Падение Западной Римской империи

Падение Западной Римской империи , также называемое падением Римской империи или падением Рима , было потерей центрального политического контроля в Западной Римской империи , процессом, в котором Империя не смогла обеспечить соблюдение своего правления, а ее обширные территория была разделена между несколькими государствами- преемниками . Римская империя потеряла силы, которые позволяли ей осуществлять эффективный контроль над своими западными провинциями ; Современные историки постулируют такие факторы, как эффективность и численность армии , здоровье и численность римского населения, сила экономики , компетентность императоров , внутренняя борьба за власть, религиозные изменения того периода и эффективность гражданской администрации. Растущее давление со стороны вторгшихся варваров за пределы римской культуры также во многом способствовало краху. Климатические изменения , а также эндемические и эпидемические заболевания стали причиной многих из этих непосредственных факторов. [ 1 ] Причины краха являются основными темами историографии древнего мира, и они определяют большую часть современных дискуссий о несостоятельности государства . [2][3][4]
In 376, a large migration of Goths and other non-Roman people, fleeing from the Huns, entered the Empire. Roman forces were unable to exterminate, expel or subjugate them (as was their normal practice). In 395, after winning two destructive civil wars, Theodosius I died. He left a collapsing field army, and the Empire divided between the warring ministers of his two incapable sons. Goths and other non-Romans became a force that could challenge either part of the Empire. Further barbarian groups crossed the Rhine and other frontiers. The armed forces of the Western Empire became few and ineffective, and despite brief recoveries under able leaders, central rule was never again effectively consolidated.
By 476, the position of Western Roman Emperor wielded negligible military, political, or financial power, and had no effective control over the scattered Western domains that could still be described as Roman. Barbarian kingdoms had established their own power in much of the area of the Western Empire. In 476, the Germanic barbarian king Odoacer deposed the last emperor of the Western Roman Empire in Italy, Romulus Augustulus, and the Senate sent the imperial insignia to the Eastern Roman Emperor Zeno.
While its legitimacy lasted for centuries longer and its cultural influence remains today, the Western Empire never had the strength to rise again. The Eastern Roman, or Byzantine, Empire, survived and remained for centuries an effective power of the Eastern Mediterranean, although it lessened in strength. Additionally, while the loss of political unity and military control is universally acknowledged, the fall of Rome is not the only unifying concept for these events; the period described as late antiquity emphasizes the cultural continuities throughout and beyond the political collapse.
Historical approaches and modern syntheses
Since 1776, when Edward Gibbon published the first volume of his The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, Decline and Fall has been the theme around which much of the history of the Roman Empire has been structured. "From the eighteenth century onward," historian Glen Bowersock wrote, "we have been obsessed with the fall: it has been valued as an archetype for every perceived decline, and, hence, as a symbol for our own fears."[5]
Another paradigm of the period
From at least the time of Henri Pirenne (1862–1935), scholars have described a continuity of Roman culture and political legitimacy long after 476.[6]: 5–7 [7] Pirenne postponed the demise of classical civilization to the 8th century. He challenged the notion that Germanic barbarians had caused the Western Roman Empire to end, and he refused to equate the end of the Western Roman Empire with the end of the office of emperor in Italy. He pointed out the essential continuity of the economy of the Roman Mediterranean even after the barbarian invasions, and suggested that only the Muslim conquests represented a decisive break with antiquity.
The more recent formulation of a historical period characterized as "Late Antiquity" emphasizes the transformations of ancient to medieval worlds within a cultural continuity.[8] In recent decades archaeologically based argument even extends the continuity in material culture and in patterns of settlement as late as the eleventh century.[9][10][11][12] Observing the political reality of lost control (and the attendant fragmentation of commerce, culture, and language), but also the cultural and archaeological continuities, the process has been described as a complex cultural transformation, rather than a fall.[13]: 34 The "perception of Late Antiquity has significantly changed: the period is no longer seen as an era of decline and crisis but as an epoch of metamorphosis in the Mediterranean region".[14][15]: 3, 4
Timespan

A synthesis by Harper (2017) gave four decisive turns of events in the transformation from the height of the empire to the early Middle Ages:
- The Antonine Plague that ended a long period of demographic and economic expansion, weakening but not toppling the empire.
- The Crisis of the Third Century, in which climatic change, renewed pandemic disease, and internal and external political instability led to the near-collapse of the imperial system. Its reconstitution included a new basis for the currency, an expanded professional government apparatus, emperors further distanced from their people, and, shortly, the rise of Christianity, a proselytizing, exclusive religion that anticipated the imminent end of the world.
- The military and political failure of the West, in which mass migration from the Eurasian steppe overcame and dismembered the western part of an internally-weakened empire. The eastern empire rebuilt itself again and began the reconquest of the West.
- In the lands around the Mediterranean the Late Antique Little Ice Age and the Plague of Justinian created one of the worst environmental cataclysms in recorded history. The imperial system crumbled in the next couple of generations and then lost vast territories to the armies of Islam, a new proselytizing, exclusive religion that also looked forward to an imminent end time. The diminished and impoverished Byzantine rump state survived amid perpetual strife between and among the followers of Christianity and Islam.[16]
The loss of centralized political control over the West, and the lessened power of the East, are universally agreed, but the theme of decline has been taken to cover a much wider time span than the hundred years from 376. For Cassius Dio, the accession of the emperor Commodus in 180 CE marked the descent "from a kingdom of gold to one of rust and iron".[17] Since the age of humanism, the process of the Fall has been thought to have begun with Constantine the Great, or with the soldier emperors who seized power through command of the army from 235 through 284, or with Commodus, or even with Augustus.[14]
Gibbon was uncertain about when decline began. "In the first paragraph of his text, Gibbon wrote that he intended to trace the decline from the golden age of the Antonines"; later text has it beginning about A.D. 180 with the death of Marcus Aurelius; while in chapter 7, he pushes the start of the decline to about 52 B.C., the time of Julius Caesar and Pompey and Cicero.[18] Gibbon placed the western empire's end with the removal of the man Gibbon referred to as "the helpless Augustulus" in 476.[19]
Arnold J. Toynbee and James Burke argue that the entire Imperial era was one of steady decay of institutions founded in republican times. Theodor Mommsen excluded the imperial period from his Nobel Prize-winning History of Rome (1854–1856). As one convenient marker for the end, 476 has been used since Gibbon, but other key dates for the fall of the Roman Empire in the West include the Crisis of the Third Century, the Crossing of the Rhine in 406 (or 405), the sack of Rome in 410, and the death of Julius Nepos in 480.[20][page needed]
Underlying causes
When Gibbon published his landmark work, it quickly became the standard.[21][22] Peter Brown has written that "Gibbon's work formed the peak of a century of scholarship which had been conducted in the belief that the study of the declining Roman Empire was also the study of the origins of modern Europe".[23] Gibbon was the first to attempt an explanation of causes of a Fall of empire.[23] Like other Enlightenment thinkers and British citizens of the age steeped in institutional anti-Catholicism, Gibbon held in contempt the Middle Ages as a priest-ridden, superstitious Dark Age. It was not until his own era, the "Age of Reason", with its emphasis on rational thought, it was believed, that human history could resume its progress.[24][25]
He began an ongoing controversy about the role of Christianity, but he gave great weight to other causes of internal decline and to attacks from outside the Empire.
The story of its ruin is simple and obvious; and, instead of inquiring why the Roman empire was destroyed, we should rather be surprised that it had subsisted so long. The victorious legions, who, in distant wars, acquired the vices of strangers and mercenaries, first oppressed the freedom of the republic, and afterwards violated the majesty of the purple. The emperors, anxious for their personal safety and the public peace, were reduced to the base expedient of corrupting the discipline which rendered them alike formidable to their sovereign and to the enemy; the vigour of the military government was relaxed, and finally dissolved, by the partial institutions of Constantine; and the Roman world was overwhelmed by a deluge of Barbarians.
— Edward Gibbon. The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, Chapter 38 "General Observations on the Fall of the Roman Empire in the West"
After a diligent inquiry, I can discern four principal causes of the ruin of Rome, which continued to operate in a period of more than a thousand years. I. The injuries of time and nature. II. The hostile attacks of the Barbarians and Christians. III. The use and abuse of the materials. And, IV. The domestic quarrels of the Romans.
— Edward Gibbon. The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, Chapter 71 "Four Causes of Decay and Destruction."
Contemporary views
Modern historiography diverges from Gibbon.[26] While most of his ideas are no longer accepted in totality, they have been foundational to later discourse and the modern synthesis with archaeology, epidemiology, climatic history, genetic science,[27] and many more new sources of history beyond the documentary sources that were all that was available to Gibbon.[14][28]
While Alexander Demandt enumerated 210 different theories on why Rome fell, twenty-first century scholarship classifies the primary possibilities more concisely:[29][30]
Climatic crisis
A recent summary interprets disease and climate change as important drivers of the political collapse of the empire. There was a Roman climatic optimum from about 200 BCE to 150 CE, when lands around the Mediterranean were generally warm and well-watered. This made agriculture prosperous, army recruitment easy, and the collection of taxes straightforward. From about 150, the climate became on average somewhat worse for most of the inhabited lands around the Mediterranean.[31][32] After about 450, the climate worsened further in the Late Antique Little Ice Age that may have directly contributed to the variety of factors that brought Rome down.[33]
The Roman Empire was built on the fringes of the tropics. Its roads and its pirate-free seas, which produced an abundance of trade, also unknowingly created an interconnected disease ecology that unleashed the evolution and spread of pathogens.[34] Pandemics contributed to massive demographic changes, economic crises, and food shortages in the crisis of the third century.[35][36][37] Heavy mortality in 165–180 from the Antonine Plague seriously impaired attempts to repel Germanic invaders, but the legions generally held or at least speedily re-instated the borders of the Empire.[38]

Migrational crisis
From 376, massive populations moved into the Empire, driven by the Huns who themselves may have been driven by climate change in the Eurasian steppe.[1][39] These barbarian invasions led ultimately to barbarian kingdoms over much of the former territory of the Western Empire. But the final blow came only with the Late Antique Little Ice Age and its aftermath,[33] when Rome was already politically fragmented and materially depleted.[40]
Political crisis
Aurelian reunited the empire in 274, and from 284 Diocletian and his successors reorganized it with more emphasis on the military. John the Lydian, writing over two centuries later, reported that Diocletian's army at one point totaled 389,704 men, plus 45,562 in the fleets, and numbers may have increased later.[41] With the limited communications of the time, both the European and the Eastern frontiers needed the attention of their own supreme commanders. Diocletian tried to solve this problem by re-establishing an adoptive succession with a senior (Augustus) and junior (Caesar) emperor in each half of the Empire, but this system of tetrarchy broke down within one generation and the hereditary principle re-established itself with generally unfortunate results. Thereafter civil war became again the main method of establishing new imperial regimes. Although Constantine the Great (in office 306 to 337) again re-united the Empire, towards the end of the fourth century the need for division was generally accepted. From then on, the Empire existed in constant tension between the need for two emperors and their mutual mistrust.[42]
Until late in the fourth century, the united Empire retained sufficient power to launch powerful attacks against its enemies in Germania and in the Sasanian Empire. Receptio of barbarians became widely practised: imperial authorities admitted potentially hostile groups into the Empire, split them up, and allotted to them lands, status, and duties within the imperial system.[43] In this way many groups provided unfree workers (coloni) for Roman landowners, and recruits (laeti) for the Roman army. Sometimes their leaders became officers. Normally the Romans managed the process carefully, with sufficient military force on hand to ensure compliance. Cultural assimilation followed over the next generation or two.

Financial crisis
The Empire suffered multiple serious crises during the third century. The rising Sassanid Empire inflicted three crushing defeats on Roman field armies and remained a potent threat for centuries.[42] Other disasters included repeated civil wars, barbarian invasions, and more mass-mortality in the Plague of Cyprian (from 250 onwards). For a short period, the Empire split into a Gallic Empire in the West (260–274), a Palmyrene Empire in the East (260–273), and a central Roman rump state; in 271, Rome abandoned the province of Dacia on the north of the Danube. The Rhine/Danube frontier also came under more effective threats from larger barbarian groupings, which had developed improved agriculture and increased their populations.[44][45] The average stature of the population in the West suffered a serious decline in the late second century; the population of Northwestern Europe did not recover, though the Mediterranean regions did.[46]
The Empire survived the "Crisis of the Third Century", directing its economy successfully towards defense, but survival came at the price of a more centralized and bureaucratic state. Excessive military expenditure, coupled with civil wars due to unstable succession, caused increased taxes to the detriment of the industry.[47] Under Gallienus (Emperor from 253 to 268) the senatorial aristocracy ceased joining the ranks of the senior military commanders. Its typical members lacked interest in military service, and showed incompetence at command.[48][49]
Under Constantine, the cities lost their revenue from local taxes, and under Constantius II (r. 337–361) their endowments of property.[50] This worsened the existing difficulty in keeping the city councils up to strength, and the services provided by the cities were scamped or abandoned.[50] Public building projects had declined since the second century. There is no evidence of state participation in, or support for, restoration and maintenance of temples and shrines. Restorations were funded and accomplished privately, which limited what was done.[12]: 36–39 A further financial abuse was Constantius's habit of granting to his immediate entourage the estates of persons condemned for treason and other capital crimes. This practice reduced future, though not immediate, income; those close to the emperor also gained a strong incentive to encourage his suspicion of conspiracies.[50]
Social crisis
The new supreme rulers disposed of the legal fiction of the early Empire (seeing the emperor as but the first among equals); emperors from Aurelian (r. 270–275) onwards openly styled themselves as dominus et deus, "lord and god", titles appropriate for a master-slave relationship.[51] An elaborate court ceremonial developed, and obsequious flattery became the order of the day. Under Diocletian, the flow of direct requests to the emperor rapidly reduced, and soon ceased altogether. No other form of direct access replaced them, and the emperor received only information filtered through his courtiers.[52] However, as Sabine MacCormack described, the court culture that developed with Diocletian was still subject to pressure from below. Imperial proclamations were used to stress the traditional limitations of the imperial office, while imperial ceremonies "left room for consensus and popular participation".[53]
Official cruelty, supporting extortion and corruption, may also have become more commonplace;[54] one example being Constantine’s law that slaves who betrayed their mistress's confidential remarks should have molten lead poured down their throats.[55][56] While the scale, complexity, and violence of government were unmatched,[57] the emperors lost control over their whole realm insofar as that control came increasingly to be wielded by anyone who paid for it.[58] Meanwhile, the richest senatorial families, immune from most taxation, engrossed more and more of the available wealth and income[59][60] while also becoming divorced from any tradition of military excellence. One scholar identifies a great increase in the purchasing power of gold, two and a half fold from 274 to the later fourth century. This may be an index of growing economic inequality between a gold-rich elite and a cash-poor peasantry.[61] "Formerly, says Ammianus, Rome was saved by her austerity, by solidarity between rich and poor, by contempt for death; now she is undone by her luxury and greed (Amm. xxxi. 5. 14 and xxii. 4.). Salvianus backs up Ammianus by affirming that greed (avaritia) is a vice common to nearly all Romans".[62] However, Lucius Calpurnius Piso Frugi (consul 133 BC) had already dated the start of Rome's moral decline to 154 BCE.[63]
Within the late Roman military, many recruits and even officers had barbarian origins. Soldiers are recorded as using possibly-barbarian rituals, such as elevating a claimant on shields.[64] Some scholars have seen this as an indication of weakness. Others disagree, seeing neither barbarian recruits nor new rituals as causing any problem with the effectiveness or loyalty of the army, at least while that army was effectively led, disciplined, trained, paid, and supplied by officers who identified as Roman.[65]
Geography
A. H. M. Jones has pointed out that the earlier scholarly views are Western.[66] Most of the weaknesses discussed by scholars were "common to both halves of the empire", with Christianity even more prevalent in the East than the West. Religious disputes were bitter, bureaucracy corrupt and extortionate, it had a caste system, and land fell out of use in the East just as it had in the West.[67] Yet the East stood its ground in the fifth century, fought back in the sixth, and even recovered some territory in the seventh. The East had only one apparent advantage: geography. It was less vulnerable, strategically, than the West. The narrowest sea crossing to its core territories was protected from the northern barbarians by the fortifications and the sea and land forces of Constantinople, while the European frontier from the mouth of the Rhine to that of the Danube is some 2000 kilometres great-circle distance and could be crossed with much less difficulty.[68] "The devastations of the barbarians impoverished and depopulated the [Western] frontier provinces, and their unceasing pressure imposed on the empire a burden of defense which overstrained its administrative machinery and its economic resources. ... [playing] a major part in the fall of the West".[67]
Height of power, systematic weaknesses as direct causes
The Roman Empire reached its greatest geographical extent under Trajan (r. 98–117), who ruled a prosperous state that stretched from Armenia to the Atlantic Ocean. The Empire had large numbers of trained, supplied, and disciplined soldiers, drawn from a growing population. It had a comprehensive civil administration based in thriving cities with effective control over public finances. The literate elite considered theirs to be the only worthwhile form of civilization, giving the Empire ideological legitimacy and a cultural unity based on comprehensive familiarity with Greek and Roman literature and rhetoric. The Empire's power allowed it to maintain extreme differences of wealth and status.[69] Its wide-ranging trade networks permitted even modest households to use goods made by professionals far away.[70]
The empire had both strength and resilience. Its financial system allowed it to raise significant taxes which, despite endemic corruption, supported a large regular army with logistics and training. The cursus honorum, a standardized series of military and civil posts organised for ambitious aristocratic men, ensured that powerful noblemen had the opportunity to become familiar with military and civil command and administration. At a lower level within the army, connecting the aristocrats at the top with the private soldiers, a large number of centurions were well-rewarded, literate, and responsible for training, discipline, administration, and leadership in battle.[71] City governments with their own properties and revenues functioned effectively at a local level; membership of city councils involved lucrative opportunities for independent decision-making, and, despite its obligations, became seen as a privilege. Under a series of emperors who each adopted a mature and capable successor, the Empire did not require civil wars to regulate the imperial succession. Requests could be submitted directly to the better emperors, and the answers had the force of law, putting the imperial power directly in touch with even humble subjects.[72] The cults of polytheist religion were hugely varied, but none claimed that theirs was the only truth. Their followers displayed mutual tolerance, producing a polyphonous religious harmony.[73] Religious strife was rare after the suppression of the Bar Kokhba revolt in 136, after which the devastated Judaea ceased to be a major centre for Jewish unrest.
Nevertheless, it remained a culture based on an early subsistence economy, with only ineffective inklings of a germ theory of disease. Despite its aqueducts, the water supply did not allow good hygiene. Sewage was disposed of on the streets, in open drains, or by scavenging animals. Even in the Roman Climatic Optimum, local harvest failures causing famines were always a possibility.[1][page needed] And even in good times, Roman women needed to have, on average, six children each in order to maintain the population.[74] Good nourishment and bodily cleanliness were privileges of the rich, advertised by their firm tread, healthy skin color, and lack of the "dull smell of the underbathed".[75] Infant mortality was very high, and diarrhoeal diseases were a major cause of death. Malaria was endemic in many areas, notably in the city of Rome itself, possibly encouraged by the enthusiasm of rich Romans for water features in their gardens.[1][page needed]
Rise of Christianity, possible decline of the armed forces
In 313, Constantine the Great declared official toleration of Christianity. This was followed over the ensuing decades by the search for a definition of Christian orthodoxy all could agree upon. Creeds were developed, but Christianity has never agreed upon an official version of its Bible or its doctrine; instead it has had many different manuscript traditions.[76] Christianity's disputes may have effected decline. Official and private action was taken against heterodox Christians (heretics) from the fourth century up to the modern era. Limited action against pagans, who were mostly ignored, was based on the contempt that accompanied Christianity's sense of triumph after Constantine.[77] Christianity opposed sacrifice and magic, and Christian emperors made laws that favored Christianity. Constantine's successors generally continued this approach, and by the end of the fourth century, Christianity had become the religion of any ambitious civil official.
The wealth of the Christian Church increased dramatically in the fifth century. Immense resources, both public and private, were used for building churches, storage barns for the grain used for charity, new hospitals for the poor, and in support of those in religious life without other income.[78] Bishops in wealthy cities were thus able to offer patronage in the long-established manner of Roman aristocrats. Ammianus described some who "enriched from the offerings of matrons, ride seated in carriages, wearing clothing chosen with care, and serve banquets so lavish that their entertainments outdo the tables of kings".
But the move to Christianity probably had no significant effects on public finances.[44] The large temple complexes, with professional full-time priests, festivals, and large numbers of sacrifices (which became free food for the masses), had also been expensive to maintain. They had already been negatively impacted by the empire's financial struggles in the third century.[79]: 353 [80]: 60 The numbers of clergy, monks, and nuns increased to perhaps half the size of the actual army, and they have been considered as a drain on limited manpower.[81][82]
The numbers and effectiveness of the regular soldiers may have declined during the fourth century. Payrolls were inflated, so that pay could be diverted and exemptions from duty sold. The soldiers' opportunities for personal extortion were multiplied by residence in cities, while their effectiveness was reduced by concentration on extortion instead of military exercises.[83] However, extortion, gross corruption, and occasional ineffectiveness[84] were not new to the Roman army. There is no consensus whether its effectiveness significantly declined before 376.[85] Ammianus Marcellinus, himself a professional soldier, repeats longstanding observations about the superiority of contemporary Roman armies being due to training and discipline, not to individual size or strength.[86] He also accuses Valentinian I of being the first emperor to increase the arrogance of the military, raising their rank and power to excess, severely punishing the minor crimes of the common soldiers, while sparing those of higher rank who felt able to commit shameful and monstrous crimes.[87] Despite a possible decrease in the Empire's ability to assemble and supply large armies,[88] Rome maintained an aggressive and potent stance against perceived threats almost to the end of the fourth century.[89]
313–376: Civil and foreign wars
Constantine settled Franks on the lower left bank of the Rhine. Their communities required a line of fortifications to keep them in check, indicating that Rome had lost almost all local control.[54] Under Constantius, bandits came to dominate areas such as Isauria, which were well within the empire.[90] The tribes of Germania also became more populous and more threatening.[44] In Gaul, which did not really recover from the invasions of the third century, there was widespread insecurity and economic decline in the 300s,[44] perhaps worst in Armorica. By 350, after decades of pirate attacks, virtually all villas in Armorica were deserted. Local use of money ceased around 360.[91] Repeated attempts to economize on military expenditure included billeting troops in cities, where they could less easily be kept under military discipline and could more easily extort from civilians.[92] Except in the rare case of a determined and incorruptible general, these troops proved ineffective in action and dangerous to civilians.[93] Frontier troops were often given land rather than pay. As they farmed for themselves, their direct costs diminished, but so did their effectiveness, and their pay gave much less stimulus to the frontier economy.[94] However, except for the provinces along the lower Rhine, the agricultural economy was generally doing well.[95]
On January 18 350, the imperial magister officiorum gave a banquet in Augustodunum while his master, Western Emperor Constans, was away hunting. During the feast Magnus Magnentius, commander of the imperial household troops, appeared in an imperial purple toga and announced himself to be the new Emperor. Constans was soon murdered and Magnentius took over most of his western domains. He made peace overtures to Constantius in the East, but these failed. In the ensuing bloody civil war Magnentius marched against Constantius with as many troops as he could mobilize, stripping the Rhine frontier of its most effective troops. Magnentius died and so did many of his men. Meanwhile, Constantius sent messages to the German tribes east of the Rhine, inviting them to attack Gaul, which they did. In the next few years a strip some 40 miles wide to the west of the Rhine was occupied by the Germans, and a further 120 miles into Gaul the surviving population and garrisons had fled.[96]

Julian (r. 360–363) won victories against Germans who had invaded Gaul. He launched a drive against official corruption, which allowed the tax demands in Gaul to be reduced to one-third of their previous amount, while all government requirements were still met.[97] In civil legislation, Julian was notable for his pro-pagan policies. Julian lifted the ban on sacrifices, restored and reopened temples, and dismantled the privileged tax status and revenue concessions of the Christians. He gave generous tax remissions to the cities which he favored, and disfavor to those who remained Christian.[98]: 62–65 [99] Julian ordered toleration of varieties of Christianity banned as heretical by Constantius;[98] possibly, he would not have been able to persecute effectively such a large and powerful group as Christians had now become.: 62 [100]: 345–346 [101]: 62
Julian prepared for civil war against Constantius, who again encouraged the Germans to attack Gaul. However Julian's campaigns had been effective and only one small Alemannic raid, speedily dealt with by Julian, resulted.[96] Constantius died before any serious fighting and Julian was acknowledged as master of the entire Empire. He launched an expensive campaign against the Sasanian Persians,.[50] He succeeded in marching to the Sassanid capital of Ctesiphon, but, at the suggestion of a Persian agent, burned his boats and supplies to show resolve in continuing operations. The Sassanids then burned crops so the Roman army had no food. Finding himself cut off without supplies in enemy territory, Julian began a land retreat, and during the Battle of Samarra, he was mortally wounded.[102][98]: 74
Julian's successor Jovian, acclaimed by a demoralized army, began his brief reign (363–364) while trapped in Mesopotamia without supplies. To purchase safe passage home, he had to concede areas of northern Mesopotamia, including the strategically important fortress of Nisibis. This fortress had been Roman since before the Peace of Nisibis in 299.[102]
The brothers Valens (r. 364–378) and Valentinian I (r. 364–375) energetically tackled the threats of barbarian attacks on all the Western frontiers.[103] They also tried to alleviate the burdens of taxation, which had risen continuously over the previous forty years; Valens in the East reduced the tax demand by half in his fourth year.[104] Both of them were Christians, and re-confiscated the temple lands which Julian had restored. But they were generally tolerant of other beliefs. Valentinian in the West refused to intervene in Christian controversy. In the East, Valens had to deal with Christians who did not conform to his ideas of orthodoxy, and persecution formed part of his response. He tolerated paganism, even keeping some of Julian's associates in their trusted positions. He confirmed the rights and privileges of the pagan priests, and confirmed the right of pagans to be the exclusive caretakers of their temples.[105]
Valentinian died of an apoplexy while shouting at envoys of Germanic leaders. His successors in the West were children, his sons Gratian (r. 375–383) and Valentinian II (r. 375–392). Gratian, "alien from the art of government both by temperament and by training", removed the Altar of Victory from the Senate House. He also rejected the pagan title of Pontifex Maximus.[106]
376–395: Invasions, civil wars, and religious discord
Battle of Adrianople
In 376, the East faced an enormous barbarian influx across the Danube, mostly Goths, who were fleeing from the Huns. They were exploited by corrupt officials rather than effectively relieved and resettled, and they took up arms and were joined by more Goths and some Alans and Huns. Valens was in Asia with his main field army preparing for an assault on the Sasanian Empire. Redirection of the army and its logistic support would have required time, and Gratian's armies were distracted by Germanic invasions across the Rhine. In 378, Valens attacked the invaders with the Eastern field army, now perhaps 20,000 men, probably much fewer than the forces that Julian had led into Mesopotamia a little over a decade before, and possibly only 10% of the soldiers nominally available in the Danube provinces.[107] In the Battle of Adrianople (9 August 378), Valens lost much of that army and his own life. All of the Balkan provinces were thus exposed to raiding, without effective response from the remaining garrisons who were "more easily slaughtered than sheep".[107] Cities were able to hold their own defensive walls against barbarians who had no siege equipment, therefore the cities generally remained intact, although the countryside suffered.[108]
Partial recovery in the Balkans, internal corruption and financial desperation
Gratian appointed a new Augustus, a proven general from Hispania called Theodosius. During the next four years, he partially re-established the Roman position in the East.[109][110] These campaigns depended on effective imperial coordination and mutual trust—between 379 and 380, Theodosius controlled not only the Eastern empire, but also, by agreement, the diocese of Illyricum.[111] Theodosius was unable to recruit enough Roman troops, relying on barbarian warbands without Roman military discipline or loyalty. (In contrast, during the Cimbrian War, the Roman Republic, controlling a smaller area than the western Empire, had been able to reconstitute large regular armies of citizens after greater defeats than Adrianople. That war had ended with the near-extermination of the invading barbarian supergroups, each supposed to have more than 100,000 warriors.[112])
The final Gothic settlement was acclaimed with relief,[110] even the official panegyrist admitting that these Goths could not be expelled or exterminated, nor reduced to unfree status.[113] Instead they were either recruited into the imperial forces, or settled in the devastated provinces along the south bank of the Danube, where the regular garrisons were never fully re-established.[114] In some later accounts, and widely in recent work, this is regarded as a treaty settlement, the first time that barbarians were given a home within the Empire, in which they retained their political and military cohesion.[115] No formal treaty is recorded, nor details of whatever agreement was actually made. When the Goths are next mentioned in Roman records, they have different leaders and are soldiers of a sort.[116] In 391, Alaric, a Gothic leader, rebelled against Roman control. Goths attacked the emperor himself, but within a year Alaric was accepted as a leader of Theodosius's Gothic troops and this rebellion was over.[117]
Theodosius's financial position must have been difficult, since he had to pay for expensive campaigning from a reduced tax base. The business of subduing barbarian warbands also demanded substantial gifts of precious metal.[118] At least one extra levy provoked desperation and rioting, in which the emperor's statues were destroyed.[119] Nevertheless, he is represented as financially generous as emperor, though frugal in his personal life.[120] By the end of the 380s, Theodosius and the court were in Mediolanum, and northern Italy was experiencing a period of prosperity for the great landowners who took advantage of the court's need for food, "turning agrarian produce into gold", while repressing and misusing the poor who grew it and brought it in.[121] Paulinus the Deacon, notary of Ambrose the bishop of Milan, described these men as creating a court where "everything was up for sale".[122] Ambrose himself preached a series of sermons aimed at his wealthy constituents, asserting that avarice leads to a breakdown in society.[123]
For centuries, Theodosius was regarded as a champion of Christian orthodoxy who decisively stamped out paganism. His predecessors Constantine, Constantius II, and Valens had all been semi-Arians, whereas Theodosius supported Nicene Christianity which eventually became the orthodox version of Christology for most later Christian churches—his Edict of Thessalonica described Arian Christians as "foolish madmen". Therefore, as far as Ambrose and the Christian literary tradition that followed him were concerned, Theodosius deserved most of the credit for the final triumph of Christianity.[124] Modern scholars see this as a Christian interpretation of history.[125][126][127][128] Theodosius did not stamp out paganism, which continued into the seventh century.[126][129][128][a]
Civil wars
Theodosius had to face a powerful usurper in the West; Magnus Maximus declared himself Emperor in 383, stripped troops from the outlying regions of Roman Britain (probably replacing some with federate chieftains and their war-bands) and invaded Gaul. His troops killed Gratian and he was accepted as Augustus in the Gallic provinces, where he was responsible for the first official executions of Christian heretics.[136] To compensate the Western court for the loss of Gaul, Hispania, and Britannia, Theodosius ceded the diocese of Dacia and the diocese of Macedonia to their control. In 387 Maximus invaded Italy, forcing Valentinian II to flee to the East, where he accepted Nicene Christianity. Maximus boasted to Ambrose of the numbers of barbarians in his forces, and hordes of Goths, Huns, and Alans followed Theodosius.[137] Maximus negotiated with Theodosius for acceptance as Augustus of the West, but Theodosius refused, gathered his armies, and counterattacked, winning the civil war in 388. There were heavy troop losses on both sides of the conflict. Later Welsh legend has Maximus's defeated troops resettled in Armorica, instead of returning to Britannia, and by 400, Armorica was controlled by Bagaudae rather than by imperial authority.[138]
Theodosius restored Valentinian II, still a very young man, as Augustus in the West. He also appointed Arbogast, a pagan general of Frankish origin, as Valentinian's commander-in-chief and guardian. Valentinian quarreled in public with Arbogast, failed to assert any authority, and died, either by suicide or by murder, at the age of 21. Arbogast and Theodosius failed to come to terms and Arbogast nominated an imperial official, Eugenius (r. 392–394), as emperor in the West. Eugenius made some modest attempts to win pagan support,[119] and with Arbogast led a large army to fight another destructive civil war. They were defeated and killed at the Battle of the Frigidus, which was attended by further heavy losses; especially among the Gothic federates of Theodosius. The north-eastern approaches to Italy were never effectively garrisoned again.[139]
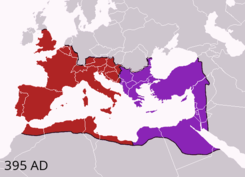
Theodosius died a few months later in early 395, leaving his young sons Honorius (r. 393–423) and Arcadius (r. 383–408) as emperors. In the immediate aftermath of Theodosius's death, the magister militum Stilicho, married to Theodosius's niece, asserted himself in the West as the guardian of Honorius and commander of the remains of the defeated Western army. He also claimed control over Arcadius in Constantinople, but Rufinus, magister officiorum on the spot, had already established his own power there. Henceforward the Empire was not under the control of one man, until much of the West had been permanently lost.[140] Neither Honorius nor Arcadius ever displayed any ability either as rulers or as generals, and both lived as the puppet rulers of their courts.[141] Stilicho tried to reunite the Eastern and Western courts under his personal control, but in doing so achieved only the continued hostility of all of Arcadius's successive supreme ministers.
Military, financial, and political ineffectiveness: the process of failure
The ineffectiveness of Roman military responses during Stilicho's rule and afterwards has been described as "shocking".[142] There is little evidence of indigenous field forces or of adequate training, discipline, pay, or supply for the barbarians who formed most of the available troops. Local defence was occasionally effective, but was often associated with withdrawal from central control and taxes. In many areas, barbarians under Roman authority attacked culturally-Roman "Bagaudae".[143][144][145] The fifth-century Western emperors, with brief exceptions, were individuals incapable of ruling effectively or even of controlling their own courts.[141] Those exceptions were responsible for brief, but remarkable resurgences of Roman power.
Corruption, in this context the diversion of finance from the needs of the army, may have contributed greatly to the Fall. The rich senatorial aristocrats in Rome itself became increasingly influential during the fifth century; they supported armed strength in theory, but did not wish to pay for it or to offer their own workers as army recruits.[146][147] They did, however, pass large amounts of money to the Christian Church.[148] At a local level, from the early fourth century, the town councils lost their property and their power, which often became concentrated in the hands of a few local despots beyond the reach of the law.[149]
395–406: Stilicho
Without an authoritative ruler, the Balkan provinces fell rapidly into disorder. Alaric was disappointed in his hopes for promotion to magister militum after the battle of the Frigidus. He again led Gothic tribesmen in arms and established himself as an independent power, burning the countryside as far as the walls of Constantinople.[150] Alaric's ambitions for long-term Roman office were never quite acceptable to the Roman imperial courts, and his men could never settle long enough to farm in any one area. They showed no inclination to leave the Empire and face the Huns from whom they had fled in 376. Meanwhile, the Huns were still stirring up further migrations, with migrating tribes often attacking the Roman Empire in turn. Alaric's group was never destroyed nor expelled from the Empire, nor acculturated under effective Roman domination.[143][144][151]
Stilicho's attempts to unify the Empire, revolts, and invasions

Alaric took his Gothic army on what Stilicho's propagandist Claudian described as a "pillaging campaign" that began first in the East.[152] Alaric's forces made their way along the coast to Athens, where he sought to force a new peace upon the Romans.[152] His march in 396 passed through Thermopylae. Stilicho sailed from Italy to Roman Greece with his remaining mobile forces, posing a clear threat to Rufinus's control of the Eastern empire. The bulk of Rufinus's forces were occupied with Hunnic incursions in Asia Minor and Syria, leaving Thracia undefended. Claudian reports that only Stilicho's attack stemmed the plundering, as he pushed Alaric's forces north into Epirus.[153] Burns' interpretation is that Alaric and his men had been recruited by Rufinus's Eastern regime, and sent to Thessaly to stave off Stilicho's threat.[139] No battle took place. Zosimus adds that Stilicho's troops destroyed and pillaged too, and let Alaric's men escape with their plunder.[b]
Many of Stilicho's Eastern forces wanted to go home and he had to let them go (though Claudian claims that he did so willingly).[154] Some went to Constantinople under the command of one Gainas, a Goth with a large Gothic following. On arrival, Gainas murdered Rufinus, and was appointed magister militum for Thrace by Eutropius, the new supreme minister and the only eunuch consul of Rome. Eutropius reportedly controlled Arcadius "as if he were a sheep".[b] Stilicho obtained a few more troops from the German frontier and continued to campaign ineffectively against the Eastern empire; again he was successfully opposed by Alaric and his men. During the next year, 397, Eutropius personally led his troops to victory over some Huns who were marauding in Asia Minor. With his position thus strengthened, he declared Stilicho a public enemy, and he established Alaric as magister militum per Illyricum. A poem by Synesius advises the emperor to display manliness and remove a "skin-clad savage" (probably Alaric) from the councils of power and his barbarians from the Roman army. We do not know if Arcadius ever became aware of the existence of this advice, but it had no recorded effect.[155] Synesius, from a province suffering the widespread ravages of a few poor but greedy barbarians, also complained of "the peacetime war, one almost worse than the barbarian war and arising from military indiscipline and the officer's greed."[156]

The magister militum in the Diocese of Africa declared for the East and stopped the supply of grain to Rome.[139] Italy had not fed itself for centuries and could not do so now. In 398, Stilicho sent his last reserves, a few thousand men, to re-take the Diocese of Africa. He strengthened his position further when he married his daughter Maria to Honorius. Throughout this period Stilicho, and all other generals, were desperately short of recruits and supplies for them.[157] In 400, Stilicho was charged to press into service any "laetus, Alamannus, Sarmatian, vagrant, son of a veteran" or any other person liable to serve.[158] He had reached the bottom of his recruitment pool.[159] Though personally not corrupt, he was very active in confiscating assets;[b] the financial and administrative machine was not producing enough support for the army.
In 399, Tribigild's rebellion in Asia Minor allowed Gainas to accumulate a significant army (mostly Goths), become supreme in the Eastern court, and execute Eutropius.[160] He now felt that he could dispense with Alaric's services and he nominally transferred Alaric's province to the West. This administrative change removed Alaric's Roman rank and his entitlement to legal provisioning for his men, leaving his army—the only significant force in the ravaged Balkans—as a problem for Stilicho.[161] In 400, the citizens of Constantinople revolted against Gainas and massacred as many of his people, soldiers and their families, as they could catch. Some Goths at least built rafts and tried to cross the strip of sea that separates Asia from Europe; the Roman navy slaughtered them.[162] By the beginning of 401, Gainas' head rode a pike through Constantinople while another Gothic general became consul.[163] Meanwhile, groups of Huns started a series of attacks across the Danube, and the Isaurians marauded far and wide in Anatolia.[164]
In 401 Stilicho travelled over the Alps to Raetia, to scrape up further troops.[165] He left the Rhine defended only by the "dread" of Roman retaliation, rather than by adequate forces able to take the field.[165] Early in spring, Alaric, probably desperate,[166] invaded Italy, and he drove Honorius westward from Mediolanum, besieging him in Hasta Pompeia in Liguria. Stilicho returned as soon as the passes had cleared, meeting Alaric in two battles (near Pollentia and Verona) without decisive results. The Goths, weakened, were allowed to retreat back to Illyricum where the Western court again gave Alaric office, though only as comes and only over Dalmatia and Pannonia Secunda rather than the whole of Illyricum.[167] Stilicho probably supposed that this pact would allow him to put Italian government into order and recruit fresh troops.[157] He may also have planned with Alaric's help to relaunch his attempts to gain control over the Eastern court.[168]

HONORI
MARIA
SERHNA
VIVATIS
STELICHO.
The letters form a Christogram.
However, in 405, Stilicho was distracted by a fresh invasion of Northern Italy. Another group of Goths fleeing the Huns, led by one Radagaisus, started the War of Radagaisus and devastated the north of Italy for six months before Stilicho could muster enough forces to take the field against them. Stilicho recalled troops from Britannia, and the depth of the crisis was shown when he urged all Roman soldiers to allow their personal slaves to fight beside them.[168] His forces, including Huns and Alans, may in the end have totalled rather less than 15,000 men.[169] Radagaisus was defeated and executed, while 12,000 prisoners from the defeated horde were drafted into Stilicho's service.[169] Stilicho continued negotiations with Alaric; Flavius Aetius, son of one of Stilicho's major supporters, was sent as a hostage to Alaric in 405.
In 406, Stilicho heard of new invaders and rebels who had appeared in the northern provinces. He insisted on making peace with Alaric, probably on the basis that Alaric would prepare to move either against the Eastern court or against the rebels in Gaul. The Senate deeply resented peace with Alaric.
In 407, Alaric marched into Noricum and demanded a large payment for his expensive efforts in Stilicho's interests. The senate, "inspired by the courage, rather than the wisdom, of their predecessors,"[170] preferred war. One senator famously declaimed Non est ista pax, sed pactio servitutis ("This is not peace, but a pact of servitude").[171] Stilicho paid Alaric four thousand pounds of gold nevertheless.[172] Stilicho sent Sarus, a Gothic general, over the Alps to face the usurper Constantine III. Sarus lost this campaign and barely escaped, having to leave his baggage to the bandits who now infested the Alpine passes.[172]
The empress Maria, daughter of Stilicho, died in 407 or early 408 and her sister Aemilia Materna Thermantia married Honorius. In the East, Arcadius died on 1 May 408 and was replaced by his son Theodosius II. Stilicho seems to have planned to march to Constantinople, and to install there a regime loyal to himself.[173] He may also have intended to give Alaric a senior official position, and to send him against the rebels in Gaul. Before he could do so, while he was away at Ticinum at the head of a small detachment, a bloody coup d'état against his supporters took place at Honorius's court. It was led by Stilicho's own creature, one Olympius.[174]
408–410: End of effective regular field armies, starvation in Italy, sack of Rome
Stilicho's fall and Alaric's reaction
Stilicho had news of the coup at Bononia, where he was probably waiting for Alaric.[175] His army of barbarian troops, including a guard of Huns and many Goths under Sarus, discussed attacking the forces of the coup, but Stilicho prevented them when he heard that the Emperor had not been harmed. Sarus's Gothic troops then massacred the Hun contingent in their sleep, and Stilicho withdrew from the quarreling remains of his army to Ravenna. He ordered that his former soldiers should not be admitted into the cities in which their families were billeted. Stilicho was forced to flee to a church for sanctuary, promised his life, and killed.[176]
Alaric was again declared an enemy of the Emperor. The conspiracy then massacred the families of the federate troops (as presumed supporters of Stilicho, although they had probably rebelled against him), and the troops defected en masse to Alaric.[177] The conspirators seem to have let their main army disintegrate,[178] and had no policy except hunting down anyone they regarded as supporters of Stilicho.[179] Italy was left without effective indigenous defence forces thereafter.[142] Heraclianus, a co-conspirator of Olympius, became governor of the Diocese of Africa. He consequently controlled the source of most of Italy's grain, and he supplied food only in the interests of Honorius's regime.[180]
As a declared 'enemy of the Emperor', Alaric was denied the legitimacy that he needed to collect taxes and hold cities without large garrisons, which he could not afford to detach. He again offered to move his men, this time to Pannonia, in exchange for a modest sum of money and the modest title of Comes. He was refused, as Olympius's clique still regarded him as a supporter of Stilicho.[181] He moved into Italy, probably using the route and supplies arranged for him by Stilicho,[175] bypassing the imperial court in Ravenna which was protected by widespread marshland and had a port, and he menaced the city of Rome itself. In 407, there was no equivalent of the determined response to the catastrophic Battle of Cannae in 216 BCE, when the entire Roman population, even slaves, had been mobilized to resist the enemy.[182]
Alaric's military operations centred on the port of Rome, through which Rome's grain supply had to pass. Alaric's first siege of Rome in 408 caused dreadful famine within the walls. It was ended by a payment that, though large, was less than one of the richest senators could have produced.[183] The super-rich aristocrats made little contribution; pagan temples were stripped of ornaments to make up the total. With promises of freedom, Alaric also recruited many of the slaves in Rome.[184]
Alaric withdrew to Tuscany and recruited more slaves.[184] Athaulf, a Goth nominally in Roman service and brother-in-law to Alaric, marched through Italy to join Alaric. A small force of Hunnic mercenaries led by Olympius killed some of Athaulf's men on this journey. Sarus was an enemy of Athaulf, and on Athaulf's arrival went back into imperial service.[185]
Alaric besieges Rome
In 409 Olympius fell to further intrigue, having his ears cut off before he was beaten to death. Alaric tried again to negotiate with Honorius, but his demands (now even more moderate, only frontier land and food[186]) were inflated by the messenger and Honorius responded with insults, which were reported verbatim to Alaric.[187] He broke off negotiations and the standoff continued. Honorius's court made overtures to the usurper Constantine III in Gaul and arranged to bring Hunnic forces into Italy, Alaric ravaged Italy outside the fortified cities (which he could not garrison), and the Romans refused open battle (for which they had inadequate forces).[188] Late in the year, Alaric sent bishops to express his readiness to leave Italy if Honorius would only grant his people a supply of grain. Honorius, sensing weakness, flatly refused.[189]
Alaric moved to Rome and captured Galla Placidia, sister of Honorius. The Senate in Rome, despite its loathing for Alaric, was now desperate enough to give him almost anything he wanted. They had no food to offer, but they tried to give him imperial legitimacy; with the Senate's acquiescence, he elevated Priscus Attalus as his puppet emperor, and he marched on Ravenna. Honorius was planning to flee to Constantinople when a reinforcing army of 4,000 soldiers from the East disembarked in Ravenna.[190] These garrisoned the walls and Honorius held on. He had Constantine's principal court supporter executed and Constantine abandoned plans to march to Honorius's defence.[191] Attalus failed to establish his control over the Diocese of Africa, and no grain arrived in Rome where the famine became even more frightful.[192] Jerome reports cannibalism within the walls.[193] Attalus brought Alaric no real advantage, failing also to come to any useful agreement with Honorius (to whom Attalus offered mutilation, humiliation, and exile). Indeed, Attalus's claim was a marker of threat to Honorius, and Alaric dethroned him after a few months.[194]
In 410 Alaric took Rome by starvation, and sacked it for three days. He invited its remaining barbarian slaves to join him, which many did. There was relatively little destruction. In some Christian holy places, Alaric's men even refrained from wanton violence, and Jerome tells the story of a virgin who was escorted to a church by the invaders, after they had given her mother a beating from which she later died. The city of Rome was the seat of the richest senatorial noble families and the centre of their cultural patronage. To pagans it was the sacred origin of the empire, and to Christians the seat of the heir of Saint Peter. At the time, this position was held by Pope Innocent I, the most authoritative bishop of the West. Rome had not fallen to an enemy since the Battle of the Allia, over eight centuries before. Refugees spread the news and their stories throughout the Empire, and the meaning of the fall was debated with religious fervour. Both Christians and pagans wrote embittered tracts, blaming paganism or Christianity respectively for the loss of Rome's supernatural protection and all attacking Stilicho's earthly failures.[195][b] Some Christian responses anticipated the imminence of the Last Judgment. Augustine of Hippo in his book "City of God" ultimately rejected the pagan and Christian idea that religion should have worldly benefits. He instead developed the doctrine that the City of God in heaven, undamaged by mundane disasters, was the true objective of Christians.[196] More practically, Honorius was briefly persuaded to set aside the laws forbidding pagans to be military officers, so that one Generidus could re-establish Roman control in Dalmatia. Generidus did this with unusual effectiveness. His techniques were remarkable for this period, in that they included training his troops, disciplining them, and giving them appropriate supplies even if he had to use his own money.[197] The penal laws were reinstated no later than 25 August 410, meaning that the overall trend of repression of paganism continued.[198]

Procopius mentions a story in which Honorius, on hearing the news that Rome had "perished", was shocked. The emperor thought that the news was in reference to his favorite chicken, which he had named "Roma". On hearing that Rome itself had fallen, he breathed a sigh of relief:
At that time they say that the Emperor Honorius in Ravenna received the message from one of the eunuchs, evidently a keeper of the poultry, that Roma had perished. And he cried out and said, "And yet it has just eaten from my hands!" For he had a very large cockerel, Roma by name; and the eunuch comprehending his words said that it was the city of Roma which had perished at the hands of Alaric, and the emperor with a sigh of relief answered quickly: "But I thought that my fowl Roma had perished." So great, they say, was the folly with which this emperor was possessed.
— Procopius, The Vandalic War (De Bellis III.2.25–26)
The Goths move out of Italy
Alaric then moved south, intending to sail to Africa. His ships were wrecked in a storm, and he shortly died of fever. His successor Athaulf, still regarded as an usurper and given only occasional and short-term grants of supplies, moved north into the turmoil of Gaul. In this region, there was some prospect of food. His supergroup of barbarians are called the Visigoths in modern works: they may now have been developing their own sense of identity.[199]
405–418: In the Gallic provinces; barbarians and usurpers, loss of Britannia, partial loss of Hispania and Gaul
The Crossing of the Rhine in 405/6 brought unmanageable numbers of Germanic and Alan barbarians (perhaps some 30,000 warriors, 100,000 people[200]) into Gaul. They may have been trying to get away from the Huns, who about this time advanced to occupy the Great Hungarian Plain.[201] For the next few years these barbarian tribes wandered in search of food and employment, while Roman forces fought each other in the name of Honorius and a number of competing claimants to the imperial throne.[202]
The remaining troops in Britannia elevated a succession of imperial usurpers. The last, Constantine III, raised an army from the remaining troops in Britannia, invaded Gaul and defeated forces loyal to Honorius led by Sarus. Constantine's power reached its peak in 409 when he controlled Gaul and beyond, he was joint consul with Honorius[203] and his magister militum Gerontius defeated the last Roman force to try to hold the borders of Hispania. It was led by relatives of Honorius; Constantine executed them. Gerontius went to Hispania, where he may have settled the Sueves and the Asding Vandals. Gerontius then fell out with his master and elevated one Maximus as his own puppet emperor. He defeated Constantine and was besieging him in Arelate when Honorius's general Constantius arrived from Italy with an army (possibly, composed mainly of Hun mercenaries).[204] Gerontius's troops deserted him, and he committed suicide. Constantius continued the siege, defeating a relieving army. Constantine surrendered in 411 with a promise that his life would be spared, and was then executed.[205]
In 410, the Roman civitates of Britannia rebelled against Constantine and evicted his officials. They asked for help from Honorius, who replied that they should look to their own defence. While the British may have regarded themselves as Roman for several generations, and British armies may at times have fought in Gaul, no central Roman government is known to have appointed officials in Britannia thereafter.[206] The supply of coinage to the Diocese of Britannia ceases with Honorius.[207]
In 411, Jovinus rebelled and took over Constantine's remaining troops on the Rhine. He relied on the support of Burgundians and Alans, to whom he offered supplies and land. In 413, Jovinus also recruited Sarus. Athaulf destroyed their regime in the name of Honorius, afterwards both Jovinus and Sarus were executed. The Burgundians were settled on the left bank of the Rhine. Athaulf then operated in the south of Gaul, sometimes with short-term supplies from the Romans.[208] All usurpers had been defeated, but large barbarian groups remained un-subdued in both Gaul and Hispania.[206] The imperial government was quick to restore the Rhine frontier. The invading tribes of 407 moved into Hispania at the end of 409; the Visigoths left Italy at the beginning of 412 and settled themselves around Narbo.
Heraclianus was still in command in the diocese of Africa. He was the last member of the clique which had overthrown Stilicho to retain power. In 413 he led an invasion of Italy, and lost to a subordinate of Constantius. He then fled back to Africa, where he was murdered by Constantius's agents.[208]
In January 414 Roman naval forces blockaded Athaulf in Narbo, where he married Galla Placidia. The choir at the wedding included Attalus, a puppet emperor without revenues or soldiers.[209] Athaulf famously declared that he had abandoned his intention to set up a Gothic empire, because of the irredeemable barbarity of his followers, and instead he sought to restore the Roman Empire.[210][194] He handed Attalus over to Honorius's regime for mutilation, humiliation, and exile. He also abandoned Attalus's supporters.[211] One of them, Paulinus Pellaeus, recorded that the Goths considered themselves merciful because they allowed him and his household to leave destitute, but alive, without being raped.[209] Athaulf moved out of Gaul, to Barcelona where his infant son by Galla Placidia was buried, and where he was assassinated by one of his household retainers, possibly a former follower of Sarus.[212][213] His ultimate successor Wallia had no agreement with the Romans; his people had to plunder in Hispania for food.[214]
Settlement of 418; barbarians within the empire

In 416 Wallia reached agreement with Constantius; he sent Galla Placidia back to Honorius and received provisions, six hundred thousand modii of wheat.[215] From 416 to 418, Wallia's Goths campaigned in Hispania on Constantius's behalf, exterminating the Siling Vandals in Baetica and reducing the Alans to the point where the survivors sought the protection of the king of the Asding Vandals. (After retrenchment they formed another barbarian supergroup, but for the moment they were reduced in numbers and effectively cowed.) In 418, by agreement with Constantius, Wallia's Goths accepted land to farm in Aquitania.[216] Constantius also reinstituted an annual council of the southern Gallic provinces, to meet at Arelate. Although Constantius rebuilt the western field army to some extent, he did so only by replacing half of its units (vanished in the wars since 395) by re-graded barbarians, and by garrison troops removed from the frontier.[217] The Notitia Dignitatum gives a list of the units of the western field army c. 425. It does not give strengths for these units, but A. H. M. Jones used the Notitia to estimate the total strength of the field armies in the West at 113,000 : Gaul, "about" 35,000; Italy, "nearly" 30,000; Britain 3,000; in Spain, 10–11,000, in the diocese of Illyricum 13–14,000, and in the diocese of Africa 23,000.[218]
Constantius had married the princess Galla Placidia (despite her protests) in 417. The couple soon had two children, Honoria and Valentinian III. Constantius was elevated to the position of Augustus in 420. This earned him the hostility of the Eastern court, which had not agreed to his elevation.[219] Nevertheless, Constantius had achieved an unassailable position at the Western court, in the imperial family, and as the able commander-in-chief of a partially restored army.[220][221]
This settlement represented a real success for the Empire - a poem by Rutilius Namatianus celebrates his voyage back to Gaul in 417 and his confidence in a restoration of prosperity. But it marked huge losses of territory and of revenue; Rutilius travelled by ship past the ruined bridges and countryside of Tuscany, and in the west the river Loire had become the effective northern boundary of Roman Gaul.[222] In the east of Gaul the Franks controlled large areas; the effective line of Roman control until 455 ran from north of Cologne (lost to the Ripuarian Franks in 459) to Boulogne. The Italian areas which had been compelled to support the Goths had most of their taxes remitted for several years.[223][224] Even in southern Gaul and Hispania large barbarian groups remained, with thousands of warriors, in their own non-Roman military and social systems. Some occasionally acknowledged a degree of Roman political control, but without the local application of Roman leadership and military power they and their individual subgroups pursued their own interests.[225]
421–433: Renewed dissension after the death of Constantius, partial loss of the Diocese of Africa
Constantius died in 421, after only seven months as Augustus. He had been careful to make sure that there was no successor in waiting, and his own children were far too young to take his place.[220] Honorius was unable to control his own court, and the death of Constantius initiated more than ten years of instability. Initially Galla Placidia sought Honorius's favour in the hope that her son might ultimately inherit. Other court interests managed to defeat her, and she fled with her children to the Eastern court in 422. Honorius himself died, shortly before his thirty-ninth birthday, in 423. After some months of intrigue, the patrician Castinus installed Joannes as Western Emperor, but the Eastern Roman government proclaimed the child Valentinian III instead, his mother Galla Placidia acting as regent during his minority. Joannes had few troops of his own. He sent Aetius to raise help from the Huns. An Eastern army landed in Italy, captured Joannes, cut his hand off, abused him in public, and killed him with most of his senior officials. Aetius returned, three days after Joannes' death, at the head of a substantial Hunnic army which made him the most powerful general in Italy. After some fighting, Placidia and Aetius came to an agreement; the Huns were paid off and sent home, while Aetius received the position of magister militum.[226]
Galla Placidia, as Augusta, mother of the Emperor, and his guardian until 437, could maintain a dominant position in court, but women in Ancient Rome did not exercise military power, and she could not herself become a general. She tried for some years to avoid reliance on a single dominant military figure, maintaining a balance of power between her three senior officers, Aetius (magister militum in Gaul), Count Boniface (governor in the Diocese of Africa), and Flavius Felix (magister militum praesentalis in Italy).[227] Meanwhile, the Empire deteriorated seriously. Apart from the losses in the Diocese of Africa, Hispania was slipping out of central control and into the hands of local rulers and Suevic bandits. In Gaul the Rhine frontier had collapsed, the Visigoths in Aquitaine may have launched further attacks on Narbo and Arelate, and the Franks, increasingly powerful although disunited, were the major power in the north-east. Armorica was controlled by Bagaudae, local leaders not under the authority of the Empire.[228] Aetius at least campaigned vigorously and mostly victoriously, defeating aggressive Visigoths, Franks, fresh Germanic invaders, Bagaudae in Armorica, and a rebellion in Noricum.[229] Not for the first time in Rome's history, a triumvirate of mutually distrustful rulers proved unstable. In 427, Felix tried to recall Boniface from Africa. Boniface refused, and overcame Felix's invading force. Boniface probably recruited some Vandal troops among others.[230]
In 428 the Vandals and Alans were united under the able, ferocious, and long-lived king Genseric; he moved his entire people to Tarifa near Gibraltar, divided them into 80 groups nominally of 1,000 people (perhaps 20,000 warriors in total),[200] and crossed from Hispania to Mauretania without opposition. They spent a year moving slowly to Numidia, defeating Boniface. He returned to Italy where Aetius had recently had Felix executed. Boniface was promoted to magister militum and earned the enmity of Aetius, who may have been absent in Gaul at the time. In 432 the two met at the Battle of Ravenna, which left Aetius's forces defeated and Boniface mortally wounded. Aetius temporarily retired to his estates, but after an attempt to murder him he raised another Hunnic army (probably by conceding parts of Pannonia to them) and in 433 he returned to Italy, overcoming all rivals. He never threatened to become an Augustus himself and thus maintained the support of the Eastern court, where Valentinian's cousin Theodosius II reigned until 450.[231]
433–454: Ascendancy of Aetius, loss of Carthage
Аэций вел энергичную кампанию, несколько стабилизировав ситуацию в Галлии и Испании. Он во многом полагался на свои силы гуннов . С жестокостью, прославленной столетия спустя в «Песни о Нибелунгах» , гунны вырезали множество бургундцев на Среднем Рейне, восстановив выживших в качестве римских союзников, первого королевства бургундцев . некоторую римскую власть Возможно, это вернуло Триру . [232] Eastern troops reinforced Carthage, temporarily halting the Vandals, who in 435 agreed to limit themselves to Numidia and leave the most fertile parts of North Africa in peace. Aetius concentrated his limited military resources to defeat the Visigoths again, and his diplomacy restored a degree of order to Hispania.[233] Однако его генерал Литорий потерпел сокрушительное поражение от вестготов в Тулузе , и новый свевский король Речиар начал энергичные нападения на то, что осталось от римской Испании. В какой-то момент Рехиар даже вступил в союз с багаудами . Это были римляне, не находившиеся под имперским контролем; на некоторые из причин их восстания можно указать из высказываний римского пленника под предводительством Аттилы , который был счастлив в своей судьбе и живо описывал «пороки приходящей в упадок империи, жертвой которой он так долго был; абсурдность римских князей, неспособных защитить своих подданных от врага народа, не желавших доверять им оружие для собственной защиты, невыносимая тяжесть налогов, еще более угнетающая из-за замысловатых и произвольных способов сбора; и противоречивые законы; утомительные и дорогостоящие формы судебного разбирательства; частичное отправление правосудия и повсеместная коррупция, которая увеличила влияние богатых и усугубила несчастья бедных». [ 234 ]
Совет Вегеция по реформированию боеспособной армии можно отнести к началу 430-х гг. [ 235 ] [ 236 ] [ самостоятельно опубликованный источник? ] [ 237 ] (хотя также предлагалась дата в 390-х годах). [ 238 ] Он выявил множество недостатков в армии, особенно отметив, что солдаты уже не были должным образом экипированы:
От основания города и до правления императора Грациана пехота носила кирасы и шлемы. Но небрежность и лень постепенно привели к полному ослаблению дисциплины, солдаты стали считать свои доспехи слишком тяжелыми, поскольку они редко надевали их. Сначала они попросили у императора разрешения отложить кирасу, а затем и шлем. Вследствие этого наши войска в боях с готами часто подвергались ливню стрел. Не была также обнаружена необходимость обязать пехоту снова носить кирасы и шлемы, несмотря на такие неоднократные поражения, которые привели к разрушению стольких великих городов. Войска, беззащитные и открытые для всего оружия противника, более склонны к бегству, чем к бою. Чего можно ожидать от пешего лучника без кирасы и шлема, который не может одновременно держать лук и щит; или от прапорщиков, тела которых обнажены и которые не могут одновременно нести щит и знамена? Пехотинец находит невыносимым вес кирасы и даже шлема. Это потому, что он редко тренируется и редко их надевает. [ 239 ]
Религиозная полемика примерно того же времени горько жалуется на притеснения и вымогательство. [ 141 ] пострадали все, кроме самых богатых римлян. Многие хотели бежать к багаудам или даже к зловонным варварам. «Хотя эти люди отличаются по обычаям и языку от тех, у кого они нашли убежище, а также непривычны, если можно так сказать, к тошнотворному запаху тел и одежды варваров, тем не менее они предпочитают странную жизнь, которую они находят там из-за несправедливости, распространенной среди римлян. Итак, вы найдете людей, переходящих повсюду, то к готам, то к багаудам или к каким-либо другим варварам, установившим свою власть где-либо ... Мы называем тех людей мятежниками и совершенно покинутыми, которых мы называем. мы сами себя принудили к преступлению, ибо по каким другим причинам они стали багаудами, как не благодаря нашим несправедливым действиям, нечестивым решениям магистратов, проскрипции и вымогательству тех, кто обратил общественные поборы к увеличению своего частного состояния и сделал это? налоговые обвинения - это возможность для грабежа?" [ 240 ]
Гильдас , монах VI века и автор книги De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae , писал, что «во время передышки от опустошения остров [Британия] был настолько наводнен изобилием товаров, что ни одна предыдущая эпоха не знала ничего подобного. выросла роскошь». [ 241 ] Тем не менее, настоятельно требовалась эффективная имперская защита от разрушительных действий варваров. Примерно в это же время власти Британии обратились за помощью к Аэцию: «Аэцию, трижды консулу: стоны британцев ». Далее последовала жалоба: «Варвары отталкивают нас обратно к морю, море отталкивает нас обратно к варварам между этими двумя видами смерти, мы либо утоплены, либо убиты». Но никакой помощи взамен они не получили». [ 241 ]
Вестготы прошли еще одну веху на своем пути к полной независимости; они вели собственную внешнюю политику , посылая принцесс для заключения (довольно неудачных) брачных союзов с Речиаром свевов и с Хунерихом , сыном вандальского короля Гензериха . [ 242 ]
В 439 году вандалы двинулись на восток, временно покинув Нумидию. Они захватили Карфаген , где основали Королевство вандалов , независимое государство с мощным флотом. Это привело к немедленному финансовому кризису в Западной империи. Африканская епархия была процветающей, обычно для ее безопасности требовалось небольшое количество войск, она приносила большие налоговые поступления и экспортировала пшеницу, чтобы прокормить Рим и многие другие регионы. [ 243 ] Римские войска собрались на Сицилии , но запланированной контратаки так и не произошло. Гунны напали на Восточную империю, [ 244 ] и «войска, посланные против Гензериха, были поспешно отозваны из Сицилии; гарнизоны на стороне Персии были истощены; и в Европе была собрана военная сила, грозная по вооружению и численности, если бы генералы понимал науку командования, а солдаты - обязанность повиновения. Армии Восточной империи были побеждены в трех последовательных сражениях... От Геллеспонта до Фермопил и предместий Константинополя [Аттила] опустошил, не встречая сопротивления, и. без пощады провинции Фракия и Македония». [ 245 ] Вторжения Аттилы на Восток были остановлены Феодосийскими стенами ; на этом сильно укрепленном восточном конце Средиземноморья не было значительных вторжений варваров через море в богатые южные районы Анатолии, Леванта и Египта. [ 246 ] Несмотря на внутренние и внешние угрозы, а также большую религиозную рознь, чем на Западе, эти провинции оставались процветающими источниками налоговых поступлений; несмотря на разрушительные действия армий Аттилы и вымогательства по его мирным договорам, налоговые поступления в целом продолжали адекватны основным государственным функциям Восточной империи. [ 247 ] [ 248 ]
Генсерих поселил своих вандалов землевладельцами. [ 249 ] В 442 году ему удалось договориться об очень выгодных условиях мира с западным двором. Он сохранил свои последние достижения, а его старший сын Гунерих был удостоен помолвки с дочерью Валентиниана III Евдокией . Она несла легитимность объединенных династий Валентиниана и Феодосия . Готскую жену Хунериха подозревали в попытке отравить тестя Гензериха; он отправил ее домой без носа и ушей, и его готский союз рано распался. [ 250 ] Римляне вернули себе Нумидию , и Рим вновь получил поставки зерна из Африки.
Потери доходов Африканской епархии были эквивалентны затратам почти 40 000 пехоты или более 20 000 кавалерии . [ 251 ] Имперскому режиму пришлось повысить налоги. Несмотря на признание того, что крестьянство больше не может платить и что не может быть собрана достаточная армия, имперский режим защищал интересы землевладельцев, перемещенных из Африки, и позволял богатым людям избегать налогов. [ 252 ] [ 253 ]
444–453: Нападения империи Аттилы Гунна.
В 444 году гунны объединились под властью Аттилы . Его подданными были гунны, численно превосходившие в несколько раз другие группы, преимущественно германские народы . [ 254 ] Его власть частично основывалась на его постоянной способности награждать своих любимых последователей драгоценными металлами. [ 255 ] и он продолжал нападать на Восточную империю до 450 г., когда ему удалось добиться огромных сумм денег и многих других уступок. [ 256 ]
Аттиле, возможно, и не нужен был какой-либо предлог, чтобы повернуться на Запад, но он получил один из них в виде просьбы о помощи от Гонории , сестры императора, которую принуждали к браку, на что она возмущалась. Аттила объявил Гонорию своей женой и половину территории Западной империи своим приданым . Столкнувшись с отказом, он в 451 году вторгся в Галлию с огромной армией. В кровопролитной битве на Каталаунских равнинах вторжение было остановлено объединенными силами варваров Западной империи. Их координировал Аэций и поддерживал те войска, которые он мог собрать. В следующем году Аттила вторгся в Италию и продолжил поход на Рим. Вспышка болезни в его армии, нехватка припасов, сообщения о том, что восточноримские войска нападали на его небоевое население в Паннонии , и, возможно, призыв Папы Льва I к миру побудил его остановить эту кампанию. Аттила неожиданно умер год спустя (453 г.), и его империя распалась, поскольку его последователи боролись за власть. Жизнь Северина Норикума дает представление об общей нестабильности и окончательном отступлении римлян на Верхний Дунай после смерти Аттилы. У римлян не было достаточных сил; варвары бессистемно вымогали, убивали, похищали и грабили римлян и друг друга. «Пока существовало римское владычество, во многих городах за государственный счет содержались солдаты для охраны пограничной стены. Когда этот обычай прекратился, эскадроны солдат и пограничная стена были уничтожены вместе. Батавис , однако, выстоял. Некоторые солдаты этого отряда отправились в Италию, чтобы принести последнюю плату своим товарищам, и никто не знал, что варвары убили их по дороге». [ 257 ]
В 454 году Валентиниан лично зарезал Аэция. «[Валентиниан] думал, что убил своего хозяина; он обнаружил, что убил своего защитника: и стал беспомощной жертвой первого заговора, который был задуман против его трона». [ 258 ] Сам Валентиниан год спустя был убит сторонниками погибшего генерала. [ 259 ] Богатый сенаторский аристократ Петроний Максим , подстрекавший к обоим убийствам, затем захватил трон. Он разорвал помолвку между принцессой Евдокией и Гунерихом , наследником вандальского престола. Это было равносильно объявлению войны вандалам. Петроний успел послать Авита просить помощи у вестготов в Галлии. [ 260 ] до прибытия флота вандалов в Италию. Петроний не смог организовать эффективную защиту, попытался бежать из города, но был растерзан толпой, которая выставляла напоказ обломки на шесте. Вандалы вошли в Рим и грабили его две недели. Несмотря на нехватку денег для защиты государства, со времени предыдущего разграбления в 410 году накопились значительные частные богатства. Вандалы уплыли с большим количеством сокровищ, а также с царевной Евдокией. Она стала женой одного короля вандалов и матерью другого, Хильдерика . [ 261 ]
Вандалы завоевали Сицилию. Их флот стал постоянной угрозой для римской морской торговли, а также для побережий и островов западного Средиземноморья. [ 262 ]
455–456: Крах Авита, дальнейшие потери в Галлии, возвышение Рицимера.
Авитус при вестготском дворе в Бурдигале объявил себя императором. Он двинулся на Рим при поддержке вестготов. Он получил признание Майориана и Рицимера , командующих оставшейся армией Италии. Это был первый случай, когда варварское королевство сыграло ключевую роль в имперской преемственности. [ 263 ] Зять Авита Сидоний Аполлинарий написал пропаганду , чтобы представить вестготского короля Теодориха II как разумного человека, с которым римский режим мог вести дела. [ 264 ] Вознаграждение Теодориха включало в себя драгоценный металл за то, что он забрал оставшиеся государственные украшения Италии. [ 265 ] и неконтролируемая кампания в Испании. Там он не только разгромил свевов, казнив своего зятя Речиара, но и разграбил римские города. [ 264 ] Бургунды расширили свое королевство в долине Роны , а вандалы захватили остатки Африканской епархии. [ 266 ] В 456 году вестготская армия была слишком сильно задействована в Испании, чтобы представлять реальную угрозу Италии. Рицимер только что уничтожил пиратский флот из шестидесяти кораблей вандалов. Майориан и Рицимер выступили против Авита и разбили его возле Плацентии . Он был вынужден стать епископом Плаценции и умер (возможно, убит) несколько недель спустя. [ 267 ]
457–467: Возрождение при Майориане, попытка вернуть Африку, контроль Рицимера.
Майориан и Рицимер теперь контролировали Италию. Рицимер был сыном свевского короля, а его мать — дочерью готского, поэтому он не мог претендовать на императорский трон. Через несколько месяцев, учитывая переговоры с новым императором Константинополя и разгром 900 аламаннских захватчиков Италии одним из его подчиненных, Майориан был провозглашен Августом. [ нужна ссылка ]
Гиббон описывает Майориана как «великого и героического персонажа». [ 268 ] Он энергично восстановил армию и флот Италии и приступил к возвращению оставшихся галльских провинций, которые не признали его возвышения. Он победил вестготов в битве при Арелате , низведя их до статуса федерации и заставив отказаться от своих притязаний на Испанию; он перешел к подчинению бургундцев, галло-римлян вокруг Лугдунума (которым были предоставлены налоговые льготы и чьи высшие должностные лица были назначены из их собственных рядов), а также свевов и багаудов в Испании. Марцеллин , magister militum в Далмации и языческий полководец хорошо оснащенной армии, признал его императором и вернул Сицилию от вандалов. [ 269 ] Эгидий также признал Майориана и взял на себя эффективную власть над северной Галлией. (Эгидий, возможно, также использовал титул «король франков»). [ 270 ] Злоупотребления в сборе налогов были устранены, а городские советы были усилены. Оба действия были необходимы для восстановления могущества Империи, но были невыгодны для самых богатых аристократов. [ 271 ] Майориан подготовил флот в Карфаген-Нова для необходимого завоевания Африканской епархии.
Флот был сожжен предателями, а Майориан заключил мир с вандалами и вернулся в Италию. Здесь Рицимер встретил его, арестовал и через пять дней казнил. Марцеллин в Далмации и Эгидий вокруг Суассона в северной Галлии отвергли как Рицимера, так и его марионеток, и сохранили некоторую версию римского правления на своих территориях. [ 272 ] Позже Рицимер уступил Нарбон и его внутренние районы вестготам в обмен на их помощь против Эгидия; это сделало невозможным марш римских армий из Италии в Испанию. Рицимер был тогда эффективным правителем Италии (но не более того) в течение нескольких лет. С 461 по 465 годы правил благочестивый итальянский аристократ Либий Север . Нет никаких записей о чем-либо значительном, чего он хотя бы пытался достичь, он никогда не был признан Востоком, в чьей помощи Рицимер нуждался, и он благополучно умер в 465 году. [ нужна ссылка ]
467–472: Антемий; Император и армия с Востока

После двух лет отсутствия западного императора Восточный двор назначил Антемия , успешного полководца, имевшего серьезные претензии на восточный трон. Он прибыл в Италию с армией при поддержке Марцеллина и его флота. Антемий женил свою дочь Алипию на Рицимере, и в 467 году он был провозглашен августом. В 468 году Восточная империя ценой огромных затрат собрала огромные силы, чтобы помочь Западу вернуть себе Африканскую епархию. Марцеллин быстро изгнал вандалов с Сардинии и Сицилии, а сухопутное вторжение изгнало их из Триполитании . Главнокомандующий с главными силами разгромил флот вандалов возле Сицилии и высадился у мыса Бон . Здесь Гензерих предложил сдаться, если ему будет предоставлено пятидневное перемирие для подготовки процесса. Он использовал передышку для подготовки полномасштабной атаки, которой предшествовали боевые корабли , которая уничтожила большую часть римского флота и убила многих его солдат. Вандалы подтвердили свое владение Африканской епархией. Вскоре они вернули себе Сардинию и Сицилию. Марцеллин был убит, возможно, по приказу Рицимера. [ 273 ] Преторианский префект Галлии Арванд ; пытался убедить Эврика, нового короля вестготов, восстать на том основании, что римской власти в Галлии все равно пришел конец король отказался.
Антемий все еще командовал армией в Италии. Кроме того, в северной Галлии британская армия во главе с неким Риотамусом действовала в имперских интересах в битве при Деоле . [ 274 ] Антемий послал своего сына Антемиола с армией через Альпы, чтобы попросить вестготов вернуть южную Галлию под контроль Рима. Это снова позволило бы Империи получить доступ к суше в Испании. Вестготы отказались и разгромили силы Риотамуса и Антемия в битве при Арле ; вместе с бургундами они захватили почти всю оставшуюся имперскую территорию в южной Галлии. [ нужна ссылка ]
Затем Рицимер поссорился с Антемием и осадил его в Риме, который сдался в июле 472 года, после нескольких месяцев голодания. [ 275 ] Антемий был схвачен и казнён (по приказу Рицимера) бургундским принцем Гундобадом . В августе Рицимер умер от легочного кровотечения . Олибрий , его новый император, назначил Гундобада своим патрицием, а затем вскоре умер сам. [ 276 ]
472–476: Последние императоры, марионетки военачальников.
После смерти Олибрия продолжалось междуцарствие до марта 473 года, когда Гундобад провозгласил Гликерия императором. Возможно, он предпринял попытку вторгнуться в Галлию; если да, то это не удалось. [ 277 ]

В 474 году Юлий Непот , племянник и преемник полководца Марцеллина, прибыл в Рим с солдатами и властью восточного императора Льва I. К тому времени Гундобад уехал оспаривать бургундский престол в Галлии. [ 277 ] Глицерий сдался без боя и ушел в отставку, чтобы стать епископом Салоны в Далмации. [ 277 ] Юлий Непот правил Италией и Далмацией из Равенны и назначил Ореста , бывшего секретаря Аттилы, magister militum .
В 475 году Орест пообещал землю в Италии различным германским наёмникам, герулам , скирианам и торкилингам , в обмен на их поддержку. Он изгнал Юлия Непота из Равенны своего собственного сына Флавия Момилла Ромула Августа ( Romulus Augustulus и 31 октября провозгласил императором ). Его фамилия «Август» была присвоена уменьшительной формой «Августул» соперниками, поскольку он был еще несовершеннолетним. Ромул никогда не был признан за пределами Италии законным правителем. [ 278 ]
В 476 году Орест отказался выполнить обещания о земле своим наемникам, поднявшим восстание под предводительством Одоакра . 23 августа 476 года Орест бежал в город Павию , где городской епископ предоставил ему убежище. Вскоре Орест был вынужден бежать из Павии, когда армия Одоакра прорвала городские стены и разорила город. Армия Одоакра преследовала Ореста до Пьяченцы , где схватила и казнила его 28 августа 476 года.
4 сентября 476 года Одоакр заставил Ромула Августула , которого его отец Орест провозгласил императором Рима, отречься от престола. Аноним Валезиан писал, что Одоакр, «пожалевший свою молодость» (ему тогда было 16 лет), сохранил Ромулу жизнь и назначил ему годовую пенсию в 6000 солидов , прежде чем отправить его жить к родственникам в Кампанию . [ 279 ] [ 280 ] Одоакр провозгласил себя правителем Италии и отправил императорские знаки отличия в Константинополь. [ 281 ]
Из 476: Последний император, крупица утверждает.
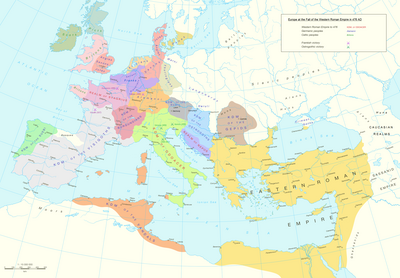
Условно считается, что Западная Римская империя прекратила свое существование 4 сентября 476 года, когда Одоакр сверг Ромула Августула и провозгласил себя правителем Италии . Эта конвенция имеет множество оговорок. В римской конституционной теории Империя по-прежнему была просто объединена под властью одного императора, что не подразумевало отказа от территориальных претензий. В районах, где конвульсии умирающей Империи сделали организованную самооборону законной, остатки государств продолжали находиться под той или иной формой римского правления после 476 года. Юлий Непот все еще претендовал на то, чтобы быть императором Запада, и контролировал Далмацию до своего убийства в 480 году. Сиагрий сын Эгидия правил Суассонскими владениями до своего убийства в 486 году. [ 282 ] Коренные жители Мавритании создали собственные королевства , независимые от вандалов и с сильными римскими чертами. Они снова добивались имперского признания во время завоеваний Юстиниана I , а позже оказали эффективное сопротивление мусульманскому завоеванию Магриба . [ 283 ] Граждане ; Британии продолжали защищаться, как приказал Гонорий они сохраняли грамотность в латыни и другие явно римские черты в течение некоторого времени, хотя они опустились до уровня материального развития, уступающего даже их доримским предкам железного века. [ 284 ] [ 285 ] [ 286 ]

Одоакр начал переговоры с восточноримским (византийским) императором Зеноном , который был занят борьбой с волнениями на Востоке. Зенон в конце концов предоставил Одоакру статус патриция и признал его своим наместником Италии. Зенон, однако, настаивал на том, что Одоакр должен был отдать дань уважения Юлию Непосу как императору Западной империи. Одоакр так и не вернул ни территории, ни реальной власти, но выпустил монеты во имя Юлия Непота по всей Италии. Убийство Юлия Непота в 480 году (Глицерий, возможно, был среди заговорщиков) побудило Одоакра вторгнуться в Далмацию, присоединив ее к своему Итальянскому королевству . В 488 году восточный император поручил беспокойному готову Теодориху (позже известному как «Великий») захватить Италию. После нескольких нерешительных кампаний в 493 году Теодорих и Одоакр согласились править совместно. Они отпраздновали свое соглашение банкетом примирения, на котором люди Теодориха убили Одоакра, а Теодорих лично разрезал Одоакра пополам. [ 287 ]
По большей части бессильный, но все же влиятельный Сенат Западной Римской империи продолжал существовать в городе Риме под властью Остготского королевства , а затем и Византийской империи, по крайней мере, еще одно столетие, прежде чем исчезнуть в неизвестную дату в начале VII века . [ 288 ]
Наследие
Римская империя была не только политическим единством, подкрепленным использованием военной силы; это была также объединенная и развитая цивилизация Средиземноморского бассейна и за его пределами. Оно включало производство, торговлю и архитектуру, широкое распространение светской грамотности, писаное право и международный язык науки и литературы. [ 287 ] Западные варвары утратили большую часть этих высших культурных практик, но их перестройка в средние века политиками, осознававшими достижения римлян, сформировала основу для дальнейшего развития Европы. [ 289 ]
Если рассматривать культурную и археологическую преемственность на протяжении и после периода утраты политического контроля, этот процесс можно описать как сложную культурную трансформацию , а не как падение. [ 290 ]
См. также
- Наследование Римской империи
- Сравнительные исследования Римской и Ханьской империй
- Упадок Византийской империи ( Падение Восточной Римской империи )
- Историография падения Западной Римской империи.
- Последний из римлян
- Позднеримская армия
- Список римских гражданских войн и восстаний
Примечания
- ^ * Многочисленные литературные источники, как христианские, так и языческие, ложно приписывают Феодосию многочисленные антиязыческие инициативы, такие как прекращение государственного финансирования языческих культов (эта мера принадлежит Грациану ) и снос храмов (почему нет первичных доказательств). ). [ 130 ]
- Феодосий также был связан с прекращением существования весталок, но ученые двадцать первого века утверждают, что девы существовали до 415 года и пострадали при Феодосии не больше, чем с тех пор, как Грациан ограничил свои финансы. [ 131 ]
- Феодосий действительно превратил языческие праздники в будни, но связанные с ними празднества продолжались. [ 132 ]
- Феодосия было связано с прекращением древних Олимпийских игр , чего он, вероятно, тоже не делал. [ 133 ] [ 134 ] Софи Ремейсен говорит, что есть несколько причин считать, что Олимпийские игры продолжались после Феодосия I, и что они завершились при Феодосии Втором , но случайно. Две дошедшие до нас схолии Лукиана связывают окончание игр с пожаром, который сжег храм Зевса Олимпийского во времена правления Феодосия Второго. [ 135 ]
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Видеть: Зосима книга 5 – через Wikisource .
Ссылки
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Харпер 2017 .
- ^ Уорд-Перкинс 2005 , с. 1.
- ^ например, Почему нации терпят неудачу. Аджемоглу Д. и Робинсон Дж.А. Профильные книги (Random House Inc.), 2012. ISBN 978-1-84668-429-6 . стр. 166–175
- ^ Даймонд, Джаред (2011). Крах . Книги о пингвинах. стр. 13–14. ISBN 978-0-14-311700-1 .
- ^ Глен Бауэрсок, «Исчезающая парадигма падения Рима», Бюллетень Американской академии искусств и наук , 1996. Том. 49 нет. 8 стр. 29–43.
- ^ Макмаллен, Рамзи (1981). Язычество в Римской империи (полное издание). Издательство Йельского университета. ISBN 978-0300029840 .
- ^ Грегори, Т. (1986). Выживание язычества в христианской Греции: критический очерк. Американский журнал филологии , 107 (2), 229–242. дои : 10.2307/294605
- ^ Браун 1978 , стр. 2–3.
- ^ Лаван, Люк (2011). Лаван, Люк; Малрайан, Майкл (ред.). Археология позднеантичного «язычества» . Брилл. п. XXIV. ISBN 978-9004192379 .
- ^ Хант 2001 , с. 256.
- ^ Грегори, Т. (1986). Выживание язычества в христианской Греции: критический очерк. Американский филологический журнал, 107 (2), 229–242. дои : 10.2307/294605
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Леоне, Анна (2013). Конец языческого города: религия, экономика и урбанизм в позднеантичной Северной Африке (иллюстрированное издание). ОУП. п. 9. ISBN 978-0199570928 .
- ^ Бауэрсок, Глен В. (1996). «Исчезающая парадигма падения Рима». Бюллетень Американской академии искусств и наук . 49 (8): 29–43. дои : 10.2307/3824699 . JSTOR 3824699 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Ребенич, Стефан (2012). «6 Поздняя античность глазами современников». У Руссо, Филипп (ред.). Спутник поздней античности . Джон Уайли и сыновья. п. 78. ИСБН 978-1118293478 .
- ^ Джонсон, Скотт Фицджеральд, изд. (2015). Оксфордский справочник поздней античности (иллюстрировано, переиздание). ОУП. п. 6. ISBN 978-0190277536 .
- ^ Харпер 2017 , с. 21.
- ^ Дион Кассий 72.36.4. Архивировано 21 февраля 2021 г. в Wayback Machine , издание Леба перевело Э. Кэри.
- ^ Груман 1960 , стр. 84–85.
- ^ Бауэрсок 1996 , с. 31.
- ^ Момильяно 1973 .
- ^ Джордан 1969 , стр. 83, 93–94.
- ^ Гиббон 1906 , стр. 279, 312.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Браун 2013 , с. 37.
- ^ Покок, JGA (1976). «Между Макиавелли и Юмом: Гиббон как гражданский гуманист и историк-философ». Дедал . 105 (3): 153–169.
- ^ Покок, Просвещение Эдварда Гиббона, 1737–1764 , 303–304; Первый упадок и падение , 304–306.
- ^ Андо 2012 , с. 60.
- ^ Дранкур, М.; Рауль, Д. (ноябрь 2016 г.). «Молекулярная история чумы» . Клиническая микробиология и инфекции . 22 (11): 911–915. дои : 10.1016/j.cmi.2016.08.031 . ПМИД 27615720 .
- ^ Ривс, Джеймс Б. (2010). «Греко-римская религия в Римской империи: старые предположения и новые подходы». Течения в библейских исследованиях . 8 (2): 240–299. дои : 10.1177/1476993X09347454 . S2CID 161124650 .
- ^ Демандт, Александр. 210 Теорий . Архивировано из оригинала 13 ноября 2017 г. Проверено 22 ноября 2018 г. , цитирую Демандт, А. (1984). Падение Рима . п. 695.
- ^ Галинский 1992 , стр. 53–73.
- ^ Harper 2017 , глава 4 «Старость мира.
- ^ Маккормик, Майкл; Бюнтген, Ульф; Кейн, Марк А.; Кук, Эдвард Р.; Харпер, Кайл; Хайберс, Питер; Литт, Томас; Мэннинг, Стёрт В.; Маевски, Пол Эндрю; Подробнее, Александр Ф.М.; Николусси, Курт; Тегель, Вилли (август 2012 г.). «Изменение климата во время и после Римской империи: реконструкция прошлого на основе научных и исторических свидетельств» . Журнал междисциплинарной истории . 43 (2): 169–220. дои : 10.1162/JINH_a_00379 . S2CID 16489531 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Харпер, 2017 , стр. 248–254.
- ^ Харпер 2017 , с. 5.
- ^ Турчин, Петр; Шайдель, Уолтер (2009). «Клады монет говорят о сокращении населения в Древнем Риме» . Труды Национальной академии наук США . 106 (41): 17276–17279. Бибкод : 2009PNAS..10617276T . дои : 10.1073/pnas.0904576106 . ПМЦ 2762679 . ПМИД 19805043 .
- ^ Харпер 2017 , стр. 112–113.
- ^ Шайдель, Уолтер (2015). «Модель демографических и экономических изменений в римском Египте после чумы Антонина». Журнал римской археологии . 15:97 . дои : 10.1017/S1047759400013854 . S2CID 160954017 .
- ^ Гиббон 1782 , Глава I: Размеры Империи в эпоху Антонинов. Глава II: Внутреннее процветание в эпоху Антонинов. Глава III: Конституция в эпоху Антонинов.
- ^ МакМайкл, Энтони (2017). «Римляне, майя и анасази: классический оптимум засухи в Америке». Изменение климата и здоровье наций . дои : 10.1093/oso/9780190262952.003.0012 . ISBN 978-0-19-026295-2 .
- ^ Харпер 2017 , стр. 264–267.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 63–64.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Хизер 2006 , с. 67.
- ^ Рейнольдс, Джулиан (2011). Защищая Рим: Мастера солдат . Корпорация Xlibris. п. 206. ИСБН 978-1-4771-6460-0 .
[...] традиционная римская политика рецепции или вербовки варваров по мере необходимости [...]
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Хизер 2006 , с. 123.
- ^ Хизер, Питер (2007). Падение Римской империи: новая история Рима и варваров . История (Электронная библиотека). Издательство Оксфордского университета. п. 87. ИСБН 978-0199978618 .
- ^ Джонгман, Виллем (2007). «Гиббон был прав: упадок и падение римской экономики» . Кризисы и Римская империя . стр. 183–199. doi : 10.1163/ej.9789004160507.i-448.38 . ISBN 978-9047420903 . S2CID 161222282 .
- ^ Грант, Майкл (1960). Мир Рима , стр. 85–86.
- ^ Letki 2012 , pp. 52–53.
- ^ Виктор, Аврелий , «XXXIII» , Де Цезарибус (на латыни), заархивировано из оригинала 2 октября 2012 г. , получено 01 июля 2012 г. ,
стих 34: И действительно, отцы, помимо общего зла римлян , подстрекал к оскорблениям собственного сословия, 34 ибо сам был первым, опасаясь за свою трезвость, чтобы управление не перешло к лучшим из дворян, запретил сенату вступать в ополчение и идти в войско . Это была сила девяти лет
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Джонс 1964 , с. 131.
- ^ Макарий Магнес , Апокритик IV: 23. Архивировано 18 декабря 2021 г. в Wayback Machine : «Поэтому вы совершаете большую ошибку, думая, что Бог гневается, если кто-то другой называется богом и получает тот же титул, что и Он Сам. Ибо даже правители не возражают против титула своих подданных, а хозяева — против рабов».
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 , стр. 110, 147.
- ^ Браун 2013 , с. 48.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б МакМаллен 1988 , стр. 137–142.
- ^ Кейт Брэдли, «Горькая цепь рабства»: размышления о рабстве в Древнем Риме», Лекции Сноудена, Греческий центр Гарвардского университета (2 ноября 2020 г.), https://chs.harvard.edu/curated-article/ Сноуден-лекции-Кит-Брэдли-горькая цепь-рабства
- ^ Кодекс Феодосиана 9.24.1.1 https://preserver.beic.it/delivery/DeliveryManagerServlet?dps_pid=IE668970
- ^ Мэтьюз 2007 , с. 253.
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 , с. 170.
- ^ Кэмерон 2011 , с. 97.
- ^ Мэтьюз 2007 , с. 278.
- ^ Рэтбоун 2009 , с. 324.
- ^ Пиганиол 1950 , стр. 66–67.
- ^ Эрнст Бадиан. Кальпурний Пизон Фруги, Луций https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780199381135.013.1312
- ^ Мэтьюз 2007 , с. 284.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 119.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , с. 1026.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Джонс 1964 , с. 1027.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , стр. 1027–1028.
- ^ Пиганиол 1950 , с. 66.
- ^ Уорд-Перкинс 2005 , стр. 87–121.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2003 , стр. 68–73.
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 , с. 110.
- ^ Гиббон, Эдвард . «2. Падение на Западе». История упадка и разрушения Римской империи . Архивировано из оригинала 15 октября 2012 г. Проверено 26 июня 2012 г.
- ^ Хэнсон, Энн Эллис. «Разделение труда». Роли мужчин в греческих и римских родах. Тамирис 1.2 (1994 г.): p=157.
- ^ Браун 2012 , стр. 220–221.
- ^ Бартон, Джон (2019). История Библии: история самой влиятельной книги в мире (иллюстрированное издание). Пингвин. п. 15. ISBN 978-0525428770 .
- ^ Браун, Питер (1998). «21 христианизация и религиозные конфликты». В Гарнси, Питер; Кэмерон, Аверил (ред.). Кембриджская древняя история . Том. 13. Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 641. ИСБН 978-0521302005 .
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 , с. 51.
- ^ Брэдбери, Скотт (1995). «Языческое возрождение Юлиана и упадок кровавых жертвоприношений». Феникс . 49 (4): 331–356. дои : 10.2307/1088885 . JSTOR 1088885 .
- ^ Браун 2003 .
- ^ Поздняя Римская империя, 284–602: Социальное, экономическое и административное исследование - 1986, А.Х.М. Джонс, том II, стр. 933, цитата: «Огромное войско духовенства и монахов было по большей части праздными ртами».
- ^ Харпер 2017 , с. 186.
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 , с. 175.
- ^ Тацит , Анналы , книга 11, глава 18. http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Tacitus/Annals/11B*.html Корбулон ... вспоминал легионы, вялые в своих трудах и повинности, поскольку они были ярыми в грабежах, к старому кодексу с его запретами выпадать на марш или начинать действия без приказа.
- ^ Никэси 1998 , с. 187.
- ^ Уорд-Перкинс 2005 , с. 37.
- ^ Книга Аммиана Марцеллина XXVII 9.2
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 , стр. 173–175, 181.
- ^ Никэси 1998 , с. 261.
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 , стр. 181–183.
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 , стр. 23, 178, 186.
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 , с. 161.
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 , стр. 190–193.
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 , с. 176.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 112–115.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Вигг Вольф, Дэвид. Поставляете умирающую империю? Монетный двор Трира в конце IV века нашей эры . С. 217–233 в «Производство и переработка монет в поздней античности / Produire et recycler la monnaie au Bas-Empire». Центральный римско-германский музей, Научно-исследовательский институт археологии Лейбница и Центр Мишеля де Буара КРААМА (UMR 6273), Университет Кана, Нормандия. 2016 Издательство Центрального римско-германского музея, Майнц SONDERPRUCK / TIRÉ À PART RGZM – КОНФЕРЕНЦИИ Том 29 Жереми Шамеруа · Пьер-Мари Гиар (реж.) 1-я Международная встреча нумизматов / 1ères Rencontres Internationales de Numismatique (15–16 мая 2014, Майнц) ISBN 978-3884672709 ISSN 1862-4812 https://www.academia.edu/27941832/Supplying_a_Dying_Empire_The_Mint_of_Trier_in_the_Late_4th_Century_AD . Архивировано 1 июня 2022 г. на Wayback Machine, доступ осуществлен 31 мая 2022 г.
- ^ Аммиан 1935 , книга XVI, глава V: «Какое добро он сделал Галлии, работавшей в крайней нищете, яснее всего видно из этого факта: когда он впервые вошел в эти края, он обнаружил, что двадцать пять золотых монет были требовали в качестве дани с каждого в качестве подушного и земельного налога, но когда он уезжал, только семь для полного удовлетворения всех повинностей и по причине этого (как будто после безобразной тьмы на них осветил ясный солнечный свет); их радость в веселье и танцах».
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Хант, Дэвид (1998). «2, Джулиан». В Кэмероне, Аверил; Гарнси, Питер (ред.). Кембриджская древняя история, том 13 . Издательство Кембриджского университета.
- ^ Бродд, Джеффри (октябрь 1995 г.). «Юлиан Отступник и его план восстановления Иерусалимского храма». Библейский обзор . Общество библейской археологии.
- ^ Брэдбери, Скотт (1995). «Языческое возрождение Юлиана и упадок кровавых жертвоприношений» (PDF) . Феникс . 49 (4): 331–356. дои : 10.2307/1088885 . JSTOR 1088885 . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 22 августа 2021 г. Проверено 27 июля 2021 г.
- ^ Гаддис 2005 , стр. 94–95.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Древний Рим: Царствование Юлиана» . Британская онлайн-энциклопедия . Архивировано из оригинала 24 марта 2019 года . Проверено 23 августа 2018 г.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 283.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , с. 147.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , стр. 26, 152.
- ^ Гиббон 1782 , Глава XXVII: Гражданские войны, правление Феодосия. Часть I. Смерть Грациана..
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б МакМаллен 1988 , с. 185.
- ^ Никэси 1998 , стр. 263 и далее.
- ^ Никэси 1998 , с. 256.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Холсолл 2007 , с. 183.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 48.
- ^ Ливий ( Титус Ливий ) (2013). История Рима . Перевод Макдевитта, Вашингтон (Уильям Александер). Архивировано из оригинала 02 февраля 2019 г. Проверено 1 февраля 2019 г.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 188.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 54.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , с. 157.
- ^ Холсолл 2007 , с. 185.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , стр. 102, 152.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 65.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Джонс 1964 , с. 162.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , стр. 162, 169.
- ^ Браун 2012 , с. 135.
- ^ Браун 2012 , стр. 136, 146.
- ^ Браун 2012 , с. 147.
- ^ Кэмерон 2010 , с. 74 (и примечание 177).
- ^ Оксфордский словарь поздней античности , стр. 1482, 1484.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Эррингтон 2006 , стр. 248–249.
- ^ Кэмерон 2010 , с. 74.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Хебблвайт 2020 , глава 8.
- ^ Кэмерон 2011 , с. 74.
- ^ Кэмерон 1993 , стр. 46–47, 72.
- ^ Теста 2007 , с. 260.
- ^ Граф 2014 , стр. 229–232.
- ^ Перротте, Тони (2004). Голые Олимпийские игры: правдивая история древних игр . Random House Digital, Inc., стр. 190 –. ISBN 978-1-58836-382-4 . Проверено 1 апреля 2013 г.
- ^ Гамлет, Ингомар. «Феодосий I. И Олимпийские игры». Никифор 17 (2004): стр. 53–75.
- ^ Ремейсен, Софи (2015). Конец греческой легкой атлетики в поздней античности . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 49.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , с. 164.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , с. 159.
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 , с. 178.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Бернс 1994 , с. 159.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , стр. 157–58, 169.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Джонс 1964 , с. 173.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Макджордж 2002 , с. 171.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Хизер 2006 , стр. 213–214, 217–218, 242, 255.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Джонс 1964 , с. 187.
- ^ MacMullen 1988 , стр. 58–121, глава 2: Энергоэффективность.
- ^ Альфёлди 2001 , с. 17.
- ^ Макджордж 2002 , стр. 171–172.
- ^ Макджордж 2002 , с. 172.
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 .
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 153.
- ^ MacMullen 1988 , стр. 58–121, глава 2. Энергоэффективность.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Джеймс 2014 , с. 54.
- ^ Куликовский 2019 , стр. 126.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 154.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , стр. 162–163.
- ^ МакМаллен 1988 , с. 189.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Бернс 1994 , с. 183.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 186.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 187.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 169.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 175.
- ^ Уорд-Перкинс 2005 , с. 60.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 173.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , с. 192.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Бернс 1994 , с. 191.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 190.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 193.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Бернс 1994 , с. 195.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Бернс 1994 , с. 198.
- ^ Гиббон, 277
- ^ Зосим, Новая история , книга 5. http://www.tertullian.org/fathers/zosimus05_book5.htm. Архивировано 11 октября 2019 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Бернс 1994 , с. 215.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 216.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 218.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Бернс 1994 , с. 227.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 219.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , стр. 224–225.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 228.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 236.
- ^ Холсолл 2007 , с. 216.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , стр. 226–227.
- ^ Коннолли 1998 , с. 189.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , стр. 233–234.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Бернс 1994 , с. 234.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 227.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 226.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 239.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , стр. 238–239.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 240.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 242.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 243.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , стр. 243–244.
- ^ Никейские и постникейские отцы: Серия II/Том VI/Письма святого Иеронима/Письмо 127 Филип Шафф и др. http://en.wikisource.org/wiki/Nicene_and_Post-Nicene_Fathers:_Series_II/Volume_VI/The_Letters_of_St._Jerome/Letter_127 . Архивировано 23 октября 2011 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Хизер 2006 , с. 239.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , стр. 228–231.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 229–232.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , стр. 196, 237–238.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 238.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 245.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Хизер 2006 , с. 198.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 202–205.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , стр. 185–189.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 128.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 244.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 205–212.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Хизер 2006 , с. 251.
- ^ Монеты таунхауса Дорчестера. Р. Рис, В: «Позднеримский таунхаус и его окрестности; Раскопки К. Д. Дрю и К. К. Коллингвуда Селби в Коллитон-парке, Дорчестер, Дорсет, 1937–8 '. Эмма Дарем и М. Фулфорд, серия 26 монографии Britannia, стр. 103–111, 2014 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Бернс 1994 , с. 257.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Eucharisticus Paulinus Pellaeus Английский перевод Г. Г. Эвелин Уайт, 1921, Ausonius классической библиотеки Леба, том. II, стр. 295–351. http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Paulinus_Pellaeus/Eucharisticus*.html
- ^ Бернс 1994 , стр. 258–259.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 259.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , стр. 259–260.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 240–241.
- ^ Бернс 1994 , с. 260.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 241.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 242.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 246–48.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , с. 197.
- ^ Мэтьюз 1975 , с. 378.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Хизер 2006 , с. 257.
- ^ Холсолл 2007 , с. 234.
- ^ Halsall 2007 , стр. 231–232.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 246.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , с. 204.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 274–278.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 261.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 260.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 283.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 285.
- ^ Холсолл 2007 , с. 240.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 290.
- ^ Холсолл 2007 , с. 244.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 288.
- ^ Гиббон 1782 , Глава XXXIV: Аттила. Часть II..
- ^ Сик О. Die Zeit des Vegetius. Гермес 1876 г. об. 11 стр. 61–83. Цитируется в Milner NP. Вегетиус: Воплощение военной науки, второе издание, Liverpool University Press, 1996. стр. xxxvii и далее.
- ^ Розенбаум, С; « Кем был Вегетиус? » опубликовано на Academia.edu в 2015 г. https://www.academia.edu/5496690/Who_was_Vegetius. Архивировано 8 марта 2021 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ^ Уолтер Гоффарт. Дата и цели книги Вегетиуса De Re Militari. В «Падении Рима и после», глава 3, стр. 49–80. Хэмблдон Пресс 1989. ISBN 1852850019
- ^ Милнер Н.П. Вегетиус: Воплощение военной науки, второе издание, Liverpool University Press, 1996. стр. xxxvii и далее.
- ^ Де Ре Милитари. Флавий Вегетий Ренат. Перевод лейтенанта Джона Кларка, 1767 г. Электронная версия Мэдса Бревика (2001 г.) http://www.digitalattic.org/home/war/vegetius/. Архивировано 21 апреля 2020 г. на Wayback Machine.
- ^ правительстве Сальвиана Бога О Пятая книга. стихи 5–7. http://www.ccel.org/ccel/salvian/govt.iv.vi.html Архивировано 27 августа 2012 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Гильдас , изд. и транс. Майкл Уинтерботтом (1978). Разрушение Британии и другие произведения Филлимор. стр. 23–24. Архивировано 5 апреля 2023 г. в Wayback Machine .
- ^ Холсолл 2007 , с. 247.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 288–290.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 291–292.
- ^ Гиббон 1782 , Глава XXXIV: Аттила. Часть I..
- ^ Уорд-Перкинс 2005 , стр. 54–62.
- ^ Уорд-Перкинс 2005 , стр. 58–62.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , стр. 206–207.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 293–294.
- ^ Гиббон 1782 , Глава XXXV: Вторжение Аттилы. Часть I. [1] .
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 298.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 295–297.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , стр. 205–206.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 330.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 332.
- ^ Гиббон 1782 , Глава XXXIV: Аттила. Часть I. [2] .
- ↑ Жизнь святого Северина. Архивировано 23 апреля 2012 г. в Wayback Machine (1914), Евгиппий, стр. 13–113, английский перевод Джорджа Робинсона, издательство Гарвардского университета, Кембридж, Массачусетс.
- ^ Бери, Дж. Б., Кембриджская средневековая история, том. Я (1924), стр. 418–419.
- ^ Гиббон , Глава XXXV: Вторжение Аттилы. Часть III. [3] .
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 375–377.
- ^ Холсолл 2007 , с. 256.
- ^ Гиббон 1782 , Глава XXXVI: Полное исчезновение Западной Империи.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , с. 379.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Хизер 2006 , с. 381.
- ^ Холсолл 2007 , с. 260.
- ^ Хизер 2006 , стр. 382–383.
- ^ Холсолл 2007 , с. 261.
- ^ Гиббон 1782 , Глава XXXVI: Полное исчезновение Западной Империи. Часть II..
- ^ Мартиндейл 1980 , стр. 708–710, глава 6 Марцеллина.
- ^ Halsall 2007 , стр. 266–267.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , с. 241.
- ^ Холсолл 2007 , с. 391.
- ^ Холсолл 2007 , с. 273.
- ^ Halsall 2007 , стр. 276–277.
- ^ Холсолл 2007 , с. 277.
- ^ Холсолл 2007 , с. 278.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Холсолл 2007 , с. 279.
- ^ «Ромул Августул – римский император» . Британская энциклопедия. Архивировано из оригинала 1 июня 2015 г. Проверено 21 июня 2022 г.
- ^ De Imperatoribus Romanis , заархивировано из оригинала 1 июня 2015 г. , получено 24 июня 2013 г.
- ^ Гиббон, с. 406
- ^ Halsall 2007 , стр. 280–281.
- ^ Джонс 1964 , с. 246.
- ^ Halsall 2007 , стр. 405–411.
- ^ Уорд-Перкинс 2005 , с. 118.
- ^ Бритты: от римлян к варварам . Алекс Вульф. стр. 345–380 в Regna and Gentes. Взаимоотношения между позднеантичными и раннесредневековыми народами и королевствами в трансформации римского мира. Под редакцией Ханса-Вернера Гетца, Йорга Янута и Вальтера Поля при сотрудничестве Сёрена Кашке. Брилл, Лейден, 2003 г. ISBN 90-04-12524-8
- ^ Halsall 2007 , стр. 284–319.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Холсолл 2007 , с. 287.
- ^ Левиллен, Филипп, изд. (2002). Папство: энциклопедия . Нью-Йорк: Рутледж. ISBN 0415922283 . OCLC 47237751 .
- ^ Уорд-Перкинс 2005 , стр. 87–122.
- ^ Бауэрсок 2001 , стр. 87–122.
Библиография
- Альфёлди, Геза (2001). «Городская жизнь, надписи и менталитет в позднеантичном Риме». В Бернсе, Томас С .; Иди, Джон В. (ред.). Городские центры и сельский контекст в поздней античности . Издательство Мичиганского государственного университета. ISBN 978-0-870-13585-9 .
- Аммиан. История . Пер. Джей Си Рольфе. Классическая библиотека Леба, Том. Я, 1935 год.
- Андо, Клиффорд (2012). «5 повествований об упадке и падении». У Руссо, Филипп (ред.). Спутник поздней античности (иллюстрировано, переиздание). Джон Уайли и сыновья. ISBN 978-1118255315 .
- Бауэрсок, Глен, Питер Браун, Олег Грабарь. Интерпретация поздней античности: очерки постклассического мира . Belknap Press издательства Гарвардского университета, 2001. ISBN 0-674-00598-8 .
- Браун, Питер (1978). Становление поздней античности . Издательство Гарвардского университета.
- Браун, Питер (2003). Возвышение христианского мира (2-е изд.). Оксфорд, издательство Блэквелл.
- Браун, Питер (2012). Сквозь игольное ушко: богатство, падение Рима и становление христианства на Западе, 350–550 гг . Издательство Принстонского университета . стр. 145–146. ISBN 978-0-691-16177-8 .
- Браун, Питер (2013). «Взгляды Гиббона на культуру и общество в пятом и шестом веках». В Бауэрсоке, Джорджия; Клайв, Джон; Граубар, Стивен Р. (ред.). Эдвард Гиббон и упадок и падение Римской империи . Издательство Гарвардского университета. стр. 37–52. doi : 10.4159/harvard.9780674733695.c5 . ISBN 978-0674733695 .
- Бернс, Томас С. Варвары у ворот Рима: исследование римской военной политики и варваров, ок. 375–425 гг. н. э., Издательство Университета Индианы, 1994 г. ISBN 978-0-253-31288-4 .
- Бёрм, Хеннинг. Западный Рим. От Гонория до Юстиниана. Архивировано 28 июля 2017 г. в Wayback Machine . Кольхаммер Верлаг 2013. ISBN 978-3-17-023276-1 ( обзор на английском языке, заархивировано 22 августа 2017 г. на Wayback Machine ).
- Бёрм, Хеннинг: Конец Римской империи: гражданские войны, имперская монархия и конец античности . В: М. Гелер – Р. Роллингер – П. Штробл (ред.): Конец империй . Спрингер 2022: 191–213. Архивировано 28 ноября 2022 г. в Wayback Machine.
- Кэмерон, Аверил (1993). Поздняя Римская империя, 284–430 гг . н.э. Кембридж, Массачусетс: Издательство Гарвардского университета. ISBN 978-0-674-51194-1 .
- Кэмерон, Алан (2010). Последние язычники Рима . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-19-974727-6 .
- Кэмерон, Аверил (2011). Средиземноморский мир в поздней античности, 395–700 гг. Н.э. (2-е изд.). Абингдон, Оксон: Рутледж. ISBN 978-0415579612 .
- Коннолли, Питер. Греция и Рим в войне. Пересмотренное издание, Greenhill Books, 1998. ISBN 978-1-85367-303-0 .
- Эррингтон, Р. Малкольм (2006). Политика Римской империи от Юлиана до Феодосия . Чапел-Хилл: Издательство Университета Северной Каролины. ISBN 0-8078-3038-0 .
- Гэддис, Майкл. Нет преступления для тех, у кого есть Христос. Религиозное насилие в христианской Римской империи. Калифорнийский университет Press, 2005. ISBN 978-0-520-24104-6 .
- Галинский, Карл. Классические и современные взаимодействия (1992) 53–73.
- Гиббон, Эдвард (1782). История упадка и разрушения Римской империи . С примечаниями преподобного Х. Х. Мильмана. 1845 г. (пересмотренный) (опубликовано в 2008 г.). Архивировано из оригинала 30 августа 2017 г.
- Гиббон, Эдвард (1906). «ХХ». В Бери, Дж. Б. (ред.). История упадка и разрушения Римской империи . Том. 3. Фред де Фау и Ко.
- Голсуорси, Адриан. Полная римская армия. ISBN 978-0-500-05124-5 . Темза и Гудзон, 2003.
- Голсуорси, Адриан. Падение Запада: медленная смерть римской сверхдержавы . ISBN 978-0-7538-2692-8 . Феникс, издательство Orion Books Ltd, 2010 г.
- Граф, Фриц (2014). «Установление закона в Феррагосто : римский визит Феодосия летом 389 года». Журнал ранних христианских исследований . 22 (2): 219–242. дои : 10.1353/earl.2014.0022 . S2CID 159641057 .
- Груман, Джеральд Дж. (1960). « Баланс и избыток как объяснение упадка и падения Гиббона». История и теория . 1 (1): 75–85. дои : 10.2307/2504258 . JSTOR 2504258 .
- Холсолл, Гай. Варварские миграции и римский Запад, 376–568 (Кембриджские средневековые учебники)
- Харпер, Кайл. Судьба Рима. Климат, болезни и конец империи . ISBN 978-0-691-19206-2 . Издательство Принстонского университета, 2017.
- Харпер, Кайл. Рабство в позднеримском мире 275–425 гг. ISBN 978-0-521-19861-5 . Издательство Кембриджского университета, 2011.
- Хизер, Питер (2006). Падение Римской империи. Новая история . Пан Книги. ISBN 978-0-330-49136-5 .
- Хебблуайт, Марк (2020). Феодосий и пределы империи . Лондон: Рутледж. дои : 10.4324/9781315103334 . ISBN 978-1-138-10298-9 . S2CID 213344890 .
- Ходжес, Ричард, Уайтхаус, Дэвид. Мухаммед, Карл Великий и происхождение Европы: археология и Пиреннская диссертация . Издательство Корнельского университета, 1983.
- Хант, Линн, Томас Р. Мартин, Барбара Х. Розенвейн, Р. По-чиа Ся, Бонни Г. Смит. Создание Запада, народов и культур, Том А: К 1500 году . Бедфорд / Сент-Мартинс, 2001 г. ISBN 0-312-18365-8 .
- Джеймс, Эдвард (2014). Европейские варвары, 200–600 гг . н.э. Лондон и Нью-Йорк: Рутледж. ISBN 978-0-58277-296-0 .
- Джонс, AHM Поздняя Римская империя, 284–602: Социальный, экономический и административный обзор [Мягкая обложка, том. 1] ISBN 0-8018-3353-1 Basil Blackwell Ltd., 1964.
- Джордан, Дэвид П. (1969). «Эра Константина» Гиббона и падение Рима». История и теория . 8 (1): 71–96. дои : 10.2307/2504190 . JSTOR 2504190 .
- Куликовский, Михаил (2019). Трагедия Империи: от Константина до разрушения Римской Италии . Кембридж, Массачусетс: Издательство Belknap Press Гарвардского университета. ISBN 978-0-67466-013-7 .
- Лаван, Люк и Майкл Малрайан, ред. (2011). Археология позднеантичного «язычества» . Лейден: Брилл. ISBN 978-90-04-19237-9 .
- Леткий Петр. Конница Диоклетиана. Происхождение, организация, тактика и вооружение . Перевод Павла Грыштара и Тристана Скупневича. Видавникдва Наполеона V ISBN 978-83-61324-93-5 . Освенцим 2012.
- Макджордж, Пенни. Поздние римские военачальники. Издательство Оксфордского университета, 2002.
- МакМаллен, Рамзи . Коррупция и упадок Рима . Издательство Йельского университета, 1988. ISBN 0-300-04799-1 .
- Мартиндейл, младший. Просопография Поздней Римской империи , том II, 395–527 гг . н.э. Издательство Кембриджского университета, 1980.
- Мэтьюз, Джон. Римская империя Аммиана Мичиганская классическая пресса, 2007. ISBN 978-0-9799713-2-7 .
- Мэтьюз, Джон. Западная аристократия и императорский двор 364–425 гг . Издательство Оксфордского университета, 1975. ISBN 0-19-814817-8 .
- Момильяно, Арнальдо. 1973. «Бесшумное падение империи в 476 году нашей эры». Итальянский исторический журнал , 85 (1973), 5–21.
- Никейси, MJ Сумерки Империи. Римская армия от правления Диоклетиана до битвы при Адрианополе . Дж. К. Гибен, 1998 г. ISBN 90-5063-448-6 .
- Рандсборг, Клавс . Первое тысячелетие нашей эры в Европе и Средиземноморье: археологический очерк . Издательство Кембриджского университета, 1991. ISBN 052138401X
- Пиганьоль, Андре (1950). «Причины падения Римской империи». Журнал общего образования . 5 (1): 62–69. JSTOR 27795332 .
- Рэтбоун, Доминик. «Прибыли и затраты. Часть IV, глава 15», стр. 299–326. В: Количественная оценка римской экономики. Методы и проблемы . Ред. Алан Боуман и Эндрю Уилсон. Oxford University Press, 2009 г., издание в мягкой обложке, 2013 г., ISBN 978-0-19-967929-4 .
- Теста, Рита Лицци (2007). «Христианский император, весталки и жреческие коллегии: новый взгляд на конец римского язычества» . Античное опоздание . 15 : 251–262. дои : 10.1484/J.AT.2.303121 . Архивировано из оригинала 07 октября 2022 г. Проверено 13 марта 2023 г.
- Уорд-Перкинс, Брайан (2005). Падение Рима и конец цивилизации . Оксфорд: Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-19-280728-1 .
- Вудс, Дэвид. «Феодосий I (379–395 н.э.)» . Де Императорибус Романис . Архивировано из оригинала 24 июля 2021 г. Проверено 29 июля 2021 г.