Большой Манчестер
Большой Манчестер | |
|---|---|
 Расположение Большого Манчестера в Англии | |
| Координаты: 53 ° 30'09 " 2 ° 18'36" с 53,50 ° с.ш. 2,3100 ° с | |
| Суверенное состояние | Великобритания |
| Учредитель страны | Англия |
| Область | Северо -Западная Англия |
| Учредил | 1 апреля 1974 года |
| Установлен | Закон местного самоуправления 1972 года |
| Часовой пояс | UTC+0 ( GMT ) |
| • Лето ( DST ) | UTC+1 ( BST ) |
| Великобритания парламент | 27 депутатов |
| Полиция | Полиция Большого Манчестера |
| Церемониальный округ | |
| Господь лейтенант | Дайан Хокинс [ 1 ] |
| Высокий шериф | Лоррейн Уорссли-Картер [ 2 ] |
| Область | 1276 км 2 (493 кв. МИ) |
| • Классифицировать | 39 -й из 48 |
| Население (2022) [ 3 ] | 2,911,744 |
| • Классифицировать | 3 -й из 48 |
| Плотность | 2282/км 2 (5,910/кв. МИ) |
| Этническая принадлежность | Список |
| Столичный округ | |
| Правительство | Большой Манчестер комбинированный авторитет |
| Мэр | Энди Бернхэм ( л ) |
| Код GSS |
|
| Itl | TLD3 |
| Веб -сайт | Большой МАНАНСКИЙ КА |
| Районы | |
 Районы Большого Манчестера Столичные районы | |
| Районы | Список |
Большой Манчестер - церемониальный округ на северо -западе Англии . Он граничит с Ланкаширом на севере, Дербишире и Западном Йоркшире на востоке, Чешире на юге и Мерсисайд на западе. Его крупнейшее поселение - город Манчестер .
Округ имеет площадь 493 кв. Миль (1277 км 2 ) [ 5 ] и очень урбанизирован, с населением 2,8 миллиона. Большинство поселений округа являются частью застроенной зоны Большого Манчестера , которая распространяется на Чешир и Мерсисайд и является вторым по численности населения городской зоны в Великобритании . Город Манчестер является крупнейшим поселением. Другими крупными поселениями являются Болтон , Рочдейл , Продажа , Солфорд , Стокпорт и Уиган . Большой Манчестер содержит десять столичных районов : Манчестер, Солфорд , Болтон , Бери , Олдхэм , Рочдейл , Стокпорт , Тамсайд , Траффорд и Уиган , советы которых сотрудничают через Большой Манчестер . Округ был создан 1 апреля 1974 года из некоторых частей северо-восточного Чешира, юго-восточного Ланкашира и небольшой части западного езды на Йоркшире .
Центр и к юго-западу от Большого Манчестера находятся низины, похожие на прибрежную равнину Западного Ланкашира на северо-западе и Чеширскую равнину на юго-западе. Север и Восток являются частью Пеннинов : западные мавры Пеннина на северо -западе, Южные Пеннины на северо -востоке и Пик район на востоке. Большинство рек округа поднимаются в Пеннинах и являются притоками Мерси и Ирвелла , последний из которых сам по себе является притоком Мерси. Округ связан с устьем Мерси Манчестерским кораблем , который в течение всей своей длины в Большом Манчестере состоит из канальных участков Мерси и Ирвелла.
То, что сейчас является Большим Манчестером, было в значительной степени сельской местностью до промышленной революции , когда регион быстро промышленный. Города и города района стали основными центрами производства хлопкового текстиля , которому помогает эксплуатация на угольном поле Ланкашира . Регион также был инженерным и научным центром, что привело к таким достижениям, как первая межгородная железная дорога и Эрнеста Резерфорда новаторская работа по ядерному делению . С момента деиндустриализации в середине 20-го века округ стал крупным центром услуг, медиа и цифровой промышленности и известен гитарой и танцевальной музыкой и ее футбольными командами. [ 6 ]
История
[ редактировать ]Британцы
[ редактировать ]Хотя Большой Манчестер не был создан до 1974 года, история его поселений уходит на годы. Существуют доказательства жилья железного века , особенно в Меллоре , [ 7 ] и известное кельтских британцев поселение по имени Чочиону , которое, как полагают, был районом Уигана , усеянный Бригантами . [ 8 ] Стретфорд также был частью земли, которая, как считается, была занята племенем кельтского бригантов и лежала на границе с Cornovii на южной стороне реки Мерси . [ 9 ] Остатки фортов 1-го века в Каслфилде в Манчестере, [ 10 ] и Каслшоу римский форт в Сэддлворте , [ 11 ] являются свидетельством римской оккупации .
Солфордшир
[ редактировать ]
От реки Мерси до Ривер Риббл был зарегистрирован как район, обследованный с Чеширом в в Дом книге 1086 года ; Считается, что область была частично обследована. [ 12 ]
Между творением Ланкашира до 18 -го века древнее подразделение Шира, с аналогичной, но меньшей площадью для нынешнего графства, было известно как Солфордшир . У подразделения ( Wapentake , которая впоследствии стала сотня) было несколько приходов, поселков и рыночных городов. Другие районы того, что стало бы окружными веками спустя, к югу от Мерси и Ручной , управлялись под Чеширом, в то время как район Сэддлворт и небольшая часть Моссели исторически являются частью Йоркшира .
Манчестерт
[ редактировать ]
В конце 18 -го по начало 19 -го века промышленная революция преобразовала местную внутреннюю систему; Мехализация позволила индустриализации текстильной торговли региона, вызвав быстрый рост хлопковой промышленности и расширение в вспомогательных сделках. [ 13 ] Район стал центральным в торговле шерстяной Англии с внутренней фланельной и фюстианской ткани, которая поощряла систему межрегиональной торговли. [ 14 ] [ 15 ] [ 16 ] В 18 -м веке немецкие торговцы придумали имя Манчестерту, чтобы покрыть регион в Манчестере и его окрестностях. [ 17 ]
Инфраструктура, такая как ряды террасного жилья, фабрик и дорог, была построена для размещения труда, транспортных товаров и производства хлопковых товаров в промышленном масштабе для мирового рынка. [ 13 ] [ 16 ] Городки в Манчестере и его окрестностях начали расширяться «удивительно» на рубеже 19 -го века в рамках процесса незапланированной урбанизации, вызванного бумом в промышленном текстильном производстве и обработке. [ 18 ] Это увеличение численности населения привело к «энергичному концентрическому росту» конфликта между Манчестером и дугой окружающих мельничных городов , сформированной из устойчивого аккреции домов, фабрик и транспортной инфраструктуры. [ 19 ] Такие места, как Бери , Олдхэм и Болтон, сыграли центральную экономическую роль в национальном уровне, и к концу 19-го века стали одними из самых важных и продуктивных городов, производящих хлопок в мире. [ 20 ] Тем не менее, это был Манчестер, который был самым густонаселенным поселением, крупным городом, крупнейшим в мире рынком для хлопковых товаров, [ 21 ] [ 22 ] и естественный центр его региона. [ 23 ] К 1835 году «Манчестер был без проблем в первом и величайшем промышленном городе в мире»; [ 22 ] и к 1848 году городской разрастание объединила город в окружающих городах и внутренних районах, чтобы сформировать единую непрерывную конфарбацию. [ 19 ] Район записан в документах по планированию Манчестерского корабля , датированного 1883 году, как «Манчестер, Солфорд и Ап-Коуншир». [ 24 ]
Conurbation был «викторианским мегаполисом, достигающим своего коммерческого пика в 1890–1915 годах». [ 25 ] В 1910 -х годах были предложены реформы местного самоуправления, чтобы управлять этим связанностью в качестве единого сущности. [ 26 ] Использование в муниципальном контексте появилось в отчете 1914 года, представленном в ответ на то, что считалось успешным созданием Лондонского округа в 1889 году. [ 26 ] В докладе предполагается, что округ должен быть создан для признания «Манчестера, известного в коммерции», и упоминается о областях, которые сформировали «существенную часть Южного Ланкашира и часть Чешира, включающие все муниципальные районы и второстепенные власти в радиусе Восемь или девять миль от Манчестера ». [ 26 ] [ 27 ]
В своих книжных городах 1915 года в эволюции городской планировщик сэр Патрик Геддес написал «гораздо больше, чем понимает Ланкашир, вырос в другом Большом Лондоне». [ 28 ] Манчестерская вечерняя хроника выдвинула на передний план вопрос «регионального единства» для этого района в апреле 1935 года под заголовком «Большой Манчестер - спасение налогоплательщиков». В нем сообщалось о «растущих требованиях по изучению возможностей большего слияния государственных услуг по всему Манчестеру и окружающим муниципалитетам». [ 29 ] Эта проблема часто обсуждалась гражданскими лидерами в этом районе, особенно из Манчестера и Солфорда . Мэр Солфорда пообещал свою поддержку этой идее, заявив, что он с нетерпением ждал того дня, когда »будет слияние основных услуг Манчестера, Солфорда и окружающих районов, составляющих Большой Манчестер». [ 29 ] Предложения были остановлены Второй мировой войной , хотя в течение десятилетия после нее, темпы предложений по реформе местного самоуправления для области ускорились. [ 30 ] В 1947 году Совет округа Ланкашир предложил систему трех « походов » для удовлетворения меняющихся потребностей графства Ланкашир, в том числе для Манчестера и окружающих районов. [ 30 ] Другие предложения включали создание совета графства Манчестер, непосредственно избранного регионального органа. В 1951 году перепись в Великобритании начала сообщать на юго -востоке Ланкашира как однородную конурбацию. [ 30 ]
Шкалы
[ редактировать ]Закон местного самоуправления 1958 года обозначал району Юго -Восточного Ланкашира (который, несмотря на его название, включала часть северо -восточного Чешира), специальной зоны обзора. Комиссия местного самоуправления по Англии представила проекты рекомендации, в декабре 1965 года, предложив новый округ, основанный на окружающей среде, включая Манчестер, с девятью наиболее местными районами, соответствующими современным районам Большого Манчестера (за исключением Уигана). Обзор был отменен в пользу Королевской комиссии по местному органу власти, прежде чем выпустить окончательный отчет. [ 31 ]
В докладе Королевской комиссии 1969 года, известном как отчет Редклифф-Мауда, было предложено удаление большей части тогдашней существующей системы местного самоуправления. Комиссия описала систему управления городскими и сельскими районами отдельно как устаревшей, отмечая, что городские районы предоставляют занятость и услуги для жителей сельских мест, а городские жители для отдыха использовали открытую сельскую местность для отдыха. Комиссия рассмотрела взаимозависимость областей на многих уровнях, включая поездки на работу, предоставление услуг и которые были прочитаны местные газеты, прежде чем предложить новый административный столичный район . [ 32 ] В этом районе была примерно такая же северная граница, что и сегодняшний Большой Манчестер (хотя входил Россендейл ), но покрыл гораздо большую территорию от Чешира (включая Маклсфилд , Уоррингтон , Олдерли Эдж , Нортвич , Мидлвич , Вильмслоу и Лимм ) и Дербишир (города Новых . Mills , Whaley Bridge , Glossop и Chapel-en-le-Frith -в докладе о меньшинстве предполагалось Бакстон ). включено [ 33 ] Столичный район должен был быть разделен на девять столичных округов, основанных на Уигане, Болтоне, Бери/Рочдейле, Уоррингтоне, Манчестере (включая Солфорд и Олд Траффорд), Олдхэм, Альтринчам, Стокпорт и Тамсейд. [ 33 ] В отчете отмечается, что «выбор даже на лейбл удобства для этого столичного района сложно». [ 34 ] Семь лет ранее, опрос, подготовленный для британской ассоциации, намеревался определить «юго-восток Ланкаширской коренной территории», отметил, что «Большой Манчестер это не ... одна из его основных характеристик-заметная индивидуальность его городов, ... все из которых есть промышленная и коммерческая история более чем местного значения ». [ 35 ] Термин selnec (или selnec ) уже использовался в качестве аббревиатуры для юго -востока Ланкашира и Северо -Восточного Чешира; Redcliffe-Maud воспринял это как «самый удобный термин», изменив его на юго-восток Ланкашир, Северо-Восток и Центральный Чешир. [ 33 ]

В соответствии с Законом о транспорте 1968 года в 1969 году был создан руководитель пассажирского транспорта Selnec (полномочия по координации и эксплуатации общественного транспорта в регионе), охватывающая область, меньшую, чем предлагаемый Selnec, и снова отличается от возможного Большого Манчестера. По сравнению с районом Redcliffe-Maud, он исключил Macclesfield, Warrington и Knutsford, но включил Glossop в Дербишире и Седлворт в Западном езде в Йоркшире . Он исключил Уиган, который находился как в районе Редклифф-Мауд, так и в возможном Большом Манчестере (но не был частью зоны обзора Закона 1958 года). [ 36 ]
Рекомендации Redcliffe-Maud были приняты правительством, контролируемым трудом в феврале 1970 года. [ 37 ] Хотя отчет Редклифф-Мауда был отклонен консервативным правительством после всеобщих выборов 1970 года , была принята приверженность реформе местного самоуправления, и была принята необходимость в столичном графстве, сосредоточенной на связанном с этим в округе, окружающей Манчестер. Первоначальное предложение нового правительства было намного меньше, чем Selnec отчета Redcliffe-Maud, с такими областями, как Уинсфорд, Нортвич, Кнутсфорд, Маклсфилд и Глоссоп, оставленные их первоначальными округами, чтобы обеспечить Совет графства достаточное количество доходов, чтобы оставаться конкурентоспособными ( Чешир будет перестали существовать). [ 37 ] Другие поздние изменения включали разделение предлагаемого Управления Бери/Рочдейл (сохранившегося в отчете Редклифф-Мауда) в столичный район Бери и столичный район Рочдейл . Первоначально планировалось сформировать один район Бери и Рочдейл (названный «Ботчдейл» местным депутатом Майклом Фидлером ) [ 38 ] [ 39 ] но были разделены на отдельные районы. Чтобы переоценить районы, район Рочдейл взял Миддлтон из Олдхэма. [ 40 ] Во время принятия законопроекта города Уитворт , Вильмслоу и Пойнтон успешно возражали против их включения в новый округ. [ 37 ]
1974–1997
[ редактировать ]


Области, которые были включены в Большой Манчестер в 1974 году, ранее сформировались части административных округов Чешир, Ланкашир, Западный езда в Йоркшире и восемь независимых округов . [ 42 ] К началу 1970 -х годов эта система разграничения была описана как «архаичная» и «крайне неадекватная, чтобы идти в ногу как с воздействием моторных путешествий, так и с огромным увеличением обязанностей местного самоуправления». [ 45 ]
Закон местного самоуправления 1972 года реформировал местное самоуправление в Англии , а Закон был принят 1 апреля 1974 года. В этом районе было названо название Большого Манчестера и обозначения округа столичного округа . Это была двухуровневая система округов и районов . [ 41 ] Акт формально, [ 46 ] Хотя Большой Совет графства Манчестер (GMCC) работал с момента выборов в 1973 году . [ 47 ] Ведущая статья в «Таймс» в день, когда вступил в силу Закон о местных органах власти, отмечала, что «новая договоренность - это компромисс, который стремится примирить знакомую географию, которая командует определенной любовью и лояльностью, с масштабом операций, на которых современное планирование планирует Методы могут работать эффективно ». [ 48 ] Франгопуло отметил, что создание Большого Манчестера «было официальным объединением региона, который посредством истории и традиций создавался для себя на протяжении многих веков ... между общинами города и деревней, каждый из которых был воплощением воплощения характер этого региона ». [ 49 ] Название Большого Манчестера было принято, будучи предпочтительным по сравнению с Selnec после публичной консультации, [ 50 ] Несмотря на то, что оппозиция утверждала, что «Большой Манчестер [...] - это миф. Айборизация. Пледно». [ 51 ]
К январе 1974 года совместная рабочая группа, представляющая Большой Манчестер, разработала свой план структуры округа , готовую к реализации Советом графства Большой Манчестер. План установил цели для предстоящего округа Метрополитен. [ 52 ] Наибольшим приоритетом было повышение качества жизни для его жителей, улучшая физическую среду и культурные объекты округа, которые пострадали после деиндустриализации-большая часть основной инфраструктуры Большого Манчестера от его роста 19-го века и была не подходит для современного образа жизни. [ 53 ] Другими целями состояли в том, чтобы обратить вспять тенденцию депопуляции в Манчестере центрального огня, инвестировать в страновые парки, чтобы улучшить плохую репутацию региона в области досуга, а также для улучшения транспортной инфраструктуры и закономерности округа. [ 54 ]

Из -за политических возражений, особенно от Чешира, Большой Манчестер охватывал только внутреннее, городское 62 из 90 бывших округов, которые Королевская комиссия рассказала как эффективная административная столичная область. [ 55 ] В этом качестве GMCC оказалась «планирующим произвольную столичную зону ... внезапно усеченной на юг», и поэтому ему пришлось договориться о нескольких проектах по использованию земель, транспорту и жилищному строительству с его соседними советами округа. [ 55 ] Однако «крупная программа экологических действий» GMCC в целом преуспела в обращении социальной депривации в трущобах города. [ 55 ] Досуг и развлекательные успехи включали в себя выставочный центр Большого Манчестера (более известный как Центр G-MEX, а теперь и фирменная Manchester Central ), преобразованная бывшая железнодорожная станция в Манчестерском центре города, используемая для культурных мероприятий, [ 56 ] и создание GMCC пяти новых страновых парков в пределах его границ. [ 57 ] Однако GMCC подвергся критике за то, что он был слишком ориентирован на манчестер со стороны представителей внешних пригородов. [ 58 ]
Через десять лет после того, как они были созданы, в основном контролируемые трудовыми советами округа и Советом Большого Лондона (GLC) было несколько громких столкновений с консервативным правительством Маргарет Тэтчер , связанные с перерасходом и высоким уровнем платы. Правительственная политика по этому вопросу рассматривалась на протяжении всего 1982 года, и Консервативная партия поместила «обещание отказаться от советов столичного графства» и GLC в своем манифесте на всеобщих выборах 1983 года . [ 59 ] [ 60 ] Совет графства Большого Манчестера был отменен 31 марта 1986 года в соответствии с Законом о местном самоуправлении 1985 года . То, что столичные советы графства контролировались лейбористской партией, привело к обвинениям в том, что их отмена была мотивирована партийной политикой: [ 59 ] Генеральный секретарь Национальной ассоциации сотрудников местного самоуправления назвал это «полностью циничным маневром». [ 61 ] Большинство функций GMCC были перенесены в десяти Большого Манчестерского столичного районного были переведены в рамках таких функций, как аварийные службы и общественный транспорт совета, хотя такие совместные советы , и продолжали работать на общенациональном уровне. [ 62 ] Ассоциация властей Большого Манчестера (AGMA) была создана, чтобы продолжить большую часть услуг округа Совета графства . [ 63 ] Столичный округ продолжает существовать в законе, и в качестве географической системы отсчета, [ 64 ] Например, в качестве административного подразделения Nuts 2 для статистических целей в Европейском Союзе . [ 65 ] Несмотря на то, что он был в районе лейтенанности с 1974 года, Большой Манчестер был включен в церемониальный округ в Законе о лейтенантах 1997 года 1 июля 1997 года. [ 66 ]
Комбинированный авторитет
[ редактировать ]В 1998 году жители Большого Лондона проголосовали на референдуме в пользу создания новой администрации Большого Лондона , с мэром и избранной палатой для округа. [ 67 ] Новая сеть местного самоуправления предложила создать новый регион Манчестер Сити, основанный на Большом Манчестере и других столичных округах в рамках постоянных усилий по реформе, в то время как в докладе, опубликованном государственной политики, Института Центром по городам предложил создание из двух административных городских регионов, основанных на Манчестере и Бирмингеме .
Регион Манчестер Сити первоначально появился в правительственных документах как один из восьми городских регионов, определенных в стратегическом документе 2004 года, продвигаясь вперед: Северный путь . [ 68 ] В июле 2007 года Казначейство опубликовало свой обзор субнационального экономического развития и регенерации , в котором говорилось, что правительство позволит тем городским регионам, которые хотят работать вместе, чтобы сформировать законодательную основу для городской региональной деятельности, включая полномочия над транспортом, навыки, навыки, планирование и экономическое развитие. [ 69 ] Регион Манчестер Сити охватывал пятнадцать округов местного самоуправления: города Манчестер и Солфорд а также столичные районы Стокпорта , , Тамсейд , Траффорд , Болтон , Бери , Олдхэм , Рочдейл и Уиган , вместе с районами , высокого пика Уоррингтона и бывших районов. Конглтон Макклсфилд , Вейл и Роял . [ 70 ]
В январе 2008 года Агма предложила создать официальную правительственную структуру для охвата большего Манчестера. [ 71 ] Проблема вспыхнула в июне 2008 года в отношении предложенной заторов в Большом Манчестере ; Сэр Ричард Лиз (лидер Совета Манчестерского городка ) сказал: «Я пришел к выводу, что [референдум по затону принять это решение ». [ 72 ] 14 июля 2008 года десять местных властей в Большом Манчестере согласились на стратегическое и интегрированное соглашение о межотборении по многонайотам ; Добровольная инициатива, направленная на то, чтобы сделать районные советы «работать вместе, чтобы оспорить искусственные пределы границ» в обмен на большую автономию со стороны центрального правительства Великобритании . [ 73 ] Референдум о фонде инновационных инноваций в Большом Манчестере состоялся в декабре 2008 года, [ 74 ] в которых избиратели «в подавляющем большинстве отклонены» планы на улучшения общественного транспорта, связанные с пиковым временем в будние дни. [ 75 ]
После заявки от Агмы, подчеркивающей потенциальные преимущества в борьбе с финансовым кризисом 2007–2008 годов было объявлено , в бюджете Великобритании в Соединенном Королевстве , что Большой Манчестер и регион города Лидс получит статус пилотного региона города, позволяя (если они желают. ), чтобы их избирательные окружные советы могли объединить ресурсы и стать установленными законодательными властями с полномочиями, сопоставимыми с авторитетом Большого Лондона. [ 76 ] Заявленная цель пилота состояла в том, чтобы оценить вклад в экономический рост и устойчивое развитие комбинированными властями. [ 77 ] Закон о местной демократии, экономическом развитии и строительстве 2009 года позволил создать комбинированный орган для Большого Манчестера с передачей полномочий по общественному транспорту, навыкам, жилье, регенерации, управлению отходами, углеродным нейтралитетом и разрешением на планирование в ожидании одобрения от десяти советов. [ 76 ] [ 78 ] Такие стратегические вопросы будут решены через расширенную систему голосования большинства , в которой участвуют десять членов, назначенных из числа советников столичных районов (один представляющий каждый район, причем каждый совет назначает одного замены) без вклада центрального правительства. Десять районных советов Большого Манчестера одобрили создание Объединенного полномочия Большого Манчестера (GMCA) 29 марта 2010 года и представили окончательные рекомендации для конституции Департаменту для общин и местного самоуправления и Департамента по транспорту и через два дня общины Секретарь Джон Денхэм одобрил Конституцию и начал 15-недельную публичную консультацию по проекту законопроекта вместе с утвержденной конституцией. [ 79 ]
Следуя запросам Ассоциации властей Большого Манчестера, которая была заменена GMCA, [ 80 ] [ 81 ] [ 82 ] Новый орган был создан 1 апреля 2011 года. [ 83 ] В тот же день транспорт для Комитета по Большому Манчестеру был также сформирован из пула из 33 советников, выделенных населением совета (примерно одного советника на 75 000 жителей), чтобы изучить управление транспортными органами Большого Манчестера и их финансах, одобрить решения и политики из указанных органов и формирования стратегических рекомендаций политики или проектов для утверждения объединенного органа. [ 76 ] 3 ноября 2014 года Джордж Осборн , канцлер казначейства , объявил, что будет одиннадцатый член GMCA - непосредственно избранного мэра Большого Манчестера , с «полномочиями над транспортом, жильем, планированием и полицейской деятельностью» с 2017 года. [ 84 ]
География
[ редактировать ]
Большой Манчестер - округ, округленный выпускной, охватывающий 493 кв. Миль (1277 км 2 ). [ 5 ] Пеннины . поднимаются на север и восток графства с западными Пеннин Маурс на северо -западе, южными Пеннинами на северо -востоке и Пик -районом на востоке Несколько угольных полей (в основном песчаников и сланцев) лежат на западе графства, в то время как Чеширская равнина на юге. [ 13 ] Реки Мерси , Ирвелл и Тейм проходят через Большой Манчестер, все из которых поднимаются в Пеннинах. [ 13 ] Другие реки пересекают регион в качестве притоков основных рек, включая Дугласа , Ирк и Рох . [ 13 ] Black Chew Head является самой высокой точкой в Большом Манчестере, которая является частью Пикового районного национального парка , поднимаясь на 1778 футов (542 м) над уровнем моря, в приходе Седлворт . [ 85 ] Большой Манчестер характеризуется своими плотными городскими и промышленными разработками, которые включают центры торговли, финансов, розничной торговли и администрирования, а также пригород и жилье, вкрапленные с транспортной инфраструктурой, такой как скоростные железы, дороги и автомагистрали и каналы. [ 13 ] Существует сочетание городских районов высокой плотности, пригородов, полусельских и сельских мест в Большом Манчестере, но землепользование в основном является городским. [ 86 ] Построенная среда Большого Манчестера использует красной кирпич и песчаник в качестве строительного материала, наряду со структурами, состоящими из современных материалов, высотных башен и зданиями 19-го, 20-го и 21-го века в городских и городских центрах. [ 13 ]

Манчестерский центр города - это коммерческое и географическое сердце Большого Манчестера, [ 87 ] [ 88 ] [ 89 ] А с прилегающими частями Солфорда и Траффорда определяется как «региональный центр» Большого Манчестера для целей городского планирования и общественного транспорта. [ 87 ] [ 89 ] [ 90 ] [ 91 ] [ 92 ] Политические и экономические связи между центром города и соседним Солфордом и Траффордом укрепились с переходом от городских и районных центров к центрам столичного уровня в Англии, [ 93 ] [ 90 ] И многоэтажные здания этой области обеспечивают ориентацию визуальной ориентации в качестве центрального делового района. [ 13 ] Тем не менее, Большой Манчестер также является полицентрическим округом с десятью столичными районами, [ 86 ] Каждый из которых имеет крупный центр города - и в некоторых случаях более одного - и многие меньшие поселения. [ 86 ] Основные города окружают Манчестерский центр города, а между ними находятся другие отдаленные города (такие как Дентон , Миддлтон и Файлсворт ), которые являются пригородными как для регионального центра, так и для основных городских центров. [ 94 ] В совокупности эти факторы делают больший Манчестер самым сложным «полицентрическим функциональным городским регионом» в Великобритании за пределами Лондона. [ 86 ] [ 58 ]
Район Большого Манчестера -это район Conurbatation или непрерывная городская зона, основанная на Большом Манчестере, как определено Управлением по национальной статистике . В 2011 году он составил около 2553 379 человек, что делает его второй по численности населенной зоны в Великобритании , и занимал площадь 630,3 км. 2 (243,4 кв. МИ) во время переписи 2011 года. [ 95 ] Европейский союз назначает Conurbation как единый гомогенный городской регион города . [ 96 ] Застроенная зона включает в себя большинство Большого Манчестера, пропущенные районы сельской местности и небольших деревень, а также незаметные городские города, такие как Уиган и Марпл . [ 95 ] За пределами границы Большого Манчестера он включает в себя несколько соседних районов поселения и несколько выбросов, связанных с развитием ленты, таких как Вильмслу и Олдерли Эдж в Чешире, Глоссопе и Хэдфилде в Дербишире и Уитворт в Ланкашире. [ 95 ] Это связанное составляет часть мегаполиса в 9,4 миллиона человек по всей северной Англии . [ 97 ] [ 98 ] [ 99 ]
Климат
[ редактировать ]Большой Манчестер испытывает умеренный морской климат , как и большинство британских островов , с относительно прохладным летом и мягкой зимой. Среднегодовое количество осадков округа составляет 806,6 мм (31,76 дюйма) [ 100 ] по сравнению с в среднем в Великобритании 1125,0 мм (44,29 дюйма), [ 101 ] и его средние дни дождя составляют 140,4 мм (5,53 дюйма в год, [ 100 ] по сравнению со средним уровнем Великобритании 154,4 мм (6,08 дюйма). [ 101 ] Средняя температура немного выше среднего для Великобритании. [ 101 ] Большой Манчестер имеет относительно высокий уровень влажности, который оценивался для оптимизированного и безразличного процесса производства текстиля, который имел место в округе. Снегопад не распространен в застроенных районах из -за эффекта городского потепления , но западные мавры Пеннина на северо -западе, южные Пеннины на северо -востоке и пик на востоке получают больше снега, и дороги, ведущие из округа к тяжелому снегопаду. [ 102 ] Они включают дорогу A62 через Standedge , [ 103 ] Пеннинская часть M62 [ 104 ] и A57 , Snake Pass , к Шеффилду . [ 105 ] В самой южной точке Большого Манчестера метеостанция Вудфорда зафиксировала температуру -17,6 ° C (0,3 ° F) 8 января 2010 года . [ 106 ]
| Месяц | Январь | Февраль | Марта | Апрель | Может | Июнь | Июль | Август | Сентябрь | Октябрь | Ноябрь | Декабрь | Год |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Запись высокой ° C (° F) | 14.3 (57.7) |
19.0 (66.2) |
21.7 (71.1) |
25.1 (77.2) |
26.7 (80.1) |
31.3 (88.3) |
37.0 (98.6) |
33.7 (92.7) |
28.4 (83.1) |
27.0 (80.6) |
17.7 (63.9) |
15.1 (59.2) |
37.0 (98.6) |
| Средний ежедневный максимум ° C (° F) | 7.3 (45.1) |
7.6 (45.7) |
10.0 (50.0) |
12.6 (54.7) |
16.1 (61.0) |
18.6 (65.5) |
20.6 (69.1) |
20.3 (68.5) |
17.6 (63.7) |
13.9 (57.0) |
10.0 (50.0) |
7.4 (45.3) |
13.5 (56.3) |
| Средний средний ° C (° F) | 4.5 (40.1) |
4.6 (40.3) |
6.7 (44.1) |
8.8 (47.8) |
11.9 (53.4) |
14.6 (58.3) |
16.6 (61.9) |
16.4 (61.5) |
14.0 (57.2) |
10.7 (51.3) |
7.1 (44.8) |
4.6 (40.3) |
10.0 (50.0) |
| Средний ежедневный минимум ° C (° F) | 1.7 (35.1) |
1.6 (34.9) |
3.3 (37.9) |
4.9 (40.8) |
7.7 (45.9) |
10.5 (50.9) |
12.6 (54.7) |
12.4 (54.3) |
10.3 (50.5) |
7.4 (45.3) |
4.2 (39.6) |
1.8 (35.2) |
6.6 (43.9) |
| Запись низкого ° C (° F) | −17.6 (0.3) |
−13.1 (8.4) |
−9.7 (14.5) |
−4.9 (23.2) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
0.8 (33.4) |
5.4 (41.7) |
3.6 (38.5) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
−10.0 (14.0) |
−14.0 (6.8) |
−15.0 (5.0) |
| Среднее количество осадков мм (дюймы) | 72.3 (2.85) |
51.4 (2.02) |
61.2 (2.41) |
54.0 (2.13) |
56.8 (2.24) |
66.1 (2.60) |
63.9 (2.52) |
77.0 (3.03) |
71.5 (2.81) |
92.5 (3.64) |
81.5 (3.21) |
80.7 (3.18) |
828.8 (32.63) |
| Средний снегопад мм (дюймы) | 24 (0.9) |
19 (0.7) |
10 (0.4) |
1 (0.0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
2 (0.1) |
15 (0.6) |
71 (2.7) |
| Средние дни осадков (≥ 1,0 мм) | 13.1 | 9.7 | 12.3 | 11.2 | 10.4 | 11.1 | 10.9 | 12.0 | 11.1 | 13.6 | 14.1 | 13.5 | 142.9 |
| Средние снежные дни | 6 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 20 |
| Средняя относительная влажность (%) | 83 | 81 | 77 | 74 | 72 | 74 | 76 | 77 | 79 | 81 | 83 | 84 | 79 |
| Средняя точка росы ° C (° F) | 2 (36) |
2 (36) |
3 (37) |
4 (39) |
7 (45) |
9 (48) |
11 (52) |
12 (54) |
10 (50) |
8 (46) |
5 (41) |
3 (37) |
6 (43) |
| Средние месячные солнечные часы | 52.5 | 73.9 | 99.0 | 146.9 | 188.3 | 172.5 | 179.7 | 166.3 | 131.2 | 99.3 | 59.5 | 47.1 | 1,416.2 |
| Средние ежедневные солнечные часы | 3.4 | 3.4 | 5.2 | 6.8 | 6.7 | 6.4 | 6.6 | 6.0 | 5.9 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 3.6 | 5.1 |
| Средний ультрафиолетовый индекс | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Источник 1: Met Office [ 107 ] NOAA (относительная влажность и снежные дни 1961–1990) [ 108 ] | |||||||||||||
| Источник 2: KNMI [ 109 ] [ 110 ] Текущие результаты - погода и наука [ 111 ] Погодный климат [ 112 ] Время и дата: средняя точка росы (1985-2015) [ 113 ] Weatheratlas [ 114 ] | |||||||||||||
Флора и фауна
[ редактировать ]
Вопреки его репутации за разрастание городов, [ 115 ] [ 116 ] Большой Манчестер имеет зеленого пояса сдерживание городского дрейфа , а также «широкий и разнообразный диапазон» дикой природы и естественной среды обитания. [ 115 ] Например, лесистые долины Болтон, Бери и Стокпорт, вересковые земли к северу и востоку от Рочдейла, Олдхэма и Сталибриджа, и тростниковые кровати между Уиганом и Ли, Харбор Флорой и Фауной национальной важности. [ 115 ] Зрелые леса, кустарника, луга, высокая вересковая пустоша, Моссленд, сельскохозяйственные земли, озера, водно -болотные угодья, речные долины, насыпь, городские парки и пригородные сады - это среды обитания, которые можно найти в Большом Манчестере, которые в дальнейшем способствуют биоразнообразию. [ 116 ] Отдел экологии Большого Манчестера классифицирует сайты, имеющие биологическое значение . [ 117 ]
21 участки специального научного интереса (SSSI) в Большом Манчестере и 12,1 кв. Миль (31 км 2 ) общей земли в Большом Манчестере [ 118 ] представляют особый интерес для таких организаций, как Центр местных записей Большого Манчестера, проект по биоразнообразию Большого Манчестера и Манчестерский полевой клуб, которые посвящены сохранению дикой природы региона и сохранению естественной истории . [ 119 ] [ 120 ] [ 121 ] Среди SSSI - Эстли и Бедфорд Мосс , которые образуют сеть древнего торфяного болота на краю чата Мосс , [ 115 ] который, в свою очередь, при 10,6 кв. Миль (27 км 2 ) содержит самую большую площадь первичных сельхозугодий в Большом Манчестере и содержит самый большой блок полу натурального леса в округе. [ 122 ] Вспышки Уигана, такие как в Пеннингтон-Флэш-Кантри Парке , являются побочным продуктом добычи угля, где оседание привело к тому, что водяные болоты собираются в полученных впадах, которые образуют важный ресурс тростника в Большом Манчестере. [ 115 ] Открытый в 1979 году, аквапарк для продажи представляет собой площадь 152 акра (62 га) в сельской местности и парковой площадке в продаже, который включает в себя искусственное озеро площадью 52 акра (21 га) у реки Мерси . [ 123 ]
Clover , Sorrel , крапия и чертополох распространены и растут в Большом Манчестере. [ 116 ] Common Heather ( Calluna vulgaris ) доминирует над нагорками, такими как Saddleworth Moor , которая находится в южном Пеннинах и Темного Пика площади национального парка Пика . [ 124 ] Канал Рочдейла содержит плавучий водный завод ( Luronium natams ), национально исчезающего водного завода. [ 115 ] В 2002 году PlantLife International запустила свою кампанию округа цветов , попросив представителей общественности выдвигать и проголосовать за эмблема дикого цветов для своего округа. Общий коттонграсс ( eriophorum angustifolium ), растение с пушистыми белыми шлейфами, местными для влажных лосты на высоких маврах, было объявлено как цветок графства Большого Манчестера. [ 125 ] [ 126 ] [ 127 ]
Дом Воробей , Старлинг и Блэкберд являются одними из самых густонаселенных видов птиц в Большом Манчестере; Сорока и дикий голубь являются обычными и размножаются в местах обитания по всему округу. [ 128 ] Слои диких попугаев можно увидеть во многих парках Южного Манчестера, [ 129 ] в том числе парк Берхфилдс, парк Уитворт и Платт Филдс Парк . [ 130 ] [ 131 ] [ 132 ] Перемещение птиц в Великобританию сделало их «только натурализованным попугаем и самым северным размножением в мире». [ 132 ] Южные Пеннины также поддерживают во всем мире важное количество золотой плюсы , Curlew , Merlin и Twite . [ 118 ] Известно, что ряд красных террапинов , вид малой черепахи, населяют озеро в парке Александры . [ 133 ]
Исторические границы округа
[ редактировать ]

Большой Манчестер состоит из частей Чешира, Ланкашира и некоторых частей Западного катания на Йоркшире. Историческая граница между Чеширом и Ланкаширом начинается с точек как реки, так и Манчестерского корабля. Южные части графства, которые являются частью Траффорда, Стокпорта и Покрытия Тамсайд Альтринчам, продажи, Стокпорт, Марпл, Чидл Халм, Хайд, Сталибридж и Уайтеншоу (которые стали частью Манчестера в 1920 -х годах), все исторически являются частью Чешира. Дентон и Оденшоу в Тамсайде были исторически частью Ланкашира. В то время как большинство графств к северу от реки Ирвелл до Чорли, Дарвен, Сент -Хеленс и Россендейл составляют большую часть исторического графства Ланкашир, включая Манчестер, Солфорд, Эклс, Болтон, Бери, Пресвич, Суинтон, Пендлбери, Wigan, Leigh, Rochdale, Oldham, Ashton-Under-Lyne, Stretford, Urmston, Old Trafford, Chadderton, Middleton, Heywood, Radcliffe, Milnrow, Horwich, Blackrod, Westhoughton, Littleborough, Atherton, Ashton-In-Makerfield и Golborne. Восточные и северо -восточные районы графства, которые включают в себя Saddleworth и части Рочдейла, являются частью исторического графства Западной поездки в Йоркшире. [ 134 ] [ 135 ]
Призывы вернуться к историческим округам
[ редактировать ]С момента формирования Большого Манчестера жители обсуждали свою личность в столичных и исторических округах посредством наследия, культуры и управления. Жители Сэддлворта в районе Олдхэм призвали к независимости от Большого Манчестера и Совета Олдхэма и новой власти, охватывающей Пеннины вокруг Большого Манчестера и Западного Йоркшира, и Общество белой розы Седлворта установило знаки с формулировкой «Историческая Западная версия Йоркшира ". [ 136 ] Петиция 2015 года призвала Уигана подать заявку на независимость от Большого Манчестера и присоединиться к Ланкаширу из -за его наследия и местоположения. [ 137 ] Было предложение о Хорвиче , Атертоне , Блэкроде и Вестхоутоне, чтобы сформировать либо новую часть Большого Манчестера, либо стать отдельной площадью в Ланкашире, возможно, под районом Чорли, хотя это не преследовалось. [ 138 ]
Управление
[ редактировать ]
Большой Манчестерский комбинированный авторитет (GMCA) является административным органом высшего уровня для местного управления Большим Манчестером. Он был основан 1 апреля 2011 года как пилотный комбинированный орган , уникальный для местного самоуправления в Соединенном Королевстве . [ 139 ] После формирования он состоял из десяти косвенно избранных членов, каждый из которых был избран непосредственно советником из одного из десяти столичных районов, которые составляют Большой Манчестер. Органа получает большую часть своих полномочий из Закона о местном органе власти 2000 года и Закона о местной демократии, экономическом развитии и строительстве 2009 года , [ 139 ] и заменил ряд одноцелевых совместных советов и Quangos в 2011 году, чтобы обеспечить официальный административный орган для Большого Манчестера власти над общественным транспортом, навыками, жильем, регенерацией, управлением отходами, углеродным нейтралитетом и разрешением на планирование. [ 139 ] Функциональные исполнительные органы, такие как транспорт для Большого Манчестера , несут ответственность за предоставление услуг в этих областях. [ 139 ] 3 ноября 2014 года была подписана передача Соглашения об комбинированном власти Большого Манчестера , чтобы пройти дальнейшие полномочия и обязанности, а также создание избранного мэра Большого Манчестера. [ 140 ] С апреля 2016 года Большой Манчестер стал первой областью Англии, которая «получила полный контроль над своими расходами на здоровье», с соглашением о передаче, которая объединяет системы здравоохранения и социального обеспечения региона под одним бюджетом под контролем местных лидеров, включая новые напрямую Большого Манчестера. Избранный мэр. [ 141 ] 4 мая 2017 года лейбористский политик Энди Бернхэм был избран первым мэром , [ 142 ] присоединившись к GMCA в качестве своего одиннадцатого члена и служит его лидером. [ 143 ]
Под GMCA находятся десять советов из десяти районов Большого Манчестера , которые находятся Болтон , Бери , город Манчестер , Олдхэм , Рочдейл , город Солфорд , Стокпорт , Тамсейд , Траффорд и Уиган . Эти районные советы обладают самыми большими полномочиями в отношении государственных услуг и контролируют такие вопросы, как налог совета , предоставление образования, социальное жилье, библиотеки и здравоохранение. Восемь из десяти столичных районов были названы в честь восьми бывших округов, которые в настоящее время составляют самые большие центры населения и большую историческую и политическую известность. [ 144 ] Например, столичный район Стокпорт сосредоточен в городе Стокпорт , бывшем округе, но включает в себя другие небольшие поселения, такие как Чидл , Гатли и Брэмхолл . [ 144 ] Имена двух из столичных районов получили нейтральное имя, потому что в то время, когда они были созданы, не было никакого соглашения о городе, которое будет выдвинуть в качестве административного центра, и ни один из них не имел округа . Эти районы- Tameside и Trafford , сосредоточенные на Эштон-Онд-Лейн и Стретфорд , соответственно, и названы со ссылкой на географическое и историческое происхождение. [ 144 ] Самым низким формальным уровнем местного самоуправления в Большом Манчестере являются приходские советы , которые охватывают различные гражданские приходы в Большом Манчестере и имеют ограниченные полномочия по сравнению с содержанием, обслуживанием и небольшими грантами.
В течение первых 12 лет после того, как округ был создан в 1974 году, в Большом Манчестере была двухуровневая система местного самоуправления, а столичные городские советы обменивали власть с Советом графства Большой Манчестер . [ 145 ] Совет графства Большого Манчестера, стратегический орган, основанный в том, что сейчас является Вестминстерским домом у садов Пикадилли , состоял из 106 членов, взятых из десяти столичных районов Большого Манчестера. [ 146 ] Это были региональные региональные услуги, работающие в субрегиональном органе, такие как транспорт, стратегическое планирование, аварийные службы и утилизация отходов. В 1986 году вместе с пятью другими округа столичными советами и Советом Большого Лондона Совет графства Большого Манчестера был отменен, и большинство его полномочий были переданы районам. [ 145 ] В период с 1986 по 2011 год районы были эффективно унитарными областями власти , но решили добровольно сотрудничать в рамках Ассоциации властей Большого Манчестера (AGMA), которая служила для создания координированного подхода по всему графству к вопросам, представляющим общий интерес для большего. Манчестер, такой как общественный транспорт и рынок общего труда, а также заявления о центральном правительстве и Европейском союзе.

Хотя используется в качестве «успешного бренда», [ 147 ] Политика Большого Манчестера характеризовалась «укоренившимся локализмом и связанным соперничеством», исторически устойчивой к регионализму . [ 58 ] Основные города в Большом Манчестере сохраняют «жесткую независимость», [ 23 ] Это означает, что Большой Манчестер вводится с использованием «межмуниципальной координации» на широко добровольной основе. [ 58 ] То, что восемь из десяти городских советов (по большей части) контролировались рабочей силой с 1986 года, помогло поддерживать это неформальное сотрудничество между районами на уровне округа. [ 148 ] После отмены Совета графства десять власти Большого Манчестера добровольно сотрудничали по вопросам политики, таких как местные транспортные планы , а также финансирование протокола Большого округа Манчестер , [ 149 ] и местные услуги проводились законодательными совместными советами . В настоящее время под руководством Большого Манчестера комбинированного полномочия эти совместные советы транспортируют Большой Манчестер (TFGM), который отвечает за планирование и координацию общественного транспорта по всему округу; Большой Манчестерский пожарная и спасательная служба , которой управляют совместное пожарное и спасательное управление; и Управление по утилизации отходов Манчестера . Эти совместные советы состоят из советников, назначенных из каждого из десяти районов (кроме Управления по утилизации отходов, которое не включает в себя столичный район Уиган ). Полиция Большого Манчестера ранее наблюдала совместная полицейская власть , но была ненадолго контролировать полицию Большого Манчестера и комиссар по преступности с 2012 года. [ 150 ] До тех пор, пока функции этого офиса не были включены в новую региональную мэрию после его создания в 2017 году. Десять городских советов являются совместными владельцами группы аэропорта Манчестера , которая контролирует аэропорт Манчестера и три других аэропорта Великобритании. [ 151 ] Другие услуги финансируются и управляются местными советами. [ 152 ]
Greater Manchester is a ceremonial county with its own Lord-Lieutenant who is the personal representative of the monarch. The Local Government Act 1972 provided that the whole of the area to be covered by the new metropolitan county of Greater Manchester would also be included in the Duchy of Lancaster – extending the duchy to include areas which are historically in the counties of Cheshire and the West Riding of Yorkshire. Until 31 March 2005, Greater Manchester's Keeper of the Rolls was appointed by the Chancellor of the Duchy of Lancaster; they are now appointed by the Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain.[153] The first Lord Lieutenant of Greater Manchester was Sir William Downward who held the title from 1974 to 1988.[154] The current Lord Lieutenant is Warren James Smith.[155] As a geographic county, Greater Manchester is used by the government (via the Office for National Statistics) for the gathering of county-wide statistics, and organising and collating general register and census material.[156]
In terms of representation in the Parliament of the United Kingdom, Greater Manchester is divided into 27 parliamentary constituencies. Most of Greater Manchester is represented in Parliament by the Labour Party, and is generally considered a Labour stronghold.[157][158]
The results of the 2024 United Kingdom general election in Greater Manchester are as follows:
| Party | Votes | % | Change from 2019 | Seats | Change from 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | 471,074 | 42.8% | 25 | |||
| Reform UK | 191,257 | 17.4% | 0 | |||
| Conservative | 173,735 | 15.8% | 0 | |||
| Liberal Democrats | 95,978 | 8.7% | 2 | |||
| Green | 89,203 | 8.1% | 0 | |||
| Workers Party | 49,976 | 4.5% | new | 0 | ||
| Others | 29,520 | 2.7% | 0 | |||
| Total | 1,100,743 | 100.0 | 27 | |||
Demography
[edit]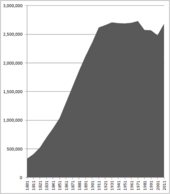

|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-1974 statistics were gathered from local government areas that now comprise Greater Manchester Source: Great Britain Historical GIS.[159] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| District | Land area | Population | Density (/km2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (km2) | (%) | People | (%) | ||
| Bolton | 140 | 11% | 298,903 | 10% | 2,138 |
| Bury | 99 | 8% | 194,606 | 7% | 1,957 |
| Manchester | 116 | 9% | 568,996 | 20% | 4,920 |
| Oldham | 142 | 11% | 243,912 | 8% | 1,714 |
| Rochdale | 158 | 12% | 226,992 | 8% | 1,435 |
| Salford | 97 | 8% | 278,064 | 10% | 2,861 |
| Stockport | 126 | 10% | 297,107 | 10% | 2,357 |
| Tameside | 103 | 8% | 232,753 | 8% | 2,256 |
| Trafford | 106 | 8% | 236,301 | 8% | 2,228 |
| Wigan | 188 | 15% | 334,110 | 11% | 1,776 |
| Greater Manchester | 1,276 | 100% | 2,911,744 | 100% | 2,282 |
Greater Manchester has a population of 2,867,800 (2021 Census),[161] making it the third most populous county in England after Greater London and the West Midlands and the highest ever for the county. The demonym of Greater Manchester is "Greater Mancunian".[162] The Manchester accent and dialect, native to Manchester, is common in the city and adjacent areas, but gives way to "slower, deeper accents" towards Greater Manchester's fringes and suburbs.[23]
Greater Manchester is home to a diverse population and is a multicultural agglomeration with an ethnic minority population comprising 8.5% of the total population in 2001.[163][164] In 2008, there were over 66 refugee nationalities in the county.[165] At the 2001 UK census, 74.2% of Greater Manchester's residents were Christian, 5.0% Muslim, 0.9% Jewish, 0.7% Hindu, 0.2% Buddhist, and 0.1% Sikh. 11.4% had no religion, 0.2% had an alternative religion and 7.4% did not state their religion. This is similar to the rest of the country, although the proportions of Muslims and Jews are nearly twice the national average.[166] It contains the Heaton Park Hebrew Congregation, a large Ashkenazi Orthodox synagogue in North Manchester.[citation needed] Greater Manchester is covered by the Roman Catholic Dioceses of Salford and Shrewsbury,[167][168][failed verification] and the Archdiocese of Liverpool.[citation needed] Much of Greater Manchester is part of the Anglican Diocese of Manchester,[169][failed verification] apart from Wigan which lies within the Diocese of Liverpool and parts of Stockport, Tameside and Trafford, which are in the Diocese of Chester.[170][failed verification]
Following the deindustrialisation of Greater Manchester in the mid-20th century, there was a significant economic and population decline in the region, particularly in Manchester and Salford.[171][172] Vast areas of low-quality squalid terraced housing that were built throughout the Victorian era were found to be in a poor state of repair and unsuited to modern needs; many inner-city districts suffered from chronic social deprivation and high levels of unemployment.[172][173] Slum clearance and the increased building of social housing overspill estates by Salford and Manchester City Councils lead to a decrease in population in central Greater Manchester.[174] During the 1970s, 1980s and 1990s, the population of Greater Manchester declined by over 8,000 inhabitants a year.[172] While Manchester's population shrank by about 40% during this time (from 766,311 in 1931 to 452,000 in 2006), the total population of Greater Manchester decreased by only 8%.[172]
Greater Manchester's housing stock comprises a variety of types. Manchester city centre is noted for its high-rise apartments,[175] while Salford has some of the tallest and most densely populated tower block estates in Europe.[176] Saddleworth has stone-built properties, including farmhouses and converted weavers' cottages.[23][177] Throughout Greater Manchester, rows of terraced houses are common, most of them built during the Victorian and Edwardian periods. House prices and labour markets differ in Greater Manchester between north and south,[178][179] such that in the 2000s, the Housing Market Renewal Initiative identified Manchester, Salford, Rochdale and Oldham as areas with terraced housing unsuited to modern needs.[179] In contrast, towns and villages in southern Greater Manchester, from Bramhall through Woodford to Altrincham constitute an arc of wealthy commuter towns.[23] Altrincham in particular, with its neighbours Bowdon and Hale, forms a "stockbroker belt, with well-appointed dwellings in an area of sylvan opulence".[180]
Education
[edit]Greater Manchester has six universities: the Manchester Metropolitan University, the University of Bolton, the University of Law, the University of Manchester the University of Salford and The University Campus of Football Business . Together with the Royal Northern College of Music they had a combined population of students of 101,165 in 2007 – the third highest number in England behind Greater London (360,890) and the West Midlands (140,980),[181] and the thirteenth highest in England per head of population.[182] The majority of students are concentrated on Oxford Road in Manchester, Europe's largest urban higher education precinct.[183]
As of 2010, further education in Greater Manchester is co-ordinated by the Greater Manchester Colleges Group, a joint venture composed of an association of 24 colleges in the region.[184] Primary and secondary education within Greater Manchester are the responsibility of the constituent boroughs which form local education authorities and administer schools. The county has several independent schools such as Bolton School, Bury Grammar School, Manchester Grammar School, Oldham Hulme Grammar School, St Bede's College, Stockport Grammar School and Chethams School of Music.[185]
Economy
[edit]

| District | GVA (£ billions) | GVA per capita (£) | GDP (£ billions) | GDP per capita (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bolton | £6.3 | £21,406 | £7.3 | £24,657 |
| Bury | £3.6 | £18,403 | £4.2 | £21,472 |
| Manchester | £26.5 | £48,107 | £28.2 | £51,330 |
| Oldham | £4.0 | £16,652 | £4.7 | £19,578 |
| Rochdale | £3.9 | £17,181 | £4.5 | £20,247 |
| Salford | £8.7 | £32,246 | £9.6 | £35,529 |
| Stockport | £7.2 | £24,370 | £8.1 | £27,425 |
| Tameside | £3.5 | £14,991 | £4.1 | £17,890 |
| Trafford | £9.6 | £40,769 | £10.4 | £44,192 |
| Wigan | £5.5 | £16,712 | £6.5 | £19,649 |
| Greater Manchester | £78.7 | £27,452 | £87.7 | £30,576 |
Much of Greater Manchester's wealth was generated during the Industrial Revolution, particularly textile manufacture.[187] The world's first cotton mill was built in the town of Royton,[188][189] and the county encompasses several former mill towns. An Association for Industrial Archaeology publication describes Greater Manchester as "one of the classic areas of industrial and urban growth in Britain, the result of a combination of forces that came together in the 18th and 19th centuries: a phenomenal rise in population, the appearance of the specialist industrial town, a transport revolution, and weak local lordship".[16] Much of the county was at the forefront of textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution and into the early-20th century;[187] Peter Smith, Baron Smith of Leigh, chair of the Greater Manchester Combined Authority said "clearly, all of the Greater Manchester area was once at the heart of a very vibrant [textiles] industry",[187] represented by former textile mills found throughout the county.[16] The territory that makes up Greater Manchester experienced a rapid decline of these traditional sectors, partly during the Lancashire Cotton famine brought on by the American Civil War, but mainly as part of the post-war economic depression and deindustrialization of Britain that occurred during the 20th century.[172][190]
Considerable industrial restructuring has helped the region to recover from deindustrialisation and the demise of the mass production of textiles.[191] Historically, the docks at Salford Quays were an industrial port, though are now (following a period of disuse) a commercial and residential area which includes the Imperial War Museum North and The Lowry theatre and exhibition centre. The BBC is now established in their new home at MediaCityUK, at Salford Quays. This is home to BBC North West, several BBC departments, including BBC Sport, Blue Peter and, since April 2012, BBC Breakfast. Rochdale and Manchester are connected to the history of the cooperative movement; the Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers (an early consumer co-operative) was founded in Rochdale in 1844,[192] and The Co-operative Group, the UK's largest mutual business and North West England's biggest company,[193] is headquartered at One Angel Square in central Manchester.[194] Despite this economic diversification, as of November 2012, government plans are under development to revive textile production in Greater Manchester, and restore it as the national home of British textile manufacture.[187]
Today, Greater Manchester is the economic centre of the North West region of England and is the largest sub-regional economy in the UK outside London and South East England.[195] Greater Manchester represents more than £82.7 billion in GDP, more than Wales, Northern Ireland or North East England.[196] Manchester city centre, the central business district of Greater Manchester, is a major centre of trade and commerce and provides Greater Manchester with a global identity, specialist activities and employment opportunities; similarly, the economy of the city centre is dependent upon the rest of the county for its population as an employment pool, skilled workforce and for its collective purchasing power.[197] Manchester today is a centre of the arts, the media, higher education and commerce. In a poll of British business leaders published in 2006, Manchester was regarded as the best place in the UK to locate a business.[198] It is the third most visited city in the United Kingdom by foreign visitors[199] and is now often considered to be the second city of the UK.[200]
At the 2001 UK census, there were 1,805,315 residents of Greater Manchester aged 16 to 74. The economic activity of these people was 40.3% in full-time employment, 11.3% in part-time employment, 6.7% self-employed, 3.5% unemployed, 5.1% students without jobs, 2.6% students with jobs, 13.0% retired, 6.1% looking after home or family, 7.8% permanently sick or disabled and 3.5% economically inactive for other reasons. The figures follow the national trend, although the percentage of self-employed people is below the national average of 8.3%.[201] The proportion of unemployment in the county varies, with the Metropolitan Borough of Stockport having the lowest at 2.0% and Manchester the highest at 7.9%.[202] In 2001, of the 1,093,385 residents of Greater Manchester in employment, the industry of employment was: 18.4% retail and wholesale; 16.7% manufacturing; 11.8% property and business services; 11.6% health and social work; 8.0% education; 7.3% transport and communications; 6.7% construction; 4.9% public administration and defence; 4.7% hotels and restaurants; 4.1% finance; 0.8% electricity, gas, and water supply; 0.5% agriculture; and 4.5% other. This was roughly in line with national figures, except for the proportion of jobs in agriculture which is only about a third of the national average of 1.5%, due to the overwhelmingly urban, built-up land use of Greater Manchester.[191][203]
Transport
[edit]


Public transport services in Greater Manchester are co-ordinated by Transport for Greater Manchester (TfGM), a public body with powers between those of a passenger transport executive and Transport for London,[204] established as SELNEC PTE in 1969 in accordance with the Transport Act 1968.[205] The original SELNEC Passenger Transport Executive was renamed as the Greater Manchester Passenger Transport Executive (GMPTE) when taken over by the Greater Manchester County Council on 1 April 1974 to co-ordinate public transport modes within the new county.[205] The council had overall responsibility for strategic planning and all policy decisions covering public transport (such as bus and rail services) and highways. GMPTE's purpose was to secure the provision of a completely integrated and efficient system of passenger transport for Greater Manchester on behalf of the county council.[205] In 1977, it was noted as the largest authority for public transport in the United Kingdom after London Transport.[205] GMPTE was renamed as Transport for Greater Manchester in April 2011 when it became a functional body of the Greater Manchester Combined Authority and obtained powers additional to those of a regular passenger transport executive from central government.[204]
Greater Manchester lies at the heart of the North West transport network. Much of the infrastructure converges at Manchester city centre with the Manchester Inner Ring Road, an amalgamation of several major roads, circulating the city centre. The county is the only place in the UK to have a fully orbital motorway,[206] the M60, which passes through all of the boroughs except Bolton and Wigan. Greater Manchester has a higher percentage of the motorway network than any other county in the country,[207] and according to the Guinness Book of World Records, it has the most traffic lanes side by side (17), spread across several parallel carriageways (M61 at Linnyshaw in Walkden, close to the M60 interchange).[208][209] Greater Manchester's 85 mi (137 km) of motorway network saw 5.8 billion vehicle kilometres in 2002 – about 6% of the UK's total, or 89,000 vehicles a day.[206] The A580 "East Lancs" road is a primary A road that connects Manchester and Salford with Liverpool. It was the UK's first purpose-built intercity highway and was officially opened by George V on 18 July 1934.[210] Throughout 2008, there were proposals for congestion charging in Greater Manchester.[211][212] Unlike the London scheme, two cordons would have been used, one covering the main urban core of the Greater Manchester Urban Area and another covering Manchester city centre.[213]
Metrolink is Greater Manchester's light rail system, which began operating in 1992. Principally used for suburban commuting, as of December 2020[update] the 57 mi (92 km) long network consists of eight lines which radiate from Manchester city centre and terminate at Altrincham, Ashton-under-Lyne, Bury, East Didsbury, Eccles, MediaCityUK, Manchester Airport, Rochdale and Trafford Centre.[214] The system is owned by TfGM and operated and maintained under contract by a Keolis / Amey consortium.[215][216] Greater Manchester has a heavy rail network of 142 route miles (229 km) with 98 stations, forming a central hub to the North West rail network.[217] Train services are provided by private operators and run on the national rail network which is owned and managed by Network Rail. There is an extensive bus network which radiates from Manchester city centre. The largest providers are Diamond Bus North West, First Greater Manchester, Go North West and Stagecoach Manchester. An extensive canal network also remains from the Industrial Revolution.
Manchester Airport, which is the third busiest in the United Kingdom, serves the county and wider region with flights to more worldwide destinations than any other airport in the UK.[218] Since 2024[update] it serves 199 routes, making the airport thirteenth globally for total destinations served.[219] The airport handled 28.07 million passengers in 2023.[220]
The three modes of public surface transport in the area are heavily used. 19.7 million rail journeys were made in the then GMPTE-supported area in the 2005/2006 financial year – an increase of 9.4% over 2004/2005; there were 19.9 million journeys on Metrolink; and the bus system carried 219.4 million passengers.[218][needs update]
The Bee Network is an integrated transport network for Greater Manchester, composed of bus, tram, cycling and walking routes. Transport for Greater Manchester (TfGM) is expected to have the complete network operational by 2024, with commuter rail services expected to be joining the network in 2030. Initially revealed in 2018, the project aims to create a London-style transport system, to encourage more people to take public transport instead of cars. The design of the network is inspired around the Greater Manchester symbol, the worker bee, with bus and tram liveries coloured yellow and black to represent this.
Greater Manchester is set to invest[when?] a further £40.7m in its walking, wheeling and cycling infrastructure as it progresses with its delivery of the largest active travel network in the country. Thirteen schemes have been allocated £23.7m in total, including a new active travel corridor along Chapel Street in Salford and a cycling and walking 'helix ramp' as part of Stockport Interchange.[221]
Sport
[edit]



Manchester hosted the 2002 Commonwealth Games which was, at a cost of £200M for the sporting facilities and a further £470M for local infrastructure, by far the biggest and most expensive sporting event held in the UK at the time and the first to be an integral part of urban regeneration.[222] A mix of new and existing facilities were used. New amenities included the Manchester Aquatics Centre, Bolton Arena, the National Squash Centre, and the City of Manchester Stadium. The Manchester Velodrome was built as part of the Manchester bid for the 2000 Summer Olympics.[223] After the Commonwealth Games the City of Manchester Stadium was converted for football use, and the adjacent warm-up track upgraded to become the Manchester Regional Arena.[224] Other facilities continue to be used by elite athletes.[222] Cambridge Policy Consultants estimate 4,500 full-time jobs as a direct consequence, and Grattan points to other long-term benefits accruing from publicity and the improvement of the area's image.[222]
Association football is "woven into the cultural fabric of Greater Manchester", by way of its numerous football clubs – two of which play in the Premier League – which draw support, visitors and economic benefits to Greater Manchester valued at £330 million per year as of 2013.[225] The Manchester Football Association is the sport's governing body in Greater Manchester, and is committed to its promotion and development.[226] Manchester United F.C. are one of the world's best-known football teams,[227] and in 2008 and 2017 Forbes estimated that they were the world's richest club.[228][229] They have won the League Championship a record twenty times (most recently in 2012–2013), the FA Cup twelve times, the Football League Cup six times and have been European Champions three times.[230] Their Old Trafford ground has hosted the FA Cup Final, England international matches and the 2003 UEFA Champions League Final between Juventus and A.C. Milan. Manchester City F.C. moved from Maine Road to the City of Manchester Stadium after the 2002 Commonwealth Games. They have won the league championship nine times (most recently in 2022–23), the FA Cup seven times, the Football League Cup eight times and have been European champions once.[231] Wigan Athletic F.C. are one of the county's younger sides and won their first major trophy in 2013, defeating Manchester City F.C. in the FA Cup final. As of season 2023–24, they play in League One, along with Bolton Wanderers F.C. In League Two are Salford City F.C. and Stockport County F.C., while Oldham Athletic A.F.C., Rochdale A.F.C. and Altrincham F.C. compete in the National League.
In rugby league, Wigan Warriors, Leigh Leopards, and Salford Red Devils compete in the Super League, the top-level professional rugby league football club competition in Europe. Wigan have won the Super League/Rugby Football League Championship twenty–one times, the Challenge Cup nineteen times, and the World Club Challenge three times.[232] Swinton Lions, and Oldham R.L.F.C. play in the second tier Championship, whilst Rochdale Hornets play in the third tier League 1 There is also a large network of junior/community rugby league clubs across the metropolitan area which act as feeder teams to the elite sides, the most notable being Manchester Rangers. In rugby union, Sale Sharks compete in the Guinness Premiership, and won the league in 2006.[233] Whitefield based Sedgley Park RUFC and Sale FC compete in National Division One, Manchester RUFC in National Division Two and Wigan side Orrell R.U.F.C. in National Division Three North.
Lancashire County Cricket Club began as Manchester Cricket Club and represents the (ancient) county of Lancashire. Lancashire contested the original 1890 County Championship. The team has won the County Championship nine times, most recently in 2011.[234] Their Old Trafford ground, near the football stadium of the same name, regularly hosts test matches. Possibly the most famous took place in 1956, when Jim Laker took a record nineteen wickets in the fourth test against Australia.[235] Cheshire County Cricket Club are a minor counties club who sometimes play in the south of the county.[236]
The National Speedway Stadium in Gorton is the home to top-flight speedway team the Belle Vue Aces,[237] and the Manchester Titans American football club.[238] Greater Manchester was previously home to the largest Greyhound racing track in the United Kingdom, the Belle Vue Stadium, which closed in 2020.[239] Professional ice hockey is held at the purpose-designed rink in Altrincham, the Altrincham Ice Dome, which host the Manchester Storm of the Elite Ice Hockey League and the Altrincham Aces of the National Ice Hockey League.[240]
Horse racing has taken place at several sites in the county. The two biggest courses were both known as Manchester Racecourse – though neither was within the boundaries of Manchester – and ran from the 17th century until 1963. Racing was at Kersal Moor until 1847 when the racecourse at Castle Irwell was opened. In 1867 racing was moved to New Barnes, Weaste, until the site was vacated (for a hefty price) in 1901 to allow an expansion to Manchester Docks. The land is now home to Dock 9 of the re-branded Salford Quays. Racing then moved back to Castle Irwell which later staged a Classic – the 1941 St. Leger – and was home to the Lancashire Oaks (nowadays run at Haydock Park) and the November Handicap, which was traditionally the last major race of the flat season. Through the late-1950s and early-1960s the track saw Scobie Breasley and Lester Piggott annually battle out the closing acts of the jockey's title until racing ceased on 7 November 1963.[241][242]
The Greater Manchester Athletics Association is the governing body of athletics in Greater Manchester, and organises events and competitions within Greater Manchester.[243] The Greater Manchester Marathon is a long-distance running event along a 26-mile and 385-yard course throughout the borough of Trafford.[244] Professional athletics takes place at the Regional Athletics Arena in Sportcity, which has hosted numerous national trials, Robin Park in Wigan, Longford Park in Stretford (home to Trafford Athletic Club), Woodbank Stadium in Stockport (home to Stockport Harriers) and the Cleavleys Track in Winton (home to Salford Harriers). The 12,000 seat Leigh Sports Village is a stadium and athletics venue home to the Leigh Harriers, Leigh Leopards Rugby League Club and the Manchester United W.F.C..[245]
The Greater Manchester Community Basketball Club is an association which represents Greater Manchester in basketball.[246] It supports a variety of teams, including Manchester Magic.[247] The Greater Manchester County Crown Green Bowling Association appoints Junior, Senior and Veteran teams to represent Greater Manchester in the sport of bowls.[248][249] Founded by Greater Manchester's ten district councils in 1996, GreaterSport is the County Sports Partnership for Greater Manchester which works closely with the sports and physical activity sectors and coordinates events such as the Greater Manchester Youth Games.[250] The Greater Manchester Sports Fund aims to ensure that people in Greater Manchester aged 12–21 competing in any kind of sport, irrespective of background, are able to obtain grants of up to £750 so that they can better fulfil their potential.[251]
Culture
[edit]Art, tourism, culture and sport provide 16% of employment in Greater Manchester, with the proportion highest in Manchester.[252] In 2014, Will Straw remarked that "Greater Manchester is a creative powerhouse", recognised for its cultural output in areas such as association football, media and digital content, and guitar and dance music.[6]
Cuisine
[edit]
There are several delicacies native to Greater Manchester.[253] Savoury dishes include black pudding, a blood sausage typically associated with Bury and Bury Market; pasty barm, a combined pasty-barm cake created in Bolton; and rag pudding, a suet pastry pudding from Oldham filled with steak and onion and steamed in a cloth or wrapper to cook; the Manchester egg was introduced in 2010.[253] Sweet dishes include Eccles cake – native to Eccles – a small round flaky pastry cake filled with currants, sugar and spice; Manchester tart, a baked tart which consists of a shortcrust pastry shell spread with raspberry jam, covered with a custard filling and topped with flakes of coconut; and Uncle Joe's Mint Balls, traditional sweet mild mints manufactured in Wigan since their inception in 1898.[253] Vimto and Tizer are soft drinks invented in Manchester in 1908 and 1924 respectively.[253] Boddingtons is a bitter developed in Manchester and promoted as the "Cream of Manchester" in a popular 1990s advertising campaign credited with raising the city's profile.[254][255][256]
The Greater Manchester Campaign for Real Ale is a branch of the national Campaign for Real Ale, an advocacy group that supports, promotes and preserves the beer and drinks industry, and recognising outstanding venues with awards; The Nursery in Heaton Norris was its National Pub of the Year in 2001, and The Baum in Rochdale was its National Pub of the Year in 2012.[257][258][259] The Manchester Food and Drink Festival was launched in 1997 as an urban beverage and gastronomy fair, principally held in Manchester city centre with further events throughout Greater Manchester;[260] smaller separate local events include the Prestwich Food and Drink Festival, the annual World Pie Eating Championship in Wigan, and the annual Ramsbottom Chocolate Festival.[261][262] As of 2020 Manchester has 1 Michelin Star restaurant: Mana,[263] which is still retained presently.[264][265] The region also has three eateries in the Bib Gourmand category.[266]
Galleries, museums and exhibitions
[edit]
The Greater Manchester Museums Group (GMMG) is a partnership of eight of the ten Museum Services in Greater Manchester.[267] Its exhibition centres include: Gallery Oldham, which has in the past featured work by Pablo Picasso;[268] Salford Museum and Art Gallery, a local museum with a recreated Victorian street;[269] and Bolton Museum, which houses material from private collectors, including geological specimens from the estate of Caroline Birley.[270] Separate from the GMMG is The Lowry at Salford Quays, which has a changing display of L. S. Lowry's work alongside travelling exhibitions. Manchester Art Gallery is a major provincial art gallery noted for its collection of Pre-Raphaelite art and housed in a Grade I listed building by Charles Barry.[271]
Greater Manchester's museums showcase the county's industrial and social heritage. The Hat Works in Stockport is the UK's only museum dedicated to the hatting industry; the museum moved in 2000 to a Grade II listed Victorian mill, previously a hat factory.[272] The Museum of Science and Industry in Manchester, amongst other displays, charts the rise of science and industry and especially the part Manchester played in its development; the Museums, Libraries and Archives Council described the displays as "pre-eminent collections of national and international importance".[273] Urbis began its life as a museum of the modern city, which attempted to explain the effects and experiences of life in the city. It was then transformed into an exhibition centre, which had its most successful year in 2006. Urbis entered its third phase since opening in 2012 as the National Football Museum.[274] Stockport Air Raid Shelters uses a mile of tunnels, built to accommodate 6,500 people, to illustrate life in the Second World War's air raid shelters.[275] The Imperial War Museum North in Trafford Park is one of the Imperial War Museum's five branches. Alongside exhibitions of war machinery are displays describing how people's lives are affected by war.[276] The Museum of Transport in Manchester, which opened in 1979, has one of the largest collections of vehicles in the country.[277] The People's History Museum is "the national centre for the collection, conservation, interpretation and study of material relating to the history of working people in Britain". The Pankhurst Museum is based in the early feminist Emmeline Pankhurst's former home and includes a parlour laid out in contemporary style.[278] Manchester United, Manchester City, and Lancashire CCC all have dedicated museums illustrating their histories. Wigan Pier, best known from George Orwell's book The Road to Wigan Pier,[279] was the name of a wharf on the Leeds and Liverpool Canal in Wigan. It will re-open as a visitor attraction in 2023, after years of closure.[280] The town is also home to the Museum of Wigan Life.[281]
Media, film and television
[edit]The Greater Manchester Film Festival was launched in 2012. It is an international film festival designed to capitalise on Greater Manchester's "huge strengths in film and television, along with its growing media presence".[282] MediaCityUK, a host venue of the Greater Manchester Film Festival,[283] is a 200-acre (81 ha) mixed-use property development site at Salford Quays; its principal tenants are mass media organisations such as ITV Granada and the BBC. One of Greater Manchester's most lucrative and acclaimed television exports is Coronation Street, which is a televised soap opera set in Weatherfield, a fictional borough of Greater Manchester,[284][285] inspired by life in Salford.[286] Created by Tony Warren, Coronation Street was first broadcast on 9 December 1960, making it the world's longest-running TV soap opera in production.[287] It has been filmed in Manchester at Granada Studios since its inception, but filming is now done at a new set at MediaCityUK.
A local television station for Greater Manchester, Channel M, was launched in February 2000, carrying a wide range of local programming, including news, sport and entertainment programming.[288] Following severe cutbacks to its local production amid heavy losses, the station ceased broadcasting in April 2012.[289][290] A smaller-scale local TV station, That's Manchester, began broadcasting in May 2015.[291]
The area has several radio stations including, BBC Radio Manchester, XS Manchester, Hits Radio Manchester, Capital Manchester, Greatest Hits Radio Manchester & The North West, Heart North West, and Smooth North West.[citation needed] There are also community-based radio stations such as Greatest Hits Radio Wigan & St Helens (covering Wigan), Greatest Hits Radio Bolton & Bury (serving Bolton and Bury), Tameside Radio (serving Tameside), Your FM (for Stockport), Rochdale Valley (for Rochdale),[292] Oldham Community Radio (for Oldham),[293] and Salford City Radio (serving Salford).
The Manchester Evening News is a regional daily newspaper covering Greater Manchester, published every day except Sunday.[294] It is owned by Reach plc and produced by MEN Media. It sells around 81,000 copies a day and gives away nearly 100,000, making it the market leader in Greater Manchester.[295] The paper was first published in 1868 by Mitchell Henry as part of his parliamentary election campaign for the Manchester constituency.[294] MEN Media "dominates Greater Manchester", reaching 7 out of 10 adults each week within the region through its portfolio of products which also includes the Oldham Advertiser, the Rochdale Observer, and the Salford Advertiser.[296]
Music, theatre and performing arts
[edit]
Greater Manchester has the highest number of theatre seats per head of population outside London. Most, if not all, of the larger theatres are subsidised by local authorities or the North West Regional Arts Board.[298] The Royal Exchange Theatre formed in the 1970s out of a peripatetic group staging plays at venues such as at the University [of Manchester] Theatre and the Apollo Theatre. A season in a temporary stage in the former Royal Exchange, Manchester was followed by funding for a theatre in the round, which opened in 1976.[299] The Lowry – Greater Manchester's most visited tourist attraction[297] – houses two theatres, used by travelling groups in all the performing arts.[252][300] The Opera House is a 1,900-seat venue hosting travelling productions, often musicals just out of the West End.[301] Its sister venue, The Palace, hosts generally similar shows. The Oldham Playhouse, one of the older theatres in the region, helped launch the careers of Stan Laurel and Charlie Chaplin. Its productions are described by the 2007 CityLife guide as 'staunchly populist' – and popular.[301] There are many other venues scattered throughout the county, of all types and sizes.[301]
Greater Manchester has four professional orchestras, all based in Manchester. The Hallé is the UK's oldest symphony orchestra (and the fourth oldest in the world),[302] supports a choir and a youth orchestra, and releases its recordings on its own record label.[303] The Hallé is based at the Bridgewater Hall but often tours, typically giving 70 performances "at home" and 40 on tour.[303] The BBC Philharmonic, one of five BBC orchestras, is based in MediaCityUK in Salford.[304] It can trace its history back to the early days of radio broadcasting in 1926.[305] The Manchester Camerata and the Northern Chamber Orchestra are smaller, though still professional, organisations.[306] The main classical venue is the 2,341-seat Bridgewater Hall in Manchester, opened in 1996 at a cost of £42m.[307] Manchester is also a centre for musical education, via the Royal Northern College of Music and Chetham's School of Music.[308]
The Manchester Arena holds over 21,000 people,[a] and is the largest indoor arena in the United Kingdom.[310] It has been voted International Venue of the Year, and for several years was the most popular venue in the world.[311] The 23,500-seat Co-op Live arena is under construction in Greater Manchester, it will open in 2023.[312] Sports grounds in Greater Manchester, such as the City of Manchester Stadium, also host large live-music events.[313] A £200 million flexible, large-scale cultural, arts, and exhibition space named Factory International was opened in 2023 on the former site of Granada Studios in central Manchester.[314][315] It is named with reference to Factory Records, a Manchester-based independent record label, founded in 1978 by Tony Wilson and Alan Erasmus. Factory Records – which featured acts such as Joy Division, New Order, and the Happy Mondays – and The Haçienda, served as a catalyst in the late-1980s for a blending of alternative rock, psychedelic rock and electronic dance music known as Madchester. Greater Manchester continues to be associated with guitar and dance music.[6]
Places of interest
[edit]

| Key | |
| Abbey/Priory/Cathedral | |
| Accessible open space | |
| Amusement/Theme Park | |
| Castle | |
| Country Park | |
| English Heritage | |
| Forestry Commission | |
| Heritage railway | |
| Historic House | |
| Places of Worship | |
| Museum (free/not free) | |
| National Trust | |
| Theatre | |
| Zoo | |
See also
[edit]- Outline of England
- Grade I listed buildings in Greater Manchester
- Grade II* listed buildings in Greater Manchester
- List of people from Greater Manchester
- List of public art in Greater Manchester
- Parliament of the United Kingdom relocation
- Healthcare in Greater Manchester
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Appointment of Lord-Lieutenant of Greater Manchester: 28 March 2022". 10 Downing Street. 28 March 2022. Archived from the original on 13 September 2022. Retrieved 13 September 2022.
- ^ "New High Sheriff of Greater Manchester chosen by the Queen". Manchester Evening News. 22 March 2022. Archived from the original on 13 September 2022. Retrieved 13 September 2022.
- ^ "Mid-2022 population estimates by Lieutenancy areas (as at 1997) for England and Wales". Office for National Statistics. 24 June 2024. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ^ "Ethnic group". Office for National Statistics. 28 March 2023. Retrieved 23 October 2023.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "UK Standard Area Measurements (SAM)". Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Straw, Will (5 March 2014). "Greater Manchester is a creative powerhouse". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 1 August 2014. Retrieved 16 December 2014.
- ^ Nevell & Redhead 2005, p. 20.
- ^ Adrian Morris. "Roman Wigan". Wigan Archaeological Society. Archived from the original on 18 February 2012. Retrieved 10 July 2008.
- ^ Bayliss 1996, p. 6.
- ^ Historic England. "Mamucium Roman fort (76731)". Research records (formerly PastScape). Retrieved 29 December 2007.
- ^ Historic England. "Castle Shaw (45891)". Research records (formerly PastScape). Retrieved 29 December 2007.
- ^ Hartwell, Hyde & Pevsner 2004, p. 18, quoting Redhead, Norman
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h "55: Manchester Conurbation". naturalengland.org.uk. 18 July 2013. Archived from the original on 21 October 2013. Retrieved 5 August 2013.
- ^ Frangopulo 1977, p. ix.
- ^ Frangopulo 1977, pp. 24–25.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d McNeil & Nevell 2000, pp. 1–3.
- ^ Frangopulo 1977, p. 268.
- ^ Aspin 1981, p. 3.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Carter 1962, p. 49.
- ^ Cowhig 1976, pp. 7–9.
- ^ Kidd 2006, pp. 12, 15–24, 224.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Hall, Peter (1998). "The first industrial city: Manchester 1760–1830". Cities in Civilization. Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 0-297-84219-6.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Schofield 2003, pp. 34–35.
- ^ Howe, Ed (26 May 2020). "What is Manchester, and how big is it?". urbinfomanc.com. Archived from the original on 1 July 2020. Retrieved 1 July 2020.
- ^ Roberts, Thomas & Williams 2014, p. 112.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Frangopulo 1977, p. 226.
- ^ Swarbrick, J. (February 1914). Greater Manchester: The Future Municipal Government of Large Cities. Institution of Municipal and County Engineers. pp. 12–15.
- ^ Frangopulo 1977, p. 229.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Frangopulo 1977, p. 227.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Frangopulo 1977, p. 228.
- ^ Frangopulo 1977, p. 231.
- ^ Frangopulo 1977, p. 234.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Redcliffe-Maud 1969, pp. 219–235.
- ^ Frangopulo 1977, p. 233.
- ^ Frangopulo 1977, p. 264.
- ^ The SELNEC Preservation Society. "The Formation of the SELNEC PTE". selnec.org.uk. Archived from the original on 20 August 2008. Retrieved 6 July 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Redcliffe-Maud & Wood 1975, pp. 46–47, 56, 157.
- ^ Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). House of Commons. 6 July 1972. col. 763–834.
- ^ "Lancashire saved from 'Botchdale'". The Times. 7 July 1972. p. 8.
- ^ "Philosophy on councils has yet to emerge". The Times. 8 July 1972. p. 2.
- ^ Jump up to: a b HMSO. Local Government Act 1972. 1972 c. 70
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Greater Manchester Gazetteer". Greater Manchester County Record Office. Places names – G to H. Archived from the original on 18 July 2011. Retrieved 17 June 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b The part of Bucklow Rural District not transferred to Greater Manchester remained in Cheshire, as part of Macclesfield municipal borough.
- ^ The part of Wigan Rural District not transferred to Greater Manchester remained in Lancashire, as part of West Lancashire district.
- ^ Clark 1973, p. 1.
- ^ Office of the Deputy Prime Minister. "Local Government Finance Statistics England No.16". local.odpm.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 7 August 2011. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ "British Local Election Database, 1889–2003". Arts and Humanities data service. 28 June 2006. Retrieved 5 March 2008.
- ^ "All change in local affairs". The Times. 1 April 1974. p. 15.
- ^ Frangopulo 1977, p. xii.
- ^ Clark 1973, p. 101.
- ^ Bowden 2015, p. NP.
- ^ Frangopulo 1977, p. 246.
- ^ Bristow & Cross 1983, p. 30.
- ^ Frangopulo 1977, pp. 246, 255.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Wannop 2002, pp. 144–145.
- ^ Parkinson-Bailey 2000, pp. 214–215.
- ^ Taylor, Evans & Fraser 1996, p. 76.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Clapson 2010, pp. 123–124.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Wilson & Game 2002, p. 61.
- ^ Walker, David (15 January 1983). "Tory plan to abolish GLC and metropolitan councils, but rates stay". The Times. p. 2.
•Haviland, Julian (5 May 1983). "Tories may abolish county councils if they win election". The Times. p. 1.
•Tendler, Stewart (16 June 1983). "Big cities defiant over police". The Times. p. 2. - ^ "Angry reaction to councils White Paper". The Times. 8 October 1983. p. 22.
- ^ Wilson & Game 2002, p. 62.
- ^ "About AGMA". Association of Greater Manchester Authorities. Archived from the original on 15 September 2008. Retrieved 5 March 2008.
- ^ Office for National Statistics (1999). Gazetteer of the old and new geographies of the United Kingdom (PDF). statistics.gov.uk. p. 48. ISBN 1-85774-298-2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 March 2008. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
"Beginners' Guide to UK Geography: Metropolitan Counties and Districts". Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2013.
"North West". The Electoral Commission. Archived from the original on 14 November 2008. Retrieved 2 March 2014. - ^ "Regional Portrait of Greater Manchester – 5.1 Spatial Structure" (PDF). Workpackage 6: e-Europe Regions Domain Reporting. BISER. September 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 October 2006. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ legislation.gov.uk. "Lieutenancies Act 1997", c.23. Archived 22 May 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Wood, Edward (11 December 1998). Research Paper 98/115 –The Greater London Authority Bill: A Mayor and Assembly for London – Bill 7 of 1998–99 (PDF). House of Commons Library. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 November 2006.
- ^ Moving Forward:The Northern Way Archived 2008-12-06 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ HM Treasury (17 July 2007). "Sub-national economic development and regeneration review". hm-treasury.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 15 December 2007. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ "A Framework for City Regions Working Paper" (PDF). Newcastle University UK. Office of the Deputy Prime Minister. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 January 2016. Retrieved 16 April 2015.
- ^ Fairley, Peter (18 January 2008). "Comment – A faster track for the city-regions". publicfinance.co.uk. Archived from the original on 5 January 2009. Retrieved 29 September 2012.
- ^ Ottewell, David (25 June 2008). "Now YOU can vote on congestion charge". Manchester Evening News. pp. 1–2.
- ^ "More than the sum of their parts – partnerships seal deal to increase economic growth". communities.gov.uk. 14 July 2008. Archived from the original on 3 August 2008. Retrieved 16 July 2008.
- ^ "Date set for C-charge referendum". news.bbc.co.uk. 29 September 2008. Archived from the original on 1 March 2009. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
- ^ Sturcke, James (12 December 2008). "Manchester says no to congestion charging". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 5 September 2013. Retrieved 12 December 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "City Region Governance: A consultation on future arrangements in Greater Manchester" (PDF). Association of Greater Manchester Authorities. 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 July 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2010.
- ^ Association of Greater Manchester Authorities. "City Region". agma.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 14 March 2010. Retrieved 18 March 2010.
- ^ HM Treasury (16 December 2009). "Greater Manchester granted city region status". hm-treasury.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 21 December 2009. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ "John Denham – Greater Manchester to be country's first ever Combined Authority". communities.gov.uk. 31 March 2010. Archived from the original on 4 May 2010. Retrieved 18 October 2010.
- ^ "Plan to end rail and road misery". The Bolton News. 31 March 2010. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ "Greater Manchester to become first 'city region'". Oldham Advertiser. 29 March 2010. Archived from the original on 5 September 2012. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ^ "Greater Manchester agrees to combined authority". Manchester City Council. 29 March 2010. Archived from the original on 3 April 2010. Retrieved 31 March 2010.
- ^ "Safeguard to prevent C-charge is welcomed". The Bolton News. 9 December 2010. Archived from the original on 14 June 2012. Retrieved 14 December 2010.
- ^ HM Treasury and The Rt Hon George Osborne MP (3 November 2014). "Manchester to get directly elected Mayor". gov.uk. Archived from the original on 3 November 2014. Retrieved 5 December 2014.
- ^ Dawson 1992, "Chapter 6: The County Tops".
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Greater Manchester Passenger Transport Authority. "The Greater Manchester Area and its Regional Context". gmltp.co.uk. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Manchester City Council (11 July 2012). "Manchester's Local Development Framework: Core Strategy Development Plan Document". manchester.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 25 February 2022. Retrieved 16 June 2013.
Part of the City Centre is in Salford and both the Regional Centre and Inner Areas cover areas of Manchester, Salford and Trafford ... Manchester City Centre is defined as the area inside the Inner Relief Route and extends to the south to encompass the Oxford Road Corridor. The City Centre also extends to Chapel Street, within the administrative boundary of Salford City Council.
- ^ Ravetz 2000, p. 50.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Association of Greater Manchester Authorities (August 2009). "Prosperity for all: The Greater Manchester Strategy" (PDF). agma.gov.uk. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 November 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Greater Manchester councils plan "unique" town centre investment strategy". localgovernmentexecutive.co.uk. 19 March 2013. Archived from the original on 21 October 2013. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Manchester City Council (1995), Manchester Unitary Development Plan, p. 105
- ^ TfGM; GMCA (2011). Greater Manchester's third Local Transport Plan 2011/12 – 2015/16 (PDF). Transport for Greater Manchester. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016.
- ^ Kellie 2010, pp. 4–5, 243.
- ^ Freeman & Snodgrass 1959, p. 155.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "2011 Census – Built-up areas". ONS. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 1 July 2013.
- ^ "State of the English Cities: Volume 1". Office of the Deputy Prime Minister. 2006. Archived from the original on 20 April 2010. Retrieved 17 December 2006.
- ^ Pedrazzini, Luisa; Akiyama, Renata Satiko (2011). From Territorial Cohesion to the New Regionalized Europe. Maggioli Editore. ISBN 9788838760341. Archived from the original on 20 February 2023. Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- ^ ESPON Archived 24 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Groom, Brian (20 June 2014). "A great northern conurbation". Financial Times. Financial Times London UK. Archived from the original on 10 December 2022. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Manchester Airport 1971–2000 weather averages". Met Office. 2001. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 15 July 2007.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "UK 1971–2000 averages". Met Office. 2001. Archived from the original on 5 July 2009. Retrieved 15 July 2007.
- ^ Frame, Don (24 February 2005). "Roads chaos as snow sweeps in Manchester". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved on 15 July 2007.
- ^ "Snow: West Yorkshire traffic and travel latest". Halifax Courier. 2 February 2009. Archived from the original on 10 November 2017. Retrieved 7 January 2017.
- ^ "Live: M62 motorway closed and 20 miles of queues as snow and high winds return to Greater Manchester". Manchester Evening News. 4 April 2012. Archived from the original on 10 November 2017. Retrieved 7 January 2018.
- ^ "Snake Pass". Peak District sightseer's guide. High Peak Interactive. 2002. Archived from the original on 12 January 2011. Retrieved 6 July 2007.
- ^ "Icy conditions hit the UK after days of heavy snow". BBC News. 7 January 2010. Archived from the original on 20 February 2023. Retrieved 7 January 2010.
- ^ "Manchester 1981-2010 Averages". Met Office. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- ^ "Manchester Ringway weather station 1961-1990" (FTP). NOAA. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "Manchester ringway extreme values". KNMI. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- ^ "Manchester ringway 1981-2010 mean extreme values". KNMI. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
- ^ "Average snowfall over the UK". Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ^ "STATION MANCHESTER". Meteo climat. Retrieved 2 January 2021.
- ^ "Climate & Weather Averages in Manchester, England, United Kingdom". Time and Date. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- ^ "Monthly weather forecast and Climate – Manchester, United Kingdom". Weather Atlas. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f "Greater Manchester Biodiversity". gmbp.org.uk. Archived from the original on 18 May 2013. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Hardy 1998, p. 7.
- ^ Manchester City Council. "Sites of Biological Importance". wildaboutmanchester.info. Archived from the original on 27 June 2012. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Defra (2002). Aitchison, J.W. (ed.). "The Commonlands of Greater Manchester: A Biological Survey" (PDF). defra.gov.uk. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 October 2012. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- ^ Greater Manchester Local Record Centre. "Welcome to Greater Manchester LRC". gmwildlife.org.uk. Archived from the original on 23 December 2012. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- ^ Greater Manchester Biodiversity Project. "What is biodiversity?". gmbp.org.uk. Archived from the original on 27 June 2017. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- ^ "Welcome to the Manchester Field Club". webspace.mypostoffice.co.uk. Archived from the original on 25 June 2013. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- ^ Salford City Council (2007). "Chat Moss". salford.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 28 September 2008. Retrieved 13 November 2007.
•"Agricultural Land Classification" (PDF). Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. July 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 February 2009. Retrieved 2 March 2014. - ^ "Appendix J River Mersey Case Study Report". The Countryside Agency. Archived from the original (DOC) on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 27 April 2007.
- ^ "South Pennine Moors". Defra. Archived from the original on 12 September 2012. Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- ^ Lashley, Brian (20 March 2003). "So what bloom best suits you?". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- ^ Devon Wildlife Trust. "Species – Cottongrass, common". devonwildlifetrust.org. Archived from the original on 26 June 2015. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- ^ Plantlife International. "North-west England". plantlife.org.uk. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- ^ Holland, Spence & Sutton 1984, pp. 28–29.
- ^ Davies, Ella; Hendry, Lisa (30 November 2021). "Wild parakeets in the UK: exotic delights or a potential problem?". nhm.ac.uk. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ Watson, Alex (14 April 2020). "The mysterious tale of the parrots of South Manchester". propermanchester.com. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ "Walk in the Park". The Whitworth. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Cooper, Matthew (16 February 2019). "Why are there so many parakeets in south Manchester? These are the wild theories that might just be true". Manchester Evening News. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ Brown, Ben (2 March 2021). "Myths of Manchester: The Terrapins & Turtles of Alexandra Park". manchestersfinest.com. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ "Greater Manchester region, England, United Kingdom". Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 2 July 2022. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
- ^ "The Beginning of the Confusion". www.forl.co.uk. Archived from the original on 15 August 2022. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
- ^ Shaw, Megan (6 December 2020). "The fight to keep these historic villages in Yorkshire nearing a sad end". YorkshireLive. Archived from the original on 12 August 2021. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- ^ Mallinson, Matt (18 March 2015). "Wigan must DITCH 'false region' Manchester and rejoin Lancashire, urges petition". Mancunian Matters. Archived from the original on 20 July 2021. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- ^ Tweed, Lyell (26 January 2021). "Vote on whether Horwich should leave Bolton Council". The Bolton News. Archived from the original on 20 July 2021. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Greater Manchester Combined Authority Final Scheme" (PDF). Association of Greater Manchester Authorities. March 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 December 2010. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ^ "Devolution to the Greater Manchester Combined Authority and transition to a directly elected mayor". gov.uk. 3 November 2014. Archived from the original on 4 November 2014. Retrieved 4 November 2014.
- ^ "Greater Manchester to control £6bn NHS budget". BBC News. 25 February 2015. Archived from the original on 25 February 2015. Retrieved 26 February 2015.
- ^ Williams, Jennifer (5 May 2017). "Andy Burnham elected as Greater Manchester's mayor". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 12 March 2018. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- ^ "What the Mayor does". greatermanchester-ca.gov.uk. 2018. Archived from the original on 6 April 2019. Retrieved 5 April 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Frangopulo 1977, p. 138.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Barlow, Max (May 1995). "Greater Manchester: conurbation complexity and local government structure". Political Geography. 14 (4): 379–400. doi:10.1016/0962-6298(95)95720-I.
- ^ Rochdale Metropolitan Borough Council, p. 65.
- ^ Walker, Jonathan (9 September 2008). "Goodbye West Midlands, hello Greater Birmingham". Birmingham Post. birminghampost.net. Archived from the original on 1 August 2012. Retrieved 24 September 2012.
- ^ Wannop 2002, p. 148.
- ^ "Greater Manchester Local Transport Plan". gmltp.co.uk. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 12 December 2006.
- ^ "Introducing new police commissioner Tony Lloyd – the most powerful man in Greater Manchester?". Manchester Evening News. 16 November 2012. Archived from the original on 22 November 2012. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ "Manchester Airports Group dividend windfall for councils". BBC News. 21 July 2013. Archived from the original on 15 October 2014. Retrieved 8 August 2013.
- ^ Hebbert, Michael; Deas, Iain (January 2000). "Greater Manchester – 'up and going'?". Policy & Politics. 28 (1): 79–92. doi:10.1332/0305573002500848.
- ^ Chancellor of the Duchy of Lancaster. "Keeper of the Rolls". duchyoflancaster.co.uk. Archived from the original on 15 December 2010. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ The Lord-Lieutenants Order 1973 (1973/1754)
- ^ "No. 58395". The London Gazette. 18 July 2007. p. 10329.
- ^ "Greater Manchester Met. C". visionofbritain.org.uk. Archived from the original on 4 September 2007. Retrieved 6 April 2007.
- ^ "Lib Dems close in on Manchester". Manchester Evening News. 11 June 2004. Archived from the original on 20 February 2023. Retrieved 26 February 2006.
- ^ "Labour party returns to Manchester". timeout.com. 2006. Archived from the original on 13 January 2008. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ "Greater Manchester Met. C: Total Population". visionofbritain.org.uk. Archived from the original on 9 May 2015. Retrieved 24 September 2012.
- ^ "Mid-Year Population Estimates, UK, June 2022". Office for National Statistics. 26 March 2024. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ^ "Censu 2021: First results". Office of National Statistics (ONS). Archived from the original on 24 August 2022. Retrieved 28 June 2022.
- ^ Clark 1973, p. 93.
- ^ "Regional Portrait of Greater Manchester – 5.3 Population Structure/Migration (demography)" (PDF). BISER Europe Regions Domain Reporting. 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 July 2011. Retrieved 18 February 2008.
- ^ "Warren Smith welcomes you to the Greater Manchester Lieutenancy". manchesterlieutenancy.org. Archived from the original on 5 July 2008. Retrieved 8 July 2008.
- ^ "Exodus: The Facts". can.uk.com. 2003. Archived from the original on 4 February 2008. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ "Greater Manchester (health authority) religion". Statistics.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 11 January 2009. Retrieved 1 February 2008.
- ^ "Catholic Diocese of Shrewsbury". Dioceseofshrewsbury.org. Archived from the original on 17 April 2009. Retrieved 7 May 2007.
- ^ "Parishes of the Diocese". Salforddiocese.org.uk. Archived from the original on 2 May 2007. Retrieved 7 May 2007.
- ^ "The Church of England Diocese of Manchester". manchester.anglican.org. Archived from the original on 27 December 2007. Retrieved 17 January 2008.
- ^ "Welcome to the Diocese of Liverpool". liverpool.anglican.org. Archived from the original on 24 February 2008. Retrieved 1 February 2008.
- ^ "Market Renewal: Manchester Salford Pathfinder" (PDF). Audit Commission. 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 August 2008. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "Shrinking Cities: Manchester/Liverpool II" (PDF). shrinkingcities.com. March 2004. p. 36. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 September 2012. Retrieved 4 March 2008.
- ^ Cooper 2005, p. 47.
- ^ Shapely, Peter (2002). "The press and the system built developments of inner-city Manchester" (PDF). Manchester Region History Review. 16. Manchester Centre for Regional History: 30–39. ISSN 0952-4320. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 December 2007. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ Qureshi, Yakub (24 November 2004). "A cut above: high rise living is back". BBC. Archived from the original on 30 December 2004. Retrieved 25 February 2008.
- ^ Cunningham, John (28 February 2001). "Tower blocks to make a comeback". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 10 May 2014. Retrieved 26 February 2008.
- ^ Dyckhoff, Tom (9 December 2011). "Let's move to: Saddleworth, Greater Manchester". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 7 January 2016. Retrieved 30 September 2012.
- ^ Kirby, Dean (24 August 2013). "Street where houses cost just £15,000 – we reveal cheapest and dearest homes in Greater Manchester". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 28 June 2017. Retrieved 24 August 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Bontje, Musterd & Pelzer 2011, p. 159.
- ^ Frangopulo 1977, p. 224.
- ^ "Table 0a – All students by institution, mode of study, level of study, gender and domicile 2006/07". Students and Qualifiers Data Tables. Higher Education Statistics Agency. 2008. Archived from the original (XLS) on 9 July 2013. Retrieved 21 March 2008.
- ^ Tight, Malcolm (July 2007). "The (Re)Location of Higher Education in England (Revisited)". Higher Education Quarterly. 61 (3): 250–265. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2273.2007.00354.x.
- ^ Hartwell 2001, p. 105.
- ^ "Manchester College's 'strong management'". manchestermule.com. 27 May 2010. Archived from the original on 6 August 2013. Retrieved 29 June 2013.
- ^ "Independent schools in Greater Manchester". www.schoolsearch.co.uk. Archived from the original on 23 February 2023. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ^ Fenton, Trevor (25 April 2023). "Regional gross domestic product: city regions". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Manchester to revive Britain's textile trade with reborn Cottonopolis". Manchester Evening News. 3 November 2012. Archived from the original on 7 November 2012. Retrieved 4 November 2012.
- ^ "Oldham's Economic Profile – Innovation and Technology". Oldham Council. Archived from the original on 13 January 2007. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ "NW Cotton Towns Learning Journey". Spinning the web. Manchester City Council. Archived from the original on 10 September 2007. Retrieved 27 October 2006.
- ^ "The rise of the 'greatest village in England'". Manchester Evening News. menmedia.co.uk. 3 November 2012. Archived from the original on 6 November 2012. Retrieved 3 November 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Regional Portrait of Greater Manchester – 6 Economic Factors" (PDF). BISER Europe Regions Domain Reporting. 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 October 2006. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ "Our History". co-operative.coop. Archived from the original on 8 November 2016. Retrieved 18 December 2014.
- ^ Roue, Lucy (27 November 2014). "200 staff to undergo consultation process at Co-operative's Manchester head office One Angel Square". manchestereveningnews.co.uk. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 18 December 2014.
- ^ Begum, Shelina (14 November 2013). "Co-op's headquarters declared greenest building in the world". manchestereveningnews.co.uk. Archived from the original on 20 March 2015.
- ^ "Manchester city region – Economic Overview". investinmanchester.com. Archived from the original on 21 March 2008. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ "Gross Domestic Product of Greater Manchester". Statista. 2023.
- ^ "The Greater Manchester Strategy: Foreword". gmep.org.uk. 2004. Archived from the original on 22 April 2008. Retrieved 9 July 2008.
- ^ "Britain's Best Cities 2005–2006 Executive Summary" (PDF). OMIS Research. 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 May 2006. Retrieved 17 July 2008.
- ^ "International Visitors To Friendly Manchester Up 10%" (Press release). Marketing Manchester. 17 September 2007. Archived from the original on 27 October 2007. Retrieved 17 July 2008.
- ^ "Manchester 'England's second city'". BBC. 12 September 2002. Archived from the original on 1 December 2008. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
• Riley, Catherine (8 July 2005). "Can Birmingham halt its decline?". The Times. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011. Retrieved 31 March 2010.
• "Manchester 'close to second city'". BBC. 29 September 2005. Archived from the original on 23 November 2008. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
• "Manchester tops second city poll". BBC. 10 February 2007. Archived from the original on 14 September 2007. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
• "Birmingham loses out to Manchester in second city face off". BBC. 2007. Archived from the original on 8 July 2009. Retrieved 18 June 2007. - ^ "Greater Manchester (health authority) economic activity". statistics.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 11 January 2009. Retrieved 3 February 2008.
- ^ "Promoting a Dynamic Economy". Greater Manchester e-Government Partnership. Archived from the original on 12 January 2008. Retrieved 12 December 2007.
- ^ "Greater Manchester (health authority) industry of employment". statistics.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 11 January 2009. Retrieved 3 February 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Kirby, Dean (1 April 2011). "All Change: Greater Manchester Passenger Transport Executive becomes Transport for Greater Manchester – With a New Logo of Course". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 4 April 2011. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Frangopulo 1977, p. 187.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Hyde, O'Rourke & Portland 2004, p. 141.
- ^ The Oldham College. "Local information: About Oldham". oldham.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 9 October 2006. Retrieved 6 March 2008.
The Metropolitan County of Greater Manchester has the most extensive motorway network in the United Kingdom
- ^ "The number's up for Britain's roads". The Daily Telegraph. October 2002. Archived from the original on 14 October 2007. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
The west side of Manchester is notoriously busy and holds the record for the widest section of motorway – an impressive 17 lanes where the M61 and M60 meet.
- ^ Matthews 1992, p. 121.
- ^ Lancashire County Council. "Early Highways Liverpool-East Lancashire Road A580". Historic Highways. lancashire.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 22 February 2008. Retrieved 19 January 2008.
- ^ Salter, Alan (5 May 2007). "C-charge details revealed". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 8 July 2008. Retrieved 25 November 2007.
- ^ "Manchester makes move towards congestion charge". The Guardian. 27 July 2007. Archived from the original on 31 August 2013. Retrieved 31 March 2010.
- ^ "Traffic Congestion charging: FAQs". BBC Manchester. Archived from the original on 18 February 2007. Retrieved 26 November 2007.
- ^ Britton, Paul (13 October 2014). "New Metrolink line to Wythenshawe and Manchester Airport to open on November 3 – a year ahead of schedule". manchestereveningnew.co.uk. Archived from the original on 18 October 2014. Retrieved 18 December 2014.
- ^ Salford City Council (February 2012). "Salford Infrastructure Delivery Plan" (PDF). salford.gov.uk. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 May 2013. Retrieved 22 January 2013.
- ^ "RATP buys Manchester Metrolink operator". Railway Gazette International. London. 2 August 2011. Archived from the original on 17 September 2011. Retrieved 7 March 2013.
- ^ Greater Manchester Passenger Transport Executive. "GMPTE – Trains". gmpte.com. Archived from the original on 15 December 2006. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "State of the City Report 2006/2007" (PDF). manchester.gov.uk. September 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 January 2008. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ "Frankfurt with almost 300 destinations and Paris CDG with over 100 airlines lead global analysis of airport operations in S17". anna aero. 15 February 2017. Retrieved 12 March 2017.
- ^ "Aircraft and passenger traffic data for UK airports". UK Civil Aviation Authority. 2020. Retrieved 9 February 2020.
- ^ "Greater Manchester to invest a further £40.7m in walking, wheeling and cycling infrastructure".
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Gratton, Chris; Simon Shibli; Richard Coleman (2005). "Sport and Economic Regeneration in Cities". Urban Studies. 42 (5–6). Urban Studies Journal Limited: 985–999. Bibcode:2005UrbSt..42..985G. doi:10.1080/00420980500107045. S2CID 154814355.
- ^ Parkinson-Bailey 2000, pp. 249–250.
- ^ "City enjoys £600m windfall". BBC Online. 16 June 2006. Archived from the original on 4 April 2012. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
"Sporting Legacy". Commonwealth Games Legacy Manchester 2002. Commonwealth Games Legacy. 2003. Archived from the original on 28 August 2007. Retrieved 23 September 2007. - ^ Jupp, Adam (11 April 2013). "£300m: The staggering amount Manchester makes from football every year". Manchester Evening News. manchestereveningnews.co.uk. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ "What we do". Manchester FA. Archived from the original on 25 October 2012. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- ^ Salazar, Jo-Ryan. "The 100 Greatest Soccer Clubs in the World". Bleacher Report. Archived from the original on 14 October 2017. Retrieved 13 October 2017.
- ^ "Soccer Team Valuations No. 1 Manchester United". Forbes. 30 April 2008. Archived from the original on 3 May 2008. Retrieved 2 May 2008.
- ^ Ozanian, Mike. "The World's Most Valuable Soccer Teams 2017". Forbes. Archived from the original on 3 October 2017. Retrieved 13 October 2017.
- ^ "Glory, Glory, Man United". The website of dreams. Archived from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 2 June 2008.
- ^ "Roll of honour". Manchester City FC. Archived from the original on 10 December 2007. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ "Honours". wiganwarriors.com. Wigan Warriors. 2008. Archived from the original on 12 April 2008. Retrieved 3 May 2008.
- ^ "BBC Rugby Union – English – Sale 45-20 Leicester". BBC. 27 May 2006. Archived from the original on 3 October 2018. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
- ^ "Champions at Last". LCCC.co.uk. Archived from the original on 4 November 2014. Retrieved 4 November 2014.
- ^ "Jim Laker". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 7 May 2008. Retrieved 2 May 2008.
- ^ "Minor County Grounds". Minor Counties Cricket Association. Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 24 July 2008. Retrieved 2 May 2008.
- ^ "National Speedway Stadium". bellevue-speedway.com. Archived from the original on 12 October 2022. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ^ "Report on National Speedway Stadium" (PDF). Resources and Governance Scrutiny Committee. Manchester City Council. 19 July 2018. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 October 2022. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ aul Britton (2 August 2020). "Belle Vue greyhound stadium to close permanently after being hard hit by coronavirus lockdown". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 12 October 2022. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ "Manchester Storm reform and replace Hull in Elite League". BBC Sport. 24 June 2015. Archived from the original on 12 October 2022. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ Ramsden 1966.
- ^ Salford Metropolitan Borough Council. "Transcript of Kersal Dale Video". Salford.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 27 May 2008. Retrieved 5 March 2008.
•Farrer, William; Brownbill, John (2003–2006) [1911]. "Townships: Broughton". The Victoria history of the county of Lancaster – Lancashire. Vol. 4. University of London & History of Parliament Trust. pp. 217–222. Archived from the original on 25 May 2011. Retrieved 25 February 2008. - ^ "Greater Manchester Athletics Association". greatermanchesteraa.co.uk. Archived from the original on 1 July 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
- ^ Greater Manchester Marathon Ltd (2012). "General Information". greatermanchestermarathon.com. Archived from the original on 8 February 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- ^ "About Us". Leigh Sports Village. Archived from the original on 12 October 2022. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ "Aims and Objectives". amaechibasketballcentre.com. Archived from the original on 1 June 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
- ^ "Manchester's basketball club prove they are magic as teams qualify for cup final". manchester.gov.uk. 6 March 2006. Archived from the original on 30 September 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
- ^ "Official Website of Greater Manchester County Crown Green Bowling Association". gmbowls.org.uk. 2 May 2011. Archived from the original on 28 May 2011. Retrieved 5 May 2011.
- ^ "County team dodge a bullet". Oldham Evening Chronicle. oldham-chronicle.co.uk. 3 May 2011. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
- ^ GreaterSport. "About GreaterSport: Greater Manchester Sports Partnership". greatersport.co.uk. Archived from the original on 22 November 2012. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- ^ "Greater Manchester Sports Fund". manchestercommunitycentral.org. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Robson, Brian (2004). "Culture and the City: A View from the 'Athens of the North'". Built Environment. 30 (3): 246–255. doi:10.2148/benv.30.3.246.54298.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Visit Manchester. "Greater Manchester local delicacies". visitmanchester.com. Archived from the original on 14 December 2013. Retrieved 27 September 2012.
- ^ Taylor, Paul (9 September 2004). "How city's pride fell to big business". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 7 July 2012.
- ^ Hall, William (28 October 2004). "Manchester united in battle over Boddingtons". Financial Times. London. Archived from the original on 10 December 2022. Retrieved 22 October 2011.(subscription required)
- ^ Taylor, Paul R (13 July 2007). "Chimney survives rubble and strife". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 10 March 2022. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ "Rochdale 'boozer' The Baum crowned Britain's best pub". BBC News. 13 February 2013. Archived from the original on 26 September 2015. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ^ Slater, Chris (12 September 2013). "Rochdale pub aims to be named Britain's best for second year running at CAMRA awards". manchestereveningnews.co.uk. Archived from the original on 20 December 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ^ "Pub of the Year – Previous Winners". camra.org.uk. Archived from the original on 20 December 2014. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ^ "Manchester Food and Drink Festival". visitmanchester.com. September 2014. Archived from the original on 18 December 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ^ "Controversy at World Pie Eating Competition". huffingtonpost.co.uk. 18 December 2014. Archived from the original on 20 December 2014. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ^ Bury Council. "Ramsbottom Annual Chocolate Festival". bury.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 20 December 2014. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ^ Rhind-Tutt, Louise (7 October 2019). "Manchester gets first Michelin star in over 40 years for Mana in Ancoats". I Love Manchester. Archived from the original on 22 August 2022. Retrieved 22 August 2022.
- ^ "mana – Manchester – a Michelin Guide Restaurant". Michelin Guide. Archived from the original on 2 September 2022. Retrieved 22 August 2022.
- ^ "Manchester's Mana Restaurant Has Retained It's Michelin Star For 2022". Secret Manchester. 16 February 2022. Archived from the original on 15 August 2022. Retrieved 22 August 2022.
- ^ "Greater Manchester restaurants fail to win a single Michelin star in 2012 guide". manchestereveningnews.co.uk. 6 October 2011. Archived from the original on 20 December 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ^ "Greater Manchester Museums Group". gmmg.org.uk. Archived from the original on 13 April 2014. Retrieved 9 April 2014.
- ^ "Past Exhibits at Gallery Oldham". galleryoldham.org.uk. Archived from the original on 3 July 2008. Retrieved 9 January 2008.
- ^ "Lark Hill Place Shops". Salford City Council. Archived from the original on 4 August 2007. Retrieved 2 May 2008.
- ^ "Caroline Birley". Bolton Museum. 7 June 2007. Archived from the original on 8 February 2012. Retrieved 23 January 2012.
- ^ Historic England. "City Art Gallery (1282980)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 14 December 2007.
•"Manchester Art Gallery: About Us". manchestergalleries.org. Archived from the original on 12 January 2008. Retrieved 9 January 2008. - ^ "About Stockport Hat Works". hatworks.org.uk. Archived from the original on 21 September 2008. Retrieved 10 January 2008.
- ^ "Museum of Science & Industry". The National Virtual Museum. 24hourmuseum.org.uk. Archived from the original on 30 October 2020. Retrieved 10 January 2008.
- ^ "Urbis visitors increase by 550%". BBC Online. 12 April 2004. Archived from the original on 10 May 2004. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
•"Visitors flock to Urbis as revamp pays off". Manchester Evening News. 6 December 2006. Archived from the original on 20 February 2023. Retrieved 10 January 2008. - ^ "About Stockport air raid shelters". airraidshelters.org.uk. Archived from the original on 18 January 2008. Retrieved 10 January 2008.
- ^ "Imperial War Museum North". north.iwm.org.uk. Archived from the original on 1 March 2013. Retrieved 10 January 2008.
- ^ "Introduction to the Museum of Transport". gmts.co.uk. Archived from the original on 21 January 2008. Retrieved 10 January 2008.
- ^ "The Pankhurst Centre". The National Virtual Museum. 24 Hour Museum. Archived from the original on 29 June 2017. Retrieved 8 July 2008.
- ^ Vallely, Paul (30 April 2004). "On the road again". The Independent. Archived from the original on 11 May 2008. Retrieved 17 January 2008.
- ^ Charles Graham (16 June 2023). "Wigan Pier revamp set to take another year to complete". Wigan Today. Archived from the original on 3 October 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "Visiting the Museum of Wigan Life". Wigan Council. Archived from the original on 3 October 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ Qureshi, Yakub (12 September 2012). "New movie-makers to star in Greater Manchester film festival". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 16 November 2021. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ Greater Manchester Film Festival (2012). "About the Festival". gmff.co.uk. Archived from the original on 25 October 2012. Retrieved 27 September 2012.
- ^ Little 1995, p. 112.
- ^ Little 2000, p. 93.
- ^ "Far cry from rain-soaked rooftops of Weatherfield". TES Connect. Times Educational Supplement. 2 March 2001. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 7 January 2011.
Salford's rows of terraced houses were the inspiration for the fictional Weatherfield in the soap Coronation Street
- ^ Hemley, Matthew (24 September 2010). "Coronation Street breaks two world records". The Stage. thestage.co.uk. Archived from the original on 3 September 2015. Retrieved 26 September 2010.
- ^ Dowling, Nicola (18 May 2004). "Channel M tunes into future". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 12 November 2012. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ "Greater Manchester's Channel M cuts staff to four". BBC News. 17 March 2010. Archived from the original on 12 June 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2011.
- ^ Plunkett, John (16 April 2012). "Manchester's Channel M closes after 12 years". The Guardian. London: Guardian News and Media. Archived from the original on 28 September 2013. Retrieved 17 September 2019.
- ^ "Placeholder for Manchester local TV appears on Freeview". a516digital.com. Archived from the original on 20 February 2023. Retrieved 9 January 2016.
- ^ "Rochdale Valley". Retrieved 6 June 2024.
- ^ "Oldham Community Radio". Retrieved 6 June 2024.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Manchester Evening News". themediabriefing.com. Archived from the original on 5 July 2011. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ "About". corporate.menmedia.co.uk. Archived from the original on 20 February 2023. Retrieved 27 September 2012.
- ^ "Projects". corporate.menmedia.co.uk. Archived from the original on 18 October 2012. Retrieved 27 September 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Brooks-Pollock, Tom (30 November 2011). "Lowry gallery and theatre is most popular tourist attraction in Greater Manchester". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 25 December 2011. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ Conway, Tony; Whitelock, Jeryl (2007). "Relationship marketing in the subsidised arts: the key to a strategic marketing focus". European Journal of Marketing. 41 (1/2): 199–222. doi:10.1108/03090560710718184. ISSN 0309-0566.
- ^ Murray 2007.
- ^ "About The Lowry". The Lowry. Archived from the original on 8 June 2008. Retrieved 2 May 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Schofield 2007.
- ^ Parkinson-Bailey 2000, p. 77.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The Hallé – History". The Hallé Concerts Society. Archived from the original on 6 July 2010. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ "Philharmonic Orchestra About the Orchestraurl". BBC. Archived from the original on 12 October 2022. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ "BBC Orchestras". BBC (Press release). February 2006. Archived from the original on 21 March 2007. Retrieved 10 July 2008.
- ^ "Manchester Camerata". Manchester Camerata. Archived from the original on 20 May 2007. Retrieved 2 May 2008.
•"About the NCO". Northern Chamber Orchestra. Archived from the original on 28 February 2009. Retrieved 2 March 2014. - ^ "Bridgewater Hall facts and figures". bridgewater-hall.co.uk. Archived from the original on 7 October 2007. Retrieved 17 January 2008.
•"Good Venue Guide; 28 – Bridgewater Hall, Manchester". Independent on Sunday. 12 April 1998. - ^ Redhead 1993, pp. 60–61.
- ^ James Holt (27 April 2022). "Manchester's AO Arena to see huge £50m revamp this summer". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 11 October 2022. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ "Largest indoor arenas in the United Kingdom in 2020, by capacity". statists. 2020. Archived from the original on 12 October 2022. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ "Pollstar Concert Industry Awards Winners Archives". Pollstar Online. 2001. Archived from the original on 12 January 2013. Retrieved 24 June 2007.
•Brown, Rachel. "M.E.N Arena's world's top venue". Manchester Evening News. M.E.N Media. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 12 August 2007.The M.E.N. Arena is the top-selling venue in the world
•"Manchester Evening News arena". smg-europe.com. Archived from the original on 10 February 2009. Retrieved 2 March 2014. - ^ Chris Slater (28 June 2022). "'It'll be the greatest music arena ever built': Manchester's Co-op Live boss gives exciting update on £365m venue – and how Harry Styles and Bruce Springsteen helped". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 11 October 2022. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ "Manchester City stadium history". MCFC.co.uk. Archived from the original on 10 December 2007. Retrieved 11 January 2008.
•"Arctic Monkeys confirm festival plans". NME. 26 January 2007. Retrieved 5 February 2007. - ^ "The Guardian view on Manchester's new cultural space: from one kind of factory to another". The Guardian. 5 December 2014. Archived from the original on 15 December 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ^ "Factory International: Manchester arts venue goes £100m over budget". BBC News. 4 October 2022. Archived from the original on 12 October 2022. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
Bibliography
[edit]- Aspin, Chris (1981). The Cotton Industry. Shire Publications. ISBN 0-85263-545-1.
- Bayliss, Don (1996). Historical Atlas of Trafford. Don Bayliss. ISBN 0-9529300-0-5.
- Bontje, Marco; Musterd, Sako; Pelzer, Peter (2011). Inventive City-Regions. Ashgate. ISBN 978-1-4094-1772-9.
- Bowden, Andrew (2015). See You In Kirk Yetholm: Tales From The Pennine Way. Rambling Man.
- Bristow, M. Roger; Cross, Donald T. (1983). English Structure Planning: A Commentary on Procedure and Practice in the Seventies. Routledge. ISBN 0-85086-094-6.
- Carter, Charles Frederick (1962). Manchester and its Region. Manchester University Press. ISBN 978-0719000218.
- Clapson, Mark (2010). Ray Hutchison (ed.). Suburbanization in Global Society. Emerald Group. ISBN 978-0-85724-347-8.
- Clark, David M. (1973). Greater Manchester Votes: A Guide to the New Metropolitan Authorities. Redrose.
- Cooper, Glynis (2005). Salford: An Illustrated History. The Breedon Books Publishing Company. ISBN 1-85983-455-8.
- Cowhig, W. T. (1976). It Happened Round Greater Manchester; Textiles. Greater Manchester Council.
- Dawson, Alan (1992). Relative hills of Britain. Cicerone Press. ISBN 1-85284-068-4.
- Frangopulo, Nicholas Joseph (1977). Tradition in action: the historical evolution of the Greater Manchester County. EP Publishing. ISBN 0-7158-1203-3.
- Freeman, Thomas Walter; Snodgrass, Catherine P. (1959). The Conurbations of Great Britain. Manchester University Press. ISBN 978-0719000546.
- Hardy, Peter B. (1998). Butterflies of Greater Manchester. PGL Enterprises. ISBN 0-9532374-0-0.
- Hartwell, Clare (2001). Pevsner Architectural Guides: Manchester. Penguin Books. ISBN 0-14-071131-7.
- Hartwell, Clare; Hyde, Matthew; Pevsner, Nikolaus (2004). Lancashire : Manchester and the South-East. The buildings of England. Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-10583-5.
- Holland, Philip; Spence, Ian; Sutton, Trevor (1984). Breeding Birds in Greater Manchester. Manchester Ornithological Society. ISBN 978-0-9509505-0-1.
- Hyde, M.; O'Rourke, A.; Portland, P. (2004). Around the M60: Manchester's Orbital Motorway. AMCD. ISBN 1-897762-30-5.
- Kellie, Euan (2010). Rebuilding Manchester. Derby: Derby Books. ISBN 978-1-85983-786-3.
- Kidd, Alan (2006). Manchester: A History. Carnegie Publishing. ISBN 1-85936-128-5.
- Little, Daran (1995). The Coronation Street Story. Boxtree. ISBN 978-1-85283-464-7.
- Little, Daran (2000). 40 Years of Coronation Street. Andre Deutsch. ISBN 978-0-233-99806-0.
- Matthews, Peter, ed. (1992). The Guinness Book of Records 1993. Guinness World Records Limited. ISBN 0-85112-978-1.
- McNeil, Robina; Nevell, Michael (2000). A Guide to the Industrial Archaeology of Greater Manchester. Association for Industrial Archaeology. ISBN 0-9528930-3-7.
- Murray, Braham (2007). The worst it can be is a disaster. Methuen Drama, A & C Black Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7136-8490-2.
- Nevell, Mike; Redhead, Norman, eds. (2005). Mellor: Living on the Edge. A Regional Study of an Iron Age and Romano-British Upland Settlement. University of Manchester Archaeological Unit, Greater Manchester Archaeological Unit, and the Mellor Archaeological Trust. ISBN 0-9527813-6-0.
- Parkinson-Bailey, John J (2000). Manchester: an Architectural History. Manchester University Press. ISBN 0-7190-5606-3.
- Ramsden, Caroline (1966). Farewell Manchester: history of Manchester Racecourse. J A Allen & Co.
- Ravetz, Joe (2000). City-Region 2020. Earthscan. ISBN 978-1-85383-606-0.
- Redcliffe-Maud, John; Wood, Bruce (1975). English local government reformed. OUP. ISBN 0-19-885091-3.
- Redcliffe-Maud, John (June 1969). Royal Commission on Local Government in England 1966–1969, Volume I: Report (Cmnd. 4040). HMSO.
- Redhead, Brian (1993). Manchester: a Celebration. Andre Deutsch Ltd. ISBN 0-233-98816-5.
- Roberts, Peter; Thomas, Kevin; Williams, Gwyndaf (2014). Metropolitan Planning in Britain: A Comparative Study. Routledge. ISBN 9781136035845.
- Rochdale Metropolitan Borough Council. Metropolitan Rochdale Official Guide. Ed. J. Burrow & Co. Ltd.
- Schofield, Jonathan (2003). City Life: Manchester the Complete Guide. City Life. ISBN 978-0-9544460-0-0.
- Schofield, Jonathan (2007). Manchester: the complete guide 2007. City Life.
- Taylor, Ian; Evans, Karen; Fraser, Penny (1996). A Tale of Two Cities: Global Change, Local Feeling, and Everyday Life in the North of England: a Study in Manchester and Sheffield. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-13828-4.
- Wannop, Urlan (2002). Regional Imperative: Regional Planning and Governance in Britain, Europe and the United States. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-11-702368-0.
- Wilson, David; Game, Chris (2002). Local Government in the United Kingdom (3rd ed.). Palgrave MacMillan. ISBN 978-0-333-94859-0.
External links
[edit]- www.agma.gov.uk, the Association of Greater Manchester Authorities
- www.gmcro.co.uk, the Greater Manchester County Record Office, for historical records relating to Greater Manchester
- www.visitmanchester.com, the official tourism website for Greater Manchester
- Greater Manchester at Curlie






