Сефевидский Иран
Охраняемые домены Ирана | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1501–1736 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
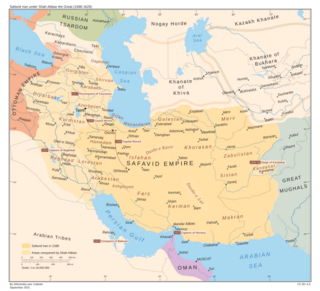 The Safavid Empire at its greatest extent, during the reign of Abbas the Great (r. 1588–1629) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Empire | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Twelver Shīʿa Islam (official) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shahanshah | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1501–1524 | Ismail I (first) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1732–1736 | Abbas III (last) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Grand Vizier | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1501–1507 | Amir Zakariya (first) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1729–1736 | Nader Qoli Beg (last) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Council of State | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Early modern period | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Establishment of the Safavid order by Safi-ad-din Ardabili | 1301 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Established | 22 December[2] 1501 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Hotak invasion | 1722 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Reconquest under Nader Shah | 1726–1729 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Disestablished | 8 March 1736 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Nader Shah crowned | 8 March 1736[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1630[4] | 2,900,000 km2 (1,100,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1650[5] | 8–10 million | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Tuman, Abbasi (incl. Abazi), Shahi[6]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
a State religion.[7] b Official language,[8] coinage,[9][10] civil administration,[11] court (since Isfahan became capital),[12] literary,[9][11][13] theological discourse,[9] diplomatic correspondence, historiography,[14] court-based religious posts,[15] poetry[16] c Court,[17][18][19] religious dignitaries, military,[14][20][21][22] mother tongue,[14] poetry.[14] d Court.[23] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Охраняемые владения Ирана , [а] обычно называемый Сефевидским Ираном , Сефевидской Персией. [б] или Империя Сефевидов , [с] была одной из крупнейших и давних иранских в VII веке империй после мусульманского завоевания Персии , которой с 1501 по 1736 год правила династия Сефевидов . [25] [26] [27] [28] Его часто считают началом современной иранской истории . [29] а также одна из пороховых империй . [30] Сефевидский шах Исмаил I учредил -двунадесятника деноминацию шиитского ислама в качестве официальной религии империи , что ознаменовало один из самых важных поворотных моментов в истории ислама . [31]
династия Иранская , основанная на суфийском ордене Сефевидов. [32] основанный курдскими шейхами , [33] она сильно породнилась с туркменкой , [34] грузинский , [35] черкесский , [36] [37] и понтийский греческий [38] высокопоставленных лиц, был тюркоязычным и тюркизированным . [39] Со своей базы в Ардебиле Сефевиды установили контроль над частями Большого Ирана и вновь подтвердили иранскую идентичность региона. [40] thus becoming the first native dynasty since the Buyids to establish a national state officially known as Iran.[41]
The Safavids ruled from 1501 to 1722 (experiencing a brief restoration from 1729 to 1736 and 1750 to 1773) and, at their height, they controlled all of what is now Iran, Republic of Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Armenia, eastern Georgia, parts of the North Caucasus including Russia, Iraq, Kuwait, and Afghanistan, as well as parts of Turkey, Syria, Pakistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan.
Despite their demise in 1736, the legacy that they left behind was the revival of Iran as an economic stronghold between East and West, the establishment of an efficient state and bureaucracy based upon "checks and balances", their architectural innovations, and patronage for fine arts.[29] The Safavids have also left their mark down to the present era by establishing Twelver Shīʿīsm as the state religion of Iran, as well as spreading Shīʿa Islam in major parts of the Middle East, Central Asia, Caucasus, Anatolia, the Persian Gulf, and Mesopotamia.[29][31]
Names
Mamalik-i Mahrusa-yi Iran (Guarded Domains of Iran) was the common and official name of the Safavid realm.[42][43] The idea of the Guarded Domains illustrated a feeling of territorial and political uniformity in a society where the Persian language, culture, monarchy, and Shia Islam became integral elements of the developing national identity.[44] The concept presumably had started to form under the Mongol Ilkhanate in the late 13th-century, a period in which regional actions, trade, written culture, and partly Shia Islam, contributed to the establishment of the early modern Persianate world.[45] Its shortened form was mamalik-i Iran ("Kingdom of Iran"), and it also had other variants, such as mamalik-i mahrusa-yi khusravani ("the Royal Guarded Domains") and mamalik-i mahrusa-yi humayun ("the Imperial Guarded Domains").[46] Simply Iran was also used.[47]
The phrase mulk-i vasi' al-faza-yi Iran ("the expansive realm of Iran") is used in both the 17th-century chronicle Khold-e barin and the 1680s travelogue Safine-ye Solaymani by the Safavid ambassador to Siam. This recurring expression highlights the authors' pride and recognition of their homeland. This expression is likely the fitting Persian way to describe an "empire" found in the writings of that time.[48]
Background

Safavid history begins with the establishment of the Safaviyya by its eponymous founder Safi-ad-din Ardabili (1252–1334). In 700/1301, Safi al-Din assumed the leadership of the Zahediyeh, a significant Sufi order in Gilan, from his spiritual master and father-in-law Zahed Gilani. Due to the great spiritual charisma of Safi al-Din, the order was later known as the Safaviyya. The Safavid order soon gained great influence in the city of Ardabil, and Hamdullah Mustaufi noted that most of the people of Ardabil were followers of Safi al-Din.
Religious poetry from Safi al-Din, written in the Old Azari language[49]—a now-extinct Northwestern Iranian language—and accompanied by a paraphrase in Persian that helps its understanding, has survived to this day and has linguistic importance.[49]
After Safī al-Dīn, the leadership of the Safaviyya passed to Sadr al-Dīn Mūsā († 794/1391–92). The order at this time was transformed into a religious movement that conducted religious propaganda throughout Iran, Syria and Asia Minor, and most likely had maintained its Sunni Shafi'ite origin at that time. The leadership of the order passed from Sadr ud-Dīn Mūsā to his son Khwādja Ali († 1429) and in turn to his son Ibrāhīm († 1429–47).
When Shaykh Junayd, the son of Ibrāhim, assumed the leadership of the Safaviyya in 1447, the history of the Safavid movement was radically changed. According to historian Roger Savory, "Sheikh Junayd was not content with spiritual authority and he sought material power."[citation needed] At that time, the most powerful dynasty in Iran was that of the Qara Qoyunlu, the "Black Sheep", whose ruler Jahan Shah ordered Junāyd to leave Ardabil or else he would bring destruction and ruin upon the city.[31] Junayd sought refuge with the rival of Kara Koyunlu Jahan Shah, the Aq Qoyunlu (White Sheep Turkomans) Khan Uzun Hassan, and cemented his relationship by marrying Uzun Hassan's sister, Khadija Begum. Junayd was killed during an incursion into the territories of the Shirvanshah and was succeeded by his son Haydar Safavi.
Haydar married Martha 'Alamshah Begom,[38] Uzun Hassan's daughter, who gave birth to Ismail I, founder of the Safavid dynasty. Martha's mother Theodora—better known as Despina Khatun[50]—was a Pontic Greek princess, the daughter of the Grand Komnenos John IV of Trebizond. She had been married to Uzun Hassan[51] in exchange for protection of the Grand Komnenos from the Ottomans.
After Uzun Hassan's death, his son Ya'qub felt threatened by the growing Safavid religious influence. Ya'qub allied himself with the Shirvanshah and killed Haydar in 1488. By this time, the bulk of the Safaviyya were nomadic Oghuz Turkic-speaking clans from Asia Minor and Azerbaijan and were known as Qizilbash "Red Heads" because of their distinct red headgear. The Qizilbash were warriors, spiritual followers of Haydar, and a source of the Safavid military and political power.
After the death of Haydar, the Safaviyya gathered around his son Ali Mirza Safavi, who was also pursued and subsequently killed by Ya'qub. According to official Safavid history, before passing away, Ali had designated his young brother Ismail as the spiritual leader of the Safaviyya.[31]
History
Founding of the dynasty by Shāh Ismāʻil I (r. 1501–1524)
Iran prior to Ismāʻil's rule

After the decline of the Timurid Empire (1370–1506), Iran was politically splintered, giving rise to a number of religious movements. The demise of Tamerlane's political authority created a space in which several religious communities, particularly Shiʻi ones, could come to the fore and gain prominence. Among these were a number of Sufi brotherhoods, the Hurufis, Nuqtavis and Musha'sha'iyyah. Of these various movements, the Safavid Qizilbash was the most politically resilient, and due to its success Shah Isma'il I gained political prominence in 1501.[52] There were many local states prior to the Iranian state established by Ismāʻil.[53] The most important local rulers about 1500 were:
- Huṣayn Bāyqarā, the Timurid ruler of Herāt
- Alwand Mīrzā, the Aq Qoyunlu Khan of Tabrīz
- Murad Beg, Aq Qoyunlu ruler of Irāq al-Ajam
- Farrokh Yaṣar, the Shah of Širvan
- Badi Alzamān Mīrzā, local ruler of Balkh
- Huṣayn Kīā Chalavī, the local ruler of Semnān
- Murād Beg Bayandar, local ruler of Yazd
- Sultan Mahmud ibn Nizam al-Din Yahya, ruler of Sistan
- Several local rulers of Mazandaran and Gilan such as: Bisotun II, Ashraf ibn Taj al-Dawla, Mirza Ali, and Kiya Husayn II.
Ismāʻil was able to unite all these lands under the Iranian Empire he created.
Rise of Shāh Ismāʻil I

The Safavid dynasty was founded about 1501 by Shāh Ismā'īl I.[55] His background is disputed: the language he used is not identical with that of his "race" or "nationality" and he was bilingual from birth.[56] Ismāʻil was of mixed Turkoman, Kurdish, Pontic Greek, and Georgian descent, and was a direct descendant of the Kurdish Ṣūfī Muslim mystic Sheikh Safi al-Din.[57] As such, he was the last in the line of hereditary Grand Masters of the Safaviyeh order, prior to its ascent to a ruling dynasty. Ismāʻil was known as a brave and charismatic youth, zealous with regards to his faith in Shīʿa Islam, and believed himself to be of divine descent – practically worshipped by his Qizilbash followers.
In 1500, Ismāʻil I invaded neighboring Shirvan to avenge the death of his father, Sheik Haydar, who had been murdered in 1488 by the ruling Shirvanshah, Farrukh Yassar. Afterwards, Ismail went on a conquest campaign, capturing Tabriz in July 1501, where he enthroned himself the Shāh of Azerbaijan,[58][59][60] proclaimed himself King of Kings (shahanshah) of Iran[61][62][63] and minted coins in his name, proclaiming Twelver Shīʿīsm as the official religion of his domain.[31] The establishment of Twelver Shīʿīsm as the state religion of Safavid Iran led to various Ṣūfī orders (tariqa) openly declaring their Shīʿīte position, and others to promptly assume Shīʿa Islam. Among these, the founder of one of the most successful Ṣūfī orders, Shāh Ni'matullāh Walī (d. 1431), traced his descent from the first Ismāʿīlī Imam, Muhammad ibn Ismāʿīl, as evidenced in a poem as well as another unpublished literary composition. Although Shāh Ni'matullāh was apparently a Sunnī Muslim, the Ni'matullāhī order soon declared its adherence to Shīʿa Islam after the rise of the Safavid dynasty.[64]
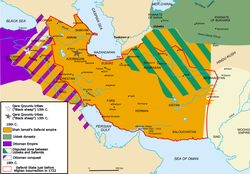
Although Ismāʻil I initially gained mastery over Azerbaijan alone, the Safavids ultimately won the struggle for power over all of Iran, which had been going on for nearly a century between various dynasties and political forces. A year after his victory in Tabriz, Ismāʻil I claimed most of Iran as part of his territory,[31] and within 10 years established a complete control over all of it. Ismāʻil followed the line of Iranian and Turkmen rulers prior to his assumption of the title "Padishah-i-Iran", previously held by Uzun Hasan and many other Iranian kings.[65] The Ottoman sultans addressed him as the king of Iranian lands and the heir to Jamshid and Kai Khosrow.[66]
Having started with just the possession of Azerbaijan, Shirvan, southern Dagestan (with its important city of Derbent), and Armenia in 1501,[67] Erzincan and Erzurum fell into his power in 1502,[68] Hamadan in 1503, Shiraz and Kerman in 1504, Diyarbakır, Najaf, and Karbala in 1507, Van in 1508, Baghdad in 1509, and Herat, as well as other parts of Khorasan, in 1510. In 1503, the kingdoms of Kartli and Kakheti were made his vassals as well.[69] By 1511, the Uzbeks in the north-east, led by their Khan Muhammad Shaybāni, were driven far to the north, across the Oxus River, where they continued to attack the Safavids. Ismāʻil's decisive victory over the Uzbeks, who had occupied most of Khorasan, ensured Iran's eastern borders, and the Uzbeks never since expanded beyond the Hindu Kush. Although the Uzbeks continued to make occasional raids into Khorasan, the Safavid empire was able to keep them at bay throughout its reign.
Start of clashes with the Ottomans


More problematic for the Safavids was the powerful neighboring Ottoman Empire. The Ottomans, a Sunni dynasty, considered the active recruitment of Turkmen tribes of Anatolia for the Safavid cause as a major threat. To counter the rising Safavid power, in 1502, Sultan Bayezid II forcefully deported many Shiʻite Muslims from Anatolia to other parts of the Ottoman realm. In 1511, the Şahkulu rebellion was a widespread pro-Shia and pro-Safavid uprising directed against the Ottoman Empire from within the empire.[70] Furthermore, by the early 1510s Ismail's expansionistic policies had pushed the Safavid borders in Asia Minor even more westwards. The Ottomans soon reacted with a large-scale incursion into Eastern Anatolia by Safavid ghazis under Nūr-ʿAlī Ḵalīfa. This action coincided with the accession to the Ottoman throne in 1512 of Sultan Selim I, Bayezid II's son, and it was the casus belli leading to Selim's decision to invade neighbouring Safavid Iran two years later.[71]
In 1514, Sultan Selim I marched through Anatolia and reached the plain of Chaldiran near the city of Khoy, where a decisive battle was fought. Most sources agree that the Ottoman army was at least double the size of that of Ismāʻil;[55] furthermore, the Ottomans had the advantage of artillery, which the Safavid army lacked. According to historian Roger Savory, "Salim's plan was to winter at Tabriz and complete the conquest of Persia the following spring. However, a mutiny among his officers who refused to spend the winter at Tabriz forced him to withdraw across territory laid waste by the Safavid forces, eight days later".[55] Although Ismāʻil was defeated and his capital was captured, the Safavid empire survived. The war between the two powers continued under Ismāʻil's son, Emperor Tahmasp I, and the Ottoman Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent, until Shah Abbās retook the area lost to the Ottomans by 1602.
The consequences of the defeat at Chaldiran were also psychological for Ismāʻil: the defeat destroyed Ismāʻil's belief in his invincibility, based on his claimed divine status.[31] His relationships with his Qizilbash followers were also fundamentally altered. The tribal rivalries among the Qizilbash, which temporarily ceased before the defeat at Chaldiran, resurfaced in intense form immediately after the death of Ismāʻil, and led to ten years of civil war (930–040/1524–1533) until Shāh Tahmāsp regained control of the affairs of the state. For most of the last decade of Ismail's reign, the domestic affairs of the empire were overseen by the Tajik vizier Mirza Shah Hossein until his assassination in 1523.[72] The Chaldiran battle also holds historical significance as the start of over 300 years of frequent and harsh warfare fueled by geo-politics and ideological differences between the Ottomans and the Iranian Safavids (as well as successive Iranian states) mainly regarding territories in Eastern Anatolia, the Caucasus, and Mesopotamia.
Early Safavid power in Iran was based on the military power of the Qizilbash. Ismāʻil exploited the first element to seize power in Iran. But eschewing politics after his defeat in Chaldiran, he left the affairs of the government to the office of the wakīl (chief administrator, vakil in Turkish). Ismāʻil's successors, most manifestly Shāh Abbās I, successfully diminished the influence of the Qizilbash on the affairs of the state.
Shāh Tahmāsp (r. 1524–1576)
Civil strife during Tahmāsp's early reign

Shāh Tahmāsp, the young titular governor of Khorasan,[73] succeeded his father Ismāʻil in 1524, when he was ten years and three months old. The succession was evidently undisputed.[72] Tahmāsp was the ward of the powerful Qizilbash amir Ali Beg Rūmlū (titled "Div Soltān Rumlu") who saw himself as the de facto ruler of the state. Rūmlū and Kopek Sultān Ustajlu (who had been Ismail's last wakīl) established themselves as co-regents of the young shah.[72] The Qizilbash, which still suffered under the legacy of the battle of Chaldiran, was engulfed in internal rivalries. The first two years of Tahmāsp's reign was consumed with Div Sultān's efforts to eliminate Ustajlu from power.[72] This court intrigue lead directly to tribal conflict. Beginning in 1526 periodic battles broke out, beginning in northwest Iran but soon involving all of Khorasan.[74] In the absence of a charismatic, messianic rallying figure like the young Ismail, the tribal leaders reclaimed their traditional prerogative and threatened to return to the time of local warlords. For nearly 10 years rival Qizilbash factions fought each other. Af first, Kopek Sultān's Ustajlu tribe suffered the heaviest, and he himself was killed in a battle.
Thus Div Soltān emerged victorious in the first palace struggle, but he fell victim to Chuha Sultān of the Takkalu, who turned Tahmāsp against his first mentor. In 1527 Tahmāsp demonstrated his desire by shooting an arrow at Div Soltān before the assembled court. The Takkalu replaced the Rumlu as the dominant tribe. They in turn would be replaced by the Shamlu, whose amir, Husain Khan, became the chief adviser. This latest leader would only last until 1534, when he was deposed and executed.[75]
At the downfall of Husain Khan, Tahmāsp asserted his rule. Rather than rely on another Turkmen tribe, he appointed a Persian wakīl. From 1553 for forty years the shah was able to avoid being ensnared in tribal treacheries. But the decade of civil war had exposed the empire to foreign danger and Tahmāsp had to turn his attention to the repeated raids by the Uzbeks.[76]
Foreign threats to the Empire
The Uzbeks, during the reign of Tahmāsp, attacked the eastern provinces of the kingdom five times, and the Ottomans under Soleymān I invaded Iran four times.[77] Decentralized control over Uzbek forces was largely responsible for the inability of the Uzbeks to make territorial inroads into Khorasan.[78] Putting aside internal dissension, the Safavid nobles responded to a threat to Herat in 1528 by riding eastward with Tahmāsp (then 17) and soundly defeating the numerically superior forces of the Uzbeks at Jām.[79] The victory resulted at least in part from Safavid use of firearms, which they had been acquiring and drilling with since Chaldiran.[80]
Notwithstanding the success with firearms at Jām, Tahmāsp still lacked the confidence to engage their archrivals the Ottomans, choosing instead to cede territory, often using scorched earth tactics in the process.[81] The goal of the Ottomans in the 1534 and 1548–1549 campaigns, during the 1532–1555 Ottoman–Safavid War, was to install Tahmāsp's brothers (Sam Mirza and Alqas Mirza, respectively) as shah in order to make Iran a vassal state. Although in those campaigns (and in 1554) the Ottomans captured Tabriz, they lacked a communications line sufficient to occupy it for long.[80] Nevertheless, given the insecurity in Iraq and its northwest territory, Tahmāsp moved his court from Tabriz to Qazvin.
In the gravest crisis of Tahmāsp's reign, Ottoman forces in 1553–54 captured Yerevan, Karabakh and Nakhjuwan, destroyed palaces, villas and gardens, and threatened Ardabil. During these operations an agent of the Samlu (now supporting Sam Mizra's pretensions) attempted to poison the shah. Tahmāsp resolved to end hostilities and sent his ambassador to Soleymān's winter quarters in Erzurum in September 1554 to sue for peace.[82] Temporary terms were followed by the Peace of Amasya in June 1555, ending the war with the Ottomans for the next two decades. The treaty was the first formal diplomatic recognition of the Safavid Empire by the Ottomans.[83] Under the Peace, the Ottomans agreed to restore Yerevan, Karabakh and Nakhjuwan to the Safavids and in turn would retain Mesopotamia (Iraq) and eastern Anatolia. Soleymān agreed to permit Safavid Shi’a pilgrims to make pilgrimages to Mecca and Medina as well as tombs of imams in Iraq and Arabia on condition that the shah would abolish the taburru, the cursing of the first three Rashidun caliphs.[84] It was a heavy price in terms of territory and prestige lost, but it allowed the empire to last, something that seemed improbable during the first years of Tahmāsp's reign.
Royal refugees: Bayezid and Humayun

Almost simultaneously with the emergence of the Safavid Empire, the Mughal Empire, founded by the Timurid heir Babur, was developing in South-Asia. The Mughals adhered (for the most part) to a tolerant Sunni Islam while ruling a largely Hindu population. After the death of Babur, his son Humayun was ousted from his territories and threatened by his half-brother and rival, who had inherited the northern part of Babur's territories.[85] Having to flee from city to city, Humayun eventually sought refuge at the court of Tahmāsp in Qazvin in 1543. Tahmāsp received Humayun as the true emperor of the Mughal dynasty, despite the fact that Humayun had been living in exile for more than fifteen years.[85][86] After Humayun converted to Shiʻi Islam (under extreme duress),[85] Tahmāsp offered him military assistance to regain his territories in return for Kandahar, which controlled the overland trade route between central Iran and the Ganges. In 1545 a combined Iranian–Mughal force managed to seize Kandahar and occupy Kabul.[87] Humayun handed over Kandahar, but Tahmāsp was forced to retake it in 1558, after Humayun seized it on the death of the Safavid governor.
Humayun was not the only royal figure to seek refuge at Tahmasp's court. A dispute arose in the Ottoman Empire over who was to succeed the aged Suleiman the Magnificent. Suleiman's favourite wife, Hürrem Sultan, was eager for her son, Selim, to become the next sultan. But Selim was an alcoholic and Hürrem's other son, Bayezid, had shown far greater military ability. The two princes quarrelled and eventually Bayezid rebelled against his father. His letter of remorse never reached Suleiman, and he was forced to flee abroad to avoid execution. In 1559 Bayezid arrived in Iran where Tahmasp gave him a warm welcome. Suleiman was eager to negotiate his son's return, but Tahmasp rejected his promises and threats until, in 1561, Suleiman compromised with him. In September of that year, Tahmasp and Bayezid were enjoying a banquet at Tabriz when Tahmasp suddenly pretended he had received news that the Ottoman prince was engaged in a plot against his life. An angry mob gathered and Tahmasp had Bayezid put into custody, alleging it was for his own safety. Tahmasp then handed the prince over to the Ottoman ambassador. Shortly afterwards, Bayezid was killed by agents sent by his own father.[88]
Legacy of Shah Tahmasp

When the young Shah Tahmāsp took the throne, Iran was in a dire state. But in spite of a weak economy, a civil war and foreign wars on two fronts, Tahmāsp managed to retain his crown and maintain the territorial integrity of the empire (although much reduced from Ismail's time). During the first 30 years of his long reign, he was able to suppress the internal divisions by exerting control over a strengthened central military force. In the war against the Uzbeks he showed that the Safavids had become a gunpowder empire. His tactics in dealing with the Ottoman threat eventually allowed for a treaty which preserved peace for twenty years.
In cultural matters, Tahmāsp presided the revival of the fine arts, which flourished under his patronage. Safavid culture is often admired for the large-scale city planning and architecture, achievements made during the reign of later shahs, but the arts of persian miniature, book-binding and calligraphy, in fact, never received as much attention as they did during his time.[89]
Tahmāsp also planted the seeds that would, unintentionally, produce change much later. During his reign he had realized while both looking to his own empire and that of the neighboring Ottomans, that there were dangerous rivalling factions and internal family rivalries that were a threat to the heads of state. Not taken care of accordingly, these were a serious threat to the ruler, or worse, could bring the fall of the former or could lead to unnecessary court intrigues. According to Encyclopædia Iranica, for Tahmāsp, the problem circled around the military tribal elite of the empire, the Qezelbāš, who believed that physical proximity to and control of a member of the immediate Safavid family guaranteed spiritual advantages, political fortune, and material advancement.[90] Despite that Tahmāsp could nullify and neglect some of his consternations regarding potential issues related to his family by having his close direct male relatives such as his brothers and sons routinely transferred around to various governorships in the empire, he understood and realized that any long-term solutions would mainly involve minimizing the political and military presence of the Qezelbāš as a whole. According to Encyclopædia Iranica, his father and founder of the Empire, Ismail I, had begun this process on a bureaucratic level as he appointed a number of prominent Persians in powerful bureaucratic positions, and one can see this continued in Tahmāsp's lengthy and close relationship with the chief vizier, Qāżi Jahān of Qazvin, after 1535.[90] While Persians continued to fill their historical role as administrators and clerical elites under Tahmāsp, little had been done so far to minimize the military role of the Qezelbāš.[90] Therefore, in 1540, Shah Tahmāsp started the first of a series of invasions of the Caucasus region, both meant as a training and drilling for his soldiers, as well as mainly bringing back massive numbers of Christian Circassian and Georgian slaves, who would form the basis of a military slave system,[91] alike to the janissaries of the neighbouring Ottoman Empire,[92] as well as at the same time forming a new layer in Iranian society composed of ethnic Caucasians.At the fourth invasion in 1553, it was now clear that Tahmāsp followed a policy of annexation and resettlement as he gained control over Tbilisi (Tiflis) and the region of Kartli while physically transplanting more than 30,000 people to the central Iranian heartlands.[90] According to Encyclopædia Iranica, this would be the starting point for the corps of the ḡolāmān-e ḵāṣṣa-ye-e šarifa, or royal slaves, who would dominate the Safavid military for most of the empire's length. As non-Turcoman converts to Islam, these Circassian and Georgian ḡolāmāns (also written as ghulams) were completely unrestrained by clan loyalties and kinship obligations, which was an attractive feature for a ruler like Tahmāsp whose childhood and upbringing had been deeply affected by Qezelbāš tribal politics.[90] In turn, many of these transplanted women became wives and concubines of Tahmāsp, and the Safavid harem emerged as a competitive, and sometimes lethal, arena of ethnic politics as cliques of Turkmen, Circassian, and Georgian women and courtiers vied with each other for the shah's attention.[90]
Although the first slave soldiers would not be organized until the reign of Abbas I, during Tahmāsp's time Caucasians would already become important members of the royal household, Harem and in the civil and military administration,[93][94] and by that becoming their way of eventually becoming an integral part of the society. One of Tahmāsp's sisters married a Circassian, who would use his court office to team up with Tahmāsp's daughter, Pari Khān Khānum to assert themselves in succession matters after Tahmāsp's death.
After the Peace of Amasya, Tasmāsp underwent what he called a "sincere repentance." Tasmāsp at the same time removed his son Ismail from his Qizilbash followers and imprisoned him at Qahqaha. Moreover, he began to strengthen Shiʻi practice by such things as forbidding in the new capital of Qazvin poetry and music which did not esteem Ali and the Twelve Imams. He also reduced the taxes of districts that were traditionally Shiʻi, regulated services in mosques and engaged Shiʻi propagandists and spies. Extortion, intimidation and harassment were practiced against Sunnis.[95]
When Tahmāsp died in 984/1576, Iran was calm domestically, with secure borders and no imminent threat from either the Uzbeks or the Ottomans. What remained unchanged, however, was the constant threat of local disaffection with the weak central authority. That condition would not change (and in fact it would worsen) until Tahmāsp's grandson, Abbas I, assumed the throne.
Chaos under Tahmasp's sons
On Tahmāsp's death support for a successor coalesced around two of his nine sons; the support divided on ethnic lines—Ismail was supported by most of the Turkmen tribes as well as his sister Pari Khān Khānum, her Circassian uncle Shamkhal Sultan as well as the rest of the Circassians, while Haydar was mostly supported by the Georgians at court although he also had support from the Turkmen Ustajlu.[96] Ismail had been imprisoned at Qahqaha since 1556 by his father on charges of plotting a coup, but his selection was ensured when 30,000 Qizilbash supporters demonstrated outside the prison.[97] Shortly after the installation of Ismail II on August 22, 1576, Haydar was beheaded.
Ismail II (r. 1576–1577)
Ismail's 14-month reign was notable for two things: continual bloodletting of his relatives and others (including his own supporters) and his reversal on religion. He had all his relatives killed except for his older brother, Mohammad Khudabanda, who, being nearly blind, was not a real candidate for the throne, and Mohammad's three sons, Hamza Mirza, Abbas Mirza and Abu Talib Mirza.[98] While the murderous actions of Ismail might be explained by political prudence (Ottoman sultans occasionally purged the bloodline to prevent succession rivals[99]), his actions against Shi’a suggest retaliation against his father, who saw himself as a pious practitioner. Ismail sought to reintroduce Sunni orthodoxy. But even here there may have been practical political considerations; namely, "concern about the excessively powerful position of Shiʻi dignitaries, which would have been undermined by a reintroduction of the Sunna."[100] His conduct might also be explained by his drug use. In any event, he was ultimately killed (according to some accounts) by his Circassian half-sister, Pari Khān Khānum, who championed him over Haydar. She is said to have poisoned his opium.[101]
Mohammad Khodabanda (r. 1578–1587)

On the death of Ismail II there were three candidates for succession: Shāh Shujā', the infant son of Ismail (only a few weeks old), Ismail's brother, Mohammad Khodabanda; and Mohammad's son, Sultan Hamza Mirza, 11 years old at the time. Pari Khān Khānum, sister of Ismail and Mohammad, hoped to act as regent for any of the three (including her older brother, who was nearly blind). Mohammad was selected and received the crown on February 11, 1579.[102] Mohammad would rule for 10 years, and his sister at first dominated the court, but she fell in the first of many intrigues which continued even though the Uzbeks and Ottomans again used the opportunity to threaten Safavid territory.
Mohammad allowed others to direct the affairs of state, but none of them had either the prestige, skill or ruthlessness of either Tahmāsp or Ismail II to rein in the ethnic or palace factions, and each of his rulers met grim ends. Mohammad's younger sister, who had a hand in elevating and deposing Ismail II and thus had considerable influence among the Qizilbash, was the first. She did not last much longer than Mohammad's installation at Qazvin, where she was murdered.[103] She was done in by intrigues by the vizier Mirza Salman Jaberi (who was a holdover from Ismail II's reign) and Mohammad's chief wife Khayr al-Nisa Begum, known as Mahd-i ‘Ulyā. There is some indication that Mirza Salman was the chief conspirator.[104] Pari Khān Khānum could master strong support among the Qizilbash, and her uncle, Shamkhal Sultan, was a prominent Circassian who held a high official position.[105] Mirza Salman left the capital before Pari Khān Khānum closed the gates and was able to meet Mohammad Khodabanda and his wife in Shiraz, to whom he offered his services.[106] He may have believed that he would rule once their enemy was disposed of, but Mahd-i ‘Ulyā proved the stronger of the two.
She was by no means content to exercise a more or less indirect influence on affairs of state: instead, she openly carried out all essential functions herself, including the appointment of the chief officers of the realm. In place of the usual royal audience, these high dignitaries had to assemble each morning at the entrance to the women's apartments in order to receive the Begum's orders. On these occasions the royal edicts were drawn up and sealed.[103]
The amirs demanded that she be removed, and Mahd-i Ulya was strangled in the harem in July 1579 on the ground of an alleged affair with the brother of the Crimean khan, Adil Giray,[103] who was captured during the 1578–1590 Ottoman war and held captive in the capital, Qazvin.[107] None of the perpetrators were brought to justice, although the shah lectured the assembled amirs on how they departed from the old ways when the shah was master to his Sufi disciples. The shah used that occasion to proclaim the 11-year-old Sultan Hamza Mirza (Mahd-i ‘Ulyā's favorite) crown-prince.[108]
The palace intrigues reflected ethnic unrest which would soon erupt into open warfare. Iran's neighbors seized the opportunity to attack. The Uzbeks struck in the Spring of 1578 but were repelled by Murtaza Quli Sultan, governor of Mashhad.[109] More seriously the Ottomans ended the Peace of Amasya and commenced a war with Iran that would last until 1590 by invading Iran's territories of Georgia and Shirvan. While the initial attacks were repelled, the Ottomans continued and grabbed considerable territory in Transcaucasia, Dagestan, Kurdistan and Lorestan and in 993/1585 they even took Tabriz.[110]
In the midst of these foreign perils, rebellion broke out in Khorasan fomented by (or on behalf of) Mohammad's son, Abbas. Ali Quli Khan Shamlu, the lala of Abbas and Ismail II's man in Herat proclaimed Abbas shah there April 1581.[111] The following year the loyal Qizilbash forces (the Turkmen and Takkalu who controlled Qazvin), with vizier Mirza Salman and crown prince Sultan Hamza Mirza at their head, confronted the rebelling Ustajlu-Shamlu coalition which had assumed control of Khorasan under the nominal rule of young Abbas.[112] The Ustajlu chief, Murshid Quli Khan, immediately acquiesced and received a royal pardon. The Shumlu leader, Ali Quli Khan, however, holed himself inside Herat with Abbas. The vizier thought that the royal forces failed to prosecute the siege sufficiently and accused the forces of sedition. The loyal Qizibash recoiled at their treatment by Mirza Salman, who they resented for a number of reasons (not least of which was the fact that a Tajik was given military command over them), and demanded that he be turned over to them. The crown prince (the vizier's son-in-law) meekly turned him over, and the Qizilbash executed him and confiscated his property.[113] The siege of Herat thus ended in 1583 without Ali Quli Khan's surrender, and Khorasan was in a state of open rebellion.
In 1585 two events occurred that would combine to break the impasse among the Qizilbash. First, in the west, the Ottomans, seeing the disarray of the warriors, pressed deep into Safavid territory and occupied the old capital of Tabriz. Crown prince Hamza Mirza, now 21 years old and director of Safavid affairs, led a force to confront the Ottomans, but in 1586 was murdered under mysterious circumstances. In the east Murshid Quli Khan, of the Ustajlu tribe, managed to snatch Abbas away from the Shamlus. Two years later in 1587, the massive invasion of Khorasan by the Uzbeks proved the occasion whereby Murshid Quli Khan would make a play for supremacy in Qazvin. When he reached the capital with Abbas a public demonstration in the boy's favor decided the issue, and Shah Mohammad voluntarily handed over the insignia of kingship to his son, who was crowned Abbas I on October 1, 1588. The moment was grave for the empire, with the Ottomans deep in Iranian territory in the west and north and the Uzbeks in possession of half of Khorasan in the east.[114]
Shah Abbas (r. 1588–1629)

The 16-year-old Abbas I was installed as nominal shah in 1588, but the real power was intended to remain in the hands of his "mentor," Murshid Quli Khan, who reorganized court offices and principal governorships among the Qizilbash[115] and took the title of wakīl for himself.[116] Abbas' own position seemed even more dependent on Qizilbash approval than Mohammad Khodabanda's was. The dependence of Abbas on the Qizilbash (which provided the only military force) was further reinforced by the precarious situation of the empire, in the vice of Ottoman and Uzbek territorial plunder. Yet over the course of ten years Abbas was able, using cautiously-timed but nonetheless decisive steps, to affect a profound transformation of Safavid administration and military, throw back the foreign invaders, and preside over a flourishing of Persian art.
Restoration of central authority
Whether Abbas had fully formed his strategy at the onset, at least in retrospect his method of restoring the shah's authority involved three phases: (1) restoration of internal security and law and order; (2) recovery of the eastern territories from the Uzbeks; and (3) recovery of the western territories from the Ottomans.[117] Before he could begin to embark on the first stage, he needed relief from the most serious threat to the empire: the military pressure from the Ottomans. He did so by taking the humiliating step of coming to peace terms with the Ottomans by making, for now, permanent their territorial gains in Iraq and the territories in the north, including Azerbaijan, Karabakh, Ganja, eastern Georgia (comprising the Kingdom of Kartli and Kakheti), Dagestan, and Kurdistan.[118][119] At the same time, he took steps to ensure that the Qizilbash did not mistake this apparent show of weakness as a signal for more tribal rivalry at the court. Although no one could have bristled more at the power grab of his "mentor" Murshid Quli Khan, he rounded up the leaders of a plot to assassinate the wakīl and had them executed. Then, having made the point that he would not encourage rivalries even purporting to favor his interests, he felt secure enough to have Murshid Quli Khan assassinated on his own orders in July 1589.[120] It was clear that Abbas' style of leadership would be entirely different from Mohammad Khodabanda's leadership.

Abbas was able to begin gradually transforming the empire from a tribal confederation to a modern imperial government by transferring provinces from mamalik (provincial) rule governed by a Qizilbash chief and the revenue of which mostly supported local Qizilbash administration and forces to khass (central) rule presided over by a court appointee and the revenue of which reverted to the court. Particularly important in this regard were the Gilan and Mazandaran provinces, which produced Iran's single most important export; silk. With the substantial new revenue, Abbas was able to build up a central, standing army, loyal only to him. This freed him of his dependence on Qizilbash warriors loyal to local tribal chiefs.[121]

What effectively fully severed Abbas's dependence on the Qizilbash, however, was how he constituted this new army. In order not to favor one Turkic tribe over another and to avoid inflaming the Turk-Persian enmity, he recruited his army from the "third force", a policy that had been implemented in its baby-steps since the reign of Tahmasp I – the Circassian, Georgian and to a lesser extent Armenian ghulāms (slaves) which (after conversion to Islam) were trained for the military or some branch of the civil or military administration. The standing army created by Abbas consisted of: (1) 10,000–15,000 cavalry ghulām regiments solely composed of ethnic Caucasians, armed with muskets in addition to the usual weapons (then the largest cavalry in the world[122]); (2) a corps of musketeers, tufangchiyān, mainly Iranians, originally foot soldiers but eventually mounted, and (3) a corps of artillerymen, tūpchiyān. Both corps of musketeers and artillerymen totaled 12,000 men. In addition the shah's personal bodyguard, made up exclusively of Caucasian ghulāms, was dramatically increased to 3,000.[123] This force of well-trained Caucasian ghulams under Abbas amounted to a total of near 40,000 soldiers paid for and beholden to the Shah.[124][125]
Abbas also greatly increased the number of cannons at his disposal, permitting him to field 500 in a single battle.[125] Ruthless discipline was enforced and looting was severely punished. Abbas was also able to draw on military advice from a number of European envoys, particularly from the English adventurers Sir Anthony Shirley and his brother Robert Shirley, who arrived in 1598 as envoys from the Earl of Essex on an unofficial mission to induce Iran into an anti-Ottoman alliance.[126] As mentioned by the Encyclopaedia Iranica, lastly, from 1600 onwards, the Safavid statesman Allāhverdī Khan, in conjunction with Robert Sherley, undertook further reorganizations of the army, which meant among other things further dramatically increasing the number of ghulams to 25,000.[127]
Abbas also moved the capital to Isfahan, deeper into central Iran. Abbas I built a new city next to the ancient Persian one. From this time the state began to take on a more Persian character. The Safavids ultimately succeeded in establishing a new Persian national monarchy.
Recovery of territory from the Uzbeks and the Ottomans

Abbas I first fought the Uzbeks, recapturing Herat and Mashhad in 1598. Then he turned against Iran's archrival, the Ottomans, recapturing Baghdad, eastern Iraq and the Caucasian provinces by 1616, all through the 1603–1618, marking the first grand Safavid pitched victory over the Ottomans. He also used his new force to dislodge the Portuguese from Bahrain (1602) and, with English help, from Hormuz (1622), in the Persian Gulf (a vital link in Portuguese trade with India). He expanded commercial links with the English East India Company and the Dutch East India Company. Thus Abbas was able to break dependence on the Qizilbash for military might indefinitely, and therefore was able to fully centralize control for the first time since the foundation of the Safavid state.
The Ottoman Turks and Safavids fought over the fertile plains of Iraq for more than 150 years. The capture of Baghdad by Ismail I in 1509 was only followed by its loss to the Ottoman Sultan Suleiman I in 1534. After subsequent campaigns, the Safavids recaptured Baghdad in 1624 during the Ottoman–Safavid War (1623–39) yet lost it again to Murad IV in 1638 after Abbas had died. Henceforth a treaty, signed in Qasr-e Shirin known as the Treaty of Zuhab was established delineating a border between Iran and Turkey in 1639, a border which still stands in northwest Iran/southeast Turkey. The 150-year tug-of-war accentuated the Sunni and Shi'a rift in Iraq.
Quelling the Georgian uprising

In 1614–16 during the Ottoman–Safavid War (1603–1618), Abbas suppressed a rebellion led by his formerly most loyal Georgian subjects Luarsab II and Teimuraz I (also known as Tahmuras Khan) in the Kingdom of Kakheti. In 1613, Abbas had appointed these trusted Georgian gholams of his on the puppet thrones of Kartli and Kakheti, the Iranian Safavid ruled areas of Georgia. Later that year, when the shah summoned them to join him on a hunting expedition in Mazandaran, they didn't show up due to the fear they would be either imprisoned or killed.[128] Ultimately forming an alliance, the two sought refuge with the Ottoman forces in Ottoman ruled Imereti. This defection of two of the shah's most trusted subjects and gholams infuriated the shah, as reported by the Safavid court historian Iskandar Beg Munshi.[128]
The following spring in 1614, Abbas I appointed a grandson of Alexander II of Imereti to the throne of Kartli, Jesse of Kakheti also known as "Isā Khān".[128] Raised at the court in Isfahan and a Muslim, he was fully loyal to the shah. Subsequently, the shah marched upon Grem, the capital of Imereti, and punished its peoples for harbouring his defected subjects. He returned to Kartli, and in two punitive campaigns he devastated Tbilisi, killed 60–70,000 Kakheti Georgian peasants, and deported between 130,000 and 200,000 Georgian captives to mainland Iran.[129][130][131][132] After fully securing the region, he executed the rebellious Luarsab II of Kartli and later had the Georgian queen Ketevan, who had been sent to the shah as negotiator, tortured to death when she refused to renounce Christianity, in an act of revenge for the recalcitrance of Teimuraz.[133][134] Kakheti lost two-thirds of its population in these years by Abbas' punitive campaign. The majority were deported to Iran, while some were slaughtered.[135]
Teimuraz returned to eastern Georgia in 1615 and defeated a Safavid force. It was just a brief setback, however, as Abbas had already been making long-term plans to prevent further incursions. He was eventually successful in making the eastern Georgian territories an integral part of the Safavid provinces. In 1619 he appointed the loyal Simon II (or Semayun Khan) on the symbolic throne of Kakheti, while placing a series of his own governors to rule of districts where rebellious inhabitants were mostly located.[128] Moreover, he planned to deport all nobles of Kartli. Iranian rule had been fully restored over eastern Georgia, but the Georgian territories would continue to produce resistance to Safavid enroachments from 1624 until Abbas' death.[136]
Suppressing the Kurdish rebellion
In 1609–10, a war broke out between Kurdish tribes and the Safavid Empire. After a long and bloody siege led by the Safavid grand vizier Hatem Beg, which lasted from November 1609 to the summer of 1610, the Kurdish stronghold of Dimdim was captured. Shah Abbas ordered a general massacre in Beradost and Mukriyan (Mahabad, reported by Eskandar Beg Monshi, Safavid Historian (1557–1642), in "Alam Ara Abbasi") and resettled the Turkic Afshar tribe in the region while deporting many Kurdish tribes to Khorasan.[137][138] Nowadays, there is a community of nearly 1.7 million people who are descendants of the tribes deported from Kurdistan to Khorasan (Northeastern Iran) by the Safavids.[139]
Contacts with Europe during Abbas's reign

Abbas's tolerance towards Christians was part of his policy of establishing diplomatic links with European powers to try to enlist their help in the fight against their common enemy, the Ottoman Empire. The idea of such an anti-Ottoman alliance was not a new one – over a century before, Uzun Hassan, then ruler of part of Iran, had asked the Venetians for military aid – but none of the Safavids had made diplomatic overtures to Europe. Shah Ismail I was the first of the Safavids to try to establish once again an alliance against the common Ottoman enemy through the earlier stages of the Habsburg–Persian alliance, but this also proved to be largely unfruitful during his reign.[140] Abbas's attitude, however, was in marked contrast to that of his grandfather, Tahmasp I, who had expelled the English traveller Anthony Jenkinson from his court on hearing he was a Christian.[141] For his part, Abbas declared that he "preferred the dust from the shoe soles of the lowest Christian to the highest Ottoman personage."[142] Abbas would take active and all measures needed in order to seal the alliances.

In 1599, Abbas sent his first diplomatic mission to Europe. The group crossed the Caspian Sea and spent the winter in Moscow before proceeding through Norway and Germany (where it was received by Emperor Rudolf II) to Rome, where Pope Clement VIII gave the travellers a long audience. They finally arrived at the court of Philip III of Spain in 1602. Although the expedition never managed to return to Iran, being shipwrecked on the journey around Africa, it marked an important new step in contacts between Iran and Europe. The Europeans began to be fascinated by the Iranians and their culture – Shakespeare's Twelfth Night (1601–02), for example, makes two references (at II.5 and III.4) to 'the Sophy', then the English term for the Shahs of Iran.[143][144] Henceforward, the number of diplomatic missions to and fro greatly increased.[145]

The shah had set great store on an alliance with Spain, the chief opponent of the Ottomans in Europe. Abbas offered trading rights and the chance to preach Christianity in Iran in return for help against the Ottomans. But the stumbling block of Hormuz remained, a vassal kingdom that had fallen into the hands of the Spanish Habsburgs when the King of Spain inherited the throne of Portugal in 1580. The Spanish demanded Abbas break off relations with the English before they would consider relinquishing the town. Abbas was unable to comply. Eventually Abbas became frustrated with Spain, as he did with the Holy Roman Empire, which wanted him to make his over 400,000 Armenian subjects swear allegiance to the Pope but did not trouble to inform the shah when the Emperor Rudolf signed a peace treaty with the Ottomans. Contacts with the Pope, Poland and Moscow were no more fruitful.[146]
More came of Abbas's contacts with the English, although England had little interest in fighting against the Ottomans. The Shirley brothers arrived in 1598 and helped reorganize the Iranian army, which proved to be crucial in the Ottoman–Safavid War (1603–18), which resulted in Ottoman defeats in all stages of the war and the first clear pitched Safavid victory of their archrivals. One of the Shirley brothers, Robert Shirley, would lead Abbas's second diplomatic mission to Europe from 1609 to 1615.[147] The English East India Company also began to take an interest in Iran, and in 1622 four of its ships helped Abbas retake Hormuz from the Portuguese in the capture of Ormuz. This was the beginning of the English East India Company's long-running interest in Iran.[148]
Succession and legacy of Abbas I
Due to his obsessive fear of assassination, Shah Abbas either put to death or blinded any member of his family who aroused his suspicion. His oldest son, the crown prince Mohammad Baqer Mirza, was executed following a court intrigue in which several Circassians were involved, while two others were blinded. Since two other sons had predeceased him, the result was a personal tragedy for Shah Abbas. When he died on 19 January 1629, he had no son capable of succeeding him.[149]
During the early 17th century the power of the Qizilbash drastically diminished, the original militia that had helped Ismail I capture Tabriz and that had gained many administrative powers over the centuries. Power was shifting to the new class of Caucasian deportees and imports, many of the hundreds of thousands ethnic Georgians, Circassians, and Armenians. This new layer of society would continue to play a vital role in Iranian history up to and including the fall of the Qajar dynasty, some 300 years after Abbas' death.
At its zenith, during the long reign of Shah Abbas I, the empire's reach comprised Iran, Iraq, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Dagestan, Kabardino-Balkaria, Bahrain, and parts of Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Turkey.
Decline

In addition to fighting its perennial enemies, their archrival the Ottomans and the Uzbeks as the 17th century progressed, Iran had to contend with the rise of new neighbors. Russian Muscovy in the previous century had deposed two western Asian khanates of the Golden Horde and expanded its influence into Europe, the Caucasus Mountains and Central Asia. Astrakhan came under Russian rule, nearing the Safavid possessions in Dagestan. In the far eastern territories, the Mughals of India had expanded into Khorasan (now Afghanistan) at the expense of Iranian control, briefly taking Kandahar.

In 1659, the Kingdom of Kakheti rose up against the Safavid Iranian rule due to a change of policy that included the mass settling of Qizilbash Turkic tribes in the region in order to repopulate the province, after Shah Abbas' earlier mass deportations of between 130,000[150] – 200,000[130][131][151] Georgian subjects to Iran's mainland and massacre of another thousand in 1616 virtually left the province without any substantial population. This Bakhtrioni Uprising was successfully defeated under personal direction of Shah Abbas II himself. However, strategically it remained inconclusive.[152] The Iranian authority was restored in Kakheti, but the Qizilbash Turkics were prevented from settling in Kakheti, which undermined the planned Iranian policies in the respective province.
More importantly, European trading companies used their superior means of maritime power to control trade routes in the western Indian Ocean. As a result, Safavid Iran's overseas links to East Africa, the Arabian peninsula and South Asia were greatly diminished.[153] Overland trade grew notably however, as Iran was able to further develop its overland trade with North and Central Europe during the second half of the seventeenth century.[154] In the late seventeenth century, Iranian merchants established a permanent presence as far north as Narva on the Baltic sea, in what now is Estonia.[155]
Iranian trade with European merchants led to the depletion of much of Iran's metal supplies. Except for Shah Abbas II, the Safavid rulers after Abbas I were therefore rendered ineffectual, and the Iranian government declined and finally collapsed when a serious military threat emerged on its eastern border in the early eighteenth century.[156] The end of the reign of Abbas II, 1666, thus marked the beginning of the end of the Safavid dynasty. Despite falling revenues and military threats, later shahs had lavish lifestyles. Soltan Hoseyn (1694–1722) in particular was known for his love of wine and disinterest in governance.[157]

The country was repeatedly raided on its frontiers – Kerman by Baloch tribes in 1698, Khorasan by the Hotakis in 1717, Dagestan and northern Shirvan by the Lezgins in 1721, constantly in Mesopotamia by Sunni peninsula Arabs. Sultan Hosein tried to forcibly convert his Afghan subjects in Qandahar from Sunni to Twelverism. In response, a Ghilzai Afghan chieftain named Mirwais Hotak revolted and killed Gurgin Khan, the Safavid governor of the region, along with his army. In 1722, an Afghan army led by Mir Wais' son Mahmud advanced on the heart of the empire and defeated the government forces at the Battle of Gulnabad. He then besieged the capital of Isfahan, until Shah Soltan Hoseyn abdicated and acknowledged him as the new king of Iran.[158][full citation needed] At the same time, the Russians led by Peter the Great attacked and conquered swaths of Safavid Iran's North Caucasian, Transcaucasian, and northern mainland territories through the Russo-Iranian War (1722-1723). The Safavids' archrivals, the neighbouring Ottomans, invaded western and northwestern Safavid Iran and took swaths of territory there, including the city of Baghdad. Together with the Russians, they agreed to divide and keep the conquered Iranian territories for themselves as confirmed in the Treaty of Constantinople (1724).[159]

The tribal Afghans rode roughshod over their conquered territory for seven years but were prevented from making further gains by Nader Shah, a former slave who had risen to military leadership within the Afshar tribe in Khorasan, a vassal state of the Safavids. Quickly making a name as a military genius both feared and respected amongst the empire's friends and enemies (including Iran's archrival the Ottoman Empire, and Russia; both empires Nader would deal with soon afterwards), Nader Shah easily defeated the Afghan Hotaki forces in the 1729 Battle of Damghan. He had removed them from power and banished them from Iran by 1729. In 1732 by the Treaty of Resht and in 1735 Treaty of Ganja, he negotiated an agreement with the government of Empress Anna Ioanovna that resulted in the return of the recently annexed Iranian territories, making most of the Caucasus fall back into Iranian hands, while establishing an Irano-Russian alliance against the common neighbouring Ottoman enemy.[160][161] In the Ottoman–Iranian War (1730–35), he retook all territories lost by the Ottoman invasion of the 1720s, as well as beyond. With the Safavid state and its territories secured, in 1738 Nader conquered the Hotaki's last stronghold in Kandahar; in the same year, in need of fortune to aid his military careers against his Ottoman and Russian imperial rivals, he started his invasion of the wealthy but weak Mughal Empire accompanied by his Georgian subject Erekle II,[162] occupying Ghazni, Kabul, Lahore, and as far as Delhi, in India, when he completely humiliated and looted the militarily inferior Mughals. These cities were later inherited by his Abdali Afghan military commander, Ahmad Shah Durrani, who would go on to found the Durrani Empire in 1747. Nadir had effective control under Shah Tahmasp II and then ruled as regent of the infant Abbas III until 1736 when he had himself crowned shah.

Immediately after Nader Shah's assassination in 1747 and the disintegration of his short-lived empire, the Safavids were re-appointed as shahs of Iran in order to lend legitimacy to the nascent Zand dynasty. However, the brief puppet regime of Ismail III ended in 1760 when Karim Khan felt strong enough to take nominal power of the country as well and officially end the Safavid dynasty.
Society
While large in terms of land area, the large proportion of deserts and mountains in its territory meant density was very low; the empire's population is estimated to have probably numbered between eight and ten million in 1650, as compared to c. 20 million for the Ottoman Empire in 1600.[163]
Safavid society was a meritocracy where officials were appointed on the basis of worth and merit, and not on the basis of birth. It was certainly not an oligarchy, nor was it an aristocracy. Sons of nobles were considered for the succession of their fathers as a mark of respect, but they had to prove themselves worthy of the position. This system avoided an entrenched aristocracy or a caste society.[164] There are numerous recorded accounts of laymen that rose to high official posts as a result of their merits.[165]
Nevertheless, the Iranian society during the Safavids was that of a hierarchy, with the Shah at the apex of the hierarchical pyramid, the common people, merchants and peasants at the base, and the aristocrats in between. The term dowlat, which in modern Persian means "government", was then an abstract term meaning "bliss" or "felicity", and it began to be used as concrete sense of the Safavid state, reflecting the view that the people had of their ruler, as someone elevated above humanity.[166]
Also among the aristocracy, in the middle of the hierarchical pyramid, were the religious officials, who, mindful of the historic role of the religious classes as a buffer between the ruler and his subjects, usually did their best to shield the ordinary people from oppressive governments.[166]
Turks and Tajiks
The power structure of the Safavid state was mainly divided into two groups: the Turkic-speaking military/ruling elite – whose job was to maintain the territorial integrity and continuity of the Iranian empire through their leadership – and the Persian-speaking administrative/governing elite – whose job was to oversee the operation and development of the nation and its identity through their high positions. Thus came the term "Turk and Tajik" to describe the Persianate, or Turko-Persian, nature of many dynasties which ruled over Greater Iran between the 12th and 20th centuries, in that these dynasties promoted and helped continue the dominant Persian linguistic and cultural identity of their states, although the dynasties themselves were of non-Persian (e.g. Turkic) origins. The relationship between the Turkic-speaking 'Turks' and Persian-speaking 'Tajiks' was symbiotic, yet some form of rivalry did exist between the two. As the former represented the "people of the sword" and the latter, "the people of the pen", high-level official posts would naturally be reserved for the Persians. Indeed, this had been the situation throughout Persian history, even before the Safavids, ever since the Arab conquest.[167][failed verification]
Shah Tahmasp introduced a change to this, when he, and the other Safavid rulers who succeeded him, sought to blur the formerly defined lines between the two linguistic groups, by taking the sons of Turkic-speaking officers into the royal household for their education in the Persian language. Consequently, they were slowly able to take on administrative jobs in areas which had hitherto been the exclusive preserve of the ethnic Persians.[168]
The third force: Caucasians

From 1540 and onwards, Shah Tahmasp initiated a gradual transformation of the Iranian society by slowly constructing a new branch and layer solely composed of ethnic Caucasians. The implementation of this branch would be completed and significantly widened under Abbas the Great (Abbas I). According to the Encyclopædia Iranica, for Tahmasp, the background of this initiation and eventual composition that would be only finalized under Shah Abbas I, circled around the military tribal elite of the empire, the Qizilbash, who believed that physical proximity to and control of a member of the immediate Safavid family guaranteed spiritual advantages, political fortune, and material advancement.[90] This was a huge impedance for the authority of the Shah, and furthermore, it undermined any developments without the agreeing or shared profit of the Qizilbash. As Tahmasp understood and realized that any long-term solutions would mainly involve minimizing the political and military presence of the Qizilbash as a whole, it would require them to be replaced by a whole new layer in society, that would question and battle the authority of the Qizilbash on every possible level, and minimize any of their influences. This layer would be solely composed of hundreds of thousands of deported, imported, and to a lesser extent voluntarily migrated ethnic Circassians, Georgians, and Armenians. This layer would become the "third force" in Iranian society, alongside the other two forces, the Turkomans and Persians.
The series of campaigns that Tahmāsp subsequently waged after realising this in the wider Caucasus between 1540 and 1554 were meant to uphold the morale and the fighting efficiency of the Qizilbash military,[169] but they brought home large numbers (over 70,000)[170] of Christian Georgian, Circassian and Armenian slaves as its main objective, and would be the basis of this third force; the new (Caucasian) layer in society.[91] According to the Encyclopædia Iranica, this would be as well the starting point for the corps of the ḡolāmān-e ḵāṣṣa-ye-e šarifa, or royal slaves, who would dominate the Safavid military for most of the empire's length, and would form a crucial part of the third force. As non-Turcoman converts to Islam, these Circassian and Georgian ḡolāmāns (also written as ghulams) were completely unrestrained by clan loyalties and kinship obligations, which was an attractive feature for a ruler like Tahmāsp whose childhood and upbringing had been deeply affected by Qizilbash tribal politics.[90] Their formation, implementation, and usage was very much alike to the janissaries of the neighbouring Ottoman Empire.[92] In turn, many of these transplanted women became wives and concubines of Tahmasp, and the Safavid harem emerged as a competitive, and sometimes lethal, arena of ethnic politics as cliques of Turkmen, Circassian, and Georgian women and courtiers vied with each other for the king's attention.[90] Although the first slave soldiers would not be organized until the reign of Abbas I, during Tahmasp's reign, Caucasians already became important members of the royal household, Harem and in the civil and military administration,[93][94] and were on their way of becoming an integral part of society. Tahmasp I's successor, Ismail II, brought another 30,000 Circassians and Georgians to Iran of which many joined the ghulam force.[171]
Following the full implementation of this policy by Abbas I, the women (only Circassian and Georgian) now very often came to occupy prominent positions in the harems of the Safavid elite, while the men who became part of the ghulam "class" as part of the powerful third force were given special training on completion of which they were either enrolled in one of the newly created ghilman regiments, or employed in the royal household.[172] The rest of the masses of deportees and importees, a significant portion numbering many hundreds of thousands, were settled in various regions of mainland Iran, and were given all kinds of roles as part of society, such as craftsmen, farmers, cattle breeders, traders, soldiers, generals, governors, woodcutters, etc., all also part of the newly established layer in Iranian society.[173]
Shah Abbas, who significantly enlargened and completed this program and under whom the creation of this new layer in society may be mentioned as fully "finalized", completed the ghulam system as well. As part of its completion, he greatly expanded the ghulam military corps from just a few hundred during Tahmāsp's era, to 15,000 highly trained cavalrymen,[174] as part of a whole army division of 40,000 Caucasian ghulams. He then went on to completely reduce the number of Qizilbash provincial governorships and systematically moved qizilbash governors to other districts, thus disrupting their ties with the local community, and reducing their power. Most were replaced by a ghulam, and within short time, Georgians, Circassians, and to a lesser extent Armenians had been appointed to many of the highest offices of state, and were employed within all other possible sections of society. By 1595, Allahverdi Khan, a Georgian, became one of the most powerful men in the Safavid state, when he was appointed the Governor-General of Fars, one of the richest provinces in Iran. And his power reached its peak in 1598, when he became the commander-in-chief of the armed forces.[175] Thus, starting from the reign of Tahmāsp I but only fully implemented and completed by Shah Abbas, this new group solely composed of ethnic Caucasians eventually came to constitute a powerful "third force" within the state as a new layer in society, alongside the Persians and the Qizilbash Turks, and it only goes to prove the meritocratic society of the Safavids.
It is estimated that during Abbas' reign alone some 130,000–200,000 Georgians,[176][131][130][132] tens of thousands of Circassians, and around 300,000 Armenians[177][178] had been deported and imported from the Caucasus to mainland Iran, all obtaining functions and roles as part of the newly created layer in society, such as within the highest positions of the state, or as farmers, soldiers, craftspeople, as part of the Royal harem, the Court, and peasantry, amongst others.
Religion
Even though the Safavids were not the first Shiʻi rulers in Iran, they played a crucial role in making Shiʻa Islam the official religion in the whole of Iran, as well as what is nowadays the Republic of Azerbaijan.[179] There were large Shiʻi communities in some cities like Qom and Sabzevar as early as the 8th century. In the 10th and 11th centuries the Buwayhids, who were of the Zaidiyyah branch of Shiʻa Islam, ruled in Fars, Isfahan and Baghdad. As a result of the Mongol conquest and the relative religious tolerance of the Ilkhanids, Shiʻi dynasties were re-established in Iran, Sarbedaran in Khorasan being the most important. The Ilkhanid ruler Öljaitü converted to Twelver Shiʻism in the 13th century.
Following his conquest of Iran and Azerbaijan, Ismail I made conversion mandatory for the largely Sunni population. The Sunni Ulema or clergy were either killed or exiled[citation needed]. Ismail I, brought in mainstream Twelver Shi'a religious leaders and granted them land and money in return for loyalty. Later, during the Safavid and especially Qajar period, the Shiʻi Ulema's power increased and they were able to exercise a role, independent of or compatible with the government.
Emergence of a clerical aristocracy
An important feature of the Safavid society was the alliance that emerged between the ulama (the religious class) and the merchant community. The latter included merchants trading in the bazaars, the trade and artisan guilds (asnāf) and members of the quasi-religious organizations run by dervishes (futuvva). Because of the relative insecurity of property ownership in Iran, many private landowners secured their lands by donating them to the clergy as so called vaqf. They would thus retain the official ownership and secure their land from being confiscated by royal commissioners or local governors, as long as a percentage of the revenues from the land went to the ulama. Increasingly, members of the religious class, particularly the mujtahids and the seyyeds, gained full ownership of these lands, and, according to contemporary historian Iskandar Munshi, Iran started to witness the emergence of a new and significant group of landowners.[180]
Akhbaris versus Usulis
The Akhbari movement "crystalized" as a "separate movement" with the writings of Muhammad Amin al-Astarabadi (died 1627 AD). It rejected the use of reasoning in deriving verdicts and believed that only the Quran, hadith, (prophetic sayings and recorded opinions of the Imams) and consensus should be used as sources to derive verdicts (fatāwā). Unlike Usulis, Akhbari did and do not follow marjas who practice ijtihad.[181]
It achieved its greatest influence in the late Safavid and early post-Safavid era, when it dominated Twelver Shiʻi Islam.[182] However, shortly thereafter Muhammad Baqir Behbahani (died 1792), along with other Usuli mujtahids, crushed the Akhbari movement.[183] It remains only a small minority in the Shiʻi world. One result of the resolution of this conflict was the rise in importance of the concept of ijtihad and the position of the mujtahid (as opposed to other ulama) in the 18th and early 19th centuries. It was from this time that the division of the Shiʻa world into mujtahid (those who could follow their own independent judgment) and muqallid (those who had to follow the rulings of a mujtahid) took place. According to author Moojan Momen, "up to the middle of the 19th century there were very few mujtahids (three or four) anywhere at any one time," but "several hundred existed by the end of the 19th century."[184]
Allamah Majlisi
Muhammad Baqir Majlisi, commonly referenced to using the title Allamah, was a highly influential scholar during the 17th century (Safavid era). Majlisi's works emphasized his desire to purge Twelver Shiʻism of the influences of mysticism and philosophy, and to propagate an ideal of strict adherence to the Islamic law (sharia).[185] Majlisi promoted specifically Shiʻi rituals such as mourning for Hussein ibn Ali and visitation (ziyarat) of the tombs of the Imams and Imamzadas, stressing "the concept of the Imams as mediators and intercessors for man with God."[186]
Government
The Safavid state was one of checks and balance, both within the government and on a local level. At the apex of this system was the Shah, with total power over the state, legitimized by his bloodline as a sayyid, or descendant of Muhammad. So absolute was his power, that the French merchant, and later ambassador to Iran, Jean Chardin thought the Safavid Shahs ruled their land with an iron fist and often in a despotic manner.[187] To ensure transparency and avoid decisions being made that circumvented the Shah, a complex system of bureaucracy and departmental procedures had been put in place that prevented fraud. Every office had a deputy or superintendent, whose job was to keep records of all actions of the state officials and report directly to the Shah. The Shah himself exercised his own measures for keeping his ministers under control by fostering an atmosphere of rivalry and competitive surveillance. And since the Safavid society was meritocratic, and successions seldom were made on the basis of heritage, this meant that government offices constantly felt the pressure of being under surveillance and had to make sure they governed in the best interest of their leader, and not merely their own.
Structure
There probably did not exist any parliament, as we know them today. But the Portuguese ambassador to the Safavids, De Gouvea, still mentions the Council of State[188] in his records, which perhaps was a term for governmental gatherings of the time.
The highest level in the government was that of the Prime Minister, or Grand Vizier (Etemad-e Dowlat), who was always chosen from among doctors of law. He enjoyed tremendous power and control over national affairs as he was the immediate deputy of the Shah. No act of the Shah was valid without the counter seal of the Prime Minister. But even he stood accountable to a deputy (vak’anevis), who kept records of his decision-makings and notified the Shah. Second to the Prime Minister post were the General of the Revenues (mostoufi-ye mamalek), or finance minister,[189] and the Divanbegi, Minister of Justice. The latter was the final appeal in civil and criminal cases, and his office stood next to the main entrance to the Ali Qapu palace. In earlier times, the Shah had been closely involved in judicial proceedings, but this part of the royal duty was neglected by Shah Safi and the later kings.[190]
Next in authority were the generals: the General of the Royal Troops (the Shahsevans), General of the Musketeers, General of the Ghulams and The Master of Artillery. A separate official, the Commander-in-Chief, was appointed to be the head of these officials.[190]
The royal court

As for the royal household, the highest post was that of the Nazir, Court Minister. He was perhaps the closest advisor to the Shah, and, as such, functioned as his eyes and ears within the Court. His primary job was to appoint and supervise all the officials of the household and to be their contact with the Shah. But his responsibilities also included that of being the treasurer of the Shah's properties. This meant that even the Prime Minister, who held the highest office in the state, had to work in association with the Nazir when it came to managing those transactions that directly related to the Shah.[190]
The second most senior appointment was the Grand Steward (Ichik Agasi bashi), who would always accompany the Shah and was easily recognizable because of the great baton that he carried with him. He was responsible for introducing all guests, receiving petitions presented to the Shah and reading them if required. Next in line were the Master of the Royal Stables (Mirakor bashi) and the Master of the Hunt (Mirshekar bashi). The Shah had stables in all the principal towns, and Shah Abbas was said to have about 30,000 horses in studs around the country.[191] In addition to these, there were separate officials appointed for the caretaking of royal banquets and for entertainment.
Chardin specifically noticed the rank of doctors and astrologers and the respect that the Shahs had for them. The Shah had a dozen of each in his service and would usually be accompanied by three doctors and three astrologers, who were authorized to sit by his side on various occasions.[190] The Chief Physician (Hakim-bashi) was a highly considered member of the Royal court,[192] and the most revered astrologer of the court was given the title Munajjim-bashi (Chief Astrologer).[193]
The Safavid court was furthermore a rich mix of peoples from its earliest days.[194] As David Blow states, foremost among the courtiers were the old nobility of Turkoman Qizilbash lords and their sons. Although already by the early years of king Abbas' reign (r. 1588–1629) they were no longer controlling the state, the Turkoman Qizilbash continued to provide many of the senior army officers and to fill important administrative and ceremonial offices in the royal household.[194] There were the Persians who still dominated the bureaucracy and under Abbas held the two highest government offices of Grand Vizier and Comptroller-General of the Revenues (mostoufi-ye mamalek), which was the nearest thing to a finance minister.[194] There were also the large number of gholams or "slaves of the shah", who were mainly Georgians, Circassians and Armenians.[194] As a result of Abbas' reforms, they held high offices in the army, the administration and the royal household. Last but by no means least there were the palace eunuchs who were also ghulams – "white" eunuchs largely from the Caucasus, and "black" eunuchs from India and Africa.[194] Under Abbas, the eunuchs became an increasingly important element at the court.[194]
During the first century of the dynasty, the primary court language remained Azeri,[189] although this increasingly changed after the capital was moved to Isfahan.[12] David Blow adds; "it seems likely that most, if not all, of the Turkoman grandees at the court also spoke Persian, which was the language of the administration and culture, as well as of the majority of the population. But the reverse seems not to have been true. When Abbas had a lively conversation in Turkish with the Italian traveller Pietro Della Valle, in front of his courtiers, he had to translate the conversation afterwards into Persian for the benefit of most of those present."[194] Lastly, due to the large amount of Georgians, Circassians, and Armenians at the Safavid court (the gholams and in the harem), the Georgian, Circassian and Armenian languages were spoken as well, since these were their mother tongues.[195] Abbas himself was able to speak Georgian as well.[196]
Local governments

On a local level, the government was divided into public land and royal possessions. The public land was under the rule of local governors, or Khans. Since the earliest days of the Safavid dynasty, the Qizilbash generals had been appointed to most of these posts. They ruled their provinces like petty shahs and spent all their revenues on their own province, only presenting the Shah with the balance. In return, they had to keep ready a standing army at all times and provide the Shah with military assistance upon his request. It was also requested from them that they appoint a lawyer (vakil) to the Court who would inform them on matters pertaining to the provincial affairs.[197] Shah Abbas I intended to decrease the power of the Qizilbash by bringing some of these provinces into his direct control, creating so called Crown Provinces (Khassa). But it was Shah Safi, under influence by his Prime Minister, Saru Taqi, that initiated the program of trying to increase the royal revenues by buying land from the governors and putting in place local commissioners.[197] In time, this proved to become a burden to the people that were under the direct rule of the Shah, as these commissioners, unlike the former governors, had little knowledge about the local communities that they controlled and were primarily interested in increasing the income of the Shah. And, while it was in the governors’ own interest to increase the productivity and prosperity of their provinces, the commissioners received their income directly from the royal treasury and, as such, did not care so much about investing in agriculture and local industries. Thus, the majority of the people suffered from rapacity and corruption carried out in the name of the Shah.[197]
Democratic institutions in an authoritarian society
In 16th and 17th century Iran, there existed a considerable number of local democratic institutions. Examples of such were the trade and artisan guilds, which had started to appear in Iran from the 1500s. Also, there were the quazi-religious fraternities called futuvva, which were run by local dervishes. Another official selected by the consensus of the local community was the kadkhoda, who functioned as a common law administrator.[198] The local sheriff (kalantar), who was not elected by the people but directly appointed by the Shah, and whose function was to protect the people against injustices on the part of the local governors, supervised the kadkhoda.[199]
Law

In Safavid Iran there was little distinction between theology and jurisprudence, or between divine justice and human justice, and it all went under Islamic jurisprudence (fiqh). The legal system was built up of two branches: civil law, which had its roots in sharia, received wisdom, and urf, meaning traditional experience and very similar to the Western form of common law. While the imams and judges of law applied civil law in their practice, urf was primarily exercised by the local commissioners, who inspected the villages on behalf of the Shah, and by the Minister of Justice (Divanbegi). The latter were all secular functionaries working on behalf of the Shah.[200]
The highest level in the legal system was the Minister of Justice, and the law officers were divided into senior appointments, such as the magistrate (darughah), inspector (visir), and recorder (vak’anevis). The lesser officials were the qazi, corresponding a civil lieutenant, who ranked under the local governors and functioned as judges in the provinces.
There were no particular place assigned for the administration of justice. Each magistrate executes justice in his own house in a large room opening on to a courtyard or a garden which is raised two or three feet above the ground. The Judge is seated at one end of the room having a writer and a man of law by his side.
Chardin also noted that bringing cases into court in Iran was easier than in the West. The judge (qazi) was informed of relevant points involved and would decide whether or not to take up the case. Having agreed to do so, a sergeant would investigate and summon the defendant, who was then obliged to pay the fee of the sergeant. The two parties with their witnesses pleaded their respective cases, usually without any counsel, and the judge would pass his judgment after the first or second hearing.[201]
Criminal justice was entirely separate from civil law and was judged upon common law administered through the Minister of Justice, local governors and the Court minister (the Nazir). Despite being based on urf, it relied upon certain sets of legal principles. Murder was punishable by death, and the penalty for bodily injuries was invariably the bastinado. Robbers had their right wrists amputated the first time, and sentenced to death on any subsequent occasion. State criminals were subjected to the karkan, a triangular wooden collar placed around the neck. On extraordinary occasions when the Shah took justice into his own hand, he would dress himself up in red for the importance of the event, according to ancient tradition.[200]
Military

The Qizilbash were a wide variety of Shiʻi Muslims (ghulāt) and mostly Turcoman militant groups who helped found the Safavid Empire. Their military power was essential during the reign of the Shahs Ismail and Tahmasp. The Qizilbash tribes were essential to the military of Iran until the rule of Shah Abbas I – their leaders were able to exercise enormous influence and participate in court intrigues (assassinating Shah Ismail II for example).
A major problem faced by Ismail I after the establishment of the Safavid state was how to bridge the gap between the two major ethnic groups in that state: the Qizilbash ("Redhead") Turcomans, the "men of sword" of classical Islamic society whose military prowess had brought him to power, and the Persian elements, the "men of the pen", who filled the ranks of the bureaucracy and the religious establishment in the Safavid state as they had done for centuries under previous rulers of Iran, be they Arabs, Mongols, or Turkmens. As Vladimir Minorsky put it, friction between these two groups was inevitable, because the Qizilbash "were no party to the national Persian tradition".
Between 1508 and 1524, the year of Ismail's death, the shah appointed five successive Persians to the office of vakil. When the second Persian vakil was placed in command of a Safavid army in Transoxiana, the Qizilbash, considering it a dishonor to be obliged to serve under him, deserted him on the battlefield with the result that he was slain. The fourth vakil was murdered by the Qizilbash, and the fifth was put to death by them.[55]
Reforms in the military

Shah Abbas realized that in order to retain absolute control over his empire without antagonizing the Qizilbash, he needed to create reforms that reduced the dependency that the shah had on their military support. Part of these reforms was the creation of the 3rd force within the aristocracy and all other functions within the empire, but even more important in undermining the authority of the Qizilbash was the introduction of the Royal Corps into the military. This military force would serve the shah only and eventually consisted of four separate branches:[202]
- Shahsevans: these were 12,000 strong and built up from the small group of qurchis that Shah Abbas had inherited from his predecessor. The Shahsevans, or "Friends of the King", were Qizilbash tribesmen who had forsaken their tribal allegiance for allegiance to the shah alone.[203]
- Ghulams: Tahmasp I had started introducing huge amounts of Georgian, Circassian and Armenian slaves and deportees from the Caucasus, of whom a sizeable amount would become part of the future ghulam system. Shah Abbas expanded this program significantly and fully implemented it, and eventually created a force of 15,000 ghulam cavalrymen and 3,000 ghulam royal bodyguards. With the advent of the brother's Shirley at Abbas' court and by the efforts of statesman Allahverdi Khan, from 1600 onwards, the ghulam fighting regiments were further dramatically expanded under Abbas reaching 25,000.[127] Under Abbas, this force amounted to a total of near 40,000 soldiers paid for and beholden to the Shah.[124][125][204] They would become the elite soldiers of the Safavid armies (like the Ottoman Janissary).[92]
- Musketeers: realizing the advantages that the Ottomans had because of their firearms, Shah Abbas was at pains to equip both the qurchi and the ghulam soldiers with up-to-date weaponry. More importantly, for the first time in Iranian history, a substantial infantry corps of musketeers (tofang-chis), numbering 12 000, was created.
- Artillery Corps: with the help of Westerners, he also formed an artillery corps of 12 000 men, although this was the weakest element in his army. According to Sir Thomas Herbert, who accompanied an English embassy to Iran in 1628, the Persians relied heavily on support from the Europeans in manufacturing cannons.[205] It wasn't until a century later, when Nader Shah became the Commander in Chief of the military that sufficient effort was put into modernizing the artillery corps and the Persians managed to excel and become self-sufficient in the manufacturing of firearms.
Despite the reforms, the Qizilbash would remain the strongest and most effective element within the military, accounting for more than half of its total strength.[205] But the creation of this large standing army, that, for the first time in Safavid history, was serving directly under the Shah, significantly reduced their influence, and perhaps any possibilities for the type of civil unrest that had caused havoc during the reign of the previous shahs.
Economy

The growth of Safavid economy was fuelled by the stability which allowed the agriculture to thrive, as well as trade, due to Iran's position between the burgeoning civilizations of Europe to its west and India and Islamic Central Asia to its east and north. The Silk Road which led through northern Iran was revived in the 16th century. Abbas I also supported direct trade with Europe, particularly England and The Netherlands which sought Persian carpet, silk and textiles. Other exports were horses, goat hair, pearls and an inedible bitter almond hadam-talka used as a spice in India. The main imports were spice, textiles (woolens from Europe, cottons from Gujarat), metals, coffee, and sugar.
In the late 17th century, Safavid Iran had higher living standards than in Europe. According to traveller Jean Chardin, for example, farmers in Iran had higher living standards than farmers in the most fertile European countries.[206]
Agriculture
According to the historian Roger Savory, the twin bases of the domestic economy were pastoralism and agriculture. And, just as the higher levels of the social hierarchy was divided between the Turkish "men of the sword" and the Persian "men of the pen"; so were the lower level divided between the Turcoman tribes, who were cattle breeders and lived apart from the surrounding population, and the Persians, who were settled agriculturalists.[207]
The Safavid economy was to a large extent based on agriculture and taxation of agricultural products. According to the French jeweller Jean Chardin, the variety in agricultural products in Iran was unrivaled in Europe and consisted of fruits and vegetables never even heard of in Europe. Chardin was present at some feasts in Isfahan were there were more than fifty different kinds of fruit. He thought that there was nothing like it in France or Italy:[208]
Tobacco grew all over the country and was as strong as that grown in Brazil. Saffron was the best in the world... Melons were regarded as excellent fruit, and there were more than 50 different sorts, the finest of which came from Khorasan. And in spite of being transported for more than thirty days, they were fresh when they reached Isfahan... After melons the finest fruits were grapes and dates, and the best dates were grown in Jahrom.
Despite this, he was disappointed when travelling the country and witnessing the abundance of land that was not irrigated, or the fertile plains that were not cultivated, something he thought was in stark contrast to Europe. He blamed this on misgovernment, the sparse population of the country, and lack of appreciation of agriculture amongst the Persians.[209]
In the period prior to Shah Abbas I, most of the land was assigned to officials (civil, military and religious). From the time of Shah Abbas onwards, more land was brought under the direct control of the shah. And since agriculture accounted for by far largest share of tax revenue, he took measures to expand it. What remained unchanged, was the "crop-sharing agreement" between whoever was the landlord, and the farmer. This agreement concisted of five elements: land, water, plough-animals, seed and labour. Each element constituted 20 percent of the crop production, and if, for instance, the farmer provided the labour force and the animals, he would be entitled to 40 percent of the earnings.[210][211] According to contemporary historians, though, the landlord always had the worst of the bargain with the farmer in the crop-sharing agreements. In general, the farmers lived in comfort, and they were well paid and wore good clothes, although it was also noted that they were subject to forced labour and lived under heavy demands.[212]
Travel and caravanserais

Horses were the most important of all the beasts of burden, and the best were brought in from Arabia and Central-Asia. They were costly because of the widespread trade in them, including to Turkey and India. The next most important mount, when traveling through Iran, was the mule. Also, the camel was a good investment for the merchant, as they cost nearly nothing to feed, carried a lot weight and could travel almost anywhere.[213]
Under the governance of the strong shahs, especially during the first half of the 17th century, traveling through Iran was easy because of good roads and the caravanserais, that were strategically placed along the route. Thévenot and Tavernier commented that the Iranian caravanserais were better built and cleaner than their Turkish counterparts.[214] According to Chardin, they were also more abundant than in the Mughal or Ottoman Empires, where they were less frequent but larger.[215] Caravanserais were designed especially to benefit poorer travelers, as they could stay there for as long as they wished, without payment for lodging. During the reign of Shah Abbas I, as he tried to upgrade the Silk Road to improve the commercial prosperity of the Empire, an abundance of caravanserais, bridges, bazaars and roads were built, and this strategy was followed by wealthy merchants who also profited from the increase in trade. To uphold the standard, another source of revenue was needed, and road toll, that were collected by guards (rah-dars), were stationed along the trading routes. They in turn provided for the safety of the travelers, and both Thevenot and Tavernier stressed the safety of traveling in 17th century Iran, and the courtesy and refinement of the policing guards.[216] The Italian traveler Pietro Della Valle was impressed by an encounter with one of these road guards:[217]
He examined our baggage, but in the most obliging manner possible, not opening our trunks or packages, and was satisfied with a small tax, which was his due...
Foreign trade and the Silk Road

The Portuguese Empire and the discovery of the trading route around the Cape of Good Hope in 1487 not only hit a death blow to Venice as a trading nation, but it also hurt the trade that was going on along the Silk Road and especially the Persian Gulf. They correctly identified the three key points to control all seaborne trade between Asia and Europe: The Gulf of Aden, The Persian Gulf and the Straits of Malacca by cutting off and controlling these strategic locations with high taxation.[218] In 1602, Shah Abbas I drove the Portuguese out of Bahrain, but he needed naval assistance from the newly arrived English East India Company to finally expel them from the Strait of Hormuz and regain control of this trading route.[219] He convinced the English to assist him by allowing them to open factories in Shiraz, Isfahan and Jask.[220][221] With the later end of the Portuguese Empire, the English, Dutch and French in particular gained easier access to Persian seaborne trade, although they, unlike the Portuguese, did not arrive as colonisers, but as merchant adventurers. The terms of trade were not imposed on the Safavid shahs, but rather negotiated.
Furthermore, the Safavids maintained a sizeable sphere of influence overseas, particularly in the Deccan region of India. The Sultanates of Ahmednagar, Bijapur, and Golconda all sought Persian suzerainty not just because of religious or cultural ties, but also because of the need for a counterweight to Mughal expansion.[222] The Persians complied, and thousands of Persians emigrated to the Deccan during the 16th and 17th centuries, continuing a process that already began under the Bahmani Sultanate of the Deccan. From here, Persian traders ventured eastwards to Southeast Asian kingdoms, most notably Ayutthaya Siam, where influential Persian families like the Bunnag helped foster cordial diplomatic relations between Thailand and Iran, as evidenced in the expedition of Suleyman's Ship.[223] The Persians were also active in the Aceh Sultanate, the Brunei Sultanate, the Demak Sultanate, and Dai Viet.[224][225][226]
In the long term, however, the seaborne trade route was of less significance to the Persians than was the traditional Silk Road. Lack of investment in ship building and the navy provided the Europeans with the opportunity to monopolize this trading route. The land-borne trade would thus continue to provide the bulk of revenues to the Iranian state from transit taxes. The revenue came not so much from exports, as from the custom charges and transit dues levied on goods passing through the country.[227] Shah Abbas was determined to greatly expand this trade, but faced the problem of having to deal with the Ottomans, who controlled the two most vital routes: the route across Arabia to the Mediterranean ports, and the route through Anatolia and Istanbul. A third route was therefore devised which circumvented Ottoman territory. By travelling across the Caspian Sea to the north, they would reach Russia. And with the assistance of the Muscovy Company they could cross over to Moscow, reaching Europe via Poland. This trading route proved to be of vital importance, especially during times of war with the Ottomans.[228]
By the end of the 17th century, the Dutch had become dominant in the trade that went via the Persian Gulf, having won most trade agreements, and managed to strike deals before the English or French were able to. They particularly established monopoly of the spice and porcelain trade between the Far East and Iran.[229] Protected by Dutch naval power, competition from Bengali silk and Sino-Japanese porcelain contributed to the decline of the Safavid economy during the late 17th century.[230][231]
Culture
| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of Iran |
|---|
 |
Jean Chardin, the 17th-century French traveler, spent many years in Iran and commented at length on their culture, customs and character. He admired their consideration towards foreigners, but he also stumbled upon characteristics that he found challenging. His descriptions of the public appearance, clothes and customs are corroborated by the miniatures, drawings and paintings from that time which have survived.[232] He considered them to be a well-educated and well-behaved people.[233]
В отличие от европейцев, они очень не любили физическую активность и не поддерживали упражнения сами по себе, предпочитая отдых и роскошь, которые могла предложить жизнь. Путешествие ценилось только с конкретной целью - добраться из одного места в другое, а не с целью увидеть новые места и познакомиться с разными культурами. Возможно, именно такое отношение к остальному миру объясняло невежество персов относительно других стран мира. Упражнения, в которых они принимали участие, были направлены на поддержание гибкости и выносливости тела, а также на приобретение навыков обращения с оружием. По стрельбе из лука заняло первое место. Второе место занимало фехтование , где запястье должно было быть твердым, но гибким, а движения – ловкими. В-третьих, было искусство верховой езды. Очень напряженным видом физических упражнений, который очень нравился персам, была охота. [234]
Искусство
Аббас I признал коммерческую выгоду от продвижения искусства: ремесленные изделия составляли большую часть внешней торговли Ирана. В этот период развивались такие ремесла, как изготовление плитки, керамики и текстиля, а также были достигнуты большие успехи в миниатюрной живописи, переплетном деле, декорировании и каллиграфии. В 16 веке ковроткачество превратилось из кочевого и крестьянского ремесла в хорошо развитую отрасль со специализацией дизайна и производства. Тебриз был центром этой промышленности. Ковры Ардебиля были созданы в память о династии Сефевидов. Элегантные барочные ковры «Полонез» были изготовлены в Иране в 17 веке.

Используя традиционные формы и материалы, Реза Аббаси (1565–1635) ввел в персидскую живопись новые сюжеты – полуобнаженных женщин, юношей, влюбленных. Его живопись и каллиграфический стиль оказали влияние на иранских художников на протяжении большей части периода Сефевидов, который стал известен как школа Исфахана. Расширение контактов с далекими культурами в 17 веке, особенно с Европой, послужило источником вдохновения для иранских художников, которые переняли моделирование, ракурс, пространственную рецессию и технику масляной живописи (шах Аббас II отправил Мухаммеда Замана учиться в Рим). Эпос « Шахнаме» («Книга королей»), блестящий образец освещения рукописей и каллиграфии, был создан во время правления шаха Тахмаспа. (Эта книга была написана Фердоуси в 1000 году нашей эры для султана Махмуда Газневи.) Другая рукопись - « Хамса» Низами , выполненная в 1539–1543 годах Ага Мираком и его школой в Исфахане.
Архитектура


В Исфахане находятся наиболее выдающиеся образцы архитектуры Сефевидов, построенные в годы после того, как шах Аббас I окончательно перенес сюда столицу в 1598 году: Императорская мечеть Масджид-э-Шах , построенная в 1630 году, Мечеть Имама (Масджид-э Имами). и Мечеть Лутфаллах Королевский дворец.
По словам Уильяма Кливленда и Мартина Бантона, [235] Провозглашение Исфахана великой столицей Ирана и материальное великолепие города привлекли интеллектуалов со всех уголков мира, что способствовало богатой культурной жизни города. Впечатляющие достижения его 400 000 жителей побудили жителей выпустить свою знаменитую фразу: «Исфахан – это половина мира».
Новая эпоха в иранской архитектуре началась с возвышением династии Сефевидов. Экономически устойчивый и политически стабильный, в этот период наблюдался процветающий рост богословских наук. Традиционная архитектура развивалась в своих моделях и методах, оставляя свое влияние на архитектуру последующих периодов.
Действительно, одним из величайших наследий Сефевидов является архитектура. В 1598 году, когда шах Аббас решил перенести столицу своей иранской империи из северо-западного города Казвин в центральный город Исфахан , он инициировал то, что впоследствии стало одной из величайших программ в иранской истории; полная перестройка города. Выбрав центральный город Исфахан, оплодотворенный Заянде-рудом (« Живоносная река »), лежащий как оазис интенсивного земледелия посреди обширной территории засушливого ландшафта, он одновременно дистанцировал свою столицу от любых будущих нападений. османами , и и узбеками в то же время получил больший контроль над Персидским заливом , который недавно стал важным торговым маршрутом для голландцев и англичан. [236]

Главным архитектором этой колоссальной задачи городского планирования был Шейх Бахаи (Баха ад-Дин аль-Амили), который сосредоточил программу на двух ключевых особенностях генерального плана Шаха Аббаса: проспекте Чахар Баг , окруженном с обеих сторон всеми известные учреждения города, такие как резиденции всех иностранных сановников. И площадь Накш-э Джахан (« Образец мира »). [237] До прихода шаха к власти в Иране существовала децентрализованная структура власти, в которой за власть боролись различные институты, включая как военных ( Кызылбаш ), так и губернаторов различных провинций, составляющих империю. Шах Аббас хотел подорвать эту политическую структуру, и воссоздание Исфахана как великой столицы Ирана было важным шагом в централизации власти. [238] Изобретательность площади, или Майдана , заключалась в том, что, построив ее, шах Аббас собрал на своем заднем дворе три основных компонента власти в Иране; власть духовенства, представленная Масджед-е Шахом , власть торговцев, представленная Императорским базаром, и, конечно же, власть самого шаха, проживающего во дворце Али Капу .
В Исфахане и других городах появились такие выдающиеся памятники, как Шейх Лотфаллах (1618 г.), Хашт Бехешт (Восьмой райский дворец) (1469 г.) и школа Чахар Баг (1714 г.). Это обширное развитие архитектуры ушло корнями в персидскую культуру и приняло форму в дизайне школ, бань, домов, караван-сараев и других городских пространств, таких как базары и площади. Это продолжалось до конца правления Каджара. [239]
Литература
При Сефевидах поэзия находилась в застое; великая средневековая газельная форма томилась в чрезмерном лиризме. Поэзии не хватало королевского покровительства другим искусствам, и она была ограничена религиозными предписаниями.
Пожалуй, самым известным историком того времени был Искандар Бег Мунши . Его «История шаха Аббаса Великого», написанная через несколько лет после смерти ее героя, достигла нюансированной глубины истории и характера.
Исфаханская школа – возрождение исламской философии

Исламская философия [240] процветала в эпоху Сефевидов в том, что ученые обычно называют школой Исфахана. Мир Дамад считается основателем этой школы. Среди светил этой школы философии выделяются имена иранских философов, таких как Мир Дамад, Мир Фендерески , Шейх Бахаи и Мохсен Файз Кашани . Школа достигла своего апогея благодаря иранскому философу Мулле Садре, который, возможно, является самым значительным исламским философом после Авиценны. Мулла Садра стал доминирующим философом исламского Востока, и его подход к природе философии имеет исключительное влияние и по сей день. [241] Он написал « Аль-Хикма аль-мутаалия фи-л-асфар аль-Аклийя аль-арбаа» («Трансцендентная философия четырех путешествий интеллекта»), [242] размышление над тем, что он назвал «метафилософией», которая привела к синтезу философский мистицизм суфизма, теологию шиитского ислама , а также перипатетическую и иллюминационистскую философию Авиценны и Сухраварди .
По словам иранолога Ричарда Нельсона Фрая : [243]
Они были продолжателями классической традиции исламской мысли, которая после Аверроэса умерла на арабском Западе. Персидские школы мысли были истинными наследниками великих исламских мыслителей золотого века ислама, тогда как в Османской империи наблюдался интеллектуальный застой в том, что касается традиций исламской философии.
Лекарство

Статус врачей при Сефевидах был как никогда высок. В то время как ни древние греки, ни римляне не придавали своим врачам высокого социального статуса, иранцы с древних времен почитали своих врачей, которые часто назначались советниками шаха. Это не изменилось с арабским завоеванием Ирана , и именно персы переняли на себя труды по философии , логике, медицине, математике, астрономии , астрологии , музыке и алхимии . [244]
К шестнадцатому веку исламская наука , под которой во многом подразумевалась персидская наука , почивала на лаврах. Труды ар-Рази (865–892) (известного на Западе как Разес) до сих пор использовались в европейских университетах в качестве стандартных учебников по алхимии, фармакологии и педиатрии . «Канон медицины» ( Авиценны ок. 980–1037) до сих пор считался одним из основных учебников по медицине в большей части цивилизованного мира. [245] Таким образом, статус медицины в период Сефевидов не сильно изменился и опирался на эти работы так же, как и раньше. Физиология по-прежнему основывалась на четырех юморах древней и средневековой медицины, а кровотечение и очищение по-прежнему оставались основными формами терапии хирургов, с чем столкнулся даже Тевено во время своего визита в Иран. [192]
Единственной областью медицины, где был достигнут некоторый прогресс, была фармакология с составлением «Тибб-э Шифаи» в 1556 году. Эта книга была переведена на французский язык в 1681 году Ангулом де Сеном под названием «Фармакопея Персика». [246]
Развлечение

С доисламских времен борьба была неотъемлемой частью иранской идентичности, а профессиональные борцы, выступавшие в Зурханехах , считались важными членами общества. В каждом городе был свой отряд борцов, называемых Пахлаванами . Их спорт также давал массам развлечение и зрелище. Шарден описал одно такое событие: [247]
Оба борца были покрыты жиром. Они присутствуют на ровной площадке, и во время состязания для волнения всегда играет небольшой барабан. Они клянутся хорошо драться и пожимают друг другу руки. После этого они хлопают себя по бедрам, ягодицам и бедрам в ритме барабана. Это для женщин и для того, чтобы привести себя в хорошую форму. После этого они объединяются, издавая великий крик и пытаясь свергнуть друг друга.
Помимо борьбы, массы собирали фехтование, канатоходцы, кукольники и акробаты, выступавшие на больших площадях, таких как Королевская площадь . Неторопливую форму развлечения можно было найти в кабаре , особенно в некоторых районах, например, возле мавзолея Харун-э велаята. Люди собирались там, чтобы выпить ликер или кофе, покурить табак или опиум, поболтать или послушать стихи. [248]
Одежда и внешний вид



Как отмечалось ранее, ключевым аспектом персидского характера была любовь к роскоши, особенно к поддержанию внешнего вида. Они украшали свою одежду камнями и украшали сбрую своих лошадей. Мужчины носили на пальцах много колец, почти столько же, сколько и их жены. Они также украшали свое оружие драгоценностями, например, кинжалами и мечами. Кинжалы носили на поясе. Описывая одежду дамы, он отмечал, что персидское платье раскрывало фигуру больше, чем европейское, но женщины выглядели по-разному в зависимости от того, находились ли они дома в присутствии друзей и семьи или находились на публике. Наедине они обычно носили вуаль, закрывавшую только волосы и спину, но, выходя из дома, они надевали манто — большие плащи, скрывавшие все их тело, кроме лица. Они часто красили ноги и руки хной . Их прическа была простой: волосы собирались в косы, концы которых часто украшались жемчугом и гроздями драгоценностей. Женщины с тонкой талией считались более привлекательными, чем женщины с более крупными фигурами. Женщины из провинций и рабыни прокалывали левую ноздрю кольцами, но родовитые персидские женщины этого не делали. [249]
Самым ценным аксессуаром мужчины был тюрбан . Хотя они длились долгое время, необходимо было иметь изменения для разных случаев, таких как свадьбы и Навруз , в то время как люди со статусом никогда не носили один и тот же тюрбан два дня подряд. Одежду, которая каким-либо образом испачкалась, меняли немедленно. [250]
Язык
Сефевиды ко времени своего возвышения говорили на азербайджанском языке, хотя они также использовали персидский язык в качестве второго языка.Языком, который в основном использовался при дворе Сефевидов и в военном ведомстве, был азербайджанский. [14] [21] Но официальный [8] языком империи, а также административным языком, языком переписки, литературы и историографии был персидский. [14] Надписи на валюте Сефевидов также были на персидском языке. [251]

Сефевиды также использовали персидский язык в качестве культурного и административного языка на всей территории империи и говорили на персидском языке двуязычно. [56] По словам Арнольда Дж. Тойнби, [252]
В период расцвета режимов Великих Моголов, Сефевидов и Османской империи правящие элементы всего этого огромного царства покровительствовали новому персидскому языку как языку «человеческих букв», а также он использовался в качестве официального языка управления в этих двух странах. -третей его владений, находившихся в пределах границ Сефевидов и Великих Моголов.
По словам Джона Р. Перри, [253]
В XVI веке тюркоязычная семья Сефевидов из Ардебиля в Азербайджане, вероятно, тюркизированного иранского происхождения, завоевала Иран и установила тюркский язык, язык двора и армии, как высокостатусный разговорный язык и широко распространенный контактный язык, влияющий на разговорную речь. Персидский язык, хотя и был письменным персидским языком высокой литературы и гражданского управления, практически не изменился по своему статусу и содержанию.
По словам Забиоллы Сафа, [21]
В повседневных делах при дворе Сефевидов, а также выдающимися военными и политическими деятелями, а также религиозными сановниками в основном использовался турецкий, а не персидский язык; и последний класс людей писал свои религиозные произведения преимущественно на арабском языке. Те, кто писал на персидском языке, либо не имели должного обучения этому языку, либо писали за пределами Ирана и, следовательно, на расстоянии от центров, где персидский язык был общепринятым разговорным языком, наделенные той жизненной силой и восприимчивостью к навыкам его использования, которые язык может иметь только в тех местах, где ему действительно место.

По словам Э. ТЕМ. Чато и др., [254]
Особый тюркский язык был засвидетельствован в Сефевидской Персии в 16-17 веках, язык, который европейцы часто называли персидско-турецким («Turc Agemi», «lingua turcica agemica»), который был любимым языком при дворе и в армии, потому что тюркского происхождения династии Сефевидов. Первоначальное название было просто тюрки, поэтому подходящим названием могло бы быть Турки-йи Асеми. На этой разновидности персидского турецкого языка, должно быть, также говорили в Кавказских и Закавказских регионах, которые в 16 веке принадлежали как османам, так и Сефевидам, и не были полностью интегрированы в империю Сефевидов до 1606 года. Хотя в целом этот язык можно было идентифицировать как среднеазербайджанский, пока невозможно точно определить границы этого языка как в лингвистическом, так и в территориальном отношении. Он определенно не был однородным – возможно, это был азербайджано-османский смешанный язык, как утверждает Белтадзе (1967:161) для перевода Евангелий на грузинскую письменность XVIII века.
По словам Рулы Джурди Абисааба, [255]
Хотя арабский язык по-прежнему оставался средством религиозно-схоластического выражения, именно при Сефевидах сложные хадисы и всевозможные доктринальные произведения переводились на персидский язык. Амили ( шиитские ученые на территории нынешнего Южного Ливана ), действовавшие через религиозные посты при дворе, были вынуждены освоить персидский язык; их ученики перевели инструкции на персидский язык. Персианизация шла рука об руку с популяризацией «основной» шиитской веры.
По словам Корнелиса Верстига, [256]
Династия Сефевидов при шахе Исмаиле (961/1501) приняла персидскую и шиитскую формы ислама в качестве национального языка и религии.
По словам Дэвида Блоу, [194]
Основным придворным языком [во время правления Аббаса I (годы правления 1588–1629)] оставался турецкий. Но это был не турецкий Стамбул. Это был турецкий диалект, диалект кызылбашских туркмен, на котором до сих пор говорят в провинции Азербайджана, на северо-западе Ирана. Эта форма турецкого языка была также родным языком шаха Аббаса, хотя он столь же легко говорил по-персидски. Кажется вероятным, что большинство, если не все, туркменских вельмож при дворе также говорили на персидском языке, который был языком управления и культуры, а также большинства населения. Но обратное, похоже, было неверным. Когда Аббас вел оживленную беседу на турецком языке с итальянским путешественником Пьетро Делла Валле на глазах у своих придворных, ему пришлось впоследствии перевести разговор на персидский язык для пользы большинства присутствующих.
Что касается использования грузинского , черкесского и армянского языков при Королевском дворе, Дэвид Блоу заявляет: [195]
Говорили также на грузинском, черкесском и армянском языках, поскольку они были родными языками многих гуламов, а также значительной части женщин гарема. Фигероа слышал, как Аббас говорил по-грузински, который он, несомненно, усвоил от своих грузинских гуламов и наложниц.
По словам Виллема Флор и Хасана Джавади, [257]
В период Сефевидов азербайджанский турецкий язык, или, как его еще называли в то время, кызылбашский турецкий язык, занимал важное место в обществе, на нем говорили как при дворе, так и в простом народе. Хотя в Сефевидском Иране широко говорили на турецком языке, этот факт редко упоминается. Обычно ни персидские, ни европейские авторы не упоминают, на каком языке люди общались друг с другом. Турецкий язык, на котором говорили в Сефевидском Иране, в основном был тем, что сейчас называют азербайджанским или азербайджанским турецким языком. Однако в то время его называли под разными именами. Казалось бы, поэт и миниатюрист Садеки Афшар (1533–1610), чьим родным языком был не азербайджанский тюркский, а чагатайский (хотя он родился в Тебризе), первым обратился к носителям кызылбаши (мотакаллемин-э гызылбаш), но он, а столетие спустя Абдул-Джамиль Насири были исключением из этого общего правила называть язык «тюркским».
По словам Стивена Дейла , [258]
Азербайджанский диалект Шаха Исмаила так и не стал государственным языком, и его использование по-прежнему ограничивалось Азербайджаном , где на нем до сих пор говорят многие иранцы. В остальном тюркская речь в Иране в значительной степени оставалась племенным/гызылбашским и провинциальным азербайджанским явлением, подчинявшимся персидскому языку как языку формального образования и доминирующей литературной культуры.
Наследие

Именно Сефевиды сделали Иран духовным бастионом шиизма, хранилищем персидских культурных традиций и самосознания иранства, действуя как мост в современный Иран. Основатель династии Шах Исмаил принял титул «царя Ирана» ( Падишах-и Иран ) с подразумеваемым представлением об иранском государстве, простирающемся от Хорасана до Евфрата и от Окса до южного побережья. Территории Персидского залива . [259] По словам профессора Роджера Сэвори : [260] [261]
Сефевиды по-разному повлияли на развитие современного иранского государства: во-первых, они обеспечили сохранение различных древних и традиционных персидских институтов и передали их в усиленной, или более «национальной», форме; во-вторых, навязав Ирану исна-ашариатский шиитский ислам в качестве официальной религии государства Сефевидов, они усилили власть муджтахидов . Таким образом, Сефевиды положили начало борьбе за власть между тюрбаном и короной, то есть между сторонниками светского правительства и сторонниками теократического правительства; в-третьих, они заложили основу союза между религиозными классами («улемами») и базаром, который сыграл важную роль как в Персидской конституционной революции 1905–1906 годов, так и снова в Исламской революции 1979 года; в-четвертых, политика, введенная шахом Аббасом I, привела к созданию более централизованной административной системы.
По словам Дональда Стрюзанда, «хотя объединение Сефевидов восточной и западной частей Иранского нагорья и навязывание шиитского ислама двунадесятников в регионе создали узнаваемого предшественника современного Ирана, само государство Сефевидов не было ни явно иранским, ни национальным». [262] Рудольф Матти пришел к выводу, что «хотя Сефевидский Иран и не был национальным государством, он содержал в себе элементы, которые позже породили его, создав множество устойчивых бюрократических черт и положив начало государственному устройству с перекрывающимися религиозными и территориальными границами». [263]
См. также
| История Ирана |
|---|
 |
| Хронология |
- Персидские государства
- Список мусульманских династий шиитов
- Обращение Сефевидов Ирана в шиитский ислам
- Ханства Кавказа
Примечания
- ^ Закрытые страны Ирана
- ^ ( / ˈ s æ f ə v ɪ d , ˈ s ɑː -/ )
- ^ Персидский : Империя Сефевидов Шаханшахи-йе Сефеви .
Ссылки
- ^ «... Орден Льва и Солнца, устройство, которое, по крайней мере, с 17 века, появлялось на национальном флаге Сефевидов: лев, олицетворяющий Али, а солнце - славу шиитской веры», Михаил Борисович Пиотровский, Дж. М. Роджерс, Комнаты Эрмитажа в Сомерсет-Хаусе, Институт искусств Курто, Рай на земле: Искусство исламских стран: Работы из Государственного Эрмитажа и коллекции Халили , Престель, 2004, с. 178.
- ^ Гереглу, Киумарс (октябрь – декабрь 2017 г.). «Хроника зарождающейся династии: новый взгляд на ранних Сафевидов в Тарихе Хаяти Табризи (961/1554)» . Журнал Американского восточного общества . 137 (4): 827. doi : 10.7817/jameroriesoci.137.4.0805 – через Columbia Academic Commons .
Интронизация шаха Исмаила состоялась в Тебризе сразу после битвы при Шаруре , 1 джумада II 907/22 декабря 1501 года.
- ^ Элтон Л. Дэниел, История Ирана (Greenwood Press, 2001), с. 95
- ^ Банг, Питер Фибигер; Бэйли, Калифорния; Шайдель, Вальтер (2020). Оксфордская всемирная история империи: Том первый: Имперский опыт . Издательство Оксфордского университета. стр. 92–94. ISBN 978-0-19-977311-4 .
- ^ Блейк, Стивен П., изд. (2013), «Сефевиды, Великие Моголов и Османская империя», Время в раннем современном исламе: календарь, церемонии и хронология в Сефевидах, Великих Моголов и Османской империи, Кембридж: Cambridge University Press, стр. 21–47, дои : 10.1017/CBO9781139343305.004 , ISBN 978-1-107-03023-7 , получено 10 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ Ферье, Р.В., Путешествие в Персию: Портрет Империи семнадцатого века Жана Шардена , с. ix.
- ^ Новая энциклопедия ислама , Ред. Сирил Глассе, (Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, 2008), 449.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Ремер, HR (1986). «Период Сефевидов». Кембриджская история Ирана , Том. 6: Периоды Тимуридов и Сефевидов. Кембридж: Издательство Кембриджского университета, стр. 189–350. ISBN 0-521-20094-6 , с. 331: «Каким бы удручающим ни было положение в стране во время падения Сефевидов, нельзя допустить, чтобы они затмили достижения династии, которая во многих отношениях стала важным фактором развития Персии в современном К ним относятся сохранение персидского языка в качестве официального языка и нынешних границ страны, приверженность двунадесятому шиизму, монархической системе, планировке и архитектурным особенностям городских центров, централизованному управлению государством. союз шиитских улемов с торговыми базарами и симбиоз персоязычного населения с важными неперсоязычными, особенно тюркоязычными меньшинствами».
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Руди Матти, « Сефевиды, заархивированные 1 сентября 2022 г. в Wayback Machine » в Энциклопедии Ираника , доступ 4 апреля 2010 г. в том, что персидские стихи заменили арабский язык на монетах». «Политическая система, возникшая при них, имела перекрывающиеся политические и религиозные границы и основной язык, персидский, который служил литературным языком и даже начал заменять арабский язык в качестве средства богословского дискурса».
- ^ Рональд Ферье, Искусство Персии . Издательство Йельского университета. 1989, с. 9.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Джон Р. Перри, «Тюркско-иранские контакты», Энциклопедия Ираника , 24 января 2006 г.: «... письменный персидский язык, язык высокой литературы и гражданского управления, остался практически неизменным по статусу и содержанию»
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Сирил Глассе (редактор), Новая энциклопедия ислама , Лэнхэм, Мэриленд: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, исправленное издание, 2003 г., ISBN 0-7591-0190-6 , с. 392: «Шах Аббас перенес свою столицу из Казвина в Исфахан . Его правление ознаменовало пик достижений династии Сефевидов в искусстве, дипломатии и торговле. Вероятно, примерно в это же время двор, который первоначально говорил на тюркском языке, начал использовать персидский"
- ^ Арнольд Дж. Тойнби, Исследование истории , V, стр. 514–515. покровительствовал новому персидскому языку как языку literae humaniores Отрывок: «В период расцвета режимов Великих Моголов, Сефевидов и Османской империи правящий элемент во всем этом огромном царстве , в то время как он также использовался в качестве официального языка управления. в тех двух третях его владений, которые лежали в пределах границ Сефеви и Великих Моголов».
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж Маццауи, Мишель Б; Кэнфилд, Роберт (2002). «Исламская культура и литература в Иране и Центральной Азии в раннее Новое время» . Тюркско-Персия в исторической перспективе . Издательство Кембриджского университета. стр. 86–87. ISBN 978-0-521-52291-5 .
Однако держава Сефевидов с ее самобытной персидско-шиитской культурой оставалась золотой серединой между двумя могущественными турецкими соседями. Государство Сефевидов, просуществовавшее по крайней мере до 1722 года, было по сути «турецкой» династией с азербайджано-турецким языком (Азербайджан был родиной семьи) в качестве языка правителей и двора, а также военного ведомства Кызылбаша. Шах Исмаил писал стихи на турецком языке. Тем не менее администрация была персидской, а персидский язык был средством дипломатической переписки (инша), беллетристики (адаб) и истории (тарих).
- ^ Руда Джурди Абисааб. «Иран и Ливан до обретения независимости» в Хоучанге Эсфандиаре Чехаби, Отношения на расстоянии: Иран и Ливан за последние 500 лет , IB Tauris 2006, стр. 76: «Хотя арабский язык все еще был средством религиозно-схоластического выражения, именно при Сефевидах сложные хадисы и доктринальные произведения всех видов переводились на персидский язык. Амили (ливанские ученые шиитской веры), действовавшие через Суд религиозные должности, были вынуждены освоить персидский язык; их ученики переводили свои инструкции на персидский язык, персидизация шла рука об руку с популяризацией «основной» шиитской веры».
- ^ Сэвори, Роджер М.; Карамустафа, Ахмет Т. (2012). «ESMĀʿĪL I ṢAFAWĪ: Его поэзия» . Энциклопедия Ираника .
- ^ Флор, Виллем; Джавади, Хасан (2013). «Роль азербайджанских тюрков в Сефевидском Иране». Иранские исследования . 46 (4): 569–581. дои : 10.1080/00210862.2013.784516 . S2CID 161700244 .
- ^ Ованнисян, Ричард Г .; Сабах, Жорж (1998). Персидское присутствие в исламском мире . Кембридж: Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 240. ИСБН 978-0521591850 .
- ^ Эксуорси, Майкл (2010). Меч Персии: Надир-шах: от воина племени до тирана-победителя . ИБ Таурис. п. 33. ISBN 978-0857721938 .
- ^ Роджер Сэвори (2007). Иран под властью Сефевидов . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 213. ИСБН 978-0-521-04251-2 .
кызылбаш обычно говорил при дворе на азари-турецком языке, как и сами сефевидские шахи; Незнание персидского языка могло способствовать отходу от чистых классических стандартов прежних времен.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Забиолла Сафа (1986), «Персидская литература в период Сефевидов», Кембриджская история Ирана , том. 6: Периоды Тимуридов и Сефевидов. Кембридж: Издательство Кембриджского университета, ISBN 0-521-20094-6 , стр. 948–965. P. 950: «В повседневных делах языком, который в основном использовался при дворе Сефевидов, а также великими военными и политическими деятелями, а также религиозными сановниками, был турецкий, а не персидский язык; и последний класс людей писал их религиозные труды в основном были на арабском языке. Те, кто писал на персидском языке, либо не имели должного обучения этому языку, либо писали за пределами Ирана и, следовательно, вдали от центров, где персидский язык был общепринятым языком, наделенные жизненной силой и восприимчивостью к навыкам его владения. использовать, которое язык может иметь только там, где он действительно принадлежит».
- ^ Прайс, Массум (2005). Разнообразные народы Ирана: Справочник . АВС-КЛИО. п. 66. ИСБН 978-1-57607-993-5 .
Шах был носителем тюркского языка и писал стихи на азербайджанском языке.
- ^ Blow 2009 , стр. 165–166 «[при дворе] также говорили на грузинском, черкесском и армянском языках, поскольку это были родные языки многих гуламов, а также значительной части женщин гарема. Фигероа слышал, как Аббас говорил по-грузински, который он, без сомнения, усвоил от своих грузинских гуламов и наложниц».
- ^ Фласкеруд, Ингвильд (2010). Визуализация веры и благочестия в иранском шиизме . А&С Черный. стр. 182–3. ISBN 978-1-4411-4907-7 .
- ^ Хелен Чапин Мец , редактор, Иран, страновое исследование . 1989. Мичиганский университет, с. 313.
- ^ Эмори К. Богл. Ислам: происхождение и вера . Издательство Техасского университета. 1989, с. 145.
- ^ Стэнфорд Джей Шоу. История Османской империи. Издательство Кембриджского университета. 1977, с. 77.
- ^ Эндрю Дж. Ньюман, Сефевидский Иран: Возрождение Персидской империи , IB Tauris (2006). [ нужна страница ]
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Матти, Руди (2017) [2008]. «Династия Сефевидов» . Энциклопедия Ираника . Нью-Йорк : Колумбийский университет . дои : 10.1163/2330-4804_EIRO_COM_509 . ISSN 2330-4804 . Архивировано из оригинала 25 мая 2022 года . Проверено 23 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Стрейзанд, Дуглас Э., Исламские пороховые империи: османы, Сефевиды и Великие Моголы (Боулдер, колонка: Westview Press, 2011) («Стреусанд»), стр. 135.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г Сэвори, Роджер (2012) [1995]. «Сафавиды». в Босворте, CE ; ван Донзель, EJ ; Генрихс, В.П .; Льюис, Б.; Пеллат, Ч. ; Шахт, Дж. (ред.). Энциклопедия ислама, второе издание . Том. 8. Лейден и Бостон : Издательство Brill . дои : 10.1163/1573-3912_islam_COM_0964 . ISBN 978-90-04-16121-4 .
- ^ Балтаджиоглу-Браммер, Айше (2021). «Возникновение Сефевидов как мистического ордена и их последующий приход к власти в четырнадцатом и пятнадцатом веках» . В Матти, Руди (ред.). Сефевидский мир . Routledge Worlds (1-е изд.). Нью-Йорк и Лондон : Рутледж . стр. 15–36. дои : 10.4324/9781003170822 . ISBN 978-1-003-17082-2 . S2CID 236371308 .
- ^
- Мэтти, Руди. (2005). В погоне за удовольствиями: наркотики и стимуляторы в истории Ирана, 1500–1900 гг . Издательство Принстонского университета. п. 18; « Сефевиды как иранцы курдского происхождения и неплеменного происхождения (...)» .
- Пикантно, Роджер. (2008). «ЭБН БАЗЗАЗ». Энциклопедия Ираника, Том. VIII, Фаск. 1 . п. 8. « Эта официальная версия содержит текстовые изменения, призванные скрыть курдское происхождение семьи Сефевидов и обосновать их претензии на происхождение от имамов».
- Аморетти, Бьянкамария Скарсия; Мэтти, Руди. (2009). «Династия Цафавидов». В Эспозито, Джон Л. (ред.) Оксфордская энциклопедия исламского мира . Издательство Оксфордского университета. « Имея курдское происхождение, Сафевиды возникли как суннитский мистический орден (...)»
- ^
- Ремер, HR (1986). «Период Сефевидов» в Джексоне, Питер; Локхарт, Лоуренс. Кембриджская история Ирана, Том. 6: Периоды Тимуридов и Сефевидов . Издательство Кембриджского университета. стр. 214, 229
- Блоу, Дэвид (2009). Шах Аббас: безжалостный король, ставший иранской легендой . ИБ Таурис. п. 3
- Сэвори, Роджер М.; Карамустафа, Ахмет Т. (1998) ESMĀĪL I ṢAFAWĪ . Энциклопедия Ираника Том. VIII, Фаск. 6 , с. 628–636
- Гереглу, Киумарс (2016). ХАЙДАР САФАВИ . Энциклопедия Ираника
- ^ Аптин Ханбаги (2006) Огонь, звезда и крест: религии меньшинств в средневековье и раннем периоде . Лондон и Нью-Йорк. ИБ Таурис. ISBN 1-84511-056-0 , стр. 130–131.
- ^ Яршатер 2001 , с. 493.
- ^ Ханбаги 2006 , с. 130.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Энтони Брайер. «Греки и туркмены: понтийское исключение», Dumbarton Oaks Papers, Vol. 29 (1975), Приложение II «Генеалогия мусульманских браков принцесс Трапезунда»
- ^ «Сефевидский Иран» в Энциклопедии Ираника , «Происхождение Сефевидов покрыто мраком. Они, возможно, имели курдское происхождение (см. Р. Савори, Иран под властью Сефевидов, 1980, стр. 2; Р. Матти, «Сефевиды» Dynasty» на сайте iranica.com), но практически они были тюркоязычными и тюркизированными».
- ^ Почему существует такая путаница в отношении происхождения этой важной династии, которая восстановила иранскую идентичность и основала независимое иранское государство после восьми с половиной веков правления иностранных династий? Роджер Сэвори , Иран под властью Сефевидов (Издательство Кембриджского университета, Кембридж, 1980), с. 3.
- ^ Херциг, Эдмунд; Стюарт, Сара (2011). Ранний исламский Иран . ИБ Таурис.
- ^ Мандат 1997 г. , с. 13.
- ^ Мандат 2017 г. , с. 443.
- ^ Мандат 1997 г. , с. 15.
- ^ Мандат 2019 г. , с. 33.
- ^ Ашраф 2024 , стр. 82–83.
- ^ Пикантный 1974 , с. 180.
- ^ Мэтью 2009 , с. 241.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Сефевидский Иран» в Энциклопедии Ираника
- ^ Питер Чаранис. «Рецензия на книгу Эмиля Янссена « Требизонда в Колхиде », Speculum , Vol. 45, № 3 (июль 1970 г.), с. 476.
- ^ Энтони Брайер, открытая цитация , с. 136.
- ^ Вирани, Шафик Н. Исмаилиты в средние века: история выживания, поиск спасения (Нью-Йорк: Oxford University Press), 2007, с. 113.
- ↑ Писатель Румлу задокументировал самые важные из них в своей истории.
- ^ Мастерс, Брюс (2009). «Багдад» . В Агостоне, Габор; Мастерс, Брюс (ред.). Энциклопедия Османской империи . Нью-Йорк : факты в архиве . п. 71. ИСБН 978-0-8160-6259-1 . LCCN 2008020716 . Архивировано из оригинала 16 мая 2016 года . Проверено 21 июня 2022 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д "Исмаил Сафави" Иранская энциклопедия
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б В. Минорский, «Поэзия шаха Исмаила I», Бюллетень Школы восточных и африканских исследований Лондонского университета, 4 октября (1942): 1006–1053.
- ^
- Ремер, HR (1986). «Период Сефевидов» в Джексоне, Питер; Локхарт, Лоуренс. Кембриджская история Ирана, Том. 6: Периоды Тимуридов и Сефевидов . Издательство Кембриджского университета. стр. 214, 229
- Блоу, Дэвид (2009). Шах Аббас: безжалостный король, ставший иранской легендой . ИБ Таурис. п. 3
- Сэвори, Роджер М.; Карамустафа, Ахмет Т. (1998) ESMĀĪL I ṢAFAWĪ . Энциклопедия Ираника Том. VIII, Фаск. 6 , с. 628–636
- Гереглу, Киумарс (2016). ХАЙДАР САФАВИ . Энциклопедия Ираника
- ^ Ричард Тэппер. «Шахсеван в Сефевидской Персии», Бюллетень Школы восточных и африканских исследований Лондонского университета, Vol. 37, № 3, 1974, с. 324.
- ^ Лоуренс Дэвидсон, Артур Гольдшмид, Краткая история Ближнего Востока , Westview Press, 2006, стр. 153.
- ^ Britannica Concision. Архивировано 20 января 2008 г. в Wayback Machine . «Династия Сефевидов», онлайн-издание 2007 г.
- ^ Джордж Ленчовски, «Иран под властью Пехлеви», Hoover Institution Press, 1978, стр. 79: «Исмаил Сафави, потомок благочестивого шейха Исхака Сафи ад-Дина (ум. 1334), захватил Тебриз, приняв титул Шаханшаха-и-Ирана».
- ^ Стефан Сперл, К. Шекл, Николас Ауд, «Поэзия Касиды в исламской Азии и Африке», Академический паб Brill; Издание Set Only (февраль 1996 г.), с. 193: «Как и шах Нимат Аллах-и Вали, он принимал выдающихся гостей, в том числе Исмаила Сефеви, который провозгласил себя шаханшахом Ирана в 1501 году после взятия Тебриза, символической и политической столицы Ирана».
- ^ Хайнц Хальм, Джанет Уотсон, Мэриан Хилл, Шиизм , перевод Джанет Уотсон, Мэриан Хилл, издание: 2, иллюстрировано, опубликовано Columbia University Press, 2004, стр. 80: «...он смог триумфально въехать в столицу Альванда Тебриз. Здесь он принял древний иранский титул Царя царей (Шаханшаха) и провозгласил шиитов правящей религией»
- ^ Вирани, Шафик Н. Исмаилиты в средние века: история выживания, поиск спасения (Нью-Йорк: Oxford University Press), 2007, 113.
- ^ HR Ремер, Период Сефевидов, в Кембриджской истории Ирана, Vol. VI, Издательство Кембриджского университета, 1986, стр. 339: «Еще одним свидетельством стремления следовать линии туркменских правителей является принятие Исмаилом титула «Падишах-и-Иран».
- ^ «Иранская идентичность III. Средневековый исламский период» в Энциклопедии Ираника. Архивировано 25 октября 2019 г. в Wayback Machine : «Цари Сефевидов называли себя, среди других наименований, «сердцем святыни Али» ( kalb-e āstān- э Али ), приняв при этом титул Шаханшаха (царя царей) Персии / Ирана ». Цитата 2: «Даже османские султаны, обращаясь к царям Ак Куюнлу и Сефевидам, использовали такие титулы, как «царь иранских земель», или «султан земель Ирана», или «царь царей Ирана, владыка персы» или «обладатели славы Джамшида, видения Фаридуна и мудрости Дары». Они обращались к шаху Исмаилу как «царю персидских земель и наследнику Джамшида и Кай-Хосроу» (Наваи, стр. . 578, 700–702, 707). Во время правления Шаха Аббаса трансформация завершена, и шиитский Иран сталкивается с двумя соседними суннитскими державами: Османской империей на западе и Королевством Узбеков на востоке».
- ^ Уорд, Стивен Р. (2014). Бессмертное, обновленное издание: Военная история Ирана и его вооруженных сил . Издательство Джорджтаунского университета. п. 43. ИСБН 978-1-62616-032-3 .
- ^ Синклер, Т.А. (1989). Восточная Турция: Архитектурное и археологическое исследование, Том II . Пиндар Пресс. п. 289. ИСБН 978-1-904597-75-9 .
- ^ Рэйфилд, Дональд (2013). Край империй: История Грузии . Книги реакции. п. 165. ИСБН 978-1-78023-070-2 .
- ^ Кристин Вудхед (2011). Османский мир . Рутледж. п. 94. ИСБН 978-1-136-49894-7 .
- ↑ Шах Исмаил I. Архивировано 25 июля 2019 г. на Wayback Machine, получено в июле 2015 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Стрейзанд, с. 146.
- ↑ Колин П. Митчелл, «Тахмасп I». Архивировано 17 мая 2015 г. в Wayback Machine Encyclopædia Iranica (15 июля 2009 г.).
- ^ HR Ремер, «Период Сефевидов» в «Периоды Тимуридов и Сефевидов» , изд. Питер Джексон и Лоуренс Локхарт, том 6 « Кембриджской истории Ирана» (Кембридж, Великобритания: издательство Кембриджского университета, 1968–1991) («Ремер»), стр. 233–234.
- ^ Ремер, с. 234.
- ^ Ромер, стр. 234–237.
- ^ Роджер Сэвори , Иран при Сефевидах , стр. 60–64.
- ^ Стрейзанд, стр. 146–147.
- ^ Колин П. Митчелл, Политическая практика в Сефевидском Иране: власть, религия и риторика (Лондон: IB Tauris, 2000), стр. 59.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Стрейзанд, с. 147.
- ^ Михаил Сванидзе, «Амасийский мирный договор между Османской империей, Ираном (1 июня 1555 г.) и Грузией», Вестник Национальной академии наук Грузии , Том. 3, с. 191–97 (2009) («Сванидзе»), с. 191.
- ^ Редактировать, с. 192
- ^ Стрейзанд, с. 50.
- ^ Макс Шербергер, «Противостояние между суннитской и шиитской империями: османско-сефевидские отношения между четырнадцатым и семнадцатым веками» в книге « Сунна и шиит в истории: разделение и экуменизм на мусульманском Ближнем Востоке» , изд. Офра Бенджио и Меир Литвак (Нью-Йорк: Palgrave Macmillan, 2011) («Шербергер»), стр. 60.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Джон Ф. Ричардс , Империя Великих Моголов (Кембридж, Великобритания: Издательство Кембриджского университета, около 1995 г.), стр. 11.
- ^ Риазул Ислам; Индо-персидские отношения: исследование политических и дипломатических отношений между Империей Великих Моголов и Ираном (Тегеран: Иранский культурный фонд, 1970), стр. 22–47.
- ^ Савори, Р., Иран при Сефевидах, с. 66.
- ^ Нахаванди и Бомати, стр. 284–286
- ^ Савори, стр. 129–131.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час я «Тахмасп I» . Проверено 12 мая 2015 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Стрейзанд, с. 148.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с «БАРДА и БАРДА-ДАРИ против военного рабства в исламском Иране» . Проверено 15 апреля 2014 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Манц, Беатрис. «Чаркас» . Энциклопедия Ираника . Архивировано из оригинала 2 ноября 2014 года . Проверено 1 апреля 2014 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Лапидус, Ира М. (2012). Исламские общества в девятнадцатом веке: глобальная история . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 494. ИСБН 978-0-521-51441-5 .
- ^ Розмари Стэнфилд Джонсон, «Выживание суннитов в Сефевидском Иране: антисуннитская деятельность во время правления Тахмаспа I», Иранские исследования, том. 27, стр. 123–133 (1994), стр. 125–126, 128–131.
- ^ Ремер. стр. 250–51.
- ^ Фаррох, Каве (2011). Иран в войне: 1500–1988 гг . Издательство Блумсбери. ISBN 978-1-78096-240-5 .
- ^ Стрейзанд, с. 149.
- ^ Ремер, с. 251.
- ^ Ремер, с. 252.
- ^ Чабер, с. 70.
- ^ Ремер, с. 253.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Ремер, с. 255.
- ^ Ремер, с. 354
- ^ Стрейзанд, стр. 149.
- ^ Аболала Судавар, «Покровительство визиря Мирзы Салмана», Мукармас. Том. 30, стр. 213–234 (2013), с. 216.
- ^ Sicker 2001 , стр. 2–3.
- ^ Ремер, с. 256.
- ^ Ремер, с. 257.
- ^ Ремер, стр. 257–258.
- ^ Ремер, с. 259.
- ^ Стрейзанд, с. 150
- ^ Чабер, с. 74.
- ^ Савори, стр. 74–76.
- ^ Стрейзанд, с. 151
- ^ Чабер, с. 77.
- ^ Чабер, с. 76.
- ^ Чабер, с. 177
- ^ Стрейзанд, стр. 151–152.
- ^ Савори, стр. 82–83.
- ^ Стрейзанд, с. 152.
- ^ Кремер, Уильям (25 января 2013 г.). «Почему мужчины перестали носить высокие каблуки?» . Новости Би-би-си . Архивировано из оригинала 17 августа 2014 года . Проверено 13 сентября 2014 г.
- ^ Савори, стр. 78–79.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Чабер 1980 , с. 79
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Бомати и Нахаванди 1998 , стр. 141–142
- ^ Бомати и Нахаванди 1998 , стр. 143
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б РМ, Сэвори. «АЛЛАХВЕРДЕ ХАН (1)» . Энциклопедия Ираника . Проверено 1 января 2016 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Митчелл, Колин П. (2011). Новые взгляды на Сефевидский Иран: Империя и общество . Тейлор и Фрэнсис. п. 69. ИСБН 978-1-136-99194-3 .
- ^ Ханбаги 2006 , с. 131
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Микаберидзе 2015 , стр. 101-1. 291, 536.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Блоу 2009 , с. 174.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Матти, Руди (7 февраля 2012 г.). «ГРУЗИЯ vii. Грузины в администрации Сефевидов» . iranicaonline.org . Проверено 14 мая 2021 г.
- ^ Суни с. 50 [ неполная короткая цитата ]
- ^ Асатиани и Бендианачвили 1997 , с. 188
- ^ «Алавердская епархия» (PDF) . Проверено 12 мая 2015 г.
- ^ Митчелл, Колин П. (2011). Новые взгляды на Сефевидский Иран: Империя и общество . Тейлор и Фрэнсис. п. 70. ИСБН 978-1-136-99194-3 .
- ^ «Сефевидский Иран» в Encyclopædia Iranica
- ^ Джалилов, О Дж (1967). Курдский героический эпос Златоруки Хан (Курдский героический эпос Хан Златорукий) (на русском языке). Москва. ISBN 978-0-89158-296-0 .
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: отсутствует местоположение издателя ( ссылка ) - ^ «Исламские группы» ( JPEG ) . Техасский университет.
- ^ Вехсе, Карл Эдуард (1856). Мемуары двора, аристократии и дипломатии Австрии . Лонгман, Браун, Грин и Лонгманс. п. 71.
- ^ Лоуренс Локхарт в «Наследии Персии» , изд. А. Дж. Арберри ( Издательство Оксфордского университета , 1953), стр. 1953. 347.
- ^ Нахаванди и Бомати, с. 114.
- ^ Шекспир, Уильям (2001). Двенадцатая ночь, или что пожелаете . Компания классической книги. п. 177. ИСБН 978-0-7426-5294-1 .
- ^ Ричард Уилсон, «Когда приходят монастыри Золотого времени»: Двенадцатая ночь и Восточное обещание Шекспира, Шекспир , Том 6, выпуск 2, июнь 2010 г., стр. 209–226.
- ^ Нахаванди, Бомати, стр. 128–130.
- ^ Нахаванди, Бомати, стр. 130–137.
- ^ Олсон, Джеймс С .; Шадл, Роберт (1996). Исторический словарь Британской империи . Издательская группа Гринвуд. п. 1005. ИСБН 978-0-313-29367-2 .
- ^ Нахаванди, Бомати, стр. 161–162.
- ^ Энциклопедия Ираника , «Аббас I Великий», стр. 75.
- ^ Мунши 1978 , с. 1116
- ^ Систани , с. 509 [ нужна полная цитата ]
- ^ Джавахишвили 1970, [ нужна страница ]
- ^ Субрахманьям, Санджай (1988). «Персы, паломники и португальцы: трудности судоходства Масулипатнам в западной части Индийского океана, 1590–1665». Современные азиатские исследования . 22 (3): 503–530. дои : 10.1017/S0026749X00009653 . S2CID 144502214 .
- ^ Котилайне, Ярмо Т. (2005). Внешняя торговля и экономическая экспансия России в XVII веке: Окна в мир . Лейден. стр. 330–360 , 450–485. ISBN 9789004138964 .
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: отсутствует местоположение издателя ( ссылка ) - ^ Утц, Аксель (2011). Культурный обмен, империалистическое насилие и благочестивые миссии: местные перспективы Танджавура и страны Ленапе, 1720–1760 (докторская диссертация). Государственный университет Пенсильвании. стр. 84–85, 93–94. ПроКвест 902171220 .
- ^ Флор, Виллем; Клоусон, Патрик (2000). «Поиски Сефевидского Ирана серебра и золота». Международный журнал исследований Ближнего Востока . 32 (3): 345–368. дои : 10.1017/S0020743800021139 . S2CID 162418783 .
- ^ Моттахеде, Рой, Мантия Пророка: религия и политика в Иране , One World, Оксфорд, 1985, 2000, стр. 204.
- ^ Эксуорси, стр. 39–55.
- ^ Аспекты алтайской цивилизации III: материалы тридцатого заседания Постоянной международной алтаистической конференции, Университет Индианы, Блумингтон, Индиана, 19–25 июня 1987 г. Психология Пресс. 1996. с. 49. ИСБН 978-0-7007-0380-7 .
- ^ Микаберидзе, Александр (2011). «Гянджинский договор (1735 г.)». Микаберидзе, Александр (ред.). Конфликт и завоевания в исламском мире: Историческая энциклопедия . АВС-КЛИО. п. 329. ИСБН 978-1598843361 .
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: отсутствует местоположение издателя ( ссылка ) - ^ «Сефевидский Иран» в Encyclopædia Iranica
- ^ Ланг, Дэвид Маршалл (1957). Последние годы грузинской монархии, 1658–1832 гг . Издательство Колумбийского университета. п. 142. ИСБН 9780231937108 .
- ^ Сефевиды, Великие Моголов и Османская империи. Архивировано 27 сентября 2021 г. в Wayback Machine Cambridge Core. См. также Список стран по численности населения в 1700 году .
- ^ Роджер Сэвори , Иран при Сефевидах , с. 183.
- ^ Сэр Э. Денисон Росс, сэр Энтони Шерли и его персидское приключение, стр. 219–220.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Роджер Сэвори , Иран при Сефевидах , с. 77.
- ^ Эксуорси, Майкл ; История Ирана (2010).
- ^ Пикантный; стр. 184–185.
- ^ Роджер Сэвори ; Иран под властью Сефевидов ; п. 65
- ^ Бабаян, доцент кафедры истории Ирана и культуры Кэтрин; Дочь Сьюзен; Бабаян, Кэтрин; Маккейб, мать; Фархад, Массуме (2004). Рабы шаха: новые элиты Сефевидского Ирана . Академик Блумсбери. ISBN 9781860647215 . Проверено 1 апреля 2014 г.
- ^ Оберлинг, Пьер, Грузины и черкесы в Иране , Гаага, 1963; стр. 127–143
- ^ Удар, Д; Шах Аббас: безжалостный король, ставший иранской легендой, с. 9.
- ^ Мэти, Рудольф П. (1999), Политика торговли в Сефевидском Иране: шелк за серебро, 1600–1730 гг. Архивировано 20 октября 2022 г. в Wayback Machine .
- ^ Удар; п. 37.
- ^ Пикантный; п. 82.
- ^ Эскандар Бег, стр. стр. 900–901. Савори, II, с. 1116
- ^ Бурнотьян, Джордж А .; Краткая история армянского народа: (с древних времен до наших дней). Архивировано 18 ноября 2022 г. в Wayback Machine (оригинал из Мичиганского университета ), Mazda Publishers, 2002 г. ISBN 978-1568591414 с. 208
- ^ Асланян, Себух. От Индийского океана до Средиземного моря: глобальные торговые сети армянских торговцев из Новой Джульфы. Архивировано 18 ноября 2022 г. в Wayback Machine University of California Press , 4 мая 2011 г. ISBN 978-0520947573 с. 1
- ^ Акинер, Ширин (2004). Каспий: политика, энергетика и безопасность . Тейлор и Фрэнсис. п. 158. ИСБН 978-0-203-64167-5 .
- ^ Савори, стр. 185–186.
- ^ Наср, Вали (2006). Возрождение шиитов: как конфликты внутри ислама будут определять будущее . Нью-Йорк: Нортон. п. 69 . ISBN 978-0-393-06211-3 .
- ^ Момен, Муджан (1985). Введение в шиитский ислам: история и доктрины двунадесятного шиизма . Оксфорд: Г. Рональд. п. 127. ИСБН 978-0-85398-201-2 .
- ^ Момен, Муджан (1985). Введение в шиитский ислам: история и доктрины двунадесятного шиизма . Оксфорд: Г. Рональд. п. 222. ИСБН 978-0-85398-201-2 .
- ^ Момен, Муджан (1985). Введение в шиитский ислам: история и доктрины двунадесятного шиизма . Оксфорд: Г. Рональд. п. 204. ИСБН 978-0-85398-201-2 .
- ^ Момен, Муджан (1985). Введение в шиитский ислам: история и доктрины двунадесятного шиизма . Оксфорд: Г. Рональд. п. 115. ИСБН 978-0-85398-201-2 .
- ^ Момен, Муджан (1985). Введение в шиитский ислам: история и доктрины двунадесятного шиизма . Оксфорд: Г. Рональд. п. 116. ИСБН 978-0-85398-201-2 .
- ^ Ферье, RW; Путешествие в Персию: портрет империи семнадцатого века Жана Шардена; стр. 71–71.
- ^ Удар, с. 173.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Удар, Дэвид. Шах Аббас: безжалостный король, ставший иранской легендой, с. 165.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Ферье, стр. 80–82.
- ^ Удар, с. 170.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Роджер Сэвори , Иран при Сефевидах , с. 221.
- ^ Удар, с. 175.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час Блоу 2009 , с. 165.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Блоу 2009 , стр. 165–166.
- ^ Блоу 2009 , стр. 118–119, 166.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Ферье; стр. 85–89.
- ^ Малькольм; том II, с. 456.
- ^ Пикантный; п. 182.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Ферье, Р.В., Путешествие в Персию: Портрет Империи семнадцатого века Жана Шардена, стр. 90–94.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Ферье п. 91.
- ^ Блоу, Дэвид; Шах Аббас: безжалостный король, ставший иранской легендой, стр. 37–38.
- ^ «Племена Шахсавана». Архивировано 8 октября 2007 г. в Wayback Machine , доктор П. Шахсаванд, профессор социологии Исламского университета Азад. Журнал «События» , «Культурные, экономические и общие события Ирана» (получено 4 сентября 2007 г.).
- ^ Ремер 1986 , с. 265
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Удар, с. 38.
- ^ Пол Байрох (1995). Экономика и всемирная история: мифы и парадоксы . Издательство Чикагского университета . п. 107. Архивировано из оригинала 12 октября 2017 г. Проверено 3 января 2020 г.
- ^ Сэвори, Р.; Иран под властью Сефевидов; стр. 186–187.
- ^ Ферье, RW; Путешествие в Персию: портрет Империи семнадцатого века работы Жана Шардена ; п. 24.
- ^ Ферье; п. 23.
- ^ Пикантный; п. 187.
- ^ Блоу, Д.; Шах Аббас: безжалостный король, ставший иранской легендой; п. 211.
- ^ Ламбтон, АКС; Землевладелец и крестьянин в Персии (Оксфорд, 1953); стр. 127–128.
- ^ Ферье; стр. 25–26.
- ^ Пикантный; п. 190.
- ^ Ферье; п. 31.
- ^ Пикантный; п. 191.
- ^ Удар; п. 210.
- ^ Роджер Сэвори , Иран при Сефевидах ; стр. 193–195.
- ^ Удар, Д; Шах Аббас: безжалостный король, ставший иранской легендой; стр. 113–131.
- ^ Удар; глава: «Английские авантюристы на службе шаха Аббаса».
- ^ Пикантный; п. 195.
- ^ Анвар, М. Сирадж (1991). «Отношения Сефевидов и Великих Моголов с государствами Декана» . Труды Индийского исторического конгресса . 52 : 255–262. JSTOR 44142611 .
- ^ Марцинковски, Кристоф. «Персы и шииты в Таиланде: от периода Аюттхая до наших дней» (PDF) .
- ^ Петру, Томаш (2016). « Земли под ветрами» как часть персидского космополиса: исследование лингвистических и культурных заимствований из персидских обществ в малайском мире» . Муссоны (27): 147–161. дои : 10.4000/муссоны.3572 .
- ^ Редактор (03.03.2020). «Четбанг, основная технология огнестрельного оружия Маджапахита» . 1001 Индонезия . Проверено 17 мая 2022 г.
- ^ Скотт, Уильям Генри (1989). «Средиземноморская связь» . Филиппинские исследования . 37 (2): 131–144. ISSN 0031-7837 . JSTOR 42634581 .
- ^ Удар; п. 212.
- ^ Пикантный; п. 196.
- ^ Пикантный; стр. 199–200.
- ^ Эксуорси, Майкл (2009). Меч Персии: Надир-шах: от воина племени до тирана-победителя . Академик Блумсбери. ISBN 9781845119829 .
- ^ «Китайско-иранские отношения iv. Период Сефевидов, 1501–1732 гг.» .
- ^ Ферье, Р.В., Путешествие в Персию: портрет империи семнадцатого века Жана Шардена , с. 110.
- ^ Ферье; стр. 111–113.
- ^ Ферье; стр. 114–115.
- ^ Уильям Л. Кливленд и Мартин П. Бантон, История современного Ближнего Востока (Westview Press, 2000), 2-е изд., стр. 56–57.
- ^ Сэвори, Роджер; Иран при Сефевидах , с. 155.
- ^ Сэр Роджер Стивенс; Страна Великой Софии , с. 172.
- ^ Пикантный; глава: Империя Сефевидов на пике своего могущества при шахе Аббасе Великом (1588–1629).
- ^ Джодидио, Филип, Иран: Архитектура для изменения общества : Умберто Аллеманди (2 августа 2006 г.).
- ^ Дабаши, Х. (1996) «Мир Дамад и основание школы Исфахана», в С.Х. Насре и О. Лимане (ред.) История исламской философии, Лондон: Routledge, гл. 34, 597–634.
- ^ Ризви, Саджад (2009). «Мулла Садра». В Залте, Эдвард Н. (ред.). Стэнфордская энциклопедия философии . Лаборатория метафизических исследований Стэнфордского университета.
- ^ Наср, Сейед Хоссейн , Садр ад-Дин Ширази и его трансцендентная теософия, история, жизнь и творчество , 2-е изд., Тегеран: Институт гуманитарных наук и культурных исследований.
- ^ Р.Н. Фрай, Золотой век Персии , Phoenix Press, 2000, стр. 234
- ^ Сэвори, Роджер: Иран при Сефевидах, стр. 220–225.
- ^ Чабер, с. 220.
- ^ Чабер, с. 222.
- ^ Ферье; п. 116.
- ^ Ферье; стр. 117–118.
- ^ Ферье; стр. 120–124.
- ^ Ферье; п. 124.
- ^ Рональд В. Ферье, Искусство Персии , издательство Йельского университета, 1989, стр. 199.
- ^ Арнольд Дж. Тойнби, Исследование истории , V, стр. 514–515.
- ^ Джон Р. Перри, «Тюркско-иранские контакты», Encyclopædia Iranica , 2006.
- ^ Да. ТЕМ. Чато, Б. Исакссон, К. Джахани. Лингвистическая конвергенция и ареал распространения: тематические исследования иранского, семитского и тюркского языков , Routledge, 2004, стр. 228, ISBN 0-415-30804-6 .
- ^ Руда Джурди Абисааб. «Иран и Ливан до обретения независимости» в Хоучанге Эсфандиаре Чехаби, Отношения на расстоянии: Иран и Ливан за последние 500 лет , IB Tauris (2006), стр. 76.
- ^ Корнелис Хенрикус Мария Верстиг, Арабский язык , издательство Колумбийского университета, 1997, стр. 71.
- ^ Хасан Джавади; Уиллем Флор (2013). «Роль азербайджанских тюрков в Сефевидском Иране». Иранские исследования . 46 (4). Рутледж: 1. doi : 10.1080/00210862.2013.784516 . S2CID 161700244 .
- ^ Дейл, Стивен Фредерик (2020). «Турки, турки и тюрки-тюрки: Анатолия, Иран и Индия в сравнительной перспективе». В Пикоке, ACS ; МакКлари, Ричард Пиран (ред.). Турецкая история и культура в Индии: идентичность, искусство и межрегиональные связи . Брилл. стр. 74–75.
- ^ Хилленбранд Р., Исламское искусство и архитектура , Лондон (1999), ISBN 0-500-20305-9 , с. 228.
- ^ Сэвори, РМ. «18 Иран, Армения и Грузия – Возвышение шиитского государства в Иране и новая ориентация в исламской мысли и культуре» . ЮНЕСКО: История человечества . Том. 5: С шестнадцатого по восемнадцатый век. Лондон, Нью-Йорк: Рутледж. п. 263.
- ^ Муджтахид: Муджтахид по-арабски означает человека, имеющего право заниматься иджтихадом или толкованием религиозных текстов. Итна ашари — число двенадцать в арабском языке, обозначающее имамитов-двунадесятников шиитского ислама. Улама: арабский для богословов.
- ^ Стрейзанд, с. 137.
- ^ Рудольф П. Мэти, Политика торговли в Сефевидском Иране: шелк за серебро, 1600–1730 (Кембридж, Великобритания: Cambridge University Press, 1999), стр. 231.
Библиография
- Аманат, Аббас (1997). Ось Вселенной: Насир ад-Дин Шах Каджар и иранская монархия, 1831–1896 гг . ИБ Таурис. ISBN 978-1845118280 .
- Аманат, Аббас (2017). Иран: современная история . Издательство Йельского университета. ISBN 978-0300112542 .
- Аманат, Аббас (2019). «Вспоминая Персидский край». В Аманате Аббас; Ашраф, Ассеф (ред.). Персидский мир: переосмысление общей сферы . Брилл. стр. 15–62. ISBN 978-90-04-38728-7 .
- Ашраф, Ассеф (2024). Создание и преобразование империи в раннем Каджаре Иране . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-1009361552 .
- Блоу, Дэвид (2009). Шах Аббас: безжалостный король, ставший иранской легендой . ИБ Таурис. ISBN 978-0857716767 .
- Локхарт, Лоуренс; Джексон, Питер , ред. (1986). Кембриджская история Ирана, том 6: Периоды Тимуридов и Сефевидов . Кембридж: Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 0-521-20094-6 .
- Ханбаги, Аптин (2006). Огонь, звезда и крест: религии меньшинств в средневековом и раннем современном Иране . ИБ Таурис. ISBN 978-1845110567 .
- Матти, Руди (2009). «Был ли Сефевидский Иран империей?». Журнал экономической и социальной истории Востока . 53 (1–2). Брилл: 233–265. дои : 10.1163/002249910X12573963244449 .
- Микаберидзе, Александр (2015). Исторический словарь Грузии (2-е изд.). Роуман и Литтлфилд. ISBN 978-1442241466 .
- Сэвори, Роджер (1974). «Государство Сефевидов и политическое устройство». Иранские исследования . 28 . Издательство Кембриджского университета: 179–212. JSTOR 4310161 . ( требуется регистрация )
- Сэвори, Роджер (2007). Иран под властью Сефевидов . Издательство Кембриджского университета . ISBN 978-0521042512 .
- Сикер, Мартин (2001). Исламский мир в упадке: от Карловицкого договора до распада Османской империи . Издательская группа Гринвуд. ISBN 978-0275968915 .
- Яршатер, Эхсан (2001). Энциклопедия Ираника Рутледж и Кеган Пол. ISBN 978-0933273566 .
Дальнейшее чтение
- Матти, Руди , изд. (2021). Сефевидский мир . Абингдон, Оксон: Рутледж . ISBN 978-1-138-94406-0 .
- Мелвилл, Чарльз , изд. (2021). Сефевидская Персия в эпоху империй . Идея Ирана, Vol. 10. Лондон: ИБ Таурис . ISBN 978-0-7556-3378-4 .
- Кристоф Марцинковски (тр.), Персидская историография и география: Бертольд Спулер об основных работах, созданных в Иране, на Кавказе, в Центральной Азии, Индии и ранней Османской Турции , Сингапур: Pustaka Nasional, 2003, ISBN 9971-77-488-7 .
- Кристоф Марцинковски (тр., редактор), Мирзы Рафиа Дастур аль-Мулук : Руководство по позднему управлению Сефевидов. Аннотированный английский перевод, комментарии об офисах и услугах и факсимиле уникальной персидской рукописи , Куала-Лумпур, ISTAC, 2002 г., ISBN 983-9379-26-7 .
- Кристоф Марцинковски, От Исфахана до Аюттайи: контакты между Ираном и Сиамом в 17 веке , Сингапур, Pustaka Nasional, 2005 г., ISBN 9971-77-491-7 .
- «Путешествия и путешествия послов» , Адам Олеарий, в переводе Джона Дэвиса (1662 г.),
- Хасан Джавади; Уиллем Флор (2013). «Роль азербайджанских тюрков в Сефевидском Иране». Иранские исследования . 46 (4). Рутледж: 569–581. дои : 10.1080/00210862.2013.784516 . S2CID 161700244 .
Внешние ссылки
- История Сефевидов в Иранской палате
- «Династия Сефевидов» , Иранская энциклопедия Руди Матти
- Файлы истории: Правители Персии
- BBC История религии
- Сайт иранской культуры и истории
- «Грузины в администрации Сефевидов» , Энциклопедия Ираника
- Художественная и культурная история Сефевидов из Метрополитен-музея.
- История искусства Сефевидов
- Исследование миграции шиитских произведений из арабских регионов в Иран в эпоху ранних Сефевидов.
- Почему история Сефевидов важна? (Иранское палатное общество)
- Историография в эпоху Сефевидов
- «Иран ix. Религии в Иране (2) Ислам в Иране (2.3) Шиизм в Иране со времен Сефевидов: период Сефевидов» , Энциклопедия Ираника Хамида Алгара