Империя Великих Моголов
Империя Великих Моголов | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1526–1857 | |||||||||||
 The empire at its greatest extent in c. 1700 under Aurangzeb | |||||||||||
| Status | Empire | ||||||||||
| Capital |
| ||||||||||
| Official languages | |||||||||||
| Common languages | See Languages of South Asia | ||||||||||
| Religion |
| ||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||
• 1526–1530 (first) | Babur | ||||||||||
• 1837–1857 (last) | Bahadur Shah II | ||||||||||
| Vicegerent | |||||||||||
• 1526–1540 (first) | Mir Khalifa | ||||||||||
• 1794–1818 (last) | Daulat Rao Sindhia | ||||||||||
| Grand Vizier | |||||||||||
• 1526–1540 (first) | Nizam-ud-din Khalifa | ||||||||||
• 1775–1797 (last) | Asaf-ud-Daula | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Early modern | ||||||||||
| 21 April 1526 | |||||||||||
| 17 May 1540–22 June 1555 | |||||||||||
| 5 November 1556 | |||||||||||
| 1526–1752 | |||||||||||
| 1680–1707 | |||||||||||
| 1738–1740 | |||||||||||
| 21 September 1857 | |||||||||||
• Mughal Emperor exiled to Burma | 7 October 1858 | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| 1690[2][3] | 4,000,000 km2 (1,500,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
• 1595 | 125,000,000[4] | ||||||||||
• 1700 | 158,000,000[5] | ||||||||||
| Currency | Rupee, Taka, dam[6]: 73–74 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||
Империя Великих Моголов была ранней современной империей в Южной Азии . На пике своего развития империя простиралась от внешних окраин бассейна реки Инд на западе, северного Афганистана на северо-западе и Кашмира на севере до высокогорья современных Ассама и Бангладеш на востоке и нагорий Плато Декан в Южной Индии . [ 7 ]
Традиционно считается, что Империя Великих Моголов была основана в 1526 году Бабуром , вождем территории современного Узбекистана , который воспользовался помощью соседних империй Сефевидов и Османской империи . [ 8 ] победить султана Дели Ибрагима Лоди в Первой битве при Панипате и захватить равнины Северной Индии . Однако имперскую структуру Великих Моголов иногда относят к 1600 году, ко времени правления внука Бабура, Акбара . [ 9 ] Эта имперская структура просуществовала до 1720 года, вскоре после смерти последнего крупного императора Аурангзеба . [ 10 ] [ 11 ] во время правления которого империя также достигла своих максимальных географических размеров. Впоследствии к 1760 году империя была преобразована в регион внутри и вокруг Старого Дели, а она была официально распущена британским владычеством после Индийского восстания 1857 года .
Although the Mughal Empire was created and sustained by military warfare,[12][13][14] it did not vigorously suppress the cultures and peoples it came to rule; rather it equalized and placated them through new administrative practices,[15][16] and diverse ruling elites, leading to more efficient, centralised, and standardized rule.[17] The base of the empire's collective wealth was agricultural taxes, instituted by the third Mughal emperor, Akbar.[18][19] These taxes, which amounted to well over half the output of a peasant cultivator,[20] were paid in the well-regulated silver currency,[17] and caused peasants and artisans to enter larger markets.[21]
The relative peace maintained by the empire during much of the 17th century was a factor in India's economic expansion.[22] The burgeoning European presence in the Indian Ocean and an increasing demand for Indian raw and finished products generated much wealth for the Mughal court.[23] There was more conspicuous consumption among the Mughal elite,[24] resulting in greater patronage of painting, literary forms, textiles, and architecture, especially during the reign of Shah Jahan.[25] Among the Mughal UNESCO World Heritage Sites in South Asia are: Agra Fort, Fatehpur Sikri, Red Fort, Humayun's Tomb, Lahore Fort, Shalamar Gardens, and the Taj Mahal, which is described as "the jewel of Muslim art in India, and one of the universally admired masterpieces of the world's heritage."[26]
Name
The closest to an official name for the empire was Hindustan, which was documented in the Ain-i-Akbari.[27] Mughal administrative records also refer to the empire as "dominion of Hindustan" (Wilāyat-i-Hindustān),[28] "country of Hind" (Bilād-i-Hind), "Sultanate of Al-Hind" (Salṭanat(i) al-Hindīyyah) as observed in the epithet of emperor Aurangzeb[29] or endonymous identification from emperor Bahadur Shah Zafar as "Land of Hind" (Hindostān) in Hindustani.[30][31] Contemporary chronicles from Qing China referred to the empire as Hindustan (Héndūsītǎn).[32] In the west, the term "Mughal" was used for the emperor, and by extension, the empire as a whole.[33]
The Mughal designation for their own dynasty was Gurkani (Gūrkāniyān), a reference to their descent from the Turco-Mongol conqueror Timur, who took the title Gūrkān 'son-in-law' after his marriage to a Chinggisid princess.[34] The word Mughal (also spelled Mogul[35] or Moghul in English) is the Indo-Persian form of Mongol. The Mughal dynasty's early followers were Chagatai Turks, and not Mongols,[36] although the dynasty claimed to be of Mongolian ancestry as its founder Babur was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan.[37] The term Mughal was applied to them in India by association with the Mongols and to distinguish them from the Afghan elite which ruled the Delhi Sultanate.[36] The term remains disputed by Indologists.[38] In Marshall Hodgson's view, the dynasty should be called Timurid/Timuri or Indo-Timuri.[36]
History
Babur and Humayun (1526–1556)
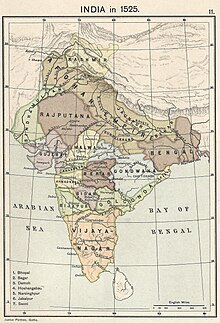
The Mughal Empire was founded by Babur (reigned 1526–1530), a Central Asian ruler who was descended from the Turco-Mongol conqueror Timur (the founder of the Timurid Empire) on his father's side, and from Genghis Khan on his mother's side.[39] Paternally, Babur belonged to the Turkicized Barlas tribe of Mongol origin.[40] Ousted from his ancestral domains in Central Asia, Babur turned to India to satisfy his ambitions.[41] He established himself in Kabul and then pushed steadily southward into India from Afghanistan through the Khyber Pass.[39] Babur's forces defeated Ibrahim Lodi in the First Battle of Panipat in 1526. Before the battle, Babur sought divine favour by abjuring liquor, breaking the wine vessels and pouring the wine down a well. However, by this time Lodi's empire was already crumbling, and it was the Rajput Confederacy which was the strongest power of Northern India under the capable rule of Rana Sanga of Mewar. He defeated Babur in the Battle of Bayana.[42] However, in the decisive Battle of Khanwa which was fought near Agra, the Timurid forces of Babur defeated the Rajput army of Sanga. This battle was one of the most decisive and historic battles in Indian history, as it sealed the fate of Northern India for the next two centuries.
After the battle, the centre of Mughal power became Agra instead of Kabul. The preoccupation with wars and military campaigns, however, did not allow the new emperor to consolidate the gains he had made in India.[43] The instability of the empire became evident under his son, Humayun (reigned 1530–1556), who was forced into exile in Persia by rebels. The Sur Empire (1540–1555), founded by Sher Shah Suri (reigned 1540–1545), briefly interrupted Mughal rule.[39] Humayun's exile in Persia established diplomatic ties between the Safavid and Mughal Courts, and led to increasing Persian cultural influence in the later restored Mughal Empire.[citation needed] Humayun's triumphant return from Persia in 1555 restored Mughal rule in some parts of India, but he died in an accident the next year.[39]
Akbar to Aurangzeb (1556–1707)

Akbar (reigned 1556–1605) was born Jalal-ud-din Muhammad[44] in the Rajput Umarkot Fort,[45] to Humayun and his wife Hamida Banu Begum, a Persian princess.[46] Akbar succeeded to the throne under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped consolidate the Mughal Empire in India. Through warfare and diplomacy, Akbar was able to extend the empire in all directions and controlled almost the entire Indian subcontinent north of the Godavari River.[citation needed] He created a new ruling elite loyal to him, implemented a modern administration, and encouraged cultural developments. He increased trade with European trading companies.[39] India developed a strong and stable economy, leading to commercial expansion and economic development.[citation needed] Akbar allowed freedom of religion at his court and attempted to resolve socio-political and cultural differences in his empire by establishing a new religion, Din-i-Ilahi, with strong characteristics of a ruler cult.[39] He left his son an internally stable state, which was in the midst of its golden age, but before long signs of political weakness would emerge.[39]
Jahangir (born Salim,[47] reigned 1605–1627) was born to Akbar and his wife Mariam-uz-Zamani, an Indian Rajput princess.[48] Salim was named after the Indian Sufi saint, Salim Chishti.[49][50] He "was addicted to opium, neglected the affairs of the state, and came under the influence of rival court cliques".[39] Jahangir distinguished himself from Akbar by making substantial efforts to gain the support of the Islamic religious establishment. One way he did this was by bestowing many more madad-i-ma'ash (tax-free personal land revenue grants given to religiously learned or spiritually worthy individuals) than Akbar had.[51] In contrast to Akbar, Jahangir came into conflict with non-Muslim religious leaders, notably the Sikh guru Arjan, whose execution was the first of many conflicts between the Mughal empire and the Sikh community.[52][53][54]

Shah Jahan (reigned 1628–1658) was born to Jahangir and his wife Jagat Gosain, a Rajput princess.[47] His reign ushered in the golden age of Mughal architecture.[55] During the reign of Shah Jahan, the splendour of the Mughal court reached its peak, as exemplified by the Taj Mahal. The cost of maintaining the court, however, began to exceed the revenue coming in.[39] His reign was called as "The Golden Age of Mughal Architecture". Shah Jahan extended the Mughal empire to the Deccan by ending the Nizam Shahi dynasty and forcing the Adil Shahis and Qutb Shahis to pay tribute.[56]
Shah Jahan's eldest son, the liberal Dara Shikoh, became regent in 1658, as a result of his father's illness.[citation needed] Dara championed a syncretistic Hindu-Muslim culture, emulating his great-grandfather Akbar.[57] With the support of the Islamic orthodoxy, however, a younger son of Shah Jahan, Aurangzeb (r. 1658–1707), seized the throne. Aurangzeb defeated Dara in 1659 and had him executed.[39] Although Shah Jahan fully recovered from his illness, Aurangzeb kept Shah Jahan imprisoned until he died in 1666.[58]: 68 Aurangzeb oversaw an increase in the Islamicization of the Mughal state. He encouraged conversion to Islam, reinstated the jizya on non-Muslims, and compiled the Fatawa 'Alamgiri, a collection of Islamic law. Aurangzeb also ordered the execution of the Sikh guru Tegh Bahadur, leading to the militarization of the Sikh community.[59][53][54] From the imperial perspective, conversion to Islam integrated local elites into the king's vision of network of shared identity that would join disparate groups throughout the empire in obedience to the Mughal emperor.[60] His campaign to conquer South and Western India nominally increased the size of Mughal Empire but had a ruinous effect on Mughal Empire.[61] This campaign also had a ruinous effect on Mughal Treasury, and Emperor's absence led to a severe decline in Governance in Northern India. Marathas started expanding northwards shortly after the death of Aurangzeb, defeated the Mughals in Delhi and Bhopal, and extended their empire up to Peshawar by 1758.[62]
Aurangzeb is considered India's most controversial king,[58] with some historians arguing his religious conservatism and intolerance undermined the stability of Mughal society,[39] while other historians question this, noting that he built Hindu temples,[63] employed significantly more Hindus in his imperial bureaucracy than his predecessors did, opposed bigotry against Hindus and Shia Muslims.[58]: 58 Despite these allegations, it has been acknowledged that Emperor Aurangzeb enacted repressive policies towards non-Muslims, which also resulted to a major rebellion by the Marathas.[64]
Decline (1707–1857)


Aurangzeb's son, Bahadur Shah I, repealed the religious policies of his father and attempted to reform the administration. "However, after he died in 1712, the Mughal dynasty began to sink into chaos and violent feuds. In 1719 alone, four emperors successively ascended the throne",[39] as figureheads under the rule of a brotherhood of nobles belonging to the Indian Muslim caste known as the Sadaat-e-Bara, whose leaders, the Sayyid Brothers, became the de facto sovereigns of the empire.[65][66]
During the reign of Muhammad Shah (reigned 1719–1748), the empire began to break up, and vast tracts of central India passed from Mughal to Maratha hands. As the Mughals tried to suppress the independence of Nizam-ul-Mulk, Asaf Jah I in the Deccan, he encouraged the Marathas to invade central and northern India.[67][68][69] The Indian campaign of Nader Shah, who had previously reestablished Iranian suzerainty over most of West Asia, the Caucasus, and Central Asia, culminated with the Sack of Delhi shattering the remnants of Mughal power and prestige, and taking off all the accumulated Mughal treasury. The Mughals could no longer finance the huge armies with which they had formerly enforced their rule. Many of the empire's elites now sought to control their affairs and broke away to form independent kingdoms.[70] But lip service continued to be paid to the Mughal Emperor as the highest manifestation of sovereignty. Not only the Muslim gentry, but the Maratha, Hindu, and Sikh leaders took part in ceremonial acknowledgements of the emperor as the sovereign of India.[71]
Meanwhile, some regional polities within the increasingly fragmented Mughal Empire, involved themselves and the state in global conflicts, leading only to defeat and loss of territory during the Carnatic Wars and the Bengal War.[citation needed]
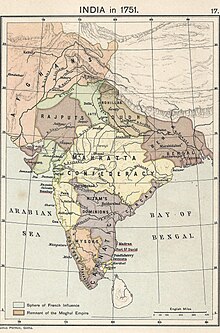
The Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II (1759–1806) made futile attempts to reverse the Mughal decline. But when the Third Battle of Panipat was fought between the Maratha Empire and the Afghans (led by Abdali) in 1761, in which the Afghans were victorious, the emperor had ignominiously taken temporary refuge with the British to the east. In 1771, the Marathas recaptured Delhi from Afghan control and in 1784 they officially became the protectors of the emperor in Delhi,[72] a state of affairs that continued until the Second Anglo-Maratha War. Thereafter, the British East India Company became the protectors of the Mughal dynasty in Delhi.[71] The British East India Company took control of the former Mughal province of Bengal-Bihar in 1793 after it abolished local rule (Nizamat) that lasted until 1858, marking the beginning of British colonial era over the Indian subcontinent. By 1857 a considerable part of former Mughal India was under the East India Company's control. After a crushing defeat in the war of 1857–1858 which he nominally led, the last Mughal, Bahadur Shah Zafar, was deposed by the British East India Company and exiled in 1858. Zafar was exiled to Rangoon, Burma.[73] His wife Zeenat Mahal and some of the remaining members of the family accompanied him. At 4 am on 7 October 1858, Zafar along with his wives, and two remaining sons began his journey towards Rangoon in bullock carts escorted by 9th Lancers under the command of Lieutenant Ommaney.[74] Through the Government of India Act 1858 the British Crown assumed direct control of East India Company-held territories in India in the form of the new British Raj. In 1876 the British Queen Victoria assumed the title of Empress of India.[citation needed]

Causes of decline
Historians have offered numerous accounts of the several factors involved in the rapid collapse of the Mughal Empire between 1707 and 1720, after a century of growth and prosperity. A succession of short-lived incompetent and weak rulers, and civil wars over the succession, created political instability at the centre. The Mughals appeared virtually unassailable during the 17th century but, once gone, their imperial overstretch became clear, and the situation could not be recovered. The seemingly innocuous European trading companies, such as the British East Indies Company, played no real part in the initial decline; they were still racing to get permission from the Mughal rulers to establish trades and factories in India.[75]
In fiscal terms, the throne lost the revenues needed to pay its chief officers, the emirs (nobles) and their entourages. The emperor lost authority, as the widely scattered imperial officers lost confidence in the central authorities, and made their deals with local men of influence. The imperial army bogged down in long, futile wars against the more aggressive Marathas, and lost its fighting spirit. Finally came a series of violent political feuds over control of the throne. After the execution of Emperor Farrukhsiyar in 1719, local Mughal successor states took power in region after region.[76]
Contemporary chroniclers bewailed the decay they witnessed, a theme picked up by the first British historians who wanted to underscore the need for a British-led rejuvenation.[77]
Modern views on the decline
Since the 1970s historians have taken multiple approaches to the decline, with little consensus on which factor was dominant. The psychological interpretations emphasise depravity in high places, excessive luxury, and increasingly narrow views that left the rulers unprepared for an external challenge. A Marxist school (led by Irfan Habib and based at Aligarh Muslim University) emphasises excessive exploitation of the peasantry by the rich, which stripped away the will and the means to support the regime.[78]
Karen Leonard has focused on the failure of the regime to work with Hindu Baniya[79], whose financial support was increasingly needed; the bankers then helped the Maratha and the British.[80] In a religious interpretation, some scholars argue that the Hindu powers revolted against the rule of a Muslim dynasty.[81] Finally, other scholars argue that the very prosperity of the Empire inspired the provinces to achieve a high degree of independence, thus weakening the imperial court.[82]
Jeffrey G. Williamson has argued that the Indian economy went through deindustrialization in the latter half of the 18th century as an indirect outcome of the collapse of the Mughal Empire, with British rule later causing further deindustrialization.[83] According to Williamson, the decline of the Mughal Empire led to a decline in agricultural productivity, which drove up food prices, then nominal wages, and then textile prices, which led to India losing a share of the world textile market to Britain even before it had superior factory technology.[84] Indian textiles, however, still maintained a competitive advantage over British textiles up until the 19th century.[85]
Administration and state
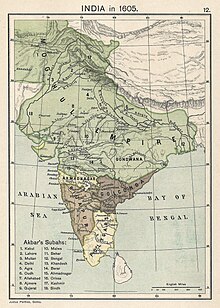
The Mughal Empire had a highly centralised, bureaucratic government, most of which was instituted during the rule of the third Mughal emperor Akbar.[86][87] The central government was headed by the Mughal emperor; immediately beneath him were four ministries. The finance/revenue ministry, headed by an official called a diwan, was responsible for controlling revenues from the empire's territories, calculating tax revenues, and using this information to distribute assignments. The ministry of the military (army/intelligence) was headed by an official titled mir bakhshi, who was in charge of military organisation, messenger service, and the mansabdari system. The ministry in charge of law/religious patronage was the responsibility of the sadr as-sudr, who appointed judges and managed charities and stipends. Another ministry was dedicated to the imperial household and public works, headed by the mir saman. Of these ministers, the diwan held the most importance, and typically acted as the wazir (prime minister) of the empire.[73][86][88]
Administrative divisions
The empire was divided into Subah (provinces), each of which was headed by a provincial governor called a subadar. The structure of the central government was mirrored at the provincial level; each suba had its own bakhshi, sadr as-sudr, and finance minister that reported directly to the central government rather than the subahdar. Subas were subdivided into administrative units known as sarkars, which were further divided into groups of villages known as parganas. Mughal government in the pargana consisted of a Muslim judge and local tax collector.[73][86] Parganas were the basic administrative unit of the Mughal empire.[89]
Mughal administrative divisions were not static. Territories were often rearranged and reconstituted for better administrative control, and to extend cultivation. For example, a sarkar could turn into a subah, and Parganas were often transferred between sarkars. The hierarchy of division was ambiguous sometimes, as a territory could fall under multiple overlapping jurisdictions. Administrative divisions were also vague in their geography – the Mughal state did not have enough resources or authority to undertake detailed land surveys, and hence the geographical limits of these divisions were not formalised and maps were not created. The Mughals instead recorded detailed statistics about each division, to assess the territory's capacity for revenue, based on simpler land surveys.[90]
Capitals
The Mughals had multiple imperial capitals, established throughout their rule. These were the cities of Agra, Delhi, Lahore, and Fatehpur Sikri. Power often shifted back and forth between these capitals.[91] Sometimes this was necessitated by political and military demands, but shifts also occurred for ideological reasons (for example, Akbar's establishment of Fatehpur Sikri), or even simply because the cost of establishing a new capital was marginal.[92] Situations where there were two simultaneous capitals happened multiple times in Mughal history. Certain cities also served as short-term, provincial capitals, as was the case with Aurangzeb's shift to Aurangabad in the Deccan.[91] Kabul was the summer capital of Mughals from 1526 to 1681.[93]
The imperial camp, used for military expeditions and royal tours, also served as a kind of mobile, "de facto" administrative capital. From the time of Akbar, Mughal camps were huge in scale, accompanied by numerous personages associated with the royal court, as well as soldiers and labourers. All administration and governance were carried out within them. The Mughal Emperors spent a significant portion of their ruling period within these camps.[94]
After Aurangzeb, the Mughal capital definitively became the walled city of Shahjahanabad (Old Delhi).[95]
Law

The Mughal Empire's legal system was context-specific and evolved throughout the empire's rule. Being a Muslim state, the empire employed fiqh (Islamic jurisprudence) and therefore the fundamental institutions of Islamic law such as those of the qadi (judge), mufti (jurisconsult), and muhtasib (censor and market supervisor) were well-established in the Mughal Empire. However, the dispensation of justice also depended on other factors, such as administrative rules, local customs, and political convenience. This was due to Persianate influences on Mughal ideology, and that the Mughal Empire governed a non-Muslim majority.[96] Scholar Mouez Khalfaoui notes that legal institutions in the Mughal Empire systemically suffered from the corruption of local judges.[97]
Legal ideology
The Mughal Empire followed the Sunni Hanafi system of jurisprudence. In its early years, the empire relied on Hanafi legal references inherited from its predecessor, the Delhi Sultanate. These included the al-Hidayah (the best guidance) and the Fatawa al-Tatarkhaniyya (religious decisions of the Emire Tatarkhan). During the Mughal Empire's peak, the Fatawa 'Alamgiri was commissioned by Emperor Aurangzeb. This compendium of Hanafi law sought to serve as a central reference for the Mughal state that dealt with the specifics of the South Asian context.[97]
The Mughal Empire also drew on Persian notions of kingship. Particularly, this meant that the Mughal emperor was considered the supreme authority on legal affairs.[96]
Courts of law
Various kinds of courts existed in the Mughal Empire. One such court was that of the qadi. The Mughal qadi was responsible for dispensing justice; this included settling disputes, judging people for crimes, and dealing with inheritances and orphans. The qadi also had additional importance in documents, as the seal of the qadi was required to validate deeds and tax records. Qadis did not constitute a single position, but made up a hierarchy. For example, the most basic kind was the pargana (district) qadi. More prestigious positions were those of the qadi al-quddat (judge of judges) who accompanied the mobile imperial camp, and the qadi-yi lashkar (judge of the army).[96] Qadis were usually appointed by the emperor or the sadr-us-sudr (chief of charities).[96][98] The jurisdiction of the qadi was availed by Muslims and non-Muslims alike.[99]
The jagirdar (local tax collector) was another kind of official approach, especially for high-stakes cases. Subjects of the Mughal Empire also took their grievances to the courts of superior officials who held more authority and punitive power than the local qadi. Such officials included the kotwal (local police), the faujdar (an officer controlling multiple districts and troops of soldiers), and the most powerful, the subahdar (provincial governor). In some cases, the emperor dispensed justice directly.[96] Jahangir was known to have installed a "chain of justice" in the Agra Fort that any aggrieved subject could shake to get the attention of the emperor and bypass the inefficacy of officials.[100]
Self-regulating tribunals operating at the community or village level were common, but sparse documentation of them exists. For example, it is unclear how panchayats (village councils) operated in the Mughal era.[96]
Economy
The economy in the Indian Subcontinent during the Mughal era performed just as it did in ancient times, though now it would face the stress of extensive regional tensions.[101] The Mughal economy was large and prosperous.[102][103] India was producing 24.5% of the world's manufacturing output up until 1750.[104][103] India's economy has been described as a form of proto-industrialization, like that of 18th-century Western Europe prior to the Industrial Revolution.[105]
Modern historians and researchers generally agreed that The Mughal empire economic policy character is resembling Laissez-faire system in dealing with tradings and bullions, to achieve the economic ends.[106][107][108] [109]
The Mughals were responsible for building an extensive road system, creating a uniform currency, and the unification of the country.[6]: 185–204 The empire had an extensive road network, which was vital to the economic infrastructure, built by a public works department set up by the Mughals which designed, constructed and maintained roads linking towns and cities across the empire, making trade easier to conduct.[102]
The main base of the empire's collective wealth was agricultural taxes, instituted by the third Mughal emperor, Akbar.[18][19] These taxes, which amounted to well over half the output of a peasant cultivator,[20] were paid in the well-regulated silver currency,[17] and caused peasants and artisans to enter larger markets.[21] In circa 1595, Modern historians estimated the state's annual revenues of Mughal empire were around 99,000,000 Rupee.[110]
Coinage

The Mughals adopted and standardised the rupee (rupiya, or silver) and dam (copper) currencies introduced by Sur Emperor Sher Shah Suri during his brief rule.[111] The currency was initially 48 dams to a single rupee in the beginning of Akbar's reign, before it later became 38 dams to a rupee in the 1580s, with the dam's value rising further in the 17th century as a result of new industrial uses for copper, such as in bronze cannons and brass utensils. The dam was initially the most common coin in Akbar's time, before being replaced by the rupee as the most common coin in succeeding reigns.[6] The dam's value was later worth 30 to a rupee towards the end of Jahangir's reign, and then 16 to a rupee by the 1660s.[112] The Mughals minted coins with high purity, never dropping below 96%, and without debasement until the 1720s.[113]
Despite India having its stocks of gold and silver, the Mughals produced minimal gold of their own but mostly minted coins from imported bullion, as a result of the empire's strong export-driven economy, with global demand for Indian agricultural and industrial products drawing a steady stream of precious metals into India.[6] Around 80% of Mughal India's imports were bullion, mostly silver,[114] with major sources of imported bullion including the New World and Japan,[113] which in turn imported large quantities of textiles and silk from the Bengal Subah province.[6]
Labour
The historian Shireen Moosvi estimates that in terms of contributions to the Mughal economy, in the late 16th century, the primary sector contributed 52%, the secondary sector 18% and the tertiary sector 29%; the secondary sector contributed a higher percentage than in early 20th-century British India, where the secondary sector only contributed 11% to the economy.[115] In terms of the urban-rural divide, 18% of Mughal India's labour force were urban and 82% were rural, contributing 52% and 48% to the economy, respectively.[116]
According to Stephen Broadberry and Bishnupriya Gupta, grain wages in India were comparable to England in the 16th and 17th centuries, but diverged in the 18th century when they fell to 20-40% of England's wages.[117][118] This, however, is disputed by Parthasarathi and Sivramkrishna. Parthasarathi cites his estimates that grain wages for weaving and spinning in mid-18th century Bengal and South India were comparable to Britain.[119] Similarly, Sivramkrishna analyzed agricultural surveys conducted in Mysore by Francis Buchanan during 1800–1801, arrived at estimates using a "subsistence basket" that aggregated millet income could be almost five times subsistence level, while corresponding rice income was three times that much.[120] That could be comparable to advance part of Europe.[121] Due to the scarcity of data, however, more research is needed before drawing any conclusion.[122][123]
According to Moosvi, Mughal India had a per-capita income, in terms of wheat, 1.24% higher in the late 16th century than British India did in the early 20th century.[124] This income, however, would have to be revised downwards if manufactured goods, like clothing, would be considered. Compared to food per capita, expenditure on clothing was much smaller though, so relative income between 1595 and 1596 should be comparable to 1901–1910.[125] However, in a system where wealth was hoarded by elites, wages were depressed for manual labour.[126] In Mughal India, there was a generally tolerant attitude towards manual labourers, with some religious cults in northern India proudly asserting a high status for manual labour. While slavery also existed, it was limited largely to household servants.[126]
Agriculture
Indian agricultural production increased under the Mughal Empire.[102] A variety of crops were grown, including food crops such as wheat, rice, and barley, and non-food cash crops such as cotton, indigo and opium. By the mid-17th century, Indian cultivators began to extensively grow two new crops from the Americas, maize and tobacco.[102]
The Mughal administration emphasised agrarian reform, which began under the non-Mughal emperor Sher Shah Suri, the work of which Akbar adopted and furthered with more reforms. The civil administration was organised hierarchically based on merit, with promotions based on performance.[127] The Mughal government funded the building of irrigation systems across the empire, which produced much higher crop yields and increased the net revenue base, leading to increased agricultural production.[102]
A major Mughal reform introduced by Akbar was a new land revenue system called zabt. He replaced the tribute system, previously common in India and used by Tokugawa Japan at the time, with a monetary tax system based on a uniform currency.[113] The revenue system was biased in favour of higher value cash crops such as cotton, indigo, sugar cane, tree crops, and opium, providing state incentives to grow cash crops, in addition to rising market demand.[6] Under the zabt system, the Mughals also conducted extensive cadastral surveying to assess the area of land under plough cultivation, with the Mughal state encouraging greater land cultivation by offering tax-free periods to those who brought new land under cultivation.[113] The expansion of agriculture and cultivation continued under later Mughal emperors including Aurangzeb, whose 1665 firman edict stated: "the entire elevated attention and desires of the Emperor are devoted to the increase in the population and cultivation of the Empire and the welfare of the whole peasantry and the entire people."[128]
Mughal agriculture was in some ways advanced compared to European agriculture at the time, exemplified by the common use of the seed drill among Indian peasants before its adoption in Europe.[129] While the average peasant across the world was only skilled in growing very few crops, the average Indian peasant was skilled in growing a wide variety of food and non-food crops, increasing their productivity.[130] Indian peasants were also quick to adapt to profitable new crops, such as maize and tobacco from the New World being rapidly adopted and widely cultivated across Mughal India between 1600 and 1650. Bengali farmers rapidly learned techniques of mulberry cultivation and sericulture, establishing Bengal Subah as a major silk-producing region of the world.[6] Sugar mills appeared in India shortly before the Mughal era. Evidence for the use of a draw bar for sugar-milling appears at Delhi in 1540, but may also date back earlier, and was mainly used in the northern Indian subcontinent. Geared sugar rolling mills first appeared in Mughal India, using the principle of rollers as well as worm gearing, by the 17th century.[131]
According to economic historian Immanuel Wallerstein, citing evidence from Irfan Habib, Percival Spear, and Ashok Desai, per-capita agricultural output and standards of consumption in 17th-century Mughal India were probably higher than in 17th-century Europe and certainly higher than early 20th-century British India.[132] The increased agricultural productivity led to lower food prices. In turn, this benefited the Indian textile industry. Compared to Britain, the price of grain was about one-half in South India and one-third in Bengal, in terms of silver coinage. This resulted in lower silver coin prices for Indian textiles, giving them a price advantage in global markets.[133]
Industrial manufacturing
South Asia during the Mughal's rule was a very fertile ground for manufacturing technologies which coveted by the Europeans before the Industrial Revolution.[134] Up until 1750, India produced about 25% of the world's industrial output.[83]
Manufactured goods and cash crops from the Mughal Empire were sold throughout the world. Key industries included textiles, shipbuilding, and steel. Processed products included cotton textiles, yarns, thread, silk, jute products, metalware, and foods such as sugar, oils and butter.[102] The growth of manufacturing industries in the Indian subcontinent during the Mughal era in the 17th–18th centuries has been referred to as a form of proto-industrialization, similar to 18th-century Western Europe before the Industrial Revolution.[105]
In early modern Europe, there was significant demand for products from Mughal India, particularly cotton textiles, as well as goods such as spices, peppers, indigo, silks, and saltpetre (for use in munitions).[102] European fashion, for example, became increasingly dependent on Mughal Indian textiles and silks. From the late 17th century to the early 18th century, Mughal India accounted for 95% of British imports from Asia, and the Bengal Subah province alone accounted for 40% of Dutch imports from Asia.[135] In contrast, there was very little demand for European goods in Mughal India, which was largely self-sufficient, thus Europeans had very little to offer, except for some woollens, unprocessed metals and a few luxury items. The trade imbalance caused Europeans to export large quantities of gold and silver to Mughal India to pay for South Asian imports.[102] Indian goods, especially those from Bengal, were also exported in large quantities to other Asian markets, such as Indonesia and Japan.[6]
Textile industry


The largest manufacturing industry in the Mughal Empire was textile manufacturing, particularly cotton textile manufacturing, which included the production of piece goods, calicos, and muslins, available unbleached and in a variety of colours. The cotton textile industry was responsible for a large part of the empire's international trade.[102] India had a 25% share of the global textile trade in the early 18th century.[136] Indian cotton textiles were the most important manufactured goods in world trade in the 18th century, consumed across the world from the Americas to Japan.[137] By the early 18th century, Mughal Indian textiles were clothing people across the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, Europe, the Americas, Africa, and the Middle East.[84] The most important centre of cotton production was the Bengal province, particularly around its capital city of Dhaka.[138]
Bengal accounted for more than 50% of textiles and around 80% of silks imported by the Dutch from Asia,[135] Bengali silk and cotton textiles were exported in large quantities to Europe, Indonesia, and Japan,[6]: 202 and Bengali muslin textiles from Dhaka were sold in Central Asia, where they were known as "Dhaka textiles".[138] Indian textiles dominated the Indian Ocean trade for centuries, were sold in the Atlantic Ocean trade, and had a 38% share of the West African trade in the early 18th century, while Indian calicos were a major force in Europe, and Indian textiles accounted for 20% of total English trade with Southern Europe in the early 18th century.[83]
The worm gear roller cotton gin, which was invented in India during the early Delhi Sultanate era of the 13th–14th centuries, came into use in the Mughal Empire sometime around the 16th century,[131] and is still used in India through to the present day.[139] Another innovation, the incorporation of the crank handle in the cotton gin, first appeared in India sometime during the late Delhi Sultanate or the early Mughal Empire.[140] The production of cotton, which may have largely been spun in the villages and then taken to towns in the form of yarn to be woven into cloth textiles, was advanced by the diffusion of the spinning wheel across India shortly before the Mughal era, lowering the costs of yarn and helping to increase demand for cotton. The diffusion of the spinning wheel and the incorporation of the worm gear and crank handle into the roller cotton gin led to greatly expanded Indian cotton textile production during the Mughal era.[141]
Once, the Mughal emperor Akbar asked his courtiers, which was the most beautiful flower. Some said rose, from whose petals were distilled the precious ittar, others, the lotus, glory of every Indian village. But Birbal said, "The cotton boll". There was a scornful laughter and Akbar asked for an explanation. Birbal said, "Your Majesty, from the cotton boll, comes the fine fabric prized by merchants across the seas that has made your empire famous throughout the world. The perfume of your fame far exceeds the scent of roses and jasmine. That is why I say the cotton boll is the most beautiful flower.[142]
Bengal Subah

The Bengal Subah province was especially prosperous from the time of its takeover by the Mughals in 1590 until the British East India Company seized control in 1757.[143] Historian C. A. Bayly wrote that it was probably the Mughal Empire's wealthiest province.[144] Domestically, much of India depended on Bengali products such as rice, silks and cotton textiles. Overseas, Europeans depended on Bengali products such as cotton textiles, silks, and opium; Bengal accounted for 40% of Dutch imports from Asia, for example, including more than 50% of textiles and around 80% of silks.[135] From Bengal, saltpetre was also shipped to Europe, opium was sold in Indonesia, raw silk was exported to Japan and the Netherlands, and cotton and silk textiles were exported to Europe, Indonesia and Japan.[6]
Akbar played a key role in establishing Bengal as a leading economic centre, as he began transforming many of the jungles there into farms. As soon as he conquered the region, he brought tools and men to clear jungles to expand cultivation and brought Sufis to open the jungles to farming.[128] Bengal was later described as the Paradise of Nations by Mughal emperors.[145] The Mughals introduced agrarian reforms, including the modern Bengali calendar.[146] The calendar played a vital role in developing and organising harvests, tax collection and Bengali culture in general, including the New Year and Autumn festivals.[citation needed] The province was a leading producer of grains, salt, fruits, liquors and wines, precious metals and ornaments.[147] After Akbar, there are notable contributive factor during the era of Aurangzeb, as Siddiqui M. Azizuddin Hussein from Jamia Millia Islamia and Maulana Azad National Urdu University, has viewed that aside from religious and legal context, Fatawa 'Alamgiri codex has provided direct contribution to the Proto-industrialization in Bengal Subah.[148]
After 150 years of rule by Mughal viceroys, Bengal gained semi-independence as a dominion under the Nawab of Bengal in 1717. The Nawabs permitted European companies to set up trading posts across the region, including firms from Britain, France, the Netherlands, Denmark, Portugal and Austria. An Armenian community dominated banking and shipping in major cities and towns. The Europeans regarded Bengal as the richest place for trade.[147] By the late 18th century, the British displaced the Mughal ruling class in Bengal.
Shipbuilding industry
Mughal India had a large shipbuilding industry, which was also largely centred in the Bengal province. Economic historian Indrajit Ray estimates the shipbuilding output of Bengal during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries at 223,250 tons annually, compared with 23,061 tons produced in nineteen colonies in North America from 1769 to 1771.[149] He also assesses ship repairing as very advanced in Bengal.[149]
An important innovation in shipbuilding was the introduction of a flushed deck design in Bengal rice ships, resulting in hulls that were stronger and less prone to leak than the structurally weak hulls of traditional European ships built with a stepped deck design. The British East India Company later duplicated the flushed deck and hull designs of Bengal rice ships in the 1760s, leading to significant improvements in seaworthiness and navigation for European ships during the Industrial Revolution.[150]
Demographics
Population
India's population growth accelerated under the Mughal Empire, with an unprecedented economic and demographic upsurge which boosted the Indian population by 60%[151] to 253% in 200 years during 1500–1700.[152] The Indian population had a faster growth during the Mughal era than at any known point in Indian history before the Mughal era.[103][151] By the time of Aurangzeb's reign, there were a total of 455,698 villages in the Mughal Empire.[153]
The following table gives population estimates for the Mughal Empire, compared to the total population of South Asia including the regions of modern India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, and compared to the world population:
| Year | Mughal Empire population |
Total Indian population |
% of South Asian population |
World population |
% of world population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1500 | — | 100,000,000[151] | — | 425,000,000[154] | — |
| 1600 | 115,000,000[153] | 130,000,000[151] | 89 | 579,000,000[154] | 20 |
| 1700 | 158,400,000[5] | 160,000,000[151] | 99 | 679,000,000[154] | 23 |
Urbanization
According to Irfan Habib Cities and towns boomed under the Mughal Empire, which had a relatively high degree of urbanization for its time, with 15% of its population living in urban centres.[155] This was higher than the percentage of the urban population in contemporary Europe at the time and higher than that of British India in the 19th century;[155] the level of urbanization in Europe did not reach 15% until the 19th century.[156]
Under Akbar's reign in 1600, the Mughal Empire's urban population was up to 17 million people, 15% of the empire's total population. This was larger than the entire urban population in Europe at the time, and even a century later in 1700, the urban population of England, Scotland and Wales did not exceed 13% of its total population,[153] while British India had an urban population that was under 13% of its total population in 1800 and 9% in 1881, a decline from the earlier Mughal era.[157] By 1700, Mughal India had an urban population of 23 million people, larger than British India's urban population of 22.3 million in 1871.[158]
Those estimates were criticised by Tim Dyson, who consider them exaggerations. According to Dyson urbanization of the Mughal empire was less than 9%.[159]
The historian Nizamuddin Ahmad (1551–1621) reported that, under Akbar's reign, there were 120 large cities and 3200 townships.[155] A number of cities in India had a population between a quarter-million and half-million people,[155] with larger cities including Agra (in Agra Subah) with up to 800,000 people, Lahore (in Lahore Subah) with up to 700,000 people,[160] Dhaka (in Bengal Subah) with over 1 million people,[161] and Delhi (in Delhi Subah) with over 600,000 people.[162]
Cities acted as markets for the sale of goods, and provided homes for a variety of merchants, traders, shopkeepers, artisans, moneylenders, weavers, craftspeople, officials, and religious figures.[102] However, several cities were military and political centres, rather than manufacturing or commerce centres.[163]
Culture

Generally, classical historiographies depicted the Mughal empire's origin was a sedentarized agrarian society. However, modern historians such as André Wink, Jos J. L. Gommans, Anatoly Khazanov, Thomas J. Barfield, and others, argued the Mughals was originated from nomadic culture.[165] Pius Malekandathil argued instead that although it was true that the Mughal has their origin as nomadic civilization, they became more sendentarized as the time passed, as exemplified by their military tradition.[166] The Mughal Empire was definitive in the early-modern and modern periods of South Asian history, with its legacy in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Afghanistan seen in cultural contributions such as:


- Centralised imperial rule that consolidated the smaller polities of South Asia.[167]
- The amalgamation of Persian art and literature with Indian art.[168]

- The development of Mughlai cuisine, an amalgamation of South Asian, Iranian and Central Asian culinary styles.
- The development of Mughal clothing, jewellery and fashion, utilizing richly decorated fabrics such as muslin, silk, brocade and velvet.
- Influence of Persian language over Old Hindi lead to the development of the Hindustani language.[169]
- The introduction of sophisticated Iranian-style waterworks and horticulture through Mughal gardening.[170]
- The introduction of Turkish baths into the Indian subcontinent.
- The evolution and refinement of Mughal and Indian architecture and in turn, the development of later Rajput and Sikh palatial architecture. A famous Mughal landmark is the Taj Mahal.
- The development of the Pehlwani style of Indian wrestling, a combination of Indian malla-yuddha and Persian varzesh-e bastani.[171][172]
- The construction of Maktab schools, where youth were taught the Quran and Islamic law such as the Fatawa 'Alamgiri in their indigenous languages.
- The development of Hindustani classical music,[173] and instruments such as the sitar.

Customs
The procession of marriage among the royal of Mughal empire were recorded in with many reports of extravagant gifts. one occasion was during the marriage of a son of emperor Akbar, Salim, with the daughter of a ruler of Bijapur, Raja Bhagwan Das, where the gift presented by Raja Bhagwan consisted of many horses, 100 elephants, many male and female slaves of Abyssinian, Caucasian, and native Indian origins, who brought with them various gold and silver utensils as dowry.[174]
Architecture
The Mughals made a major contribution to the Indian subcontinent with the development of their distinctive architectural style. This style was derived from earlier Indo-Islamic architecture as well as from Iranian and Central Asian architecture (particularly Timurid architecture), while incorporating further influences from Hindu architecture.[175][176] Mughal architecture is distinguished, among other things, by bulbous domes, ogive arches, carefully-composed and polished façades, and the use of hard red sandstone and marble as construction materials.[175][177]
Furthermore, William Dalrymple mentioned that during the final days of the Mughal fall of Delhi in 1857, an ice house structure existed in Delhi.[178] Emperor Shah Jahan has recorded to establish an ice-houses in Sirmaur, north of Delhi.[179]
Many monuments were built during the Mughal era by the Muslim emperors, especially Shah Jahan, including the Taj Mahal—a UNESCO World Heritage Site considered "the jewel of Muslim art in India and one of the universally admired masterpieces of the world's heritage",[26] attracting 7–8 million unique visitors a year. The palaces, tombs, gardens and forts built by the dynasty stand today in Agra, Aurangabad, Delhi, Dhaka, Fatehpur Sikri, Jaipur, Lahore, Kabul, Sheikhupura, and many other cities of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Bangladesh,[180] such as:

| India | Pakistan | Bangladesh | Afghanistan |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Art and literature

The Mughal artistic tradition, mainly expressed in painted miniatures, as well as small luxury objects, was eclectic, borrowing from Iranian, Indian, Chinese and Renaissance European stylistic and thematic elements.[181] Mughal emperors often took in Iranian bookbinders, illustrators, painters and calligraphers from the Safavid court due to the commonalities of their Timurid styles, and due to the Mughal affinity for Iranian art and calligraphy.[182] Miniatures commissioned by the Mughal emperors initially focused on large projects illustrating books with eventful historical scenes and court life, but later included more single images for albums, with portraits and animal paintings displaying a profound appreciation for the serenity and beauty of the natural world.[183] For example, Emperor Jahangir commissioned brilliant artists such as Ustad Mansur to realistically portray unusual flora and fauna throughout the empire.
The literary works Akbar and Jahangir ordered to be illustrated ranged from epics like the Razmnama (a Persian translation of the Hindu epic, the Mahabharata) to historical memoirs or biographies of the dynasty such as the Baburnama and Akbarnama, and Tuzk-e-Jahangiri. Richly finished albums (muraqqa) decorated with calligraphy and artistic scenes were mounted onto pages with decorative borders and then bound with covers of stamped and gilded or painted and lacquered leather.[184] Aurangzeb (1658–1707) was never an enthusiastic patron of painting, largely for religious reasons, and took a turn away from the pomp and ceremonial of the court around 1668, after which he probably commissioned no more paintings.[185]

Language
According to Qazvini, by the time of Shah Jahan, the emperor was only familiar with a few Turki words and showed little interest in the study of the language as a child.[186] Though the Mughals were of Turko-Mongol origin, their reign enacted the revival and height of the Persian language in the Indian subcontinent, and by the end of the 16th-century Turki (Chagatai) was understood by relatively few at court.[187] Accompanied by literary patronage was the institutionalisation of Persian as an official and courtly language; this led to Persian reaching nearly the status of a first language for many inhabitants of Mughal India.[188][189] Muzaffar Alam argues that the Mughals used Persian purposefully as the vehicle of an overarching Indo-Persian political culture, to unite their diverse empire.[190] Persian had a profound impact on the languages of South Asia; one such language, today known as Hindustani, developed in the imperial capital of Delhi in the late Mughal era. It began to be used as a literary language in the Mughal court from the reign of Shah Jahan, who described it as the language of his dastans (prose romances) and replaced Persian as the informal language of the Muslim elite.[191][192] According to Mir Taqi Mir, "Urdu was the language of Hindustan by the authority of the King."[193][194]
Military
Gunpowder warfare

Mughal India was one of the three Islamic gunpowder empires, along with the Ottoman Empire and Safavid Persia.[36][195][196] By the time he was invited by Lodi governor of Lahore, Daulat Khan, to support his rebellion against Lodi Sultan Ibrahim Khan, Babur was familiar with gunpowder firearms and field artillery, and a method for deploying them. Babur had employed Ottoman expert Ustad Ali Quli, who showed Babur the standard Ottoman formation—artillery and firearm-equipped infantry protected by wagons in the centre and the mounted archers on both wings. Babur used this formation at the First Battle of Panipat in 1526, where the Afghan and Rajput forces loyal to the Delhi Sultanate, though superior in numbers but without the gunpowder weapons, were defeated. The decisive victory of the Timurid forces is one reason opponents rarely met Mughal princes in pitched battles throughout the empire's history.[197] In India, guns made of bronze were recovered from Calicut (1504) and Diu (1533).[198] Fathullah Shirazi (c. 1582), a Persian polymath and mechanical engineer who worked for Akbar, developed an early multi-gun shot. As opposed to the polybolos and repeating crossbows used earlier in ancient Greece and China, respectively, Shirazi's rapid-firing gun had multiple gun barrels that fired hand cannons loaded with gunpowder. It may be considered a version of a volley gun.[199]

By the 17th century, Indians were manufacturing a diverse variety of firearms; large guns in particular, became visible in Tanjore, Dacca, Bijapur and Murshidabad.[200]
Rocketry and explosives
In the sixteenth century, Akbar was the first to initiate and use metal cylinder rockets known as bans, particularly against war elephants, during the Battle of Sanbal.[201][202] In 1657, the Mughal Army used rockets during the Siege of Bidar.[203] Prince Aurangzeb's forces discharged rockets and grenades while scaling the walls. Sidi Marjan was mortally wounded when a rocket struck his large gunpowder depot, and after twenty-seven days of hard fighting, Bidar was captured by the Mughals.[203]
In A History of Greek Fire and Gunpowder, James Riddick Partington described Indian rockets and explosive mines:[198]
The Indian war rockets ... were formidable weapons before such rockets were used in Europe. They had bam-boo rods, a rocket body lashed to the rod and iron points. They were directed at the target and fired by lighting the fuse, but the trajectory was rather erratic. The use of mines and counter-mines with explosive charges of gunpowder is mentioned for the times of Akbar and Jahangir.
Science
A new curriculum for the madrasas which stressed the importance of uloom-i-muqalat (Rational Sciences) and introduced new subjects such as geometry, medicine, philosophy, and mathematics. The new curriculum produced a series of eminent scholars, engineers and architects.[204] [205]
Astronomy

While there appears to have been little concern for theoretical astronomy, Mughal astronomers made advances in observational astronomy and produced some Zij treatises. Humayun built a personal observatory near Delhi. According to Sulaiman Nadvi, Jahangir and Shah Jahan intended to build observatories too but were unable to do so. The astronomical instruments and observational techniques used at the Mughal observatories were mainly derived from Islamic astronomy.[206][207] In the 17th century, the Mughal Empire saw a synthesis between Islamic and Hindu astronomy, where Islamic observational instruments were combined with Hindu computational techniques.[206][207]
During the decline of the Mughal Empire, the Hindu king Jai Singh II of Amber continued the work of Mughal astronomy. In the early 18th century, he built several large observatories called Yantra Mandirs, to rival Ulugh Beg's Samarkand observatory, and to improve on the earlier Hindu computations in the Siddhantas and Islamic observations in Zij-i-Sultani. The instruments he used were influenced by Islamic astronomy, while the computational techniques were derived from Hindu astronomy.[206][207]
Chemistry
Sake Dean Mahomed had learned much of Mughal chemistry and understood the techniques used to produce various alkali and soaps to produce shampoo. He was also a notable writer who described the Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II and the cities of Allahabad and Delhi in rich detail and also made note of the glories of the Mughal Empire.
In Britain, Sake Dean Mahomed was appointed as shampooing surgeon to both Kings George IV and William IV.[208]
Metallurgy

The society within Mughal empire operated the Karkhanas, which functioned as workshops for craftsmen. These Karkhanas were producing arms, ammunition, and also various items for the court and emperor's need such as clothes, shawls, turbans, jewelry, gold and silverware, perfumes, medicines, carpets, beddings, tents, and for the imperial stable-harnesses for the horses in irons, copper and other metals.[210][211][212]
Another aspects of remarkable invention in Mughal India is the lost-wax cast, hollow, seamless, celestial globe. It was invented in Kashmir by Ali Kashmiri ibn Luqman in 998 AH (1589–90 CE). Twenty other such globes were later produced in Lahore and Kashmir during the Mughal Empire. Before they were rediscovered in the 1980s, it was believed by modern metallurgists to be technically impossible to produce hollow metal globes without any seams.[213] A 17th-century celestial globe was also made by Diya’ ad-din Muhammad in Lahore, 1668 (now in Pakistan).[214] It is now housed at the National Museum of Scotland.[citation needed]
List of Mughal Emperors
| Portrait | Titular Name | Birth Name | Birth | Reign | Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 
|
Babur بابر |
Zahir al-Din Muhammad ظهیر الدین محمد |
14 February 1483 Andijan, Uzbekistan | 20 April 1526 – 26 December 1530 | 26 December 1530 (aged 47) Agra, India |
2 
|
Humayun همایوں |
Nasir al-Din Muhammad نصیر الدین محمد |
6 March 1508 Kabul, Afghanistan | 26 December 1530 – 17 May 1540
22 February 1555 – 27 January 1556 (10 years 3 months 25 days) |
27 January 1556 (aged 47) Delhi, India |
3 
|
Akbar the Great اکبر |
Jalal al-Din Muhammad جلال الدین محمد |
15 October 1542 Umerkot, Pakistan | 11 February 1556 – 27 October 1605
(49 years 9 months 0 days) |
27 October 1605 (aged 63) Agra, India |
4 
|
Jahangir جهانگیر |
Nur al-Din Muhammad نور الدین محمد |
31 August 1569 Agra, India | 3 November 1605 – 28 October 1627
(21 years 11 months 23 days) |
28 October 1627 (aged 58) Jammu and Kashmir, India |
5 
|
Shah Jahan شاہ جهان |
Shihab al-Din Muhammad شهاب الدین محمد |
5 January 1592 Lahore, Pakistan | 19 January 1628 – 31 July 1658
(30 years 8 months 25 days) |
22 January 1666 (aged 74) Agra, India |
6 
|
Aurangzeb اورنگزیب Alamgir |
Muhi al-Din Muhammad محی الدین محمد |
3 November 1618 Gujarat, India | 31 July 1658 – 3 March 1707
(48 years 7 months 0 days) |
3 March 1707 (aged 88) Ahmednagar, India |
7 
|
Azam Shah اعظم شاه |
Qutb al-Din Muhammad قطب الدين محمد |
28 June 1653 Burhanpur, India | 14 March 1707 – 20 June 1707 | 20 June 1707 (aged 53) Agra, India |
8 
|
Bahadur Shah بهادر شاہ |
Qutb al-Din Muhammad قطب الدین محمد |
14 October 1643 Burhanpur, India | 19 June 1707 – 27 February 1712
(4 years, 253 days) |
27 February 1712 (aged 68) Lahore, Pakistan |
9 
|
Jahandar Shah جهاندار شاہ |
Muiz al-Din Muhammad معز الدین محمد |
9 May 1661 Deccan, India | 27 February 1712 – 11 February 1713
(0 years, 350 days) |
12 February 1713 (aged 51) Delhi, India |
10
|
Farrukh Siyar فرخ سیر |
Muin al-Din Muhammad موئن الدین محمد Puppet King Under the Sayyids of Barha |
20 August 1685 Aurangabad, India | 11 January 1713 – 28 February 1719
(6 years, 48 days) |
19 April 1719 (aged 33) Delhi, India |
11
|
Rafi ud-Darajat رفیع الدرجات |
Shams al-Din Muhammad شمس الدین محمد Puppet King Under the Sayyids of Barha |
1 December 1699 | 28 February 1719 – 6 June 1719
(0 years, 98 days) |
6 June 1719 (aged 19) Agra, India |
12
|
Shah Jahan II شاہ جهان دوم |
Rafi al-Din Muhammad رفع الدين محمد Puppet King Under the Sayyids of Barha |
5 January 1696 | 6 June 1719 – 17 September 1719
(0 years, 105 days) |
18 September 1719 (aged 23) Agra, India |
13
|
Muhammad Shah محمد شاه |
Nasir al-Din Muhammad نصیر الدین محمد Puppet King Under the Sayyids of Barha |
7 August 1702 Ghazni, Afghanistan | 27 September 1719 – 26 April 1748
(28 years, 212 days) |
26 April 1748 (aged 45) Delhi, India |
14 
|
Ahmad Shah Bahadur احمد شاہ بهادر |
Mujahid al-Din Muhammad مجاهد الدین محمد |
23 декабря 1725 г., Дели , Индия. | 29 апреля 1748 г. - 2 июня 1754 г.
(6 years, 37 days) |
1 января 1775 г. (49 лет) Дели , Индия |
15 
|
Аламгир II Аламгир II |
Азиз ад-Дин Мухаммад Уважаемый Улуддин Мухаммад. |
6 июня 1699 г., Бурханпур, Индия. | 3 июня 1754 г. - 29 ноября 1759 г.
(5 лет, 180 дней) |
29 ноября 1759 г. (60 лет) Котла Фатех Шах, Индия. |
16 
|
Шах Джахан III Шах Джахан III |
Мухи аль-Миллат Мохи-уль-Мулат |
1711 | 10 декабря 1759 г. - 10 октября 1760 г.
(282 дня) |
1772 г. (60–61 год) |
17 
|
Шах Алам II Шах Алам II |
Джалал ад-Дин Мухаммад Али Гаухар Джалалуддин Али Гохар |
25 июня 1728 года, Дели , Индия. | 10 октября 1760 г. - 31 июля 1788 г.
(27 лет, 301 день) |
19 ноября 1806 г. (78 лет) Дели , Индия |
18 
|
Шах Джахан IV Джахан Шах IV |
Бидар Бахт Махмуд Шах Бахадур Джахан Шах Бидар Бахт Махмуд Шах Бахадур Джахан Шах |
1749 г. , Дели , Индия. | 31 июля 1788 г. - 11 октября 1788 г.
(63 дня) |
1790 (40–41 год) Дели , Индия. |
17 
|
Шах Алам II Шах Алам II |
Джалал ад-Дин Мухаммад Али Гаухар Джалалуддин Али Гохар Король-марионетка Империи маратхов |
25 июня 1728 года, Дели , Индия. | 16 октября 1788 г. - 19 ноября 1806 г.
(18 лет, 339 дней) |
19 ноября 1806 г. (78 лет) Дели , Индия |
19 
|
Акбар Шах II Акбар Шах II |
Муин ад-Дин Мухаммад Мирза Акбар Марионеточный король Ост-Индской компании |
22 апреля 1760 г., Мукундпур , Индия. | 19 ноября 1806 г. - 28 сентября 1837 г.
(30 лет, 321 день) |
28 сентября 1837 г. (77 лет) Дели , Индия |
20 
|
Бахадур Шах II Зафар Бахадур Шах Зафар |
Абу Зафар Сирадж ад-Дин Мухаммад Абу Зафар Сираджуддин Мухаммад |
24 октября 1775 г., Дели , Индия. | 28 сентября 1837 г. - 21 сентября 1857 г.
(19 лет, 360 дней) |
7 ноября 1862 г. (87 лет) Рангун, Мьянма |
См. также
- История Индии
- Флаги Империи Великих Моголов
- Список монгольских государств
- Генеалогия Великих Моголов
- Ислам в Южной Азии
Ссылки
Сноски
Цитаты
- ^ Синополи, Карла М. (1994). «Монументальность и мобильность в столицах Великих Моголов» . Азиатские перспективы . 33 (2): 294. ISSN 0066-8435 . JSTOR 42928323 . Архивировано из оригинала 1 мая 2022 года . Проверено 11 июня 2021 г.
- ^ Турчин, Петр; Адамс, Джонатан М.; Холл, Томас Д. (2006). «Ориентация исторических империй и современных государств Восток-Запад» . Журнал исследований мировых систем . 12 (2): 219–229. дои : 10.5195/JWSR.2006.369 . ISSN 1076-156X .
- ^ Рейн Таагепера (сентябрь 1997 г.). «Модели расширения и сокращения крупных государств: контекст для России» . Ежеквартальный журнал международных исследований . 41 (3): 475–504. дои : 10.1111/0020-8833.00053 . ISSN 0020-8833 . JSTOR 2600793 . Архивировано из оригинала 19 ноября 2018 года . Проверено 6 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Дайсон, Тим (2018). История населения Индии: от первых современных людей до наших дней . Издательство Оксфордского университета. стр. 70–71. ISBN 978-0-19-256430-6 .
Мы видели, что существует значительная неопределенность относительно численности населения Индии около 1595 года. Серьезные оценки варьируются от 116 до 145 миллионов (в среднем 125 миллионов). Однако реальная цифра может даже выходить за пределы этого диапазона. Соответственно, хотя кажется вероятным, что население выросло в течение семнадцатого века, маловероятно, что мы когда-либо сможем иметь хорошее представление о его численности в 1707 году.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Йожеф Бёроч (2009). Европейский Союз и глобальные социальные изменения . Рутледж . п. 21. ISBN 978-1-135-25580-0 . Проверено 26 июня 2017 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час я дж Ричардс, Джон Ф. (1995). Империя Великих Моголов . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-0-521-56603-2 .
- ^ Стейн, Бертон (2010), История Индии , John Wiley & Sons, стр. 159–, ISBN 978-1-4443-2351-1 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 г. , получено 15 июля 2019 г. Цитата: «Королевство, определенное и управляемое таким образом, представляло собой обширную территорию площадью около 750 000 квадратных миль [1 900 000 км²]. 2 ], простирающийся от границы со Центральной Азией на севере Афганистана до северных нагорий плато Декан и от бассейна Инда на западе до Ассамского нагорья на востоке».
- ^ Гилберт, Марк Джейсон (2017), Южная Азия в мировой истории , Oxford University Press, стр. 62, ISBN 978-0-19-066137-3 , получено 15 июля 2019 г. Цитата: «Затем Бабур ловко дал османам свое обещание не нападать на них в обмен на их военную помощь, которую он получил в виде новейших боевых изобретений, фитильного ружья и литых пушек, а также инструкторов, чтобы обучить своих людей пользоваться ими».
- ^ Стейн, Бертон (2010), История Индии , John Wiley & Sons, стр. 159–, ISBN 978-1-4443-2351-1 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года , получено 15 июля 2019 года. Цитата: «Другая возможная дата начала режима Великих Моголов — 1600 год, когда институты, определявшие режим, были прочно установлены и когда сердце империи было оба этих события были определены внуком Бабура Акбаром».
- ^ Стейн, Бертон (2010), История Индии , John Wiley & Sons, стр. 159–, ISBN 978-1-4443-2351-1 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года , получено 15 июля 2019 года. Цитата: «Императорская карьера дома Великих Моголов традиционно считается завершенной в 1707 году, когда умер император Аурангзеб, потомок Бабура в пятом поколении. Ему исполнилось пятьдесят лет. Год правления начался в 1658 году, когда государство Великих Моголов казалось таким же сильным, как и прежде, или даже более сильным. Но в последние годы правления Аурангзеба государство было поставлено на грань разрушения, из-за чего оно рухнуло через полтора десятилетия после его смерти к 1720 году. Правление Великих Моголов в значительной степени закончилось, и завершилась эпоха двух столетий империи».
- ^ Ричардс, Джон Ф. (1995), Империя Великих Моголов , издательство Кембриджского университета, стр. xv, ISBN 978-0-521-56603-2 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 г. , получено 1 июля 2019 г. Цитата: «К последней дате (1720 г.) основная структура централизованного государства была безвозвратно разрушена».
- ^ Стейн, Бертон (2010), История Индии , John Wiley & Sons, стр. 159–, ISBN 978-1-4443-2351-1 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 г. , получено 15 июля 2019 г. Цитата: «Хвастовство таких прародителей подчеркнуло центральный характер режима Великих Моголов как государства-воина: он родился в войне и поддерживался войной до восемнадцатого века. века, когда война уничтожила его».
- ^ Робб, Питер (2011), История Индии , Macmillan, стр. 108–, ISBN 978-0-230-34549-2 Цитата: «Государство Великих Моголов было подготовлено к войне и добилось успеха, пока оно выигрывало сражения. Оно контролировало территорию частично через свою сеть крепостей, от своих укреплённых столиц в Агре, Дели или Лахоре, которые определяли его центральные земли, до преобразованных и расширенных форты Раджастана и Декана. Воля императоров часто исполнялась в боях. Сотни армейских разведчиков были важным источником информации, но административная структура империи также определялась и направлялась на войну. Местные военные контрольно-пропускные пункты или таны поддерживали порядок. Назначаемые напрямую имперские военные и гражданские командиры (фождары) контролировали кавалерию и пехоту или администрацию в каждом регионе. Крестьянство, в свою очередь, часто было вооружено, могло оказывать поддержку региональным властям и было склонно к восстанию по собственной инициативе: постоянно. от правителей требовалось умиротворение».
- ^ Гилберт, Марк Джейсон (2017), Южная Азия в мировой истории , Oxford University Press, стр. 75–, ISBN 978-0-19-066137-3 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года , получено 15 июля 2019 года. Цитата: «С помощью Сефевидов и Османской империи Моголы вскоре присоединятся к этим двум державам в триумвирате воинственных, экспансионистских и эффективных в военном и бюрократическом отношении государств раннего Нового времени. , которые теперь часто называют «пороховыми империями» из-за их общего умения использовать такое оружие для завоевания земель, которые они стремились контролировать».
- ^ Ашер, Кэтрин Б.; Талбот, Синтия (2006), Индия до Европы , Cambridge University Press, стр. 115–, ISBN 978-0-521-80904-7 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года , получено 15 июля 2019 года.
- ^ Робб, Питер (2011). История Индии . Макмиллан. стр. 99–100. ISBN 978-0-230-34549-2 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Ашер, Кэтрин Б.; Талбот, Синтия (2006), Индия до Европы , Cambridge University Press, стр. 152–, ISBN 978-0-521-80904-7 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года , получено 15 июля 2019 года.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Штейн, Бертон (2010), История Индии , John Wiley & Sons, стр. 164–, ISBN 978-1-4443-2351-1 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 г. , получено 15 июля 2019 г. Цитата: «Ресурсной базой нового порядка Акбара были доходы от земли»
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Ашер, Кэтрин Б.; Талбот, Синтия (2006), Индия до Европы , издательство Кембриджского университета, стр. 158–, ISBN 978-0-521-80904-7 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 г. , получено 15 июля 2019 г. Цитата: «Империя Великих Моголов базировалась внутри большой территории и получала подавляющую часть своих доходов от сельского хозяйства».
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Штейн, Бертон (2010), История Индии , John Wiley & Sons, стр. 164–, ISBN 978-1-4443-2351-1 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 г. , получено 15 июля 2019 г. Цитата: «... более половины продукции с полей в его владениях, после того как производственные затраты были оплачены, по оценкам, было взято из крестьянских производителей посредством официальных налогов и неофициальных поборов, причем платежи взимались деньгами, а для этого требовалась хорошо регулируемая серебряная валюта».
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Ашер, Кэтрин Б.; Талбот, Синтия (2006), Индия до Европы , Cambridge University Press, стр. 152–, ISBN 978-0-521-80904-7 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 г. , получено 15 июля 2019 г. Цитата: «Его условие об уплате земельного налога наличными вынудило крестьян войти в рыночные сети, где они могли получить необходимые деньги, в то время как стандартизация имперской валюты сделала обмен товары за деньги проще».
- ^ Ашер, Кэтрин Б.; Талбот, Синтия (2006), Индия до Европы , Cambridge University Press, стр. 152–, ISBN 978-0-521-80904-7 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 г. , получено 15 июля 2019 г. Цитата: «Прежде всего, длительный период относительного мира, установленный властью Акбара и поддерживаемый его преемниками, способствовал экономическому расширению Индии».
- ^ Ашер, Кэтрин Б.; Талбот, Синтия (2006), Индия до Европы , Cambridge University Press, стр. 186–, ISBN 978-0-521-80904-7 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 г. , получено 15 июля 2019 г. Цитата: «По мере того как европейское присутствие в Индии росло, их требования к индийским товарам и торговым правам увеличивались, что приносило еще большее богатство и без того богатым индийским судам».
- ^ Ашер, Кэтрин Б.; Талбот, Синтия (2006), Индия до Европы , Cambridge University Press, стр. 186–, ISBN 978-0-521-80904-7 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 г. , получено 15 июля 2019 г. Цитата: «Элита тратила все больше и больше денег на предметы роскоши и роскошный образ жизни, а правители время от времени строили целые новые столицы».
- ^ Ашер, Кэтрин Б.; Талбот, Синтия (2006), Индия до Европы , Cambridge University Press, стр. 186–, ISBN 978-0-521-80904-7 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 г. , получено 15 июля 2019 г. Цитата: «Все эти факторы привели к усилению покровительства искусству, включая текстиль, живопись, архитектуру, ювелирные изделия и оружие, для удовлетворения церемониальных требований королей и принцев».
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Центр, Всемирное наследие ЮНЕСКО. «Тадж-Махал» . Центр всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО . Архивировано из оригинала 1 февраля 2018 года . Проверено 7 мая 2020 г.
- ^ Ванина, Евгения (2012). Средневековые индийские пейзажи: пространство, время, общество, человек . Книги Примуса. п. 47. ИСБН 978-93-80607-19-1 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 19 октября 2015 г.
- ^ Харди, П. (1979). «Современные европейские и мусульманские объяснения обращения в ислам в Южной Азии: предварительный обзор литературы». В Левционе, Неемия (ред.). Обращение в ислам . Холмс и Мейер. п. 69. ИСБН 978-0-8419-0343-2 . Архивировано из оригинала 3 апреля 2023 года . Проверено 19 марта 2023 г.
- ^ «Название памятника/места: Могила Аурангзеба» (PDF) . asiaurangabad.in . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 23 сентября 2015 года.
- ^ Парвез, Аслам; Фаруки, Атхар (2017). Жизнь и поэзия Бахадур Шаха Зафара . Нью-Дели, Индия: Hay House India. ISBN 978-93-85827-47-1 . OCLC 993093699 .
- ^ «Коллектив истории Индии» . 30 декабря 2023 г. Архивировано из оригинала 30 декабря 2023 г.
- ^ Моска, Мэтью (2013). От пограничной политики к внешней политике: вопрос Индии и трансформация геополитики в цинском Китае . Издательство Стэнфордского университета. стр. 78–94. ISBN 978-0-8047-8538-9 . Архивировано из оригинала 7 ноября 2023 года . Проверено 7 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Фонтана, Микела (2011). Маттео Риччи: Иезуит при дворе Мин . Издательство Rowman & Littlefield. п. 32. ISBN 978-1-4422-0588-8 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 19 октября 2015 г.
- ^ Захир уд-Дин Мохаммад (2002). Такстон, Уилер М. (ред.). Бабурнама: Мемуары Бабура, принца и императора . Нью-Йорк: Современная библиотека. п. XLVI . ISBN 978-0-375-76137-9 .
В Индии династия всегда называла себя Гуркани, в честь титула Темура Гуркян, персидской формы монгольского kürägän , «зять», титула, который он принял после женитьбы на чингизидской принцессе.
- ^ Джон Уолбридж. Бог и логика в исламе: Халифат разума . п. 165.
Империя Персидских Моголов.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Ходжсон, Маршалл Г.С. (2009). Исламское предприятие . Том. 3. Издательство Чикагского университета. п. 62. ИСБН 978-0-226-34688-5 .
- ^ Кэнфилд, Роберт Л. (2002). Тюркско-Персия в исторической перспективе . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 20. ISBN 978-0-521-52291-5 .
- ^ Хаскин, французский Хаскен; Дик ван дер Мей (2004). Читая Азию: новые исследования в области азиатских исследований . Рутледж. п. 104. ИСБН 978-1-136-84377-8 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час я дж к л Берндл, Клаус (2005). Национальная географическая визуальная история мира . Национальное географическое общество. стр. 318–320. ISBN 978-0-7922-3695-5 .
- ^ Жерар Шалиан, Глобальная история войны: от Ассирии до XXI века , University of California Press , Калифорния, 2014, стр. 151
- ^ Бэйли, Кристофер. Появление Европы. Восхождение Моголов . п. 151. ИСБН 0-7054-0982-1 .
- ^ Худжа, Рима (2006). История Раджастана . Рупа. п. 454. ИСБН 978-81-291-1501-0 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 16 июня 2022 г.
Из мемуаров Бабура мы узнаем, что успехи Санги против авангарда Великих Моголов под командованием Абдул Азиза и других сил в Баяне... серьезно деморализовали боевой дух войск Бабура, расположившихся лагерем недалеко от Сикри.
- ^ Бэйли, Кристофер. Появление Европы. Восхождение Моголов . п. 154. ИСБН 0-7054-0982-1 .
- ^ Боллхэтчет, Кеннет А. «Акбар» . Британская энциклопедия . Архивировано из оригинала 25 мая 2023 года . Проверено 17 июля 2017 г.
- ^ Смит, Винсент Артур (1917). Акбар Великий Могол, 1542–1605 гг . Оксфорд в Clarendon Press. стр. 13–14.
- ^ Бегум, Гульбадан (1902). История Хумаюна (Хумаюн-Нама) . Перевод Бевериджа, Аннет С. Королевского азиатского общества. стр. 237–239 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Мохаммада, Малика (2007). Основы сложной культуры в Индии . Аакар Книги. п. 300. ИСБН 978-81-89833-18-3 .
- ^ Гилберт, Марк Джейсон (2017). Южная Азия в мировой истории . Издательство Оксфордского университета . п. 79. ИСБН 978-0-19-976034-3 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 22 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Мухаммад-Хади (1999). Предисловие к «Джахангирнаме» . Перевод Такстона, Уилера М. Издательство Оксфордского университета. п. 4. ISBN 978-0-19-512718-8 .
- ^ Джахангир, император Индостана (1999). Джахангирнама: Мемуары Джахангира, императора Индии . Перевод Такстона, Уилера М. Издательство Оксфордского университета. п. 65. ИСБН 978-0-19-512718-8 .
- ^ Фаруки, Мунис Д. (2012). Принцы Империи Великих Моголов, 1504–1719 гг . Издательство Кембриджского университета. стр. 268–269. ISBN 978-1-107-02217-1 .
- ^ Робб, Питер (2011), История Индии , Международное высшее образование Macmillan, стр. 97–98, ISBN 978-0-230-34424-2
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Ашер, Кэтрин Б.; Талбот, Синтия (2006). Индия раньше Европы . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 267. ИСБН 0-521-80904-5 . OCLC 61303480 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «BBC – Религии – Сикхизм: Истоки сикхизма» . Би-би-си . 30 сентября 2009 г. Архивировано из оригинала 17 августа 2018 г. . Проверено 19 февраля 2021 г.
- ^ Мехта, Джасвант Лал (1984) [Впервые опубликовано в 1981 году]. Расширенное исследование истории средневековой Индии . Том. II (2-е изд.). Стерлинг Паблишерс Пвт. ООО с. 59. ИСБН 978-81-207-1015-3 . OCLC 1008395679 .
- ^ Сингхал, Дамодар П. (1983). История индийского народа . Метуэн. п. 193. ИСБН 978-0-413-48730-8 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 4 мая 2021 г.
- ↑ Дара Шико. Архивировано 3 апреля 2023 года в Wayback Machine. Средневековая исламская цивилизация: энциклопедия , авторы: Джозеф В. Мери, Джере Л. Бахарах. Рутледж, 2005. ISBN 0-415-96690-6 . стр. 195–196.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Трушке, Одри (2017). Аурангзеб: жизнь и наследие самого противоречивого короля Индии . Издательство Стэнфордского университета . ISBN 978-1-5036-0259-5 .
- ^ Робб, Питер (2011). История Индии . Международное высшее образование Макмиллана. п. 98. ИСБН 978-0-230-34424-2 .
- ^ Абхишек Кайкер (2020). Король и народ: суверенитет и народная политика в Дели Великих Моголов . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-19-007067-0 . Архивировано из оригинала 3 апреля 2023 года . Проверено 19 марта 2023 г.
- ^ Саркар Джадунатх (1928). Краткая история Аурангзиба .
- ^ Микаберидзе, Александр (2011). Конфликт и завоевания в исламском мире: Историческая энциклопедия [2 тома]: Историческая энциклопедия . АВС-КЛИО. п. 43. ИСБН 978-1-59884-337-8 .
- ^ Копленд, Ян; Маббетт, Ян; Рой, Асим; и др. (2013). История государства и религии в Индии . Рутледж. п. 119. ИСБН 978-1-136-45950-4 .
- ^ Вергезе, Аджай; Фоа, Роберто Стефан (5 ноября 2018 г.). «Доколониальное этническое насилие: пример индуистско-мусульманского конфликта в Индии» (PDF) . Бостонский университет. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 7 апреля 2023 года . Проверено 7 апреля 2023 г.
- ^ Одри Трушке (2021). Язык истории: санскритские рассказы об индо-мусульманском правлении . Издательство: Издательство Колумбийского университета. ISBN 978-0-231-55195-3 . Архивировано из оригинала 3 апреля 2023 года . Проверено 19 марта 2023 г.
- ^ Мухаммад Ясин (1958). Социальная история исламской Индии, 1605–1748 гг . Издательство Верхней Индии. п. 18. Архивировано из оригинала 3 апреля 2023 года . Проверено 27 марта 2023 г.
стали виртуальными правителями и суверенами «де-факто», когда начали создавать и свергать императоров. Между собой у них сложилось что-то вроде общего братства.
- ^ Издательство Колумбийского университета (2000). Колумбийские хронологии азиатской истории и культуры . Издательство Колумбийского университета. п. 285. ИСБН 978-0-231-11004-4 . Архивировано из оригинала 3 апреля 2023 года . Проверено 19 марта 2023 г.
- ^ Ричард М. Итон (2013). Итон, Ричард М.; Фаруки, Мунис Д.; Гилмартин, Дэвид; Кумар, Сунил (ред.). Расширение границ в очерках Южной Азии и всемирной истории в честь Джона Ф. Ричардса . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 21. дои : 10.1017/CBO9781107300002 . ISBN 978-1-107-03428-0 .
Я считаю всю эту армию (маратхов) своей..... Я войду с ними в соглашение и доверю им Мулукгири (набег) на той стороне Нармады.
- ^ Пагади, Сету Мадхаварао (1970). «Отношения маратхов и низамов: письма Низам-уль-Мулька» . Летопись Бхандаркарского института восточных исследований . 51 (1/4): 94.
Суд Великих Моголов был враждебен Низам-уль-Мульку..... Низам не вмешивался в деятельность маратхов в малва и Гуджарате.....Низам-уль-Мульк считал маратхами армия...
- ^ Сальма Ахмед Фаруки (2011). Всеобъемлющая история средневековой Индии: с двенадцатого по середину восемнадцатого века . Пирсон Образовательная Индия. п. 309. ИСБН 978-8131732021 .
Еще более тревожным был тот факт, что утверждение независимости распространилось и на другие части империи, и губернаторы Хайдарабада, Бенгалии и Авада вскоре также основали независимые королевства.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Босе, Сугата ; Джалал, Аиша (2004). Современная Южная Азия: история, культура, политическая экономия (2-е изд.). Рутледж. п. 41 . ISBN 978-0-203-71253-5 .
- ^ Ратод, Н.Г. (1994). Великий маратх Махададжи Сциндия Нью-Дели: Саруп и сыновья. п. 8. ISBN 978-81-85431-52-9 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Конерманн, Стефан (4 августа 2015 г.), «Империя Великих Моголов» , Онлайн-энциклопедия ранней современной истории , Brill, doi : 10.1163/2352-0272_emho_com_024206 , заархивировано из оригинала 26 марта 2022 г. , получено 28 марта 2022 г.
- ^ Далримпл, Уильям (2007). Последний Могол . Книги о пингвинах. ISBN 978-0-14-310243-4 .
- ^ Кирстен Маккензи; Роберт Олдрич (2013). История западных империй Рутледжа (электронная книга) . Тейлор и Фрэнсис. п. 333. ИСБН 9781317999874 . Проверено 14 марта 2024 г.
- ^ Ричардс, Дж. Ф. (1981). «Государственные финансы Великих Моголов и досовременная мировая экономика». Сравнительные исследования в обществе и истории . 23 (2): 285–308. дои : 10.1017/s0010417500013311 . JSTOR 178737 . S2CID 154809724 .
- ^ Сэр Уильям Уилсон Хантер (1908). Императорский географический справочник Индии . Кларендон Пресс. п. 107.
- ^ Хабиб, Ирфан (март 1969 г.). «Потенциалы капиталистического развития в экономике Индии Великих Моголов». Журнал экономической истории . 29 (1): 32–78. дои : 10.1017/s0022050700097825 . JSTOR 2115498 . S2CID 91170802 .
- ^ «Как неудачное обрезание, совершенное Моголами в Бании, и неспособность защититься от сил Шиваджи Лута после захвата материка привели к упадку империи Великих Моголов» .
- ^ Леонард, Карен (апрель 1979 г.). «Теория «Великой фирмы» упадка Империи Великих Моголов» . Сравнительные исследования в обществе и истории . 21 (2): 151–167. дои : 10.1017/s0010417500012792 . JSTOR 178414 . S2CID 54775994 . Архивировано из оригинала 21 декабря 2019 года . Проверено 6 июля 2019 г.
- ^ Халлисси, Роберт К. (1977). Восстание раджпутов против Аурангзеба . Университет Миссури Пресс. стр. ix, x, 84. ISBN. 978-0-8262-0222-2 .
- ^ Клод Марковиц (2004) [Впервые опубликовано в 1994 году под названием Histoire de l'Inde Moderne ]. История современной Индии, 1480–1950 гг . Гимн Пресс. стр. 172–173. ISBN 978-1-84331-004-4 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Джеффри Г. Уильямсон , Дэвид Клингингсмит (август 2005 г.). «Деиндустриализация Индии в 18 и 19 веках» (PDF) . Гарвардский университет . Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 13 декабря 2016 года . Проверено 18 мая 2017 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Джеффри Г. Уильямсон (2011). Торговля и бедность: когда третий мир отстал . МТИ Пресс . п. 91. ИСБН 978-0-262-29518-5 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 15 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Бродберри, Стивен; Гупта, Бишнуприя (2005). Хлопчатобумажный текстиль и большое расхождение: Ланкашир, Индия и изменение конкурентного преимущества, 1600–1850 гг. (PDF) . Возникновение, организация и институциональная основа рынков факторов производства . Утрехтский университет. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 10 сентября 2016 г. Проверено 5 декабря 2016 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Робинсон, Фрэнсис (2009), «Империя Великих Моголов» , Оксфордская энциклопедия исламского мира , Oxford University Press, doi : 10.1093/acref/9780195305135.001.0001 , ISBN 978-0-19-530513-5 , заархивировано из оригинала 29 марта 2022 года , получено 28 марта 2022 года.
- ^ Бертон-Пейдж, Дж.; Ислам, Риазул; Атар Али, М.; Моосви, Ширин; Морленд, Вашингтон; Босворт, CE; Шиммель, Аннемари; Кох, Эбба; Холл, Маргарет (24 апреля 2012 г.), «Mug̲h̲als» , Энциклопедия ислама (2-е изд.), Brill, doi : 10.1163/1573-3912_islam_com_0778 , заархивировано из оригинала 31 марта 2022 г. , получено 31 марта 2022 г.
- ^ Гладден, EN (2019). История государственного управления, том II: от одиннадцатого века до наших дней . Рутледж. стр. 234–236. ISBN 978-0-429-42321-5 .
- ^ Майкл, Бернардо А. (2012). Государственное строительство и территории в Южной Азии . Гимн Пресс. п. 67. дои : 10.7135/upo9780857285324.005 . ISBN 978-0-85728-532-4 .
- ^ Майкл, Бернардо А. (2012). Государственное строительство и территории в Южной Азии . Гимн Пресс. стр. 69, 75, 77–78. дои : 10.7135/upo9780857285324.005 . ISBN 978-0-85728-532-4 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Синополи, Карла М. (1994). «Монументальность и мобильность в столицах Великих Моголов» . Азиатские перспективы . 33 (2): 294–295. ISSN 0066-8435 . JSTOR 42928323 . Архивировано из оригинала 1 мая 2022 года . Проверено 11 июня 2021 г.
- ^ Синополи, Карла М. (1994). «Монументальность и мобильность в столицах Великих Моголов» . Азиатские перспективы . 33 (2): 304–305. ISSN 0066-8435 . JSTOR 42928323 . Архивировано из оригинала 1 мая 2022 года . Проверено 11 июня 2021 г.
- ^ Самрин, Фара (2005). «Город Кабул при Великих Моголов» . Труды Индийского исторического конгресса . 66 : 1307. JSTOR 44145943 . Архивировано из оригинала 29 июня 2021 года . Проверено 14 декабря 2021 г.
- ^ Синополи, Карла М. (1994). «Монументальность и мобильность в столицах Великих Моголов» . Азиатские перспективы . 33 (2): 296 и 298. ISSN 0066-8435 . JSTOR 42928323 . Архивировано из оригинала 1 мая 2022 года . Проверено 11 июня 2021 г.
- ^ Босворт, Клиффорд Эдмунд (2008). Исторические города исламского мира . Брилл. п. 127. ИСБН 978-90-04-15388-2 . ОСЛК 231801473 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж Чаттерджи, Нандини (1 декабря 2019 г.), «Суды, Моголы» , Энциклопедия ислама, Три , Брилл, doi : 10.1163/1573-3912_ei3_com_25171 , заархивировано из оригинала 13 декабря 2021 г. , получено 13 декабря 2021 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Халфауи, Муэз. «Империя Великих Моголов и право» . Оксфордские исламские исследования онлайн . Архивировано из оригинала 13 декабря 2021 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2021 г.
- ^ Конерманн, Стефан (4 августа 2015 г.), «Империя Великих Моголов» , Интернет-энциклопедия ранней современной истории , Brill, doi : 10.1163/2352-0272_emho_com_024206 , заархивировано из оригинала 26 марта 2022 г. , получено 25 марта 2022 г.
- ^ Чаттерджи, Нандини (2014). «Размышления о религиозных различиях и допустимом включении в законы Великих Моголов» . Журнал права и религии . 29 (3): 396–415. дои : 10.1017/мл.2014.20 . hdl : 10871/15975 . ISSN 0748-0814 . S2CID 143513602 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2021 г.
- ^ Итон, Ричард М. (2019). Индия в персидскую эпоху: 1000–1765 гг . Издательство Калифорнийского университета. п. 272. ИСБН 978-0-520-97423-4 . OCLC 1243310832 .
- ^ Шмидт, Карл Дж. (2015). Атлас и обзор истории Южной Азии . Рутледж. ISBN 978-1-317-47681-8 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час я дж Шмидт, Карл Дж. (2015). Атлас и обзор истории Южной Азии . Рутледж. стр. 100–. ISBN 978-1-317-47681-8 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 9 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Мэддисон, Ангус (2003). Исследования Центра развития Мировая экономика Историческая статистика: Историческая статистика . Издательство ОЭСР. стр. 256–. ISBN 978-92-64-10414-3 . Архивировано из оригинала 20 января 2023 года . Проверено 9 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Джеффри Г. Уильямсон и Дэвид Клингингсмит, Деиндустриализация Индии в 18 и 19 веках. Архивировано 29 марта 2017 года в Wayback Machine , Сеть глобальной экономической истории, Лондонская школа экономики.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Рой, Тиртханкар (2010). «Длительная глобализация и производители текстиля в Индии» . В Лексе Херме ван Воссе; Эльс Химстра-Куперус; Элиза ван Недервен Мееркерк (ред.). Эшгейтский спутник по истории текстильщиков, 1650–2000 гг . Издательство Эшгейт . п. 255. ИСБН 978-0-7546-6428-4 . Архивировано из оригинала 2 июля 2023 года . Проверено 15 августа 2017 г.
- ^ JJL Gommans (2002 , стр. 75)
- ^ Стрейзанд 2018 , с. «...Правители Великих Моголов придерживались более либерального экономического подхода, извлекая выгоду из процветания...».
- ^ А. Бэйли, К.; Фибигер Банг, Питер; Шайдель, Уолтер, ред. (2020). Оксфордская всемирная история империй, том второй: История империй . Издательство Оксфордского университета. п. 775. ИСБН 9780197532775 . Проверено 18 апреля 2024 г.
- ^ М. Атар Али (2008)
- ^ Хорхе Флорес (2015 , стр. 73)
- ^ «Изображение оригинальной рупии Великих Моголов , представленное Шер Шахом Сури» . Архивировано из оригинала 5 октября 2002 года . Проверено 4 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Ирфан Хабиб ; Дхарма Кумар ; Тапан Райчаудхури (1987). Кембриджская экономическая история Индии (PDF) . Том. 1. Издательство Кембриджского университета . п. 464. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 4 августа 2017 года . Проверено 11 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Ричардс, Джон Ф. (2003). Бесконечная граница: экологическая история раннего современного мира . Издательство Калифорнийского университета. стр. 27–. ISBN 978-0-520-93935-6 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 9 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Трейси, Джеймс Д. (1997). Политическая экономия торговых империй: государственная власть и мировая торговля, 1350–1750 гг . Издательство Кембриджского университета. стр. 97–. ISBN 978-0-521-57464-8 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 9 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Моосви 2015 , с. 433.
- ^ Мэддисон, Ангус (1971). Классовая структура и экономический рост: Индия и Пакистан со времен Великих Моголов . Тейлор и Фрэнсис . п. 33. ISBN 978-0-415-38259-5 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 22 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Бродберри, Стивен; Гупта, Бишнуприя (2003). «Великое расхождение раннего Нового времени: заработная плата, цены и экономическое развитие в Европе и Азии 1500–1800 гг.» (PDF) . п. 34. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 24 мая 2022 года . Проверено 22 января 2021 г.
- ^ Партхасарати, Прасаннан (2011). Почему Европа разбогатела, а Азия нет: глобальное экономическое расхождение, 1600–1850 гг . п. 42.
- ^ Партхасарати, Прасаннан (2011). Почему Европа разбогатела, а Азия нет: глобальное экономическое расхождение, 1600–1850 гг . п. 39.
- ^ Сиврамкришна, Саши (2009). «Определение уровня жизни в бывшем Майсуре, Южная Индия, на основе путешествия Фрэнсиса Бьюкенена 1800–01: эмпирический вклад в великое расхождение» . Журнал экономической и социальной истории . 52 (4): 726. Архивировано из оригинала 2 мая 2022 года . Проверено 22 января 2021 г.
- ^ Сиврамкришна, Саши (2009). «Определение уровня жизни в бывшем Майсуре, Южная Индия, на основе путешествия Фрэнсиса Бьюкенена 1800–01: эмпирический вклад в великое расхождение» . Журнал экономической и социальной истории . 52 (4): 731. Архивировано из оригинала 2 мая 2022 года . Проверено 22 января 2021 г.
- ^ Партхасарати, Прасаннан (2011). Почему Европа разбогатела, а Азия нет: глобальное экономическое расхождение, 1600–1850 гг . п. 45.
- ^ Сиврамкришна, Саши (2009). «Определение уровня жизни в бывшем Майсуре, Южная Индия, на основе путешествия Фрэнсиса Бьюкенена 1800–01: эмпирический вклад в великое расхождение» . Журнал экономической и социальной истории . 52 (4): 729. Архивировано из оригинала 2 мая 2022 года . Проверено 22 января 2021 г.
- ^ Моосви 2015 , с. 432.
- ^ Моосви 2015 , с. 450.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Моосви, Ширин (декабрь 2011 г.). «Мир труда в Индии Великих Моголов (ок. 1500–1750)» . Международное обозрение социальной истории . 56 (С19): 245–261. дои : 10.1017/S0020859011000526 .
- ^ Пагаза, Игнатий; Аргириадес, Деметрий (2009). Добиться необходимых перемен: спасти нашу планету Земля . ИОС Пресс. п. 129. ИСБН 978-1-58603-958-5 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Ладден, Дэвид (1999). Аграрная история Южной Азии . Издательство Кембриджского университета . п. 96. ИСБН 978-0-521-36424-9 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 29 апреля 2019 г.
- ^ Ирфан Хабиб ; Дхарма Кумар ; Тапан Райчаудхури (1987). Кембриджская экономическая история Индии (PDF) . Том. 1. Издательство Кембриджского университета . п. 214. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 4 августа 2017 года . Проверено 5 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Ирфан Хабиб ; Дхарма Кумар ; Тапан Райчаудхури (1987). Кембриджская экономическая история Индии (PDF) . Том. 1. Издательство Кембриджского университета . п. 217. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 4 августа 2017 года . Проверено 5 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Ирфан Хабиб (2011), Экономическая история средневековой Индии, 1200–1500 , стр. 53. Архивировано 22 сентября 2023 года в Wayback Machine , Pearson Education.
- ^ Сунеджа, Вивек (2000). Понимание бизнеса: многомерный подход к рыночной экономике . Психология Пресс . п. 13. ISBN 978-0-415-23857-1 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 9 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Партхасарати, Прасаннан (2011), Почему Европа разбогатела, а Азия нет: глобальное экономическое расхождение, 1600–1850 гг. , Cambridge University Press, стр. 39–45, ISBN 978-1-139-49889-0 , заархивировано из оригинала 4 апреля 2023 года , получено 9 августа 2017 года.
- ^ Эндрю де ла Гарса (2016 , стр. 114-115)
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Ом Пракаш , « Империя Великих Моголов. Архивировано 18 ноября 2022 года в Wayback Machine », История мировой торговли с 1450 года , под редакцией Джона Дж. Маккаскера , том. 1, Macmillan Reference, США, 2006, стр. 237–240, Всемирная история в контексте . Проверено 3 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Ангус Мэддисон (1995), Мониторинг мировой экономики, 1820–1992 , ОЭСР , стр. 30
- ^ Партхасарати, Прасаннан (2011), Почему Европа разбогатела, а Азия нет: глобальное экономическое расхождение, 1600–1850 гг ., Cambridge University Press, стр. 2, ISBN 978-1-139-49889-0
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Ричард Максвелл Итон (1996), Расцвет ислама и границы Бенгалии, 1204–1760 , стр. 202. Архивировано 4 апреля 2023 года в Wayback Machine , University of California Press.
- ^ Лаквете, Анджела (2003). Изобретение хлопкоочистительной машины: машина и миф в довоенной Америке . Балтимор: Издательство Университета Джона Хопкинса. стр. 1–6. ISBN 978-0-8018-7394-2 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 3 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Ирфан Хабиб (2011), Экономическая история средневековой Индии, 1200–1500 , стр. 53–54. Архивировано 22 сентября 2023 года в Wayback Machine , Pearson Education.
- ^ Ирфан Хабиб (2011), Экономическая история средневековой Индии, 1200–1500 , стр. 54. Архивировано 22 сентября 2023 года в Wayback Machine , Pearson Education.
- ^ Доктор Мохамед Наср. Мода и дизайн при Великих Моголов Акбаре Аурангзебу. Историческая перспектива .
- ^ Рой, Тиртханкар (ноябрь 2011 г.). «Где находится Бенгалия? Расположение индийского региона в мировой экономике раннего Нового времени». Прошлое и настоящее (213): 115–146. дои : 10.1093/pastj/gtr009 .
- ^ Бэйли, Калифорния (1988). Индийское общество и создание Британской империи . Новая Кембриджская история Индии. Том. II.1. Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 51. ИСБН 978-0-521-38650-0 . Архивировано из оригинала 8 февраля 2023 года . Проверено 8 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ «Рай народов» . Дакка Трибьюн . Архивировано из оригинала 3 июня 2016 года . Проверено 30 апреля 2016 г.
- ^ Даниял, Шоаиб. «Бенгальский Новый год: как Акбар изобрел современный бенгальский календарь» . Прокрутка.в . Архивировано из оригинала 26 апреля 2022 года . Проверено 30 апреля 2016 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Нанда, Дж. Н. (2005). Бенгалия: уникальный штат . Концептуальное издательство. п. 10. ISBN 978-81-8069-149-2 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 5 мая 2016 г.
- ^ Хусейн, Сиддики М. Азизуддин (2002). Структура политики при Аурангзебе 1658-1707 гг . Дистрибьюторы Kanishka Publishers, Университета Самбалпура библиотека . п. 158. ИСБН 978-8173914898 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Рэй, Индраджит (2011). Бенгальская промышленность и британская промышленная революция (1757–1857) . Рутледж. п. 174. ИСБН 978-1-136-82552-1 .
- ^ «Технологический динамизм в застойном секторе: безопасность на море во время ранней промышленной революции» (PDF) . Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 11 декабря 2019 года . Проверено 3 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и Колин МакЭведи ; Ричард Джонс (1978). Атлас мировой истории народонаселения (PDF) . Нью-Йорк: факты в архиве . стр. 184–185. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 12 ноября 2020 г. Проверено 7 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Ангус Мэддисон (2001), Мировая экономика: перспектива тысячелетия , стр. 236 Архивировано 11 ноября 2020 года в Wayback Machine , Центр развития ОЭСР.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Ирфан Хабиб ; Дхарма Кумар ; Тапан Райчаудхури (1987). Кембриджская экономическая история Индии (PDF) . Том. 1. Издательство Кембриджского университета . п. 170. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 4 августа 2017 года . Проверено 4 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Жан-Ноэль Бирабен, 1980, «Очерк эволюции человечества», Население, Избранные статьи, Том. 4, стр. 1–13.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Эрали, Авраам (2007). Мир Великих Моголов: жизнь в последний золотой век Индии . Книги Пингвинов Индия. стр. 5–. ISBN 978-0-14-310262-5 .
- ^ Маланима, Паоло (2009). Досовременная европейская экономика: тысяча лет (10–19 вв.) . Издательство «Брилл» . п. 244. ИСБН 978-90-04-17822-9 .
- ^ Ирфан Хабиб ; Дхарма Кумар ; Тапан Райчаудхури (1987). Кембриджская экономическая история Индии (PDF) . Том. 1. Издательство Кембриджского университета . п. 165. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 4 августа 2017 года . Проверено 4 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Бродберри, Стивен; Гупта, Бишнуприя (2010). «ВВП Индии до 1870 года: некоторые предварительные оценки и сравнение с Великобританией» (PDF) . Уорикский университет . п. 23. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 11 ноября 2020 г. . Проверено 12 октября 2015 г.
- ^ Дайсон, Тим (2018). История населения Индии: от первых современных людей до наших дней . стр. 63–65.
- ^ Ирфан Хабиб ; Дхарма Кумар ; Тапан Райчаудхури (1987). Кембриджская экономическая история Индии (PDF) . Том. 1. Издательство Кембриджского университета . п. 171. Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 4 августа 2017 года . Проверено 4 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Роб, штат Мэриленд Абдур; Асадуззаман, Мэриленд (декабрь 1997 г.). «Исторический рост урбанизации в Дакке». Обзор социальных наук . 14 (2). Университет Дакки : 126.
- ^ Моосви, Ширин (2008). Люди, налогообложение и торговля в Индии Великих Моголов . Издательство Оксфордского университета. п. 131. ИСБН 978-0-19-569315-7 .
- ^ Чаудхури, КН (2008). «Некоторые размышления о городе и стране в Индии Великих Моголов». Современные азиатские исследования . 12 (1): 77–96. дои : 10.1017/S0026749X00008155 . ISSN 0026-749X . S2CID 146558617 .
- ^ Фаруки, Шамсур Рахман (2003). «Долгая история литературной культуры урду, часть 1». В Поллоке, Шелдон (ред.). Литературные культуры в истории . Издательство Калифорнийского университета. п. 806. ИСБН 0-520-22821-9 .
- ^ Кошик Рой и Питер Лорге (2014 , стр. 146)
- ^ Пиус Малекандатил (2016). Индийский океан в создании Индии раннего Нового времени (Иллюстрированное издание). Рутледж. п. 194. ИСБН 978-1351997454 . Проверено 19 июля 2024 г.
...Армия Великих Моголов потеряла большую часть своего посткочевого населения...
- ^ Империя Великих Моголов — MSN Encarta . Архивировано из оригинала 28 октября 2009 года.
- ^ «Конференция по индо-персидской литературе: SOAS: Литературная культура Северной Индии (1450–1650)» . СОАС . Архивировано из оригинала 23 сентября 2009 года . Проверено 28 ноября 2012 г.
- ^ «Ислам: Империя Великих Моголов (1500-е, 1600-е годы)» . Религии . Би-би-си. Архивировано из оригинала 13 августа 2018 года . Проверено 10 июня 2018 г.
- ^ Фатма, Садаф (2012). «Водопроводные сооружения в садах Великих Моголов». Труды Индийского исторического конгресса . 73 : 1268–1278. JSTOR 44156328 .
- ^ Альтер, Джозеф С. (май 1992 г.). « Санньяси и индийский борец: анатомия отношений». Американский этнолог . 19 (2): 317–336. дои : 10.1525/ae.1992.19.2.02a00070 . ISSN 0094-0496 .
- ^ Альтер, Джозеф С. (1992). Тело борца: идентичность и идеология в Северной Индии . Издательство Калифорнийского университета. п. 2 . ISBN 978-0-520-07697-6 .
Борьба в современной Индии представляет собой синтез двух разных традиций: персидской формы искусства, принесенной в Южную Азию Моголами, и местной индуистской формы.
- ^ «Влияние Великих Моголов на индийскую музыку» . Индус . 8 февраля 2000 г. Архивировано из оригинала 26 декабря 2019 г. . Проверено 5 апреля 2019 г.
- ^ Харбанс Мухия (2008). Моголы Индии . Джон Уайли и сыновья. п. 150. ИСБН 978-0470758151 . Проверено 11 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Петерсен, Эндрю (1996). «Моголы». Словарь исламской архитектуры . Рутледж. стр. 199–205. ISBN 9781134613663 .
- ^ Ашер, Кэтрин Бланшард (1992). Архитектура Индии Великих Моголов . Новая Кембриджская история Индии, Часть I. Том. 4. Издательство Кембриджского университета . стр. 1–2, 15–17. ISBN 9780521267281 .
- ^ Блум, Джонатан М.; Блер, Шейла С., ред. (2009). "Архитектура". Энциклопедия исламского искусства и архитектуры Grove . Том. 1. Издательство Оксфордского университета. п. 182. ИСБН 9780195309911 .
- ^ Уильям Дэлримпл (2009). Последний Могол: Падение Дели, 1857 год . А&С Черный. ISBN 978-1408806883 . Проверено 23 июля 2024 г.
...Ледяной Дом, в котором укрывался Захир...
- ^ Кешавлал Х. Камдар (1933). История правления Великих Моголов в Индии, 1526-1761 гг . MC Котари. п. 141 . Получено 8 августа.
- ^ Росс Марлей; Кларк Д. Неер (1999). Патриоты и тираны: десять азиатских лидеров . Роуман и Литтлфилд. п. 269. ИСБН 978-0-8476-8442-7 .
- ^ Крилл, Розмари и Джаривала, Капил. Индийский портрет, 1560–1860 , стр. 23–27, Национальная портретная галерея, Лондон , 2010, ISBN 978-1855144095 ; Пляж, Майло Кливленд (1987), Живопись Ранних Великих Моголов , издательство Гарвардского университета, стр. 33–37, ISBN 978-0-674-22185-7 , книги Google. Архивировано 26 марта 2023 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ^ Соучек, Присцилла (1987). «Персидские художники в Индии Великих Моголов: влияния и трансформации». Мукарнас . 4 : 166–181. дои : 10.2307/1523102 . JSTOR 1523102 .
- ^ Блант, Уилфрид (1948). «Художники естествознания Великих Моголов». Журнал Берлингтон . 90 (539): 48–50. JSTOR 869792 .
- ^ Сардар, Марика (октябрь 2003 г.). «Искусство Великих Моголов после 1600 года» . МЕТ . Архивировано из оригинала 4 февраля 2019 года.
- ^ Лости, Дж. П. Рой, Малини (редакторы), Индия Великих Моголов: Искусство, культура и империя , 2013, стр. 147, 149, Британская библиотека, ISBN 978-0712358705
- ^ Банарши Прасад Саксена (1932). История Шахджахана Дихли, 1932 год . Индиан Пресс Лимитед.
- ^ Сейллер 2011 , стр. 329.
- ^ «2. Культура и политика персидского языка в доколониальном Индостане» , «Литературные культуры в истории» , University of California Press, стр. 158–167, 2019 г., doi : 10.1525/9780520926738-007 , ISBN 978-0-520-92673-8 , S2CID 226770775 , заархивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 г. , получено 26 июля 2021 г.
- ^ Абиди, Саха; Гаргеш, Равиндер (2008), Качру, Брадж Б; Качру, Ямуна; Шридхар, С.Н. (ред.), «Персидский язык в Южной Азии» , Язык в Южной Азии , Кембридж: Издательство Кембриджского университета, стр. 105, номер домена : 10.1017/cbo9780511619069.007 , ISBN 978-0-511-61906-9 , заархивировано 22 сентября 2023 года , получено 26 июля 2021 года.
- ^ Алам, Музаффар (2004). Языки политического ислама: Индия 1200–1800 гг . Издательство Чикагского университета. стр. 134, 144. ISBN. 0-226-01100-3 . OCLC 469379391 .
- ^ Фаруки, Шамсур Рахман (2003). «Долгая история литературной культуры урду, Часть 1: Наименование и размещение литературной культуры». В Поллоке, Шелдон (ред.). Литературные культуры в истории . Издательство Калифорнийского университета. стр. 807–808, 811. doi : 10.1525/9780520926738-019 . ISBN 978-0-520-22821-4 . S2CID 226765648 .
- ^ Мэтьюз, Дэвид. «Урду» . Энциклопедия Ираника . Архивировано из оригинала 29 апреля 2011 года . Проверено 26 июля 2021 г.
- ^ Артур Дадни (2015). Дели: страницы забытой истории . Хэй Хаус. ISBN 978-93-84544-31-7 . Архивировано из оригинала 9 июня 2023 года . Проверено 19 мая 2023 г.
- ^ С.Р. Шарма · (2014). Жизнь, времена и поэзия Мира . Издательство Партридж. п. 4. ISBN 978-1-4828-1478-1 . Архивировано из оригинала 16 июля 2023 года . Проверено 19 мая 2023 г.
- ^ Стрейзанд, Дуглас Э. (2011). Исламские пороховые империи: Османы, Сефевиды и Моголы . Филадельфия: Вествью Пресс. ISBN 978-0-8133-1359-7 .
- ^ Чарльз Т. Эванс. «Пороховые империи» . Общественный колледж Северной Вирджинии. Архивировано из оригинала 26 мая 2011 года . Проверено 28 декабря 2010 г.
- ^ Стрейзанд, Дуглас Э. (2011). Исламские пороховые империи: Османы, Сефевиды и Моголы . Филадельфия: Вествью Пресс. п. 255. ИСБН 978-0-8133-1359-7 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Партингтон, Джеймс Риддик (1999) [Впервые опубликовано в 1960 году]. История греческого огня и пороха . Балтимор: Издательство Университета Джонса Хопкинса. п. 226 . ISBN 978-0-8018-5954-0 .
- ^ Сумка, АК (2005). «Фатхуллах Ширази: Пушка, Многоствольная пушка и Яргу». Индийский журнал истории науки . 40 (3): 431–436. ISSN 0019-5235 .
- ^ Партингтон, Джеймс Риддик (1999) [Впервые опубликовано в 1960 году]. История греческого огня и пороха . Балтимор: Издательство Университета Джонса Хопкинса. п. 225 . ISBN 978-0-8018-5954-0 .
- ^ Свати Шивал; Доламани Саху (2022). «ПОЛИТИЧЕСКАЯ ИСТОРИЯ МОГОЛОВ: ВЛИЯНИЕ НА ЮЖНУЮ АЗИЮ» . Исследовательский журнал IJRTS . 23 (23): 113. ISSN 2347-6117 . Проверено 16 июля 2024 г.
- ^ Мугалистан Сипахи (19 июня 2010 г.). «Исламская империя Великих Моголов: Боевые слоны, часть 3» . Архивировано из оригинала 21 декабря 2021 года . Проверено 28 ноября 2012 г. - через YouTube.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Гулам Яздани (1995). Бидар: его история и памятники (1-е изд.). Мотилал Банарсидас. п. 15. ISBN 8120810716 .
- ^ Хан, Насир Раза. Искусство и архитектурные традиции Индии и Ирана: общность и разнообразие. Рутледж, 2022.
- ^ Насир Раза Хан (2022). Искусство и архитектурные традиции Индии и Ирана. Общность и разнообразие . Рутледж Индия. ISBN 9781032134819 . Проверено 20 марта 2024 г.
... Ширази и другие пересмотрели учебные программы медресе. В новой программе...
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Шарма, Вирендра Натх (1995), Савай Джай Сингх и его астрономия , Motilal Banarsidass Publ., стр. 8–9, ISBN 978-81-208-1256-7
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Бабер, Захир (1996), Наука Империи: научные знания, цивилизация и колониальное правление в Индии , State University of New York Press , стр. 82–89, ISBN 978-0-7914-2919-8
- ^ Тельчер, Кейт (2000). «Хирург-мойщик и персидский принц: два индейца в Британии начала девятнадцатого века». Интервенции: Международный журнал постколониальных исследований . 2 (3): 409–423. дои : 10.1080/13698010020019226 . ISSN 1469-929Х . S2CID 161906676 .
- ^ «НЕБЕСНЫЙ ГЛОБУС, СДЕЛАННЫЙ МОГАЛЬСКИМ АСТРОЛАБИСТОМ МУХАММАДОМ САЛИХОМ ИЗ ТХАТТЫ, ДАТИРОВАННЫЙ 1074 ГОДОМ хиджры/1663 годом нашей эры» . www.orientalartauctions.com . Проверено 18 июня 2024 г.
- ^ Верма, Трипта (1994). Карханас при Великих Моголов, от Акбара до Аурангзеба: исследование экономического развития . Публикации Прагати. п. 18. ISBN 978-81-7307-021-1 .
- ^ Шарма, Шри Рам (1951). Правительство и администрация Великих Моголов . Хинд Китабс. п. 61.
- ^ Сумит (2012). «Обзор Джайпура «Чхапахана» восемнадцатого века на основе записей Джайпура «Карханаджат»» . Труды Индийского исторического конгресса . 73 : 421–430. ISSN 2249-1937 . JSTOR 44156233 .
- ^ Сэвидж-Смит, Эмили (1985), Исламские небесные глобусы: их история, конструкция и использование , Smithsonian Institution Press, Вашингтон, округ Колумбия
- ^ «Небесный глобус» . Национальные музеи Шотландии . Архивировано из оригинала 14 июня 2020 года . Проверено 15 октября 2020 г.
Источники
- Эндрю де ла Гарса (2016). Империя Великих Моголов в войне Бабура, Акбара и индийской военной революции, 1500-1605 гг . Тейлор и Фрэнсис. ISBN 978-1-317-24531-5 . Проверено 6 декабря 2023 г.
- Конан, Мишель (2007). Ближневосточные садовые традиции: единство и разнообразие: вопросы, методы и ресурсы в мультикультурной перспективе . Думбартон-Оукс. ISBN 978-0-88402-329-6 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 13 июня 2019 г.
- Хорхе Флорес (2015). Падшах Великих Моголов: иезуитский трактат о дворе и домашнем хозяйстве императора Джахангира . Том 6 «Правители и элиты». Брилл. п. 74. ИСБН 978-9004307537 . Проверено 13 июля 2024 г.
- Кошик Рой; Питер Лорге (17 декабря 2014 г.). Китайско-индийская война - от классической эпохи до 1870 года (электронная книга) . Тейлор и Фрэнсис. п. 196. ИСБН 978-1-317-58710-1 . Проверено 5 декабря 2023 г.
- Моосви, Ширин (2015) [Впервые опубликовано в 1987 году]. Экономика Империи Великих Моголов, ок. 1595: статистическое исследование (2-е изд.). Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-19-908549-1 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 13 июня 2019 г.
- Морье, Джеймс (1812). «Путешествие по Персии, Армении и Малой Азии» . Ежемесячный журнал . Том. 34. Р. Филлипс. Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 19 октября 2015 г.
- Резерфорд, Алекс (2010). Империя Великих Моголов: Братья на войне: Братья на войне . Заголовок. ISBN 978-0-7553-8326-9 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 10 июня 2019 г.
- Сейллер, Джон (2011). «Могольская рукопись «Дивана» Наваи». Артибус Азия . 71 (2): 325–334.
Дальнейшее чтение
- Алам, Музаффар. Кризис империи Великих Моголов в Северной Индии: Авад и Пенджаб, 1707–48 (1988)
- Али, М. Атар (1975), «Уход империи: Дело Великих Моголов», Modern Asian Studies , 9 (3): 385–396, doi : 10.1017/s0026749x00005825 , JSTOR 311728 , S2CID 143861682 , о причинах ее крах
- Ашер, CB; Талбот, К. (2008), Индия до Европы , издательство Кембриджского университета , ISBN 978-0-521-51750-8
- Блэк, Джереми. «Моголы наносят двойной удар», History Today (апрель 2012 г.) 62 № 4, стр. 22–26. полный текст онлайн
- Блейк, Стивен П. (ноябрь 1979 г.), «Родовая бюрократическая империя Великих Моголов», Журнал азиатских исследований , 39 (1): 77–94, doi : 10.2307/2053505 , JSTOR 2053505 , S2CID 154527305
- Дейл, Стивен Ф. Мусульманские империи Османов, Сефевидов и Великих Моголов (Cambridge UP, 2009)
- Далримпл, Уильям (2007). Последний Могол: Падение династии: Дели, 1857 г. Random House Digital, Inc. ISBN 978-0-307-26739-9 .
- Фаруки, Мунис Д. (2005), «Забытый принц: Мирза Хаким и формирование Империи Великих Моголов в Индии», Журнал экономической и социальной истории Востока , 48 (4): 487–523, doi : 10.1163 /156852005774918813 , JSTOR 25165118 , об Акбаре и его брате
- Дж. Дж. Л. Гомманс (2002). Война Великих Моголов Индийские границы и дороги в Империи 1500–1700 гг . Тейлор и Фрэнсис. ISBN 9781134552757 . Архивировано из оригинала 2 января 2011 года . Проверено 18 апреля 2024 г.
- Гордон, С. Новая Кембриджская история Индии , II, 4: Маратхи 1600–1818 (Кембридж, 1993).
- Хабиб, Ирфан. Атлас Империи Великих Моголов: политические и экономические карты (1982).
- Марковиц, Клод, изд. (2004) [Впервые опубликовано в 1994 году под названием Histoire de l'Inde Moderne ]. История современной Индии, 1480–1950 (2-е изд.). Лондон: Гимн Пресс. ISBN 978-1-84331-004-4 . Архивировано из оригинала 22 сентября 2023 года . Проверено 19 октября 2015 г.
- Меткалф, Б. ; Меткалф, TR (2006), Краткая история современной Индии (2-е изд.), Cambridge University Press , ISBN 978-0-521-68225-1 , архивировано из оригинала 2 июля 2023 года , получено 19 октября 2015 года.
- Ричардс, Джон Ф. (1996). Империя Великих Моголов . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-0-521-56603-2 . Архивировано из оригинала 1 февраля 2023 года . Проверено 19 октября 2015 г.
- Маджумдар, Рамеш Чандра (1974). Империя Великих Моголов . Б.В. Бхаван.
- Ричардс, Дж. Ф. (апрель 1981 г.), «Государственные финансы Великих Моголов и досовременная мировая экономика», Сравнительные исследования в обществе и истории , 23 (2): 285–308, doi : 10.1017/s0010417500013311 , JSTOR 178737 , S2CID 154809724
- Робб, П. (2001), История Индии , Лондон: Пэлгрейв, ISBN 978-0-333-69129-8
- Шривастава, Аширбади Лал. Империя Великих Моголов, 1526–1803 (1952) онлайн.
- Штейн, Б. (1998), История Индии (1-е изд.), Оксфорд: Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-0-631-20546-3
- Штейн, Б. (2010), Арнольд, Д. (редактор), История Индии (2-е изд.), Оксфорд: Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-1-4051-9509-6 , заархивировано из оригинала 12 июля 2023 года , получено 19 октября 2015 года.
Культура
- Беринстейн, В. Индия Великих Моголов: великолепие Павлиньего трона (Лондон, 1998).
- Буш, Эллисон. Поэзия королей: классическая литература на хинди Индии Великих Моголов (2011), отрывок и текстовый поиск. Архивировано 29 мая 2016 года в Wayback Machine.
- Пароди, Лаура Э. (2021). «Кабул, забытая столица Великих Моголов: сады, город и двор на рубеже шестнадцатого века». Мукарнас Онлайн . 38 (1): 113–153. дои : 10.1163/22118993-00381P05 . S2CID 245040517 .
- Дайана Престон; Майкл Престон (2007). Тадж-Махал: страсть и гений в сердце Империи Великих Моголов . Уокер и компания. ISBN 978-0-8027-1673-6 .
- Шиммель, Аннемари . Империя Великих Моголов: история, искусство и культура (Реакция 2006)
- Уэлч, Южная Каролина; и др. (1987). Альбом императоров: изображения Индии Великих Моголов . Нью-Йорк: Метрополитен-музей . ISBN 978-0-87099-499-9 . Архивировано из оригинала 27 сентября 2018 года . Проверено 9 октября 2013 г.
Общество и экономика
- Чаудхури, КН (1978), «Некоторые размышления о городе и стране в Индии Великих Моголов», Современные азиатские исследования , 12 (1): 77–96, doi : 10.1017/s0026749x00008155 , JSTOR 311823 , S2CID 146558617
- Хабиб, Ирфан. Атлас Империи Великих Моголов: политические и экономические карты (1982).
- Хабиб, Ирфан. Аграрная система Индии Великих Моголов (1963 г., исправленное издание 1999 г.).
- Джей Си Шарман (2019). Империи слабых: реальная история европейской экспансии и создания нового мирового порядка . Издательство Принстонского университета. ISBN 978-0691182797 .
- Хистерман, Дж. К. (2004), «Социальная динамика Империи Великих Моголов: краткое введение», Журнал экономической и социальной истории Востока , 47 (3): 292–297, doi : 10.1163/1568520041974729 , JSTOR 25165051
- Хан, Иктидар Алам (1976), «Средние классы в Империи Великих Моголов», социолог , 5 (1): 28–49, doi : 10.2307/3516601 , JSTOR 3516601
- М. Атар Али (2008). «Политика Великих Моголов - критика ревизионистских подходов» . Современные азиатские исследования . 27 (5). Издательство Кембриджского университета: 699–710. дои : 10.1017/S0026749X00001256 . ISSN 1469-8099 . Проверено 18 апреля 2024 г.
....контраст между восточным деспотическим государством и западным государством laissez faire.
- Масанори Сато (Масатецу Сато); Нариаки Накадзато (Нариаки Накадзато); Цукаса Мизусима (1998). Великих Моголов до Британской Индии 14 (на японском языке) . От Империи
- вторая публикация Великих Моголов до Британской Индии . От Империи Всемирная история Чуокорон-Синша 14. 2009.
- Ротермунд, Дитмар. Экономическая история Индии: от доколониальных времен до 1991 года (1993)
- Олег Игоревич Красов (2022 г.). Земельное право в странах Азии (электронная книга) . Норма. п. 75. ИСБН 9785001562566 . Проверено 18 апреля 2024 г.
- Стрейзанд, Дуглас Э. (2018). Исламские пороховые империи Османы, Сефевиды и Великие Моголы . Тейлор и Фрэнсис. ISBN 9780429979217 . Проверено 24 апреля 2024 г.
Первоисточники
- Бернье, Франсуа (1891). Путешествие по Империи Великих Моголов, 1656–1668 гг . Арчибальд Констебль, Лондон.
- Хиро, Дилип, редактор, Журнал императора Бабура (Penguin Classics, 2007)
- Бабурнама: Мемуары Бабура, принца и императора изд. У.М. Такстон-младший (2002); это была первая автобиография в исламской литературе.
- Джексон, А.В. и др., ред. История Индии (1907), т. 9. Исторические рассказы об Индии иностранных путешественников, классические, восточные и западные, онлайн-издание AVW Jackson.
- Джоуэр (1832 г.). Тезкере аль вакиат или Частные мемуары императора Великих Моголов Хумаюна. Написаны на персидском языке Джухером, конфиденциальным слугой Его Величества . Перевод майора Чарльза Стюарта. Джон Мюррей, Лондон.
Старые истории
- Эллиот, сэр Его Величество, под редакцией Доусона, Джона. История Индии, рассказанная ее собственными историками. Мухаммадский период ; опубликовано лондонской компанией Trubner Company 1867–1877. (Интернет-копия в Гуманитарном институте Паккарда - Другие персидские тексты в переводе; исторические книги: список авторов и список названий)
- Адамс, WH Давенпорт (1893). Воины Полумесяца . Лондон: Хатчинсон.
- Холден, Эдвард Синглтон (1895). Могольские императоры Индостана, 1398–1707 гг . Нью-Йорк: Сыновья К. Скрибнера.
- Маллесон, Великобритания (1896 г.). Акбар и возникновение империи Великих Моголов . Оксфорд: Кларендон Пресс.
- Мануччи, Никколао ; тр. с французского Франсуа Катру (1826 г.). История династии Моголов в Индии, 1399–1657 гг . Лондон: Дж. М. Ричардсон.
- Лейн-Пул, Стэнли (1906). История Индии: от правления Акбара Великого до падения Империи Великих Моголов (Том 4) . Лондон, общество Гролье.
- Мануччи, Никколао ; тр. Уильям Ирвин (1907). История-ду-Могор; или, Могулская Индия 1653–1708, Vol. 1 . Лондон, Дж. Мюррей.
- Мануччи, Никколао ; тр. Уильям Ирвин (1907). История-ду-Могор; или, Могулская Индия 1653–1708, Том. 2 . Лондон, Дж. Мюррей.
- Мануччи, Никколао ; тр. Уильям Ирвин (1907). История-ду-Могор; или, Могулская Индия 1653–1708, Том. 3 . Лондон, Дж. Мюррей.
- Оуэн, Сидни Дж (1912). Падение империи Великих Моголов . Лондон, Дж. Мюррей.
Внешние ссылки
- Индия Великих Моголов: интерактивный опыт от Британского музея
- Империя Великих Моголов , интервью BBC Radio 4 с Санджаем Субрахманьямом, Сьюзан Стронг и Чандрикой Каул ( В наше время , 26 февраля 2004 г.)
- «Акбар» Сунила Хилнани из передачи BBC Radio 4 «Воплощения: Индия в 50 жизнях».