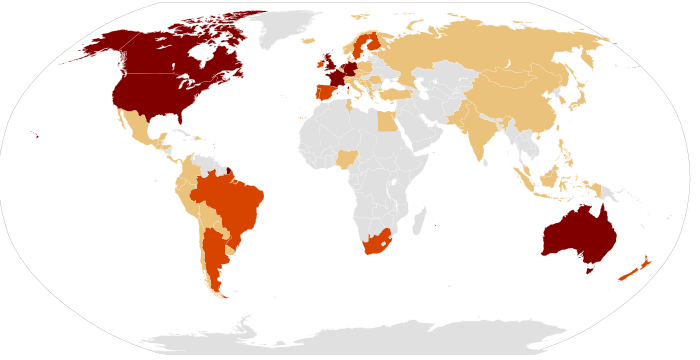
Занимайте движение
| Занимайте движение | |
|---|---|
| Часть ответа на финансовый кризис 2007–2008 годов , кризис субстандартного ипотечного кредитования и «арабскую весну». | |
 Всемирные протесты движения Occupy 15 октября 2011 г. | |
| Date | 17 September 2011 – 9 November 2016 (5 years, 1 month, 3 weeks and 2 days) |
| Location | Worldwide (List of locations) |
| Caused by | Economic and social inequality, corporate influence over government, inter alia. |
| Methods | |
| Casualties and losses | |
| Arrests: 7,700+[1] Injuries: 400+[2] Deaths: 32[3][4][5][6][7] | |
| www | |
Движение Occupy было международным популистским общественно-политическим движением , которое выражало оппозицию социальному и экономическому неравенству и ощущаемому отсутствию реальной демократии во всем мире. Его цель заключалась в первую очередь в продвижении социальной и экономической справедливости и различных форм демократии. Движение имело множество различных сфер применения, поскольку местные группы часто преследовали разные цели, но его главная забота заключалась в том, как крупные корпорации и глобальная финансовая система контролируют мир таким образом, что это приносит непропорционально большую выгоду меньшинству, подрывает демократию и вызывает нестабильность. [ 12 ]
Первый протест Occupy, получивший широкое внимание, Occupy Wall Street в парке Зуккотти , Нижний Манхэттен , начался 17 сентября 2011 года. К 9 октября протесты Occupy прошли или продолжались в более чем 951 городе в 82 странах и в более чем 600 населенных пунктах. в Соединенных Штатах . [ 13 ] [ 14 ] [ 15 ] [ 16 ] Although the movement became most active in the United States, by October 2011 Occupy protests and occupations had started in dozens of other countries across every widely inhabited continent. For the first month, overt police repression remained minimal, but this began to change by 25 October 2011, when police first attempted to forcibly remove Occupy Oakland. By the end of 2011 authorities had cleared most of the major camps, with the last remaining high-profile sites – in Washington, D.C., and in London – evicted by February 2012.[21]
The Occupy movement took inspiration in part from the Arab Spring,[22][23] from the 2009 Iranian Green Movement, and from the Spanish Indignados Movement, as well as from the overall global wave of anti-austerity protests of 2010 and following. The movement commonly used the slogan "We are the 99%" and the #Occupy hashtag format; it organized through websites such as the now defunct Occupy Together.[24][25] According to The Washington Post, the movement, which Cornel West described as a "democratic awakening", is difficult to distill to a few demands.[26][27] On 12 October 2011, the Los Angeles City Council became one of the first governmental bodies in the United States to adopt a resolution stating its informal support of the Occupy movement.[28] In October 2012, Andy Haldane the Executive Director of Financial Stability at the Bank of England stated that the protesters were right to criticise and had persuaded bankers and politicians "to behave in a more moral way".[29]
Background
[edit]In 2009 and 2010, students across the University of California occupied campus buildings in protest against budget cuts, tuition hikes, and staff cutbacks that had resulted from the Great Recession of 2008. According to Dissent Magazine, "It was in the context of the California student movement that the slogan 'Occupy Everything, Demand Nothing' first emerged."[30] The Huffington Post noted that, "During one incident in March of 2010, 150 protesters were arrested for trying to occupy part of Interstate 80 in protest of the budget cuts and tuition hikes, displaying a banner that read 'Occupy everything,' while shutting down the roadway for an hour, and were crushed by the same kind of overwhelming police force that was later mobilized against Occupy encampments across the country."[31] Adbusters editor Micah White, who designed the original Occupy Wall Street concept, traveled to California for the protests and took part in the occupation of Wheeler Hall. In an article for Adbusters, he wrote with enthusiasm about the "revolutionary potential of [the students'] struggle".[32]
The Spanish Indignados movement began in mid-May 2011, with camps at Madrid and elsewhere. According to sociologist Manuel Castells, by the end of the month there were already hundreds of camps around Spain and across the world.[33] For some journalists and commentators the camping in Spain marked the start of the global occupy movement, though it is much more commonly said to have begun in New York during September.[34][35] On 30 May 2011, a leader of the Indignados, inspired by the Arab Spring, 5.18 Movement of 1980, and June Democracy Movement of 1987[36][37] called for a worldwide protest on 15 October.[38] In mid-2011, the Canadian-based group Adbusters Media Foundation, best known for its advertisement-free anti-consumerist magazine Adbusters, proposed a peaceful occupation of Wall Street to protest corporate influence on democracy, address a growing disparity in wealth, and the absence of legal repercussions in the 2007–2008 financial crisis.[39] Adbusters co-founder Kalle Lasn registered the OccupyWallStreet.org web address on 9 June.[40] According to Micah White, the senior editor of the magazine, "[we] basically floated the idea in mid-July into our [email list] and it was spontaneously taken up by all the people of the world, it just kind of snowballed from there."[39]
One of the inspirations for the movement was the Democracy Village set up in 2010, outside the British Parliament in London. The protest received additional attention when the internet hacker group Anonymous encouraged its followers to take part in the protests, calling protesters to "flood lower Manhattan, set up tents, kitchens, peaceful barricades and Occupy Wall Street".[41][42][43] They promoted the protest with a poster featuring a dancer atop Wall Street's iconic Charging Bull.[44][45] The first protest was held at Zuccotti Park in New York City on 17 September 2011,[46] the tenth anniversary of the re-opening of Wall Street trading after the 11 September 2001 attacks. The protests were preceded by a similar Occupy Dataran movement in Kuala Lumpur in July, seven weeks before Occupy Wall Street.[47][48][49]
"We are the 99%" slogan
[edit]
The phrase "The 99%" is a political slogan used by participants in the Occupy movement.[50] It was originally launched as a Tumblr blog page in late August 2011.[51][52] It refers to the concentration of wealth among the top 1% of income earners compared to the other 99 percent;[53] the top 1 percent of income earners nearly tripled their after-tax income over the last thirty years, according to a Congressional Budget Office (CBO) report.[54]
The report was released just as concerns of the Occupy Wall Street movement were beginning to enter the national political debate.[55] According to the CBO, between 1979 and 2007 the incomes of the top 1% of Americans grew by an average of 275%. During the same time period, the 60% of Americans in the middle of the income scale saw their income rise by 40%. Since 1979 the average pre-tax income for the bottom 90% of households has decreased by $900, while that of the top 1% increased by over $700,000, as federal taxation became less progressive. From 1992 to 2007 the top 400 income earners in the U.S. saw their income increase 392% and their average tax rate reduced by 37%.[56] In 2009, the average income of the top 1% was $960,000 with a minimum income of $343,927.[57][58][59]
In 2007, the richest 1% of the American population owned 34.6% of the country's total wealth, and the next 19% owned 50.5%. Thus, the top 20% of Americans owned 85% of the country's wealth and the bottom 80% of the population owned 15% —an example of the Pareto principle. Financial inequality (total net worth minus the value of one's home)[60] was greater than inequality in total wealth, with the top 1% of the population owning 42.7%, the next 19% of Americans owning 50.3%, and the bottom 80% owning 7%.[61]
However, after the Great Recession which started in 2007, the share of total wealth owned by the top 1% of the population grew from 34.6% to 37.1%, and that owned by the top 20% of Americans grew from 85% to 87.7%. The Great Recession also caused a drop of 36.1% in median household wealth but a drop of only 11.1% for the top 1%, further widening the gap between the 1% and the 99%.[61][62][63] During the economic expansion between 2002 and 2007, the income of the top 1% grew 10 times faster than the income of the bottom 90%. In this period 66% of total income gains went to the 1%, who in 2007 had a larger share of total income than at any time since 1928.[64] This is in stark contrast with surveys of U.S. populations that indicate an "ideal" distribution that is much more equal, and a widespread ignorance of the true income inequality and wealth inequality.[65]
Goals
[edit]During the early weeks, the movement was frequently criticized by the news media for having no clearly defined goals. Speaking on 7 October 2011, Kalle Lasn of Adbusters said that, in the early stages, the lack of demands was the "mysterious part" that allowed the movement to grow.[66] By late October, Adbusters had been trying to "rally it around a single, clear demand" for a Robin Hood tax, with a global march in support of the Robin Hood tax planned for 29 October.[67][68] Naomi Wolf argued that the impression created by much of the media that the protestors did not have clear demands was false. Wolf argued that they did have clear demands including a desire to end what they saw as the corrupting effect of money on politics.[69] The New Yorker magazine stated that the claims of Kalle Lasn and Micah M. White were specific: tighten banking-industry regulations, ban high-frequency trading, arrest all 'financial fraudsters' responsible for the 2008 crash, and form a presidential commission to investigate and prosecute corruption in politics.[40] According to Bloomberg Businessweek, protesters wanted more and better jobs, more equal distribution of income, bank reform, and a reduction of the influence of corporations on politics.[70] The movement has also been described as broadly anticapitalist.[71][72]
Some commentators such as David Graeber and Judith Butler criticized the idea that the movement must have clearly defined demands; they argued that issuing demands is counterproductive for the Occupy movement, because doing so would legitimize the very power structures the movement seeks to challenge.[73][74] In late November, the London contingent of the Occupy movement released their first statement on corporations, in which they called for measures to end tax evasion by wealthy firms. The reason for the delay in articulating a clear demand was given as the time it takes to reach a consensus with the sometimes slow processes of participatory democracy.[75] In November "Occupy London Stock Exchange", an offshoot of Occupy London, said that they were working on a global collaboration of various occupations that reflected the voices of diverse movements worldwide.[76] The global movement has been called the reinvention of politics, revolution, and utopia in the twenty-first century.[77]
Methods
[edit]Activists have used web technologies and social media like IRC, Facebook, Twitter, and Meetup to coordinate events.[78][79][80]
The Community Environmental Legal Defense Fund released a model community bill of rights, promoting laws that strip corporations of their personhood rights and elevating the rights of citizens, for occupy organizers to adopt locally.[81] In December 2011, Occupy Homes embarked on a movement to assist home owners who had lost or were scheduled to lose their homes due to foreclosure as a result of what they called the illegal practices used by banks that took advantage of consumers. The group planned to occupy foreclosed homes, disrupt bank auctions, and block evictions.[82]
Structure
[edit]

The movement has been described as having an "overriding commitment" to participatory democracy.[83] Much of the movement's democratic process occurs in "working groups," where any protester is able to have their say. Important decisions are often made at General assemblies,[84] which can themselves be informed by the findings of multiple working groups. Decisions are made using the consensus model of participatory democracy. This often features the use of hand signals to increase participation and operating with discussion facilitators rather than leaders – a system that can be traced in part to the Quaker movement several centuries ago, to participatory democracy in ancient Athens, and to the spokescouncils of the 1999 anti-globalization movement.[85][86]
At the assemblies, working group proposals are made to meeting participants, who comment upon them using a process called a stack; a queue of speakers that anyone can join. In New York City, Occupy Wall Street uses what is called a progressive stack, in which people from marginalized groups are sometimes allowed to speak before people from dominant groups, with facilitators, or stack-keepers, urging speakers to "step forward, or step back" based on which group they belong to, meaning that women and minorities get to go to the front of the line, while white males must often wait for a turn to speak.[86][87] The progressive stack concept has been criticized by some outside the movement as "forced equality" and "unfair".[88]
Nonviolence
[edit]The occupy movement began with a commitment to nonviolence.[89][90][91] Frequent references were made to the writings of nonviolent theorist Dr. Gene Sharp whose work was reported to have influenced nonviolent struggle movements in Serbia and the Arab Spring.[92] Study groups were organised across the US Occupy camps discussing Sharp's 198 methods of nonviolent action[93] and his book From Dictatorship to Democracy.[94][95][96] A subsequent film about his work How to Start a Revolution by Ruaridh Arrow which premiered in Boston on 18 September was screened in Occupy camps across the US and Europe.[97][98][99][100] Sharp himself warned that many of the tactics the movement were employing were not effective. In an Al Jazeera interview, he said, "The [Occupy] protesters don't have a clear objective, something they can actually achieve. If they think they will change the economic system by simply staying in a particular location, then they are likely to be very disappointed. Protest alone accomplishes very little."[101]
In late May 2011, sociologist Manuel Castells congratulated Spanish occupiers for the fact that not a single violent incident had been reported after 11 days of camping all over Spain.[33] Castells said that nonviolence was of fundamental importance, and was echoed by various other sociologists and social historians including Lester Kurtz, Prof. Maurice Isserman and Prof. Tom Juravich.[33][102][103] Juravich and others have, however, said that conflict can be important in attracting attention, with much to be gained if occupiers are seen as victims of the violence, providing occupiers keep their own aggression strictly within limits.[102] In the words of one occupier, it can help them gain media coverage if they "make things a little sexy and badass" . The Direct Action Working Group of Occupy Wall Street endorsed diversity of tactics from the earliest days of the encampment.[104] Not all occupiers have upheld the commitment to nonviolence, with aggressive tactics being used in Spain from as early as 15 June, and with some journalists saying the New York branch of the movement did initially accept protestors who had not signed up to nonviolence.[105][106]
In September, sympathetic coverage given to the movement by the media was substantially increased after the circulation of a video of pepper spray being used by a police commander against peaceful female protestors.[102] In early October, Naomi Klein congratulated New York occupiers for their commitment to nonviolence.[107] By November 2011, media sources began to report an increase in violence, with allegations of sexual assault and incidents of violence from occupiers against the police, including one officer allegedly stabbed with scissors.[102][108] Some occupy camps responded by requiring that all occupiers sign a resolution to be nonviolent if they wished to stay.[103] Rick Hampton for USA Today said the vast majority of occupy members have been nonviolent.[102] Reviewing the global movement in December 2011, Anthony Barnett said its nonviolence remained an immense strength.[34] One protester who did not take part stated, "It was organized by a very militant anarchist segment of the movement; I support the idea of taking a building, especially for housing those who don't have housing. But I don't support it with the kind of triumphal attitude I saw expressed."[106][109][110]
Social media
[edit]From the beginning the Occupy movement relied heavily on social media to disperse information and gather support. Occupy accounts were very successful in achieving these goals. The social media accounts eventually became hierarchical and failed their purpose.[111] Some [who?] believe, in order to have been more successful, the social media accounts should have been more heavily regulated and kept to a standard. In addition, a study was published that followed how Occupy user interests changed in time from 1 June 2011 to 31 August 2012. It showed 40% of users produced Occupy related content during peak activity of the movement. But it was not sustained over the following year, with the user ratio dropping to less than 5% in the last three months of the study period.[112]
Responses to the movement from celebrities were both in-person and online. Some find it controversial that rich celebrities made appearances at the Occupy Wall Street Movement, but Kanye West justified his appearance as helping give power back to the people.[113]
Many hold[who?] that the success of OWS has led to the success of Bernie Sanders and his political platform, disrupting the political conversation about environmental impact and economic equality. Some[who?] believe that there was social media blockage of Sanders' presidential campaign, in favor of more airtime for Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton.[114]
Chronology of events
[edit]The WikiLeaks endorsed news site WikiLeaks Central began promoting the idea of a "US Day of Rage,"[115] on 10 March 2011. The Canadian editor-in-chief Heather Marsh modeled the concept after the Days of Rage being held at that time in the Middle East and North Africa.[115] Early promotion by the WikiLeaks Twitter and blog was reported[116] as being instrumental in the group's success.[116] It was renamed Occupy Wall Street after the idea publicized on an email list[117] on 13 July 2011 by Vancouver-based non-profit Canadian group Adbusters.[39][118][119] The Occupy Wall Street protests began on 17 September 2011 in downtown Manhattan.[120] On 9 October 2011, activists in cities in over 25 countries repeated calls for a global protest on 15 October.[78][121] A list of events for 15 October included 951 cities in 82 countries.[122] On 15 October events were held in many cities worldwide.[123]
17 September to 14 October 2011
[edit]On 17 September 2011, 1,000 protesters gathered in lower Manhattan walking up and down Wall Street. About 100 to 200 people stayed overnight in Zucotti Park, two blocks north of Wall Street. By 19 September, seven people had been arrested.[124] At least 80 arrests were made on 24 September after protesters started marching uptown and forcing the closure of several streets. Most of the 80 arrests were for blocking traffic, though some were also charged with disorderly conduct and resisting arrest. Police officers also used a technique called kettling which involves using orange nets to isolate protesters into smaller groups.[125] Videos which showed several penned-in female demonstrators being hit with pepper spray by a police official were widely disseminated, sparking controversy. That police official, later identified as Deputy Inspector Anthony Bologna, was shown in other videos hitting a photographer with a burst of spray.

Public attention to the pepper-sprayings resulted in a spike of news media coverage, a pattern that was to be repeated in the coming weeks following confrontations with police. Clyde Haberman, writing in The New York Times, said that "If the Occupy Wall Street protesters ever choose to recognize a person who gave their cause its biggest boost, they may want to pay tribute to Anthony Bologna," calling the event "vital" for the still nascent movement.[126] On 1 October 2011, protesters set out to march across the Brooklyn Bridge. The New York Times reported that more than 700 arrests were made. Some said the police had tricked protesters, allowing them onto the bridge, and even escorting them partway across. Jesse A. Myerson, a media coordinator for Occupy Wall Street said, "The cops watched and did nothing, indeed, seemed to guide us onto the roadway." According to Fox News, a spokesman for the New York Police Department, Paul Browne, said that protesters were given multiple warnings to stay on the sidewalk and not block the street, and were arrested when they refused.[127][unreliable source?]
On 4 October, a group of protesters who were arrested on the bridge filed a lawsuit against the city, alleging that officers had violated their constitutional rights by luring them into a trap and then arresting them.[128] In June 2012, a federal judge ruled that the protesters had not received sufficient warning of arrest pending entrance onto the Brooklyn Bridge. Although video evidence showed the police warning protesters by bullhorn,[129] after reviewing it, Judge Jed S. Rakoff sided with plaintiffs, saying, "a reasonable officer in the noisy environment defendants occupied would have known that a single bull horn could not reasonably communicate a message to 700 demonstrators".[130]
On 5 October 2011, joined by union members, students, and the unemployed, the demonstration swelled to the largest yet with an estimated 15,000 marchers joining the protest. Smaller protests continued in cities and on college campuses across the country. Thousands of union workers joined protesters marching through the Financial District. The march was mostly peaceful—until after nightfall, when scuffles erupted. About 200 protesters tried to storm barricades blocking them from Wall Street and the Stock Exchange. Police responded with pepper spray and penned the protesters in with orange netting. Inspired by Occupy Wall Street, British protesters organized an occupation of the London Stock Exchange to bring attention to what they saw as unethical behavior on the part of banks. One of the organizers of the protest said the protests were to be focused against "increasing social and economic injustice in this country". In his opinion, "the Government has made sure to maintain the status quo and let the people who caused this crisis get off scot-free, whilst conversely ensuring that the people of this country pay the price, in particular those most vulnerable."[131][132][133]
15 October to 4 November
[edit]
On 15 October 2011 global protests were staged around the world, with thousands of protesters staging demonstrations in 900 cities including Auckland, Sydney, Hong Kong, Taipei, Tokyo, São Paulo, Paris, Madrid, Berlin, Hamburg, Leipzig, Boston and many other cities. In Frankfurt, 5,000 people protested at the European Central Bank and in Zurich, Switzerland's financial hub, protesters carried banners reading "We won't bail you out yet again" and "We are the 99 percent." Protests were largely peaceful; however, a protest in Rome that drew thousands turned violent.[134] Thousands of Occupy Wall Street protesters gathered in Times Square in New York City and rallied for several hours.[135][136] Several hundred protesters were arrested across the U.S., mostly for refusing to obey police orders to leave public areas. In Chicago there were 175 arrests, about 100 arrests in Arizona (53 in Tucson, 46 in Phoenix), and more than 70 in New York City, including at least 40 in Times Square.[137] Multiple arrests were reported in Chicago, and about 150 people camped out by city hall in Minneapolis.[138]
In the early morning hours of 25 October, police cleared and closed an Occupy Oakland encampment in Frank Ogawa Plaza in Oakland, California.[139][140] The raid was chaotic and violent, but Oakland Police Chief Howard Jordan expressed his pleasure concerning the operation because neither the police nor the public suffered any injuries.[141][142] A street march that afternoon protesting the closure culminated in a confrontation between police and protesters, who sought to re-establish the Ogawa Plaza encampment. During this confrontation, protester Scott Olsen, a former Marine and Iraq War veteran, suffered a skull fracture caused by a tear-gas projectile or smoke canister fired by police.[142][143] By 29 October 2011, there were around 2,300 Occupy protest camps across around 2,000 cities worldwide.[144] On 2 November, protesters in Oakland, California, shut down the Port of Oakland, the fifth busiest port in the nation. Police estimated that about 3,000 demonstrators were gathered at the port and 4,500 had marched across the city; however, a member of the Occupy movement was quoted by the BBC as estimating as many as 30,000 may have taken part.[145]
On 4 November 2011, "Occupy the Roads" (OTR) started traveling throughout the U.S. to bring the message of Occupy, in order to educate the people on various issues facing the general public and shine a light on the inequities and political injustice. OTR has been to every major Occupy Event in support of all occupied cities, traveling over 31,000 miles and visiting 42 States and 160 cities since inception. One side of the RV (named the "V"- from the chant "Whose V? RV") has been decorated with stickers, posters, and event notices from around the country representing a billboard for the Occupy movement. On the other side is 31 ft of graphics in support for Chelsea Manning and WikiLeaks.[146]
5 to 25 November
[edit]On 5 November, protesters held "Bank Transfer Day", marching on banks and other financial institutions to urge Americans to move their money from big corporate banks to smaller community credit unions. It was reported that an estimated 600,000 people took their money out of major banks.[147] On 11 November, Remembrance Day in Canada, police forcibly removed tents from Victoria Park in Halifax, Nova Scotia and arrested 15 protestors.[148] On the night of 14 November, a coordinated crackdown was undertaken by authorities around the world, with several camps being forcibly cleared including Zuccotti Park in New York, Oakland,[149] Oregon,[150] Denver and Zurich. For some of the other camps such as the one at St Pauls in London, no physical action was taken, but on 15 November authorities stepped up legal action to gain authorization for a forcible eviction. Financial Times editor Richard Lambert suggested that the shift to confrontational tactics by authorities would be more likely to spur on the movement rather than cause it to disband.[17][18][151] However, John Gapper, chief business commentator at the FT, offered a different view. Gapper said that it may be advantageous that the camps were being closed down, as they were beginning to alienate even members of the public who were initially fully sympathetic with the movement.[152] During a demonstration at UC Davis on 18 November 2011, campus police Lieutenant John Pike used pepper spray on seated students.[153] The incident drew national attention and led to further demonstrations, petitions, and calls for Chancellor Linda P.B. Katehi to resign. (See: UC Davis pepper-spray incident)[154][155] On 22 November, occupiers mic checked President Obama to draw his attention to the treatment they had received from the police, including thousands of arrests.[156]
26 November to 31 December 2011
[edit]
By December, occupiers had begun to divert their energies beyond protest camps and a narrow focus on the banks, instead seeking to engage further with mainstream politics and joining forces with established activist groups to support causes broadly compatible with the interests of "the 99%". Interviewing one of the informal leaders of the movement, Financial Times journalist Shannon Bond found that issues of concern included: "the unemployment rate, household debt, student debt, the lack of prospects for people graduating from college and foreclosures".[157] In the U.S., Occupy Homes joined with other existing human rights activists groups and began to occupy foreclosed homes, disrupt bank auctions, and block evictions.[82] On 1 December, two evicted activists in Portland, Oregon, planted a table on the plaza of Portland's City Hall and lit a candle, igniting a Prayer Vigil/Occupation of City Hall that lasted 18 months. On 22 December The Washington Post reported that some of the cities which had forcefully disbanded occupy camps were now facing legal challenges.[158]
1 January 2012 to 2016
[edit]On 2 January 2012, Occupy Nigeria began, sparked by Nigeria's President Goodluck Jonathan announcing the ending of fuel subsidies in the country. There was support from the global movement, but most of the activity took place in Nigeria itself, with a report from CSM saying strikes were effectively shutting down whole cities. On 16 January Jonathan responded by announcing he would bring prices back down by partially restoring the fuel subsidy.[159]
While students have been involved with Occupy since its inception, early 2012 has seen increasing formal interaction between the Occupy movement and academia. In the US, universities including Columbia and Roosevelt have begun offering courses about the movement, in the case of Columbia the course includes field work where students join in with Occupy activities. In Great Britain, Occupy's outwork teams are planning school visits to give talks about the movement and related issues.[160][161]
On 23 January, EGT LLC (Export Grain Terminal) and the International Longshore and Warehouse Union (ILWU) reached a tentative agreement, mediated by Washington state governor Christine Gregoire.[162][163] The agreement resolved a year-long dispute, paving the way for ILWU Local 21 workers to work inside the $200 million grain terminal at the Port of Longview in south-west Washington state. This came after "Occupy the Ports" protests which shut down multiple ports on the west coast of the United States on 12 December. The goals of those protests included support of longshoremen and truckers in disputes with EGT and terminal operator SSA Marine (partially owned by Goldman Sachs).[164]

A worldwide poll conducted in January 2012 found that only one third (37%) of respondents were familiar with the movement. Of the respondents who were aware of the movement, supporters of the movement outweighed those in opposition two to one.[165] In late January, Occupy protested at the World Economic Forum.[166][167] On 17 March, Occupy Wall Street attempted to mark six months of the movement, by reoccupying Zuccotti Park, the location of the first Occupy camp. Protestors were soon cleared away by police, who made over 70 arrests.[168] On 1 May, the Occupy movement marked a resurgence with a May Day general strike that took place in cities across the U.S., including New York; Washington, D.C.; Chicago; and Los Angeles.[169] This included a revival of the Free University of New York.[170]

The longest US "re-occupation" started on 1 December 2011, when evicted activists from the Occupy Portland camp set up a table on the plaza of Portland's City Hall and lit a candle, igniting the 24/7 Prayer Vigil to Lift the Camping Ban, referring to the city's anti-"camping" ordinances that were cited during the eviction.[171] The activists claimed the laws, which prohibit the use of "bedding, sleeping bags, or other sleeping matter,"[172] are immoral and that they're obligated to challenge them. The occupiers claim that sleep is human right and is essential for mental, physical and emotional health, citing that human beings need to spend nearly a third of their lives sleeping. Prohibiting sleep by making it illegal for people to protect themselves and their belongings from the elements causes sleep deprivation; it is inhumane, unconstitutional, and amounts to torture.[173][174][175] The activists said the prayer vigil would continue until "bedding matter" was again legal. The vigil was staffed around the clock until 23 July 2013, when Mayor Charlie Hales ordered the removal of the vigil and associated encampments on the abutting sidewalks.[176]
The Occupy movement has "already transformed beyond recognition from its original state" and "campaigns have emerged outside the constraint of the trademark Occupy tactics."[177] These campaigns include Occupy Sandy which has provided needed relief to the New York area since Hurricane Sandy hit,[178] Occupy London's Occupy Economics group that hosted, and was praised by the Bank of England's Executive Director for Financial Stability,[179] Occupy the SEC, which monitors US financial regulatory matters,[180] The Rolling Jubilees program of Strike Debt,[181] which is raising money to retire "zombie debt," debt, such as medical bills, that the individual cannot re-pay,[182] Occupy University, which has developed and made accessible free educational materials,[183] and the Debt Collective, a successor of Strike Debt, worked to get students of a fraudulent for-profit college absolved of their debt with some success.[184][185]
On 3 April 2016, hundreds of supporters of Bernie Sanders protested outside of CNN's Headquarters in Los Angeles. Sanders supporters were protesting CNN's coverage of the 2016 United States presidential elections, specifically in regard to the amount of airtime Sanders has received. Known as Occupy CNN, protestors are claiming that major media networks have intentionally blacked out Sanders' presidential campaign in favor of giving much more airtime to candidates such as Hillary Clinton and Donald Trump.[186]
In Switzerland, the Occupy spirit lives on by annual online and offline celebrations each year on 17 September[187] in the village of St. Imier where modern anarchism began with the International Congress of 1872.[188] The Occupy Cafe along with the Decentrale Co-operative[189] continues to assist those wishing to participate in the continuing "decentralisation of the power" of banks and corporate entities; and, to encourage global activism through developing trust and value networks.[190][191][192]
Present day activities
[edit]This section needs to be updated. (May 2020) |
After an approximate two-year hiatus in activism on location, the Occupy Movement organized the Occupy ICE phase in order to protest the actions of US Immigration and Customs Enforcement office regarding the detention of undocumented immigrants presenting themselves at the southern US border points to seek asylum. While small groups of protesters emerged across the country in protest against the separation of families who were detained during immigration processing, a group swarmed the ICE facility in SoHo, causing it to shut down temporarily. In Oregon, hundreds of Occupy ICE activists took over a portion of the grounds of the Portland ICE building. The blockade caused the building to shut down for several days, with ICE staff citing "safety concerns".[193] On 25 June, Feds ordered the protesters to vacate government environs or face arrest.[194] On 28 June 2018, Federal officers moved in the early morning to remove or arrest protesters blockading the building. Eight were arrested.[195]
On 19 August 2018, Occupy Kalamazoo began an encampment in Bronson Park to address homelessness.[196] The group's efforts notably received support from local Commissioner Shannon Sykes, who criticized her colleagues in government for "failing to create more affordable housing."[197]
Protests by country
[edit]Armenia
[edit]
On 20 February 2012[198] near Margaryan Maternity Clinic, where kiosks were being built by the city authorities. The place of protests was promptly dubbed "Mashtots park" – a name under which it is now widely known by the Armenian society.[199]
Armenak Dovlatyan, Leader of the Greens party, believed that the "Occupy" demonstrations were the most successful civic action in the history of Armenia.[200]
Australia
[edit]
"Occupy" demonstrations took place in Canberra, Wollongong,[201] Perth,[202] Sydney,[203] Brisbane,[204] and Melbourne,[205] as well as smaller towns around the country. At the Occupy Melbourne protest on 21 October 2011, approximately 150 protesters defied police orders to clear the area and were subsequently removed with force. 95 arrests were made, and 43 reports of police violence were filed.[206] Occupiers returned the following day in a walk against police violence, re-occupying multiple sites since. Occupy Sydney had an ongoing occupation in Martin Place since their initial police eviction, marking almost 21 months in July 2013. The Occupy Sydney camp was removed on 3 July 2013, but it returned on 4 July. It was again removed on 5 July.[207]
Belgium
[edit]In Brussels, a large Occupy demonstration took place on 15 October involving between 6,500 and 8,000 participants. The protest was largely peaceful, although seven people were arrested following vandalisation of the Dexia bank headquarters and financial tower.[208] The Occupy Antwerp (Antwerpen) movement had its first gathering on Saturday 22 October at the Groenplaats, next to the cathedral. About 150–200 people attended a speaker's corner. The left-wing socialist party (PVDA) was present and served free soup as well as information about its proposed "millionaires' tax". There have been four Occupy protests in Leuven. Three took place on the Grand Market in the centre of the city and one took place at a building of the city's Catholic university. The number of protesters in these rallies varied from 100 to 250. These protests have not included prolonged camping, but the protesters say that it is a possibility in the future.[209][210] Occupy Ghent (Gent) began on 29 October with 400 people in the South Park (Zuidpark). They received a visit by supporters attending the "second day of Socialism" (de Tweede Dag van het Socialisme), also held in Ghent on the same day.[211]
Brazil
[edit]
The 2013 protests in Brazil (also known as the Come to the street and Brazilian Spring) were a series of public demonstrations in several Brazilian cities, initiated mainly by the Movimento Passe Livre (Free Fare Movement), a local entity that advocates for free public transportation. During a 2015 movement "Ocupe Estelita", a police officer was suspended for shooting protesters with rubber bullets for knocking off his cap.[212]
Canada
[edit]
Occupy protests have taken place in at least 20 Canadian cities since 15 October 2011. On that day, 5,000 people gathered in Vancouver to protest perceived social injustice, while 150 stayed the night in front of the Vancouver Art Gallery.[213][214] 2,000 people marched in Toronto on 15 October and around 100 continued to occupy St James Park,[215][216] and 1,000 gathered in Montreal to march down Ste-Catherine Street; 85 tents were set up in Victoria square.[217] Beginning on 23 October 2011 approximately 40 people occupied Memorial Park on Minto Street in downtown Sudbury and still continue to do so.[218] On 20 October 2011, over 100 people occupied the front of City Hall in Prince George, British Columbia.[219] Events have been concentrated in provincial urban areas, and there have yet to be any demonstrations in the territories of Yukon, Northwest Territories, or Nunavut.[118][220] A relatively small group of occupiers successfully occupied Harbourside Park in St John's Newfoundland for the entire 2012 Winter season. This site, known also as "King's Beach" is symbolically significant as the birthplace of the British Empire, and the encampment is seen by some protesters to represent an occupation of colonialism vis-a-vis its birth site. There are currently a number of court proceedings across Canada on whether or not the eviction of protestors and violence from police is an infringement of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.[221]
Colombia
[edit]Around 800 student protestors began occupying universities across Colombia on 12 November 2011.[222]
Czech Republic
[edit]On 28 April 2012, a week after demonstrations of unions and civic associations (more than one hundred thousand protesters)[223] the camp "Occupy Klárov" in Prague was started.[224] Pirate Party participated in the occupation.[225] Police dissolved the camp a month later.[226]
Cyprus
[edit]
On 19 November 2011, protesters started the "No Borders Camp" Or "Occupy Buffer Zone", a permanent occupation of the United Nations controlled buffer zone in the centre of the capital, Nicosia, demanding an end to the decades-long division of the Island.[227] The movement used the Twitter hashtag "OccupyBufferZ". By June 2012 the occupation of the buffer zone was essentially over.
Denmark
[edit]On 15 October 2011, 2,000 protesters showed up on the square in front of the city hall of Copenhagen, protesting in sympathy with OWS. Immediately after the demonstration an "Occupy Copenhagen" camp was established. The camp, internally nicknamed "Plaza One Love", lived through harsh climate conditions and a couple of eviction attempts for two months, until it was torn down by the Municipality of Copenhagen and Danish police, on 21 December. The movement has shifted to a mobile camp tactic, and still holds GA every Wednesday and other activities throughout the week.[228]
France
[edit]Some 300 protesters started occupying Paris's financial district, La Défense, on 4 November 2011.[229] Since then, their camp has been torn down by several police forces. According to French protestors, relations with the police have varied considerably. Some police joined them for coffee and friendly discussion, but otherwise were hostile and confiscated blankets and food, leaving protesters sleeping in the cold outdoors without protection. On 11 November, following a call made on social networks, some 400 additional people joined the occupation.[230] Occupy protests have also begun at Nantes, Lyon, Grenoble, Marseille,[231] Perpignan and more than 50 cities.[232]
Germany
[edit]
The Occupy movement began in Germany on 15 October 2011 with protests in Berlin, focused outside the Reichstag, as well as Frankfurt, Hamburg and Düsseldorf. Occupy Frankfurt subsequently took residence in front of the European Central Bank, and Occupy Berlin established a protest camp at St. Mary's Church.[233] On 12 November major Occupy protests took place in Berlin and Frankfurt.[234] Police reported that around 9,000 people peacefully protested near the headquarters of the European Central Bank, and that "several thousand" people took to the streets of Berlin; organisers of the protests claimed that turnout was around 8,000 in Berlin and 10,000 in Frankfurt.[234]
Hong Kong
[edit]An Occupy movement in Hong Kong, named 'Occupy Central', began on 15 October 2011 with protesters occupying the plaza beneath the HSBC Main Building in Central, an iconic landmark of the territory's central business district.[235][236] Despite the fact that the protesters were peaceful, HSBC filed a lawsuit for their eviction. On 13 August 2012, the High Court ruled that the protesters must leave the occupied area. On 11 September 2012, the protesters were evicted from the plaza by court bailiffs, ending one of the world's longest continuously occupied Occupy protest camps.
Israel
[edit]Italy
[edit]On 15 October 2011, about 200,000 people gathered in Rome to protest against economic inequality and the influence of the European Commission, the European Central Bank and the International Monetary Fund on government.[237] Many other protests occurred in other Italian cities the same day.[238] In Rome masked and hooded militants wearing makeshift body armor, in black bloc fashion, participated in the protests centered in St John Lateran square and committed numerous violent acts, throwing Molotov cocktails and other homemade explosives, burning and blowing up cars, burning buildings, and smashing up property such as ATMs and shop windows.[64] The Roman Catholic church Santi Marcellino e Pietro al Laterano received extensive damage, including a statue of the Virgin Mary being thrown into the street and destroyed.[64]
Several unexploded petrol bombs were reportedly found on several streets by Italian police.[64] Over 1,000,000 euros of damage (equivalent to over 1.3 million dollars) was recorded.[64] At least 135 people were injured in the resulting clashes, including 105 police officers, several of whom were left in critical condition,[239] and two news crews from Sky Italia.[64][240] Two protesters had their fingers amputated by exploding smoke bombs.[64] Almost 20 people have been arrested in connection with the violence.[64] After the 15 October demonstration, people occupied the Santa Croce in Gerusalemme square and started camping as in other cities worldwide. The name of this Rome's group, related to international Occupy movement, is Accampata Roma.[241]
Malaysia
[edit]The Occupy Dataran movement first held their assembly at Dataran Merdeka (Independence Square) seven weeks before Occupy Wall Street on 30 July 2011[242] to create an alternative to the current representative democracy[243] using the popular assembly model based on principles of participatory democracy.[244] As part of the 15 October 2011 global protests, over 200 people[245] took part in 15 October's Occupy Dataran, the largest assembly to date.[246] In late October, the movement spread to Penang with Occupy Penang[247] and Kelantan with Occupy Kota Bharu.
Mexico
[edit]Occupy began in Mexico City on 11 October 2011, with a hunger strike in front of the Mexican Stock Exchange highrise. Edur Velasco, a 56-year-old labor economist and university professor, was on a 42-day-long hunger strike sitting in a tent outside Mexico City's stock market, demanding that the government guarantee greater access to higher education among the youth.[248] Days after his initiative, it came as a surprise to see the multiplication of tents setting up outside the stock exchange building. Police remained discreetly around the corner sitting in their trucks.[249]
Occupy Mexico did not achieve the level of popularity it gained in other areas. This is attributed to the fact that Mexico's Occupy protesters, which were focused on poverty and workers' rights, failed to resonate with a public enthralled by the violence of the Mexican Drug War.[250] In contrast, an anti-violence movement led by Javier Sicilia during the time that the Occupy protests occurred, drew thousands onto the streets of Mexico City.[250] The Occupy Movement was almost entirely ignored by Mexico's mainstream politicians.[250] By late January 2012, most of the tents were empty and only a few protesters remained outside the Stock Exchange.[250]
Mongolia
[edit]S. Ganbaatar, the head of Mongolia's Confederation of Trade Unions (CTU), has announced that the association joins the worldwide occupy protests of Wall Street and other high streets on 20 October 2011.[251] He claimed that bankers are charging higher interest rates from customers and corporates. In the most recent data in September 2011, the weighted average annual MNT lending rate is 16% in Mongolia.[252]
Nepal
[edit]Also known as Baluwatar Satyagraha, Occupy Baluwatar is a peaceful protest movement calling on the Nepali state to better address the widespread problem of impunity and gender-based violence. Since 28 December 2012, protesters have gathered outside the prime minister's official residence in Baluwatar from 9:00 to 11:00 am daily. The protesters created a coherent set of demands, divided into short- and long-term goals, which they presented to then prime minister Baburam Bhattarai. The short-term demands called on the state, including the police and the judiciary, to properly investigate and prosecute the guilty in five specific cases which took place immediately prior to the movement's start. The long-term demands focused on policy reform in the arenas of migration and rape laws, among others.
Netherlands
[edit]
In the Netherlands, Occupy protests took place in many cities, most notably Amsterdam,[253] The Hague,[254] Rotterdam,[255] and Utrecht[256]
New Zealand
[edit]
In October 2011, Occupy protests began in six New Zealand cities (Auckland, New Plymouth, Wellington, Christchurch, Dunedin, and Invercargill) with protests in Auckland drawing up to 3,000 supporters.[257] A seventh Occupy protest started on 19 November in the Lower Hutt suburb of Pomare by a group called "Pomare Community Voice" to highlight what they call the "loss of community" caused by the demolition of state homes in the area.[258][259] On 23 January, police moved in on four sites in Auckland. Two arrests were made, and police said campers were in breach of council bylaws regarding camping. The sites were at Aotea Square, 360 Queen St, Victoria Park and Albert Park.[260]
Nigeria
[edit]Occupy Nigeria is an anti-fuel subsidy removal protest that started in Nigeria on 2 January 2012 in response to fuel subsidy removal by the Federal government of Nigeria on 1 January 2012. It is a movement against corruption in Government & public service, insensitive & inhuman treatment of Nigerians by Government & Security agents. The movement ended on 16 January 2012 following agreement between the government and the organized labour leaders which saw a partial restoration of the subsidy regime. Fuel pump price in Nigeria has since then been fixed at the official rate of 97 naira per litre while it practically sells for as high as 130 naira in some major cities including Port Harcourt, one of the cities in the oil-producing states in Nigeria.
Norway
[edit]The Occupy movement in Norway began on 15 October with protests in Oslo and Bergen as part of the Global Day of Action.[261][262]
Philippines
[edit]The Pandi housing takeover is sometimes seen as part of the global Occupy movement and its opposition to social inequality.[263][264]
In March 2017, thousands of urban poor from the Kalipunan ng Damayang Mahihirap (Kadamay) led the occupation of vacant government shelters in Pandi, Bulacan, Philippines.[263] President Rodrigo Duterte announced in April that protesters may be allowed stay in the occupied homes,[265] though members of Kadamay reported that they continued to be harassed and red-tagged, and have been excluded in the process to legalize their ownership of the housing units.[263]
Republic of Ireland
[edit]
Protests were held in Dublin,[266] Cork, and Galway.[267] The Irish Times described the movement in the following terms: "The group has no hierarchical structure, has set up a Facebook page and Twitter account – with the social media links attracting a very mixed, and sometimes critical, reaction." The protest in Dublin was organized by "Pots & Pans – Ireland", and #OccupyDameStreet protest group, who then invited Real Democracy Now! Shell to Sea, Tir na Saor and many other non-political groups to participate and all set up camp outside the Central Bank of Ireland in solidarity with the Occupy Wall Street movement in New York. On 22 October it was reported that over 2,000 people took part in a demonstration organized by Occupy Dame Street.[268] This camp survived through the winter, but was removed by an Garda Síochána (Irish police) on 13 March 2012, days before the annual St. Patrick's Day Parade. On the morning of 16 May 2012 at approximately 4:30 am, the Occupy camp in Eyre Square in Galway, the longest-lasting of the Occupy groups in Ireland, was removed by An Garda Síochána and Galway City Council. The camp was removed because the group was illegally occupying a public amenity. At the time the camp was dismantled, there were only 6 protesters at the camp. The camp had lasted for 215 days.[269][270]
South Africa
[edit]In South Africa, a movement called Taking Back South Africa! sprung up as an initiative primarily aimed at protesting and inciting mass action against the economic and social inequality in the country. It consists of a loose informal affiliation of on-the-ground groups and individuals across South Africa as well as internet-based groups. During the 2016 Fees Must Fall movement, protest groups also adopted the slogan #Occupy4FreeEducation in response to the government's perceived lack of interest in dealing with the issue.[271][272]
South Korea
[edit]Hundreds of protesters held rallies in the South Korean capital of Seoul on 15 and 22 October in 2011 under the slogan of "Occupy Seoul". Protesters focused on issues such as a recent free trade agreement with the United States as well as costs of tuition and rent.[273][274][275]
Although there was considerable support from public, there were also criticisms regarding the nature of the protest. Unlike the original Occupy movement which started out as the anti-capitalist protest, many of the catchphrases of Occupy Seoul contained anti-government or anti-American messages. One of the observers has argued that "South Korea overcame the 2008 financial crisis relatively well and there was no serious crisis in financial sector. It is hard to find the legitimate basis of the protest."[276]
Spain
[edit]A series of protests demands a radical change in Spanish politics, as protesters do not consider themselves to be represented by any traditional party nor favoured by the measures approved by politicians.[277] Spanish media have related the protests to the economic crisis, Stéphane Hessel's Time for Outrage!,[277] the NEET troubled generation and current protests in the Middle East and North Africa,[278] Greece,[279] Portugal[280] as well as the Icelandic protest and riots in 2009.[281]
Switzerland
[edit]On 15 October 2011, between 500 and 1,000 Occupy protesters demonstrated in front of the offices of UBS and Credit Suisse on the Paradeplatz in Zurich.[282] 100 protesters later established an occupation on the nearby Lindenhof, which was evicted by the police on 15 November.
Taiwan
[edit]Turkey
[edit]
The initial protests in Istanbul on 28 May 2013 were led by about 50 environmentalists[283] against replacing Taksim Gezi Park with a reconstruction of the Ottoman Era Taksim Military Barracks (the scene of pro Sultan riots in 1909). The current protests developed into riots after the heavy handed police intervention which featured significant use of tear gas and water cannons.[284] The oppressive reaction to the protests caused the protests to widen with many more people to become involved,[285] people from many different walks of life including a wide range of political interest groups, secular and religious people, students, gays, feminists, football fans, women in head scarves, whole families, all finding reason to join the protests.[286]
What started as an environmentalist protest against plans to replace Taksim Gezi Park developed into wider anti-government demonstrations. Demands issued on 4 June included:
- The end of police brutality,
- The end of the sale of public facilities such as parks, forests and beaches to private investors,
- The right of public expression,
- Media responsibility in informing the public of events, and other demands.[287] The protests (up to 500.000 in Istanbul and 30.000 people in Ankara) also spread to other cities in Turkey, and protests were seen in other countries with significant Turkish communities.
United Kingdom
[edit]England
[edit]

As part of the 15 October 2011 global protests, protesters gathered in London, Bristol, and Birmingham in England, together with Glasgow and Edinburgh in Scotland (See Scotland heading below).[289] The London Stock Exchange in Paternoster Square was the initial target for the protesters of Occupy London on 15 October 2011.[131][132][133] Attempts to occupy the square were thwarted by police.[132][290] Police sealed off the entrance to the square as it is private property, and a High Court injunction had been granted against public access to the square.[291] 2,500–3,000 people gathered nearby outside St Paul's Cathedral, with 250 camping overnight.[290] A canon of St. Paul's, Reverend Giles Fraser, said he was happy for people to "exercise their right to protest peacefully" outside the cathedral and an indefinite encampment was established.[290] Additional smaller protests occurred in Birmingham[292] and Nottingham.[293] As of 17 October an indefinite encampment had also been established on College Green in Bristol.[294]

On 29 October a camp was also established in Victoria Gardens, Brighton, and grew from six tents to around twenty within one week.[295] Further Occupy camps took place in Liverpool[296] Bath, Bournemouth University, Bradford, Leeds, Sheffield, Thanet,[297] Newcastle upon Tyne, Plymouth, Exeter, Norwich,[298] The Occupy Thanet protests also focused on local issues,[299] including the closure of shops in the town and the Dreamland Margate amusement park, a lack of employment opportunities[299] and perceived disparities in the allocation of education resources.[299] Lancaster in England and Cardiff in Wales.[300] On 8 January 2012, Lancaster Police arrested four members of Occupy Lancaster who were occupying a disused hotel in the city centre.[301]
On 11 November, police arrested 179 people believed to be EDL supporters[302] on Armistice Day after apparent threats to the St Paul's camp were posted on Facebook. 176 were released without charge and 3 were bailed "pending further inquiries".[303]
On 15 November, an Occupy camp was established in the centre of Leicester near the Highcross shopping centre.[304] On 25 November an Occupy camp was established in Liverpool near the Walker Art Gallery.[305][306] Starting on 30 November 2011 following a national strike action, a body of students occupied the University of Sheffield Arts Tower in solidarity with, but not limited to, the Occupy movement.[307][308]
On 17 October 2014 a new camp was established in Parliament Square, Westminster by a group called Occupy Democracy. The camp was part of a campaign for greater transparency in democracy as well as an end to lobbying.[309] The camp lasted two days until police swept in, giving protestors 30 minutes to leave or face arrest. Any items that could be used for sleeping have been deemed illegal under the Police Reform and Social Responsibility Act 2011, created after the original occupation. The eviction was live streamed, showing police dragging protesters away.[310] Police said there was one arrest. Fifty to a hundred protesters remained in the park overnight.[311] On their website, the group said their goal is "to direct the energy from current single issue struggles into a critical mass that can radically challenge the corrupt and unrepresentative system".[312]
Northern Ireland
[edit]In Northern Ireland, Occupy Belfast initiated its protest outside the offices of Invest NI on 21 October 2011. Occupy Belfast took residence at Writer's Square, in the Cathedral Quarter.[313] It also took control of a disused building owned by the Bank of Ireland, renaming it the People's Bank, with plans to open a library and homeless accommodation to be a community hub.[314] It was expected that an Occupy Derry would take place in the near future.
Occupy Coleraine took over the University of Ulster Common Room for three weeks in December 2013.[315] The group protested the demolition of the historic student-teacher shared space, due for refurbishment as a senior management corporate dining room.[316]
Scotland
[edit]Occupy camps were established in the financial district of St. Andrew Square, Edinburgh on 15 October 2011. St. Andrews Square is the home of the Royal Bank of Scotland headquarters in the Dundas House mansion. Edinburgh City Council subsequently officially backed Occupy Edinburgh and the Occupy movement worldwide. Protesters from Occupy Glasgow set up in the civic George Square on 15 October but after the council obtained a court order moved to Kelvingrove Park, where the council agreed to provide running water, toilets and safety fences.
Wales
[edit]In Wales, Occupy Cardiff originally set its campsite outside Cardiff Castle but it was disbanded by police, and some protesters were arrested. Charges were later dropped following calls from trade unionists, lawyers and politicians including Plaid Cymru leader Leanne Wood, Labour Party politician Tony Benn and demonstrations outside Cardiff magistrate's court.[317] Occupy Cardiff set up a new camp in the city, outside the offices of Welsh Labour and a number of trade unions at the Transport House, Cathedral Road.[300][318]
United States
[edit]
The Occupy Wall Street protests began in New York City on 17 September 2011.[319] By 9 October, similar demonstrations were either ongoing or had been held in 70 major cities and over 600 communities across the U.S.[16] The movement rejects existing political institutions and attempts to create alternative ones through direct action and direct democracy.[73][320][321] Occupy protesters' slogan, "We are the 99%", asserts that the "99%" pay for the mistakes of the "1%". The original location of choice by the protesters was 1 Chase Plaza, the site of the "Charging Bull" statue, but when police discovered the planned site, it was fenced off and nearby Zuccotti Park was chosen. There was scant media coverage till 24 September when a large march forcing the closure of several streets resulted in 80 arrests. Police used a technique called "netting", the use of orange plastic nets to corral protesters, and the march received extensive media coverage when a video of several "netted" young women being pepper sprayed was widely circulated.[322]
Media coverage was again sparked on 1 October, when New York City protesters attempted to march across the Brooklyn Bridge and more than 700 arrests were made. Some said the police had tricked protesters, allowing them onto the bridge and even escorting them partway across before they began to make mass arrests. On 25 October, police officers cleared two Occupy Oakland protest camp sites. Protest organizers said that many of the troublemakers were not part of the Occupy movement.[323] The raid was described as "violent and chaotic at times"[324] and resulted in over 102 arrests. Scott Olsen, a former Marine and Iraq War veteran, suffered a skull fracture caused by a projectile which witnesses claimed was a tear gas or smoke canister fired by the police.[325] On 2 November, protesters in Oakland, California, shut down the Port of Oakland, the fifth busiest port in the nation. Police estimated that about 3,000 demonstrators were gathered at the port and 4,500 had marched across the city.[145]

At about 1:00 am on 15 November, police cleared the Zuccotti Park encampment. Many journalists complained that the police had made a deliberate decision to keep journalists away from the park during the raid.[326] New York City journalists responded to what they perceived as "alarming suppression, abuse and arrests of reporters" by forming "The Coalition for the First Amendment" to "monitor police-press relations as a way of spotlighting police activities that threaten constitutional protections".[327] Executive Director Alison Bethel McKenzie of the International Press Institute commented: "It is completely unacceptable to hinder reporting on a subject that is undoubtedly of public interest. Such reporting is vital to democracy, and authorities at every level of government – federal, state and local – must honour their constitutional obligation not to infringe upon the freedom of the press."[328]
On 6 December, Occupy Homes, an offshoot of Occupy Wall Street, embarked on a "national day of action" to protest the mistreatment of homeowners by big banks, who they say made billions of dollars off the housing bubble by offering predatory loans and indulging in practices that allegedly took advantage of consumers. In more than two dozen cities across the nation the movement took on the housing crisis by re-occupying foreclosed homes, disrupting bank auctions and blocking evictions.[82] On 17 September 2012, protesters returned to Zuccotti Park to mark the one-year anniversary of the beginning of the occupation.[329][330][331]
Reactions
[edit]Political
[edit]- Brazil—President Dilma Rousseff said, "We agree with some of the expressions that some movements have used around the world [in] demonstrations like the ones we see in the US and other countries."[332]
- Canada—Finance Minister Jim Flaherty expressed sympathy with the protests, stating "There's growing worry about a lack of opportunities for the younger generation – particularly in the United States – and it's up to governments to ensure youth are able to capitalize on their education and find good jobs." He later commented, "I can understand some legitimate frustration arising out of that."[333]
- India—Prime Minister Manmohan Singh described the protests as "a warning for all those who are in charge of the processes of governance".[334]
- Iran—Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei voiced his support for the Occupy Movement saying, "Ultimately, it will grow so that it will bring down the capitalist system and the West."[335]
- United Kingdom—On 21 October 2011, former Prime Minister Gordon Brown said the protests were about fairness. "There are voices in the middle who say, 'Look, we can build a better financial system that is more sustainable, that is based on a better and proportionate sense of what's just and fair and where people don't take reckless risks or, if they do, they're penalized for doing so.'"[336] On 6 November 2011, Opposition leader Ed Miliband: "The challenge is that they reflect a crisis of concern for millions of people about the biggest issue of our time: the gap between their values and the way our country is run." He mentioned that he is "determined that mainstream politics, and the Labour Party in particular, speaks to that crisis and rises to the challenge".[337] On Saturday 26 November 2011, Edinburgh City Council set a worldwide precedent by voting in favour of the motion to support the aims and sentiments of Occupy Edinburgh and the Occupy movement as a whole. This motion was presented by the Scottish Green Party, was seconded by the Scottish Labour Party and was slightly amended by the Scottish National Party (SNP) and Scottish Liberal Democrats. The only party not to back the motion was the Scottish Conservative Party. "We regard this as a fantastic step forward in the opening of dialogue with the Scottish government.", stated Occupy Edinburgh.[338]
- United States—President Barack Obama spoke in support of the movement, but also asked protesters not to "demonize" finance workers.[67] Local authorities in the United States have collaborated to develop strategies to respond to the Occupy movement and its encampments, and political leaders in eighteen United States cities consulted on cracking down on the Occupy movement, according to Oakland Mayor Jean Quan, who participated in a conference call.[339] Within a span of less than 24 hours, municipal authorities in Denver, Salt Lake City, Portland, Oakland, and New York City sent in police to crack down on the encampments of the Occupy movement.[340] In a markedly different approach, the city administration and police in New Haven, Connecticut, have worked with Occupy New Haven[341] to ensure the safety of protesters occupying the upper section of the New Haven Green.[342][343] Until 18 April 2012, Occupy New Haven,[341] has been running continuously on the Green for 186 days until they were removed by police.[344][345] A 2017 book released by Brookings Institution senior fellow Richard V. Reeves called Dream Hoarders: How the American Upper Middle Class Is Leaving Everyone Else in the Dust, Why That Is a Problem, and What to Do about It, presented data which showed that, "...more than a third of the demonstrators on the May Day 'Occupy' march in 2011 had annual earnings of more than $100,000. But, rather than looking up in envy and resentment, the upper middle class would do well to look at their own position compared to those falling further and further behind."[346]
- Venezuela—President Hugo Chávez condemned the "horrible repression" of the activists and expressed solidarity with the movement.[347]
Media
[edit]Foreign Affairs has had various articles covering the movement.[348][349][350][351] In the January/February 2012 issue, Francis Fukuyama argued that the Occupy movement was not as influential as the right-wing Tea Party movement. "One of the most puzzling features of the world in the aftermath of the financial crisis," he wrote, "is that so far, populism has taken primarily a right-wing form, not a left-wing one."[352] In contrast, a survey for the think tank Center for American Progress suggested that the Occupy movement has succeeded in substantially boosting the coverage of the job crisis in the American media.[353]
Other
[edit]Egyptian protesters from Tahrir Square have lent their support of the movement. A message of solidarity issued by a collective of Cairo-based protesters declared: "As the interests of government increasingly cater to the interests and comforts of private, transnational capital, our cities and homes have become progressively more abstract and violent places, subject to the casual ravages of the next economic development or urban renewal scheme. An entire generation across the globe has grown up realizing, rationally and emotionally, that we have no future in the current order of things."[354] In early December 2011, Fox News reported that business magnate Richard Branson told them the movement is a "good start", that OWS have been protesting for valid reasons, and that if the business community takes some of their concerns on board they will have made a difference.[355][unreliable source?]
On 15 December 2011, Jesse Jackson said that Jesus Christ, Mahatma Gandhi, and Martin Luther King Jr. were all occupiers, and that: "Occupy is a global spirit, which is now sweeping the nation and the world, fighting for justice for all of God's children".[35][356] A global survey of 23 countries published by Ipsos on 20 January 2012 found that around 40% of the world's citizens are familiar with the movement. Over twice as many reported a favourable response to the movement compared to those who dislike it. Support for the movement varied markedly among countries, with South Korea (67%), Indonesia (65%), and India (64%) reporting the highest sympathy – and Australia (41%), Japan (41%), and Poland (37%) reporting the lowest.[165]
Impact
[edit]Some known impacts to date include the following:
Social impact
[edit]In the United States, the protests have helped shift the focus of national dialogue from the federal budget deficit to economic problems many ordinary Americans face, such as unemployment,[357] the large amount of student and other personal debt that burdens middle class and working class Americans,[358] and other major issues of social inequality, such as homelessness.[359] The movement appears to have generated a national conversation about income inequality, as evidenced by the fact that print and broadcast news mentioned the term "income inequality" more than five times more often during the last week of October 2011 than during the week before the occupation began.[360] Longer term effects are much less clear, as according to Google search trends, in the years since 2012 interest has waned. Occupy movement raised awareness regarding what organizers consider undeserved wealth and lack of fairness in American society.[361] Labor unions have become bolder in the tactics they employ and have been using digital social media more effectively thanks to the Occupy movement.[362] In New York City, the Occupy Wall Street protest has also provided hundreds of protesters to help in picket actions conducted by labor unions.[362]
Offshoots of the Occupy movement, such as Rolling Jubilee, a project of Strike Debt, have bought millions in "zombie debt," money that individuals owe that they have no financial means to pay, including medical debt, to free the debtors from the obligation to pay it off.[363] As of September 2014, Rolling Jubilee claims to have cancelled more than $15 million in medical debt and $4 million in private student loan debt.[364] Noam Chomsky argues that the movement "spontaneously created something that doesn't really exist in the country: communities of mutual support, cooperation, open spaces for discussion . . . just people doing things and helping each other".[365] As of April 2015, Rolling Jubilee reports it has cleared nearly $32 million in debt.[366]
On 10 November 2011, The Daily Telegraph reported that the word "occupy" had been the "most commonly used English word on the internet and in print" over the past 12 months according to a top ten list published by media analysis company Global Language Monitor.[367][368] In January 2012, members of the American Dialect Society voted with an overwhelming majority for "Occupy" as the word of the year for 2011.[369] Numerous news shows and radio shows have been using the term "1%" and "99%" TV shows such as The Middle, Revenge and, The Office have made references to Occupy, and, in July 2012, the City of Vancouver added the word to its list of reserve names for civic assets such as streets and buildings.[370] In December 2012, the Television show Conan launched a contest called "Occupy Conan".
Political impact
[edit]On 27 December 2011, the Financial Times argued that the movement had had a global impact, altering "the terms of the political debate".[371] However, some sympathetic commentators such as Anthony Barnett have suggested that in Spain, where the movement once had the support of well over 70% of the population with millions taking part, the popularity of Occupy is now past its peak and has achieved no consequences of any significance.[34] However, there were numerous successes at local levels,[372] and The Economist has reported that Spanish protesters caused their government to pass various laws including new limits on the amounts banks can "claw back" from defaulting borrowers.[105] In November 2011, U.S. Congressman Ted Deutch, member of the House Judiciary Committee, introduced the "Outlawing Corporate Cash Undermining the Public Interest in our Elections and Democracy (OCCUPIED) Constitutional Amendment," which would overturn the United States Supreme Court decision in Citizens United v. FEC recognizing corporate constitutionally protected free speech rights and would ban corporate money from the electoral process.[373][374]
In March 2012, former U.S. Vice President Al Gore called on activists to "occupy democracy", explaining that "Our democracy has been hacked. It no longer works to serve the best interests of the people of this country."[375] Also in November 2011, Paul Mason said that the Occupy movement had started to dynamically shape the global policy response to the late-2000s financial crisis, being mentioned so often at the 2011 G20 summit that if Occupy had been a brand "it would have a profile to die for among the super-elite".[376] Various journalists along with Jared Bernstein former chief economist and economic adviser to Vice President Joe Biden, have suggested that Occupy influenced the President's January 2012 State of the Union address, with the movement creating the political space for Obama to shift to the economic left and speak about the desirability of the rich paying a greater share of the tax burden. Inequality had remained a central theme of President Obama's reelection campaign, yet he no longer mentioned the Occupy movement by name, which analysts[who?] said reflected the fact that by early 2012 Occupy had become a divisive issue, unpopular with some of the public.[353][377][378][379]
By 2015, income inequality had become a major part of the political discourse in the United States, which The Atlantic declared "The Triumph of Occupy Wall Street".[380]
National monitoring and crackdown
[edit]Government documents released in December 2012 pursuant to Freedom of Information Act requests by the Partnership for Civil Justice Fund reveal FBI monitoring of what became known as the Occupy movement since at least August 2011, a month before the protests began.[381][382] The FBI, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, local police, regional law enforcement "counterterrorism" fusion centers, and private security forces of major banks formed the Domestic Security Alliance Council (DSAC) to collect and share information about, and to share plans to target and to arrest Occupy protesters. Banks met with the FBI to pool information about participants of the Occupy movement collected by corporate security, and the FBI offered to bank officials its plans to prevent Occupy events that were scheduled for a month later.[381][383]
FBI officials met with New York Stock Exchange representatives on 19 August 2011, notifying them of planned peaceful protests.[384] FBI officials later met with representatives of the Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond and Zions Bank about planned protests.[384] The FBI used informants to infiltrate and monitor protests; information from informants and military intelligence units was passed to DSAC, which then gave updates to financial companies.[385] Surveillance of protestors was also carried out by the Joint Terrorism Task Force.[386][387] DSAC also coordinated with security firms hired by banks to target OWS leaders.[388]
Lawsuits
[edit]Following actions by police and municipal officials to use force in closing various Occupy tent camps in public spaces, lawsuits have been filed, while others are being planned.[389] Civil liberties organizations filed separate law suits against the FBI for refusing to turn over documents requested pursuant to the Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) regarding the FBI's role in surveillance of the Occupy movement and the FBI's sharing of intelligence about Occupy events with private corporate security officials.[390] The FBI withheld documents requested under the FOIA citing the reason that the withholding was "in the interest of national defense or foreign policy".[390]
In 2013, MIT doctoral student Ryan Shapiro, collecting research on the role of the FBI in the Occupy movement, sent the FBI three FOIA requests regarding "a potential plan to gather intelligence against the leaders of [Occupy Wall Street-related protests in Houston] and obtain photographs, then formulate a plan to kill the leadership [of the protests] via suppressed sniper rifles". When the FBI refused the request, Shapiro filed a federal complaint in Washington, D.C., and subsequently obtained 17 pages (most of the requested documentation was ruled withheld due to the possibility to "disclose the identity of a confidential source".) The redacted FBI document confirmed the Houston plot and contradicted an earlier claim by the FBI that it had never opened an investigation on the Occupy movement.[391][392]
Criticism
[edit]There have been criticisms of the Occupy movement. One such critique concerns itself with the way in which the Occupy movement has focused its demands around a narrowly modern understanding of freedom that differs little from the claims of mainstream liberal pluralism:
The modern ideology of freedom ... provides its point of departure. This singular dominance of the modern becomes clear in the long list of demands that follow. Practicality dominates and there is not a single demand for relief from the ontological dominance of modern practices and subjectivities that abstract, codify, rationalize and objectify our lives. Though the ideals and demands ... are laudable, they are not that much different in form from the Millennium Goals of the United Nations.[393]
International activists involved in the Occupy movement have seen it stall due a lack of synergy to work with other alternative movements calling for change. The biggest criticism is that the movement is without depth, without a lasting vision of an alternative future.
In her critique of the Occupy movement, American political philosopher Jodi Dean argues that the focus on autonomy, leaderlessness and horizontality paved the way for conflicts and disillusionment within the movement:
Emphasis on autonomy encouraged people to pursue multiple, separate and even conflicting goals rather than work toward common ones. Celebration of horizontality heightened skepticism toward organizing structures like the General Assembly and the Spokes Council, ultimately leading to the dissolution of both. assertions of leaderlessness as a principle incited a kind of paranoia around leaders who emerged but could not be acknowledged or held accountable as leaders. So rather than solving the problem of left political organization by focusing on process and immediate questions of action, as anarchism suggests, Occupy Wall Street in fact poses it anew. It pushes us to think again about the role of a communist party.[394]
Remarks from Occupy Wall Street participant Justine Tunney, a Google software engineer, who called on President Obama to appoint Eric Schmidt "CEO of America", have also sparked criticism, including from the vast majority of other Occupy participants, many of whom have observed that her politics are inconsistent with horizontalism.[395][396][397]
Many Occupy Wall Street protests have included antisemitic slogans and signage such as "Jews control Wall Street" or "Zionist Jews who are running the big banks and the Federal Reserve". As a result, the Occupy Wall Street Movement has been consistently confronted with accusations of antisemitism.[398][399][400][401] However, Abraham Foxman, national director of the Anti-Defamation League stated that "it's not surprising that in a movement that deals with economic issues you're going to get bigots that believe in this stereotype...[however,] they are not expressing or representing a larger view."[399]
A 2017 book released by Brookings Institution senior fellow Richard V. Reeves called Dream Hoarders: How the American Upper Middle Class Is Leaving Everyone Else in the Dust, Why That Is a Problem, and What to Do about It, presented data which showed that:
...more than a third of the demonstrators on the May Day 'Occupy' march in 2011 had annual earnings of more than $100,000.[346]
Reeves commented on this fact saying, "...rather than looking up in envy and resentment, the upper middle class would do well to look at their own position compared to those falling further and further behind."[346]
See also
[edit]Other U.S. protests
[edit]Other international protests
[edit]Related articles
[edit]- Bioregionalism
- Bonus Army
- Cascadia movement
- Corruption Perceptions Index
- Coxey's Army
- Empowered democracy
- GameStop short squeeze
- Grassroots movement
- Green Feather Movement
- Guy Fawkes mask
- Hooverville
- Income inequality in the United States
- List of countries by distribution of wealth
- List of countries by income equality
- List of protests in the 21st century
- March Against Monsanto
- Cecily McMillan
- Neoliberalism
- Occupy (book)
- Peace Convoy
- Plutocracy
- Selected Historical income tax rates in the U.S. (1913–2010)
- Wealth inequality in the United States
References
[edit]- ^ "OccupyArrests". OccupyArrests.com. Archived from the original on 6 January 2012. Retrieved 3 January 2012.
- ^ "FOTO in VIDEO: 'Elitna skupina moških nadzira financni sistem'". 24ur.com. Retrieved 16 October 2011.
- ^ "Man found dead in tent during Occupy Okla. City protest; police say death not suspicious". The Washington Post. 21 October 2011. Archived from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 1 November 2011.
- ^ "Woman Dies at Occupy Vancouver Site". Associated Press. 6 November 2011. Archived from the original on 6 November 2011. Retrieved 9 November 2011.
- ^ Collins, Terry (11 November 2011). "2 Deaths at Occupy Protests in Calif. and Vermont". ABC News. Archived from the original on 11 November 2011.
- ^ Duthiers, Vladimir; Karimi, Faith (13 January 2012). "No deal in Nigeria as protests widen". CNN. Retrieved 19 January 2012.
- ^ "Two deaths near Occupy camps in Oakland and Burlington". BBC News. 11 November 2011. Retrieved 4 November 2012.
- ^ The 99% declaration Archived 3 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Unite the 99%.
- ^ Wall Street protesters: We're in for the long haul Bloomberg Businessweek. Retrieved 3 October 2011.
- ^ Lessig, Lawrence (5 October 2011). "#OccupyWallSt, Then #OccupyKSt, Then #OccupyMainSt". HuffPost. Retrieved 6 October 2011.
- ^ [8][9][10][11]
- ^ Thompson, Derek (15 October 2011). "Occupy the World: The '99 Percent' Movement Goes Global". The Atlantic. Retrieved 15 October 2011.
- ^ Adam, Karla (15 October 2011). "Occupy Wall Street protests go global". The Washington Post. Retrieved 8 November 2011.
- ^ Adam, Karla (16 October 2011). "Occupy Wall Street protests continue worldwide". The Washington Post.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Joanna Walters in Seattle (8 October 2011). "Occupy America: protests against Wall Street and inequality hit 70 cities". The Observer. UK. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Bond, Shannon (15 November 2011). "Authorities move against Occupy protest". Financial Times. Retrieved 15 November 2011. (registration required)
- ^ Jump up to: a b Davies, Lizzy (15 November 2011). "Occupy movement: city-by-city police crackdowns so far". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 16 November 2011.
- ^ Burgis, Tom (28 February 2012). "Authorities clear St Paul's Occupy camp". Financial Times. Retrieved 22 March 2012. (registration required)
- ^ "Riot police smash Occupy Wall Street demo". ITN. 22 March 2012. Archived from the original on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 22 March 2012.
- ^ [17][18][19][20]
- ^ "Where now for the Occupy protesters?". Channel 4 News. 4 November 2011. Retrieved 15 November 2011.
- ^ Shenker, Jack; Gabbatt, Adam (25 October 2011). "Tahrir Square protesters send message of solidarity to Occupy Wall Street". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 15 November 2011.
- ^
"Occupy Together". Occupy Together. Archived from the original on 14 May 2013. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
occupytogether.org is not currently being maintained but you can use the Wayback Machine to view an archive of this site.
- ^ Berkowitz, Ben (19 October 2011). "From a single hashtag, a protest circled the world". Brisbane Times. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- ^ "Cornel West on Occupy Wall Street: It's the Makings of a U.S. Autumn Responding to the Arab Spring". Democracy Now!. 29 September 2011. Retrieved 30 September 2011.
- ^ Matchar, Emily (24 February 2011). "Will Occupy Wall Street's spark reshape our politics?". The Washington Post. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- ^ Wilson, Simone (12 October 2011). "City Council Unanimously Passes Occupy L.A. Resolution – Protesters Struggle to Distance Themselves From Democrats, Unions – Los Angeles News – The Informer". Blogs.laweekly.com. Archived from the original on 30 March 2012. Retrieved 6 March 2012.
- ^ Kirkup, James (29 October 2012). "Occupy protesters were right, says Bank of England official". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 12 January 2022. Retrieved 30 October 2012.
- ^ "From Master Plan to No Plan: The Slow Death of Public Higher Education". dissentmagazine.org. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ^ Kingkade, Tyler (11 November 2011). "Occupy Cal Berkeley Protest Draws Thousands, As Two Years of Occupation Come Home". HuffPost. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ^ "An Open Letter to Students". adbusters.org. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Castells, Manuel (6 June 2011). "Translation of 27 May 2011 speech by Manuel Castells". Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Anthony Barnett (writer) (16 December 2011). "The Long and the Quick of Revolution". openDemocracy.net. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Walker, Peter (15 December 2011). "Jesse Jackson cheers on Occupy London protesters". The Guardian. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ Frayer, Lauren Inspired by Arab Protests, Spain's Unemployed Rally for Change, in voanews, 19 May 2011
- ^ "From Europe to the US, protesters are inspired by Arab spring". The National (Abu Dhabi). 5 October 2011. Archived from the original on 20 October 2011. Retrieved 16 October 2011.
- ^ Pérez-Lanzac, Carmen (30 May 2011). "Democracia Real Ya prepara una convocatoria mundial para el 15 de octubre". El País. Retrieved 16 October 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Fleming, Andrew (27 September 2011). "Adbusters sparks Wall Street protest Vancouver-based activists behind street actions in the U.S". The Vancouver Courier. Archived from the original on 11 October 2012. Retrieved 30 September 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Schwartz, Mattathias (28 November 2011). "Pre-Occupied". The New Yorker. Retrieved 19 January 2012.
- ^ Saba, Michael (17 September 2011). "Twitter #occupywallstreet movement aims to mimic Iran". CNN tech. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ [Barack Obama, Louis Farrakhan], Anonymous (17 September 2011). An Anonymous Message Concerning #occupywallstreet (Internet video). user TheAnonMessage via YouTube. Archived from the original on 3 February 2012.
- ^ Adbusters (23 August 2011). "Anonymous Joins #OCCUPYWALLSTREET "Wall Street, Expect Us!" says video communique". Adbusters. Archived from the original on 9 October 2011. Retrieved 9 October 2011.
- ^ Beeston, Laura (11 October 2011). "The Ballerina and the Bull: Adbusters' Micah White on 'The Last Great Social Movement'". The Link. Retrieved 12 October 2011.
- ^ Schneider, Nathan (29 September 2011). "Occupy Wall Street: FAQ". The Nation. Retrieved 12 October 2011.
- ^ Batchelor, Laura (6 October 2011). "Occupy Wall Street lands on private property". CNNMoney. Retrieved 7 October 2011.
Many of the Occupy Wall Street protesters might not realize it, but they really got lucky when they decided to gather together at Zuccotti Park in downtown Manhattan
- ^ "New democratic occupation". The Star, 20 November 2011. Archived from the original on 23 June 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2012.
- ^ "The Great Occupation". Esquire Magazine. January 2012. Archived from the original on 14 March 2012.
- ^ "Photos of the first Occupy Dataran". Retrieved 28 December 2011 – via Facebook.
- ^ "Occupy Prescott protesters call for more infrastructure investment". Western News&Info, Inc. Archived from the original on 4 April 2012. Retrieved 17 November 2011.
- ^ «Мы — 99 процентов творцов» . Мать Джонс и Фонд национального прогресса . Проверено 17 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Фридман, Ури (18 ноября 2011 г.). «99 процентов мира» . Внешняя политика . Группа «Сланец». Архивировано из оригинала 22 октября 2011 года . Проверено 18 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Протесты на Уолл-стрит распространяются» . Новости CBS . Архивировано из оригинала 5 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 17 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Груша, Роберт (25 октября 2011 г.). «По данным исследования, люди с самыми высокими доходами удвоили долю национального дохода» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 17 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Ирвин, Нил (26 октября 2011 г.). «CBO: Доходы людей с самыми высокими доходами растут гораздо быстрее, чем у всех остальных» . Вашингтон Пост . Проверено 17 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Это неравенство, глупо, авторы Дэйв Гилсон и Кэролин Перо в журнале Mother Jones, март/апрель 2011 г.
- ^ Лухбы, Тами (29 октября 2011 г.). «Кто этот 1 процент?» . CNN . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «Налоговые данные показывают, что 1 процент самых богатых людей пострадал в 2008 году, но доходы остались высоко концентрированными на вершине». Центр бюджетных и политических приоритетов . Проверено в октябре 2011 г.
- ^ Самые высокооплачиваемые удвоили долю национального дохода, исследование показало, что New York Times Роберта Пира, 25 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Финансовое богатство» определяется экономистами как «общая чистая стоимость за вычетом стоимости дома», включая инвестиции и другие ликвидные активы.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Оккупай Уолл-стрит и риторика равенства Forbes, 1 ноября 2011 г., Дебора Л. Джейкобс
- ^ Недавние тенденции в благосостоянии домохозяйств в Соединенных Штатах: рост долга и сжатие среднего класса - обновленная информация к 2007 году, Эдвард Н. Вольф, Институт экономики Леви Бард-колледжа, март 2010 г.
- ^ Дж. Уильям Домхофф из факультета социологии Калифорнийского университета в Санта-Барбаре. «Богатство, доход и власть» .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д и ж г час «Рим подсчитывает цену насилия после глобальных протестов» . Би-би-си. 16 октября 2011 года . Проверено 17 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Нортон, М.И., и Ариели, Д. Построение лучшей Америки - по одному квинтилю богатства за раз. Перспективы психологической науки, январь 2011 г. 6: 9–12
- ^ Пивен, Бен (7 октября 2011 г.). «Оккупируй Уолл-стрит: весь день, всю неделю» . Аль Джазира . Проверено 21 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Бонд, Шеннон (16 октября 2011 г.). «Обама поддерживает протестующих» . Файнэншл Таймс . Проверено 21 октября 2011 г. ( требуется регистрация )
- ^ «29 ОКТЯБРЯ – ГЛОБАЛЬНЫЙ МАРШ #ROBINHOOD» . Адбастеры . 17 октября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 20 октября 2011 года . Проверено 21 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Вольф, Наоми (25 ноября 2011 г.). «Шокирующая правда о подавлении Occupy» . Хранитель . Лондон . Проверено 30 ноября 2011 г.
- ↑ Occupy Wall Street: это не хиппи, Роджер Ловенштейн, Bloomberg Businessweek, 27 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Клевер , Джошуа. «Хватай пони» . Лос-Анджелесский обзор книг . Архивировано из оригинала 6 февраля 2012 года . Проверено 13 февраля 2012 г.
- ^ Гупта, Арун. «Путешествие Оккупай» . В эти времена . Архивировано из оригинала 19 января 2012 года . Проверено 13 февраля 2012 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Гребер, Дэвид. «Оккупируйте анархистские корни Уолл-стрит» . Аль Джазира . Проверено 13 февраля 2012 г.
- ^ Батлер, Джудит (2 февраля 2012 г.). «Оккупай как форма» . АРК Музы . Проверено 13 февраля 2012 г. : «Таким образом, формулирование требований, которые могут быть удовлетворены, фундаментально зависит от приписывания легитимности тем, кто имеет власть удовлетворить требования. тех авторитетов, которые разоблачены».
- ^ Уокер, Питер (28 ноября 2011 г.). «Оккупай Лондон» излагает программу действий по изменению экономического мира . Хранитель . Проверено 28 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Помогите нам составить глобальное заявление движения Occupy» . Хранитель . Лондон. 15 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 30 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Сукете, Хосе Педро (2012) « Другой мир возможен? Возвращение к утопии », Новые глобальные исследования
- ^ Jump up to: а б «За пределами Уолл-стрит: протесты «Оккупай» становятся глобальными» . Си-Эн-Эн. 7 октября 2011 года . Проверено 7 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Доктор медицинских наук Коновер, К. Дэвис, Э. Феррара, К. Маккелви, Ф. Менцер и А. Фламмини (2013). «Геопространственные характеристики коммуникационной сети социального движения» . ПЛОС ОДИН . 8 (3): e55957. arXiv : 1306.5473 . Бибкод : 2013PLoSO...855957C . дои : 10.1371/journal.pone.0055957 . ПМК 3590214 . ПМИД 23483885 .
- ^ Доктор медицинских наук Коновер, Э. Феррара, Ф. Менцер и А. Фламмини (2013). «Цифровая эволюция движения «Оккупай Уолл-стрит» . ПЛОС ОДИН . 8 (5): e64679. arXiv : 1306.5474 . Бибкод : 2013PLoSO...864679C . дои : 10.1371/journal.pone.0064679 . ПМЦ 3667169 . ПМИД 23734215 .
- ^ Линзи, Томас (14 октября 2011 г.). «Превращение профессии в долгосрочные перемены» . Да! Журнал. Архивировано из оригинала 8 декабря 2011 года . Проверено 9 декабря 2011 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Кристи, Лес (6 декабря 2011 г.). «Протестующие Occupy захватывают отчужденные дома» . CNNMoney . Проверено 7 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ Миллер, Джеймс (25 октября 2011 г.). «Захватят ли экстремисты Уолл-стрит?» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 21 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Асамблеа», испанское слово, обозначающее собрание, — общий термин, часто используемый вместо «генеральное собрание».
- ^ Шнайдер, Натан (31 октября 2011 г.). «От «Оккупай Уолл-стрит» к «Оккупай повсюду» . Нация . Проверено 4 января 2012 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Пенни, Лаура (16 октября 2011 г.). «Протест путем консенсуса» . Новый государственный деятель . Проверено 11 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Зельцер, Сара (29 октября 2011 г.). «Где женщины на акции Occupy Wall Street?» . Нация . Архивировано из оригинала 31 октября 2011 года . Проверено 11 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Хинкль, А. Бартон (4 ноября 2011 г.). «Протестующие OWS имеют странные представления о справедливости» . Рассылка Ричмонд Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 15 августа 2012 года . Проверено 11 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Борьба Occupy Wall Street за ненасилие» . Салон . 17 октября 2011 года . Проверено 30 сентября 2013 г.
- ^ «Каждый имеет право безопасно занимать пространство» . OccupyWallSt.org . Проверено 30 сентября 2013 г.
- ^ «Принципы солидарности» . Генеральная ассамблея Нью-Йорка. Архивировано из оригинала 2 октября 2013 года . Проверено 30 сентября 2013 г.
- ^ Эрроу, Руарид (21 февраля 2011 г.). «Джин Шарп: автор свода правил ненасильственной революции» . Би-би-си . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «Мероприятия в центре Накул» . ТИА Архитекторы. 26 апреля 2012 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ лингалинг. «Новое руководство по освобождению от Джина Шарпа в Институте Альберта Эйнштейна» . Оккупируйте Окленд . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «» «Ненасильственная революция» - скоро начнется изучение/обсуждение книги / Оккупай Нэшвилл» . Оккупанашвилл.орг. 22 ноября 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 19 января 2013 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «Исследовательская/дискуссионная группа Джина Шарпа» . Альянс МУДРЕЦ. 26 апреля 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 22 февраля 2013 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ Occuplsx (29 ноября 2011 г.). «Джин Шарп | Захвати Лондонскую фондовую биржу» . Occupylsx.org. Архивировано из оригинала 15 апреля 2013 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «Фильм: Как начать революцию» . Occupymaine.org. Архивировано из оригинала 22 февраля 2013 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ « Как начать революцию». Показ фильма «Оккупай Бостон» сегодня вечером в 19:00» . Оккупируйте Бостон. 9 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «Фильм: «Как начать революцию» в Пикфорде » Occupy Bellingham» . Occupybellinghamwa.org. 10 марта 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 9 мая 2013 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «Вопросы и ответы: Джин Шарп – Мнение» . Аль Джазира . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д и Хэмптон, Рик (14 ноября 2011 г.). « Движение «Оккупай» сталкивается с вызовом со стороны агрессивных маргиналов» . США сегодня . Проверено 4 января 2012 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Суикорд, Джефф (16 ноября 2011 г.). «Движение Occupy работает над сохранением доверия» . Голос Америки . Проверено 4 января 2012 г.
- ^ Маквей, Карен. «Оккупай Уолл-стрит: комитет прямого действия, обеспечивающий успех протеста» . Хранитель . Лондон . Проверено 19 января 2015 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Возмущение Испании: самые ярые протестующие Европы» . Экономист . 14 июля 2011 года . Проверено 4 января 2012 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Деверо, Райан (3 февраля 2012 г.). «Оккупай Уолл-стрит: «Существует воинствующая враждебность, порожденная прямыми действиями» » . Хранитель . Лондон . Проверено 8 февраля 2012 года .
- ^ Кляйн, Наоми (6 октября 2011 г.). «Оккупируй Уолл-стрит: самое важное в мире сейчас» . Нация . Проверено 4 января 2012 г.
- ^ Дженкинс, Коллин и Джонстон, Синтия (1 января 2012 г.). «Полиция Нью-Йорка арестовала десятки протестующих против Уолл-стрит» . Рейтер . Проверено 4 января 2012 г.
- ^ Гудейл, Глория (30 января 2012 г.). «Насилие на выходных в Окленде: движение Occupy вернулось или сломлено? (+видео)» . Христианский научный монитор . Проверено 8 февраля 2012 года .
- ^ Харрисон, Лэрд (1 февраля 2012 г.). «Движение «Оккупай» раскололось из-за конфронтационной тактики» . Рейтер . Проверено 8 февраля 2012 года .
- ^ Гербаудо, Паоло (февраль 2017 г.). «Команды социальных сетей как цифровые авангарды: вопрос лидерства в управлении ключевыми аккаунтами Facebook и Twitter групп Occupy Wall Street, Indignados и UK Uncut» . Информация, коммуникация и общество . 20 (2): 185–202. дои : 10.1080/1369118X.2016.1161817 . S2CID 147100385 .
- ^ Коновер, Майкл Д.; Феррара, Эмилио; Менцер, Филиппо; Фламмини, Алессандро (29 мая 2013 г.). «Цифровая эволюция движения «Оккупай Уолл-стрит» . ПЛОС ОДИН . 8 (5): e64679. arXiv : 1306.5474 . Бибкод : 2013PLoSO...864679C . дои : 10.1371/journal.pone.0064679 . ПМЦ 3667169 . ПМИД 23734215 .
- ^ «Знаменитости делают модным движение Occupy Wall Street». Дейли Стар . 22 октября 2011 г. ПроКвест 899857024 .
- ^ «Сторонники Берни Сандерса протестуют против освещения выборов в здании CNN в Голливуде» . 3 апреля 2016 года . Проверено 27 октября 2016 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Марш, Хизер (10 марта 2011 г.). «@USDayofRage объявляет о создании страницы в Facebook» . Центральный Wikileaks . Архивировано из оригинала 14 марта 2011 года . Проверено 10 марта 2011 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Дорлинг, Филип (29 октября 2011 г.). «Ассанж все еще может оказаться в центре внимания» . Сидней Морнинг Геральд . Проверено 29 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Флеминг, Эндрю (27 сентября 2011 г.). «Реклама Adbusters вызывает протест на Уолл-стрит» . Ванкуверский курьер . Архивировано из оригинала 11 октября 2012 года . Проверено 18 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Митинги «Оккупай Канаду» распространяются в период экономического «пробуждения» » . Канадская радиовещательная корпорация. 13 октября 2011 года . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ Ярдли, Уильям (27 ноября 2011 г.). «Брендинг движения Occupy» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 9 декабря 2011 года .
- ^ Шрайбер, Дэн. «Оккупай СФ» . Хроники Сан-Франциско . Архивировано из оригинала 6 октября 2011 года.
- ^ 15 октября: #Объединившись, мы заново изобретем мир .
- ↑ «Возмущённые» протесты в субботу станут глобальными. Архивировано 5 декабря 2011 года в Wayback Machine . 15 октября 2011 г. AFP через Францию 24 . Цитата статьи: «В субботу протестующие выйдут на улицы по всему миру, вдохновленные движениями «Оккупай Уолл-стрит» и «Возмущенные», чтобы выразить свой гнев против предполагаемой корпоративной жадности и правительственных сокращений».
- ^ «Возмущенные» протесты по всей Азии . 15 октября 2011 г. Бангкок Пост . Цитата статьи: «Протестующие по всему Азиатско-Тихоокеанскому региону в субботу присоединились к мировым демонстрациям, вдохновленным движениями «Оккупай Уолл-стрит» и «Возмущенные».
- ^ Марцинек, Лаура (19 сентября 2011 г.). «Районы Уолл-стрит заблокированы, поскольку полиция арестовала семерых в знак протеста» . Блумсберг Бизнесуик . Архивировано из оригинала 23 сентября 2011 года . Проверено 19 сентября 2011 г.
- ^ Мойнихан, Колин (24 сентября 2011 г.). «80 арестовано по мере продвижения протеста в финансовом районе на север» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 24 сентября 2011 г.
- ^ Розен, Дэниел Эдвард, «Полиция Нью-Йорка Рэя Келли выходит из-под контроля?» , The [New York] Observer , 11 января 2011 г., 18:39. 3 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «700 человек арестованы после протеста на Уолл-стрит на Бруклинском мосту в Нью-Йорке» . Канал «Фокс Ньюс». 1 октября 2011 года . Проверено 1 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Харрис, Элизабет А. (5 октября 2011 г.). «Ссылаясь на полицейскую ловушку, протестующие подали иск» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . п. А25 . Проверено 17 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Битва за Бруклинский мост» . Поделиться . 4 октября 2011 года . Проверено 19 января 2015 г.
- ^ Деверо, Райан (8 июня 2012 г.). «Протестующие Occupy Wall Street одержали юридическую победу в арестах на Бруклинском мосту» . Хранитель . Лондон . Проверено 9 декабря 2012 года .
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Протесты Occupy Wall Street приходят в Лондон» . Хранитель . Ассоциация прессы . 12 октября 2011 года . Проверено 12 октября 2011 г.
Протесты против глобальной финансовой системы, вызвавшие массовые демонстрации на Уолл-стрит в Нью-Йорке, в эти выходные распространятся на лондонский Сити. [...] так называемая OccupyLSX [...] Мы солидарны с Occupy Wall Street, протестующими в Испании, Греции и на Ближнем Востоке, которые начали это движение.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с «Антикорпоративные протесты охватят Лондон» . Сидней Морнинг Геральд . Агентство Франс-Пресс . 12 октября 2011 года . Проверено 12 октября 2011 г.
Протесты против корпоративной власти, охватившие США, обрушатся на Великобританию в субботу митингом перед Лондонской фондовой биржей. Движение «Оккупай Лондонскую фондовую биржу» (OccupyLSX) [...] поддерживается британской группой, выступающей против жесткой экономии UK Uncut, базирующейся в Лондоне Ассамблеей испанского движения 15М и Сетью народных ассамблей «Всемирный день действий».
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Оккупай Лондонскую фондовую биржу привлекает 9000 подписчиков на Facebook» . Метро . 12 октября 2011 года . Проверено 12 октября 2011 г.
Группа под названием Occupy London Stock Exchange сообщила, что страница в Facebook, посвященная протестам, привлекла более 9000 подписчиков и более 3500 подтвержденных посещений. Организации, проводящие кампанию, в том числе группа прямого действия UK Uncut, подтвердили, что поддержат акцию в самом сердце финансового центра столицы в субботу.
- ^ « Протесты под лозунгом «Оккупай» приобретают глобальный характер и становятся жестокими» . Новости CBS . 15 октября 2011 года . Проверено 19 октября 2011 г.
- ↑ Хоули, Крис (16 октября 2011 г.) «Тысячи протестующих «Оккупай» заполняют Нью-Йорк Таймс-сквер». Чикаго Сан-Таймс . Проверено в октябре 2011 года. Архивировано 18 октября 2011 года в Wayback Machine.
- ^ «Оккупай Уолл-стрит собрала 300 000 долларов» . Новости CBS . 17 октября 2011 года . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Сотни арестованы в ходе протестов «Оккупай»» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Ассошиэйтед Пресс 1. 13 июля 2011 г. Проверено 19 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Оккупируй Уолл-стрит: как долго это может продолжаться?» . Си-Эн-Эн. 18 октября 2011 года . Проверено 19 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Бульва, Демиан (25 октября 2011 г.). «Полиция очищает лагеря движения «Оккупай Окленд», арестовывает десятки людей» . Хроники Сан-Франциско . Архивировано из оригинала 25 октября 2011 года . Проверено 25 октября 2011 г.
- ^ МакКинли, Джесси; Гуднаф, Эбби (26 октября 2011 г.). «Некоторые города начинают подавлять протесты «Оккупай»» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 27 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Фарук, Саджид (25 октября 2011 г.). «Оккупай Окленд закрывается» . Проверено 25 октября 2011 г. «Рейд временами был жестоким и хаотичным, но начальник полиции Окленда Говард Джордан сказал, что он доволен тем, как все прошло, поскольку ни население, ни его офицеры не пострадали».
- ^ Jump up to: а б Бендер, Кристен (25 октября 2011 г.). «Ранним утренним полицейским рейдом была вытеснена группа «Оккупай Окленд»» . Сан-Хосе Меркьюри Ньюс . Проверено 25 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Габбатт, Адам (26 октября 2011 г.). «Травмы Скотта Олсена требуют пересмотра, поскольку протесты Occupy Oakland продолжаются» . Хранитель . Великобритания . Проверено 29 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Бартон, Крис (29 октября 2011 г.). « Протест «Оккупай Окленд» говорит многими голосами» . Новозеландский Вестник . Проверено 8 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Столкновения протестующих US Occupy с полицией в порту Окленда» . Би-би-си. 3 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 4 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Оккупируйте дороги | Экономическая и социальная справедливость» . Архивировано из оригинала 10 мая 2012 года . Проверено 29 сентября 2015 г.
- ^ «Оккупай Уолл-стрит: график протестов» . Неделя . 21 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 9 декабря 2012 года .
- ^ «Аресты, когда полицейские Галифакса выселяют протестующих Occupy» . Новости КТВ . Канадская телевизионная сеть. 11 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 20 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «RAW ВИДЕО: Кадры с вертолета, на которых более 100 000 участников движения «Оккупай Окленд» возвращают себе шоссе» . Хроники Сан-Франциско . Архивировано из оригинала 4 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 3 ноября 2011 г. - через YouTube.
- ^ Бартон, Крис. « Протест «Оккупай Окленд» говорит многими голосами» . Архивировано из оригинала 16 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 14 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Ламберт, Ричард (15 ноября 2011 г.). «Его лагеря больше нет, но движение Occupy будет расти» . Файнэншл Таймс . Проверено 15 ноября 2011 г. ( требуется регистрация )
- ^ Гаппер, Джон (16 ноября 2011 г.). «Лучший способ захватить Уолл-стрит» . Файнэншл Таймс . Проверено 16 ноября 2011 г. ( требуется регистрация )
- ^ «Начальник полиции ОГД отправлен в административный отпуск» . Дэвис Энтерпрайз . 20 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 24 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Открытое письмо канцлеру Линде П. Б. Катехи | Велосипедная баррикада UCDavis» . Bicyclebarricade.wordpress.com. 19 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 24 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Протестующие молча наблюдают, как канцлер UCD уходит после пресс-конференции» . CBS Сакраменто. 19 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 24 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Монтополи, Брайан (22 ноября 2011 г.). « Проверка микрофона: протестующие Occupy прерывают Обаму» . ЦБС . Проверено 4 января 2012 г.
- ^ Бонд, Шеннон (7 декабря 2011 г.). «Occupy» нацелена за пределы Уолл-стрит» . Файнэншл Таймс . Проверено 9 декабря 2011 года . ( требуется регистрация )
- ^ «Города, которые распустили лагеря Occupy, теперь сталкиваются с судебными исками по поводу свободы слова и применения силы» . Вашингтон Пост . 22 декабря 2011 года . Проверено 4 января 2012 г. [ мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ Сэмпсон, Оветта (16 января 2012 г.). «Победа операции «Оккупируй Нигерию»: президент снизит цены на топливо» . Христианский научный монитор . Проверено 17 января 2012 г.
- ^ Ричардсон, Ханна (20 января 2012 г.). «Движение протеста «Оккупай» зайдет в школы» . Би-би-си . Проверено 8 февраля 2012 года .
- ^ Кестертон, Майкл (6 февраля 2012 г.). «Университет предлагает курс «Оккупируй Уолл-стрит», на котором студенты зарабатывают зачетные баллы, работая «в поле» » . Глобус и почта . Торонто . Проверено 8 февраля 2012 года .
- ^ Олсен, Эрик (23 января 2012 г.). «ILWU и EGT достигли предварительного соглашения по трудовому спору в Лонгвью» . Ежедневные новости (лонгвью) . Проверено 21 февраля 2012 г.
- ^ Олсен, Эрик (28 января 2012 г.). «Порт Лонгвью подписывает соглашение ILWU и EGT» . Ежедневные новости (лонгвью) . Проверено 21 февраля 2012 г.
- ^ Габбатт, Адам (12 декабря 2011 г.). «Оккупай стремится закрыть порты западного побережья – как это произошло» . Хранитель . Лондон . Проверено 21 февраля 2012 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Пока протестующие под лозунгом «Оккупай» обещают новые стратегии на 2012 год, граждане мира находятся в неведении, но сочувствуют» . Ипсос . 20 января 2012 года . Проверено 20 января 2012 г.
- ^ Фороохар, Рана (13 февраля 2012 г.). «Компании — новые страны» . Время . Архивировано из оригинала 2 февраля 2012 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ Пилас, Пан (25 января 2012 г.). «Меркель заявила на форуме в Давосе, что Европа решит проблему долга» . США сегодня . Проверено 21 февраля 2012 г.
- ^ Деверо, Райан (18 марта 2012 г.). «Десятки арестованных, поскольку Occupy Wall Street отмечает годовщину новыми протестами» . Хранитель . Лондон . Проверено 22 марта 2012 г.
- ^ Гоуэн, Энни (1 мая 2012 г.). «Движение Occupy возвращается на первомайские протесты в округе Колумбия, Нью-Йорке и по всей территории США», — The Washington Post . Проверено 2 мая 2012 г.
- ^ Свободный университет Нью-Йорка . Проверено 16 июля 2012 г. Архивировано 12 июля 2012 г. в Wayback Machine.
- ↑ «Оккупай Портленд» превращается в молитвенное бдение в мэрии против постановления, запрещающего кемпинг . Орегонец . Проверено 12 августа 2013 г.
- ^ 14A.50.020 Кемпинг запрещен на территории общественной собственности и права проезда . Portlandonline.com (11 июня 2003 г.). Проверено 12 августа 2013 г.
- ^ Активист сна выигрывает в суде . Портлендский оккупант (25 августа 2012 г.). Проверено 12 августа 2013 г.
- ^ Монитор зала | Монитор зала . Портленд Меркьюри. Проверено 12 августа 2013 г.
- ↑ Активист записывает происходящее на длительной акции протеста против закона о кемпингах в центре Портленда . Орегонец . Проверено 12 августа 2013 г.
- ^ Несение бдения | Город . Портленд Меркьюри. Проверено 12 августа 2013 г.
- ^ Хог, Илиза (14 марта 2012 г.). «Оккупай мертв! Да здравствует Оккупай!» . Нация . ISSN 0027-8378 . Архивировано из оригинала 12 марта 2018 года . Проверено 11 марта 2018 г.
- ^ Фойер, Алан (9 ноября 2012 г.). «Там, где FEMA потерпело неудачу, там была Occupy» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 13 февраля 2013 г.
- ^ «Чиновник Банка Англии разбивает свою палатку вместе с Occupy» . Файнэншл Таймс . 31 октября 2012 года . Проверено 13 февраля 2013 г.
- ^ «Удивительное письмо Occupy о правиле Волкера» . Рейтер . 14 февраля 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 15 февраля 2012 года . Проверено 13 февраля 2013 г.
- ^ «Забастовка долга» . Проверено 13 февраля 2013 г.
- ^ «Прокатный юбилей — это искра, а не решение» . Нация . 27 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 13 февраля 2013 г.
- ^ Эрл, Итан (28 сентября 2013 г.). «Наследие Occupy: огромное бормотание возможностей» . Независимый . Проверено 1 ноября 2017 г.
- ^ «Активисты перестают выплачивать студенческие кредиты» . НПР Эд. 31 марта 2015 года . Проверено 1 июля 2015 г.
- ^ ДиГанги, Кристина (11 июня 2015 г.). «Некоторые коринфские студенты не удовлетворены новыми мерами по облегчению бремени федерального долга» . Деньги.com . Архивировано из оригинала 13 мая 2021 года . Проверено 1 июля 2015 г.
- ^ «Сторонники Берни Сандерса протестуют против освещения выборов в здании CNN в Голливуде» . CBS Лос-Анджелес . 3 апреля 2016 года . Проверено 4 апреля 2016 г.
- ^ «Децентрализуйте сбор сейчас для 99%» . 11 августа 2015 года. Архивировано из оригинала 19 сентября 2016 года . Проверено 23 августа 2016 г. .
- ^ Стеклофф. «История Первого Интернационала Г. М. Стеклова» .
- ^ «Синергихаб» . Архивировано из оригинала 29 января 2019 года . Проверено 14 февраля 2022 г.
- ^ Кафе «Оккупай» .
- ^ «Сент-Имье 2016» .
- ^ «Добро пожаловать в FairNetwork!!» . Архивировано из оригинала 14 марта 2016 года . Проверено 29 августа 2016 г.
- ^ «Occupy Ice: активисты блокируют здание Портленда из-за разлучения семей» . Хранитель . 20 июня 2018 г.
- ^ «Федералы приказывают протестующим Occupy ICE PDS покинуть лагерь на своей территории или им грозит арест» . Орегонец . 25 июня 2018 г.
- ^ Сильва, Даниэлла (28 июня 2018 г.). «Федеральные чиновники предлагают вновь открыть здание ICE, закрытое после протестов» .
- ^ Барретт, Малачи (24 августа 2018 г.). «Бездомные протестующие продолжают оккупировать общественную собственность Каламазу» . mlive.com.
- ^ «Время лагеря для бездомных в Бронсон-парке истекает» . Mlive.com . 10 сентября 2018 года . Проверено 17 апреля 2019 г.
- ^ «Оккупай…Армению? Протестующие борются за спасение ереванского общественного парка» . Франция 24. Архивировано из оригинала 26 марта 2012 года . Проверено 23 апреля 2012 г.
- ^ «Обращение в аппарат омбудсмена» . WordPress.com. Архивировано из оригинала 22 февраля 2013 года . Проверено 23 апреля 2012 г.
- ^ «Активисты оккупировали парк Маштоца – Ереван: Не портите наши парки!» . Тамблер. Архивировано из оригинала 19 апреля 2012 года . Проверено 23 апреля 2012 г.
- ^ «Оккупай Вуллонгонг» . Проверено 17 ноября 2011 г. - через Facebook.
- ^ «Протестующие оккупируют Перт во время CHOGM» . Австралийская радиовещательная корпорация. 22 октября 2011 года . Проверено 22 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Кэмпион, Викки (21 марта 2011 г.). «Сидячая забастовка в центральном деловом районе Сиднея» . «Дейли телеграф» . Австралия . Проверено 22 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Постоянные новости о том, как протест США Оккупай Уолл-стрит проходит в Брисбене» . News.com.au. 21 октября 2011 года . Проверено 22 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Питер, Бай (22 октября 2011 г.). «Полиция и протестующие Occupy Melbourne снова столкнулись» . News.com.au. Проверено 22 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Леви, Меган и Прейсс, Бенджамин (21 октября 2011 г.). «Протестующие арестованы, когда в центральном деловом районе царит хаос» . Возраст . Проверено 22 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Сиднейский объект оккупации снова демонтирован» . Yahoo!7 Новости . 5 июля 2013 года . Проверено 5 июля 2013 г.
- ^ Автор: ВММА. « Демонстрация «Негодующих» в Брюсселе – Het Nieuwsblad» . Nieuwsblad.be. Архивировано из оригинала 4 сентября 2012 года . Проверено 12 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Оккупай Левен, оккупируй Левенс Гроте Маркт» . Гва.бе. 8 ноября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 29 октября 2011 года . Проверено 12 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Автор: ВММА. « Оккупай Левен» поддерживает протест – Het Nieuwsblad» . Nieuwsblad.be. Архивировано из оригинала 28 октября 2011 года . Проверено 12 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Оккупай Гент привлекает 400 человек в Зюйдпарк» . De Wereld Morgen.be . 29 октября 2011 года . Проверено 2 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Макки, Роберт (2 октября 2015 г.). «Бразильский протестующий застрелен резиновой пулей за то, что сбил с офицера фуражку (опубликовано в 2015 г.)» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . ISSN 0362-4331 . Проверено 11 октября 2020 г.
- ^ Берритт, Дэн (15 октября 2011 г.). «Оккупай Ванкувер» собирает 5000 человек в центре города в знак протеста против жадности» . Новости1130. Архивировано из оригинала 18 октября 2011 года . Проверено 4 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Дагган, Эван (27 октября 2011 г.). «Протестующие «Оккупай Ванкувер» заявляют, что не двигаются» . Ванкувер Сан . Архивировано из оригинала 29 октября 2011 года.
- ^ Протестующие Occupy Toronto обосновались в парке Сент-Джеймс , The Star , 16 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Оккупируйте Торонто. Оккупируйте Торонто. Проверено 10 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «Оккупай Монреаль продолжается на площади Виктории» . Канадская радиовещательная корпорация. 17 октября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 20 декабря 2011 года . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ Маллиган, Кэрол. «Движение «Оккупантов» достигло города» . Звезда Садбери . Архивировано из оригинала 13 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 17 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ [1] Архивировано 11 апреля 2013 г. на archive.today «Принц Джордж занят».
- ^ «Вот как выглядит демократия: оккупация Уолл-стрит и Бэй-стрит» . Глобус и почта . Торонто . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Канадская хартия прав и свобод» . Pch.gc.ca. 5 ноября 2010 года. Архивировано из оригинала 9 января 2012 года . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Студенты разбили лагерь посреди университета» . Зритель . 11 ноября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 19 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 20 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «В Праге проходит крупнейший антиправительственный протест с 1997 года» . aktualne.cz. 21 апреля 2012 г.
- ^ «Оккупай Кларов. В Праге растет лагерь недовольных» . current.cz 28 апреля 2012 г.
- ^ «Пираты примут участие в акции «Оккупай Кларов»» . Пираты.cz. 28 апреля 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 21 июня 2012 года . Проверено 30 мая 2012 г.
- ^ «Полиция в Кларове разогнала лагерь движения Occupy» . current.cz 27 мая 2012 г.
- ^ Бахчели, Саймон (24 ноября 2011 г.). «Оккупай улицу Ледра получила благословение ООН» . Кипрская почта . Архивировано из оригинала 28 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 25 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Йенс Антон Тингстрем Клинкен и Каспер Иверсен (15 октября 2011 г.). «Статья в Politiken от 15 октября 2011 г.» . Политика (на датском языке) . Проверено 9 декабря 2012 года .
- ^ «Плохие времена для возмущенной обороны» . Мир . 11 ноября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 11 мая 2012 года . Проверено 11 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Новые выглядят как возмущенные из Минобороны» . Мир . 11 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 11 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Восемь человек взяты под стражу после того, как полиция разогнала одного» . Francetv.fr . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Демонстрация Indignés. Париж, 10 декабря 2011 — Only Photos — блог уличного фотографа» . Толькоphotos.org. Архивировано из оригинала 26 мая 2012 года . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ Бек, Ульрих (28 октября 2011 г.). «Бессильный, но законный» . Ежедневная газета . Проверено 28 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Джаффе, Грег (12 ноября 2011 г.). «Немецкая полиция сообщает, что более 10 000 человек протестуют против засилья банков» . Вашингтон Пост . Архивировано из оригинала 9 декабря 2018 года . Проверено 12 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Бальфур, Фредерик (16 октября 2011 г.). «Протестующие Occupy Central Hong Kong начинают свой второй день» . Блумберг ЛП . Проверено 18 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ « В Гонконге продолжаются протесты под лозунгом «Оккупай Централ» . Канал НовостиАзия. 11 ноября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 15 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 18 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Как и ожидалось» . Il Fatto Quotidiano . 16 октября 2011 года . Проверено 16 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Мирные инициативы в других городах» . РУЧКА. 15 октября 2011 года . Проверено 15 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Анархисты захватывают протесты в Риме» . Ежедневный зверь . 15 октября 2011 года . Проверено 15 ноября 2010 г.
- ^ «Десятки раненых в Риме из-за роста движения «Оккупай» – Мир – NZ Herald News» . Новозеландский Вестник . 17 марта 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 15 октября 2011 года . Проверено 17 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «accampataroma.altervista.org» . Accampataroma.altervista.org. 16 ноября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 23 июля 2013 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ Альхаджри, Аляа (15 октября 2011 г.). «Оккупация Датаран заканчивается мирно» . Солнце . Архивировано из оригинала 2 ноября 2011 года.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: bot: исходный статус URL неизвестен ( ссылка ) - ^ М. Кумар (16 октября 2011 г.). « Демо-версия «Оккупай Датаран» провалилась после того, как появилось менее сотни участников» . Звезда . Архивировано из оригинала 30 октября 2012 года . Проверено 8 ноября 2018 г.
- ^ «Молодежь собирается в Куала-Лумпуре в рамках движения, вдохновленного движением «Оккупай»» . Китайская газета . 16 октября 2011 г. [ постоянная мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ «Сингапур является лидером азиатской сдержанности в осуждении корпоративной жадности» . Рейтер . 16 октября 2011 г.
- ↑ Группа «Оккупай Датаран» разогнана полицией. Архивировано 18 октября 2011 г. в Wayback Machine , Малайзиякини, 16 октября 2011 г.
- ^ « Оккупай Пенанг привлекает молодежную группу» . Anilnetto.com. 30 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Лица и причины Occupy» . Глобус и почта . Торонто. 17 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Готов умереть за перемены» . Рейтер . 17 ноября 2011 г. Архивировано из оригинала 21 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д Пэриш Фланнери, Натаниэль. «Оккупировать Мексику? Как насчет «Положить конец войне с наркотиками»?» . ГлобалПост . Проверено 5 марта 2015 г.
- ^ «С.Ганбаатар присоединится к движению «Оккупируй Уолл-Стрит»» . English.news.mn. Архивировано из оригинала 23 октября 2011 года . Проверено 22 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Ежемесячный статистический бюллетень Монголбанка, стр. 28» (PDF) . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 27 октября 2011 года.
- ^ «Демонстрации оккупации сегодня в Амстердаме и Гааге» . Фольскрант . Архивировано из оригинала 17 октября 2011 года . Проверено 15 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Грут, Виллемиен. «Оккупай Уолл-стрит достигает Гааги» . Радио Нидерландов по всему миру . Архивировано из оригинала 12 октября 2011 года . Проверено 14 октября 2011 г.
- ↑ На площади Beursplein в Роттердаме палаток нет, но в Амстердаме и Гааге , NRC Handelsblad.
- ^ «Сравнение компараторов | Независимое сравнение Виллема за 5 лет» . Оккупация.nl .
- ^ Питерс, Том и Брэддок, Джон (17 октября 2011 г.). «Новая Зеландия: Акции протеста в шести городах» . wsws.org . Проверено 29 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Община займет Помаре в знак протеста против сноса домов» (пресс-релиз). Scoop.co.nz. 18 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ Истон, Пол (18 ноября 2011 г.). «Планируется протест «Оккупай Помаре»» . Вещи (компания) . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ Бесвик, Анджела (23 января 2011 г.). «Протестующие Occupy утверждают, что у полиции был тот же номер значка» . 3news.co.nz. Архивировано из оригинала 19 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 23 января 2012 г.
- ^ В Осло прошла акция протеста « Оккупай Норвегию» . Информационное агентство Синьхуа. 16 октября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 октября 2011 года . Проверено 1 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ В Осло прошла акция протеста « Оккупай Норвегию» . АПА. 16 октября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 17 октября 2011 года . Проверено 1 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Безана, Стивен (3 февраля 2020 г.). «Помимо жилья: городская беднота занята движением в PH» . Народная коалиция за продовольственный суверенитет . Проверено 19 октября 2021 г.
- ^ Дизон, Хейзел М. (апрель 2019 г.). «Захват жилья на Филиппинах: как городская беднота заявила о своем праве на жилье» (PDF) . Радикальный жилищный журнал . 1 (1): 105–129. дои : 10.54825/LDXD9655 . S2CID 246350082 .
- ^ «Дутерте позволяет Кадамаю иметь дома Булакана» . Новости АБС-ЦБН .
- ↑ Протестующие маршируют по столице , The Belfast Telegraph , 15 октября 2011 г.
- ↑ Движение распространяется на площадь Эйр в Голуэе , The Irish Times , 17 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Люди превыше прибыли – Объединенный левый альянс. «Более 2000 человек принимают участие в демонстрации «Захвати улицу Дам | Люди важнее прибыли – Объединенный левый альянс»» . Peoplebeforeprofit.ie. Архивировано из оригинала 25 октября 2011 года . Проверено 28 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Радио и телевидение Ирландии (16 мая 2012 г.). «Лагерь протестующих «Оккупай Голуэй» сносится Гарда» . Новости РТЭ . Проверено 16 мая 2012 г.
- ^ «Гардаи демонтирует последний лагерь Оккупай» . Granthamjournal.co.uk. Архивировано из оригинала 23 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 16 мая 2012 г.
- ^ «Вернем Южную Африку! 2011» . Takebacksa.wordpress.com. 14 апреля 2011 года . Проверено 6 марта 2012 г.
- ^ «Вернем Южную Африку! 2011: Всемирная революция» . 23 февраля 2012 года . Проверено 6 марта 2012 г. - через Facebook.
- ^ «#ОккупайСеул» . Occupyseoul.hourb.com. Архивировано из оригинала 16 декабря 2011 года . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Сеул присоединяется к движению Occupy Wall Street» . Информационное агентство Синьхуа. 15 октября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 октября 2011 года . Проверено 15 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Южнокорейские активисты проводят очередную акцию протеста «Оккупай Сеул»» . Корейский вестник . 23 октября 2011 г. Архивировано из оригинала 14 ноября 2011 г. Проверено 15 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Пак, Хун Сан (15 октября 2011 г.). «Движения «Оккупай» сегодня в 80 странах; Сеул присоединяется к ночной акции протеста» . Донг-а Ильбо . Проверено 31 марта 2013 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Возмущённые на улице» . СТРАНА . 17 мая 2011 г. Архивировано из оригинала 22 мая 2011 г. . Проверено 22 мая 2011 г.
- ^ «Митинг испанской молодежи в Мадриде отражает протесты в Египте» . Би-би-си. 18 мая 2011 года . Проверено 22 мая 2011 г.
- ^ «По следам испанских «возмущенных»» (на греческом языке). skai.gr. 25 мая 2011 года . Проверено 26 мая 2011 г.
- ^ « Geração à rasca» — это отсылка к Испании – JN» . Проверено 22 мая 2011 г.
- ^ «The sábados de Islandia llegaron al 15-M (исландские субботы появляются в 15-м)» . Эль Паис . 17 мая 2011 г. Архивировано из оригинала 22 мая 2011 г. . Проверено 22 мая 2011 г.
- ^ Брэдли, Саймон (15 октября 2011 г.). «Швейцарские возмущенные выходят на улицы» . SWI swissinfo.ch . Проверено 12 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Это началось с Таксима и распространилось по всей стране / 3 – Галерея фотоновостей» . Хюрриет Дейли Ньюс . Проверено 2 июня 2013 г.
- ^ «Премьер-министр Турции обвиняет протестующих в том, что они идут «рука об руку с терроризмом» » . Австралийская радиовещательная корпорация. 4 июня 2013 года . Проверено 6 июня 2013 г.
- ^ Маллен, Джетро; Куллинан, Сюзанна (4 июня 2013 г.). «Что движет волнениями и протестами в Турции?» . CNN . Проверено 16 сентября 2013 г.
- ^ Коцев, Виктор (2 июня 2013 г.). «Как протесты повлияют на Турцию внутри страны и за рубежом» . Атлантика . Проверено 2 июня 2013 г.
- ^ «Немедленные требования Таксим Солидарности» . Whatishappeninginistanbul.com. 6 июня 2013 года. Архивировано из оригинала 10 июня 2013 года . Проверено 26 июня 2013 г.
- ^ «Протесты Occupy London в финансовом районе» . Новости Би-би-си. 15 октября 2011 года . Проверено 15 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Оккупай Лондон: протест продолжается второй день» . Новости Би-би-си . Лондон. 16 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Дэвис, Кэролайн (16 октября 2011 г.). «Протесты против движения «Оккупай Лондон» продолжаются второй день» . Хранитель . Лондон.
- ^ «Оккупация фондовой биржи заблокирована» . УэльсОнлайн . Уэльс. 15 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Оккупируй Бирмингем, Великобритания – оккупируй Бирмингем с 15.10.11» . Оккупируйтебирмингем.co.uk. Архивировано из оригинала 30 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 15 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Оккупируй Ноттингем – культура Ноттингема» . Leftlion.co.uk . Проверено 19 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Моррис, Стивен (16 октября 2011 г.). «Активисты Occupy Bristol разбили лагерь» . Хранитель . Лондон . Проверено 15 октября 2011 г.
- ^ « Протестующие «Оккупай Брайтон» разбили лагерь в знаменитых садах» . Брайтон и Хоув Аргус . 31 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Оккупируй Ливерпуль» . Оккупируйте Ливерпуль . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Протестующие Occupy Thanet заявляют, что выступают от имени 99 процентов» . Это Кент. 31 января 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 5 мая 2013 года . Проверено 25 марта 2012 г.
- ^ «Occupy Wiki – Оккупации продолжаются» . Архивировано из оригинала 12 октября 2017 года . Проверено 14 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с «Молодой и злой – и есть что сказать» . Нортклифф Медиа Лимитед. 3 февраля 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 7 февраля 2012 года . Проверено 25 марта 2012 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Оккупай Кардифф» разбивает новый лагерь в Транспортном доме» . Новости Би-би-си . 20 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 25 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Куинн, Бен (9 января 2012 г.). «Четверо арестованы на акции протеста Occupy в Ланкастере» . Хранитель . Лондон . Проверено 29 января 2012 г.
- ^ «Арестовано 170 сторонников EDL» . Independent.co.uk . 11 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Лавиль, Сандра (11 ноября 2011 г.). «Полиция арестовывает членов EDL, чтобы «предотвратить запланированное нападение» в Лондоне» . Хранитель .
- ^ «Антикапиталисты разбили лагерь в центре Лестера» . Лестер Меркьюри . 15 ноября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 16 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 17 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Протестующие Occupy Liverpool обещают остаться на зиму» . Новости Би-би-си . 29 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 6 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Мирные протестующие против правительства срезают лагерь возле галереи Ливерпуля» . Ливерпульское Эхо . 28 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 6 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Университет Шеффилда не запрещает протесты » . Новости Би-би-си . 5 декабря 2011 года . Проверено 6 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Студенты Шеффилда прекратили протест после отмены судебного запрета» . Новости Би-би-си . 6 декабря 2011 года . Проверено 6 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ Таунсенд, Марк (3 января 2015 г.). «Забор на Парламентской площади подавляет права протестующих, - говорит Occupy Democracy» . Хранитель . Проверено 2 мая 2023 г.
- ^ «#London #Occupy2 #TarpaulinRevolution, день третий #PoliceBrutality #ONN #OLSX» . Бэмбюзер . Проверено 19 января 2015 г.
- ^ Джонстон, Крис. «Полиция пытается очистить площадь Парламента от протестующих Occupy» . Хранитель . Проверено 19 января 2015 г.
- ^ «Демократическое действие – займите площадь Парламента» . сайт Оккуплондон.org.uk . Проверено 19 января 2015 г.
- ^ «Оккупируйте Белфаст, создайте «Народный банк» » . Ярко-зеленый. 30 января 2012 года . Проверено 18 апреля 2011 г.
- ^ Блэк, Ребекка. «Протестующие студенты Occupy Colraine заявляют, что борьба еще не окончена» . Белфастский телеграф . Проверено 24 сентября 2014 г.
- ^ Благородно, Кайли. «Мои герои 2013 года: студенты, принявшие участие в акции «Оккупай Колрейн». " . Ох, так сложно . Беспристрастный репортер. Архивировано из оригинала 28 января 2014 года . Проверено 24 сентября 2014 г.
- ^ Протестующие Occupy Cardiff заявляют о своей победе после того, как CPS отказалась от дела . Хранитель . Проверено 12 августа 2013 г.
- ^ Occupy Cardiff разбивает новый лагерь в Transport House . BBC News (20 ноября 2011 г.). Проверено 12 августа 2013 г.
- ^ Уолтерс, Джоанна (8 октября 2011 г.). «Оккупай Америку: протесты против Уолл-стрит и неравенства охватили 70 городов» . Наблюдатель . Лондон . Проверено 13 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Беннетт, Дрейк (26 октября 2011 г.). «Дэвид Гребер, антилидер движения «Оккупай Уолл-стрит»» . Деловая неделя . Архивировано из оригинала 29 октября 2011 года . Проверено 13 февраля 2012 г. : «Хотя предстояло еще несколько недель планирования, важная битва была выиграна. Шоу будут вести горизонтали, и выбор, который последует за этим - решение не иметь лидеров или даже назначенных представителей полиции, ежедневных генеральных прокуроров и бесчисленные встречи рабочих групп, которые до сих пор составляют основу протестов в парке Зуккотти, — все это вытекало из этого».
- ^ Гребер, Дэвид (15 ноября 2011 г.). «Оккупация и дар анархизма демократии» . Комментарий Guardian бесплатен . Проверено 13 февраля 2012 г.
- ^ Габбатт, Адам (14 ноября 2011 г.). «Оккупай Окленд: демонстранты готовятся к действиям полиции – понедельник, 11 ноября 2011 г.» . Хранитель . Лондон . Проверено 13 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ МакКинли, Джесси (26 октября 2011 г.). «Некоторые города начинают подавлять протесты «Оккупай»» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 27 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Фарук, Саджид (25 октября 2011 г.). «Оккупай Окленд закрывается» . Архивировано из оригинала 27 октября 2011 года . Проверено 25 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Хендерсон, Питер; Рандевич, Ноэль (29 октября 2011 г.). «Протестующие в Окленде планируют марш, мэр извиняется» . Рейтер . Проверено 29 октября 2011 г.
Олсен, 24 года, [...] был ранен в голову баллончиком со слезоточивым газом, выпущенным во вторник полицией, сообщили организаторы протеста.
- ^ Уокер, Питер; Уэллс, Мэтт (15 ноября 2011 г.). «Оккупай Уолл-стрит: полиция выселяет протестующих – как это было» . Хранитель . Лондон.
- ^ Сделано вручную Питером О.Э. Беккером для Нью-Йоркского пресс-клуба. «Коалиция за первую поправку» . Нью-Йоркский пресс-клуб. Архивировано из оригинала 10 апреля 2012 года . Проверено 6 марта 2012 г.
- ^ «IPI: В США арестованы журналисты – TrustMedia» . Траст.орг. Архивировано из оригинала 17 января 2012 года . Проверено 6 марта 2012 г.
- ^ Мойнихан, Колин (17 сентября 2012 г.). «185 арестованных в годовщину Оккупай Уолл-стрит» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 26 сентября 2012 г.
- ^ Барр, Меган (17 сентября 2012 г.). «Через год после начала лагеря в Оккупации царит хаос» . Сиэтл Таймс . Ассошиэйтед Пресс . Проверено 26 сентября 2012 г.
- ^ Уокер, Хантер (18 сентября 2012 г.). «Незанятое: следующее утро в парке Зуккотти» . Нью-Йоркский обозреватель . Политическая сеть . Проверено 26 сентября 2012 г.
- ↑ Возмущены в Бразилии: демонстрации мирные и пользуются поддержкой президента. Архивировано 7 августа 2016 года в Wayback Machine , Ла-Терсера , 15 октября 2011 года. Проверено 20 октября 2011 года.
- ^ «Протесты «Оккупай Уолл-стрит» охватили Канаду» . Канада.com. 15 октября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 16 декабря 2011 года . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Оккупай Уолл-стрит протестует против предупреждения: премьер-министр» . Profit.ndtv.com. 16 декабря 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 21 января 2012 года . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ Лах, Эрик (12 октября 2011 г.). «Аятолла Хаменеи на Occupy Wall Street: «Это разрушит капиталистическую систему и Запад» » . ГлобалПост . Проверено 5 января 2012 г.
- ^ Линч, Дэвид Дж. (21 октября 2011 г.). «Протесты экс-главы Великобритании Гордена Брауна в штатах требуют справедливости» . Bloomberg LP Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Эд Милибэнд предупреждает о «сигналах опасности» протеста Святого Павла » . Би-би-си. 6 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Оккупируйте Эдинбург в восторге от официального признания» . Ekklesia.co.uk. 26 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «Мэр Окленда Джин Куан признает, что 18 городов консультировались по поводу репрессий #Occupy» . Альтернативный сайт.орг. 15 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ «После свержения протестующие «Оккупай Окленд» возвращаются» . Еда на вынос. 15 ноября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 9 декабря 2011 года . Проверено 28 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Что такое оккупационное движение?» . Оккупируйтеnewhaven.org . 13 ноября 2012 года . Проверено 24 января 2013 г.
- ^ Робинсон, Натан. «В Нью-Хейвене лагерь «Оккупай» остается в живых и сохраняет неравенство в повестке дня, 30 декабря 2011 г., «В Нью-Хейвене лагерь «Оккупай» остается в живых и сохраняет неравенство в повестке дня » . ХаффПост . Проверено 23 января 2012 г.
- ^ «Оккупация готовится к зиме», 5 января 2012 г., «Оккупация готовится к зиме» » . Нью-Хейвен Индепендент . 5 января 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 23 мая 2012 года . Проверено 23 января 2012 г.
- ^ «Официальный сайт «Оккупай Нью-Хейвен»» . Проверено 23 января 2012 г.
- ^ Лагерь «Оккупай Нью-Хейвен» очищен; 13 протестующих арестованы (видео, фото) . 18 апреля 2012 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Ривз, Ричард В. (2017). Хранители мечты: как американский верхний средний класс оставляет всех остальных в пыли, почему это проблема и что с этим делать . Издательство Брукингского института. п. 7. ISBN 978-0-8157-2912-9 .
- ^ «Чавес осуждает «репрессии» протестов на Уолл-стрит » . Хранитель . Лондон. 9 октября 2011 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ Хардт, Майкл и Негри, Антонио (11 октября 2011 г.). «Борьба за «настоящую демократию» в центре движения «Оккупай Уолл-стрит» . Иностранные дела . Проверено 6 марта 2012 г.
- ^ Тарроу, Сидней (10 октября 2011 г.). «Почему Occupy Wall Street — это не чаепитие левых» . Иностранные дела . Проверено 6 марта 2012 г.
- ^ Маквей, Рори (10 октября 2011 г.). «Как работает организация Occupy Wall Street» . Иностранные дела . Проверено 6 марта 2012 г.
- ^ Фукуяма, Фрэнсис (1 января 2012 г.). «Будущее истории» . Иностранные дела . Проверено 6 марта 2012 г.
- ^ «Фрэнсис Фукуяма об упадке среднего класса - Официальный блог PNHP» . Pnhp.org. 6 января 2012 года . Проверено 6 марта 2012 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Гарофоли, Джо (26 января 2012 г.). «Речь Обамы перекликается с темами движения Occupy» . Хроники Сан-Франциско . Проверено 8 февраля 2012 года .
- ^ «Движению Occupy – оккупанты площади Тахрир с вами» . Хранитель . Лондон. 25 октября 2011 года . Проверено 13 декабря 2011 г.
- ^ « Один процент» Ричарда Брэнсона поддерживает протесты «Оккупай» . Канал «Фокс Ньюс». 22 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 11 ноября 2012 г.
- ^ Джексон, Джесси (15 декабря 2011 г.). Джесси Джексон выступает на Occupy London: «Occupy – это дух, время которого пришло» – видео . Хранитель . Проверено 6 января 2012 года .
- ^ «Победа OWS уже одержана: протесты помогли перевести национальный диалог от дефицита к реальным проблемам, с которыми сталкиваются американцы» . Салон . 27 октября 2011 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «Важная победа Occupy Wall Street: перевод разговора с «национального дефицита» на «личный долг» » . Тиккун. 9 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «4 профессии, охватывающие бездомных (поскольку города все чаще не могут о них позаботиться: невозможно отделить бездомность от борьбы Occupy Wall Street за экономическую справедливость)» . АльтерНет. 8 ноября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 2 мая 2012 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ Байерс, Дилан (11 ноября 2011 г.). «Оккупай Уолл-стрит побеждает» . Политик . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ Деван, Шейла (11 октября 2011 г.). «99 процентов и 53 процента противостоят друг другу» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 15 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Теплица, Стивен (8 ноября 2011 г.). «Движение «Оккупай» вдохновляет профсоюзы применять смелую тактику» . Нью-Йорк Таймс .
- ^ «Зомби-долг» Часть 1,1 миллиона долларов по счетам за медицинские услуги в Луисвилле, купленным протестующими на Уолл-стрит: счета за медицинские услуги Луисвилля среди тех, кто уничтожен некоммерческой группой The Courier -Journal, 10 мая 2013 г.
- ^ Лиз Плезант, Криста Хиллстром и Джеймс Тримарко (17 сентября 2014 г.). Occupy Offshoot отменяет грабительские студенческие кредиты на сумму 4 миллиона долларов и создает Союз должников . Да! Проверено 17 сентября 2014 г.
- ^ «Хомский: «Оккупай Уолл-Стрит» создал в США то, чего на самом деле не существовало — солидарность» . Демократия сейчас! . 14 мая 2012 года . Проверено 15 ноября 2014 г.
- ↑ Продолжение юбилейных операций , дата обращения 24 апреля 2015 г.
- ^ Уордроп, Мюррей (10 ноября 2011 г.). « «Оккупай» — наиболее часто используемое слово в англоязычных СМИ, утверждает исследование» . «Дейли телеграф» . Лондон. Архивировано из оригинала 12 января 2022 года . Проверено 15 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ «Главные слова 2011 года» . Глобальный языковой монитор. 9 ноября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 2 января 2013 года . Проверено 4 ноября 2012 г.
- ^ Галлман, Стефани (8 января 2012 г.). «Лингвисты назвали слово «оккупировать» словом 2011 года» . CNN . Проверено 9 января 2012 г.
- ^ «Протокол Ванкуверского комитета по именованию гражданских активов» (PDF) . Город Ванкувер, Канада. 5 июля 2012 г. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 22 февраля 2013 г. . Проверено 28 октября 2012 г.
- ^ От редакции (27 декабря 2011 г.). «Капитализм мертв, да здравствует капитализм» . Файнэншл Таймс . Проверено 21 октября 2011 г. ( требуется регистрация )
- ^ Шнайдер, Натан (19 декабря 2011 г.). «Спасибо, анархисты» . Нация . Проверено 4 января 2012 г.
- ^ «Представитель Дойч представляет ОККУПИРОВАННУЮ поправку к конституции, запрещающую корпоративные деньги на выборах и заявляющую, что корпорации не являются людьми» . Веб-страница члена палаты представителей Теда Дойча . Конгресс США . 18 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «Представитель Дойч вносит ОККУПИРОВАННУЮ поправку к конституции, запрещающую корпоративные деньги в политике» . Думайте о прогрессе . 18 ноября 2011 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «Эл Гор с Шоном Паркером на SXSW: «Захватывайте демократию!» . Новости CNET. 12 марта 2012 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ Мейсон, Пол (2 ноября 2011 г.). «#OWS: Лидеры брендов не могут позволить себе игнорировать» . Би-би-си . Проверено 4 января 2012 г.
- ^ Янг, Гэри (25 января 2012 г.). «Состояние союза: президент Обама борется с неравенством» . Хранитель . Лондон . Проверено 8 февраля 2012 года .
- ^ «Бывший советник Обамы: внимание к неравенству в США в год выборов. Состояние Союза занимает отпечаток Уолл-стрит» . Демократия сейчас. 25 января 2012 года . Проверено 23 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ Альтман, Роджер (21 марта 2012 г.). «Больше никаких бездействий в отношении неравенства доходов» . Файнэншл Таймс . Проверено 22 марта 2012 г. ( требуется регистрация )
- ^ Левитин, Михаил (10 июня 2015 г.). «Триумф захвати Уолл-стрит» . Атлантика . Проверено 1 июля 2015 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Вольф, Наоми (29 декабря 2012 г.). «Раскрыто: как ФБР координировало подавление Occupy» . Хранитель . Проверено 1 ноября 2017 г.
- ↑ Фонд «Партнерство в интересах гражданского правосудия», 22 декабря 2012 г., « Документы ФБР раскрывают секретный общенациональный мониторинг оккупации »
- ↑ Грант, Дрю (24 декабря 2012 г.). «То, что вы параноик, не означает, что ФБР не следило за вами: издание Occupy Wall Street». Нью-Йоркский обозреватель .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Брауди, Брайан (26 декабря 2012 г.). «ФБР передало информацию об оккупационном движении финансовым учреждениям». Американский банкир
- ↑ Грей, Барри (27 декабря 2012 г.). «Протесты Occupy, преследуемые контртеррористическими подразделениями ФБР» . Мировой социалистический веб-сайт. Проверено 27 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ Грей, 2012
- ↑ Уилкинс, Бретт (24 декабря 2012 г.). «ФБР расследовало движение Occupy Wall Street как «внутренних террористов»». Цифровой журнал. Проверено 27 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «В новом отчете Occupy ФБР и тактика национальной безопасности названы «оруэлловскими» за работу с охранными фирмами, нанятыми частными банками» . Интернэшнл Бизнес Таймс . 30 декабря 2012 г. Проверено 31 декабря 2012 г.
- ^ «Протестующие Occupy предъявляют иск за свободу слова и силу» . США сегодня .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Американский союз гражданских свобод (14 сентября 2012 г.). «Документы FOIA показывают, что ФБР следило за протестующими против оккупации, некоторые документы все еще секретны по соображениям национальной безопасности» .
- ^ «ФБР согласилось с тайником информации о предполагаемом заговоре об убийстве» . Служба новостей здания суда . 6 февраля 2015 г.
- ^ Гершман, Джейкоб (18 марта 2014 г.). «ФБР приказано обосновать сокрытие запрошенных записей о предполагаемом снайперском заговоре «Оккупай»» . Уолл Стрит Джорнал . Проверено 23 марта 2014 г.
- ^ Стегер, Манфред Б.; Джеймс, Пол (2013). «Уровни субъективной глобализации: идеологии, воображения, онтологии» . Перспективы глобального развития и технологий . 12 (1–2): 37–38. дои : 10.1163/15691497-12341240 .
- ^ Дин, Джоди (2012). Коммунистический горизонт . Версо. п. 210. ИСБН 978-1844679546 .
- ^ « Эрик Шмидт в качестве генерального директора Америки: петиции основателей Occupy Wall Street» . Тех Таймс . 21 марта 2014 года . Проверено 19 января 2015 г.
- ^ Мимс, Кристофер (27 марта 2014 г.). «Почему активист Occupy, ставший сотрудником Google, считает, что Эрик Шмидт должен управлять США» . Кварц . Проверено 19 января 2015 г.
- ^ «Основатель OWS призывает Обаму назначить Эрика Шмидта из Google «генеральным директором Америки» » . дезинформация . Архивировано из оригинала 19 января 2015 года . Проверено 19 января 2015 г.
- ^ Рубин, Дженнифер (17 октября 2011 г.). «Оккупай Уолл-стрит: кого-нибудь волнует антисемитизм?» . Вашингтон Пост .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Бергер, Джозеф (21 октября 2011 г.). «Крики антисемитизма, но не в парке Зуккотти» . Нью-Йорк Таймс .
- ^ «Протестующий OWS заявляет: «Евреи контролируют Уолл-стрит». В Зуккотти-парке Рэнт» . Новости CBS . 12 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Гринвальд, Абэ (11 октября 2011 г.). «Оккупай Уолл-стрит имеет проблему антисемитизма» . Комментаторский журнал .
Дальнейшее чтение
[ редактировать ]- Берг, А.Г. и Остри, доктор юридических наук (сентябрь 2011 г.) «Равенство и эффективность» в области финансов и развития (Вашингтон, округ Колумбия: Международный валютный фонд )
- Бирн, Джанет (редактор). (2012) Справочник Occupy , Back Bay Books ISBN 978-0316220217
- Гибсон, Морган Роджерс (2013) (2013). «Анархизм захватывающего движения». Австралийский журнал политической науки . 48 (3): 335–348. дои : 10.1080/10361146.2013.820687 . S2CID 144776094 .
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: числовые имена: список авторов ( ссылка ) - Марлис, Гласиус; Плейерс, Джеффри (2013). «Момент 2011 года: Демократия, социальная справедливость, достоинство» . Развитие и изменения . 44 (3): 547–567. дои : 10.1111/деч.12034 .
- Голдин, Фрэнсис и др. (2014). Представьте себе: жизнь в социалистических США. Многолетник Харпер . ISBN 0062305573
- Майкл А. Гулд-Вартофски (2015). Оккупанты: создание 99-процентного движения . Издательство Оксфордского университета . ISBN 0199313911
- Гребер, Дэвид (9 февраля 2012 г.). «О жестокой полиции мира: открытое письмо Крису Хеджесу» . Проверено 9 февраля 2012 года .
- Шрам, Сэнфорд Ф. (2015). Возвращение обычного капитализма: неолиберализм, нестабильность, оккупация . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0190253028 .
- Хенкель, Скотт (2015). «Преимущества отсутствия лидера», в Т. Комер, под ред. Что будет после Occupy?: Региональная политика сопротивления .
- Митчелл, WJT, Харкорт, Бернард Э. и Майкл Тауссиг (2013). Оккупируй: три расследования непослушания . Издательство Чикагского университета . ISBN 022604274X
- Ингар Солты (2014). «Разрушает ли глобальный кризис брак капитализма и либеральной демократии? (Не)легитимная политическая власть и новые глобальные антикапиталистические массовые движения в контексте интернационализации государства», в книге М. Лакич, редактор, « Политика». Пересмотр власти: государственная власть и гражданский активизм между легитимностью и насилием (LIT), стр. 161–204. Разрушает ли глобальный кризис брак капитализма и либеральной демократии? (Ил-)Легитивная политическая власть и новые глобальные антикапиталистические массовые движения в контексте интернационализации государства
- Стегер, Манфред Б.; Джеймс, Пол (2013). «Уровни субъективной глобализации: идеологии, воображения, онтологии» . Перспективы глобального развития и технологий . 12 (1–2): 17–40. дои : 10.1163/15691497-12341240 .
- Ричард Г. Уилкинсон и Кейт Пикетт (2009). Духовный уровень: почему более равные общества почти всегда добиваются лучших результатов . Аллен Лейн.
- Горизонтализм и оккупационные движения . Марина Ситрин. Несогласие , весна 2012 г.
- Вольф, Ричард и Барсамян, Дэвид (8 мая 2012 г.). Оккупируйте экономику: вызов капитализму. Издательство City Lights . ISBN 0872865673
Внешние ссылки
[ редактировать ]- Архив Occupywallstreet.net , официального сайта Occupy Wall Street.
- Occupy.com