Индо-Греческое царство
Индо-греческое царство | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 г. до н. э. – 10 г. н. э. | |||||||||||||
Слон и кадуцей на монете Деметрия I , основателя Индо-Греческого царства.
| |||||||||||||
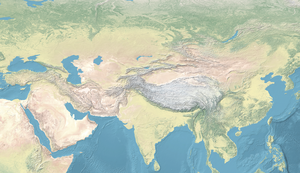
![Территория индо-греков около 150 г. до н.э.[1]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f4/Map_of_the_Indo-Greeks.png/250px-Map_of_the_Indo-Greeks.png) Территория индо-греков около 150 г. до н.э. [ 1 ] | |||||||||||||
| Капитал | Александрия на Кавказе (современный Баграм ) [ 2 ] | ||||||||||||
| Общие языки | Греческий ( греческий алфавит ) Пали ( сценарий Харошти ) санскрит Пракрит ( сценарий Брахми ) | ||||||||||||
| Религия | буддизм индуизм эллинизм Зороастризм | ||||||||||||
| Правительство | Монархия | ||||||||||||
| Базилевс | |||||||||||||
• 200 – 180 гг. до н.э. | Деметрий I (первый) | ||||||||||||
• 25 г. до н. э. – 10 г. н. э. | Уровень III (последний) | ||||||||||||
| Историческая эпоха | Античность | ||||||||||||
• Учредил | 200 г. до н.э. | ||||||||||||
• Упразднено | 10 год нашей эры | ||||||||||||
| Область | |||||||||||||
| 150 г. до н.э. [ 3 ] | 1 100 000 км 2 (420 000 квадратных миль) | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Сегодня часть | Афганистан Пакистан Индия | ||||||||||||
| Индо-Греческое царство (200 г. до н.э. – 10 г. н.э.) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Часть серии о |
| Индо-Греческое царство |
|---|
 |
Индо -греческое царство , или Греко-Индийское царство , также известное как царство Явана (также Яванараджья [ 4 ] после слова Йона , происходящего от ионийцев ), было королевством эллинистической эпохи, греческим охватывающим различные части современного Афганистана , Пакистана и северо-западной Индии . [ 5 ] [ 6 ] [ 7 ] [ 8 ] [ 9 ] [ 10 ] Он существовал с ок. 200 г. до н.э. – ок. 10 год нашей эры .
Термин «Индо-греческое царство» в общих чертах описывает ряд различных эллинистических государств, правивших из региональных столиц, таких как Таксила , Сагала , Пушкалавати и Александрия на Кавказе (ныне Баграм ). [ 11 ] [ 12 ] [ 13 ] На другие центры лишь намекают; например, и » Птолемея «География номенклатура более поздних царей предполагают, что некий Феофил на юге индо-греческой сферы влияния, возможно, также когда-то был царской резиденцией.
Царство было основано, когда греко-бактрийский царь Деметрий I Бактрийский вторгся в Индию из Бактрии примерно в 200 г. до н. э. [ 14 ] Греки к востоку от Империи Селевкидов в конечном итоге были отделены от Греко-Бактрийского царства и Индо-греческих царств на северо-западе Индийского субконтинента. [ 15 ]
В течение двух столетий своего правления индо-греческие цари объединили греческий и индийский языки и символы , как видно на их монетах, а также смешали греческие и индийские идеи, как видно из археологических находок. [ 16 ] Распространение индо-греческой культуры имело последствия, которые ощущаются до сих пор, особенно под влиянием греко-буддийского искусства . [ 17 ] Этническая принадлежность индо-греков также могла быть в некоторой степени гибридной. Евтидемом я был, по словам Полибия, [ 18 ] магнезийский грек . Его сын, Деметрий I , основатель Индо-греческого царства, следовательно, был греком по национальности, по крайней мере, по отцу. Был заключен брачный договор того же Деметрия с дочерью селевкидского правителя Антиоха III . Этническая принадлежность более поздних индо-греческих правителей иногда менее ясна. [ 19 ] Например, предполагалось, что Артемидор (80 г. до н.э.) имел индо-скифское происхождение, хотя сейчас его считают обычным индо-греческим царем. [ 20 ]
Менандра I Сотера , самого известного среди индо-греческих царей, часто называют просто «Менандр», несмотря на то, что действительно существовал еще один индо-греческий царь, известный как Менандр II. Столица Менандра I находилась в Сагале в Пенджабе (современный Сиалкот). После смерти Менандра большая часть его империи распалась, а индо-греческое влияние значительно сократилось. Многие новые королевства и республики к востоку от реки Рави начали чеканить новые монеты, изображающие военные победы. [ 21 ] Наиболее известными образовавшимися образованиями были Республика Яудхейя , Арджунаяны и Аудумбары . Говорят, что Яудхеи и Арджунаяны одержали «победу мечом». [ 22 ] династия Датта и династия Митра последовали Вскоре в Матхуре .
Индо-греки в конечном итоге исчезли как политическое образование около 10 г. н. э. после вторжений индо-скифов , хотя отдельные участки греческого населения, вероятно, оставались на несколько столетий дольше под последующим правлением индо-парфян , кушанов , [ а ] и индо-скифы , чье государство западных сатрапов просуществовало, охватывая местных греков , до 415 г. н.э.
Фон
[ редактировать ]Первоначальное присутствие Греции на Индийском субконтиненте
[ редактировать ]
Греки впервые начали заселять северо-западную часть Индийского субконтинента во времена Персидской империи Ахеменидов . Дарий Великий завоевал эту территорию, но вместе со своими преемниками также завоевал большую часть греческого мира, который в то время включал всю западную часть Анатолийского полуострова . Когда греческие деревни восставали под персидским игом, они иногда подвергались этническим чисткам путем переселения в дальнюю часть империи. Таким образом, в индийских частях Персидской империи появилось множество греческих общин. [ нужна ссылка ]
В четвертом веке до нашей эры Александр Македонский разгромил и завоевал Персидскую империю. В 326 г. до н.э. сюда входила северо-западная часть Индийского субконтинента вплоть до реки Гифазис . Александр основал сатрапии и основал несколько поселений, в том числе Буцефалу ; он повернул на юг, когда его войска отказались идти дальше на восток. [ 23 ] Индийские сатрапии Пенджаба были оставлены под властью Пора и Таксила , которые были вновь подтверждены Трипарадисским договором в 321 г. до н. э., а оставшиеся греческие войска в этих сатрапиях были оставлены под командованием генерала Александра Евдема . После 321 г. до н.э. Евдем сверг Таксила, пока он не покинул Индию в 316 г. до н.э. На юге греческими колониями Инда правил также другой полководец: Пейтон, сын Агенора , [ 24 ] до его отъезда в Вавилон в 316 г. до н.э.
Около 322 г. до н.э. греки (описанные в индийских источниках как Йона или Явана ), возможно, тогда участвовали вместе с другими группами в восстании Чандрагупты Маурья против династии Нанды и дошли до Паталипутры для захвата города из Нанды. Мудраракшаса , Вишакхадутты с а также джайнская работа Парисиштапарвана говорят о союзе Чандрагупты с гималайским царем Парваткой, которого часто отождествляют Порусом . [ 25 ] и согласно этим сообщениям, этот союз дал Чандрагупте составную и мощную армию, состоящую из яванов (греков), камбоджа , шаков (скифов), киратов (непальцев), парасиков (персов) и баликов (бактрианцев), которые взяли Паталипутру . [ 26 ] [ 27 ] [ 28 ]
В 305 году до нашей эры Селевк I повел армию к Инду , где столкнулся с Чандрагуптой . Противостояние закончилось мирным договором и «соглашением о смешанных браках» ( Эпигамия , греческий : Ἐπιγαμία), что означает либо династический брак, либо соглашение о смешанных браках между индийцами и греками. Соответственно, Селевк уступил свои восточные территории Чандрагупте, возможно, до Арахозии , и получил 500 боевых слонов (которые сыграли ключевую роль в победе Селевка в битве при Ипсе ): [ 29 ]
Индийцы занимают частично некоторые из стран, расположенных вдоль Инда, которые прежде принадлежали персам: Александр лишил их ариан и основал там свои поселения. Но Селевк Никатор отдал их Сандрокотту по брачному контракту и получил взамен пятьсот слонов.
The details of the marriage agreement are not known,[31] but since the extensive sources available on Seleucus never mention an Indian princess, it is thought that the marital alliance went the other way, with Chandragupta himself or his son Bindusara marrying a Seleucid princess, in accordance with contemporary Greek practices to form dynastic alliances. An Indian Puranic source, the Pratisarga Parva of the Bhavishya Purana, described the marriage of Chandragupta with a Greek ("Yavana") princess, daughter of Seleucus,[32] before accurately detailing early Mauryan genealogy:
"Chandragupta married with a daughter of Suluva, the Yavana king of Pausasa. Thus, he mixed the Buddhists and the Yavanas. He ruled for 60 years. From him, Vindusara was born and ruled for the same number of years as his father. His son was Ashoka."

Chandragupta, however, followed Jainism until the end of his life. He got in his court for marriage the daughter of Seleucus Nicator, Berenice (Suvarnnaksi), and thus, he mixed the Indians and the Greeks. His grandson Ashoka, as Woodcock and other scholars have suggested, "may in fact have been half or at least a quarter Greek."[35]
Also several Greeks, such as the historian Megasthenes,[36] followed by Deimachus and Dionysius, were sent to reside at the Mauryan court.[37] Presents continued to be exchanged between the two rulers.[38] The intensity of these contacts is testified by the existence of a dedicated Mauryan state department for Greek (Yavana) and Persian foreigners,[39] or the remains of Hellenistic pottery that can be found throughout northern India.[40]
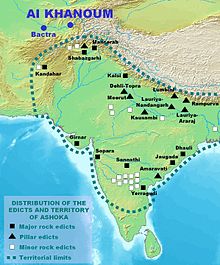
On these occasions, Greek populations apparently remained in the northwest of the Indian subcontinent under Mauryan rule. Chandragupta's grandson Ashoka, who had converted to the Buddhist faith declared in the Edicts of Ashoka, set in stone, some of them written in Greek,[41][42] that Greek populations within his realm also had converted to Buddhism:[43]
Here in the king's domain among the Greeks, the Kambojas, the Nabhakas, the Nabhapamkits, the Bhojas, the Pitinikas, the Andhras and the Palidas, everywhere people are following Beloved-of-the-Gods' instructions in Dharma.
— Rock Edict Nb13 (S. Dhammika).
In his edicts, Ashoka mentions that he had sent Buddhist emissaries to Greek rulers as far as the Mediterranean (Edict No. 13),[44][45] and that he developed herbal medicine in their territories, for the welfare of humans and animals (Edict No. 2).[46]

The Greeks in India even seem to have played an active role in the propagation of Buddhism, as some of the emissaries of Ashoka such as Dharmaraksita,[47] or the teacher Mahadharmaraksita,[48] are described in Pali sources as leading Greek ("Yona", i.e., Ionian) Buddhist monks, active in Buddhist proselytism (the Mahavamsa, XII).[49] It is also thought that Greeks contributed to the sculptural work of the Pillars of Ashoka,[50] and more generally to the blossoming of Mauryan art.[51] Some Greeks (Yavanas) may have played an administrative role in the territories ruled by Ashoka: the Junagadh rock inscription of Rudradaman records that during the rule of Ashoka, a Yavana King/ Governor named Tushaspha was in charge in the area of Girnar, Gujarat, mentioning his role in the construction of a water reservoir.[52][53]
Again in 206 BC, the Seleucid emperor Antiochus led an army to the Kabul valley, where he received war elephants and presents from the local king Sophagasenus:[54]
He (Antiochus) crossed the Caucasus (the Caucasus Indicus or Paropamisus: mod. Hindú Kúsh) and descended into India; renewed his friendship with Sophagasenus the king of the Indians; received more elephants, until he had a hundred and fifty altogether; and having once more provisioned his troops, set out again personally with his army: leaving Androsthenes of Cyzicus the duty of taking home the treasure which this king had agreed to hand over to him.
Greek rule in Bactria
[edit]
Alexander had also established several colonies in neighbouring Bactria, such as Alexandria on the Oxus (modern Ai-Khanoum) and Alexandria of the Caucasus (medieval Kapisa, modern Bagram). After Alexander's death in 323 BC, Bactria came under the control of Seleucus I Nicator, who founded the Seleucid Empire. The Greco-Bactrian kingdom was founded when Diodotus I, the satrap of Bactria (and probably the surrounding provinces) seceded from the Seleucid Empire around 250 BC. The preserved ancient sources (see below) are somewhat contradictory and the exact date of Bactrian independence has not been settled. Somewhat simplified, there is a high chronology (c. 255 BC) and a low chronology (c. 246 BC) for Diodotos' secession.[57] The high chronology has the advantage of explaining why the Seleucid king Antiochus II issued very few coins in Bactria, as Diodotos would have become independent there early in Antiochus' reign.[58] On the other hand, the low chronology, from the mid-240s BC, has the advantage of connecting the secession of Diodotus I with the Third Syrian War, a catastrophic conflict for the Seleucid Empire.
Diodotus, the governor of the thousand cities of Bactria (Latin: Theodotus, mille urbium Bactrianarum praefectus), defected and proclaimed himself king; all the other people of the Orient followed his example and seceded from the Macedonians.
The new kingdom, highly urbanized and considered one of the richest of the Orient (opulentissimum illud mille urbium Bactrianum imperium "The extremely prosperous Bactrian empire of the thousand cities" Justin, XLI,1[60]), was to further grow in power and engage into territorial expansion to the east and the west:
The Greeks who caused Bactria to revolt grew so powerful on account of the fertility of the country that they became masters, not only of Ariana, but also of India, as Apollodorus of Artemita says: and more tribes were subdued by them than by Alexander... Their cities were Bactra (also called Zariaspa, through which flows a river bearing the same name and emptying into the Oxus), and Darapsa, and several others. Among these was Eucratidia, which was named after its ruler.
— (Strabo, XI.XI.I[61])

When the ruler of neighbouring Parthia, the former satrap and self-proclaimed king Andragoras, was eliminated by Arsaces, the rise of the Parthian Empire cut off the Greco-Bactrians from direct contact with the Greek world. Overland trade continued at a reduced rate, while sea trade between Greek Egypt and Bactria developed.
Diodotus was succeeded by his son Diodotus II, who allied himself with the Parthian Arsaces in his fight against Seleucus II:
Soon after, relieved by the death of Diodotus, Arsaces made peace and concluded an alliance with his son, also by the name of Diodotus; some time later he fought against Seleucos who came to punish the rebels, and he prevailed: the Parthians celebrated this day as the one that marked the beginning of their freedom
— (Justin, XLI,4)[62]
Euthydemus, a Magnesian Greek according to Polybius[63] and possibly satrap of Sogdiana, overthrew Diodotus II around 230 BC and started his own dynasty. Euthydemus's control extended to Sogdiana, going beyond the city of Alexandria Eschate founded by Alexander the Great in Ferghana:
"And they also held Sogdiana, situated above Bactriana towards the east between the Oxus River, which forms the boundary between the Bactrians and the Sogdians, and the Iaxartes River. And the Iaxartes forms also the boundary between the Sogdians and the nomads.
— Strabo XI.11.2[64]

Euthydemus was attacked by the Seleucid ruler Antiochus III around 210 BC. Although he commanded 10,000 horsemen, Euthydemus initially lost a battle on the Arius[65] and had to retreat. He then successfully resisted a three-year siege in the fortified city of Bactra (modern Balkh), before Antiochus finally decided to recognize the new ruler, and to offer one of his daughters to Euthydemus's son Demetrius around 206 BC.[66] Classical accounts also relate that Euthydemus negotiated peace with Antiochus III by suggesting that he deserved credit for overthrowing the original rebel Diodotus, and that he was protecting Central Asia from nomadic invasions thanks to his defensive efforts:
...for if he did not yield to this demand, neither of them would be safe: seeing that great hordes of Nomads were close at hand, who were a danger to both; and that if they admitted them into the country, it would certainly be utterly barbarised.
Following the departure of the Seleucid army, the Bactrian kingdom seems to have expanded. In the west, areas in north-eastern Iran may have been absorbed, possibly as far as into Parthia, whose ruler had been defeated by Antiochus the Great. These territories possibly are identical with the Bactrian satrapies of Tapuria and Traxiane.
To the north, Euthydemus also ruled Sogdiana and Ferghana, and there are indications that from Alexandria Eschate the Greco-Bactrians may have led expeditions as far as Kashgar and Ürümqi in Chinese Turkestan, leading to the first known contacts between China and the West around 220 BC. The Greek historian Strabo too writes that:
they extended their empire even as far as the Seres (Chinese) and the Phryni

Several statuettes and representations of Greek soldiers have been found north of the Tien Shan, on the doorstep to China, and are today on display in the Xinjiang museum at Urumqi (Boardman[67]).
Greek influences on Chinese art have also been suggested (Hirth, Rostovtzeff). Designs with rosette flowers, geometric lines, and glass inlays, suggestive of Hellenistic influences,[68] can be found on some early Han dynasty bronze mirrors.[69]
Numismatics also suggest that some technology exchanges may have occurred on these occasions: the Greco-Bactrians were the first in the world to issue cupro-nickel (75/25 ratio) coins,[70] an alloy technology only known by the Chinese at the time under the name "White copper" (some weapons from the Warring States period were in copper-nickel alloy[71]). The practice of exporting Chinese metals, in particular iron, for trade is attested around that period. Kings Euthydemus, Euthydemus II, Agathocles and Pantaleon made these coin issues around 170 BC and it has alternatively been suggested that a nickeliferous copper ore was the source from mines at Anarak.[72] Copper-nickel would not be used again in coinage until the 19th century.
The presence of Chinese people in the Indian subcontinent from ancient times is also suggested by the accounts of the "Ciñas" in the Mahabharata and the Manu Smriti.
The Han dynasty explorer and ambassador Zhang Qian visited Bactria in 126 BC, and reported the presence of Chinese products in the Bactrian markets:
"When I was in Bactria (Daxia)", Zhang Qian reported, "I saw bamboo canes from Qiong and cloth made in the province of Shu (territories of southwestern China). When I asked the people how they had gotten such articles, they replied, "Our merchants go buy them in the markets of Shendu (India)."
Upon his return, Zhang Qian informed the Chinese emperor Han Wudi of the level of sophistication of the urban civilizations of Ferghana, Bactria and Parthia, who became interested in developing commercial relationships with them:
The Son of Heaven on hearing all this reasoned thus: Ferghana (Dayuan) and the possessions of Bactria (Daxia) and Parthia (Anxi) are large countries, full of rare things, with a population living in fixed abodes and given to occupations somewhat identical with those of the Chinese people, and placing great value on the rich produce of China
— (Hanshu, Former Han History)
A number of Chinese envoys were then sent to Central Asia, triggering the development of the Silk Road from the end of the 2nd century BC.[73]

The Indian emperor Chandragupta, founder of the Mauryan dynasty, had re-conquered northwestern India upon the death of Alexander the Great around 322 BC. However, contacts were kept with his Greek neighbours in the Seleucid Empire, a dynastic alliance or the recognition of intermarriage between Greeks and Indians were established (described as an agreement on Epigamia in Ancient sources), and several Greeks, such as the historian Megasthenes, resided at the Mauryan court. Subsequently, each Mauryan emperor had a Greek ambassador at his court.
Chandragupta's grandson Ashoka converted to the Buddhist faith and became a great proselytizer in the line of the traditional Pali canon of Theravada Buddhism, directing his efforts towards the Indian and the Hellenistic worlds from around 250 BC. According to the Edicts of Ashoka, set in stone, some of them written in Greek, he sent Buddhist emissaries to the Greek lands in Asia and as far as the Mediterranean. The edicts name each of the rulers of the Hellenistic world at the time.
The conquest by Dharma has been won here, on the borders, and even six hundred yojanas (4,000 miles) away, where the Greek king Antiochos rules, beyond there where the four kings named Ptolemy, Antigonos, Magas and Alexander rule, likewise in the south among the Cholas, the Pandyas, and as far as Tamraparni.
— (Edicts of Ashoka, 13th Rock Edict, S. Dhammika)
Some of the Greek populations that had remained in northwestern India apparently converted to Buddhism:
Here in the king's domain among the Greeks, the Kambojas, the Nabhakas, the Nabhapamkits, the Bhojas, the Pitinikas, the Andhras and the Palidas, everywhere people are following Beloved-of-the-Gods' instructions in Dharma.
— (Edicts of Ashoka, 13th Rock Edict, S. Dhammika)
Furthermore, according to Pali sources, some of Ashoka's emissaries were Greek Buddhist monks, indicating close religious exchanges between the two cultures:
When the thera (elder) Moggaliputta, the illuminator of the religion of the Conqueror (Ashoka), had brought the (third) council to an end… he sent forth theras, one here and one there: …and to Aparantaka (the "Western countries" corresponding to Gujarat and Sindh) he sent the Greek (Yona) named Dhammarakkhita... and the thera Maharakkhita he sent into the country of the Yona.
— (Mahavamsa XII)
Greco-Bactrians probably received these Buddhist emissaries (At least Maharakkhita, lit. "The Great Saved One", who was "sent to the country of the Yona") and somehow tolerated the Buddhist faith, although little proof remains. In the 2nd century AD, the Christian dogmatist Clement of Alexandria recognized the existence of Buddhist Sramanas among the Bactrians ("Bactrians" meaning "Oriental Greeks" in that period), and even their influence on Greek thought:
Thus philosophy, a thing of the highest utility, flourished in antiquity among the barbarians, shedding its light over the nations. And afterwards it came to Greece. First in its ranks were the prophets of the Egyptians; and the Chaldeans among the Assyrians;[74] and the Druids among the Gauls; and the Sramanas among the Bactrians ("Σαρμαναίοι Βάκτρων"); and the philosophers of the Celts; and the Magi of the Persians, who foretold the Saviour's birth, and came into the land of Judea guided by a star. The Indian gymnosophists are also in the number, and the other barbarian philosophers. And of these there are two classes, some of them called Sramanas ("Σαρμάναι"), and others Brahmins ("Βραφμαναι").
— Clement of Alexandria, "The Stromata, or Miscellanies" Book I, Chapter XV[75]
Rise of the Shungas (185 BC)
[edit]
In India, the Maurya dynasty was overthrown around 185 BC when Pushyamitra Shunga, the commander-in-chief of Mauryan Imperial forces and a Brahmin, assassinated the last of the Mauryan emperors Brihadratha.[76][77] Pushyamitra Shunga then ascended the throne and established the Shunga Empire, which extended its control as far west as the Punjab.
Buddhist sources, such as the Ashokavadana, mention that Pushyamitra was hostile towards Buddhists and allegedly persecuted the Buddhist faith. A large number of Buddhist monasteries (viharas) were allegedly converted to Hindu temples, in such places as Nalanda, Bodhgaya, Sarnath or Mathura. While it is established by secular sources that Hinduism and Buddhism were in competition during this time, with the Shungas preferring the former to the latter, historians such as Etienne Lamotte[78] and Romila Thapar[79] argue that Buddhist accounts of persecution of Buddhists by Shungas are largely exaggerated. Some Puranic sources however also describe the resurgence of Brahmanism following the Maurya dynasty, and the killing of millions of Buddhists, such as the Pratisarga Parva of the Bhavishya Purana:[80]
"At this time [after the rule of Chandragupta, Bindusara and Ashoka] the best of the brahmanas, Kanyakubja, performed sacrifice on the top of a mountain named Arbuda. By the influence of Vedic mantras, four Kshatriyas appeared from the yajna (sacrifice). (...) They kept Ashoka under their control and annihilated all the Buddhists. It is said there were 4 million Buddhists and all of them were killed by uncommon weapons".
History
[edit]Sources
[edit]
Some narrative history has survived for most of the Hellenistic world, at least of the kings and the wars;[83] this is lacking for India. The main Greco-Roman source on the Indo-Greeks is Justin, who wrote an anthology drawn from the Roman historian Pompeius Trogus, who in turn wrote, from Greek sources, at the time of Augustus Caesar.[84] In addition to these dozen sentences, the geographer Strabo mentions India a few times in the course of his long dispute with Eratosthenes about the shape of Eurasia. Most of these are purely geographical claims, but he does mention that Eratosthenes' sources say that some of the Greek kings conquered further than Alexander; Strabo does not believe them on this, nor does he believe that Menander and Demetrius son of Euthydemus conquered more tribes than Alexander[85] There is half a story about Menander in one of the books of Polybius which has not come down to us intact.[86]
There are Indian literary sources, ranging from the Milinda Panha, a dialogue between a Buddhist sage Nagasena and Indianized names that may be related to Indo-Greek kings such as Menander I. Names in these sources are consistently Indianized, and there is some dispute whether, for example, Dharmamitra represents "Demetrius" or is an Indian prince with that name. There was also a Chinese expedition to Bactria by Chang-k'ien under the Emperor Wu of Han, recorded in the Records of the Grand Historian and Book of the Former Han, with additional evidence in the Book of the Later Han; the identification of places and peoples behind transcriptions into Chinese is difficult, and several alternate interpretations have been proposed.[87][full citation needed]
Other evidence of the broader and longer influence of Indo-Greeks is possibly suggested by Yavanarajya inscription, dated to the 1st-century BC. It mentions Yavanas, a term which is derived from "Ionians", and which at that time most likely means "Indo-Greeks".[88]
Expansion of Demetrius into India
[edit]
Demetrius I, the son of Euthydemus is generally considered the Greco-Bactrian king who first launched the Greek expansion into India. He is therefore the founder of the Indo-Greek realm. The true intents of the Greek kings in occupying India are unknown, but it is thought that the elimination of the Maurya Empire by the Sunga greatly encouraged this expansion. The Indo-Greeks, in particular Menander I who is said in the Milindapanha to have converted to Buddhism, also possibly received the help of Indian Buddhists.[90]
There is an inscription from his father's reign already officially hailing Demetrius as victorious. He also has one of the few absolute dates in Indo-Greek history: after his father held off Antiochus III for two years, 208–6 BC, the peace treaty included the offer of a marriage between Demetrius and Antiochus' daughter.[91] Coins of Demetrius I have been found in Arachosia and in the Kabul Valley; the latter would be the first entry of the Greeks into India, as they defined it. There is also literary evidence for a campaign eastward against the Seres and the Phryni; but the order and dating of these conquests is uncertain.[92]
Demetrius I seems to have conquered the Kabul valley, Arachosia and perhaps Gandhara;[93] he struck no Indian coins, so either his conquests did not penetrate that far into India or he died before he could consolidate them. On his coins, Demetrius I always carries the elephant-helmet worn by Alexander, which seems to be a token of his Indian conquests.[94] Bopearachchi believes that Demetrius received the title of "King of India" following his victories south of the Hindu Kush.[95] He was also given, though perhaps only posthumously, the title Ἀνίκητος ("Aniketos", lit. Invincible) a cult title of Heracles, which Alexander had assumed; the later Indo-Greek kings Lysias, Philoxenus, and Artemidorus also took it.[96] Finally, Demetrius may have been the founder of a newly discovered Yavana era, starting in 186/5 BC.[97]
First bilingual and multi-religion monetary system
[edit]
After the death of Demetrius, the Bactrian kings Pantaleon and Agathocles struck the first bilingual coins with Indian inscriptions found as far east as Taxila[99] so in their time (c. 185–170 BC) the Bactrian kingdom seems to have included Gandhara.[100] These first bilingual coins used the Brahmi script, whereas later kings would generally use Kharoshthi. They also went as far as incorporating Indian deities, variously interpreted as Hindu deities or the Buddha.[98] They also included various Indian devices (lion, elephant, zebu bull) and symbols, some of them Buddhist such as the tree-in-railing.[101] These symbols can also be seen in the Post-Mauryan coinage of Gandhara.

The Hinduist coinage of Agathocles is few but spectacular. Six Indian-standard silver drachmas were discovered at Ai-Khanoum in 1970, which depict Hindu deities.[102] These are early Avatars of Vishnu: Balarama-Sankarshana with attributes consisting of the Gada mace and the plow, and Vasudeva-Krishna with the Vishnu attributes of the Shankha (a pear-shaped case or conch) and the Sudarshana Chakra wheel.[102] These first attempts at incorporating Indian culture were only partly preserved by later kings: they all continued to struck bilingual coins, sometimes in addition to Attic coinage, but Greek deities remained prevalent. Indian animals however, such as the elephant, the bull or the lion, possibly with religious overtones, were used extensively in their Indian-standard square coinage. Buddhist wheels (Dharmachakras) still appear in the coinage of Menander I and Menander II.[103][104]
Several Bactrian kings followed after Demetrius' death, and it seems likely that the civil wars between them made it possible for Apollodotus I (from c. 180/175 BC) to make himself independent as the first proper Indo-Greek king (who did not rule from Bactria). Large numbers of his coins have been found in India, and he seems to have reigned in Gandhara as well as western Punjab. Apollodotus I was succeeded by or ruled alongside Antimachus II, likely the son of the Bactrian king Antimachus I.[105]
Rule of Menander I
[edit]
The next important Indo-Greek king was Menander I who is considered to have been the most successful of the Indo-Greek kings, and who expanded the kingdom to its greatest extent by means of his various conquests.[106][107] The finds of his coins are the most numerous and occur across the greatest geographical area, more than any of the other Indo-Greek kings. Coins stamped with Menander's likeness can be found as far away as Eastern Punjab over 600 miles distant. Menander seems to have begun a second wave of conquests, and it seems likely that the easternmost conquests were made by him.[108]
Thus from 165 BCE until his death in 130 BCE, Menander I ruled Punjab with Sagala as his capital.[109][110] Menander subsequently made an expedition across northern India to Mathura, where the Yavnarajya inscription was recorded. However, it is not known if this was a contiguous empire, or ruled through key city centers or polis. Soon after, Eucratides I king of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom began warring with the Indo-Greeks in the north western frontier.
According to Apollodorus of Artemita, quoted by Strabo, the Indo-Greek territory for a while included the Indian coastal provinces of Sindh and possibly Gujarat.[111] With archaeological methods, the Indo-Greek territory can however only be confirmed from the Kabul Valley to the eastern Punjab, so Greek presence outside was probably short-lived or non-existent.


Some sources also claim that the Indo-Greeks may have reached the Shunga capital Pataliputra in northern India.[114] However, the nature of this expedition is a matter of controversy. The only recorded primary account regarding this campaign was written in the Yuga Purana, however this text was written as a forthcoming prophecy of an impending conflict. It is not known if the expedition was carried out, or if the Yavanas (Indo-Greeks) were successful in this campaign.
"After having conquered Saketa, the country of the Panchala and the Mathuras, the Yavanas, wicked and valiant, will reach Kusumadhvaja ("The town of the flower-standard", Pataliputra). The thick mud-fortifications at Pataliputra being reached, all the provinces will be in disorder, without doubt. Ultimately, a great battle will follow, with tree-like engines (siege engines)."
— Yuga Purana (Gargi-Samhita, Paragraph 5)
However the claim that the Yavanas held Pataliputra is not supported by numismatic or historical accounts, and is even contradicted by some inscriptions. King Kharavela of Kalinga, during his forth year reigning, was recorded in the Hathigumpha inscription to have routed a demoralized Indo-Greek army back to Mathura. It is not known which Indo-Greek was leading the army at the time, however it is presumed to be Menander I or perhaps even a later ruler.[115] Then during his twelfth year in power, Kharavela is recorded to have battled the Shunga Empire and defeated the emperor Brhaspatimitra, known as Pushyamitra Shunga.[116] Kharavela is then stated to have sacked the capital Pataliputra, and reclaimed the Jain idols and treasures that had been plundered from Kalinga and taken to Pataliputra. Based on the chronology and date during 1st century BC, it is postulated that Menander was the one leading the Indo-Greeks during Kharavela's reign.
"Then in the eighth year, (Kharavela) with a large army having sacked Goradhagiri causes pressure on Rajagaha (Rajagriha). On account of the loud report of this act of valour, the Yavana (Greek) King Dimi[ta] retreated to Mathura having extricated his demoralized army."
— Hathigumpha inscription (lines 7-8)
The important Bactrian king Eucratides seems to have attacked the Indo-Greek kingdom during the mid 2nd century BC. A Demetrius, called "King of the Indians", seems to have confronted Eucratides in a four-month siege, reported by Justin, but he ultimately lost.[b]
It is uncertain who this Demetrius was, and when the siege happened. Some scholars believe that it was Demetrius I."(Demetrius I) was probably the Demetrius who besieged Eucratides for four months", D.W. Mac Dowall, pp. 201–202, Afghanistan, ancien carrefour entre l'est et l'ouest. This analysis goes against Bopearachchi, who has suggested that Demetrius I died long before Eucratides came to power.</ref> In any case, Eucratides seems to have occupied territory as far as the Indus, between ca. 170 BC and 150 BC.[117] His advances were ultimately reclaimed by the Indo-Greek king Menander I,[118]
Menander is also remembered in Buddhist literature, where he is called Milinda. He is described in the Milinda Panha as a convert to Buddhism and that he became an arhat[119] whose relics were enshrined in a manner reminiscent of a Buddha.[120][121] He also introduced a new coin type, with Athena Alkidemos ("Protector of the people") on the reverse, which was adopted by most of his successors in the East.[122]
Following the death of Menander his empire was greatly reduced due to the emergence of new kingdoms and republics within India.[22] The most eminent entities to reform were the Yaudheya and the Arjunayanas, which were military confederations that had been annexed by the Maurya Empire. These republics began to mint new coins mentioning military victories, that were reminiscent of Indo-Greek type coins. Along with numismatic evidence, the Junagadh rock inscription of Rudradaman details the conquests of the Saka King Rudradaman I of the Western Satraps over the Yaudheya Republic, reaffirming their independence.[123]
From the mid-2nd century BC, the Scythians, in turn being pushed forward by the Yuezhi who were completing a long migration from the border of China, started to invade Bactria from the north.[124] Around 130 BC the last Greco-Bactrian king Heliocles was probably killed during the invasion and the Greco-Bactrian kingdom proper ceased to exist. The Parthians also probably played a role in the downfall of the Bactrian kingdom, and supplanted the Scythians.
There are however no historical recordings of events in the Indo-Greek kingdom after Menander's death around 130 BC, since the Indo-Greeks had now become very isolated from the rest of the Graeco-Roman world. The later history of the Indo-Greek states, which lasted to around the shift BC/AD, is reconstructed almost entirely from archaeological and numismatical analyses.[125]
Western accounts
[edit]Greek presence in Arachosia, where Greek populations had been living since before the acquisition of the territory by Chandragupta from Seleucus, is mentioned by Isidore of Charax. He describes Greek cities there, one of them called Demetrias, probably in honour of the conqueror Demetrius.[126]
Apollodotus I (and Menander I) were mentioned by Pompeius Trogus as important Indo-Greek kings.[127] It is theorized that Greek advances temporarily went as far as the Shunga capital Pataliputra (today Patna) in eastern India. Senior considers that these conquests can only refer to Menander:[128] Against this, John Mitchener considers that the Greeks probably raided the Indian capital of Pataliputra during the time of Demetrius,[129] though Mitchener's analysis is not based on numismatic evidence.

Of the eastern parts of India, then, there have become known to us all those parts which lie this side of the Hypanis, and also any parts beyond the Hypanis of which an account has been added by those who, after Alexander, advanced beyond the Hypanis, to the Ganges and Pataliputra.
The seriousness of the attack is in some doubt: Menander may merely have joined a raid led by Indian Kings down the Ganges,[132] as Indo-Greek presence has not been confirmed this far east.
To the south, the Greeks may have occupied the areas of the Sindh and Gujarat, including the strategic harbour of Barygaza (Bharuch),[133] conquests also attested by coins dating from the Indo-Greek ruler Apollodotus I and by several ancient writers (Strabo 11; Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, Chap. 41/47):[134]
The Greeks... took possession, not only of Patalene, but also, on the rest of the coast, of what is called the kingdom of Saraostus and Sigerdis.
— Strabo 11.11.1[135]
The Periplus further explains ancient Indo-Greek rule and continued circulation of Indo-Greek coinage in the region:
"To the present day ancient drachmae are current in Barygaza, coming from this country, bearing inscriptions in Greek letters, and the devices of those who reigned after Alexander, Apollodorus [sic] and Menander."
— Periplus Chap. 47[136]
Narain however dismisses the account of the Periplus as "just a sailor's story", and holds that coin finds are not necessarily indicators of occupation.[137] Coin hoards further suggest that in Central India, the area of Malwa may also have been conquered.[138]
Rule in Mathura
[edit]
From numismatic, literary and epigraphic evidence, it seems that the Indo-Greeks also had control over Mathura during the period between 185 BCE and 85 BCE, and especially during the rule of Menander I (165–135 BC).[140] Ptolemy mentioned that Menander's ruler extended to Mathura (Μόδυρα).[140]
Slightly northwest of Mathura, numerous Indo-Greek coins were found in the city of Khokrakot (modern Rohtak), belonging to as many as 14 different Indo-Greek kings, as well as coin molds in Naurangabad,[141] suggesting Indo-Greek occupation of Haryana in the 2nd-1st centuries BC.[142][143]

An inscription in Mathura discovered in 1988,[145] the Yavanarajya inscription, mentions "The last day of year 116 of Yavana hegemony (Yavanarajya)". The "Yavanarajya" probably refers to the rule of the Indo-Greeks in Mathura as late as around 70–60 BC (year 116 of the Yavana era).[139] The extent of Indo-Greek rule in Mathura has been disputed, but it is also known that no remains of Sunga rule have been found in Mathura,[139] and their territorial control is only proved as far as the central city of Ayodhya in northern central India, through the Dhanadeva-Ayodhya inscription.[146] Archeological excavations of cast die-struck coins have also revealed the presence of a Mitra dynasty (coin issuers who did not name themselves "kings" on their coins) in Mathura sometime between 150 BC to 20 BC.[139] Additionally, coins belonging to a Datta dynasty have also been excavated in Mathura. Whether these dynasties ruled independently or as satraps to larger kingdoms is unknown.
Figurines of foreigners in Mathura
[edit]Several figures of foreigners appear in the terracottas of Mathura art from the 4th to the 2nd century BCE, which are either described simply as "foreigners" or Persian or Iranian because of their foreign features.[148][149][150] These figurines might reflect the increased contacts of Indians with foreigners during this period.[149] Several of these seem to represent foreign soldiers who visited India during the Mauryan period and influenced modellers in Mathura with their peculiar ethnic features and uniforms.[151] A helmeted head of a soldier, probably Indo-Greek, is also known, and dated to the 1st century BCE, now in the Mathura Museum.[147] One of the terracotta statuettes, usually nicknamed the "Persian nobleman" and dated to the 2nd century BCE, can be seen wearing a coat, scarf, trousers and a turban.[152][153][154][148]
Mathura may then have been conquered by the Mitra dynasty, or ruled independently by the Datta dynasty during the 1st century BC.[155] In any case Mathura was under the control of the Indo-Scythian Northern Satraps from the 1st century of the Christian era.
Indian sources
[edit]The term Yavana is thought to be a transliteration of "Ionians" and is known to have designated Hellenistic Greeks (starting with the Edicts of Ashoka, where Ashoka writes about "the Yavana king Antiochus"),[156] but may have sometimes referred to other foreigners as well after the 1st century AD.[157]
Patanjali, a grammarian and commentator on Pāṇini, around 150 BC, describes in the Mahābhāsya, the invasion in two examples using the imperfect tense Sanskrit, denoting a recent or ongoing events:[158][159]
- "Arunad Yavanah Sāketam" ("The Yavanas (Greeks) were besieging Saketa")
- "Arunad Yavano Madhyamikām" ("The Yavanas were besieging Madhyamika" (the "Middle country")).

The Brahmanical text of the Yuga Purana describes events in the form of a prophecy, which may have been historical,[161][162][163] relates the attack of the Indo-Greeks on the capital Pataliputra,[164] a magnificent fortified city with 570 towers and 64 gates according to Megasthenes,[165] and describes the ultimate destruction of the city's walls:[166]
Then, after having approached Saketa together with the Panchalas and the Mathuras, the Yavanas, valiant in battle, will reach Kusumadhvaja ("The town of the flower-standard", Pataliputra). Then, once Puspapura (another name of Pataliputra) has been reached and its celebrated mud-walls cast down, all the realm will be in disorder.
Accounts of battles between the Greeks and the Shunga in Central India are also found in the Mālavikāgnimitram, a play by Kālidāsa which is thought to describe an encounter between a Greek cavalry squadron and Vasumitra, the grandson of Pushyamitra, during the latter's reign, by the Sindh River or the Kali Sindh River.[168]
According to the Yuga Purana, the Yavanas thereafter will retreat following internal conflicts:
"The Yavanas (Greeks) will command, the Kings will disappear. (But ultimately) the Yavanas, intoxicated with fighting, will not stay in Madhadesa (the Middle Country); there will be undoubtedly a civil war among them, arising in their own country (Bactria), there will be a terrible and ferocious war." (Gargi-Samhita, Yuga Purana chapter, No7).[167]
According to Mitchener, the Hathigumpha inscription indicates the presence of the Indo-Greeks led by a ruler listed as "ta" from Mathura during the 1st century BCE.[169] Although, the name of the king has been omitted and undeciphered. The remaining syllables [ta] has been disputed. It has been argued by Tarn to be referencing the ruler Demetrius. However this interpretation is disputed by other historians like Narain, which point out the discrepancies in chronology and the fact Demetrius didn't venture past Punjab.[170] Instead most historians now theorize it to be the Indo-Greek ruler Menander I, or perhaps a later Yavana king from Mathura.
"Then in the eighth year, (Kharavela) with a large army having sacked Goradhagiri causes pressure on Rajagaha (Rajagriha). On account of the loud report of this act of valour, the Yavana (Greek) King Dimi[ta] retreated to Mathura having extricated his demoralized army."
— Hathigumpha inscription, line 8, probably in the 1st century BC. Original text is in Brahmi script.[171]
But while this inscription may be interpreted as an indication that Demetrius I was the king who made conquests in Punjab, it is still true that he never issued any Indian-standard coins, only numerous coins with elephant symbolism, and the restoration of his name in Kharosthi on the Hathigumpha inscription: Di-Mi-Ta, has been doubted.[172] The "Di" is a reconstruction, and it may be noted that the name of another Indo-Greek king, Amyntas, is spelt A-Mi-Ta in Kharosthi and may fit in.
Therefore, Menander remains the likeliest candidate for any advance east of Punjab.
Consolidation
[edit]Menander is considered to have been probably the most successful Indo-Greek king, and the conqueror of the largest territory.[106] The finds of his coins are the most numerous and the most widespread of all the Indo-Greek kings. Menander is also remembered in Buddhist literature, where he is called Milinda, and is described in the Milinda Panha as a convert to Buddhism:[174] he became an arhat[119] whose relics were enshrined in a manner reminiscent of the Buddha.[120][121] He also introduced a new coin type, with Athena Alkidemos ("Protector of the people") on the reverse, which was adopted by most of his successors in the East.[122]
Fall of Bactria and death of Menander
[edit]
From the mid-2nd century BC, the Scythians, in turn being pushed forward by the Yuezhi who were completing a long migration from the border of China, started to invade Bactria from the north.[124] Around 130 BC the last Greco-Bactrian king Heliocles was probably killed during the invasion and the Greco-Bactrian kingdom proper ceased to exist. The Parthians also probably played a role in the downfall of the Bactrian kingdom.
Immediately after the fall of Bactria, the bronze coins of Indo-Greek king Zoilos I (130–120 BC), successor of Menander in the western part of the Indian territories, combined the club of Herakles with a Scythian-type bowcase and short recurve bow inside a victory wreath, illustrating interaction with horse-mounted people originating from the steppes, possibly either the Scythians (future Indo-Scythians), or the Yuezhi (future Kushans) who had invaded Greco-Bactria.[175] This bow can be contrasted to the traditional Hellenistic long bow depicted on the coins of the eastern Indo-Greek queen Agathokleia. It is now known that 50 years later, the Indo-Scythian Maues was in alliance with the Indo-Greek kings in Taxila, and one of those kings, Artemidoros seems to claim on his coins that he is the son of Maues,[176] although this is now disputed.[20]
Preservation of the Indo-Greek realm
[edit]The extent of Indo-Greek rule is still uncertain and disputed. Probable members of the dynasty of Menander include the ruling queen Agathokleia, her son Strato I, and Nicias, though it is uncertain whether they ruled directly after Menander.[177]


Other kings emerged, usually in the western part of the Indo-Greek realm, such as Zoilos I, Lysias, Antialcidas and Philoxenos.[178] These rulers may have been relatives of either the Eucratid or the Euthydemid dynasties. The names of later kings were often new (members of Hellenistic dynasties usually inherited family names) but old reverses and titles were frequently repeated by the later rulers.

Immediately after the fall of Bactria, the bronze coins of Indo-Greek king Zoilos I (130–120 BC), successor of Menander in the western part of the Indian territories, combined the club of Herakles with a Scythian-type bowcase and short recurve bow inside a victory wreath, illustrating interaction with horse-mounted people originating from the steppes, possibly either the Scythians (future Indo-Scythians), or the Yuezhi (future Kushans) who had invaded Greco-Bactria.[175] This bow can be contrasted to the traditional Hellenistic long bow depicted on the coins of the eastern Indo-Greek queen Agathokleia. It is now known that 50 years later, the Indo-Scythian Maues was in alliance with the Indo-Greek kings in Taxila, and one of those kings, Artemidoros seems to claim on his coins that he is the son of Maues,[176] although this is now disputed.[20]
While all Indo-Greek kings after Apollodotus I mainly issued bilingual (Greek and Kharoshti) coins for circulation in their own territories, several of them also struck rare Greek coins which have been found in Bactria. The later kings probably struck these coins as some kind of payment to the Scythian or Yuezhi tribes who now ruled there, though if as tribute or payment for mercenaries remains unknown.[179] For some decades after the Bactrian invasion, relationships seem to have been peaceful between the Indo-Greeks and these relatively hellenised nomad tribes.
Interactions with Indian culture and religions
[edit]Indo-Greeks in the regions of Vidisha and Sanchi (115 BC)
[edit]

- Vidisha
It is around this time, in 115 BC, that the embassy of Heliodorus, from king Antialkidas to the court of the Sungas king Bhagabhadra in Vidisha, is recorded. In the Sunga capital, Heliodorus established the Heliodorus pillar in a dedication to Vāsudeva. This would indicate that relations between the Indo-Greeks and the Sungas had improved by that time, that people traveled between the two realms, and also that the Indo-Greeks readily followed Indian religions.[182]
- Sanchi
Also around the same period, circa 115 BC, decorative reliefs were introduced for the first time at nearby Sanchi, 6 km away from Vidisha, by craftsmen from the northwest.[183] These craftsmen left mason's marks in Kharoshthi, mainly used in the area around Gandhara, as opposed to the local Brahmi script.[183] This seems to imply that these foreign workers were responsible for some of the earliest motifs and figures that can be found on the railings of the stupa.[183] These early reliefs at Sanchi, (those of Sanchi Stupa No.2), are dated to 115 BC, while the more extensive pillar carvings are dated to 80 BC.[184] These reliefs have been described as "the oldest extensive stupa decoration in existence".[185] They are considered the origin of Jataka illustrations in India.[186]
| Early reliefs at Sanchi, Stupa No.2 (circa 115 BC) | |
Sanchi, Stupa No 2 Mason's marks in Kharoshti point to craftsmen from the north-west (region of Gandhara) for the earliest reliefs at Sanchi, circa 115 BC.[183][184][187] |
|
Indo-Greeks and Bharhut (100-75 BC)
[edit]

A warrior figure, the Bharhut Yavana, appeared prominently on a high relief on the railings of the stupa of Bharhut circa 100 BC.[194][195] The warrior has the flowing head band of a Greek king, a northern tunic with Hellenistic pleats, he hold a grape in his hand, and has a Buddhist triratana symbol on his sword.[194] He has the role of a dvarapala, a Guardian of the entrance of the Stupa. The warrior has been described as a Greek,[194] Some have suggested that he might even represent king Menander.[189][190][191]
Also around that time, craftsmen from the Gandhara area are known to have been involved in the construction of the Buddhist torana gateways at Bharhut, which are dated to 100–75 BC:[196] this is because mason's marks in Kharosthi have been found on several elements of the Bharhut remains, indicating that some of the builders at least came from the north, particularly from Gandhara where the Kharoshti script was in use.[192][197][198]
Cunningham explained that the Kharosthi letters were found on the balusters between the architraves of the gateway, but none on the railings which all had Indian markings, summarizing that the gateways, which are artistically more refined, must have been made by artists from the North, whereas the railings were made by local artists.[193]
Sanchi Yavanas (50–1 BC)
[edit]
Again in Sanchi, but this time dating to the period of Satavahana rule circa 50–1 BC, one frieze can be observed which shows devotees in Greek attire making a dedication to the Great Stupa of Sanchi.[199][200] The official notice at Sanchi describes "Foreigners worshiping Stupa". The men are depicted with short curly hair, often held together with a headband of the type commonly seen on Greek coins. The clothing too is Greek, complete with tunics, cloaks, and sandals, typical of the Greek travelling costume.[201] The musical instruments are also quite characteristic, such as the double flute called aulos. Also visible are carnyx-like horns.[202] They are all celebrating at the entrance of the stupa.
The actual participation of Yavanas/Yonas (Greek donors)[203] to the construction of Sanchi is known from three inscriptions made by self-declared Yavana donors:
- The clearest of these reads "Setapathiyasa Yonasa danam" ("Gift of the Yona of Setapatha"),[204][205] Setapatha being an uncertain city, possibly a location near Nasik,[206] a place where other dedications by Yavanas are known, in cave No.17 of the Nasik Caves complex, and on the pillars of the Karla Caves not far away.
- A second similar inscription on a pillar reads: "[Sv]etapathasa (Yona?)sa danam", with probably the same meaning, ("Gift of the Yona of Setapatha").[206][207]
- The third inscription, on two adjacent pavement slabs reads "Cuda yo[vana]kasa bo silayo" ("Two slabs of Cuda, the Yonaka").[208][206]
Decline
[edit]King Philoxenus (100–95 BC) briefly occupied the whole Greek territory from the Paropamisadae to Western Punjab, after that the territories fragmented again between smaller Indo-Greek kings. Throughout the 1st century BC, the Indo-Greeks progressively lost ground to the Indians in the east, and the Scythians, the Yuezhi, and the Parthians in the West. About 20 Indo-Greek kings are known during this period,[213] down to the last known Indo-Greek rulers, Strato II and Strato III, who ruled in the Punjab region until around 10 AD.[214]
Loss of Hindu Kush territories (70 BC–)
[edit]

Around eight "western" Indo-Greek kings are known; most of them are distinguished by their issues of Attic coins for circulation in the neighbouring region.
One of the last important kings in the Paropamisadae (part of the Hindu Kush) was Hermaeus, who ruled until around 80 BC; soon after his death the Yuezhi or Sakas took over his areas from neighbouring Bactria. When Hermaeus is depicted on his coins riding a horse, he is equipped with the recurve bow and bow-case of the steppes and RC Senior believes him to be of partly nomad origin. The later king Hippostratus may however also have held territories in the Paropamisadae.
After the death of Hermaeus, the Yuezhi or Saka nomads became the new rulers of the Paropamisadae, and minted vast quantities of posthumous issues of Hermaeus up to around 40 AD, when they blend with the coinage of the Kushan king Kujula Kadphises.[215] The first documented Yuezhi prince, Sapadbizes, ruled around 20 BC, and minted in Greek and in the same style as the western Indo-Greek kings, probably depending on Greek mints and chelators.
Loss of Central territories (48/47 BC)
[edit]

Around 80 BC, an Indo-Scythian king named Maues, possibly a general in the service of the Indo-Greeks, ruled for a few years in northwestern India before the Indo-Greeks again took control. He seems to have been married to an Indo-Greek princess named Machene.[216] King Hippostratus (65–55 BC) seems to have been one of the most successful subsequent Indo-Greek kings until he lost to the Indo-Scythian Azes I, who established an Indo-Scythian dynasty in 48/47 BC.[c] Various coins seem to suggest that some sort of alliance may have taken place between the Indo-Greeks and the Scythians.[d]
Although the Indo-Scythians clearly ruled militarily and politically, they remained surprisingly respectful of Greek and Indian cultures. Their coins were minted in Greek mints, continued using proper Greek and Kharoshthi legends, and incorporated depictions of Greek deities, particularly Zeus.[217] The Mathura lion capital inscription attests that they adopted the Buddhist faith, as do the depictions of deities forming the vitarka mudra on their coins. Greek communities, far from being exterminated, probably persisted under Indo-Scythian rule. There is a possibility that a fusion, rather than a confrontation, occurred between the Greeks and the Indo-Scythians: in a recently published coin, Artemidorus seems to present himself as "son of Maues"[218] ( but this is now disputed),[219] and the Buner reliefs show Indo-Greeks and Indo-Scythians reveling in a Buddhist context.
The last known mention of an Indo-Greek ruler is suggested by an inscription on a signet ring of the 1st century AD in the name of a king Theodamas, from the Bajaur area of Gandhara, in modern Pakistan. No coins of him are known, but the signet bears in kharoshthi script the inscription "Su Theodamasa", "Su" being explained as the Greek transliteration of the ubiquitous Kushan royal title "Shau" ("Shah", "King").[220]
Loss of Eastern territories (10 AD)
[edit]

The Indo-Greek kingdoms lost most of their eastern territories in the 1st century BC following the death of Menander.[221] The Arjunayanas and the Yaudheya Republic mention military victories on their coins ("Victory of the Arjunayanas", "Victory of the Yaudheyas"). These entities would remain independent until being conquered by the Saka King Rudradaman I of the Western Satraps.
Rudradaman (...) who by force destroyed the Yaudheyas who were loath to submit, rendered proud as they were by having manifested their' title of' heroes among all Kshatriyas.
They would again win independence until being conquered by Samudragupta (350-375 CE) of the Gupta Empire, and would disintegrate soon after.
During the 1st century BC, the Trigartas, Audumbaras[222] and finally the Kunindas[223] also started to mint their own coins, usually in a style highly reminiscent of Indo-Greek coinage.[224][225][226]
The Yavanas may have ruled as far as the area of Mathura from the time of Menander I until the middle of the 1st century BC: the Maghera inscription, from a village near Mathura, records the dedication of a well "in the one hundred and sixteenth year of the reign of the Yavanas", which corresponds to circa 70 BC.[227] In the 1st century BC, however, they lost the area of Mathura, either to the Mitra rulers under the Shunga Empire or to the Datta dynasty.[155]
Fleeing the Sakas in the west, the Indo-Greeks continued to rule a territory in the eastern Punjab. The kingdom of the last Indo-Greek kings Strato II and Strato III was conquered by the Northern Satrap Saka ruler Rajuvula around 10 AD.[228]
Later contributions
[edit]



 , circa AD 120.
, circa AD 120.Some Greek nuclei may have continued to survive until the 2nd century AD.[230]
Nahapana had at his court a Greek writer named Yavanesvara ("Lord of the Greeks"), who translated from Greek to Sanskrit the Yavanajataka ("Saying of the Greeks"), an astrological treatise and India's earliest Sanskrit work in horoscopy.[231]
Buddhist caves
[edit]A large number of Buddhist caves in India, particularly in the west of the country, were artistically hewn between the 1st century BC and the 2nd century AD. Numerous donors provided the funds for the building of these caves and left donatory inscriptions, including laity, members of the clergy, government officials. Foreigners, mostly self-declared Yavanas, represented about 8% of all inscriptions.[232]
- Karla Caves
Yavanas from the region of Nashik are mentioned as donors for six structural pillars in the Great Buddhist Chaitya of the Karla Caves built and dedicated by Western Satraps ruler Nahapana in 120 AD,[233] although they seem to have adopted Buddhist names.[234] In total, the Yavanas account for nearly half of the known dedicatory inscriptions on the pillars of the Great Chaitya.[235] To this day, Nasik is known as the wine capital of India, using grapes that were probably originally imported by the Greeks.[236]




 ). Shivneri Caves 1st century AD.
). Shivneri Caves 1st century AD.- Shivneri Caves
Two more Buddhist inscriptions by Yavanas were found in the Shivneri Caves.[237] One of the inscriptions mentions the donation of a tank by the Yavana named Irila, while the other mentions the gift of a refectory to the Sangha by the Yavana named Cita.[237] On this second inscription, the Buddhist symbols of the triratna and of the swastika (reversed) are positioned on both sides of the first word "Yavana(sa)".
- Pandavleni Caves
One of the Buddhist caves (Cave No.17) in the Pandavleni Caves complex near Nashik was built and dedicated by "Indragnidatta the son of the Yavana Dharmadeva, a northerner from Dattamittri", in the 2nd century AD.[238][239][240] The city of "Dattamittri" is thought to be the city of Demetrias in Arachosia, mentioned by Isidore of Charax.[238]
| The "Yavana cave", Cave No.17 of Pandavleni Caves, near Nashik (2nd century AD) | |
 Cave No.17 has one inscription, mentioning the gift of the cave by Indragnidatta the son of the Yavana (i.e. Greek or Indo-Greek) Dharmadeva:
| |
- Manmodi Caves
In the Manmodi Caves, near Junnar, an inscription by a Yavana donor appears on the façade of the main Chaitya, on the central flat surface of the lotus over the entrance: it mentions the erection of the hall-front (façade) for the Buddhist Samgha, by a Yavana donor named Chanda:[241]
"yavanasa camdānam gabhadā[ra]"
"The meritorious gift of the façade of the (gharba) hall by the Yavana Chanda"
These contributions seem to have ended when the Satavahana King Gautamiputra Satakarni vanquished the Western Satrap ruler Nahapana, who had ruled over the area where these inscriptions were made, c. AD 130. This victory is known from the fact that Gautamiputra Satakarni restruck many of Nahapana's coins, and that he is claimed to have defeated a confederacy of Shakas (Western Kshatrapas), Pahlavas (Indo-Parthians), and Yavanas (Indo-Greeks), in the inscription of his mother Queen Gotami Balasiri at Cave No. 3 of the Nasik Caves:[245][246]
...Siri-Satakani Gotamiputa (....) who crushed down the pride and conceit of the Kshatriyas; who destroyed the Sakas, Yavanas and Palhavas; who rooted out the Khakharata race; who restored the glory of the Satavahana family...
Inscriptions of the 3rd century (AD 210–325) at the Nagarjunakonda Buddhist complex in southern India again mention the involvement of the Yavanas with Buddhism:[248] an inscription in a monastery (Site No.38) describes its residents as Acaryas and Theriyas of the Vibhajyavada school, "who had gladdened the heart of the people of Kasmira, Gamdhara, Yavana, Vanavasa,[249] and Tambapamnidipa".[250]
Yavana era for Buddha sculptures
[edit]
Several Gandhara Buddha statues with dated inscriptions, are now thought to have been dated in the Yavana era (originating c. 186 BC). One of the statues of the Buddha from Loriyan Tangai has an inscription mentioning "the year 318". The era in question is not specified, but it is now thought, following the discovery of the Bajaur reliquary inscription and a suggestion by Richard Salomon which has gained wide acceptance,[252] that it is dated in the Yavana era beginning in 186 BC, and gives a date for the Buddha statue of c. AD 143.[251]

The inscription at the base of the statue is:
sa 1 1 1 100 10 4 4 Prothavadasa di 20 4 1 1 1 Budhagosa danamu(khe) Saghorumasa sadaviyasa
"In year 318, the day 27 of Prausthapada, gift of Buddhaghosa, the companion of Samghavarma"
— Inscription of the Buddha of Loriyan Tangai.[251]
This would make it one of the earliest known representations of the Buddha, after the Bimaran casket (1st century AD), and at about the same time as the Buddhist coins of Kanishka.[251]
Another statue of Buddha, the Buddha of Hashtnagar, is inscribed from the year 384, also probably in the Yavana era, which is thought to be AD 209. Only the pedestal is preserved in the British Museum, the statue itself, with folds of clothing having more relief than those of the Loriyan Tangai Buddha, having disappeared.[251]
Ideology
[edit]
Buddhism flourished under the Indo-Greek kings, and their rule, especially that of Menander, has been remembered as benevolent. It has been suggested, although direct evidence is lacking, that their invasion of India was intended to show their support for the Mauryan empire with which they may have had a long history of marital alliances,[e] exchange of presents,[f] demonstrations of friendship,[g] exchange of ambassadors[h] and religious missions[i]. The historian Diodorus even wrote that the king of Pataliputra had "great love for the Greeks".[259][260]
The Greek expansion into Indian territory may have been intended to protect Greek populations in India,[261] and to protect the Buddhist faith from the religious persecutions of the Shungas.[262] The city of Sirkap founded by Demetrius combines Greek and Indian influences without signs of segregation between the two cultures.
The first Greek coins to be minted in India, those of Menander I and Apollodotus I bear the mention "Saviour king" (ΒΑΣΙΛΕΩΣ ΣΩΤΗΡΟΣ), a title with high value in the Greek world which indicated an important deflective victory. For instance, Ptolemy I had been Soter (saviour) because he had helped save Rhodes from Demetrius the Besieger, and Antiochus I because he had saved Asia Minor from the Gauls. The title was also inscribed in Pali as ("Tratarasa") on the reverse of their coins. Menander and Apollodotus may indeed have been saviours to the Greek populations residing in India, and to some of the Indians as well.[263]
Also, most of the coins of the Greek kings in India were bilingual, written in Greek on the front and in Pali on the back (in the Kharosthi script, derived from Aramaic, rather than the more eastern Brahmi, which was used only once on coins of Agathocles of Bactria), a tremendous concession to another culture never before made in the Hellenic world.[264] From the reign of Apollodotus II, around 80 BC, Kharosthi letters started to be used as mintmarks on coins in combination with Greek monograms and mintmarks, suggesting the participation of local technicians to the minting process.[265] Incidentally, these bilingual coins of the Indo-Greeks were the key in the decipherment of the Kharoshthi script by James Prinsep (1835) and Carl Ludwig Grotefend (1836).[266][267] Kharoshthi became extinct around the 3rd century AD.
In Indian literature, the Indo-Greeks are described as Yavanas (in Sanskrit),[268][269][270] or Yonas (in Pali)[271] both thought to be transliterations of "Ionians". In the Harivamsa the "Yavana" Indo-Greeks are qualified, together with the Sakas, Kambojas, Pahlavas and Paradas as Kshatriya-pungava i.e. foremost among the Warrior caste, or Kshatriyas. The Majjhima Nikaya explains that in the lands of the Yavanas and Kambojas, in contrast with the numerous Indian castes, there were only two classes of people, Aryas and Dasas (masters and slaves).
Religion
[edit]


In addition to the worship of the Classical pantheon of the Greek deities found on their coins (Zeus, Herakles, Athena, Apollo...), the Indo-Greeks were involved with local faiths, particularly with Buddhism, but also with Hinduism and Zoroastrianism.[276]
Interactions with Buddhism
[edit]Chandragupta Maurya, the founder of the Mauryan Empire, conquered the Greek satraps left by Alexander, which belonged to Seleucus I Nicator of the Seleucid Empire. The Mauryan Emperor Ashoka would then establish the largest empire in the Indian Subcontinent through an aggressive expansion. Ashoka converted to Buddhism following the destructive Kalinga War, abandoning further conquests in favor of humanitarian reforms.[277] Ashoka erected the Edicts of Ashoka to spread Buddhism and the 'Law of Piety' throughout his dominion. In one of his edicts, Ashoka claims to have converted his Greek population along with others to Buddhism.
Here in the king's domain among the Greeks, the Kambojas, the Nabhakas, the Nabhapamkits, the Bhojas, the Pitinikas, the Andhras and the Palidas, everywhere people are following Beloved-of-the-Gods' instructions in Dharma.[278]
The last Mauryan Emperor Brihadratha was assassinated by Pushyamitra Shunga, the former senapati or "army lord" of the Mauryan Empire and founder of the Shunga Empire. Pushyamitra is alleged to have persecuted Buddhism in favor of Hinduism, likely in attempt to further remove the legacy of the Mauryan Empire.[279]
... Pushyamitra equipped a fourfold army, and intending to destroy the Buddhist religion, he went to the Kukkutarama (in Pataliputra). ... Pushyamitra therefore destroyed the sangharama, killed the monks there, and departed. ... After some time, he arrived in Sakala, and proclaimed that he would give a ... reward to whoever brought him the head of a Buddhist monk.[280]
It is possible that Menander I Soter or the "Saviour king", choose Sakala as his capital due to the Buddhist presence there. Menander I, is stated to have converted to Buddhism[281] in the Milinda Panha, which records the dialogue between Menander and the Buddhist monk Nagasena. Menander is claimed to have obtained the title of an arhat.
And afterwards, taking delight in the wisdom of the Elder, he (Menander) handed over his kingdom to his son, and abandoning the household life for the house-less state, grew great in insight, and himself attained to Arahatship!
— The Questions of King Milinda, Translation by T. W. Rhys Davids.
The wheel he represented on some of his coins was most likely Buddhist Dharmachakra,.[282]
Another Indian text, the Stupavadana of Ksemendra, mentions in the form of a prophecy that Menander will build a stupa in Pataliputra.[283]
Plutarch also presents Menander as an example of benevolent rule, and explains that upon his death, the honour of sharing his remains was claimed by the various cities under his rule, and they were enshrined in "monuments" (μνημεία, probably stupas), in a parallel with the historic Buddha:[284]
But when one Menander, who had reigned graciously over the Bactrians, died afterwards in the camp, the cities indeed by common consent celebrated his funerals; but coming to a contest about his relics, they were difficultly at last brought to this agreement, that his ashes being distributed, everyone should carry away an equal share, and they should all erect monuments to him.
The Butkara stupa was "monumentalized" by the addition of Hellenistic architectural decorations during Indo-Greek rule in the 2nd century BC.[275] A coin of Menander I was found in the second oldest stratum (GSt 2) of the Butkara stupa suggesting a period of additional constructions during the reign of Menander.[286] It is thought that Menander was the builder of the second oldest layer of the Butkara stupa, following its initial construction during the Mauryan Empire.[287]
"Followers of the Dharma"
[edit]
Several Indo-Greek kings use the title "Dharmikasa", i.e. "Follower of the Dharma", in the Kharoshti script on the obverse of their coins. The corresponding legend in Greek is "Dikaios" ("The Just"), a rather usual attribute on Greek coins. The expression "Follower of the Dharma" would of course resonate strongly with Indian subjects, used to this expression being employed by pious kings, especially since the time of Ashoka who advocated the Dharma in his inscriptions. The seven kings using "Dharmakasa", i.e. "Follower of the Dharma", are late Indo-Greek kings, from around 150 BC, right after the reign of Menander I, and mainly associated with the area of Gandhara: Zoilos I (130–120 BC), Strato (130–110 BC), Heliokles II (95–80 BC), Theophilos (130 or 90 BC), Menander II (90–85 BC), Archebios (90–80 BC) and Peukolaos (c. 90 BC).[288] The attribute of Dharmika was again used a century later by a known Buddhist practitioner, Indo-Scythian king Kharahostes, to extoll on his coins the virtues of his predecessor king Azes.[289]
Blessing gestures
[edit]From the time of Agathokleia and Strato I, circa 100 BC, kings and divinities are regularly show on coins making blessing gestures,[290] which often seem similar to the Buddhist Vitarka mudra.[291] As centuries passed, the exact shapes taken by the hand becomes less clear. This blessing gesture was also often adopted by the Indo-Scythians.[292]
-
Philoxenus (c. 100 BC), unarmed, making a blessing gesture.
-
Nicias making a blessing gesture.
-
Strato I in combat gear, making a blessing gesture, circa 100 BC.
-
Various blessing gestures: divinities (top), kings (bottom).
Vaishnavites
[edit]The Heliodorus pillar is a stone column that was erected around 113 BC in central India[citation needed] in Vidisha near modern Besnagar, by Heliodorus, a Greek ambassador of the Indo-Greek king Antialcidas[230] to the court of the Shunga king Bhagabhadra. The pillar originally supported a statue of Garuda. In the dedication, the Indo-Greek ambassador explains he is a devotee of "Vāsudeva, the God of Gods". Historically, it is the first known inscription related to the Bhagavata cult in India.[180]
Art
[edit]
In general, the art of the Indo-Greeks is poorly documented, and few works of art (apart from their coins and a few stone palettes) are directly attributed to them. The coinage of the Indo-Greeks however is generally considered some of the most artistically brilliant of Antiquity.[293] The Hellenistic heritage (Ai-Khanoum) and artistic proficiency of the Indo-Greek world would suggest a rich sculptural tradition as well, but traditionally very few sculptural remains have been attributed to them. On the contrary, most Gandharan Hellenistic works of art are usually attributed to the direct successors of the Indo-Greeks in India in the 1st century AD, such as the nomadic Indo-Scythians, the Indo-Parthians and, in an already decadent state, the Kushans[294] In general, Gandharan sculpture cannot be dated exactly, leaving the exact chronology open to interpretation.

The possibility of a direct connection between the Indo-Greeks and Greco-Buddhist art has been reaffirmed recently as the dating of the rule of Indo-Greek kings has been extended to the first decades of the 1st century AD, with the reign of Strato II in the Punjab.[295] Also, Foucher, Tarn, and more recently, Boardman, Bussagli and McEvilley have taken the view that some of the most purely Hellenistic works of northwestern India and Afghanistan, may actually be wrongly attributed to later centuries, and instead belong to a period one or two centuries earlier, to the time of the Indo-Greeks in the 2nd–1st century BC:[j]

This is particularly the case of some purely Hellenistic works in Hadda, Afghanistan, an area which "might indeed be the cradle of incipient Buddhist sculpture in Indo-Greek style".[296] Referring to one of the Buddha triads in Hadda, in which the Buddha is sided by very Classical depictions of Herakles/Vajrapani and Tyche/Hariti, Boardman explains that both figures "might at first (and even second) glance, pass as, say, from Asia Minor or Syria of the first or second century BC (...) these are essentially Greek figures, executed by artists fully conversant with far more than the externals of the Classical style".[297]
Alternatively, it has been suggested that these works of art may have been executed by itinerant Greek artists during the time of maritime contacts with the West from the 1st to the 3rd century AD.[298]
The Greco-Buddhist art of Gandhara, beyond the omnipresence of Greek style and stylistic elements which might be simply considered an enduring artistic tradition,[299] offers numerous depictions of people in Greek Classical realistic style, attitudes and fashion (clothes such as the chiton and the himation, similar in form and style to the 2nd century BC Greco-Bactrian statues of Ai-Khanoum, hairstyle), holding contraptions which are characteristic of Greek culture (amphoras, "kantaros" Greek drinking cups), in situations which can range from festive (such as Bacchanalian scenes) to Buddhist-devotional.[300][301]

Uncertainties in dating make it unclear whether these works of art actually depict Greeks of the period of Indo-Greek rule up to the 1st century BC, or remaining Greek communities under the rule of the Indo-Parthians or Kushans in the 1st and 2nd century AD. Benjamin Rowland thinks that the Indo-Greeks, rather than the Indo-Scythians or the Kushans, may have been the models for the Bodhisattva statues of Gandhara[302]
Economy
[edit]Very little is known about the economy of the Indo-Greeks, although it seems to have been rather vibrant.[303][304]
Coinage
[edit]The abundance of their coins would tend to suggest large mining operations, particularly in the mountainous area of the Hindu-Kush, and an important monetary economy. The Indo-Greek did strike bilingual coins both in the Greek "round" standard and in the Indian "square" standard,[305] suggesting that monetary circulation extended to all parts of society. The adoption of Indo-Greek monetary conventions by neighbouring kingdoms, such as the Kunindas to the east and the Satavahanas to the south,[306] would also suggest that Indo-Greek coins were used extensively for cross-border trade.
Tribute payments
[edit]
It would also seem that some of the coins emitted by the Indo-Greek kings, particularly those in the monolingual Attic standard, may have been used to pay some form of tribute to the Yuezhi tribes north of the Hindu-Kush.[179] This is indicated by the coins finds of the Qunduz hoard in northern Afghanistan, which have yielded quantities of Indo-Greek coins in the Hellenistic standard (Greek weights, Greek language), although none of the kings represented in the hoard are known to have ruled so far north.[307] Conversely, none of these coins have ever been found south of the Hindu-Kush.[308]
Trade with China
[edit]
The Indo-Greek kings in Southern Asia issued the first known cupro-nickel coins, with Euthydemus II, dating from 180 to 170 BC, and his younger brothers Pantaleon and Agathocles around 170 BC. As only China was able to produce cupro-nickel at that time, and as the alloy ratios are exclusively similar, it has been suggested that the metal was the result of exchanges between China and Bactria.[309]
An indirect testimony by the Chinese explorer Zhang Qian, who visited Bactria around 128 BC, suggests that intense trade with Southern China was going through northern India. Zhang Qian explains that he found Chinese products in the Bactrian markets, and that they were transiting through northwestern India, which he incidentally describes as a civilization similar to that of Bactria:
"When I was in Bactria", Zhang Qian reported, "I saw bamboo canes from Qiong and cloth (silk?) made in the province of Shu. When I asked the people how they had gotten such articles, they replied: "Our merchants go buy them in the markets of Shendu (northwestern India). Shendu, they told me, lies several thousand li southeast of Bactria. The people cultivate land, and live much like the people of Bactria".
— Sima Qian, "Records of the Great Historian", trans. Burton Watson, p. 236.
Recent excavations at the burial site of China's first Emperor Qin Shi Huang, dating back to the 3rd century BCE, also suggest Greek influence in the artworks found there, including in the manufacture of the famous Terracotta army. It is also suggested that Greek artists may have come to China at that time to train local artisans in making sculptures.[310][311]
Indian Ocean trade
[edit]Maritime relations across the Indian Ocean started in the 3rd century BC, and further developed during the time of the Indo-Greeks together with their territorial expansion along the western coast of India. The first contacts started when the Ptolemies constructed the Red Sea ports of Myos Hormos and Berenike, with destination the Indus delta, the Kathiawar peninsula or Muziris. Around 130 BC, Eudoxus of Cyzicus is reported (Strabo, Geog. II.3.4)[312] to have made a successful voyage to India and returned with a cargo of perfumes and gemstones. By the time Indo-Greek rule was ending, up to 120 ships were setting sail every year from Myos Hormos to India (Strabo Geog. II.5.12).[313]
Armed forces
[edit]
The coins of the Indo-Greeks provide rich clues on their uniforms and weapons. Typical Hellenistic uniforms are depicted, with helmets being either round in the Greco-Bactrian style, or the flat kausia of the Macedonians (coins of Apollodotus I).
Military technology
[edit]Their weapons were spears, swords, longbow (on the coins of Agathokleia) and arrows. Around 130 BC, the Central Asian recurve bow of the steppes with its gorytos box started to appear for the first time on the coins of Zoilos I, suggesting strong interactions (and apparently an alliance) with nomadic peoples, either the Yuezhi or the Scythians.[314] The recurve bow becomes a standard feature of Indo-Greek horsemen by 90 BC, as seen on some of the coins of Hermaeus.
Generally, Indo-Greek kings are often represented riding horses, as early as the reign of Antimachus II around 160 BC. The equestrian tradition probably goes back to the Greco-Bactrians, who are said by Polybius to have faced a Seleucid invasion in 210 BC with 10,000 horsemen.[315] Although war elephants are never represented on coins, a harness plate (phalera) dated to the 3rd–2nd century BC, today in the Hermitage Museum, depicts a helmetted Greek combatant on an Indian war elephant.
The Milinda Panha, in the questions of Nagasena to king Menander, provides a rare glimpse of the military methods of the period:
-(Nagasena) Has it ever happened to you, O king, that rival kings rose up against you as enemies and opponents?
-(Menander) Yes, certainly.
-Then you set to work, I suppose, to have moats dug, and ramparts thrown up, and watch towers erected, and strongholds built, and stores of food collected?
-Not at all. All that had been prepared beforehand.
-Or you had yourself trained in the management of war elephants, and in horsemanship, and in the use of the war chariot, and in archery and fencing?
-Not at all. I had learnt all that before.
-But why?
-With the object of warding off future danger.— (Milinda Panha, Book III, Chap 7)
The Milinda Panha also describes the structure of Menander's army:
Now one day Milinda the king proceeded forth out of the city to pass in review the innumerable host of his mighty army in its fourfold array (of elephants, cavalry, bowmen, and soldiers on foot).
— (Milinda Panha, Book I)
Size of Indo-Greek armies
[edit]
The armed forces of the Indo-Greeks engaged in battles with other Indian kingdoms. The ruler of Kalinga, King Kharavela, states in the Hathigumpha inscription that during the 8th year of his reign he led a large army in the direction of a Yavana King, and that he forced their demoralized army to retreat to Mathura.
"Then in the eighth year, (Kharavela) with a large army having sacked Goradhagiri causes pressure on Rajagaha (Rajagriha). On account of the loud report of this act of valour, the Yavana (Greek) King Dimi[ta] retreated to Mathura having extricated his demoralized army."
— Hathigumpha inscription, lines 7–8, probably in the 1st century BCE. Original text is in Brahmi script.[171]
The name of the Yavana king is not clear, but it contains three letters, and the middle letter can be read as ma or mi.[316] R. D. Banerji and K.P. Jayaswal read the name of the Yavana king as "Dimita", and identify him with Demetrius I of Bactria. However, according to Ramaprasad Chanda, this identification results in "chronological impossibilities".[317] The Greek ambassador Megasthenes took special note of the military strength of Kalinga in his Indica in the middle of the 3rd century BC:
The royal city of the Calingae (Kalinga) is called Parthalis. Over their king 60,000 foot-soldiers, 1,000 horsemen, 700 elephants keep watch and ward in "procinct of war."
— Megasthenes fragm. LVI. in Plin. Hist. Nat. VI. 21. 8–23. 11.[318]
An account by the Roman writer Justin gives another hint of the size of Indo-Greek armies, which, in the case of the conflict between the Greco-Bactrian Eucratides and the Indo-Greek Demetrius II, he numbers at 60,000 (although they allegedly lost to 300 Greco-Bactrians):
Eucratides led many wars with great courage, and, while weakened by them, was put under siege by Demetrius, king of the Indians. He made numerous sorties, and managed to vanquish 60,000 enemies with 300 soldiers, and thus liberated after four months, he put India under his rule
— Justin, XLI,6[319]
The Indo-Greek armies would be conquered by Indo-Scythians, a nomadic tribe from Central Asia.
Legacy
[edit]
From the 1st century AD, the Greek communities of central Asia and the northwestern Indian subcontinent lived under the control of the Kushan branch of the Yuezhi, apart from a short-lived invasion of the Indo-Parthian kingdom.[321] The Kushans founded the Kushan Empire, which was to prosper for several centuries. In the south, the Greeks were under the rule of the Western Kshatrapas. The Kalash tribe of the Chitral Valley claim to be descendants of the Indo-Greeks; although this is disputed.

It is unclear how much longer the Greeks managed to maintain a distinct presence in the Indian sub-continent. The legacy of the Indo-Greeks was felt however for several centuries, from the usage of the Greek language and calendrical methods,[322] to the influences on the numismatics of the Indian subcontinent, traceable down to the period of the Gupta Empire in the 4th century.[323]
The Greeks may also have maintained a presence in their cities until quite late. Isidorus of Charax in his 1st century AD "Parthian stations" itinerary described an "Alexandropolis, the metropolis of Arachosia", thought to be Alexandria Arachosia, which he said was still Greek even at such a late time:
Beyond is Arachosia. And the Parthians call this White India; there are the city of Biyt and the city of Pharsana and the city of Chorochoad and the city of Demetrias; then Alexandropolis, the metropolis of Arachosia; it is Greek, and by it flows the river Arachotus. As far as this place the land is under the rule of the Parthians.[324]
The Indo-Greeks may also have had some influence on the religious plane as well, especially in relation to the developing Mahayana Buddhism. Mahayana Buddhism has been described as "the form of Buddhism which (regardless of how Hinduized its later forms became) seems to have originated in the Greco-Buddhist communities of India, through a conflation of the Greek Democritean–Sophistic–Pyrrhonist tradition with the rudimentary and unformalized empirical and skeptical elements already present in early Buddhism".[325]
Chronology
[edit]
Today 36 Indo-Greek kings are known. Several of them are also recorded in Western and Indian historical sources, but the majority are known through numismatic evidence only. The exact chronology and sequencing of their rule is still a matter of scholarly inquiry, with adjustments regular being made with new analysis and coin finds (overstrikes of one king over another's coins being the most critical element in establishing chronological sequences).
There is an important evolution of coin shape (round to square) and material (from gold to silver to brass) across the territories and the periods, and from Greek type to Indian type over a period of nearly 3 centuries. Also, the quality of coinage illustration decreases down to the 1st century AD. Coinage evolution is an important point of Indo-Greek history, and actually one of the most important since most of these kings are only known by their coins, and their chronology is mainly established by the evolution of the coin types.
The system used here is adapted from Osmund Bopearachchi, supplemented by the views of R C Senior and occasionally other authorities.[326]
See also
[edit]- Greco-Bactrian kingdom
- Yavana era
- Yavana kingdom
- Seleucid Empire
- Greco-Buddhism
- Gandharan Buddhism
- Indo-Scythians
- India (Herodotus)
- Indo-Parthian kingdom
- Kandahar Greek Inscription
- Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription
- Kushan Empire
- Roman commerce
- Timeline of Indo-Greek kingdoms
- Gandhara kingdom
- Partition of Babylon
References
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ "When the Greeks of Bactria and India lost their kingdom they were not all killed, nor did they return to Greece. They merged with the people of the area and worked for the new masters; contributing considerably to the culture and civilization in southern and central Asia." Narain, "The Indo-Greeks" 2003, p. 278
- ^ Justin refers to an incident in which Eucratides with a small force of 300 was besieged for four months by "Demetrius, king of the Indians" with a large army of 60,000. The numbers are obviously an exaggeration. Eucratides managed to break out and went on to conquer India.
- ^ G.K. Jenkins, using overstrikes and monograms, showed that, contrary to what Narai would write two years later, Apollodotus II and Hippostratus were posterior, by far, to Maues. (...) He reveals an overstike if Azes I over Hippostratus. (...) Apollodotus and Hippostratus are thus posterior to Maues and anterior to Azes I, whose era we now starts in 57 BC." Bopearachchi, p. 126-127.
- ^ "It is curious that on his copper Zoilos used a bow and quiver as a type. A quiver was a badge used by the Parthians (Scythians) and had been used previously by Diodotos, who we know had made a treaty with them. Did Zoilos use Scythian mercenaries in his quest against Menander perhaps?" Senior, Indo-Scythian coins, p. xxvii
- ^ Marital alliances:
- Discussion on the dynastic alliance in Tarn, pp. 152–153: "It has been recently suggested that Ashoka was grandson of the Seleucid princess, whom Seleucus gave in marriage to Chandragupta. Should this far-reaching suggestion be well founded, it would not only throw light on the good relations between the Seleucid and Maurya dynasties, but would mean that the Maurya dynasty was descended from, or anyhow connected with, Seleucus... when the Mauryan line became extinct, he (Demetrius) may well have regarded himself, if not as the next heir, at any rate as the heir nearest at hand". Also: "The Seleucid and Maurya lines were connected by the marriage of Seleucus' daughter (or niece) either to Chandragupta or his son Bindusara" John Marshall, Taxila, p20. This thesis originally appeared in "The Cambridge Shorter History of India": "If the usual oriental practice was followed and if we regard Chandragupta as the victor, then it would mean that a daughter or other female relative of Seleucus was given to the Indian ruler or to one of his sons, so that Ashoka may have had Greek blood in his veins." The Cambridge Shorter History of India, J. Allan, H. H. Dodwell, T. Wolseley Haig, p33.[254]
- Description of the 302 BC marital alliance in:[255] "The Indians occupy in part some of the countries situated along the Indus, which formerly belonged to the Persians: Alexander deprived the Ariani of them, and established there settlements of his own. But Seleucus Nicator gave them to Sandrocottus in consequence of a marriage contract, and received in return five hundred elephants." The ambassador Megasthenes was also sent to the Mauryan court on this occasion.
- ^ Exchange of presents:
- Classical sources have recorded that Chandragupta sent various aphrodisiacs to Seleucus: "And Theophrastus says that some contrivances are of wondrous efficacy in such matters as to make people more amorous. And Phylarchus confirms him, by reference to some of the presents which Sandrakottus, the king of the Indians, sent to Seleucus; which were to act like charms in producing a wonderful degree of affection, while some, on the contrary, were to banish love" Athenaeus of Naucratis, "The deipnosophists" Book I, chapter 32 [256]
- Ashoka claims he introduced herbal medicine in the territories of the Greeks, for the welfare of humans and animals (Edict No2).
- Bindusara asked Antiochus I to send him some sweet wine, dried figs and a sophist: "But dried figs were so very much sought after by all men (for really, as Aristophanes says, "There's really nothing nicer than dried figs"), that even Amitrochates, the king of the Indians, wrote to Antiochus, entreating him (it is Hegesander who tells this story) to buy and send him some sweet wine, and some dried figs, and a sophist; and that Antiochus wrote to him in answer, "The dry figs and the sweet wine we will send you; but it is not lawful for a sophist to be sold in Greece" Athenaeus, "Deipnosophistae" XIV.67 [257]
- ^ Treaties of friendship:
- When Antiochos III, after having made peace with Euthydemus, went to India in 209 BC, he is said to have renewed his friendship with the Indian king there and received presents from him: "He crossed the Caucasus (Hindu Kush) and descended into India; renewed his friendship with Sophagasenus the king of the Indians; received more elephants, until he had a hundred and fifty altogether; and having once more provisioned his troops, set out again personally with his army: leaving Androsthenes of Cyzicus the duty of taking home the treasure which this king had agreed to hand over to him."[258]
- ^ Ambassadors:
- Known ambassadors to India are Megasthenes, Deimakos and Dionysius.
- ^ Religious missions:
- In the Edicts of Ashoka, king Ashoka claims to have sent Buddhist emissaries to the Hellenistic west around 250 BC.
- ^ On the Indo-Greeks and the Gandhara school:
- 1) "It is necessary to considerably push back the start of Gandharan art, to the first half of the first century BC, or even, very probably, to the preceding century.(...) The origins of Gandharan art... go back to the Greek presence. (...) Gandharan iconography was already fully formed before, or at least at the very beginning of our era" Mario Bussagli "L'art du Gandhara", p331–332
- 2) "The beginnings of the Gandhara school have been dated everywhere from the first century B.C. (which was M.Foucher's view) to the Kushan period and even after it" (Tarn, p. 394). Foucher's views can be found in "La vieille route de l'Inde, de Bactres a Taxila", pp340–341). The view is also supported by Sir John Marshall ("The Buddhist art of Gandhara", pp5–6).
- 3) Also the recent discoveries at Ai-Khanoum confirm that "Gandharan art descended directly from Hellenized Bactrian art" (Chaibi Nustamandy, "Crossroads of Asia", 1992).
- 4) On the Indo-Greeks and Greco-Buddhist art: "It was about this time (100 BC) that something took place which is without parallel in Hellenistic history: Greeks of themselves placed their artistic skill at the service of a foreign religion, and created for it a new form of expression in art" (Tarn, p. 393). "We have to look for the beginnings of Gandharan Buddhist art in the residual Indo-Greek tradition, and in the early Buddhist stone sculpture to the South (Bharhut etc...)" (Boardman, 1993, p. 124). "Depending on how the dates are worked out, the spread of Gandhari Buddhism to the north may have been stimulated by Menander's royal patronage, as may the development and spread of the Gandharan sculpture, which seems to have accompanied it" McEvilley, 2002, "The shape of ancient thought", p. 378.
Citations
[edit]- ^ Schwartzberg, Joseph E. (1978). A Historical atlas of South Asia. University of Chicl.uchicago.edu/reference/schwartzberg/pager.html?object=182.
- ^ name=Indo-Greek: 30em">Tarn, William Woodthorpe (1966), "Alexandria of the Caucasus and Kapisa", The Greeks in Bactria and India, Cambridge University Press, pp. 460–462, doi:10.1017/CBO9780511707353.019, ISBN 978051170735
- ^ Taagepera, Rein (1979). "Size and Duration of Empires: Growth-Decline Curves, 600 B.C. to 600 A.D.". Social Science History. 3 (3/4): 132. doi:10.2307/1170959. JSTOR 1170959.
- ^ Wilson, John (1877). Indian Caste. Times of India Office. p. 353.
- ^ Jackson J. Spielvogel (14 September 2016). Western Civilization: Volume A: To 1500. Cengage Learning. p. 96. ISBN 978-1-305-95281-2.
The invasion of India by a Greco-Bactrian army in ... led to the creation of an Indo-Greek kingdom in northwestern India (present-day India and Pakistan).
- ^ Erik Zürcher (1962). Buddhism: its origin and spread in words, maps, and pictures. St Martin's Press. p. 45.
Three phases must be distinguished, (a) The Greek rulers of Bactria (the Oxus region) expand their power to the south, conquer Afghanistan and considerable parts of north-western India, and establish an Indo-Greek kingdom in the Panjab where they rule as 'kings of India'; i
- ^ Heidi Roupp (4 March 2015). Teaching World History: A Resource Book. Routledge. p. 171. ISBN 978-1-317-45893-7.
There were later Indo-Greek kingdoms in northwest India. ...
- ^ Hermann Kulke; Dietmar Rothermund (2004). A History of India. Psychology Press. p. 74. ISBN 978-0-415-32919-4.
They are referred to as 'Indo-Greeks' and there were about forty such kings and rulers who controlled large areas of northwestern India and Afghanistan. Their history ...
- ^ Los Angeles County Museum of Art; Pratapaditya Pal (1986). Indian Sculpture: Circa 500 B.C.-A.D. 700. University of California Press. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-520-05991-7.
Since parts of their territories comprised northwestern India, these later rulers of Greek origin are generally referred to as Indo-Greeks.
- ^ Joan Aruz; Elisabetta Valtz Fino (2012). Afghanistan: Forging Civilizations Along the Silk Road. Metropolitan Museum of Art. p. 42. ISBN 978-1-58839-452-1.
The existence of Greek kingdoms in Central Asia and northwestern India after Alexander's conquests had been known for a long time from a few fragmentary texts from Greek and Latin classical sources and from allusions in contemporary Chinese chronicles and later Indian texts.
- ^ Mortimer Wheeler Flames over Persepolis (London, 1968). Pp. 112 ff. It is unclear whether the Hellenistic street plan found by Sir John Marshall's excavations dates from the Indo-Greeks or from the Kushans, who would have encountered it in Bactria; Tarn (1951, pp. 137, 179) ascribes the initial move of Taxila to the hill of Sirkap to Demetrius I, but sees this as "not a Greek city but an Indian one"; not a polis or with a Hippodamian plan.
- ^ "Menander had his capital in Sagala" Bopearachchi, "Monnaies", p. 83.
- ^ McEvilley supports Tarn on both points, citing Woodcock: "Menander was a Bactrian Greek king of the Euthydemid dynasty. His capital (was) at Sanghol in the Punjab, "in the country of the Yonakas (Greeks)"." McEvilley, p. 377. However, "Even if Sagala proves to be a city, it does not seem to be Menander's capital for the Milindapanha states that Menander came down to Sagala to meet Nagasena, just as the Ganges flows to the sea."
- ^ Thonemann, Peter (2016-01-14). The Hellenistic World: Using Coins as Sources. Cambridge University Press. p. 97. ISBN 978-1-316-43229-7.
- ^ "Indo-Greek Campaigns".
- ^ "A vast hoard of coins, with a mixture of Greek profiles and Indian symbols, along with interesting sculptures and some monumental remains from Taxila, Sirkap and Sirsukh, point to a rich fusion of Indian and Hellenistic influences", India, the Ancient Past, Burjor Avari, p. 130
- ^ Ghose, Sanujit (2011). "Cultural links between India and the Greco-Roman world". Ancient History Encyclopedia
- ^ 11.34
- ^ ("Notes on Hellenism in Bactria and India". W. W. Tarn. Journal of Hellenic Studies, Vol. 22 (1902), pp. 268–293).
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Osmund Bopearachchi Was Indo-Greek Artemidoros the son of Indo-Sctythian Maues
- ^ "Most of the people east of the Ravi already noticed as within Menander's empire -Audumbaras, Trigartas, Kunindas, Yaudheyas, Arjunayanas- began to coins in the first century BC, which means that they had become independent kingdoms or republics.", Tarn, The Greeks in Bactria and India
- ^ Jump up to: a b Tarn, William Woodthorpe (2010-06-24). The Greeks in Bactria and India. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781108009416.
- ^ India, the Ancient Past, Burjor Avari, pp. 92-93
- ^ :"To the colonies settled in India, Python, the son of Agenor, was sent." Justin XIII.4[usurped]
- ^ Chandragupta Maurya and His Times, Radhakumud Mookerji, Motilal Banarsidass Publ., 1966, pp. 26-27 [1]
- ^ Chandragupta Maurya and His Times, Radhakumud Mookerji, Motilal Banarsidass Publ., 1966, p. 27 [2]
- ^ History Of The Chamar Dynasty, Raj Kumar, Gyan Publishing House, 2008, p. 51 [3]
- ^ "Kusumapura was besieged from every direction by the forces of Parvata and Chandragupta: Shakas, Yavanas, Kiratas, Kambojas, Parasikas, Bahlikas and others, assembled on the advice of Chanakya" in Mudrarakshasa 2. Sanskrit original: "asti tava Shaka-Yavana-Kirata-Kamboja-Parasika-Bahlika parbhutibhih Chankyamatipragrahittaishcha Chandergupta Parvateshvara balairudidhibhiriva parchalitsalilaih samantaad uprudham Kusumpurama". From the French translation, in "Le Ministre et la marque de l'anneau", ISBN 2-7475-5135-0
- ^ India, the Ancient Past, Burjor Avari, pp. 106-107
- ^ "Strabo 15.2.1(9)".
- ^ Barua, Pradeep. The State at War in South Asia. Vol. 2. U of Nebraska Press, 2005. pp13-15 via Project MUSE (subscription required)
- ^ Jump up to: a b Foreign Influence on Ancient India, Krishna Chandra Sagar, Northern Book Centre, 1992, p. 83 [4]
- ^ Pratisarga Parva p. 18. Original Sanskrit of the first two verses: "Chandragupta Sutah Paursadhipateh Sutam. Suluvasya Tathodwahya Yavani Baudhtatapar".
- ^ "A minor rock edict, recently discovered at Kandahar, was inscribed in two scripts, Greek and Aramaic", India, the Ancient Past, Burjor Avari, p. 112
- ^ "The treaty between the two kings was settled with a marriage agreement by which a daughter of Seleucus Nicator entered the house of Chandragupta. Since she hardly had become the wife of any lesser person than the Indian emperor himself or his son and heir Bindusāra, the fascinating possibility arises that Aśoka, the greatest of the Mauryan emperors, may in fact, have been half or at least a quarter Greek." Vassiliades, 2016, p. 21, quoting Woodcock, "The Greeks in India", p. 17
- ^ India, the Ancient Past, Burjor Avari, pp. 108-109
- ^ "Three Greek ambassadors are known by name: Megasthenes, ambassador to Chandragupta; Deimachus, ambassador to Chandragupta's son Bindusara; and Dyonisius, whom Ptolemy Philadelphus sent to the court of Ashoka, Bindusara's son", McEvilley, p. 367
- ^ Classical sources have recorded that following their treaty, Chandragupta and Seleucus exchanged presents, such as when Chandragupta sent various aphrodisiacs to Seleucus: "And Theophrastus says that some contrivances are of wondrous efficacy in such matters as to make people more amorous. And Phylarchus confirms him, by reference to some of the presents which Sandrakottus, the king of the Indians, sent to Seleucus; which were to act like charms in producing a wonderful degree of affection, while some, on the contrary, were to banish love" Athenaeus of Naucratis, "The deipnosophists" Book I, chapter 32 Ath. Deip. I.32. Mentioned in McEvilley, p. 367
- ^ "The very fact that both Megasthenes and Kautilya refer to a state department run and maintained specifically for the purpose of looking after foreigners, who were mostly Yavanas and Persians, testifies to the impact created by these contacts.", Narain, "The Indo-Greeks", p. 363
- ^ "It also explains (...) random finds from the Sarnath, Basarth, and Patna regions of terra-cotta pieces of distinctive Hellenistic or with definite Hellenistic motifs and designs", Narain, "The Indo-Greeks" 2003, p. 363
- ^ "The second Kandahar edict (the purely Greek one) of Ashoka is a part of the "corpus" known as the "Fourteen-Rock-Edicts"" Narain, "The Indo-Greeks" 2003, p. 452
- ^ "It is also in Kandahar that were found the fragments of a Greek translation of Edicts XII and XIII, as well as the Aramean translation of another edict of Ashoka", Bussagli, p. 89
- ^ "Within Ashoka's domain Greeks may have had special privileges, perhaps ones established by the terms of the Seleucid alliance. Rock Edict Thirteen indicates the existence of a Greek principality in the northwest of Ashoka's empire—perhaps Kandahar, or Alexandria-of-the-Arachosians—which was not ruled by him and for which he troubled to send Buddhist missionaries and published at least some of his edicts in Greek", McEvilley, p. 368
- ^ "Thirteen, the longest and most important of the edicts, contains the claim, seemingly outlandish at first glance, that Ashoka had sent missions to the lands of the Greek monarchs—not only those of Asia, such as the Seleucids, but those back in the Mediterranean also", McEvilley, p. 368
- ^ "When Ashoka was converted to Buddhism, his first thought was to despatch missionaries to his friends, the Greek monarchs of Egypt, Syria, and Macedonia", Rawlinson, Intercourse between India and the Western world, p. 39, quoted in McEvilley, p. 368
- ^ «В Rock Edict Two Ашока даже утверждает, что основал больницы для людей и животных в эллинистических королевствах», МакЭвилли, стр. 368
- ^ «Один из самых известных из этих эмиссаров, Дхармаракшита, который, как говорят, обратил тысячи людей, был греком (Mhv.XII.5 и 34)», МакЭвилли, стр. 370
- ^ «Махавамса рассказывает, что «знаменитый греческий учитель Махадхармараксита во втором веке до нашей эры возглавил делегацию из 30 000 монахов из Александрии Кавказской (Александра Йонас, или греков, цейлонский текст) на самом деле говорится) открытию великой ступы Руанвалли в Анурадхапуре», McEvilley, p. 370, цитируя Вудкока, «Греки в Индии», с. 55
- ^ Полный текст главы XII Mahavamsa Click.
- ^ «Лучшие колонны были выполнены греческими или персидско-греческими скульпторами; другие - местными мастерами под иностранным контролем или без него» Маршалл, «Буддийское искусство Гандхары», стр. 4
- ^ «Ряд иностранных ремесленников, таких как персы или даже греки, работали вместе с местными мастерами, и некоторые из их навыков копировались с жадностью» Бурджор Авари, «Индия, древнее прошлое», стр. 118
- ^ Иностранное влияние на Древнюю Индию Кришна Чандра Сагар, стр. 138
- ^ Идея Древней Индии: Очерки религии, политики и археологии Упиндера Сингха с. 18
- ^ «Антиох III, заключив мир с Евтидемом I после прерванной осады Бактры, возобновил с Софагасеном союз, заключенный его предком Селевком I», Bopearachchi, Monnaies , с. 52
- ^ Полибий (1962) [1889]. «11.39» . Истории . Эвелин С. Шакбург (переводчик). Макмиллан, Перепечатка Блумингтона.
- ^ Полибий; Фридрих Отто Хульч (1889). Истории Полибия . Макмиллан и компания. п. 78 .
- ^ Дж. Д. Лернер, Влияние упадка Селевкидов на Восточно-Иранское нагорье: основы Аршакидской Парфии и Греко-Бактрии (Штутгарт, 1999).
- ^ Флорида Холт, Громовой Зевс (Беркли, 1999)
- ^ Джастин XLI, параграф 4. [узурпировал]
- ^ Джастин XLI, пункт 1 [узурпировал]
- ^ Jump up to: а б Страбон XI.XI.I
- ^ Джастин XLI [узурпировал]
- ^ Jump up to: а б Полибий 11.34
- ^ Страбон 11.11.2
- ^ Полибий 10.49, Битва при Арии
- ^ Полибий 11.34 Осада Бактры
- ^ Об изображении греческого коленопреклоненного воина: «Бронзовая статуэтка коленопреклоненного воина, не греческой работы, но одетая в вариант греческого фригийского шлема. Из захоронения, предположительно IV века до н.э., к северу от Тянь-Шаньский хребет». Урумчинский музей Синьцзяна. (Бордман «Распространение классического искусства в древности»)
- ^ Уведомление Британского музея о вазе Чжоу (2005 г., приложенное изображение): «Красная глиняная чаша, украшенная накладкой и инкрустированная стеклянной пастой. Период Восточного Чжоу, IV – III века до н.э. Эта чаша, вероятно, предназначалась для копирования более ценный и, возможно, иностранный сосуд из бронзы или даже серебра мало использовался в Китае. Его популярность в конце периода Восточной Чжоу, вероятно, была связана с иностранным влиянием».
- ^ «То, что Китай получил от греко-иранского мира - гранат и другие растения «Чанг-Киен», тяжелое снаряжение катафракта, следы влияния греков на ханьское искусство (например) знаменитое белое бронзовое зеркало период Хань с греко-бактрийскими узорами (...) в Музее Виктории и Альберта »(Тарн, Греки в Бактрии и Индии , стр. 363–364)
- ^ Медно-никелевые монеты в Греко-Бактрии. Архивировано 6 марта 2005 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ^ Древнее китайское оружие. Архивировано 7 марта 2005 г. в Wayback Machine. Алебарда из медно-никелевого сплава периода Воюющих царств.
- ^ А. А. Мосс, стр. 317-318 Нумизматическая хроника 1950 г.
- ^ К.Майкл Хоган, Шелковый путь, Северный Китай , Мегалитический портал, изд. А. Бернэм
- ^ Виглас, Кателис (2016). «Халдейское и неоплатоническое богословие» . Электронный журнал философии и культуры Philosophia (14): 171–189.
Название «Халдеи» обычно относится к халдейскому народу, жившему в земле Вавилонии , и особенно к халдейским «волхвам» Вавилона… «Халдеи» были хранителями священной науки: астрологических знаний. и гадание, смешанное с религией и магией. Их считали последними представителями вавилонских мудрецов... В классической античности название «халдеи» обозначало прежде всего жрецов вавилонских храмов. В эллинистические времена термин «Халдей» был синонимом слов «математик» и «астролог»... Неоплатоники связывали халдейские оракулы с древними халдеями, получая пришедший с Востока престиж и узаконивая свои существования как носителей и продолжателей древней традиции.
- ^ Климент Александрийский «Строматы, или Сборники», Книга I, Глава XV
- ^ "Генерал Пушьямитра, стоящий у истоков династии Шунга. Он был поддержан браминами и даже стал символом брахманического поворота против буддизма Маурьев. Столица затем была перенесена в Паталипутру (сегодняшняя Патна )", Буссагли, с. 99
- ^ Пушьямитра описывается как «сенапати» (главнокомандующий) Брихадратхи в Пуранах.
- ^ Э. Ламотт: История индийского буддизма, Институт востоковедения, Лувен-ла-Нёв, 1988 (1958), стр. 109.
- ^ Ашока и упадок Маурьев, Ромила Тапар, Oxford University Press, 1960, стр. 200
- ^ Jump up to: а б Энциклопедия индийских традиций и культурного наследия, Anmol Publications, 2009, стр. 18
- ^ Пратисарга Парва с. 18
- ^ Джайразбхой, Рафик Али (1995). Иностранное влияние в древнем Индо-Пакистане . Книжный дом Синда. п. 100. ИСБН 978-969-8281-00-7 .
Аполлодот, основатель Греко-Индийского царства (ок. 160 г. до н. э.).
- ^ См . Полибий , Арриан , Ливий , Кассий Дион и Диодор . Юстин, о котором вскоре пойдет речь, дает краткое изложение истории эллинистической Македонии, Египта, Азии и Парфии.
- ^ Дату Трогуса см. в ОКР по «Трогусу» и Ярдли/Девелин, стр. 2; поскольку отец Трога руководил дипломатическими миссиями Юлия Цезаря до того, как была написана история (Юстин 43.5.11), дата Сеньора в следующей цитате слишком ранняя: «Западные источники для описания бактрийской и индо-греческой истории : Полибий, грек, родившийся около 200 г. до н. э.; Страбон, римлянин, опиравшийся на утерянную историю Аполлодора Артемитского (ок. 130–87 до н. э.), и Юстин, опиравшийся на Трога, писателя, жившего после 87 г. до н. э.», Старший. , Индо-скифские монеты IV , с. х; Степень, в которой Страбон цитирует Аполлодора, оспаривается, за исключением трех мест, которые он называет Аполлодором (и они могут быть у него через Эратосфена). Полибий говорит о Бактрии, а не об Индии.
- ^ Страбон, География 11.11.1 стр. 516 Кейсобон . 15.1.2, с. 686 Казобон , «племена» — это версия слова «этна » Джонса (Лёб).
- ^ Список классических свидетельств см. в «Индексе Тарна II»; но это охватывает Индию, Бактрию и несколько источников по эллинистическому Востоку в целом.
- ^ Тарн, приложение. 20; Нараин (1957) стр. 136, 156 и другие .
- ^ Соня Ри Кинтанилья (2007). История ранней каменной скульптуры в Матхуре: ок. 150 г. до н.э. – 100 г. н.э. БРИЛЛ Академик. стр. 254–255. ISBN 978-90-04-15537-4 .
- ^ Говорят, что Деметрий основал Таксилу (археологические раскопки), а также Сагалу в Пенджабе, которую он, кажется, назвал Евтидемией, в честь своего отца («город Сагала, также называемый Евтидемией» (Птолемей, География, VII 1) )
- ^ Путешествие по прошлому Индии Чандра Маули Мани, Северный книжный центр, 2005, с. 39
- ^ Полибий 11.34
- ^ Обычно считается, что первые завоевания Деметрия произошли еще при жизни его отца; разница была больше фактической даты. Тарн и Нараин договорились, что они начнутся примерно со 180; Бопеараччи перенес это число обратно на 200, и ему последовала большая часть более поздней литературы, но см. Брилла «Новый Поли : Энциклопедия древнего мира» (Бостон, 2006), «Деметрий», §10, в котором вторжение помещается «вероятно в 184 год». . Д.Х. МакДауэлл, «Роль Деметрия в Арахосии и Кабулской долине», опубликованная в томе: О. Бопеарачи, Ланды (редактор), Афганистан Ancien Carrefour Entre L'Est Et L'Ouest (Brepols 2005), обсуждает надпись, посвященную Евтидему, «Величайшему из всех царей», и его сыну Деметрию, которого называют не царем, а «Победоносным» (Каллиникос). Считается, что это указывает на то, что Деметрий был генералом своего отца во время первых завоеваний. Неизвестно, были ли завоеваны первыми Кабулская долина или Арахозия, и была ли последняя провинция отнята у Селевкидов после их поражения от римлян в 190 г. до н.э. Как ни странно, в упомянутых провинциях найдено больше монет Евтидема I, чем Деметрия I. Календарь «Йонас» подтверждается надписью, указывающей на тройной синхронизм, который начался в 186/5 г. до н.э.; какое событие отмечается, само по себе неясно. Ричард Саломон «Индо-греческая эпоха 186/5 г. до н. э. в надписи буддийского реликвария», в Ancien Carrefour . Афганистан, цитирует
- ^ «Деметрий занял большую часть дельты Инда, Саураштру и Катч», Бурджор Авари, стр. 130
- ^ «Иначе невозможно было бы объяснить, почему на всех его портретах Деметриос увенчан скальпом слона», Bopearachchi, Monnaies , с. 53
- ^ «Мы думаем, что завоевания этих регионов к югу от Гиндукуша принесли Деметрию I титул «царя Индии», данный ему Аполлодором Артемитским ». Бопеараччи, с. 52
- ^ О Геракле см. Лилиан Б. Лоулер « Orchesis Kallinikos » Transactions and Proceedings of the American Philological Association , Vol. 79. (1948), стр. 254–267, с. 262; об Артемидоре см. К. Уолтон Доббинс « Торговля Каписене и Гандхары после падения индо-греческого правления » Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient , Vol. 14, № 3. (декабрь 1971 г.), стр. 286–302 (оба JSTOR ). Тарн, с. 132, утверждает, что Александр не принимал в качестве титула, а лишь прославлялся им, но см. Питер Грин , Эллинистический век , с. 7; см. также Сеньор, Индо-скифские монеты, с. xii. Ни одна бесспорная монета самого Деметрия I не использует этот титул, но он используется на одной из родословных монет, выпущенных Агафоклом, на реверсе которых изображен классический профиль Деметрия, увенчанный скальпом слона, с легендой DEMETRIOS ANIKETOS, а также на реверс Геракла, коронующего себя, с легендой «О царе Агафокле» (Бопперахчи, «Монне», стр. 179 и табл. 8). Тарн, Греки в Бактрии и Индии, гл. IV.
- ^ «Теперь кажется наиболее вероятным, что Деметриос был основателем недавно открытой греческой эпохи 186/5», Старший, индо-скифские монеты IV.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Холт, Фрэнк Ли (1988). Александр Македонский и Бактрия: формирование греческой границы в Центральной Азии . Архив Брилла. ISBN 9004086129 .
- ^ МакДауэлл, 2004 г.
- ^ «Единственное, что кажется достаточно достоверным, это то, что Таксила была частью владений Агафокла», Bopearachchi, Monnaies , стр. 59
- ^ Кришан, Юврадж; Тадиконда, Калпана К. (1996). Образ Будды: его происхождение и развитие . Бхаратия Видья Бхаван. п. 22. ISBN 9788121505659 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Иконография Баларамы, Нилакантх Пурушоттам Джоши, Abhinav Publications, 1979, стр. 22 [5]
- ^ Стэнтон, Андреа Л.; Рамсами, Эдвард; Сейболт, Питер Дж.; Эллиотт, Кэролайн М. (2012). Культурная социология Ближнего Востока, Азии и Африки: Энциклопедия . Публикации SAGE. п. 28. ISBN 9781452266626 .
- ^ Сингх, Нагендра Кр; Мишра, АП (2007). Энциклопедия восточной философии и религии: Буддизм . Издательство «Глобал Вижн». стр. 351, 608–609. ISBN 9788182201156 .
- ^ Бопеараччи, Монеты , с. 63
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Нумизматы и историки единодушны во мнении, что Менандр был одним из величайших, если не величайшим, и самым знаменитым из индо-греческих царей. Монет с именем Менандра несравненно больше, чем монет любого другого индо-греческого царя. Греческий царь» Бопеарачи , «Monnaies Greco-Bactriennes et Indo-Grecques», с. 76.
- ^ «Менандр» . Британская онлайн-энциклопедия .
Менандр, также пишется Минедра или Менадра, палийский Милинда (процветал в 160 г. до н. э.? – 135 г. до н. э.?), величайший из индо-греческих царей и наиболее известный западным и индийским классическим авторам. Считается, что он был покровителем буддийской религии и предметом важного буддийского труда «Милинда-панха» («Вопросы Милинды»). Менандр родился на Кавказе, но греческий биограф Плутарх называет его царем Бактрии, а греческий географ и историк Страбон включает его в число бактрийских греков, «покоривших больше племен, чем Александр [Великий]».
- ^ «Конечно, есть доля правды в Аполлодоре и Страбоне, когда они приписывают Менандру продвижение греков Бактрии за пределы Гипаниса и даже до Ганга и Палиботры (...) Что яваны продвинулись даже дальше на востоке. , в долину Ганга-Джамуна, примерно в середине второго века до нашей эры, подтверждается совокупными свидетельствами индийских источников», Нараин, «Индо-греки», с. 267.
- ^ Ахир, округ Колумбия (1971). Буддизм в Пенджабе, Харьяне и Химачал-Прадеше . Общество Маха Бодхи Индии. п. 31 . OCLC 1288206 .
Деметрий умер в 166 г. до н. э., а Аполлодот, который был близким родственником короля, умер в 161 г. до н. э. После его смерти Менандр основал королевство в Пенджабе. Таким образом, с 161 г. до н.э. Менандр был правителем Пенджаба до своей смерти в 145 или 130 г. до н.э.
- ^ Мэгилл, Фрэнк Нортен (2003). Словарь мировой биографии, Том 1 . Тейлор и Фрэнсис. п. 717. ИСБН 9781579580407 .
МЕНАНДР Родился: ок. 210 г. до н. э.; вероятно Каласи, Афганистан Умер: ок. 135 г. до н.э.; вероятно, на северо-западе Индии. Области достижений: Правительство и религия. Вклад: Менандр расширил греко-бактрийские владения в Индии больше, чем любой другой правитель. Он стал легендарной фигурой как великий покровитель буддизма в палийской книге «Милиндапанха». Ранняя жизнь – Менандр (не путать с более известным греческим драматургом с таким же именем) родился где-то в плодородной местности к югу от Паропайсадов или нынешних гор Гиндукуш в Афганистане. Единственное упоминание об этом месте содержится в полулегендарной Милиндапанхе (первый или второй век нашей эры), в которой говорится, что он родился в деревне Каласи недалеко от Аласанды, примерно в двухстах йоджанах (около восемнадцати миль) от города Сагала (вероятно, Сиалкот). в Пенджабе). Аласанда относится к Александрии в Афганистане, а не к египетской.
- ^ «Греки... овладели не только Паталеной , но и на остальной части побережья так называемым царством Сараоста и Сигердиса ». Страбон 11.11.1 ( Страбон 11.11.1 )
- ^ Баумс, Стефан (2017). Основы гандхарской хронологии, основанные на реликтовых надписях, в «Проблемах хронологии в гандхарском искусстве» . Археопресс. }
- ^ Монеты греческих и скифских царей Бактрии и Индии в Британском музее, стр.50 и табл. XII-7 [6]
- ^ Роше, Людо (1986), Пураны , стр. 254: « Юга [Пурана] важна прежде всего как исторический документ. Это прозаическая хроника [...] империи Магадха , вплоть до распада Сунгов и прихода саков . уникален в своем описании вторжения и ухода яванов в Магадху».
- ^ Сен, Сайлендра Нат. (1999). Древняя индийская история и цивилизация (второе изд.). Нью-Дели: Нью Эйдж Интернэшнл. ISBN 81-224-1198-3 . OCLC 133102415 .
- ^ Саху, Северная Каролина (1959). «Бахасатимита из надписи Хатигумфа». Труды Индийского исторического конгресса . 22 : 84–87. ISSN 2249-1937 . JSTOR 44304273 .
- ^ Бопеараччи, с. 72
- ^ «Как показал Бопеараччи, Менандр смог перегруппироваться и вернуть территорию, которую завоевал Евкратид, возможно, после смерти Евкратида (1991, стр. 84–6). Бопеаракчи демонстрирует, что переход в дизайне монет Менандра был ответом к изменениям, внесенным Евкратидом».
- ^ Jump up to: а б «(В Милиндапанхе) Менандр объявлен архатом», МакЭвилли, стр. 378.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Плутарх, который говорит о захоронении мощей Менандра под памятниками или ступами, очевидно, читал или слышал какое-то буддийское повествование о смерти греческого короля», МакЭвилли, стр. 377.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Заявление Плутарха о том, что, когда умер Менандр, «города праздновали (...) договорились, что они должны разделить прах поровну и уйти, и должны воздвигнуть ему памятники во всех своих городах», важно и напоминает историю о Будда», Нараин, «Индо-греки» 2003, с. 123, «Это безошибочно буддистское и напоминает аналогичную ситуацию во время кончины Будды», Нараин, «Индо-греки», 2003, стр. 123. 269.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Бопеараччи, «Монеты», с. 86.
- ^ Рудрадаман (...), который силой уничтожил яудхеев, которые не хотели подчиняться, возгордился, проявив свой «титул» героев среди всех кшатриев. - Надпись на скале Джунагадх
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Приблизительно к 130 г. до н.э. кочевники из региона Яксарта вышли за северную границу самой Бактрии», МакЭвилли, с. 372.
- ^ Старший, Индо-скифские монеты и история IV , с. xxxiii
- ^ В I веке до нашей эры географ Исидор из Харакса упоминает парфян, правящих греческим населением и городами в Арахозии : «За пределами Арахозии. И парфяне называют это Белой Индией; там есть город Бийт, город Фарсана и город от Хорочоада и города Деметриады, затем Александрополя, столицы Арахосии, греческой, и по нему протекает река; Арахот. До этого места земля находится под властью парфян». «Парфянские станции», I век до н. э. Упоминается в Бопеарачи, «Monnaies Greco-Bactriennes et Indo-Grecques», стр. 52. Исходный текст в пункте 19 Парфянских станций.
- ^ Помпей Трог, Пролог к книге XLI.
- ^ «Когда Страбон упоминает, что «Те, кто после Александра продвинулись за Гипанис к Гангу и Полиботре (Паталипутре)», это может относиться только к завоеваниям Менандра.», Старший, Индо-скифские монеты и история , с. XIV
- ^ Митченер, Юга Пурана , 2000, с. 65: «Поэтому в соответствии с вышеизложенным обсуждением мы можем сделать вывод, что такое событие (вторжения в Паталипутру) произошло после правления Шалишуки Маурья (ок. 200 г. до н. э.) и до правления Пушьямитры Шунги (187 г. до н. э.). Соответственно, вторжения Яваны будут происходить во время правления индо-греческих царей Евтидема (ок. 230–190 до н.э.) или Деметрия (ок. 205–190 в качестве соправителя и 190–171 до н.э. в качестве верховного правителя).
- ^ По мнению Тарна, слово «наступление» (Проелонтес) может означать только военную экспедицию. Это слово обычно означает «идти вперед»; согласно LSJ , это может, но не обязательно, подразумевать военную экспедицию. См. LSJ, подраздел προέρχομαι. Страбон 15-1-27
- ^ Jump up to: а б МакЭвилли, 2002, Форма древней мысли, с. 371
- ^ АК Нараин и Кей, 2000 г.
- ^ «Менандер стал правителем королевства, простирающегося вдоль побережья западной Индии, включая всю Саураштру и гавань Барукачча . Его территория также включала Матхуру, Пенджаб, Гандхару и долину Кабула», Буссагли, стр. 101)
- ^ Тарн, стр. 147–149.
- ^ Страбон о масштабах завоеваний греко-бактрийцев/индо-греков: «Они овладели не только Паталеной , но и на остальной части побережья тем, что называется царством Сараоста и Сигердиса . короче говоря, Аполлодор говорит, что Бактриана является украшением Арианы в целом и, более того, они простирали свою империю даже до Серов и Фриний ». Страбон 11.11.1 ( Страбон 11.11.1 )
- ^ Полный текст, перевод Шоффа 1912 года.
- ^ «Рассказ о Перипле - это всего лишь рассказ моряка», Нараин (стр. 118–119).
- ^ «Отличительная серия индо-греческих монет была найдена в нескольких местах в центральной Индии: в том числе в Девасе, примерно в 22 милях к востоку от Удджайна . Таким образом, это еще раз подтверждает вероятность индо-греческого присутствия в малва. Митченер, «Юга Пурана», с. 64
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д История ранней каменной скульптуры в Матхуре: ок. 150 г. до н.э. – 100 г. н.э., Соня Ри Кинтанилья, BRILL, 2007, стр. 8–10 [7]
- ^ Jump up to: а б Кинтанилья, Соня Ри (2007). История ранней каменной скульптуры в Матхуре: ок. 150 г. до н. э. — 100 г. н. э . БРИЛЛ. п. 9. ISBN 9789004155374 .
- ^ «Отливки для монет индо-греков также были обнаружены в Гураме и Наурангабаде». Конференция по истории Пенджаба, Пенджабский университет , 1990, Материалы, том 23, стр. 45
- ^ История и историки в Древней Индии, Дилип Кумар Гангули, Abhinav Publications, 1984, стр. 108
- ^ Энциклопедия туристических ресурсов Индии, Том 1, Манохар Саджнани, Издательство Gyan, 2001 , стр. 93
- ^ Искусство и архитектура Индийского субконтинента, Джеймс К. Харл, издательство Йельского университета, 1994 , стр. 67
- ^ Опубликовано в «Возвращение к Индо-Греку Менандру или Полю Демьевилю», Journal Asiatique 281 (1993), стр. 113
- ^ Древняя индийская история и цивилизация, Сайлендра Нат Сен, New Age International, 1999, стр. 169
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Голова солдата в шлеме, вероятно, индо-греческого, I век до н.э., Музей Матхуры» в Джа, Двиджендра Нараян (1977). Древняя Индия: вводный план . Народный паб. Дом. п. xi. ISBN 9788170070399 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Вишну, Аша (1993). Материальная жизнь Северной Индии: на основе археологических исследований, публикации Миттала с 3-го по 1-й век до н.э. п. 141. ИСБН 9788170994107 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Иранские головы. В Матхуре были обнаружены несколько терракотовых мужских голов, которые изображают иранский народ, с которым индейцы вступили в более тесный контакт в четвертом и третьем веках до нашей эры. Агравала называет их представителями иранского народа, потому что их черты лица отражают иностранное этническое родство. ." Шривастава, Сурендра Кумар (1996). Терракотовое искусство северной Индии . Публикации Паримала. п. 81.
- ^ «В Матхуре также был обнаружен особый класс терракотовых голов, черты лица которых отражают этническое родство с иностранцами». Дхаваликар, Мадукар Кешав (1977). Шедевры индийской терракоты . Тарапоревала. п. 23.
- ^ "Солдатские головы. В период Маурьев военная деятельность была более заметна в общественной жизни. Возможно, иностранные солдаты часто посещали Индию и привлекали индийских моделистов своими этническими особенностями и необычной униформой. Из Матхуры в Уттар-Прадеше и Басарха в Бихаре, Сообщалось о некоторых терракотовых головах, изображающих солдат. С художественной точки зрения терракотовые головы солдат Басарха выполнены лучше, чем те, что из Матхуры». в Шривастава, Сурендра Кумар (1996). Терракотовое искусство северной Индии . Публикации Паримала. п. 82.
- ^ Вишну, Аша (1993). Материальная жизнь Северной Индии: на основе археологических исследований, публикации Миттала с 3-го по 1-й век до н.э. п. XV. ISBN 9788170994107 .
- ^ «Фигура персидского юноши (35.2556) в пальто, шарфе, брюках и тюрбане — редкая вещь». Музей, Археологический музей Матхуры (1971). Введение в музей Матхуры: иллюстрированный путеводитель . Археологический музей. п. 14.
- ^ Шарма, Рамеш Чандра (1994). Великолепие искусства и музея Матхуры . ДК Принтмир. п. 58. [ постоянная мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ Jump up to: а б История ранней каменной скульптуры в Матхуре: ок. 150 г. до н.э. – 100 г. н.э., Соня Ри Кинтанилья, BRILL, 2007, с. 170
- ^ «Поскольку ионийцы были либо первой, либо самой доминирующей группой среди греков, с которой люди на востоке вступали в контакт, персы называли их всех Яуна , а индийцы использовали Йону и Явану для них », Нараин, Индо -Греки , с. 249
- ^ «Термин (Явана) имел точное значение вплоть до христианской эпохи , когда постепенно его первоначальное значение было потеряно и, как и слово Млечча, оно выродилось в общий термин для иностранца» Нараин, стр. 18
- ^ «Индо-греческие, индо-скифские и индо-парфянские монеты в Смитсоновском институте», Bopearachchi , стр. 16.
- ^ Тарн, стр. 145–146
- ^ «Напряженная поза и расположение у входа в пещеру (Рани Гумфа) позволяют предположить, что мужская фигура является стражем или дварапалой . Агрессивная поза фигуры и ее западное платье (короткий килт и ботинки) указывают на то, что скульптура может быть это явана , иностранец из греко-римского мира». в книге «Раннее скульптурное искусство на индийском побережье: исследование культурной передачи и синкретизма» (300 г. до н. э. – 500 г. н. э.), Сунил Гупта, DK Printworld (P) Limited, 2008, стр. 85
- ^ «Но реальная история индо-греческого вторжения становится ясной только при анализе материала, содержащегося в историческом разделе Гарги Самхиты, Юга Пурана» Нараин, стр. 110, Индо-греки . Также «Текст Юга Пураны, как мы показали, дает явный ключ к периоду и характеру вторжения в Паталипутру, в котором принимали участие индо-греки, поскольку в нем говорится, что Панчалы и Матхуры были другими силами. которые напали на Сакету и уничтожили Паталипутру», Нараин, с. 112
- ^ «Для любого ученого, занимающегося изучением присутствия индо-греков или индо-скифов до христианской эры, Юга Пурана является важным исходным материалом» Дилип Кумер Гхош, генеральный секретарь Азиатского общества , Калькутта , 2002 г.
- ^ «...еще одно подтверждение вероятности того, что этот рассказ о вторжении яванов в Сакету и Паталипутру - в союзе с Панчалами и Матхурами - действительно является историческим» Митченер, Юга Пурана , стр. 65.
- ^ «Наступление греков на Паталипутру записано с индийской стороны в Юга-пуране», Тарн, стр. 145
- ^ «Самый большой город в Индии - это тот, который называется Палимботра, во владениях Прасианцев ... Мегасфен сообщает нам, что этот город простирался в населенных кварталах на огромную длину с каждой стороны на восемьдесят стадий, и что его ширина составляла пятнадцать стадий, и что кругом ее окружал ров, имеющий шестьсот футов ширины и тридцать локтей глубины, и что стена была увенчана 570 башнями и имела шестьдесят четыре ворот». Приб. Индийский 10. «О Паталипутре и нравах индейцев», цитирование текста Мегасфена. Архивировано 10 декабря 2008 г., в Wayback Machine.
- ^ «Текст Юга Пураны, как мы показали, дает явный ключ к периоду и характеру вторжения в Паталипутру, в котором принимали участие индо-греки, поскольку в нем говорится, что Панчалы и Матхуры были другими силами которые напали на Сакету и уничтожили Паталипутру», Нараин, Индо-греки , с. 112.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Сунга, Канвас, Республиканские королевства и монархии, Махамегхаваханас, Дилип Кумар Чакрабарти , стр. 6 [8]
- ^ «Индо-греческие, индо-скифские и индо-парфянские монеты в Смитсоновском институте», Bopearachchi , стр. 16. Также: «Калидас рассказывает в своей Малавикагнимитре (5.15.14–24), что Пуспамитра поручил своему внуку Васумитре охранять свою жертвенную лошадь, которая бродила по правому берегу реки Синдху и была захвачена кавалеристами Яваны, причем последний впоследствии был побежден Васумитра, упомянутая в этом контексте, может относиться к реке Инд : но такое расширение власти Шунги кажется маловероятным, и более вероятно, что оно обозначает одну из двух рек в центральной Индии — реку Синдху, которая является притоком реки Синдху. Ямуна , или река Кали-Синдху , которая является притоком Чамбала » . Юга Пурана, Митченер, 2002 г.)»
- ^ «Имя Димита почти наверняка является адаптацией имени «Деметриос», и, таким образом, надпись указывает на присутствие явана в Магадхе, вероятно, примерно в середине I века до нашей эры». Митченер, «Юга Пурана» , с. 65.
- ^ «Надпись Хатигумфы, кажется, не имеет ничего общего с историей индо-греков; определенно, она не имеет ничего общего с Деметрием I», Нараин, Индо-греки , стр. 50.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Перевод в Epigraphia Indica 1920 с. 87
- ^ PLGupta: Кушанские монеты и история, DKPrintworld, 1994, стр. 184, примечание 5
- ^ «Нумизматы и историки считают, что Менандр был одним из величайших, если не величайшим, и самым прославленным из индо-греческих царей», Bopearachchi, «Monnaies», стр. 76
- ^ «Менандер, вероятный завоеватель Паталипутры, похоже, был буддистом, и его имя входит в список важных королевских покровителей буддизма наряду с Ашокой и Канишкой», МакЭвилли, стр. 375.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Сапоги, копыта и колеса: и социальная динамика, стоящая за войной в Южной Азии, Сайкат К. Бозе, Vij Books India Pvt Ltd, 2015, с. 226 [9]
- ^ Jump up to: а б На пороге эпохи: искусство в мире до Кушаны, Дорис Шринивасан, BRILL, 2007, стр. 101 [10]
- ^ Бопеараччи, Монеты , с. 88
- ^ Старший, Индо-скифские монеты и история IV , с. xi
- ^ Jump up to: а б "П.Бернар считает, что эти эмиссии предназначались для коммерческого обмена с Бактрией, контролируемой тогда юэчами, и были постгреческими монетами, оставшимися верными греко-бактрийской чеканке. Несколько иная точка зрения (...) Г. Ле Ридер считает, что эти выбросы использовались для уплаты дани кочевникам севера, которые, таким образом, были заинтересованы в том, чтобы не продолжать свои набеги в направлении Индо-греческого царства», Bopearachchi, «Monnaies», с. 76.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Осмунд Бопеаракчи , 2016, Появление изображений Вишну и Шивы в Индии: нумизматические и скульптурные свидетельства
- ^ Герман Кульке и Дитмар Ротермунд (2004). История Индии . Рутледж. п. 73. ИСБН 978-0-415-32920-0 .
- ^ Древняя индийская история и цивилизация, Саилендра Нат Сен, New Age International, 1999, стр. 170
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д Энциклопедия индийской археологии Амалананды Гоша , BRILL, с. 295
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Буддийские пейзажи в Центральной Индии: холм Санчи и археология религиозных и социальных изменений, с третьего века до нашей эры по пятый век нашей эры, Джулия Шоу, Left Coast Press, 2013 , стр. 90
- ^ «Перила ступы Санчи № 2, которая представляет собой самое старое из существующих обширных украшений ступы, (и) датируется примерно вторым веком до нашей эры» Составляющие сообщества: буддизм Тхеравады и религиозные культуры Южной и Юго-Восточной Азии, Джон Клиффорд Холт , Джейкоб Н. Киннард, Джонатан С. Уолтерс, SUNY Press, 2012 с. 197
- ^ Дидактическое повествование: Иконография Джатаки в Дуньхуане с каталогом изображений Джатаки в Китае, Александр Питер Белл, LIT Verlag Münster, 2000 стр. 15 и далее
- ^ Буддийские пейзажи в Центральной Индии: холм Санчи и археология религиозных и социальных изменений, с третьего века до нашей эры по пятый век нашей эры, Джулия Шоу, Left Coast Press, 2013 , стр. 88ff
- ^ Индийская статуэтка из Помпеи, Мирелла Леви Д'Анкона, в журнале Arts of Asia, Vol. 13, нет. 3 (1950) с. 171
- ^ Jump up to: а б Лица власти: образ Александра и эллинистическая политика, Эндрю Стюарт, Калифорнийский университет Press, 1993 , с. 180
- ^ Jump up to: а б Популярные противоречия в мировой истории: исследование интригующих вопросов истории [4 тома]: исследование интригующих вопросов истории, Стивен Л. Дэнвер, ABC-CLIO, 2010, стр. 91
- ^ Jump up to: а б Буддийское искусство и древности Химачал-Прадеша, до 8 века нашей эры, Омаканда Ханда, Indus Publishing, 1994 , стр. 48
- ^ Jump up to: а б Распространение классического искусства в древности, Джон Бордман, Princeton University Press, стр. 115
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Эти маленькие балясины представляют значительный интерес, поскольку их скульптурные статуи намного превосходят по художественному замыслу и исполнению статуи перил. Они также примечательны тем, что на их основаниях или капителях выгравированы арианские буквы - особенность, которая безошибочно указывает на Найдены буквы p, s, a и b, из которых первые три встречаются дважды. Теперь, если бы на перилах работали одни и те же скульпторы, мы могли бы с уверенностью ожидать, что в качестве частных знаков будут использоваться одни и те же буквы алфавита. Но дело обстоит как раз наоборот, поскольку все 27 знаков, обнаруженных на любых частях перил, являются индийскими буквами. Единственный вывод, к которому я могу прийти. Эти факты заключаются в том, что иностранные художники, работавшие над скульптурами ворот, определенно не работали над какой-либо частью перил. Поэтому я делаю вывод, что раджа Сунгаса , спонсор ворот, должно быть, послал свою собственную группу. рабочих для их изготовления, а меньшие дары в виде колонн и перил были выполнены местными художниками». в книге Александра Каннингема «Ступа Бхархута: буддийский памятник, украшенный многочисленными скульптурами, иллюстрирующими буддийские легенды и историю третьего века до нашей эры». п. 8 (общественное достояние)
- ^ Jump up to: а б с «Распространение классического искусства в древности», Джон Бордман, 1993, стр. 112.
- ^ Дидактическое повествование: Иконография Джатаки в Дуньхуане с каталогом изображений Джатаки в Китае, Александр Питер Белл, LIT Verlag Münster, 2000 стр. 18
- ^ Буддийская архитектура, Хуу Фуок Ле, Графикол, 2010, с. 149 и далее
- ^ «Есть свидетельства того, что эллинистические скульпторы были в контакте с Санчи и Бхархутом» в книге «Образ Будды: его происхождение и развитие», Юврадж Кришан, Бхаратия Видья Бхаван, 1996, стр. 9
- ^ Хуу Фуок Ле (2010). Буддийская архитектура . Графикол. п. 161. ИСБН 9780984404308 .
- ^ Арора, Удай Пракаш (1991). Греко-Индика, культурные контакты Индии . Рамананд Видья Бхаван. п. 12. ISBN 9788185205533 .
В древней Индии не было недостатка в скульптурах, изображающих греков или человеческие фигуры греческого типа. Помимо пресловутой Гандхары, Санчи и Матхура также создали множество скульптур, свидетельствующих о внимательном наблюдении за греками.
- ^ Эти «иностранцы, похожие на греков», также описаны в книге Сьюзен Хантингтон «Искусство древней Индии», стр. 100
- ^ «Греки, очевидно, представили гиматий и хитон, которые можно увидеть на терракотах из Таксилы, а также короткий килт, который носил солдат на рельефе Санчи». Иностранное влияние на индийскую культуру: с ок. 600 г. до н.э. – 320 г. н.э., Manjari Ukil Originals, 2006, стр. 162
- ^ «Сцена показывает музыкантов, играющих на различных инструментах, некоторые из них весьма необычны, например, греческая двойная флейта и духовые инструменты с головой дракона из Западной Азии» в «Археологии мореплавания в древней Южной Азии», Химаншу Прабха Рэй, Cambridge University Press. , 2003 с. 255
- ^ Пурататтва, номер 8 . Индийское археологическое общество. 1975. с. 188.
Ссылка на Йону в надписях Санчи также имеет огромную ценность. (...) Одна из надписей объявляет о даре Сетапатиа Йоны, «Сетапатияса Йонаса данам», т.е. о даре Йоны, жителя Сетапатхи. Слово Йона здесь не может быть ничем, кроме греческого донора.
- ^ Epigraphia Indica Vol.2 с. 395 надпись 364
- ^ Джон Машалл, Памятники Санчи, с. 348 надпись №475
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Идея древней Индии: очерки религии, политики и археологии, SAGE Publications India, Upinder Singh, 2016 , стр. 18
- ^ Джон Машалл, Памятники Санчи, с. 308 надпись №89
- ^ Джон Машалл, Памятники Санчи, с. 345 надпись №433
- ^ Коутсворт, Джон; Коул, Хуан; Ханаган, Майкл П.; Пердью, Питер С.; Тилли, Чарльз; Тилли, Луиза (16 марта 2015 г.). Глобальные связи: Том 1, До 1500 года: Политика, обмен и социальная жизнь в мировой истории . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 138. ИСБН 978-1-316-29777-3 .
- ^ Атлас всемирной истории . Издательство Оксфордского университета. 2002. с. 51. ИСБН 978-0-19-521921-0 .
- ^ Фов, Жерун (2021). Европейский справочник по изучению Центральной Азии . Там же Пресс. п. 403. ИСБН 978-3-8382-1518-1 .
- ^ Тёрёк, Тибор (июль 2023 г.). «Интеграция лингвистических, археологических и генетических перспектив раскрывает происхождение угров» . Гены . 14 (7): Рисунок 1. doi : 10.3390/genes14071345 . ISSN 2073-4425 . ПМЦ 10379071 . ПМИД 37510249 .
- ^ «Известно, что в течение столетия, последовавшего за Менандром, более двадцати правителей чеканили монеты», Нараин, «Индо-греки» 2003, стр. 270
- ^ Бернард (1994), с. 126.
- ^ "Воскресший Кадфис, основатель Кушанской империи, сменил там (в Паропамисадах) кочевников, чеканивших подражания Гермею" Бопеараччи, "Монне", с. 117
- ^ «Сам Мауэс выпускал совместные монеты с Мачене, (...) вероятно, дочерью одного из индо-греческих домов» Старший, Индо-скифы , с. xxxvi
- ^ «Индо-скифские завоеватели, которые также переняли греческие типы, чеканили деньги со своими именами». Бопеарачи, «Моне», с. 121
- ^ Описано в RC Senior «Упадок индо-греков» [11] . См. также этот источник. Архивировано 15 октября 2007 г. на Wayback Machine.
- ^ Осмунд Бопеарачи , Резонный каталог, стр. 172-175
- ^ «Мы видим двух греков парфянского периода, первой половины первого века нашей эры, которые использовали индийскую форму своих имен: царя Теодамаса на его перстне-печатке, найденном в Баджауре, и Федора, сына Теороса, на двух серебряных чашах из Таксила». Тарн, с. 389.
- ^ «Большинство людей к востоку от Рави уже заметили, что они находятся в империи Менандра - Аудумбары, Тригарты, Кунинды, Яудхеи, Арджунаяны - начали чеканить монеты в первом веке до нашей эры, что означает, что они стали независимыми королевствами или республиками»., Тарн , с. 324.
- ^ «Чеканка первых (аудумбаров), для которых их торговля имела важное значение, начинается где-то в первом веке до нашей эры; они иногда имитируют типы Деметрия и Аполлодота I», Тарн, стр. 325.
- ^ Кунинды, должно быть, были включены в Греческую империю не только из-за их географического положения, но и потому, что они начали чеканить монеты в то время, когда произошло окончание греческого правления и установление их независимости», Тарн, стр. 238.
- ^ «Еще одно свидетельство коммерческого успеха греческих драхм можно увидеть в том факте, что они повлияли на чеканку монет Аудумбара и Кунинда», Нараин Индо-греки , стр. 114
- ^ «Богатые Аудумбары (...) некоторые из их монет после окончания греческого правления имитировали греческие типы», Тарн, стр. 239.
- ^ «Позже, в первом веке, правитель Куниндов Амогабхути выпустил серебряные монеты, «которые могли конкурировать на рынке с более поздним индо-греческим серебром»», Тарн, стр. 325.
- ↑ Надпись на санскрите гласит: «Yavanarajyasya sodasuttare varsasate 100 10 6». Р. Саломон, «Индо-греческая эпоха 186/5 г. до н.э. в надписи на буддийском реликварии», в «Афганистане, ancien carrefour entre l'est et l'ouest», стр. 373
- ^ «Около 10 г. н. э., при совместном правлении Стратона II и его сына Стратона в районе Сагалы, последнее греческое королевство пало от атак Раджувулы, индо-скифского сатрапа Матхуры.», Бопеараччи, «Монне», п. 125
- ^ Epigraphia Indica Vol.18 стр. 328 Надпись №10
- ^ Jump up to: а б Шейн Уоллес Греческая культура в Афганистане и Индии: старые свидетельства и новые открытия , 2016, стр. 210
- ^ Мак Эвилли «Форма древней мысли», стр. 385 («Яванаджатака - самый ранний сохранившийся санскритский текст по астрологии, составляющий основу всех более поздних индийских разработок в гороскопии», сам цитирует Дэвида Пингри «Яванаджатака Сфужидхваджи», стр. 5)
- ^ Буддийская архитектура, Ли Хуу Фуок, Grafikol 2009, стр. 98–99
- ^ Памятники всемирного наследия и связанные с ними постройки в Индии, Том 1. Али Джавид, Табассум Джавид, Algora Publishing, 2008 , стр. 42
- ^ * Надпись № 7: «(Этот) столб (является) даром Явана Сихадхая из Дхенукатаки» в «Проблемах древней индийской истории: новые перспективы и восприятия», Шанкар Гоял - 2001, стр. 104
* Надпись № 4: «(Этот) столб (является) даром Явана Дхаммадхьи от Дхенукатаки»
Описание в «Эллинизме в Древней Индии» Гауранги Натха Банерджи, с. 20 - ^ Индийская эпиграфия Том 18 стр. 326–328 и Epigraphia Indica Vol.7 [Epigraphia Indica Vol.7, стр. 53–54
- ^ Филпотт, Дон (2016). Мир вина и еды: Путеводитель по сортам, вкусам, истории и сочетаниям . Роуман и Литтлфилд. п. 133. ИСБН 9781442268043 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Греко-индейцы Западной Индии: исследование надписей буддийских пещерных храмов Яваны и Йонаки, «Индийский международный журнал буддийских исследований», NS 1 (1999–2000) S._1_1999-2000_pp._83-109 {{p. |87–88}}
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Индийская эпиграфия с. 90 и далее
- ^ Эллинизм в Древней Индии, Гауранга Натх Банерджи, с. 20
- ^ Римская империя и Индийский океан: древняя мировая экономика и королевства Африки, Аравии и Индии, Рауль Маклафлин, Перо и меч, 2014, стр. 170
- ^ Jump up to: а б Религии и торговля: религиозное формирование, трансформация и межкультурный обмен между Востоком и Западом, BRILL, 2013, с. 97 Примечание 97
- ^ Журнал Эпиграфического общества Индии . Общество. 1994. стр. iv.
- ^ Археологическое исследование Западной Индии . Центральная правительственная пресса. 1879. стр. 43–44.
- ^ Карттунен, Клаус (2015). «Йоны и яваны в индийской литературе» . Студия Ориенталия . 116 : 214.
- ^ Упиндер Сингх (2008). История древней и раннесредневековой Индии: от каменного века до XII века. Пирсон Образовательная Индия. ISBN 978-81-317-1120-0 . п. 383
- ^ Надпись в пещере Насик № 1. «(О нем) кшатрий, который пылал, как бог любви, подчинил саков, явавов и палхавов» на парсидском языке древней Индии. Ходивала, Шапурджи Кавасджи, с. 16
- ^ Эпиграфия Индика, стр. 61–62
- ^ Тивари, Шив Кумар (2002). Племенные корни индуизма . Саруп и сыновья. п. 311. ИСБН 9788176252997 .
- ^ Лонгхерст, AH (1932). Великая Ступа в Нагарджунаконде на юге Индии . Индийский антиквар. п. 186.
- ^ Сингх, Упиндер (2016). Идея Древней Индии: очерки религии, политики и археологии . Публикации SAGE Индия. стр. 45–55. ISBN 9789351506478 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д и Проблемы хронологии в искусстве Гандхары, Джухён Ри, стр. 35–51, 2017 г.
- ^ Проблемы хронологии в искусстве Гандхары с. 39
- ^ Проблемы хронологии в искусстве Гандхары с. 37
- ^ Источник
- ^ Страбон 15.2.1 (9)
- ^ Преподобный. Тип. I.32
- ^ Афиней, «Дейпнософисты» XIV.67.
- ^ Полибий 11.39
- ^ Историк Диодор писал, что царь Паталипутры , по-видимому, царь Маурьев, «любил греков»: «Ямбул, пробравшись в некую деревню, был затем приведен туземцами в присутствие царя Палиботры, города который находился на расстоянии многих дней пути от моря. И поскольку царь любил греков («Филэлленос») и был предан учению, он счел Ямбула достойным сердечного приема и, наконец, получив разрешение на охранную грамоту; перешел сначала в Персию, а затем благополучно прибыл в Грецию» Диодор 2,60.
- ^ «Диодор свидетельствует о великой любви царя Палиботры, по-видимому, царя Маурьев, к грекам» Нараин, «Индо-греки», с. 362.
- ^ «Очевидно, что для греков, выживших в Индии и пострадавших от притеснений шунга (для которых они были чужеземцами и еретиками), Деметриос должен был явиться спасителем» Марио Буссагли, с. 101
- ^ «Теперь, я думаю, мы можем понять, что означало греческое «завоевание» и как греки смогли преодолеть такие необычайные расстояния. В некоторые части Индии, возможно, в большие части, они пришли не как завоеватели, а как друзья или «спасители»; в частности, для буддийского мира они казались его защитниками» (Тарн, стр. 180).
- ^ Тарн с. 175. Также: «Люди, которых нужно было «спасать», на самом деле обычно были буддистами, и общая враждебность греков и буддистов к царю Сунга бросила их в объятия друг друга», Tarn p. 175. «Менандр пришёл спасти их от гнета царей Сунга», Тарн с. 178.
- ^ Уайтхед, «Индо-греческие монеты», стр. 3–8.
- ^ Бопеараччи с. 138
- ^ Саломон, Ричард (1998). Индийская эпиграфика: Руководство по изучению надписей на санскрите, пракрите и других индоарийских языках . Издательство Оксфордского университета. стр. 210–211. ISBN 978-0-19-535666-3 .
- ^ Уайтхед, с. VI.
- ^ «В древнеиндийской литературе этих индо-греков называли яванами» с. 9 + примечание 1 «Этот термин имел точное значение вплоть до христианской эпохи, когда постепенно его первоначальное значение было утрачено и, подобно слову Млекха , оно выродилось в общий термин для обозначения иностранца» с. 18, Нараин «Индогреки»
- ^ «Однако все греки в Индии были известны как яваны», Бурджор Авари, «Индия, древнее прошлое», стр. 130
- ^ «Термин Явана вполне мог быть впервые применен индийцами к грекам различных городов Малой Азии, которые были заселены в районах, прилегающих к северо-западной Индии» Нараин «Индо-греки», с. 227
- ^ «Из санскритского Явана существуют другие формы и производные, а именно Йона, Йонака, Джавана, Явана, Джонон или Джононка, Я-ба-на и т. д. Йона - это нормальная пракритская форма от Яваны», Нараин « Индо-греки», с. 228
- ^ Авари, Бурджор (2016). Индия: Древнее прошлое: история Индийского субконтинента с 7000 г. до н.э. по 1200 г. н.э. Рутледж. п. 167. ИСБН 9781317236733 .
- ^ Овер (2000), стр. 83–86, параграф. 173-179.
- ^ Монеты греческих и скифских царей Бактрии и Индии в Британском музее, с. 50 и пл. XII-7 [12]
- ^ Jump up to: а б «De l'Indus à l'Oxus: Archéologie de l'Asie Centrale», Пьерфранческо Каллиери, стр. 212: «Распространение со второго века до нашей эры эллинистических влияний в архитектуре Свата также подтверждается археологическими поисками в святилище Буткара I, ступа которого в то же время была «монументализирована» базальными элементами и декоративными нишами, заимствованными из эллинистической архитектуры».
- ^ Тарн, с. 391: "Где-то я встречал злобное утверждение, что каждый грек в Индии в конце концов стал буддистом (...) Гелиодор, посол, был Бхагаваттой, поклонником Вишну-Кришны как верховного божества (...) Феодор-меридрах, установивший некоторые реликвии Будды «в целях безопасности многих людей», несомненно, был буддистом». Изображения зороастрийского божества Митры , изображенного в лучистой фригийской шапке , широко встречаются на индо-греческих монетах западных царей. Этот Зевс-Митра также изображен сидящим (с глориолой вокруг головы и небольшим выступом на макушке, изображающим шапку) на многих монетах Гермея , Антиалкида или Гелиокла II .
- ^ Вклад императора Ашоки Маурья в развитие гуманитарного идеала в войне 30 апреля 1995 г. Статья Джеральда Дрейпера «Международное обозрение Красного Креста», № 305.
- ^ Rock Edict Nb13 (С. Дхаммика)
- ^ Лахири, Бела (1974). Коренные штаты северной Индии, около 200 г. до н.э. – 320 г. н.э. Университет Калькутты
- ^ Стронг, Джон С. (1989). Легенда о царе Ашоке: исследование и перевод Ашокаваданы. Принстон: Издательство Принстонского университета. ISBN 0-691-01459-0 .
- ^ «Вполне возможно, что «Дикайос», что в легенде Харости переводится как Драмайка, может быть связано с принятием им буддийской веры». Нараин, «Индогреки», 2003, с. 124
- ^ «Вероятно, колесо на некоторых монетах Менандра связано с буддизмом», Нараин, Индо-греки , стр. 122
- ↑ Ступавадана, глава 57, т.15. Цитаты в E.Seldeslachts.
- ^ МакЭвилли, с. 377
- ^ Плутарх «Политические заповеди», стр. 147–148.
- ^ Справочник по востоковедению, Курт А. Берендт, BRILL, 2004, стр. 49 знаков
- ^ «Царь Менандр, построивший предпоследний ярус ступы Буткара в первом веке до нашей эры, был индо-греком». Альбиния, Алиса (2012). Империи Инда: История реки .
- ^ Иностранное влияние на индийскую жизнь и культуру (ок. 326 г. до н.э. – ок. 300 г. н.э.) Сатьендра Натх Наскар, Abhinav Publications, 1996, стр. 69 [13]
- ^ Перекресток Азии, Элизабет Эррингтон, Фонд Древней Индии и Ирана, Музей Фицуильяма, Фонд Древней Индии и Ирана, 1992, стр. 16
- ^ Упоминается в «Греко-бактрийских и индо-греческих монетах», Осмунд Бопеарачи, Национальная библиотека, 1991 г.
- ^ Культурная социология Ближнего Востока, Азии и Африки: Энциклопедия, Андреа Л. Стэнтон, Эдвард Рамсами, Питер Дж. Сейболт, Кэролайн М. Эллиотт, SAGE Publications, 2012 стр. 28 [14]
- ^ Франкфор, Анри-Поль (1 января 2022 г.). «Благословляющий» жест руки в изображениях божеств и царей в искусстве Бактрии и Гандхары (2 век до н.э. – 1 век н.э.): Знак рогов» . Бюллетень Азиатского института .
- ^ «Необычайный реализм их портретной живописи. Портреты Деметрия, Антимаха и Евкратида являются одними из самых замечательных, дошедших до нас из древности» Эллинизм в Древней Индии, Банерджи, стр. 134
- ^ "Так же, как Франк Хлодвиг не принимал участия в развитии галло-римского искусства , так и индо-скиф Канишка не имел прямого влияния на развитие индо-греческого искусства; кроме того, мы имеем теперь определенные доказательства того, что во время его правления это искусство уже было стереотипным, а не декадентским» Эллинизм в Древней Индии, Банерджи, стр. 147.
- ^ «Сохранение в I веке нашей эры греческой администрации и, предположительно, некоторых элементов греческой культуры в Пенджабе теперь необходимо принимать во внимание при любом обсуждении роли греческого влияния в развитии гандхарской скульптуры», Перекресток Азия, стр. 14
- ^ Бордман, с. 141
- ^ Бордман, с. 143.
- ^ «Другие, датируя эту работу первыми двумя веками нашей эры, после упадка греческой автономии на Северо-Западе, вместо этого связывают ее с римской имперской торговлей, которая тогда только закреплялась в таких местах, как Барбарикум (современный Карачи ) в Устье Инда Было высказано предположение, что одно из посольств индийских королей и римских императоров, возможно, пригласило мастера-скульптора для наблюдения за работой в зарождающейся буддийской чувствительности Махаяны (в которой Будда стал рассматриваться как своего рода божество). и что «группы иностранных рабочих из восточных центров Римской империи » были привезены в Индию» (Мак Эвилли «Форма древней мысли», цитируя Бенджамина Роуленда «Искусство и архитектура Индии», стр. 121 и А. С. Сопера). Римский стиль в Гандхаре» Американский журнал археологии 55 (1951), стр. 301–319).
- ^ Бордман, с. 115
- ^ МакЭвилли, стр. 388-390.
- ^ Бордман, 109–153.
- ^ «Примечательно, что одежда статуй гандхарских бодхисаттв не имеет никакого сходства с одеждой кушанских царских портретных статуй, которые во многом связаны с парфянским костюмом. Наряды изображений гандхары должны быть созданы по образцу одежды местной местной знати. , князей индийской или индо-греческой расы, не имевших кровной связи со скифскими правителями. Очевидно также, что типы лиц не имеют отношения к чертам кушанов, какими мы их знаем по их монетам и фрагментарным портретным статуям.", Бенджамин Роуленд-младший, предисловие к «Диасническому искусству Кушана», Джон Розенфилд, 1967.
- ^ «Эти крошечные территории индо-греческих царей, должно быть, были оживленными и процветающими коммерческими местами», Индия: древнее прошлое , Бурджор Авари, стр. 130
- ^ «Без сомнения, греки Бактрии и Индии управляли процветающей экономикой. На это ясно указывают их чеканка монет и денежный обмен, который они установили с другими валютами». Нараин, «Индогреки», 2003, с. 275.
- ^ Бопеараччи, «Монеты», с. 27
- ^ Рэпсон, clxxxvi-
- ^ Бопеараччи, «Монеты», с. 75.
- ^ Фуссман, JA 1993, с. 127 и Бопеарачи, «Греко-бактрийские проблемы поздних индо-греческих царей», Num. Хрон. 1990, стр. 79–104)
- ^ Jump up to: а б Наука и цивилизация в Китае: Химия и химическая технология Джозефа Нидхэма, Гвей-Джен Лу с. 237 и далее
- ^ «Контакты Запада с Китаем начались задолго до Марко Поло, говорят эксперты» . Новости Би-би-си . 12 октября 2016 г. Проверено 16 апреля 2017 г.
- ^ «Мавзолей первого императора Китая сотрудничает с BBC и каналом National Geographic, чтобы представить новаторские доказательства того, что Китай находился в контакте с Западом во время правления первого императора» . businesswire.com . 12 октября 2016 г. Проверено 16 апреля 2017 г.
- ^ «Страбон II.3.4‑5 о Евдоксе» .
- ^ «Поскольку александрийские купцы уже плывут с флотом через Нил и Персидский залив до Индии, эти регионы также стали гораздо лучше известны нам сегодня, чем нашим предшественникам. Во всяком случае, когда Галл был префектом Египта, я сопровождал его и поднялся по Нилу до Сиены и границ Эфиопии, и я узнал, что из Миос-Хормоса в Индию отплывало до ста двадцати кораблей, тогда как прежде, при Птолемеях, только очень немногие отважились отправиться в путешествие и заняться торговлей индийскими товарами». Страбон II.5.12
- ^ «Любопытно, что на своей меди Зойлос использовал в качестве типа лук и колчан. Колчан был знаком, использовавшимся парфянами (скифами), а ранее использовался Диодотом, который, как мы знаем, заключил с ними договор. Возможно, Зойлос использовал скифских наемников в своих поисках против Менандра?» Старший, Индо-скифские монеты, с. xxvii
- ^ «Полибий 10.49, Битва при Арии» .
- ^ П. Л. Гупта 1994 г.
- ^ Судхакар Чаттопадхьяя (1974). Некоторые ранние династии Южной Индии . Мотилал Банарсидасс. стр. 44–50. ISBN 978-81-208-2941-1 .
- ^ «Мегастен Индика» . Архивировано из оригинала 10 декабря 2008 года.
- ^ «Джастин XLI» . Архивировано из оригинала 28 августа 2003 года.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: неподходящий URL ( ссылка ) - ^ Тарн, с. 494.
- ^ «Хотя индо-греческие монархии, похоже, прекратили свое существование в первом веке до нашей эры, греческое присутствие в Индии и Бактрии оставалось сильным», МакЭвилли, стр. 379
- ^ «Использование греческих месяцев саками и более поздними правителями указывает на вывод, что они использовали систему датировки, начатую их предшественниками». Нараин, «Индогреки» 2003, с. 190
- ^ «Свидетельства завоевания Саурастра во время правления Чандрагупты II можно увидеть в его редких серебряных монетах, которые более непосредственно имитируют монеты западных сатрапов... они сохраняют некоторые следы старых надписей греческими буквами, в то время как на реверсе они заменяют чайтью с полумесяцем и звездой типом Гупта (павлин). в Рэпсоне «Каталог индийских монет в Британском музее. Андхрас и т. д.», стр. Кли
- ^ «Парфянские станции», I век нашей эры. Оригинальный текст в пункте 19 Парфянских станций
- ^ МакЭвилли, Томас С. (2012). Форма древней мысли: сравнительные исследования греческой и индийской философии . Саймон и Шустер. п. 503. ИСБН 9781581159332 .
- ^ При каждом короле информация из Бопеарачи взята из Monnaies Gréco-Bactriennes et Indo-Grecques, Catalog Raisonné (1991) или иногда из SNG9 (1998). Хронология Сениора взята из «Последовательности индо-греческих и индо-скифских царей во втором и первом веках до н. э.» , Приложение ONS179 (2004 г.), тогда как комментарии (вплоть до времен Гиппострата) взяты из «Упадка индо-греков » (1998 г. ). ).
- ^ О. Бопеарачи, «Греко-бактрийские и индо-греческие монеты, Резонный каталог», Bibliothèque Nationale, Париж, 1991, стр. 453
- ^ История ранней каменной скульптуры в Матхуре: ок. 150 г. до н.э. – 100 г. н.э., Соня Ри Кинтанилья, BRILL, 2007, с. 9 [15]
Цитируемые работы
[ редактировать ]- Авари, Бурджор (2007). Индия: Древнее прошлое. История Индийского субконтинента с ок. 7000 г. до н.э. – 1200 г. н.э. Рутледж. ISBN 978-0-415-35616-9 .
- Банерджи, Гауранга Натх (1961). Эллинизм в древней Индии . Дели: Мунши Рам Манохар Лал. ISBN 978-0-8364-2910-7 . ОСЛК 1837954.
- Бернар, Пол (1994). «Греческие королевства Средней Азии». В: История цивилизаций Центральной Азии, Том II. Развитие оседлых и кочевых цивилизаций: 700 г. до н.э. - 250 г. н.э. , стр. 99–129. Харматта, Янош, изд., 1994. Париж: Издательство ЮНЕСКО. ISBN 92-3-102846-4 .
- Бордман, Джон (1994). Распространение классического искусства в древности . Принстон, Нью-Джерси: Издательство Принстонского университета. ISBN 978-0-691-03680-9 .
- Бопеараччи, Осмунд (1991). Греко-бактрийские и индо-греческие монеты, Каталог Raisonné (на французском языке). Национальная библиотека Франции. ISBN 978-2-7177-1825-6 .

- Бопеараччи, Осмунд (1998). СНГ 9 . Нью-Йорк: Американское нумизматическое общество. ISBN 978-0-89722-273-0 .
- Бопеараччи, Осмунд (2003). От Инда до Окса, Археология Центральной Азии (на французском языке). Латте: Ассоциация имаго-музеев латте. ISBN 978-2-9516679-2-1 .
- Бопеараччи, Осмунд (1993). Индо-греческие, индо-скифские и индо-парфянские монеты в Смитсоновском институте . Вашингтон: Национальная нумизматическая коллекция, Смитсоновский институт . OCLC 36240864 .
- Буссагли, Марио; Франсин Тиссо; Беатрис Арналь (1996). Искусство Гандхары (на французском языке). Париж: Универсальный французский книжный магазин. ISBN 978-2-253-13055-0 .
- Камбон, Пьер (2007). Афганистан, найденные сокровища (на французском языке). Музей Гиме . ISBN 978-2-7118-5218-5 .
- Эррингтон, Элизабет; Джо Крибб; Мэгги Кларингбулл; Фонд Древней Индии и Ирана ; Музей Фицуильяма (1992). Перекресток Азии: трансформация образа и символа в искусстве древнего Афганистана и Пакистана . Кембридж: Фонд Древней Индии и Ирана. ISBN 978-0-9518399-1-1 .
- Фачценна, Доменико (1980). Буткара I (Сват, Пакистан) 1956–1962, Том III 1 . Рим: IsMEO (Итальянский институт Ближнего и Дальнего Востока).
- Фольц, Ричард (2010). Религии Шелкового пути: домодернистские модели глобализации . Нью-Йорк: Пэлгрейв Макмиллан. ISBN 978-0-230-62125-1 .
- Киоун, Дэмиен (2003). Словарь буддизма . Нью-Йорк: Издательство Оксфордского университета . ISBN 978-0-19-860560-7 .
- Ловенштейн, Том (2002). Видение Будды: Буддизм, путь к духовному просветлению . Лондон: Дункан Бэрд. ISBN 978-1-903296-91-2 .
- Маршалл, сэр Джон Хьюберт (2000). Буддийское искусство Гандхары: история ранней школы, ее зарождения, роста и упадка . Нью-Дели: Мунширам Манохарлал. ISBN 978-81-215-0967-1 .
- Маршалл, Джон (1956). Таксила. Иллюстрированный отчет об археологических раскопках, проведенных в Таксиле (3 тома) . Дели: Мотилал Банарсидасс.
- МакЭвилли, Томас (2002). Форма древней мысли. Сравнительные исследования греческой и индийской философии . Allworth Press и Школа визуальных искусств. ISBN 978-1-58115-203-6 .
- Митчинер, Джон Э.; Помогите (1986). Юга Пурана: критически отредактированная, с английским переводом и подробным введением. Калькутта, Индия: Азиатское общество. ISBN 978-81-7236-124-2 . ОСЛК 15211914.
- Нараин, АК (1957). Индо-греки . Оксфорд: Кларендон Пресс.
- переиздано Оксфордом, 1962, 1967, 1980 гг.; переиздан (2003 г.), «переработан и дополнен» издательством BR Publishing Corporation, Нью-Дели.
- Нараин, АК (1976). Типы монет индо-греческих царей . Чикаго, США: Издательство Ares Publishing. ISBN 978-0-89005-109-2 .
- Пури, Байдж Натх (2000). Буддизм в Средней Азии . Дели: Мотилал Банарсидасс. ISBN 978-81-208-0372-5 .
- Розенфилд, Джон М. (1967). Династические искусства кушанов . Беркли, Калифорния: Издательство Калифорнийского университета. ISBN 978-81-215-0579-6 .
- Саломон, Ричард (январь – март 1982 г.). «Надпись «Авака» и происхождение эпохи Викрама». Журнал Американского восточного общества . 102 (1): 59–68. дои : 10.2307/601111 . JSTOR 601111 .
- Селдеслахтс, Э. (2003). Конец пути для индо-греков? . Ираника Антика, Том XXXIX, 2004 г.
- Старший, RC (2006). Индо-скифские монеты и история. Том IV . Классическая нумизматическая группа, Inc. ISBN 978-0-9709268-6-9 .
- Тарн, WW (1938). Греки в Бактрии и Индии . Издательство Кембриджского университета.
- Второе издание с дополнениями и исправлениями (1951 г.). Переиздано с обновленным предисловием Фрэнка Ли Холта (1985), Ares Press, Чикаго. ISBN 0-89005-524-6
- Афганистан, древний перекресток между востоком и западом (на французском и английском языках). Бельгия: Бреполи. 2005. ISBN 978-2-503-51681-3 .
- Токио Кокурицу Хакубуцукан ; Хёго Кенрицу Бидзюцукан (2003). Александр Великий: культурные контакты Востока и Запада от Греции до Японии . Токио: Токио Кокурицу Хакубуцукан.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: несколько имен: список авторов ( ссылка ) - Вассилиадес, Деметриос (2000). Греки в Индии – обзор философского понимания . Нью-Дели: Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers Pvt Limited. ISBN 978-81-215-0921-3 .
- Вассилиадес, Деметриос (2016). Греки и буддизм: межкультурная встреча . Афины: Индо-эллинское общество культуры и развития. ISBN 978-618-82624-0-9 .
Внешние ссылки
[ редактировать ]- Индо-греческая история и монеты
- Древняя чеканка Греко-Бактрийского и Индо-Греческого царств.
- Текст профессора Николаса Симса-Вильямса (Лондонский университет) с упоминанием прихода кушанов и замены греческого языка.
- Реконструкция индо-греческих армий в военных играх
- Влияние греко-индийской культуры на западную цивилизацию
- о Греко-Бактрийском и Индо-Греческом царствах Некоторые новые гипотезы Антуана Симонена
- Греко-бактрийские и индо-греческие царства в древних текстах
- Индо-греки
- Древняя история Афганистана
- Древняя Индия
- Эллинистические государства
- Этнические группы в Индии
- Древние народы Пакистана
- Заведения 180-х гг. до н.э.
- 10-е годы
- Государства и территории, основанные во 2 веке до нашей эры.
- Государства и территории, упраздненные в I веке.
- Разрушения I века
- Бывшие королевства







![Иностранец на лошади. Медальоны датированы примерно 115 г. до н.э.[184]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e5/Sanchi_Stupa_2_man_on_horse.jpg/166px-Sanchi_Stupa_2_man_on_horse.jpg)
![Лакшми с лотосом и двумя детьми-помощниками, вероятно, заимствована из аналогичных изображений Венеры[188]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/66/Lakshmi_Sanchi_Stupa_2.jpg/180px-Lakshmi_Sanchi_Stupa_2.jpg)