic ended, in many parts its most significant occurrence since the main pandemic in late 1918. Northwestern Europe was particularly affected. All-cause mortality in the Netherlands approximately doubled in January 1922 alone.[114]: 168 In Helsinki, a major epidemic (the fifth since 1918) prevailed between November and December 1921.[167] The flu was also widespread in the United States, its prevalence in California reportedly greater in early March 1922 than at any point since the pandemic ended in 1920.[114]: 172
In the years after 1920, the disease, a novel one in 1918, assumed a more familiar nature, coming to represent at least one form of the "seasonal flu". The virus, H1N1, remained endemic, occasionally causing more severe or otherwise notable outbreaks as it gradually evolved over the years.[168] The period since its initial appearance in 1918 has been termed a "pandemic era", in which all flu pandemics since its emergence have been caused by its own descendants.[169] Following the first of these post-1918 pandemics, in 1957, the virus was totally displaced by the novel H2N2, the reassortant product of the human H1N1 and an avian influenza virus, which thereafter became the active influenza A virus in humans.[168]
In 1977, an influenza virus bearing a very close resemblance to the seasonal H1N1, which had not been seen since the 1950s, appeared in Russia and subsequently initiated a "technical" pandemic that principally affected those 26 years of age and younger.[170][171] While some natural explanations, such as the virus remaining in some frozen state for 20 years,[171] have been proposed to explain this unprecedented[172] phenomenon, the nature of influenza itself has been cited in favor of human involvement of some kind, such as an accidental leak from a lab where the old virus had been preserved for research purposes.[171] Following this miniature pandemic, the reemerged H1N1 became endemic once again but did not displace the other active influenza A virus, H3N2 (which itself had displaced H2N2 through a pandemic in 1968).[170][168] For the first time, two influenza A viruses were observed in cocirculation.[173] This state of affairs has persisted even after 2009, when a novel H1N1 virus emerged, sparked a pandemic, and thereafter took the place of the seasonal H1N1 to circulate alongside H3N2.[173]
Potential origins
Despite its name, historical and epidemiological data cannot identify the geographic origin of the Spanish flu.[2] However, several theories have been proposed.
United States
The first confirmed cases originated in the United States. Historian Alfred W. Crosby stated in 2003 that the flu originated in Kansas,[174] and author John M. Barry described a January 1918 outbreak in Haskell County, Kansas, as the point of origin in his 2004 article.[80]
A 2018 study of tissue slides and medical reports led by evolutionary biology professor Michael Worobey found evidence against the disease originating from Kansas, as those cases were milder and had fewer deaths compared to the infections in New York City in the same period. The study did find evidence through phylogenetic analyses that the virus likely had a North American origin, though it was not conclusive. In addition, the haemagglutinin glycoproteins of the virus suggest that it originated long before 1918, and other studies suggest that the reassortment of the H1N1 virus likely occurred in or around 1915.[175]
Europe


The major U.K. troop staging and hospital camp in Étaples in France has been theorized by virologist John Oxford as being at the center of the Spanish flu.[177] His study found that in late 1916 the Étaples camp was hit by the onset of a new disease with high mortality that caused symptoms similar to the flu.[178][177] According to Oxford, a similar outbreak occurred in March 1917 at army barracks in Aldershot,[179] and military pathologists later recognized these early outbreaks as the same disease as the Spanish flu.[180][177] The overcrowded camp and hospital at Étaples was an ideal environment for the spread of a respiratory virus.
The hospital treated thousands of victims of poison gas attacks, and other casualties of war, and 100,000 soldiers passed through the camp every day. It also was home to a piggery and poultry was regularly brought in from surrounding villages to feed the camp. Oxford and his team postulated that a precursor virus, harbored in birds, mutated and then migrated to pigs kept near the front.[179][180]
A report published in 2016 in the Journal of the Chinese Medical Association found evidence that the 1918 virus had been circulating in the European armies for months and possibly years before the 1918 pandemic.[181] Political scientist Andrew Price-Smith published data from the Austrian archives suggesting the influenza began in Austria in early 1917.[182]
A 2009 study in Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses found that Spanish flu mortality simultaneously peaked within the two-month period of October and November 1918 in all fourteen European countries analyzed, which is inconsistent with the pattern that researchers would expect if the virus had originated somewhere in Europe and then spread outwards.[120]
China
In 1993, Claude Hannoun, the leading expert on the Spanish flu at the Pasteur Institute, asserted the precursor virus was likely to have come from China and then mutated in the United States near Boston and from there spread to Brest, France, Europe's battlefields, the rest of Europe, and the rest of the world, with Allied soldiers and sailors as the main disseminators.[183] Hannoun considered several alternative hypotheses of origin, such as Spain, Kansas, and Brest, as being possible, but not likely.[183]
In 2014, historian Mark Humphries argued that the mobilization of 96,000 Chinese laborers to work behind the British and French lines might have been the source of the pandemic. Humphries, of the Memorial University of Newfoundland in St. John's, based his conclusions on newly unearthed records. He found archival evidence that a respiratory illness that struck northern China (where the laborers came from) in November 1917 was identified a year later by Chinese health officials as identical to the Spanish flu.[184][185] Unfortunately, no tissue samples have survived for modern comparison.[186] Nevertheless, there were some reports of respiratory illness on parts of the path the laborers took to get to Europe, which also passed through North America.[186]
China was one of the few regions of the world seemingly less affected by the Spanish flu pandemic, where several studies have documented a comparatively mild flu season in 1918.[187][188][189] (Although this is disputed due to lack of data during the Warlord Period, see Around the globe.) This has led to speculation that the Spanish flu pandemic originated in China,[189][190] as the lower rates of flu mortality may be explained by the Chinese population's previously acquired immunity to the flu virus.[173][189] In the Guangdong Province it was reported that early outbreaks of influenza in 1918 disproportionately impacted young men. The June outbreak infected children and adolescents between 11 and 20 years of age, while the October outbreak was most common in those aged 11 to 15.[191]
A report published in 2016 in the Journal of the Chinese Medical Association found no evidence that the 1918 virus was imported to Europe via Chinese and Southeast Asian soldiers and workers and instead found evidence of its circulation in Europe before the pandemic.[181] The 2016 study found that the low flu mortality rate (an estimated one in a thousand) recorded among the Chinese and Southeast Asian workers in Europe suggests that the Asian units were not different from other Allied military units in France at the end of 1918 and, thus, were not a likely source of a new lethal virus.[181] Further evidence against the disease being spread by Chinese workers was that workers entered Europe through other routes that did not result in a detectable spread, making them unlikely to have been the original hosts.[175]
Epidemiology and pathology
Transmission and mutation
The basic reproduction number of the virus was between 2 and 3.[192] The close quarters and massive troop movements of World War I hastened the pandemic, and probably both increased transmission and augmented mutation. The war may also have reduced people's resistance to the virus. Some speculate the soldiers' immune systems were weakened by malnourishment, as well as the stresses of combat and chemical attacks, increasing their susceptibility.[193][194] A large factor in the worldwide occurrence of the flu was increased travel. Modern transportation systems made it easier for soldiers, sailors, and civilian travelers to spread the disease.[195] Another was lies and denial by governments, leaving the population ill-prepared to handle the outbreaks.[196]
The severity of the second wave has been attributed to the circumstances of the First World War.[197] In civilian life, natural selection favors a mild strain. Those who get very ill stay home, and those mildly ill continue with their lives, preferentially spreading the mild strain. In the trenches, natural selection was reversed. Soldiers with a mild strain stayed where they were, while the severely ill were sent on crowded trains to crowded field hospitals, spreading the deadlier virus. The second wave began, and the flu quickly spread around the world again. Consequently, during modern pandemics, health officials look for deadlier strains of a virus when it reaches places with social upheaval.[198] The fact that most of those who recovered from first-wave infections had become immune showed that it must have been the same strain of flu. This was most dramatically illustrated in Copenhagen, which escaped with a combined mortality rate of just 0.29% (0.02% in the first wave and 0.27% in the second wave) because of exposure to the less-lethal first wave.[199] For the rest of the population, the second wave was far more deadly; the most vulnerable people were those like the soldiers in the trenches – adults who were young and fit.[200]
After the lethal second wave struck in late 1918, new cases dropped abruptly. In Philadelphia, for example, 4,597 people died in the week ending 16 October, but by 11 November, influenza had almost disappeared from the city. One explanation for the rapid decline in the lethality of the disease is that doctors became more effective in the prevention and treatment of pneumonia that developed after the victims had contracted the virus. However, John Barry stated in his 2004 book The Great Influenza: The Epic Story of the Deadliest Plague In History that researchers have found no evidence to support this position.[80] Another theory holds that the 1918 virus mutated extremely rapidly to a less lethal strain. Such evolution of influenza is a common occurrence: there is a tendency for pathogenic viruses to become less lethal with time, as the hosts of more dangerous strains tend to die out.[80] Fatal cases did continue into 1919, however. One notable example was that of ice hockey player Joe Hall, who, while playing for the Montreal Canadiens, fell victim to the flu in April after an outbreak that resulted in the cancellation of the 1919 Stanley Cup Finals.[201]
Signs and symptoms
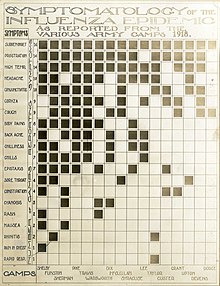
The majority of the infected experienced only the typical flu symptoms of sore throat, headache, and fever, especially during the first wave.[202] However, during the second wave, the disease was much more serious, often complicated by bacterial pneumonia, which was often the cause of death.[202] This more serious type would cause heliotrope cyanosis to develop, whereby the skin would first develop two mahogany spots over the cheekbones which would then over a few hours spread to color the entire face blue, followed by black coloration first in the extremities and then further spreading to the limbs and the torso.[202] After this, death would follow within hours or days due to the lungs being filled with fluids.[202] Other signs and symptoms reported included spontaneous mouth and nosebleeds, miscarriages for pregnant women, a peculiar smell, teeth and hair falling out, delirium, dizziness, insomnia, loss of hearing or smell, and impaired vision.[202] One observer wrote, "One of the most striking of the complications was hemorrhage from mucous membranes, especially from the nose, stomach, and intestine. Bleeding from the ears and petechial hemorrhages in the skin also occurred".[203]
The majority of deaths were from bacterial pneumonia,[204][205][206] a common secondary infection associated with influenza. This pneumonia was itself caused by common upper respiratory-tract bacteria, which were able to get into the lungs via the damaged bronchial tubes of the victims.[207] The virus also killed people directly by causing massive hemorrhages and edema in the lungs.[206] Modern analysis has shown the virus to be particularly deadly because in animal trials it triggers an overreaction of the body's immune system (sometimes referred to as a cytokine storm).[80] The strong immune reactions of young adults were postulated to have ravaged the body, whereas the weaker immune reactions of children and middle-aged adults resulted in fewer deaths among those groups.[208]
Misdiagnosis
Because the virus that caused the disease was too small to be seen under a microscope at the time, there were problems with correctly diagnosing it.[209] The bacterium Haemophilus influenzae was instead mistakenly thought to be the cause, as it was big enough to be seen and was present in many, though not all, patients.[209] For this reason, a vaccine that was used against that bacillus did not make an infection rarer but did decrease the death rate.[210]
During the deadly second wave there were also fears that it was in fact plague, dengue fever, or cholera.[211] Another common misdiagnosis was typhus, which was common in circumstances of social upheaval, and was therefore also affecting Russia in the aftermath of the October Revolution.[211] In Chile, the view of the country's elite was that the nation was in severe decline, and therefore doctors assumed that the disease was typhus caused by poor hygiene, and not an infectious one, causing a mismanaged response which did not ban mass gatherings.[211]
The role of climate conditions

Studies have shown that the immune system of Spanish flu victims could have been weakened by adverse climate conditions which were particularly unseasonably cold and wet for extended periods of time during the duration of the pandemic. This affected especially WWI troops exposed to incessant rains and lower-than-average temperatures for the duration of the conflict, and especially during the second wave of the pandemic. Ultra-high-resolution climate data combined with highly detailed mortality records analyzed at Harvard University and the Climate Change Institute at the University of Maine identified a severe climate anomaly that impacted Europe from 1914 to 1919, with several environmental indicators directly influencing the severity and spread of the Spanish flu pandemic.[10] Specifically, a significant increase in precipitation affected all of Europe during the second wave of the pandemic, from September to December 1918. Mortality figures follow closely the concurrent increase in precipitation and decrease in temperatures. Several explanations have been proposed for this, including the fact that lower temperatures and increased precipitation provided ideal conditions for virus replication and transmission, while also negatively affecting the immune systems of soldiers and other people exposed to the inclement weather, a factor proven to increase likelihood of infection by both viruses and pneumococcal co-morbid infections documented to have affected a large percentage of pandemic victims (one fifth of them, with a 36% mortality rate).[212][213][214][215][216] A six-year climate anomaly (1914–1919) brought cold, marine air to Europe, drastically changing its weather, as documented by eyewitness accounts and instrumental records, reaching as far as the Gallipoli campaign, in Turkey, where ANZAC troops suffered extremely cold temperatures despite the normally Mediterranean climate of the region. The climate anomaly likely influenced the migration of H1N1 avian vectors which contaminate bodies of water with their droppings, reaching 60% infection rates in autumn.[217][218][219] The climate anomaly has been associated with an anthropogenic increase in atmospheric dust, due to the incessant bombardment; increased nucleation due to dust particles (cloud condensation nuclei) contributed to increased precipitation.[220][221][222]
Responses
Public health management
While systems for alerting public health authorities of infectious spread did exist in 1918, they did not generally include influenza, leading to a delayed response.[225] Nevertheless, actions were taken. Maritime quarantines were declared on islands such as Iceland, Australia, and American Samoa, saving many lives.[225] Social distancing measures were introduced, for example closing schools, theatres, and places of worship, limiting public transportation, and banning mass gatherings.[226] Wearing face masks became common in some places, such as Japan, though there were debates over their efficacy.[226] There was also some resistance to their use, as exemplified by the Anti-Mask League of San Francisco. Vaccines were also developed, but as these were based on bacteria and not the actual virus, they could only help with secondary infections.[226] The actual enforcement of various restrictions varied.[227] To a large extent, the New York City health commissioner ordered businesses to open and close on staggered shifts to avoid overcrowding on the subways.[228]
A later study found that measures such as banning mass gatherings and requiring the wearing of face masks could cut the death rate up to 50 percent, but this was dependent on their being imposed early in the outbreak and not being lifted prematurely.[229]
Medical treatment
As there were no antiviral drugs to treat the virus, and no antibiotics to treat the secondary bacterial infections, doctors would rely on a random assortment of medicines with varying degrees of effectiveness, such as aspirin, quinine, arsenics, digitalis, strychnine, epsom salts, castor oil, and iodine.[230] Treatments of traditional medicine, such as bloodletting, ayurveda, and kampo were also applied.[231]
Information dissemination
Due to World War I, many countries engaged in wartime censorship, and suppressed reporting of the pandemic.[232] For example, the Italian newspaper Corriere della Sera was prohibited from reporting daily death tolls.[233] The newspapers of the time were also generally paternalistic and worried about mass panic.[233] Misinformation also spread along with the disease. In Ireland there was a belief that noxious gases were rising from the mass graves of Flanders Fields and being "blown all over the world by winds".[234] There were also rumors that the Germans were behind it, for example by poisoning the aspirin manufactured by Bayer, or by releasing poison gas from U-boats.[235]
Mortality
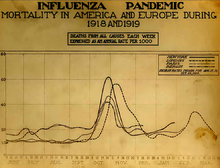
Around the globe

The Spanish flu infected around 500 million people, about one-third of the world's population.[2] Estimates as to how many infected people died vary greatly, but the flu is regardless considered to be one of the deadliest pandemics in history.[238][239] An early estimate from 1927 put global mortality at 21.6 million.[4] An estimate from 1991 states that the virus killed between 25 and 39 million people.[95] A 2005 estimate put the death toll at 50 million (about 3% of the global population), and possibly as high as 100 million (more than 5%).[203][240] However, a 2018 reassessment in the American Journal of Epidemiology estimated the total to be about 17 million,[4] though this has been contested.[241] With a world population of 1.8 to 1.9 billion,[242] these estimates correspond to between 1 and 6 percent of the population.
Estimates done in 2021 by John M. Barry have the total death toll alone at well above 100 million.[7]
A 2009 study in Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses based on data from fourteen European countries estimated a total of 2.64 million excess deaths in Europe attributable to the Spanish flu during the major 1918–1919 phase of the pandemic, in line with the three prior studies from 1991, 2002, and 2006 that calculated a European death toll of between 2 million and 2.3 million. This represents a mortality rate of about 1.1% of the European population (c. 250 million in 1918), considerably higher than the mortality rate in the U.S., which the authors hypothesize is likely due to the severe effects of the war in Europe.[120] The excess mortality rate in the U.K. has been estimated at 0.28%–0.4%, far below this European average.[4]
Some 12–17 million people died in India, about 5% of the population.[243] The death toll in India's British-ruled districts was 13.88 million.[244] Another estimate gives at least 12 million dead.[245] The decade between 1911 and 1921 was the only census period in which India's population fell, mostly due to devastation of the Spanish flu pandemic.[246][247] While India is generally described as the country most severely affected by the Spanish flu, at least one study argues that other factors may partially account for the very high excess mortality rates observed in 1918, citing unusually high 1917 mortality and wide regional variation (ranging from 0.47% to 6.66%).[4] A 2006 study in The Lancet also noted that Indian provinces had excess mortality rates ranging from 2.1% to 7.8%, stating: "Commentators at the time attributed this huge variation to differences in nutritional status and diurnal fluctuations in temperature."[248]
In Finland, 20,000 died out of 210,000 infected.[249] In Sweden, 34,000 died.[250]
In Japan, the flu killed nearly 500,000 people over two waves between 1918 and 1920, with nearly 300,000 excess deaths between October 1918 and May 1919 and 182,000 between December 1919 and May 1920.[145]
In the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia), 1.5 million were assumed to have died among 30 million inhabitants.[251] In Tahiti, 13% of the population died during one month. Similarly, in Western Samoa 22% of the population of 38,000 died within two months.[252]
In Istanbul, capital of the Ottoman Empire, 6,403[253] to 10,000[101] died, giving the city a mortality rate of at least 0.56%.[253]
In New Zealand, the flu killed an estimated 6,400 Pākehā (or "New Zealanders primarily of European descent") and 2,500 indigenous Māori in six weeks, with Māori dying at eight times the rate of Pākehā.[254][255]
In Australia, the flu killed around 12,000[256] to 20,000 people.[257] The country's death rate, 2.7 per 1,000 people, was one of the lowest recorded compared with other countries at the time; however, as much as 40 percent of the population were infected, and a mortality rate of 50 percent was recorded by some Aboriginal communities.[258][257] New South Wales and Victoria saw the greatest relative mortality, with 3.19 and 2.40 deaths per 1,000 people respectively, while Western Australia, Queensland, Southern Australia, and Tasmania experienced rates of 1.70, 1.14, 1.13, and 1.09 per 1,000 respectively. In Queensland, at least one-third of deaths recorded were in the Aboriginal population.[124]
In the U.S., about 28% of the population of 105 million became infected, and 500,000 to 850,000 died (0.48 to 0.81 percent of the population).[259][260][261] Native American tribes were particularly hard hit. In the Four Corners area, there were 3,293 registered deaths among Native Americans.[262] Entire Inuit and Alaskan Native village communities died in Alaska.[263] In Canada, 50,000 died.[264]
In Brazil, 300,000 died, including president Rodrigues Alves.[265]
In the UK, as many as 250,000 died; in France, more than 400,000.[266]
In Ghana, the influenza epidemic killed at least 100,000 people.[267] Tafari Makonnen (the future Haile Selassie, Emperor of Ethiopia) was one of the first Ethiopians who contracted influenza but survived.[268][269] Many of his subjects did not; estimates for fatalities in the capital city, Addis Ababa, range from 5,000 to 10,000, or higher.[270]
The death toll in Russia has been estimated at 450,000, though the epidemiologists who suggested this number called it a "shot in the dark".[95] If it is correct, Russia lost roughly 0.4% of its population, meaning it suffered the lowest influenza-related mortality in Europe. Another study considers this number unlikely, given that the country was in the grip of a civil war, and the infrastructure of daily life had broken down; the study suggests that Russia's death toll was closer to 2%, or 2.7 million people.[271]
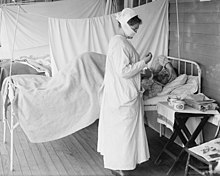
Devastated communities
Even in areas where mortality was low, so many adults were incapacitated that much of everyday life was hampered. Some communities closed all stores or required customers to leave orders outside. There were reports that healthcare workers could not tend the sick nor the gravediggers bury the dead because they too were ill. Mass graves were dug by steam shovel and bodies buried without coffins in many places.[272]
Bristol Bay, a region of Alaska populated by indigenous people, suffered a death rate of 40 percent of the total population, with some villages entirely disappearing.[273]
Nenana, Alaska, managed to avoid the extent of the pandemic between 1918 and 1919, but the flu at last reached the town in spring 1920. Reports suggested that during the first two weeks of May, the majority of the town's population became infected; 10% of the population were estimated to have died, most of whom were Alaska Natives.[274]
Several Pacific island territories were hit particularly hard. The pandemic reached them from New Zealand, which was too slow to implement measures to prevent ships, such as Talune, carrying the flu from leaving its ports. From New Zealand, the flu reached Tonga (killing 8% of the population), Nauru (16%), and Fiji (5%, 9,000 people).[275] Worst affected was Western Samoa, formerly German Samoa, which had been occupied by New Zealand in 1914. 90% of the population was infected; 30% of adult men, 22% of adult women, and 10% of children died. By contrast, Governor John Martin Poyer prevented the flu from reaching neighboring American Samoa by imposing a blockade.[275] The disease spread fastest through the higher social classes among the indigenous peoples, because of the custom of gathering oral tradition from chiefs on their deathbeds; many community elders were infected through this process.[276]
In Iran, the mortality was very high: according to an estimate, between 902,400 and 2,431,000, or 8% to 22% of the total population died.[277] The country was going through the Persian famine of 1917–1919 concurrently.
In Ireland, during the worst 12 months, the Spanish flu accounted for one-third of all deaths.[278][279]
In South Africa it is estimated that about 300,000 people amounting to 6% of the population died within six weeks. Government actions in the early stages of the virus' arrival in the country in September 1918 are believed to have unintentionally accelerated its spread throughout the country.[280] Almost a quarter of the working population of Kimberley, consisting of workers in the diamond mines, died.[281] In British Somaliland, one official estimated that 7% of the native population died.[282] This huge death toll resulted from an extremely high infection rate of up to 50% and the extreme severity of the symptoms.[95]
Other areas
In the Pacific, American Samoa[283] and the French colony of New Caledonia[284] succeeded in preventing even a single death from influenza through effective quarantines. However, the outbreak was delayed into 1926 for American Samoa and 1921 for New Caledonia as the quarantine period ended.[285] On American Samoa, at least 25% of the island residents were clinically attacked and 0.1% died, and on New Caledonia, there was widespread illness and 0.1% population died.[285] Australia also managed to avoid the first two waves with a quarantine.[225] Iceland protected a third of its population from exposure by blocking the main road of the island.[225] By the end of the pandemic, the isolated island of Marajó, in Brazil's Amazon River Delta had not reported an outbreak.[286] Saint Helena also reported no deaths.[287]

Estimates for the death toll in China have varied widely,[288][95] a range which reflects the lack of centralized collection of health data at the time due to the Warlord period. China may have experienced a relatively mild flu season in 1918 compared to other areas of the world.[189][173][289] However, some reports from its interior suggest that mortality rates from influenza were perhaps higher in at least a few locations in China in 1918.[271] At the very least, there is little evidence that China as a whole was seriously affected by the flu compared to other countries in the world.[290]
The first estimate of the Chinese death toll was made in 1991 by Patterson and Pyle, which estimated a toll of between 5 and 9 million. However, this 1991 study was criticized by later studies due to flawed methodology, and newer studies have published estimates of a far lower mortality rate in China.[187][291] For instance, Iijima in 1998 estimates the death toll in China to be between 1 and 1.28 million based on data available from Chinese port cities.[292] The lower estimates of the Chinese death toll are based on the low mortality rates that were found in Chinese port cities (for example, Hong Kong) and on the assumption that poor communications prevented the flu from penetrating the interior of China.[288] However, some contemporary newspaper and post office reports, as well as reports from missionary doctors, suggest that the flu did penetrate the Chinese interior and that influenza was severe in at least some locations in the countryside of China.[271]
Although medical records from China's interior are lacking, extensive medical data were recorded in Chinese port cities, such as then British-controlled Hong Kong, Canton, Peking, Harbin and Shanghai. These data were collected by the Chinese Maritime Customs Service, which was largely staffed by non-Chinese foreigners, such as the British, French, and other European colonial officials in China.[293] As a whole, data from China's port cities show low mortality rates compared to other cities in Asia.[293] For example, the British authorities at Hong Kong and Canton reported a mortality rate from influenza at a rate of 0.25% and 0.32%, much lower than the reported mortality rate of other cities in Asia, such as Calcutta or Bombay, where influenza was much more devastating.[293] Similarly, in the city of Shanghai – which had a population of over 2 million in 1918 – there were only 266 recorded deaths from influenza among the Chinese population in 1918.[293] If extrapolated from the extensive data recorded from Chinese cities, the suggested mortality rate from influenza in China as a whole in 1918 was likely lower than 1% – much lower than the world average (which was around 3–5%).[293] In contrast, Japan and Taiwan had reported a mortality rate from influenza around 0.45% and 0.69% respectively, higher than the mortality rate collected from data in Chinese port cities, such as Hong Kong (0.25%), Canton (0.32%), and Shanghai.[293]
However, it is noted that the influenza mortality rate in Hong Kong and Canton are under-recorded, because only the deaths that occurred in colony hospitals were counted.[293] Similarly, in Shanghai, these statistics are limited to that area of the city under the control of the health section of the Shanghai International Settlement, and the actual death toll in Shanghai was much higher.[293] The medical records from China's interior indicate that, compared to cities, rural communities have substantially higher mortality rate.[294] A published influenza survey in Houlu County, Hebei Province, found that the case fatality rate was 9.77% and 0.79% of county population died from influenza in October and November 1918.[295]
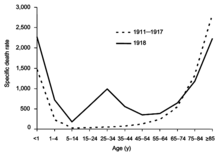
Patterns of fatality
The pandemic mostly killed young adults. In 1918–1919, 99% of pandemic influenza deaths in the U.S. occurred in people under 65, and nearly half of deaths were in young adults 20 to 40 years old. In 1920, the mortality rate among people under 65 had decreased sixfold to half the mortality rate of people over 65, but 92% of deaths still occurred in people under 65.[296] This is unusual since influenza is typically most deadly to weak individuals, such as infants under age two, adults over age 70, and the immunocompromised. In 1918, older adults may have had partial protection caused by exposure to the 1889–1890 flu pandemic, known as the "Russian flu".[297] According to historian John M. Barry, the most vulnerable of all – "those most likely, of the most likely", to die – were pregnant women. He reported that in thirteen studies of hospitalized women in the pandemic, the death rate ranged from 23% to 71%.[298] Of the pregnant women who survived childbirth, over one-quarter (26%) lost the child.[299] Another oddity was that the outbreak was widespread in the summer and autumn (in the Northern Hemisphere); influenza is usually worse in winter.[300]
There were also geographic patterns to the disease's fatality. Some parts of Asia had 30 times higher death rates than some parts of Europe, and generally, Africa and Asia had higher rates, while Europe and North America had lower ones.[301] There was also great variation within continents, with three times higher mortality in Hungary and Spain compared to Denmark, two to three times higher chance of death in Sub-Saharan Africa compared to North Africa, and possibly up to ten times higher rates between the extremes of Asia.[301] Cities were affected worse than rural areas.[301] There were also differences between cities, which might have reflected exposure to the milder first wave giving immunity, as well as the introduction of social distancing measures.[302]
Another major pattern was the differences between social classes. In Oslo, death rates were inversely correlated with apartment size, as the poorer people living in smaller apartments died at a higher rate.[303] Social status was also reflected in the higher mortality among immigrant communities, with Italian Americans, a recently arrived group at the time, were nearly twice as likely to die compared to the average Americans.[301] These disparities reflected worse diets, crowded living conditions, and problems accessing healthcare.[301] Paradoxically, however, African Americans were relatively spared by the pandemic.[301]
More men than women were killed by the flu, as they were more likely to go out and be exposed, while women would tend to stay at home.[302] For the same reason men also were more likely to have pre-existing tuberculosis, which severely worsened the chances of recovery.[302] However, in India the opposite was true, potentially because Indian women were neglected with poorer nutrition, and were expected to care for the sick.[302]
A study conducted by He et al. (2011) used a mechanistic modeling approach to study the three waves of the 1918 influenza pandemic. They examined the factors that underlie variability in temporal patterns and their correlation to patterns of mortality and morbidity. Their analysis suggests that temporal variations in transmission rate provide the best explanation, and the variation in transmission required to generate these three waves is within biologically plausible values.[304] Another study by He et al. (2013) used a simple epidemic model incorporating three factors to infer the cause of the three waves of the 1918 influenza pandemic. These factors were school opening and closing, temperature changes throughout the outbreak, and human behavioral changes in response to the outbreak. Their modeling results showed that all three factors are important, but human behavioral responses showed the most significant effects.[305]
Effects
World War I
Academic Andrew Price-Smith has made the argument that the virus helped tip the balance of power in the latter days of the war towards the Allied cause. He provides data that the viral waves hit the Central Powers before the Allied powers and that both morbidity and mortality in Germany and Austria were considerably higher than in Britain and France.[182] A 2006 Lancet study corroborates higher excess mortality rates in Germany (0.76%) and Austria (1.61%) compared to Britain (0.34%) and France (0.75%).[248]
Kenneth Kahn at Oxford University Computing Services writes that "Many researchers have suggested that the conditions of the war significantly aided the spread of the disease. And others have argued that the course of the war (and subsequent peace treaty) was influenced by the pandemic." Kahn has developed a model that can be used on home computers to test these theories.[306]
Economic

Many businesses in the entertainment and service industries suffered losses in revenue, while the healthcare industry reported profit gains.[307] Historian Nancy Bristow has argued that the pandemic, when combined with the increasing number of women attending college, contributed to the success of women in the field of nursing. This was due in part to the failure of medical doctors, who were predominantly men, to contain and prevent the illness. Nursing staff, who were mainly women, celebrated the success of their patient care and did not associate the spread of the disease with their work.[308]
A 2020 study found that U.S. cities that implemented early and extensive non-medical measures (quarantine, etc.) suffered no additional adverse economic effects due to implementing those measures.[309][310] However, the validity of this study has been questioned because of the coincidence of WWI and other problems with data reliability.[311]
Long-term effects
A 2006 study in the Journal of Political Economy found that "cohorts in utero during the pandemic displayed reduced educational attainment, increased rates of physical disability, lower income, lower socioeconomic status, and higher transfer payments received compared with other birth cohorts."[312] A 2018 study found that the pandemic reduced educational attainment in populations.[313] The flu has also been linked to the outbreak of encephalitis lethargica in the 1920s.[314]
Survivors faced an elevated mortality risk. Some survivors did not fully recover from physiological conditions resulting from infection.[315]
Legacy

Despite the high morbidity and mortality rates that resulted from the epidemic, the Spanish flu began to fade from public awareness over the decades until the arrival of news about bird flu and other pandemics in the 1990s and 2000s.[316][317] This has led some historians to label the Spanish flu a "forgotten pandemic".[174] However, this label has been challenged by the historian Guy Beiner, who has charted a complex history of social and cultural forgetting, demonstrating how the pandemic was overshadowed by the commemoration of the First World War and mostly neglected in mainstream historiography, yet was remembered in private and local traditions across the globe.[317]
There are various theories of why the Spanish flu was "forgotten". The rapid pace of the pandemic, which killed most of its victims in the United States within less than nine months, resulted in limited media coverage. The general population was familiar with patterns of pandemic disease in the late 19th and early 20th centuries: typhoid, yellow fever, diphtheria, and cholera all occurred near the same time. These outbreaks probably lessened the significance of the influenza pandemic for the public.[318] In some areas, the flu was not reported on, the only mention being that of advertisements for medicines claiming to cure it.[319]
Additionally, the outbreak coincided with the deaths and media focus on the First World War.[320] Another explanation involves the age group affected by the disease. The majority of fatalities, from both the war and the epidemic, were among young adults. The high number of war-related deaths of young adults may have overshadowed the deaths caused by flu.[296]
When people read the obituaries, they saw the war or postwar deaths and the deaths from the influenza side by side. Particularly in Europe, where the war's toll was high, the flu may not have had a tremendous psychological impact or may have seemed an extension of the war's tragedies.[296] The duration of the pandemic and the war could have also played a role. The war, however, had initially been expected to end quickly but lasted for four years by the time the pandemic struck.
In literature and other media

Despite the toll of the pandemic, it was never a large theme in American literature.[321] Alfred Crosby suspects that it may be due to the fact that it occurred after World War I, which was the most important event in that generation's lives.[322] Katherine Anne Porter's 1939 novella Pale Horse, Pale Rider is one of the most well-known fictional accounts of the pandemic.[321] The 2006 novel The Last Town on Earth focuses on a town which attempts to limit the spread of the flu by preventing people from entering or leaving.[323] The Pull of the Stars is a 2020 novel by Emma Donoghue set in Dublin during the Spanish flu. Its final draft was submitted in March 2020, and publishers fast-tracked publication because of the then ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.[324]
Comparison with other pandemics
The Spanish flu killed a much lower percentage of the world's population than the Black Death, which lasted for many more years.[325]
The recent COVID-19 pandemic is estimated to have killed 17.5 - 31.4 million.[326]
| Name | Date | World pop. | Subtype | Reproduction number[329] | Infected (est.) | Deaths worldwide | Case fatality rate | Pandemic severity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spanish flu[330] | 1918–20 | 1.80 billion | H1N1 | 1.80 (IQR, 1.47–2.27) | 33% (500 million)[331] or >56% (>1 billion)[332] | 17[333]–100[334][335] million | 2–3%,[332] or ~4%, or ~10%[336] | 5 |
| Asian flu | 1957–58 | 2.90 billion | H2N2 | 1.65 (IQR, 1.53–1.70) | >17% (>500 million)[332] | 1–4 million[332] | <0.2%[332] | 2 |
| Hong Kong flu | 1968–69 | 3.53 billion | H3N2 | 1.80 (IQR, 1.56–1.85) | >14% (>500 million)[332] | 1–4 million[332] | <0.2%[332][337] | 2 |
| 1977 Russian flu | 1977–79 | 4.21 billion | H1N1 | ? | ? | 0.7 million[338] | ? | ? |
| 2009 swine flu pandemic[339][340] | 2009–10 | 6.85 billion | H1N1/09 | 1.46 (IQR, 1.30–1.70) | 11–21% (0.7–1.4 billion)[341] | 151,700–575,400[342] | 0.01%[343][344] | 1 |
| Typical seasonal flu[t 1] | Every year | 7.75 billion | A/H3N2, A/H1N1, B, ... | 1.28 (IQR, 1.19–1.37) | 5–15% (340 million – 1 billion)[345] 3–11% or 5–20%[346][347] (240 million – 1.6 billion) |
290,000–650,000/year[348] | <0.1%[349] | 1 |
Notes
| ||||||||
Research
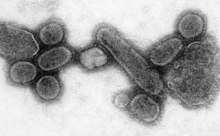
The origin of the Spanish flu pandemic, and the relationship between the near-simultaneous outbreaks in humans and swine, have been controversial. One hypothesis is that the virus strain originated at Fort Riley, Kansas, in viruses in poultry and swine which the fort bred for food; the soldiers were then sent from Fort Riley around the world, where they spread the disease.[350] Similarities between a reconstruction of the virus and avian viruses, combined with the human pandemic preceding the first reports of influenza in swine, led researchers to conclude the influenza virus jumped directly from birds to humans, and swine caught the disease from humans.[351][352]
Others have disagreed,[353] and more recent research has suggested the strain may have originated in a nonhuman, mammalian species.[354] An estimated date for its appearance in mammalian hosts has been put at the period 1882–1913.[355] This ancestor virus diverged about 1913–1915 into two clades (or biological groups each descended from a common ancestor), which gave rise to the classical swine and human H1N1 influenza lineages. The last common ancestor of human strains dates between February 1917 and April 1918. Because pigs are more readily infected with avian influenza viruses than are humans, they were suggested as the original recipients of the virus, passing the virus to humans sometime between 1913 and 1918.

An effort to recreate the Spanish flu strain (a strain of influenza A subtype H1N1) was a collaboration among the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, the USDA ARS Southeast Poultry Research Laboratory, and Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City. The effort resulted in the announcement (on 5 October 2005) that the group had successfully determined the virus' genetic sequence, using historic tissue samples recovered by pathologist Johan Hultin from an Inuit female flu victim buried in the Alaskan permafrost and samples preserved from American soldiers[356] Roscoe Vaughan and James Downs.[357][358][352]
This enabled researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Mount Sinai School of Medicine, led by Dr Terrence Tumpey, to synthesize RNA segments from the H1N1 virus and ultimately reconstruct infective virus particles.[359] These were subsequently used to experimentally infect mice, ferrets, and macaques giving valuable insights into influenza virus biology and pathogenesis, providing important information about how to prevent and control future pandemics.[360]
On 18 January 2007, Kobasa et al. (2007) reported that monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) infected with the recreated flu strain exhibited classic symptoms of the 1918 pandemic, and died from an overreaction of the immune system.[361] This may explain why the Spanish flu had its surprising effect on younger, healthier people, as a person with a stronger immune system would potentially have a stronger overreaction.[362]
In December 2008, research by Yoshihiro Kawaoka of the University of Wisconsin linked the presence of three specific genes (termed PA, PB1, and PB2) and a nucleoprotein derived from Spanish flu samples to the ability of the 1918 flu virus to invade the lungs and cause pneumonia. These genes were inserted into a modern H1N1 strain and triggered similar symptoms in animal testing.[363]
In 2008 an investigation used the virus sequence to obtain the Hemagglutinin (HA) antigen and observe the adaptive immunity in 32 survivors of the 1918 flu pandemic, all of them presented seroreactivity and 7 of 8 further tested presented memory B cells able to produce antibodies that bound to the HA antigen highlighting the ability of the immunological memory many decades after.[364][352]
In June 2010, a team at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine reported the 2009 flu pandemic vaccine provided some cross-protection against the Spanish flu pandemic strain.[365]
One of the few things known for certain about influenza in 1918 and for some years after was that it was, except in the laboratory, exclusively a disease of human beings.[366]
In 2013, the AIR Worldwide Research and Modeling Group "characterized the historic 1918 pandemic and estimated the effects of a similar pandemic occurring today using the AIR Pandemic Flu Model". In the model, "a modern-day 'Spanish flu' event would result in additional life insurance losses of between US$15.3–27.8 billion in the United States alone", with 188,000–337,000 deaths in the United States.[367]
In 2018, Michael Worobey, an evolutionary biology professor at the University of Arizona who is examining the history of the 1918 pandemic, revealed that he obtained tissue slides created by William Rolland, a physician who reported on a respiratory illness likely to be the virus while a pathologist in the British military during World War One.[368] Rolland had authored an article in the Lancet during 1917 about a respiratory illness outbreak beginning in 1916 in Étaples, France.[369][370] Worobey traced recent references to that article to family members who had retained slides that Rolland had prepared during that time. Worobey extracted tissue from the slides to potentially reveal more about the origin of the pathogen.[27]
Sex differences in mortality
The high mortality rate of the influenza pandemic is one aspect that sets the pandemic apart from other disease outbreaks. Another factor is the higher mortality rate of men compared with women. Men with an underlying condition were at significantly more risk. Tuberculosis was one of the deadliest diseases in the 1900s, and killed more men than women. But with the spread of influenza disease, the cases of tuberculosis cases in men decreased. Many scholars have noted that tuberculosis increased the mortality rate of influenza in males, decreasing their life expectancy. During the 1900s tuberculosis was more common in males than females, but studies show that when influenza spread the tuberculosis mortality rate among females changed. The death rate of tuberculosis in females increased significantly and would continue to decline until post-pandemic.[371]
Death rates were particularly high in those aged 20–35. The only comparable disease to this was the Black Death, or bubonic plague, in the 1300s. As other studies have shown, tuberculosis and influenza had comorbidities and one affected the other. The ages of males dying of the flu show that tuberculosis was a factor, and as males primarily had this disease at the time of the pandemic, they had a higher mortality rate. Life expectancy dropped in males during the pandemic but then increased two years after the pandemic.[372]
Island of Newfoundland
One major cause of the spread of influenza was social behavior. Men had more social variation and were mobile more than women due to their work. Even though there was a higher mortality rate in males, each region showed different results, due to such factors as nutritional deficiency. In Newfoundland, the pandemic spread was highly variable. Influenza did not discriminate who was infected, indeed it attacked the socioeconomic status of people. Although social variability allowed the disease to move quickly geographically, it tended to spread faster and affect men more than women due to labor and social contact. Newfoundland's leading cause of death before the pandemic was tuberculosis and this is known to be a severe underlying condition for people and increases the |mortality rate when infected by the influenza disease. There was diverse labor in Newfoundland, men and women had various occupations that involved day-to-day interaction. But, fishing had a major role in the economy and so males were more mobile than females and had more contact with other parts of the world. The spread of the pandemic is known to have begun in the spring of 1918, but Newfoundland did not see the deadly wave until June or July, which aligns with the high demand for employment in the fishery. The majority of men were working along the coast during the summer and it was typical for entire families to move to Newfoundland and work. Studies show a much higher mortality rate in males compared with females. But, during the first, second, and third waves of the pandemic, the mortality shifted. During the first wave, men had a higher mortality rate, but the mortality rate of females increased and was higher during the second and third waves. The female population was larger in certain regions of Newfoundland and therefore had a bigger impact on the death rate.[373]
Influenza pandemic among Canadian soldiers
Records indicate the most deaths during the first wave of the pandemic were among young men in their 20s, which reflects the age of enlistment in the war. The mobility of young men during 1918 was linked to the spread of influenza and the biggest wave of the epidemic. In late 1917 and throughout 1918, thousands of male troops gathered at the Halifax port before heading to Europe. Any soldier that was ill and could not depart was added to the population of Halifax, which increased the case rate of influenza among men during the war. To determine the cause of the death during the pandemic, war scientists used the Commonwealth War Graves Commission (CWGC), which reported under 2 million men and women died during the wars, with a record of those who died from 1917 to 1918. The movement of soldiers during this time and the transportation from United States between Canada likely had a significant effect on the spread of the pandemic.[374]
See also
- 1918 flu pandemic in India – Known in India as "Bombay Fever"
- 2009 swine flu pandemic – 2009–2010 pandemic of swine influenza caused by H1N1 influenza virus
- Anti-Mask League of San Francisco – 1919 San Francisco organization
- COVID-19 pandemic – Pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2
- Pandemic – Widespread, often global, epidemic of severe infectious disease
- List of epidemics
- List of Spanish flu cases
Footnotes
References
Citations
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Yang W, Petkova E, Shaman J (March 2014). "The 1918 influenza pandemic in New York City: age-specific timing, mortality, and transmission dynamics". Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses. 8 (2). National Institutes of Health: 177–188. doi:10.1111/irv.12217. PMC 4082668. PMID 24299150.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Taubenberger & Morens 2006.
- ^ "Pandemic Influenza Risk Management WHO Interim Guidance" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2013. p. 25. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 January 2021. Retrieved 21 August 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Spreeuwenberg P, Kroneman M, Paget J (December 2018). "Reassessing the Global Mortality Burden of the 1918 Influenza Pandemic". American Journal of Epidemiology. 187 (12). Oxford University Press: 2561–2567. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy191. PMC 7314216. PMID 30202996.
- ^ Rosenwald MS (7 April 2020). "History's deadliest pandemics, from ancient Rome to modern America". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 7 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ^ CDC (17 December 2019). "The Discovery and Reconstruction of the 1918 Pandemic Virus". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 19 September 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Barry JM (2021). The Great Influenza: The Story of the Deadliest Pandemic in History. Penguin Books. pp. 397–398. ISBN 978-0-14-303649-4.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Mayer J (29 January 2019). "The Origin Of The Name 'Spanish Flu'". Science Friday. Retrieved 30 July 2021.
Etymology: In ancient times, before epidemiology science, people believed the stars and "heavenly bodies" flowed into us and dictated our lives and health—influenza means 'to influence' in Italian, and the word stems from the Latin for 'flow in.' Sickness, like other unexplainable events, was attributed to the influence of the stars... But the name for the infamous 1918 outbreak, the Spanish flu, is actually a misnomer.
- ^ Gagnon, Miller & et al 2013, p. e69586.
- ^ Jump up to: a b More AF, Loveluck CP, Clifford H, Handley MJ, Korotkikh EV, Kurbatov AV, et al. (September 2020). "The Impact of a Six-Year Climate Anomaly on the "Spanish Flu" Pandemic and WWI". GeoHealth. 4 (9): e2020GH000277. Bibcode:2020GHeal...4..277M. doi:10.1029/2020GH000277. ISSN 2471-1403. PMC 7513628. PMID 33005839.
- ^ Marshall L (9 October 2023). "1918 flu pandemic myth debunked by skeletal remains". CU Boulder Today. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ Brundage JF, Shanks GD (December 2007). "What really happened during the 1918 influenza pandemic? The importance of bacterial secondary infections". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 196 (11): 1717–18, author reply 1718–19. doi:10.1086/522355. PMID 18008258.
- ^ Morens DM, Fauci AS (April 2007). "The 1918 influenza pandemic: insights for the 21st century". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 195 (7): 1018–1028. doi:10.1086/511989. PMID 17330793.
- ^ "Influenza Pandemic Plan. The Role of WHO and Guidelines for National and Regional Planning" (PDF). World Health Organization. April 1999. pp. 38, 41. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 December 2020.
- ^ Michaelis M, Doerr HW, Cinatl J (August 2009). "Novel swine-origin influenza A virus in humans: another pandemic knocking at the door". Medical Microbiology and Immunology. 198 (3): 175–183. doi:10.1007/s00430-009-0118-5. PMID 19543913. S2CID 20496301.
- ^ Mermel LA (June 2009). "Swine-origin influenza virus in young age groups". Lancet. 373 (9681): 2108–2109. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61145-4. PMID 19541030. S2CID 27656702. Archived from the original on 27 July 2021. Retrieved 5 April 2021.
- ^ Davis 2013, p. 7: "In short, although the Spanish flu 'had nothing "Spanish" about it,' from a strictly epidemiological perspective, its discursive link to the Iberian nation is beyond dispute. The importance of narrative for a historically informed appreciation of the epidemic stems from the importance of this discursive link and is tied directly to the scientific uncertainty about the etiological agent of the epidemic;"
- ^ "Biblical Hebrew Words and Meaning". hebrewversity. 14 March 2018. Retrieved 11 August 2021.
in the original Hebrew the people of Israel asked: "Ma'n Hu?" {?מן הוא} – English for 'what is it?' and that is the origin of the name 'manna'
- ^ Spinney 2018, p. 65: "In Freetown, a newspaper suggested that the disease be called manhu until more was known about it. Manhu, a Hebrew word meaning 'what is it?'
- ^ Cole F (1994), Sierra Leone and World War 1, University of London, School of Oriental and African Studies, p. 213, 10731720, retrieved 11 August 2021 – via ProQuest Dissertations Publishing,
local interpretations of the crisis had become deeply reminiscent of the increasing disobedience of the Israelites in the wilderness of Sin. It was therefore urged that the epidemic be called 'Man hu,' (an obvious corruption of "manna") meaning 'what is it?'
- ^ Sierra Leone Weekly News, vol. XXXV, 9 July 1918, p. 6 quoted in Mueller JW (1998), p. 8.
- ^ Hammond JA, Rolland W, Shore TH (14 July 1917). "Purulent Bronchitis". The Lancet. 190 (4898): 41–46. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(01)56229-7. ISSN 0140-6736. Alt URL
- ^ Radusin M (September 2012). "The Spanish flu--Part I: the first wave". Vojnosanitetski Pregled. 69 (9): 812–817. PMID 23050410.
the Purple Death … name resulted from the specific skin colour in the most severe cases of the diseased, who by the rule also succumbed to the disease, and is also at the same time the only one which does not link this disease with the Iberian peninsula. This name is actually the most correct.
- ^ McCord CP (November 1966). "The Purple Death. Some things remembered about the influenza epidemic of 1918 at one army camp". Journal of Occupational Medicine. 8 (11). Industrial Medical Association: 593–598. PMID 5334191.
- ^ Getz D (19 September 2017). Purple death : the mysterious Spanish flu of 1918. Square Fish. ISBN 978-1-250-13909-2. OCLC 1006711971.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Oxford JS, Gill D (2 September 2019). "A possible European origin of the Spanish influenza and the first attempts to reduce mortality to combat superinfecting bacteria: an opinion from a virologist and a military historian". Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics. 15 (9): 2009–2012. doi:10.1080/21645515.2019.1607711. PMC 6773402. PMID 31121112.
Two papers were published in The Lancet in 1917 describing an outbreak of disease constituting 'almost a small epidemic'. The first paper was written by physicians at a hospital center in northern France,3 and the second by a team at an army hospital in Aldershot, in southern England. In both earlier instances and in the 1918 pandemic the disease was characterized by a 'dusky' cyanosis, a rapid progression from quite minor symptoms to death
- ^ Jump up to: a b Cox J, Gill D, Cox F, Worobey M (April 2019). "Purulent bronchitis in 1917 and pandemic influenza in 1918". The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 19 (4): 360–361. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(19)30114-8. PMID 30938298. S2CID 91189842.
- ^ Honigsbaum M (June 2018). "Spanish influenza redux: revisiting the mother of all pandemics". Lancet. 391 (10139): 2492–2495. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31360-6. PMID 29976462. S2CID 49709093.
Labelled 'purulent bronchitis' for want of a better term, the disease proved fatal in half the cases and many soldiers also developed cyanosis. 2 years later, British respiratory experts, also writing in The Lancet, but this time in the wake of the pandemic, would decide the disease had been 'fundamentally the same condition' as 'Spanish' influenza
- ^ Dennis Shanks G, Mackenzie A, Waller M, Brundage JF (July 2012). "Relationship between "purulent bronchitis" in military populations in Europe prior to 1918 and the 1918-1919 influenza pandemic". Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses. 6 (4): 235–239. doi:10.1111/j.1750-2659.2011.00309.x. PMC 5779808. PMID 22118532.
- ^ Storey, C (21 September 2020). "OLD NEWS: Influenza was an old foe long before 1918". Arkansas Democrat-Gazette. Opinion. Retrieved 7 August 2021.
I came across this seemingly astute analysis in the Dec. 21, 1913, Gazette.... It was a 'Special Cable to the Gazette Through the International News Service.' Grip Is a Disease Without a Country; All Nations Repudiate Malady: Each Blaming Other Kingdoms, London, Dec. 20. — The grip is a disease without a country, according to a new book just issued which is devoted to the malady. Every country tries to make it out a native of another land.... Eighteenth-century Italian writers say Dr. Hopkirk spoke of "una influenza di freddo" (influence of cold), and English physicians, mistaking the word influenza for the name of the disease itself, used it. The same term is also used in Germany, where a host of dialect names still prevail, such as lightning catarrh and fog plague.
- ^ "Grippe is not new". Los Angeles Herald. 14 January 1899. p. 6 col. 6. Retrieved 7 August 2021 – via California Digital Newspaper Collection.
French doctors gave it the name of "la grippe," which is now anglicized into "the grip" ... It is known all over the world, and there is a disposition in every nation to shift the odium of it upon some other country. Then the Russians call it the Chinese catarrh, the Germans often call it the Russian pest, the Italians name it the German disease, and the French call it sometimes the Italian fever and sometimes the Spanish catarrh.
- ^ Davis 2013, p. 27: "On May 21, 1918, El Liberal published a scant article titled 'Can One Live? The Fashionable Illness.' Likely the first account in Spain of the Spanish flu, it begins: 'For several days, Madrid has been affected by an epidemic, which fortunately is mild; but which, from what it appears, intends to kill doctors from overwork'.... The following day, El Sol and ABC published their first stories about the epidemic: 'What is the Cause? An Epidemic in Madrid' and 'Benign Epidemic. The Sickbay in Madrid,' respectively."
- ^ Alfeirán X (7 December 2015). "La fiebre de los tres días" [The three-day fever]. La Voz de Galicia (in Spanish). A Coruña. Retrieved 29 July 2021.
Las primeras noticias aparecieron en la prensa de Madrid el 21 de mayo de 1918.
[The first news appeared in the press of Madrid on 21 May 1918.] - ^ McClure J (1 May 2009). "Spanish flu of 1918 no three-day fever. Try 365-day worldwide plague". York Daily Record. Retrieved 29 July 2021.
- ^ Calleja S (29 July 2021). "La fiebre de los tres días" [The three-day fever]. Diario de León (in Spanish). León, Spain. Retrieved 21 October 2018.
- ^ "Impacto de la gripe de 1918 en España". Comité Asesor de Vacunas de la Asociación Española de Pediatría [Vaccine Advisory Committee of the Spanish Association of Pediatrics] (in Spanish). Retrieved 29 July 2021.
En España, se le llamó al principio 'la fiebre de los tres días', atendiendo a la creencia, como en otros países, de que la gripe era una enfermedad leve. Las primeras noticias sobre la gripe, llamando la atención sobre que algo distinto estaba ocurriendo, aparecieron en la prensa a finales de mayo. Por ej. en el diario ABC el 22 de mayo mediante una escueta nota en la página 24: 'Los médicos han comprobado, en Madrid, la existencia de una epidemia de índole gripal, muy propagada, pero, por fortuna, de carácter leve'.
[In Spain, it was initially called 'the three-day fever', based on the belief, as in other countries, that the flu was a mild illness. The first reports about the flu, drawing attention to the fact that something different was happening, appeared in the press at the end of May. For example, in the newspaper ABC on 22 May, through a brief note on page 24: "The doctors have verified, in Madrid, the existence of an epidemic of a influenza nature, very widespread, but, fortunately, of a mild nature.'] - ^ Killingray D, Phillips H (2 September 2003). The Spanish Influenza Pandemic of 1918-1919: New Perspectives. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-56640-2.
In the popular mind calamities often need to have their origin and cause identified and other countries or peoples credited with blame. This xenophobic response has been common in Europe, that impulse to blame others or the silent places of the Asian heartlands for the source of disease.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Hoppe T (November 2018). ""Spanish Flu": When Infectious Disease Names Blur Origins and Stigmatize Those Infected". American Journal of Public Health. 108 (11): 1462–1464. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2018.304645. PMC 6187801. PMID 30252513.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Bax D (2020). "Pandemie – Welt im Fieber" [Pandemic - World in Fever]. Der Freitag (in German) (13). Retrieved 31 July 2021.
In Großbritannien wurde die Krankheit dagegen als 'Flandrische Grippe' bezeichnet, weil sich viele —en in den Schützengräben von Flandern ansteckten.
[In Britain, on the other hand, the disease was called the 'Flanders flu' because many soldiers became infected in the trenches of Flanders.] - ^ Reynolds JR (1866). A System of Medicine. Vol. 1. Macmillan. pp. 30–31.
One is, that every epidemic owns one unknown source, whence it spreads; each nation, in turn, attributing to its neighbour from whom it derived the disease, the unenviable honour of originating it. Thus the Italians have termed it the German disease; the Germans, the Russian pest; the Russians, the Chinese Catarrh;
- ^ Harrison MA, Claiborne JH Jr, eds. (January 1890). "Editorials: La Grippe". Gaillard's Medical Journal. 50: 217.
The outbreak immediately preceding the present one was in 1879, and has been well described by Da Costa. Like every other disease about whose pathology we know very little, this malady has not a scientifically correct name, but at different times and in different countries has received names which are almost purely local; thus the Russians have called it the Chinese catarrh, because it has often invaded Russia from China. The Germans call it the Russian pest, while the Italians in turn call it the German disease.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Davis KC (2018). More deadly than war : the hidden history of the Spanish flu and the First World War (First ed.). New York: Henry Holt and Company. ISBN 978-1-250-14512-3. OCLC 1034984776.
The Russians called it the Chinese flu. In Japan, it was wrestler's fever. In South Africa, it was known as either the white man's sickness or kaffersiekte blacks' disease. Soldiers fighting in the Great War called it the three-day fever—a highly inaccurate description—and when it first struck in the spring of 1918, German soldiers called it Flanders fever, after one of the war's most notorious and deadly battlefields
- ^ Porras-Gallo & Davis 2014, p. 51.
- ^ Galvin 2007.
- ^ Own Correspondent (2 June 1918). "The Spanish Epidemic". The Times. London. Retrieved 29 July 2021.
The unknown disease which appeared in Madrid a fortnight ago spread with remarkable rapidity.... It is reported that there are well over 100,000 victims in Madrid alone.... Although the disease is clearly of a gripal character...
- ^ "The Spanish Influenza; A Sufferer's Symptoms". The Times. London. 25 June 1918. Retrieved 29 July 2021.
- ^ "Public Notice; 'Spanish Influenza' Epidemic". The Times. London. 28 June 1918. Retrieved 11 August 2021.
- ^ Arnold C (13 September 2018). "Eat More Onions!". Lapham's Quarterly. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
daily newspapers carried an increasing number of advertisements for influenza-related remedies as drug companies played on the anxieties of readers and reaped the benefits. From the Times of London to the Washington Post, page after page was filled with dozens of advertisements for preventive measures and over-the-counter remedies. 'Influenza!' proclaimed an advert extolling the virtues of Formamint lozenges.
- ^ Daniels R (29 April 2018) [1998 Mill Hill Essays]. "In Search of an Enigma: The "Spanish Lady"". NIMR History. Archived from the original on 29 April 2018. Retrieved 9 August 2021 – via web.archive.org.
In turn, when Russia reported on the situation in Moscow, Pravda printed "Ispanka (The Spanish Lady) is in town" and the name has stuck.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Trilla A, Trilla G, Daer C (September 2008). "The 1918 "Spanish flu" in Spain". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 47 (5): 668–673. doi:10.1086/590567. PMID 18652556.
- ^ "Spanish flu facts". Channel 4 News. Archived from the original on 27 January 2010.
- ^ Anderson S (29 August 2006). "Analysis of Spanish flu cases in 1918–1920 suggests transfusions might help in bird flu pandemic". American College of Physicians. Archived from the original on 25 November 2011. Retrieved 2 October 2011.
- ^ Barry 2004, p. 171.
- ^ Spinney L (29 September 2018). "The centenary of the 20th century's worst catastrophe". The Economist. Science & technology. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved 3 August 2021.
On June 29th 1918 Martín Salazar, Spain's inspector-general of health, stood up in front of the Royal Academy of Medicine in Madrid. He declared, not without embarrassment, that the disease which was ravaging his country was to be found nowhere else in Europe. In fact, that was not true. The illness in question, influenza, had been sowing misery in France and Britain for weeks, and in America for longer, but Salazar did not know this because the governments of those countries, a group then at war with Germany and its allies, had made strenuous efforts to suppress such potentially morale-damaging news.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ "Madrid Letter". Journal of the American Medical Association. 71 (19): 1594. 9 November 1918.
- ^ Radusin M (September 2012). "The Spanish flu--Part I: the first wave". Vojnosanitetski Pregled. 69 (9): 812–817. PMID 23050410.
'The Serbian Newspaper' wrote in the period October 23 / November 5, 1918 at the peak of the second, deadliest wave of the pandemic: 'Various countries have been assigning the origin of this imposing guest to each other for quite some time, and at one point in time they agreed to assign its origin to the kind and neutral Spain, which had been fighting off this honour just as much as German submarines, so imposing in their search for hospitality off Spanish shores.'
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Vázquez-Espinosa E, Laganà C, Vázquez F (October 2020). "The Spanish flu and the fiction literature". Revista Espanola de Quimioterapia. 33 (5): 296–312. doi:10.37201/req/049.2020. PMC 7528412. PMID 32633114.
French journalists had, initially, called it the 'American flu'; but the fact that the American soldiers were his allies in the warlike conflict advised not to assign such a link to them.... Another most popular name in Madrid, was the 'Soldado de Nápoles' (Naples soldier), a popular song in the zarzuela (popular musical genre or 'género chico' in Spain) called La canción del olvido (The forgotten song) due both, were 'highly contagious'. Today, there are many authors who avoid such a name (the Spanish flu) and they aptly refer to it as the '1918- 1819[sic] influenza pandemic'
- ^ Müller S (2020). "Spanische Grippe" [The Spanish Flu]. www.fes.de (in German). Bonn: Friedrich Ebert Foundation. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
In Europa wurde die Spanischer Grippe auch als 'Blitzkatarrh', als 'Flandern-Fieber', 'flandische Grippe', bei Engländern und Amerikanern als 'three-day'- oder 'knock-me-down'-Fieber, und in Frankreich als 'la grippe', als 'bronchite purulente' (eitrige Bronchitis) oder beim französische Militärärzte als 'Krankheit 11' (maladie onze) bezeichnet. Die Benennung von Krankheiten und insbesondere Seuchen nach ihrem vermuteten Ursprungsort ist nichts Ungewöhnliches. Es ist der Versuch, einem Geschehen auf die Spur zu kommen. Zugleich werden auf diese Weise Krankheiten als etwas Äußerliches gekennzeichnet, als etwas Fremdes, das eingedrungen ist oder eingeschleppt wurde.
[In Europe, the Spanish flu was also referred to as 'Blitzkatarrh', as 'Flanders fever', 'Flanders flu', in English and Americans as 'three-day' or 'knock-me-down' fever, and in France as 'la flu', as 'bronchite purulente' (purulent bronchitis) or by French military doctors as 'disease 11' (maladie onze). The naming of diseases and especially epidemics according to their presumed place of origin is nothing unusual. It is an attempt to track down what is happening. At the same time, in this way, diseases are marked as something external, as something foreign that has invaded or been introduced.] - ^ Jump up to: a b Cotter C (23 April 2020). "From the 'Spanish Flu' to COVID-19: lessons from the 1918 pandemic and First World War". Humanitarian Law & Policy. International Committee of the Red Cross. Retrieved 7 August 2021.
Many other nicknames were given to the pandemic, many based on nationality or race: 'Spanish Lady', 'French Flu', 'Naples Soldier', 'Purple Death', 'War Plague', 'Flanders Grippe', 'Kirghiz Disease', 'Black Man's Disease', 'Hun Flu', 'German Plague', 'Bolshevik Disease' or even the 'Turco-Germanic bacterium criminal entreprise'. These discriminatory epithets reflect the many rumors and theories that quickly spread about the origins of the pathology.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Spinney 2018, p. 58.
- ^ Davis 2013, pp. 103–36.
- ^ Landgrebe P (29 December 2018). "100 Years After: The Name of Death". History Campus. Archived from the original on 16 August 2020. Retrieved 16 August 2020.
- ^ Rodríguez LP, Palomba AL (5 March 2019). "How is the adjective 'Spanish' used in other languages?". El País (English ed.). Madrid. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
The use of 'Spanish' can often have negative connotations, with the adjective often unfairly used to describe unwelcome events and problems. The most obvious example is the so-called 'Spanish flu,' a reference to the 1918 influenza pandemic...
- ^ O'Reilly T (13 May 2020). "How the Spanish Flu wasn't Spanish at all". CBC Radio. Under the Influence. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
Medical professionals and officials in Spain protested. They said the Spanish people were being falsely stigmatized.... If you've ever wondered about the staying power of a brand, the 'Spanish Flu' is a case in point. A full 100 years later, the 'Spanish Flu' is still referenced — and still remains a source of irritation in Spain.
- ^ Takon L (7 April 2020). "Fighting words: how war metaphors can trigger racism". The Lighthouse. Macquarie University. Retrieved 8 August 2021.
the names given to this disease in different parts of the world reflected prevailing concerns about certain ethnic groups and ideologies. The disease was called the 'Singapore fever' in Penang and the Bolshevik disease in Poland.
- ^ Филлипс Х (1990). Черный октябрь: влияние эпидемии испанского гриппа 1918 года на Южную Африку . Правительственная типография, Южная Африка. ISBN 978-0-7970-1580-7 .
In one area where Blacks were the first victims, the accusatory term 'Kaffersiekte' was coined; in another district, where the position was reversed, Blacks returned the compliment with, White man's sickness'
- ^ Примечания: Говоря о "Spring Throb", это звучит хорошо... [Говоря о «весеннем сэкибу», что-то звучит хорошо...]. = Майнити Симбун [ Утренняя газета Mainichi Shimbun ] (на японском языке). 15 мая 2020 г. Проверено 8 августа 2021 г. В следующем месяце ряд борцов сумо отсутствовали из-за высокой температуры или по другим причинам на летних площадках Токио. Общественность назвала это «гриппом сумо» или «гриппом борцов сумо», но на самом деле это загадочное инфекционное заболевание считается «испанкой», которая начала распространяться в Соединенных Штатах с начала тот же год. [В следующем месяце ряд борцов сумо отсутствовали на летнем турнире в Токио из-за высокой температуры. Люди называли это «гриппом сумо» или «гриппом рестлера», но на самом деле эта загадочная инфекция, как полагают, является испанским гриппом, который начал распространяться в Соединенных Штатах в начале того же года.]
- ^ «Как испанский грипп 1918-20 годов опустошил Японию» . Япония сегодня . 6 мая 2020 г. Проверено 8 августа 2021 г.
Первые пациенты в Японии, как сообщил Шукан Гендай (2–9 мая), начали проявлять симптомы примерно в апреле 1918 года. Первоначально болезнь называлась «Сумо Казэ» (простуда сумо), потому что группа борцов сумо заразилась ею во время занятий спортом. тур по Тайваню. Трое известных борцов, Масагоиши, Тёсюнада и Вакагияма, умерли, не успев вернуться из Тайваня. По мере распространения инфекции летний турнир по сумо, который должен был проводиться на территории храма Ясукуни, был отменен.
- ^ Дионн и Туркмен 2020 , стр. 213–230.
- ^ «ВОЗ публикует передовой опыт в названии новых инфекционных заболеваний человека» . www.who.int . 8 мая 2015 года . Проверено 4 августа 2021 г.
- ^ «Пандемический грипп: развивающаяся проблема» . Всемирная организация здравоохранения . 22 мая 2018 г. Архивировано из оригинала 20 марта 2020 г. . Проверено 20 марта 2020 г.
- ^ «Пандемия гриппа 1918–1919 годов» . Британская энциклопедия . 4 марта 2020 г. Архивировано из оригинала 20 марта 2020 г. . Проверено 20 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Ходош С (18 марта 2020 г.). «Чему пандемия гриппа 1918 года может научить нас о COVID-19, в четырех диаграммах» . ПопНаука . Архивировано из оригинала 24 декабря 2020 года . Проверено 20 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Мюллер Дж.В. (1998). Что в имени. Испанский грипп в странах Африки к югу от Сахары и что местные имена говорят о восприятии этой пандемии . Испанский грипп 1918–1998 годов: размышления о пандемии гриппа 1918 года спустя 80 лет. Кейптаун, Южная Африка . Проверено 13 августа 2021 г.
- ^ Филлипс Х (8 октября 2014 г.). «Пандемия гриппа (Африка)» . энциклопедия.1914-1918-online.net . Международная энциклопедия Первой мировой войны (WW1) . Проверено 13 августа 2021 г.
- ^ Министерство здравоохранения Великобритании (1920 г.). Отчет о пандемии гриппа, 1918–1919 гг . Канцелярский офис HM.
В то время дул сильный западный ветер, и считалось, что именно он является переносчиком болезни, поэтому болезнь назвали «болезнью ветра».
- ^ Афхами А.А. (5 февраля 2019 г.). Современная инфекция: империализм и общественное здравоохранение в иранскую эпоху холеры . Джу Пресс. ISBN 978-1-4214-2722-5 .
В Тегеране болезнь получила название «болезнь ветра» (нахуши-йи бад) из-за ее первоначального возникновения во время сильного порыва западного ветра и быстрого распространения.
- ^ Архив внутренней медицины . Том. 24. Чикаго : Американская медицинская ассоциация . 1919.
Поскольку это включало период большой эпидемии гриппа, когда обычно преобладали инфекции типа IV, можно увидеть, что доля фиксированных типов среди носителей и среди случаев не далека от одного и того же.
- ^ Управление главного хирурга США (1920 г.). Отчет главного хирурга армии военному министру за финансовый год, закончившийся 30 июня 1919 года . Годовые отчеты военного ведомства. Том. Государственная типография IUS.
13 сентября 1918 года были зарегистрированы первые случаи крупной эпидемии гриппа, и в течение следующих 10 недель было госпитализировано более 4100 пациентов.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д и ж Барри 2004б .
- ^ Спинни 2018 , с. 64: «В… Родезии (Зимбабве)… официальные лица назвали новое заболевание «гриппом (vera)», добавив латинское слово vera, означающее «истинный»… Немецкие врачи… назвали его «псевдогриппом»»
- ^ Кросс А (29 марта 2020 г.). «Взгляд на искусство и музыку, созданные во времена пандемии» . Глобал Ньюс (Канада) . Проверено 9 августа 2021 г.
Еще одна рифма смертельно опасного происхождения появилась во время всемирной пандемии гриппа в 1889-1890 годах. Конечно, болезнь можно остановить, изолировав дом от отравленного воздуха снаружи, в школах появился совет по безопасности: была маленькая девочка, и у нее была маленькая птичка; И она назвала его красивым именем Энца; Но однажды оно улетело, но не осталось; Ибо, когда она подняла окно, грипп-Энца
- ^ Университетские библиотеки. «Экспонат Первой мировой войны: пандемия гриппа» . content.lib.washington.edu . Университет Вашингтона . Проверено 9 августа 2021 г.
- ^ Хаким Дж. (сентябрь 2002 г.). Война, мир и весь этот джаз . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-19-515335-4 .
Прилетела Энца — скажи это быстро, и это станет «гриппом». Это был запоминающийся стишок, под который мальчики и девочки прыгали на скакалке.
- ^ Хонигсбаум М (18 октября 2016 г.). Жизнь с Энзой: забытая история Британии и великой пандемии гриппа 1918 года . Спрингер. ISBN 978-0-230-23921-0 .
Популярный стишок для прыжков на детской площадке отражает легкость, с которой передается эта «новая болезнь»: у меня была маленькая птичка; Его звали Энца; Я открыл окно; И грипп-энза. Когда грипп распространился из Глазго в Абердин и из Ливерпуля в лондонский Майл-Энд, вскоре детские площадки по всей стране раздались эхом под песнопения.
- ^ Мартовский ПК (4 сентября 1932 г.). «Рассказ генерала Марча: взгляд на Вудро Вильсона» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . п. XX3, раздел «Специальные возможности».
- ^ «Пандемия гриппа 1918 года унесла жизни сотен тысяч американцев. Белый дом никогда не говорил об этом ни слова» . Время . Проверено 10 августа 2021 г.
В книге Кросби «Забытая пандемия в Америке: грипп 1918 года» Вильсон в октябре 1918 года спросил начальника штаба армии генерала Пейтона Марча, слышал ли он о популярном стишке о прыжках со скакалкой, пародирующем вирус, и процитировал его часть.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Спинни 2018 , с. 36.
- ^ «Грипп 1918 года (эпидемия испанки)» . Птичий птичий грипп . Архивировано из оригинала 21 мая 2008 года.
- ^ Шейдлоуэр Н. (17 марта 2020 г.). «Как Нью-Йорк пережил пандемию испанского гриппа 1918 года» . Нетронутый Нью-Йорк . Архивировано из оригинала 29 сентября 2020 года . Проверено 8 октября 2020 г.
- ^ Биллингс 1997 .
- ^ «Мемуары Герберта Гувера: годы приключений, 1874–1920 гг. (Нью-Йорк: Macmillan Company. 1951. стр. xi, 496) и Герберт Гувер и русские военнопленные Первой мировой войны: исследование дипломатии и помощи», 1918–1919. Эдвард Ф. Уиллис (Стэнфорд: Издательство Стэнфордского университета. 1951. стр. VIII, 67.)». Американский исторический обзор : 12. 2011. doi : 10.1086/ahr/57.3.709 . ISSN 1937-5239 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Спинни 2018 , с. 37.
- ^ «Странная эпидемия охватила Северный Китай; банки и магазины шелка в Пекине закрыты – у Японии просят еще один кредит» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 1 июня 1918 г. ISSN 0362-4331 . Архивировано из оригинала 24 июня 2020 года . Проверено 22 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д и ж Паттерсон и Пайл, 1991 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Статистика смертности за 1918 год: девятнадцатый годовой отчет» (PDF) . Бюро переписи населения США . 1920. с. 28. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 11 июля 2020 года . Проверено 29 мая 2020 г.
- ^ Эркорека А (март 2010 г.). «Пандемия испанского гриппа в Западной Европе (1918-1920 гг.) и возраст жертв» . Грипп и другие респираторные вирусы . 4 (2): 81–89. дои : 10.1111/j.1750-2659.2009.00125.x . ПМК 5779284 . ПМИД 20167048 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Спинни 2018 , с. 38.
- ^ Байерли CR (апрель 2010 г.). «Военные США и пандемия гриппа 1918-1919 годов» . Отчеты общественного здравоохранения . 125 Приложение 3 (Приложение 3): 82–91. дои : 10.1177/00333549101250S311 . ПМЦ 2862337 . ПМИД 20568570 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Спинни 2018 , с. 39.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Ататюрк победил испанский грипп раньше оккупантов» . www.sozcu.com.tr (на турецком языке). 23 апреля 2020 года. Архивировано из оригинала 8 ноября 2020 года . Проверено 2 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ Спинни 2018 , с. 40.
- ^ Барри Дж. М. (2005). Великий грипп . США: Книги Пингвина. п. 270. ИСБН 0-670-89473-7 .
15 сентября произошла первая смерть от гриппа в Нью-Йорке.
- ^ Флинн М. (12 марта 2020 г.). «Что произойдет, если парады не будут отменены во время пандемии? Филадельфия узнала об этом в 1918 году, и это привело к катастрофическим результатам» . Вашингтон Пост . Архивировано из оригинала 4 июля 2020 года . Проверено 9 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Спинни 2018 , с. 41.
- ^ Спинни 2018 , с. 42.
- ^ Кеннер Р. (18 января 2010 г.). «Грипп 1918 года» . Американский опыт . 10 сезон. 5 серия . ПБС . ВГБХ . Архивировано из оригинала 27 мая 2020 года. Стенограмма . Проверено 27 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Эпидемический грипп» . п. 93. Архивировано из оригинала 4 июля 2020 года . Проверено 4 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д Чандра С., Кристенсен Дж., Лихтман С. (6 ноября 2020 г.). «Связность и сезонность: пандемии гриппа 1918 года и COVID-19 в глобальной перспективе» . Журнал глобальной истории . 15 (3): 408–420. дои : 10.1017/S1740022820000261 . S2CID 228988279 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Бутсма MC, Фергюсон, Нью-Мексико (май 2007 г.). «Влияние мер общественного здравоохранения на пандемию гриппа 1918 года в городах США» . Труды Национальной академии наук Соединенных Штатов Америки . 104 (18): 7588–7593. Бибкод : 2007PNAS..104.7588B . дои : 10.1073/pnas.0611071104 . ПМЦ 1849868 . ПМИД 17416677 .
- ^ «Еженедельные отчеты общественного здравоохранения за 29 НОЯБРЯ 1918 г.» . Отчеты общественного здравоохранения . 33 (48): 2093–2152. Ноябрь 1918 года. ЧВК 1999834 . ПМИД 19314645 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Еженедельные отчеты общественного здравоохранения за 6 ДЕКАБРЯ 1918 г.» . Отчеты общественного здравоохранения . 33 (49): 2153–2209. Декабрь 1918 года. ЧВК 1999845 . ПМИД 19314646 .
- ^ Чандра С., Кристенсен Дж., Чандра М., Панет Н. (март 2021 г.). «Возрождение пандемии и четыре волны избыточной смертности, совпавшие с пандемией гриппа 1918 года в Мичигане: выводы о COVID-19» . Американский журнал общественного здравоохранения . 111 (3): 430–437. дои : 10.2105/AJPH.2020.305969 . ПМЦ 7893337 . ПМИД 33566641 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д и ж г Джордан Э.О. (1927). Эпидемический грипп: обзор . Чикаго: Американская медицинская ассоциация.
- ^ «Вот точные факты о гриппе и его последствиях в городе, штате, стране и мире» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . 9 февраля 1919 года. Архивировано из оригинала 24 июля 2020 года . Проверено 10 мая 2020 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Воан WT (июль 1921 г.). «Грипп: эпидемиологическое исследование» . Американский журнал гигиены . ISBN 978-0-598-84038-7 . Архивировано из оригинала 24 июля 2020 года.
- ^ «Еженедельные отчеты общественного здравоохранения за 21 ФЕВРАЛЯ 1919 г.» . Отчеты общественного здравоохранения . 34 (8): 313–376. Февраль 1919 года. ЧВК 1996943 . ПМИД 19314657 .
- ^ «Статистика смертности за 1919 год: Двадцатый годовой отчет» (PDF) . Бюро переписи населения США . 1921. с. 30. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 12 июля 2020 года . Проверено 11 мая 2020 г.
- ^ Пирс, округ Колумбия, Паллаги П.К., Маккоу Дж.М., МакВернон Дж., Мэтьюз Дж.Д. (март 2011 г.). «Понимание смертности во время пандемии гриппа 1918-1919 годов в Англии и Уэльсе» . Грипп и другие респираторные вирусы . 5 (2): 89–98. дои : 10.1111/j.1750-2659.2010.00186.x . ПМЦ 4954464 . ПМИД 21306572 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д Ансарт С., Пелат С., Боэль П.Ю., Каррат Ф., Флахо А., Валлерон А.Дж. (май 2009 г.). «Бремя смертности от пандемии гриппа 1918-1919 годов в Европе» . Грипп и другие респираторные вирусы . 3 (3): 99–106. дои : 10.1111/j.1750-2659.2009.00080.x . ПМЦ 4634693 . ПМИД 19453486 .
- ^ Чоуэлл Г., Эркорека А., Вибуд С., Эчеверри-Давила Б. (июль 2014 г.). «Пространственно-временные закономерности избыточной смертности от пандемии гриппа 1918-1919 годов в Испании» . БМК Инфекционные болезни . 14 (371): 371. дои : 10.1186/1471-2334-14-371 . ПМК 4094406 . ПМИД 24996457 .
- ^ Нуньес Б, Сильва С, Родригес А, Рокетт Р, Батиста И, Ребелу-де-Андраде Х (декабрь 2018 г.). «Пандемия гриппа 1918-1919 годов в Португалии: региональный анализ смертности» . Американский журнал эпидемиологии . 187 (12): 2541–2549. дои : 10.1093/aje/kwy164 . ПМЦ 7314274 . ПМИД 30099487 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Холбрук С. (август 2022 г.). «Общественное здравоохранение в федерации: уроки испанского гриппа в Австралии» . Социальная история медицины . 35 (3): 818–846. дои : 10.1093/shm/hkac005 . ПМЦ 9383459 . ПМИД 36046217 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д Шанкс ГД. «Опыт Австралии во время пандемии гриппа 1918-1919 годов: извлеченные уроки» (PDF) . Университет Отаго .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Керсон П., Маккракен К. (2006). «Австралийский взгляд на пандемию гриппа 1918-1919 годов» . Бюллетень общественного здравоохранения Нового Южного Уэльса . 17 (7–8): 103–107. дои : 10.1071/NB06025 . ПМИД 17136138 .
- ^ «Еженедельные отчеты общественного здравоохранения за 22 августа 1919 г.» . Отчеты общественного здравоохранения . 34 (34): 1927–1968. Август 1919 года. ЧВК 1996930 . ПМИД 19314683 .
- ^ Хо П.Л., Чоу К.Х. (ноябрь 2009 г.). «Бремя смертности от пандемии гриппа 1918-1920 годов в Гонконге» . Грипп и другие респираторные вирусы . 3 (6): 261–263. дои : 10.1111/j.1750-2659.2009.00105.x . ПМЦ 4941390 . ПМИД 19903207 .
- ^ «Еженедельные отчеты общественного здравоохранения за 30 мая 1919 г.» . Отчеты общественного здравоохранения . 34 (22): 1171–1241. Май 1919 года. ЧВК 1996920 . ПМИД 19314671 .
- ^ «Еженедельные отчеты общественного здравоохранения за 1 АВГУСТА 1919 г.» . Отчеты общественного здравоохранения . 34 (31): 1673–1742. Август 1919 года. ЧВК 1996928 . ПМИД 19314680 .
- ^ «Еженедельные отчеты общественного здравоохранения за 29 АВГУСТА 1919 г.» . Отчеты общественного здравоохранения . 34 (35): 1969–2012. Август 1919 года. ЧВК 1996931 . ПМИД 19314684 .
- ^ «Еженедельные отчеты общественного здравоохранения за 15 августа 1919 г.» . Отчеты общественного здравоохранения . 34 (33): 1823–1926. Август 1919 года. ЧВК 1996932 . ПМИД 19314682 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Чоуэлл Дж., Симонсен Л., Флорес Дж., Миллер М.А., Вибуд К. (ноябрь 2014 г.). «Схема смертности во время пандемии гриппа 1918 года в Чили» . Новые инфекционные заболевания . 20 (11): 1803–1811. дои : 10.3201/eid2011.130632 . ПМК 4214284 . ПМИД 25341056 .
- ^ Кристина Дж., Поллеро Р., Пеллегрино А. (май 2019 г.). «Пандемия гриппа 1918 года в Монтевидео: самая южная столица Америки» . Грипп и другие респираторные вирусы . 13 (3): 219–225. дои : 10.1111/irv.12619 . ПМК 6468140 . ПМИД 30422393 .
- ^ Наера РФ (2 января 2019 г.). «Грипп в 1919 году и 100 лет спустя» . Колледж врачей Филадельфии . Архивировано из оригинала 24 июля 2020 года . Проверено 23 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ «Еженедельные отчеты общественного здравоохранения за 15 августа 1919 г.» . Отчеты общественного здравоохранения . 34 (33): 1823–1926. Август 1919 г. doi : 10.2307/4575271 . JSTOR 4575271 . ЧВК 1996932 . ПМИД 19314682 .
- ^ «ПРЕДУПРЕЖДАЕТ О ГРИППЕ» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 15 августа 1919 г. с. 6 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «ПРОТЕМА С КОПЛЭНДОМ» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 27 августа 1919 г. с. 9 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «СИНИЕ ОЖИДАЮТ ВОЗВРАЩЕНИЕ ГРИППА» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 14 сентября 1919 г. с. 4 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «ПАРИЖ БОЯТСЯ ВОЗВРАЩЕНИЯ ЭПИДЕМИИ «ГРИППА»» . Солнце . 19 августа 1919 г. с. 4 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «Британцы готовятся к гриппу» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 30 октября 1919 г. с. 17 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «ГРИП ЭПИДЕМИЯ В ЯПОНИИ» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 28 декабря 1919 г. с. 6 . Проверено 17 марта 2023 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «В Японии постепенно распространяется грипп» . Рекламодатель Гонолулу . 10 января 1920 г. с. 3 . Проверено 17 марта 2023 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «ГРИПП В ЯПОНИИ» . Сидней Морнинг Геральд . 28 января 1920 г. с. 10 . Проверено 17 марта 2023 г.
- ^ «ГРИПП» . Возраст . 26 января 1920 г. с. 5 . Проверено 17 марта 2023 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Ричард С.А., Сугая Н., Симонсен Л., Миллер М.А., Вибуд С. (август 2009 г.). «Сравнительное исследование пандемии гриппа 1918-1920 годов в Японии, США и Великобритании: влияние смертности и последствия для планирования пандемии» . Эпидемиология и инфекции . 137 (8): 1062–1072. дои : 10.1017/S0950268809002088 . ПМК 2704924 . ПМИД 19215637 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Воан WT (июль 1921 г.). «Грипп: эпидемологическое исследование» . Американский журнал гигиены. п. 91. Архивировано из оригинала 6 октября 2020 года . Проверено 13 августа 2020 г. .
- ^ «ЗАРЕГИСТРИРОВАНО 300 СЛУЧАЕВ «ГРИППА»» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 28 сентября 1919 г. с. 5 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «В Чикаго распространяется грипп» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 15 января 1920 г. с. 1 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «525 НОВЫХ СЛУЧАЕВ В ЧИКАГО» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 17 января 1920 г. с. 11 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «Служба здравоохранения сообщает, что грипп находится под контролем во всех частях страны» . Вечерняя звезда . 21 января 1920 г. стр. А2 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «РАСПРОСТРАНЯЕТСЯ ЭПИДЕМИЯ ЧИКАГСКОГО ГРИППА» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 18 января 1920 г. с. 14 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «УВЕЛИЧЕНИЕ СЛУЧАЕВ ГРИППА В ЧИКАГО» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 21 января 1920 г. с. 32 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «ГРИПП ПОКАЗЫВАЕТ БОЛЬШОЙ РОСТ» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 21 января 1920 г. с. 32 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «РАСПРОСТРАНЯЕТСЯ В ДРУГИХ ГОРОДАХ» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 23 января 1920 г. с. 2 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «ТЕМЫ ВРЕМЕНИ» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 22 января 1920 г. с. 16 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «СЛУЧАЙНОСТИ ГРИППА РАСТУТ ПО ВСЕЙ СТРАНЕ» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 25 января 1920 г. с. 2 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «КОПЛЭНД ОЖИДАЕТ РОСТ ЧАСТОТЫ ГРИППА» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 27 января 1920 г. с. 1 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ «Грипп проверен в 25 штатах» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . 8 февраля 1920 г. с. 15 . Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ Статистика смертности, 1920 год. Двадцать первый годовой отчет (PDF) . Бюро переписи населения США (отчет). 1922 г. - через CDC.
- ^ Шмитт Р.К., Нордайк ЕС (1999). «Смерть от гриппа на Гавайях, 1918–1920 годы» . Гавайский исторический журнал . 33 : 101–117 – через eVols.
- ^ Грабовский М.Л., Косиньска Б., Кнап Ю.П., Брыдак Л.Б. (октябрь 2017 г.). «Смертельная пандемия испанского гриппа в Польше» . Монитор медицинских наук . 23 : 4880–4884. дои : 10.12659/MSM.906280 . ПМЦ 5649514 . ПМИД 29021518 .
- ^ Эркорека А (март 2010 г.). «Пандемия испанского гриппа в Западной Европе (1918-1920 гг.) и возраст жертв» . Грипп и другие респираторные вирусы . 4 (2): 81–89. дои : 10.1111/j.1750-2659.2009.00125.x . ПМК 5779284 . ПМИД 20167048 .
- ^ Чоуэлл Дж., Вибуд С., Симонсен Л., Миллер М.А., Уртадо Дж., Сото Дж. и др. (июль 2011 г.). «Пандемия гриппа 1918-1920 годов в Перу» . Вакцина . 29 Приложение 2 (Приложение 2): B21–B26. doi : 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.02.048 . ПМК 3144394 . ПМИД 21757099 .
- ^ Ким Т (2017). «Пандемия гриппа 1918 года и профилактические меры японского генерал-губернаторства Кореи против эпидемий» . Журнал гуманитарных наук Сеульского национального университета (на корейском языке). 74 (1): 203–207 – через Korea Journal Central.
- ^ Се Ю.Х. (октябрь 2009 г.). «Избыточная смертность и иммунозащита во время пандемии гриппа 1918-1920 годов, Тайвань» . Новые инфекционные заболевания . 15 (10): 1617–1619. дои : 10.3201/eid1510.080811 . ПМЦ 2866376 . ПМИД 19861055 .
- ^ Николс СМ, Юинг Э.Т., Гастон К.Х., Маринари М., Лессофф А., Хейссен Д. (апрель 2022 г.). «Что было дальше?: Размышления о последствиях пандемии гриппа 1918–1919 годов в эпоху COVID» . Журнал позолоченного века и прогрессивной эпохи . 21 (2): 126 – через Cambridge Core.
- ^ Линнанмяки Э (2005). Испанский грипп в Финляндии — Пандемия гриппа 1918-1920 гг. (на финском языке). Хельсинки: Финское литературное общество. стр. 69. ISBN 9789517467162 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Таубенбергер Дж.К., Моренс Д.М. (апрель 2010 г.). «Грипп: пандемия прошлого и будущего» . Отчеты общественного здравоохранения . 125 Приложение 3 (Приложение 3): 16–26. дои : 10.1177/00333549101250S305 . ПМЦ 2862331 . ПМИД 20568566 .
- ^ Моренс Д.М., Таубенбергер Дж.К., Фаучи А.С. (июль 2009 г.). «Стойкое наследие вируса гриппа 1918 года» . Медицинский журнал Новой Англии . 361 (3): 225–229. дои : 10.1056/NEJMp0904819 . ПМК 2749954 . ПМИД 19564629 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Таубенбергер Дж.К., Моренс Д.М. (апрель 2009 г.). «Пандемический грипп, включая оценку риска H5N1» . Revue Scientifique et Technique . 28 (1): 187–202. doi : 10.20506/rst.28.1.1879 . ПМК 2720801 . ПМИД 19618626 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Розо М., Гронвалл ГК (август 2015 г.). «Возвращающийся штамм H1N1 1977 года и дебаты о приобретении функции» . мБио . 6 (4). дои : 10.1128/mBio.01013-15 . ПМЦ 4542197 . ПМИД 26286690 .
- ^ Кунг ХК, Джен К.Ф., Юань В.К., Тянь С.Ф., Чу СМ (1978). «Грипп в Китае в 1977 году: рецидив вируса гриппа А подтипа H1N1» . Бюллетень Всемирной организации здравоохранения . 56 (6): 913–918. hdl : 10665/261795 . ПМК 2395678 . ПМИД 310732 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д Сондерс-Гастингс PR, Кревски Д. (декабрь 2016 г.). «Обзор истории пандемического гриппа: понимание закономерностей возникновения и передачи» . Патогены . 5 (4): 66. doi : 10.3390/pathogens5040066 . ПМК 5198166 . ПМИД 27929449 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Кросби 2003 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Воробей М., Кокс Дж., Гилл Д. (2019). «Истоки великой пандемии» . Эволюция, медицина и общественное здравоохранение . 2019 (1): 18–25. дои : 10.1093/emph/eoz001 . ПМК 6381288 . ПМИД 30805187 . S2CID 67863937 .
- ^ «Грипп: многотысячелетний и вредный вирус, открытый только в 1933 году» . Культура Франции (на французском языке). 16 января 2019 года . Проверено 29 июля 2021 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Валентин В. (20 февраля 2006 г.). «Истоки пандемии 1918 года: пример Франции» . Национальное общественное радио . Архивировано из оригинала 30 апреля 2009 года . Проверено 13 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ Oxford JS (декабрь 2001 г.). «Так называемая Великая пандемия испанского гриппа 1918 года могла возникнуть во Франции в 1916 году» . Философские труды Лондонского королевского общества. Серия Б, Биологические науки . 356 (1416). Королевское общество : 1857–1859. дои : 10.1098/rstb.2001.1012 . ПМЦ 1088561 . ПМИД 11779384 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Коннор С. (8 января 2000 г.). «Эпидемия гриппа произошла в пересыльном лагере Великой войны» . Хранитель . Великобритания. Архивировано из оригинала 8 августа 2009 года . Проверено 9 мая 2009 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Оксфорд Дж.С., Ламбкин Р., Сефтон А., Дэниелс Р., Эллиот А., Браун Р. и др. (январь 2005 г.). «Гипотеза: соединение солдат, газа, свиней, уток, гусей и лошадей на севере Франции во время Великой войны обеспечило условия для возникновения «испанской» пандемии гриппа 1918-1919 годов» (PDF) . Вакцина . 23 (7): 940–945. doi : 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.06.035 . ПМИД 15603896 . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 12 марта 2020 года . Проверено 12 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Шанкс Г.Д. (январь 2016 г.). «Нет доказательств происхождения пандемии гриппа 1918 года среди китайских рабочих/солдат во Франции» . Журнал Китайской медицинской ассоциации . 79 (1): 46–48. дои : 10.1016/j.jcma.2015.08.009 . ПМИД 26542935 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Прайс-Смит 2008 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Ханнун С. (1993). «Грипп». Документы конференции Института Пастера . Испанский грипп 1918 года. Медико-хирургическая энциклопедия Ed Techniques (EMC), Инфекционные заболевания. Полет. 8-069-А-10.
- ^ Хамфрис 2014 .
- ^ Вергано Д (24 января 2014 г.). «Пандемия гриппа 1918 года, унесшая жизни 50 миллионов человек, возникла в Китае, говорят историки» . Нэшнл Географик . Архивировано из оригинала 26 января 2014 года . Проверено 4 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Спинни 2018 , с. 143.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Киллинрей Д., Филлипс Х. (2003). Пандемия испанского гриппа 1918–1919 годов: новые перспективы . Рутледж. ISBN 978-1-134-56640-2 . Архивировано из оригинала 9 мая 2021 года . Проверено 9 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ Лэнгфорд С. (2005). «Пандемия гриппа 1918–1919 годов возникла в Китае?». Обзор народонаселения и развития . 31 (3): 473–505. дои : 10.1111/j.1728-4457.2005.00080.x . JSTOR 3401475 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д Ченг К.Ф., Люнг ПК (июль 2007 г.). «Что произошло в Китае во время пандемии гриппа 1918 года?» . Международный журнал инфекционных заболеваний . 11 (4): 360–364. дои : 10.1016/j.ijid.2006.07.009 . ПМИД 17379558 .
- ^ Вергано Д. «Историки утверждают, что пандемия гриппа 1918 года, унесшая жизни 50 миллионов человек, возникла в Китае» . Нэшнл Географик . Архивировано из оригинала 3 марта 2020 года . Проверено 5 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Ченг К.Ф., Люнг ПК (июль 2007 г.). «Что произошло в Китае во время пандемии гриппа 1918 года?» . Международный журнал инфекционных заболеваний . 11 (4): 360–364. дои : 10.1016/j.ijid.2006.07.009 . ПМИД 17379558 .
- ^ Миллс CE, Робинс Дж. М., Липсич М. (декабрь 2004 г.). «Заразность пандемического гриппа 1918 года» . Природа . 432 (7019): 904–906. Бибкод : 2004Natur.432..904M . дои : 10.1038/nature03063 . ПМК 7095078 . ПМИД 15602562 .
- ^ Куреши 2016 , с. 42.
- ^ Эвальд 1994 .
- ^ «Пандемия испанского гриппа 1918 года» . Историческая пресса . Архивировано из оригинала 13 января 2021 года . Проверено 20 февраля 2021 г.
- ^ Иллинг С. (20 марта 2020 г.). «Самый важный урок пандемии гриппа 1918 года: говорить чертову правду» . Вокс . Архивировано из оригинала 25 марта 2020 года.
Джон М. Барри: Правительство лгало. Они лгали обо всем. Мы были в состоянии войны, и они лгали, потому что не хотели разрушать военные действия. Руководители общественного здравоохранения говорили людям, что это обычный грипп под другим названием. Они просто не рассказали людям правду о происходящем.
- ^ Гладуэлл 1997 , с. 55.
- ^ Гладуэлл 1997 , с. 63.
- ^ Международный центр Фогарти. «Летняя вспышка гриппа 1918 года могла обеспечить частичную защиту от смертельной осенней пандемии» . Fic.nih.gov. Архивировано из оригинала 27 июля 2011 года . Проверено 19 мая 2012 г.
- ^ Гладуэлл 1997 , с. 56.
- ^ Джойс Дж. (март 2020 г.). «Финал Кубка Стэнли 1919 года и самая смертоносная пандемия в современной истории» . Спортнет . Архивировано из оригинала 31 марта 2020 года . Проверено 23 марта 2023 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д и Спинни, 2018 , стр. 45–47.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Кноблер 2005 .
- ^ Моррис Д.Э., Клири Д.В., Кларк С.С. (2017). «Вторичные бактериальные инфекции, связанные с пандемиями гриппа» . Границы микробиологии . 8 : 1041. дои : 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01041 . ПМЦ 5481322 . ПМИД 28690590 .
- ^ «Бактериальная пневмония стала причиной большинства смертей во время пандемии гриппа 1918 года» . Национальные институты здравоохранения . 23 сентября 2015 года. Архивировано из оригинала 22 апреля 2016 года . Проверено 17 апреля 2016 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Таубенбергер и др. 2001 , стр. 1829–39.
- ^ Моренс Д.М., Таубенбергер Дж.К., Фаучи А.С. (октябрь 2008 г.). «Преобладающая роль бактериальной пневмонии как причины смерти при пандемическом гриппе: значение для готовности к пандемическому гриппу» . Журнал инфекционных болезней . 198 (7): 962–970. дои : 10.1086/591708 . ПМЦ 2599911 . ПМИД 18710327 .
- ^ Барри 2004 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Спинни 2018 , с. 61.
- ^ «Министерство здравоохранения штата Вашингтон пессимистично оценивает пандемию гриппа в отчете губернатору от 1 января 1919 года» . www.historylink.org . Архивировано из оригинала 21 июля 2020 года . Проверено 21 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Спинни 2018 , с. 62.
- ^ Фоксман Э.Ф., Сторер Дж.А., Фицджеральд М.Е., Васик Б.Р., Хоу Л., Чжао Х. и др. (январь 2015 г.). «Температурно-зависимая врожденная защита от вируса простуды ограничивает репликацию вируса при теплой температуре в клетках дыхательных путей мыши» . Труды Национальной академии наук Соединенных Штатов Америки . 112 (3): 827–832. Бибкод : 2015PNAS..112..827F . дои : 10.1073/pnas.1411030112 . ПМЦ 4311828 . ПМИД 25561542 .
- ^ Лоуэн AC, Стил Дж (июль 2014 г.). «Роль влажности и температуры в формировании сезонности гриппа» . Журнал вирусологии . 88 (14): 7692–7695. дои : 10.1128/JVI.03544-13 . ПМК 4097773 . ПМИД 24789791 .
- ^ Браун Дж.Д., Гёкджян Г., Поулсон Р., Валейка С., Сталкнехт Д.Э. (апрель 2009 г.). «Вирус птичьего гриппа в воде: инфекционность зависит от pH, солености и температуры» . Ветеринарная микробиология . 136 (1–2): 20–26. дои : 10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.10.027 . ПМИД 19081209 .
- ^ Фоксман Э.Ф., Сторер Дж.А., Ваная К., Левченко А., Ивасаки А. (июль 2016 г.). «Две интерферон-независимые стратегии защиты хозяина, индуцированные двухцепочечной РНК, подавляют вирус простуды при теплой температуре» . Труды Национальной академии наук Соединенных Штатов Америки . 113 (30): 8496–8501. Бибкод : 2016PNAS..113.8496F . дои : 10.1073/pnas.1601942113 . ПМЦ 4968739 . ПМИД 27402752 .
- ^ Клугман К.П., Чиен Ю.В., Мадхи С.А. (август 2009 г.). «Пневмококковая пневмония и грипп: смертельная комбинация» . Вакцина . 27 Приложение 3 (с3): C9–C14. doi : 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.06.007 . ПМИД 19683658 .
- ^ Бенгтссон Д., Сафи К., Аврил А., Фидлер В., Викельски М., Гуннарссон Г. и др. (февраль 2016 г.). «Влияет ли инфекция вируса гриппа А на поведение при передвижении во время остановки у дикого хозяина-резервуара?» . Королевское общество открытой науки . 3 (2): 150633. Бибкод : 2016RSOS....350633B . дои : 10.1098/rsos.150633 . ПМЦ 4785985 . ПМИД 26998334 .
- ^ Тольф С., Бенгтссон Д., Родригес Д., Латорре-Маргалеф Н., Вилле М., Фигейредо М.Е. и др. (2012). «Птицы и вирусы на перепутье: эпиднадзор за вирусом гриппа А у португальских водоплавающих птиц» . ПЛОС ОДИН . 7 (11): е49002. Бибкод : 2012PLoSO...749002T . дои : 10.1371/journal.pone.0049002 . ПМК 3492218 . ПМИД 23145046 .
- ^ Такер М.А., Бенинг-Гезе К., Фаган В.Ф., Фрикселл Дж.М., Ван Муртер Б., Альбертс С.К. и др. (январь 2018 г.). «Перемещение в антропоцене: глобальное сокращение перемещений наземных млекопитающих» . Наука . 359 (6374): 466–469. Бибкод : 2018Sci...359..466T . дои : 10.1126/science.aam9712 . hdl : 10174/25640 . ПМИД 29371471 .
- ^ Блейкмор Э. (3 октября 2020 г.). «Катастрофическому эффекту гриппа 1918 года, возможно, способствовал своеобразный приток холодного воздуха в Европу во время Первой мировой войны» . Вашингтон Пост . Архивировано из оригинала 11 декабря 2020 года . Проверено 29 ноября 2020 г. .
- ^ Кент Л. (28 сентября 2020 г.). «Как условия окружающей среды, такие как холодная и влажная погода, могут влиять на пандемии и что это значит для COVID-19» . CNN . Архивировано из оригинала 2 декабря 2020 года . Проверено 29 ноября 2020 г. .
- ^ Пауэлл А. (5 октября 2020 г.). «Шестилетний потоп связан с испанским гриппом и смертями во время Первой мировой войны» . Гарвардская газета . Архивировано из оригинала 27 ноября 2020 года . Проверено 29 ноября 2020 г. .
- ^ «Марлевая маска для остановки распространения чумы» . Вашингтон Таймс . 27 сентября 1918 г. с. 3. Архивировано из оригинала 8 октября 2020 года . Проверено 5 октября 2020 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Хаук Дж., Геллис К. (22 ноября 2020 г.). «Мы празднуем День Благодарения в условиях пандемии. Вот как мы это делали в 1918 году – и что произошло дальше» . США сегодня . Архивировано из оригинала 21 ноября 2020 года.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д Спинни, 2018 , стр. 83–84.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Спинни, 2018 , стр. 87–88.
- ^ Спинни 2018 , с. 91.
- ^ «Как Нью-Йорк победил смертельный грипп 1918 года без вакцин, ограничений, масок и закрытия школ» . силивный . 20 сентября 2021 г. Проверено 23 сентября 2021 г.
- ^ Бутсма MC, Фергюсон, Нью-Мексико (май 2007 г.). «Влияние мер общественного здравоохранения на пандемию гриппа 1918 года в городах США» . Труды Национальной академии наук Соединенных Штатов Америки . 104 (18): 7588–7593. Бибкод : 2007PNAS..104.7588B . дои : 10.1073/pnas.0611071104 . ПМЦ 1849868 . ПМИД 17416677 . S2CID 11280273 .
- ^ Спинни 2018 , стр. 109–10.
- ^ Спинни 2018 , стр. 111–12.
- ^ Флекно Д., Чарльз Уэйкфилд Б., Симмонс А. (июнь 2018 г.). «Чума и войны: пандемия испанского гриппа как урок истории». Медицина, конфликты и выживание . 34 (2): 61–68. дои : 10.1080/13623699.2018.1472892 . ПМИД 29764189 . S2CID 21694687 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Спинни 2018 , с. 92.
- ^ Спинни 2018 , с. 69.
- ^ Спинни 2018 , с. 70.
- ^ Таубенбергер и Моренс 2006 , с. 19.
- ^ Таубенбергер и Моренс 2006 , с. 17.
- ^ Всемирное здравоохранение O (декабрь 2005 г.). «Десять вещей, которые вам нужно знать о пандемическом гриппе (обновление от 14 октября 2005 г.)» (PDF) . Relevé Épidémiologique Hebdomadaire . 80 (49–50): 428–431. ПМИД 16372665 . Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 27 июля 2021 года . Проверено 11 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Джилани Т.Н., Джамиль Р.Т., Сиддики А.Х. (14 декабря 2019 г.). «Грипп H1N1 (свиной грипп)» . СтатПерлс . Остров сокровищ, Флорида: StatPearls. ПМИД 30020613 . Архивировано из оригинала 12 марта 2020 года . Проверено 11 марта 2020 г. - через NCBI .
- ^ Джонсон и Мюллер 2002 .
- ^ Чандра С., Кристенсен Дж. (июль 2019 г.). «Re: «Переоценка глобального бремени смертности от пандемии гриппа 1918 года» ». Американский журнал эпидемиологии . 188 (7): 1404–1406. дои : 10.1093/aje/kwz044 . ПМИД 30824934 . и ответ Шпреувенберг П., Кронеман М., Пейджет Дж. (июль 2019 г.). «Ответ авторов» (PDF) . Американский журнал эпидемиологии . 188 (7): 1405–1406. дои : 10.1093/aje/kwz041 . ПМИД 30824908 . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 12 марта 2020 года . Проверено 12 марта 2020 г.
- ^ «Исторические оценки населения мира» . Архивировано из оригинала 9 июля 2012 года . Проверено 29 марта 2013 г.
- ^ Мэр С. (октябрь 2000 г.). «Эксперты по гриппу предупреждают о необходимости планов по борьбе с пандемией» . БМЖ . 321 (7265): 852. doi : 10.1136/bmj.321.7265.852 . ПМЦ 1118673 . ПМИД 11021855 .
- ^ Чандра, Кульджанин и Рэй, 2012 .
- ^ Арнольд Д. (декабрь 2019 г.). «Смерть и современная империя: эпидемия гриппа 1918–1919 годов в Индии». Труды Королевского исторического общества . 29 : 181–200. дои : 10.1017/S0080440119000082 .
- ^ Шривацан А (12 марта 2020 г.). «Почему 1918 год имеет значение в войне с короной в Индии» . мята . Архивировано из оригинала 18 апреля 2020 года . Проверено 7 июня 2020 г.
- ^ «Что история пандемий говорит нам о коронавирусе» . Индостан Таймс . 15 апреля 2020 года. Архивировано из оригинала 21 апреля 2020 года . Проверено 7 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Мюррей Си Джей, Лопес А.Д., Чин Б., Фихан Д., Хилл К.Х. (декабрь 2006 г.). «Оценка потенциальной глобальной смертности от пандемического гриппа на основе данных реестра естественного движения населения во время пандемии 1918-20 годов: количественный анализ» . Ланцет . 368 (9554). Эльзевир : 2211–2218 гг. дои : 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69895-4 . ПМИД 17189032 . S2CID 22787011 . Архивировано из оригинала 27 сентября 2020 года . Проверено 30 сентября 2020 г.
- ^ «Историалилия Паперейта 1» . historiallinenyhdistys.fi . ISSN 1456-8055 . Архивировано из оригинала 6 февраля 2020 года . Проверено 24 июня 2020 г.
- ^ Оман М (1990). Испанский грипп: шведская эпидемия 1918–1920 годов и ее международная подоплека (на шведском языке). Уппсала; Стокгольм: Ubsaliensis Academiae; Дистрибьютор, Almqvist & Wiksell International. ISBN 978-91-554-2587-6 . OCLC 22451542 .
- ^ Фитри Э (28 октября 2009 г.). «Изучение истории Индонезии в поисках ответов на свиной грипп» . Джакарта Глобус . Архивировано из оригинала 2 ноября 2009 года . Проверено 28 марта 2017 г.
- ^ Кон 2007 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б «ВЛИЯНИЕ ИСПАНКИ НА МИР И ОСМАНСКУЮ ИМПЕРИЮ» (на турецком языке). Архивировано из оригинала 8 ноября 2020 года . Проверено 2 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ «Столетие гриппа 1918 года: Как пережить пандемию» . Архивировано из оригинала 9 июля 2019 года . Проверено 19 июня 2019 г.
- ^ Райс Дж., Брайдер Л. Черный ноябрь: пандемия гриппа 1918 года в Новой Зеландии (второе, исправленное и дополненное издание). Крайстчерч, Новая Зеландия. ISBN 978-1-927145-91-3 . ОСЛК 960210402 .
- ^ Радусин М. (октябрь 2012 г.). «Испанский грипп — часть II: вторая и третья волна» . Войносанитецкий Преглед . 69 (10): 917–927. ПМИД 23155616 . Архивировано из оригинала 9 июля 2020 года . Проверено 23 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Эпидемии и пандемии в Виктории: исторические перспективы» . Парламент Виктории . 23 апреля 2020 г. Проверено 14 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ «Пандемия гриппа» . Национальный музей Австралии . Проверено 14 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ «1918–1920 - Пандемия гриппа и пневмонии - по всей стране ~ 820 000–850 000 - Самые смертоносные американские катастрофы и события с большими человеческими жертвами» . Январь 1918 года. Архивировано из оригинала 30 мая 2020 года . Проверено 22 мая 2020 г.
- ^ Великая пандемия: Соединенные Штаты в 1918–1919 годах , Министерство здравоохранения и социальных служб США.
- ^ «Безмолвный захватчик – Цифровые коллекции – Национальная медицинская библиотека» . Архивировано из оригинала 24 июля 2020 года . Проверено 15 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ «Эпидемия гриппа сильно поразила Юту в 1918, 1919 годах» . Новости Дезерета . 28 марта 1995 года. Архивировано из оригинала 30 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 7 июля 2012 г.
- ^ «Великая пандемия 1918 года: государство за государством» . 5 марта 2018 г. Архивировано из оригинала 6 мая 2009 г. . Проверено 4 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «Смертельный вирус бушует по всей Канаде в конце Первой мировой войны» . История ЦБК.
- ^ «Испанский грипп в Бразилии - Элизио Аугусто де Медейрос и Силва, бизнесмен, писатель и член AEILIJ» (на португальском языке). Газета «Сегодня». Архивировано из оригинала 2 февраля 2014 года . Проверено 22 января 2014 г.
- ^ «Птичий грипп», унесший жизни 40 миллионов человек . Новости Би-би-си . 19 октября 2005 г. Архивировано из оригинала 7 ноября 2017 г. . Проверено 26 апреля 2009 г.
- ^ Хейс 1998 .
- ^ Маркус Х (1996). Хайле Селласси I: Годы становления, 1892–1936 . Трентон, Нью-Джерси: Red Sea Press. стр. 36 и далее.
- ^ Панкхерст 1991 , стр. 48f.
- ^ Панкхерст 1991 , с. 63.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Спинни, 2018 , стр. 167–69.
- ^ «Вирусы массового поражения» . Удача. Си-Эн-Эн. 1 ноября 2004 г. Архивировано из оригинала 6 мая 2009 г. Проверено 30 апреля 2009 г.
- ^ Спинни 2018 , с. 134.
- ^ «Пандемия гриппа поразила Ненану 100 лет назад» . nps.gov . 27 октября 2021 г. Проверено 12 апреля 2022 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Денун 2004г .
- ^ Уишарт С. (июль – август 2018 г.). «Как распространился грипп 1918 года» . New Zealand Geographic (152): 23. Архивировано из оригинала 3 августа 2018 года . Проверено 3 августа 2018 г.
- ^ Афхами 2003 ; Афхами 2012 .
- ^ Фитцджеральд Дж. «Коронавирус: забытые уроки пандемии испанского гриппа» . Ирландские Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 5 мая 2020 года . Проверено 14 июня 2020 г.
Тем не менее, эпидемия «испанки» 1918–1919 годов привела к дополнительным смертям в Ирландии примерно на 25 000 человек, многие из которых были молодыми людьми. Это было почти столько же смертей, сколько погибло среди ирландцев, сражавшихся во время Первой мировой войны.
- ^ «Официальное статистическое управление Ирландии» . Центральное статистическое управление Ирландии . Архивировано из оригинала 14 июня 2020 года . Проверено 14 июня 2020 г.
Всего смертей в Ирландии в 1916 году: 50 627.
- ^ Филлипс Х (10 марта 2020 г.). «Южная Африка провалила испанский грипп в 1918 году. История не должна повториться в отношении COVID-19» . Разговор . Архивировано из оригинала 13 июня 2020 года . Проверено 26 мая 2020 г.
- ^ Спинни 2018 , с. 72.
- ^ Панкхерст 1991 , стр. 51 и далее.
- ^ Белл Д., Николл А., Фукуда К., Хорби П., Монто А., Хайден Ф. и др. (январь 2006 г.). «Нефармацевтические вмешательства при пандемическом гриппе, международные меры» . Новые инфекционные заболевания . 12 (1): 81–87. дои : 10.3201/eid1201.051370 . ПМК 3291414 . ПМИД 16494722 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Шанкс Г.Д., Брандейдж Дж.Ф. (февраль 2013 г.). «Тихоокеанские острова, избежавшие пандемии гриппа 1918-1919 годов и их последующей смертности» . Эпидемиология и инфекции . 141 (2): 353–356. дои : 10.1017/S0950268812000866 . ПМЦ 9152047 . ПМИД 22564320 . S2CID 23794327 .
- ^ Райан Дж, изд. (2009). Пандемический грипп: чрезвычайное планирование и готовность населения . Бока-Ратон, Флорида: CRC Press. п. 24.
- ^ "Колониальный годовой отчет", 1919 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Иидзима В. (2003). «Испанка в Китае, 1918–1920: предварительное исследование». В Phillips H, Killingray D (ред.). Пандемия испанского гриппа 1918 года: новые перспективы . Лондон и Нью-Йорк: Рутледж. стр. 101–09.
- ^ Киллинрей Д., Филлипс Х. (2003). Пандемия испанского гриппа 1918–1919 годов: новые перспективы . Рутледж. ISBN 978-1-134-56640-2 . Архивировано из оригинала 27 июля 2021 года . Проверено 9 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ Киллинрей Д., Филлипс Х. (2003). Пандемия испанского гриппа 1918–1919 годов: новые перспективы . Рутледж. ISBN 978-1-134-56640-2 . Архивировано из оригинала 27 июля 2021 года . Проверено 9 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ Иидзима В. (1998). Испанский грипп в Китае, 1918–1920 гг . OCLC 46987588 .
- ^ Иидзима В. (1998). Испанский грипп в Китае, 1918–1920 гг . Испанский грипп 1918–1998 годов: размышления о пандемии гриппа 1918 года спустя 80 лет. Кейптаун, Южная Африка. Архивировано из оригинала 11 апреля 2020 года . Проверено 11 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д и ж г час Киллинрей Д., Филлипс Х. (2003). Пандемия испанского гриппа 1918–1919 годов: новые перспективы . Рутледж. п. 105. ИСБН 978-1-134-56640-2 . Архивировано из оригинала 27 июля 2021 года . Проверено 9 ноября 2020 г.
- ^ Алита Х.П., Лин Т., Бинь Ж., Сяо-тин Ли (2010). «Анализ эпидемии испанского гриппа 1918 года в Китае на основе литературных источников» . Журнал медицинской информатики . 31 (1): 47–50. Архивировано из оригинала 29 июля 2021 года . Проверено 29 июля 2021 г.
- ^ Хонг, Нью-Хэмпшир (2015). «Эпидемический анализ гриппа 1918 года в Китае - исследование округа Хуолу в провинции Чжили». Исторические исследования в Аууи .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Симонсен и др. 1998 год .
- ^ Ханссен О (1923). Исследования появления гриппа (1918-1922 , особенно в Бергене ) . Сочинения, опубликованные фондом Клауса Хансена, № III. Берген: Больница Хаукеланд, 1923 г. (Письма, опубликованные Фондом Клауса Хансена, № III, Больница Хаукеланд в Бергене (на норвежском языке). Григ. стр. 66.
- ^ Кноблер С.Л., Мак А., Махмуд А., Лемон С.М. «Форум Медицинского института (США) по микробным угрозам» . НКБИ . Проверено 17 августа 2021 г.
- ^ Барри 2004 , с. 239.
- ^ «Основные факты о свином гриппе» . Центры США по контролю и профилактике заболеваний . Архивировано из оригинала 5 мая 2009 года . Проверено 30 апреля 2009 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д и ж Спинни, 2018 , стр. 180–82.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д Спинни, 2018 , стр. 183–84.
- ^ Мамелунд SE (февраль 2006 г.). «Социально нейтральная болезнь? Отдельный социальный класс, благосостояние семьи и смертность от испанского гриппа в двух социально контрастирующих приходах Кристиании 1918-19». Социальные науки и медицина . 62 (4): 923–940. doi : 10.1016/j.socscimed.2005.06.051 . ПМИД 16084634 .
- ^ Он и др. 2011
- ^ Он и др. 2013 .
- ^ «Пандемия испанского гриппа и ее связь с Первой мировой войной» . Столетие Первой мировой войны . Оксфордский университет JISC. Архивировано из оригинала 5 августа 2020 года . Проверено 11 августа 2020 г. .
- ^ Гаррет 2007 .
- ^ Линдли Р. «Забытая американская пандемия: историк доктор Нэнси К. Бристоу об эпидемии гриппа 1918 года» . хнн.нас . Архивировано из оригинала 8 августа 2014 года . Проверено 4 августа 2014 г.
- ^ «Чему испанский грипп может научить нас о пандемии COVID-19?» . Всемирный экономический форум . 2 апреля 2020 года. Архивировано из оригинала 9 апреля 2020 года . Проверено 8 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ Коррейя С., Лак С., Вернер Э. (2020). «Пандемии подавляют экономику, а меры общественного здравоохранения — нет: данные о гриппе 1918 года» . Серия рабочих документов SSRN . arXiv : 2207.11636 . дои : 10.2139/ssrn.3561560 . ISSN 1556-5068 . S2CID 216202133 . Архивировано из оригинала 27 июля 2021 года . Проверено 14 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ Кемп Дж. (7 апреля 2020 г.). «RPT-COLUMN-Коронавирусные ограничения: можем ли мы извлечь уроки из пандемии гриппа 1918 года? Кемп» . Рейтер . Проверено 17 августа 2021 г.
- ^ Миндаль Д. (1 августа 2006 г.). «Окончилась ли пандемия гриппа 1918 года? Долгосрочные последствия внутриутробного воздействия гриппа на население США после 1940 года». Журнал политической экономии . 114 (4): 672–712. дои : 10.1086/507154 . ISSN 0022-3808 . S2CID 20055129 .
- ^ Бич Б, Ферри Дж.П., Сааведра М.Х. (2018). «Шок плода или отбор? Пандемия гриппа 1918 года и развитие человеческого капитала» . nber.org . Серия рабочих документов. дои : 10.3386/w24725 . Архивировано из оригинала 18 июня 2018 года . Проверено 18 июня 2018 г.
- ^ Виленский, Фоли и Гилман 2007 .
- ^ Фоттрелл К. (25 августа 2020 г.). «Еще одно предупреждение от гриппа 1918 года для COVID-19: «Выживание не означает, что человек полностью выздоровел» » . МаркетВотч . Архивировано из оригинала 24 августа 2020 года.
- ^ Хонигсбаум 2008 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Бейнер Дж. (2021). «Повторное открытие великого гриппа между предзабыванием и постзабыванием». В Байнере Дж. (ред.). Пандемическое пробуждение: забытый и незабытый «испанский» грипп 1918–1919 годов . Издательство Оксфордского университета. стр. 346–376. ISBN 9780192843739 .
- ^ Морриси 1986 .
- ^ Бенедикт и Брейтуэйт 2000 , с. 38.
- ^ Кросби 2003 , стр. 320–22.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Почему так мало романов посвящено пандемии 1918 года?» . Смитсоновский журнал . Проверено 6 июня 2023 г.
- ^ Кросби 2003 , с. 315.
- ^ Хансен Л. (24 сентября 2006 г.). «Вид Маллена из «Последнего города на Земле» » . ЭНЕРГЕТИЧЕСКИЙ ЯДЕРНЫЙ РЕАКТОР . Проверено 11 июня 2023 г.
- ^ Корриган М. (20 июля 2020 г.). «Грипп 1918 года вдохновил Донохью на роман «Притяжение звезд» — тревожный роман о пандемии» . ЭНЕРГЕТИЧЕСКИЙ ЯДЕРНЫЙ РЕАКТОР . Проверено 6 июня 2023 г.
- ^ Мейер Р. (29 апреля 2016 г.). «Вымирание человечества не так уж и маловероятно» . Атлантика . Архивировано из оригинала 1 мая 2016 года . Проверено 6 февраля 2018 года .
- ^ «Истинное число погибших от пандемии» . Экономист . 25 октября 2022 г. Проверено 31 июля 2023 г.
- ^ Хиллеман М.Р. (август 2002 г.). «Реалии и загадки вирусного гриппа человека: патогенез, эпидемиология и контроль». Вакцина . 20 (25–26): 3068–87. дои : 10.1016/S0264-410X(02)00254-2 . ПМИД 12163258 .
- ^ Поттер CW (октябрь 2001 г.). «История гриппа». Журнал прикладной микробиологии . 91 (4): 572–9. дои : 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01492.x . ПМИД 11576290 . S2CID 26392163 .
- ^ Биггерстафф М., Кошемес С., Рид С., Гамбхир М., Финелли Л. (сентябрь 2014 г.). «Оценки репродуктивной численности сезонного, пандемического и зоонозного гриппа: систематический обзор литературы» . БМК Инфекционные болезни . 14 (1): 480. дои : 10.1186/1471-2334-14-480 . ПМЦ 4169819 . ПМИД 25186370 .
- ^ Миллс CE, Робинс Дж. М., Липсич М. (декабрь 2004 г.). «Заразность пандемического гриппа 1918 года» . Природа . 432 (7019): 904–6. Бибкод : 2004Natur.432..904M . дои : 10.1038/nature03063 . ПМК 7095078 . ПМИД 15602562 .
- ^ Таубенбергер Дж. К., Моренс Д. М. (январь 2006 г.). «Грипп 1918 года: мать всех пандемий» . Новые инфекционные заболевания . 12 (1): 15–22. дои : 10.3201/eid1201.050979 . ПМЦ 3291398 . ПМИД 16494711 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д и ж г час «Отчет Комитета по обзору функционирования Международных медико-санитарных правил (2005 г.) в отношении пандемии (H1N1) 2009 г.» (PDF) . 5 мая 2011 г. с. 37. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 14 мая 2015 года . Проверено 1 марта 2015 г.
- ^ Шпреувенберг П., Кронеман М., Пейджет Дж. (декабрь 2018 г.). «Переоценка глобального бремени смертности от пандемии гриппа 1918 года» . Американский журнал эпидемиологии . 187 (12): 2561–2567. дои : 10.1093/aje/kwy191 . ПМК 7314216 . ПМИД 30202996 .
- ^ Моренс Д.М., Фаучи А.С. (апрель 2007 г.). «Пандемия гриппа 1918 года: взгляд на XXI век» . Журнал инфекционных болезней . 195 (7): 1018–28. дои : 10.1086/511989 . ПМИД 17330793 .
- ^ Джонсон Н.П., Мюллер Дж. (2002). «Обновление отчетов: глобальная смертность от пандемии «испанского» гриппа 1918-1920 годов». Бюллетень истории медицины . 76 (1): 105–15. дои : 10.1353/bhm.2002.0022 . ПМИД 11875246 . S2CID 22974230 .
- ^ Лин II РГ, Карламангла С (6 марта 2020 г.). «Почему вспышка коронавируса вряд ли станет повторением испанского гриппа 1918 года» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс .
- ^ Шварцманн С.В., Адлер Дж.Л., Салливан Р.Дж., Морской пехотинец В.М. (июнь 1971 г.). «Бактериальная пневмония во время эпидемии гриппа в Гонконге 1968-1969 гг.». Архив внутренней медицины . 127 (6): 1037–41. дои : 10.1001/archinte.1971.00310180053006 . ПМИД 5578560 .
- ^ Михаэлис М., Дорр Х.В., Синатл Дж. (август 2009 г.). «Новый вирус свиного гриппа А у людей: еще одна пандемия стучится в дверь» . Медицинская микробиология и иммунология . 198 (3): 175–83. дои : 10.1007/s00430-009-0118-5 . ПМИД 19543913 . S2CID 20496301 .
- ^ Дональдсон Л.Дж., Раттер П.Д., Эллис Б.М., Гривз Ф.Е., Миттон О.Т., Пебоди Р.Г. и др. (декабрь 2009 г.). «Смертность от пандемического гриппа A/H1N1 2009 в Англии: исследование общественного здравоохранения» . БМЖ . 339 : b5213. дои : 10.1136/bmj.b5213 . ПМК 2791802 . ПМИД 20007665 .
- ^ «Первые глобальные оценки смертности от пандемии H1N1 в 2009 году, опубликованные в результате сотрудничества под руководством CDC» . Центры по контролю и профилактике заболеваний (CDC). 25 июня 2012 года . Проверено 7 июля 2012 г.
- ^ Келли Х., Пек Х.А., Лори К.Л., Ву П., Нишиура Х., Коулинг Б.Дж. (5 августа 2011 г.). «Повозрастная кумулятивная заболеваемость пандемическим гриппом H1N1 2009 была одинаковой в разных странах до вакцинации» . ПЛОС ОДИН . 6 (8): e21828. Бибкод : 2011PLoSO...621828K . дои : 10.1371/journal.pone.0021828 . ПМК 3151238 . ПМИД 21850217 .
- ^ Давуд Ф.С., Юлиано А.Д., Рид С., Мельцер М.И., Шей Д.К., Ченг П.Ю. и др. (сентябрь 2012 г.). «Оценочная глобальная смертность, связанная с первыми 12 месяцами циркуляции вируса пандемического гриппа A H1N1 в 2009 году: моделирование» . «Ланцет». Инфекционные болезни . 12 (9): 687–95. дои : 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70121-4 . ПМИД 22738893 .
- ^ Райли С., Квок КО, Ву К.М., Нин Д.Ю., Коулинг Б.Дж., Ву Дж.Т. и др. (июнь 2011 г.). «Эпидемиологические характеристики пандемического гриппа 2009 года (H1N1) на основе парных сывороток из продольного когортного исследования сообщества» . ПЛОС Медицина . 8 (6): e1000442. дои : 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000442 . ПМК 3119689 . ПМИД 21713000 .
- ^ Вонг Дж.Й., Келли Х., Ип Д.К., Ву Дж.Т., Люнг Г.М., Коулинг Б.Дж. (ноябрь 2013 г.). «Риск летальности от гриппа А (H1N1pdm09): систематический обзор» . Эпидемиология . 24 (6): 830–41. дои : 10.1097/EDE.0b013e3182a67448 . ПМК 3809029 . ПМИД 24045719 .
- ^ «Европейское ВОЗ – Грипп» . Всемирная организация здравоохранения (ВОЗ). Июнь 2009 г. Архивировано из оригинала 17 июня 2009 г. Проверено 12 июня 2009 г.
- ^ «Основные факты о гриппе» . Центры по контролю и профилактике заболеваний . 28 октября 2019 г. Проверено 10 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Токарс Дж.И., Олсен С.Дж., Рид С. (май 2018 г.). «Сезонная заболеваемость симптоматическим гриппом в США» . Клинические инфекционные болезни . 66 (10): 1511–1518. дои : 10.1093/cid/cix1060 . ПМЦ 5934309 . ПМИД 29206909 .
- ^ «Грипп: Информационный бюллетень» . Всемирная организация здравоохранения (ВОЗ). 6 ноября 2018 года. Архивировано из оригинала 17 декабря 2019 года . Проверено 25 января 2020 г.
- ^ «Уровни смертности от H1N1 сравнимы с сезонным гриппом» . Малазийский инсайдер . Вашингтон, округ Колумбия, США. Рейтер. 17 сентября 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 20 октября 2009 года . Проверено 26 сентября 2009 г.
- ^ «Программа открытых коллекций: заражение испанским гриппом в Северной Америке, 1918–1919» . Архивировано из оригинала 20 ноября 2016 года . Проверено 22 ноября 2016 г.
- ^ Хардер Т.С., Ортруда В. «Глава вторая: Птичий грипп» . Отчет о гриппе 2006 г. опубликовано в Интернете. Архивировано из оригинала 9 августа 2017 года . Проверено 26 октября 2007 г.
Иногда вирус содержит как гены, адаптированные к птицам, так и гены, адаптированные к человеку. Пандемические штаммы H2N2 и H3N2 вируса птичьего гриппа содержали сегменты РНК . «В то время как пандемические вирусы человеческого гриппа 1957 (H2N2) и 1968 (H3N2) возникли в результате реассортации между человеческими и птичьими вирусами, вирус гриппа, вызвавший «испанку» в 1918 году, по-видимому, полностью произошел из птичьего источника (Belshe 2005). .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Таубенбергер и др. 2005 .
- ^ Антонович, Худ и Бейкер 2006 .
- ^ Вана и Вестовер 2008 .
- ^ Дос Рейс, Хэй и Гольдштейн, 2009 .
- ^ «Исследователи реконструируют вирус пандемического гриппа 1918 года; усилия направлены на повышение готовности» . Центры по контролю и профилактике заболеваний США. Архивировано из оригинала 19 октября 2011 года . Проверено 2 сентября 2009 г.
- ^ «На пути к убийце: ученые открывают ключ к разгадке вируса испанского гриппа» . Национальный музей здоровья и медицины . Архивировано из оригинала 2 мая 2020 года . Проверено 23 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Колата Г. (16 февраля 1999 г.). «Ученые обнаружили признаки эпидемии гриппа 1918 года» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 22 марта 2020 года . Проверено 23 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Джордан Д., Тампи Т., Джестер Б. «Самый смертоносный грипп: полная история открытия и реконструкции пандемического вируса 1918 года» . archive.cdc.gov . Проверено 22 июня 2024 г.
- ^ Таубенбергер Дж.К., Балтимор Д., Доэрти П.С., Маркел Х., Моренс Д.М., Вебстер Р.Г. и др. (ноябрь 2012 г.). «Реконструкция вируса гриппа 1918 года: неожиданные награды из прошлого» . мБио . 3 (5). дои : 10.1128/mBio.00201-12 . ПМЦ 3448162 . ПМИД 22967978 .
- ^ Кобаса и др. 2007 .
- ^ «Исследования на обезьянах показали, что воскресший грипп 1918 года погиб, повернув тело против самого себя» . США сегодня . Архивировано из оригинала 5 марта 2009 года . Проверено 14 августа 2008 г.
- ^ Фокс 2008 .
- ^ Ю Х, Цибане Т., МакГроу П.А., Хаус Ф.С., Кифер С.Дж., Хикар, доктор медицинских наук и др. (сентябрь 2008 г.). «Нейтрализующие антитела, полученные из В-клеток людей, переживших пандемию гриппа 1918 года» . Природа . 455 (7212): 532–536. Бибкод : 2008Natur.455..532Y . дои : 10.1038/nature07231 . ПМЦ 2848880 . ПМИД 18716625 .
- ^ Фокс 2010 .
- ^ Кросби 1976 , с. 295.
- ^ Мадхав 2013 .
- ^ Брансвелл Х (5 декабря 2018 г.). «Полученное в темноте электронное письмо приведет к семейному сокровищу столетней давности и надежде раскрыть тайну смертельного гриппа» . Стат . Архивировано из оригинала 5 декабря 2018 года . Проверено 5 декабря 2018 г.
- ^ Хаммонд Дж. А., Роллан В., Шор, TH (14 июля 1917 г.). «Гнойный бронхит: исследование случаев заболевания среди британских войск на базе во Франции» (PDF) . Ланцет . 190 (4898): 41–45. дои : 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)56229-7 . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 26 августа 2019 года.
- ^ «Пандемия гриппа 1918 года» . Столетие Первой мировой войны . Оксфорд, Англия: Оксфордский университет. Архивировано из оригинала 9 декабря 2018 года . Проверено 8 декабря 2018 г.
- ^ Савчук Л.А. (август 2009 г.). «Краткое сообщение: Переосмысление влияния пандемии гриппа 1918 года на половые различия в смертности» . Американский журнал физической антропологии . 139 (4): 584–590. дои : 10.1002/ajpa.21022 . ПМИД 19280673 . Архивировано из оригинала 27 июля 2021 года . Проверено 10 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ Ноймер А., Гаренн М. (сентябрь 2000 г.). «Влияние эпидемии гриппа 1918 года на половые различия в смертности в Соединенных Штатах» . Обзор народонаселения и развития . 26 (3): 565–581. дои : 10.1111/j.1728-4457.2000.00565.x . ПМК 2740912 . ПМИД 19530360 .
- ^ Паскофф Т., Саттеншпиль Л. (январь 2019 г.). «Половозрастные различия в смертности во время пандемии гриппа 1918 года на острове Ньюфаундленд» . Американский журнал биологии человека . 31 (1): e23198. дои : 10.1002/ajhb.23198 . ПМИД 30488509 . S2CID 54122685 . Архивировано из оригинала 19 октября 2020 года . Проверено 10 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ Ревеган А., Богерт К., Ян М., Ганьон А., Херринг Д.А. (10 сентября 2015 г.). «Первая волна пандемии гриппа 1918 года среди солдат канадского экспедиционного корпуса» . Американский журнал биологии человека . 27 (5): 638–645. дои : 10.1002/ajhb.22713 . ПМИД 25820782 . S2CID 11033776 . Архивировано из оригинала 27 июля 2021 года . Проверено 10 декабря 2020 г.
Библиография
- Антонович Дж., Худ М.Э., Бейкер CH (апрель 2006 г.). «Молекулярная вирусология: был ли грипп 1918 года птичьего происхождения?» . Природа . 440 (7088): E9, обсуждение E9-E9, обсуждение 10. Бибкод : 2006Natur.440E...9A . дои : 10.1038/nature04824 . ПМИД 16641950 . S2CID 4382489 .
- Афхами А (2003). «Скомпрометированные конституции: иранский опыт борьбы с пандемией гриппа 1918 года» . Бюллетень истории медицины . 77 (2): 367–392. дои : 10.1353/bhm.2003.0049 . ПМИД 12955964 . S2CID 37523219 . Архивировано из оригинала 31 марта 2020 года . Проверено 3 октября 2017 г. – Материалы в открытом доступе, предоставленные Отделением психиатрии и поведенческих наук в Health Sciences Research Commons.
- Афхами А. (29 марта 2012 г.) [15 декабря 2004 г.]. «Грипп » В Яршатер Э (ред.). Энциклопедия Ираника Фаск. 2. Том. XIII (Интернет-изд.). Нью-Йорк: Издательство Персидской библиотеки. стр. 100-1 140–43. Архивировано 27 ноября. из оригинала Получено 3 октября.
- Барри Дж. М. (2004). Великий грипп: эпическая история величайшей чумы в истории . Викинг Пингвин. ISBN 978-0-670-89473-4 .
- Барри Дж. М. (январь 2004 г. b). «Место возникновения пандемии гриппа 1918 года и ее последствия для общественного здравоохранения» . Журнал трансляционной медицины . 2 (1): 3. дои : 10.1186/1479-5876-2-3 . ПМК 340389 . ПМИД 14733617 .
- Бейнер Г. , изд. (2022). Пандемические пробуждения: забытая и незабытая «испанка» 1918-1919 годов . Оксфорд и Нью-Йорк: Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 9780192843739 .
- Бенедикт М.Л., Брейтуэйт М. (2000). «Год смертельного гриппа» . Перед лицом катастрофы: правдивые истории канадских героев из архивов Маклина . Нью-Йорк: Викинг. п. 38 . ISBN 978-0-670-88883-2 .
- Биллингс М. (1997). «Пандемия гриппа 1918 года» . Вирусология в Стэнфордском университете. Архивировано из оригинала 27 июня 2009 года . Проверено 1 мая 2009 г.
- Бристоу Н.К. (2012). Американская пандемия: затерянные миры эпидемии гриппа 1918 года . Нью-Йорк: ОУП. ISBN 978-0-19-023855-1 . OCLC 1231722653 .
- Чандра С., Кулянин Г., Рэй Дж. (август 2012 г.). «Смертность от пандемии гриппа 1918-1919 годов: случай Индии» . Демография . 49 (3): 857–865. дои : 10.1007/s13524-012-0116-x . ПМИД 22661303 . S2CID 39247719 .
- Кросби А.В. (1976). Эпидемия и мир, 1918 год . Вестпорт, Коннектикут: Greenwood Press. ISBN 978-0-8371-8376-3 .
- Кросби А.В. (2003). Забытая пандемия Америки: грипп 1918 года (2-е изд.). Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-0-521-54175-6 . Архивировано из оригинала 3 июня 2020 года . Проверено 3 мая 2020 г. - через Google Книги.
- Дэвис Р.А. (2013). Испанский грипп: повествование и культурная идентичность Испании, 1918 год . Пэлгрейв Макмиллан. ISBN 978-1-137-33921-8 . Архивировано из оригинала 27 июля 2021 года . Проверено 9 ноября 2020 г. - через Google Книги.
- Денун Д (2004). «Новые экономические порядки: земля, труд и зависимость». В Denoon D (ред.). Кембриджская история жителей островов Тихого океана . ЧАШКА. п. 247. ИСБН 978-0-521-00354-4 .
- Дионн КЮ, Туркменский ФФ (2020). «Политика пандемии других: рассмотрение COVID-19 в глобальном и историческом контексте» . Международная организация . 74 (S1): E213–E230. дои : 10.1017/S0020818320000405 . S2CID 230561266 .
- Дос Рейс М., Хэй А.Дж., Гольдштейн Р.А. (октябрь 2009 г.). «Использование неоднородных моделей нуклеотидных замен для выявления событий смены хозяина: применение к происхождению «испанского» вируса пандемического гриппа 1918 года» . Журнал молекулярной эволюции . 69 (4). ООО «Спрингер Сайенс энд Бизнес Медиа»: 333–345. Бибкод : 2009JMolE..69..333D . дои : 10.1007/s00239-009-9282-x . ПМК 2772961 . ПМИД 19787384 .
- Эвальд П.В. (1994). Эволюция инфекционных заболеваний . ОУП. ISBN 978-0-19-506058-4 .
- Ганьон А., Миллер М.С., Холлман С.А., Бурбо Р., Херринг Д.А., Эрн DJ и др. (2013). «Повозрастная смертность во время пандемии гриппа 1918 года: разгадка тайны высокой смертности среди молодых людей» . ПЛОС ОДИН . 8 (8): e69586. Бибкод : 2013PLoSO...869586G . дои : 10.1371/journal.pone.0069586 . ПМЦ 3734171 . ПМИД 23940526 .
- Фокс М (29 декабря 2008 г.). «Исследователи раскрывают тайны пандемии гриппа 1918 года» . Рейтер . Архивировано из оригинала 9 ноября 2020 года . Проверено 2 сентября 2009 г.
- Фокс М (16 июня 2010 г.). «Прививка от свиного гриппа защищает от гриппа 1918 года: исследование» . Рейтер . Архивировано из оригинала 18 июня 2010 года . Проверено 30 июня 2017 г.
- Гэлвин Дж. (31 июля 2007 г.). «Пандемия испанского гриппа: 1918 год» . Популярная механика . Архивировано из оригинала 20 сентября 2011 года . Проверено 2 октября 2011 г.
- Гаррет Т.А. (2007). Экономические последствия пандемии гриппа 1918 года: последствия для современной пандемии (PDF) . Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 22 сентября 2020 г. Проверено 22 ноября 2016 г.
- Гладуэлл М. (29 сентября 1997 г.). «Мёртвая зона» . Житель Нью-Йорка . Архивировано из оригинала 15 декабря 2020 года . Проверено 16 марта 2020 г.
- Хейс Дж. Н. (1998). Бремя болезней: эпидемии и реакция человека в западной истории . Издательство Университета Рутгерса. п. 274. ИСБН 978-0-8135-2528-0 . Архивировано из оригинала 27 июля 2021 года . Проверено 3 мая 2020 г. - через Google Книги.
- He D, Dushoff J, Day T, Ma J, Earn DJ (2011). «Механистическое моделирование трех волн пандемии гриппа 1918 года». Теоретическая экология . 4 (2): 283–88. Бибкод : 2011ThEco...4..283H . дои : 10.1007/s12080-011-0123-3 . ISSN 1874-1738 . S2CID 2010776 .
- He D, Dushoff J, Day T, Ma J, Earn DJ (сентябрь 2013 г.). «Вывод о причинах трех волн пандемии гриппа 1918 года в Англии и Уэльсе» . Слушания. Биологические науки . 280 (1766): 20131345. doi : 10.1098/rspb.2013.1345 . ПМК 3730600 . ПМИД 23843396 .
- Хонигсбаум М (2008). Жизнь с Энзой: забытая история Британии и великой пандемии гриппа 1918 года . Пэлгрейв Макмиллан. ISBN 978-0-230-21774-4 .
- Хамфрис М.О. (2014). «Пути заражения: Первая мировая война и истоки пандемии гриппа 1918 года». Война в истории . 21 (1): 55–81. дои : 10.1177/0968344513504525 . S2CID 159563767 .
- Джонсон Н.П., Мюллер Дж. (2002). «Обновление отчетов: глобальная смертность от пандемии «испанского» гриппа 1918-1920 годов». Бюллетень истории медицины . 76 (1): 105–115. дои : 10.1353/bhm.2002.0022 . ПМИД 11875246 . S2CID 22974230 .
- Ноблер С., Мак А., Махмуд А., Лемон С., ред. (2005). «1: История гриппа» . Угроза пандемического гриппа: готовы ли мы? Краткое содержание семинара (2005 г.) . Вашингтон, округ Колумбия: Издательство национальных академий. стр. 60–61. Архивировано из оригинала 23 декабря 2020 года . Проверено 20 августа 2019 г.
- Кобаса Д., Джонс С.М., Шинья К., Каш Дж.К., Коппс Дж., Эбихара Х. и др. (январь 2007 г.). «Аберрантный врожденный иммунный ответ при летальном заражении макак вирусом гриппа 1918 года» . Природа . 445 (7125): 319–323. Бибкод : 2007Natur.445..319K . дои : 10.1038/nature05495 . ПМИД 17230189 . S2CID 4431644 .
- Кон Г.К. (2007). Энциклопедия чумы и мора: с древнейших времен до наших дней (3-е изд.). Издательство информационной базы. п. 363. ИСБН 978-0-8160-6935-4 . Архивировано из оригинала 1 января 2016 года . Проверено 29 октября 2015 г. - через Google Книги.
- Мадхав Н. (февраль 2013 г.). «Моделирование современной пандемии испанского гриппа» (PDF) . ЭЙР по всему миру . Архивировано из оригинала 26 февраля 2020 года . Проверено 5 мая 2020 г.
- Подробнее А.Ф., Лавлак К.П., Клиффорд Х., Хэндли М.Дж., Коротких Е.В., Курбатов А.В. и др. (сентябрь 2020 г.). «Влияние шестилетней климатической аномалии на пандемию испанского гриппа и Первую мировую войну» . ГеоЗдоровье . 4 (9): e2020GH000277. Бибкод : 2020GHeal...4..277M . дои : 10.1029/2020GH000277 . ISSN 2471-1403 . ПМЦ 7513628 . ПМИД 33005839 .
- Морриси CR (1986). «Эпидемия гриппа 1918 года» . Военно-морская медицина . 77 (3): 11–17.
- Ноймер А., Карреон Д., Джонсон Н. (апрель 2010 г.). «Под сомнение гипотезу о салицилатах и пандемической смертности от гриппа в 1918-1919 годах» . Клинические инфекционные болезни . 50 (8): 1203, ответ автора 1203. doi : 10.1086/651472 . ПМИД 20233050 .
- Панкхерст Р. (1991). Введение в медицинскую историю Эфиопии . Трентон: Red Sea Press. ISBN 978-0-932415-45-5 .
- Паттерсон К.Д., Пайл Г.Ф. (1991). «География и смертность от пандемии гриппа 1918 года». Бюллетень истории медицины . 65 (1): 4–21. ПМИД 2021692 .
- Поррас-Галло М., Дэвис Р.А., ред. (2014). «Пандемия испанского гриппа 1918–1919 годов: перспективы Пиренейского полуострова и Америки» . Рочестерские исследования по истории медицины . Том. 30. Издательство Рочестерского университета. ISBN 978-1-58046-496-3 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 января 2021 года . Проверено 9 ноября 2020 г. - через Google Книги.
- Прайс-Смит А.Т. (2008). Заражение и хаос . Кембридж, Массачусетс: MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-66203-1 .
- Куреши А.И. (2016). Болезнь, вызванная вирусом Эбола: от зарождения до вспышки . Академическая пресса. ISBN 978-0-12-804242-7 – через Google Книги.
- Райс Г.В. (2005). Черный ноябрь; Пандемия гриппа 1918 года в Новой Зеландии (2-е изд.). Университет Кентербери Пресс. ISBN 978-1-877257-35-3 .
- Симонсен Л., Кларк М.Дж., Шенбергер Л.Б., Арден Н.Х., Кокс Н.Дж., Фукуда К. (июль 1998 г.). «Смертность от пандемического и эпидемического гриппа: закономерности изменения возрастного распределения». Журнал инфекционных болезней . 178 (1): 53–60. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.327.2581 . дои : 10.1086/515616 . JSTOR 30114117 . ПМИД 9652423 .
- Спинни Л. (2018). Бледный всадник: испанский грипп 1918 года и как он изменил мир . Лондон: Винтаж. ISBN 978-1-78470-240-3 . OCLC 1090305029 .
- Старко К.М. (ноябрь 2009 г.). «Салицилаты и смертность от пандемического гриппа, фармакология, патология и исторические данные 1918-1919 годов» . Клинические инфекционные болезни . 49 (9): 1405–1410. дои : 10.1086/606060 . ПМИД 19788357 . Разместить резюме в: Американское общество инфекционистов (3 октября 2009 г.). «Неправильное употребление аспирина могло усугубить пандемию гриппа 1918 года» . ScienceDaily . Архивировано из оригинала 9 января 2021 года.
- Чжуан В., Лю Дж., Ли В. (2010). «hsa-миР-33-5p как терапевтическая мишень способствует апоптозу клеток рака молочной железы посредством селенопротеина Т» . Границы в медицине . 50 (8): 651473. дои : 10.1086/651473 . ПМК 8110722 . ПМИД 33987194 .
- Таубенбергер Дж.К., Рид А.Х., Янчевски Т.А., Фаннинг Т.Г. (декабрь 2001 г.). «Интеграция исторических, клинических и молекулярно-генетических данных для объяснения происхождения и вирулентности вируса испанского гриппа 1918 года» . Философские труды Лондонского королевского общества. Серия Б, Биологические науки . 356 (1416): 1829–1839. дои : 10.1098/rstb.2001.1020 . ПМЦ 1088558 . ПМИД 11779381 .
- Таубенбергер Дж.К., Рид А.Х., Лоренс Р.М., Ван Р., Джин Дж., Фаннинг Т.Г. (октябрь 2005 г.). «Характеристика генов полимеразы вируса гриппа 1918 года» . Природа . 437 (7060): 889–893. Бибкод : 2005Natur.437..889T . дои : 10.1038/nature04230 . ПМИД 16208372 . S2CID 4405787 .
- Таубенбергер Дж. К., Моренс Д. М. (январь 2006 г.). «Грипп 1918 года: мать всех пандемий» . Новые инфекционные заболевания . 12 (1): 15–22. дои : 10.3201/eid1201.050979 . ПМЦ 3291398 . ПМИД 16494711 .
- Вана Г., Вестовер К.М. (июнь 2008 г.). «Происхождение вируса испанского гриппа 1918 года: сравнительный геномный анализ». Молекулярная филогенетика и эволюция . 47 (3): 1100–1110. Бибкод : 2008МОЛПЭ..47.1100В . дои : 10.1016/j.ympev.2008.02.003 . ПМИД 18353690 .
- Виленский Дж. А., Фоли П., Гилман С. (август 2007 г.). «Дети и летаргический энцефалит: исторический обзор» . Детская неврология . 37 (2): 79–84. doi : 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2007.04.012 . ПМИД 17675021 . Архивировано из оригинала 17 апреля 2020 года . Проверено 22 ноября 2016 г.
Дальнейшее чтение
- Бейнер Г. (2006). «На морозе и обратно: новый интерес к великому гриппу» . Культурная и социальная история . 3 (4): 496–505. doi : 10.1191/1478003806cs070ra (неактивен 31 января 2024 г.). Архивировано из оригинала 24 июля 2020 года . Проверено 29 мая 2020 г.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI неактивен по состоянию на январь 2024 г. ( ссылка ) - Бейнер Г., изд. (2022), Пандемическое пробуждение: забытый и незабытый «испанский» грипп 1918–1919 годов , Оксфорд и Нью-Йорк: Oxford University Press, ISBN 9780192843739
- Браун Дж. (2018). Грипп: столетняя охота за лечением самой смертельной болезни в истории . Нью-Йорк: Атрия. ISBN 978-1-5011-8124-5 .
- Байерли CR (2005). Лихорадка войны: эпидемия гриппа в армии США во время Первой мировой войны . Нью-Йорк: Издательство Нью-Йоркского университета. ISBN 0814799248 .
- Чандра С., Кристенсен Дж., Лихтман С. (ноябрь 2020 г.). «Связность и сезонность: пандемии гриппа 1918 года и COVID-19 в глобальной перспективе» . Журнал глобальной истории . 15 (3): 408–20. дои : 10.1017/S1740022820000261 . S2CID 228988279 .
- Кольер Р. (1974). Чума испанской дамы – пандемия гриппа 1918–1919 годов . Атенеум. ISBN 978-0-689-10592-0 .
- Дэвис КС (2018). Более смертоносно, чем война: скрытая история испанского гриппа и Первой мировой войны . Генри Холта и компании ISBN 978-1250145123 .
- Дорратолтай Н. (29 марта 2018 г.). Каррелл Х (ред.). «Чему пандемия гриппа 1918 года может научить сегодняшних страховщиков» . Группа исследований и моделирования AIR. Архивировано из оригинала 7 ноября 2020 года . Проверено 28 мая 2019 г.
- Дункан К. (2003). Охота на грипп 1918 года: поиск вируса-убийцы одним ученым . Университет Торонто Пресс. ISBN 978-0-8020-8748-5 . Архивировано из оригинала 24 июля 2020 года . Проверено 3 мая 2020 г.
- Хамфрис М.О. (2013). Последняя чума: испанский грипп и политика общественного здравоохранения в Канаде . Университет Торонто Пресс. ISBN 978-1-4426-1044-6 .
- Джонсон Н. (2006). Великобритания и пандемия гриппа 1918–1919 годов: мрачный эпилог . Лондон и Нью-Йорк: Рутледж. ISBN 978-0-415-36560-4 .
- Джонсон Н. (2003). «Измерение пандемии: смертность, демография и география» . Popolazione e Storia . 4 (2): 31–52.
- Джонсон Н. (2003). «Шотландский грипп – шотландский опыт смертности от испанки ». Шотландский исторический обзор . 83 (2): 216–26. дои : 10.3366/шр.2004.83.2.216 .
- Колата Г (1999). Грипп: история великой пандемии гриппа 1918 года и поиска вируса, вызвавшего ее . Нью-Йорк: Фаррар, Штраус и Жиру. ISBN 978-0-374-15706-7 .
- Маленький Джей (2007). Если я умру, не успев проснуться: дневник Фионы МакГрегор об эпидемии гриппа, Торонто, Онтарио, 1918 год . Дорогая Канада . Маркхэм, Онтарио: Scholastic Canada. ISBN 978-0-439-98837-7 .
- Ноймер А., Гаренн М. (2000). «Влияние эпидемии гриппа 1918 года на половые различия в смертности в Соединенных Штатах» . Обзор народонаселения и развития . 26 (3): 565–581. дои : 10.1111/j.1728-4457.2000.00565.x . ПМК 2740912 . ПМИД 19530360 .
- Оксфорд Дж.С., Сефтон А., Джексон Р., Иннес В., Дэниэлс Р.С., Джонсон Н.П. (февраль 2002 г.). «Первая мировая война, возможно, привела к появлению «испанского» гриппа». «Ланцет». Инфекционные болезни . 2 (2): 111–114. дои : 10.1016/S1473-3099(02)00185-8 . ПМИД 11901642 .
- Оксфорд Дж.С., Сефтон А., Джексон Р., Джонсон Н.П., Дэниелс Р.С. (декабрь 1999 г.). «Кто эта леди?» . Природная медицина . 5 (12): 1351–1352. дои : 10.1038/70913 . ПМИД 10581070 . S2CID 5065916 .
- Петтит Д., Дженис Б. (2008). Жестокий ветер: пандемия гриппа в Америке, 1918–1920 гг . Мерфрисборо, Теннесси: Timberlane Books. ISBN 978-0-9715428-2-2 .
- Филипс Х (2010). «Вновь появляющаяся тень 1918 года: тенденции в историографии пандемии гриппа 1918-1919 годов» . Канадский бюллетень истории медицины . 21 (1): 121–134. дои : 10.3138/cbmh.21.1.121 . ПМИД 15202430 .
- Филлипс Х (1 сентября 2014 г.). «Недавняя волна историографии «испанки» гриппа». Социальная история медицины . 27 (4): 789–808. дои : 10.1093/shm/hku066 .
- Филлипс Х., Киллинрей Д., ред. (2003). Пандемия испанского гриппа 1918 года: новые перспективы . Лондон и Нью-Йорк: Рутледж.
- Филлипс Х (ноябрь 2020 г.). « 17, 18, 19: религия и наука в трех пандемиях: 1817, 1918 и 2019 годах» . Журнал глобальной истории . 15 (3): 434–43. дои : 10.1017/S1740022820000315 . S2CID 228999483 .
- Поттер CW (октябрь 2001 г.). «История гриппа» . Журнал прикладной микробиологии . 91 (4): 572–579. дои : 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01492.x . ПМИД 11576290 . S2CID 26392163 .
- Бирге-младший, Kärtner FX (май 2007 г.). «Эффективная оптимизация многослойных покрытий для сверхбыстрой оптики с использованием аналитических градиентов дисперсии». Прикладная оптика . 46 (14): 2656–2662. дои : 10.2307/132645 . JSTOR 132645 . ПМИД 17446914 .
- Такель П., Сасслер С., Майзель Р., Лейкам А. (2006). «Распространение пандемии гриппа 1918 года в Хартфорде, штат Коннектикут» . История социальных наук . 30 (2): 167–196. дои : 10.1017/S0145553200013432 . JSTOR 40267904 .
- Тумпей Т.М., Гарсиа-Састре А. , Микуласова А., Таубенбергер Дж.К., Суэйн Д.Е., Палезе П. и др. (октябрь 2002 г.). «Существующие противовирусные препараты эффективны против вирусов гриппа с генами пандемического вируса 1918 года» . Труды Национальной академии наук Соединенных Штатов Америки . 99 (21): 13849–13854. Бибкод : 2002PNAS...9913849T . дои : 10.1073/pnas.212519699 . ПМК 129786 . ПМИД 12368467 .
Видео
- Мы слышали звонки: грипп 1918 года – НИЗ с людьми, пережившими испанский грипп. интервью
- Презентация Нэнси Бристоу о пандемии гриппа и Первой мировой войне, 1 ноября 2019 г. , C-SPAN
- «Испанка: предупреждение из истории» . Кембриджский университет . 30 ноября 2018 г. Архивировано из оригинала 27 октября 2021 г.
- Доктор Уайз о гриппе (1919) – 18-минутный театральный информационный фильм ( немой Великобритании ), созданный Советом местного самоуправления , предшественником Министерства здравоохранения . Из Национального архива Британского института кино .
Внешние ссылки
- Эпидемия американского гриппа 1918–1919 годов: цифровая энциклопедия - крупнейшая цифровая коллекция газет, архивных рукописей и интерпретативных эссе, исследующих влияние эпидемии на 50 городов США ( Мичиганский университет ).


