Глоссарий ботанических терминов
(Перенаправлен из хасмофита )
Эта статья требует дополнительных цитат для проверки . ( декабрь 2022 г. ) |
Этот глоссарий ботанических терминов является списком определений терминов и концепций, имеющих отношение к ботанике и растениям в целом. Условия морфологии растений включены здесь, а также в более специфический глоссарий морфологии растений и глоссария морфологии листьев . Для других связанных терминов см. Глоссарий фитопатологии , Глоссарий терминов лишайников и список латинских и греческих слов, обычно используемых в систематических именах .
А
[ редактировать ]- ab-
- Префикс, означающий «позиция вдали от». [ 1 ]
- абаксиальный
- Поверхность органа, обращенного от оси органа, например, нижняя поверхность бокового органа, такая как лист или лепесток. [ 2 ] Контрастный адаксиальный .
- прервать
- Отказаться от развития структуры или органа. [ 3 ]
- запас
- Естественное выпадение органа, которое является зрелым или выдержанным, как зрелый фрукт или старый лист. [ 4 ]
- зона обмена
- орган, Специализированный слой ткани, который позволяет сбросить когда он созрел или стареет. Такая ткань обычно образуется, например, у основания черешка или цветоножки .
- акаалесцентный
- Не имея очевидного стебля или, по крайней мере, ни один не видим над поверхностью земли. [ 2 ] Примеры включают некоторые виды оксалиса , [ 5 ] Нолина , [ 6 ] и Юкка . [ 7 ] Антоним : Caulescent (обладает стеблем).
- начисление
- Увеличение в размере с возрастом, например, чашечка , которая продолжает расти после того, как венчика упала, [ 2 ] Например, в Physal Peruviana .
- accust
- Лежа против другой части растения; При нанесении на семядоли это означает, что край семядолей лежит вдоль сложенного извещания в семени. [ 8 ]
- -еааа
- Суффикс добавлен к слову общего названия , чтобы сформировать название таксономической семьи ; [ 9 ] Например, Rosaceae - это семейство роз, из которого тип рода - Роза . [ 10 ]
- Аченец
- Сухие, односетированные неотъемлемые фрукты [ 11 ] в котором истинный фрукт не является так называемой «ягодкой», а ахен, которые являются так называемыми «семенами» на инфрукции , например, в роде Fragaria .
- ацикул
- Стройная или игла в форме. [ 11 ] Смотрите также форму листьев .
- акропетальный
- Перемещение от корней к листьям, например, молекулярных сигналов в растениях.
- Арофилл
- Регулярные листья зрелого растения, полученные над основанием, в отличие от батифиллы .
- акростахоид
- (Описывает тип Sorus ), покрывающего всю абаксиальную поверхность листья , обычно плотно, как в Elaphoglossum и Acrostichum .
- актино-
- Префикс, который указывает на радиальную картину, форму или морфологию.
- актинодромический
- (из венения листьев ) ладонь или радиально расположенное венеция с тремя или более первичными венами , возникающими у основания листа или рядом с ним, и достигая края у большинства видов, но не все.
- актиноморфный
- Обычный или радиально симметричный; [ 12 ] может быть раздирается в похожих половинах как минимум в двух плоскостях. Применяется, например, к стеле и цветам, в которых сегменты перианта в каждом обороте одинаковы по размеру и форме. Сравните регулярно . Контрастные асимметричные , нерегулярные и зигоморфные .
- Акулеат
- Вооружен колючкой , [ 13 ] Например, стебель розы.
- проницательность
- Длинная, сужающаяся точка, особенно вершина заостренного листа.
- закайтировать
- Сужание постепенно до точки, с вогнутыми сторонами, приближающимися к точке. [ 13 ] Контрастные острые и мукронат . Смотрите также форму листьев .
- острый
- 1. резко заостренные, но не вытянутые, с прямыми сторонами приближаются к точке. [ 13 ] Контраст заострен . Смотрите также форму листьев .
- 2. Сходиться под углом менее 90 °. Контраст тупой .
- объявление-
- Префикс, означающий «близко или к»; Также означает «добавлено». [ 13 ]
- адаксиальный
- Поверхность органа, обращенного к оси органа, [ 13 ] Например, верхняя поверхность бокового органа, такая как лист или лепесток. Контраст абасиал .
- Адельфия
Пакет или структура тычинок, образующих одну единицу в ацелушном цвете; Например, трубка из тычинки вокруг плитки гибискуса .
- Adelphous
- Наличие органов, особенно нити , таких как тычинки , соединенные с одной или несколькими Adelphiae , будь то в виде групп или трубок, таких как обычно в таких семьях, как Malvaceae . Использование термина не является последовательным; Некоторые авторы включают в себя тщательно сгруппированные филаменты, в то время как другие включают только Adelphiae, в которых нити связаны минимально на их основаниях. Смотрите, например, Sims: «... филаменты настолько пристально нажаты, что они появляются в монадельфузах ...». [ 14 ] Сравните производные термины, такие как Monadelphous , наличие тычинок, растущих в одной связке или трубке, например, в гибискусе , и Diadelphous , растущий в двух группах.
- приверженый
- Немного объединен с органом другого рода, [ 13 ] Обычно к части другого оборота, например, чашельник, связанный с лепестой . Контрастные аднате .
- Аднате
- Вырос или тщательно слитый до органа другого рода, [ 13 ] Особенно на краю , например, вычистка, слитая с лепестой. Аднатные пыльники S имеют свои половинки, прикрепленные к нити в течение большей части их длины. Контраст connate .
- случайный
- Производится в непредсказуемом или необычном положении, [ 13 ] Например, случайный бутон , произведенный из стебля а не из более типичной уклоны листа , . Авентаризация корней может развиваться из узлов S простратных стеблей некоторых видов растений или из гипокотиля , а не от лучика прорастающего монокотидона .
- Адвентив
- Введено случайно [ 13 ] (обычно ссылаясь на сорняк ).
- антенна
- Воздуха; выращивание или носится над поверхностью земли или воды. [ 15 ]
- эстиция
- Расположение Чапала S и лепесток или их доли в невыразимом цветочном бутоне . Контрастная вернация .
- Аф - (связанный)
- С близостью к другим, сродни; Часто используется для предварительно признанного, но неназванного таксона, который считается близким к этому имени, возможно, гибридный или экстремальный вариант.
- совокупные фрукты
- Кластер фруктов , образованный из свободного кокрана одного цветка, например, ежевика . Сравните несколько фруктов .
- AGOHORIC
- Растения, которые распространяются через случайный транспорт.
- Сельскохозяйственная травка
- Смотрите сорняк .
- Агриофит
- Виды растений, которые вторглись в местную растительность и могли выжить там без вмешательства человека. Они установлены там в естественных местах обитания, оставаясь частью естественной растительности даже после того, как влияние человека прекратилось, и не зависят от людей в их дальнейшем существовании. [ 16 ]
- агрофический
- Расческа, подобная серии вен, разбивается с одной стороны первичной или вторичной вены.
- агростология
- Научное исследование трав, в самом строгом смысле только те виды, которые являются членами семейства Poaceae . Более широкие употребления иногда также включают в себя травяные или граминоидные виды из семейств Cyperaceae , Juncaceae и Typhaceae .
- инструменты
- Наличие крыла или крыльев.
- альбом
- Более старое название для эндосперма цветущих растений. За исключением ткани для хранения питательных веществ, это не похоже на белок ( яичный белок ) эмбрионов животных.
- альбуминовая
- ( семян ), содержащих эндосперм .
- -Посен
- Суффикс добавлен в стебель общего имени или описательного имени, чтобы сформировать имя таксономического приказа .
- чужак
- Любое завод, введенный в область за пределами его естественного ассортимента. Часто используется взаимозаменяемо или в сочетании с иностранным , экзотическим , не нативным и не местным .
- алкалоид
- Любой из слабо определенных классов органических соединений, обнаруженных в тканях многих видов растений. Алкалоидные молекулы имеют один или несколько щелочных атомов азота в их углеродных структурах. Многие алкалоиды коммерчески важны, как лекарства или яды, например, кофеин , морфин , хинин и стрихнин , каждый из которых встречается естественным образом у определенных растений.
- Аллелопатия
- Секреция растения биохимических веществ, которые влияют на рост и размножение близлежащих растений.
- аллопатрический
- Географически отдельные, непересекающиеся диапазоны распределения. [ 17 ] Контрастный симпатрический .
- альтернативный
- 1. (Прил.) (Из листьев или цветов ), несмотря на отдельные, на разных уровнях вдоль стебля , включая спиральные части. Контраст напротив .
- 2. (Подготовка.) Происходит между чем -то другим, например, вычислительную сцену с лепестой .
- альтернативный
- Конфигурация, где части цветка, например, тычинки S, чередуются в положении с лепестой . [ 18 ]
- Мститель
- Синоним Catkin .
- амфитропный
- (яйцеклеток ) согнута так, чтобы оба конца были рядом друг с другом. Контрастные анатропные , кампилотропные и ортотропные .
- Amplocycaul
- С расширенным основанием и сжиманием стебля, обычно листьев.
- Амилумская звезда
- вегетативное распространение тела, наполненного крахмалом (амилум) и расположено вокруг нижних узлов определенных каменныхвортов .
- Анастомоз
- Ветвясь, а затем присоединиться, как с венецией листьев .
- Анастомоз
- Соединение или слияние двух или более вен , которые обычно расходятся или разветвляются, тем самым формируя сеть.
- анатропный
- (яйцеклеток ) перевернута так, чтобы микропил сталкивался с плацентой (это наиболее распространенная ориентация яйцеклеток в цветущих растениях). Контрастные амфитропные , кампилотропные и ортотропные .
- Ancipital
- Плоский, с двумя краями (по сравнению с круглым). [ 19 ]
- Андродиологический
- Наличие бисексуальных цветов и мужских цветов на отдельных людях. Контрастные андромонооочистные , многогамодиоцированные , многогамоно -эфирные и многогамные .
- андроцей
- Коллективное название для мужских репродуктивных частей цветка ; Вычин -тычинка цветка рассматривается коллективно. Контрастная гинеция . Сокращенный A ; Например, A 3+3 указывает на шесть тычинок в двух оборотах .
- Андрогинофор
- Стейбель, несущий как , так и гиноэциум цветка над уровнем вставки перианта андроциум .
- Андрогин
- Имея мужские и женские цветы в том же соцветии .
- Андрофор
- Стейбель или колонна, поддерживающие вычин S в определенных цветах.
- Andromonoecrious
- Наличие бисексуальных цветов и мужских цветов на одном отдельном растении. Контрастные андродиологические , гиномонооочистные , полигамодиоцированные , полигамомонооочистные и полигамные .
- анемофильный
- к опылению ветром . Адаптировано
- анемофилия
- к опылению ветром . Адаптация
- Angiosperm
- растение Цветущее ; Растение с развивающимися семенами, заключенным в яичник .
- анизомери
- Состояние наличия цветочного оборота с другим (обычно меньшим) количеством частей от других цветочных оборотов.
- анизотомный
- Ветвление, с ветвями, имеющими неравные диаметры, такие как туловище и его ветвь. Контрастные изотомические .
- ежегодный
- Завод, который завершает свой жизненный цикл (т.е. прорастает, воспроизводит и умирает) в течение одного года или вегетационного периода.
- кольцо
- 1. Кольцевая структура; в виде кольца. Пластики иногда прикрепляются к кольцу, называемому кольцом или диском в верхней части клюва Achene . В некоторых пыльцевых зернах экзин вокруг отверстий либо толще, либо более тонкой. В порах эта граница называется кольцом. У определенных цветов есть кольцевые сужения в устье цветка, например, в Унией и Аристолохии .
- 2. Кольцо специализированных клеток на спорангии .
- передний
- Расположено перед, к вершине . Сравните дистальный .
- Антемиоид
- В Compositae стиль с щеткой , похожий на щеткий пучок с широкими волосками на кончике каждой ветви стиля.
- пыль
- Пыльцевая часть тычинки .
- антеридий
- В Bryophytes специализированный гаметофитный орган, который производит мужские гаметы .
- Антеридиофор
- В печеночных сторонах ордена Marchantiales мужской гаметофор , специализированная, преследующая структура, которая несет в себе антеридию .
- Антерод
- Стерильный пыльник стаминоде .
- Антез
- 1. (Из цветка) период, в течение которого пыльца представлена и/или стигма восприимчива.
- 2. (из цветущего растения) период, в течение которого присутствуют цветы в антезе. Не определено для некоторых случаев, например, когда пыльца выпускается в зародыше.
- Anthocarp
- Тип фруктов , в котором какая -то часть цветов сохраняется к перикарпу , например, в Nyctaginaceae .
- Антофор
- Подобная стеблу структуру, междоуздор, расположенная между чашечкой и другими частями цветка.
- антиклинальная
- Указывая вверх, вдали от или перпендикулярно поверхности. Контрастная периклинальная .
- Антрорс
- Направлено вперед или вверх, например, волосы на стебле. Контрастные отступы .
- Апетальный
- Отсутствует лепесток с.
- вершина
Наконечник; точка, которая далека от точки привязанности.
- Афанантаус
- (цветов) незаметные или неподходящие, в отличие от фанерантоса или эффектного.
- Афлебия
Несовершенные или нерегулярные окончания листьев, обычно встречающиеся на папоротниках и окаменелостях папоротников из каменноугольного периода .
- афиллею
- Безлистно; не имея листьев. [ 20 ]
- апикальный
- На вершине структуры , обычно побег , стебель или ствол дерева, например, апикальная меристема или апикальная бутона .
- апикулировать
- Особенно листьев, заканчиваясь короткой треугольной точкой. Смотрите также форму листьев .
- апифилия
- Форма опыления , в которой пыльца распределяется медоносными пчелами .
- или-
- Префикс, означающий «от, отдельный, без».
- апокарпов
- (Гиноэциум ) , состоящий из одного или нескольких ковров , которые свободны друг от друга (или почти так), например, у членов Ranunculaceae и Dilleniaceae .
- апомиксис
Тип бесполого воспроизведения, при котором жизнеспособные семян S или споры производятся беспорядком, без оплодотворения , так что генетический материал, который они содержат, является клоном генетического материала родителя. Завод, произведенный таким образом, называется апомиктом .
- апоморфия
- В кладистике «другая форма» из формы предка (то есть инновации ) использования при определении членства в кладе .
- Апопетально
- Имея отдельный лепесток , не слитый ( симпатичный ).
- апофил
- Периант или другие сегменты бесплатно, а не объединены. Сравните симфиллею , гамофиллею и полифиллею .
- апофиз
- 1. Внешняя часть шкалы конуса .
- 2. В результате роста органа или увеличения стебля .
- придаток
- Вторичная часть, прикрепленная к основной структуре; Внешний рост, который редко имеет какую -либо очевидную функцию, следовательно, аппендикуляция .
- аппендикуляция
- Наличие характера или придатка .
- прижатый
- Прижатый внимательно, но не слился, например, листья к стеблу.
- водное растение
- Растение, естественная среда обитания которого является вода, живущая в воде или на воде для всей или существенной части его срока службы; Обычно ограничены свежими или внутренними водами.
- аракноидальный
- Паутинка, от того, что он покрыт тонкими белыми волосками.
- древесный
- Дерево -похожее на рост или общий вид.
- дендрарий
Таксономически организованная коллекция деревьев .
- Археофит
- Не нативное растение, которое, тем не менее, присутствовало в определенной географической области в течение некоторого времени. Контрастные неофит .
- Архегоний
- Многоклеточная гаплоидная структура или орган фазы гаметофита определенных растений, производящих и содержащие яйцеклетку или женскую гамету. Соответствующий мужской орган называется Antheridium .
- Архегониофор
- В печеночных сторонах ордена Marchantiales, женский гаметофор : специализированная, преследующая структура, которая несет архигонию и спорофиты .
- арктотоид
- В Compositae стиль с кольцом широких волосков , несущихся на стержне стиля, проксимального к ветвям стиля.
- Ареолат
- или составленное из ареол S, как ареолат -лишайник Наличие .
- Ареол
- 1. Пространство между резьбами сети, например, часть поверхности листья, определенная каждым из элементов сети вен ; Как и в случае с кактусами, площадь между венщиками листа.
- 2. Структура на узеле ствола кактуса , специализированная морфологически ветвь ; Область кактуса, на которой позвоночник , глохид и цветы. носят
- Арил
- Мембранный или мясистый придаток , образованный расширением FUNICLE , который частично или полностью покрывает семя , например, мясистый внешний слой плода личи или который встречается у членов Sapindaceae .
- Аристат
- С жестким, похожим на щетину AWN или наконечника. Смотрите также форму листьев .
- статья
- Сегмент соединенного стебля или фрукта с трудностями между семенами; часть органа, которая легко отделяется от остальной части органа в соединении или артикуляции.
- Шартикулировать
- Сотавано; свободно отделяется, оставляя чистый шрам; Например, листья некоторых папоротников, где они присоединяются к корневище .
- восходящий
- 1. (Из стебля ) распространяется горизонтально, затем направлен вверх; Восходящий стебель более или менее простит возле его основания, затем вертел .
- 2. (Из яйцеклеток ) прикреплено несколько над основанием.
- асцидиат
- В форме, как кувшин, как и в случае с листьями растений кувшины, например, видам Непента и сарачении . [ 21 ]
- Асексуальное воспроизведение
- Воспроизведение, которое не связано с гаметией . Часто используется взаимозаменяемо с вегетативным размножением .
- Асперропо
- Имея грубую текстуру песчаника; Например, некоторые поверхности листьев.
- асимметричный
- Неправильный или неравный; не хватает какой -либо плоскости симметрии ; Например, цветы канны .
- ослаблять
- Сужение постепенно. Смотрите также форму листьев .
- ушную раковину
- в форме уха Доля , особенно небольшой, округлый, боковой придаток листового или листоподобного органа.
- Auciculate
- Прикреплено к основанию с ушными придатками ( ушными точками ). Смотрите также форму листьев .
- Аутогам
- Самоопыление, самоопределение-в цветущих растениях
- ав
- 1. Любой длинный, похожий на щетину придаток .
- 2. В Poaceae придаток, заканчивающегося или на задней части гляния или леммы какого -то травяного шипа .
- 3. В Geraniaceae часть стиля , которая остается прикрепленной к ковлю , которая отделяется от карпофора (колонка).
- 4. Обычно прямой, жесткий элемент паппуса , варьирующийся от жестко похожих на щетину до жесткого и игольчащего. В Strophanthus это клюв семени , стип комы Awn - .
- опор
- Верхний угол между одной частью растения и другой, например, стебель и лист.
- подмышки
- На оси; плаценты оси , на центральной яичника .
- подмышечный
- Приносится или возникает из оселки , обычно ссылаясь на пазую листа.
- ось
- Главный стебель целого растения или соцветия ; Кроме того, линия, вдоль которой простирается этот стебель.

В заросе листья тетрадении Riparia имеют свои верхние поверхности, повернутые в сторону стебля и паучин . Нижняя поверхность абаксиальна («вдали от оси»), а верхняя поверхность является адаксиальной .


Welwitschia mirabilis представляет пример , роста привычки необычную у столь крупных видов растений.

Схематические диаграммы прикачного расположения семядолей и ущерба в семени эрисимума (ранее Cheiranthus )

гераниума Цветы являются актиноморфными , имеют пять осей симметрии, в отличие от двух оси симметрии зигоморфных цветов большинства видов родственного рода Pelargonium .

Папоротник с заостренными листочками

Adelphous Panemens в цвете Gossypium tomentosum

Watsonia Flower Slit Open и с одной вычинкой , наклонившейся вверх, чтобы показать свою привязанность к лепеспе

Диаграмма кокосового фрукта. Альбук ( эндосперм ) помечен Альбом .
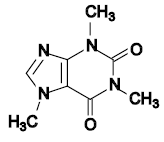
Кофеин является алкалоидом с четырьмя атомами азота в его углеродном скелете.

Лист Ротманнии с тщательным анастомозы венением

Андрогинозный цветок Сандерсонии Аурантиака срезан в продольном продольном уровне, чтобы показать андроциум , который включает в себя пыльник , окружающий зеленый центральный пиститель


Вид NEEA , семейный Nyctaginaceae , представляет собой пример антокарпа : чашечка и стиль остаются вокруг созревающих фруктов.

Афанантовые цветы дубов, таких как Quercus Robur , являющиеся анемофильными , не нуждаются в замешательстве для опыляющих животных.

Апикальный бутон популярного (тополя) стрельбы

По -видимому, отдельные орехи Ochrosia Borbonica на самом деле являются апокарповными карпель , два из каждого цветов.

Апофизы на кончиках конуса Araucaria cunninghamii имеют шипы.

Волосы на листьях Meniocus linifolius (ранее Alyssum linifolium ) являются звездчатыми и прижатыми к поверхности листа.

Аракноидальные листья неопознанного Газании вида



Инфрукция дикой ржи, выдающиеся показывая

Анатомия AWN и щетинки на виде австралийской травы Rytidosperma longifolium

Подмышечные почки в листе
Беременный
[ редактировать ]- баккат
- Фрукты появляются как ягода, которая может быть или не быть настоящей ягодой. [ 22 ]
- бакулиформ
- Похожий на удивление; дольше, чем широкое. Сравните цилиндрический .
- обновой
- Сзади, как в рыбном крючке .
- колютый
- Направляя Барб , в одном направлении.
- штанги
- Имея колючие волосы ( шарниров ).
- лаять
- ткани на стебле и корне древесных Защитный внешний слой деревьев и кустарников; Включает всю живую и неживую ткани, внешнюю по отношению к камбиуму .
- базал
- Расположены или прикреплены к основанию или близко к основанию (диаграммы растения или филогенетического дерева ).
- базис
- Что -то прикрепленное его основанием, например, пыльника , прикрепленной к нити . Сравните Dorsifixed .
- базипетальный
- Последовательное последовательно от вершины к основанию (т.е. с самым молодым к основанию), например, цветов в соцветии . Кроме того, переход от листьев к корням, например, молекулярных сигналов в растениях.
- батифилл
- Специализированный лист, производимый у основания растения, обычно, когда растение незрелое, и который служит для привязки растения на подложку; особенно примечательно в папоротнике Teratophyllum . Контрастная акрофилл .
- клюв
- Выдающаяся, заостренная терминальная проекция, особенно ковша или фрукты .
- ягода
- Тип неотъемлемых фруктов с семенами , погруженным в мякоть, например, помидор .
- с а-
- Префикс, означающий «два», например , с двумя бороздками или бороздками.
- Биеннале
- Завод, который завершает его жизненный цикл (т.е. прорастает, размножается и умирает) в течение двух лет или вегетационных сезонов. Растения двухлетних лет обычно образуют базальную розетку листьев в первый год, а затем цветет и фрукты во второй год.
- бифид
- Разветвленный; Разрежьте два на половину его длины. Сравните Trifid .
- двулистный
- (из составного листа ), имеющая точно две листочки , обычно в симметричной паре, например, лист колофосперма мопане . Сравните джагте -лопастный лист , например, большинство видов баухинии .
- двуфузовый
- Вьющиеся с щепоткой посередине.
- билабайт
- Имея две губы, например, форма лепестки во многих нерегулярных цветах.
- двусторонний
- 1. Имея две различимыми сторонами, такие как две лица дорсивентрального листа.
- 2. расположены на противоположных сторонах, например, листья на стебле ; Сравните дистич и противоположность .
- 3. Двутерно -симметричный, как в листе с симметричным контуром.
- двугнездный
- Имея два места , например, в пыльнике или яичниках .
- биномиал
- Использование имен, состоящих из двух слов для формирования научного имени (или комбинации) в латинской форме. Например, где первое - это название род , к которому принадлежит вид , а второй - это специфический эпитет, данный этому виду, чтобы отличить его от других в том же роде.
- Биномиальная номенклатура
- Система номенклатуры, в которой научное название вида ( а не таксона в любом другом ранге) представляет собой комбинацию двух имен, первым, первым, является общее название . Второе имя называется ботанически как конкретный эпитет . Обратите внимание, что два имени вместе (не только второе имя) составляют название вида.
- Бипиннат
- Вдвойне верно ; Например, составной лист с отдельной листовой листовой , стерно разделенной.
- Bipinnatisect
- Лист Pinnatisect . с глубоко рассеченными сегментами
- бисексуал
- С репродуктивными органами как мужчин, так и женщин; Обычно цветы с вычинкой S и Carpel S; Синонимично с гермафродитой , синоучительным и моноклинным . Бисексуальные цветы встречаются только на монодомных растениях. См. Также Андрогин , моноичная и репродуктивная морфология растений .
- Bitegmic
- (яйцеклеток ) покрыта двумя целыми положениями. Контрастные унитегмические .
- Biternate
- Тернат , с каждым делением, разделенным на три.
- двустворчатые
- Имея два клапана или шарнирные части. Контрастная Trivalve .
- лезвие
- Пластинка за или сплющенная часть листа , исключением стебля или черешка .
- цвести
- Тонкий белый или голубоватый восковой порошок, возникающий на части растений, обычно стебли, листья и фрукты. Его легко удаляется путем потирания.
- Боле
- Ствол . дерева, обычно часть под самой низкой ветвью Сравните навес .
- Бострехоид
- Расположен на конической поверхности (как оболочка улитки); Используется для описания соцветия , в котором зачатки расположены практически спиральным образом на внешней стороне длинных, сужающихся конических рахисов .
- приклетнее
- Модифицированный лист, связанный с цветом или соцветия , и различающийся по форме, размеру или цвету от других листьев (и без подмышечной бутоны ).
- Bracteate
- Обладая применением .
- браколь
- Небольшой приетка, носился по отдельности или в паре на цветоносе или чашечке ; Синоним с Браклетом .
- Брактеолат
- Обладая бракольскими (браклеттами).
- брактоза
- Имея много или эффектный брак с. [ 23 ]
- браклет
- Смотрите Bracteole .
- ветви
- Небольшая ветвь .
- Брувидеса
- Растение, которое теряет все свои листья лишь кратко перед тем, как выращивать новые, так что оно безлистно в течение короткого времени, например, примерно две недели.
- кольца
- Прямые, жесткие волосы (гладкие или минутные зубы); Верхняя часть AWN ( когда последняя согнута и имеет нижнюю, толстую и обычно скрученную часть, называемую колонкой ).
- брохидодромный
- , Венеция листьев в котором вторичные вены не заканчиваются на краю листьев , но соединены в последовательности выдающихся дуг .
- брош
Ширина одного просвета ретикулума пыльцы и половины ширины окружающего мури (стен), следовательно, гетероброкат и гоморосхат , где люмин имеет разные или похожие размеры, соответственно.
- Бриофит
- Неофициально любое растение, которое представляет собой мх , Хорн или печеночный . Формально эти растения размещаются в трех отдельных подразделениях: Hornworts ( Anthocerophyta ), печеночные вещества ( Marchantiophyta ) и Mosses ( Bryophyta ).
- лампочка
- Толстый орган хранения, обычно под землей, состоящий из оснований стебля и листьев (внутренних мясистых).
- бульбель
- Луковица , возникающая из другой лампы. Смотрите Bulblet .
- Бульбил
- Небольшая лиственная лампочка или клубень , образованная в пазух листьев или ушной палочки ; Средство вегетативного распространения.
- булочка
- Луковица , возникающая из другой луковицы; бульбель .
- прозрачный
- 1. Имея округленную или похожие на волдырь; арочный или сводчатый.
- 2. (из листа), имеющая арочную ткань листьев между каждой боковой веной, то есть вены кажутся подавленными на поверхности листа.
- зарубежный
- Деформация или узел в ветвях или стволе дерева, иногда востребованной в деревообработке. [ 24 ]
- бурр
- 1. Колючий фрукт .
- 2. Грубая или колючая пропагула, состоящая из семян или фруктов, и связанных с ними цветочных частей или прицветников .
- Подпорная корень
- Корень , растущий из надземного стебля или ствола, и оказание поддержки, например, Ficus macrophylla .


Барб S встречается на шипах некоторых видов кактусов, как показано здесь, увеличенные.


Бифолиальные . составные листья дерева Mopane, colophospermum mopane , предполагают общее название «дерево бабочек»

Поперечное сечение кремнеолета Arabidopsis thaliana , показывая его билокуляцию , образованную из двух ковров , морфологически кремневинг, а не стручка


Структура листья избитого соединения

Этот африканский баобаб, Adansonia Digitata , имеет огромный боле под относительно скромным навесом , который типичен для этого вида.



Подпорная корень зрелого вдали
В
[ редактировать ]- кадритный
- Рано падая, например, чашелистики отка , которые падают, когда лепесток начинает открываться. Сравните постоянную и беглую .
- Caespitose
- Tufted или Turf-подобные, например, форма роста некоторых трав и умен.
- калькарат
- обладая шпорой .
- известко
- Тип почвы или тип подложки лишайника, который богат или в основном состоит из карбоната кальция .
- калцельт
- В форме, как тапочка. [ 25 ]
- Кальцик
- Растение, которое процветает в известковой почве. Также кальцифил , кальцифит . Антоним : кальцификация . [ 25 ]
- каллоза
- Закален; утолщен; бездушная.
- каллус
1. Выступающая масса ткани
- 2. недифференцированный рост тканей, образованный в ответ на ранения; может быть выращено in vitro .
- 3. В орхидеях, плотистые расстройства из лаблама , которые могут быть по -разному формируются от сосов до тарелок.
- 4. В травах закаленное удлинение от основания цветока ( образованного из сустава рахиллы и/или основания леммы ) , которое может или не может удлиняться и часто покрывается волосами или щетинками.
- калицифловый
- Наличие лепесток и тычинки , прикрепленных к чашечке .
- Каликофилл
- Листоподобная структура, сформированная из доли чашеля или чашечки, которая увеличивается, как правило, многократная, до или после антеза , особенно когда большинство других чашелистиков или доли чашечки сохраняют свой первоначальный размер. Более экстремальные, чем начисленная чашечка, каликофиллы обнаружены в Rubiaceae . Сравните Semaphyll и Pterophyll .
- calyculate
- Имея Epicalyx .
- calyculus
- 1. Кубковая структура, образованная из прицветника , напоминающей внешнюю чашечку .
- 2. В некоторых астеасеаи круг прицветников ниже инвента .
- Калиптра
- Капюшон или крышка. Смотрите OperCulum .
- чашечка
Коллективный термин для чапала S одного цветка; Внешний винщик цветочного, обычно зеленый. Сравните Corolla .
- чашечная трубка
- Трубка, образованная слиянием чашелистиков ( чашечка ), по крайней мере, у основания.
- Камбий
- Тканевый слой, который обеспечивает частично недифференцированные клетки для роста растений.
- Кампанулят
- Колокол.
- Камптодром
- Пиннат Венеция, в которой кривая вторичной вены к полям, в некоторых случаях становится почти параллельными с ними и не воссоединяется с другими венами, чтобы сформировать петли.
- Кампилотропный
- Когда яйцеклетка ориентирована поперечно (т.е. с ее осью под прямым углом к его стеблу) и с изогнутым эмбрионным мешочком . Сравните Amphitropus , Anatropous и Orthotropous .
- каналкулировать
- Направлены; имея продольную канавку.
- ясно
- Приближаясь к белому цвету, как в листе, покрытом белым или шерстью.
- навес
- Ветви и листва дерева; Корона . Также относится к защитному верхнему слою леса. Сравните туловище .
- капилляр
- 1. Трубка, пор или проход с узким, внутренним поперечным сечением.
- 2. стройный; Подобные волосам.
- случаться
- 1. (из соцветия ), имеющая ручку, похожая на ручку, с цветами, неспоненными и агрегированными в плотный кластер.
- 2. (Стигмы ) как голова булавки.
- глава
- Плотный скопление сидячих или субсильных цветов или цветочниц , например, цветочная голова в семействе романи . Смотрите псевдантиум .
- капсула
- Сухие фрукты, образованные из двух или более объединенных ковров и разжигающих при созревании (обычно, расщепляя на куски или открываясь на вершине за зубами или полями).
- кардоид
- В Asteraceae есть стиль с кольцом широких волос, несущих на стержне стиля под ветвями стиля.
- карина
- Смотрите Кил .
- Карильный канал
- Продольная полость в , совпадающего гребнем с стволе equisetum и вымершей Equisetopsida на поверхности стебля.
- Карнеус
- Плоть, особенно применительно к некоторым цветам.
- Карноз, карноус
- Мясистые или мякоть в текстуре, особенно применительно к некоторым тканям или органам. Контрастные коричневые и роговые .
- Кароподиум
- Род цветущих растений в семействе Apiaceae . Родный диапазон: Турция в Иран. Не путать с Carpopodium
- коврик
- Основной женский репродуктивный орган у покрытосеменных , состоящий из одного спорофилла или единого локуса составного яичника , со стилем и стигмой . Гиноцециум является коллективным термином для всех ковров одного цветов .
- Carpellary
- Ссылаясь на ковры или связанные конструкции или расстройства ковров, например, стаминоды, прикрепленные к коврам в Nymphaeaceae, часто называли грузоподобными прикреплениями . Текущее и прошлое использование терминов «Carpellary Actadentments», Paracarpels и STAMinode S запутывается и варьируется среди авторов.
- Карпоподиум
- На Achene S (Cypselae) удлинение основания гинециума , которое выглядит отчетливым; зона обсадки , где Ахене отделяется от сосуда .
- 2. Род Carpopodium в семействе Brassicaceae ; Не путать с кароподиумом .
- хрящевой
- Жестко и жестко; гристой. Сравните куронный и коричневый .
- Карункул
- Небольшой кусочек ткани, похожей на плоть, обычно комковатая или бородавка, растущая на тестировании возле Хилума . Контрастная арил .
- Caryopsis
- Сухой, неотъемлемый , односетированный фрукт , в котором семенное пальто тесно связано с фруктовой стеной, например, в большинстве трав.
- Каспарианская полоса
- Непрерывная полоса суберин в радиальных первичных клеточных стенках эндодермы в стеблях и корнях сосудистых растений, которые образуют барьер проницаемости для пассивной диффузии внешней воды и растворителей в сосудистую ткань.
- кассид
- Капюшона, шлема или капота; Обычно ссылаясь на цветочную анатомию, например, в цветах aconitum , сатирия и т. Д.
- касторный
- Каштановый, красновато-коричневый. [ 26 ]
- Случайный инопланетянин
- Экзотическое растение, которое появляется без видимой человеческой помощи, но не развивает устойчивую популяцию (ы) или то, что сохраняется только путем повторного нового введения. Сравните инопланетянин .
- Катафилла
- Любая структура растений, которая является морфологически листом , но имеет максимум случайную или переходную фотосинтетическую функцию. Они либо проливаются, когда их основная функция была завершена, либо включена в структуры, где, когда они мертвы, они служат защитной или поддерживающей цели.
- CATENALULET
- В форме цепи; сформированы из частей или клеток, соединенных, как будто прикованные вместе, например, некоторые диатомовые , водоросли и цианобактерии, такие как Анабана . Смотрите также Concatenate .
- Кэткин
- Шип , например , , обычно брюшной, в котором в основном маленькие цветы являются унисексуальными и без заметного перианта в ивах , тополях , дубах и казуаринах . Отдельные цветы часто имеют чешуйчатый приступ и, как правило, насыщены ветром . Кэткинс обычно проливают как единое целое.
- хвостат
- Имея узкий, похожий на хвостовой придаток или наконечник, например, капельный наконечник . Контрастная заостренная , киспидат и мукронат .
- Caudex
Стебель ; растения, древесный особенно Также используется для подвода , или, в частности, базальной структуры ствола или органа хранения, из которого возникает новый рост. Сравните лигнотубер .
- Cahiblliform
- Стебель -похожий на caudex -; Иногда используется для обозначения « pachycaul », что означает «толстый стеблен».
- калека
- обладая хорошо развитым стеблем над землей, аналогично Cauline . Антоним : Acaulescent (отсутствие кажущегося стебля).
- Покрытие
Наличие цветов или фруктов, растущих непосредственно из ветвей дерева или ствола. [ 27 ]
- каулин
- Принесенный на воздушном стебле или каулисе , как с листьями, цветами или фруктами (при нанесении к последним двум органам, обычно относящимся к более старым стебли.
- Caulirosulate
- В конце стебля или Caulis , как и в случае с листьями или прицветниками.
- клетка
- 1. Основная микроскопическая единица структуры растений, как правило, состоит из компартментов в вязкой жидкости, окруженной клеточной стенкой .
- 2. полость пыльника или яичника .
- CENANTHOSS
- (от перианта ), в котором отсутствуют как вычинки , так и Pistil , т.е. цветок ни от андроиума , ни гиноциума .
- центрифекция
- Двухцветного органа, прикрепленного его центром, например, волосами или пыльника .
- Серачевой
- Наличие воскового внешнего вида, цвета или текстуры, например, цветы многих видов Ceropegia и восковые плоды некоторых видов Myrica .
- неровно
- Кивает, падает головой или лицом вниз; склонен, наклоняясь или кланяйтесь вперед. наклона Применяется ко многим видам с кивающей привычкой , такими как многие нарциссов и дирамы виды . Многие виды растений несут специфический эпитет " cernua ".
- объект
- Альтернативное написание Caespitose , означающее тщательное или подобное газону, например, форма роста некоторых трав.
- камера
- Полость яичника .
- направлено
- Затонув под поверхностью, что приводит к закругленному каналу.
- чартационный
- Наличие текстуры бумаги.
- chasmogamous
- Цветов, которые опыляются, когда периант открыт. Сравните Cleistogamous .
- хасмофит
- Завод, адаптированный к росту в расщелинах или впах, например, в лицевых лицах. Сравните Cremnophyte . [ 28 ] [ 29 ]
- химера
- Человек, состоящий из двух или более генетически различных тканей, чаще всего в результате трансплантата , а иногда и мутациями, которые происходят во время клеточного деления или клеточных трансферов во время развития семян.
- хироптерофильный
- Облигается летучими мышами .
- Хлорофилл
- Любая из различных химических пигментов в хлоропластах , которые необходимы для фотосинтеза .
- хлоропласт
- Органель , присутствующая в растительных клетках, которые содержат хлорофилл .
- хлороз
- Ненормальная отсутствие или бледность цвета в обычно зеленом органе.
- реснички
Очень маленькие волосы или волосы, похожие на волосы, более или менее ограничены краем органа , как с ресницами; В подвижных клетках, мелкие, похожие на волос выступы, которые помогают подвижности .
- сжигание
- Ясененный, сероватый, обычно из-за покрытия коротких волос; Несколько темнее, чем ясно .
- Цирминат
- Спирально спиральный с кончиком внутреннего, например, цирнированная вернация развивающихся листьев большинства папоротников.
- цирроз
- (листа), заканчивающегося в усике на вершине .
- Циррус
- См . Стремление .
- Cladode
- ветвь Фотосинтетическая . или стебель , часто похожие на листья и обычно с листвами, либо отсутствующими, либо значительно уменьшенными Сравните Phyllode .
- сорт
- Основная категория рейтинга таксонов между разделением и порядком .
- клатрат
- В форме, как сеть или решетка; пронзено отверстиями, как с клеткой.
- клават
- Клубная.
- Клавункула
- В Apocynaceae увеличенная, барабанная стигма , из которой стороны и нижняя поверхность являются зонами восприимчива. Связно с пыльником или нет.
- когтя
- 1. Узкая, похожая на стебель, базальная часть лепестки , чашелистика или прицветника .
- 2. В Мелалеуке , объединенной части вычинного пакета.
- Клистогамный
- Наличие цветов, которые самоопределяются и никогда не открываются полностью, или которые самоопыляются перед открытием. Сравните chasmogamous .
- альпинист
- Завод, растущий, более или менее прямой, опираясь на или обволачиваясь вокруг другой структуры для поддержки, или цепляясь за усики .
- скалолазание
- Смотрите альпиниста .
- Клайн
Непрерывное морфологическое изменение формы внутри вида или иногда между двумя видами.
- клон
- Растение, полученное из бесполого вегетативного размножения родительского растения, при этом обоих растений имеют идентичные генетические композиции.
- коалцизм
- Наличие растений слитых или выращиваемых вместе, чтобы сформировать единый блок.
- кохлериформа
- Вогнутый и в форме ложки.
- Стюйт
- Стучаемо, как оболочка улитки.
- монастырь
- Аранжированная колония водорослей , которая действует как один организм.
- коноцит
- Одна клетка с множественными ядрами , сформированными, когда ядерное деление не сопровождалось цитокинезом .
- Coleoptile
- Один тип оболочки в структуре семян монокотидонов . Колеоптиль представляет собой защитную оболочку или крышку ( Pileus ), как правило, более или менее заостренная, которая покрывает монокотидольный плюмул , когда он появляется из почвы. Обычно он становится зеленым и способствует фотосинтезу до тех пор, пока его функция не будет заменена основным ростом рассады. Сравните это с Coleorhiza , которая остается под землей до тех пор, пока она не заменена, когда появляются корни.
- Coleorhiza
- Один тип оболочки в структуре семян монокотидонов . Coleorhiza соединяет колеоптиль стерлингом и защищает монокотидочное лучику во время прорастания. В отличие от Coleoptile, Coleorhiza связана с корнем и не выходит из почвы во время прорастания. Контрастная Coleoptile .
- Колхима
- Специализированная ткань, состоящая из живых клеток с неравномерно утолщенными целлюлозными и пектиновыми клеточными стенками , которая выполняет опорную функцию в органах, таких как листья и молодые стебли, которые состоят из первичных растений.
- коллитер
- Многоклеточные железистые волосы, которые обычно производят слизистое вещество и расположены на чашелевых S, Stypules или черешках , или на близлежащих частях стебля S; обычно встречается на растениях в порядке денианов .
- Колумелла
- В цветущих растениях центральная ось конуса или фруктов , например, в Каллитрисе .
- столбец
- 1. Структура, простирающаяся над яичником и включает в себя стиль и вычинки , также известную как гиностег , например, в орхидеях и молочных водорослях .
- 2. в травах, нижняя, упорная и обычно скрученная часть AWN , отличная от тонкой верхней части или щетины.
- столбец
- В форме, как колонна.
- кома
- 1. Пучок волос из Testa или Funiculus на одном или обоих концах некоторых семян, например, в Strophanthus , Asclepias или Alstonia .
- 2. Стерильный флакт , например, в Cracum , дыхание или преступный .
- 3. Стерильный цветок S, например, в Muscari и Leopoldia , на вершине некоторых соцветий .
- 4. Пучок волос у основания некоторых цветов, например, в pfaffia gnaphalioides .
- 5. Пучок волос на вершине или основание некоторых шипов .
- 6. An axil tuft of hairs in inflorescences in some Poaceae, e.g. in Eragrostis comata6
- коммерческое название
- Имя часто отсутствует ботаническое положение и не управляемое ICNCP . Термин, как правило, применяется к таким именам, как названия товарных знаков, имена, охватываемые правами заводчиков, патентами и рекламными именами, которые часто используются для повышения продажи завода.
- Коммиссуру
- Шв или лицо, на котором прилипают два ковена . Смотрите также трещину и шов .
- сообщество
- Экологическая сборка растений, которые характерно встречаются вместе.
- сложный
- Состоит из нескольких частей, например, лист, состоящий из нескольких листовок , гиноэциум, состоящий из нескольких ковров , или соцветия, состоящей из нескольких меньших соцветий.
- Составной ладонь
- Наличие листовки , которые излучают из центральной точки (обычно в верхней части черешка ), например, раскидывающие пальцы, излучающие из ладони. Сравните ладон .
- сжатый
- Сплющенные вдоль, либо в боковом (из стороны в сторону), либо дорсально (спереди к спине).
- конкатенат
- Объединился в цепной форме. См. Также Concatenate и Catenate .
- совместный
- Иметь одинаковый цвет повсюду; равномерно окрашен.
- поместить
- Расположены так, что две стороны плоской поверхности сложены вдоль средней линии, чтобы лицом к лицу. См. Также Ptyxis , Aestivation и Vernation .
- конус
- Тип фруктов , обычно древесных , яйцевидных до глобулярных , включая чешуйки , привилегирование или брактеолы, расположенные вокруг центральной оси, например, в спортивных гриппах , особенно хвойных деревьях и казуарине .
- конфлоризация
- Редко используемый термин, описывающий существенные различия между общей структурой соцветия и структурой его отдельных ветвей, например, голова с несколькими цветами для бутылочных цветов членов рода Callistemon .
- Конноги
- Слитый к другому органу (или органам) того же вида, например, лепесток в гомопетальной трубке венчик . Сравните аднате .
- соединительный
- Часть пыльника , которая соединяет клетки пыльников.
- конноги
- Вступая в контакт или сходиться.
- конспецифический
- Принадлежит к тому же виду .
- смежный
- Прилегающий, трогательный, но не объединенный.
- заклинание
- (из чапала S или лепестки ) тип эстиции ввода , в котором одна сторона каждого сегмента перекрывает один из соседних сегментов, а другая сторона перекрывается другим соседним сегментом. Смотрите .
- искажен
- Вывернулся из нормальной формы.
- Сложно
- 1. Ссылаясь на расположение цветочных или лиственных органов в зародыше , когда каждый орган или сегмент имеет один край, перекрывающий соседний орган или сегмент; Форма именения . Смотрите Cortort .
- 2. (из листьев ) тип вернации , при котором один лист свертывается внутри другого.
- 3. Тип вернации двух листьев в узле , в котором обнажается половина каждого листа, а другая половина обернута внутри другого листа.
- Коркл
- Растение эмбрион , плюмуле или плюмуле плюс дочист .
- корпус
- В форме сердца, с максимальной ступенькой; основания листа , как зарезанная часть сердца. Контрастные акцидовые .
- Корисоус
- Кожие; Жесткий и жесткий, но гибкий. Сравните куронный .
- корм
Мясистая, опухшая основание стебля , обычно под землей и функционирующая в хранении пищевых резервов, с почками голыми или покрытыми очень тонкими чешуйками; тип корневища .
- Кормель
- Небольшой корм (или кормлет), образующийся у основания растущего большего корма. [ 30 ]
- роговой
- Возбужденная в текстуре; Жесткий и жесткий, но несколько жесткий. Сравните Coriaceous .
- венчик
- Коллективный термин для лепестки цветочного цвета . Сравните Calyx .
- Корона
- 1. В цветущих растениях кольцо сооружений, которое может быть объединено в трубке, возникающее из венчика или перианта цветка и стоящего между периантыми долями и тычиной . Труба нарциссов - это корона.
- 2. В травах закаленное кольцо ткани, преодолевающее лемму у некоторых видов.
- кора
Область ткани, расположенная между поверхностными клетками и сосудистым цилиндром . [ 31 ]
- кортикол
- Растет на коре или на дереве с литой коры. Сравните Lignicolous .
- Corymb
Соцветие с ветвями , возникающими в разных точках, но достигая примерно одинаковой высоты, придавая кластеру цветов плоский вид.
- коста
- Ребро .
- STORTAPALMATE
- Имея определенную коста (среднюю жилью), в отличие от типичного листа ладони или вентилятора, но с . радиально, как в ладонном листе
- Стюдол
- Первичный лист или листья эмбриона растения, которые при прорастании развиваются в лист семян или первый набор листьев.
- Craspedodromous
- Вентравное венеция , в котором вторичные вены заканчиваются на краю , часто как зубы.
- кратерариформа
- В форме блюдца или мелкой чашки; полусферический или более мелкий.
- CREMNOPHITET
- Завод, адаптированный к росту, особенно на то, что на лицевых лицах или расщелинах. Сравните хасмофит . [ 28 ] [ 29 ]
- Смягчить
- Наличие тупых или округлых зубов; Стина .
- сферат
- Минично.
- Crisped
- Мелко скручивается, как и с краями листьев и лепестков.
- Кристарк -ячейка
- Склереид , который содержит дружный и имеет лигнин, отложенный экзентрически на клеточной стенке , чтобы сформировать форму чашки или в поперечном сечении , форма.
- корона
- Смотрите навес .
- крест
- Сделать что -то межрелище; Акт гибридизации.
- крестообразный
- Поперечная форма.
- кровяный
- Тяжелый, тонкий и хрупкий.
- кост
- Образуя близко применяемый поверхностный слой или кору.
- криптогам
- Любое из «нижних растений», которые производят споры и не имеют вычин , яичников или семян ; Буквально растения, чьи сексуальные репродуктивные органы не являются заметными. Эта группа, как правило, включает в себя папоротники , бриофиты и водоросли , а иногда и грибы (включая лишайные грибы). Сравните фанерогам .
- CUCULLATE
- Капюшон или капюшона, обычно ссылаясь на форму листьев или лепестков, например, Pelargonium cucullatum . Аналогичным образом, полученные термины включают Cuculliform и Cuccularis .
- кальм
- В травах, сплесках, спешках и некоторых других монокотиледонах , воздушном стебле , несущем соцветие , строго простирающееся от основания растения до самого низкого инволюционного прицветника (или основания соцветия).
- культ
- Растение, чье происхождение или отбор обусловлено в первую очередь из -за намеренной человеческой деятельности.
- сорта
- Термин, полученный из «культивируемого сорта», обозначающего сборку культивируемых растений, явно отличающихся одним или несколькими признаками (морфологические, физиологические, цитологические, химические или другие). При воспроизведении (как сексуально, так и в асексальном) сборка сохраняет свои отличительные символы. Сортов может возникнуть в культивировании или ввести из дикой природы. Это вариант, который представляет садоводческий интерес или ценность. Имена сортов написаны с помощью отдельных кавычек вокруг них, например, «Синий ковер» или «Альба». Все новые имена, установленные после 1 января 1959 года, должны быть на общем языке (то есть не на латыни), но имена, установленные на латыни, до этой даты сохраняются в латинской форме.
- СОТВЕТСТВИЯ ЭПИТЕТ
- Определяющая часть имени, которая деновирует сортом . Сортировки обозначены фантазийными (QV) эпитетами, добавленными либо к научному названию, либо к общему названию таксона, к которому они принадлежат; Они не выделены курсивом, но помещены в одиночные кавычки, например, Rubus nitidoides 'Merton Rany'. «Мертон Ранний» - это эпитет сорта.
- клин
- Клин в форме, с прямыми сторонами, сходящимися у основания.
- чашка
- Чашка в форме конструкции, состоящая из коаллеровых принуждений , таких как чашка желудь . Смотрите Calybium .
- чашка
- В форме, как куполка .
- Купулатус
- Подшипники .
- Купулиформ
- Почти полусферический, в форме, как купола или купол.
- квадрат
- Тяжелый, заостренный наконечник, жесткий и более грозный, чем , следовательно , слизь
- Крус
- Окучился с помощью порога , как с некоторыми листьями.
- кутикула
- Гидроизоляционный слой, покрывающий эпидермис поверхностей воздушных растений и состоит из полимеров CUIN , и/или восков CUTAN и.
- резка
- Апикальный или кончик структуры побега , корня , листа который вырезан из растения и используется для асексуального вегетативного распространения.
- Цитий
Соцветие , цветов унисексуальных окруженных инволюционными прицветниками , особенно цветов эйфхорбии .
- циатофилл
- В Евфхорбии , прицветника, подобная структуре, на которой сидит инволюция , обычно, но не всегда встречается в два. Иногда они могут быть ярко окрашены и запутаны с лепестой .
- цилиндрический
- Подобный стержням и в два-три раза длиннее шириной. Сравните бакулиформу .
- цинароид
- Смотрите Carduoid .
- Cyme
Тип соцветия , при котором основная ось и все боковые ветви заканчиваются цветом ( каждый боковой может быть неоднократно разветвлен).
- Кормуляция
- Имея в тарелке или тарелках.
- Cypsela
- Тип сухих, односетированных, неотъемлемых фруктов , образованных из нижнего яичника .

Дайант Чиненсис имеет привычку к росту.


Структура цветка орхидеи в роду Praecoxanthus , с моллусом маркированной

Бородатая мозоль цветока видов травы хризопогон

Сканирующая электронная микрофотография карпоподиума у основания аченоподобного плода Zyzyura Mayana , Asteraceae

Дерные листовые бутоны лиственных деревьев обычно защищены катафиллом , которые проливаются при прорастании зачатка.


Caudex растет в значительной степени of Dioscorea Elephantipes выше поверхности почвы. Многие виды, которые образуют хвостам, выращивают их под землей.

Цветы, выращивающие из ветви сизигия Муреи , пример цветной кости

Некоторые члены рода Espeletia демонстрируют привычку к росту, которая является Caulirosulate .


Хлоропласт -капиллара в клетках листьев мха

Не все хлоропласты S просты по форме. Хлоропласты спирогиры являются спиральными в трубчатых клетках их водорослей.


Так называемые «мясистые листья» кактусов, например, на этой Opuntia tomentosa , на самом деле являются Cladode S (ветви). Истинные листья - это рост позвоночника на кладодах, которые на этом молодом кладоде все еще мясисты.



Curcuma Pseudomontana с из красной комы прицветниками

Pfaffia gnaphalioides цветы с базальными комами волосами

Кома на вершине Muscari Armeniacum , несущая стерильные цветы

Коническое соединение соцветия Aeonium arboreum представляет собой соединенную метелку, состоящую из незначительных метелок, некоторые из которых в свою очередь составляют.

Калифорнийский Buckeye ( Aesculus Californica ) имеет составной лист ладонь , листочки, излучающиеся из центральной точки.


Casuarina equisetifolia мужские и женские цветы и конус s

Гамопетальный цветок Watsonia распадается между двумя лепестками, чтобы показать коннатную формацию трубки Corolla ; Сравните привязанность Adnate на вычин с подходящими лепестками



Семейдон S саженцев Koelreuteria . Одно растение показывает первые новые листья над своими семядолями, а остальные показывают различные молодые этапы новых семядолей.


Nymphoides Crenata имеет Crenate Leaf Fargins.

Mimetes Cucullatus , так названный в честь формы с капюшоном, кукулята его белых цветов

Муррайя Паникулата имеет листья с Cuneate (клино в форме) основания.


Круспидат Листья диплома Бигелови вар. Cuspidatus

Euphorbia milii является коммерчески выращенным для эстетического появления его ярко окрашенных, прицветников, похожих на притяжение называемые циатофиллом , , которые находятся под соцветия .
Дюймовый
[ редактировать ]- лиственная
- Расширение и падение сезонно, как с корой , листьями или лепестками . Контрастирует .
- отклонить
- Изгибаясь вниз, а затем вверх на кончике. Часто квалифицированный, например, отказаться от Асцендента.
- разместить
- Разделен на более чем один уровень, например, в бипиннатных листьях, в которых листовка того, что в противном случае было бы верным листом, сами по себе разделены.
- декартат
- 1. (Intr. V.), Чтобы сбросить внешнюю кору дерева, обычно сезонно в рамках естественного цикла роста.
- 2. (Tr. V.), Чтобы лишить кожуру, кору, кору или другие поверхностные ткани из растения или из собранного материала, например, при извлечении волокна из собранных листьев агавы .
- утечка
- Наличие ветвей, растущих горизонтально вдоль земли, но которые поднимаются на концах.
- бегать
- Простираясь вниз за точку вставки , например, когда основание листа или грибковой жабры продлевается вниз вдоль стебля в поднятой линии или узком крыле.
- декаус
- Синоним Decussate ; Использование Decussant сомнительно и встречается редко, вероятно, в качестве ошибки. Формально правильное использование декаусса .
- отключен
- Напротив последовательных пар, несущих под прямым углом до последнего; обычно применяется к расположению листьев .
- определенный
- Постоянного числа, например, вдвое больше тычинок , чем лепесток или чашелистика (или меньше), или соцветия, заканчивающейся цветом или прерванным цветочным зачаткой , как правило, соцветие в цимозе . Контраст неопределенный .
- дефлексный
- Склонился вниз. Контраст инфлексирован .
- разряжение
- Раскрыться в зрелости, чтобы освободить содержимое; Относится например, на открытие фруктов для освобождения семян , пыльников для освобождения пыльцы и спорангии для выпуска споров . Контрастные неотъемлемые .
- Дельтоид
- В форме, как греческая буква с верхней , то есть, как более или менее равносторонний треугольник.
- Дендроид
- Дерево -похожее; разветвляется как дерево.
- зубчатый
- Зубчатые , особенно в отношении листьев края .
- зубчатый
- Мелко зубчатые ; уменьшительная форма зубчатой .
- пустынный
- Населяя пустыню.
- определять
- Ограничен, обычно в росте. Контраст неопределенно .
- Диадельфус
- Ссылаясь на класс ацелушной структуры, в которой вычислительные или аналогичные органы связаны в двух ацелиатах вместо одного.
- диаспора
- Любая репродуктивная часть растения, адаптированная для рассеивания, и для создания новых растений; Может быть распространение, такая как семя , или другие части, такие как специализированные почки , ветви, соцветия или фрукты.
- сказал
- Цимоза со всеми соцветия ветвями под терминальным цветом в регулярных противоположных парах. Сравните моночазию и плейочазиум .
- Дихламдис
- Имея периант , который разделен на отдельную чашечку и венчик . Сравните Homochlamydeous .
- дихотомический
- Разбрызгивание в две равные ветви. Это может быть результатом равного разделения растущего наконечника или может быть симподиальным , в котором растущий кончик прерывается и заменен. Обычно относится к способу роста ветви, как у Aloidendron Dichotomum , но также и к другим органам, таким как паттерны венения на листьях, шипы различных видов кариссы (которые морфологически являются ветвями), и талли или гифы различных водорослей и водорослей и водорослей и водорослей и водорослей и водорослей и водорослей и водорослей и водорослей. грибы.
- DiCotyledon
Цветущее растение, эмбрион которого имеет два или более семядолей (листья семян). Контрастная монокотидон .
- тип
- С сегментами, распространяющимися из общего центра, как пальцы руки. См. Также ладонь и ладонь . Смотрите также форму листьев .
- цифрообразная
- В форме, как палец.
- диморфный
- Встречается в двух разных формах (относительно формы и/или размера), например, вычин S, листьев или листьев. См. Также мономорфное (имеющее одну форму) и полиморфной (имея множество форм).
- диологически
- (из сосудистых растений) Имеющие мужские и женские репродуктивные структуры, которые развиваются только у разных людей и никогда не на одном человеке. Контраст монодом .
- диоки
- (из бриофита гаметофита ), имеющие мужские и женские репродуктивные структуры, которые развиваются только на разных людях и никогда не на одном человеке. Контрастные моночны .
- диплоид
- Наличие двух полных наборов хромосом в ядре клеток спорофита , то есть по одному набору от каждого из родительских гамет . Это часто выражается символически как 2n , где n = количество хромосом в гаплоидной гамете.
- диплостемонис
- Наличие вычин , расположенного в двух оборотах , с внешним оборотом чередуются с лепестками , в то время как внутренний оборот напротив лепесток. Сравните Obdiplostemonous и Haplostemonous .
- диск
Пластина или кольцо структур, полученных из сосуда , и происходящее между оборотами цветочных частей. В некоторых группах, особенно Sapindales , нектар находится в форме выдающегося диска. В ромашках центральная часть капитула - это диск, поэтому цветы, которые там называют цветами или цветами .
- дисковидный
- Напоминающий диск или тарелку, имея как толщину, так и параллельные грани и с округлым краем. Также используется для описания цветочной головки Asteraceae , где нет Ray Florets, а только цветочки диска.
- обеспокоенный
- ( листьев ), имеющие верхнюю и нижнюю поверхность разных цветов.
- разъединенный
- Встречается в широко разделенных географических областях, отчетливо отдельно; Применяется к прерывистому диапазону, в котором одна или несколько популяций отделены от других потенциально межредирующих популяций с достаточным расстоянием, чтобы исключить поток генов между ними.
- disk floret
- A floret occurring most typically in the disk of the capitulum of flowers in the family Asteraceae, and to some extent in other plants that bear a flowering head with a disk, such as Scabiosa.
- dissected
- Deeply divided; cut into many segments.
- dissepiment
- A partition or septum in a plant part, usually referring to septa between the loculi of capsules or of other fruits with multiple partitions.
- distal
- Remote from the point of origin or attachment; the free end. Contrast proximal.
- distichous
- Arranged in two opposite rows (and hence in the same plane).
- distinct
- Separate or free; not united.
- distyly
- The condition in which the flowers of a species occur in two forms that differ only by the length of the style and stamens, and flowers of only one of these forms appear on any one plant. Compare heterostyly.
- diurnal
- Of the day; occurring or opening in the daytime.
- divaricate
- Wide-spreading.
- divergent
- Spreading in different directions, generally upward.
- division
- A taxonomic rank below kingdom in the standard taxonomic hierarchy. "Division" is generally used only for plants, and is the approximate botanical equivalent of the term phylum, which is used for animals and other kingdoms.
- domatia
Any hollow structure formed by a plant that is inhabited by animals such as ants or mites.
- dorsal
- From Latin dorsum, a ridge or the back of an animal. Partly because the term originally referred to animals rather than plants, usage in botany is arbitrary according to context and source. In general "dorsal" refers to "the rear or back or upper surface", but in botanical usage such concepts are not always clearly defined and may be contradictory. For example:
- facing away from the axis (abaxial) in a lateral organ of an erect plant
- facing away from the substrate in any part of an erect plant, for example the upper surface of a more or less horizontal leaf (adaxial) or the upper part of the crown of the plant
- facing away from the substrate in a prostrate or climbing plant or floating leaves such as those of Nymphaea.
- dorsifixed
- Attached at or by the back, e.g. anthers on a filament.
- dorsiventral
- Having structurally and visibly different upper and lower surfaces, e.g. some leaves. Compare bilateral and isobilateral.
- drip tip
- A long, narrow, acuminate, caudate, or cuspidate extension at the tip of a leaf or leaflet. Commonly an adaptation to rainy conditions, as it promotes shedding of water by its dripping from the narrow tip. The term drip tip is not anatomically descriptive in the way that acuminate or cuspidate are, for example; rather, it is a description of the functional shape that aids dripping, regardless of the specific geometry of the shape itself.
- drupe
- A type of succulent fruit formed from one carpel; the single seed is enclosed by a stony layer of the fruit wall, e.g. in peaches and olives. Also called a kernel.
- drupelet
- A small drupe formed from one of the carpels in an apocarpous flower. Drupelets usually form a compound fruit, as in Rubus, but they may become widely separated, as in Ochna.
- druse
- A globular mass of calcium oxalate crystals, usually with the crystals radiating from an organic core.


машина Декартизирующая , собирающая волокно из листьев



Зубные листья Ziziphus mauritiana

Astragalus Austriacus считается диадельфузной, потому что у него одна тычинка, не привязанная к основной Адельфии (Bunch).


Разнообразные листья обесцвечивания брахиланы различаются по цвету между их верхней и нижней поверхностями.

Диск цветочки, открывающиеся в столице культивируемого гелианта . Они постепенно открываются от края до центра диска.

Dissepiment developing in tissue of carpels where they meet to form locules in the capsule of the ovary of Lilium

Boophone disticha has conspicuously distichous leaves.

Domatia at the bases of the thorns of Vachellia drepanolobium, the whistling thorn, with visible access holes


E
[edit]- -eae
- A suffix added to the stem of a generic name to form the name of a tribe, e.g. Aster → Astereae.
- ebracteate
- Lacking bracts; synonymous with ebracteolate.
- ecological amplitude
- The range of environmental conditions in which an organism can survive.
- edaphic
- Of or influenced by the soil.
- eglandular
Not having glands.
- elaiosome
- An external structure attached to the seed of many species of plants. Elaiosomes generally look fleshy and in some species they are rich in oils or other nutritious materials. Their functions vary and are not always obvious; commonly they attract ants or other animals that aid in dispersal, but they may also repel other animals from eating the seed.[32]
- elephophily
- A form of pollination whereby pollen or spores are distributed by the feet of elephants, as in Rafflesia arnoldii.
- ellipsoid
- A three-dimensional shape that is elliptical in all sections through the long axis.
- elliptical
Planar, shaped like a flattened circle, symmetrical about both the long and the short axis, tapering equally both to the tip and the base; oval.
- emarginate
- Typically in reference to leaf margins: notched or recessed at some part of the edge, such as the apex; the recess usually is broad and shallow. The location of a leaf's emargination(s) might be one or more of apical, lateral or basal
- embryo
- The young plant contained by a seed prior to germination.
- emergent
- A plant taller than the surrounding vegetation or, among aquatic plant species, one that bears flowers and commonly leaves above the surface of the water. Aquatic examples include water lilies, reeds, and papyrus. Some pondweeds such as Stuckenia are not emergent until they flower, at which time only their flowers appear above the water surface.
- enation
- Leaf-like outgrowth from a surface.[33]
- enantiostyly
- The condition in which the gynoecium protrudes laterally, to the right (dextrostyly) or to the left (sinistrostyly) of the androecium, e.g. Senna.
- endemic
- Having a natural distribution restricted to a particular geographic region. Compare native.
- endocarp
- The innermost layer of the wall of a fruit; in a drupe, the stony layer surrounding the seed.
- endodermis
- The innermost layer of the cortex of vascular plant roots, also present in the stems of pteridophytes. The radial walls are impregnated with suberin to form a permeability barrier known as the Casparian strip.
- endosperm
- 1. (angiosperms) A nutritive tissue surrounding the embryo of the seed, usually triploid, originating from the fusion of both polar nuclei with one gamete after the fertilization of the egg.
- 2. (gymnosperms) The prothallus within the embryo sac.
- endospory
- The production of spores that germinate into a reduced multicellular gametophyte contained within the spore wall. Contrast exospory.
- ensiform
- Shaped like the blade of a sword.
- entire
- 1. Not divided.
- 2. (of a margin) Smooth and not lobed or toothed (though possibly wavy or scalloped). See also entire in Glossary of leaf morphology
- entomophily
- A form of pollination whereby pollen or spores are distributed by insects.
- epecophyte
- Species of recent appearance, usually numerous and constant in the country, but confined to artificial habitats, such as meadows and ruderal vegetation and are dependent on humans for existence.[34]
- ephemeral
- Short-lived. See also caducous.
- epicalyx
- An involucre resembling an outer calyx, e.g. as in Hibiscus.
- epicarp
- The outer layer of the wall of a fruit, i.e. the "skin".
- epicormic
- Used to refer to buds, shoots, or flowers developing from the old wood of trees, especially after injury or fire.
- epicotyl
- The part of the plant axis or stem between the cotyledonary node and the first foliage leaves.
- epicuticular wax
- A layer of crystalline or amorphous wax deposited on the surface of the cuticle.
- epidermis
- An organ's outermost layer of cells, usually only one cell thick.
- epigynous
- Borne on the ovary; describes floral parts when attached above the level of the ovary and arising from tissue fused to the ovary wall. Compare hypogynous and perigynous.
- epilithic
- Growing on stone. Compare lithophytic, a plant growing on stone.
- epipetalous
- Of stamens that are attached to the petals.
- epipetric
- Growing on rock or stone, lithophytic, epilithic.
- epiphloedal
- Growing on the surface of bark. Contrast endophloedal (growing inside, not on, the bark) and epilithic (growing on rock, not bark).
- epiphyte
- A plant, alga or fungus that grows on another plant without deriving nourishment from it but using it for support.
- epiphytic
- Of an epiphyte; living on the surface of a plant. Compare epilithic, lithophytic.
- episepalous
- Of stamens that are attached to the sepals.
- epitepalous
- Of stamens that are attached to the tepals.
- epithet
- The adjectival component in a binomial scientific name, usually more specifically called a specific epithet; the final word or combination of words in a name of more than one word (other than a term denoting rank) that denominates an individual taxon. The simplest and commonest example is the second word in a two-word name of a species, such as "mirabilis" in Welwitschia mirabilis.
- epizoochory
- A type of seed dispersal that occurs when seeds or fruits physically adhere to the outside of vertebrate animal bodies.
- epruinose
- Not pruinose.
- equitant
- (of a leaf) Folded lengthwise and clasping another leaf.
- erect
- Upright, more or less perpendicular to the ground or point of attachment. Compare patent (spreading) and erecto-patent, between erect and patent.
- ericoid
- Having leaves like those of the European heaths (Erica); small and sharply pointed.
- erose
- (of a margin) Irregular as though nibbled or worn away.
- ethelochoric
- Deliberate introduction by seedlings, seeds or plants in a new habitat by humans.
- etiolation
- Weak growth due to lack of light, resulting in elongated stems and yellowish color.[35]
- even-pinnate
- Having an even number of leaflets in a compound leaf; synonymous with paripinnate.
- evergreen
- Not deciduous; having leaves all year.
- ex
- In nomenclature, indicating that the preceding author proposed the name but did not legitimately publish it, and that the succeeding author referred to the first author when legitimately publishing the name. See Author citation (botany).
- exalbuminous
- In seeds of a given species, having no endosperm, i.e. no albumen, e.g. in Fabaceae and Combretaceae.
- exocarp
- The outer layer of the pericarp, often the skin of fleshy fruits.
- exospory
- The production of spores that germinate into free-living multicellular gametophytes. Contrast endospory.
- exotesta
- The outer layer of the testa (seed coat). It is derived from the outer integument of the ovule.
- exotic
- Not native; introduced from another region or country.
- exserted
- Projected beyond, e.g. stamens beyond the corolla tube.
- exstipulate
- Lacking stipules.
- extrastaminal
- Outside the stamens or androecium, usually referring to the location of a nectary disk.
- extrorse
- (of anther locules) Opening toward the outside of the flower. Contrast introrse and latrorse.

Plants of the genus Corydalis bear seeds with attached elaiosomes, which have various functions, commonly attracting ants. On some Corydalis species, elaiosomes that attract ants also repel mice.[32]

Ficus lyrata is an example of a doubly-emarginate leaf with lateral and apical emargination; it also might be seen as a basally emarginate.

Petals of Heracleum sphondylium are variously emarginate at their tips. Flowers in the middle of the inflorescence have slightly emarginate petals, whereas flowers at the periphery are so deeply emarginate as to be almost cleft in two.



Iris pseudacorus has clearly ensiform leaves: narrow, straight-edged, sword-shaped.



Tillandsia recurvata growing as a harmless, non-parasitic epiphloedal epiphyte on a tree trunk that is also infested with an epiphloedal foliose lichen

Seeds or fruits are dispersed by epizoochory when they stick to the fur of animals.

The bases of equitant leaves enclose later leaves on the stem.

Sections of exalbuminous seeds

Aloe marlothii flowers with stamens and stigmata of mature flowers exserted from the mouths of the floral tubes
F
[edit]- F1 hybrid
- A single cross; a plant breeding term for the result of a repeatable cross between two pure bred lines.
- F2 hybrid
- A plant breeding term for the result of a plant arising from a cross between two F1 hybrids; may also refer to self-pollination in a population of F1 hybrids.
- fabiform
- Shaped like a kidney bean.
- facultative
- Able to perform a particular life function, or to live generally, in more than one way.[36] Compare obligate.
- falcate
- Curved like the blade of a scythe.
- family
- A taxonomic group of one or more genera with features, ancestry, or both in common. It is the term for the principal rank between order and genus.
- farina
- Powdery, pale yellow, crystalline secretion consisting of flavonoids in Primula and other species.
- farinaceous
- Powderiness that is mealy.
- fascicle
A cluster of flowers, leaves, needles, vascular tissue, etc., e.g. a tuft of leaves all arising from the same node.
- fasciculate
- Branching in clusters, e.g. a bundle of sticks or needles; having fascicles.
- fastigiate
- 1. In Plant morphology, the habit of a plant that consists in part, of a bundle of erect, more or less parallel branches or stems, particularly if they form or taper to a peak or point. (Latin fastigiatus,meaning "having a peak".
- 2. In palynology, the form of a pollen grain that has a fastigium, a pointed apex over a hollow between the layers of the pollen outer wall.
- faucal
- Pertaining to the fauces; located in the throat of a calyx or corolla.
- fauces
- The throat of a calyx or corolla; the conspicuously widened portion between the mouth and the apex of the tube. In Boraginaceae, the site of distinctive appendages.
- faveolate
- Honeycombed; having regular, angled pits. Compare foveolate.
- felted
- Having interlocked hairs to the extent of being matted.[28]
- female flower
- See pistillate flower.
- fenestrate
- Having translucent or transparent areas that let light through; this variously affects the behavior of animal visitors or permits photosynthesis in many arid-region plants that grow only to the soil surface. Also refers loosely to perforations, for which perforate is the more precise term.
- ferruginous
- Ruddy or rust-colored.
- fertile
- Capable of producing fruit; of flowers when they produce seed, or of anthers containing pollen.
- fertilization
- The union of male and female gametes during sexual reproduction.
- fiber
- 1. A fiber cell.
- 2. Any flexible, strong, stringy, and very elongate structure.
- fiber cell
- A type of cell that is found in sclerenchyma; it is much elongated, and dies soon after an extensive modification of its cell wall. The cell wall is usually thickly lignified but is sometimes gelatinous.
- filament
- 1. The stalk of a stamen.
- 2. Any very narrow, thread-like structure that is one or a few cells thick.
- filamentous
- Consisting of filaments or fibers; hairlike.
- filiform
- Thread-like, e.g. stamen filaments or leaf shapes.
- fimbria
Slender, hair-like projection; fringe.
- fimbriate
- Fringed, e.g. where the ends of a petal are split into two or more divisions.[37] Having fimbriae.
- fissure
- A split or crack, often referring to fissured bark; a line or opening of dehiscence.
- fistule
- A tube-shaped cavity.
- fistulose
- Hollow; usually applied to a tube-shaped cavity, as in a reed.
- flabellate
- Fan-shaped, e.g. a flabellate (fan-shaped) leaf.
- flaccid
- Limp; tending to wilt. Compare turgid.
- flexistyly
- Depending on the degree of maturation of the stamens, the style moves up or down (cataflexistyle or (ana-)hyperflexisyle).
- flexuous
- flexuose
- Bent alternately in different directions; zigzag.
- floccose
- Having a soft and wooly covering of hairs.
- flora
- 1. All the plants growing in a certain region or country.
- 2. An enumeration of them, generally with a guide to their identification (e.g. the Flora of North America, Flora of China, Flora of Victoria, Flora of New South Wales, and so on). In this case, flora is written with a capital F.
- floral envelope
- See perianth.
- floral leaves
- The upper leaves at the base of the flowering branches.
- floral diagram
- A graphical means to describe flower structure, usually a schematic cross-section through a young flower.
- floral formula
- A description of flower structure using numbers, letters, and various symbols.
- floral tube
- An imprecise term sometimes used as a synonym of hypanthium, corolla tube, or calyx tube.
- floret
- A small flower, usually referring to the individual true flowers clustered within an inflorescence, particularly those of the Poaceae grasses and the pseudanthia of family Asteraceae.
- flower
- The sexual reproductive structure of the angiosperms, typically with a gynoecium, androecium, perianth, and an axis.
- foliate
- Preceded by a number to signify having a certain number of leaflets, e.g. 3-foliate means "having three leaflets".
- foliicolous
- A growth habit of certain lichens, algae, and fungi that prefer to grow on the leaves of vascular plants.
- follicle
- A dry fruit formed from one carpel splitting along a single suture to which the seeds are attached, e.g. from the pod of a legume.[38]
- foliole
- A small, leaf-like appendage on the front or back.[of what?]
- foliose
- Leaf-like; flattened like a leaf.
- forb
- Any non-woody flowering plant that is not a grass, sedge, or rush.
- forest
- Vegetation dominated by trees with single trunks, including closely arranged trees with or without an understory of shrubs and herbs.
- forma (in common usage, form)
- A taxonomic category subordinate to species and within the taxonomic hierarchy, below variety (varietas), and usually differentiated by a minor character.
- foveolate
- Having regular tiny pits. Compare faveolate.
- free
- Not united with other organs of the same type; not attached at one end.
- free central
- (of placentation) Ovules attached to a free-standing column in the center of a unilocular ovary.
- frond
- A leaf of a fern, cycad, or palm.
- frutescent
- Shrub-like (fruticose) or becoming shrub-like.
- fruticose
- Shrubby; having the branching character of a shrub.
- fruit
- A seed-bearing structure, present in all angiosperms, formed from the mature ovary and sometimes associated floral parts upon fertilization.
- fugacious
- Disappearing, falling off, or withering. Compare persistent and caducous.
- funicle (funiculus)
- The stalk of an ovule.
- funnelform
- Having a form gradually widening from the base to the apex; funnel-shaped.
- furcate
- Forked, usually applied to a terminal division; with two long lobes.
- fused
- Joined together.
- fusiform
- Rod-shaped and narrowing gradually from the middle toward each end; spindle-shaped.

Astragalus falcatus has conspicuously falcate pods; not many falcate anatomical structures are so markedly curved.

Rhigozum obovatum bears its leaves in well-defined fascicles.


Favolaschia calocera, the orange pore fungus, has conspicuously faveolate fruiting bodies.

Emerging leaves of Oldenburgia grandis are heavily felted.

Fenestrate leaves of Darlingtonia californica

In the wild, the leaves of Fenestraria commonly are covered in soil, except for the transparent fenestration; this permits photosynthesis while reducing damage from exposure to intrense sunlight and herbivores.

Digitalis ferruginea owes its specific name to its ferruginous (rust-colored) flowers.

Calochortus fimbriatus has fimbriate flowers.


The pseudanthium of Zinnia elegans is typical of many Asteraceae in that it includes two types of florets, ray florets and disk florets.


Foveolate seeds of Physochlaina physaloides
G
[edit]- galbulus
- In gymnosperms, a fleshy cone (megastrobilus); chiefly relates to cones borne by junipers and cypresses, which are often mistakenly called berries.
- galea
- An overhanging, helmet-shaped, structure that protects the reproductive parts from precipitation, wind or unwanted visitors.
- gall
- Abnormal outgrowth on external plant tissues, caused by various parasites, from viruses, fungi and bacteria, to other plants, insects and mites.
- gamete
- A cell or nucleus that fuses with another of the opposite sex during sexual reproduction.
- gametophore
- Specialized structures on the gametophytes of some bryophyte species, for example many species in the order Marchantiales; in such species the gametes are produced on the gametophores.
- gametophyte
- The haploid multicellular phase in the alternation of generations of plants and algae that bears gametes. In bryophytes the gametophyte is the dominant vegetative phase; in ferns and their allies it is a small free-living plant known as the prothallus; in gymnosperms and angiosperms the gametophytes are reduced to microscopic structures dependent on the sporophyte, male gametophytes contained in pollen grains and females contained within the ovules.
- gamopetalous
- with joined or fused petals
- gamophyllous
- a single perianth-whorl of united segments. Compare symphyllous (synonym), apophyllous, and polyphyllous.
- gemma
- an asexual reproductive structure found in liverworts and mosses.
- gene pool
- The complete range of genetic variation found within a population.
- genus
A group of one or more species with features or ancestry (or both) in common. Genus is the principal category of taxa intermediate in rank between family and species in the standard nomenclatural hierarchy.
- generic name
- The name of a taxonomic genus, such as Acacia and Eucalyptus.
- genotype
- The genetic make-up of an individual.
- geophilous
- Growing or rooting in the ground.
- germination
- 1. of seeds, describing the complex sequence of physiological and structural changes that occur from resting to growth stage.
- 2. of a pollen grain; production of a pollen tube when contacting a stigma receptive to it.
- 3. of a spore of fungi/bacterium; change of state – from resting to vegetative.
- gibbous (gibbose)
- (of part of an organ) Swollen, usually with a pouch-like enlargement at the base.
- glabrescent
- Becoming glabrous, almost glabrous; glabrate.
- glabrous
- Lacking surface ornamentation such as hairs, scales or bristles; smooth.
- gland
- A secretory structure within or on the surface of a plant.
- glandular hair
- A hair tipped with a gland.
- glaucous
- Describing the external surface of a plant part that has a whitish covering, in some cases with a blueish cast. Often applied to plants with a wooly or arachnoid surface, but properly referring to pruinose surfaces, meaning those with a waxy bloom. The surfaces of the young leaves of many eucalypts provide good examples, and so do some xerophytes.
- globose
Roughly spherical. See also subglobose.
- globulose
- Approximately spherical.
- glochid
- A tiny barbed hair or bristle, e.g. the fine defensive hairs in cactus species such as Opuntia.
- glumes
- bracts subtending the floret(s) of a sedge, or similar plant; in grasses forming the lowermost organs of a spikelet (there are usually 2 but 1 is sometimes reduced; or rarely, both are absent).
- glutinous
- Sticky.
- graft
- 1. The artificial union of plant parts.
- 2. A plant shoot suitable for grafting; loosely, a scion, sucker, or branch.
- graft chimaera (sometimes graft hybrid)
- A taxon whose members consist of tissue from two or more different plants in intimate association originated by grafting. The addition sign "+" is used to indicate a graft-chimaera either as a part of a formula (e.g. Crataegus monogyna + Mespilus germanica) or in front of an abbreviated name (e.g. + Crataegomespilus 'Dardari'). The nomenclature of graft hybrids is governed by the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants.
- graminaceous
Of or relating to grass.
- graminoid
- An herbaceous plant with a grass-like morphology.
- granular
- (of a surface) Covered with small rounded protuberances.
- grass
- A plant of the family Poaceae.
- grassland
- Low vegetation dominated by grasses.
- groundcover
- 1. Dense vegetation that covers the ground.
- 2. A term applied to describe a plant that covers the soil surface so densely that it smothers all beneath it.
- group
- A formal category equivalent to or below the rank of genus which distinguishes
- an assemblage of two or more cultivars within a species or hybrid;
- plants derived from a hybrid in which one or more of the parent species is not known or is of uncertain origin; or,
- a range of cultivated plants of a species or hybrid which may exhibit variation but share one or more characters, which makes it worth distinguishing them as a unit.
- guard cell
- Each of two cells surrounding the stoma which control gas exchange between the apoplast of the plant and the external environment.
- guttate
- Having droplet-shaped spots. Compare punctate and maculate.
- guttation
- The secretion of liquid water from uninjured plant parts. See hydathode.
- guttulate
- Having or appearing to be spotted with oil droplets; of spores, having oil droplets inside.
- gymnosperm
- A seed-bearing plant with unenclosed ovules borne on the surface of a sporophyll. Gymnosperms are among the oldest clades of vascular plants, and today are represented by approximately 1,000 extant species worldwide, including, among others, conifers, Ginkgo, Gnetum and cycads. Compare angiosperm.
- gynaecium
- Alternative term for gynoecium, but with partly different etymology.
- gynobasic
- Of a style, arising near the base of the gynoecium, e.g. between the lobes of the ovary.
- gynodioecious
- Of a species, with some plants bearing only bisexual flowers and others bearing only female flowers.
- gynomonoecious
- Of a species, with bisexual flowers and female flowers on the same plant.
- gynoecium
- The collective term for the female reproductive parts of a flower or for the carpels of a flower, whether united or free. Contrast androecium. Abbreviation: G. For instance, G indicates a superior ovary; G(5) indicates having five fused carpels.
- gynophore
- A stalk supporting the gynoecium and situated above the level of insertion of the other floral parts.
- gynostegium
- A compound organ in milkweeds (Asclepiadaceae) and orchids formed by fusion of the filaments of the stamens with the style. Also known as the column.


Gametophores (red male antheridia and brown female archegonia) borne on a gametophyte of a Chara species of green algae

Longitudinal section of immature male pine cone, showing male gametophytes (pollen grains) developing between the cone scales

Glandular hairs on the stem of Geranium dissectum

The leaves, buds, and young stalks of Eucalyptus macrocarpa are glaucous, covered with a thick waxy pruinosity.


Glumes of a grass species with a fairly large inflorescence

Scanning electron micrograph of a stoma on the leaf of Haemanthus. The two lip-shaped cells on either side of the pore are the guard cells.


Examples of gymnosperms
LEFT1-Welwitschia mirabilis
2-Cycas revoluta
3-Taxus baccata
4-Ginkgo biloba
RIGHT
1-Cupressus sempervirens
2-Sequoiadendron giganteum
3-Agathis dammara
4-Araucaria heterophylla
H
[edit]- habit
- The general external appearance of a plant, including size, shape, texture, and orientation.
- habitat
- The place where a plant lives; the environmental conditions of its home.
- hair
- A single elongated cell or row of cells borne on the surface of an organ.
- half-inferior ovary
- An ovary partly below and partly above the level of attachment of the other floral parts. Compare inferior ovary and superior ovary.
- halonate
- Having a transparent coating, or being of a spore's outer layer.
- halophyte
- A plant adapted to living in highly saline habitats; a plant that accumulates high concentrations of salt in its tissues.
- hand-pollination
- The controlled act of pollination that excludes the possibility of open-pollination.
- haploid
- Having one set of chromosomes, e.g. the complement of chromosomes in each of the cells of the gametophyte, the nucleus of a gamete, and the spores. This is expressed symbolically as n, where n = the gametic number of chromosomes. Compare diploid, triploid, and tetraploid.
- haplostemonous
- Having a single series of stamens equal in number to the proper number of petals, and alternating with them. Compare diplostemonous and obdiplostemonous.
- harmomegathy
- process by which pollen grains in arid environments close off their apertures to avoid losing water
- hastate
- Triangular in outline, the basal lobes pointing outward, so that the base appears truncate; may refer only to the base of a leaf with such lobes. Compare sagittate, which refers to basal lobes pointing backward.
- haustorium
- In parasitic plants, a structure developed for penetrating the host's tissues.
- head
- See capitulum, a pseudanthium.
- heathland
- Vegetation dominated by small shrubs which usually have ericoid leaves.
- helicoid
- Coiled; of a cymose inflorescence, when the branching is repeatedly on the same side (the apex is often recurved). Compare scorpioid.
- heliophilous
- Requiring or tolerating strong, direct sunlight.
- hemerochory
- A plant that has been transported voluntarily or involuntarily by humans in a territory which it could not have colonized by its own natural mechanisms of dissemination, or at least much more slowly.[34]
- hemi-legume
- A legume fruit in which the seed or seeds and one valve of the pod are dispersed as a unit. The valve catches the wind and blows away with the seeds, as in Acacia tenuifolia and Peltogyne paniculata.
- herb
- Any vascular plant that does not develop a woody stem at any point during its life cycle, e.g. a daffodil.
- herbaceous
- Not woody; usually green and soft in texture.
- herbarium
A collection of preserved, usually pressed and dried, plant material used for identification and comparison; also a building in which such collections are stored.
- hermaphrodite
- A synonym of bisexual.
- hesperidium
- A form of berry that occurs most familiarly in the genus Citrus. The fruit tends to be large for a berry, ranging from not much more than a centimeter in small fruited genera such as Murraya, to 15 cm or more in some varieties of Citrus. The outer rind typically is thick and tough with many oil glands, while the carpels within are packed with juicy fibers.
- heteroblastic
- Having parts, especially leaves, that are distinctly different between the juvenile and adult stages.
- heterophyllous
- Having more than one leaf type on the same plant. For example, leaves adapted to the open air and leaves adapted to being under water in Ranunculus aquatilis.[39]
- heterophylly
- A plant which is heterophyllous.[40]
- heteromorphic
- Having two or more distinct morphologies (e.g. of different size and shape). Compare isomorphic.
- heterospory
- The production of spores of two different sizes (small and large) by the sporophytes of land plants. Compare homospory.
- heterostyly
- The condition of a species having flowers with different style and stamen lengths, but with all the flowers of any one plant being identical. See distyly.
- hilum
- The scar on a seed coat where it separates from its stalk (funicle).
- hip
- The fruit of a rose plant.
- hippocrepiform
- Horseshoe-shaped.
- hirsute
- Bearing coarse, rough, longish hairs. See indumentum.
- hispid
- Bearing long, erect, rigid hairs or bristles, harsh to touch.
- hoary
- Covered with a greyish to whitish layer of very short, closely interwoven hairs, giving a frosted appearance.
- holotype
- A type chosen by the author of a name. Compare lectotype.
- homochlamydeous
- Having a perianth which is not divided into a separate calyx and corolla. Contrast dichlamydeous.
- homospory
- The production of spores of only one size by the sporophytes of land plants. Compare heterospory.
- hort.
Of gardens, an author citation used in two ways:
1. as a name misapplied by gardeners- 2. as an invalid name derived from horticultural writings of confused authorship.
- husk
- Protective outer covering of certain seeds, for example, the leafy outer covering of an ear of maize (corn), the leathery covering of the walnut, or the spiky covering of the chestnut.
- hyaline
- Translucent; usually delicately membranous and colorless.
- hybrid
- Plant produced by the crossing of parents belonging to two different named groups, e.g. genera, species, varieties, subspecies, forma and so on; i.e. the progeny resulting within and between two different plants. An F1 hybrid is the primary product of such a cross. An F2 hybrid is a plant arising from a cross between two F1 hybrids (or from the self-pollination of an F1 hybrid).
- hybrid formula
- The names of the parents of a hybrid joined by a multiplication sign, e.g. Cytisus ardonoi × C. purgans.
- hydrophily
- Form of pollination whereby pollen is distributed by the flow of waters.
- hypanthium
- Tube or cup-like structure in a flower that includes the bases of sepals, petals, and stamens, and may or may not be connected (adnate) to the ovary.
- hyper-resupinate
- In botany, describing leaves or flowers that are in the usual position but are borne on a petiole or pedicel that is twisted 360 degrees. The term is used to describe organs, such as orchid flowers, that are usually resupinate. Compare resupinate.
- hypocarpium
- Enlarged fleshy structure that forms below the fruit from the receptacle or hypanthium.
- hypocotyl
- Of an embryo or seedling, the part of the plant axis below the cotyledon and node, but above the root. It marks the transition from root to stem development.
- hypocrateriform
- Salver-shaped. Synonym of salverform. From Greek kratḗrion: a vessel.
- hypogynous
- Borne below the ovary; used to describe floral parts inserted below the ovary's level of insertion. Compare epigynous and perigynous.
- hysteranthous
- Type of growth in which new leaves appear after flowering. Also spelled histeranthous. Compare proteranthous and synanthous.

Epidermal hairs on plant leaves

Multicellular hairs on the edge of a sepal of Veronica sublobata


Markedly hastate leaf of Salvia canariensis

The swollen haustorium of Viscum capense renders the end of the branch stunted compared to the lower part of the branch.

The fruit of Poncirus is a typical hesperidium.

Heteroblastic growth is common in Eucalyptus species with leaves that are isobilateral in the mature tree; they generally start life with dorsiventral leaves. Some of these saplings are in the transient stage in which they have both forms of leaves, dorsiventral on lower branches, and isobilateral above.


A hypocarpium forms below the fruits of Sassafras albidum.

Flowers, fruit and propagule of a Rhizophora "mangle" or mangrove. The apparent root of the propagule is in fact meristematic tissue developing from the hypocotyl. The new plant develops largely from this tissue, especially if it has successfully penetrated into mud in which the new plant can establish itself.
I
[edit]- idioblast
- A cell, especially of a leaf, differing markedly from surrounding cells. They often synthesise specialized products such as crystals.
- illegitimate name (nomen illeg.)
- A name not abiding by the rules of the botanical Codes, e.g. later homonyms, cultivars that have been Latinised after 1 Jan 1959; cultivar names with more than 10 syllables or 30 letters; cultivar names that use confusing names of other plants, e.g. Camellia 'Rose'.
- imbricate
- From the Latin for "tiled". Overlapping each other; of perianth parts, edges overlapping in the bud (the convoluted arrangement is a special form of imbrication). Dormant buds of many deciduous species are imbricately covered with protective cataphylls called bud scales. Compare with subimbricates meaning lightly overlapping
- imparipinnate
- A pinnate leaf with an odd number of pinnae (terminated by a single leaflet). Compare paripinnate.
- in
- In nomenclature, where the preceding author published the name in an article or book, authored or edited by the succeeding author.
- -inae
- The suffix added to the stem of a generic name to form the name of a subtribe: for instance, Corydalinae from Corydalis + -inae.
- inbreeding
- The production of offspring between closely related parents leading to a high degree of similarity; self-fertilization is the most intense form of inbreeding.
- incertae sedis
- Of unknown taxonomic affinity; relationships obscure.
- incised
- Cut deeply and (usually) unevenly (a condition intermediate between toothed and lobed).
- included
- Enclosed, not protruding, e.g. stamens within the corolla.
- incomplete flower
- A flower which lacks one or more of its usual parts, such as carpels, sepals, petals, pistils, or stamens.
- incurved
- Bent or curved inward; of leaf margins, when curved toward the adaxial side.
- ined.
- An abbreviation of Latin inedita, an unpublished work. Used to indicate that a botanical name appeared only in a manuscript that was not published, so the name is invalid.
- indefinite
- variable in number, and as a rule numerous, e.g. more than twice as many stamens as petals or sepals, but no particular standard number of stamens. In another usage it is a synonym for the preferable term indeterminate, meaning the condition in which an inflorescence is not terminated by a flower, but continues growing until limited by physiological factors. Compare numerous. Contrast definite.
- indehiscent
- Not opening in any definite manner at maturity; usually referring to fruit. Contrast dehiscent.
- indeterminate
- usually referring to a stem or inflorescence in which there is no particular terminal bud or meristem that stops growth and ends the extension of the stem, which continues until physiological factors stop the growth. Racemes of some Xanthorrhoeaceae, such as many Aloes, and of many Iridaceae, such as Watsonias, are indeterminate. Contrast determinate.
- indigenous
- Native to the area, not introduced, and not necessarily confined to the region discussed or present throughout it (hardly distinct from ‘native' but usually applied to a smaller area). For example, the Cootamundra Wattle is native to Australia but indigenous to the Cootamundra region of southern New South Wales. Compare endemic.
- indumentum
- Collective term for a surface covering of any kind of trichomes, e.g. hairs, scales.
- induplicate
- Folded upward, or folded with the two adaxial surfaces together.
- indusium
- 1. Membrane covering the sori of some ferns.[41]
- 2. Cup enclosing the stigma in Goodeniaceae.[41]
- inferior ovary
- An ovary at least partly below the level of attachment of other floral parts. Compare superior ovary and half-inferior ovary.
- inflated
- Swollen, like a bladder.
- inflexed
- Bent sharply upward or forward. Compare deflexed.
- inflorescence
- several flowers closely grouped together to form an efficient structured unit; the grouping or arrangement of flowers on a plant.
- infraspecific
- denotes taxonomic ranks below species level, for example subspecies.
- infrageneric
- denoting taxonomic ranks below the genus level, for example, subgenera, sections, and series.
- infructescence
- the grouping or arrangement of fruits on a plant.
- infundibular (infundibuliform)
- funnel-shaped, for example in the corolla of a flower.
- inrolled
- rolled inward.
- insectivorous
- catching, and drawing nutriment from, insects.
- insertion, point of
- The point at which one organ or structure (such as a leaf) is joined to the structure which bears it (such as a stem).
- inserted
- growing out from
- integument
- in general, any covering, but especially the covering of an ovule.
- intercalary
- (e.g. of growth) occurring between the apex and the base of an organ
- intercalary meristem
- a meristem located between the apex and the base of an organ
- interjugary glands
- in pinnate leaves, glands occurring along the leaf rachis between the pinnae (occurring below the single, and often slightly larger, gland at or just below the insertion of the pinnae). Compare jugary.
- internode
- The portion of a stem between two nodes.
- interpetiolar
- (of stipules) Between the petioles of opposite leaves, e.g in Rubiaceae.
- intramarginal
- inside but close to the margin. For example, an intramarginal vein is one that parallels, and is very close to, the leaf margin.
- intrastaminal
- inside the stamens or androecium, usually referring to the location of a nectary disk.
- introrse
- of anther locules, with opening toward the center of flower (at least in bud). Compare extrorse and latrorse.
- invalid
- Use of names not validly published according to the Code, i.e. they are not strictly 'names' in the sense of the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature.
- involucre
- A structure surrounding or supporting, usually a head of flowers. In Asteraceae, it is the group of phyllaries (bracts) surrounding the inflorescence before opening, then supporting the cup-like receptacle on which the head of flowers sits. In Euphorbiaceae it is the cuplike structure that holds the nectar glands, nectar, and head of flowers, and sits above the bract-like cyathophyll structure. Involucres occur in Marchantiophyta, Cycads, fungi, and many other groups.
- involute
- Rolled inward, for example when the margins of a leaf are rolled toward the adaxial (usually upper) surface. Compare revolute.
- iridescent
- Having a reflective colored sheen produced by structural coloration, as in the speculum of the mirror orchid Ophrys speculum.
- irregular
- Not able to be divided into two equal halves through any vertical plane. See also asymmetrical. Compare zygomorphic, actinomorphic, and regular.
- isobifacial
- (of flat structures, especially leaves) Having both surfaces similar, usually referring to cell types or to the number and distribution of stomata.
- isomerous
- Having an equal number of parts in the whorls.
- isomorphic
- with all features morphologically similar, i.e. of similar size and shape. Compare heteromorphic.
- isotomic
- Having branches of equal diameter. Compare anisotomic.


Petals of Mespilus germanica are imbricate before the flower opens.

Doubly imparipinnate compound leaf of Melia azedarach

Deeply incised leaves of Pelargonium graveolens

Indefinite stamens of Hypericum

Indehiscent pods of Libidibia ferrea; unlike most Fabaceae species, the plant depends on the pods being crushed by large ungulates to disperse the seeds.


The leaves of Syagrus palms are 'induplicately folded, in contrast to many other palm genera with reduplicate leaves.

Stamens of Calotropis gigantea are inserted at the base of the corolla.

The intramarginal veins near the margins of this leaf are outlined in white.

Two of these three green Asteraceae involucres encase unopened flower heads, and the third supports the open colorful head of emerging flowers. The imbricate phyllaries around the heads of this Malacothrix coulteri suggest the keeled scales of a snake, giving the plant its common name: "snake's head".

This Begonia leaf shows unusual iridescence for a plant.
J
[edit]- joint
- A node or junction of two parts; articulation.
- jugary
- associated with a jugum or something yoke-like; see for example jugary gland.
- jugary gland
- A gland occurring on the rachis of a pinnate or bipinnate leaf on a jugum, the junction or attachment of pairs of pinnae or pinnules, as in some Acacia species. Compare interjugary.
- jugate
- yoke-like; describing a structure of paired items joined together as in a jugum or something yoke-like, such as some leaves and fruit.
- jugum
- applied to various yoke-like organs, usually in the sense of their being paired, such as a pair of pinnae on a rachis.
- juvenile leaves
- Leaves formed on a young plant, typically differing from the adult leaves in form.

Vachellia karroo bipinnate leaf
A. Rachilla
B. Pinnule
C. Jugary glands
D. Juga (plural of jugum)
E. Base of petiole
F. Petiolary gland
G. Rachis

Jugate leaf of Bauhinia glabra

Jugate fruit of Tabernaemontana elegans

K
[edit]- keel
A prominent longitudinal ridge like the keel of a boat, e.g. the structure of the corolla formed by the fusion of the lower edge of the two abaxial anterior petals of flowers in the Fabaceae.
- kernel
- See drupe.
- kettle trap
- another term for the kettle-like pitchers of any of the carnivorous pitcher plants, in which they trap their prey.
- key innovation
- A novel phenotypic trait that allows subsequent evolutionary radiation and success of a taxonomic group.
- kidney shape
- A term describing a kidney-shaped object such as a bean or a leaf; more formally, oblately cordate, or crescent-shaped with the ends rounded.
- kingdom
- the highest generally employed category of the taxonomic hierarchy, above that of division (phylum). The Plant Kingdom includes vascular plants, bryophytes and green algae and is also known as the clade Viridiplantae.
- Klausenfrucht
- Klausen or Klausenfrucht (german) is a special type of fruits in Lamiaceae and Boraginaceae. A dry, dehiscent fruit formed from a superior ovary with axil or basal placentation, with an adherent calyx, from more than one carpel and usually breaking apart into 1-seeded units by separating each carpel by false septa. One unit is a half carpel, mostly there are four units, seeds. English terms are eremocarp, schizocarp, mericarp or nutlets.
- knee
- abrupt bend in a root or stem, commonly at a node; a cypress knee, or pneumatophore, is a type of bend or knob in the root of some plants, especially conifers such as some of the Taxodioideae, that shows as a projection of the root above ground level or mud level.

One form of the kettle traps of a pitcher plant

Kidney-shaped leaf of Cucurbita maxima

Typical knee at a node in a grass stem

Unusually dense stand of cypress knees around the parent tree
L
[edit]- labellum
- lip; one of three or five petals which is (usually) different from the others, e.g. in Orchidaceae, Zingiberaceae, Cannaceae and Stylidiaceae.
- labiate
- lipped; where a corolla is divided into two parts, called an upper and lower lip, the two resembling an open mouth with lips.
- lacerate
- jagged, as if torn.
- laciniate
- Of lobes – with ends irregularly divided into deeply divided, narrow, pointed segments; Of margins – deeply divided into pointed segments in an irregular manner.
- lacuna
- An empty space, hole, cavity, pit, depression, or discontinuity.
- lamella
Thin, plate-like layer.
Composed of an assemblage of many layers.
- lamina
- the blade of a leaf or the expanded upper part of a petal, sepal or bract.
- lanate
- covered in or composed of wooly hairs.
- lanceolate
- longer than broad, narrowly ovate, broadest in the lower half and tapering to the tip, like a lance or spear head; (sometimes, and incorrectly, used to mean narrowly elliptic).
- lanuginose
- covered in long hairs that cross and/or interweave with each other. More commonly the term lanate is used.[42]
- lateral
- attached to the side of an organ, e.g. leaves or branches on a stem. For more detail see dorsal.
- latex
- a milky fluid that exudes from such plants such as spurges, figs and dandelions.
- laticiferous
- latex-bearing, producing a milky juice.
- latrorse
- a type of anther dehiscence in which the anthers open laterally toward adjacent anthers. Compare introrse and extrorse.
- lauroid
- resembling Laurus, the laurel genus, particularly its leaves.
- lax
- loose, not compact.
- leaf
- an outgrowth of a stem, usually flat and green; its main function is food manufacture by photosynthesis. Abbreviation: lvs.
- leaf gap
- a parenchymatous area in the stele above (distal to) a leaf trace.
- leaf scar
- A healing layer forming on a stem where a leaf has fallen off.
- leaf trace
- A vascular bundle connecting the stele to a leaf.
- leaflets
- The ultimate segments of a compound leaf.
- legume
- 1. a fruit characteristic of the family Fabaceae, formed from one carpel and either dehiscent along both sides, or indehiscent.
- 2. a crop species in the family Fabaceae.
- 3. a plant of the family Fabaceae.
- lemma
- the lower of 2 bracts enclosing a grass flower.
- lenticel
- Typically lenticular (lens-shaped) porous tissue in bark with large intercellular spaces that allows direct exchange of gases between the internal tissues and atmosphere through the bark.
- lenticellate
- Having lenticels
- lenticular
- 1. lens-shaped.
- 2. covered in lenticels.
- lepidote
- covered with small scales.
- leprose
- powdery
- liana
- a woody climbing plant, rooted in the ground (liane is also used).
- liane
- a woody climbing plant, rooted in the ground. See also liana.
- ligneous
- having hard lignified tissues or woody parts, woody
- lignum
- Dead wood, typically in the context of a substrate for lichens.
- lignicolous
- Growing on wood tissue after bark as fallen or been stripped off (compare to corticolous).
- lignotuber
- a woody swelling of the stem below or just above the ground; contains adventitious buds from which new shoots can develop, e.g. after fire.
- ligulate
- 1. bearing a ligule.
- 2. strap-shaped.
- ligule
- 1. A small membranous appendage on the top of the sheath of grass leaves.
- 2. A minute adaxial appendage near the base of a leaf, e.g. in Selaginella.
- 3. An extended, strap-like corolla in some daisy florets.
- linea, line, British line, Paris line
- Various pre-metric units somewhat larger than 2 mm, used in botany into the 20th century. See Line (unit) and Paris line.
- linear
- Very narrow in relation to its length, with the sides mostly parallel. See Leaf shape.
- lingulate
- tongue-shaped.
- lip
- A labellum.
- lithophytic
- A plant growing on rocks; an epilithic plant.
- lobe
- Part of a leaf (or other organ), often rounded and formed by incisions to about halfway to the midrib.
- lobulate
- Having, consisting of or relating to a lobe or lobes.
- loculicidal
- (of a fruit) Dehiscing through the centers of loculi. Compare septicidal.
- locule
- A chamber or cavity containing seeds within an ovary, pollen within an anther or spores in a sporangium.
- lodicule
- One of two or three minute organs at the base of the ovary of a grass flower, representing parts of a strongly reduced perianth.
- lomentum or loment
- A pod-like indehiscent fruit that develops constrictions between the segments and at maturity breaks into one-seeded segments instead of splitting open.
- longicidal
- (of anthers) Opening lengthwise by longitudinal slits. Compare poricidal.
- lunate
- Crescent-shaped.
- lumen
- The cavity bounded by a plant cell wall.
- lyrate
- Lyre-shaped; deeply lobed, with a large terminal lobe and smaller lateral ones.

Labiate flowers of Prunella vulgaris

Laciniate, deeply incised, leaves of Pelargonium crispum

Most Euphorbias are laticiferous and instantly exude latex when even mildly punctured.

A leaf scar on Juglans regia, showing the layer of corky protective tissue that remained after the leaf separated along the abscission zone. It also shows the leaf traces of the vascular bundles that broke off when the abscission zone failed. The axillary bud associated with the leaf shows just above the scar.

The dark horizontal lines on silver birch bark are lenticels.

Lignotubers of Lambertia formosa growing sprouts after a bush fire

Ligule between the leaf sheath and leaf of a grass

Loculicidal dehiscence of a fruit capsule. The locule walls split at the back, and the valves separate, bearing the septa on their centers.

M
[edit]- maculate
- Spotted; marked with spots.
- male flower
- See staminate flower.
- mallee
- A growth habit in which several woody stems arise separately from a lignotuber; a plant with such a growth habit, e.g. many Eucalyptus species; vegetation characterized by such plants.
- mangrove
- Any shrub or small tree growing in salt or brackish water, usually characterized by pneumatophores; any tropical coastal vegetation characterized by such species.
- margin
- The edge of a structure, as in the edge of a leaf blade.
- marginal
- Occurring at or very close to a margin.
- marsh
- A waterlogged area or swamp.
- mast
- Edible fruit and nuts produced by woody species of plants (e.g. acorns and beechmast) which is consumed on the ground by wildlife species and some domestic animals.
- mealy
- Covered with coarse, floury powder.
- medulla
- pith. See also medullary rays in wood.
- megasporangium
- the larger of two kinds of sporangium produced by heterosporous plants, producing large spores that contain the female gametophytes. Compare microsporangium.
- megaspore
- the larger of two kinds of spores produced by a heterosporous plant, giving rise to the female gametophyte. Compare microspore.
- megasporophyll
- in hetersoporous plants, a modified leaf bearing one or more megasporangia. Compare microsporophyll.
- megastrobilus
- the larger of two kinds of cones or strobili produced by gymnosperms, being female and producing the seeds. Compare microstrobilus.
- membranous
- thin, translucent and flexible, seldom green.
- mericarp
- one segment of a fruit (a schizocarp) that splits at maturity into units derived from the individual carpels, or a carpel, usually 1-seeded, released by the break-up at maturity of a fruit formed from 2 or more joined carpels.
- meristem
- Any actively dividing plant tissue.
- mesic
- Moist, avoiding both extremes of drought and wet; pertaining to conditions of moderate moisture or water supply; applied to organisms (vegetation) occupying moist habitats.
- mesocarp
- The fleshy portion of the wall of a succulent fruit inside the skin and outside the stony layer (if any), surrounding the seed(s); sarcocarp.
- mesomorphic
- Soft and with little fibrous tissue, but not succulent.
- mesophyll
- 1. The parenchyma tissues between the upper and lower epidermis. They vary in function, but usually include the photosynthetic tissue of a leaf.
- 2. In ecology, the blade of a leaf or leaflet that has a surface area 4500–18225 mm2; a plant, or vegetation, that has mesophyll (sized) leaves.
- mesophyllous
- (of vegetation) Of moist habitats and having mostly large and soft leaves.
- mesophyte
- A plant thriving under intermediate environmental conditions of moderate moisture and temperature, without major seasonal fluctuations.
- micropyle
- Opening at apex of ovule.
- microsporangium
- The smaller of two kinds of sporangium produced by a heterosporous plant, producing microspores that contain the male gametophyte. Compare megasporangium.
- microspore
- The smaller of two kinds of spores produced by a heterosporous plant. Compare megaspore.
- microsporophyll
- In heterosporous plants, a modified leaf bearing one or more microsporangia. Compare megasporophyll.
- microstrobilus
- The smaller of two kinds of cones or strobilus produced by gymnosperms, being male and producing the pollen. Compare megastrobilus.
- midrib
The central and usually most prominent vein of a leaf or leaf-like organ.
- midvein
- See midrib.
- monad
- A single individual that is free from other individuals, not united with them into a group. The term is usually used for pollen to distinguish single grains from tetrads or polyads.
- monadelphous
- A term describing stamen filaments that are fused for the greater part of their length, forming a tube around the style.
- moniliform
- Resembling a string of beads.
- monocarpic
- Flowering and setting seed only once before dying. See also semelparous.
- monochasium
- A cymose inflorescence with the branches arising singly. Compare dichasium and pleiochasium.
- monocot
- An abbreviation of monocotyledon.
- monocotyledon
- A flowering plant whose embryo contains one cotyledon (seed-leaf). Compare dicotyledon.
- monoecious
- (of vascular plants) Hermaphroditic, with all flowers bisexual, or with male and female reproductive structures in separate flowers but on the same plant, or of an inflorescence that has unisexual flowers of both sexes. Contrast dioecious.
- monoicous
- (of bryophyte gametophytes) Hermaphroditic or bisexual, where both male and female reproductive structures develop on the same individual. Contrast dioicous.
- monograph
- Of a group of plants, a comprehensive treatise presenting an analysis and synthesis of taxonomic knowledge of that taxon; the fullest account possible (at the time) of a family, tribe or genus. It is generally worldwide in scope and evaluates all taxonomic treatments of that taxon including studies of its evolutionary relationships with other related taxa, and cytological, genetic, morphological, palaeobotanical and ecological studies. The term is often incorrectly applied to any systematic work devoted to a single taxon. Compare revision.
- monomorphic
- Of one type, rather than several. See also dimorphic (two types) and polymorphic (many types).
- monophyllous
- Having a single leaf.
- monopodial
- A mode of stem growth and branching in which the main axis is formed by a single dominant meristem. Contrast sympodial.
- monostromatic
- Being a single cell thick, as in the alga Monostroma.
- monothecous
- having a sole compartment or cell. Compare Dithecous.
- monotypic
- Containing only one taxon of the next lower rank, e.g. a family with only one genus, or a genus that includes only a single species.
- morphology
- The shape or form of an organism or part thereof.
- mucro
A sharp, short point, generally at the tip of a leaf or the tip of the midrib of a compound leaf.[28]
- mucronate
- Terminating in a mucro.
- multiple fruit
- A cluster of fruits produced from more than one flower and appearing as a single fruit, often on a swollen axis, as with many species of the family Moraceae. Compare aggregate fruit.
- muricate
- Covered with short, hard protuberances.
- mutation
- In times before the nature of genetic encoding was understood, mutation was regarded as an abrupt, and sometimes heritable, variation from the norm of a population; for example a plant might unexpectedly produce "double" flowers, a novel color, or a habit of growth uncharacteristic of the species or variety. Advances in genetics and molecular biology in the mid-twentieth century, showed that biological mutations comprise and reflect changes in the nucleic acid molecules that encode the genome of an organism or virus. The nucleic acid affected could be DNA in the chromosomes, or it could be extrachromosomal DNA (typically DNA in the mitochondria or chloroplasts). In RNA viruses a mutation would be a change to the genetic information that the RNA encodes.
- mycelium
- The "vegetative" (nonreproductive) part of a fungus, mostly composed of aggregations of hyphae. It functions in substrate decomposition and absorption of nutrients.
- mycorrhiza
One of several types of symbiotic association between a fungus and the roots of a plant.
- mycotroph
A plant that obtains most or all of its carbon, water, and nutrients by associating with a fungus.

Maculate leaves

Eucalyptus socialis, showing its mallee habit, a single tree with several trunks growing from an underground lignotuber

Mast from beeches on the forest floor

Apical meristem in root tip:
1: Meristem2: Columella
showing statocytes with statoliths
3: Lateral part of the tip
4: Dead cells
5: Elongation zone

Mesophyll as seen in the cross section of a dicotyledonous leaf
A-Lower epidermisB-Lower palisade mesophyll
C-Upper epidermis
D-Upper palisade mesophyll
E- Spongy mesophyll
F-Leaf vein

Longitudinal section of Pinus ovule
A=GametophyteB=Egg cell
C=Micropyle
D=Integument
E=Megasporangium

Strobilus of a Selaginella
A-MegasporeB-Microsporangium
C-Megasporangium
D-Microspore
E-Sporophyll

Moniliform pods on Vachellia nilotica



Fungal mycelium grown in culture dish

N
[edit]- native
- Naturally occurring in an area, but not necessarily confined to it. Compare endemic.
- natural hybrid
- A hybrid taxon produced by chance in the wild.
- naturalised
- Describing a plant, introduced from another region, that grows and reproduces readily in competition with the natural flora.
- nectar
- A usually sweet, nutrient-rich fluid produced by the flowers of many plants and collected by bees and other pollinators.
- nectary
A specialized gland that secretes nectar.
- neophyte
- A plant that has recently been introduced to a geographic area. Contrast archaeophyte.
- nerve
- Another name for a vein.
- node
- The part of a stem from which leaves or branches arise.
- nomen conservandum
- (Latin) A conserved name, usually a name that became so much better known than the correct name, that a substitution was made.
- nomen illegitimum
- A name that is either superfluous at its time of publication because the taxon to which it was applied already has a name, or the name has already been applied to another plant (a homonym).
- nomen invalidum
- A name that is not validly published, and technically is therefore not a botanical name. Abbreviation: nom. inval. See valid publication.
- nomen nudum
- A name not published in accordance with the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, usually without a diagnosis or description of the entity to which it applies, and without reference to either; such a name should not be used.
- nomenclature
- The naming of things; often restricted to the correct use of scientific names in taxonomy; a system that sets out provisions for the formation and use of names.
- noxious
- Of plants, containing harmful or unwholesome qualities. Applied in conjunction with 'weed' to specifically describe a plant which legislation deems harmful to the environment. Each state and territory in Australia has specific legislation governing noxious weeds.
- nucellus
- The tissue of the ovule of a seed plant that surrounds the female gametophyte. It is enclosed by integuments and is not of epidermal origin.
- numerous
- Stamens are described as numerous when there are more than twice as many as sepals or petals, especially when there is no set number of them. Compare indefinite.
- nut
- A hard, dry, indehiscent fruit containing only one seed.
- nutlet
- 1. A small nut.
- 2. One of the lobes or sections of the mature ovary of some members of the Boraginaceae, Verbenaceae, and Lamiaceae.

Hoya carnosa secretes so much nectar that it falls in drops if no pollinators remove it.

The small green petals of Helleborus argutifolius act as floral nectaries. The sepals function as petals.

Some Senna species have extrafloral nectaries that attract ants to defend them from pests.

Plant stem nodes and internodes
O
[edit]- ob-
- A prefix meaning "inversely"; usually the same shape as that described by the word stem, but attached by the narrower end. See obcordate, oblanceolate and obovate.
- obconic
- (of a fruit, hypanthium, pistil, or calyx) Shaped like an inverted cone, attached at the apex.
- obcordate
- (of a leaf blade) Broad and notched at the tip; heart-shaped but attached at the pointed end.
- obdiplostemonous
- Having stamens arranged in two whorls, and having twice as many stamens as petals, with the outer whorl being opposite the petals. Compare diplostemonous and haplostemonous.
- oblanceolate
- Having a lanceolate shape but broadest in the upper third.
- oblate
- Having a spherical shape but flattened at the poles.
- obligate
- (of parasites) Unable to survive without a host. Contrast facultative.
- oblique
- Slanting; of a leaf or stem, larger on one side of the midrib than the other, in other words asymmetrical.
- obloid
- Having a three-dimensional oblong shape, e.g. a fruit.
- oblong
- Having a length a few times greater than the width, with sides almost parallel and ends rounded.
- obovate
- (of a leaf) Having a length about 1.5 times the width, and widest above the center.
- obsolete
- Not evident, or at most rudimentary or vestigial.
- obtrapeziform
- trapeziform, but attached by the narrower trapezoidal base (e.g. of a leaf)
- obtuse
- Blunt or rounded; having converging edges that form an angle of more than 90°. Compare acute.
- ocrea
A sheath formed from two stipules encircling the node in members of the Polygonaceae.
- odd-pinnate
Having an odd number of leaflets in a compound pinnate leaf, such that there is only one terminal leaflet.
- oft.
- An abbreviation of "often". Compare usu. and s.t..
- -oideae
- A suffix added to the stem of a generic name to form the name of a subfamily, e.g. Fumaria → Fumarioideae.
- olim
- Formerly, e.g. "olim B", formerly in the Berlin herbarium (Herbarium Berolinense).
- ontogeny
- The sequence of developmental stages through which an organism passes as it grows.
- operculum (calyptra)
- A lid or cover that becomes detached at maturity, e.g. in Eucalyptus, a cap covering the bud and formed by the fusion or cohesion of perianth parts.
- opposite
- 1. Describing leaves or flowers borne at the same level but on directly opposite sides of their common axis.
- 2. Describing the occurrence of something on the same radius as something else, e.g. anthers opposite sepals. Compare alternate.
- opus utique oppressum
Listed after the botanical name of a plant, or the name of a publication, this indicates that a publication is listed in the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants as a suppressed work. Botanical names of the specified rank in the publication are considered not validly published (article 34).
- orbicular
- Flat and more or less circular.
- order
- A group of one or more families sharing common features, ancestry, or both.
- ortet
- The original single parent plant from which a clone ultimately derives.
- orthotropous
- Describes an ovule that is erect, with the micropyle directed away from the placenta; atropous. Compare amphitropous, anatropous, and campylotropous.
- oval
- See elliptical.
- ovary
- The basal portion of a carpel or group of fused carpels, enclosing the ovules.
- ovate
- Shaped like a section through the "long axis" of an egg and attached by the wider end.
- ovoid
- Egg-shaped, with wider portion at base; 3-dimensional object, ovate in all sections through long-axis.
- ovule
- Loosely, the seed before fertilization; a structure in a seed plant within which one or more megaspores are formed (after fertilization it develops into a seed).





Open flower of Eucalyptus macrocarpa, next to a shed operculum

Opposite arrangement (phyllotaxis) of leaves

Orbicular leaves of Dombeya rotundifolia

P
[edit]- pachycaul
- with a disproportionately thick trunk
- pachycladous
- with disproportionately thick stems
- palate
- An expanded lower lip of a flower that nearly or entirely blocks the opening of a flower tube, as in a snapdragon flower.[43]
- palea
1. The upper of two bracts enclosing a grass flower, major contributors to chaff in harvested grain.
- 2. Chaffy scales on the receptacles of many Asteraceae.
- 3. Chaffy scales on the stipe of many ferns.
- paleate
- Bearing paleae or chaffy scales, as in description of the receptacle of a capitulum of a plant in the Asteraceae.
- paleaceous
- Chaff-like in texture.
- palmate
- 1. leaf with veins radiating out from a central point (usually at the top of a petiole), resembling spread out fingers pointing away from the palm.
- 2. A compound palmate leaf has leaflets that radiate from a central point (usually at the top of a petiole).
- palmatifid
- Deeply divided into several lobes arising from more or less the same level.
- palmatisect
- Intermediate between palmate and palmatifid, i.e. the segments are not fully separated at the base; often more or less digitate.
- pandurate
- shaped like the body of a fiddle (mainly, of plant leaves)
- panicle
A compound raceme; an indeterminate inflorescence in which the flowers are borne on branches of the main axis or on further branches of these.
- papilionate
- Butterfly-like; having a corolla like that of a pea.
- papilla
A small, elongated protuberance on the surface of an organ, usually an extension of one epidermal cell.
- pappus
- In daisy florets, a tuft or ring of hairs or scales borne above the ovary and outside the corolla (representing the reduced calyx); a tuft of hairs on a fruit.
- paracarpel
- Ill-defined term, variously interpreted and applied to: organs attached to carpels; staminodes close to the gynoecium; and to a pistillode in a staminate flower
- paraperigonium
An anomalous secondary outgrowth of the perianthal meristem with ramifying vasculature. See also perigonium, perianth, and corona.[44]
- parasite
- An organism living on or in a different organism, from which it derives nourishment. Some plant species are parasitic. Compare saprophyte and epiphyte.
- parenchyma
- A versatile ground tissue composed of living primary cells which performs a wide variety of structural and biochemical functions in plants.
- parietal
- Attached to the marginal walls of a structure, e.g. ovules attached to placentas on the wall of the ovary. See placentation.
- paripinnate
- Having an even number of leaflets (or pinnae), i.e. terminated by a pair of pinnae as opposed to a single pinna. Compare imparipinnate.
- parthenocarpy
- The development or production of fruit without fertilization. Compare stenospermocarpy.
- patent
Spreading; standing at 45–50° to the axis. See also erecto-patent.
- patulous
- See patent.
- pauciflor
- Having few flowers per inflorescence. Compare pluriflor and uniflor.
- pectinate
- Pinnately divided with narrow segments closely set like the teeth of a comb.
- pedate
- Having a terminal lobe or leaflet, and on either side of it an axis curving outward and backward, bearing lobes or leaflets on the outer side of the curve.
- pedicel
The stalk of a flower; may also be applied to the stalk of a capitulum in the Asteraceae.
- peduncle
The stalk of an inflorescence.
- peltate
- Shield-like, with the stalk attached to the lower surface and not to the margin.
- pellucid
- Transmitting light; for example, said of tiny gland dots in the leaves of e.g. Myrtaceae and Rutaceae that are visible when held in front of a light.
- pendulous
- Hanging, for example an ovule attached to a placenta on the top of the ovary. Compare suspended.
- penicillate
- Tufted like an artist's brush; with long hairs toward one end.
- penninervation
With pinnately arranged veins.
- pentamerous
- In five parts, particularly with respect to flowers, five parts in each whorl. See also trimerous and tetramerous.
- pepo
- A type of berry formed from an inferior ovary and containing many seeds, usually large with a tough outer skin (e.g. a cucumber, pumpkin or watermelon).
- perennating
- Of an organ that survives vegetatively from season to season. A period of reduced activity between seasons is usual.
- perennial
- A plant whose life span extends over several years.
- perfect
- (of a flower) Bisexual; containing both male and female reproductive parts in the same inflorescence. Contrast imperfect.
- perfoliate
- With its base wrapped around the stem (so that the stem appears to pass through it), e.g. of leaves and bracts.
- perforate
- With many holes. Used to describe the texture of pollen exine, and also to indicate that tracheary elements have a perforation plate. See also fenestrate.
- perforation plate
- in a tracheary element, part of the cell wall that is perforated; present in vessel members but not in tracheids. Should not be confused with a pit.
- perianth
- The collective term for the calyx and corolla of a flower (generally used when the two are too similar to be easily distinguishable). Abbreviation: P; for instance, P 3+3 indicates the calyx and corolla each have 3 elements, i.e. 3 sepals + 3 petals.
- pericarp
- The wall of a fruit, developed from the ovary wall.
- periclinal
- Curved along parallel to a surface. Compare anticlinal.
- pericycle
- A cylinder of parenchyma or sclerenchyma cells that lies just inside the endodermis and is the outer most part of the stele of plants.
- perigonium
- In flowering plants, synonym of perianth.
- 2. In mosses, the leaves surrounding the antheridia, also called a splash-cup, e.g. in Polytrichum juniperinum.
- perigynium
- A sac from a modified tubular bract, or when fully closed an utricle, around the pistillate flower of sedges
- perigynous
- Borne around the ovary, i.e. of perianth segments and stamens arising from a cup-like or tubular extension of receptacle (free from the ovary but extending above its base). Compare epigynous and hypogynous.
- persistent
- Remaining attached to the plant beyond the usual time of falling, for instance sepals not falling after flowering, flower parts remaining through maturity of fruit. Compare deciduous and caducous.
- perule
1. The scales covering a leaf or flower bud, or a reduced scale-like leaf surrounding the bud. Buds lacking perulae are referred to as "naked".
- 2. In Camellias the final bracts and sepals become indistinguishable and are called perules.
- 3. A kind of sac formed by the adherent bases of the two lateral sepals in certain orchids.
- petal
- In a flower, one of the segments or divisions of the inner whorl of non-fertile parts surrounding the fertile organs, usually soft and conspicuously colored. Compare sepal, tepal.
- petalody
- The transformation of reproductive organs of flower into petals.
- petaloid
- Like a petal; soft in texture and colored conspicuously.
- petiolary (or petiolar)
- Associated with a petiole, as in petiolary glands.
- petiolate
- (of a leaf) Having a petiole. Contrast sessile.
- petiole
- The stalk of a leaf.
- petiolule
- The stalk of a leaflet.
- petricolous
- Rock-dwelling; living on or among rocks.
- phaneranthous
- Showy, as in showy flowers that advertise to pollinators, as opposed to aphananthous (unshowy)
- phanerogam
- Gymnosperms and angiosperms; plants producing stamens and gynoecia; literally plants with conspicuous sexual reproductive organs. Compare cryptogams.
- phenology
- The study of the timing of seasonal biological phenomena, such as flowering, leaf emergence, fruit ripening and leaf fall.
- phloem
- Specialized conducting tissue in vascular plants that transports sucrose from the leaves to other plant organs.
- photosynthesis
- Process by which energy from sunlight is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into simple sugars in cells containing chloroplasts. All plants, except certain parasites, can perform photosynthesis.
- phyllary
- Individual bract within an involucre or involucel.
- phyllid
- Leaf-like extension of the stem in Bryophytes
- phyllode
A leaf with the blade much reduced or absent, and in which the petiole and or rachis perform the functions of the whole leaf, e.g. many acacias. Compare cladode.
- phyllopodium
- (in ferns) A short outgrowth of the stem on which the frond is borne and which remains attached to the rhizome after the frond has been shed.
- phylloplane
- the surface of a leaf, considered as a habitat for organisms.
- phyllosphere
- The above-ground surface of plants as a habitat for epiphytic microorganisms.
- phylum
- A level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum.
- phytomelan
A black, inert, organic material that forms a crust-like covering of some seeds, commonly found in Asparagales, Asteraceae, etc.
- pileate
- Having a cap, a pileus.
- pileus
- A cap or cap-shaped structure, such as the cap of mushrooms or the plumule of some monocotyledons.
- piliform
- Having the shape of a cap, a pileus.
- pilose
- covered with soft, weak, thin and clearly separated hairs, which are usually defined as long and sometimes ascending.
- pinna
A primary segment of a compound leaf.
- pinnate
- A compound leaf with leaflets arranged on each side of a common petiole or axis; also applied to how the lateral veins are arranged in relation to the main vein.
- pinnatifid
- Pinnately lobed.
- pinnatisect
- pinnately divided almost to midrib but segments still confluent.
- pinnule or pinnula
- Usage varies:
ultimate free division (or leaflets) of a compound leaf,
or
a pinnate subdivision of a multipinnate leaf. - pistil
- 1. a single carpel when the carpels are free.
- 2. a group of carpels when the carpels are united by the fusion of their walls.
- pistillate flower
- a flower containing one or more pistils but no fertile stamens. Sometimes called a female flower. Contrast with staminate flower
- pistillode
- A sterile or rudimentary pistil such as may appear in a staminate flower.
- pit
- In tracheary elements, a section of the cell wall where the secondary wall is missing, and the primary wall is present. Pits generally occur in pairs and link two cells.
- pith
- The central region of a stem, inside the vascular cylinder; the spongy parenchymatous central tissue in some stems and roots.
- placenta
- The tissue within an ovary to which the ovules are attached.
- placentation
- The arrangement of ovules inside ovary; for example axile, free-central, parietal, marginal, basal, or apical.
- Plant Breeders Rights (PBR)
- These rights, governed by Plant Breeder's Rights Acts give the plant breeder legal protection over the propagation of a cultivar, and the exclusive rights to produce and to sell it, including the right to license others to produce and sell plants and reproductive material of a registered, deliberately bred variety. Compare UPOV.
- Plant Variety Rights (PVR)
- Governed by the Plant Variety Rights the registration of new varieties is now governed by Plant Breeders Rights.
- plastochron
- The time between successive leaf initiation events.
- pleiochasium
- pl. pleiochasia. An inflorescence in which several buds come out at the same time. Compare monochasium and dichasium.
- plicate
- Pleated; folded back and forth longitudinally like a fan, such as the leaves of fan palm species. The concept often appears in specific names in forms such as Kumara plicatilis and Acacia plicata. Commonly such names are not correctly appropriate, but are applied to distichous structures rather than plicate.
- -plinerved
- (of leaves) A suffix indicating that the main nerves are lateral and arise from a point distinctly above the base of the leaf. Combined with a numerical prefix to form words like 3-plinerved, 5-plinerved, and so on. Such leaves are especially characteristic of the family Melastomataceae. See for example Dissotis.
- plumose
- Like a feather; with fine hairs branching from a main axis.
- plumule
- The part of an embryo that gives rise to the shoot system of a plant. Compare radicle.
- pluriflor
- Having many flowers per inflorescence. See also pauciflor and uniflor.
- pluriovulate
- Having many ovules as in placentae, carpels, or ovaries.
- pneumatophore
- A vertical appendage, aerial at low tide, on the roots of some plants. Pneumatophore functions are unclear, but possibly related to gas exchange, or to root anchoring. Pneumatophores typically occur on mangrove roots, but some versions occur on species of conifers, such as some in the Taxodioideae.
- pod
- 1. A legume, the fruit of a leguminous plant, a dry fruit of a single carpel, splitting along two sutures.
- 2. A siliqua and silicula, the fruit of Brassicaceae, a dry fruit composed of two carpels separated by a partition.
- podocarpium
- In four genera of the coniferous family Podocarpaceae (Acmopyle, Dacrycarpus, Falcatifolium, and Podocarpus), a group of fleshy fused bracts beneath the female cone, often brightly-colored, which swell to enclose the developing seeds above and attract fruit-eating animals.[45]
- pollen
- powdery mass shed from anthers (of angiosperms) or microsporangia (of gymnosperms); the microspores of seed plants; pollen-grains.
- pollen-mass
- pollen-grains cohering by a waxy texture or fine threads into a single body; pollinium, e.g. in orchids.
- pollen transmitting tissue
- the tissue in the style of a flower through which the pollen tubes grow.
- pollination
- The transfer of pollen from a male organ (such as an anther) to the receptive region of a female organ (such as a stigma).
- pollinium
- See pollen-mass.
- polygamodioecious
- Having bisexual and male flowers on some plants and bisexual and female flowers on others. Compare androdioecious, andromonoecious, dioecious, monoecious, polygamomonoecious, and polygamous.
- polygamomonoecious
- having male, female, and bisexual flowers on the same plant. Compare androdioecious, andromonoecious, polygamodioecious, and polygamous.
- polygamous
- having bisexual and unisexual flowers on the same plant.
- polymorphic
- Of several different kinds (in respect to shape and/or size), hence polymorphism. See also monomorphic (a single type) and dimorphic (two types)
- polyphyllous
- having many leaves or perianth segments. Compare symphyllous, gamophyllous, and apophyllous.
- polyploid
- with more than two of the basic sets of chromosomes in the nucleus; any sporophyte with cells containing three or more complete sets of chromosomes. Various combinations of words or numbers with '-ploid' indicate the number of haploid sets of chromosomes, e.g. triploid = 3 sets, tetraploid = 4 sets, pentaploid = 5 sets, hexaploid = 6 sets, and so on.
- polystemonous
- having numerous stamens; the number of stamens being at least twice the number of sepals or petals, but not strictly three or four times that number.
- pome
- A fruit that has developed partly from the ovary wall but mostly from the hypanthium (e.g. an apple).
- population
- 1. All individuals of one or more species within a prescribed area.
- 2. A group of organisms of one species, occupying a defined area and usually isolated to some degree from other similar groups.
- 3. In statistics, the whole group of items or individuals under investigation.
- poricidal
- Opening by pores, as with the capsule of a poppy or the anthers in several families of plants. Compare longicidal.
- posterior
- Positioned behind or toward the rear. Contrast anterior.
- prickle
A hard, pointed outgrowth from the surface of a plant (involving several layers of cells but not containing a vein); a sharp outgrowth from the bark, detachable without tearing wood. Compare thorn.
- primary vein
- The single vein or array of veins that is conspicuously larger than any others in a leaf. In pinnate venation, the single primary vein can generally be found in the middle of the leaf; in palmate venation, several such veins radiate from a point at or near the base of the leaf.
- procumbent
- Spreading along the ground but not rooting at the nodes; not as close to the ground as prostrate.
- propagule
- Any structure capable of generating a new plant; includes seeds, spores, bulbils, etc.
- pro parte
- In part. In nomenclature, used to denote that the preceding taxon includes more than one currently recognized entity, and that only one of those entities is being considered.
- prophyll
- A leaf formed at the base of a shoot, usually smaller than those formed later.
- prostrate
- Lying flat on the ground; commonly rooting at nodes that touch the soil surface.
- protandrous
- Having male sex organs which mature before the female ones, e.g. a flower shedding pollen before the stigma is receptive. Compare protogynous.
- proteranthous
- With new leaves appearing before flowers. See also hysteranthous and synanthous.
- prothallus
- A gametophyte plant, usually flattened and delicate, e.g. in ferns and fern allies.
- protogynous
- Having female sex organs which mature before the male ones, e.g. a flower shedding pollen after the stigma has ceased to be receptive. Compare protandrous.
- proximal
- Near the point of origin or attachment. Compare distal.
- pruinose
- Covered with a powdery, waxy material; having a bloom.
- pseudanthium
- A type of inflorescence occurring in the Asteraceae and Euphorbiaceae, in which multiple flowers are grouped together to form a flower-like structure, commonly called a head or capitulum.
- pseudo-
- A prefix meaning "false, not genuine", e.g. a pseudo-bulb is a thickened, bulb-like internode in orchids, but not an actual bulb.
- pseudobasifixed
- (of an anther) Connected to the filament of the stamen by connective tissue which extends in a tube around the filament tip. See also basifixed and dorsifixed.
- pseudostipule
- An enlarged, persistent axillary bud scale that resembles a stipule; common in Bignoniaceae.
- pseudoverticillate
- Having the appearance of being whorled (verticillate), without actually being so.
- puberulous
Covered with minute soft erect hairs.
- pubescent
- Downy; covered with short, soft hairs, especially erect hairs.
- pulverulent
- Having powdery or crumbly particles as if pulverized.
- pulvinate
- Having a pulvinus.
- pulvinus
- a swelling at either end of a petiole of a leaf or petiolule of a leaflet, e.g. in Fabaceae, that permits leaf movement.
- punctate
- (from Latin puncta= puncture or prick-mark) marked with an indefinite number of dots, or with similarly small items such as translucent glands or tiny hollows.
- punctiform
- Dot-like or in the shape of a prick-mark.
- pungent
- Having a sharp, hard point.
- pustule
- A blister-like swelling.
- pustulate
- Having pustules.
- pyramidal
- (of a growth habit) Conical or pyramid-shaped. Most familiar in some coniferous trees, especially species adapted to snowy climates
- pyrene
- The stone of a drupe, consisting of the seed surrounded by the hardened endocarp.
- pyriform
- Pear-shaped; a term for solid shapes that are roughly conical in shape, broadest one end and narrowest at the other. As a rule the distal third of their length is the broadest, and they are narrowest near the proximal end, the base, where the stalk, if any, attaches.
- pyrophile
- Plants which need fire for their reproduction.
- pyrophyte
- Plants which have adapted to tolerate fire.

The thick trunk of Brachychiton rupestris accumulates moisture as a means of survival of droughts, and presents a marked example of a pachycaul habit.

This Curio articulatus is pachycladous in that it has a disproportionately thick stem.

A maple (Acer platanoides) leaf has palmate venation, as its veins radiate out from a central point, like fingers from the palm of a hand.


Asclepias physocarpa shedding seeds, each with its silky pappus

Doubly paripinnate leaves of Delonix regia


Stephania japonica is a vine with peltate leaves.

Perfoliate leaves of Smyrnium perfoliatum with stems passing through them

The leaves of Aponogeton madagascariensis are perforate.

The perigonium of a moss (red in this case), also called a splash-cup, surrounds the antheridia and aids in dispersal of sperm.

Liquidambar styraciflua bud emerging from its protective brown imbricate cataphyll scales, also known as perules


Petiolary glands on the petiole of a cherry leaf

Rock-splitting roots of the petricolous large-leaved rock fig, Ficus abutilifolia

The phaneranthous habit of the red flowering gum, Corymbia ficifolia, can attract pollinators such as the honey eater, Anthochaera chrysoptera, from a considerable distance.

Seedlings of Acacia fasciculifera bear leaves that illustrate the ancestral function of their phyllodes as petioles.


Glandular pilose hairs on the stem of Aquilegia grata


Simple pinnate leaf of Ekebergia capensis


Electron micrographs of sections of wood of a conifer (Picea abies) show pits in the tracheid walls.



Longitudinal section of maize kernel (scale=1.4 mm):
A=pericarp, B=aleurone, C=stalk, D=endosperm, E=coleorhiza, F=radicle, G=hypocotyl, H=plumule, I=scutellum, J=coleoptile
A=pericarp, B=aleurone, C=stalk, D=endosperm, E=coleorhiza, F=radicle, G=hypocotyl, H=plumule, I=scutellum, J=coleoptile

Pneumatophores on a species of mangrove

The sharp projections on the trunk of the knobthorn, Senegalia nigrescens, are prickles rather than thorns, botanically speaking.

Procumbent growth habit of Sagina procumbens, growing mainly along the soil surface, but without rooting

Carpobrotus and other prostrate plants growing on sand in Sicily, striking root and binding the soil as they grow

Floral stages of the protandrous species: Geranium incanum. The flower at first has intensely colored petals, and both androecium and gynoecium. After a day or so in bloom, it sheds the stamens and the color of the petals becomes somewhat paler.



Punctiform glands on the undersurface of a Plectranthus leaf


Q
[edit]- quadrate
- More or less square.

R
[edit]- raceme
An indeterminate inflorescence in which the main axis produces a series of flowers on lateral stalks, the oldest at the base and the youngest at the top. Compare spike. Also racemiform or racemoid - having the form of a raceme.
- rachilla (rhachilla)
- 1. the axis of a grass spikelet, above the glumes; see spikelet.
- 2. the rachis of higher order in leaves that are compound more than once
- rachis
The axis of an inflorescence or a pinnate leaf; for example ferns; secondary rachis is the axis of a pinna in a bipinnate leaf distal to and including the lowermost pedicel attachment.
- radial
- With structures radiating from a central point as spokes on a wheel (e.g. the lateral spines of a cactus).
- radiate
- (of daisies, of a capitulum) With ray floret surrounding disc florets.
- radical
- Springing from the root; clustered at base of stem.
- radicle
- The part of an embryo giving rise to the root system of a plant. Compare plumule.
- rainforest
- A moist temperate or tropical forest dominated by broad-leaved trees that form a continuous canopy.
- ramet
- An individual member of a clone.
- ramicaul
- a single-leafed stem, as in Pleurothallis orchids.[46]
- ramify
- To divide or spread out into individual branches or branchlike parts.
- ray
- 1. zygomorphic (ligulate) flowers in a radiate flowerhead, that is, ray-florets/flowers, for example Asteraceae.
- 2. each of the branches of an umbel.
- receptacle
- the axis of a flower, in other words, floral axis; torus; for example in Asteraceae, the floral base or receptacle is the expanded tip of the peduncle on which the flowers are inserted.
- recumbent
- bent back toward or below the horizontal.
- recurved
- bent or curved backward or downward.
- reduplicate
- folded outward, or with the two abaxial surfaces together.
- reflexed
- bent sharply back or down.
- registered name
- a cultivar name accepted by the relevant International Cultivar Registration Authority.
- registration
- 1. the act of recording a new cultivar name with an International Cultivar Registration Authority.
- 2. recording a new cultivar name with a statutory authority like the Plant Breeder's Rights Office.
- 3. recording a trademark with a trade marks office.
- regular
- See actinomorphic.
- reniform
- Kidney-shaped.
- replum
- a framework-like placenta to which the seeds attach, and which remains after each valve drops away.
- resupinate
- Describing leaves or flowers that are in an inverted position because the petiole or pedicel, respectively, is twisted 180 degrees. compare: hyper-resupinate.
- reticulate
- forming a network (or reticulum), e.g. veins that join one another at more than one point.
- retrorse
- Bent backward or downward. Compare antrorse.
- retuse
- Having a blunt (obtuse) and slightly notched apex.
- revision
- an account of a particular plant group, like an abbreviated or simplified monograph. Sometimes confined to the plants of a particular region. Similar to a monograph in clearly distinguishing the taxa and providing a means for their identification. Compare monograph.
- revolute
- rolled under (downward or backward), for example when the edges of leaves are rolled under toward the midrib. Compare involute.
- rhachis
- See rachis.
- rhizodermis
- the root epidermis, the outermost primary cell layer of the root
- rhizome
- a perennial underground stem usually growing horizontally. See also stolon. Abbreviation: rhiz.
- rhizomatous
- (adj.) having above-ground stems that are derived from below-ground stems (rhizomes). Compare arhizomatous (arhizomatic).
- rhizosphere
- the below-ground surface of plants and adjacent soil as a habitat for microorganisms.
- rhytidome
- the dead region of the bark and root that lies outside the periderm.
- rhombic
- like a rhombus: an oblique figure with four equal sides. Compare trapeziform and trullate.
- rhomboid
- a four-sided figure with opposite sides parallel but with adjacent sides an unequal length (like an oblique rectangle); see also rhombic.
- rhomboidal
- a shape, for instance of a leaf, that is roughly diamond-shaped with length equal to width.
- rimose
- with many cracks, as in the surface of a crustose areolate lichen.
- root
- a unit of a plant's axial system which is usually underground, does not bear leaves, tends to grow downward, and is typically derived from the radicle of the embryo.
- root hairs
- outgrowths of the outermost layer of cells just behind the root tips, functioning as water-absorbing organs.
- root microbiome
- the dynamic community of microorganisms associated with plant roots.
- rootstock
- 1. the part of a budded or grafted plant which supplies the root system, also simply called a stock.
- 2. plants selected to produce a root system with some specific attribute, e.g. a virus-free rootstock.
- rosette
- when parts are not whorled or opposite but appear so, due to the contractions of internodes, e.g. the petals in a double rose or a basal cluster of leaves (usually close to the ground) in some plants.
- rostellate
- possessing a beak (rostellum). Synonym of rostrate.
- rostrate
- with a beak.
- rotate
- circular and flattened; for example a corolla with a very short tube and spreading lobes (for instance some Solanaceae).
- ruderal
- a plant that colonises or occupies disturbed waste ground. See also weed.
- rudiment
- In the structure of a plant, an item that is at best hardly functional, either because it is immature and has not yet completed its development (such as a leaf still incompletely formed inside a bud), or because its role in the organism's morphology cannot be completed and therefore is futile (such as the leaf rudiment at the tip of a phyllode, that will be shed while immature, because the leaf function will be taken over by the phyllode). Compare cataphyll and vestige.
- rudimentary
- Being of the nature of a rudiment; at most barely functional because incompletely developed; begun, but far from completed, either temporarily or permanently. Compare vestigial.
- rugose
- Wrinkled, either covered with wrinkles, or crumpled like a wrinkled leaf, either as a stiffening structure, or in response to disease or insect damage.
- rugulose
- Finely wrinkled.
- ruminate
- (usually applied to endosperm) Irregularly grooved or ridged; appearing chewed, e.g. the endosperm in certain members of Myristicaceae.
- runcinate
- Sharply pinnatifid or cleft, with the segments directed downward.
- runner
- See stolon.
- rupicolous
- Rupestral, saxicolous, growing on or among rocks. Compare epilithic and lithophytic.
- rush
- A plant of the family Juncaceae or, more loosely, applied to various monocotyledons.

Bulbinella latifolia racemes. The flowers are already open at the bottom; at the top, the axis is still growing and budding.

Rachis of Vachellia karroo bipinnate leaf, with components labelled as follows:
A. Rachilla (the diminutive of rachis)B. Pinnule
C. Jugary glands
D. Juga (plural of jugum)
E. Base of petiole
F. Petiolary gland
G. Rachis

Radicles emerging from germinating seeds

Reniform kidney bean seeds



Typical rhizome. This one is a specimen of Iris pseudacorus.





The runcinate lobes of a Taraxacum officinale leaf point downward, i.e. toward the stem.
S
[edit]- saccate
- Pouched or shaped like a sack.
- sagittate
- Shaped like the head of an arrow; narrow and pointed but gradually enlarged at the base into two straight lobes directed downward; may refer only to the base of a leaf with such lobes. Compare hastate.
- salverform
- Shaped like a salver - Trumpet-shaped; having a long, slender tube and a flat, abruptly expanded limb
- samara
- A dry, indehiscent fruit with its wall expanded into a wing, e.g. in the genus Acer.
- samphire
- A common name given to various edible coastal plants, such as Salicornia spp. (Amaranthaceae), Crithmum maritimum (Apiaceae) and Limbarda crithmoides (Asteraceae).
- sanguine
- (from Latin sanguineus) Blood-colored: crimson; the color of blood.
- saprophyte
A plant, or loosely speaking, a fungus or similar organism, deriving its nourishment from decaying organic matter such as dead wood or humus, and usually lacking chlorophyll. Compare parasite, saprotroph, and epiphyte.
- saprotroph
An organism deriving its nourishment from decaying organic matter. Contrast parasite and epiphyte.
- sarment
- A long, slender, prostrate stolon, commonly called a runner.
- sarmentose
- Reproducing by sarments; strawberry plants are the most familiar example.
- saxicolous
- Growing on stone, like some lichens.
- scabrid .
Rough to the touch, with short hard protrusions or hairs.
- scalariform
- Ladder-like in structure or appearance.
- scale
- 1. A reduced or rudimentary leaf, for example around a dormant bud.
- 2. A flattened epidermal outgrowth, such as those commonly found on the leaves and rhizomes of ferns.
- scandent
- Climbing, by whatever means. See also: scandent in Wiktionary.
- scape
Usages vary, e.g.: a leafless peduncle arising directly from the ground, or a stem-like flowering stalk of a plant with radical leaves.
- scapose
- Having the floral axis more or less erect with few or no leaves; consisting of a scape.
- scarious
- Dry and membranous.
- schizocarp
- A dry fruit formed from more than one carpel but breaking apart into individual carpels (mericarp) when ripe. For illustration, see mericarp
- scion
- The aerial part of a graft combination, induced by various means to unite with a compatible understock or rootstock.
- sclereid
- A cell with a thick, lignified, cell wall that is shorter than a fiber cell and dies soon after the thickening of its cell wall.
- sclerenchyma
- A strengthening or supporting tissue composed of sclereids or of a mixture of sclereids and fibers.
- sclerophyll
A plant with hard, stiff leaves; any structure stiffened with thick-walled cells.
- scorpioid
- (of a cymose inflorescence) Branching alternately on one side and then the other. Compare helicoid.
- scrobiculate
- Having very small pits.
- scrubland
- Dense vegetation dominated by shruba.
- scurf
- Minute, loose, membranous scales on the surface of some plant parts, such as leaves.
- secondary metabolite
- Chemicals produced by a plant that do not have a role in so-called primary functions such as growth, development, photosynthesis, reproduction, etc.
- secretory tissue
- The tissues concerned with the secretion of gums, resins, oils and other substances in plants.
- section (sectio)
- The category of supplementary taxa intermediate in rank between subgenus and series. It is a singular noun always written with a capital initial letter, in combination with the generic name.
- secund
- Having all the parts grouped on one side or turned to one side (applied especially to inflorescences).
- sedge
- A plant of the family Cyperaceae.
- seed
- A ripened ovule, consisting of a protective coat enclosing an embryo and food reserves; a propagating organ formed in the sexual reproductive cycle of gymnosperms and angiosperms (together, the seed plants).
- segment
- A part or subdivision of an organ, e.g. a petal is a segment of the corolla. A term sometimes used when the sepals and petals are indistinguishable.
- self-pollination
- (also selfing) The acceptance by stigmas of pollen from the same flower or from flowers on the same plant, which means they are self-compatible.
- semaphyll
- A structure such as a bract or sepal (if the remainder of the perianth is inconspicuous) which has become modified to attract pollinators.
- semelparity
- When a plant flowers once then dies.
- semiterete
- Rounded on one side but flat on the other. See also terete.
- senecioid
- See anthemoid.
- sensitive
- A descriptive term for stigmas that, in response to touch, close the two lobes of the stigma together, ending the receptivity of the stigma, at least for the time that the lobes are closed together. Mimulus is perhaps the best-known example.
- sensu
- In the sense of.
- sensu auct.
- (of a plant group or name) As cited by a named authority.
- sensu amplo
- (of a plant group or name) In a generous or ample sense.
- sensu lato
- (of a plant group) In a broad sense.
- sensu strictissimo
- (of a plant group) In the narrowest sense.
- sensu stricto
- (of a plant group) In a narrow sense.
- sepal
- In a flower, one of the segments or divisions of the outer whorl of non-fertile parts surrounding the fertile organs; usually green. Compare petal, tepal.
- septicidal
- (of a fruit) Dehiscing along the partitions between loculi. Compare loculicidal.
- septum
A partition, e.g. the membranous wall separating the two valves of the pod of Brassicaceae.
- seriate
- Arranged in rows.
- sericeous
- Silky with dense appressed hairs.
- series
- The category of supplementary taxa intermediate in rank between section and species. It is often used as a plural adjective, as in "Primula subgenus Primula sect. Primula series Acaules".
- serrate
- Toothed with asymmetrical teeth pointing forward; like the cutting edge of a saw.
- serrulate
- Finely serrate.
- sessile
- Attached without a stalk, e.g. of a leaf without a petiole or a stigma, when the style is absent.
- seta
A bristle or stiff hair (in Bryophytes, the stalk of the sporophyte). A terminal seta is an appendage to the tip of an organ, e.g. the primary rachis of a bipinnate leaf in Acacia.
- sheath
- A tubular or rolled part of an organ, e.g. the lower part of the leaf in most grasses.[47]
- sheathing
- When the rolled or tubular part of a plant contains another it is described as sheathing.[47]
- shoot
- The aerial part of a plant; a stem and all of its dependent parts (leaves, flowers, etc.).
- shrub
- A woody perennial plant without a single main trunk, branching freely, and generally smaller than a tree.
- sigmoid
- Shaped like the letter 'S'.
- silicula or silicle
- A fruit like a siliqua, but stouter, not more than twice as long as wide.
- silique
- siliqua
- A dry, dehiscent fruit (in contrast to a silicula, more than twice as long as wide) formed from a superior ovary of two carpels, with two parietal placentas and divided into two loculi by a 'false' septum.
- silky
- Densely covered with fine, soft, straight, appressed hairs, with a lustrous sheen and satiny to the touch.
- silviculture
- The science of forestry and the cultivation of woodlands for commercial purposes and wildlife conservation.
- simple
- Undivided or unsegmented, e.g. a leaf not divided into leaflets (note, however, that a simple leaf may still be entire, toothed or lobed) or an unbranched hair or inflorescence.
- sinuate
- Having deep, wave-like depressions along the margins, but more or less flat. Compare undulate.
- sinus
- A notch or depression between two lobes or teeth in the margin of an organ.
- solitary
- Single, of flowers that grow one plant per year, one in each axil, or widely separated on the plant; not grouped in an inflorescence.
- sorus
A cluster of sporangia. Sori typically occur in ferns, some Algae and some fungi. In many fern species the sorus is covered by a protective indusium.
- sp.
- An abbreviation of species (singular), often used when the genus is known but the species has not been determined, as in "Brassica sp." See spp..
- spp.
- An abbreviation of species (plural), often used to collectively refer to more than one species of the same genus, as in "Astragalus spp." See sp..
- spadix
- A spicate (spike-like) inflorescence with the flowers crowded densely, even solidly, around a stout, often succulent axis. Particularly typical of the family Araceae
- spathe
A large bract ensheathing an inflorescence. Traditionally any broad, flat blade.
- spathulate or spatulate
- Spoon-shaped; broad at the tip with a narrowed projection extending to the base.
- species
- A group, or populations of individuals, sharing common features and/or ancestry, generally the smallest group that can be readily and consistently recognized; often, a group of individuals capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. The basic unit of classification, the category of taxa of the lowest principal rank in the nomenclatural hierarchy. Strict assignment to a species is not always possible, as it is subject to particular contexts, and the species concept under consideration.
- specific epithet
- Follows the name of the genus, and is the second word of a botanical binomial. The generic name and specific epithet together constitute the name of a species, i.e. the specific epithet is not the species name.
- speirochoric
- Unintentional introduction by seeds.[48] Compare agochoric.
- spica
Another name for a spike.
- spike
An unbranched, indeterminate inflorescence in which the flowers are without stalks. Compare raceme.
- spikelet
- A subunit of a spike inflorescence, especially in grasses, sedges, and some other monocotyledons, consisting of one to many flowers and associated bracts or glumes.
- spine
A stiff, sharp structure formed by the modification of a plant organ that contains vascular tissue, e.g. a lateral branch or a stipule; includes thorns.
- spinescent
- Ending in a spine; modified to form a spine.
- spiral
- Of arrangement, when plant parts are arranged in a succession of curves like the thread of a screw, or coiled in a cylindrical or conical manner.
- splash-cup (sporangia)
- A cup-like structure in fungi such as Nidulariaceae and in cryptogams such as some mosses. The cups function in spore dispersal, in which the energy of raindrops falling into the cup causes the water to splash outward carrying the spores.[49]
- sporangium (sporangia)
- A structure in which spores are formed and from which the mature spores are released
- sporangiophore
- An organ bearing sporangia, e.g. the cones of Equisetum.
- spore
- A haploid propagule, produced by meiosis in diploid cells of a sporophyte that can germinate to produce a multicellular gametophyte.
- sporocarp
- A fruiting body containing spores.
- sporophyll
- In pteridophytes, a modified leaf that bears a sporangium or sporangia.
- sporophyte
- The diploid multicellular phase in the alternation of generations of plants and algae that produces the spores. Compare gametophyte.
- sport
- A naturally occurring variant of a species, not usually present in a population or group of plants; a plant that has spontaneously mutated so that it differs from its parent plant.
- spreading
- Extending horizontally, e.g. in branches. Standing out at right angles to an axis, e.g. in leaves or hairs.
- spur
- 1. a short shoot.
- 2. a conical or tubular outgrowth from the base of a perianth segment, often containing nectar.
- squamule
Small scales.
- squamulose
- Covered with small scales (squamules).
- squarrose
- Having tips of leaves, stems, etc. radiating or projecting outward, e.g. in the moss Rhytidiadelphus squarrosus.
- s.t.
- An abbreviation for "sometimes". Compare usu. and oft..
- stalk
- The supporting structure of an organ, usually narrower in diameter than the organ itself.
- stamen
The male organ of a flower, consisting (usually) of a stalk called the filament and a pollen-bearing head called the anther.
- staminate flower
A flower with stamens but no pistil.
- staminode
- A sterile stamen, often rudimentary, sometimes petal-like. Commonly has a function in attracting pollinators that feed on the staminodes.
- staminophore
- A structure, around the apex of eucalypt, myrtaceae hypanthia, that supports the stamens.
- standard
- The large posterior petal of pea-flowers.
- standard specimen
- A representative specimen of a cultivar or other taxon which demonstrates how the name of that taxon should be used.
- stele
- The primary vascular system (including phloem, xylem, and ground tissue) of plant stems and roots.
- stellate
- Star-shaped.
- stem
- The plant axis, either aerial or subterranean, which bears nodes, leaves, branches, and flowers.
- stem-clasping
- See amplexicaul.
- stenospermocarpy
- The development or production of fruit that is seedless or has minute seeds because of the abortion of seed development. Compare parthenocarpy.
- sterile
- Infertile, as with a stamen that does not bear pollen or a flower that does not bear seed.
- stigma
- The pollen-receptive surface of a carpel or group of fused carpels, usually sticky; usually a point or small head at the summit of the style.
- stipe
- Generally a small stalk or stalk-like structure. The stalk of a frond of a fern; the stalk supporting the pileus of a mushroom; the stalk of a seaweed such as a kelp; the stalk-like support of a gynaecium or a carpel
- stipella
One of two small secondary stipules at the base of leaflets in some species.
- stipitate
- stalked; borne on a stipe; of an ovary, borne on a gynophore.
- stipulate
- Bearing stipules.
- stipule
- A small appendage at the bases of leaves in many dicotyledons.
- stock
- See rootstock.
- stolon
A slender, prostrate or trailing stem, producing roots and sometimes erect shoots at its nodes. See also rhizome.
- stoloniferous
- Having stolons.
- stoma
A pore or small hole in the surface of a leaf (or other aerial organ) allowing the exchange of gases between tissues and the atmosphere.
- stone cell
- a sclereid cell, such as the cells that form the tissue of nut shells and the stones of drupes.
- striate
- Striped with parallel, longitudinal lines or ridges.
- strigillose
- Minutely strigose.
- strigose
- Covered with appressed, straight, rigid, bristle-like hairs; the appressed equivalent of hispid.
- strobilus
A cone-like structure consisting of sporophylls (e.g. conifers and club mosses) or sporangiophores (e.g. in Equisetopsida) borne close together on an axis.
- style
- An elongated part of a carpel or a group of fused carpels between the ovary and the stigma.
- stylodium
- An elongate stigma that resembles a style; a false style, e.g. commonly found in the Poaceae and Asteraceae.
- stylopodium
- A swelling on top of the ovary, at the base of the styles commonly found in flowers of the Apiaceae.
- stylulus
- The elongated apex of a free carpel which functions like the style of a syncarpous ovary, allowing pollen tubes from its stigma to enter the locule of only that carpel.
- subacute
- Having a tapered but not sharply pointed form; moderately acute. See also acute.
- subcoriaceous
- Slightly leathery or coriaceous.
- subgenus
- A category of supplementary taxa intermediate between genus and section. The name of a subgenus is a singular noun, always has a capital initial letter and is used in combination with the generic name, e.g. Primula subgenus Primula.
- subglobose
- Inflated, but less than spherical. See also globose.
- suborbicular
- Nearly orbicular, flat and almost circular in outline. See also orbicular.
- subpetiolate
- (of a leaf) Having an extremely short petiole, and may appear sessile.
- subquadrangular
- Not quite square. Compare quadrangular.
- subshrub
A small shrub which may have partially herbaceous stems, but generally a woody plant less than 1 metre (3.3 ft) high.
- subspecies
- A taxonomic category within a species, usually used for geographically isolated or morphologically distinct populations of the same species. Its taxonomic rank occurs between species and variety.
- subtend
- To stand beneath or close to, as in a bract at the base of a flower.
- subulate
- Narrow and tapering gradually to a fine point.
- succulent
- 1. Juicy or fleshy.
- 2. A plant with a fleshy habit.
- sucker
- A shoot of more or less subterranean origin; an erect shoot originating from a bud on a root or a rhizome, sometimes at some distance from the stem of the plant.
- suffrutex
A subshrub or undershrub.
- sulcate
- Furrowed; grooved. May be single (monosulcate), two (bisulcate) or many (polysulcate).
- superficial
- On the surface.
- superior ovary
- An ovary borne above the level of attachment of the other floral parts, or above the base of a hypanthium. Compare inferior ovary and half-inferior ovary.
- suspended
- Of an ovule, when attached slightly below the summit of the ovary. Compare pendulous.
- suture
- A junction or seam of union. See fissure and commissure.
- sward
- Extensive, more or less even cover of a surface, e.g. a lawn grass. Compare tussock.
- sympatric
- Having more or less similar or overlapping ranges of distribution.
- sympodial
- A mode of growth in which the main axis is repeatedly terminated and replaced with a lateral branch. Examples occur in the family Combretaceae, including the genera Terminalia and Combretum. Compare monopodial.
- syconium
- A hollow infructescence containing multiple fruit, such as that of a fig.
- syn-
A prefix meaning "with, together".
- symmetrical
- Capable of being divided into at least two equal, mirror-image halves (e.g. zygomorphic) or having rotational symmetry (e.g. regular or actinomorphic). Compare irregular and asymmetrical.
- sympetalous
- Having united (connate or fused) petals, not free (apopetalous). See also syntepalous (having fused tepals).
- symphyllous
- a single perianth-whorl of united segments. Compare gamophyllous (synonym), apophyllous, and polyphyllous.
- synangium
- A fused aggregate of sporangia, e.g. in the trilocular sporangia of the whisk fern Psilotum.
- synanthous
- A type of growth in which new leaves and flowers appear and die back at the same time. See also hysteranthous and proteranthous.
- synaptospermy
- The dispersal of diaspores as units, where each bears more than one seed, for example where each diaspore comprises an entire inflorescence, as in Brunsvigia or multi-seeded fruit as in Tribulus zeyheri. Ephemeral synaptospermy is the term for when the diaspores split into units containing fewer or single seeds each, as in most tumbleweeds. True synaptospermy is when the diaspore generally remains entire until germination, as commonly happens in species of Grielum.
- syncarpous
- (of a gynoecium) Composed of united carpels.
- synonym
- An outdated or 'alternative' name for the same taxon.
- synoecious
- A synonym of bisexual.
- syntepalous
- Having fused tepals. See also sympetalous (having fused petals).


Salverform flowers of Plumbago auriculata

Trametes versicolor, the turkey tail fungus, is a saprotroph that consumes dead wood in forests. Its common name comes from the conspicuously patterned brackets, but the main body of the saprotroph consists of the largely invisible mycelium that penetrates the dead wood and digests it.


Micrograph of the scabrid undersurface of the leaf of Stipa pulcherrima.


Involucral bracts of Syncarpha species are as scarious as tissue paper, but look like live petals for years, so they are known as "Everlastings" and valued for dried arrangements.

Isolated sclereid or stone cell in plant tissue
Sclereids in gritty particles of pear tissue

Sepals on Geranium thunbergii, five separated behind the petals of an open flower, and a connected set enclosing an unopened bud



Silky foliage of the silvertree, Leucadendron argenteum


Spadix of Amorphophallus maximus within its spathe. The female flowers are around the bottom of the spadix, the male flowers above, and the sterile top part is the major source of pollinator attractants.


Drosera spatulata leaves are markedly spathulate.

The flowering spike of this Salvia nemorosa differs from a raceme in that the flowers are practically sessile.


Spinescent leaves of Salsola australis: stiff, narrowed, and with lobes ending in spiny points

Bird nest fungi, Nidulariaceae, bear examples of splash-cups with spores that are spread by raindrops.


Staminate flowers of Shepherdia canadensis



The large, succulent, acaulescent, linear, cuspidate mottled leaves of a Gasteria species and the small, succulent, cordate leaves of a Crassula species contrast with the linear, herbaceous leaves of a Hypoxis species.

Suckers around the trunk of Dypsis lutescens

Sulcate (specifically polysulcate) grooves along the stem of Scorzonera cana

Superior ovary ovary in an Aloe species. One flower is sectioned to display the pistil and hypanthium.

The suture along the concave curve of the pod of a Crotalaria incana, along which the seeds are attached, is where the single carpel has folded shut.

T
[edit]- taproot
- The primary descending root of a plant with a single dominant root axis.
- tartareous
- Having a surface that is course, thick, rough, and crumbling.
- taxon
A group or category in a system of biological classification.
- taxonomy
- The study of the principles and practice of classification.
- tegmen
- The inner layer of the testa (seed coat). It develops from the inner integument of the ovule.
- tendril
- Any slender organ modified from a stem, leaf, leaflet, or stipule and used by climbing plants to cling to an object.
- tepal
- A segment of a perianth, either sepal or petal; usually used when all perianth segments are indistinguishable in appearance.
- terete
Circular in cross-section; more or less cylindrical without grooves or ridges.
- terminal
- Situated at the tip or apex.
- ternate
- In groups of three; of leaves, arranged in whorls of three; of a single leaf, having the leaflets arranged in groups of three.
- terrestrial
- Of or on the ground; of a habitat, on land as opposed to in water (aquatic), on rocks (lithophytic), or on other plants (epiphytic).
- tessellate
- With cracks or fissures arranged in squares so as to give a chequered appearance. Usually applied to the appearance of the bark of a tree
- testa
- The seed coat.
- tetrad
- A group of four; usually used to refer to four pollen grains which remain fused together through maturity (e.g. in the Epacridaceae).[50]
- tetragonal
- Square; having four corners; four-angled, e.g. the cross-sections of stems of herbaceous Lamiaceae.
- tetramerous
- In four parts, particularly with respect to flowers; four parts in each whorl. See also trimerous and pentamerous.
- tetraploid
- Having four complete sets of chromosomes in each sporophyte cell.
- tetraspore
- The asexual spore of red algae. It is so named because each sporangium produces just four spores. See Rhodophyceae.[51]
- thalamus
1. A synonym for receptacle.
- 2. The inflorescence disk of members of the Asteraceae.
- 3. A calyx, as used by Carl Linnaeus.
- having a thallus-like structure; in the form of a thallus; thalloid
- thallus
A vegetative structure that is not differentiated into stem and leaves, as in lichens, algae, thallose liverworts, and certain vascular plants, e.g. Lemna
- theca
- One of the usually two synangia in which pollen is produced in flowering plants. It consists of two fused sporangia known as pollen sacs. The wall between the pollen sacs disintegrates before dehiscence, which is usually by a common slit.
- thorn
- A sharp, stiff point, usually a modified stem, that cannot be detached without tearing the subtending tissue; a spine. Compare prickle.
- throat
- The opening of a corolla or perianth.
- Тирс
- Разветвленное соцветие, в котором основная ось является неопределенной ( ракемос ), а боковые ветви определяют ( цимоза ).
- Томанеллеус
- Минично Томентоза.
- начинка
Плотное покрытие коротких матовых волос. Томантоза часто используется в качестве общего термина для нести индукторного , но это не рекомендуемое использование.
- зубчатый
- Наличие более или менее регулярно вырезанного маржи .
- торус
- Смотрите сосуд .
- передача ткани
- См. Ткани, передающей пыльцу .
- трапециформ
- 1. Как трапеция (четырехсторонняя фигура с двумя параллельными сторонами неравной длины).
- 2. Как трапеция (четырехсторонняя фигура или четырехугольник , ни одна пара сторон не равна); Иногда используется ошибочно в качестве синонима для ромбики .
- дерево
- Древесное растение, обычно с одним отдельным стволом и обычно более 2–3 метра (6,6–9,8 фута) ростом.
- триада
- Группа из трех человек.
- Треугольный
- Планарный и с 3 стороны.
- племя
- Таксономическая группировка, которая занимает ранжирование между родом и семьей .
- Трихом
- В нефиламентных растениях любой рост, похожий на волосы от эпидермиса , например, волосы или щетина; Иногда ограничивается неразветвленными эпидермальными ротами.
- трихотомический
- 3-й или разветвленный на три. Сравните дихотомический .
- Трифид
- Разделите на три части. Смотрите также Bifid .
- Триполиат
- Сложный лист из трех листовок ; Например, лист клевера .
- Трифолиолат
- Смотрите трилиат .
- Тригонный
- Треугольный по поперечному сечению и тупо углубляется. Сравните трикутрость .
- Тримин
- В трех частях, особенно в отношении цветов; Имея три части в каждом обозревании. См. Также тетрамообразное и пентаматическое .
- резкий
- Имея три нерва или вены .
- Triplinerved
- (из листьев), имеющие три основных нерва с боковыми нервами, возникающими с середины над основанием листа.
- триперист
- (пыльцы) с тремя полями.
- Трикутровый
- Более или менее треугольный по поперечному сечению, но с острым углом (с 3 различными продольными хребтами). Сравните тригон .
- Trivalve
- Разделен на три клапана . Также Тривавар . Смотрите также двустворчатую .
- тривиальное имя
- Второе слово в двух частях научного названия организма. Сравните конкретный эпитет .
- Трофофилл
- Вегетативный, производственный питательный лист или микрофилл , основной функцией которого является фотосинтез . Это не специализировано и не модифицировано для какой -либо другой функции. Сравните спорофилл .
- Триль
- Яйцевидная , но уклоняется, как с каплярной катиной ; обратно пропорциональная змея в форме. Сравните Rhombic .
- усечь
- Отрезать прямо; наличие внезапно поперечного конца.
- ствол
- Вертикальный, большой и обычно древесный главный стебель дерева.
- ферма
- Компактный кластер цветов или фруктов, возникающий из одного центра; очевидно во многих рододендронах .
- клубень
- Любой из многих типов специализированных вегетативных подземных органов хранения. Они накапливают пищу, воду или защиту от смерти от пожара, засухи или других трудных времен. ПУБОТЫ Обычно хорошо отличаются от других органов растений; Например, неформально морковь обычно не рассматривается как клубень, а просто опухший корень. В этом они отличаются от клубня сладкого картофеля, который не имеет особой корневой функции. Точно так же корм , как правило, не рассматриваются как клубни, даже если они являются подземными стеблями хранения. Кубки хранят пищу для растения, а также играют важную роль в вегетативном размножении . Как правило, они из двух основных типов: клубни ствола образуются путем набухания подземного стебля, растущего из корня, или из таких структур, как подземные столоны . Стволовые клубни обычно производят пропагандистские почки на своих узлах STEM , образуя сезонный самостоятельный орган , например, картофель . Основным другим классом является корневый клубень , также называемый тубероидом . Они отличаются от клубней STEM по таким функциям, как это, как и любой нормальный корень, они не образуют узлы.
- бугорку
- Небольшой растущий рост или выпуклость ткани.
- туберкуляция
- Покрыты бугорками . Смотрите Warty . [ 52 ]
- тубероид
- Альтернативное название для подземного органа хранения, образованного припухлом корня; встречается во многих орхидеях .
- КУБОРТА
- Напоминающий клубень или производительность клубней.
- трубчатый
- Имея форму трубки или цилиндра .
- погружен
- Плотно фаскуляция на кончике.
- туника
- Внешнее покрытие некоторых ламп и корм .
- туникат
- (из луковиц ), состоящий из концентрических пальто.
- турбинат
- В форме вращающегося верхнего или свеклы .
- тургидный
- Опухший с жидкостью; раздутый; твердый. Сравните Flaccid .
- Tussock
- Плотный пучок растительности, обычно хорошо отделенный от соседних болот, например, в некоторых травах. Сравните Sward .
- Двухчисленные
- Наличие листьев, расположенных в двух рядах в одной плоскости, на противоположных сторонах ветви. Смотрите дистич .
- тип
- Предмет (обычно гербарный образец), к которому навсегда прикреплено название таксона, то есть назначенный представитель названия растения. Важно при определении приоритета имен, доступных для конкретного таксона.
- тип рода
- В номенклатуре один род таксономическая семья . , на котором основана
-
Leucaena Leucocephala Taproot, выставленная в дорожке
-
-
Усильники Pepo Cucurbita , некоторые поддерживают стебель на кадре, некоторые не смогли найти точку привязанности
-
Nerine Bowenii , показывающий отсутствие видимых чашелителей и нижних яичников . Чашелистики включены в венчик как тепал с .
-
Terete Raceme of Kniphofia, показанная вместе с поперечным сечением плодоножки. A: соцветие ; B: Terete Peduncle ; C: поперечное сечение Terete Peduncle
-
Gymnosporia buxifolia имеет истинную шипую , то есть модифицированные ветви. У некоторых видов такие ветви в комплекте с почками и листьями.
-
Сладкий картофельный клубень , показывая их корневыми клубнями. Морфологически они отличаются от клубней ствола картофеля, например, в том, что корневые клубни не имеют узлов , которые несут почки. Однако корневые клубни некоторых видов растений могут производить случайные бутоны для вегетативного размножения .
-
Клубни оксис , клубни ствола
-
Квормы крокосмии растущих несут типичную тунику , образованную из катафиллов, из узлов CORM. Иллюстрация показывает все ещеживые катафиллы в виде белой ткани, тогда как функциональная, твердая, устойчивая тунику является коричневой.
-
Турбинат (вращающиеся верхние) корни сахарной свеклы
-
Haworthia Lockwoodii , с его листьями тущими и зелеными после сезонных дождей, хранят воду против предстоящего сухого периода.
В
[ редактировать ]- зонтик
- Соцветие растворя , в котором все отдельные цветочные стеблы возникают в кластере в верхней части цветоножки и имеют примерно одинаковую длину; В простой зонтике каждый стебель неразветвлен и несет только один цветок. Зубель таракоза выглядит похожей на обычную зонтику, но его цветы открываются центробежными.
- Форма
- Закругленная высота, например, посреди вершины зонтика или грибы ; Центральный босс или выпуклость, например, масштабе конуса в .
- Грива
- Наличие Umbo , с коническим или тупым проекцией, возникающим из более плоской поверхности, как на верхней части гриба или в масштабе соснового конуса .
- неразмерный
- Крючок.
- неведущий
- Иметь крючок на вершине.
- поднятый
- Низкий кустарник , часто с цветущими ветвями, которые умирают зимой. Сравните подтехруб .
- пособия
- Растительная жизнь растет под лесным навесом .
- Внешний
- Волнистый и не плоский. Сравните сияние .
- Uniflor
- Имея один цветок (Uniflory). Сравните Пауцифлор ( мало ) и плюрифлор ( многие ).
- универсальный
- Наличие одного локуля или камеры, например, яичник в семействах Proteaceae и Fabaceae .
- универсальный
- Расположен в одном ряду или серии. Неразветвленный. Uniseriate .
- Uniseriate
- Расположен в одном ряду или серии. Неразветвленный. Универсальный .
- унисексуал
- Одного пола; с несущими собой только мужчины или только женские репродуктивные органы, диологические , диоики . См. Сексуальное размножение в растениях .
- Unitegmic
- (яйцеклеток ) покрыта одним целым . См. Также Bitegmic , имея два целых числа.
- Урцеолат
- В форме, как урна или кувшин , с опухшим средним и сужающим верхом. Примеры включают кувшины многих видов кувшина растений родов сарачении и Nepenthes .
- использовать.
- Аббревиатура обычно . Сравните ST и Oft. Полем
- утрику
- 1. Небольшой мочевой пузырь; Мембранный яичник мочевой мешок от стенки яичника, тонкий перикарп, становится более или менее мочевым пузырем или надуваемым при зрелости, охватывающем или фрукты.
- 2. В Sedges , плод, при котором плод свободно заключается в модифицированную трубчатую прицветнику, см. Перигиний .




Кувшины вида Nepenthes Ventricosa, как правило, заметно ульцелат .
V
[ редактировать ]- Vallecular Canal
- Канал смолы, совпадающий с продольной канавкой в семенах Asteraceae . Продольная полость в коре стеблей Equisetum , совпадающая с канавкой на поверхности стебля.
- бдительный
- (от чашелистиков и лепестков в зародыше) встречаются с краем до края, но не перекрываются.
- клапан
- Часть органа, который фрагментирует или расщепляет открытую, например, зубы, похожие на части перикарпа в разделенной (Decisced) капсуле или стручке при созревании.
- наш.
- Аббревиатура варьет .
- вариант
- Растение или группа растений, показывающих некоторую меру отличия от характеристик, связанных с конкретным таксоном .
- разнообразно
- Нерегулярно отмечен с пятнами или пятнами другого цвета.
- разнообразие
Таксономическое звание ниже видов и между рядами подвида и формы .
- сосудистый
- Ссылаясь на проводящие ткани ( ксилема и флоэма ) сосудистых растений s.
- сосудистый пакет
- Пакет сосудистой ткани в первичных стеблях сосудистых растений S, состоящий из специализированных проводящих клеток для транспортировки воды ( ксилем ) и ассимиляции ( флоэма ).
- маленькое судно
- Контейнер, используемый ботаниками для сбора полевых образцов.
- вена
Прядь сосудистой ткани, например, в листьях сосудистых растений .
- Вена
- Небольшая вена ; Конечное (видимое) разделение вены.
- вуаль
- Губчатая ткань, покрывающая корни орхидей и воздушные некоторых других эпифитов .
- велюрино
- Смотрите бархатисто .
- бархатистый
- Плотно покрытый тонкими, короткими, мягкими, прятельскими волосками.
- венеция
- Расположение вен в листе.
- вентральный
- От латинского вентера , что означает «живот». Противоположность дорсальному . Отчасти потому, что термин, первоначально упоминаемый животным, а не растениям, использование ботаники является произвольным в соответствии с контекстом и источником. В целом «вентрал» относится к «животу или нижней части», но при ботаническом использовании такие понятия не всегда четко определены и могут быть противоречивыми. Например:
- лицом к оси ( адаксиальному ) при ссылке на боковой орган прямого растения
- Взглянув в сторону подложки в любой части прямого растения, например, нижняя поверхность более или менее горизонтального листа ( абаксиальное )
- Взгляд к подложке на заводе по прострадному или скалолазанию.
- вернация
- Расположение неожиданных листьев в бутоне ; Порядок, в котором листья разворачиваются из бутона.
- краска
- Имея блестящую или полированную поверхность, как будто покрыта лаком и гладкой или гладкой текстурой. [ 53 ]
- Вернониоид
- В семье Asteraceae стиль с широкими волосками, несущихся на абаксиальных поверхностях ветвей стиля.
- Вернуриформ
- Бородавка в форме.
- бородавка
- Имея бородавки.
- Веррукулоза
- Минично верракоза ; Минично -бородатая.
- универсальный
- (от пыльника ) свободно размахивается о точке привязанности к нити .
- вертилятный
- Расположенные в одном или нескольких оборотах , то есть несколько подобных частей, расположенных в той же точке оси , например, расположение листьев. Сравните Pseudoverticillate (появляясь обороты или вертилята, но на самом деле не так).
- Verticillaster
- Тип псевдовертиллиллического соцветия , типичный для Lamiaceae , в котором псевдо-толсты образуются из пар противоположных циментов .
- везикулярный
- (из волос), похожий на мочевой пузырь; Весечно, неся такие волосы.
- судно
- Капиллярная трубка, образованная из серии открытых клеток в воде, проводящей ткани растения.
- рудиментарный
- Уменьшен в форме и функции из нормального или наследственного состояния.
- Вирлоселея
- Мелко ворсин.
- ворсинку
- Изобилует или покрыты длинными, мягкими, прямыми волосками; Шаглые с мягкими волосками.
- виноградный
- 1. Скандальные растения , поднимающиеся с помощью стеблей или бегунов .
- 2. такой стебель или бегун. [ 28 ] [ 54 ]
- 3. член рода Vitis .
- девственница
Палочка, твигги, особенно ссылаясь на прямые стебли. В микологии , ссылаясь на кучу с излучающими ребрами или линиями.
- Viridiplantae
- Клада автотрофных организмов, которые включают зеленые водоросли , харофиты и наземные растения , которые имеют целлюлозу в их клеточной стенке , хлоропласты , полученные из первичного эндосимбиоза с цианобактериями , которые содержат хлорофиллы A и B и не имеют фикобилинов .
- викон
- Липкий; покрыт толстой, сиропо -секрецией.
- Вита
Масляная трубка в плодах некоторых растений. [ 55 ]
- Вивипарус
- 1. Ссылаясь на семена или фрукты, которые прорастают перед тем, как сбрасывать от родительского растения.
- 2. Развитие заводов на нефлоральных органах, например, листья.
-
A: Phloem
Б: Камбий
C: Xylem
D: волокнистая оболочка сосудистого пакета -
-
Цветочные стебли и чашелевые трубки Pueraria phaseoloides покрыты сережными ( бархатистыми ) волосками.
-
Листья вертилята и появляющиеся ветвики FORB
-
-
Asparagus virgatus обязана своим специфическим эпитетом Virgatus из -за волнения его побег девственницы .
В
[ редактировать ]- достойный
- Поверхность, покрытая небольшими круглыми выпуклостями, особенно в фруктах, листьях, веточках и коре. Смотрите Tuberculate .
- Уотерск
- Прямое , , сильное или эпикормическое побег развивающийся от основания куста или дерева, но отличается от присоски .
- сорняк
- 1. Любое растение, растущее там, где оно не разыскивается; обычно ассоциируется с нарушенными средами обитания. Смотрите также Рудерал .
- 2. Нежелательное растение, которое растет среди сельскохозяйственных культур .
- 3. Натурализованные, экзотические или экологически «индивидуальные» коренные виды за пределами сельскохозяйственного или садового контекста, который в результате вторжения отрицательно влияет на выживание или регенерацию коренных видов в естественных или частично естественных сообществах растительности Полем [ 56 ]
- дикий
- Происходит из известной дикой или чисто естественной среды обитания ( дикая местность ).
- прозвенел
- Кольцо органов носило на том же уровне на оси (например, листья, примытки или цветочные детали).
- крыло
- 1. Мембранное расширение фруктов или семян, которое помогает в рассеивании, например, на сосны . семенах
- 2. Тонкий фланцевой фланце, простирающийся за пределы нормального контура структуры, например, на колонне некоторых орхидей , на стеблях, на черешках.
- 3. Один из двух боковых лепестков цветочника подсемейства Faboideae из семейства Fabaceae , расположенного между лепесткам Adaxial Standard (Banner) и двумя лепестками с абаксиальными килями.
- Вуди
- жесткий и лигнированный ; не травянистый
- шерсти
- шерстяное
- овец Очень плотно покрытый длинными, более или менее спутанными или переплетенными волосками, напоминающими шерсть .
-
Вертилятные необычны обороты . листьев на Brabejum stellatifolium среди деревьев в его родном регионе
-
ED ED Семена Catalpa Bignonioides - почти все крыло. Тафты на кончиках увеличивают аэродинамическое сопротивление , тем самым улучшая рассеивание ветра.
-
Листья некоторых видов цитрусовых имеют крылатые черешки.
-
Листья Senecio haworthii имеют необычайно густое шерстяное пальто.
Х
[ редактировать ]- ксероморф
- Растение со структурными особенностями (например, жесткие или сочные листья) или функциональные адаптации, которые предотвращают потерю воды путем испарения; Обычно ассоциируется с засушливыми средами обитания, но не обязательно устойчиво к засухе. Сравните ксерофит .
- ксерофит
- Растение, как правило, живет в сухой среде обитания, обычно показывает ксероморфную или сочную адаптацию; Растение, способное переносить длительные периоды засухи. Сравните Xeromorph .
- ксилем
- Специализированная вода ткани у сосудистых растений .
С
[ редактировать ]- Зонат
- Имея легкие и темные круглые полосы или кольца, обычно на листьях или цветах.
- Зигоморфный
- Двусторонняя симметричная; симметрично только по одной вертикальной плоскости; относится к цветам, в которых сегменты перианта в каждом обороте различаются по размеру и форме. Контрастные актиноморфные и нерегулярные .
- Zygote
- Оплодотворенная ячейка, продукт слияния двух гамет .
-
Зонатные маркировки на листьях сада разнообразного пеларгония Zonale
-
Как и большинство рода Pelargonium , и в отличие от большинства членов рода Geranium , Pelargonium Quercifolium носит цветы, которые являются двусторонними симметричными . Соответственно, потому что иго из быка двусторонне симметричны, такие цветы, как говорят, являются зигоморфными , что буквально означает «яговая форма».
Смотрите также
[ редактировать ]- Цветочная формула - сокращения, используемые при описании деталей цветов
- Глоссарий биологии
- Глоссарий морфологии растений
- Глоссарий морфологии листьев
- Глоссарий лишайных терминов
- Глоссарий микологии
- Глоссарий научного именования
- Морфология растений
Ссылки
[ редактировать ]- ^ Новый Оксфорд Словарь V1 2007 , с. 2
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в Harris & Harris 2001 , p. 3
- ^ Новый Оксфорд Словарь V1 2007 , с. 7
- ^ Новый Оксфорд Словарь V1 2007 , с. 8
- ^ Shreve & Wiggins 1964 , p. 738.
- ^ Shreve & Wiggins 1964 , p. 355.
- ^ Shreve & Wiggins 1964 , p. 351.
- ^ Новый Оксфорд Словарь V1 2007 , с. 16
- ^ Turtland et al. 2018 , статья 18 .
- ^ IP 2022 .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Harris & Harris 2001 , p. 4
- ^ Harris & Harris 2001 , с. 4–5.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в дюймовый и фон глин час я Harris & Harris 2001 , p. 5
- ^ Симс 1803 , [с. 93] .
- ^ Harris & Harris 2001 , p. 6
- ^ Cappers & Neef 2012 , с. 95
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 15
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 16
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 17
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 20
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 24
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 27
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 35
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 39
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 41
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 46
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 47
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в дюймовый и Джексон 1928 .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Jaeger 1959 .
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 58
- ^ Beentje 2010 , с. 33.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Ханзава, Битти и Холмс 1985 .
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 78
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Schulze & Zwölfer 2012 , p. 261.
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 83.
- ^ Скопированное определение из прилагательного биологии. Смотрите историю этой страницы для атрибуции.
- ^ Скопированное определение из прилагательного биологии Fimbriate . Смотрите историю этой страницы для атрибуции.
- ^ Рендл 1911 .
- ^ Hickey & King 2000 , p. 20, 87.
- ^ Hickey & King 2000 , p. 20
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Carolin & Tindale 1994 , p. 23
- ^ Beentje 2010 , с. 67
- ^ "Глоссарий: P" . Иди ботаника . Нативное траст завода. Архивировано из оригинала 28 сентября 2023 года . Получено 4 января 2024 года .
- ^ Meerow et al. 1999 .
- ^ Eckenwalder 2009 , с. 648–661.
- ^ Pell & Angell 2016 , с. 169
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Beentje 2010 , с. 107
- ^ Kucewicz, Maćkiewicz & żorzek-Sokolnik 2010 .
- ^ Броди 1951 .
- ^ Пляж 1914a .
- ^ Пляж 1914b .
- ^ "Tuberculate" . Словарь ботаники . Получено 7 января 2024 года .
- ^ Harris & Harris 2001 , p. 132.
- ^ Новый Оксфорд Словарь V2 2007 , с. 3534.
- ^ Beentje 2010 , с. 129
- ^ Carr, GW, в Foreman & Walsh, 1993.
Библиография
[ редактировать ]- Аллаби, Майкл (2012). Словарь растительных наук . Издательство Оксфордского университета . ISBN 978-0-19-960057-1 - через Google Books (только предварительный просмотр) .
- Пляж, Чендлер Б., изд. (1914a). " Тетрада ". Новая студенческая справочная работа . Чикаго: FE Compton and Co.
- Пляж, Чендлер Б., изд. (1914b). « Тетраспоре ». Новая студенческая справочная работа . Чикаго: FE Compton and Co.
- Beentje, Henk (2010). Глоссарий завода Kew, иллюстрированный словарь терминов растений . Ричмонд, Лондон: Kew Publishing . ISBN 978-1-84246-422-9 .
- Броди, Гарольд Дж. (Май 1951 г.). «Механизм рассеивания брызг в растениях» . Канадский журнал ботаники . 29 (3). Оттава, Онтарио: Канадская научная публикация : 224–234. doi : 10.1139/b51-022 .
- Cappers, René TJ; Neef, рендер (2012). Справочник или раститель палеоэологии . Barkuis publicing. ISBN 9789492444264 - через Google Books (только предварительный просмотр) .
- Каролин, Роджер С .; Тиндейл, Мэри Д. (1994). Флора региона Сиднея (4 -е изд.). Чатвуд, Новый Южный Уэльс: Рид. ISBN 0730104001 Полем OCLC 32821788 .
- Дон, Джордж (1831). Общая история дихламдиозных растений ... расположено в соответствии с естественной системой . Тол. 1. Лондон . Получено 15 декабря 2022 года - через библиотеку наследия биоразнообразия .
- Экенвалдер, Джеймс Э. (2009). Звуки мира: полная ссылка . Лондон: Timber Press . ISBN 978-0-88192-974-4 .
- Гиффорд, Эрнест М.; Фостер, Адрианс С. (1989). Морфология и эволюция сосудистых растений (3 -е изд.). WH Freeman . ISBN 978-0-7167-1946-5 .
- Ханзава, Фрэнсис М.; Битти, Эндрю Дж.; Холмс, Энн (ноябрь 1985 г.). «Двойная функция Elaiosoma of Corydalis aurea (Fumariaceae): привлечение дисперсионных агентов и отталкивание Peromyscus maniculatus , семенного хищника». Американский журнал ботаники . 72 (11). Сент -Луис, Миссури: Ботаническое общество Америки : 1707–1711. doi : 10.1002/j.1537-2197.1985.tb08442.x . JSTOR 2443727 .
- Харрис, Джеймс Г.; Харрис, Мелинда Вульф (2001). Терминология идентификации растений: иллюстрированный глоссарий (2 -е изд.). Весеннее озеро, штат Юта, США: издательство Спринг -Лейк. ISBN 0-9640221-6-8 .
- Хикки, Майкл; Кинг, Клайв (2000). Кембридж иллюстрировал глоссарий ботанических терминов . Кембридж, Англия: издательство Кембриджского университета . ISBN 978-0-521-79401-5 - через Google Books .
- Хьюз, Колин (2017). «О проекте по полевым руководствам» . Виртуальный поля гербарий (gerbaria ald.lants.ox.ac.uk) . Оксфордский университет Гербария . Архивировано с оригинала 5 марта 2017 года . Получено 4 марта 2017 года .
- * «Характеристики растений» . Виртуальный поля гербарий (gerbaria ald.lants.ox.ac.uk) . Архивировано с оригинала 5 марта 2017 года . Получено 4 марта 2017 года . В Хьюзе (2017) .
- IPNI (2022). "Rosaceae Juss., Gen. Pl. [Jussieu] 334 (1789), Nom. Cons" . Международный индекс названий заводов (IPNI) . Королевские ботанические сады, Кью ; Гербария и библиотеки Гарвардского университета ; Австралийский национальный ботанический сад . Получено 24 декабря 2022 года .
- Джексон, Бенджамин Дэйдон (1928). Глоссарий ботанических терминов с их деривацией и акцентом . Нью -Йорк: Hafner Publishing Co. Inc. Получено 15 декабря 2022 года - через библиотеку наследия биоразнообразия .
- Jaeger, Edmund Carroll (1959). Источник биологических названий и терминов . Спрингфилд, Иллинойс, США: Томас. ISBN 978-0-398-06179-1 - через интернет -архив .
- Куцевич, Магдалена; Maćkiwicz, Catarzyna; źróbek-Sokolnik, Anna (2010). «Избранные аспекты крошечной экологии семян Vetch [ Vicia Hirsuta (L.) Grey SF]: генеративное воспроизведение и влияние зрелости семян и хранения семян на прорастание » Acta Agrobotanica 63 (1). Варшава: Ботаническое общество полиции: 205–2 Doi : 10.5586/ a.2
- Леллингер, Дэвид Б. (2002). Современный многоязычный глоссарий для таксономической птеридологии (Pteridologia) (на английском, испанском, французском и португальском языках). Тол. 3. American Fern Society, Inc. ISBN 978-0-933500-02-0 Полем Получено 15 декабря 2022 года - через библиотеку наследия биоразнообразия .
- Meerow, Alan W . ; Фэй, Майкл Ф . ; Парень, Чарльз Л.; Ли, Цинь-Бао; Заман, Фарида Q.; Чейз, Марк У. (сентябрь 1999). «Систематика amaryllidaceae на основе кладистического анализа данных пластидной последовательности». Американский журнал ботаники . 86 (9). Сент -Луис, Миссури: Ботаническое общество Америки : 1325–1345. doi : 10.2307/2656780 . JSTOR 2656780 . PMID 10487820 .
- Neotropikey (2017). «Глоссарий ботанических терминов» . www.kew.org . Королевские ботанические сады, Кью . Архивировано из оригинала 21 января 2017 года . Получено 18 февраля 2017 года .
- Новый более короткий оксфордский английский словарь по историческим принципам (A - M) . Тол. 1 (6 -е изд.). Оксфорд, Англия: издательство Оксфордского университета . 2007. ISBN 978-0-19-920687-2 Полем Получено 17 декабря 2022 года - через интернет -архив .
- Новый более короткий оксфордский английский словарь по историческим принципам (N - Z) . Тол. 2 (6 -е изд.). Оксфорд, Англия: издательство Оксфордского университета . 2007. ISBN 978-0-19-920687-2 Полем Получено 16 декабря 2022 года - через интернет -архив .
- NYBG (2019). «Глоссарий для сосудистых растений» . William & Lynda Steere Herbarium, Нью -Йорк Ботанический сад . Получено 20 сентября 2019 года .
- Пелл, Сьюзен К.; Ангелл, Бобби (2016). Словарь ботаника: 1300 терминов объяснены и проиллюстрированы . Портленд, Орегон, США: Timber Press . ISBN 978-1-604-69563-2 .
- Рендл, Альфред Бартон (1911). " Фрукты ". В Чисхолме, Хью (ред.). Encyclopædia Britannica . Тол. 11 (11 -е изд.). Издательство Кембриджского университета. С. 257–258.
- Шульце, Эрнст-Детлеф; Zwölfer, Helmut, eds. (2012). Потенциалы и ограничение экосистемного анализа, вымирания и натурализации видов растений . Спрингер Берлин Гейдельберг . ISBN 9783642716300 Полем Получено 16 декабря 2022 года - через Google Books (только предварительный просмотр) .
- Шрив, Форрест ; Виггинс, Ира Л. (1964). Растительность и флора пустыни Сонора . Тол. 1. Стэнфорд, Калифорния, США: издательство Стэнфордского университета . ISBN 9780804701631 Полем OCLC 710084 - через интернет -архив .
- Симпсон, Майкл Г. (август 2011 г.). Систематика растений . Академическая пресса . ISBN 978-0-08-051404-8 - через Google Books (только предварительный просмотр) .
- Симс, Джон (1803). Ботанический журнал Кертиса, или цветочный сад, отображаемый: в которых самые декоративные иностранные растения, культивируемые на открытой земле, зеленый дом и плита, точно представлены в их естественных цветах ... Vol. 17. Лондон: Т. Кертис . Получено 15 декабря 2022 года - через Google Books .
- Стерн, Уильям Т. (1983). Ботанический латынь (3 -е изд.). Newton Abbot & London & North Pomfret, Вермонт, США: Дэвид и Чарльз . ISBN 0-7153-8548-8 Полем Получено 15 декабря 2015 года - через интернет -архив .
- Turland, NJ; Wiersema, JH; Барри, Фр; Greuter, W.; Hawksworth, DL; Herendeen, PS; Knapp, S.; Kusber, W.-H.; Li, D.-Z.; Marhold, K.; Май, TW; McNeill, J.; Монро, Ам; Prado, J.; Цена, MJ; Смит, Гф, ред. (2018). Международный кодекс номенклатуры для водорослей, грибов и растений (Шэньчжэнь Кодекс), принятый девятнадцатым международным ботаническим конгрессом Шэньчжэнь, Китай, июль 2017 года . Regnum gelatabile. Тол. 159. Глашуттен, Германия : Книги Кельц. doi : 10.12705/code.2018 . ISBN 978-3-946583-16-5 Полем OCLC 1043552267 . Получено 21 декабря 2022 года .
Внешние ссылки
[ редактировать ]Посмотрите категория: li: растения в вики, свободный словарь.
- Глоссарий в Apweb
- Глоссарий ботанических терминов ( на английском языке во флоре и т. Д. )
- Садовая сеть
- Эфорас
- Категорический глоссарий для проекта «Флора Северной Америки»
Королевские ботанические сады в Кью
[ редактировать ]Австралия и Новая Зеландия
[ редактировать ]- Университет Сиднея: Eflora - Glossary
- Florabase (Западная Австралия)
- Флора Австралии онлайн Глоссарий
- Флора Австралийских сокращений
- Флора S Australia
- Ботаника Слово дня - иллюстрированное с новой Зеландией
- Новозеландская сеть сохранения растений
Африка
[ редактировать ]- Herman, PPJ (2015). «Ботанический глоссарий» (PDF) . Санби . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 18 октября 2020 года . Получено 21 мая 2020 года .
- Растения Южной Африки ( архивировано 17 октября 2016 года на машине Wayback )


























