Священная Римская империя
| 800/962 [ А ] –1806 | |
| Quaternion Eagle (1510) | |
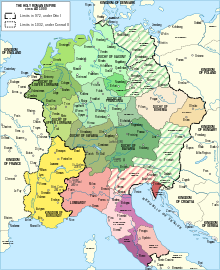
 The Holy Roman Empire at its greatest territorial extent imposed over modern borders, c. 1200–1250 | |
| Capital | Multicentral[3]
Rome (de jure) Aachen (800–1562) Palermo (de facto) (1194–1254) Innsbruck (1508–1519) Vienna (1550s–1583, 1612–1806) Frankfurt (1562–1806) Prague (1583–1612) Regensburg (1594–1806) Wetzlar (1689–1806) |
| Common languages | German, Medieval Latin (administrative/liturgical/ Various[c] |
| Religion | Various official religions: Roman Catholicism (1054–1806)[d] Lutheranism (1555–1806) Calvinism (1648–1806) |
| Government | Elective monarchy Mixed monarchy (after Imperial Reform)[17] |
| Emperor | |
• 800–814 | Charlemagne[a] (first) |
• 962–973 | Otto I |
• 1519–1556 | Charles V |
• 1792–1806 | Francis II (last) |
| Legislature | Imperial Diet |
| Historical era | Middle Ages to early modern period |
| 25 December 800 | |
• East Frankish Otto I is crowned Emperor of the Romans | 2 February 962 |
• Conrad II assumes crown of the Kingdom of Burgundy | 2 February 1033 |
| 25 September 1555 | |
| 24 October 1648 | |
| 1648–1789 | |
| 2 December 1805 | |
| 6 August 1806 | |
| Area | |
| 1150[e] | 1,100,000 km2 (420,000 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 1700[18] | 23,000,000 |
• 1800[18] | 29,000,000 |
| Currency | Multiple: thaler, guilder, groschen, Reichsthaler |
Священная Римская империя , [ f ] Также известная как Священная Римская империя немецкой нации после 1512 года, была политикой в Центральной и Западной Европе , обычно возглавляемой императором Священной Римской . [ 19 ] Он развивался в раннем средневековье и длился почти тысячу лет до его роспуска в 1806 году во время наполеоновских войн . [ 20 ]
25 декабря 800 года папа Лео III короновал Франклянского короля Карла Великого в качестве римского императора, возродив титул в Западной Европе более чем через три столетия после падения древней Западной Римской империи в 476 году. [ 21 ] Заголовок истек в 924 году, но был возрожден в 962 году, когда Отто, я был коронован императором папой Джона XII Карла Великого и Каролингскую империю , , создавая себя как преемник [ 22 ] и начинать постоянное существование империи на протяжении более восьми веков. [ 23 ] [ 24 ] [ G ] С 962 года до 12 -го века империя была одной из самых мощных монархий в Европе. [ 25 ] Функционирование правительства зависело от гармоничного сотрудничества между императором и вассалами; [26] this harmony was disturbed during the Salian period.[27] The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power under the House of Hohenstaufen in the mid-13th century, but overextension of its power led to a partial collapse.[28][29]
Scholars generally describe an evolution of the institutions and principles constituting the empire, and a gradual development of the imperial role.[30][31] While the office of emperor had been reestablished, the exact term for his realm as the "Holy Roman Empire" was not used until the 13th century,[32] although the emperor's theoretical legitimacy from the beginning rested on the concept of translatio imperii, that he held supreme power inherited from the ancient emperors of Rome.[30] Nevertheless, in the Holy Roman Empire, the imperial office was traditionally elective by the mostly German prince-electors. In theory and diplomacy, the emperors were considered the first among equals of all Europe's Catholic monarchs.[33]
A process of Imperial Reform in the late 15th and early 16th centuries transformed the empire, creating a set of institutions which endured until its final demise in the 19th century.[34][35] According to historian Thomas Brady Jr., the empire after the Imperial Reform was a political body of remarkable longevity and stability, and "resembled in some respects the monarchical polities of Europe's western tier, and in others the loosely integrated, elective polities of East Central Europe." The new corporate German Nation, instead of simply obeying the emperor, negotiated with him.[36][37] On 6 August 1806, Emperor Francis II abdicated and formally dissolved the empire following the creation – the month before, by French emperor Napoleon – of the Confederation of the Rhine, a confederation of German client states loyal not to the Holy Roman emperor but to France.
Name and general perception

Since Charlemagne, the realm was merely referred to as the Roman Empire.[38] The term sacrum ("holy", in the sense of "consecrated") in connection with the medieval Roman Empire was used beginning in 1157 under Frederick I Barbarossa ("Holy Empire"): the term was added to reflect Frederick's ambition to dominate Italy and the Papacy.[39] The form "Holy Roman Empire" is attested from 1254 onward.[40]
The exact term "Holy Roman Empire" was not used until the 13th century, before which the empire was referred to variously as universum regnum ("the whole kingdom", as opposed to the regional kingdoms), imperium christianum ("Christian empire"), or Romanum imperium ("Roman empire"),[32] but the Emperor's legitimacy always rested on the concept of translatio imperii,[h] that he held supreme power inherited from the ancient emperors of Rome.[30]
In a decree following the Diet of Cologne in 1512, the name was changed to the Holy Roman Empire of the Germanic Nation (German: Heiliges Römisches Reich Deutscher Nation, Latin: Sacrum Imperium Romanum Nationis Germanicae),[38] a form first used in a document in 1474.[39] The adoption of this new name coincided with the loss of imperial territories in Italy and Burgundy to the south and west by the late 15th century,[41] but also to emphasize the new importance of the German Imperial Estates in ruling the Empire due to the Imperial Reform.[42] The Hungarian denomination "German Roman Empire" (Hungarian: Német-római Birodalom) is the shortening of this.[43]
By the end of the 18th century, the term "Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation" fell out of official use. Contradicting the traditional view concerning that designation, Hermann Weisert has argued in a study on imperial titulature that, despite the claims of many textbooks, the name "Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation" never had an official status and points out that documents were thirty times as likely to omit the national suffix as include it.[44]
In a famous assessment of the name, the political philosopher Voltaire remarked sardonically: "This body which was called and which still calls itself the Holy Roman Empire was in no way holy, nor Roman, nor an empire."[45]
In the modern period, the Empire was often informally called the German Empire (Deutsches Reich) or Roman-German Empire (Römisch-Deutsches Reich).[46] After its dissolution through the end of the German Empire, it was often called "the old Empire" (das alte Reich). Beginning in 1923, early twentieth-century German nationalists and Nazi Party propaganda would identify the Holy Roman Empire as the "First" Reich (Erstes Reich, Reich meaning empire), with the German Empire as the "Second" Reich and what would eventually become Nazi Germany as the "Third" Reich.[47]
David S. Bachrach opines that the Ottonian kings actually built their empire on the back of military and bureaucratic apparatuses as well as the cultural legacy they inherited from the Carolingians, who ultimately inherited these from the Late Roman Empire. He argues that the Ottonian empire was hardly an archaic kingdom of primitive Germans, maintained by personal relationships only and driven by the desire of the magnates to plunder and divide the rewards among themselves but instead, notable for their abilities to amass sophisticated economic, administrative, educational and cultural resources that they used to serve their enormous war machine.[48][49]
Until the end of the 15th century, the empire was in theory composed of three major blocs – Italy, Germany and Burgundy. Later territorially only the Kingdom of Germany and Bohemia remained, with the Burgundian territories lost to France. Although the Italian territories were formally part of the empire, the territories were ignored in the Imperial Reform and splintered into numerous de facto independent territorial entities.[50][30][37] The status of Italy in particular varied throughout the 16th to 18th centuries. Some territories like Piedmont-Savoy became increasingly independent, while others became more dependent due to the extinction of their ruling noble houses causing these territories to often fall under the dominions of the Habsburgs and their cadet branches. Barring the loss of Franche-Comté in 1678, the external borders of the Empire did not change noticeably from the Peace of Westphalia – which acknowledged the exclusion of Switzerland and the Northern Netherlands, and the French protectorate over Alsace – to the dissolution of the Empire. At the conclusion of the Napoleonic Wars in 1815, most of the Holy Roman Empire was included in the German Confederation, with the main exceptions being the Italian states.
History
| History of Germany |
|---|
 |
Early Middle Ages
Carolingian Empire

As Roman power in Gaul declined during the 5th century, local Germanic tribes assumed control.[51] In the late 5th and early 6th centuries, the Merovingians, under Clovis I and his successors, consolidated Frankish tribes and extended hegemony over others to gain control of northern Gaul and the middle Rhine river valley region.[52][53] By the middle of the 8th century, the Merovingians were reduced to figureheads, and the Carolingians, led by Charles Martel, became the de facto rulers.[54] In 751, Martel's son Pepin became King of the Franks, and later gained the sanction of the Pope.[55][56] The Carolingians would maintain a close alliance with the Papacy.[57]
In 768, Pepin's son Charlemagne became King of the Franks and began an extensive expansion of the realm. He eventually incorporated the territories of present-day France, Germany, northern Italy, the Low Countries and beyond, linking the Frankish kingdom with Papal lands.[58][59]
Although antagonism about the expense of Byzantine domination had long persisted within Italy, a political rupture was set in motion in earnest in 726 by the iconoclasm of Emperor Leo III the Isaurian, in what Pope Gregory II saw as the latest in a series of imperial heresies.[60] In 797, the Eastern Roman Emperor Constantine VI was removed from the throne by his mother, Empress Irene, who declared herself sole ruler. As the Latin Church only regarded a male Roman emperor as the head of Christendom, Pope Leo III sought a new candidate for the dignity, excluding consultation with the patriarch of Constantinople.[61][62]
Charlemagne's good service to the Church in his defense of Papal possessions against the Lombards made him the ideal candidate. On Christmas Day of 800, Pope Leo III crowned Charlemagne emperor, restoring the title in the West for the first time in over three centuries.[61][62] This can be seen as symbolic of the papacy turning away from the declining Byzantine Empire toward the new power of Carolingian Francia. Charlemagne adopted the formula Renovatio imperii Romanorum ("renewal of the Roman Empire"). In 802, Irene was overthrown and exiled by Nikephoros I and henceforth there were two Roman emperors.
After Charlemagne died in 814, the imperial crown passed to his son, Louis the Pious. Upon Louis' death in 840, it passed to his son Lothair, who had been his co-ruler. By this point the territory of Charlemagne was divided into several territories (cf. Treaty of Verdun, Treaty of Prüm, Treaty of Meerssen and Treaty of Ribemont), and over the course of the later 9th century the title of emperor was disputed by the Carolingian rulers of the Western Frankish Kingdom or West Francia and the Eastern Frankish Kingdom or East Francia, with first the western king (Charles the Bald) and then the eastern (Charles the Fat), who briefly reunited the Empire, attaining the prize.[63] In the 9th century, Charlemagne and his successors promoted the intellectual revival, known as the Carolingian Renaissance. Some, like Mortimer Chambers,[64] opine that the Carolingian Renaissance made possible the subsequent renaissances (even though by the early 10th century, the revival already diminished).[65]
After the death of Charles the Fat in 888, the Carolingian Empire broke apart, and was never restored. According to Regino of Prüm, the parts of the realm "spewed forth kinglets", and each part elected a kinglet "from its own bowels".[63] The last such emperor was Berengar I of Italy, who died in 924.
Post-Carolingian Eastern Frankish Kingdom
Around 900, East Francia's autonomous stem duchies (Franconia, Bavaria, Swabia, Saxony, and Lotharingia) reemerged. After the Carolingian king Louis the Child died without issue in 911, East Francia did not turn to the Carolingian ruler of West Francia to take over the realm but instead elected one of the dukes, Conrad of Franconia, as Rex Francorum Orientalium.[66] On his deathbed, Conrad yielded the crown to his main rival, Henry the Fowler of Saxony (r. 919–936), who was elected king at the Diet of Fritzlar in 919.[67] Henry reached a truce with the raiding Magyars, and in 933 he won a first victory against them in the Battle of Riade.[68]
Henry died in 936, but his descendants, the Liudolfing (or Ottonian) dynasty, would continue to rule the Eastern kingdom or the Kingdom of Germany for roughly a century. Upon Henry the Fowler's death, Otto, his son and designated successor,[69] was elected king in Aachen in 936.[70] He overcame a series of revolts from a younger brother and from several dukes. After that, the king managed to control the appointment of dukes and often also employed bishops in administrative affairs.[71] He replaced leaders of most of the major East Frankish duchies with his own relatives. At the same time, he was careful to prevent members of his own family from making infringements on his royal prerogatives.[72][73]
Formation of the Holy Roman Empire

In 951, Otto came to the aid of Queen Adelaide of Italy, defeating her enemies, marrying her, and taking control over Italy.[74] In 955, Otto won a decisive victory over the Magyars in the Battle of Lechfeld.[75] In 962, Otto was crowned emperor by Pope John XII,[75] thus intertwining the affairs of the German kingdom with those of Italy and the Papacy. Otto's coronation as emperor marked the German kings as successors to the empire of Charlemagne, which through the concept of translatio imperii, also made them consider themselves as successors to Ancient Rome. The flowering of arts beginning with Otto the Great's reign is known as the Ottonian Renaissance, centered in Germany but also happening in Northern Italy and France.[76][77]
Otto created the imperial church system, often called "Ottonian church system of the Reich", which tied the great imperial churches and their representatives to imperial service, thus providing "a stable and long-lasting framework for Germany".[78][79] During the Ottonian era, imperial women played a prominent role in political and ecclesiastic affairs, often combining their functions as religious leader and advisor, regent or co-ruler, notably Matilda of Ringelheim, Eadgyth, Adelaide of Italy, Theophanu, and Matilda of Quedlinburg.[80][81][82][83]
In 963, Otto deposed John XII and chose Leo VIII as the new pope (although John XII and Leo VIII both claimed the papacy until 964, when John XII died). This also renewed the conflict with the Byzantine emperor, especially after Otto's son Otto II (r. 967–983) adopted the designation imperator Romanorum. Still, Otto II formed marital ties with the east when he married the Byzantine princess Theophanu.[84] Their son, Otto III, came to the throne only three years old, and was subjected to a power struggle and series of regencies until his age of majority in 994. Up to that time, he remained in Germany, while a deposed duke, Crescentius II, ruled over Rome and part of Italy, ostensibly in his stead.
In 996 Otto III appointed his cousin Gregory V the first German pope.[85] A foreign pope and foreign papal officers were seen with suspicion by Roman nobles, who were led by Crescentius II to revolt. Otto III's former mentor Antipope John XVI briefly held Rome, until the Holy Roman emperor seized the city.[86]
Otto died young in 1002, and was succeeded by his cousin Henry II, who focused on Germany.[87] Otto III's (and his mentor Pope Sylvester's) diplomatic activities coincided with and facilitated the Christianization and the spread of Latin culture in different parts of Europe.[88][89] They coopted a new group of nations (Slavic) into the framework of Europe, with their empire functioning, as some remark, as a "Byzantine-like presidency over a family of nations, centred on pope and emperor in Rome". This has proved a lasting achievement.[90][91][92][93] Otto's early death though made his reign "the tale of largely unrealized potential".[94][95]
Henry II died in 1024 and Conrad II, first of the Salian dynasty, was elected king only after some debate among dukes and nobles. This group eventually developed into the college of electors.
The Holy Roman Empire eventually came to be composed of four kingdoms:
- Kingdom of Germany (part of the empire since 962),
- Kingdom of Italy (from 962 until 1801),
- Kingdom of Bohemia (from 1002 as the Duchy of Bohemia and raised to a kingdom in 1198),
- Kingdom of Burgundy (from 1032 to 1378).
High Middle Ages
Investiture Controversy
Kings often employed bishops in administrative affairs and often determined who would be appointed to ecclesiastical offices.[96] In the wake of the Cluniac Reforms, this involvement was increasingly seen as inappropriate by the Papacy. The reform-minded Pope Gregory VII was determined to oppose such practices, which led to the Investiture Controversy with King Henry IV (r. 1056–1106, crowned emperor in 1084).[96]

Henry IV repudiated the pope's interference and persuaded his bishops to excommunicate the pope, whom he famously addressed by his birth name "Hildebrand" rather than his papal name "Gregory".[97] The pope, in turn, excommunicated the king, declared him deposed, and dissolved the oaths of loyalty made to Henry.[23][97] The king found himself with almost no political support and was forced to make the famous Walk to Canossa in 1077,[98] by which he achieved a lifting of the excommunication at the price of humiliation. Meanwhile, the German princes had elected another king, Rudolf of Swabia.[99]
Henry managed to defeat Rudolf, but was subsequently confronted with more uprisings, renewed excommunication, and even the rebellion of his sons. After his death, his second son, Henry V, reached an agreement with the Pope and the bishops in the 1122 Concordat of Worms.[100] The political power of the Empire was maintained, but the conflict had demonstrated the limits of the ruler's power, especially in regard to the Church, and it robbed the king of the sacral status he had previously enjoyed. The pope and the German princes had surfaced as major players in the political system of the Holy Roman Empire.
Ostsiedlung
As the result of Ostsiedlung, less populated regions of Central Europe (i.e. sparsely populated border areas in present-day Poland and Czechia) received a significant number of German speakers. Silesia became part of the Holy Roman Empire as the result of the local Piast dukes' push for autonomy from the Polish Crown.[101] From the late 12th century, the Duchy of Pomerania was under the suzerainty of the Holy Roman Empire[102] and the conquests of the Teutonic Order made that region German-speaking.[103]
Hohenstaufen dynasty


When the Salian dynasty ended with Henry V's death in 1125, the princes chose not to elect the next of kin, but rather Lothair III, the moderately powerful but already old duke of Saxony. When he died in 1137, the princes again aimed to check royal power; accordingly they did not elect Lothair's favoured heir, his son-in-law, Henry the Proud of the Welf family, but Conrad III of the Hohenstaufen family, the grandson of Emperor Henry IV and nephew of Emperor Henry V. This led to over a century of strife between the two houses. Conrad ousted the Welfs from their possessions, but after his death in 1152, his nephew Frederick Barbarossa succeeded him and made peace with the Welfs, restoring his cousin Henry the Lion to his – albeit diminished – possessions.
The Hohenstaufen rulers increasingly lent land to "ministeriales", formerly non-free servicemen, who Frederick hoped would be more reliable than dukes. Initially used mainly for war services, this new class of people would form the basis for the later knights, another basis of imperial power. A further important constitutional move at Roncaglia was the establishment of a new peace mechanism for the entire empire, the Landfrieden, with the first imperial one being issued in 1103 under Henry IV at Mainz.[104][105]
This was an attempt to abolish private feuds, between the many dukes and other people, and to tie the emperor's subordinates to a legal system of jurisdiction and public prosecution of criminal acts – a predecessor of the modern concept of "rule of law". Another new concept of the time was the systematic founding of new cities by the emperor and by the local dukes. These were partly a result of the explosion in population; they also concentrated economic power at strategic locations. Before this, cities had only existed in the form of old Roman foundations or older bishoprics. Cities that were founded in the 12th century include Freiburg, possibly the economic model for many later cities, and Munich.
Frederick Barbarossa was crowned emperor in 1155. He emphasized the "Romanness" of the empire, partly in an attempt to justify the power of the emperor independent of the (now strengthened) pope. An imperial assembly at the fields of Roncaglia in 1158 reclaimed imperial rights in reference to Justinian I's Corpus Juris Civilis. Imperial rights had been referred to as regalia since the Investiture Controversy but were enumerated for the first time at Roncaglia. This comprehensive list included public roads, tariffs, coining, collecting punitive fees, and the seating and unseating of office-holders. These rights were now explicitly rooted in Roman law, a far-reaching constitutional act.
Frederick's policies were primarily directed at Italy, where he clashed with the free-minded cities of the north, especially the Duchy of Milan. He also embroiled himself in another conflict with the Papacy by supporting a candidate elected by a minority against Pope Alexander III (1159–1181). Frederick supported a succession of antipopes before finally making peace with Alexander in 1177. In Germany, the emperor had repeatedly protected Henry the Lion against complaints by rival princes or cities (especially in the cases of Munich and Lübeck). Henry gave only lackluster support to Frederick's policies, and, in a critical situation during the Italian wars, Henry refused the emperor's plea for military support. After returning to Germany, an embittered Frederick opened proceedings against the duke, resulting in a public ban and the confiscation of all Henry's territories. In 1190, Frederick participated in the Third Crusade, dying in the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia.[106]
During the Hohenstaufen period, German princes facilitated a successful, peaceful eastward settlement of lands that were uninhabited or inhabited sparsely by West Slavs. German-speaking farmers, traders, and craftsmen from the western part of the Empire, both Christians and Jews, moved into these areas. The gradual Germanization of these lands was a complex phenomenon that should not be interpreted in the biased terms of 19th-century nationalism. The eastward settlement expanded the influence of the empire to include Pomerania and Silesia, as did the intermarriage of the local, still mostly Slavic, rulers with German spouses. The Teutonic Knights were invited to Prussia by Duke Konrad of Masovia to Christianize the Prussians in 1226. The monastic state of the Teutonic Order (German: Deutschordensstaat) and its later German successor state of the Duchy of Prussia was never part of the Holy Roman Empire.
Under the son and successor of Frederick Barbarossa, Henry VI, the Hohenstaufen dynasty reached its apex, with the addition of the Norman kingdom of Sicily through the marriage of Henry VI and Constance of Sicily. Bohemia and Poland were under feudal dependence, while Cyprus and Lesser Armenia also paid homage. The Iberian-Moroccan caliph accepted his claims over the suzerainty over Tunis and Tripolitania and paid tribute. Fearing the power of Henry, the most powerful monarch in Europe since Charlemagne, the other European kings formed an alliance. But Henry broke this coalition by blackmailing English king Richard the Lionheart. The Byzantine emperor worried that Henry would turn his Crusade plan against his empire, and began to collect the alamanikon to prepare against the expected invasion. Henry also had plans for turning the Empire into a hereditary monarchy, although this met with opposition from some of the princes and the pope. The emperor suddenly died in 1197, leading to the partial collapse of his empire.[107][108][109] As his son, Frederick II, though already elected king, was still a small child and living in Sicily, German princes chose to elect an adult king, resulting in the dual election of Frederick Barbarossa's youngest son Philip of Swabia and Henry the Lion's son Otto of Brunswick, who competed for the crown. After Philip was murdered in a private squabble in 1208, Otto prevailed for a while, until he began to also claim Sicily.[clarification needed]

Pope Innocent III, who feared the threat posed by a union of the empire and Sicily, was now supported by Frederick II, who marched to Germany and defeated Otto. After his victory, Frederick did not act upon his promise to keep the two realms separate. Though he had made his son Henry king of Sicily before marching on Germany, he still reserved real political power for himself. This continued after Frederick was crowned emperor in 1220. Fearing Frederick's concentration of power, the pope finally excommunicated him. Another point of contention was the Crusade, which Frederick had promised but repeatedly postponed. Now, although excommunicated, Frederick led the Sixth Crusade in 1228, which ended in negotiations and a temporary restoration of the Kingdom of Jerusalem.
Despite his imperial claims, Frederick's rule was a major turning point toward the disintegration of central rule in the Empire. While concentrating on establishing a more centralized state in Sicily, he was mostly absent from Germany and issued far-reaching privileges to Germany's secular and ecclesiastical princes: in the 1220 Confoederatio cum principibus ecclesiasticis, Frederick gave up a number of regalia in favour of the bishops, among them tariffs, coining, and the right to build fortification. The 1232 Statutum in favorem principum mostly extended these privileges to secular territories. Although many of these privileges had existed earlier, they were now granted globally, and once and for all, to allow the German princes to maintain order north of the Alps while Frederick concentrated on Italy. The 1232 document marked the first time that the German dukes were called domini terræ, owners of their lands, a remarkable change in terminology as well.
Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia was a significant regional power during the Middle Ages. In 1212, King Ottokar I (bearing the title "king" since 1198) extracted a Golden Bull of Sicily (a formal edict) from Emperor Frederick II, confirming the royal title for Ottokar and his descendants, and the Duchy of Bohemia was raised to a kingdom.[110] Bohemia's political and financial obligations to the Empire were gradually reduced.[111] Charles IV set Prague to be the seat of the Holy Roman emperor.
Interregnum

After the death of Frederick II in 1250, the German kingdom was divided between his son Conrad IV (died 1254) and the anti-king, William of Holland (died 1256). Conrad's death was followed by the Interregnum, during which no king could achieve universal recognition, allowing the princes to consolidate their holdings and become even more independent as rulers. After 1257, the crown was contested between Richard of Cornwall, who was supported by the Guelph party, and Alfonso X of Castile, who was recognized by the Hohenstaufen party but never set foot on German soil. After Richard's death in 1273, Rudolf I of Germany, a minor pro-Hohenstaufen count, was elected. He was the first of the Habsburgs to hold a royal title, but he was never crowned emperor. After Rudolf's death in 1291, Adolf and Albert were two further weak kings who were never crowned emperor.
Albert was assassinated in 1308. Almost immediately, King Philip IV of France began aggressively seeking support for his brother, Charles of Valois, to be elected the next king of the Romans. Philip thought he had the backing of the French Pope, Clement V (established at Avignon in 1309), and that his prospects of bringing the empire into the orbit of the French royal house were good. He lavishly spread French money in the hope of bribing the German electors. Although Charles of Valois had the backing of pro-French Henry, Archbishop of Cologne, many were not keen to see an expansion of French power, least of all Clement V. The principal rival to Charles appeared to be Count Palatine Rudolf II.
But the electors, the great territorial magnates who had lived without a crowned emperor for decades, were unhappy with both Charles and Rudolf. Instead Count Henry of Luxembourg, with the aid of his brother, Archbishop Baldwin of Trier, was elected as Henry VII with six votes at Frankfurt on 27 November 1308. Though a vassal of King Philip, Henry was bound by few national ties, and thus suitable as a compromise candidate. Henry VII was crowned king at Aachen on 6 January 1309, and emperor by Pope Clement V on 29 June 1312 in Rome, ending the interregnum.
Changes in political structure

During the 13th century, a general structural change in how land was administered prepared the shift of political power toward the rising bourgeoisie at the expense of the aristocratic feudalism that would characterize the Late Middle Ages. The rise of the cities and the emergence of the new burgher class eroded the societal, legal and economic order of feudalism.[112]
Peasants were increasingly required to pay tribute to their landlords. The concept of property began to replace more ancient forms of jurisdiction, although they were still very much tied together. In the territories (not at the level of the Empire), power became increasingly bundled: whoever owned the land had jurisdiction, from which other powers derived. Jurisdiction at the time did not include legislation, which was virtually nonexistent until well into the 15th century. Court practice heavily relied on traditional customs or rules described as customary.
During this time, territories began to transform into the predecessors of modern states. The process varied greatly among the various lands and was most advanced in those territories that were almost identical to the lands of the old Germanic tribes, e.g., Bavaria. It was slower in those scattered territories that were founded through imperial privileges.
In the 12th century the Hanseatic League established itself as a commercial and defensive alliance of the merchant guilds of towns and cities in the empire and all over northern and central Europe. It dominated marine trade in the Baltic Sea, the North Sea and along the connected navigable rivers. Each of the affiliated cities retained the legal system of its sovereign and, with the exception of the Free imperial cities, had only a limited degree of political autonomy. By the late 14th century, the powerful league enforced its interests with military means, if necessary. This culminated in a war with the sovereign Kingdom of Denmark from 1361 to 1370. The league declined after 1450.[i][113][114]
Late Middle Ages
Rise of the territories after the Hohenstaufens

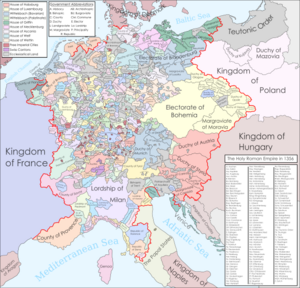
The difficulties in electing the king eventually led to the emergence of a fixed college of prince-electors (Kurfürsten), whose composition and procedures were set forth in the Golden Bull of 1356, issued by Charles IV (reigned 1355–1378, King of the Romans since 1346), which remained valid until 1806. This development probably best symbolizes the emerging duality between emperor and realm (Kaiser und Reich), which were no longer considered identical. The Golden Bull also set forth the system for election of the Holy Roman Emperor. The emperor now was to be elected by a majority rather than by consent of all seven electors. For electors the title became hereditary, and they were given the right to mint coins and to exercise jurisdiction. Also it was recommended that their sons learn the imperial languages – German, Latin, Italian, and Czech.[j][16] The decision by Charles IV is the subject of debates: on one hand, it helped to restore peace in the lands of the Empire, that had been engulfed in civil conflicts after the end of the Hohenstaufen era; on the other hand, the "blow to central authority was unmistakable".[115] Thomas Brady Jr. opines that Charles IV's intention was to end contested royal elections (from the Luxembourghs' perspective, they also had the advantage that the King of Bohemia had a permanent and preeminent status as one of the Electors himself).[116][117] At the same time, he built up Bohemia as the Luxembourghs' core land of the Empire and their dynastic base. His reign in Bohemia is often considered the land's Golden Age. According to Brady Jr. though, under all the glitter, one problem arose: the government showed an inability to deal with the German immigrant waves into Bohemia, thus leading to religious tensions and persecutions. The imperial project of the Luxembourgh halted under Charles's son Wenceslaus (reigned 1378–1419 as King of Bohemia, 1376–1400 as King of the Romans), who also faced opposition from 150 local baronial families.[118]
The shift in power away from the emperor is also revealed in the way the post-Hohenstaufen kings attempted to sustain their power. Earlier, the Empire's strength (and finances) greatly relied on the Empire's own lands, the so-called Reichsgut, which always belonged to the king of the day and included many Imperial Cities. After the 13th century, the relevance of the Reichsgut faded, even though some parts of it did remain until the Empire's end in 1806. Instead, the Reichsgut was increasingly pawned to local dukes, sometimes to raise money for the Empire, but more frequently to reward faithful duty or as an attempt to establish control over the dukes. The direct governance of the Reichsgut no longer matched the needs of either the king or the dukes.
The kings beginning with Rudolf I of Germany increasingly relied on the lands of their respective dynasties to support their power. In contrast with the Reichsgut, which was mostly scattered and difficult to administer, these territories were relatively compact and thus easier to control. In 1282, Rudolf I thus lent Austria and Styria to his own sons. In 1312, Henry VII of the House of Luxembourg was crowned as the first Holy Roman Emperor since Frederick II. After him all kings and emperors relied on the lands of their own family (Hausmacht): Louis IV of Wittelsbach (king 1314, emperor 1328–1347) relied on his lands in Bavaria; Charles IV of Luxembourg, the grandson of Henry VII, drew strength from his own lands in Bohemia. It was thus increasingly in the king's own interest to strengthen the power of the territories, since the king profited from such a benefit in his own lands as well.
Imperial Reform

The "constitution" of the Empire still remained largely unsettled at the beginning of the 15th century. Feuds often happened between local rulers. The "robber baron" (Raubritter) became a social factor.[119]
Simultaneously, the Catholic Church experienced crises of its own, with wide-reaching effects in the Empire. The conflict between several papal claimants (two anti-popes and the "legitimate" Pope) ended only with the Council of Constance (1414–1418); after 1419 the Papacy directed much of its energy to suppressing the Hussites. The medieval idea of unifying all Christendom into a single political entity, with the Church and the Empire as its leading institutions, began to decline.
With these drastic changes, much discussion emerged in the 15th century about the Empire itself. Rules from the past no longer adequately described the structure of the time, and a reinforcement of earlier Landfrieden was urgently needed.[120]
The vision for a simultaneous reform of the Empire and the Church on a central level began with Sigismund (reigned 1433–1437, King of the Romans since 1411), who, according to historian Thomas Brady Jr., "possessed a breadth of vision and a sense of grandeur unseen in a German monarch since the thirteenth century". But external difficulties, self-inflicted mistakes and the extinction of the Luxembourg male line made this vision unfulfilled.[121]
Frederick III was the first Habsburg to be crowned Holy Roman Emperor, in 1452.[122] He had been very careful regarding the reform movement in the empire. For most of his reign, he considered reform as a threat to his imperial prerogatives. He avoided direct confrontations, which might lead to humiliation if the princes refused to give way.[123] After 1440, the reform of the Empire and Church was sustained and led by local and regional powers, particularly the territorial princes.[124] In his last years, he felt more pressure on taking action from a higher level. Berthold von Henneberg, the Archbishop of Mainz, who spoke on behalf of reform-minded princes (who wanted to reform the Empire without strengthening the imperial hand), capitalized on Frederick's desire to secure the imperial election for his son Maximilian. Thus, in his last years, he presided over the initial phase of Imperial Reform, which would mainly unfold under his Maximilian. Maximilian himself was more open to reform, although naturally he also wanted to preserve and enhance imperial prerogatives. After Frederick retired to Linz in 1488, as a compromise, Maximilian acted as mediator between the princes and his father. When he attained sole rule after Frederick's death, he would continue this policy of brokerage, acting as the impartial judge between options suggested by the princes.[125][35]
Creation of institutions

Major measures for the Reform were launched at the 1495 Reichstag at Worms. A new organ was introduced, the Reichskammergericht, that was to be largely independent from the Emperor. A new tax was launched to finance it, the Gemeine Pfennig, although this would only be collected under Charles V and Ferdinand I, and not fully.[126][127][128]
To create a rival for the Reichskammergericht, in 1497 Maximilian establish the Reichshofrat, which had its seat in Vienna. During Maximilian's reign, this council was not popular though. In the long run, the two Courts functioned in parallel, sometimes overlapping.[129][130]
In 1500, Maximilian agreed to establish an organ called the Reichsregiment (central imperial government, consisting of twenty members including the Electors, with the Emperor or his representative as its chairman), first organized in 1501 in Nuremberg. But Maximilian resented the new organization, while the Estates failed to support it. The new organ proved politically weak, and its power returned to Maximilian in 1502.[131][130][132]
The most important governmental changes targeted the heart of the regime: the chancery. Early in Maximilian's reign, the Court Chancery at Innsbruck competed with the Imperial Chancery (which was under the elector-archbishop of Mainz, the senior Imperial chancellor). By referring the political matters in Tyrol, Austria as well as Imperial problems to the Court Chancery, Maximilian gradually centralized its authority. The two chanceries became combined in 1502.[7] In 1496, the emperor created a general treasury (Hofkammer) in Innsbruck, which became responsible for all the hereditary lands. The chamber of accounts (Raitkammer) at Vienna was made subordinate to this body.[133] Under Paul von Liechtenstein, the Hofkammer was entrusted with not only hereditary lands' affairs, but Maximilian's affairs as the German king too.[134]
Reception of Roman law

At the 1495 Diet of Worms, the Reception of Roman Law was accelerated and formalized. The Roman Law was made binding in German courts, except in the case it was contrary to local statutes.[136] In practice, it became the basic law throughout Germany, displacing Germanic local law to a large extent, although Germanic law was still operative at the lower courts.[137][138][139][140] Other than the desire to achieve legal unity and other factors, the adoption also highlighted the continuity between the Ancient Roman empire and the Holy Roman Empire.[141] To realize his resolve to reform and unify the legal system, the emperor frequently intervened personally in matters of local legal matters, overriding local charters and customs. This practice was often met with irony and scorn from local councils, who wanted to protect local codes.[142]
The legal reform seriously weakened the ancient Vehmic court (Vehmgericht, or Secret Tribunal of Westphalia, traditionally held to be instituted by Charlemagne but this theory is now considered unlikely[143][144]), although it would not be abolished completely until 1811 (when it was abolished under the order of Jérôme Bonaparte).[145][146]
National political culture

Maximilian and Charles V (despite the fact both emperors were internationalists personally[150][151]) were the first who mobilized the rhetoric of the Nation, firmly identified with the Reich by the contemporary humanists.[119] With encouragement from Maximilian and his humanists, iconic spiritual figures were reintroduced or became notable. The humanists rediscovered the work Germania, written by Tacitus. According to Peter H. Wilson, the female figure of Germania was reinvented by the emperor as the virtuous pacific Mother of Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation.[152] Whaley further suggests that, despite the later religious divide, "patriotic motifs developed during Maximilian's reign, both by Maximilian himself and by the humanist writers who responded to him, formed the core of a national political culture."[153]
Maximilian's reign also witnessed the gradual emergence of the German common language, with the notable roles of the imperial chancery and the chancery of the Wettin Elector Frederick the Wise.[154][155] The development of the printing industry together with the emergence of the postal system (the first modern one in the world[156]), initiated by Maximilian himself with contribution from Frederick III and Charles the Bold, led to a revolution in communication and allowed ideas to spread. Unlike the situation in more centralized countries, the decentralized nature of the Empire made censorship difficult.[157][158][159][160]
Terence McIntosh comments that the expansionist, aggressive policy pursued by Maximilian I and Charles V at the inception of the early modern German nation (although not to further the aims specific to the German nation per se), relying on German manpower as well as utilizing fearsome Landsknechte and mercenaries, would affect the way neighbours viewed the German polity, although in the longue durée, Germany tended to be at peace.[161]
Imperial power

Maximilian was "the first Holy Roman Emperor in 250 years who ruled as well as reigned". In the early 1500s, he was true master of the Empire, although his power weakened during the last decade before his death.[162][163] Whaley notes that, despite struggles, what emerged at the end of Maximilian's rule was a strengthened monarchy and not an oligarchy of princes.[164] Benjamin Curtis opines that while Maximilian was not able to fully create a common government for his lands (although the chancellery and court council were able to coordinate affairs across the realms), he strengthened key administrative functions in Austria and created central offices to deal with financial, political and judicial matters – these offices replaced the feudal system and became representative of a more modern system that was administered by professionalized officials. After two decades of reforms, the emperor retained his position as first among equals, while the empire gained common institutions through which the emperor shared power with the estates.[165]
By the early 16th century, the Habsburg rulers had become the most powerful in Europe, but their strength relied on their composite monarchy as a whole, and not only the Holy Roman Empire (see also: Empire of Charles V).[166][167] Maximilian had seriously considered combining the Burgundian lands (inherited from his wife Mary of Burgundy) with his Austrian lands to form a powerful core (while also extending toward the east).[168] After the unexpected addition of Spain to the Habsburg Empire, at one point he intended to leave Austria (raised to a kingdom) to his younger grandson Ferdinand.[169] His elder grandson Charles V later gave Spain and most of the Burgundian lands to his son Philip II of Spain, the founder of the Spanish branch, and the Habsburg hereditary lands to his brother Ferdinand, the founder of the Austrian branch.[170]
In France and England, from the 13th century onward, stationary royal residences had begun to develop into capital cities that grew rapidly and developed corresponding infrastructure: the Palais de la Cité and the Palace of Westminster became the respective main residences. This was not possible in the Holy Roman Empire because no real hereditary monarchy emerged, but rather the tradition of elective monarchy prevailed (see: Imperial election) which, in the High Middle Ages, led to kings of very different regional origins being elected (List of royal and imperial elections in the Holy Roman Empire). If they wanted to control the empire and its rebellious regional rulers, they could not limit themselves to their home region and their private palaces. As a result, kings and emperors continued to travel around the empire well into modern times,[171] using their temporary residences (Kaiserpfalz) as transit stations for their itinerant courts. From the late Middle Ages onward, the weakly fortified pfalzen were replaced by imperial castles. It was only King Ferdinand I, the younger brother of the then Emperor Charles V, who moved his main residence to the Vienna Hofburg in the middle of the 16th century, where most of the following Habsburg emperors subsequently resided. Vienna did not become the capital of the empire, just of a Habsburg hereditary state (the Archduchy of Austria). The emperors continued to travel to their elections and coronations at Frankfurt and Aachen, to the Imperial Diets at different places and to other occasions. The Perpetual Diet of Regensburg was based in Regensburg from 1663 to 1806. Rudolf II resided in Prague, the Wittelsbach emperor Charles VII in Munich. A German capital in the true sense only existed in the Second German Empire from 1871, when the Kaiser, Reichstag and Reichskanzler resided in Berlin.
Early capitalism
While particularism prevented the centralization of the Empire, it gave rise to early developments of capitalism. In Italian and Hanseatic cities like Genoa and Pisa, Hamburg and Lübeck, warrior-merchants appeared and pioneered raiding-and-trading maritime empires. These practices declined before 1500, but they managed to spread to the maritime periphery in Portugal, Spain, the Netherlands and England, where they "provoked emulation in grander, oceanic scale".[172] William Thompson agrees with M.N. Pearson that this distinctively European phenomenon happened because in the Italian and Hanseatic cities which lacked resources and were "small in size and population", the rulers (whose social status was not much higher than the merchants) had to pay attention to trade. Thus the warrior-merchants gained the state's coercive powers, which they could not gain in Mughal or other Asian realms – whose rulers had few incentives to help the merchant class, as they controlled considerable resources and their revenue was land-bound.[173]
In the 1450s, the economic development in Southern Germany gave rise to banking empires, cartels and monopolies in cities such as Ulm, Regensburg, and Augsburg. Augsburg in particular, associated with the reputation of the Fugger, Welser and Baumgartner families, is considered the capital city of early capitalism.[174][175] Augsburg benefitted majorly from the establishment and expansion of the Kaiserliche Reichspost in the late 15th and early 16th century.[157][156] Even when the Habsburg empire began to extend to other parts of Europe, Maximilian's loyalty to Augsburg, where he conducted a lot of his endeavours, meant that the imperial city became "the dominant centre of early capitalism" of the 16th century, and "the location of the most important post office within the Holy Roman Empire". From Maximilian's time, as the "terminuses of the first transcontinental post lines" began to shift from Innsbruck to Venice and from Brussels to Antwerp, in these cities, the communication system and the news market started to converge. As the Fuggers as well as other trading companies based their most important branches in these cities, these traders gained access to these systems as well.[176] The 1557, 1575 and 1607 bankruptcies of the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs though damaged the Fuggers substantially. Moreover, "Discovery of water routes to India and the New World shifted the focus of European economic development from the Mediterranean to the Atlantic – emphasis shifted from Venice and Genoa to Lisbon and Antwerp. Eventually American mineral developments reduced the importance of Hungarian and Tyrolean mineral wealth. The nexus of the European continent remained landlocked until the time of expedient land conveyances in the form of primarily rail and canal systems, which were limited in growth potential; in the new continent, on the other hand, there were ports in abundance to release the plentiful goods obtained from those new lands." The economic pinnacles achieved in Germany in the period between 1450 and 1550 would not be seen again until the end of the 19th century.[177]
In the Netherlands part of the empire, financial centres evolved together with markets of commodities. Topographical development in the 15th century made Antwerp a port city.[178] Boosted by the privileges it received as a loyal city after the Flemish revolts against Maximilian, it became the leading seaport city in Northern Europe and served as "the conduit for a remarkable 40% of world trade".[179][180][181] Conflicts with the Habsburg-Spanish government in 1576 and 1585 though made merchants relocate to Amsterdam, which eventually replaced it as the leading port city.[182][178]
Reformation and Renaissance

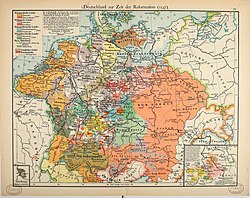
In 1516, Ferdinand II of Aragon, grandfather of the future Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, died.[183] Charles initiated his reign in Castile and Aragon, a union which evolved into Spain, in conjunction with his mother Joanna of Castile.
In 1519, already reigning as Carlos I in Spain, Charles took up the imperial title as Karl V. The Holy Roman Empire would end up going to a more junior branch of the Habsburgs in the person of Charles's brother Ferdinand, while the senior branch continued to rule in Spain and the Burgundian inheritance in the person of Charles's son, Philip II of Spain. Many factors contribute to this result. For James D. Tracy, it was the polycentric character of the European civilization that made it hard to maintain "a dynasty whose territories bestrode the continent from the Low Countries to Sicily and from Spain to Hungary – not to mention Spain's overseas possessions".[184] Others point out the religious tensions, fiscal problems and obstruction from external forces including France and the Ottomans.[185] On a more personal level, Charles failed to persuade the German princes to support his son Philip, whose "awkward and withdrawn character and lack of German language skills doomed this enterprise to failure".[186]
Before Charles's reign in the Holy Roman Empire began, in 1517, Martin Luther launched what would later be known as the Reformation. The empire then became divided along religious lines, with the north, the east, and many of the major cities – Strasbourg, Frankfurt, and Nuremberg – becoming Protestant while the southern and western regions largely remained Catholic.
At the beginning of Charles's reign, another Reichsregiment was set up again (1522), although Charles declared that he would only tolerate it in his absence and its chairman had to be a representative of his. Charles V was absent in Germany from 1521 to 1530. Similar to the one set up in the early 1500s, the Reichsregiment failed to create a federal authority independent of the emperor, due to the unsteady participation and differences between princes. Charles V defeated the Protestant princes in 1547 in the Schmalkaldic War, but the momentum was lost and the Protestant estates were able to survive politically despite military defeat.[187] In the 1555 Peace of Augsburg, Charles V, through his brother Ferdinand, officially recognized the right of rulers to choose Catholicism or Lutheranism (Zwinglians, Calvinists and radicals were not included).[188] In 1555, Paul IV was elected pope and took the side of France, whereupon an exhausted Charles finally gave up his hopes of a world Christian empire.[189][190]
Baroque period


Germany would enjoy relative peace for the next six decades. On the eastern front, the Turks continued to loom large as a threat, although war would mean further compromises with the Protestant princes, and so the Emperor sought to avoid it. In the west, the Rhineland increasingly fell under French influence. After the Dutch revolt against Spain erupted, the Empire remained neutral, de facto allowing the Netherlands to depart the empire in 1581. A side effect was the Cologne War, which ravaged much of the upper Rhine. Emperor Ferdinand III formally accepted Dutch neutrality in 1653, a decision ratified by the Reichstag in 1728.
After Ferdinand died in 1564, his son Maximilian II became Emperor, and like his father accepted the existence of Protestantism and the need for occasional compromise with it. Maximilian was succeeded in 1576 by Rudolf II, who preferred classical Greek philosophy to Christianity and lived an isolated existence in Bohemia. He became afraid to act when the Catholic Church was forcibly reasserting control in Austria and Hungary, and the Protestant princes became upset over this.
Imperial power sharply deteriorated by the time of Rudolf's death in 1612. When Bohemians rebelled against the Emperor, the immediate result was the series of conflicts known as the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648), which devastated the empire. Foreign powers, including France and Sweden, intervened in the conflict and strengthened those fighting the Imperial power, but also seized considerable territory for themselves. Accordingly, the empire could never return to its former glory, leading Voltaire to make his infamous quip that the Holy Roman Empire was "neither Holy nor Roman nor an Empire."[191]
Still, its actual end did not come for two centuries. The Peace of Westphalia in 1648, which ended the Thirty Years' War allowed Calvinism, but Anabaptists, Arminians and other Protestant communities would still lack any support and continue to be persecuted well until the end of the empire. The Habsburg emperors focused on consolidating their own estates in Austria and elsewhere.
At the Battle of Vienna (1683), the Army of the Holy Roman Empire, led by the Polish King John III Sobieski, decisively defeated a large Turkish army, stopping the western Ottoman advance and leading to the eventual dismemberment of the Ottoman Empire in Europe. The army was one third forces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and two thirds forces of the Holy Roman Empire.
Modern period
Prussia and Austria

By the rise of Louis XIV, the Habsburgs were chiefly dependent on their hereditary lands to counter the rise of Prussia, which possessed territories inside the Empire. Throughout the 18th century, the Habsburgs were embroiled in various European conflicts, such as the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–1714), the War of the Polish Succession (1733–1735), and the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748). The German dualism between Austria and Prussia dominated the empire's history after 1740.
French Revolutionary Wars and final dissolution

From 1792 onward, revolutionary France was at war with various parts of the Empire intermittently.
The German mediatization was the series of mediatizations and secularizations that occurred between 1795 and 1814, during the latter part of the era of the French Revolution and then the Napoleonic Era. "Mediatization" was the process of annexing the lands of one imperial estate to another, often leaving the annexed some rights. For example, the estates of the Imperial Knights were formally mediatized in 1806, having de facto been seized by the great territorial states in 1803 in the so-called Rittersturm. "Secularization" was the abolition of the temporal power of an ecclesiastical ruler such as a bishop or an abbot and the annexation of the secularized territory to a secular territory.

The empire was dissolved on 6 August 1806, when the last Holy Roman Emperor Francis II (from 1804, Emperor Francis I of Austria) abdicated, following a military defeat by the French under Napoleon at the Battle of Austerlitz in 1805 (see Treaty of Pressburg). Napoleon reorganized much of the Empire into the Confederation of the Rhine, a French satellite. Francis' House of Habsburg-Lorraine survived the demise of the empire, continuing to reign as Emperors of Austria and Kings of Hungary until the Habsburg empire's final dissolution in 1918 in the aftermath of World War I.
The Napoleonic Confederation of the Rhine was replaced by a new union, the German Confederation in 1815, following the end of the Napoleonic Wars. It lasted until 1866 when Prussia founded the North German Confederation, a forerunner of the German Empire which united the German-speaking territories outside of Austria and Switzerland under Prussian leadership in 1871. This state developed into modern Germany.
The abdication indicated that the Kaiser no longer felt capable of fulfilling his duties as head of the Reich, and so declared:
"That we consider the tie that has bound us to the body politic of the German Reich to be broken, that we have expired the office and dignity of the head of the Reich through the unification of the confederated Rhenish estates and that we are thereby relieved of all the duties we have assumed towards the German Reich Consider counted, and lay down the imperial crown worn by the same until now and conducted imperial government, as is hereby done."[192]
The only princely member states of the Holy Roman Empire that have preserved their status as monarchies until today are the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg and the Principality of Liechtenstein. The only Free Imperial Cities still existing as states within Germany are Hamburg and Bremen. All other historic member states of the Holy Roman Empire were either dissolved or have adopted republican systems of government.
Demographics
Population
Overall population figures for the Holy Roman Empire are extremely vague and vary widely. The empire of Charlemagne may have had as many as 20 million people.[193] Given the political fragmentation of the later Empire, there were no central agencies that could compile such figures. Nevertheless, it is believed the demographic disaster of the Thirty Years' War meant that the population of the Empire in the early 17th century was similar to what it was in the early 18th century; by one estimate, the Empire did not exceed 1618 levels of population until 1750.[194]
In the early 17th century, the electors held under their rule the following number of Imperial subjects:[195]
- Habsburg Monarchy: 5,350,000 (including 3 million in the Bohemian crown lands)[196][full citation needed]
- Electorate of Saxony: 1,200,000
- Duchy of Bavaria (later Electorate of Bavaria): 800,000
- Electoral Palatinate: 600,000
- Electorate of Brandenburg: 350,000
- Electorates of Mainz, Trier, and Cologne: 300–400,000 altogether[197]
While not electors, the Spanish Habsburgs had the second highest number of subjects within the Empire after the Austrian Habsburgs, with over 3 million in the early 17th century in the Burgundian Circle and Duchy of Milan.[k][l]
Peter Wilson estimates the Empire's population at 20 million in 1700, of whom 5 million lived in Imperial Italy. By 1800 he estimates the Empire's population at 29 million (excluding Italy), with another 12.6 million held by the Austrians and Prussians outside of the Empire.[18]
According to a contemporary estimate of the Austrian War Archives for the first decade of the 18th century, the Empire – including Bohemia and the Spanish Netherlands – had a population of close to 28 million with a breakdown as follows:[198]
- 65 ecclesiastical states with 14 percent of the total land area and 12 percent of the population;
- 45 dynastic principalities with 80 percent of the land and 80 percent of the population;
- 60 dynastic counties and lordships with 3 percent of the land and 3.5 percent of the population;
- 60 imperial towns with 1 percent of the land and 3.5 percent of the population;
- Imperial knights' territories, numbering into the several hundreds, with 2 percent of the land and 1 percent of the population.
German demographic historians have traditionally worked on estimates of the population of the Holy Roman Empire based on assumed population within the frontiers of Germany in 1871 or 1914. More recent estimates use less outdated criteria, but they remain guesswork. One estimate based on the frontiers of Germany in 1870 gives a population of some 15–17 million around 1600, declined to 10–13 million around 1650 (following the Thirty Years' War). Other historians who work on estimates of the population of the early modern Empire suggest the population declined from 20 million to some 16–17 million by 1650.[199]
A credible estimate for 1800 gives 27–28 million inhabitants for the Empire (which at this point had already lost the remaining Low Countries, Italy, and the Left Bank of the Rhine in the 1797 Treaty of Campo Fornio) with an overall breakdown as follows:[200]
- 9 million Austrian subjects (including Silesia, Bohemia and Moravia);
- 4 million Prussian subjects;
- 14–15 million inhabitants for the rest of the Empire.
There are also numerous estimates for the Italian states that were formally part of the Empire:
| State | Population |
|---|---|
| Duchy of Milan (Spanish) | 1,350,000 |
| Piedmont-Savoy | 1,200,000[m] |
| Republic of Genoa | 650,000 |
| Grand Duchy of Tuscany | 649,000 |
| Duchy of Parma-Piacenza | 250,000 |
| Duchy of Modena-Reggio | 250,000 |
| County of Gorizia and Gradisca (Austrian) | 130,000[196][full citation needed] |
| Republic of Lucca | 110,000 |
| Total | c. 4,600,000 |
| State | Population |
|---|---|
| Piedmont-Savoy | 2,400,000[n] |
| Duchy of Milan (Austrian) | 1,100,000[o] |
| Grand Duchy of Tuscany | 1,000,000 |
| Republic of Genoa | 500,000 |
| Duchy of Parma-Piacenza | 500,000 |
| Duchy of Modena-Reggio | 350,000 |
| Republic of Lucca | 100,000 |
| Total | c. 6,000,000 |
Largest cities
Largest cities or towns of the Empire by year:
- 1050: Regensburg 40,000 people. Rome 35,000. Mainz 30,000. Speyer 25,000. Cologne 21,000. Trier 20,000. Worms 20,000. Lyon 20,000. Verona 20,000. Metz 16,000 people. Florence 15,000.[203]
- 1300–1350: Milan 120,000 people. Florence 110,000 people. Genoa 90,000 people. Prague 77,000 people. Cologne 60,000 people. Marseille 40,000 people. Verona 40,000 people. Padua 35,000 people. Erfurt 32,000 people. Metz 32,000 people. Regensburg 30,000 people. Speyer 25,000 people. Mainz 24,000 people. Aachen 21,000 people. Magdeburg 20,000 people. Nuremberg 20,000 people. Vienna 20,000 people. Danzig (now Gdańsk) 20,000 people. Straßburg (now Strasbourg) 20,000 people. Worms 20,000 people. Lübeck 15,000 people. Regensburg 11,000 people.[204][205][206][207]
- 1500: Milan 100,000 people. Genoa 70,000 people. Prague 70,000.Florence 50,000 people. Cologne 45,000. Antwerp 40,000 people. Cremona 40,000 people. Nuremberg 38,000. Augsburg 30,000. Mantua 28,000 people. Lübeck 25,000. Breslau (now Wrocław) 25,000. Regensburg 22,000. Augsburg 20,000 people. Vienna 20,000. Straßburg (now Strasbourg) 20,000. Parma 19,000 people. Magdeburg 18,000. Modena 18,000 people. Pavia 16,000 people. Ulm 16,000. Hamburg 15,000.[208]
- 1600: Milan 150,000.[209] Prague 100,000. Vienna 50,000. Augsburg 45,000. Cologne 40,000. Nuremberg 40,000. Hamburg 40,000. Magdeburg 40,000. Breslau (now Wrocław) 40,000. Straßburg (now Strasbourg) 25,000. Lübeck 23,000. Ulm 21,000. Regensburg 20,000. Frankfurt am Main 20,000. Munich 20,000.[208]
Religion

Catholicism constituted the single official religion of the Empire until 1555; the Holy Roman Emperor was always Catholic.
Lutheranism was officially recognized in the Peace of Augsburg of 1555, and Calvinism in the Peace of Westphalia of 1648. Those two constituted the only officially recognized Protestant denominations, while various other Protestant confessions such as Anabaptism, Arminianism, etc. coexisted illegally within the Empire. Anabaptism came in a variety of denominations, including Mennonites, Schwarzenau Brethren, Hutterites, the Amish, and multiple other groups.
Following the Peace of Augsburg, the official religion of a territory was determined by the principle cuius regio, eius religio according to which a ruler's religion determined that of his subjects. The Peace of Westphalia abrogated that principle by stipulating that the official religion of a territory was to be what it had been on 1 January 1624, considered to have been a "normal year". Henceforth, the conversion of a ruler to another faith did not entail the conversion of his subjects.[210]
In addition, all Protestant subjects of a Catholic ruler and vice versa were guaranteed the rights that they had enjoyed on that date. While the adherents of a territory's official religion enjoyed the right of public worship, the others were allowed the right of private worship (in chapels without either spires or bells). In theory, no one was to be discriminated against or excluded from commerce, trade, craft or public burial on grounds of religion. For the first time, the permanent nature of the division between the Christian churches of the empire was more or less assumed.[210]
A Jewish minority existed in the Holy Roman Empire. The Holy Roman Emperors claimed the right of protection and taxation of all the Jews of the empire, but there were also large-scale massacres of Jews, especially at the time of the First Crusade and during the wars of religion in the 16th century.
Institutions
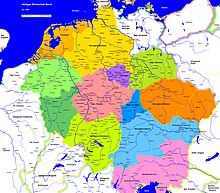
The Holy Roman Empire was neither a centralized state nor a nation-state. Instead, it was divided into dozens – eventually hundreds – of individual entities governed by kings,[p] dukes, counts, bishops, abbots, and other rulers, collectively known as princes. There were also some areas ruled directly by the Emperor.
From the High Middle Ages onwards, the Holy Roman Empire was marked by an uneasy coexistence with the princes of the local territories who were struggling to take power away from it. To a greater extent than in other medieval kingdoms such as France and England, the emperors were unable to gain much control over the lands that they formally owned. Instead, to secure their own position from the threat of being deposed, emperors were forced to grant more and more autonomy to local rulers, both nobles and bishops. This process began in the 11th century with the Investiture Controversy and was more or less concluded with the 1648 Peace of Westphalia. Several Emperors attempted to reverse this steady dilution of their authority but were thwarted both by the papacy and by the princes of the Empire.
Imperial estates
The number of territories represented in the Imperial Diet was considerable, numbering about 300 at the time of the Peace of Westphalia. Many of these Kleinstaaten ("little states") covered no more than a few square miles, or included several non-contiguous pieces, so the Empire was often called a Flickenteppich ("patchwork carpet"). An entity was considered a Reichsstand (imperial estate) if, according to feudal law, it had no authority above it except the Holy Roman Emperor himself. The imperial estates comprised:
- Territories ruled by a hereditary nobleman, such as a prince, archduke, duke, or count.
- Territories in which secular authority was held by an ecclesiastical dignitary, such as an archbishop, bishop, or abbot. Such an ecclesiastic or Churchman was a prince of the Church. In the common case of a prince-bishop, this temporal territory (called a prince-bishopric) frequently overlapped with his often larger ecclesiastical diocese, giving the bishop both civil and ecclesiastical powers. Examples are the prince-archbishoprics of Cologne, Trier, and Mainz.
- Free imperial cities and Imperial villages, which were subject only to the jurisdiction of the emperor.
- The scattered estates of the free Imperial Knights and Imperial Counts, immediate subject to the Emperor but unrepresented in the Imperial Diet.
A sum total of 1,500 Imperial estates has been reckoned.[211] For a list of Reichsstände in 1792, see List of Imperial Diet participants (1792).
The most powerful lords of the later empire were the Austrian Habsburgs, who ruled 240,000 km2 (93,000 sq mi) of land within the Empire in the first half of the 17th century, mostly in modern-day Austria and Czechia. At the same time the lands ruled by the electors of Saxony, Bavaria, and Brandenburg (prior to the acquisition of Prussia) were all close to 40,000 km2 (15,000 sq mi); the Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg (later the Elector of Hanover) had a territory around the same size. These were the largest of the German realms. The Elector of the Palatinate had significantly less at 20,000 km2 (7,700 sq mi), and the ecclesiastical Electorates of Mainz, Cologne, and Trier were much smaller, with around 7,000 km2 (2,700 sq mi). Just larger than them, with roughly 7,000–10,000 km2 (2,700–3,900 sq mi), were the Duchy of Württemberg, the Landgraviate of Hessen-Kassel, and the Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin. They were roughly matched in size by the prince-bishoprics of Salzburg and Münster. The majority of the other German territories, including the other prince-bishoprics, were under 5,000 km2 (1,900 sq mi), the smallest being those of the Imperial Knights; around 1790 the Knights consisted of 350 families ruling a total of only 5,000 km2 (1,900 sq mi) collectively.[212] Imperial Italy was less fragmented politically, most of it c. 1600 being divided between Savoy (Savoy, Piedmont, Nice, Aosta), the Grand Duchy of Tuscany (Tuscany, bar Lucca), the Republic of Genoa (Liguria, Corisca), the duchies of Modena-Reggio and Parma-Piacenza (Emilia), and the Spanish Duchy of Milan (most of Lombardy), each with between half a million and one and a half million people.[201] The Low Countries were also more coherent than Germany, being entirely under the dominion of the Spanish Netherlands as part of the Burgundian Circle, at least nominally.
| Ruler | 1648 | 1714 | 1748 | 1792 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austrian Habsburgs | 225,390 km2 (32.8%) | 251,185 km2 (36.5%) | 213,785 km2 (31.1%) | 215,875 km2 (31.4%) |
| Brandenburg Hohenzollerns | 70,469 km2 (10.2%) | 77,702 km2 (11.3%) | 124,122 km2 (18.1%) | 131,822 km2 (19.2%) |
| Other secular prince-electors[r] | 89,333 km2 (13.1%) | 122,823 km2 (17.9%) | 123,153 km2 (17.9%) | 121,988 km2 (17.7%) |
| Other German rulers | 302,146 km2 (44.0%) | 235,628 km2 (34.3%) | 226,278 km2 (32.9%) | 217,653 km2 (31.7%) |
| Total | 687,338 | 687,338 | 687,338 | 687,338 |
King of the Romans

A prospective Emperor first had to be elected King of the Romans (Latin: Rex Romanorum; German: römischer König). German kings had been elected since the 9th century; at that point they were chosen by the leaders of the five most important tribes (the Salian Franks of Lorraine, Ripuarian Franks of Franconia, Saxons, Bavarians, and Swabians). In the Holy Roman Empire, the main dukes and bishops of the kingdom elected the King of the Romans.
The imperial throne was transferred by election, but Emperors often ensured their own sons were elected during their lifetimes, enabling them to keep the crown for their families. This only changed after the end of the Salian dynasty in the 12th century.
In 1356, Emperor Charles IV issued the Golden Bull, which limited the electors to seven: the King of Bohemia, the Count Palatine of the Rhine, the Duke of Saxony, the Margrave of Brandenburg, and the archbishops of Cologne, Mainz, and Trier. During the Thirty Years' War, the Duke of Bavaria was given the right to vote as the eighth elector, and the Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg (colloquially, Hanover) was granted a ninth electorate; additionally, the Napoleonic Wars resulted in several electorates being reallocated, but these new electors never voted before the Empire's dissolution. A candidate for election would be expected to offer concessions of land or money to the electors in order to secure their vote.
After being elected, the King of the Romans could theoretically claim the title of "Emperor" only after being crowned by the Pope. In many cases, this took several years while the King was held up by other tasks: frequently he first had to resolve conflicts in rebellious northern Italy or was quarreling with the Pope himself. Later Emperors dispensed with the papal coronation altogether, being content with the styling Emperor-Elect: the last Emperor to be crowned by the Pope was Charles V in 1530.
The Emperor had to be male and of noble blood. No law required him to be a Catholic, but as the majority of the Electors adhered to this faith, no Protestant was ever elected. Whether and to what degree he had to be German was disputed among the Electors, contemporary experts in constitutional law, and the public. During the Middle Ages, some Kings and Emperors were not of German origin, but since the Renaissance, German heritage was regarded as vital for a candidate in order to be eligible for imperial office.[214]
Imperial Diet (Reichstag)

The Imperial Diet (Reichstag, or Reichsversammlung) was not a legislative body as is understood today, as its members envisioned it to be more like a central forum, where it was more important to negotiate than to decide.[215] The Diet was theoretically superior to the emperor himself. It was divided into three classes. The first class, the Council of Electors, consisted of the electors, or the princes who could vote for King of the Romans. The second class, the Council of Princes, consisted of the other princes. The Council of Princes was divided into two "benches", one for secular rulers and one for ecclesiastical ones. Higher-ranking princes had individual votes, while lower-ranking princes were grouped into "colleges" by geography. Each college had one vote.
The third class was the Council of Imperial Cities, which was divided into two colleges: Swabia and the Rhine. The Council of Imperial Cities was not fully equal with the others; it could not vote on several matters such as the admission of new territories. The representation of the Free Cities at the Diet had become common since the late Middle Ages. Nevertheless, their participation was formally acknowledged only as late as 1648 with the Peace of Westphalia ending the Thirty Years' War.
Imperial courts
The Empire also had two courts: the Reichshofrat (also known in English as the Aulic Council) at the court of the King/Emperor, and the Reichskammergericht (Imperial Chamber Court), established with the Imperial Reform of 1495 by Maximilian I. The Reichskammergericht and the Aulic Council were the two highest judicial instances in the Old Empire. The Imperial Chamber court's composition was determined by both the Holy Roman Emperor and the subject states of the Empire. Within this court, the Emperor appointed the chief justice, always a highborn aristocrat, several divisional chief judges, and some of the other puisne judges.[216]
The Aulic Council held standing over many judicial disputes of state, both in concurrence with the Imperial Chamber court and exclusively on their own. The provinces Imperial Chamber Court extended to breaches of the public peace, cases of arbitrary distraint or imprisonment, pleas which concerned the treasury, violations of the Emperor's decrees or the laws passed by the Imperial Diet, disputes about property between immediate tenants of the Empire or the subjects of different rulers, and finally suits against immediate tenants of the Empire, with the exception of criminal charges and matters relating to imperial fiefs, which went to the Aulic Council. The Aulic Council even allowed the emperors the means to depose rulers who did not live up to expectations.[130][129]
Imperial circles
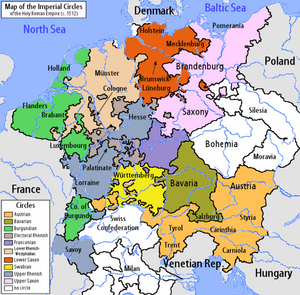
As part of the Imperial Reform, six Imperial circles were established in 1500; four more were established in 1512. These were regional groupings of most (though not all) of the various states of the Empire for the purposes of defense, imperial taxation, supervision of coining, peace-keeping functions, and public security. Each circle had its own parliament, known as a Kreistag ("Circle Diet"), and one or more directors, who coordinated the affairs of the circle. Not all imperial territories were included within the imperial circles, even after 1512; the Lands of the Bohemian Crown were excluded, as were Switzerland, the imperial fiefs in northern Italy, the lands of the Imperial Knights, and certain other small territories like the Lordship of Jever.
Army
The Army of the Holy Roman Empire (German: Reichsarmee, Reichsheer or Reichsarmatur; Latin: exercitus imperii) was created in 1422 and as a result of the Napoleonic Wars came to an end even before the Empire. It should not be confused with the Imperial Army (Kaiserliche Armee) of the Emperor.
Despite appearances to the contrary, the Army of the Empire did not constitute a permanent standing army that was always at the ready to fight for the Empire. When there was danger, an Army of the Empire was mustered from among the elements constituting it,[217] in order to conduct an imperial military campaign or Reichsheerfahrt. In practice, the imperial troops often had local allegiances stronger than their loyalty to the Emperor.
Administrative centres

Throughout the first half of its history the Holy Roman Empire was reigned over by a travelling court. Kings and emperors toured between the numerous Kaiserpfalzes (Imperial palaces), usually resided for several weeks or months and furnished local legal matters, law and administration. Most rulers maintained one or a number of favourites Imperial palace sites, where they would advance development and spent most of their time: Charlemagne (Aachen from 794), Otto I (Magdeburg, from 955),[218] Frederick II (Palermo 1220–1254), Wittelsbacher (Munich 1328–1347 and 1744–1745), Habsburger (Prague 1355–1437 and 1576–1611; and Vienna 1438–1576, 1611–1740 and 1745–1806).[22][219][220]
This practice eventually ended during the 16th century, as the emperors of the Habsburg dynasty chose Vienna and Prague and the Wittelsbach rulers chose Munich as their permanent residences (Maximilian I's "true home" was still "the stirrup, the overnight rest and the saddle", although Innsbruck was probably his most important base; Charles V was also a nomadic emperor).[221][222][223] Vienna became Imperial capital during the 1550s under Ferdinand I (reigned 1556–1564). Except for a period under Rudolf II (reigned 1570–1612) who moved to Prague, Vienna kept its primacy under his successors.[221][224] Before that, certain sites served only as the individual residence for a particular sovereign. A number of cities held official status, where the Imperial Estates would summon at Imperial Diets, the deliberative assembly of the empire.[225][226]
The Imperial Diet (Reichstag) resided variously in Paderborn, Bad Lippspringe, Ingelheim am Rhein, Diedenhofen (now Thionville), Aachen, Worms, Forchheim, Trebur, Fritzlar, Ravenna, Quedlinburg, Dortmund, Verona, Minden, Mainz, Frankfurt am Main, Merseburg, Goslar, Würzburg, Bamberg, Schwäbisch Hall, Augsburg, Nuremberg, Quierzy-sur-Oise, Speyer, Gelnhausen, Erfurt, Eger (now Cheb), Esslingen, Lindau, Freiburg, Cologne, Konstanz and Trier before it was moved permanently to Regensburg.[227]
Until the 15th century the elected emperor was crowned and anointed by the Pope in Rome, among some exceptions in Ravenna, Bologna and Reims. Since 1508 (emperor Maximilian I) Imperial elections took place in Frankfurt am Main, Augsburg, Rhens, Cologne or Regensburg.[131][228]
In December 1497 the Aulic Council (Reichshofrat) was established in Vienna.[229]
In 1495 the Reichskammergericht was established, which variously resided in Worms, Augsburg, Nuremberg, Regensburg, Speyer and Esslingen before it was moved permanently to Wetzlar.[230]
Foreign relations
The Habsburg royal family had its own diplomats to represent its interests. The larger principalities in the Holy Roman Empire, beginning around 1648, also did the same. The Holy Roman Empire did not have its own dedicated ministry of foreign affairs and therefore the Imperial Diet had no control over these diplomats; occasionally the Diet criticised them.[231]
When Regensburg served as the site of the Diet, France and, in the late 1700s, Russia, had diplomatic representatives there.[231] The kings of Denmark, Great Britain, and Sweden had land holdings in Germany and so had representation in the Diet itself.[232] The Netherlands also had envoys in Regensburg. Regensburg was the place where envoys met as it was where representatives of the Diet could be reached.[233]
Имперские семьи и династии
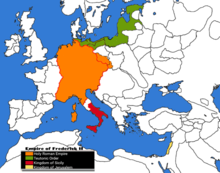
В некоторых избирательных округах Священной Римской империи были дополнительные королевские или имперские территории, которые иногда были с самого начала, вне юрисдикции Священной Римской империи. Генрих VI , унаследовав как немецкие устремления к имперскому суверенитету, так и мечту нормандских сицилийских королей о гегемонии в Средиземноморье, имел амбициозный дизайн для мировой империи. Бутчер отмечает, что политика в браке также сыграла здесь важную роль: «Семейная политика Стауфера варьировалась от Иберии до России, от Скандинавии до Сицилии, от Англии до Византии и до государств крестоносцев на востоке. Генри уже отбрасывал глаза. Африка и Греция, в Азию и Сирию и, конечно, на Иерусалиме ». Его аннексия Сицилия изменила стратегический баланс на итальянском полуострове. Император, который хотел сделать все свои земли наследственными, также утверждал, что папские качества были имперскими феодами. После его смерти в возрасте 31 года он не смог передать свою сильную позицию своему сыну Фредерику II , который был избран только королем римлян. [ 234 ] [ 235 ] [ 236 ] Союз между Сицилией и Империей, таким образом, оставался личным союзом. [ 237 ] Фредерик II стал королем Сицилии в 1225 году благодаря браку с Изабеллой II (или Иоландом) Иерусалима и восстановил Вифлеем и Назарет для христианской стороны посредством переговоров с Аль-Камилом . Мечта о мировой империи Хоэнстауфен закончилась смертью Фредерика в 1250 году. [ 238 ] [ 239 ]
В свои ранние дни империя обеспечила основную среду для христианства, чтобы проникнуть в сферы язычников на севере и на востоке (скандинавцы, мадьяры, славянские люди и т. Д.). [ 240 ] В эпоху реформ Империя, по своей природе, была оборонительной и не агрессивной, желая как внутреннего мира, так и безопасности от вторжения сил, что даже воинственные принцы, такие как Максимилиан, я ценил. [ 241 ] В ранней современной эпохе ассоциация с церковью (Церковь универсал для Люксембургов и католическая церковь для габсбургов), а также ответственность императора за защиту Центральной Европы оставалась реальностью. Даже спусковым крючком для концепции имперской реформы под Сигизмунд была идея помощи Церкви поставить свой дом в порядок. [ 242 ] [ 243 ] [ 244 ]
Традиционно немецкие династии использовали потенциал имперского названия, чтобы привлечь Восточную Европу в склад, в дополнение к их землям к северу и югу от Альп. Стратегии брака и наследства, следуя (обычно защитной) войне, сыграли отличную роль как для люксембургов, так и для габсбургов. Это было под сигизмунд из Люксембурга , которая вышла замуж за Мэри, королевы Реднала и законного наследника Венгрии , а затем укрепил свою власть с браком с способной и хорошо связанной благородной женщиной Барбарой из Килли , [ 245 ] что личная империя императора расширилась до царства за пределами границы Священной Римской империи: Венгрия. Этот последний монарх династии Люксембург (который носил четыре королевских короны) сумел получить империю, почти сопоставимую по масштабе с более поздней империей Габсбурга, хотя в то же время они потеряли королевство Бургундии и контроль над итальянскими территориями. Основное внимание Люксембургам на Востоке, особенно Венгрии, позволило новым бургундским правителям из династии Валуа поощрять недовольство немецких князей. Таким образом, габсбурги были вынуждены переориентироваться на Западе. Двоюродный брат и предшественник Фредерика III, Альберт II из Германии (который был зятом Сигизмунда и наследником в его браке с Элизабет из Люксембурга ) удалось объединить короны Германии, Венгрии, Богемии и Хорватии под его правлением, но он умер, но он умер, но он умер, но он умер, но он умер молодой. [ 246 ] [ 247 ] [ 248 ]
Во время его правления, Максимилиан я сфокусировался как на Востоке, так и на Западе. Успешное расширение (с заметной ролью в отношении политики в браке) при Максимилионе укрепило свою позицию в империи, а также создало большее давление на имперскую реформу , чтобы они могли получить больше ресурсов и скоординировали помощь от немецких территорий, чтобы защитить свои сферы и Встречи, такие как Франция. [ 249 ] [ 250 ] С тех пор, как он стал королем римлян в 1486 году, империя оказала важную помощь для его деятельности в Бургундских Нидерландах, а также с богемией, Венгрией и другими восточными государствами. [ 251 ] В царствованиях его внуков Хорватия и оставшаяся наводнятка венгерского королевства выбрали Фердинанда в качестве их правителя после того, как ему удалось спасти Силезию и Богемию от судьбы Венгрии против османской. Симмс отмечает, что их выбор был договорным, связывая правительство Фердинанда в этих королевствах и территориях с его избраниями в качестве короля римлян и его способность защищать Центральную Европу. [ 252 ] [ 253 ] В свою очередь, имперское правление Габсбургов также «зависело от того, чтобы удерживать эти дополнительные обширные земли в качестве независимых источников богатства и престижа». [ 254 ]
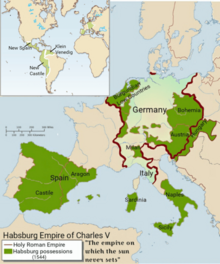
Более поздние австрийские габсбурги из Фердинанда я был осторожен, чтобы сохранить различие между их династической империей и Священной Римской империей. Питер Уилсон утверждает, что институты и структуры, разработанные имперской реформой, в основном служили немецким землям, и, хотя монархия Габсбурга «оставалась тесно связана с Империей», габсбурги преднамеренно воздержались от включения других их территорий в свои рамки. «Вместо этого они разработали свои собственные институты для управления тем, что фактически было параллельной династической территориальной империей и которая дала им огромное превосходство ресурсов, в свою очередь, позволяя им сохранить почти непрерывную сцепление на имперский титул в течение следующих трех веков . " [ 255 ] Фердинанд заинтересовался в том, чтобы удержать богемию отдельно от имперской юрисдикции и установления связи между богемией и Империей. Когда он отказался от права имперского избирателя как короля богемии (что дало ему половину его дохода [ 256 ] ), он смог дать богемию (а также связанные с ними территории, такие как верхняя и нижняя Альсатия, Силезия и Моравия) тот же привилегированный статус, что и Австрия, поэтому подтверждая его превосходную позицию в Империи. [ 160 ] [ 257 ] Габсбурги также пытались мобилизовать имперскую помощь Венгрии (которая в течение 16 -го века стоила династии больше денег в расходов на оборону, чем общий доход, который он принес). [ 258 ]
С 1542 года Charles V и Ferdinand смогли собрать общий налог на копейки, или Türkenhilfe (Turkish Aid), предназначенный для защиты империи от османов или Франции. Но, как Венгрия, в отличие от богемии, не была частью империи, имперская помощь в Венгрии зависела от политических факторов. Обязанность действовало только в том случае, если Вене или империю угрожали. [ 126 ] [ 259 ] [ 260 ] [ 127 ] Уилсон отмечает, что «в начале 1520 -х годов Рейхстаг колебался, чтобы проголосовать за помощь королю Венгрии Луи II, потому что он считал его иностранным принцем. Это изменилось, когда Венгрия перешла к Габсбургам после смерти Луи в битве в 1526 году и главной цели. Императорское налогообложение в течение следующих 90 лет заключалось в том, чтобы субсидировать стоимость защиты венгерской границы от османов. Войска, которые в конечном итоге выселили османов из Венгрии между 1683 и 1699 годами. Кодекс имперского права 1532 года использовался в некоторых частях Венгрии до середины 17-го века, но в остальном у Венгрии была своя правовая система и не импортировала австрийские сопротивлялся использованию германских названий, таких как GRAF для подсчета до 1606 года, и очень немногие приобрели личный статус имперского принца ». [ 261 ]
Отвечая на мнение, что династические проблемы Габсбурга были нанесены вреда Священной Римской империи, Уэйли пишет, что «не было фундаментальной несовместимости между династическим и участием в империи, ни для габсбургов, ни для саксов или других». [ 262 ] Имперские стратегии брака имели два раза в двух обоюдоострении для Священной Римской империи. Испанская связь была примером: хотя она предоставила влиятельного партнера в защиту христианского христианского языка от османов, это позволило Карлу V перенести бургундские Нидерланды , Франч-Комте, а также другие имперские феи, такие как Милан , его сыну Филиппу II ' S испанская империя. [ 263 ] [ 264 ]
Помимо имперских семей, другие немецкие князья также обладали иностранными землями, и иностранные правители также могут приобрести имперские феи и, таким образом, стать имперскими принцами. Это явление способствовало фрагментации суверенитета, в котором имперские вассалы оставались полусуверными, одновременно укрепляя взаимосвязи (и шансы на взаимное вмешательство) между Королевством Германии и империей в целом с другими королевствами, такими как Денарда и Шведена, которые приняли Статус имперских вассалов от имени их немецких владений (которые были подвергнуты имперским законам). Две скандинаньские монархи выполнили обязательства по оказанию помощи империи в войнах 17 -го и начала 18 -го веков. Они также импортировали немецкие княжеские семьи в качестве правителей, хотя в обоих случаях это не производило прямые союзы. Дания последовательно пыталась воспользоваться своим влиянием в имперских учреждениях, чтобы получить новые имперские феи вдоль Эльбы , хотя эти попытки, как правило, не преуспели. [ 265 ]
Смотрите также
- Семейное древо немецких монархов
- Список государств в Священной Римской империи
- Список государственных лидеров в Священной Римской империи 10-го века
- Список государственных лидеров в Священной Римской империи 11-го века
- Список государственных лидеров в Священной Римской империи 12-го века
- Список государственных лидеров в Священной Римской империи 13-го века
- Список государственных лидеров в Священной Римской империи 14-го века
- Список государственных лидеров в Священной Римской империи 15-го века
- Список государственных лидеров в Священной Римской империи 16-го века
- Список государственных лидеров в Священной Римской империи 17-го века
- Список государственных лидеров в Священной Римской империи 18-го века
- Список государственных лидеров в Священной Римской империи 19-го века
- Список войн с участием Священной Римской империи
- Последовательность Римской империи
Ссылки
Примечания
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в Некоторые историки называют началом империи 800, с коронацией Франканского короля Карла Великого («Чарльз Великий»). [ 1 ] Другие называют начало коронацией Отто Великого в 962 году. [ 2 ]
- ^ Регенсбург, место «Вечной диеты» после 1663 года, стало рассматриваться как неофициальная столица Империи несколькими европейскими державами с долю в Империи - Франции, Англии, Нидерландах, России, Швеции, Дардии - и они хранил там более или менее постоянных посланников, потому что это было единственное место в Империи, где делегаты всех крупных и средних немецких штатов собрались и могли быть достигнуты для лоббирования и т. Д. Сами императоры Габсбурга использовали Регенсбург таким же образом. ( Härter 2011 , с. 122–123, 132)
- ^ Немецкий , низкий немецкий , итальянский , чешский , польский , голландский , французский , фризский , ромасяный , словенский , сорбийский , идиш и другие языки. Согласно « Золотому быку» 1356 года, сыновья принц-элькторов были рекомендованы изучить языки немецкого , латинского , итальянского и чешского . [ 16 ]
- ^ Согласно перспективе восточной православной церкви , до c. Великий раскол 1054 года (постепенный процесс), Священная Римская империя (наряду с остальной частью Западной Европы ) была православным христианином, находясь под церковной юрисдикцией Патриархата Рима до того, как Папа Лео Икс сломал общение с другими церквями. В качестве яркого примера, император Генрих II († 1024) управлял государством и умер незадолго до раскола, но все же почитается как святой как католиками , так и православными.
- ^ Немецкая «Римская» империя: из -за феодальной организации царство, контролируемое императором, трудно определить, а тем более мера. По оценкам, достигается пика около 1050 при около 1,0 мм 2 К. ( Taagepera 1997 , p. 494)
- ^ Латинский : крестцовый румым империя ; Немецкий : Священная Римская империя , произносится [ˈhaɪlɪəs ˈʁøːmɪʃəs ˈʁaɪç]
- ^ В то время как Карл Великий и его преемники приняли вариации названия Императора , никто не назвал себя римским императором до Отто II в 983 году. «Природа империи» . Encyclopædia Britannica Online . Получено 15 февраля 2014 года .
- ^ "Передача правила"
- ^ Перевод предоставления привилегий торговцам в 1229 году: «Средневековые источники: привилегии, предоставленные немецким купцам в ноябрьском, 1229» . Fordham.edu. Архивировано из оригинала 14 августа 2014 года . Получено 13 апреля 2020 года .
- ^ Поэтому мы решили отличить короля Боем, граф Палатин Рене, правителя избранного из Электрика или наследников и преемников, которые, вероятно, узнают, начинают знать седьмой год грамматического итальянского и сланного инструктора по лингвису, так что это так Четырнадцатый год года в такой данной ему Богом благодаря ученым . ( Zeumern 1908 )
- ^ 1,35 миллиона населения, данное для герцогства Милана. ( Смит 1920 , стр. 19)
- ^ Популяции 1,6 миллиона и 1,5 миллиона, приведенных для областей в пределах границ современной Бельгии и Нидерландов, соответственно, около 1600 года; Испанские активы в бургундском круге также включали в себя Franche-Comte, Luxembourg и другие небольшие территории. ( Avakov 2015 )
- ^ Цифра в 800 000 дается Смитом для «Савойя в Италии», не разъясняясь о том, относится ли это ко всему государству Савойя или только его итальянские территории Пьемонта и долины Аоста (таким образом, исключая Савой и округ Ниццы. ) Однако Hanlon 2014 , с. 87 дает население Пьемонта в начале 17 -го века как 700 000, а Supor Savoy - 400 000, без числа, не данных для Aosta или NICE; Указывая о том, что использование Смита «Савойя из Италии» действительно относится только к Пьемонту и Аосте.
- ^ За исключением 500 000 жителей острова Сардиния, который не был частью империи.
- ^ Назван в источнике как «Австрийская ломбардия». Большая часть бывшего герцогства была аннексирована Венецианской Республикой в начале 18 -го века.
- ^ Единственным принцем позволил назвать себя «королем» территории в Империи, был королем богемии (после 1556 года обычно сам Император). Некоторые другие принцы были королями в силу королевств, которые они контролировали за пределами империи
- ^ Изучившись по данным областям, фигуры Уилсона включают только немецкие и чешские, говорящие о районе Рейха, за исключением французских (например, австрийских Нидерландов , Франч-Комтэ ) и итальянских (например , Тоскана , Пьемонт-Савой ). Это очевидно в том, как территории избирателей и «других немецких правителей» добавляют к заявленной общей сумме рейха, и в том, как область Рейха не меняется с данного 687 338 км. 2 (265 383 кв. МИ) Всего с 1648 по 1792 год, несмотря на то, что многие французские территории бургундского круга в это время было потеряно . Цифры также исключают земли, удерживаемые за пределами империи (включая немецкие), такие как прусские территории Хохензоллерна.
- ^ В 1648 году: Саксония, Бавария и избирательный палатинат. На более поздние даты: Саксония, Бавария, избирательный лав и Ганновер.
Цитаты
- ^ «Карл Великий | Император Священного Римского» . Encyclopædia Britannica Online . Получено 16 октября 2023 года .
- ^ Kleinhenz 2004 , p. 810; «Отто можно считать первым правителем Священной Римской империи, хотя этот термин использовался до двенадцатого века».
- ^ Аретин, Карл Отмар Фрейерр (31 декабря 1983 г.). Шидер, Теодор; Брунн, Герхард (ред.). «Рейх без капитала? Мульти -центр функционирует функции капитала в рейхе до 1806 года» . Столичные города в европейской национальной государствах : 5–14. Doi : 10.1515/9783486992878-003 . ISBN 978-3-4869-9287-8 .
- ^ «Союз правительства в« Федерианском » . Treccani.it . Получено 4 мая 2022 года .
- ^ «Генрих VI, король Сицилии и император в« Federiciana » . Treccani.it . Получено 4 мая 2022 года .
- ^ Камп, Норберт. «Фредерик II из Свабии, император, король Сицилии и Иерусалим, король римлян в« Федериане » » . Treccani.it . Получено 4 мая 2022 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в Brady 2009 , p. 211.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Pavlac & Lott 2019 , с. 249
- ^ Sciences, Neuhausen Academy of (2021). Вклад в историю, язык, язык и культуру баварцы (на немецком языке). BOD - Книги по требованию. п. 106 ISBN 978-3-0006-9644-2 .
- ^ Шмитт, Оливер Йенс (2021). Правило и политика в Юго -Восточной Европе с 1300 по 1800 год (на немецком языке). Walter de Gruyter Gmbh & Co Kg. п. 659 . ISBN 978-3-1107-4443-9 .
- ^ Бухманн, Бертран Майкл (2002). Хоф, правительство, городская администрация: Вена как место австрийской центральной администрации с начала до падения монархии (на немецком языке). Издатель по истории и политике. п. 37 ISBN 978-3-4865-6541-6 .
- ^ Клопсток, Фридрих Готлиб (1974). Работы и письма: Историческое критическое издание (на немецком языке). W. de Gruyter. п. 999 . Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Pihlajamäki, Heikki; Даббер, Маркус Д.; Годфри, Марк (2018). Оксфордский справочник европейской юридической истории . Издательство Оксфордского университета. п. 762. ISBN 978-0-1910-8838-4 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Джонстон, Уильям М. (1983). Австрийский разум: интеллектуальная и социальная история, 1848–1938 . Калифорнийский университет. п. 13 ISBN 978-0-5200-4955-0 .
- ^ PAVLAC & LOTT 2019 , с. 278
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Ůrek 2014 .
- ^ Wilson 2016 , с. V - XXVI.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в Wilson 2016 , с. 496.
- ^ Кой, Джейсон Филип; Маршке, Бенджамин; Сабеан, Дэвид Уоррен (2010). Священная Римская империя, пересмотренная . Berghahn Books. п. 2 ISBN 978-1-8454-5992-5 .
- ^ «Священная Римская империя» . Encyclopædia Britannica Online . Получено 15 февраля 2014 года .
- ^ "Карл Великий" . История 9 ноября 2009 года. Архивировано с оригинала 6 сентября 2022 года . Получено 19 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Кантор 1993 , с. 212–215.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Гаскон, Бамбер. «История Священной Римской империи» . История мира .
- ^ Дэвис 1996 , с. 316–317.
- ^ Петерс, Эдвард (1977). Европа: мир средневековья . Прентис-Холл. п. 418. ISBN 978-0-1329-1898-5 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Вейлер, Бьорн Ку; Маклин, Саймон (2006). Представления власти в средневековой Германии 800–1500 . Isd. п. 126. ISBN 978-2-5035-1815-2 Полем Получено 9 марта 2022 года .
- ^ Громкий, Грэм А.; Schenk, Jochen (2017). Происхождение немецких княжеств, 1100–1350: эссе немецких историков . Тейлор и Фрэнсис. п. 49 ISBN 978-1-3170-2200-8 .
- ^ Streissguth, Tom (2009). Средневековья . Greenhaven Publishing. п. 154 ISBN 978-0-7377-4636-5 .
- ^ Уилсон 1999 , с. 18
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в дюймовый Whaley 2012a , с. 17–21.
- ^ Брайс 1890 , с. 2–3.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Гарипзанов 2008 .
- ^ Breverton 2014 , с. 104
- ^ Wilson 2016b , p. 79
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Brady 2009 , с. 104–106.
- ^ Brady 2009 , с. 128, 129.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Johnson 1996 , p. 23
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Уилсон 1999 , с. 2
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Whaley 2011 , с. 17
- ^ Морау 1999 , полковник 2025–2028.
- ^ Whaley 2011 , с. 19–20.
- ^ Schulze 1998 , с. 52–55.
- ^ «Немецкая империя-губчатая католическая лексика» . lexikon.katholik.hu . Получено 3 августа 2022 года .
- ^ Уилсон 2006 , с. 719.
- ^ Вольтер 1773 , с. 338.
- ^ Jorio & Braun 2016 .
- ^ Lauryssens 1999 , p. 102
- ^ Бахрах, Дэвид С. (2014). Война в Германии десятого века . Boydell & Brewer Ltd. с. 3, 5, 12, 60, 73, 103, 180, 254. ISBN 978-1-8438-3927-9 Полем Получено 31 июля 2022 года .
- ^ Браун, Уоррен (февраль 2015 г.). «Война в Германии десятого века [Обзор книги]» . Ранняя средневековая Европа . 23 (1): 117–120. doi : 10.1111/emed.12090 . ISSN 0963-9462 . Архивировано из оригинала 31 июля 2022 года . Получено 31 июля 2022 года .
- ^ Брайс 1890 , с. 183.
- ^ Innes 2000 , с. 167–170.
- ^ Брайс 1890 , с. 35.
- ^ Дэвис 1996 , с. 232, 234.
- ^ Брайс 1890 , с. 35–38.
- ^ McKitterick 2018 , с. 48–50.
- ^ «Франция: история, карта, флаг, капитал и факты » Encyclopædia Britannica 16 Там 2023.
- ^ Брайс 1890 , с. 38–42.
- ^ Джонсон 1996 , с. 22
- ^ Kohn 2006 , с. 113–114.
- ^ Даффи 1997 , с. 62–63.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Брайс, с. 44, 50–52
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный McKitterick 2018 , p. 70
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Коллинз 2014 , с. 131.
- ^ Chambers, Mortimer (1974). Западный опыт . Кнопф. п. 204. ISBN 978-0-3943-1806-6 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Витт, Рональд Г. (2012). Две латинские культуры и основание ренессансного гуманизма в средневековой Италии . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 27. ISBN 978-0-5217-6474-2 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Тейлор и Хансен-Тейлор 1894 , с. 117
- ^ Тейлор и Хансен-Тейлор 1894 , с. 118
- ^ Тейлор и Хансен-Тейлор 1894 , с. 121.
- ^ Hoyt & Chodorowow 1976 , p. 197
- ^ Magill 1998 , p. 706.
- ^ Кантор 1993 , с. 212–213.
- ^ Бернхардт, Джон В. (2002). Независимое царство и королевские монастыри в ранней средневековой Германии, C. 936–1075 . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 23. ISBN 978-0-5215-2183-3 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Уикхем, Крис (2016). Средневековая Европа . Издательство Йельского университета. п. 131. ISBN 978-0-3002-2221-0 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Кантор 1993 , с. 214–215.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Magill 1998 , p. 707.
- ^ Такер, Спенсер С. (2009). Глобальная хронология конфликта: от древнего мира до современного Ближнего Востока [6 томов]: от древнего мира до современного Ближнего Востока . ABC-Clio. п. 412. ISBN 978-1-8510-9672-5 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Geanakoplos, Deno John (1979). Средневековая западная цивилизация и византийские и исламские миры: взаимодействие трех культур . DC Heath. п. 207. ISBN 978-0-6690-0868-5 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ "Отто I - Legacy Britannica" . www.britannica.com . Получено 2 марта 2022 года .
- ^ Биография, немецкий. «Отто И. - немецкая биография» . www.deutsche-biography.de (на немецком языке) . Получено 5 марта 2022 года .
- ^ Дэвидс, Адельберт (2002). Императрица Феофано: Византия и Запад на рубеже первого тысячелетия . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 188. ISBN 978-0-5215-2467-4 Полем Получено 9 марта 2022 года .
- ^ Янсен С. (2002). Чудовищный полк женщин: женщины -правители в ранней современной Европе . Спрингер. п. 153. ISBN 978-0-2306-0211-3 Полем Получено 9 марта 2022 года .
- ^ Маклин, Саймон (2017). Отонианское королевство . Издательство Оксфордского университета. п. 169. ISBN 978-0-1988-0010-1 Полем Получено 9 марта 2022 года .
- ^ Дигби, Генри 1891 (1891). Католики Мерес: книги VII-IX . П. О'Ши. п. 939 . Отступление 9 марта 2022 года .
- ^ Magill 1998 , p. 708.
- ^ McBrien 2000 , p. 138.
- ^ Швиди 1914 .
- ^ Кантор 1993 , с. 215–217.
- ^ Bideleux, Robert; Джеффрис, Ян (2006). История Восточной Европы: кризис и перемены . Routledge. п. 119. ISBN 978-1-1347-1985-3 Полем Получено 30 мая 2022 года .
- ^ Льюис, Арчибальд Росс (1988). Кочевники и крестоносцы, 1000–1368 г. н.э. Издательство Джорджтаунского университета. п. 83. ISBN 978-0-2533-4787-9 Полем Получено 30 мая 2022 года .
- ^ Фрид, Йоханнес (2015). Средневековья . Гарвардский университет издательство. п. 138. ISBN 978-0-6747-4467-7 Полем Получено 30 мая 2022 года .
- ^ Роуленд, Кристофер; Бартон, Джон (2002). Апокалиптический в истории и традициях . Bloomsbury Academic. п. 173. ISBN 978-0-8264-6208-4 Полем Получено 30 мая 2022 года .
- ^ Arnason, Johann P.; Wittrock, Björn (2005). Евразийские преобразования, от десятого до тринадцатого века: кристаллизации, расхождения, эпохи Возрождения . Брилль п. 100. ISBN 978-9-0474-1467-4 Полем Получено 30 мая 2022 года .
- ^ Немецкий польский диалог: письма польских и немецких епископов и международные заявления . Редакция Атлантический-Форум. 1966. с. 9 Получено 30 мая 2022 года .
- ^ Эммерсон, Ричард К. (2013). Ключевые фигуры в средневековой Европе: энциклопедия . Routledge. п. 497. ISBN 978-1-1367-7518-5 Полем Получено 30 мая 2022 года .
- ^ Muldoon, J. (1999). Империя и порядок: концепция империи, 800–1800 . Спрингер. п. 35. ISBN 978-0-2305-1223-8 Полем Получено 30 мая 2022 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Barraclough 1984 , с. 101–134.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Barraclough 1984 , p. 109
- ^ Barraclough 1984 , с. 122–124.
- ^ Barraclough 1984 , p. 123.
- ^ Barraclough 1984 , с. 123–134.
- ^ Чисхолм, Хью , изд. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica . Тол. 25 (11 -е изд.). Издательство Кембриджского университета.
- ^ Herrmann 1970 , p. 530.
- ^ Хаффнер 2019 , с. 6–10.
- ^ Смаил и Гибсон 2009 .
- ^ Арнольд 1995 , с. 398.
- ^ Hunyadi & Laszlovszky 2001 , p. 129
- ^ Boettcher, Carl-Heinz (2005). Путь Европы в современные времена: от мирового государства до мира государства (на немецком языке). Röhrig Universitätsverlag. п. 342. ISBN 978-3-8611-0390-5 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Элерс, Йоахим (2003). "Генрих VI." В Шнайдмюллере, Бернд; Weinfurter, Stefan (Eds.). Немецкие правители средневековья: исторические портреты Генриха I до Максимилиана I (919–1519) (на немецком языке). Чек. С. ISBN 978-3-4065-0958-2 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Koenigsberger, HG (2014). Средневековая Европа 400–1500 . Routledge. п. 105. ISBN 978-1-3178-7088-3 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ PAVLAC & LOTT 2019 , с. 17
- ^ Грант, Жанна (2014). Для общего блага: богемный земельный закон и начало революции Гуссита . Брилль п. 8. ISBN 978-9-0042-8326-8 Полем Получено 2 ноября 2022 года .
- ^ Ротштейн 1995 , с. 9–.
- ^ Szepesi 2015 .
- ^ Ротбард 2009 .
- ^ Шварцвальд, Джек Л. (2015). Крышка и восстановление Европы, 476–1648 гг . Макфарланд. п. 116. ISBN 978-1-4766-6230-5 Полем Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Брэди 2009 , с. 73.
- ^ Махони, Уильям (2011). История Чехии и Словакии . ABC-Clio. п. 51. ISBN 978-0-3133-6306-1 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Brady 2009 , с. 73, 74.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Whaley 2011 , с. 278
- ^ Харди 2018 .
- ^ Брэди 2009 , с. 75–81.
- ^ Drees, Clayton J. (2000). Поздний средневековый возраст кризиса и обновления, 1300–1500 гг.: Биографический словарь . Bloomsbury Publishing USA. ISBN 978-1-56750-749-2 .
- ^ Уилсон, Питер Х. (2016b). Священная Римская империя: тысяча лет истории Европы . Пингвин Книги Limited. п. 79. ISBN 978-0-1419-5691-6 Полем Получено 21 января 2022 года .
- ^ Смит, Уильям Брэдфорд (2008). Реформация и немецкое территориальное государство: Верхняя Франкония, 1300–1630 . Университет Рочестер Пресс. п. 45. ISBN 978-1-5804-6274-7 Полем Получено 21 января 2022 года .
- ^ Уилсон 2016 , с. 79
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Трейси, Джеймс Д. (2016). Балканские войны: Габсбург Хорватия, Османская Босния и венецианская Далматия, 1499–1617 . Роуман и Литтлфилд. п. 163. ISBN 978-1-4422-1360-9 Полем Получено 17 января 2022 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Агостон, Габор (2021). Последнее мусульманское завоевание: Османская империя и ее войны в Европе . ПРИЗНАЯ УНИВЕРСИТЕТА ПРИСЕТА. п. 312. ISBN 978-0-6912-0538-0 Полем Получено 17 января 2022 года .
- ^ Whaley 2012a , p. [1] .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Pavlac & Lott 2019 , с. 143.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный в Brady 2009 , p. 429.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Herbs 2000 , pp. 19-30.
- ^ Whaley 2011 , с. 61.
- ^ Berenger & Simpson 2014 , с.
- ^ Госман, Мартин; Alasdair, A.; Макдональд, а.; Макдональд, Аласдейр Джеймс; Вандерджагт, Ари Йохан (2003). Принцы и княжеская культура: 1450–1650 . Брилль п. 298. ISBN 978-9-0041-3572-7 Полем Архивировано из оригинала 24 октября 2021 года . Получено 24 октября 2021 года .
- ^ Ходнет, Эндрю Артур (2018). Другие Ленднхнехта . Государственный университет Северной Каролины. п. 81.
- ^ Burdick, William Livesey (2004). Принципы римского права и их отношение к современному праву . The Lawbook Exchange, Ltd. с. 19, 20. ISBN 978-1-5847-7253-8 Полем Получено 19 ноября 2021 года .
- ^ Ли, Даниэль (2016). Популярный суверенитет в ранней современной конституционной мысли . Издательство Оксфордского университета. п. 243. ISBN 978-0-1910-6244-5 Полем Получено 20 ноября 2021 года .
- ^ Торнхилл, Крис (2007). Немецкая политическая философия: метафизика права . Routledge. п. 12. ISBN 978-1-1343-8280-4 Полем Получено 20 ноября 2021 года .
- ^ Haivry, Ofir (2017). Джон Селден и западная политическая традиция . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 118. ISBN 978-1-1070-1134-2 Полем Получено 20 ноября 2021 года .
- ^ Мусуракис, Джордж (2017). Исторический и институциональный контекст римского права . Routledge. п. 435. ISBN 978-1-3518-8840-0 Полем Получено 20 ноября 2021 года .
- ^ Zoller, Elisabeth (2008). Введение в публичное право: сравнительное исследование . Брилль п. 64. ISBN 978-9-0041-6147-4 Полем Получено 20 ноября 2021 года .
- ^ Hodnet 2018 , с. 79–81.
- ^ Спенс, Льюис (1993). Энциклопедия оккультизма . Kensington Publishing Corporation. п. 133. ISBN 978-0-8065-1401-7 Полем Получено 12 декабря 2021 года .
- ^ Palgrave, Francis (2013). Собранные исторические произведения сэра Фрэнсиса Пэлгрейва, издательство К. Кембриджского университета. С. XIV, 203–204. ISBN 978-1-1076-2636-2 Полем Получено 12 декабря 2021 года .
- ^ Beccaria, Cesare Marchese Di; Беккария, Чезаре; Стивенсон, Брайан (2008). По преступлениям и наказаниям и другим произведениям . Университет Торонто Пресс. п. 133. ISBN 978-0-8020-8990-8 Полем Получено 12 декабря 2021 года .
- ^ Рипли, Джордж; Датский, Чарльз Андерсон (1869). Новая американская циклопдия: популярный словарь общих знаний D. Эпплтон. П. 43 Получено 12 декабря
- ^ Стидер, Питер (8 мая 2017 г.). «Об истории происхождения почетных ворот Дюрера для Императора Максимилиана» . План Германского национального музея : 128–142 страницы. Doi : 10.11588/azgnm.1954.38143 . Получено 7 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Hirschi, Caspar (2011). Происхождение национализма: альтернативная история от древнего Рима до ранней современной Германии . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 45. ISBN 978-1-1395-0230-6 Полем Получено 7 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Брандт, Беттина (2010). Германия и их сыновья: представления нации, пола и политики в современности (на немецком языке). Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht. п. 37. ISBN 978-3-5253-6710-0 Полем Получено 8 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Альберт, Рабил младший (2016). Ренессанс гуманизм, том 2: Фонды, формы и наследие . Университет Пенсильвании Пресс. ISBN 978-1-5128-0576-5 Полем Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Quevedo, Франциско де; Бриттон, Р.К. (1989). Франциско де Кеведо: Мечты и циферблаты . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-1-8003-4588-1 Полем Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Уилсон 2016 , с. 263.
- ^ Whaley, Joachim (2009). «Whaley On Silver,« Marketing Maximilian: визуальная идеология Императора Священного Римского »| H-German | H-Net» . Networks.h-net.org . Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Tennant, Elaine C.; Джонсон, Кэрролл Б. (1985). Габсбургский канцелярный язык в перспективе, том 114 . Калифорнийский университет. стр. 1, 3, 9. ISBN 978-0-5200-9694-3 Полем Архивировано из оригинала 27 сентября 2021 года . Получено 21 сентября 2021 года .
- ^ Визингер, Питер. «Развитие немецкого письменного языка с 16 по 18 веков под влиянием конфессий» . Журнал германистов Румынии (ZGR) (17–18 / 2000 (9 -й год)): 155–162. Doi : 10.1515/jbgsg-2018-0014 . S2CID 186566355 . Архивировано из оригинала 23 января 2008 года . Получено 8 ноября 2021 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Мейнель, Кристоф; Сак, Харальд (2014). Цифровая связь: коммуникация, мультимедиа, безопасность . Springer Science & Business Media. п. 31. ISBN 978-3-6425-4331-9 Полем Архивировано из оригинала 26 сентября 2021 года . Получено 20 сентября 2021 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Метциг, Грегор (2016). Коммуникация и конфронтация: дипломатия и устранение императора Maximilians I (1486–1519) (на немецком языке). Walter de Gruyter Gmbh & Co Kg. Стр 978-3-1104-5673-8 Полем Получено 29 января 2022 года .
- ^ Скотт, Хэмиш М. (2015). Оксфордский справочник ранней современной европейской истории, 1350–1750 . Издательство Оксфордского университета. п. 173. ISBN 978-0-1995-9725-3 Полем Получено 12 декабря 2021 года .
- ^ Headrick, Daniel R. (2000). Когда информация достигла совершеннолетия: технологии знаний в эпоху разума и революции, 1700–1850 . Издательство Оксфордского университета. п. 184. ISBN 978-0-1980-3108-6 Полем Получено 12 декабря 2021 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Whaley 2011 , с. 370.
- ^ «Круглый стол H-German на Смит, Германия: нация в свое время до, во время и после национализма, 1500–2000 | H-German | H-Net» . Networks.h-net.org . Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Брэди 2009 , с. 110, 128.
- ^ Форстер, Марк Р. "Форстер на Брэди-младший,« Немецкие истории в эпоху Реформаций, 1400–1650 '| H-German | H-Net » . Networks.h-net.org . Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Whaley 2012a , p. 75
- ^ Curtis 2013 , с. 46–52.
- ^ Аш, Рональд Дж. (28 октября 2021 г.). «Монархи» . Ранняя современная культура суда : 17–36. doi : 10.4324/9780429277986-3 . ISBN 978-0-4292-7798-6 Полем S2CID 240193601 .
- ^ Thackeray, Frank W.; Финдинг, Джон Э. (2012). События, которые сформировали современный мир: из европейского эпохи Возрождения до войны с террором [5 томов]: от Европейского Ренессанса до войны с террором . ABC-Clio. п. 133. ISBN 978-1-5988-4902-8 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Holleger 2012 , с.
- ^ Брэди, Томас А.; Брэди, Томас А. младший (2009). Немецкие истории в эпоху Реформаций, 1400–1650 . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 112. ISBN 978-0-5218-8909-4 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Уилсон 2004 , с. 27
- ^ Карл Отмар фон Аретин: Рейх без столицы? (Империя без капитала?), В: Столичные города в европейских государствах (столицы в европейских государствах), Ed T Schieder & G Brunn, Munich/Vienna, 1983, с. 1–29
- ^ Брэди, Томас А. младший (1997). Трейси, Джеймс Д. (ред.). Политическая экономия торговых империй: государственная власть и мировая торговля, 1350–1750 . Издательство Кембриджского университета. С. 117–160. ISBN 978-0-5215-7464-8 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Томпсон, Уильям Р. (2000). Появление глобальной политической экономии (PDF) . Лондон: Routledge. п. 67. ISBN 0-4152-1452-1 Полем Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 19 сентября 2013 года . Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Ertl, Alan (2007). Политический экономический фонд демократического капитализма: от Бытия до созревания . Universal-Publishers. С. 189–191. ISBN 978-1-5994-2424-8 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Kypta, Ulla; Брух, Джулия; Skambraks, Tanja (2019). Методы в премерской экономической истории: тематические исследования Священной Римской империи, c. 1300 - C. 1600 . Спрингер Природа. п. 116. ISBN 978-3-0301-4660-3 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Behringer, Wolfgang (2011). «Ядро и периферия: Священная Римская империя как вселенная общения». Священная Римская империя, 1495–1806 (PDF) . Оксфорд: издательство Оксфордского университета. С. 347–358. ISBN 978-0-1996-0297-1 Полем Архивировано (PDF) из оригинала 9 октября 2022 года . Получено 7 августа 2022 года .
- ^ ERTL 2007 , стр. 189-191.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный ERTL 2007 , с. 188-189.
- ^ Poitras, Geoffrey (2000). Ранняя история финансовой экономики, 1478–1776 гг . Эдвард Элгар. п. 48. ISBN 978-1-8406-4455-5 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Очки, Эдвард; Кортит, Карима; Nijcamp, Peter (2020). Городские империи: города как глобальные правители в новом городском мире . Переродил. п. 148. ISBN 978-0-4298-9236-3 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Хамерс, Джель (5 сентября 2022 г.). "Беспокойный брак . повторный За Böhlaau Verlag: 421–4 doi : 10.7767/977820521032.421 . ISBN 978-3-2052-1602-5 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Смит, Алан К. (2019). Создание мировой экономики: торговец, колониализм и мировая торговля, 1400–1825 . Routledge. п. 103. ISBN 978-0-4297-1042-1 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Mullett 2010 , с. 81.
- ^ Трейси, Джеймс Д. (2018). Голландия под правилом Габсбурга, 1506–1566: формирование политического тела . Univ of California Press. п. 46. ISBN 978-0-5203-0403-1 Полем Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Nexon, Daniel H. (2009). Борьба за власть в ранней современной Европе: религиозный конфликт, династические империи и международные изменения . ПРИЗНАЯ УНИВЕРСИТЕТА ПРИСЕТА. п. 135. ISBN 978-0-6911-3793-3 Полем Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Whaley 2011 , с. 326.
- ^ Холборн, Хаджо (1982). История современной Германии: Реформация . ПРИЗНАЯ УНИВЕРСИТЕТА ПРИСЕТА. п. 48. ISBN 978-0-6910-0795-3 Полем Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Whaley 2012a , p. 334.
- ^ Macculloch, Diarvad (2005). Реформация . Пингвин. п. 362. ISBN 978-1-1015-6395-3 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Isom-Verhaaren, Christine (2011). Союзники с неверным: Османский и французский альянс в шестнадцатом веке . Bloomsbury Publishing. п. 58. ISBN 978-0-8577-3227-9 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Ренна, Томас (сентябрь 2015 г.). «Священная Римская империя не была ни святой, ни римской, ни империей» . Мичиганский академик . 42 (1): 60–75. doi : 10.7245/0026-2005-42.1.60 . ISSN 0026-2005 . Получено 31 марта 2023 года .
- ^ «Объяснение Франца II, чтобы сложить корону Священной Римской империи - викирус» . de.wikisource.org (на немецком языке) . Получено 28 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Жареный 2016 , с. 56
- ^ Parker 2008 , p. 1058.
- ^ Уилсон 2009 , с. 18–23.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Уилсон, с. 788
- ^ Уилсон 2009 , с. 17
- ^ Benecke 1974 , p. 162.
- ^ Whaley 2012a , p. 633.
- ^ Whaley 2012b , p. 351.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Смит 1920 , с. 19
- ^ Случаев 1824 , с. 197
- ^ Пуга, Диего; Trefler, Daniel, «Международная торговля и институциональные изменения: смерть в Венеции» (PDF) , Венецианский семинар MIT , архивируя из оригинала (PDF) 3 сентября 2015 г.
- ^ Tallier 2009 , p. 290.
- ^ Клаус 1997 .
- ^ Уран 2010 , с. 587.
- ^ Legauy 1995 , p. 104
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Поток 2011 , с. 118
- ^ Лук 1981 .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Whaley 2012a , с. 624–625.
- ^ Gumpelzhaier 1796 .
- ^ Whaley 2012b , p. 188.
- ^ Уилсон 2004 , с. 307
- ^ Hirschi 2005 , с. 393–399.
- ^ Малетке 2001 , с. 22
- ^ «Общество Императорского камерного суда, Wetzlar» . Музей и исследовательский центр Императорского камерного суда (Reichskammergericht) . 4 июля 2015 года . Получено 7 сентября 2021 года .
- * Corvisier & Childs 1994 , p. 306
- ^ Туллнер, Матиас (2013). История государства Саксония-Анхальт (на немецком языке). Springer Publishing House. п. 27. ISBN 978-3-3229-7346-7 Полем Получено 6 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Ehlers et al. 2016 , с. 31–.
- ^ «Семь немецких городов, которых вы никогда не знали, были когда -то столицы» . Местный . 18 августа 2016 года. Архивировано с оригинала 20 июня 2019 года . Получено 20 июня 2019 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Pavlac & Lott 2019 , с. 27
- ^ Бенеце, Герхард (2019). Максимилиан I (1459–1519): аналитическая биография . Routledge. п. 25. ISBN 978-1-0000-0840-1 Полем Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Грант, Нил (1970). Чарльз V, Император Священного Римского . Ф. Уоттс. п. 74. ISBN 978-0-5310-0937-6 Полем Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Патруч, Джозеф Ф. (2010). Ученик Королевы: Эрцлерхесса Элизабет, Императрица Мария, Габсбурги и Священная Римская империя, 1554–1569 . Брилль п. 11. ISBN 978-9-0041-8030-7 Полем Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Gagliardo 1980 , стр. 22–23.
- ^ Брокманн 2006 , с. 15
- ^ Schindling 1986 , p. 64
- ^ Angermeier 1984 .
- ^ Hochedlinger, Mata & Winkelbauer 2019 .
- ^ Баркер 1911 , с. 341.
- ^ Jump up to: а беременный Уилсон 1999 , с. 70
- ^ Уилсон 1999 , с. 69
- ^ Материнал 2011 , с. 122-123, 132.
- ^ Boettcher 2005 , p. 342.
- ^ Wilson 2016b , p. 2028.
- ^ Ertl, Alan W. (2008). На пути к пониманию Европы: политическая экономическая наука континентальной интеграции . Universal-Publishers. п. 202. ISBN 978-1-5994-2983-0 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Houben, Hubert (2002). Роджер II из Сицилии: правитель между Востоком и Западом . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 7. ISBN 978-0-5216-5573-6 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ О'Коннелл, Моник; Dursteler, Eric R. (2016). Средиземноморский мир: от падения Рима до роста Наполеона . Jhu Press. п. 102. ISBN 978-1-4214-1901-5 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Ван, Клив; Клив, Томас Кертис Ван (1972). Император Фредерик II из Хохенстауфена, иммутатор Мунди . Кларендон Пресс. п. 120. ISBN 978-0-1982-2513-3 Полем Получено 15 октября 2022 года .
- ^ Wilson 2016 , с. 69.
- ^ Уилсон 1999 , с. 52–53.
- ^ Wilson 2016 , с. Lxxv.
- ^ Брэди 2009 , с. 72
- ^ Джонсон 1996 , с. 52
- ^ Populer, Michèle (1993). «Малиуш (Элемер). Кайзер Сигисминд в Унгарне 1387–1437» . Revue Belge de Philologie et d'Istoire . 71 (4): 953–957 . Получено 5 июля 2022 года .
- ^ Whaley 2012a , с. 18–19.
- ^ Отец, Роберто (2022). История европейской интеграции за 2500 лет: древние происхождение обновляется в нынешних aetertas Tektime. П. 85. ISBN 978-8-8354-3496-2 Полем Получено 6 августа 2022 года .
- ^ Ирганг, Винфрид. «Seepoints - Обзор: Император Сигисминд (1368–1437) - издание 14 (2014), № 11» . seepoint.de .
- ^ Whaley, Joachim (2018). Священная Римская империя: очень короткое представление . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-1910-6563-7 Полем Получено 6 августа 2022 года .
- ^ Whaley 2012a , с. 18–19, 69.
- ^ Блюдрс, Патрик. Максимилиан I и Священная Римская империя: власть царя римлян (1486–1490) (тезис). С. 1–39 . Получено 6 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ Leustean, Lucian N. (2014). Православное христианство и национализм в юго-восточной Европе девятнадцатого века . Fordham Univ Press. п. 255. ISBN 978-0-8232-5608-2 Полем Получено 6 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ Симмс, Брендан (2013). Европа: борьба за превосходство, с 1453 по настоящее время . Основные книги. п. 1737. ISBN 978-0-4650-6595-0 Полем Получено 6 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ Уилсон 2016 , с. 221
- ^ Уилсон 2016 , с. II
- ^ Эванс 2006 , с. 82
- ^ Evans & Wilson 2012 , с. 126
- ^ Андерсон, Перри (2013). Линии абсолютистского состояния . Verso Books. п. 303. ISBN 978-1-7816-8010-0 Полем Получено 6 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ Zmora, Hillay (2002). Монархия, аристократия и государство в Европе 1300–1800 . Routledge. п. 50. ISBN 978-1-1347-4798-6 Полем Получено 17 января 2022 года .
- ^ Ninness, Richard J. (2020). Немецкие имперские рыцари: благородные неудачи между княжеской властью и короной, 1479–1648 . Routledge. п. 106. ISBN 978-1-0002-8502-4 Полем Получено 17 января 2022 года .
- ^ Уилсон , стр. II-IT30.
- ^ «Whaley On Silver,« Marketing Maximilian: визуальная идеология Императора Священного Римского »| H-German | H-Net» . Networks.h-net.org . Получено 26 февраля 2022 года .
- ^ Дауни, Кирстин (2014). Изабелла: Королева воинов . Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. п. 307. ISBN 978-0-3855-3412-3 Полем Получено 6 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ Данделет, Томас Джеймс (2014). Ренессанс империи в ранней современной Европе . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 78. ISBN 978-0-5217-6993-8 Полем Получено 6 сентября 2022 года .
- ^ Wilson 2016 , с. II - AI29.
Источники
- Angermeier, Heinz (1984). Реформа Рейх 1410–1555: государственная проблема в Германии между средневековью и настоящим (на немецком языке). Ч. Бек. ISBN 978-3-4063-0278-7 .
- Арнольд, Бенджамин (1995). «14 Западная империя 1125–1197». В Лускомбе, Дэвид; Райли-Смит, Джонатан (ред.). Новая Кембриджская средневековая история, том 4: c. 1024 - C. 1198, часть 2 . Тол. 4. doi : 10.1017/chol9780521414111.016 . ISBN 978-0-5214-1411-1 .
- Аваков, Александр В. (2015). Две тысячи лет экономической статистики . Тол. 1. Нью -Йорк: Алгора.
- Баркер, Эрнест (1911). . В Чисхолме, Хью (ред.). Encyclopædia Britannica . Тол. 14 (11 -е изд.). Издательство Кембриджского университета. С. 341–342.
- Barraclough, Джеффри (1984). Происхождение современной Германии . Нью -Йорк: WW Norton & Co. Inc. ISBN 978-0-3933-0153-3 .
- Бенеце, Г. (1974). Общество и политика в Германии, 1500–1750 . Routledge & Kegan Paul.
- Беренгер, Джин; Симпсон, Калифорния (2014). История империи Габсбурга 1273–1700 . Routledge. с. 120, 121. ISBN 978-1-3178-9570-1 Полем Архивировано из оригинала 5 октября 2021 года . Получено 5 октября 2021 года .
- Брэди, Томас А. младший (2009). Немецкие истории в эпоху Реформаций, 1400–1650 . Издательство Кембриджского университета. с. 104–106, 116. ISBN 978-1-1394-8115-1 Полем Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- БЕРЕРТОН, Терри (2014). Все, что вы когда -либо хотели знать о Tudors, но боялись спросить . Amberley Publishing . ISBN 978-1-4456-3845-4 .
- Брокманн, Стивен (2006). Нюрнберг: воображаемый капитал . Рочестер, Нью -Йорк: Камден Хаус. ISBN 978-1-5711-3345-8 .
- Брайс, Джеймс (1890). Священная Римская империя . Макмиллан.
- Кантор, Норман Ф. (1993). Цивилизация средневековья . Harper Perennial. ISBN 978-0-0609-2553-6 .
- Cipolla, Carlo M. (1981). Борьба с чумой в Италии семнадцатого века . Мэдисон: Университет Висконсин Пресс.
- Клаус, Эдда (1997). Возрождение коммуникационной сети: Европа во время Каролингов (диссертация M.SC). HDL : 1866/803 .
- Коллинз, Пол (2014). Рождение Запада: Рим, Германия, Франция и создание Европы в десятом веке . Publicaffairs. ISBN 978-1-6103-9368-3 Полем OL 28037381M .
- Кертис, Бенджамин (2013). Габсбурги: история династии . Блумсбери . п. 36
- Corvisier, André; Чайлдс, Джон (1994). Словарь военной истории и искусство войны .
- Дэвис, Норман (1996). История Европы . Оксфорд.
- Дело де Лас, Ид (1824). Журнал личной жизни и разговоров императора Наполеона в Сент -Хелене . Тол. 3. Х. Колберн.
- Даффи, Имон (1997). Святые и грешники: история пап . Издательство Йельского университета.
- Элерс, Каспар; Frachenecker, Helmut; Пяффген, Бернд; Шиффер, Рудольф (2016). Немецкие королевские дворцы . Том 5 Том: Бавария: Частичный том 3: Баварская Свабия. Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht. ISBN 978-3-6473-6523-7 .
- Эрбе, Майкл (2000). "Городской". Габсбург 1493–1918 . Штутгарт : Колхаммер Верлаг . ISBN 3-1701-1866-8 .
- Эванс, Роберт Дж.В. (2006). Австрия, Венгрия и Габсбурги: Центральная Европа c. 1683–1867 . УП Оксфорд. п. 82 ISBN 978-0-1992-8144-2 .
- Эванс, Роберт Дж.В .; Шайх, Майкл; Уилсон, Питер Х. , ред. (2011). Священная Римская империя, 1495–1806 . США: издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-1996-0297-1 .
- Эванс, Роберт Дж.В .; Уилсон, Питер , ред. (2012). Священная Римская империя, 1495–1806: европейская перспектива . Брилль ISBN 978-9-0042-0683-0 Полем OL 25270288M .
- Фол, Джон (2011). Горшки Лаурате в Священной Римской империи: биоблиологический справочник . Уолтер Грюйтер. п. CXVII . ISBN 978-3-1109-1274-6 .
- Фрид, Йоханнес (2016). Карл Великий . Гарвардский университет издательство.
- Gagliardo, John H. (1980). Рейх и нация. Священная Римская империя как идея и реальность, 1763–1806 . Издательство Университета Индианы.
- Garipzanov, Ildar H. (2008). Символический язык власти в мире Каролинга (ок. 751–877) . Лейден: Брилл.
- Gumpelzhaimer, HSG (1796). Рейх Матрикель из всех кругов: наряду с обычными матрицами Имперского и Рейха -камерного суда с изменениями (на немецком языке). Ультра
- Хаффнер С. (2019). Восстание и падение Пруссии . Планкетт озеро.
- Хэнлон, Грегори (2014). Герой Италии: Одоардо Фарнезе, герцог Пармы, его солдаты и его подданные в тридцатилетней войне . Routledge.
- Харди Д. (2018). Ассоциативная политическая культура в Священной Римской империи: Верхняя Германия, 1346–1521 . Оксфордские исторические монографии. УП Оксфорд. ISBN 978-0-1925-6217-3 .
- Хартер, Карл. «Постоянная имперская диета в европейском контексте, 1663–1806». В Evans, Schaich & Wilson (2011) .
- Herrmann, Joachim (1970). Славян в Германии (на немецком языке). Берлин: Akademie-Verlag Gmbh.
- Hirschi, Caspar (2005). Национальные соревнования . Геттинген : Уоллштейн Верлаг.
- Хохедлингер, Майкл; Мата, Петр; Винкельбауэр, Томас (2019). Административная история габсбургской монархии в начале современного периода . Том. Том 1: Суд и династия, Император и Рейх, Центральные администрации, военная система и государственные княжеские финансы. Вена: Böhlau Verlag. ISBN 978-3-2052-3246-9 .
- Холлегер, Манфред (2012). "Я" В Мишеле, Ева; Стернат, Мария Луиз (ред.). PDF . доклад; Альбертин. стр. 32–33. ISBN 978-3-7913-5172-8 Полем Получено 2 декабря 2021 года .
- Хойт, Роберт С.; Chodorow, Stanley (1976). Европа в средние века . Харкорт Брэйс Йованович.
- Хуньяди, Zsolt; Laszlovszky, József (2001). Крестовые походы и военные приказы: расширение границ средневекового латинского христианства . Центральный Европейский университет издательство. ISBN 978-9-6392-4142-8 .
- Иннес, Мэтью (2000). Государство и общество в раннем средневековье: Средняя долина Рейнс, 400–1000 . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-1-1394-2558-2 .
- Джонсон, Лонни (1996). Центральная Европа: враги, соседи, друзья . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-1980-2607-5 .
- Йорио, Марко; Браун, Беттина (25 апреля 2016 г.), «Священная Римская империя» , Историческая лексика Швейцарии (HLS) , полученная 7 сентября 2021 года.
- Кляйнхенц, Кристофер (2004). Средневековая Италия: энциклопедия . Routledge. ISBN 978-1-1359-4880-1 .
- Кон, Джордж С. (2006). Словарь войн . Infobase. ISBN 978-1-4381-2916-7 .
- Куриан, Джордж Томас (2010). Энциклопедия христианской литературы . Пресс чучела. ISBN 978-0-8108-7283-7 .
- Lauryssens, Stan (1999). Человек, который изобрел третий рейх: жизнь и времена Артура Моеллера ван ден Брук . Страуд: Саттон. ISBN 978-0-7509-1866-4 .
- Легау, Жан Пьер (1995). «6. Городская жизнь» . В Джонс, Майкл Се (ред.). Новая Кембриджская средневековая история, том 6, c. 1300 - C.1 415 . Тол. 6. издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-0-5213-6290-0 .
- Магилл, Фрэнк (1998). Словарь мировой биографии . Тол. II Лондон: Фицрой Дирборн.
- Малетке, Клаус (2001). Отношения между Францией и Святой империей в 17 веке (на французском языке). Париж: Чемпион.
- McBrien, Richard P. (2000). Жизнь пап: понтифики от Святого Петра до Бенедикта XVI . HarperCollins.
- McKitterick, R. (2018). Франко королевства под каролингами 751–987 . Тейлор и Фрэнсис. ISBN 978-1-3178-7248-1 .
- Морау, Питер (1999) [1977]. "Святая империя". Лексикон средневековья . Том. 4. Мюнхен и Цюрих: Артемида.
- Маллетт, Майкл (2010). Исторический словарь реформации и контрреформации . Пресс чучела. ISBN 978-0-8108-7393-3 .
- Паркер, Джеффри (2008). «Кризис и катастрофа: глобальный кризис семнадцатого века пересмотрел» . Американский исторический обзор . 113 (4): 1053–1079. doi : 10.1086/ahr.113.4.1053 .
- Павлак, Брайан А.; Лотт, Элизабет С. (2019). Священная Римская империя: историческая энциклопедия [2 тома] . ABC-Clio. п. 143. ISBN 978-1-4408-4856-8 Полем Архивировано из оригинала 21 сентября 2021 года . Получено 21 сентября 2021 года .
- Ротбард, Мюррей Н. (23 ноября 2009 г.). «Великая депрессия 14 -го века» . Институт Мизеса . Получено 14 марта 2019 года .
- Ротштейн, Стэнли Уильям (1995). Класс, культура и раса в американских школах: справочник . Гринвуд. ISBN 978-0-3132-9102-9 .
- Шиндлинг, Антон (1986). «Развитие вечной диеты в Регенсбурге». Журнал современной истории . 58 : 64–75. doi : 10.1086/243149 . S2CID 144471373 .
- Schulze, Hans K. (1998). Основные структуры конституции в средние века [ основные структуры конституции в средние века ] (на немецком языке). Том . Штутгарт: Колхаммер Верлаг .
- Смаиль, Даниэль Лорд; Гибсон, Келли (2009). Месть в средневековой Европе: читатель . Университет Торонто Пресс. п. 156. ISBN 978-1-4426-0126-0 .
- Суин, Дуглас Брук Уилтон (1914). - через Wikisource .
- Смит, сохраненный (1920). Социальное происхождение Реформации . Кольер.
- Szepesi, Istvan (2015). «Отражение нации: историография гансейтических учреждений» (PDF) . Ватерлоо Исторический обзор . 7 doi : 10.15353/whr.v7.33 . S2CID 148667574 . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 17 октября 2021 года . Получено 7 сентября 2021 года .
- Taagepera, Rein (сентябрь 1997 г.). «Расширение и схема сжатия больших полиций: контекст для России» (PDF) . Международные исследования ежеквартально . 41 (3): 494. DOI : 10.1111/0020-8833.00053 . JSTOR 2600793 .
- Tellier, Luc-Normand (2009). Городская мировая история: экономическая и географическая перспектива . ISBN 978-2-7605-2209-1 .
- Тейлор, Баярд; Хансен-Тейлор, Мари (1894). История Германии с самых ранних времен до наших дней . Нью -Йорк: D. Appleton & Co. p. 117
- Вольтер (1773) [1756]. «Глава LXX» . Эссе о таможне и нациях Esprit (по -французски). Полет. 3 (новое изд.). Неучутл. п. 338. OCLC 797016561 .
Это тело названо и до сих пор называется Священной Римской империей, никоим образом не было ни святым, ни римской, ни империей
- Whaley, Joachim (2011). Германия и Священная Римская империя: Том II: Мир Вестфалии для роспуска Рейха, 1648–1806 . УП Оксфорд. ISBN 978-0-1916-2822-1 Полем Получено 5 февраля 2022 года .
- Whaley, Joachim (2012a). Германия и Священная Римская империя, том I: Максимилиан I к миру Вестфалии, 1493–1648 . Тол. И. Оксфорд: уп. ISBN 978-0-1987-3101-6 .
- Whaley, Joachim (2012b). Германия и Священная Римская империя, том II: Мир Вестфалии для роспуска Рейха, 1648–1806 . Тол. II Оксфорд: Оуп. ISBN 978-0-1996-9307-8 .
- Уилсон, Питер Х. (1999). Священная Римская империя 1495–1806 . Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1-3492-7649-3 .
- Уилсон, Питер Х. (2004). От Рейха до революции: немецкая история, 1558–1806 .
- Уилсон, Питер Х. (декабрь 2006 г.). «Подкрепление престижа Габсбургов: конец Священной Римской империи в 1806 году». Международный обзор истории . 28 (4): 709–736. doi : 10.1080/07075332.2006.9641109 . S2CID 154316830 .
- Уилсон, Питер Х. (2009). Трагедия Европы: история тридцатилетней войны . Аллен Лейн.
- Уилсон, Питер Х. (2016). Сердце Европы: история Священной Римской империи . Belknap Press. ISBN 978-0-6740-5809-5 .
- , ed . Zeumern, Karl
- Ůrek, Ваклов (31 декабря 2014 г.). «Языки царя. Роль языка в общении династической пропаганды во время Карла IV» [языки царя. Роль языка в династической пропагандистской коммуникации во время Карла IV]. Обзор Французского института истории в Германии (на французском языке) (6). DOI : 10,4000/IFHA .
Дальнейшее чтение
- Арнольд, Бенджамин (1991). Князья и территории в средневековой Германии . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-0-5215-2148-2 Полем OL 7744146M .
- Брайс, Джеймс (1864). Священная Римская империя . Макмиллан. OCLC 1347435 . OL 17729330M .
- Кой, Джейсон Филип; Маршке, Бенджамин; Сабеан, Дэвид Уоррен, ред. (2010). Священная Римская империя, пересмотренная . Berghahn Books. ISBN 978-1-8454-5992-5 Полем OL 38653949M .
- Дональдсон, Джордж. Германия: полная история (Gotham Books, Нью -Йорк, 1985)
- Хан, Ганс Иоахим. Немецкая мысль и культура: от Священной Римской империи до сегодняшнего дня (издательство Манчестерского университета, 1995).
- Скрибнер, Боб. Германия: новая социальная и экономическая история, вып. 1: 1450–1630 (1995)
- Столлберг-Рилингер, Барбара . Священная Римская империя: короткая история . Принстон, Нью -Джерси: издательство Принстонского университета, 2018.
- Сокровище, Джеффри. Создание современной Европы, 1648–1780 (3 -е изд. 2003). С. 374–426.
- Зофи, Джонатан В., изд. Священная Римская империя: справочник словаря (Greenwood Press, 1980)
Внешние ссылки
- Священная Римская империя
- 960 -е годы в Священной Римской империи
- 962 учреждения
- 1806 Открытие в Европе
- 1806 Открытие в Священной Римской империи
- Христианский
- Христианские государства
- Христианская терминология
- Ранний современный период
- Бывшие конфедерации
- Бывшие империи
- Бывшие монархии Европы
- История католицизма в Европе
- История Центральной Европы
- Средний возраст
- Штаты и территории расстроены в 1806 году
- Штаты и территории созданы в 800 году
- Штаты и территории созданы в 962 году
- Западное христианство