Наследование Римской империи

Продолжение, преемственность и возрождение Римской империи — постоянная тема истории Европы и Средиземноморского бассейна . Он отражает неизгладимые воспоминания о власти, престиже и единстве, связанных с Римской империей.
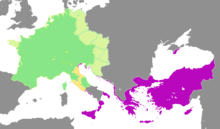
Некоторые государства заявляли о своей непосредственной преемственности с Римской империей, используя ее название или его вариацию в качестве своего исключительного или неисключительного самоописания. Шли столетия и происходило все больше политических расколов, идея институциональной преемственности становилась все более спорной. Наиболее стойкими и значительными претендентами на продолжение Римской империи на Востоке были Османская империя и Российская империя , которые обе претендовали на правопреемство Византийской империи после 1453 года; а на Западе — Священная Римская империя с 800 по 1806 год.
Помимо заявлений о продолжении существования, мнение о том, что Империя закончилась, привело к различным попыткам возродить ее или присвоить ее наследие, особенно в случае с православной Россией . Словарь « Третьего Рима », где «Первый Рим» — это Рим в Италии , а «Второй Рим» — это Константинополь в Византийской империи, использовался для передачи таких утверждений о законном преемственности.
Историография и номенклатура
[ редактировать ]В Западной Европе точка зрения на низложение Ромула Августула в 476 году нашей эры как исторический водораздел, ознаменовавший падение Западной Римской империи и, таким образом, начало Средневековья , была представлена Леонардо Бруни в начале 15 века, подкрепленная Кристофом Целлариусом в конце 17 века и зацементирован Эдвардом Гиббоном в конце 18 века. На практике это не более чем историографическая условность, поскольку имперская идея надолго пережила Западную Римскую империю в большей части Западной Европы и достигла территорий, которые никогда не находились под римским правлением в период классической античности .
Падение Константинополя в 1453 году исторически и широко считается концом Восточной Римско-Византийской империи и концом средневековья. [1] Тем не менее, спустя столетия после падения Константинополя возникли два заметных притязания на правопреемство Восточной Римской империи: Османская империя и Российская империя; в частности, Мехмед II, османский султан, захвативший Константинополь, обосновал свое принятие титула императора римлян ( Кайзер-и Рум ) правом завоевания , [2] что соответствовало византийской имперской идеологии, которая считала, что контроль над Константинополем является ключевым фактором легитимации императора. [3] а также был поддержан современным историографом Георгием Трапезундским . [4] [5] Притязания Мехмеда II были также признаны Геннадием Схоларием после того, как Мехмед II назначил его вселенским патриархом Константинополя в 1454 году, через год после падения Константинополя. [6] [7] Притязания Мехмеда II не были приняты Римско-католической церковью или христианскими государствами Европы в то время, и хотя Мехмед II намеревался реализовать свои претензии, начав завоевание Италии, его смерть в 1481 году ознаменовала последний раз, когда Османское государство пытался завоевать Италию или сам Рим; скорее последующие османские императоры вместо этого боролись с конкурирующими претендентами на римский титул (Священная Римская империя и Российская империя). По мере того как Османская империя продолжала разрыв с греко-римской легитимностью в пользу укрепления своей исламской легитимности, претензии Османской империи на Римскую империю исчезли; последнее официальное использование названия Кайзер-и Рум было в 18 веке.
Имена
[ редактировать ]Этот раздел нуждается в дополнительных цитатах для проверки . ( апрель 2023 г. ) |

The empire that modern historiography calls the "Byzantine Empire" never used that expression, and kept calling itself the Roman Empire, Empire of the Romans, or Romania until the fall of Constantinople.[citation needed] Following the establishment of the Holy Roman Empire in 800, Christian Western Europeans were reluctant to apply the "Roman" epithet to the Eastern Empire and frequently called it "Empire of the Greeks" or "Greek Empire", even though they also used Romania – the latter also for the Latin Empire of the 13th century.[citation needed] By contrast, Muslims in the Levant and farther east typically referred to the people of the Eastern Empire as "Romans" (Rum), and to Western Europeans, including those from the Holy Roman Empire, as "Franks" (Farang).[citation needed]
The name Byzantium refers to the ancient city on the Bosporus, now called Istanbul, which Constantine renamed Constantinople in 330. It was not used thereafter, except in rare historical or poetic contexts, until it first took its new meaning in 1557 when the German scholar Hieronymus Wolf published his Corpus Historiæ Byzantinæ, a collection of historical sources about the Eastern Empire. Then from 1648 onwards, Philippe Labbe and fellow French Jesuits published the 24-volume De Byzantinæ historiæ scriptoribus,[8] and in 1680 Du Cange produced his own Historia Byzantina. These endeavors further entrenched the use of the "Byzantine" label among French authors, including Montesquieu in the 18th century.[9] Outside France in the Western world, it only came into general use around the mid-19th century, after Barthold Georg Niebuhr and his continuators published the 50-volume Corpus Scriptorum Historiae Byzantinae.[10]
Similarly, what historians call the "Carolingian Empire" and "Holy Roman Empire" – in French and Spanish, "Holy Roman Germanic Empire" (Saint Empire romain germanique, Sacro Imperio Romano Germánico) was the Roman Empire, Empire of the Romans or simply Empire to their own subjects and rulers, with "Frankish" or "of the Franks" sometimes added depending on context. Only in 1157 did the twists and turns of the Investiture Controversy lead to the practice of calling the Empire, though not the Emperor himself, "holy" (sacrum).[11][12] The reference to Germany (Heiliges Römisches Reich Deutscher Nation, Sacrum Imperium Romanum Nationis Germanicæ), which first appeared in the late 15th century, was never much used in official Imperial documents,[13] and even then was a misnomer since the Empire's jurisdiction in Italy had not entirely disappeared. Other colloquial designations in the early Modern era included "German Empire" (Deutsches Reich) or "Roman-German Empire" (Römisch-Deutsches Reich).[14]
In 1773, a few decades before the Holy Roman Empire's demise, Voltaire made the famous quip that it "was in no way holy, nor Roman, nor an empire."[15]
Roman imperial legitimacy
[edit]In the early decades of the Roman Empire, legitimacy was largely defined by the institutions inherited from the Roman Republic, initially together with a form of hereditary succession within the Julio-Claudian dynasty. As the old Republican institutions gradually lost relevance, many later Emperors derived their legitimacy from acclamation by the army, and during the Nerva–Antonine dynasty, adoption by their predecessor. The Roman Empire itself was long defined by its eponymous capital, but this equation became blurred after the crisis of the Third Century as the administrative center was moved to Mediolanum (Milan), then further fragmented into various locations (e.g. Nicomedia, Sirmium, Augusta Treverorum, Serdica) before being reconsolidated by Constantine the Great in Byzantium, renamed and dedicated as Constantinople in 330 - while Ravenna replaced Milan as Western political capital in 402. Meanwhile, the Empire was Christianized in the course of the 4th century, which partly redefined the authority of the Emperor as he became the protector of the new state religion.
Thus, the Imperial identity, and therefore the question of which polity could rightfully claim to be the Roman Empire, rested not on a single criterion but on a variety of factors: dominant territorial power and the related attributes of peace and order; rule over Rome and/or Constantinople; protection of justice and of the Christian faith (against paganism, heresy, and later Islam); as well as, albeit only intermittently, considerations of dynastic succession or of ethnic nationalism.
Conflicting claims
[edit]The multidimensionality of the imperial claim, together with the unique prestige of the imperial title, explains the recurrence of often intractable conflicts about which polities and rulers could rightfully assume them. These conflicts lost their potency in the course of the Early modern period, however, as improved communications and literacy increasingly undermined any claim of universal supremacy.
A letter of Carolingian Emperor Louis II to Byzantine Emperor Basil I, probably drafted in Roman circles close to the Papacy in response to a lost original and surviving in 13th-century copy kept at the Vatican Library, articulates how the debate was framed in its time (ca. 871). The following quotes are from a full translation by scholar Charles West.[16]
Territorial rule over Constantinople is not the exclusive criterion for a rightful Imperial claim:
Over here with us, in truth, many books have been read, and many are tirelessly being read, yet never have we found that boundaries were set out, or that forms or precepts were issued, so that no-one is to be called Emperor (Basileus) except whoever happens to hold the helm of rule (imperium) in the city of Constantinople.
While the Empire as an idea is unitary, there is no established doctrine that there should be only one Emperor at any time, especially if the two Emperors are on friendly terms. Whether on purpose or not, Louis's description of two Emperors of a single Empire matches the doctrine underlying the Tetrarchy or the division between Eastern and Western Empire between 395 and 476:
You say also that the four patriarchal sees [of Constantinople, Alexandria, Antioch and Jerusalem] have a tradition handed down from the God-bearing Apostles to commemorate a single empire (imperium) during mass, and you advise us that we should persuade them that they should call us emperors. But neither does reason demand this, nor does it need to be done. Firstly, since it is not fitting for us to instruct others on how we should be called. Secondly, because we know that, without any persuasion on our part, both patriarchs and all other people under this heaven, except Your Fraternity, both office-holders and private citizens, do call us by this name, as often as we receive letters and writings from them. And we find that our uncles, glorious kings [i.e. Charles the Bald and Louis the German], call us emperor without any envy and say without any doubt that we are the emperor, not taking age into account – for they are older than us – but considering instead unction and the blessing by which, through the laying on of hands and prayer of the highest pontiff, we are divinely raised to this height and to the rulership of the Roman principality (romani principatus imperium), which we hold by heavenly permission. But however this may be, if the patriarchs do make mention of a single empire during the holy sacraments, they should be praised as acting entirely appropriately. For there is indeed one empire of the Father, the Son and the Holy Ghost, of which the church on earth is a part. But God has not granted this church to be steered (gubernari)either by me or you alone, but so that we should be bound to each other with such love that we cannot be divided, but should seem to exist as one.
Louis's claim is ancient enough to be justified by tradition since it has already held for several generations:
We are justified in feeling some astonishment that your Serenity believes we are aspiring for a new or recent title (appellatio). For as much as it pertains to the lineage of our descent (genus), it is neither new nor recent, for it comes from our great-grandfather of glorious memory [i.e. Charlemagne]. He did not usurp it, as you maintain, but received the imposition and the unction of his hands by the will of God, and by the judgement of the church and of the highest pontiff, as you will easily find written in your books. (...) Indeed none doubts that the dignity of our empire (imperium) is ancient, who is aware that we are the successor of ancient emperors, and who knows the wealth of divine piety.
Louis defends the Carolingian principle of dynastic succession as validated by tradition. Furthermore, Louis thinks that there should be no exclusive ethnic criterion for the Imperial dignity. Here Louis apparently refers to a claim by Basil that the Emperor should be a Roman and not from a non-Roman ethnicity (gens):
It is only right to laugh at what you said about the imperial name being neither hereditary (paternum) nor appropriate for a people (neque genti convenire). How is it not hereditary, since it was hereditary for our grandfather? In what way is it inappropriate for a people (gens), since we know – mentioning only a few for the sake of brevity – that Roman emperors were created from the people (gens) of Hispania [e.g. Theodosius I], Isauria [e.g. Leo III], and Khazaria [e.g. Leo IV]? And though you will not truthfully assert that these nations (nationes) are more outstanding in religion or virtues than the people (gens) of the Franks, yet you do not refuse to accept them nor disdain to talk of emperors coming from them. (...) Your beloved Fraternity moreover indicates you are surprised that we are called emperor of the Romans, not of the Franks. But you should know that if we were not emperor of the Romans, we should not be emperor of the Franks either. We derive this title and dignity from the Romans, amongst whom the first summit of glory and exaltation shone out, whose people (gens) and whose city we divinely received to govern, and whose church, the mother of all the churches of God, we received to defend and raise up. (...) Since things are so, why do you take such effort to criticise us, because we come from the Franks and have charge of the reins of the Roman empire (imperium), since in every people (gens) anyone who fears God is acceptable to Him? For certainly the elder Theodosius and his sons Arcadius and Honorius, and Theodosius the younger, the son of Arcadius, were raised from Spaniards to the summit of the Roman empire.
Using a modern vocabulary, Louis thought that those populations (gens) he cited (e.g. Spaniards, Isaurian etc.) were not Romans and that only the inhabitants of the city of Rome were Romans, not recognizing that those populations would have been seen as Romans, being citizens of the empire. While for Basil, the population (gens) of the Franks would not make good emperors because they were not citizens of the empire.
Empire and Christianity
[edit]Since the 4th century and particularly since the Edict of Thessalonica in 380, the defense and promotion of Christianity has been a key driver of Imperial identity. After that date, the territorial scope of the Empire or any of its continuating entities has never exactly coincided with that of Christendom, and the discrepancies led to enduring conflicts of legitimacy. The most consequential of these was the East-West Schism, which crystallized in 1054 as a consequence of longstanding fights over governance and jurisdiction (known as ecclesiastical differences) and over doctrine (theological differences), and can be fairly viewed as a delayed effect of the problem of two emperors arising from the creation of the Carolingian Empire in 800.
Earlier examples include the preference of several barbarian kingdoms during the Migration Period for Arianism after the competing Nicene Creed had regained dominance in Constantinople: the Burgundians until 516, Vandals until 534, Ostrogoths until 553, Suebi until the 560s, Visigoths until 587, and Lombards intermittently until 652. The adoption of Arianism protected these kingdoms' rulers from the religious disputes and policy initiatives of Constantinople, while being more acceptable to their majority-Catholic subjects than paganism.[citation needed]

On two occasions, the Eastern (Byzantine) Emperors reunited their church with its Western (Roman Catholic) counterpart, on political motivations and without durable effect. At the Second Council of Lyon in 1274, Emperor Michael VIII aimed to appease the Papacy to keep his Frankish adversaries in check, particularly Charles I of Anjou's plans to re-invade the Empire; the union was never widely accepted in Constantinople, and was reversed at the Council of Blachernae in 1285 after both Michael and Charles had died. At the Council of Ferrara/Florence in 1438–39, Emperor John VIII negotiated under the threat of Ottoman conquest, but the union agreement was again resisted in Constantinople and only proclaimed by Isidore of Kiev in December 1452, four years after John's death and too late to prevent the fall of Constantinople a few months later.
Conversely, the Ottoman Sultans' policies as self-proclaimed Emperors of the Romans (i.e. in the language of the time, of the Eastern Orthodox Christians) supported the independence of the Orthodox Church from Rome and occasionally favored reforms to keep religiously inspired separatism in check, e.g. the revival of the Serbian Patriarchate of Peć in 1557. The initial instrument of that policy, Gennadius Scholarius, had been a prominent opponent of the union of the Eastern and Western churches in the 1440s and early 1450s.
The link between Empire and Christianity has a durable legacy: to this day, Rome remains the seat of the Catholic Church, and Constantinople (Istanbul) that of the Ecumenical Patriarchate with a widely recognized status of primus inter pares within the Eastern Orthodox Church. In 2018, the negotiations over autocephaly of the Orthodox Church of Ukraine led to a schism between Moscow and Constantinople as the Russian Orthodox Church unilaterally severed full communion with the Ecumenical Patriarchate. A similar schism had occurred in 1996 over the Estonian Apostolic Orthodox Church, but unlike in 2018 it was resolved after a few months.
The Imperial connection extends, through the legacy of the Ottoman Empire, to Islam as well. Istanbul was also until 1923 the seat of the only widely recognized Caliphate of the last half-millennium, and keeps most of the surviving Relics of Muhammad as the Sacred Trust in Topkapı Palace, close to the location of the former Roman Imperial palace.
Continuation in the East
[edit]Roman/Byzantine Empire until 1204
[edit]
There is seamless continuity between the Roman and Byzantine Empires, to the extent that the date at which the former ends and the latter begins is essentially a matter of historiographical convention. The Byzantines consistently and near-exclusively called themselves Romans, before and after they adopted Greek as principal state language in the 7th century. Traditional Western European historiography retains 395 as the date of beginning of the Byzantine Empire, when Theodosius I was succeeded by Arcadius in the East and Honorius in the West.[citation needed] Alternative conventions date the transition from Rome to Byzantium at the translation of the imperial capital from Rome to Constantinople in 330, or at the reign of Heraclius marking the end of late antiquity.[citation needed]
Even though the Byzantine Empire went through numerous political upheavals, and faced periods of dramatic contraction in the 7th and late 11th centuries, it exhibited unquestionable institutional continuity until 1204, not least because its central and defining seat of power, Constantinople, was never conquered during this period. Conversely, in the Eastern Mediterranean territories that ceased being part of the Empire during that period, there emerged almost no competing claim of Imperial legitimacy. In their different ways, the Avars and Slavs in Southeastern Europe, and the Sasanians and Muslims in the Levant and Northern Africa, had different models of governance and no appetite for posing as Romans. This may also be linked to their inability to conquer the Imperial capital despite numerous attempts, as is suggested by the counter-example of the Ottoman Sultans claiming the Imperial title after 1453.
Bulgarian Empire
[edit]In the period before 1204, the only significant competing Imperial claim in the East appeared in 913, when Simeon I the Great, ruler of Bulgaria, was crowned "Emperor and Autocrat of all Bulgarians and Romans" (Car i samodǎržec na vsički bǎlgari i gǎrci in the modern vernacular) by the Patriarch of Constantinople and imperial regent Nicholas Mystikos outside of the Byzantine capital. The decade 914–927 was then spent in a destructive Byzantine–Bulgarian war over the Imperial claim and other matters of conflict. The Bulgarian monarch was eventually recognized as "Emperor of the Bulgarians" (basileus tōn Boulgarōn) by the Byzantine Emperor Romanos I Lakapenos in 924, following the convention also adopted with the Carolingian Empire that basileus (a Greek word that can translate as king or emperor depending on context) was not an equal title to that of the Emperor as long as it did not explicitly confer authority over the "Romans". Constantinople's recognition of the basileus dignity of the Bulgarian monarch and the patriarchal dignity of the Bulgarian patriarch was again confirmed at the conclusion of permanent peace and a Bulgarian–Byzantine dynastic marriage in 927. The Bulgarian title "tsar" (Caesar) was adopted by all Bulgarian monarchs up to the fall of Bulgaria under Ottoman rule.
During the Second Bulgarian Empire, 14th-century literary compositions portrayed the then capital of Tarnovo, now Veliko Tarnovo, as successor of both Rome and Constantinople.[17] Bulgarian contemporaries called the city "Tsarevgrad Tarnov", the Imperial city of Tarnovo, echoing the Bulgarian name then used for Constantinople, Tsarigrad.[18]
Fourth Crusade and its aftermath
[edit]
The Fourth Crusade and sack of Constantinople in 1204 marked a major rupture in the history of the Eastern Roman/Byzantine Empire, and opened a period of fragmentation and competing claims of Imperial legitimacy. The crusading (Latin) invaders divided most of the Empire among themselves by a formal treaty of partition, under which the Latin Empire of Constantinople's direct rule did not extend greatly further than the city itself. It included the Straits and their immediate hinterland, e.g. Adrianople and Nicomedia, but neither Salonica nor Nicaea. Other territories of the former Empire were not conquered by the Latin crusaders, and remained held by various holdovers of the former (Greek) Empire.
Several of the polities emerging from that fragmentation claimed to be the rightful successor of the prior Empire, on various motives: the Latin Empire held the Imperial capital; the rulers of the Empire of Trebizond stemmed from the formerly Imperial Komnenos family; those of the Despotate of Epirus (briefly the Empire of Thessalonica) were from the Angelos family, even though they renounced the imperial claim by accepting Nicaean overlordship in 1248; the Empire of Nicaea successfully claimed the patriarchate in 1206, and eventually prevailed through skillful management of alliances and its recapture of Constantinople in 1261.
Latin Empire of Constantinople
[edit]The Latin Empire had its own line of Imperial succession, initially dominated by the House of Flanders then by the French House of Courtenay. It was embattled almost from the start, as the city was never able to recover from the trauma of 1204. Despite its theoretical suzerainty, the Latin Empire was not even politically dominant among the crusader states, which were referred to as Latin or Frankish by Easterners.
After being expelled from Constantinople in 1261, its titular Emperors occasionally held territorial power in parts of modern Greece. Jacques des Baux was Prince of Achaea in 1381–1383, and the last recorded claimant to the Latin Imperial title.[citation needed]
Late Byzantine era
[edit]
The Palaiologos dynasty prolonged the Roman Imperial experience from its recovery of Constantinople in 1261 until the Ottoman conquest in 1453. The Empire shrunk considerably during that period, and at the end it was only the imperial city itself without any hinterland, plus most of the Peloponnese (then referred to as Morea) typically under the direct rule of one of the Emperor's sons with the title of Despot. This line of Imperial succession ceased in 1453; even though the Despotate of the Morea lingered on a few more years, until the Ottomans conquered it in 1460, its rulers at the time did not claim Imperial authority.
Serbian Empire
[edit]In 1345, the Serbian King Stefan Dušan proclaimed himself Emperor (Tsar) and was crowned as such at Skopje on Easter 1346 by the newly created Serbian Patriarch, as well as by the Patriarch of All Bulgaria and the Archbishop of Ohrid. His imperial title was recognized by, among others, the Bulgarian Empire, much diminished following the Battle of Velbazhd in 1330, albeit not by the Byzantine Empire. In Serbia, the title of "Emperor of Serbs and Romans" (in its final simplified form; цар Срба и Римљана / car Srba i Rimljana in modern Serbian) was only employed thereafter by Stefan Dušan's son Stefan Uroš V until his death in 1371. A half-brother of Dušan, Simeon Uroš, and then his son Jovan Uroš, used the same title until the latter's abdication in 1373, while ruling as dynasts in Thessaly.
Empire of Trebizond
[edit]The Empire of Trebizond, one of the entities that had emerged from the fragmentation of the early 13th century, survived until Ottoman conquest in 1461. Its Komnenos rulers claimed the Imperial title for themselves in competition to the ones in Constantinople, even though they did not receive any meaningful international recognition.
A separate polity on the Crimean coast of the Black Sea, the Principality of Theodoro, only fell to the Ottomans in 1475. There is no indication that its rulers made any claim of being Roman Emperors.
Andreas Palaiologos's cessions
[edit]
Andreas Palaiologos, a nephew of the last Byzantine Emperor Constantine XI Palaiologos and the head of what remained of the Palaiologos family, started calling himself Emperor of Constantinople in 1483 and, possibly childless, sold what he viewed as his imperial title to Charles VIII of France in 1494.[19] The following Kings of France kept the claim until Charles IX in 1566, when it went into disuse. Charles IX wrote that the imperial Byzantine title "is not more eminent than that of king, which sounds better and sweeter."[20]
In his last will in 1502, Andreas Palaiologos again ceded his self-awarded imperial title, this time to Ferdinand II of Aragon and Isabella I of Castile.[21] Other pretenders to the Byzantine throne have appeared following his death that year, with increasingly dubious claims as centuries went by. Charles I Gonzaga, Duke of Mantua, who also claimed descent from the Palaiologos family, declared in 1612 his intent to reclaim Constantinople but only succeeded in provoking an uprising in the Mani Peninsula, which lasted until 1619.
Ottoman Empire after 1453
[edit]

After the conquest of Constantinople in 1453, Mehmed II declared himself Roman Emperor: Kayser-i Rum, literally "Caesar of the Romans", the standard title for earlier Byzantine Emperors in Arab, Persian and Turkish lands.[22] In 1454, he ceremonially established Gennadius Scholarius, a staunch antagonist of Catholicism and of the Sultan's European enemies, as Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople and ethnarch (milletbashi) of the Rum Millet, namely Greek Orthodox Christians within the Empire. In turn, Gennadius endorsed Mehmed's claim of Imperial succession.[23][24]
Mehmed's claim rested principally with the idea that Constantinople was the rightful seat of the Roman Empire, as it had been for more than a millennium even if the 1204–1261 period is subtracted. Contemporary scholar George of Trebizond wrote that "the seat of the Roman Empire is Constantinople ... and he who is and remains Emperor of the Romans is also the Emperor of the whole world".[25] An additional though questionable claim of legitimacy referred to the past alliances between the Ottoman dynasty and Byzantine Imperial families. Byzantine Princess Theodora Kantakouzene had been one of the wives of Orhan I, and an unsupported but widespread story portrayed Mehmed as a descendant of John Tzelepes Komnenos.[19]
George of Trebizond addressed Mehmed in a poem:[26]
No one can doubt that he is emperor of the Romans. He who holds the seat of empire in his hand is emperor of right; and Constantinople is the centre of the Roman Empire.
Mehmed's imperial plans went further and aimed at conquering Rome itself, thus reuniting the Empire in a way it hadn't been for nearly eight centuries. His Italian campaign started in 1480 with the invasion of Otranto, but was cut short by Mehmed's sudden death on 3 May 1481.[27] None of his successors renewed that endeavor. Instead, they repeatedly (albeit never successfully) attempted to conquer the capital of the rival contenders to the Imperial Roman title, with a first siege of Vienna in 1529 and a second one in 1683.
Being the rightful heir of the Roman/Byzantine Empire became part of the identity of the Sultanate, along with its Turkish and Muslim heritage, even though that dimension was played down by Western observers. According to Turkish scholar F. Asli Ergul:[28]
Although this title was not recognized by either the Greeks or the Europeans, the Ottoman dynasty, by defining itself as Rum [Roman], internalized the hegemonic and multi-cultural structure of the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire). Obviously it was a declaration of the Ottoman Sultan's seizure of the heritage of the Eastern Roman Empire.
Additionally, over the centuries, many Greeks abandoned Orthodoxy and embraced Islam, to the point that today, in part because of the intermingling of ethnic Greeks with Turks in the Ottoman Empire, genetic studies have found that modern Turks are closer, genetically, to Mediterranean and Middle Eastern people than to Central Asians.[28]
In diplomatic exchanges with the Holy Roman Empire, the Ottomans initially refused to acknowledge the latter's Imperial claim, because they saw themselves as the only rightful successors of Rome. In the Treaty of Constantinople (1533), the Austrian negotiators agreed not to make any mention of the Holy Roman Empire, only referring to Ferdinand I as King of Germany and Charles V as King of Spain. The Ottomans abandoned that requirement in the Treaty of Sitvatorok in 1606, and similarly to the Russian Empire in the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca in 1774.
Chinese usage during the Ming dynasty referred to the Ottomans as Lumi (魯迷), derived from Rûmi, literally "Roman". It is important to emphasize that in China there is the concept of "conquest dynasty", with the Chinese considering dynasties of non-Han ethnic origin as the Yuan dynasty (Mongolian origin) and Qing dynasty (Manchu origin) as Chinese dynasties, this concept (when used for non-Chinese foreign people) may have influenced the Chinese to see the Ottomans as a Roman dynasty [29]
Continuation in the West
[edit]Political fragmentation and imperial overlordship
[edit]

By the start of the 5th century, the Western Roman Empire remained close to its maximum territorial extent, notwithstanding the loss of the Agri Decumates during the crisis of the Third Century, but Roman rule had become fragile and many areas were depopulated. In the early years of the century, the Empire withdrew from Great Britain, leaving it open to Anglo-Saxon settlement. Mounting foreign incursions soon resulted in permanent settlement of Germanic and other ethnic groups into territories that became gradually autonomous, were sometimes acknowledged or even encouraged by treaty (foedus) by the Western Empire, and often embarked on expansion by further conquest.
The Vandals crossed the Rhine in 406, the Pyrenees in 409, the Strait of Gibraltar in 428, and established the Vandal Kingdom in Northern Africa and the Western Mediterranean islands by the mid-5th century; the Suebi, initially moving alongside the Vandals, established their Western Iberian kingdom in 409; the Visigothic Kingdom was initially established by treaty in 418 in the Garonne Valley, and soon expanded into the Iberian Peninsula; the Alemanni expanded into Alsace and beyond, from their initial base in the Agri Decumates; in the 440s, the Kingdom of the Burgundians was established around the Rhone; an autonomous Kingdom of Soissons was carved out from 457 by Roman military commanders between the Seine and Somme rivers; last but not least, the Franks, which had been established north of the Rhine in 358 by treaty with Emperor Julian, expanded into what is now Belgium and Northern France. As a consequence, when the last Western Emperor Romulus Augustulus was deposed by military commander Odoacer in 476, his direct rule did not extend much beyond the current Northern borders of Italy. Another military leader, Julius Nepos, briefly Romulus Augustulus's predecessor, held territory in Dalmatia and kept the Imperial title until his assassination in 480.
In a symbolic act that would fascinate later historians, Odoacer sent back the Imperial regalia or accessories of Romulus Augustulus to the Eastern Emperor Zeno in Constantinople. Far from signaling the end of imperial rule in Italy, this meant that Odoacer acknowledged Zeno's overlordship and did not claim full sovereignty. Like previous foederati leaders, he adopted the title of King (Rex) and ruled in the name of the remaining Emperors, namely Zeno and also Julius Nepos while the latter was still alive. This arrangement was kept by Theodoric the Great, who vanquished and killed Odoacer in 493 and replaced him as King of Italy.

Political boundaries kept moving in the later 5th and 6th centuries. Clovis I, king of the Franks (d. 511), conquered Alemannia, the Kingdom of Soissons and most of the Visigothic Kingdom north of the Pyrenees, and his sons conquered the Kingdom of the Burgundians in 534, thus creating a vast kingdom of Francia, which was periodically divided between various members of the Merovingian dynasty. Meanwhile, Eastern Emperor Justinian I reestablished direct Imperial rule in Southern Spain, North Africa and especially Italy, reconquered during the hard-fought Gothic War (535–554). Later in the 6th century, Emperor Maurice sponsored Gundoald, a member of Clovis's Merovingian dynasty, in his claim to the Frankish kingdom, which ended unsuccessfully in 585 at Saint-Bertrand-de-Comminges.
Even though it was out of the Empire's direct military reach, Francia kept acknowledging the overlordship of Constantinople throughout the 6th century. At a ceremony in early 508 in Tours, Clovis received the insignia sent by Emperor Anastasius I which established his service to the Empire as Consul. Similarly, in the early 6th century, King Gundobad of the still-independent Burgundians, despite being an Arian, was Magister militum in the name of the Emperor.[30] The Gesta pontificum Autissiodorensium, a compendium of information about the Bishops of Auxerre first compiled in the late 9th century, keeps referring to the reigning Roman Emperor up to Desiderius (d. 621), listed as bishop "in the reigns of Phocas and Heraclius" (imperantibus Foca, atque Heraclio).[31][32] No such deference appears to have existed in the Visigothic Kingdom at the same time. Chris Wickham portrays the Visigothic king Euric (466–484) as "the first major ruler of a 'barbarian' polity in Gaul - the second in the Empire after Geiseric - to have a fully autonomous political practice, uninfluenced by any residual Roman loyalties."[33] A century and a half later in the 620s, Isidore of Seville articulated for the Visigothic Kingdom, by then a Catholic monarchy following the conversion of Reccared I in 587, a vision of Christian monarchy on an equal status with the Eastern Roman Empire that would have seminal influence on later Western European political thinking.[34]: 236
Imperial rule in the West eroded further from the late 6th century. In Britain, to the extent discernible from scarce documentation, Roman rule was at best a distant memory. In Francia, references to Imperial overlordship disappear at the time of Merovingian renewal in the early 7th century under Chlothar II and Dagobert I. In the Iberian Peninsula, the Visigothic King Suintila expelled the last Imperial forces from Southern Spain in 625. In Italy, the Lombards invaded in 568, and the resulting Kingdom of the Lombards was hostile to the Empire whose territorial footprint shrunk gradually.
Papal pivot
[edit]The Roman Papacy was to become the instrument of the Imperial idea's revival in the West. Rome was increasingly isolated from Constantinople following the devastations of Gothic War (535–554), subsequent imperial choices to favor Ravenna over Rome,[34]: 149 and the Lombard invasion of Italy starting in 568, which limited its communications with the main imperial outposts in Ravenna and Sicily.[34]: 141 The Column of Phocas on the Roman Forum, dedicated in 608, counts among the last monumental expressions of (eastern) imperial power in Rome. In 649, in breach of tradition, Pope Martin I was elected and consecrated without waiting for imperial confirmation.[34]: 218 Constans II was the last (eastern) emperor to visit Rome for centuries, in 663, and plundered several of the remaining monuments to adorn Constantinople. Meanwhile, and for various reasons, Catholicism finally triumphed over Arianism in the Western kingdoms: in the Visigothic Iberian Peninsula with the conversion of Reccared I in 587, and in Lombard-held Italy, after some back-and-forth, following the death of King Rothari in 652. Pope Gregory I (590-604) established the foundations for the papacy's incipient role as leader of Christianity in the West, even though at the time there was no conception of an alternative imperial authority to be established there in competition with Constantinople.[34]: 182
The promotion of iconoclasm by Emperor Leo III the Isaurian from 726 led to a deepening rupture between the Eastern Empire and the Papacy. Pope Gregory II saw iconoclasm as the latest in a series of imperial heresies. In 731, his successor Pope Gregory III organized a synod in Rome which declared iconoclasm punishable by excommunication. Leo III responded in 732/33 by confiscating all papal patrimonies in south Italy and Sicily, and further removed the bishoprics of Thessalonica, Corinth, Syracuse, Reggio, Nicopolis, Athens, and Patras from papal jurisdiction,[citation needed] instead subjecting them to the Patriarch of Constantinople. This was in effect an act of triage: it strengthened the imperial grip in Southern Italy, but all but guaranteed the eventual destruction of the exarchate of Ravenna, which soon occurred at Lombard hands. In effect, the papacy had been "cast out of the empire".[35] Pope Zachary, in 741, was the last pope to announce his election to a Byzantine ruler or seek their approval.[36]

The Popes needed to quickly reinvent their relationship to secular authority. Even though the neighboring Lombard kings were no longer heretical, they were often hostile. The more powerful and more distant Franks, which had by and large been allies of the Empire, were an alternative option as potential protectors. In 739, Gregory III sent a first embassy to Charles Martel seeking protection against Liutprand, King of the Lombards, but the Frankish strongman had been Liutbrand's ally in the past and had asked him in 737 to ceremonially adopt his son. The Papacy had more luck with the latter, Pepin the Short, who succeeded Charles in October 741 together with his elder brother Carloman (who withdrew from public life and became a monk in 747). Pope Zachary was pressed into action by the final Lombard campaign against the exarchate of Ravenna, whose fall in mid-751 sealed the end of Byzantine rule in Central Italy. He was in contact with the Frankish ruling elites through the venerable Boniface, Archbishop of Mainz, and other clerics such as Burchard of Würzburg and Fulrad. In March 751 he moved to depose Childeric III, the last Merovingian King, following which Pepin was dedicated as King of France in Soissons. In 754, Zachary's successor Pope Stephen II undertook the first-ever papal visit north of the Alps, met Pepin in Ponthion and anointed him as king at Saint-Denis on July 28, setting the template for later rites of coronation of French Kings. Stephen further legitimized the Carolingian dynasty by also anointing Pepin's sons Charles and Carloman, by prohibiting the election of any non-descendant of Pepin as king, and by proclaiming that "the Frankish nation is above all nations".[37] This in return prompted the Donation of Pepin in 756, cementing the Popes' rule over the Papal States over the next eleven centuries. Subsequently, in 773–774, Pepin's son and successor Charlemagne conquered the Lombard Kingdom of Italy.
Holy Roman Empire
[edit]
The coronation of Charlemagne by Pope Leo III, in Rome on Christmas Day 800, was explicitly intended as establishing continuity with the Roman Empire that still existed in the East. In Constantinople, Irene of Athens had blinded and deposed her son Emperor Constantine VI a few years earlier. With no precedent of a woman being sole holder of the imperial title, her critics in the West (e.g. Alcuin) viewed the imperial throne as vacant rather than recognizing her as Empress. Thus, as Peter H. Wilson put it, "it is highly likely Charlemagne believed he was being made Roman Emperor" at the time of his coronation; however, Charlemagne's imperial title rested on a different base from any of the Roman emperors until him, as it was structurally reliant on the partnership with the Papacy, embodied in the act of his coronation by the Pope.[11]
Meanwhile, the accession to the Byzantine throne of Nikephoros I in 802 confirmed the conflict of legitimacy between the Frankish and Byzantine incarnations of the Roman Empire, known in historiography as the problem of two emperors (in German, Zweikaiserproblem). According to Theophanes the Confessor, Charlemagne had attempted to prevent that conflict with a project to marry Irene, but this was not completed. The territorial conflicts were addressed in the following years through a series of negotiations known as the Pax Nicephori, but the broader conflict with Constantinople about Imperial legitimacy proved extremely durable.
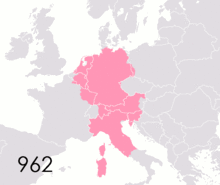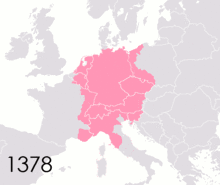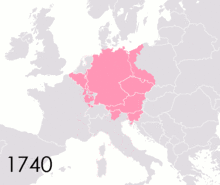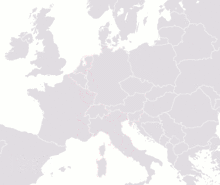


Political authority fragmented within the Empire following Charlemagne's death. The eventual outcome was an association of the Imperial dignity with the easternmost ("German") lands of the Carolingian geography, but that was not self-evident at the start and took a long time to happen. From 843 to 875, the holders of the Imperial title only ruled over Northern Italy and, at the start, the "middle kingdom" of Lotharingia. On Christmas Day 875, exactly 75 years after Charlemagne, Charles the Bald of West Francia was crowned Emperor in Rome by Pope John VIII, adopting the motto renovatio imperii Romani et Francorum, which raised the prospect of an Empire centered on what is today France. Charles died soon afterwards in 877, and his successor Charles the Fat only briefly managed to reunite all the Carolingian domains, and after his death in 888 the Western part of Francia was dominated by the non-Carolingian Robertians, later the Capetian dynasty. For over seven decades, the Emperors' authority was then mostly confined to Northern Italy, until Otto I revived the Imperial idea and was crowned by Pope John XII in Rome in 962. From then on, all Emperors had dynastic roots in the Germanic-speaking lands (even though Frederick II was born in Italy, Henry VII in Valenciennes, Charles IV in Prague, Charles V in Ghent, Ferdinand I in Spain, Charles VII in Brussels, Francis I in Nancy, and Francis II in Florence).
During the millennium of the Holy Roman Empire, several specific attempts were made to recall the Empire's classical heritage. Emperor Otto III reigned from Rome from 998 to his death in 1002, and made a short-lived attempt to revive ancient Roman institutions and traditions in partnership with Pope Sylvester II, who chose his papal name as an echo of the time of Constantine the Great. Frederick II took a keen interest in Roman antiquity, sponsored archaeological excavations, organized a Roman-style triumph in Cremona in 1238 to celebrate his victory at the battle of Cortenuova, and had himself depicted in classical imagery.[38] Similarly, Maximilian I was highly mindful of classical references in his "memorial" projects of the 1510s that included the three monumental woodblock prints of the Triumphal Arch, Triumphal Procession and Large Triumphal Carriage.
Papacy and the imperial title
[edit]
According to his biographer Einhard, Charlemagne was unhappy about his coronation, a fact that later historians have interpreted as displeasure about the Pope's assumption of the key role in the legitimation of Imperial rule. Instead of the traditional recognition by popular acclamation, Leo III had crowned Charlemagne at the outset of the ceremony, just before the crowd acclaimed him. In September 813, Charlemagne tried to override that precedent by himself crowning his son Louis the Pious in Aachen, but the principle of Papal coronation survived and was renewed in 962 when Otto I restored the Empire and its rituals after decades of turmoil and received the Imperial Crown from Pope John XII.
The interdependence between Pope and Emperor led to conflict after the Papacy started asserting its position with the Gregorian Reform of the mid-11th century. The Investiture Controversy (1076-1122) included episodes of dramatic confrontation, in which the pope attempted to deprive the emperor of his imperial dignity. The Dictatus papae, a papal document issued in 1075 shortly after the election of Gregory VII, states that the pope "alone may use the Imperial Insignia", that "All princes shall kiss the feet of the Pope alone", and that "It may be permitted to him to depose emperors". Following Emperor Henry IV's walk to Canossa in January 1077, Gregory VII pronounced his absolution but referred to him as rex Teutonicorum ("king of the Germans"), thus omitting the imperial title and the fact that Henry was king (rex) of several realms, including Burgundy and Italy.[39] Wars of Guelphs and Ghibellines, the respective partisans of the Pope and the Emperor, lasted until the 15th century. In 1527, the Pope's involvement in the Italian Wars led to the traumatic sack of Rome by Charles V's imperial troops, after which the Papacy's influence in international politics was significantly reduced.
Kingdoms and the imperial title
[edit]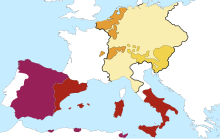

Early in the Empire's history, Louis the Pious formally established the supremacy of the Empire over Catholic kingdoms through the document issued in 817 and later known as Ordinatio Imperii. The view at the time was that the Empire covered all Western Christendom under one authority. (The British Isles, Brittany, and the Kingdom of Asturias were omitted in this vision.) Under Louis's arrangement, only his elder son Lothair would hold the title of Emperor, and Lothair's younger brothers Pepin and Louis should obey him even though they were kings, respectively, of Aquitaine and Bavaria. That document was controversial from the start, not least as it did not conform to Frankish succession law and practices. Following Louis the Pious's death in June 840, the Battle of Fontenoy (841), Oaths of Strasbourg (842) and Treaty of Verdun (843) established a different reality, in which the Imperial title remained undivided but its holder competed with kings for territory, even though at the time all were still bound by the family links of the Carolingian dynasty and the bounds of Catholic Christianity.
Following the gradual demise of the Carolingian dynasty in the late 9th and 10th centuries, the rivalry between the Empire and individual kingdoms developed on these early precedents. The Kingdom of France, developing from Charles the Bald's West Francia, was continually reluctant to acknowledge the Emperor's senior status among European monarchs. As Latin Christendom expanded in the High Middle Ages, new kingdoms appeared outside of the Empire and would similarly bid for territory and supremacy. France itself was instrumental in the developments that led to the Empire's political decline from the 16th to the early 19th centuries.
Modern-era nationalist revivals
[edit]A number of political regimes have claimed various forms of successorship of the Roman Empire, even though they acknowledged a significant time lag between what they viewed as the Empire's extinction and their own efforts to revive it. These attempts have increasingly been framed in nationalist terms, in line with the times.
Despite its name, European imperialism has typically not invoked the memories of the Roman Empire, with the only exception of Italy for a few decades in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Thus, European colonial empires are not mentioned in this section.
Imperial Russia
[edit]
Ivan III of Russia in 1472 married Sophia (Zoé) Palaiologina, a niece of the last Byzantine Emperor Constantine XI, and styled himself Tsar (Царь, "Caesar") or imperator. In 1547, Ivan IV cemented the title as "Tsar of All Rus" (Царь Всея Руси). In 1589, the Metropolitanate of Moscow was granted autocephaly by the Patriarchate of Constantinople and thus became the Patriarchate of Moscow, thanks to the efforts of Boris Godunov. This sequence of events supported the narrative, encouraged by successive rulers, that Muscovy was the rightful successor of Byzantium as the "Third Rome", based on a mix of religious (Orthodox), ethno-linguistic (East Slavic) and political ideas (the autocracy of the Tsar).[40][41] Supporters of that view also asserted that the topography of the seven hills of Moscow offered parallels to the seven hills of Rome and the seven hills of Constantinople.
In 1492, Zosimus, Metropolitan of Moscow, in a foreword to his Presentation of the Paschalion, referred to Ivan III as "the new Tsar Constantine of the new city of Constantine — Moscow."[42] In a panegyric letter to Grand Duke Vasili III composed in 1510, Russian monk Philotheus (Filofey) of Pskov proclaimed, "Two Romes have fallen. The third stands. And there will be no fourth. No one shall replace your Christian Tsardom!"[40]
Imperial Spain
[edit]The Hispano-Gothic Monarchy, recognized himself politically and legally as the heir and successor of Roman Empire in Hispania,[43] using the Roman symbols of monarchy.[44] Additionally, two Roman usurpers of the Visigothic Kingdom attempted to claim imperial authority: Burdunellus (496) and Petrus (506).[45][46]
During the Middle Ages in Spain, some iberian monarchs, mostly from Kings of Castile and Kings of Leon, used the title of Imperator totius Hispaniae,[47] in which there were claims, not only of the suzerainty over the other kings of the peninsula (both Christian and Muslim), but also the king's equality with the rulers of the Byzantine Empire and Holy Roman Empire.
The last titular holder heir to the rank of Eastern Roman emperor, Andreas Palaiologos, sold his imperial title, along with his domains in Morea,[48] to the Catholic Monarchs of Spain (Ferdinand II of Aragon and Isabella I of Castile)[49][50] in his will, written on 7 April 1502,[51] designating them, and their successors (the future Spanish monarchs) as his universal heirs.[52] Andreas argue that The Spanish kings held, through the Aragonese line, the ownership of the duchy of Athens and Neopatria, also because in Spanish noble circles there was a belief that the Álvarez de Toledo family (cousins of Ferdinand of Aragon) descended from the ancient Byzantine imperial lineage of the Komnenos. He was hoping that the Spanish Army would launch a crusade (during Ottoman–Venetian wars) from their south-Italians domains in Apulia, Calabria, and Sicily to conquer the Peloponnese, before moving on to Thrace, Macedonia, and Constantinople; however, no Spanish monarch is known to have used the Byzantine imperial titles.[48] In 1510, Pope Julius II revoked Alexander VI's granting of the title of King of Jerusalem to Louis XII of France, and transferred it to Ferdinand the Catholic (which was included in his title of King of Naples after Treaty of Blois).[53][54] This gave a step to make the confrontation with the Ottoman Empire in the Mediterranean in the Spanish-Ottoman wars, against Turkish claims of being Rome Successor.[48]
During this times of the Catholic Monarchy, Antonio de Nebrija conceived Spain, after the end of the Reconquista and its political unification of Castille and Aragon, as the heir of the Roman empire, because there was a direct lineage from the Roman emperors and the Visigothic kings (considered their legal successors of Hispania), also appealed to a literary legitimisation in which Castilian replaced Latin as the language of the Empire.[55]

With the succession of Charles I of Spain to the throne of Castile and Aragon, the peninsular territories were included in a greater inheritance that included the Burgundians (the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Burgundy, Franche-Comté) and the Austrians (Tyrol, Austria, Styria, Carinthia, Carniola), to which in 1519 was added the title of Holy Roman Emperor. It was the first time, since the coronation of Charlemagne in 800, and after the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, in which the Romano-Germanic and Byzantine crowns coincided in the same person.[48] The followers of the Empire of Charles V (and his imperial ideal of being the universal monarch of Christendom, the Universitas Christiana)[56] created maps, like the Europa regina, in which Hispania is the head, crowned with the Holy Roman Empire's insignia, its Carolingian crown (inherited of its Roman claims).[57][58][59]
During Bourbon Spain, following the Renaissance tradition, the Spanish Bourbons, like Philip V, in their attempts to stablish the Enlightenment programme, conceived the Spanish empire to be the equal of the Roman empire. So, they started to recover the cultural hegemony, lost under the last Austrian rulers, by imitating Rome political power, institutions and symbols.[55]
With all of this history in the Spanish Monarchy,[60] Spanish nationalism claims that there is a legitimate ideological-dynastic (titles of Emperor of Constantinople and King of Jerusalem in the Spanish Crown, also in the past have been Holy Roman Emperor), geostrategic (kingdom of Naples and Sicily together, the conquests of North African plazas in Barbary, like Melilla, Ceuta, Mazalquivir, Oran, Bugia and Peñón of Algiers) and cultural basis (being a Latin country) to claim the inhertiance of the Roman Empire. Also, because many cities and institutions in the Kingdom of Spain still use the Roman double-headed eagle to this day, like the city of Toledo, the province of Toledo and the province of Zamora.[61] and the manual of history of Edebé editorial (conservative nationalist) establishes a continuity between the Iberians, Rome, the Visigoths, and the peninsular Christian kingdoms as direct heirs of this Roman imperial tradition as Hispano-romans.[62] This claim is also reinforced by the history of Spanish colonization of the Americas, which a lot of Hispanists claim is the definitive proof that Spain is the most accurate heir of Rome's imperial legacy, as Spain was important for the culture of a continent, America (the New World), like Rome was to Europe (the Old World), some even claim that Spain surpassed Rome, since it also knew how to unify diverse peoples for centuries and maintaining cultural unity despite the imperial collapse.[63][64][65][66] Even today there are opinions in which Philip VI of Spain is considered the nearest heir of Rome.[67][68]
Рисорджименто и фашистская Италия.
[ редактировать ]Итальянский националистический провидец Джузеппе Мадзини продвигал идею «Третьего Рима» во время Рисорджименто . Говоря об объединении Италии и установлении Рима в качестве столицы, он сказал: «После Рима императоров, после Рима Пап наступит Рим народа». [69] После объединения Италии в Королевство Италия некоторые итальянские деятели называли это государство Третьим Римом. [70] После объединения Рим был выбран столицей, несмотря на его относительную отсталость, поскольку он вызывал престиж бывшей Империи. Мадзини говорил о необходимости Италии как Третьего Рима, имеющего имперские устремления, которые должны быть реализованы в Итальянской империи . [71] Мадзини сказал, что Италия должна «вторгнуться и колонизировать тунисские земли», поскольку это «ключ к Центральному Средиземноморью», и он считал, что Италия имеет право доминировать в Средиземном море , как это сделал древний Рим. [71]
В своих речах Бенито Муссолини повторял риторику Рисорджименто и называл свой режим «Третьим Римом» или Новой Римской империей . [72] Терца Рома (Третий Рим) также было названием плана Муссолини по расширению Рима в сторону Остии и моря. Соседство ЕВРО стало первым шагом в этом направлении. [73]
Неримские интерпретации
[ редактировать ]
Некоторые политические режимы XIX и начала XX веков определяли себя со ссылкой на продолжателей Римской империи, но не на саму (классическую) Римскую империю. Все они предполагали националистическую интерпретацию этих продолжателей и недооценивали степень, в которой последние изображали себя римлянами.
- Французский Наполеон I претендовал на наследие Франкской империи , как Меровинги , удобно забывая тот факт, что они признавали господство Константинополя, так и Каролинги , чье наследие было легко присвоить, поскольку он завоевал их центральные земли на территории нынешней Бельгии и Западной Германии. Таким образом, после своей императорской коронации на пост императора Франции 2 декабря 1804 года он использовал как символику пчел из захоронения Хильдерика I (которое было раскопано в 1653 году в Турне ), так и псевдокаролингский стиль для своей коронационной короны. , которую он назвал Короной Карла Великого . Даже после своего первого поражения Наполеон снова позаимствовал пчел, вдохновленных Меровингами, для составления флага Эльбы .
- Австрийская империя , а после нее и Австрийская республика , заимствовали образы и символику Священной Римской империи после ее распада в 1806 году. По сей день императорский орел является символом австрийского правительства, как и в Германии. .
- В Греции идея Мегали («Великая идея») возникла вскоре после Войны за независимость с целью воссоздания Византийской империи , понимаемой как этнически-греческое государство со столицей в Константинополе. Идея впервые возникла во время дебатов премьер-министра Иоанниса Колеттиса с королем Отто , предшествовавших обнародованию конституции 1844 года. [74] Эти националистические устремления определяли международные отношения Греции и, в значительной степени, внутреннюю политику на протяжении большей части первого столетия после обретения независимости. Выражение было новым в 1844 году, но концепция имела корни в греческом народном сознании – «Греция двух континентов и пяти морей» (Европа и Азия, Ионическое, Эгейское, Мраморное, Черное и Ливийское моря соответственно). [74] Попытки реализовать эту идею после поражения Османской империи в Первой мировой войне закончились катастрофой в результате греко-турецкой войны (1919–1922) .
- Определенные связи между Германской империей 1871 года и наследием Священной Римской империи были показаны в пропаганде и действиях, таких как творческая реставрация Императорского дворца Гослара в 1870-х годах. [75] [76] Нацистскую Германию впоследствии некоторые деятели во время ее режима называли Третьим рейхом ( Drittes Reich ), пришедшим на смену Священной Римской империи и Германской империи. Ссылка на Священную Римскую империю была неуклюжей, поскольку не соответствовала нацистской идеологии. В 1939 году циркуляр, не предназначенный для публикации, запрещал дальнейшее использование выражения «Третий Рейх». [77]
- В Болгарии в 1908 году титула царя принятие Фердинандом I было прежде всего ссылкой на Первую и Вторую Болгарские империи ; [78] : 297 в отличие от России, на западные языки оно переводилось как «царь», а не как «император». [79]
Наднационализм и римская имперская идея
[ редактировать ]В XX веке несколько политических мыслителей и политиков связали многоуровневое управление и многоязычие Римской империи в различных ее последовательных воплощениях с современными правовыми концепциями федерализма и наднационализма . [ нужны разъяснения ]
Лига Наций
[ редактировать ]Французский историк Луи Эйзенман в статье 1926 года под названием « Имперская идея в истории Европы » изобразил недавно созданную Лигу Наций как современное выражение «имперской идеи», которая была деградирована националистическим дрейфом Германской Габсбургов империи . монархия и Российская империя . Он утверждал, что окончательный упадок трех империй и создание Лиги представляют собой обновление имперской идеи Pax Romana . [80]
Евросоюз
[ редактировать ]
Воспоминания о Римской империи сопровождали Европейский Союз с момента его создания в рамках Плана Шумана 1950 года . [ нужна ссылка ] Римская империя снабдила Европейский Союз, как и многие другие страны, римскими правовыми концепциями и их языком – латынью . Таким образом, латынь в некоторых случаях использовалась в качестве неофициального языка франка в Европейском Союзе . [ нужна ссылка ] например, институты ЕС используют латинские понятия в текстах и названиях.
Сравнение Европейского Союза со Священной Римской империей, в негативном или позитивном свете, является обычным приемом в политических комментариях. [81] [82] Европейский Союз рассматривается как реинкарнация иностранной и властной Римской империи в некоторых европейских странах, особенно в Соединенном Королевстве . Выход Великобритании из Союза или Брексит в 2020 году по-разному сравнивали с восстанием в Боудике. [83] [84] или с окончанием римского правления в Британии . [85] регулярно формулируется иной негативный взгляд на Европейский Союз как на новую Римскую империю В христианских фундаменталистских кругах, особенно в Соединенных Штатах, . Согласно этой точке зрения, ЕС, как и другие наднациональные организации, такие как Организация Объединенных Наций и Всемирный банк , пытаясь возродить Римскую империю, сигнализирует о приближающемся конце времени , восхищении или Втором пришествии . Иногда Европейский Союз изображают как «Четвертый Рейх», еще больше подчеркивая его демоническую природу. Эту критику часто изображают как маргинальную, несмотря на то, что она широко распространена среди американских евангелистов на протяжении нескольких десятилетий. [86]
См. также
[ редактировать ]- Цезарь (титул) - императорский титул в Римской империи.
- Август (титул) - древнеримский титул
- Базилевс - греческий титул, примерно означающий «монарх».
- Король римлян - титул, используемый немецкими монархами средневековья и раннего Нового времени.
- Империум - Тип власти в Древнем Риме.
- Римский император - правитель Римской империи в имперский период.
- Обновление Римской империи - Намерение восстановить Римскую империю.
- Translatio imperii - Линейная последовательность передачи власти
- Византия После Византии - книга Николае Йорги, 1935 г.
- Наследие Римской империи
- Nova Roma - организация римских возрожденцев и реконструкторов.
- Панлатинизм - Идеология, способствующая объединению романских народов.
- Союз Средиземноморья – Межправительственная организация
- Наследование Византийской империи - претензии на византийское наследие и наследство
- Последний римский император - легендарная фигура, которая появится на земле, чтобы восстановить Священную Римскую империю в качестве библейского катехона, останавливающего приход Антихриста, впервые упоминается в 7 веке в Апокалипсисе Псевдо-Мефодия.
Ссылки
[ редактировать ]- ^ Фостер, Чарльз (22 сентября 2006 г.). «Завоевание Константинополя и конец империи» . Современный обзор . Архивировано из оригинала 11 июня 2009 года.
Это конец средневековья.
- ^ «Миллиет Интернет – Пазар» . Milliyet.com.tr. 19 декабря 2004 г. Архивировано из оригинала 31 октября 2007 г. Проверено 9 апреля 2017 г.
- ^ Никол, Дональд М. (1967). «Византийский взгляд на Западную Европу». Греческие, римские и византийские исследования . 8 (4): 315–339.
- ^ «washingtonpost.com: Константинополь: город желаний всего мира, 1453–1924» . www.washingtonpost.com . Архивировано из оригинала 24 июля 2019 года . Проверено 9 апреля 2017 г.
- ^ Кроули, Роджер (2009). Константинополь: Последняя великая осада, 1453 год . Фабер и Фабер. ISBN 978-0571250790 .
- ^ «Геннадий II Схоларий | патриарх Константинопольский» . Британская энциклопедия . Архивировано из оригинала 31 октября 2017 года . Проверено 9 апреля 2017 г.
- ^ «Список Вселенских Патриархов – Вселенский Патриархат» . www.patriarchate.org . Архивировано из оригинала 2 июля 2017 года . Проверено 9 апреля 2017 г.
- ^ «Коллекция «Византийского Лувра»» . Кантара .
- ^ Фокс, Клинтон Р. (март 1996 г.). «Что такое византийское?» . Целатор . 10 (3).
- ^ Джон Х. Россер (2011). Исторический словарь Византии . Лэнхэм, Массачусетс: Пугало. п. 2. ISBN 978-0-8108-7567-8 .
- ^ Jump up to: Перейти обратно: а б Питер Х. Уилсон (2017). Священная Римская империя: тысяча лет истории Европы . Книги о пингвинах.
- ^ Питер Мороу , Священная Империя , в: Лексикон Средневековья , Мюнхен и Цюрих: Артемида 1977–1999, том. 4, столбцы 2025–2028 гг.
- ^ Питер Х. Уилсон, «Укрепление престижа Габсбургов: конец Священной Римской империи в 1806 году», в The International History Review , Vol. 28, № 4 (декабрь 2006 г.), с. 719.
- ^ Марко Хорио. «Священная Римская империя – Глава 1: Территория и институты» . Священная Римская империя . Исторический лексикон Швейцарии .
- ^ Вольтер (1773) [1756]. «Глава LXX» . Очерки о нравственности и духе наций . Полет. 3 (новое изд.). Невшатель. п. 338.
Эта организация, которая называлась и которую до сих пор называют Священной Римской империей, никоим образом не была ни святой, ни римской, ни империей.
- ^ «Письмо императора Италии Людовика II императору Византии Василию I, ок. 871 г.; перевод Чарльза Уэста» (PDF) . Май 2016.
- ^ Иван Дуйчев (1972). Болгарское средневековье (Болгарское средневековье) . София: Наука и искусство. п. 430.
- ^ Иван Божилов (Иван Божилов); Васил Гюзелев (1999), История Средневековой Болгарии VII–XIV вв. (История Средневековой Болгарии VII–XIV вв.) , София: Анубис, с. 620–621, ISBN 954-426-204-0
- ^ Jump up to: Перейти обратно: а б Джон Джулиус Норвич (1995). Византия – упадок и падение . Нью-Йорк: Альфред А. Кнопф. п. 446. ИСБН 0-679-41650-1 .
- ^ Дэвид Поттер, История Франции, 1460–1560: возникновение национального государства , 1995, стр. 33
- ^ Полихроны Киприаноса Энепекида, Винерское завещание Андреаса Палеолога, vom 7. Апрель 1502 г.
- ^ Ильбер Ортайлы (28 мая 2011 г.). «Константинополь Великий и Царьград» . Национальность .
- ^ «Геннадий II Схоларий» . Британская энциклопедия . Проверено 13 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Дмитрий Кицикис , Турецко-греческая империя. Взгляд на историю Османской империи в свете реальности Промежуточного региона – Стамбул, İletişim Yayınları, 1996.
- ^ Роджер Кроули (2009). Константинополь: Последняя великая осада, 1453 год . Фабер и Фабер. стр. 13–. ISBN 978-0-571-25079-0 .
- ^ Халил Иналджик (1973). Османская империя: классический век 1300-1600 гг . стр. 56–57.
- ^ Бансон, Мэтью. «Как 800 мучеников Отранто спасли Рим» . Католические ответы . Архивировано из оригинала 17 декабря 2013 года . Проверено 30 мая 2014 г.
- ^ Jump up to: Перейти обратно: а б Мэтью Нэми (20 июля 2020 г.). «Когда закончилась Римская империя: в 1917 или 1922 году?» . Православная история .
- ^ Вада, Хиронори (октябрь 1958 г.) «Миндай но тэппо денрай до Осумана тейкоку: синкифу до Сайики точи дзинбуцуряку [на японском языке]» . Кейогиджуку Университет 31 (1/2/3/4): 692–719.
- ^ Женевьева Бюрер-Тьерри; Шарль Мерио (2010). Франция до Франции (481–888) . Париж: Белин. п. 128.
- ^ «Геста епископов Осера» . ГитЛаб .
- ^ Жесты епископов Осера . Париж: Les Belles Lettres. 2002.
- ^ Крис Уикэм (2009). Наследие Рима: освещение темных веков 400–1000 гг . Книги о пингвинах. п. 86.
- ^ Jump up to: Перейти обратно: а б с д и Джудит Херрин (1987). Становление христианского мира . Классика пингвинов.
- ^ Имон Даффи (1997). Святые и грешники: История Пап . Нью-Хейвен, Коннектикут: Издательство Йельского университета.
- ^ Фредерик Дж. Баумгартнер (2003). За запертыми дверями: история папских выборов . Пэлгрейв Макмиллан. ISBN 0-312-29463-8 .
- ^ Женевьева Бюрер-Тьерри; Шарль Мерио (2010). Франция до Франции (481–888) . Париж: Белин. п. 321.
- ^ Родерик Конвей Моррис (5 июля 2008 г.). «При Фридрихе II произошло первое возрождение римской культуры» . Нью-Йорк Таймс .
- ^ Рольф Гроссе (2014). От Франкского королевства к зарождению Франции и Германии 800-1214 гг . Прессы Universitaires du Nord. п. 83.
- ^ Jump up to: Перейти обратно: а б Mashkov, AD Moscow is the Third Rome (МОСКВА – ТРЕТИЙ РИМ) . Russian Soviet Encyclopedia .
- ^ Парри, Кен; Меллинг, Дэвид, ред. (1999). Блэквеллский словарь восточного христианства . Молден, Массачусетс: Blackwell Publishing. п. 490. ИСБН 978-0-631-23203-2 .
- ^ "ЗОСИМА" . www.pravenc.ru . Retrieved 1 November 2019 .
В «Изложении пасхалии» митрополит провозглашает Москву новым К-полем, Московского вел. князя именует «государем и самодержцем всея Руси, новым царем Константином новому граду Константинову Москве, и всей Русской земле, и иным многим землям государем».
- ^ «Главная - Монархия в истории - Монархия в истории Испании» . www.casareal.es . Проверено 16 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ «Испания — Вестготское королевство | Британика» . www.britanica.com . Проверено 17 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ Коллинз, Роджер (2004). Вестготская Испания, 409-711 гг . Оксфорд, Оксана, Великобритания: Паб Blackwell. ISBN 0-631-18185-7 . OCLC 52814206 .
- ^ Томпсон, Э.А. (1982). Римляне и варвары: упадок Западной империи . Мэдисон: Издательство Университета Висконсина. ISBN 0-299-08700-Х . OCLC 7836251 .
- ^ Рейли 1988, 137.
- ^ Jump up to: Перейти обратно: а б с д Флористан, Хосе М. (1 января 2005 г.), «Арагонская корона и Византийская империя палеологов»
- ^ Сеттон, Кеннет М. (1976–1984). Папство и Левант, 1204–1571 гг . Филадельфия: Американское философское общество. ISBN 0-87169-114-0 . ОСЛК 2698253 .
- ^ Энепекид, Полихронис Киприану (1960). Das Wiener Завещание Андреаса Палеолога от 7 апреля 1502 г. [ Венское завещание Андреаса Палеолога от 7 апреля 1502 г. ] (на немецком языке). Мюнхен: CH Бек. OCLC 761003148 .
- ^ Норвич, Джон Джулиус. Византия — упадок и падение
- ^ Фрайберг, Джек (2014). Темпьетто Браманте, римский Ренессанс и испанская корона . Нью-Йорк, штат Нью-Йорк. ISBN 978-1-316-07315-5 . OCLC 894226999 .
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: отсутствует местоположение издателя ( ссылка ) - ^ «Почему король Испании является королем Иерусалима?» . abc (на испанском языке). 22 января 2020 г. Проверено 16 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ ГЕРБ КОРОЛЯ ФЕРДИНАНА КАТОЛИЧЕСКОГО, Неаполитанское королевство (?), 1504-1512 гг. Хайме Эгигурен
- ^ Jump up to: Перейти обратно: а б Сервантес, Виртуальная библиотека Мигеля де. «Образ Рима в Испании: ученые, художники и архитекторы Италии XVI-XVIII веков». Виртуальная библиотека Мигеля де Сервантеса (на испанском языке) . Проверено 17 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ «Забытая история империи Карла V, Европейского Союза, исчезнувшего из-за националистов» . abc (на испанском языке). 6 декабря 2020 г. Проверено 17 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ Европейскость в латинской литературе раннего Нового времени , Изабелла Вальзер-Бюрглер, стр.60
- ^ Вендехорст и Вестфаль (2006), с. 63
- ^ Вернер (2009), с. 244-245
- ^ «Главная - Монархия в истории - Монархия в истории» . www.casareal.es . Проверено 17 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ Аюсо, Мигель (июнь 2018 г.). «ИСТОРИЧЕСКАЯ НЕВОЗМОЖНОСТЬ ИСПАНСКОГО НАЦИОНАЛИЗМА: Традиционная испанская мысль перед лицом национализма» . Журнал американской и аргентинской истории . 53 (1): 143–165. ISSN 2314-1549 .
- ^ Альваро Аргуэльес Сантовенья (2014). Испанский национализм: генеалогия, развитие и постоянство в учебниках истории для средней школы (магистерская диссертация) (на испанском языке). Университет Кантабрии.
- ^ «Так была выкована Испанская империя, Рим Америки перед лицом хищников» . abc (на испанском языке). 19 апреля 2018 года . Проверено 16 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ Ибаньес, Альберто Хиль (13 октября 2021 г.). «Существовала Священная Римская империя Испании» . Обзор прессы (на испанском языке) . Проверено 17 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ Феанар (13 сентября 2015 г.). «Политически некорректно: Испания как наследница Рима: десять элементов, с помощью которых Испания цивилизовала Америку» . Политически некорректно . Проверено 16 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ Довале, Эктор Мануэль Васкес, Выживание древней и вестготской Испании в испанском национализме XIX века
- ^ Арндт, Гэри (7 октября 2020 г.). «Кто нынешний римский император?» . Всё Везде . Проверено 17 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ «Кто был последним римским императором?» . Кошачий флаг . 21 мая 2017 года . Проверено 17 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ «Римский семинар» . Архивировано из оригинала 4 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 17 марта 2023 г.
- ^ Кристофер Дагган. Сила судьбы: история Италии с 1796 года . Нью-Йорк, Нью-Йорк, США: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2008. с. 304.
- ^ Jump up to: Перейти обратно: а б Сильвана Патриарка, Люси Риалл. Возвращение к Рисорджименто: национализм и культура в Италии девятнадцатого века. п. 248.
- ^ Мартин Кларк, Муссолини: Профили у власти (Лондон: Pearson Longman, 2005), 136.
- ↑ Речь, произнесенная в Кампидольо на инаугурации первого губернатора Рима 31 декабря 1925 года , Интернет-архив, копия страницы с речью Муссолини.
- ^ Jump up to: Перейти обратно: а б История Греции Британская энциклопедия онлайн
- ^ Уорик Болл. Рим на Востоке: трансформация империи . Лондон, Англия, Великобритания: Routledge, 2000. с. 449.
- ^ Крейг М. Уайт. Великая немецкая нация: истоки и судьба . АвторДом, 2007. с. 169.
- ^ Рейнхард Боллмус: Офис Розенберга и его оппоненты. Исследования борьбы за власть в национал-социалистической системе правления. Штутгарт 1970, стр. 236.
- ^ Иржи Лоуда и Майкл Маклаган (1981), Линии преемственности , Лондон: Orbis Publishing Ltd.
- ^ «Фердинанд, царь Болгарии» , Британская энциклопедия , март 2024 г.
- ^ Луи Эйзенманн (декабрь 1926 г.), «Имперская идея в истории Европы» , «Славянское обозрение » , 5 (14), перевод RWSW: 242–257, JSTOR 4202072 Цитата: «Но на самом деле то, что исчезло в муках Великая война была не столько самой имперской идеей, сколько формами, в которых она утвердилась в истории на протяжении этих двух тысяч лет. Как это ни парадоксально, но то, что придает ей историческую ценность и силу, не является политической структурой. Империя или имя, достоинство и власть Императора; это концепция наднационального политического и морального организма, который возвышается над разнообразием наций, чтобы смягчить и смягчить его воздействие, который объединяет и примиряет народы и общества; Это идея о том, что человеческое общество, каким бы сложным и разделенным в интересах оно ни было, не может существовать без высшей власти, которая, хотя и высокая и далекая, олицетворяет для общественного сознания эти идеалы порядка, мир и братство, к которым стремится цивилизованное человечество, несмотря на все препятствия, часто не подозревая об этом, а иногда даже не желая этого.Эта идея не погибла в великом катаклизме империй. Напротив, он вышел из печи очищенным, расширенным и обновленным, более ясным и более сознательным, чем когда-либо прежде; и именно эта идея сегодня (...) реализуется на последовательных этапах Лиги Наций. Читатель может быть склонен рассматривать эту попытку соединить Империю с Лигой Наций как просто произвольную или безрассудную. (...)Лишенная своих бренных форм, Имперская Идея остается одной из исторических и моральных сил нового мира; освобожденная отныне от своего материализма, очищенная и одухотворенная, она, таким образом, была возвращена в ту промежуточную сферу между небом и землей, из которой честолюбие государей унизило ее и в которую ее восстанавливают желания и надежды свободных наций. (...) Ибо, действительно, мы не насилуем историческую истину и не поддаемся чрезмерно воображению или энтузиазму, если видим в Лиге Наций законного наследника древней Империи, той Империи, которая оставалась единой на протяжении долгих столетий. Пакс Романа».
- ^ Питер Уилсон (20 января 2016 г.), «Священная Римская империя может помочь вдохновить новый Европейский Союз» , Financial Times , заархивировано из оригинала 10 декабря 2022 г.
- ^ Далибор Рогач (7 мая 2019 г.). «Священный Римский союз» . Американский интерес .
- ^ Клиффорд Лонгли (9 декабря 2019 г.). «Есть ли в Боудикке ключ к разгадке нашей загадки Брексита?» . Планшет .
- ^ Дейзи Данн (4 марта 2020 г.), «Боевой дух Боудики, королевы воинов, живет в Британии после Брексита» , The Telegraph
- ^ Том Холланд (9 апреля 2019 г.). «Первый Брексит в Британии был самым трудным» . УнХерд .
- ^ Орестис Линдермайер (1995), « Зверь из Откровения: американское фундаменталистское христианство и Европейский Союз» , Etnofoor , 8 (1): 27–46, JSTOR 25757855
- История Рима
- Римская империя
- История Римской империи
- Наследие Римской империи
- Падение Западной Римской империи
- христианские государства
- Византийская империя
- История восточного православия
- Константинополь
- Каролингская империя
- Священная Римская империя
- Раскол между Востоком и Западом
- Латинская империя
- Христианский мессианизм
- Немецкий национализм
- 16 век в Московском княжестве.
- Политика Российской Империи
- Русский национализм
- Итальянское объединение
- Итальянский фашизм
- Римская историография









