Северо-Западная Англия
Северо-Западная Англия | |
|---|---|
Сверху слева направо: Ливерпуль ; Манчестер ; Блэкпул ; Честер ; Лес Боуленд ; Моркам Бэй ; Озерный край | |
 Северо-Западная Англия выделена красным на бежевой политической карте Англии. | |
| Координаты: 54 ° 04'30 "N 02 ° 45'00" W / 54,07500 ° N 2,75000 ° W | |
| Суверенное государство | Великобритания |
| Страна | Англия |
| Объединенные органы власти | |
| Районы |
|
| Округа | |
| Правительство | |
| • Тип | Совет руководителей местных органов власти |
| • Тело | Совет лидеров Северо-Западного региона |
| • Палата общин | 75 депутатов (из 650) |
| Область | |
| • Общий | 5 759 квадратных миль (14 915 км ) 2 ) |
| • Земля | 5 447 квадратных миль (14 108 км ) 2 ) |
| • Вода | 22 квадратных миль (57 км ) 2 ) |
| • Классифицировать | 6-е место |
| Население (2021) [2] | |
| • Общий | 7,422,295 |
| • Классифицировать | 3-й |
| • Плотность | 1360/кв. миль (526/км) 2 ) |
| Этническая принадлежность ( 2021 ) | |
| • Этнические группы | Список |
| Религия (2021) | |
| • Религия | Список |
| Код ГСС | E12000002 |
| ITL-код | ДВУ |
| ВДС | оценка на 2021 год [4] |
| • Общий | 196,0 миллиардов фунтов стерлингов |
| • Классифицировать | 3-й |
| • На душу населения | £26,411 |
| • Классифицировать | 4-й |
| ВВП (номинальный) | оценка на 2021 год [5] |
| • Общий | 220,3 миллиарда фунтов стерлингов |
| • Классифицировать | 3-й |
| • На душу населения | £29,681 |
| • Классифицировать | 4-й |
| Эта статья является частью серии, посвященной Политика Соединенного Королевства на |
 |
|---|
Англия является одним из девяти официальных регионов Англии и состоит из церемониальных графств Чешир Северо- Западная , Камбрия , Большой Манчестер , Ланкашир и Мерсисайд . В 2021 году население Северо-Запада составляло 7 417 397 человек. [3] Это третий по численности населения регион Соединенного Королевства после Юго-Востока и Большого Лондона . Крупнейшие населенные пункты — Манчестер и Ливерпуль .
Подразделения
[ редактировать ]Официальный регион состоит из следующих подразделений :
| Местные власти | Графство | Комбинированная власть или нет |
|---|---|---|
| Камберленд † и Вестморленд и Фернесс † | Камбрия | Н/д |
| Восточный Чешир †, Западный Чешир и Честер † и Уоррингтон † | Чешир | Н/д |
| Хэлтон † | Ливерпульский городской регион | |
| Ноусли , Ливерпуль , Сент-Хеленс , Сефтон и Уиррал | Мерсисайд * | |
| Болтон , Бери , Манчестер , Олдхэм , Рочдейл , Солфорд , Стокпорт , Теймсайд , Траффорд и Уиган. | Большой Манчестер * | |
| Блэкпул †, Блэкберн с Дарвеном †, Бернли , Западный Ланкашир , Чорли , Саут-Риббл , Филд , Город Престон , Уайр , Город Ланкастер , Риббл-Вэлли , Пендл , Россендейл и Хиндберн | Ланкашир | Н/д |
После упразднения советов графств Большого Манчестера и Мерсисайда в 1986 году власть была передана столичным районам , что сделало их эквивалентными унитарным органам власти. В апреле 2011 года Большой Манчестер получил административный орган высшего уровня в виде Объединенного управления Большого Манчестера , что означает, что 10 районов Большого Манчестера снова стали органами власти второго уровня.
География
[ редактировать ]Северо-Западная Англия ограничена на востоке Пеннинами и на западе Ирландским морем . Регион простирается от шотландских границ на севере до региона Уэст-Мидлендс на юге. К юго-западу от него находится Северный Уэльс . Среди наиболее известных физико-географических особенностей Северо-Запада — Озерный край и Чеширская равнина . Самая высокая точка Северо-Западной Англии (и самая высокая вершина в Англии) — Скафелл-Пайк , Камбрия, на высоте 3209 футов (978 м).
Уиндермир — самое большое естественное озеро в Англии, а Брод-Крэг-Тарн на Брод-Крэге — самое высокое озеро Англии. Васт-Уотер — самое глубокое озеро Англии, его глубина составляет 74 метра.
Сочетание сельского и городского ландшафта, два крупных агломерации с центрами Ливерпуля и Манчестера занимают большую часть юга региона. Север региона, включающий Камбрию и северный Ланкашир, в основном сельский, как и крайний юг, который включает части Чеширской равнины и Пикового округа.
В состав региона входят части трех национальных парков (весь Озерный край , а также небольшие части Пик-Дистрикт и Йоркшир-Дейлс ) и три зоны выдающейся природной красоты (все Арнсайд и Силвердейл , а также побережье Солуэй и почти все леса Боуленд ).
Погода
[ редактировать ]Погода в этой части Англии обычно классифицируется как морская, влажная и умеренная, с умеренным годовым диапазоном температур. Среднегодовое количество осадков в Великобритании обычно колеблется от 800 до 1400 мм. Температуры в целом близки к средним по стране. [6] В Камбрии обычно самая суровая погода с большим количеством осадков в горных районах Озерного края и Пеннинских островов. Зимой самая суровая погода наблюдается в более открытых и возвышенных районах Северо-Запада, опять же в основном в Озерном крае и Пеннинских районах. [ нужна ссылка ]
Демография
[ редактировать ]
Население, плотность и поселения
[ редактировать ]Источник: Управления национальной статистики в 2008 году. Среднегодовые оценки численности населения [7]
| Регион/округ | Население | Плотность населения | Крупнейший город/город | Крупнейшая городская территория |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Большой Манчестер | 2,629,400 | 2016/км 2 | Манчестер (510 700) (оценка 2012 г.) | Городской район Большого Манчестера (2 240 230) |
| Ланкашир | 1,449,600 | 468/км 2 | Блэкпул (147 663) | Престон / Чорли / Лейланда городской район (335 000) |
| Мерсисайд | 1,353,600 | 2118/км 2 | Ливерпуль (491 500) [8] | Городской район Ливерпуля (816 000) |
| Чешир | 1,003,600 | 424/км 2 | Уоррингтон (202 228) | Уоррингтон (202 228) |
| Камбрия | 496,200 | 73/км 2 | Карлайл (71773) | Карлайл (71773) |
Население Северо-Западной Англии составляет чуть более 13% от общей численности населения Англии. 37,86% населения Северо-Запада проживает в Большом Манчестере, 21,39% в Ланкашире, 20,30% в Мерсисайде, 14,76% в Чешире и 7,41% проживают в крупнейшем по площади графстве Камбрия. [7]
Этническая принадлежность
[ редактировать ]
По оценкам Управления национальной статистики за 2009 год , [9] 91,6% (6 323 300) жителей региона называют себя «белыми»: 88,4% (6 101 100) белых британцев , 1,0% (67 200) белых ирландцев и 2,2% (155 000) белых других . Во время промышленной революции сотни тысяч валлийцев мигрировали на северо-запад Англии, чтобы работать на угольных шахтах. Части с особенно высоким населением валлийского происхождения в результате этого включают Ливерпуль , Честер , Скелмерсдейл , Уиднес , Хейлвуд , Уолласи , Эштон-ин-Мейкерфилд и Биркенхед . [10] [11]
Население смешанной расы составляет 1,3% (93 800) населения региона. Здесь проживает 323 800 выходцев из Южной Азии , что составляет 4,7% населения, и 1,1% чернокожих (80 600 человек). 0,6% населения (39 900 человек) составляют китайцы и 0,5% (36 500 человек) принадлежат к другой этнической группе.
North West England is a very diverse region, with Manchester and Liverpool amongst the most diverse cities in Europe. 19.4% of Blackburn with Darwen's population are Muslim, the third-highest among all local authorities in the United Kingdom and the highest outside London. Areas such as Moss Side in Greater Manchester are home to a 30%+ Black British population. In contrast, the town of St. Helens in Merseyside, unusually for a city area, has a very low percentage of ethnic minorities with 98% identifying as White British.[12] The City of Liverpool, over 800 years old, is one of the few places in Britain where ethnic minority populations can be traced back over dozens of generations: being the closest major city in England to Ireland, it is home to a significant ethnic Irish population, with the city being home to one of the first ever Afro-Caribbean communities in the UK, as well as the oldest Chinatown in Europe.[citation needed]
| Ethnic group | Year | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1971 estimations[13] | 1981 estimations[14] | 1991[15] | 2001[16] | 2011[17] | 2021[18] | |||||||
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| White: Total | – | 98.7% | 6,580,840 | 97.5% | 6,480,131 | 96.3% | 6,355,495 | 94.43% | 6,361,716 | 90.2% | 6,347,394 | 85.6% |
| White: British | – | – | – | – | – | – | 6,203,043 | 92.17% | 6,141,069 | 87% | 6,019,385 | 81.2% |
| White: Irish | – | – | – | – | – | – | 77,499 | 64,930 | 61,422 | 0.8% | ||
| White: Irish Traveller/Gypsy | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 4,147 | – | 5,741 | 0.1% |
| White: Roma | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 7,359 | 0.1% |
| White: Other | – | – | – | – | – | – | 74,953 | 151,570 | 253,487 | 3.4% | ||
| Asian or Asian British: Total | – | – | – | – | 174,878 | 2.6% | 256,762 | 3.81% | 437,485 | 6.2% | 622,685 | 8.4% |
| Asian or Asian British: Indian | – | – | – | – | 55,823 | 72,219 | 107,353 | 140,413 | 1.9% | |||
| Asian or Asian British: Pakistani | – | – | – | – | 77,150 | 116,968 | 189,436 | 303,611 | 4.1% | |||
| Asian or Asian British: Bangladeshi | – | – | – | – | 15,016 | 26,003 | 45,897 | 60,859 | 0.8% | |||
| Asian or Asian British: Chinese | – | – | – | – | 17,803 | 26,887 | 48,049 | 54,051 | 0.7% | |||
| Asian or Asian British: Asian Other | – | – | – | – | 9,086 | 14,685 | 46,750 | 63,751 | 0.9% | |||
| Black or Black British: Total | – | – | – | – | 47,478 | 0.7% | 41,637 | 0.61% | 97,869 | 1.38% | 173,918 | 2.3% |
| Black or Black British: African | – | – | – | – | 9,417 | 15,912 | 59,278 | 126,608 | 1.7% | |||
| Black or Black British: Caribbean | – | – | – | – | 21,763 | 20,422 | 23,131 | 25,919 | 0.3% | |||
| Black or Black British: Other | – | – | – | – | 16,298 | 5,303 | 15,460 | 21,391 | 0.3% | |||
| Mixed: Total | – | – | – | – | – | – | 62,539 | 0.92% | 110,891 | 1.57% | 163,245 | 2.1% |
| Mixed: White and Caribbean | – | – | – | – | – | – | 22,119 | 39,204 | 46,962 | 0.6% | ||
| Mixed: White and African | – | – | – | – | – | – | 9,853 | 18,392 | 30,011 | 0.4% | ||
| Mixed: White and Asian | – | – | – | – | – | – | 17,223 | 30,529 | 47,829 | 0.6% | ||
| Mixed: Other Mixed | – | – | – | – | – | – | 13,344 | 22,766 | 38,443 | 0.5% | ||
| Other: Total | – | – | – | – | 24,373 | 0.4% | 13,331 | 0.19% | 44,216 | 0.62% | 110,156 | 1.5% |
| Other: Arab | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 24,528 | 43,865 | 0.6% | |
| Other: Any other ethnic group | – | – | – | – | 24,373 | 0.4% | 13,331 | 0.19% | 19,688 | 66,291 | 0.9% | |
| Non-White: Total | – | 1.3% | 168,695 | 2.5% | 246,729 | 3.7% | 374,269 | 5.6% | 690,461 | 9.8% | 1,070,004 | 14.4% |
| Total | – | 100% | 6,749,535 | 100% | 6,726,860 | 100% | 6,729,764 | 100% | 7,052,177 | 100% | 7,417,398 | 100% |
Place of birth
[edit]The table below is not how many people belong to each ethnic group (e.g. a BBC News article in 2008 claimed there are over 25,000 ethnic Italians in Manchester alone whilst only 6,000 Italian-born people live in the North West).[19] The proportion of people residing in North West England born outside the UK was 11.7% in 2021, compared with 8.2% in 2011 and 5.1% in 2001. Below are the fifteen largest overseas-born groups in the region according to the 2021 census, alongside the two previous censuses:

| Place of birth | 2021[20] | 2011[21] | 2001[22] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 125,110 | 79,289 | 46,529 | |
| 76,688 | 51,999 | 4,864 | |
| 60,180 | 48,676 | 34,600 | |
| 38,379 | 48,456 | 56,887 | |
| 33,918 | 3,052 | 484 | |
| 29,092 | 13,903 | 3,011 | |
| 23,876 | 19,485 | 13,746 | |
| 23,305 | 7,434 | 6,325 | |
| 22,792 | 20,561 | 6,439 | |
| 22,169 | 22,094 | 19,931 | |
| 17,237 | 5,673 | 3,473 | |
| 14,724 | 8,436 | 3,473 | |
| 12,981 | 10,500 | 7,740 | |
| 12,770 | 9,692 | 9,052 | |
| 10,995 | 9,028 | 7,037 | |
| Overall – all overseas-born | 865,445 | 577,232 | 341,593 |
Religion
[edit]| Religion | 2021[23] | 2011[24] | 2001[25] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Christianity | 3,895,779 | 52.5% | 4,742,860 | 67.3% | 5,249,686 | 78.0% |
| Islam | 563,105 | 7.6% | 356,458 | 5.1% | 204,261 | 3.0% |
| Hinduism | 49,749 | 0.7% | 38,259 | 0.5% | 27,211 | 0.4% |
| Judaism | 33,285 | 0.4% | 30,417 | 0.4% | 27,974 | 0.4% |
| Buddhism | 23,028 | 0.3% | 20,695 | 0.3% | 11,794 | 0.2% |
| Sikhism | 11,862 | 0.2% | 8,857 | 0.1% | 6,487 | 0.1% |
| Other religion | 28,103 | 0.4% | 19,166 | 0.3% | 10,625 | 0.2% |
| No religion | 2,419,624 | 32.6% | 1,397,916 | 19.8% | 705,045 | 10.5% |
| Religion not stated | 392,862 | 5.3% | 437,549 | 6.2% | 486,681 | 7.2% |
| Total population | 7,417,397 | 100% | 7,052,177 | 100% | 6,729,764 | 100% |
One in five of the population in the North West is Catholic,[26] a result of large-scale Irish emigration in the nineteenth century[27][28] as well as the high number of English recusants in Lancashire.[citation needed]
Social deprivation
[edit]Of the nine regions of England, the North West has the fourth-highest GVA per capita—the highest outside southern England. Despite this the region has above average multiple deprivation with wealth heavily concentrated on very affluent areas like rural Cheshire, rural Lancashire, and south Cumbria. As measured by the Indices of deprivation 2007, the region has many more Lower Layer Super Output Areas in the 20% most deprived districts than the 20% least deprived council districts.[29] Only North East England shows more indicators of deprivation than the North West, but the number of affluent areas in the North West is very similar to Yorkshire and the Humber.
The most deprived local authority areas in the region (based on specific wards within those borough areas) are, in descending order—Liverpool, Manchester, Knowsley, Blackpool, Salford, Blackburn with Darwen, Burnley, Rochdale, Barrow-in-Furness, Halton, Hyndburn, Oldham, Pendle, St Helens, Preston, Bolton, Tameside, Wirral, Wigan, Copeland, Sefton, and Rossendale.
In 2007 when Cheshire still had district councils, the least deprived council districts in the region by council district, in descending order, were—Congleton, Ribble Valley, Macclesfield, and South Lakeland.[30] These areas have Conservative MPs, except South Lakeland has a Lib Dem and Labour MPs. At county level, before it was split into two, Cheshire was the least deprived, followed by Trafford, and by Warrington and Stockport.
In March 2011, the overall unemployment claimant count was 4.2% for the region. Inside the region the highest was Liverpool with 6.8%, followed by Knowsley on 6.3%, Halton with 5.5% and Rochdale with 5.1%. The lowest claimant count is in Eden (Cumbria) and Ribble Valley (Lancashire) each with 1.3%, followed by South Lakeland with 1.4%.[31]
Elections
[edit]
In the 2019 general election, the Conservatives gained ten seats, from the Labour Party, with no other seats changing hands. Labour held 42 of their 52 seats, albeit many with slimmed down majorities. They remain the dominant party in the region by seat count, with the Conservatives total now standing at 27. The Conservatives made two gains in Cheshire, three gains in Lancashire, five gains in Greater Manchester, notably including Andy Burnham's former seat of Leigh.
In the 2017 general election, the area was dominated by the Labour Party. Fifty-five per cent of the region's electorate voted Labour, 36.3% Conservative, 5.4% Liberal Democrat, 1.9% UKIP and 1.1% Greens; however, by number of parliamentary seats, Labour have 54, the Conservatives have 20, and the Liberal Democrats have 1. The Lib Dems' North West seat is in south Cumbria; Labour dominates Greater Manchester, and the Conservatives' vote is concentrated in affluent suburban areas such as Cheadle, Hazel Grove and Altrincham and Sale West. Labour seats also predominate in Merseyside. In Cheshire the 2015 result was reversed, with Labour winning seven seats and the Conservatives four, whilst Lancashire is competitive between Labour and Conservative (8 seats each); the Labour seats in Lancashire are concentrated in the south of the county along the M65. For the region, the Labour gained 3 seats; there was a 5.2% swing from Conservative to Labour.
In the 2015 general election, Liverpool Walton was the safest seat in the UK, with a 72% majority, and in 2017 this was repeated with a 77% majority for Dan Carden (Labour), when an astonishing 85.7% of the electorate voted for him (the Conservatives came second with 8.6%). In the by-election of 2012, Manchester Central has the record for the lowest turnout in the UK—18%. Gwyneth Dunwoody, for Crewe and Nantwich, was the longest serving female MP until her death in 2008.
In the final European Elections in the UK in 2019, 31.23% voted for the Brexit Party, with Labour polling 21.91%, the Liberal Democrats 17.15% and the Green Party 12.48%. The Conservatives came fifth in the region with 7.55% of votes cast.[32]
Language and dialect
[edit]The earliest known language spoken in the North West was a dialect of the Brythonic language spoken across much of Britain from at least the Iron Age up to the arrival of English in the first millennium AD. Fragments of this early language are seen in the inscriptions and place names of the Roman era. In some parts of the region, the Brythonic dialect developed into the medieval language known today as Cumbric, which continued to be spoken perhaps as late as the 12th century in the north of Cumbria. This early Celtic heritage remains today in place names such as Carlisle, Penrith and Eccles, and many river names such as Cocker, Kent and Eden.
English may have been spoken in the North West from around the 7th century AD, when the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Northumbria first appears to have made inroads west of the Pennines. The language at this time would have been the Northumbrian dialect of Old English. The high percentage of English place names in the region as a whole suggests English became almost ubiquitous over the coming centuries, particularly in the area south of the Lake District. Manchester, Liverpool, Lancaster, Blackburn and Preston are among the region's many English place names. In the 9th to the 11th centuries, Danes from the east and Norsemen from Ireland and Scotland began settling in the area. The North West is really the only area of England where Norse settlement was significant and their influence remains in the place names and dialect of the region. Elements like fell, thwaite and tarn, which are particularly common in Cumbria, are all Norse. The numerous Kirkbys and place names with "holm" and "dale" show the Scandinavian influence throughout the North West.
Through the Middle Ages the dialects of the North West would have been considerably different from those spoken in the Midlands and south. It was only with the spread of literacy (particularly with the publication of the King James Bible) that Standard English spread to the region. Even so, local dialects continued to be used and were relatively widespread until the 19th and 20th centuries.
In modern times, English is the most spoken language in the North West, with a large percentage of the population fluent in it, and close to 100% conversational in it. To the north-east of the region, within the historic boundaries of Cumberland, the Cumbrian dialect is dominant. The historical county of Lancashire covered a vast amount of land, and the Lancashire dialect and accent is still predominant throughout the county, and stretches as far north as Furness in South Cumbria to parts of north Greater Manchester and Merseyside in the south of the region. The region boasts some of the most distinctive accents in the form of the Scouse accent, which originates from Liverpool and its surrounding areas, and the Manc accent, deriving from the central Manchester district. Both of these descend from the Lancashire dialect but have some distinctions from it, especially Scouse. The region's accents are among those referred to as 'Northern English'.
Large immigrant populations in the North West result in the presence of significant immigrant languages. South Asian languages such as Urdu, Hindi and Punjabi are widespread, with the largest number of speakers residing in Preston, Blackburn and Manchester. The Chinese once made up the largest minority in the region (as Liverpool has one of the oldest Chinese settlements in Europe), and still do to the far north where Chinese is spoken by small but significant communities. Since the enlargement of the EU, over one million Poles have immigrated to the UK, a large number of them settling in the North West. Places such as Crewe as well as larger cities make Polish written information available for the public, to much controversy. Other immigrant languages with a presence in the North West are Spanish, mainly amongst the Latin American communities in Liverpool and Manchester,[citation needed] as well as various other Eastern European and Asian languages.
The most taught languages in schools across the North West are English, French and Spanish. German and Italian are available at more senior levels and, in cities such as Manchester and Liverpool, even Urdu and Mandarin are being taught to help maintain links between the local minority populations.[citation needed]
Eurostat NUTS
[edit]In the Eurostat Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS), North West is a level-1 NUTS region, coded "UKD", which (since 2015) is subdivided as follows:[33][34]
| NUTS 1 | Code | NUTS 2 | Code | NUTS 3 | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North West | UKD | Cumbria | UKD1 | West Cumbria (Allerdale, Barrow-in-Furness, Copeland) | UKD11 |
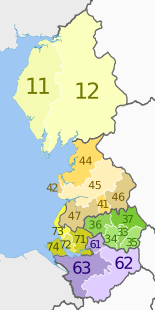 | East Cumbria (Carlisle, Eden, South Lakeland) | UKD12 | |||
| Cheshire | UKD6 | Warrington | UKD61 | ||
| Cheshire East | UKD62 | ||||
| Cheshire West and Chester | UKD63 | ||||
| Greater Manchester | UKD3 | Manchester | UKD33 | ||
| Greater Manchester South West (Salford and Trafford) | UKD34 | ||||
| Greater Manchester South East (Stockport and Tameside) | UKD35 | ||||
| Greater Manchester North West (Bolton and Wigan) | UKD36 | ||||
| Greater Manchester North East (Bury, Oldham and Rochdale) | UKD37 | ||||
| Lancashire | UKD4 | Blackburn with Darwen | UKD41 | ||
| Blackpool | UKD42 | ||||
| Lancaster and Wyre | UKD44 | ||||
| Mid Lancashire (Fylde, Preston, Ribble Valley and South Ribble) | UKD45 | ||||
| East Lancashire (Burnley, Hyndburn, Pendle and Rossendale) | UKD46 | ||||
| Chorley and West Lancashire | UKD47 | ||||
| Merseyside | UKD7 | East Merseyside (Knowsley, St. Helens and Halton) | UKD71 | ||
| Liverpool | UKD72 | ||||
| Sefton | UKD73 | ||||
| Wirral | UKD74 | ||||
Cities and towns
[edit]
|
|
Population > 400,000
|
Population > 100,000
|
Population > 70,000
|
|
Population > 50,000
|
|
Population > 30,000

|
|
Population > 20,000
|
|
Population > 10,000
|
|
Population > 5,000
|
|
Metropolitan areas
[edit]The five largest metropolitan areas in the North West are as follows:
- Greater Manchester metropolitan area – 2,556,000[35]
- Liverpool/Birkenhead metropolitan area – 2,241,000[35]
- Blackburn/Burnley – 391,000[35]
- Preston – 354,000[35]
- Blackpool −304,000[35]
Liverpool and Manchester are sometimes considered parts of a single large polynuclear metropolitan area,[36][37][38] or megalopolis but are usually treated as separate metropolitan areas.[35] In some studies, part of Wigan in Greater Manchester is considered part of the Liverpool metropolitan area.[35]
Politics
[edit]The North West of England has historically been held by the Labour Party.
National politics
[edit]In the 2019 United Kingdom general election, the Labour Party won a plurality of seats in the North West.
Elected regional assembly
[edit]
It is one of the two regions (along with Yorkshire and the Humber) that were expected to hold a referendum on the establishment of an elected regional assembly. However, when the North East region of England rejected having an elected regional assembly in a referendum, further referendums were cancelled and the proposals for elected regional assemblies in England put on hold. The regional leaders' forum, 4NW is based on Waterside Drive in Wigan.
European Parliament
[edit]The former North West England European Parliament constituency had the same boundaries as the Region.
History
[edit]Ten English regions were established by the government in 1994. At that time, Merseyside, which already had its own Government Office, formerly the Merseyside Task Force, was regarded as a separate region. In 1998, Merseyside was merged into the North West region. This action was controversial in some quarters.[39] Regional Government Offices were abolished in April 2011 by the Coalition Government.
Scientific heritage
[edit]Sir Ernest Marsden (of Blackburn) and Hans Geiger conducted the Geiger–Marsden experiment at the University of Manchester in 1909, where the Geiger counter was invented, which demonstrated the existence of the atomic nucleus. Sir J. J. Thomson of Cheetham Hill discovered the electron (given its name in 1891 by George Johnstone Stoney) in April 1897 and received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1906; his son George Paget Thomson would win the Nobel Prize for Physics 1937 for discovering electron diffraction (at the University of Aberdeen). John Dalton, from Cumbria and moved to Manchester, developed atomic theory. William Sturgeon of Lancashire invented the electromagnet in 1825.
Sydney Chapman, a mathematician from Eccles, in 1930 explained the ozone–oxygen cycle in the stratosphere, being the first to propose that atmospheric oxygen or ozone molecules absorb (harmful UVB and UVC) ultraviolet wavelengths of light in photolysis, to produce reactive single atoms which accumulate to form the ozone layer.
Graphene was discovered at the University of Manchester in 2004 under Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov.

At the Calico Printers' Association in Manchester in 1941, John Rex Whinfield and James Tennant Dickson discovered polyethylene terephthalate, known as PET, a common polyester compound found in plastic bottles and food, and also known as Terylene or Dacron. Cheslene and Crepes of Macclesfield discovered crimplene, the fabric that is now referred to as polyester. ICI Dyestuffs at Hexagon House, in Blackley in north Manchester, discovered Procion dyes. At the Winnington Laboratory on 27 March 1933, Eric Fawcett and Reginald Gibson discovered polythene in an ICI laboratory in Northwich, when reacting benzaldehyde with ethene at a pressure of 2,000 atmospheres; the process was improved in 1935 by Michael Perrin.
Halothane, the world's first synthetic inhalation general anaesthetic gas, was discovered in 1951 at ICI's Widnes Laboratory by Wallasey's Charles Suckling, and first tested on a patient in Manchester in 1956; it works by binding to the GABA receptor. John Charnley of Bury invented the hip replacement in 1962 at Wrightington Hospital, Lancashire, north-west of Wigan. Clatterbridge Hospital in Bebington has a cyclotron (linear accelerator), and is the only hospital in the UK to offer proton therapy.
Alderley Park opened in October 1957, and ICI Pharmaceuticals was formed in the same year. In 1962 Dora Richardson of ICI discovered tamoxifen. ICI Alderley Park later discovered Anastrozole, Fulvestrant, Goserelin and Bicalutamide, later made by Zeneca. James Black discovered beta blockers—propranolol (Inderal) at Alderley Park in 1962. The Wellcome Foundation, a provider of much of Britain's medical research, was based from 1966 to 1997 at Crewe Hall in Crewe Green.
Clifford Cocks and James H. Ellis from Cheshire, with Malcolm J. Williamson, invented the RSA (algorithm) in 1973 at GCHQ, used for public-key cryptography. Richard Owen from Lancaster coined the word dinosaur in 1842, and he founded the Natural History Museum, London, opening in 1881.
Industrial heritage
[edit]
The Liverpool & Manchester Railway was the world's first passenger inter-city railway in 1830. Manchester Liverpool Road railway station is the world's oldest surviving railway station, having opened on 15 September 1830; the Stockton & Darlington Railway had opened in 1825. Chat Moss was a problem to constructing the railway, with Edge Hill Tunnel and Sankey Viaduct; the line was bitterly opposed by William Molyneux, 2nd Earl of Sefton. The Bridgewater Canal was the first recognised canal of the modern era. Francis Egerton, 3rd Duke of Bridgewater had visited France and noted their canals. John Gilbert had the innovative idea to use water pumped out of his coal mines to fill a canal from the Duke's Worsley mines to Manchester. It was designed by James Brindley and built in 1761.
The Bridgewater Foundry in Patricroft (Salford), can claim to be the world's first factorywith an assembly line type arrangement in 1836. Joseph Huddart of Cumbria was the first to mechanise the production of rope in 1793. The spinning jenny was invented in 1764 in Lancashire by James Hargreaves, a mechanical advance on the spinning wheel.
The University of Manchester built the world's first programmable computer, the Manchester Baby, on 21 June 1948; the Williams–Kilburn tube on the machine was the world's first computer memory, and the beginning of random-access memory (RAM); the baby computer was made from 550 Mullard valves. The first commercially available computer, the Ferranti Mark 1, was made in Manchester and sold in February 1951 to the University of Manchester. The world's first transistor computer was the Manchester Transistor Computer in November 1953. Atlas was another important computer developed at the University of Manchester, largely developed by Tom Kilburn; at the time in 1962 it was most powerful computer in the world. The government had dropped its financial support of this computer, and was only funded by Ferranti—the total development cost was around £1m. Britain was leading the world at this time in computing, with the only main competitor being IBM; after the mid-1950s America took over the industry. The spreadsheet was invented in 1974, known as the Works Record System, and used an Adabas database on an IBM 3270 at ICI in Northwich; it was developed by Robert Mais and it was around four years before (the more well-known) VisiCalc in 1978. The University of Manchester has collected 25 Nobel prizes, though recent years have been less notable.
Parsonage Colliery at Leigh had the UK's deepest mine—1,260 metres in 1949. Macclesfield was the base of UK's silk weaving industry. John Benjamin Dancer of Manchester invented microphotography in 1839, which would lead to microform in the 1920s. Frank Hornby from Liverpool invented Meccano in 1901, where Meccano Ltd would be based for over 60 years. Bryant & May's site in Garston was the last wooden match factory in the UK, closing in 1994 to become The Matchworks business centre off the A561 west of the former Speke airport. Cottonopolis was the industrial name for Manchester and the local area. Manchester at one time was the world's richest city. The CIS Tower, built by John Laing in 1962, was Europe's tallest building, and Britain's tallest building until 1963, and Manchester's tallest building until 2006.
Kirkby was planned in the 1950s as the largest trading estate in Britain—1,800 acres. Trafford Park is the world's first planned industrial estate. Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers opened their first co-operative outlet on 21 December 1844.

Alastair Pilkington invented the float glass method of manufacture in 1957 at St Helens, announcing it in January 1959. It was manufactured from 1961, and 80% of the world's glass is made with the process; the former site closed in 2014 and it is made now at the Green Gate site. Pears soap, made at Port Sunlight, is the world's first registered brand, and world's oldest brand in existence. Elihu Thomson, born in Manchester who subsequently moved to America, formed Thomson-CSF which became Thales Group in 2000. The British part (British Thomson-Houston) would later become part of GEC; he invented the arc lamp. Henry Brunner from Liverpool would join with Ludwig Mond in the 1860s to form a chemical company which became ICI in 1926. Mossbay Steelworks in Workington, when opened in 1877, were the world's first large-scale steelworks; its austenitic manganese steel (mangalloy) was produced from 1877 until 1974, with Britain's railways converting from iron to steel by the 1880s. Track was made there for the UK's railways (exclusively from the 1970s onwards, with the steel made in Teesside) until August 2006; much of the rails made were exported (from 1882), with its main competitor being Voestalpine of Austria, and a plant (bought by British Steel in 1999) in Hayange, France, who make all of SNCF's railway tracks, and the Katowice Steelworks in Poland. Workington was thought to make the best quality rail track in the world.
Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti, born in Liverpool in 1864, was an electrical engineer who designed the layout for Deptford Power Station, the first alternating current power station in the world in 1887, and whose design all others would follow; his later company Ferranti, of Oldham, would later be an industry leader in Britain's defence electronics, on the FTSE 100 Index. Ferranti's design of increasing AC voltage to high tension at the power station, to be stepped-down at a transformer at substations before entering properties, is the system all electricity networks take today; the system reduces wasteful heating of electricity transmission cables.

The Chain Home radar transmitters were built by Metrovick at its Trafford Park Works, which became part of AEI in 1929, GEC in 1968, and as Alstom it was closed in June 2000. 2ZY, the first broadcasts in the north of England, were made from the Metrovick factory in November 1922, which became part of the BBC National Programme in 1927. GEC opened its first factory in Manchester in 1888, moving to Salford in 1895 at the Peel Works, and had built the Osram electric light company in 1893. The Metropolitan-Vickers F.2 of Trafford Park Works, Manchester was the first axial-flow jet engine, with a nine-stage compressor, first running in 1941. It would end up as the Armstrong Siddeley Sapphire and the American-built Wright J65. The F.2 gas turbine would power MGB.2009 the first gas-turbine-powered vessel in 1947. No. 1 Parachute Training School RAF—the main parachute training site for the war—was at RAF Ringway (the Central Landing Establishment and Airborne Forces Experimental Establishment) now Manchester Airport; many aircraft were built there too, and the Ford Trafford Park Factory built 34,000 aircraft engines—mostly Merlin engines; the nearby Metropolitan-Vickers factory built many Lancasters.
Calder Hall was the world's first nuclear power station in 1956. There are approximately 430 nuclear power stations around the world, and the UK is the third most experienced operator of nuclear reactors after the US and France, and is the world's ninth largest producer of nuclear-generated electricity, with nine stations operating in the UK producing around 10GW. New-build nuclear power stations will either be the AP1000 (Toshiba Westinghouse NuGeneration) or EPR design (developed by Areva). BNFL bought Pittsburgh-based Westinghouse Electric Company in 1999; it was sold in October 2006 for £5.4 billion to Toshiba. British Energy was sold in 2009 for £12.5 billion to EDF; Centrica (British Gas) had also wanted to buy it; 26 Magnox reactors were built in the UK, followed by 14 AGR reactors.
Operation Hurricane on 3 October 1952, Britain's first nuclear bomb, detonated on HMS Plym on the Montebello Islands in the state of Western Australia, was made of plutonium-239 mostly made at Windscale (which began production in 1950), with some possibly from Chalk River Laboratories in Ontario, Canada (where the Tube Alloys project was later moved).

W. T. Glover & Co. of Salford were important electricity cable manufacturers throughout the early 20th century. BAE Systems Wind Tunnel Department at Warton—one of its four wind tunnels—the High Speed Wind Tunnel—can test speeds intermittently up to Mach 3.8 (trisonic)—the second fastest in the UK, to the University of Manchester's Aero-Physics Laboratory which has a hypersonic wind tunnel up to Mach 6. Osborne Reynolds of Owens College (which became the Victoria University of Manchester in 1904), known worldwide for his Reynolds number (introduced elsewhere by the mathematician George Gabriel Stokes), showed in the early 1880s that wind tunnels (invented by Francis Herbert Wenham in 1871) could model large-scale objects accurately. BAE Systems Regional Aircraft assembled Britain's last airliner, the British Aerospace 146 (Avro RJX), at Woodford in November 2001. The Merlin-powered Avro Tudor G-AGPF, which took off from what is now Manchester Airport on 14 June 1945, was Britain's first pressurised civilian aircraft; only 38 were built and it was designed for the North Atlantic route. On 13 May 1949, VN799 the English Electric Canberra first flew from Warton: Warton at the time was a former USAAF wartime maintenance base; the German Arado Ar 234 was technically the world's first jet bomber; the Canberra would be the first jet aircraft to make a non-stop crossing of the Atlantic on 21 February 1951.
Robert Whitehead of Bolton invented the modern-day torpedo in 1866. Sir William Pickles Hartley of Lancashire founded Hartley's Jam in 1871, building a purpose-built village at Aintree. Sir Henry Tate also came from Lancashire, joining Abram Lyle in 1921, of whose Golden syrup tins are claimed to be Britain's oldest brand; he established the Tate Gallery in 1897. Robert Hope-Jones of the Wirral invented the Wurlitzer organ. The Christys' & Co factory in Stockport was the largest hat-making factory in the world in the nineteenth century; it became part of Associated British Hat Manufacturers and is now in Oxfordshire. The company owner's son founded Christy in 1850 in Droylsden (now in Tameside), which invented the industrially produced towel.

Britain's most popular car, the Ford Escort, was made throughout its life (until 21 July 2000) at Halewood by Ford; 5 million were made there from 1967. In 1998, production of its replacement the Focus was transferred to Saarlouis and Valencia, which signalled the end of the site's ownership by Ford. The Jaguar X-Type was first made there in May 2001, until late 2009. In the UK, the Mondeo has sold 1.4m since 1993, and is made in Valencia in Spain.
Starchaser Industries of Hyde is hoping to send a British citizen into space, on a British rocket; BAC at Preston had proposed its MUSTARD re-usable spacecraft in 1964, which although not built had given NASA a concept.
Culture
[edit]

The Suffragette movement came from Manchester—the Women's Social and Political Union. Arthur Wynne, born in Liverpool, invented the crossword in December 1913. On 13 August 1964, Britain carried out its last two executions at Strangeways and Walton Prison. Under the Museums Act 1845, the UK's second and third public municipal libraries were at Warrington in 1848 and at Salford Museum and Art Gallery in 1850; Canterbury had been first in 1847. The first Trades Union Congress was held in 1868 at the Mechanics' Institute, Manchester. The World Pie Eating Championship is held in Wigan each year.
Ann Lee from Manchester started the USA Shakers movement, founded out of the Quakers, which itself has strong links to Pendle Hill in Lancashire. Joseph Livesey of Preston was the founder of Britain's temperance movement, and the word teetotal was first coined in Preston in 1833. The crumbly Cheshire cheese is thought to be the oldest in Britain. Heaton Park in north Manchester is the largest municipal park in Europe. Jelly Babies were invented in Lancaster in 1864, at Fryers of Lancashire. The first KFC outlet in the UK was on Fishergate in Preston in May 1965, opened by the entrepreneur Ray Allen. Oldham claims to be the site of the first fried potatoes in the UK in 1860. The UK's biggest dance music festival takes place on the August Bank Holiday at Creamfields on Daresbury Estate. Ingvar Kamprad's IKEA opened its first UK store in Warrington on 1 October 1987; the UK was the 20th country at the time that IKEA had been established. The International Cheese Awards are held at the end of July in Nantwich.
Liverpool and Manchester, the two largest cities in the North West by population, are known for being the birthplace of beat music (also called "Merseybeat") during the 1960s to 1970s, and the development of the Madchester music scene from the 1980s, and 1990s respectively.
A Taste of Honey was an influential 1960s film set in Salford, depicting working class poverty in ways not previously seen at the cinema, known as kitchen sink realism; Walter Greenwood's Love on the Dole, a 1930s book also set in Salford, was thought by the BBFC to be too sordid a depiction of poverty to be made into a film; Mike Leigh, from Salford, has produced films on a similar subject.
Transport
[edit]
Transport policy
[edit]As part of the national transport planning system,the North West Regional Assembly was, before its abolition in 2008, required to produce a Regional Transport Strategy (RTS) to provide long term planning for transport in the region. This involved region wide transport schemes, such as those carried out by the Highways Agency and Network Rail.[40] Within the region, the local transport authorities plan for the future by producing Local Transport Plans (LTPs) which outline their strategies, policies and implementation programmes.[41] The most recent LTP is that for the period 2006–11. In the North West region, the following transport authorities have published their LTP online: Blackburn with Darwen U.A,[42] Blackpool U.A.,[43] Cheshire,[44] Cumbria,[45] Greater Manchester,[46] Halton U.A.,[47] Lancashire,[48] Merseyside[49] and Warrington U.A.[50] Since 1 April 2009, when the county of Cheshire was split into two unitary councils[51] the Cheshire transport authority ceased to exist, however it is the most recent LTP for the area.
Road
[edit]
Regionwide
[edit]
Regionwide, the principal road link is the M6, which enters the region, from Scotland, near Carlisle in the north and leaves it, for the English Midlands, near Crewe in the south. It connects such towns and cities as Penrith, Kendal, Lancaster, Preston, Warrington, Liverpool and Manchester. The M6 intersects many of the North West's motorways and A-roads, carrying almost 120,000 vehicles per day (41,975,000 per year).[52]
Britain's most severe steep road is Hardknott Pass in Cumbria and the highest road in the UK is the former A6293 at 2,780 ft at Milburn, Cumbria; the highest classified road in England was the A689 east of Nenthead in Cumbria on the Durham boundary.

Greater Manchester and Merseyside
[edit]
The Greater Manchester and Merseyside areas are home to almost 4 million people; over half of the region's population. The road networks intertwining these metropolitan areas are extremely important to the economy and are largely motorway, including the M62 which crosses the entire country (east to west, Hull to Liverpool); this motorway directly connects the cities of Manchester and Liverpool, carrying 78,000 vehicles in the North West per day.[53]
The Merseyside-Manchester region has many other motorways that serve many millions on a daily basis: the M61 connects Manchester to Preston; the M56 runs south of Manchester to Cheshire and Wales; the M57 and M58 motorways run north of Liverpool and connect towns such as St. Helens and Wigan; the M60 is Manchester's ring road; and the M67 and M66 motorways run east and north respectively, both of these roads are under 10 mi (16 km) and link Manchester to smaller outlying settlements. On top of this there are countless numbers of A-roads, B-roads and minor roads which circle, entwine and serve these two major metropolises.
Cumbria
[edit]
In Cumbria the M6 runs all the way down the east of the county connecting the very north of England to the Lancashire border. The A590 links Barrow-in-Furness to Kendal with around 14,000 vehicles per day.[54] The A595 runs all the way along the West Cumbrian coast beginning near Barrow and ending in Carlisle, linking towns such as Whitehaven and Workington. The A591 road runs from Kendal to the centre of the county connecting Lake District settlements like Windermere, Ambleside and Keswick. Other important A-roads include the A5092, A66, A596 and formerly the A74, until this was upgraded to motorway standard as an extension of the M6 between 2006 and 2008 to meet the A74(M) at the Scottish border.
Lancashire
[edit]The Lancashire economy relies strongly on the M6, which also runs from north to south (Lancaster to Chorley). Other motorways in the region include the M55, which connects the city of Preston and the town of Blackpool at 11.5 mi (18.5 km) in length. The M65 motorway runs from east to west, starting in the town of Colne, running past Burnley, Accrington, Blackburn and terminating in Preston. The Lancaster-Morecambe area is served by the A683, A6, A588 and A589 roads. The Blackpool-Fylde-Fleetwood area is home to the A583, A584, A585, A586, A587 and A588 roads. The city of Preston and its surroundings are served by the A6, A59, A582, A583, A584 and, to the very south-east, the M61 motorway. To the east of the county are the A59, A6119, A677, A679, A666, A680, A56, A646 and A682. The M66 begins 500 m (0.3 mi) inside the county border near Edenfield, providing an important link between east Lancashire and Manchester.
Cheshire
[edit]In Cheshire, there are four motorways: the M6, the M56 (linking Chester to the east), the M53 (linking Chester to Birkenhead) and the M62, which runs just along the county's northern border with Merseyside and Greater Manchester. The Cheshire road system is made up of 3,417 mi (5,499 km) of highway and the principal road (M6) carries 140,000[55] vehicles in the county daily, linking the North West to the West Midlands.
The county town of Chester is served by the A55, A483 and A494 roads, amongst others. To the west of the M6, Crewe, Northwich and Sandbach are served by the A54, A51, A49, A533, A556 and A530 roads; these all eventually link up connecting the towns to the larger cities, including Stoke-on-Trent to the south. To the east of the M6 in Cheshire lies the Peak District and towns such as Macclesfield and Congleton, which are served by the A6, A537, A536, A34, A523 and A566 roads.
Air
[edit]


The biggest international airport in the region is Manchester Airport, which serves 28.2 million passengers annually; more than some of the world's major aviation hubs. The airport is home to three terminals, plus the World Freight Terminal, which serve destinations worldwide. The largest airlines at the airport (in terms of numbers of flights in 2007) were Flybe, BMI, British Airways, Jet2.com and Lufthansa; several long-haul carriers such as American Airlines, Delta Air Lines, Virgin Atlantic, Singapore Airlines and Emirates also operate from the airport. Manchester Airports Group is owned approximately one-third by Manchester Council and one-third by the other nine Greater Manchester councils. In 2007, Manchester had a recorded 222,703 aircraft movements.[56] The airport is also a hub for major holiday airlines such as First Choice Airways and Thomson Airways; it was previously served by Thomas Cook Airlines and Monarch Airlines.
The region's second largest airport, but is the oldest and fastest growing, is Liverpool John Lennon Airport, which serves over 5 million passengers annually. The airport serves destinations primarily in the UK and Europe and is a major hub for EasyJet and Ryanair.
The only other significant passenger airport in the region was Blackpool Airport, which was refurbished in 2006 and handled around half a million passengers annually. Destinations ranged from the Canary Islands in Spain to the Republic of Ireland. Commercial flights ended there in March 2017.
- Cumbria
- Barrow/Walney Island Airport – Operated by BAE Systems Submarines, private use
- Carlisle Lake District Airport – Operated by Stobart Group, public use
- Greater Manchester
- City Airport Manchester – Operated by City Airport Manchester Ltd, public use
- Manchester Airport – Major international airport operated by Manchester Airport Group, destinations worldwide
- Woodford Aerodrome – Operated by BAE Systems Regional Aircraft, now closed
- Lancashire
- Blackpool Airport – Operated by Balfour Beatty, public use (commercial flights withdrawn)
- Warton Aerodrome – Operated by BAE Systems, private use
- Merseyside
- Liverpool John Lennon Airport – International airport operated by Liverpool Airport plc, destinations worldwide
- RAF Woodvale – Operated by the Royal Air Force, military use
- Southport Birkdale Sands airstrip – Sand runway located on Southport beach (infrequent use, subject to prior permission)
Rail
[edit]

The main connection by train is the West Coast Main Line, connecting most of the North West. Other important lines are the Liverpool to Manchester Lines and the North TransPennine, which connects Liverpool to Manchester through Warrington. East-west connections in Lancashire are carried via the Caldervale Line to Blackpool. Liverpool and Manchester both have extensive local passenger rail networks operating high-frequency commuter trains. The quietest railway station in the region, by usage, is Reddish South, the 4th quietest in Britain.
The InterCity branded service in the UK began between London and Manchester in the mid-1960s; the new Euston station opened in 1968. With the new electrification of the line in the late 1960s, passenger numbers doubled.
The region saw the last steam-train service on the UK network – the Fifteen Guinea Special on 11 August 1968, withthree Black Five locomotives.
Water
[edit]- Mersey Ferry Royal Daffodil
- Liverpool Cruise Terminal
- Leeds and Liverpool Canal
- Isle of Man Steam Packet
- Isle of Man Steam Packet route map
- MS Norbay operates Liverpool to Dublin

Sea ferries depart from the following ports: Port of Liverpool (Gladstone Dock), Bootle to Dublin (P&O Ferries) and Douglas on the Isle of Man (Isle of Man Steam Packet); Birkenhead (Twelve Quays Terminal) to Belfast and Dublin (Norfolkline Irish Sea Ferries – former Norse Merchant Ferries); Fleetwood to Larne (Stena Line) in Northern Ireland; and Heysham Port to Douglas (Isle of Man Steam Packet).
The world's first hovercraft service took place on 20 July 1962, from Leasowe (Moreton) to Rhyl, operated by British United Airways in a Vickers-Armstrongs VA-3, powered by two turboprop engines.
Leeds and Liverpool Canal has run into Liverpool city centre, via Liverpool Canal Link at Pier Head, since 2009.
Liverpool Cruise Terminal in the city centre provides long-distance passenger cruises; Fred. Olsen Cruise Lines, MS Black Watch and Cruise & Maritime Voyages MS Magellan all use the terminal to depart to Iceland, France, Spain and Norway.

Economy
[edit]The North West is historically linked with the textiles industry, mainly before the mid 20th century. The Greater Manchester region produces the most economic output according to GVA in 2014 with £57,395m, followed by Merseyside £28,257m, Lancashire with £27,668m, Cheshire £25,803m and Cumbria with £10,747m.
According to research by Cushman & Wakefield in 2008, Manchester is the second best city to locate a business in the UK whilst Liverpool is the eleventh best city.[57] The Financial Times stated that the North West economy, led by the redevelopment of Manchester and Liverpool, is a genuine rival to "overheated London".[58]
The area's electricity, formerly looked after by MANWEB and NORWEB, is now looked after by ScottishPower Energy Networks and United Utilities respectively. The Morecambe Bay gas field provides 6% of the UK's natural gas.
Cheshire
[edit]This section has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|


Cheshire is linked with the salt industry. AstraZeneca, the fifth largest pharmaceutical company in the world, has a manufacturing site in the north-east of Macclesfield on Hurdsfield Ind Est (former ICI Pharmaceuticals) off the A523, where it makes Zoladex (goserelin); it was formerly ICI until June 1993 when it became Zeneca. Vauxhall, home of the Astra, is on a former airfield next to the M53, and Essar Energy (former Shell, partly in Thornton-le-Moors) are in Ellesmere Port. Industrial inspection organisation SGS UK is based on junction 8 of the M53 at Rossmore Business Park. Innospec (former Octel) is west of the refinery near junction 9 of the M53 (A5032); Innospec also has a site at Widnes (former Aroma Fine Chemicals) which makes Lilestralis. Encirc Glass (former Aventas group) make glass bottles to the east of the refinery at Elton; the Shell Technology Centre on the southern side of the railway, off the A5117 and the M56 Hapsford Interchange on the east side of the refinery, closed in 2014; to the east is the large site of CF Fertilisers UK (former Shellstar) who make the Nitram brand of fertiliser.
Lex Autolease, the UK's largest vehicle leasing company, is in the east of Chester, towards Hoole. Ball Packaging Europe is based on the A483 at Chester Business Park, near the A55 junction in Eccleston, which has a main office of Marks & Spencer; east of M&S, south of the A55 bypass is Sira, which issues ATEX product approvals. To the north at Dunkirk at the end of the M56 on the A5117, is Max Spielmann (including the former Klick) in Lea-by-Backford; further north at Capenhurst, next to the railway, Urenco Group have a uranium enrichment plant, partly in Ledsham. Sandbach used to be home of ERF and Fodens trucks. Tata Chemicals Europe (former Brunner Mond) next to the A530, next to the railway, is partly in Lostock Gralam just west of Northwich; there is another main site at Winnington on the A533 north-west of Northwich. British Salt is in Middlewich; Bisto used to be made there by Centura Foods (RHM), but production moved to Worksop (Nottinghamshire) in 2008. Henkel UK (the consumer adhesive division, maker of Pritt and Sellotape) is on the Winsford Ind Estate in the east of Winsford, home of the UK's largest salt mine at Meadowbank run by Salt Union, who are owned by Compass Minerals.
Mornflake is in Crewe on the B5071, Focus closed in July 2011, and Orion Optics make telescopes. Bentley Motors (owned by Volkswagen since 1998) have their main plant in the west of the town between the A530 and A532, next to the railway to Chester. Crewe Works built the HST (Class 43) power cars, and now carries out maintenance for Bombardier. Unipart Rail is on the B5071 next to Crewe railway station. Bargain Booze is at the A532/A5020 roundabout in the east of the town, and further along the A532 Whitby Morrison are the world's leading manufacturer of ice cream vans. Air Products have a main HQ off the A534 in central Crewe near the Virgin Trains training academy. UK Fuels (fuel cards) are off the A532, north of Crewe railway station.
BAE Systems Global Combat Systems at Radway Green, Barthomley north of M6 junction 16, south of Alsager makes small arms ammunition, and Freshpack make pies next to the A5011 towards the east of the town; Twyford Bathrooms (owned since 2001 by the Finnish Sanitec) are off the B5077, but their enormous factory next to the railway closed in early 2011, with production moving overseas. Amec is south of Knutsford at Booths Hall off the A537, now the HQ of Amec Foster Wheeler; also in the town is Edmundson Electrical. Between Knutsford and Wilmslow in Mobberley off the B5085, close to the southern approach of Manchester Airport, is a large site of Harman Technology (known worldwide as Ilford Photo). Four Seasons Health Care is in central Wilmslow; north of the town on the A538 is a large £60m mass spectrometry research site of the Waters Corporation, built in 2014 on a former research site of Ciba-Geigy Pharmaceuticals (who formed Novartis in 1996), next to the River Bollin. Pets at Home is next to the railway at Handforth near Wilmslow and the Stockport boundary near Handforth Dean (A34). Boalloy Industries are on Radnor Park Ind Est in West Heath in west Congleton north of the A534/A34 junction, make trailers, and pioneered the Tautliner curtain-sided trailer design in the 1970s. Reginox UK (kitchen sinks) are in the north of Congleton; Siemens Industry Automation & Drive Technologies UK make variable-speed drives, exporting 98% of production, on Eaton Bank Trading Est near the River Dane. OK Diner is in Macclesfield (previously in Middlewich); Tullis Russell at Bollington makes the paper for all Royal Mail stamps, and has done for many years.

Ineos Fluor (the site was previously owned by ICI Chemicals) is at Runcorn which produces chlorine and caustic soda from Cheshire salt, piped from Lostock Gralam, south of Northwich; most of the chlorine in the UK comes from this plant; it also makes hydrofluoroalkanes (HFAs) for metered-dose inhalers and the anaesthetic halothane. There is Ineos Chlor and Ineos Vinyls. BNFL and its subsidiary Sellafield Ltd (former British Nuclear Group), and ABB are based in Daresbury near Runcorn, although most of BNG's operations take place at Sellafield in Cumbria. Daresbury is also home of the EMMA and ALICE FFAG accelerators. Diageo bottles Guinness at Preston Brook, between the A56 and A533, and nearby Saint-Gobain UK make Isover insulation. Kawneer UK (part of Alcoa) make architectural aluminium systems (curtain walls) off the A533 at Astmoor in north Runcorn. APPH (aircraft undercarriage) is based off the A558 on Manor Park in Sandymoor near TALL Security Print, the UK's leading provider of business cheques; further to the west is Yokogawa Electric UK. Schachihata UK (Xstamper and Artline) are based at Ashville Ind Est on the A557 at junction 12 of the M56 next to the Weaver Navigation and the 3,200 ft Weaver Viaduct south of Runcorn towards Sutton Weaver. Croda Enterprise Technology Group does its important R&D in Halebank, Widnes, south of Ditton. The Thermphos factory on the A557 south of Widnes closed in 2013.
United Utilities is based in the west of Warrington at Lingley Mere Business Park in Great Sankey, next to the St Helens boundary; in Lingley Green to the south on the A57 was the former HQ of North West Water; to the north, Amazon have a fulfilment centre. Unilever makes Persil and Surf washing powders next to the Bank Quay railway station; next door between the A5061 and River Mersey is PQ Silicas (former Joseph Crosfield). Cogent Skills (the UK's SSC for science) is in the south of Warrington off the A5060, on the other side of the railway from Bank Quay. New Balance UK is at Centre Park, off the A5060 in south-west Warrington, with a factory at Flimby, on the Cumbria coast. Konftel UK is at Thelwall. ASICS UK (sportswear) is on the Gemini Business Park, off the A574 in Burtonwood and Westbrook north of Warrington, next to the M62 and a large IKEA and M&S on Gemini Retail Park; next door is KYB UK, part of the world's largest (Japanese) manufacturer of shock absorbers; nearby is Krauss-Maffei UK (injection moulding machines); AlphaBiolabs provide the DNA paternity testing for The Jeremy Kyle Show on Carina Park in Westbrook.[59]
Burtonwood Brewery (the HQ of Thomas Hardy Burtonwood, who developed Britain's alcopop drinks in the 1990s) is on the B5204 in the west of Burtonwood, towards St Helens borough. Birchwood Park has to be the main technical business park in the North West. The Bank of England MPC's Agency for the North West is on Birchwood Park near the HQ of GB Oils, the UK's leading fuel oil supplier (owned by DCC), and the operator of Gulf Oil petrol stations in the UK. Electricity North West (the North West's distribution network operator) is near by, with ESR Technology, who did work for the Philae space probe and owns the National Centre of Tribology at Whittle House in Risley, with TalkTalk Business to the west, near International Nuclear Services and Sellafield Ltd at Hinton House. Terberg Matec UK (Dutch) supply lifts for bin wagons next to M62 junction 11. Also west of the park is Nuvia UK (part of Soletanche Freyssinet). Betfred (having the largest turnover in the region—£13.3bn) is at the western end of Birchwood itself, next to the M6 and Birchwood railway station. Birchwood was built on the former ROF Risley.
Lancashire
[edit]This article may contain an excessive amount of intricate detail that may interest only a particular audience. Specifically, move to Lancashire#Economy. (May 2023) |

The ONS 2010 Annual Business Survey states that 30.3% of jobs in the British aerospace industry are based in Lancashire.[60] The main private employer in the county is BAE Systems Military Air & Information who have two sites east and west of Preston for the manufacture of military aircraft. Samlesbury (4000 employees) makes air-frames; the front fuselage, canards and tailfin of the Eurofighter. Warton, BAE Systems' main site (former English Electric, then BAC), is in Bryning-with-Warton (6500 employees).[61] BAE builds a Eurofighter every two weeks (takt time). Rolls-Royce make turbofan blades in Barnoldswick (950 employees).[62] Nearby Weston EU manufacture components in Foulridge (250)[63] and engine maintenance contractor Euravia are in Kelbrook (100).[64] Safran Aircelle make engine nacelles and thrust reversers in Burnley (800), and mostly make thrust reversers for the Trent 700.[65] GE subsidiary Unison Engine Components (320),[64] are the largest of several others in the area.
Westinghouse (BNFL) make nuclear fuel at the Springfields site at Salwick, off the A583 in Newton-with-Clifton. The boiler firm BAXI have a factory in the south of Preston, and next door, Assystem UK (engineering consultancy) are off the B5258 in Bamber Bridge. AB InBev have a brewery on the B6230 in nearby in Samlesbury (former Whitbread, and brews Stella Artois); further east the BAE Systems factory is between the A677 and A59, mainly in Balderstone. To the north-east of Preston, Bodycare Group make toiletries at the Red Scar Business Park on the B6243, near junction 31a of the M6, where Goss International UK make printing presses. Webb Ivory (charity fundraising, owned by Findel plc) is off the A6 in Avenham, in the south of Preston. Alstom Transport (former GEC Traction) is at TLS Preston; company's main Trafford Park site closed in the early 1990s. Bosal was the UK's leading manufacturer of car exhausts on Walton Summit, between the M6 and M61 until they closed operations. The Pilkington European Technical Centre is at Lathom.
Voith Paper has a site in Stubbins, at the northern end of the M66, off the A676. Silentnight (600)[64] is in Barnoldswick, where Hope Technology make mountain bike components; nearby Johnson Matthey makes automotive catalysts. At Whitworth on the A671, BCH engineer equipment for the food processing industry (Nestlé and Mars).
Brands originating in Lancashire include TVR, Reebok, Jaguar Cars and Warburtons. Leyland Trucks manufactures several truck ranges from Leyland, home of Enterprise plc, and where Albion Automotive (part of American Axle) make crankshafts at Farington. CCA Occasions makes greeting cards on the B5253 on the Moss Side Ind Estate and nearby Dr Oetker makes Chicago Town and Pizza Ristorante pizzas (330);[66] 40% of the UK's frozen pizzas are made here, and the Pizza Ristorante brand, solely made in Lancashire, is Italy's best-selling frozen pizza with 20% of the Italian market.[67] Nearby, Nitecrest is the UK's leading manufacturer of gift, payment, loyalty and phone cards, and exports most of its products.
Walker's make Monster Munch at junction 5 of the M58 on the Pimbo Ind Est in Up Holland; nearby SCA Hygiene has their Skelmersdale Mill which makes kitchen towel, with Uretek UK (polyurethane). To the east is Frederick's Dairies in East Pimbo, who make Cadbury's ice creams, near TAAG Steelwork, who built the Olympic Energy Centre. To the west, Turtle Wax Europe are next to M58 junction 4 on Gillibrands Ind Est. The Co-operative Bank are administered from Delf House in the centre of Skelmersdale.
Victrex make PEEK (a thermoplastic) just north of Blackpool at Cleveleys. Next door, AGC Chemicals Europe,[68] owned by Asahi Glass Co., makes ETFE (fluon) for electrical wire insulation, and silica gel off the B5268 at Thornton-Cleveleys. HTI Group in Fleetwood makes toys and owns Barbie.
Ennis Prismo make traffic white line products at Chorley; Walmsleys is a paper manufacturer off the A675 in Withnell. DXC Technology (former CSC) have sites in Chorley and Preston. Along the M65, Fort Vale based in Simonstone (near Burnley) (300) are a world leader in valves and fittings for road tankers.[69] Close by, office furniture manufacturer Senator International (800)[64][70] are the largest in the UK in their field. Off the A646 in Habergham Eaves, east of Burnley, is AMS Neve, a renowned manufacturer of audio mixing desks. Telecoms provider Daisy Group (former Pipex, 400),[64] based in Nelson is one of the UK's fastest growing companies, on Lomeshaye Ind Est north of M65 junction 12 in Brierfield;[71] Cott Beverages (former Macaw Soft Drinks before 2006) is off junction 12 of the M65 in Brierfield, west of Nelson, next to Pendle Water. Jura UK (Swiss coffee machines) is off the A6068 in Colne. At Horrocksford near Clitheroe, Hanson Cement have their large Ribblesdale Cement works, next to the River Ribble, which supplied construction of the Liverpool Metropolitan Cathedral. Bensons for Beds (previously in Burtonwood near Warrington) and Sleepmasters (both owned by Steinhoff International) are in the north of Accrington, off junction 8 (A56) of the M65, near Huncoat railway station. Kleeneze (owned by Findel plc) is based with Express Gifts off the A678 in Clayton-le-Moors off the M65 Hyndburn Interchange between Blackburn and Burnley, north of Accrington with a main distribution centre off the A679 in Church on the other side of the M65 in the west of Accrington, with both sites next to the Leeds-Liverpool Canal. Off the A678 near the River Calder in Altham (north east of Clayton le Moors) is Senator who claim to be the UK's largest manufacturer of office furniture; Simon Jersey designed and made the Team GB clothing for the 2016 Olympics opening and closing ceremonies.
In Blackpool is the Federation of Small Businesses (FSB), Amber Taverns, Premium Bonds and National Savings and Investments. Dennis Eagle makes bin wagons in Marton; Tangerine Confectionery are based at Little Marton, with another factory to the east, just south of the main government building site. The Service Personnel and Veterans Agency (MoD's pensions, former Veterans Agency) is off the A585 in east Blackpool at the B268 roundabout at Norcross in the south of Anchorsholme. The NS & I office of Blackpool is on the A583, off the M55 Marton Circle, in Little Marton on the eastern edge of the town. Disability Living Allowance, replaced by Personal Independence Payment, is administered by the DWP, with the Disablement Services Authority at Warbreck House west of the A587, accessed from the B5265 and next to Bispham High School. At the end of the M55 (junction 4) off the A5230 in Westby-with-Plumptons is DWP's large Peel Park Control Centre, on the Blackpool boundary. Amber Taverns is near Blackpool North railway station. To the north of Peel Park, next to the Clifton Retail Park in Mereside is Glasdon (roadside furniture), off the A583.Burton's Biscuit Company (owned since November 2013 by the Ontario Teachers' Pension Plan) have many head office functions in Layton, Blackpool and a factory off the B5124, in the south of Warbreck, next to the railway line, which makes Maryland Cookies, Cadbury Fingers and Wagon Wheels (with another main factory in Torfaen, south Wales); it is the UK's second largest biscuit maker and was founded in Blackpool.
Crown Paints is in Darwen (500).[64] DS Smith have the Hollins paper mill just south of junction 4 of the M65, off the A666 in Darwen, which is set to close. Across the M65 to the north Apeks make diving equipment at Blackamoor. Graham & Brown at Blackburn make fancy wallpaper, next to the Leeds & Liverpool Canal, and off the A6077 is CWV (Coloroll and Crown Wallpaper); Capita Group runs TV Licensing in the middle of the town; Lucite International has its main plant on the A666 in the north of the town centre, where it makes Lucite; this site, under ICI Acrylics, manufactured the perspex for wartime aircraft canopies from 1940, becoming Ineos Acrylics from 1999 until 2002 and the company is the world's largest manufacturer of methyl methacrylate (MMA); ICI Acrylics invented the process to make perspex in 1936; the granular form of Perspex was known by ICI as Leukon. Tensar International, invented and manufacture geogrids for construction, off the A6077 near junction 5 of the M65 in Blackburn near the B6231 roundabout; nearby is Castle Metals UK; also on the Shadsworth Business Park is Evertaut, who make auditorium seating.
Greater Manchester
[edit]Tyco UK is based on the A62 in Newton Heath. Joseph Holt's Brewery is off the A665 next to Strangeways prison; Boddingtons' Strangeways Brewery closed in 2006. Avecia (biotechnology) is off the A664 in the Hexagon Tower in Blackley near the North Manchester General Hospital. North of the hospital at Crumpsall was B3 Cable Solutions, the UK's only former manufacturer of telecommunications cables, based next to the River Irk. Heineken (former Scottish & Newcastle) have their large Royal Brewery in Moss Side next to the A5103, north of the B5219 junction. Admiral Sportswear are in Northenden. British Textile Technology Group is in Didsbury. Timpson is in Wythenshawe; Sharwood's used to make their sauces there until Premier Foods moved production to Bury St Edmunds in 2008. Duerr's make honey and jam at the Roundthorn Ind Estate in Wythenshawe, off the A560.
Shell UK (retail) was at Rowlandsway House in Wythenshawe until 2011 and has moved to Brabazon House nearby on the Concord Business Park; Royal Dutch Shell, by revenue ($458bn) in 2010, was the world's largest company, with ExxonMobil second. Electrium make their Wylex fuse boxes on the B5168 and B5166 in Wythenshawe, north of the Sharston Interchange of the M56; to the west is a plant of the Heimbach Group. PZ Cussons (formerly in Cheadle Heath) is off the Airport Interchange of the M56, with a manufacturing site on the former Agecroft Colliery next to the railway in Pendlebury, Salford, off the A6044. Nearby in Moss Nook is Franke UK, the world's largest manufacturer of domestic sinks and Simon Carves (process engineering), and Renold plc is an international chain company based on the B5166, off the Manchester Airport spur of the M56. Amazon have a fulfilment centre off the A538 west of the airport, south of the Hale Four Seasons Roundabout of the M56.
N Brown Group (JD Williams) is one of Britain's main clothing manufacturers and retailers, and based incentral Manchester near the A62/A665 junction and Sir Owen William's Daily Express Building, and owns well-known brands. Gazprom Energy is on Quay Street (A34) towards the River Irwell.

JJB Sports is at Marsh Green near the River Douglas, set up by former footballer Dave Whelan who owns Wigan Athletic F.C.; also in Wigan are The Tote, Shearings Holidays and Girobank, and R&R Ice Cream (former Richmond Foods) make De Roma ice cream. Contitech UK (part of Continental AG) makes industrial belts off the A587 in Bickershaw, between Wigan and Leigh. Bulldog Tools make spades on the A577 in the east of Wigan. Electrium (Volex) make electrical wiring off the A578, north of Westleigh. Ainscough Crane Hire is the UK's largest lifting services company on Bradley Hall Est in Standish, next to the WCML. Off the A580 at the A573 roundabout at Golborne, at Stone Cross Park south of the borough, is Alpla UK (plastic bottles) and Sofology (furniture).
Makro is in Eccles. Akcros Chemicals are off the A576. Cooper & Stollbrand make premium garments next to the River Irwell on Cambridge Ind Est in Lower Broughton. On the Bolton boundary in north of the borough in Little Hulton, Eaton Transmissions closed in 2006, with production moving to Tczew in Poland. Colgate closed its toothpaste factory in October 2008, on the A5066, and is now called Soapworks, near the former Pomona Docks in Ordsall. Pentair Safety Systems have a main site in Linnyshaw, west of the M61 Worsley Braided Interchange.

Sock Shop is in Bolton, and MBDA (Matra BAe Dynamics Alenia, owned 37.5% by BAE Systems) makes missiles in Lostock near the Horwich Link Interchange of the M61; it is the historic main manufacturing site of Britain's aircraft-launched missiles; MBDA Lostock is MBDA's largest production site (of the whole company) and makes the air-to-air ASRAAM (found on the Eurofighter) and the air-to-surface active radar homing Brimstone (missile) designed by GEC-Marconi in the 1990s, and previously made the Rapier surface-to-air missile, and the De Havilland Firestreak, Britain's first (infrared homing) air-to-air missile. Cash Generator is south of the borough off the A575 in Farnworth, north of the Salford boundary; Cosatto (nursery equipment) is on the A575 Moses Gate, in East Farnworth. dabs.com, an e-commerce site owned by BT, is in Wingates (Westhoughton), west of Bolton off the A6 and the Horwich Link Interchange of the M61, next to Krones UK (German) on the Wingates Ind Est, which produces machinery for bottling manufacture; nearby is a hologram factory of De La Rue. Benteler UK (carbon steel tubes) is next to the River Croal off the A58 at Tonge Moor next to Astley Bridge in north Bolton and to the south PMT Industries makes paper drying machines. Watson Steel Structures (Severfield, opposite MBDA in Lostock) built steel structures for Olympic Stadium, the Velodrome, the Basketball Arena, the ArcelorMittal Orbit, and the Handball Centre, as well as numerous well-known steel structures around the UK, such as Aspire, and the Clyde Arc.
BAE Systems built aircraft in Chadderton and Woodford in Stockport (former Avro) off the A5102 (the eastern half of the airfield is in Cheshire East); the BAe 146 (Avro RJ) was manufactured at Woodford until 2001. Senior Aerospace BWT at Adlington, Cheshire off the A523 at the eastern end of Woodford Aerodrome, make air-conditioning systems for business jets. DNV UK (engineering standards), National Tyre Service (at the A5145/A6 junction) and Britain's first internet bank Smile (founded by the Co-op in 1999) are nearby in Stockport. Wienerberger UK, the Austrian brick company who own Baggeridge, are based at the Cheadle Royal Business Park at the B5358/A34 junction, as is Umbro, and Agilent Technologies UK (biomedical equipment), and Chiesi UK (respiratory medicine). DBS Civilian HR (the former Pay and Personnel Agency) is off A555 at Cheadle Hulme. Adidas UK is in Bramhall Moor, Hazel Grove off the A5143, and further south is NXP Semiconductors UK which make MOSFETs; on the opposite side of the railway is MAN Diesel & Turbo, which is next to Stepping Hill Hospital. BASF UK is in Handforth next to the A34/A555 junction on the Cheshire boundary. Thales Underwater Systems (former Ferranti Thomson Sonar Systems) is in Cheadle Heath. McVitie's make their Jaffa Cakes, Penguins and chocolate digestives at a factory in South Manchester on the A6.[72] JYSK UK (mattresses) are off the A523 near the A6 junction. Pilkington's Tiles are based on Bredbury Park Ind Est, near a main factory of Renold Chain on the A6017 off the M60 Bredbury Interchange; also in Bredbury off the A6017 is Janome UK (sewing machines).
Russell Hobbs is in the south of the borough at Failsworth on the A62, west of the M60 Hollinwood Interchange; nearby to the Hollinwood railway station in Oldham, Trinity Mirror (former Mirror Colour Print before 2006) prints the Mirror and Independent for the north of England, as well as the Manchester Evening News and Liverpool Echo. Diodes Semiconductors (former Zetex) based off the A669 in Alder Root, Chadderton, is a leader in LED lighting. Money Controls, in Royton in the north of the borough, make currency detectors, being owned by Crane Payment Solutions, and Pulse Home Products (makes Breville, owned by Jarden in Florida) is on the B6195. BAE Chadderton was next to the M60 and B6393, and a railway, and closed in March 2012; later a repair facility, it built the Lancaster and Vulcan. Mölnlycke Health Care UK on the B6194 in central Oldham make surgical clothing and masks. Shop Direct have their Shaw National Distribution Centre.
Revolution Bars Group (former Inventive Leisure before December 2014), who own the Revolution pub chain, are in Ashton-under-Lyne. Kerry Foods at Godley Hill (Hyde) on the A57 make Richmond and Wall's sausages. Robertson's (now owned by Premier Foods since it was bought from Rank Hovis McDougall) moved their marmalade (Golden Shred) and jam processing from Droylsden to Histon (Cambridgeshire) in October 2008. Brother Europe (typewriters and sewing machines) are at Hooley Hill on the A6017 next to Guide Bridge railway station, east of the Snipe Interchange of the M60. Outdoor Sports Company owner of Mountain Equipment, Ronhill (running clothing), and Sprayway, are based off the B6468 in Hyde.
Cotton Traders are in Altrincham, and Dulux Decorator Centres is in West Timperley. Britannia Hotels is on the A538 in Hale near the A5144 junction. LyondellBasell UK (former Basell Polyolefins), makes polypropylene resin at Carrington Works, off the A6144 (former motorway) in Carrington, off the Carrington Interchange of the M60, which was set up to exploit the British-invented Catarole process, later bought by Shell in 1955. Ethel Austin is in Altrincham (formerly Knowsley until 2010). Virtalis (virtual reality) is off the B5397 near Dane Road Metrolink station in Sale. S2Blue, a radio jingles company run by Steve England, is off the A6144 near the B5165 junction, in Ashton upon Mersey in the former studios of Alfasound (having moved from Leek in 2013). HomeForm Group, owner of Möben Kitchens, Sharps Bedrooms and Dolphin Bathrooms until 2011, was on the A56 in Old Trafford. Itron UK (flow metering) have a plant at the A56/A5014 junction at Gorse Hillin Stretford; further along the A5014 there is Kelloggs UK HQ next to the Old Trafford cricket ground. Regatta and Craghoppers are on Barton Dock Road (B5211), near the Trafford Centre (the base of The Peel Group), on the other side of the A5081. Holt Lloyd, known as Holts, the largest car care company in the world in the 1980s, now owned by Honeywell Consumer Products Group, is based on Barton Dock Road (B5211), at Merlin Park on the south of Trafford Park, off the M60 Lostock Circle. On Trafford Park near the A576 Centenary Bridge SCA makes household tissue products (owned by P&G before 2007), and next door is P&G's Manchester Plant which makes its Pampers nappies. The Fragrance Shop is based near Trafford Ecology Park, on Trafford Park. Soreen is made south of Trafford Park, next to the Bridgewater Canal off the A5081 Parkway Circle roundabout; next door UK Data Capture (Lockheed Martin) processed all the 2011 census data.

Kelloggs is in Trafford Park (Manchester); to the north Adidas have their European distribution centre, and nearby TDG was on the industrial estate, until bought by Norbert Dentressangle in 2011. DHL Freight UK is at Manchester International Freight Terminal, west of the Old Trafford football ground. Chemtura (chemicals, former site of Ciba-Geigy) is between the A576 and B5214 towards the north end of the industrial park. Lucchini UK (railway wheelsets and axles) are on Trafford Park off the B5214, and are a main supplier for UK trains. Ocean Finance is on Trafford Park (previously in Tamworth). Hot Animation, who made Bob the Builder, are on Hanover Business Park in the east of Altrincham, in Broadheath; to the south towards the Bridgewater Canal, across a former railway, on the Altrincham Ind Est, Girlguiding UK run their trading service.

JD Sports is west of the Pilsworth Interchange of the M66 in Unsworth south of Bury; Birthdays is west of the Heap Bridge Interchange; Tetrosyl Group Ltd, UK maker of car care products are at Walmersley, off the A56 and also at junction 2 (A58) of the M66. At A6053/A56 junction in Redvales, to the south of Bury is Melba Swintex, a main supplier of street furniture—traffic cones and barriers, claiming to be a world leader. Milliken make airbags on the A58, south-west of Bury.
PTG (Holroyd Machine Tools) базируется на развязке M62 Milnrow ; неподалеку от автомагистрали A6193 находится компания Takeuchi Manufacturing UK (строительное оборудование). Premier Foods производит ресторан Sarson's на автомагистрали A669 недалеко от железнодорожной станции Миллс-Хилл в Миддлтоне ; на противоположной стороне железной дороги Vita Group производит пенополиуретан (Vitafoam, крупнейший поставщик в Великобритании). Сервисный центр Voith Paper находится на автомагистрали A576 , к западу от центра города Миддлтон. Кооператив и базируется в Манчестере Рочдейле . Minky Homecare ( уборка дома ) и Freudenberg Household Products UK находятся в центре Рочдейла, рядом с автомагистралью A671 . Zen Internet находится в доме Сэндбрук в парке Сэндбрук, в конце автомагистрали A627(M) от автомагистрали A664 в Стоунифилде на юге Рочдейла, а по соседству находится штаб-квартира кооперативной аптеки . Магазин We Buy Any Car находится в Каслтоне , недалеко от автомагистрали A664, на юго-западе Рочдейла, там же, где находится Carcraft . Компания Guenther Bakeries (до 2005 года принадлежавшая компании Golden West, входящей в состав RHM) на юге Хейвуда, к востоку от большого распределительного парка Хейвуда, производит булочки для Макдональдс (еще один ресторан в Банбери).
Мерсисайд
[ редактировать ]
Пилкингтон находится в Сент-Хеленсе ; Knauf Insulation UK находится к юго-западу от центра города. Alumasc Exterior Building Products находится на B5204, недалеко от железнодорожной станции Сент-Хеленс-Джанкшен в Саттоне . Kalzip , подразделение Tata Steel Europe , производит алюминиевые крыши в Хейдоке ; GCE Group UK, производящая контроллеры медицинских газов и регуляторы для дайвинга , находится на автомагистрали A599 недалеко от острова М6 Хейдок; на северо-западе находится крупный центр развития Sainsbury's RDC; Дальше по автомагистрали A49, перед средней школой Эштон-ин-Мейкерфилд и Бирчалл, находится Speedy Hire , крупнейшая фирма по аренде автомобилей в Великобритании. Vimto принадлежит компании Nichols plc из Ньютон-ле-Уиллоуз , хотя на самом деле производится компанией Cott Beverages в северном Лестершире .
Littlewoods находятся в Гарстоне и принадлежат Shop Direct Group в Спике . Штаб-квартиры Princes , Johnsons Cleaners UK , Maersk Line UK , Beetham Organization , John West Foods , Bibby Line , Home Bargains , Royal Liver Assurance и TJ Hughes находятся в Ливерпуле. По направлению к исторически Эйнтри компании Jacob's базируются и их крекеры, а также производят Twiglets на своем участке в Hartley's Village в Фазакерли , а неподалеку находится Sportech PLC , владелец футбольных бассейнов ; Trigon Snacks производит Big D (арахис) в Эйнтри и делает это с 1970-х годов на Greylaw Ind Est недалеко от B5187, недалеко от католического спортивного колледжа архиепископа Бека . HMRC (бывшей налоговой службы) Национальное подразделение по делам о несостоятельности находится в Regian House (ранее в Queen's Dock ) напротив железнодорожной станции Ливерпуль-Джеймс-стрит Ливерпуля и рядом с Управлением карьеры в вооруженных силах . Бюро судимости находится на скамье подсудимых Принца и с 2013 года является частью новой Службы раскрытия информации и запрета (вместе с бывшей ISA в Дарлингтоне). Агентство оборонных законопроектов находился в Мерси-Хаусе рядом с железнодорожной станцией Сент-Джеймс, теперь являющемся частью DBS Finance .
Компания Tangerine Confectionery производит зефир «Принцесса» на Эдж-лейн (A5047) в восточном Ливерпуле, к западу от технологического парка Уэвертри. Home Bargains находится рядом с автомагистралью A580 к западу от развязки 4 автомагистрали M57, на границе Ноусли в парке Стоунбридж . Дж. Ф. Реншоу (Renshaw Napier), имеющий королевский ордер, делает глазурь для торта на трассе A562 рядом с женской больницей Ливерпуля в Эдж-Хилл; в Великобритании 90% марципана производится на этой фабрике. В Спике на автомагистрали A561, к западу от завода JLR , частично в Ноусли, Novartis производит такие вакцины, как Fluvirin , а непосредственно к югу MedImmune (принадлежащая AstraZeneca ) производит компоненты вакцины против гриппа ( FluMist ); Briggs Automotive Company находится на Speke Hall Ind Est вместе с HP Chemie Pelzer UK (автомобильная акустика ). В Хантс-Кросс, на северной стороне железнодорожной линии, крупный производственный завод Eli Lilly Speke Operations производит антибиотики, такие как капреомицин , а в 1981 году произвел первый в мире биосинтетический продукт, производя биологический инсулин, а также производил биосинтетический человеческий инсулин. гормон роста с 1985 года; После войны до 1962 года завод принадлежал компании The Distillers Company , где производился пенициллин, а затем и талидомид . Рядом с перекрестком A561/A562 NWDA. финансируемый в 2006 году был построен Национальный центр биопроизводства, На южной стороне автомагистрали A561 в Спике находится торговый парк Estuary. Дальше на юг находятся Prinovis UK и B&M (ранее в Блэкпуле) в Ливерпульском международном бизнес-парке; на бывшем аэродроме Спик находится магазин Direct рядом с Национальным центром биопроизводства.

Jaguar Land Rover имеет 166 акров своей основной производственной площадки (ранее принадлежавшей Ford ) в Хейлвуде , где производятся Freelander и Range Rover Evoque . Getrag Ford Transmissions производит 400 000 автоматических и механических коробок передач по соседству к востоку от завода JLR в Хейлвуде для автомобилей Ford, Volvo и Mazda. Magna Decoma , расположенная к западу от JLR Halewood и к востоку от Novartis, производит интерьеры и экстерьеры автомобилей. Dairy Crest производит Vitalite и Utterly Butterly на автомагистрали A5207 в Киркби , недалеко от развязки M57 Randles Farm, напротив бывшего участка Этель Остин ; к востоку от Dairy Crest находится Yorkshire Copper Tube , главный британский производитель медных трубок , принадлежащий итальянской KME Group ; Counterline производит прилавки общественного питания в бизнес-парке Ноусли; Clarke Energy находится на трассе A5208 . Дальше на север, в поместье рядом с автомагистралью A5208, находится распределительный центр QVC UK , все три которого находятся в Киркби. Дальше на север, рядом с границей Ланкашира, находится Goodrich Actuation Systems на Хайтон-Инд-Эст (в бывшем карьере Хайтон) на северо-западной стороне автомагистрали M62. Остров Тарбок (рядом с автомагистралью A5080) в Тарбоке . По соседству Halewood International , производящая Lambrini , Red Square, Lamb's Navy Rum и некоторые алкогольные напитки , находится в Уайтфилд-Лейн-Энд , на юге Хайтона , на перекрестке M62/M57. Belling Ltd (принадлежит Glen Dimplex ) находится в Уистоне , рядом с большой больницей Уистона ; Glen Dimplex Whiston — единственный в Великобритании производитель плит, около 350 000 штук в год (до 2001 года Stoves plc), а также владеет LEC холодильниками . Manesty производит таблетки для лекарств на трассе B5194 в бизнес-парке Ноусли. Общенациональный ритейлер модной одежды Matalan имеет головной офис и главный распределительный центр на севере Knowsley Ind Est (до 2014 года в Скелмерсдейле); Поместье Ноусли Инд находится на территории бывшего ROF Киркби . У Camelot Group есть центр выплаты призов Ливерпуля в бизнес-парке Kings на автомагистрали A57, к западу от развязки M57 Forest House.

Чай Typhoo производится в Мортоне рядом с автомагистралью A551, рядом с железнодорожной станцией Мортона , и на том же месте находится Manor Bakeries ( Premier Foods , бывшая Lyons Cakes , до апреля 1995 года), которая делает мини-булочки фабрика Burton's Biscuit Company , а также закрытая в 1995 году . Декабрь 2011 года: производство печенья Cadbury ( Cadbury Fingers ) и Wagon Wheels , где до сих пор находится завод по переработке шоколада. Основные исследовательские лаборатории Bristol-Myers Squibb UK расположены к востоку от пекарни Мортон, недалеко от железнодорожной станции Лисоу . CML Group (часть Teledyne ) производит композиты и компоненты самолетов на автомагистрали A41 в Бромборо недалеко от загородного парка Истхэм ; на юге находится Einhell UK (электроинструменты). Stiebel Eltron UK (тепловые насосы) неподалеку, недалеко от Meyer Prestige , производящего кухонную посуду (который также владеет Circulon и Anolon ), а у Givaudan UK есть фабрика по производству парфюмерии. Компания FMC Lithium , расположенная к востоку от автомагистрали A41 в Международном бизнес-парке Wirral, производит бутиллитий и другие металлоорганические соединения. В Port Sunlight компания Unilever производит и исследует моющие средства и шампуни, такие как Timotei и Sunsilk , а также Comfort и Persil Liquid . Каммелл Лэрд в Биркенхеде строил корабли, в том числе две «Поларис подводные лодки класса Резолюшн» в 1960-х годах; на Двенадцати набережных у автомагистрали A554 находится компания Faiveley Transport UK (железнодорожные электрические компоненты). RFD Beaufort (известная в 1980-х годах как Beaufort Air-Sea Equipment) производит G-костюмы для истребителей и спасательных плотов . Нефтеперерабатывающий завод Истхэма у развязки 6 автомагистрали M53, в Истхэме в Уиррале, к северу от Хутон-парка (в Чешире), принадлежит компании Nynas .

Понтинс находится в Эйнсдейле , Сефтон. HMRC в St John's House на A5057 в Бутле - это национальный офис по налогообложению индивидуальных сберегательных счетов (ISA) и других сберегательных схем, благотворительных организаций ( Gift Aid ), трастов нерезидентов и постоянного проживания статуса ; напротив находится Совета Сефтона Дом Магдалины . Неподалеку к западу от автомагистрали A5057 HSE и Управления по ядерному регулированию головной офис находится в Редгрейв-Корт , недалеко от главного здания колледжа Хью Бэрда . The Triad Главный офис Налогового управления находился в здании в Бутле, рядом с торговым центром Strand , и этим объектом до сих пор управляет HMRC. Unipart Dorman производит светодиодные светофоры возле железнодорожной станции Meols Cop в Бловике , к востоку от Саутпорта; к северу, в Кроссенсе , компания Railex производит шкафы для документов .
Камбрия
[ редактировать ]Подводные лодки и корабли Королевского флота производятся компанией BAE Systems Submarine Solutions в Барроу-ин-Фернесс . Побережье Камбрии известно как британское энергетическое побережье из-за большого количества энергии, производимой на побережье графства; Селлафилд - это электростанция, расположенная в Западной Камбрии и вносящая основной вклад в «Энергетический берег», а Барроу-ин-Фернесс - крупный город, вносящий вклад в «Энергетический берег» с электростанцией ( Электростанция Рузкот ), Газовые терминалы ( Rampside Gas Terminal ) и морская ветряная электростанция ( Walney Wind Farm ), которая находится примерно в 14 км (8,6 миль) к западу от береговой линии города и оснащена одними из крупнейших ветряных турбин на Земле. В научно-технологическом парке Вестлейкс недалеко от автомагистрали A595 к югу от Уайтхейвена находится Управление по выводу из эксплуатации ядерных объектов (в Хердус-Хаусе).
Британская служба перемещения скота находится в Уоркингтоне, рядом с Tata Steel Projects , недалеко от территории Национальной ядерной лаборатории на Дервент-Хау, Индиана-Эст. Iggesund Paperboard находится к югу от Уоркингтона, недалеко от автомагистрали A596 ; по соседству находится Eastman Chemical . Amcor Flexibles Cumbria (до 2009 года бывшая Alcan) на юге Уоркингтона печатает пакеты для хрустящих продуктов и обертки для кондитерских изделий для распространения на фабриках Великобритании.
Озерный край популярен среди отдыхающих. Управление по выводу из эксплуатации ядерных объектов находится недалеко от Уайтхейвена. Компания Lakeland , производящая кухонную утварь, находится в Уиндермире. Stobart Group находится в Карлайле . M-Sport , раллийная команда в Довенби-холле и пивоварня Jennings Brewery находятся в Кокермуте . Джеймс Кроппер , ведущий европейский производитель цветной бумаги, находится в Бернсайде , к северу от Кендала, на реке Кент , недалеко от автомагистрали A591 . Главный завод шин Pirelli в Великобритании (для престижных автомобилей) находится на трассе B5299 на юге Карлайла; к югу, в Каммерсдейле , рядом с рекой Калдью , у компании Stead McAlpin есть большой текстильный завод, ранее принадлежавший Джону Льюису . BSW Timber компания Великобритании , крупнейшая лесопильная , имеет большой участок к северу от Карлайла в Карго в Кингмуре , рядом с Карлайлом Кингмуром TMD на WCML. У БиллерудКорснеса была бумажная фабрика в Битэме на автомагистрали А6, рядом с рекой Бела на юге графства. Sealy UK производит кровати и матрасы на трассе B5031 рядом с железнодорожной станцией Аспатрия на севере Камбрии, к западу от Карлайла; по соседству Первое молоко приготовить Чеддер из Озерного края . Дальше на восток вдоль автомагистрали A596 компания Innovia Films (бывшая British Rayophane) имеет большую площадку в Уигтоне . GSK Ulverston, построенная в 1949 году как Glaxo для производства пенициллина с новым заводом, который будет построен, производит цефалоспориновые антибиотики, включая цефуроксим и цефтазидим .
Образование
[ редактировать ]Среднее образование
[ редактировать ]Средние школы в основном являются общеобразовательными, но в Траффорде сохраняется полностью избирательная школьная система, а есть еще несколько гимназий в Ланкашире, Уиррале, Ливерпуле и Камбрии .
В средней школе региона обучается около 345 000 человек, что является третьим по величине показателем в Англии после Юго-Восточной Англии и Большого Лондона . Это примерно в три раза больше, чем в Северо-Восточной Англии . школы, Что касается прогулов то самые упорные прогульщики находятся в Манчестере с показателем 7,3%, за ним следуют Ноусли с 6,9% и Блэкпул с 6,6%. Самый низкий уровень прогулов наблюдается в Саут-Риббле - 2,4%, за ним следует Риббл-Вэлли с 2,9% (оба в Ланкашире).
На уровне А в 2010 году Траффорд показал лучшие результаты и, как и его результаты на GCSE, является одним из лучших мест в Англии. Район с самыми низкими показателями снова оказался в Ноусли, за ним следует Рочдейл. Ноусли добился ужасных результатов на уровне A; Halewood Academy , последняя шестиклассная школа, закрылась в 2016 году; В настоящее время в Ноусли нет школьных программ A-level, их предоставляет Общественный колледж Ноусли . Для традиционных графств Ланкашир показывает отличные результаты на A-level, являясь одним из лучших в Англии. Области, показавшие результаты выше среднего по Англии (в порядке результатов): Блэкпул, Уоррингтон, Уиган, Чешир-Уэст и Честер, Бери, Камбрия, Уиррал и Стокпорт. Блэкпул не особенно хорошо сдает экзамены GCSE, но дает гораздо лучшие результаты на уровне A — даже лучше, чем Чешир-Уэст и Честер , и третий лучший результат в регионе. [ нужна ссылка ]



- Десять лучших государственных школ Северо-Запада (результаты уровня A за 2015 г.)
- Гимназия для девочек Альтринчам (1223)
- Гимназия для мальчиков Альтринчама
- Школа Blue Coat , Ливерпуль
- Ланкастерская женская гимназия
- Школа Blue Coat CofE , Олдхэм
- Вирралская гимназия для девочек
- Вирралская гимназия для мальчиков
- Средняя школа Лорето , Альтринчам
- Средняя школа Вест-Кирби
- Королевская гимназия Клитеро [ нужна ссылка ]
Районы, в которых школьники с наибольшей вероятностью будут посещать университеты, - это Траффорд и Чешир, за которыми следуют Уиррал, Сефтон, Стокпорт и Бери. Четыре из этих областей являются или были частью Чешира. [ нужна ссылка ]
Колледжи
[ редактировать ]



- Колледж Аквинского , Стокпорт
- Колледж шестого класса Эштона , Эштон-андер-Лайн
- Колледж шестого класса Барроу-ин-Фернесс , Барроу-ин-Фернесс
- Блэкбернский колледж , Блэкберн
- Блэкпул и колледж Файлд , Блэкпул
- Блэкпульский колледж шестого класса , Блэкпул
- Болтонский колледж , Болтон
- Болтонский колледж шестого класса , Болтон
- Колледж Бернли , Бернли
- Бери-колледж , Бери
- Карлайлский колледж , Карлайл
- Кармел Колледж , Сент-Хеленс
- Колледж шестого класса Чидла и Марпл , Чидл
- Колледж Фернесс , Барроу-ин-Фернесс
- Шестой класс средней школы Хейзел Гроув , Стокпорт
- Колледж Святого Креста (Великобритания) , Бери
- Колледж Хопвуд Холл , Рочдейл
- Колледж Хью Бэрда , Бутл
- Кендалский колледж, Кендал
- Колледж короля Георга V , Саутпорт
- Колледж Ланкастера и Моркама , Ланкастер
- Ливерпульский общественный колледж , Ливерпуль
- Лорето-колледж , Манчестер
- Колледж Маклсфилда , Маклсфилд
- Манчестерский колледж , Манчестер
- Колледж Мид Чешир , Нортвич
- Колледж Олдхэма , Олдхэм
- Колледж шестого класса Олдхэма , Олдхэм
- Престонский колледж , Престон
- Колледж Пристли , Уоррингтон
- Колледж Рейнфорд , Сент-Хеленс
- Риверсайд-Колледж , Уиднес
- Колледж Раншоу , Лейланд
- Солфордский городской колледж , Солфорд
- Колледж Южного Чешира , Крю
- Саутпортский колледж , Саутпорт
- Колледж сэра Джона Дина , Нортвич
- Стокпортский колледж , Стокпорт
- Колледж Сент-Хеленс , Сент-Хеленс
- Колледж Святого Джона Ригби , Уиган
- Колледж Святой Марии , Блэкберн
- Шестой класс колледжа Св. Уилфрида C of E, Блэкберн
- Томас Уизем, шестой класс , Бернли
- Траффордский колледж , Траффорд
- Колледж Западного Чешира , Элсмир-Порт
- Колледж Уигана и Ли , Уиган
- Колледж Уинстенли , Уиган
- Колледж Ксавье , Манчестер
Двумя основными колледжами высшего образования в регионе являются Блэкберн-колледж и Блэкпул, а также Филд-колледж . Есть сорок три колледжа FE. Региональный LSC находился в центре Манчестера; теперь это SFA и YPLA.
Университеты
[ редактировать ]

Университеты Северо-Запада перечислены ниже:
- Манчестерский университет , Манчестер – крупнейший университет с одним факультетом в Великобритании, в котором обучается 36 907 студентов.
- Манчестерский столичный университет , Манчестер – также один из крупнейших университетов страны с 40 420 студентами – второй по величине университет в регионе.
- UCLAN , Престон – Университет Центрального Ланкашира в Престоне, 28 850 студентов – третий по величине университет в регионе.
- Ливерпульский университет Джона Мурса , Ливерпуль – 24 085 студентов.
- Ливерпульский университет , Ливерпуль – 20 765 студентов.
- Университет Солфорда , Солфорд – 20 185 студентов.
- Ланкастерский университет , Ланкастер – 17 415 студентов.
- Юридический университет , Честер, Манчестер
- Университет Эдж-Хилл , Ормскирк – 15 645 студентов.
- Честерский университет , Честер и Уоррингтон – 15 095 студентов.
- Университет Болтона , Болтон – 8540 студентов.
- Ливерпульский университет Хоупа , Ливерпуль – 8 205 студентов.
- Университет Камбрии - новейший университет региона, расположенный в Камбрии, некоторых частях Ланкашира и Лондона и ранее известный как Институт искусств Камбрии .
Более 60% студентов вузов региона являются уроженцами региона. Следующим по количеству студентов на северо-западе регионом является Йоркшир и Хамбер , поэтому примерно 80% студентов университетов в этом районе - выходцы с севера Англии. Среди студентов региона самая высокая доля студентов из так называемых районов с низким уровнем участия. [ нужна ссылка ]
Местные СМИ
[ редактировать ]
- ТВ
- Liverpool TV — местная телевизионная станция, обслуживающая городской регион Ливерпуля и его окрестности. Станция принадлежит и управляется компанией Local Television Limited и должна транслировать 35 часов в неделю первых местных программ.
- «Это Манчестер» — местная телевизионная станция, обслуживающая Большой Манчестер. Он принадлежит и управляется компанией That's TV и вещает на канале Freeview 7 из студии The Flint Glass Works в пригороде Анкоутс в Манчестере.
- Региональные новостные программы для острова Мэн, северо-западной Англии и юга Камбрии — North West Tonight ( BBC North West ) и Granada Reports ( ITV Granada ), обе базируются в Солфорд-Куэйс с осени 2011 года и весны 2013 года соответственно.
- Региональные новостные программы для севера Камбрии – Look North ( BBC North East и Cumbria ) в Ньюкасле и Lookaround ( ITV Tyne Tees & Border ) в Гейтсхеде .
- Региональные новостные программы для района Вест-Крэйвен в Ланкашире, исторически находившегося в Западном райдинге Йоркшира - Look North и ITV News Calendar, оба базирующиеся в Лидсе . Оба транслируются с передатчика «Скиптон» , который является частью группы передатчиков «Эмли Мур» .
- NB Digital TV поставляется из Уинтер-Хилл на юге региона и Колдбека в Камбрии. Переход на цифровое вещание произошел в середине 2009 года в Камбрии и в конце 2009 года на юге региона.
- Радио
- Службы местного радио BBC в регионе включают радиостанции BBC в Манчестере , Мерсисайде , Ланкашире , Камбрии и Стоуке (охватывающие юг Чешира ).
- Национальное радио исходит из Холма Мосса (для Мерсисайда, Большого Манчестера и Чешира) и Сэндейла для Камбрии. Главный СВЧ-передатчик региона (и Англии) находится за границей в Кирклисе , в Мурсайд-Эдж .
- К коммерческим радиостанциям относятся:
- Heart North West (транслируется на Манчестер, Ланкашир и Мерсисайд через региональную службу - ранее 105.4 Century FM и Real Radio - и на Барроу-ин-Фернесс , Моркам и Ланкастер , ранее The Bay) .
- Сеть Hits Radio базируется в Каслфилде , Манчестер; в число его станций входят Hits Radio Manchester (ранее Key 103), Rock FM (Престон) и Radio City (Ливерпуль), при этом студии Castlefield также обеспечивают большинство программ для Hits Radio UK .
- Столица Манчестер и Ланкашир (созданная из бывшей Galaxy Manchester и 2BR , последняя ранее поглотила 106,5 Central Radio и The Bee ), а также столица Ливерпуль (бывшая Juice FM), с Уирралом и Чеширом, которые служили частью Capital North West и North. Уэльс .
- Smooth North West (региональная служба) и Smooth Lake District ( Кендал )
- Greatest Hits Radio North West вещает на Мерсисайд , Олдхэм и Рочдейл , Болтон и Бери , Стокпорт , Уиган и Сент-Хеленс , Блэкпул , Уоррингтон и Ранкорн на FM, а также на Ливерпуль, Манчестер и центральный Ланкашир через DAB и ранее AM. Локализованная версия для Камбрии была запущена на DAB в 2021 году, затем в апреле 2023 года CFM был переименован в Greatest Hits Radio Cumbria & South West Scotland , а в канале DAB теперь есть Hits Radio. Некоторые программы радиосети Greatest Hits Radio транслируются из Каслфилда или Сент-Джонс-Бикон в Ливерпуле.
- XS Манчестер
- Chester's Dee Radio (Честер) и брат Cheshire's Silk 106.9 (Маклсфилд)
Великобритании Сигнал времени поступает с радиостанции Анторн на северо-западном побережье Камбрии, где есть три атомных часа .


- Газеты
- Блэкпулский вестник , Блэкпул
- Болтонские новости , Болтон
- Бери Таймс , Бери
- Лидер Chester Evening , Честер
- Ланкашир Ивнинг Пост , Престон
- Ланкаширский телеграф , Блэкберн
- Ливерпуль Эхо , Ливерпуль
- Manchester Evening News , Манчестер
- Новости и звезда Карлайл
- North-West Evening Mail , Барроу-ин-Фернесс
- Oldham Evening Chronicle , Олдхэм
- Посетитель Саутпорта , Саутпорт
- Репортер , [73] Сент-Хеленс
- Звезда , [74] Сент-Хеленс
- Вестморленд Газетт , Кендал
- Уиган Ивнинг Пост , Уиган

У Guardian Media Group есть типография в Trafford Park Printers рядом с автомагистралью A5081 (развязка M60 9) между каналом Бриджуотер и кольцевой развязкой A576 , на которой печатается газета Guardian (50% акций принадлежит Telegraph и 50% Guardian Print Center ); до 2008 года он печатал Telegraph и известен также как GPC Manchester. С 2008 года Telegraph печатается на огромном сайте Newsprinters в Ноусли. Газетные типографии имеют участок рядом с Dairy Crest в Ноусли и печатают заголовки Times , Telegraph и Sun рядом с B5202.
Broughton Printers , принадлежащая Northern & Shell, печатает газеты Express и Star в Фулвуде на шоссе B6241 к югу от перекрестка M55/M6, на том же сайте, что и Lancashire Evening Post .
- Журналы
Приновис в Ливерпуле (Спик) печатает нормально! , журнал Sun on Sunday ( Fabulous ) и Sunday Times журнал .
Городские и городские побратимы
[ редактировать ]| Эштон-андер-Лайн | Шомон , Франция |
| Блэкберн | Альтена , Германия Перонн , Франция |
| Блэкпул | Ботроп , Германия |
| Болтон | Ле-Ман , Франция Падерборн , Германия |
| Бернли | Витри-сюр-Сен , Франция |
| Хоронить | Ангулем , Франция Датун , Китай Тюль , Франция Шорндорф , Германия Вудбери , Нью-Джерси, США |
| Карлайл | Фленсбург , Германия Слупск , Польша |
| Карнфорт | Сайи-сюр-ла-Лис , Франция |
| Чаддертон | Гестахт , Германия |
| Честер | Санс , Франция Лёррах , Германия Сенигаллия , Италия |
| Чорли | Секешфехервар , Венгрия |
| Далтон-ин-Фернесс | Далтон , Пенсильвания, США |
| Дентон | Монтиньи-ле-Бретонне , Франция |
| Дройлсден | Вильмомбль , Франция |
| Дукинфилд | Шампаньоль , Франция |
| Элсмир Порт | Ройтлинген , Германия |
| Фэйлсворт | Ландсберг-ам-Лех , Германия |
| Флитвуд | Флитвуд , Пенсильвания, США |
| Хэлтон | Лейрия , Португалия Марцан-Хеллерсдорф , Германия Тунлин , Китай Усти-над-Лабем , Чехия |
| Хейвуд | Боль , Германия |
| Кендал | Килларни , Ирландия Ринтельн , Германия |
| Ноусли | Мёрс , Германия |
| Ланкастер | Ольборг , Дания Рендсбург , Германия |
| Ливерпуль | Кёльн , Германия Рио-де-Жанейро , Бразилия Дублин , Ирландия Odesa , Ukraine Шанхай, Китай |
| Лонгдендейл | Руппихтерот , Германия |
| Манчестер | Амстердам , Нидерланды Хемниц , Германия Кордова , Испания Фейсалабад , Пакистан Лос-Анджелес, Калифорния, США Пуэрто Кабесас , Никарагуа Реховот , Израиль Санкт-Петербург , Россия Ухань , Китай |
| Моссли | Хем , Франция |
| Олдем | Крань , Словения |
| Освальдтвистл | Фалькенберг , Швеция |
| Престон | Алмело , Нидерланды Калиш , Польша Ним , Франция Реклингхаузен , Германия |
| Рочдейл | Билефельд , Германия Львов , Украина Сахивал , Пакистан Туркуэн , Франция |
| Салфорд | Клермон-Ферран , Франция Люнен , Германия Нарбонна , Франция Сент-Уан , Франция |
| Седберг | Зрече , Словения |
| Сефтон | Гданьск , Польша Монс , Бельгия |
| Сталибридж | Армантьер , Франция |
| Стокпорт | Безье , Франция Хайльбронн , Германия |
| Сент-Хеленс | Штутгарт , Германия Шалон-сюр-Сон , Франция |
| Тамсайд | Бэнгбу , Китай Мутаре , Зимбабве |
| Улверстон | Альберт , Франция |
| Уоррингтон | Хильден , Германия Округ Лейк , Иллинойс, США Наход , Чехия |
| Уайтхейвен | Козлодуй , Болгария |
| Уиган | Анже , Франция |
| Уоркингтон | Зельм , Германия Валь-де-Рей , Франция |
| Реа Грин | Сен-Брис-ле-Вино , Франция |
Спорт
[ редактировать ]
Современный дартс был изобретен в 1896 году плотником из Ланкашира Брайаном Гэмлином из Бери, 44 года. Оултон-Парк , расположенный в центральном Чешире, является местом проведения чемпионата Великобритании по кузовным гонкам в июне . Международная федерация нетбола расположена в Манчестере, где расположены Национальный центр сквоша и Национальный центр велосипедного спорта ( Манчестерский велодром и Британский велосипедный спорт ) в Спортсити . Первые собачьи бега в Великобритании прошли в июле 1926 года в Манчестере на специально построенном овальном стадионе Belle Vue . Национальный музей футбола находится в Манчестере.
Футбол
[ редактировать ]Следующие футбольные клубы базируются на Северо-Западе и соревнуются в Премьер-лиге или Футбольной лиге (четырех высших дивизионах системы английских футбольных лиг ) начиная с сезона 2023–24 . Национальная лига также включена.
| Команда | Расположение | Лига 2022–23 |
|---|---|---|
| Бернли | Бернли , Ланкашир | Премьер-лига |
| Эвертон | Ливерпуль , Мерсисайд | Премьер-лига |
| Ливерпуль | Ливерпуль , Мерсисайд | Премьер-лига |
| Манчестер Сити | Манчестер , Большой Манчестер | Премьер-лига |
| Манчестер Юнайтед | Манчестер , Большой Манчестер | Премьер-лига |
| Блэкберн Роверс | Блэкберн , Ланкашир | Чемпионат |
| Престон Норт Энд | Престон, Ланкашир | Чемпионат |
| Блэкпул | Блэкпул , Ланкашир | Первая лига |
| Болтон Уондерерс | Болтон , Большой Манчестер | Первая лига |
| Карлайл Юнайтед | Карлайл , Камбрия | Первая лига |
| Флитвуд Таун | Флитвуд , Ланкашир | Первая лига |
| Уиган Атлетик | Уиган , Большой Манчестер | Первая лига |
| Аккрингтон Стэнли | Аккрингтон , Ланкашир | вторая лига |
| Курган | Барроу-ин-Фернесс , Камбрия | вторая лига |
| Крю Александра | Крю , Чешир | вторая лига |
| Моркам | Моркам , Ланкашир | вторая лига |
| Солфорд Сити | Солфорд , Большой Манчестер | вторая лига |
| Округ Стокпорт | Стокпорт , Большой Манчестер | вторая лига |
| Транмер Роверс | Биркенхед , Мерсисайд | вторая лига |
| Рочдейл | Рочдейл , Большой Манчестер | Национальная лига |
Команды Северо-Запада выиграли 64 из 124 титулов английской футбольной лиги (чуть более 50%), больше, чем в любом другом регионе, причем «Манчестер Юнайтед» выиграл больше, чем любая другая команда.
Лига регби
[ редактировать ]Следующие клубы лиги регби базируются на Северо-Западе и участвуют в Суперлиге или чемпионате (три высших дивизиона британской системы лиг регби по состоянию на 2021 год ) .
Команды Суперлиги
[ редактировать ]- Ли Центурионс (Ли, Большой Манчестер)
- Салфорд Сити Редс (Солфорд, Большой Манчестер)
- Сент-Хеленс (Сент-Хеленс, Мерсисайд)
- Уоррингтон Вулвз (Уоррингтон, Чешир)
- Уиган Уорриорз (Уиган, Большой Манчестер)
Команды чемпионата
[ редактировать ]- Суинтон Лайонс (Суинтон, Большой Манчестер)
- Олдхэм Рауидс (Олдхэм, Большой Манчестер)
- Уайтхейвен (Уайтхейвен, Камбрия)
- Уиднес Викинги (Уиднес, Чешир)
Команды первой лиги
[ редактировать ]- Barrow Raiders (Барроу-ин-Фернесс, Камбрия)
- Рочдейл Хорнетс (Рочдейл, Большой Манчестер)
- Уоркингтон-Таун (Уоркингтон, Камбрия)
Плавание
[ редактировать ]Британское плавание имеет один из трех центров интенсивной подготовки в Центральных бассейнах Гранд в Стокпорте.
Гольф
[ редактировать ]Гольф-клуб Royal Birkdale находится в Саутпорте, а также гольф-клуб Royal Lytham & St Annes . Гольф-клуб Royal Liverpool находится в Хойлейке.
См. также
[ редактировать ]- Камбрический язык
- Энвиролинк Северо-Запад
- Список школ на северо-западе Англии
- Агентство развития Северо-Запада
- Очертание Англии
Ссылки
[ редактировать ]- ^ «Стандартные измерения площади (последние) для административных территорий Соединенного Королевства» . Открыть географический портал . Управление национальной статистики. 24 апреля 2024 г. Проверено 6 мая 2024 г.
- ^ Парк, Нил (21 декабря 2022 г.). «Оценки численности населения Великобритании, Англии, Уэльса, Шотландии и Северной Ирландии» . Управление национальной статистики . Проверено 25 августа 2023 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Перепись Великобритании (2021 г.). «Профиль территории переписи 2021 года – Северо-Западный регион (E12000002)» . Номис . Управление национальной статистики . Проверено 14 августа 2023 г.
- ^ Фентон, Тревор (25 апреля 2023 г.). «Региональная валовая добавленная стоимость (сбалансированная) на душу населения и доходы» . Управление национальной статистики . Проверено 14 августа 2023 г.
- ^ Фентон, Тревор (25 апреля 2023 г.). «Валовой внутренний продукт региона: все регионы ИТЛ» . Управление национальной статистики . Проверено 15 августа 2023 г.
- ^ «Рисунок 2: Тенденции межгодовых изменений (A) среднегодовых осадков (мм) и (B) среднегодовой температуры (°C) в период 2001–2015 гг.». дои : 10.7717/peerj.9797/рис-2 .
{{cite web}}: Отсутствует или пусто|url=( помощь ) - ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Управление национальной статистики» . Статистика.gov.uk . Архивировано из оригинала 16 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 17 мая 2012 г.
- ^ «Профиль рынка труда – Ливерпуль» . Управление национальной статистики. 5 октября 2018 года. Архивировано из оригинала 13 февраля 2019 года . Проверено 5 октября 2018 г.
- ^ «Текущие оценки – оценки численности населения по этническим группам на середину 2009 г. (экспериментальная)» . Управление национальной статистики . Архивировано из оригинала 10 августа 2011 года . Проверено 21 мая 2011 г.
- ^ Коллинсон, Дон (28 февраля 2015 г.). «День Святого Давида: почему связи «Ливерпуля» с Уэльсом настолько сильны?» . Архивировано из оригинала 21 февраля 2017 года . Проверено 29 мая 2017 г.
- ^ «Об Эштон-ин-Мейкерфилде» . Архивировано из оригинала 5 августа 2018 года . Проверено 29 мая 2017 г.
- ^ «Веб-архив правительства Великобритании» . Архивировано из оригинала 16 марта 2012 года . Проверено 19 ноября 2011 г.
- ^ Объяснение этнических различий: изменение моделей неблагополучия в Великобритании (1-е изд.). Издательство Бристольского университета. 2003. дои : 10.2307/j.ctt1t8915s . JSTOR j.ctt1t8915s .
- ^ Равенство, Комиссия по расовым вопросам (1985). «Этнические меньшинства в Британии: статистические сведения о характере расселения» . Комиссия по расовому равенству : Таблица 2.1.
- ^ Данные взяты из службы данных Casweb Соединенного Королевства переписи населения Соединенного Королевства 1991 года по этническим данным для Англии, Шотландии и Уэльса. Архивировано 5 апреля 2022 года в Wayback Machine (таблица 6).
- ^ «Управление национальной статистики; основные статистические данные переписи 2001 года» . webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk . Проверено 24 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «Перепись 2011 года: этнические группы, местные власти в Англии и Уэльсе» . webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk . Проверено 24 июня 2022 г.
- ^ «Этническая группа – Управление национальной статистики» . ons.gov.uk. Проверено 29 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ Зеленый, . Дэвид (29 ноября 2003 г.). «Итальянцы восстают из-за закрытия церкви» . Новости Би-би-си. Архивировано из оригинала 22 ноября 2008 года . Проверено 27 января 2008 г.
- ^ «TS012: Страна рождения (подробно)» . Управление национальной статистики . Проверено 28 марта 2023 г.
- ^ «QS203EW: Страна рождения (подробно)» . nomisweb.co.uk . Номис . Проверено 30 января 2013 г.
- ^ «UV008: Страна рождения» . nomisweb.co.uk . Номис . Проверено 30 января 2013 г.
- ^ «TS030 – Запрос на редактирование религии» . nomisweb.co.uk . Проверено 29 ноября 2022 г.
- ^ «KS209EW (Религия) – Номинации – nomisweb.co.uk . Получено 18 октября.
- ^ «KS007 — Религия — Номинации — nomisweb.co.uk . Получено 18 октября.
- ^ «Голосование католиков в Британии помогло привести Блэра к победе» . Ипсос МОРИ . 23 мая 2005 г. Архивировано из оригинала 4 января 2015 г. . Проверено 16 октября 2011 г.
Конечно, существуют значительные региональные различия: католики наиболее распространены в Лондоне, Шотландии и особенно на северо-западе (где каждый пятый — католик).
- ^ Чейни, Дэвид М. «Великобритания, статистика по епархиям и католическому населению [католическая иерархия]» . Архивировано из оригинала 15 января 2018 года . Проверено 19 июня 2014 г.
- ^ Кевин Филлипс, Войны кузенов (Нью-Йорк: Basic Books, 1999), 480–84. Филлипс отмечает: «Покорение [ирландцев] в семнадцатом веке было почти полным... В первой четверти восемнадцатого века [после Договора о Союзе] католические епископы были запрещены, а священники должны были зарегистрироваться. Католики проиграли их право голосовать, занимать должности, владеть ружьем или лошадью стоимостью более 5 фунтов или жить в городах, не платя специальных сборов... И снова ирландцы были вытеснены на запад, в более бедные земли, исход, который стал прообразом настроения Американские индейцы в течение следующих двух столетий».
- ^ «Данные LSOA за 2007 год» (PDF) . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 6 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 17 мая 2012 г.
- ^ «Данные о лишениях за 2007 год» (PDF) . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 6 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 17 мая 2012 г.
- ^ Количество истцов [ мертвая ссылка ]
- ^ голосов, Северо-Запад. «Информация о результатах голосования на Северо-Западе» . Northwestvotes.gov.uk . Архивировано из оригинала 9 мая 2021 года . Проверено 17 декабря 2020 г.
- ↑ NUTS (Номенклатура территориальных единиц статистики), по регионам, версия 2013 г. Архивировано 12 марта 2016 г. на Wayback Machine, по состоянию на 11 марта 2016 г.
- ↑ NUTS: Справочник Северо-Запада (Англия). Архивировано 16 октября 2015 г. в Wayback Machine , Управление национальной статистики, по состоянию на 11 марта 2016 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г «Британская городская структура: данные о населении» (PDF) . Проект ESPON 1.4.3 Исследование городских функций . Европейская сеть наблюдения за пространственным планированием . Март 2007. с. 119. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 24 сентября 2015 года . Проверено 22 февраля 2010 г.
- ^ «Сокращение городов и растущие регионы – новые тенденции новых отношений между деревней и городом в Великобритании и Германии (Манчестерская электронная школа – Манчестерский университет)» . Escholar.manchester.ac.uk. Архивировано из оригинала 25 апреля 2012 года . Проверено 17 мая 2012 г.
- ^ «Всемирный географический справочник: Соединенное Королевство - крупнейшие города (по географическим показателям...» Архивировано из оригинала 5 января 2013 года.
- ^ Мартин Уэйнрайт (23 октября 2006 г.). «Ищете тишины и покоя? Вот где это найти | Новости Великобритании» . Хранитель . Лондон. Архивировано из оригинала 15 декабря 2013 года . Проверено 17 мая 2012 г.
- ^ «Северо-Западная Англия - Карта истории городов, погода, места для посещения» . Самое главное – узнайте о нашем мире больше . Архивировано из оригинала 17 августа 2021 года . Проверено 17 августа 2021 г.
- ^ «Региональная транспортная стратегия: национальная картина» . Правительственное учреждение Йоркшира и Хамбера . Архивировано из оригинала 11 июня 2009 года . Проверено 8 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «Процесс ЛТП» . Департамент транспорта . Архивировано из оригинала 9 октября 2007 года . Проверено 8 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «Блэкберн с Дарвеном, План местного транспорта на 2006–2011 годы» . Блэкберн с городским советом Дарвена . Архивировано из оригинала 7 июня 2011 года . Проверено 8 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «План местного транспорта Блэкпула на 2006–2011 годы» . Совет Блэкпула . Архивировано из оригинала 3 мая 2007 года . Проверено 8 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «План местного транспорта Чешира на 2006–2011 годы» . Совет графства Чешир . Архивировано из оригинала 19 октября 2007 года . Проверено 8 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «План местного транспорта Камбрии на 2006–11 годы» . Совет графства Камбрия . Архивировано из оригинала 11 апреля 2008 года . Проверено 8 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «План местного транспорта Большого Манчестера на 2006–11 годы» . LTP Большого Манчестера. Архивировано из оригинала 20 июля 2011 года . Проверено 8 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «План местного транспорта Холтона на 2006–11 годы» . Городской совет Хэлтона . Архивировано из оригинала 14 июня 2008 года . Проверено 8 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «План местного транспорта Ланкашира на 2006–2011 годы» . Совет графства Ланкашир . Архивировано из оригинала 10 августа 2009 года . Проверено 8 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «План местного транспорта Мерсисайда на 2006–2011 годы» . Мерсисайд ЛТП. Архивировано из оригинала 9 мая 2009 года . Проверено 8 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «План местного транспорта Уоррингтона на 2006–2011 годы» . Городской совет Уоррингтона . Архивировано из оригинала 8 января 2009 года . Проверено 8 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «Домашняя страница Совета графства Чешир» . Совет графства Чешир . Архивировано из оригинала 27 февраля 2007 года . Проверено 8 мая 2009 г.
- ^ «Окончательный стратегический отчет – Зона 9, M6 (от перекрестка 11a до перекрестка 20)» . Стратегия управления маршрутами . Агентство автомобильных дорог . Архивировано из оригинала 30 сентября 2007 года . Проверено 16 октября 2007 г.
- ^ «Статистика дорожного движения 2006» . Департамент транспорта. Архивировано из оригинала (XLS) 6 марта 2008 года . Проверено 16 октября 2007 г.
- ^ «Обходной канал высокого и низкого Ньютона A590» . Агентство автомобильных дорог . Архивировано из оригинала 30 сентября 2007 года . Проверено 16 октября 2007 г.
- ^ «Дорожная полиция» . Веб-сайт полиции Чешира. Архивировано из оригинала 27 сентября 2007 года . Проверено 16 октября 2007 г.
- ^ «Ежегодная статистика аэропортов CAA за 2007 год» . Caa.co.uk. Архивировано из оригинала 16 мая 2012 года . Проверено 17 мая 2012 г.
- ^ «Лондон и Манчестер лидируют в опросе о бизнесе в Великобритании» . Веб-страницы Cushman & Wakefield . Кушман и Уэйкфилд . 24 сентября 2008 г. Архивировано из оригинала 27 ноября 2008 г. Проверено 24 сентября 2008 г.
- ^ «Жизнь на Северо-Западе» . АстраЗенека . Архивировано из оригинала 26 октября 2011 года . Проверено 20 сентября 2011 г.
- ^ «Кто проводит тестирование ДНК Джереми Кайла?» . АльфаБиолабс . 29 апреля 2019 года . Проверено 19 января 2021 г.
- ^ «Аэрокосмическая промышленность» . Совет графства Ланкашир - офис главы исполнительной власти. Архивировано из оригинала 1 сентября 2011 года . Проверено 10 июня 2012 г.
- ^ «Годовые продажи BAE Systems упали на 14%» . Новости Би-би-си. 16 февраля 2012 года. Архивировано из оригинала 11 мая 2012 года . Проверено 10 июня 2012 г.
- ^ «Где в мире? Барнольдсвик» . Роллс-Ройс. Архивировано из оригинала 31 декабря 2011 года . Проверено 10 июня 2012 г.
- ^ «Аэрофирма Pendle Weston EU продана за 54 миллиона фунтов стерлингов» . Ланкаширский телеграф . 30 ноября 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 27 марта 2012 года . Проверено 10 июня 2012 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж «Крупнейшие фирмы Восточного Ланкашира планируют нанять персонал в 2011 году» . Ланкаширский телеграф . 9 января 2011 года. Архивировано из оригинала 26 августа 2014 года . Проверено 10 июня 2012 г.
- ^ «Aircelle Ltd. получает признание «Бизнес года» в Ланкашире, Англия» . Эйрсель. 18 ноября 2008 г. Архивировано из оригинала 16 ноября 2008 г. Проверено 10 июня 2012 г.
- ^ «40 новых рабочих мест — это именно то, что прописал доктор» . Лейланд Гардиан. 25 февраля 2009 г. Архивировано из оригинала 2 июня 2013 г. Проверено 14 июня 2012 г.
- ^ Хенли, Джон (21 июня 2011 г.). «Насколько хороша пицца доктора Эткера?» . Хранитель . Архивировано из оригинала 27 августа 2014 года . Проверено 14 июня 2012 г.
- ^ Сэлвидж, Рэйчел (29 апреля 2023 г.). «Фирма сбрасывает в реку Ланкашир почти 800 кг «вечной химии» в год» . Хранитель .
- ^ «Премия Lancashire Telegraph Business Awards: победитель в области экспорта Fort Vale Engineering» . Ланкаширский телеграф . 14 ноября 2011 г. Архивировано из оригинала 2 апреля 2012 г. Проверено 16 июня 2012 г.
- ^ «Сенатор получил награду «Бизнес года»» . Ланкаширский телеграф . 6 декабря 2006 г. Архивировано из оригинала 26 августа 2014 г. Проверено 16 июня 2012 г.
- ^ «Группа празднует десятилетие ромашек» . Коммуникационный бизнес. 5 октября 2011 г. Архивировано из оригинала 14 декабря 2021 г. . Проверено 7 июня 2012 г.
- ^ "О" . Юнайтед Бисквитс. Архивировано из оригинала 27 мая 2012 года . Проверено 17 мая 2012 г.
- ^ «Сент-Хеленс сегодня: новости, спорт, работа, недвижимость, автомобили, развлечения и многое другое» . Sthelensreporter.co.uk . Архивировано из оригинала 13 мая 2012 года . Проверено 17 мая 2012 г.
- ^ «Звезда Сент-Хеленс - Новости, спорт, Лига регби Сэйнтс, Недвижимость на продажу, аренда в Сент-Хеленс, Мерсисайд» . Sthelensstar.co.uk . Архивировано из оригинала 21 мая 2012 года . Проверено 17 мая 2012 г.
Внешние ссылки
[ редактировать ] по Северо-Западной Англии от Wikivoyage Путеводитель
по Северо-Западной Англии от Wikivoyage Путеводитель