Римская республика
Римская республика Res publica Romana | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| в. 509 г. до н.э. – 27 г. до н.э. | |||||||||
Денарий 54 г. до н. э., изображающий первого римского консула Луция Юния Брута в окружении двух ликторов и которому предшествует акценс . [1] | |||||||||
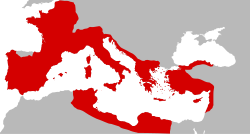 Roman provinces on the eve of the assassination of Julius Caesar, 44 BC | |||||||||
| Capital | Rome | ||||||||
| Official languages | Latin | ||||||||
| Religion | Roman polytheism | ||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Roman | ||||||||
| Government | Consular republic | ||||||||
| Consuls | |||||||||
• 509 BC (first) | |||||||||
• 27 BC (last) | |||||||||
| Legislature | Assemblies | ||||||||
| Historical era | Classical antiquity | ||||||||
| c. 509 BC | |||||||||
• Dissolution of the Latin League | 338 BC[2] | ||||||||
| 82 BC | |||||||||
• Julius Caesar named dictator for life | February 44 BC | ||||||||
| 15 March 44 BC | |||||||||
| 2 September 31 BC | |||||||||
| 16 January 27 BC | |||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| 326 BC[3] | 10,000 km2 (3,900 sq mi) | ||||||||
| 50 BC[3] | 1,950,000 km2 (750,000 sq mi) | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Римская республика ( лат . Res publica Romana [ˈreːs ˈpuːblɪka roːˈmaːna] ) — эпоха классической римской цивилизации, начавшаяся со свержения ( Римского королевства традиционно датируемая 509 г. до н. э.) и завершившаяся в 27 г. до н. э. созданием Римской империи после Война Акциума . В этот период контроль Рима расширился от ближайших окрестностей города до гегемонии над всем Средиземноморским миром .
Римское общество в то время представляло собой прежде всего культурную смесь латинского и этрусского обществ, а также сабинских, осканских и греческих культурных элементов, что особенно заметно в древнеримской религии и ее Пантеоне . Ее политическая организация развивалась примерно в то же время, что и прямая демократия в Древней Греции , с коллективными и ежегодными магистратурами, контролируемыми сенатом . [4] Выборы проводились ежегодно, но республиканская система представляла собой выборную олигархию , а не демократию ; небольшое количество влиятельных семей в значительной степени монополизировали должности магистратуры. Римские институты претерпели значительные изменения по всей республике, чтобы адаптироваться к трудностям, с которыми она столкнулась, например, создание промагистратов для управления завоеванными провинциями или состав сената.
Unlike the Pax Romana of the Roman Empire, throughout the republican era Rome was in a state of quasi-perpetual war. Its first enemies were its Latin and Etruscan neighbours, as well as the Gauls, who sacked Rome in 387 BC. After the Gallic sack, Rome conquered the whole Italian Peninsula in a century and thus became a major power in the Mediterranean. Its greatest strategic rival was Carthage, against which it waged three wars. Rome defeated Carthage at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC, becoming the dominant power of the ancient Mediterranean world. It then embarked on a long series of difficult conquests, defeating Philip V and Perseus of Macedon, Antiochus III of the Seleucid Empire, the Lusitanian Viriathus, the Numidian Jugurtha, the Pontic king Mithridates VI, Vercingetorix of the Arverni tribe of Gaul, and the Egyptian queen Cleopatra.
At home, during the Conflict of the Orders, the patricians, the closed oligarchic elite, came into conflict with the more numerous plebs; this was resolved peacefully, with the plebs achieving political equality by the 4th century BC. The late Republic, from 133 BC onward, saw substantial domestic strife, often anachronistically seen as a conflict between optimates and populares, referring to conservative and reformist politicians, respectively. The Social War between Rome and its Italian allies over citizenship and Roman hegemony in Italy greatly expanded the scope of civil violence. Mass slavery also contributed to three Servile Wars. Tensions at home coupled with ambitions abroad led to further civil wars. The first involved Marius and Sulla. After a generation, the Republic fell into civil war again in 49 BC between Julius Caesar and Pompey. Despite his victory and appointment as dictator for life, Caesar was assassinated in 44 BC. Caesar's heir Octavian and lieutenant Mark Antony defeated Caesar's assassins in 42 BC, but they eventually split. Antony's defeat alongside his ally and lover Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the Senate's grant of extraordinary powers to Octavian as Augustus in 27 BC—which effectively made him the first Roman emperor—marked the end of the Republic.
History
[edit]Founding
[edit]Rome had been ruled by monarchs since its foundation. These monarchs were elected, for life, by the men of the Roman Senate. The last Roman monarch was called Tarquin the Proud, who in traditional histories was expelled from Rome in 509 BC because his son, Sextus Tarquinius, raped a noblewoman, Lucretia.[5][6][7] The tradition asserted that the monarchy was abolished in a revolution led by the semi-mythical Lucius Junius Brutus and the king's powers were then transferred to two separate consuls elected to office for a term of one year; each was capable of checking his colleague by veto.[8] Most modern scholarship describes these accounts as the quasi-mythological detailing of an aristocratic coup within Tarquin's own family[9] or a consequence of an Etruscan occupation of Rome rather than a popular revolution.[10]
Rome in Latium
[edit]Early campaigns
[edit]
 |
|---|
| Periods |
|
| Constitution |
| Political institutions |
| Assemblies |
| Ordinary magistrates |
| Extraordinary magistrates |
| Public law |
| Senatus consultum ultimum |
| Titles and honours |
According to Rome's traditional histories, Tarquin made several attempts to retake the throne, including the Tarquinian conspiracy, which involved Brutus's own sons, the war with Veii and Tarquinii, and finally the war between Rome and Clusium. The attempts to restore the monarchy did not succeed.[11]
The first Roman republican wars were wars of expansion. One by one, Rome defeated both the persistent Sabines and the local cities. Rome defeated its rival Latin cities in the Battle of Lake Regillus in 496 BC, the Battle of Ariccia in 495 BC, the Battle of Mount Algidus in 458 BC, and the Battle of Corbio in 446 BC. But it suffered a significant defeat at the Battle of the Cremera in 477 BC, wherein it fought against the most important Etruscan city, Veii; this defeat was later avenged at the Battle of Veii in 396 BC, wherein Rome destroyed the city.[12][13][13] By the end of this period, Rome had effectively completed the conquest of its immediate Etruscan and Latin neighbours and secured its position against the immediate threat posed by the nearby Apennine hill tribes.
Plebeians and patricians
[edit]Beginning with their revolt against Tarquin, and continuing through the early years of the Republic, Rome's patrician aristocrats were the dominant force in politics and society. They initially formed a closed group of about 50 large families, called gentes, who monopolised Rome's magistracies, state priesthoods, and senior military posts. The most prominent of these families were the Cornelii, Aemilii, Claudii, Fabii, and Valerii. The leading families' power, privilege and influence derived from their wealth, in particular from their landholdings, their position as patrons, and their numerous clients.[14]
The vast majority of Roman citizens were commoners of various social degrees. They formed the backbone of Rome's economy, as smallholding farmers, managers, artisans, traders, and tenants. In wartime, they could be summoned for military service. Most had little direct political influence. During the early Republic, the plebs (or plebeians) emerged as a self-organised, culturally distinct group of commoners, with its own internal hierarchy, laws, customs, and interests.[15] Plebeians had no access to high religious and civil office.[a] For the poorest, one of the few effective political tools was their withdrawal of labour and services, in a "secessio plebis"; the first such secession occurred in 494 BC, in protest at the abusive treatment of plebeian debtors by the wealthy during a famine.[b] The patrician Senate was compelled to give them direct access to the written civil and religious laws and to the electoral and political process. To represent their interests, the plebs elected tribunes, who were personally sacrosanct, immune to arbitrary arrest by any magistrate, and had veto power over legislation.[c]
Celtic invasion of Italy
[edit]By 390 BC, several Gallic tribes were invading Italy from the north. The Romans met the Gauls in pitched battle at the Battle of Allia River around 390–387 BC. The battle was fought at the confluence of the Tiber and Allia rivers, 11 Roman miles (10 mi or 16 km) north of Rome. The Romans were routed and subsequently Rome was sacked by the Senones.[16] There is no destruction layer at Rome around this time, indicating that if a sack occurred, it was largely superficial.[17][better source needed]
Roman expansion in Italy
[edit]
Wars against Italian neighbours
[edit]
From 343 to 341 BC, Rome won two battles against its Samnite neighbours, but was unable to consolidate its gains, due to the outbreak of war with former Latin allies. In the Latin War (340–338 BC), Rome defeated a coalition of Latins at the battles of Vesuvius and the Trifanum. The Latins submitted to Roman rule.[18]
A Second Samnite War began in 327 BC.[19] The war ended with Samnite defeat at the Battle of Bovianum in 305 BC. By 304 BC, Rome had annexed most Samnite territory and begun to establish colonies there, but in 298 BC the Samnites rebelled, and defeated a Roman army, in a Third Samnite War. After this success, it built a coalition of several previous enemies of Rome.[20] The war ended with Roman victory in 290 BC.
At the Battle of Populonia, in 282 BC, Rome finished off the last vestiges of Etruscan power in the region.
Rise of the plebeian nobility
[edit]In the 4th century, plebeians gradually obtained political equality with patricians. The first plebeian consular tribunes were elected in 400. The reason behind this sudden gain is unknown,[d] but it was limited as patrician tribunes retained preeminence over their plebeian colleagues.[22] In 385 BC, the former consul and saviour of the besieged capital, Marcus Manlius Capitolinus, is said to have sided with the plebeians, ruined by the sack and largely indebted to patricians. According to Livy, Capitolinus sold his estate to repay the debt of many of them, and even went over to the plebs, the first patrician to do so. Nevertheless, the growing unrest he had caused led to his trial for seeking kingly power; he was sentenced to death and thrown from the Tarpeian Rock.[23][24]
Between 376 BC and 367 BC, the tribunes of the plebs Gaius Licinius Stolo and Lucius Sextius Lateranus continued the plebeian agitation and pushed for an ambitious legislation, known as the Leges Liciniae Sextiae. The most important bill opened the consulship to plebeians.[25] Other tribunes controlled by the patricians vetoed the bills, but Stolo and Lateranus retaliated by vetoing the elections for five years while being continuously reelected by the plebs, resulting in a stalemate.[e] In 367 BC, they carried a bill creating the Decemviri sacris faciundis, a college of ten priests, of whom five had to be plebeians, thereby breaking patricians' monopoly on priesthoods. The resolution of the crisis came from the dictator Camillus, who made a compromise with the tribunes: he agreed to their bills, and they in return consented to the creation of the offices of praetor and curule aediles, both reserved to patricians. Lateranus became the first plebeian consul in 366 BC; Stolo followed in 361 BC.[26][27][28]
Soon after, plebeians were able to hold both the dictatorship and the censorship. The four-time consul Gaius Marcius Rutilus became the first plebeian dictator in 356 BC and censor in 351 BC. In 342 BC, the tribune of the plebs Lucius Genucius passed his leges Genuciae, which abolished interest on loans, in a renewed effort to tackle indebtedness; required the election of at least one plebeian consul each year; and prohibited magistrates from holding the same magistracy for the next ten years or two magistracies in the same year.[29][30][31] In 339 BC, the plebeian consul and dictator Quintus Publilius Philo passed three laws extending the plebeians' powers. His first law followed the lex Genucia by reserving one censorship to plebeians, the second made plebiscites binding on all citizens (including patricians), and the third required the Senate to give its prior approval to plebiscites before they became binding on all citizens.[32]
During the early Republic, consuls chose senators from among their supporters. Shortly before 312 BC, the lex Ovinia transferred this power to the censors, who could only remove senators for misconduct, thus appointing them for life. This law strongly increased the power of the Senate, which was by now protected from the influence of the consuls and became the central organ of government.[33][34][f] In 312 BC, following this law, the patrician censor Appius Claudius Caecus appointed many more senators to fill the new limit of 300, including descendants of freedmen, which was deemed scandalous. Caecus also launched a vast construction program, building the first aqueduct, the Aqua Appia, and the first Roman road, the Via Appia.[35]
In 300 BC, the two tribunes of the plebs Gnaeus and Quintus Ogulnius passed the lex Ogulnia, which created four plebeian pontiffs, equalling the number of patrician pontiffs, and five plebeian augurs, outnumbering the four patricians in the college.[36] The Conflict of the Orders ended with the last secession of the plebs around 287. The dictator Quintus Hortensius passed the lex Hortensia, which reenacted the law of 339 BC, making plebiscites binding on all citizens, while also removing the requirement for prior Senate approval.[37] These events were a political victory of the wealthy plebeian elite, who exploited the economic difficulties of the plebs for their own gain: Stolo, Lateranus, and Genucius bound their bills attacking patricians' political supremacy with debt-relief measures.[38] As a result of the end of the patrician monopoly on senior magistracies, many small patrician gentes faded into history during the 4th and 3rd centuries BC due to the lack of available positions. About a dozen remaining patrician gentes and 20 plebeian ones thus formed a new elite, called the nobiles, or Nobilitas.[39]
Pyrrhic War
[edit]
By the early 3rd century BC, Rome had established itself as the major power in Italy, but had not yet come into conflict with the dominant military powers of the Mediterranean: Carthage and the Greek kingdoms.[40] In 282, several Roman warships entered the harbour of Tarentum, triggering a violent reaction from the Tarentine democrats, who sank some. The Roman embassy sent to investigate the affair was insulted and war was promptly declared.[41] Facing a hopeless situation, the Tarentines (together with the Lucanians and Samnites) appealed to Pyrrhus, king of Epirus, for military aid. A cousin of Alexander the Great, he was eager to build an empire for himself in the western Mediterranean and saw Tarentum's plea as a perfect opportunity.[42]
Pyrrhus and his army of 25,500 men (with 20 war elephants) landed in Italy in 280 BC. The Romans were defeated at Heraclea, as their cavalry were afraid of Pyrrhus's elephants. Pyrrhus then marched on Rome, but the Romans concluded a peace in the north and moved south with reinforcements, placing Pyrrhus in danger of being flanked by two consular armies; Pyrrhus withdrew to Tarentum. In 279 BC, Pyrrhus met the consuls Publius Decius Mus and Publius Sulpicius Saverrio at the Battle of Asculum, which remained undecided for two days. Finally, Pyrrhus personally charged into the melee and won the battle but at the cost of an important part of his troops; he allegedly said, "if we are victorious in one more battle with the Romans, we shall be utterly ruined."[43][g]
He escaped the Italian deadlock by answering a call for help from Syracuse, where tyrant Thoenon was desperately fighting an invasion from Carthage. Pyrrhus could not let them take the whole island, as it would have compromised his ambitions in the western Mediterranean, and so declared war. The Carthaginians lifted the siege of Syracuse before his arrival, but he could not entirely oust them from the island as he failed to take their fortress of Lilybaeum.[44] His harsh rule soon led to widespread antipathy among the Sicilians; some cities even defected to Carthage. In 275 BC, Pyrrhus left the island before he had to face a full-scale rebellion.[45] He returned to Italy, where his Samnite allies were on the verge of losing the war. Pyrrhus again met the Romans at the Battle of Beneventum. This time, the consul Manius Dentatus was victorious and even captured eight elephants. Pyrrhus then withdrew from Italy, but left a garrison in Tarentum, to wage a new campaign in Greece against Antigonus II Gonatas of Macedonia. His death in battle at Argos in 272 BC forced Tarentum to surrender to Rome.
Punic Wars and expansion in the Mediterranean
[edit]First Punic War (264–241 BC)
[edit]

Rome and Carthage were initially on friendly terms, lastly in an alliance against Pyrrhus, [46][47][48] but tensions rapidly rose after the departure of the Epirote king. Between 288 and 283 BC, Messina in Sicily was taken by the Mamertines, a band of mercenaries formerly employed by Agathocles. They plundered the surroundings until Hiero II, the new tyrant of Syracuse, defeated them (in either 269 or 265 BC). In effect under a Carthaginian protectorate, the remaining Mamertines appealed to Rome to regain their independence. Senators were divided on whether to help. A supporter of war, the consul Appius Claudius Caudex, turned to one of the popular assemblies to get a favourable vote by promising plunder to the voters.[h] After the assembly ratified an alliance with the Mamertines, Caudex was dispatched to cross the strait and lend aid.[49]

Messina fell under Roman control quickly.[50] Syracuse and Carthage, at war for centuries, responded with an alliance to counter the invasion and blockaded Messina, but Caudex defeated Hiero and Carthage separately.[51][52] His successor, Manius Valerius Maximus, landed with an army of 40,000 men and conquered eastern Sicily, which prompted Hiero to shift his allegiance and forge a long-lasting alliance with Rome. In 262 BC, the Romans moved to the southern coast and besieged Akragas. In order to raise the siege, Carthage sent reinforcements, including 60 elephants—the first time they used them—but still lost the battle.[53] Nevertheless, Rome could not take all of Sicily because Carthage's naval superiority prevented it from effectively besieging coastal cities. Using a captured Carthaginian ship as blueprint, Rome therefore launched a massive construction program and built 100 quinqueremes in only two months. It also invented a new device, the corvus, a grappling engine that enabled a crew to board an enemy ship.[54] The consul for 260 BC, Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Asina, lost the first naval skirmish of the war against Hannibal Gisco at Lipara, but his colleague Gaius Duilius won a great victory at Mylae. He destroyed or captured 44 ships and was the first Roman to receive a naval triumph, which also included captive Carthaginians for the first time.[55] Although Carthage was victorious on land at Thermae in Sicily, the corvus gave a strong advantage to Rome on the waters. The consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio (Asina's brother) captured Corsica in 259 BC; his successors won the naval battles of Sulci in 258, Tyndaris in 257 BC, and Cape Ecnomus in 256.[56]

To hasten the end of the war, the consuls for 256 BC decided to carry the operations to Africa, on Carthage's homeland. The consul Marcus Atilius Regulus landed on the Cap Bon peninsula with about 18,000 soldiers. He captured the city of Aspis, repulsed Carthage's counterattack at Adys, and took Tunis. The Carthaginians hired Spartan mercenaries, led by Xanthippus, to command their troops.[58] In 255, the Spartan general marched on Regulus, crushing the Roman infantry on the Bagradas plain; only 2,000 soldiers escaped, and Regulus was captured. The consuls for 255 nonetheless won a naval victory at Cape Hermaeum, where they captured 114 warships. This success was spoilt by a storm that annihilated the victorious navy: 184 ships of 264 sank, 25,000 soldiers and 75,000 rowers drowned. The corvus considerably hindered ships' navigation and made them vulnerable during tempest. It was abandoned after another similar catastrophe in 253 BC. These disasters prevented any significant campaign between 254 and 252 BC.[59]

Hostilities in Sicily resumed in 252 BC, with Rome's taking of Thermae. The next year, Carthage besieged Lucius Caecilius Metellus, who held Panormos (now Palermo). The consul had dug trenches to counter the elephants, which once hurt by missiles turned back on their own army, resulting in a great victory for Metellus. Rome then besieged the last Carthaginian strongholds in Sicily, Lilybaeum and Drepana, but these cities were impregnable by land. Publius Claudius Pulcher, the consul of 249, recklessly tried to take the latter from the sea, but suffered a terrible defeat; his colleague Lucius Junius Pullus likewise lost his fleet off Lilybaeum. Without the corvus, Roman warships had lost their advantage. By now, both sides were drained and could not undertake large-scale operations. The only military activity during this period was the landing in Sicily of Hamilcar Barca in 247 BC, who harassed the Romans with a mercenary army from a citadel he built on Mt. Eryx.[61]
Unable to take the Punic fortresses in Sicily, Rome tried to decide the war at sea and built a new navy, thanks to a forced borrowing from the rich. In 242 BC, 200 quinqueremes under consul Gaius Lutatius Catulus blockaded Drepana. The rescue fleet from Carthage was soundly defeated by Catulus. Exhausted and unable to bring supplies to Sicily, Carthage sued for peace. Carthage had to pay 1,000 talents immediately and 2,200 over ten years and evacuate Sicily. The fine was so high that Carthage could not pay Hamilcar's mercenaries, who had been shipped back to Africa. They revolted during the Mercenary War, which Carthage suppressed with enormous difficulty. Meanwhile, Rome took advantage of a similar revolt in Sardinia to seize the island from Carthage, in violation of the peace treaty. This led to permanent bitterness in Carthage.[62]
Second Punic War
[edit]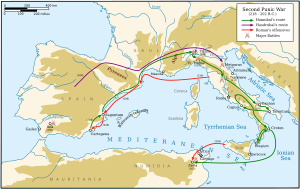
After its victory, the Republic shifted its attention to its northern border as the Insubres and Boii were threatening Italy.[63] Meanwhile, Carthage compensated the loss of Sicily and Sardinia with the conquest of Southern Hispania (up to Salamanca), and its rich silver mines.[64] This rapid expansion worried Rome, which concluded a treaty with Hasdrubal in 226, stating that Carthage could not cross the Ebro river.[65][66] But the city of Saguntum, south of the Ebro, appealed to Rome in 220 to act as arbitrator during a period of internal strife. Hannibal took the city in 219,[67] triggering the Second Punic War.[68]
Initially, the Republic's plan was to carry war outside Italy, sending the consuls P. Cornelius Scipio to Hispania and Ti. Sempronius Longus to Africa, while their naval superiority prevented Carthage from attacking from the sea.[69] This plan was thwarted by Hannibal's bold move to Italy. In May 218, he crossed the Ebro with a large army of about 100,000 soldiers and 37 elephants.[70] He passed in Gaul, crossed the Rhone, then the Alps, possibly through the Col de Clapier.[71] This exploit cost him almost half of his troops,[72] but he could now rely on the Boii and Insubres, still at war with Rome.[73] Publius Scipio, who had failed to block Hannibal on the Rhone, sent his elder brother Gnaeus with the main part of his army in Hispania according to the initial plan, and went back to Italy with the rest to resist Hannibal in Italy, but he was defeated and wounded near the Ticino river.[74]

Hannibal then marched south and won three outstanding victories. The first one was on the banks of the Trebia in December 218, where he defeated the other consul Ti. Sempronius Longus. More than half the Roman army was lost. Hannibal then ravaged the country around Arretium to lure the new consul C. Flaminius into a trap at Lake Trasimene. This clever ambush resulted in the death of the consul and the complete destruction of his army of 30,000 men. In 216, the new consuls L. Aemilius Paullus and C. Terentius Varro mustered the biggest army possible, with eight legions—some 80,000 soldiers, twice as many as the Punic army—and confronted Hannibal, who was encamped at Cannae, in Apulia. Despite his numerical disadvantage, Hannibal used his heavier cavalry to rout the Roman wings and envelop their infantry, which he annihilated. In terms of casualties, the Battle of Cannae was the worst defeat in Roman history: only 14,500 soldiers escaped, and Paullus was killed as well as 80 senators.[76][i] Soon after, the Boii ambushed the army of the consul-elect for 215, L. Postumius Albinus, who died with all his army of 25,000 men in the Battle of Silva Litana.[77]
These disasters triggered a wave of defection among Roman allies, with the rebellions of the Samnites, Oscans, Lucanians, and Greek cities of Southern Italy.[78] In Macedonia, Philip V also made an alliance with Hannibal in order to take Illyria and the area around Epidamnus, occupied by Rome. His attack on Apollonia started the First Macedonian War. In 215, Hiero II of Syracuse died of old age, and his young grandson Hieronymus broke the long alliance with Rome to side with Carthage. At this desperate point, the aggressive strategy against Hannibal the Scipiones advocated was abandoned in favour of a slow reconquest of the lost territories, since Hannibal could not be everywhere to defend them.[79] Although he remained invincible on the battlefield, defeating all the Roman armies on his way, he could not prevent Claudius Marcellus from taking Syracuse in 212 after a long siege, nor the fall of his bases of Capua and Tarentum in 211 and 209.
In Hispania, Publius and Gnaeus Scipio won the battles of Cissa in 218, soon after Hannibal's departure, and Dertosa against his brother Hasdrubal in 215, which enabled them to conquer the eastern coast of Hispania. But in 211, Hasdrubal and Mago Barca successfully turned the Celtiberian tribes that supported the Scipiones, and attacked them simultaneously at the Battle of the Upper Baetis, in which the Scipiones died.[80] Publius's son, the future Scipio Africanus, was then elected with a special proconsulship to lead the Hispanic campaign, winning a series of battles with ingenious tactics. In 209, he took Carthago Nova, the main Punic base in Hispania. The next year, he defeated Hasdrubal at the Battle of Baecula.[80] After his defeat, Carthage ordered Hasdrubal to reinforce his brother in Italy. Since he could not use ships, he followed the same route as his brother through the Alps, but the consuls M. Livius Salinator and C. Claudius Nero were awaiting him and defeated him in the Battle of the Metaurus, where Hasdrubal died.[81] It was the turning point of the war. The campaign of attrition had worked well: Hannibal's troops were now depleted; he only had one elephant left (Surus) and retreated to Bruttium, on the defensive. In Greece, Rome contained Philip V without devoting too many forces by allying with the Aetolian League, Sparta, and Pergamon, which also prevented Philip from aiding Hannibal. The war with Macedon resulted in a stalemate, with the Treaty of Phoenice signed in 205.
In Hispania, Scipio continued his successful campaign at the battles of Carmona in 207, and Ilipa (now Seville) in 206, which ended the Punic threat on the peninsula.[82] Elected consul in 205, he convinced the Senate to invade Africa with the support of the Numidian king Masinissa, who had defected to Rome. Scipio landed in Africa in 204. He took Utica and then won the Battle of the Great Plains, which prompted Carthage to open peace negotiations. The talks failed because Scipio wanted to impose harsher terms on Carthage to prevent it from rising again as a threat. Hannibal was therefore sent to face Scipio at Zama. Scipio could now use the heavy Numidian cavalry of Massinissa—which had hitherto been so successful against Rome—to rout the Punic wings, then flank the infantry, as Hannibal had done at Cannae. Defeated for the first time, Hannibal convinced the Carthaginian Senate to pay the war indemnity, which was even harsher than that of 241: 10,000 talents in 50 instalments. Carthage also had to give up all its elephants, all its fleet but ten triremes, and all its possessions outside its core territory in Africa (what is now Tunisia), and it could not declare war without Roman authorisation. In effect, Carthage was condemned to be a minor power, while Rome recovered from a desperate situation to dominate the western Mediterranean.
Roman supremacy in the Greek East
[edit]| Macedonian Wars |
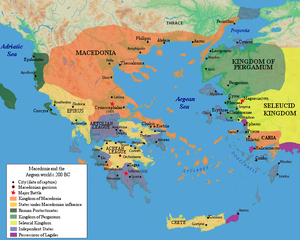 |
Rome's preoccupation with its war with Carthage provided an opportunity for Philip V of Macedonia, in the north of the Greek peninsula, to attempt to extend his power westward. He sent ambassadors to Hannibal's camp in Italy, to negotiate an alliance as common enemies of Rome.[83] But Rome discovered the agreement when Philip's emissaries were captured by a Roman fleet.[83] The First Macedonian War saw the Romans involved directly in only limited land operations, but they achieved their objective of occupying Philip and preventing him from aiding Hannibal.
The past century had seen the Greek world dominated by the three primary successor kingdoms of Alexander the Great's empire: Ptolemaic Egypt, Macedonia and the Seleucid Empire. In 202, internal problems led to a weakening of Egypt's position, disrupting the power balance among the successor states. Macedonia and the Seleucid Empire agreed to an alliance to conquer and divide Egypt.[84] Fearing this increasingly unstable situation, several small Greek kingdoms sent delegations to Rome to seek an alliance.[85] Rome gave Philip an ultimatum to cease his campaigns against Rome's new Greek allies. Doubting Rome's strength, Philip ignored the request, and Rome sent an army of Romans and Greek allies, beginning the Second Macedonian War.[86] In 197, the Romans decisively defeated Philip at the Battle of Cynoscephalae, and Philip was forced to give up his recent Greek conquests.[87] The Romans declared the "Peace of the Greeks", believing that Philip's defeat now meant that Greece would be stable, and pulled out of Greece entirely.[88]
With Egypt and Macedonia weakened, the Seleucid Empire made increasingly aggressive and successful attempts to conquer the entire Greek world.[89] Now not only Rome's allies against Philip, but even Philip himself, sought a Roman alliance against the Seleucids.[90] The situation was exacerbated by the fact that Hannibal was now a chief military advisor to the Seleucid emperor, and the two were believed to be planning outright conquest not just of Greece, but also of Rome.[91] The Seleucids were much stronger than the Macedonians had ever been, because they controlled much of the former Persian Empire and had almost entirely reassembled Alexander the Great's former empire.[91]
Fearing the worst, the Romans began a major mobilization, all but pulling out of recently conquered Spain and Gaul.[91] This fear was shared by Rome's Greek allies, who now followed Rome again for the first time since that war.[91] A major Roman-Greek force was mobilized under the command of the great hero of the Second Punic War, Scipio Africanus, and set out for Greece, beginning the Roman–Seleucid War. After initial fighting that revealed serious Seleucid weaknesses, the Seleucids tried to turn the Roman strength against them at the Battle of Thermopylae, but were forced to evacuate Greece.[90] The Romans pursued the Seleucids by crossing the Hellespont, the first time a Roman army had ever entered Asia.[90] The decisive engagement was fought at the Battle of Magnesia, resulting in complete Roman victory.[90][92] The Seleucids sued for peace, and Rome forced them to give up their recent Greek conquests. Rome again withdrew from Greece, assuming (or hoping) that the lack of a major Greek power would ensure a stable peace. In fact, it did the opposite.[93]
Conquest of Greece
[edit]

In 179, Philip died.[95] His talented and ambitious son, Perseus, took the throne and showed a renewed interest in conquering Greece.[96] With its Greek allies facing a major new threat, Rome declared war on Macedonia again, starting the Third Macedonian War. Perseus initially had some success against the Romans, but Rome responded by sending a stronger army which decisively defeated the Macedonians at the Battle of Pydna in 168.[97] The Macedonians capitulated, ending the war.[98]
Convinced now that the Greeks (and therefore the rest of the region) would not have peace if left alone, Rome decided to establish its first permanent foothold in the Greek world, and divided Macedonia into four client republics.[99] Yet Macedonian agitation continued. The Fourth Macedonian War, 150 to 148 BC, was fought against a Macedonian pretender to the throne who was again destabilizing Greece by trying to reestablish the old kingdom. The Romans swiftly defeated the Macedonians at the second battle of Pydna.
The Achaean League, seeing the direction of Roman policy trending towards direct administration, met at Corinth and declared war "nominally against Sparta but in reality, against Rome".[100] It was swiftly defeated: in 146, the same year as the destruction of Carthage, Corinth was besieged and destroyed, forcing the league's surrender. Rome decided to divide Macedonia into two new, directly administered Roman provinces, Achaea and Macedonia.[101]
Third Punic War
[edit]For Carthage, the Third Punic War was a simple punitive mission after the neighbouring Numidians allied to Rome robbed and attacked Carthaginian merchants. Treaties had forbidden any war with Roman allies; viewing defence against banditry as "war action", Rome decided to annihilate Carthage.[102] Carthage was almost defenceless, and submitted when besieged.[103] But the Romans demanded complete surrender and removal of the city into the desert hinterland, far from any coastal or harbour region; the Carthaginians refused. The city was besieged and completely destroyed.[104] Rome acquired all of Carthage's North African and Iberian territories. The Romans rebuilt Carthage 100 years later as a Roman colony, by order of Julius Caesar. It flourished, becoming one of the most important cities in the Roman Empire.[105]
Social troubles and first civil war
[edit]Views on the structural causes of the Republic's collapse differ. One enduring thesis is that Rome's expansion destabilized its social organization between conflicting interests; the Senate's policymaking, blinded by its own short-term self-interest, alienated large portions of society, who then joined powerful generals who sought to overthrow the system.[106] Two other theses have challenged this view. The first blames the Romans' inability to conceive of plausible alternatives to the traditional republican system in a "crisis without alternative".[107] The second instead stresses the continuity of the republic: until its disruption by Caesar's civil war and the following two decades of civil war created conditions for autocratic rule and made return to republican politics impossible: and, per Erich S. Gruen, "civil war caused the fall of the republic, not vice versa".[108]
A core cause of the Republic's eventual demise was the loss of elite's cohesion from c. 133 BC: the ancient sources called this moral decay from wealth and the hubris of Rome's domination of the Mediterranean.[109] Modern sources have proposed multiple reasons why the elite lost cohesion, including wealth inequality and a growing willingness by aristocrats to transgress political norms, especially in the aftermath of the Social War.[110]
Gracchan period
[edit]In the winter of 138–137 BC, a first slave uprising, known as the First Servile War, broke out in Sicily. After initial successes, the slaves led by Eunus and Cleon were defeated by Marcus Perperna and Publius Rupilius in 132 BC.[111]
In this context, Tiberius Gracchus was elected plebeian tribune in 133 BC. He attempted to enact a law to limit the amount of land anyone could own and establish a commission to distribute public lands to poor rural plebs.[112] The aristocrats, who stood to lose an enormous amount of money, bitterly opposed this proposal. Tiberius submitted this law to the Plebeian Council, but it was vetoed by fellow tribune Marcus Octavius.[113] Tiberius induced the plebs to depose Octavius from his office on the grounds that Octavius acted contrary to the manifest will of the people, a position that was unprecedented and constitutionally dubious.[114][115] His law was enacted and took effect,[j] but, when Tiberius ostentatiously stood for reelection to the tribunate, he was murdered by his enemies.[118]
Tiberius's brother Gaius was elected tribune ten years later in 123 and reelected for 122. He induced the plebs to reinforce rights of appeal to the people against capital extrajudicial punishments and institute reforms to improve the people's welfare. While ancient sources tend to "conceive Gracchus' legislation as an elaborate plot against the authority of the Senate... he showed no sign of wanting to replace the Senate in its normal functions".[119] Amid wide-ranging and popular reforms to create grain subsidies, change jury pools, establish and require the Senate to assign provinces before elections, Gaius proposed a law that would grant citizenship rights to Rome's Italian allies.[120] He stood for election to a third term in 121 but was defeated. During violent protests over repeal of an ally's colonisation bill, the Senate moved the first senatus consultum ultimum against him, resulting in his death, with many others, on the Aventine.[121] His legislation (like that of his brother) survived; the Roman aristocracy disliked the Gracchan agitation but accepted their policies.[122]
In 121, the province of Gallia Narbonensis was established after the victory of Quintus Fabius Maximus over a coalition of Arverni and Allobroges in southern Gaul in 123. Lucius Licinius Crassus founded the city of Narbo there in 118.[123]
Rise of Marius
[edit]

Rome fought the Jugurthine War from 111 to 104 BC against the North African kingdom of Numidia (in what is now Algeria and Tunisia). In 118, its king, Micipsa, died, and an illegitimate son, Jugurtha, usurped the throne.[125] Numidia had been a loyal ally of Rome since the Punic Wars.[126] Initially, Rome mediated a division of the country. But Jugurtha renewed his offensive, leading to a long and inconclusive war with Rome.[127] Gaius Marius was a legate under the consul directing the war and was elected consul in 107 BC over the objections of the aristocratic senators, relying on support from the businessmen and poor. Marius had the Numidian command reassigned to himself through the popular assembly and, with the capture of Jugurtha at the end of a long campaign, ended the war; in the aftermath, the Romans largely withdrew from the province after installing a client king.[128] Marius's victory played on existing themes of senatorial corruption and incompetence, contrasted especially against the military failure of senatorial leadership in the Cimbrian War.[129]
The Cimbrian War (113–101) was a far more serious affair than the earlier Gallic clashes in 121. The Germanic tribes of the Cimbri and the Teutons[130] migrated from northern Europe into Rome's northern territories,[131] and clashed with Rome and its allies. The defeat of various aristocrats in the conflict, along with Marius's reputation for military victory, led to his holding five successive consulships with little to enable him to lead armies against the threat.[132] At the Battle of Aquae Sextiae and the Battle of Vercellae, Marius led the Roman armies, which virtually annihilated both tribes, ending the threat.[133]
During the Cimbrian War, further conflicts embroiled the Republic: A Second Servile War waged in Sicily from 104 to 101;[111] a campaign was waged against pirates in Cilicia; Rome campaigned in Thrace, adding lands to the province of Macedonia; and Lycaonia was annexed to Rome.[134]
First civil wars
[edit]In 91, the Social War broke out between Rome and its former allies in Italy: the main causes of the war were Roman encroachment on allied lands due to the Republic's land redistribution programmes, harsh Roman treatment of the non-citizen allies, and Roman unwillingness to share in the spoils of the empire.[135] After the assassination, in Rome, of a conservative tribune who sought to grant the Italians citizenship, the allies took up arms:[136] most ancient writers explain the conflict in terms of demands for full citizenship, but contemporary rebel propaganda coins indicate it may have been a primarily anti-Roman secessionist movement.[137] The Romans were able to stave off military defeat by conceding the main point almost immediately, tripling the number of citizens.[138] More recent scholarship also has stressed the importance of the war on the allies in destabilising Roman military affairs by blurring the distinction between Romans and foreign enemies.[139]
Further civil conflict emerged, starting in 88. One of the consuls that year, L. Cornelius Sulla, was assigned to take an army against the Pontic king Mithridates. The local governor there was defeated, but C. Marius induced a tribune to promulgate legislation reassigning Sulla's command to Marius. Sulla responded by suborning his army, marching on Rome (the city was undefended but politically outraged), and declaring Marius and 11 of his allies outlaws before departing east to war with Mithridates.[140] Marius, who had escaped into exile, returned, and with L. Cornelius Cinna, took control of the city.[141]
After the Marians took control of the city, they started to purge their political enemies.[142] They elected, in irregular fashion, Marius and Cinna to the consulship of 86 BC. Marius died a fortnight after assuming office. Cinna took control of the state: his policies are unclear and the record is muddled by Sulla's eventual victory.[143] The Cinnan regime declared Sulla a public enemy and ostensibly replaced him in command in the east. Instead of cooperating with his replacement, which Sulla viewed as illegitimate, he made peace with Mithridates and prepared to return to Italy.[144] By 85 BC, the Cinnans in Rome started preparations to defend the peninsula from invasion.[144]
In 83, he returned from the east with a small but experienced army.[145] Initial reactions were negative across the peninsula, but after winning a number of victories he was able to overcome resistance and capture the city. In the Battle of the Colline Gate, just outside Rome,[146] Sulla's army defeated the Marian defenders and then proceeded to "run riot... killing for profit, pleasure, or personal vengeance anyone they pleased".[147] He then instituted procedures to centralise the killing, creating lists of proscribed persons who could be killed for their property without punishment.[148] After establishing political control, Sulla had himself made dictator and passed a series of constitutional reforms intended to strengthen the position of the magistrates and the senate in the state and replace custom with new rigid statute laws enforced by new permanent courts.[149][150] Sulla resigned the dictatorship in 81 after election as consul for 80. He then retired, and died in 78 BC.[151]
Sullan republic
[edit]Cn. Pompey Magnus served the Sullan regime during a short conflict triggered by the republic's own consul, M. Aemilius Lepidus, in 77 BC[152] and afterwards led troops successfully against the remaining anti-Sullan forces in the Sertorian War; he brought the war successfully to a close in 72 BC. While Pompey was in Spain, the Republic faced agitation both foreign and domestic. The main domestic political struggle was the restoration of tribunician powers stripped during Sulla's dictatorship.[153] After rumours of a pact between Sertorius's ostensible republic-in-exile,[154] Mithridates, and various Mediterranean pirate groups, the Sullan regime feared encirclement and stepped up efforts against the threats: they reinforced Pompey in Spain and fortified Bithynia. In spring 73 BC, Mithridates did so, invading Bithynia.[155]
In 73, a slave uprising started in southern Italy under Spartacus, a gladiator, who defeated the local Roman garrisons and four legions under the consuls of 72.[156] At the head of some 70,000 men, Spartacus led them in a Third Servile War—they sought freedom by escape from Italy—before being defeated by troops raised by M. Licinius Crassus.[157] Although Pompey and Crassus were rivals, they were elected to a joint consulship in 70. During their consulship, they brought—with little opposition—legislation to dismantle the tribunician disabilities imposed by Sulla's constitutional reforms.[158] They also shepherded legislation to settle the contentious matter of jury reform.[159]
L. Licinius Lucullus, one of Sulla's ablest lieutenants, had fought against Mithridates during the first Mithridatic war before Sulla's civil war. Mithridates also had fought Rome in a second Mithridatic war (83–82 BC).[160] Rome for its part seemed equally eager for war and the spoils and prestige that it might bring.[161] After his invasion of Bithynia in 73, Lucullus was assigned against Mithridates and his Armenian ally Tigranes the Great in Asia Minor.[162] Fighting a war of manoeuvre against Mithridates' supply lines, Lucullus was able force Mithridates from an attempted siege of Cyzicus and pursue him into Pontus and thence into Armenia.[163] After defeat forced the Romans from large parts of Armenia and Pontus in 67, Lucullus was replaced in command by Pompey.[164] Pompey moved against Mithridates in 66.[165] Defeating him in battle and securing the submission of Tigranes,[166] Mithridates fled to Crimea, where he was betrayed and killed by his son Pharnaces in 63.[167] Pompey remained in the East to pacify and settle Roman conquests in the region, also extending Roman control south to Judaea.[168]
End of the Republic
[edit]First Triumvirate
[edit]Pompey returned from the Third Mithridatic War at the end of 62 BC. In the interim, before his return to Italy, the senate had successfully suppressed a conspiracy and insurrection led by a senator, Lucius Sergius Catilina, to overthrow that year's consuls.[169] In the aftermath of the conspiracy, which was abetted by popular discontent, the Senate moved legislation to temper unrest in Italy: expanding the grain dole and implementing other reforms.[170] Pompey, landing in Brundisium, publicly dismissed his troops, indicating that he had no desire to follow Sulla's example and dominate the republic by force, as some conservative senators had feared.[171] He attempted to have his eastern settlements passed by the Senate; ratification was not forthcoming, due to the opposition of Lucullus, Crassus, and Cato the Younger.[172]
After Julius Caesar's election as one of the consuls of 59 BC, Pompey, Caesar, and Crassus engaged in a political alliance (traditionally dubbed by scholars as the First Triumvirate).[173] The alliance greatly benefited the three men: Caesar passed legislation to distribute state lands as poor relief while also providing land for Pompey's veterans; he also had Pompey's eastern settlements ratified; for Crassus, he secured relief for tax farmers and a place on agrarian commission.[174] Caesar won for himself the political support needed to acquire a profitable provincial command in Gaul and secure his political future.[175]
Attempting first to pass portions of his programme through the Senate, Caesar found the curia obstinate. He thus unveiled his alliance with Pompey and Crassus and moved his legislation before the people instead.[176] Political opposition to the allies was immense.[177]
Caesar also facilitated the election of the former patrician Publius Clodius Pulcher to the tribunate for 58. Clodius set about depriving Caesar's senatorial enemies of two of their more obstinate leaders in Cato and Cicero. Clodius attempted to try Cicero for executing citizens without a trial during the Catiline conspiracy, resulting in Cicero going into self-imposed exile. Clodius also passed a bill that forced Cato to lead the invasion of Cyprus, which would keep him away from Rome for some years. Clodius also passed a law to expand the previous partial grain subsidy to a fully free grain dole for citizens.[178]

After his term as consul in 59, Caesar was appointed to a five-year term as the proconsular Governor of Cisalpine Gaul (part of current northern Italy), Transalpine Gaul (current southern France) and Illyria (part of the modern Balkans).[179] Caesar sought cause to invade Gaul (modern France and Belgium), which would give him the dramatic military success he sought. When two local tribes began to migrate on a route that would take them near (not into) the Roman province of Transalpine Gaul, Caesar had the barely sufficient excuse he needed for his Gallic Wars, fought between 58 and 49.
Caesar defeated large armies at major battles 58 and 57. In 55 and 54 he made two expeditions into Britain, the first Roman to do so. Caesar then defeated a union of Gauls at the Battle of Alesia,[180][181] completing the Roman conquest of Transalpine Gaul. By 50, all of Gaul lay in Roman hands.
Clodius formed armed gangs that terrorised the city and eventually began to attack Pompey's followers, who in response funded counter-gangs formed by Titus Annius Milo. The political alliance of the triumvirate was crumbling. Domitius Ahenobarbus ran for the consulship in 55, promising to take Caesar's command from him. Eventually, the triumvirate was renewed at Lucca. Pompey and Crassus were promised the consulship in 55, and Caesar's term as governor was extended for five years. Beginning in the summer of 54, a wave of political corruption and violence swept Rome.[182] This chaos reached a climax in January of 52, when Milo murdered Clodius in a gang war.
In 53, Crassus launched a Roman invasion of the Parthian Empire (modern Iraq and Iran). After initial successes,[183] his army was cut off deep in enemy territory, surrounded and slaughtered at the Battle of Carrhae, in which Crassus himself perished. Crassus's death destabilized the Triumvirate. While Caesar was fighting in Gaul, Pompey proceeded with a legislative agenda for Rome that revealed that he was at best ambivalent towards Caesar.[184] Pompey's wife, Julia, who was Caesar's daughter, died in childbirth. This event severed the last remaining bond between Pompey and Caesar. In 51, some Roman senators demanded that Caesar not be permitted to stand for consul unless he turned over control of his armies to the state. Caesar chose civil war over laying down his command and facing trial.
Caesar's civil war and dictatorship
[edit]
On 1 January 49, an agent of Caesar presented an ultimatum to the senate. The ultimatum was rejected, and the senate then passed a resolution declaring that if Caesar did not lay down his arms by July of that year, he would be considered an enemy of the Republic.[185] Meanwhile, the senators adopted Pompey as their new champion against Caesar, passing a senatus consultum ultimum that vested Pompey with dictatorial powers. On 10 January, Caesar with his veteran army crossed the river Rubicon, the legal boundary of Roman Italy beyond which no commander might bring his army, in violation of Roman laws, and by the spring of 49 swept down the Italian peninsula towards Rome. His rapid advance forced Pompey, the consuls and the senate to abandon Rome for Greece. Caesar entered the city unopposed. Afterwards Caesar turned his attention to the Pompeian stronghold of Hispania (modern Spain)[186] but decided to tackle Pompey himself in Greece.[187] Pompey initially defeated Caesar, but failed to follow up on the victory, and was decisively defeated at the Battle of Pharsalus in 48.[188][189] Pompey fled again, this time to Egypt, where he was murdered.
Pompey's death did not end the civil war. In 46 Caesar lost perhaps as much as a third of his army, but ultimately came back to defeat the Pompeian army of Metellus Scipio in the Battle of Thapsus, after which the Pompeians retreated yet again to Hispania. Caesar then defeated the combined Pompeian forces at the Battle of Munda.
With Pompey defeated and order restored, Caesar wanted to achieve undisputed control over the government. The powers he gave himself were later assumed by his imperial successors.[190] Caesar held both the dictatorship and the tribunate, and alternated between the consulship and the proconsulship.[190] In 48, he was given permanent tribunician powers. This made his person sacrosanct, gave him the power to veto the senate, and allowed him to dominate the Plebeian Council. In 46, Caesar was given censorial powers,[191] which he used to fill the senate with his partisans. He then raised the membership of the Senate to 900.[192] This robbed the senatorial aristocracy of its prestige, and made it increasingly subservient to him.[193] Caesar began to prepare for a war against the Parthian Empire. Since his absence from Rome would limit his ability to install consuls, he passed a law that allowed him to appoint all magistrates, and later all consuls and tribunes. This transformed the magistrates from representatives of the people to representatives of the dictator.[192]
Caesar was now the primary figure of the Roman state, enforcing and entrenching his powers. His enemies feared that he had ambitions to become an autocratic ruler. Arguing that the Roman Republic was in danger, a group of senators led by Gaius Cassius and Marcus Brutus hatched a conspiracy and assassinated Caesar at a meeting of the Senate on 15 March 44. Virtually all the conspirators fled the city after Caesar's death in fear of retaliation.
Second Triumvirate
[edit]The civil wars that followed destroyed what was left of the Republic.[196]
After the assassination, Caesar's three most important associates, Mark Antony, Caesar's co-consul, Octavian, Caesar's adopted son and great-nephew, and Lepidus, Caesar's magister equitum, formed an alliance known as the Second Triumvirate.[197] The conspirators were defeated at the Battle of Philippi in 42.
Following Philippi, Rome's territories were divided between the triumvirs, but the agreement was fragile. Antony detested Octavian and spent most of his time in the East, while Lepidus favoured Antony but felt himself obscured by his colleagues. Following the defeat of Sextus Pompeius, a dispute between Lepidus and Octavian regarding the allocation of lands broke out and, in 36 BC, Lepidus was forced into exile in Circeii and stripped of all his offices except that of pontifex maximus. His former provinces were awarded to Octavian.
Antony, meanwhile, married Caesar's lover, Cleopatra of Ptolemaic Egypt, intending to use wealthy Egypt as a base to dominate Rome. The ambitious Octavian built a power base of patronage and then launched a campaign against Antony. Another civil war broke out between Octavian on one hand and Antony and Cleopatra on the other. This culminated in the latter's defeat at Actium in 31 BC; Octavian's forces then chased Antony and Cleopatra to Alexandria, where they both committed suicide in 30 BC.
Octavian was granted a series of special powers, including sole imperium within the city of Rome, permanent consular powers, and credit for every Roman military victory. In 27, he was granted the use of the name "Augustus", from which point he is generally considered the first Roman Emperor.[198]
Constitutional system
[edit]| Part of the Politics series |
| Republicanism |
|---|
The constitutional history of the Roman Republic began with the revolution that overthrew the monarchy in 509 BC and ended with constitutional reforms that transformed the Republic into what would effectively be the Roman Empire, in 27 BC. The Roman Republic's constitution was a constantly evolving, unwritten set of guidelines and principles passed down mainly through precedent, by which the government and its politics operated.[199]
Senate
[edit]
The senate's authority derived from the senators' esteem and prestige.[200] This esteem and prestige were based on both precedent and custom, as well as the senators' calibre and reputation. The senate passed decrees called senatus consulta. These were officially "advice" from the senate to a magistrate, but in practice, the magistrates usually followed them.[201] Through the course of the middle republic and Rome's expansion, the senate became more dominant in the state: the only institution with the expertise to administer the empire effectively, it controlled state finances, assignment of magistrates, external affairs, and deployment of military forces. Also, a powerful religious body, it received reports of omens and directed Roman responses thereto.[202]
When its prerogatives started to be challenged in the 2nd century, the senate lost its customary preapproval for legislation. Moreover, after the precedent set in 121 BC with the killing of Gaius Gracchus, the senate claimed to assume the power to issue a senatus consultum ultimum: such decrees directed magistrates to take whatever actions were necessary to safeguard the state, irrespective of legality, and signalled the senate's willingness to support that magistrate if such actions were later challenged in the courts.[203]
Its members were usually appointed by censors, who ordinarily selected newly elected magistrates for membership in the senate, making the senate a partially elected body. Status was not hereditary and there were always some new men, though sons of former magistrates found it easier to be elected to the qualifying magistracies. During emergencies, a dictator could be appointed for the purpose of appointing senators (as was done after the Battle of Cannae). However, by the end of the republic men such as Caesar and the members of the Second Triumvirate usurped these powers for themselves.[202]
Legislative assemblies
[edit]
The legal status of Roman citizenship was limited and a vital prerequisite to possessing many important legal rights, such as the right to trial and appeal, marry, vote, hold office, enter binding contracts, and to special tax exemptions. An adult male citizen with the full complement of legal and political rights was called optimo iure (lit. 'having the greatest rights'). Citizens who were optimo iure elected their assemblies, whereupon the assemblies elected magistrates, enacted legislation, presided over trials in capital cases, declared war and peace, and forged or dissolved treaties. There were two types of legislative assemblies: the comitia ('committees'), which were assemblies of all citizens optimo jure, and the consilia ("councils"), which were assemblies of specific groups of citizens optimo jure.[204]
Citizens were organized on the basis of centuries and tribes, which each gathered into their own assemblies. The Comitia Centuriata ('Centuriate Assembly') was the assembly of the centuries (that is., soldiers). The Comitia Centuriata's president was usually a consul. The centuries voted, one at a time, until a measure received support from a majority. The Comitia Centuriata elected magistrates who had imperium (consuls and praetors). It also elected censors. Only the Comitia Centuriata could declare war and ratify the results of a census.[205] It served as the highest court of appeal in certain judicial cases.
The assembly of the tribes, that is, the citizens of Rome, the Comitia Tributa, was presided over by a consul, and composed of 35 tribes. Once a measure received support from a majority of the tribes, voting ended. While it did not pass many laws, the Comitia Tributa did elect quaestors, curule aediles, and military tribunes.[206] The Plebeian Council[207] was identical to the assembly of the tribes but excluded the patricians. They elected their own officers, plebeian tribunes and plebeian aediles. Usually, a plebeian tribune would preside over the assembly. This assembly passed most laws and could act as a court of appeal.
Magistrates
[edit]Each republican magistrate held certain constitutional powers. Each was assigned a provincia by the Senate. This was the scope of that particular office holder's authority. It could apply to a geographic area or to a particular responsibility or task.[208] The powers of a magistrate came from the people of Rome (both plebeians and patricians).[209] Imperium was held by both consuls and praetors. Strictly speaking, it was the authority to command a military force, but in reality, it carried broad authority in other public spheres, such as diplomacy and the justice system. In extreme cases, those with the imperium power could sentence Roman Citizens to death. All magistrates also had the power of coercitio (coercion). Magistrates used this to maintain public order by imposing punishment for crimes.[210] Magistrates also had both the power and the duty to look for omens. This power could also be used to obstruct political opponents.
One check on a magistrate's power was collega ('collegiality'). Each magisterial office was held concurrently by at least two people. Another such check was provocatio. While in Rome, all citizens were protected from coercion, by provocatio, an early form of due process. It was a precursor to habeas corpus. If any magistrate tried to use the powers of the state against a citizen, that citizen could appeal the magistrate's decision to a tribune. In addition, once a magistrate's one-year term of office expired, he would have to wait ten years before serving in that office again. This created problems for some consuls and praetors, and these magistrates occasionally had their imperium extended. In effect, they retained the powers of the office (as a promagistrate) without officially holding that office.[211]
In times of military emergency, a dictator was appointed for a term of six months.[212] Constitutional government was dissolved, and the dictator was the absolute master of the state. When the dictator's term ended, constitutional government was restored.
The censor was a magistrate in ancient Rome who was responsible for maintaining the census, supervising public morality, and overseeing certain aspects of the government's finances.[213] The power of the censor was absolute: no magistrate could oppose his decisions, and only another censor who succeeded him could cancel those decisions. The censor's regulation of public morality is the origin of the modern meaning of the words censor and censorship.[214] During the census, they could enroll citizens in the senate or purge them from the senate.[215]
The consuls of the Roman Republic were the highest-ranking ordinary magistrates. Each served for one year.[216] Consular powers included the kings' former imperium and appointment of new senators. Consuls had supreme power in both civil and military matters. While in the city of Rome, the consuls were the head of the Roman government. They presided over the senate and the assemblies. While abroad, each consul commanded an army.[217] His authority abroad was nearly absolute.
Since the tribunes were considered the embodiment of the plebeians, they were sacrosanct. Their sacrosanctity was enforced by a pledge the plebeians took to kill anyone who harmed or interfered with a tribune during his term of office. It was a capital offense to harm a tribune, disregard his veto, or otherwise interfere with him.[218]
Praetors administered civil law[219] and commanded provincial armies. Aediles were officers elected to conduct domestic affairs in Rome, such as managing public games and shows. The quaestors usually assisted the consuls in Rome, and the governors in the provinces. Their duties were often financial.
Military
[edit] |
| Part of a series on the |
| Military of ancient Rome |
|---|
Rome's military secured Rome's territory and borders and helped to impose tribute on conquered peoples. Rome's armies had a formidable reputation; but Rome also "produced [its] share of incompetents"[220] and catastrophic defeats. Nevertheless, it was generally the fate of Rome's greatest enemies, such as Pyrrhus and Hannibal,[221] to win early battles but lose the war.
Hoplite armies
[edit]During this period, Roman soldiers seem to have been modelled after those of the Etruscans to the north,[222] who themselves are believed to have copied their style of warfare from the Greeks. Traditionally, the introduction of the phalanx formation into the Roman army is ascribed to the city's penultimate king, Servius Tullius (ruled 578–534).[223] The phalanx was effective in large, open spaces, but not on the hilly terrain of the central Italian peninsula. In the 4th century, the Romans replaced it with the more flexible manipular formation. This change is sometimes attributed to Marcus Furius Camillus and placed shortly after the Gallic invasion of 390; more likely, it was copied from Rome's Samnite enemies to the south.[224]
Manipular legion
[edit]

During this period, an army formation of around 5,000 men (of both heavy and light infantry) was known as a legion. Maniples were units of 120 men each drawn from a single infantry class. They were typically deployed into three discrete lines based on the three heavy infantry types:
- The first line maniple was the hastati, infantry soldiers who wore a bronze breastplate and a bronze helmet and carried an iron-clad wooden shield. They were armed with a sword and two throwing spears.
- The second line were the principes. They were armed and armoured in the same manner as the hastati, but wore a lighter coat of mail.
- The triarii formed the third line. They were the last remnant of the hoplite-style troops in the Roman army. They were armed and armoured like the principes, but carried a lighter spear.[227]
The three infantry classes[228] may have retained some slight parallel to social divisions within Roman society, but at least officially the three lines were based upon age and experience rather than social class. Young, unproven men served in the first line, older men with some military experience in the second, and veteran troops of advanced age and experience in the third.
The heavy infantry of the maniples was supported by a number of light infantry and cavalry troops, typically 300 horsemen per manipular legion.[228] The cavalry was drawn primarily from the richest class of equestrians. There was an additional class of troops that followed the army without specific martial roles and was deployed to the rear of the third line. Its role in accompanying the army was primarily to supply any vacancies that might occur in the maniples. The light infantry consisted of 1,200 unarmoured skirmishing troops drawn from the youngest and lower social classes. They were armed with a sword, a small shield, and several light javelins.
Rome's military confederation with the other peoples of the Italian peninsula meant that half of its army was provided by the Socii. According to Polybius, Rome could draw on 770,000 men at the beginning of the Second Punic War, of which 700,000 were infantry and 70,000 met the requirements for cavalry.
A small navy had operated at a fairly low level after about 300, but it was massively upgraded about 40 years later, during the First Punic War. After a period of frenetic construction, the navy mushroomed to more than 400 ships on the Carthaginian ("Punic") pattern. Once completed, it could accommodate up to 100,000 sailors and embarked troops for battle. The navy thereafter declined in size.[229]
In 217, near the beginning of the Second Punic War, Rome was forced to effectively ignore its long-standing principle that its soldiers must be both citizens and property owners. Severe social stresses, population decline, and the greater collapse of the middle classes meant that the Roman state was forced to arm its soldiers at the expense of the state, which it had not had to do before. The distinction between the heavy infantry types began to blur, perhaps because the state was now assuming the responsibility of providing standard-issue equipment. In addition, the shortage of available manpower led to a greater burden upon Rome's allies for the provision of allied troops.[230] Eventually, the Romans were forced to begin hiring mercenaries to fight alongside the legions.[231]
Late Republican legions
[edit]
The organisation of the legions evolved throughout the Republican period. In 107, all citizens, regardless of their wealth or social class, were made eligible for entry into the Roman army. The distinction among the three heavy infantry classes, which had already blurred, had collapsed into a single class of heavy legionary infantry. The heavy infantry legionaries were drawn from citizen stock, while non-citizens came to dominate the ranks of the light infantry. The army's higher-level officers and commanders were still drawn exclusively from the Roman aristocracy.[232] Unlike earlier in the Republic, legionaries were no longer fighting on a seasonal basis to protect their land. Instead, they received standard pay and were employed by the state on a fixed-term basis. As a consequence, military duty began to appeal most to the poorest sections of society, to whom a salaried pay was attractive.
The legions of the late Republic were almost entirely heavy infantry. The main legionary sub-unit was a cohort of approximately 480 infantrymen, further divided into six centuries of 80 men each.[233] Each century comprised 10 "tent groups" of eight men. Cavalry were used as scouts and dispatch riders rather than as battlefield forces.[234] Legions also contained a dedicated group of artillery crew of perhaps 60 men. Each legion was normally partnered with an approximately equal number of allied (non-Roman) troops.[235]
The army's most obvious deficiency lay in its shortage of cavalry, especially heavy cavalry.[236] Particularly in the East, Rome's slow-moving infantry legions were often confronted by fast-moving cavalry troops and found themselves at a tactical disadvantage.
After Rome's subjugation of the Mediterranean, its navy declined in size, although it underwent short-term upgrading and revitalisation in the late Republic to meet several new demands. Julius Caesar assembled a fleet to cross the English Channel and invade Britannia. Pompey raised a fleet to deal with the Cilician pirates who threatened Rome's Mediterranean trading routes. During the civil war that followed, as many as 1,000 ships were either constructed or pressed into service from Greek cities.[229]
Social structure
[edit]
Citizen families were headed by the family's oldest male, the pater familias, who was lawfully entitled to exercise complete authority (patria potestas) over family property and all family members.[237] Citizenship offered legal protection and rights, but citizens who offended Rome's traditional moral code could be declared infamous and lose certain legal and social privileges.[238] Citizenship was also taxable, and undischarged debt was potentially a capital offence. A form of limited, theoretically voluntary slavery (debt bondage, or nexum) allowed wealthy creditors to negotiate payment of debt through bonded service. Poor, landless citizens of the lowest class (proletarii) might contract their sons to a creditor, patron or third party employer to obtain an income or pay off family debts. Nexum was abolished only when slave labour became more readily available, most notably during the Punic wars.[239][240][241]

Slaves could be bought, sold, acquired through warfare, or born and raised in slavery. There were no legal limits on the slave-owner's power over them. A few slaves were freed by their owners, becoming freedmen and in some circumstances citizens too.[242] This degree of social mobility was unusual in the ancient world but itself limited; for example, freedmen were seen as permanently tainted, and their children could not become magistrates.[243] Freedmen could play notable roles in various crafts and trades, particularly those who had been manumitted by the upper classes.[244] Freed slaves and the master who freed them retained certain legal and moral mutual obligations.
At the other extreme were the senatorial families of the landowning nobility, both patrician and plebeian, bound by shifting allegiances and mutual competition. A plebiscite of 218 forbade senators and their sons to engage in substantial trade or money-lending.[245][246] A wealthy equestrian class emerged, not subject to the same trading constraints as senators.[247]
One of Rome's fundamental social and economic institutions was the client-patron relationship; its obligations were largely moral and social rather than legal, but permeated society, including in politics.
Citizen men and citizen women were expected to marry, produce as many children as possible, and improve—or at worst, conserve—their family's wealth, fortune, and public profile. Marriage offered opportunities for political alliance and social advancement. Patricians usually married in a form known as confarreatio, which transferred the bride from her father's legal control (manus) to that of her husband.[248] Patrician status could be inherited only through birth; an early law, introduced by the reactionary Decemviri but rescinded in 445, sought to prevent marriages between patricians and plebeians.[k] Among ordinary plebeians, different marriage forms offered married women considerable more freedom than their patrician counterparts, until manus marriage was replaced by free marriage, in which the wife remained under her absent father's legal authority, not her husband's.[249] Infant mortality was high. Towards the end of the Republic, the birthrate began to fall among the elite. Some wealthy, childless citizens resorted to adoption to provide male heirs for their estates and to forge political alliances. Adoption was subject to the senate's approval.
Trade and economy
[edit]Farming
[edit]The Republic was created during a time of warfare, economic recession, food shortages, and plebeian debt. In wartime, plebeian farmers were liable to conscription. In peacetime, most depended on whatever cereal crops they could produce on small farming plots, allotted to them by the state, or by patrons. Soil fertility varied from place to place, and natural water sources were unevenly distributed. In good years, a small holder might trade a small surplus, to meet his family's needs, or to buy the armatures required for his military service. In other years, crop failure through soil exhaustion, adverse weather, disease or military incursions could lead to poverty, unsupported borrowing, and debt. Nobles invested much of their wealth in ever-larger, more efficient farming units, exploiting a range of soil conditions through mixed farming techniques. As farming was labour-intensive, and military conscription reduced the pool of available manpower, over time the wealthy became ever more reliant on the increasingly plentiful slave labour provided by successful military campaigns.[250][251][252] Large, well-managed agricultural estates helped provide for clients and dependents, support an urban family home, and fund the owner's public and military career, in the form of cash for bribes and security for loans. Later Roman moralists idealised farming as an intrinsically noble occupation.[253][254][255]
In law, land taken by conquest was ager publicus (public land). In practise, much of it was exploited by the nobility, using slaves rather than free labour. Rome's expansionist wars and colonisations were at least partly driven by the land-hunger of displaced peasants, who must otherwise join the swelling, dependent population of urban plebs.[256] At the end of the second Punic War, Rome added the fertile ager Campanus, suitable for intense cultivation of vines, olives and cereals. Like the grain-fields of Sicily—seized after the same conflict—it was likely farmed extra-legally by leading landowners, using slave gangs. A portion of Sicily's grain harvest was sent to Rome as tribute, for redistribution by the aediles.[257][258] The urban plebs increasingly relied on firstly subsidised, then free grain.[259]

With the introduction of aqueducts (from 312), suburban market-farms could be supplied with runoff or waste aqueduct water. Perishable commodities such as flowers (for perfumes, and festival garlands), fresh grapes, vegetables and orchard fruits, and small livestock such as pigs and chickens, could be farmed close to municipal and urban markets.[251] Food surpluses, no matter how obtained, kept prices low.[260][261] Faced with increasing competition from provincial and allied grain suppliers, many Roman farmers turned to more profitable crops, especially grapes for wine production. By the late Republican era, Roman wine had been transformed from an indifferent local product for local consumption to a major domestic and export commodity, with some renowned, costly and collectable vintages.[262][263]
Roman writers have little to say about large-scale stock-breeding but make passing references to its profitability. Drummond speculates that this focus on agriculture rather than livestock might reflect elite preoccupations with historical grain famines, or long-standing competition between agriculturalists and pastoralists.[264][265] Though meat and hides were valuable by products of stock-raising, cattle were primarily reared to pull carts and ploughs, and sheep were bred for their wool, the mainstay of the Roman clothing industry. Horses, mules and donkeys were bred as civil and military transport. Pigs bred prolifically and could be raised at little cost by any small farmer with rights to pannage. Their central dietary role is reflected by their use as sacrifices in cults and funerals.[264]
Religion
[edit]

Republican Rome's religious practices harked back to Rome's quasi-mythical history.[267][268] Romulus, a son of Mars, founded Rome after Jupiter granted him favourable bird-signs regarding the site.[269] Numa Pompilius, Rome's second king, had established its basic religious and political institutions after direct instructions from the gods, given through augury, dreams and oracle. Each king thereafter was credited with some form of divinely approved innovation, adaptation or reform.[l] An Imperial-era source claims that the Republic's first consul, Brutus, effectively abolished human sacrifice to the goddess Mania, instituted by the last king, Tarquinius.[m]
Romans acknowledged the existence of innumerable deities who controlled the natural world and human affairs. The Roman state's well-being depended on its state deities, whose opinions and will could be discerned by priests and magistrates, trained in augury, haruspicy, oracles and the interpretation of omens. The gods were thought to communicate their wrath (ira deorum) through prodigies (unnatural or aberrant phenomena).
Individuals, occupations and locations had their own protective tutelary deity, or several. Each was associated with a particular, highly prescriptive form of prayer and sacrifice. Piety (pietas) was the correct, dutiful and timely performance of such actions. The well-being of each Roman household was thought to depend on daily cult to its Lares and Penates (guardian deities, or spirits), ancestors, and the divine generative essence embodied within its pater familias. A family which neglected its religious responsibilities could not expect to prosper.[270]
Roman religious authorities were unconcerned with personal beliefs or privately funded cults unless they offended natural or divine laws or undermined the mos maiorum (roughly, "the way of the ancestors"); the relationship between gods and mortals should be sober, contractual, and of mutual benefit. Undignified grovelling, excessive enthusiasm (superstitio) and secretive practices were "weak-minded" and morally suspect.[271] Magical practices were officially banned, as attempts to subvert the will of the gods for personal gain but were probably common among all classes. Private cult organisations that seemed to threaten Rome's political and priestly hierarchy were investigated by the Senate, with advice from the priestly colleges. The Republic's most notable religious suppression was that of the Bacchanalia, a widespread, unofficial, enthusiastic cult to the Greek wine-god Bacchus. The cult organisation was ferociously suppressed, and its deity was absorbed within the official cult to Rome's own wine god, Liber.[272] The official recognition, adoption and supervision of foreign deities and practices had been an important unitary feature in Rome's territorial expansion and dominance since the days of the kings.[267][268]
Priesthoods
[edit]With the abolition of monarchy, some of its sacral duties were shared by the consuls, while others passed to a Republican rex sacrorum ("king of the sacred rites"), a patrician "king", elected for life, with great prestige but no executive or kingly powers.[273] Rome had no specifically priestly class or caste. As every family's pater familias was responsible for his family's cult activities, he was effectively the senior priest of his own household. In the early Republic, the patricians, as "fathers" to the Roman people, claimed the right of seniority to lead and control the state's relationship with the divine. Patrician families, in particular the Cornelii, Postumii and Valerii, monopolised the leading state priesthoods. The patrician Flamen Dialis employed the "greater auspices" (auspicia maiora) to consult with Jupiter on significant matters of state.
Twelve "lesser flaminates" (Flamines minores) were open to plebeians or reserved to them. They included a Flamen Cerealis in service of Ceres, goddess of grain and growth, and protector of plebeian laws and tribunes.[274] The priesthoods of local urban and rustic Compitalia street festivals, dedicated to the lares of local communities, were open to freedmen and slaves.[275].

The Lex Ogulnia (300) gave patricians and plebeians more-or-less equal representation in the augural and pontifical colleges;[39] other important priesthoods, such as the Quindecimviri ("The Fifteen"), and the epulones[n] were opened to any member of the senatorial class.[278] To restrain the accumulation and potential abuse of priestly powers, each gens was permitted one priesthood at a time, and the censors monitored the senators' religious activities.[278] Magistrates who held an augurate could claim divine authority for their position and policies.[279] In the late Republic, augury came under the control of the pontifices, whose powers were increasingly woven into the civil and military cursus honorum. Eventually, the office of pontifex maximus became a de facto consular prerogative.[280]
Some cults may have been exclusively female; for example, the rites of the Good Goddess (Bona Dea). Towards the end of the second Punic War, Rome rewarded priestesses of Demeter from Graeca Magna with Roman citizenship for training respectable, leading matrons as sacerdotes of "Greek rites" to Ceres.[281] Every matron of a family (the wife of its pater familias) had a religious duty to maintain the household fire, which was considered an extension of Vesta's sacred fire, tended in perpetuity by the chaste Vestal Virgins. The Vestals also made the sacrificial mola salsa employed in many State rituals, and represent an essential link between domestic and state religion. Rome's survival was thought to depend on their sacred status and ritual purity.[282]
Temples and festivals
[edit]
Rome's major public temples were within the city's sacred, augural boundary (pomerium), which had supposedly been marked out by Romulus, with Jupiter's approval. The Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus ("Jupiter, Best and Greatest") stood on the Capitoline Hill. Among the settled areas outside the pomerium was the nearby Aventine Hill. It was traditionally associated with Romulus's unfortunate twin, Remus, and in later history with the Latins, and the Roman plebs. The Aventine seems to have functioned as a place for the introduction of "foreign" deities.[274] In 392, Camillus established a temple there to Juno Regina, Etruscan Veii's protective goddess. Later introductions include Summanus, c. 278, Vortumnus c. 264, and at some time before the end of the 3rd century, Minerva.[284][o] While Ceres's Aventine temple was most likely built at patrician expense, to mollify the plebs, the patricians brought the Magna Mater ("Great mother of the Gods") to Rome as their own "Trojan" ancestral goddess, and installed her on the Palatine.[285]
Говорят, что Ромул поставил свой аугурационный шатер на вершине Палатина. Под его южными склонами пролегала священная дорога , ведущая к бывшему дворцу королей ( Regia ), Дому весталок и храму Весты . Рядом находились святилище Луперкаля и пещера, где, как говорят, волчица вскормила Ромула и Рема. На равнинной территории между Авентином и Палатином находился Большой цирк , где проводились гонки на колесницах и религиозные игры. В число его святынь и храмов входили храмы местного бога Солнца Сола , богини луны Луны , бога хранения зерна Консуса и малоизвестной богини Мурсии .
В то время как римляне отмечали прохождение лет именами своих правящих консулов, в их календарях отмечались годовщины основания религии определенным божествам, дни, когда официальная деятельность была разрешена ( фас ), и те дни, когда она не была разрешена ( нефас ). Римляне соблюдали восьмидневную неделю; На девятый день суды были закрыты, а рынки прошли. Каждым месяцем руководило определенное, обычно главное божество. Древнейшие календари были лунными.
В армии
[ редактировать ]
Перед любой кампанией или битвой римские полководцы пользовались покровительством или гаруспиками , чтобы узнать мнение богов относительно вероятного исхода. Военный успех был достигнут за счет сочетания личного и коллективного virtus (грубо говоря, «мужской добродетели») и божественной воли. Триумфальные полководцы переоделись Юпитером Капитолийским и возложили к его ногам лавры победителя. Религиозная небрежность или недостаток добродетели вызвали божественный гнев и привели к военной катастрофе. [287] [288] Военные присяги посвящали жизнь присягнувшим богам и народу Рима; Ожидалось, что побежденные солдаты покончат с собой, а не выживут в плену. Примеры преданности в исполнении Дециев Мурес, в которых солдаты предлагали и отдавали свои жизни Ди инфери (богам подземного мира) в обмен на римскую победу, отмечались как высшее благо.
Города, поселки и виллы
[ редактировать ]Город Рим
[ редактировать ]
Жизнь в Римской республике вращалась вокруг города Рима. Важнейшие правительственные, административные и религиозные учреждения были сосредоточены в его центре, на Капитолийском и Палатинском холмах и вокруг них . Город быстро перерос свою первоначальную священную границу ( померий ) и первые городские стены . Рима Первый акведук (312), построенный во время кризиса Пунических войн, обеспечивал обильное снабжение чистой водой. Строительство дополнительных акведуков привело к расширению города и созданию общественных бань ( терм ) как центральной черты римской культуры. [п] В городе также было несколько театров , [289] гимназии , а также множество таверн и борделей. Жилая площадь была в цене. Некоторые простые граждане и вольноотпущенники со средним доходом могли жить в скромных домах, но большая часть населения жила в многоквартирных домах ( insulae, буквально «острова» ), где более состоятельные люди могли арендовать целый первый этаж, а самые бедные — один, возможно, одинокий. комната без окон наверху, с небольшим количеством удобств или вообще без них. Дворяне и богатые меценаты жили в просторных, благоустроенных городских домах; от них ожидалось, что они будут держать «дом открытых дверей» для своих коллег и клиентов. Полуобщественный атриум обычно служил местом встреч и средством демонстрации богатства, художественного вкуса и религиозного благочестия. Дворянские атрии были также площадкой для демонстрации масок предков ( предков ). [д]
В большинстве римских городов и поселков были форумы и храмы, как и в самом городе Риме. Акведуки доставляли воду в городские центры. [290] Землевладельцы обычно проживали в городах и оставляли свои поместья на попечение управляющих фермами.
Культура
[ редактировать ]Одежда
[ редактировать ]
в греческом стиле Основной римской одеждой была туника , которую носили до колен и с короткими рукавами (или без рукавов) для мужчин и мальчиков, а также до щиколотки и с длинными рукавами для женщин и девочек. Тога была чисто римской и стала знаком мужского гражданства, показателем социального положения. [292] Конвенция также предписывала тип, цвет и стиль кальцеи (ботинок), соответствующих каждому уровню мужского гражданства.
Самые белые и объемные тоги носили представители сенаторского сословия. Высокопоставленные магистраты, священники и дети граждан имели право на тогу претекста с пурпурной каймой . Триумфальные генералы носили полностью фиолетовую, расшитую золотом тогу-пикту , связанную с образом Юпитера и бывших римских царей – но только в течение одного дня; Республиканские нравы одновременно способствовали проявлениям конкуренции и пытались сдерживать их , чтобы сохранить хотя бы условное равенство между сверстниками и уменьшить потенциальную угрозу классовой зависти. [293] Большинство римских граждан, особенно низший класс плебса, предпочитали более удобную и практичную одежду, такую как туники и плащи.
Роскошная и яркая одежда всегда была доступна тем, кто мог ее себе позволить, особенно женщинам из праздных слоев общества. Существуют материальные свидетельства существования золотой парчи ( ламе ) еще в VII веке. [294] К III веку значительное количество шелка-сырца импортировалось из Китая . [295] Тирский пурпур , квазисвященный цвет, официально использовался для границы тоги претекста и для сплошной фиолетовой тоги пикты . [296] [297]
Для большинства римлян даже самая дешевая льняная или шерстяная одежда представляла собой значительную статью расходов. Изношенная одежда передавалась по социальной лестнице, пока не превращалась в лохмотья, которые использовались для лоскутного шитья. [298] Шерсть и лен были основой римской одежды, которую моралисты идеализировали как простую и скромную. [299] Для большинства женщин подготовка и плетение шерсти были частью ежедневного ведения домашнего хозяйства либо для семейного использования, либо для продажи. В традиционалистских, богатых семьях семейные веретена и ткацкие станки располагались в полуобщественной приемной ( атриуме ), чтобы mater familias и ее familia могли продемонстрировать свое трудолюбие и бережливость: в значительной степени символическая и моральная деятельность для представителей их класса. а не практическая необходимость. [р]
По мере развития Республики ее торговля, территории и богатство увеличивались. Римские консерваторы выразили сожаление по поводу очевидного размывания традиционных классовых различий в одежде и растущего аппетита римлян к роскошным тканям и экзотическим «иностранным» стилям среди всех классов, включая их собственный. Ближе к концу республики ультратрадиционалист Катон Младший публично протестовал против потакания своим прихотям своих сверстников и потери республиканских «мужских добродетелей» , надев «скудную» темную шерстяную тогу без туники и обуви. [299] [с]
Еда и столовая
[ редактировать ]
Современное изучение особенностей питания в республике затруднено различными факторами. Сохранилось немного письменных источников, и поскольку различные компоненты их рациона более или менее вероятно сохранились, на археологические данные нельзя полагаться. [300] В ранней республике основная еда ( сена ) по существу состояла из своего рода каши , бобовых . [301] Самый простой вариант будет сделан из эммера , воды, соли и жира. Богатые обычно ели бобовые с яйцами , сыром и медом , а иногда их также подавали с мясом или рыбой . В течение республиканского периода сена превратилась в два блюда: основное блюдо и десерт с фруктами и морепродуктами (например, моллюсками , креветками ). К концу республики трапеза обычно подавалась из трех частей: закуска ( gustatio ), основное блюдо ( primae mensae ) и десерт ( secundae mensae ).
В период средней и поздней республики к вину все чаще относились как к необходимости, а не как к роскоши. В Древнем Риме вино обычно смешивали с водой непосредственно перед употреблением, поскольку брожение не контролировалось и крепость алкоголя была высокой. Кислое вино, смешанное с водой и травами ( поска ), было популярным напитком среди низших сословий и основной частью рациона римского солдата. [302] Пиво ( cerevisia ) было известно, но считалось вульгарным и ассоциировалось с варварами . [303] [304]
С 123 г. до н. э. Римское государство ежемесячно раздавало порцию немолотой пшеницы (до 33 кг), известную как frumentatio , почти 200 000 человек. [305]
Образование и язык
[ редактировать ]Родным языком Рима была ранняя латынь , язык италийских латинян . Большая часть сохранившейся латинской литературы написана на классической латыни , высоко стилизованном и отточенном литературном языке , который развился из ранней разговорной латыни I века. Большинство говорящих на латыни использовали вульгарную латынь , которая значительно отличалась от классической латыни грамматикой, словарным запасом и, в конечном итоге, произношением. [306]
После различных военных завоеваний на греческом Востоке римляне адаптировали ряд греческих образовательных заповедей к своей собственной молодой системе. [307] Напряженная и дисциплинированная физическая подготовка помогла подготовить мальчиков гражданского класса к их будущему гражданству и военной карьере. Девочки обычно получали инструкции [308] от своих матерей в искусстве прядения, ткачества и шитья. Школьное обучение более формального типа началось примерно в 200 году. Образование началось примерно в шесть лет, и в следующие шесть-семь лет мальчики и девочки должны были научиться читать, писать и считать. К двенадцати годам они будут изучать латынь, греческий язык, грамматику и литературу, а затем обучаться публичным выступлениям. Эффективное ораторское искусство и хорошая латынь высоко ценились среди элиты и были необходимы для карьеры в области права или политики. [309] [310]
Искусство
[ редактировать ]В III веке греческое искусство, захваченное в качестве военных трофеев, стало популярным, и многие римские дома были украшены пейзажами греческих художников. [311]
Со временем римская архитектура претерпела изменения по мере изменения городских требований, а технологии гражданского строительства и строительства стали развиваться и совершенствоваться. Такие факторы, как богатство и высокая плотность населения в городах, заставили древних римлян открыть для себя новые архитектурные решения. Использование сводов и арок в сочетании с глубоким знанием строительных материалов позволило им добиться беспрецедентных успехов в строительстве впечатляющей инфраструктуры общественного пользования. Они были воспроизведены в меньшем масштабе в наиболее важных городах Римской республики. Административная структура и богатство Империи сделали возможными очень крупные проекты даже в местах, удаленных от основных центров. [312]
Литература
[ редактировать ]
Ранняя римская литература находилась под сильным влиянием греческих авторов. Начиная с середины республики, римские авторы следовали греческим моделям, создавая пьесы в свободной и стихотворной форме, а также другие пьесы на латыни; например, Ливий Андроник писал трагедии и комедии. Самыми ранними латинскими произведениями, сохранившимися в первозданном виде, являются комедии Плавта , написанные в середине Республики. Произведения известных, популярных драматургов иногда заказывали для исполнения на религиозных праздниках; многие из них были пьесами сатиров , основанными на греческих моделях и греческих мифах. Можно сказать, что поэт Невий написал первую римскую эпическую поэму, хотя Энний был первым римским поэтом, написавшим эпос адаптированным латинским гекзаметром. только фрагменты эпоса Энния « Анналы Однако сохранились Вергилия » », однако и Невий, и Энний оказали влияние на более поздний латинский эпос, особенно на «Энеиду . Лукреций в своей работе «О природе вещей » изложил положения эпикурейской философии.
Литературная деятельность политика, поэта и философа Цицерона была чрезвычайно плодовитой и настолько повлияла на современную и более позднюю литературу, что период с 83 по 43 год до нашей эры был назван «Эпохой Цицерона». Его ораторское искусство продолжает влиять на современных ораторов, в то время как его философские работы, особенно латинская адаптация Цицерона греческих платонических и эпикурейских произведений, повлияли на многих более поздних философов. [313] [314] Среди других выдающихся писателей этого периода — грамматик и историк религии Варрон , политик, генерал и военный комментатор Юлий Цезарь , историк Саллюстий и любовный поэт Катулл .
Спорт и развлечения
[ редактировать ]
было Марсово поле площадкой для легкой атлетики в Риме, где молодежь собиралась, чтобы играть и заниматься спортом, включая прыжки, борьбу, бокс и скачки. [315] Предпочтительными физическими нагрузками также были конный спорт, метание и плавание. [316] В сельской местности развлечения включали рыбалку и охоту. [317] Настольные игры, в которые играли в Риме, включали кости (Tesserae или Tali ), римские шахматы ( Latrunculi ), римские шашки (Calculi), крестики-нолики (Terni Lapilli), а также Ludus duodecim scriptorum и Tabula, предшественники нард. [318] Другие мероприятия включали гонки на колесницах, музыкальные и театральные представления. [319]
См. также
[ редактировать ]- История Римской империи - События и люди в Римской империи
- Римская торговля - основной сектор римской экономики.
- Римские концепции гражданства
- Римская экономика - Экономика Древнего Рима
Примечания
[ редактировать ]- ↑ Некоторые историки, в частности Тим Корнелл , оспорили эту точку зрения, заявив, что в ранней республике Fasti Consulares носили явно плебейские имена. Поэтому они утверждают, что плебеи были исключены из высших должностей Децемвиратом только в 451 г. до н.э. Совсем недавно Кори Бреннан отверг эту теорию, заявив, что консульские плебеи не позволили бы децемвирам так легко лишить их власти. См. Бреннан 2000 , стр. 24–25. «Плебейские» имена в фастах он приписывает патрицианским родам , которые впоследствии вымерли или стали плебеями.
- ^ Традиционная дата первого отделения указана Ливием как 494 год; Было предложено много других дат, и, вероятно, имело место несколько таких событий. См. Корнелл, 1995 , стр. 215–218, 256–261, 266.
- ^ Обсуждение обязанностей и правового статуса плебейских трибунов и эдилов см. Lintott 1999b , стр. 92–101
- ↑ Тем не менее предполагалось, что Луций Атилий Луск в 444 году и Квинт Антоний Меранда в 422 году также были плебеями. [21]
- ^ Ливий упоминает по крайней мере двух патрициев, благосклонных к трибунам: Марка Фабия Амбуста , тестя Столо, и диктатора 368 г. до н.э. Публия Манлия Капитолия , который назначил первого плебейского магистра всадника , Гая Лициния Кальвуса.
- ^ Аппий Цек — сложный персонаж, реформы которого трудно интерпретировать. Например, Моммзен считал себя революционером, но был озадачен его неприятием закона Огулния , который противоречил его предыдущей «демократической» политике. Тейлор, напротив, думал, что защищает интересы патрициев, поскольку вольноотпущенники оставались клиентурой своих покровителей. Совсем недавно Хумм описывал свою деятельность как продолжение реформ, предпринятых со времен Столо и Латерана.
- ^ Между рассказами Кассия Диона, Дионисия и Плутарха есть существенные различия, но последний традиционно используется в академической литературе.
- ^ Конкретное собрание, на котором проводились консультации, вызвало множество дискуссий в академической литературе. Голсуорси 2001 , с. 69 выступает за Центуриатное собрание . Скаллард 1989а , с. 542 также предпочитает центурию племенам. Неясно, объявили ли римляне войну официально; они, возможно, оправдали конфликт выполнением недавно ратифицированного Мамертинского союза.
- ^ Полиб. , iii.117 сообщает о 70 000 погибших. Ливий , XXII.49 сообщает о 47 700 убитых и 19 300 пленных.
- ^ Деятельность Гракчанской земельной комиссии археологически задокументирована на обнаруженных пограничных камнях со списком членов комиссии. [116] Учитывая места находок, ученые оценивают распределение более чем 3200 квадратных километров государственных земель, в основном сосредоточенных на юге Италии. [117]
- ^ Плебей, заключивший такой брак, вероятно, был бы богат: см. Cornell 1995 , p. 255
- ↑ Говорят, что царь Нума Помпилиус встречался с нимфой Эгерией . Мифы, окружающие короля Сервия Туллия, включают его божественное отцовство от Лара из королевского дома или от Вулкана , бога огня; и его роман с богиней Фортуной .
- ^ Макробий описывает шерстяные фигурки ( мании ), вывешенные у святилищ на перекрестках во время популярного фестиваля Компиталия , как замену древних человеческих жертвоприношений , когда-то проводившихся на том же фестивале и запрещенных первым консулом Рима Л. Юнием Брутом . Какова бы ни была правда об этом жертвоприношении и его отмене, юнии праздновали культ своих предков во время Ларенталии, а не обычной Паренталии , даже в I веке до нашей эры; см. Taylor 1925 , стр. 302 и далее.
- ^ Основана в 196 году для того, чтобы взять на себя управление растущим числом игр и фестивалей понтификов.
- ^ О Камилле и Юноне см. Бенко 2004 , с. 27
- ^ О самом раннем вероятном развитии римских общественных бань см. Fagan 1999 , стр. 42–44.
- ^ «Архитектура древних римлян от начала до конца была искусством формирования пространства вокруг ритуала:» Лотт 2004 , с. 1, со ссылкой на Brown 1961 , с. 9. Некоторые римские ритуалы включают в себя действия, которые можно было бы назвать, выражаясь современным языком, религиозными; некоторые — это то, что в современных терминах можно понимать как светское — правильный и привычный способ ведения дел. Для римлян оба вида деятельности были скорее законными обычаями ( mos maiorum ), а не религиозными, а не светскими.
- ↑ На самом деле она была женским эквивалентом романтизированного гражданина-фермера: см. Flower 2004 , стр. 153, 195–197.
- ↑ В истории Рима, написанной Аппианом , раздираемая раздорами Поздняя республика колеблется на грани хаоса; большинство из них, кажется, одеваются так, как им нравится, а не так, как следует: «Ибо теперь римский народ сильно перемешан с иностранцами, существует равное гражданство для вольноотпущенников, и рабы одеваются так же, как их хозяева. За исключением сенаторов, свободные граждане и рабы носить тот же костюм». См. Ротфус 2010 , с. 1
Ссылки
[ редактировать ]Цитаты
[ редактировать ]- ^ Кроуфорд 1974 , стр. 455, 456.
- ^ Латинская лига .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Тагепера 1979 .
- ^ Момильяно 1989 , стр. 110–11.
- ^ Корнелл 1995 , стр. 215–18. Корнелл предлагает краткое изложение «прозаического повествования Ливия» и производных литературных произведений, касающихся изгнания королей.
- ^ Дион. Хэл. Муравей. ПЗУ. , 4.64–85.
- ^ Ливий , 1.57–60.
- ^ Корнелл 1995 , стр. 226–228.
- ^ Корнелл 1995 , стр. 215–218, 377–378; Драммонд 1989 , с. 178.
- ^ Форсайт 2005 , стр. 148–149.
- ^ Корнелл 1995 , стр. 215–17.
- ^ Флор. Эпит. , т. 11–12.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Грант 1978 , стр. 37–41.
- ^ Корнелл 1995 , стр. 289–291.
- ^ Корнелл 1995 , стр. 256–59. Плебс («масса») изначально был уничижительным термином, но был принят как знак гордости теми, кого он должен был оскорбить. Возможно, это не относилось к более богатым простолюдинам.
- ^ Крута 2000 , стр. 189.
- ^ Тревес 2012 .
- ^ Грант 1978 , стр. 48–49.
- ^ Грант 1978 , с. 52.
- ^ Грант 1978 , с. 53.
- ^ Бреннан 2000 , с. 50.
- ^ Корнелл 1989a , с. 338.
- ^ Ливий , VI.11, 13–30.
- ^ Корнелл 1989a , стр. 331–32.
- ^ Корнелл 1989a , с. 337. Корнелл считает, что Ливий перепутал содержание закона Лициния Секстия 366 г. до н. э. и закона Генуция 342 г. до н. э.
- ^ Ливий , VI.36–42.
- ^ Бротон 1952–1986 , том. 1 стр. 108–114.
- ^ Бреннан 2000 , стр. 59–61.
- ^ Livy , vii.42 .
- ^ Корнелл 1989a , с. 337.
- ^ Brennan 2000 , стр. 65–67, показывая, что десятилетнее правило в то время было лишь временным.
- ^ Корнелл 1989a , стр. 342–43.
- ^ Cornell 1989b , стр. 393–94, с указанием более ранней даты, до 318 г. до н.э.
- ^ Хамм 2005 , стр. 185–226 .
- ^ МакБейн 1980 .
- ^ Корнелл 1989a , с. 343.
- ^ Девелин 1978 .
- ^ Корнелл 1989a , стр. 340–41.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Корнелл 1995 , с. 342.
- ^ Грант 1978 , с. 78.
- ^ Дион. Хэл. Муравей. ПЗУ. , XIX.5–6.
- ^ Франке 1989 , стр. 456–57.
- ^ Дион. Хэл. Муравей. ПЗУ. , хх.3; Плут. Пирр. , 21.9, источник цитаты; Дио , х.5.
- ^ Франке 1989 , стр. 473–480.
- ^ Дион. Хэл. Муравей. ПЗУ. , хх.8.
- ^ Полиб. , III.22–26.
- ^ Livy , vii.27.
- ^ Скаллард 1989a , стр. 517–37.
- ^ Скаллард 1989a , с. 542.
- ^ Скаллард 1989a , с. 543.
- ^ Полиб. , 1.11–12.
- ^ Скаллард 1989a , с. Однако 545 утверждает, что Каудексу не удалось прорвать блокаду; он не получил триумфа, и его сменил Маний Валерий Максим , который вместо этого одержал победу и получил прозвище «Мессалла».
- ^ Скаллард 1989a , с. 547.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2001 , с. 113.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2001 , с. 84.
- ^ Скаллард 1989a , стр. 548–54.
- ^ Тацит Анналы II.49.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2001 , с. 88.
- ^ Скаллард 1989a , стр. 554–57.
- ^ Кроуфорд 1974 , стр. 292–93.
- ^ Скаллард 1989a , стр. 559–64.
- ^ Скаллард 1989a , стр. 565–69.
- ^ Отверстия 2011a , с. 217.
- ^ Отверстия 2011a , с. 215.
- ^ Скаллард 1989b , стр. 28–31.
- ^ Отверстия 2011a , стр. 101-1. 216–19.
- ^ Скаллард 1989b , стр. 33–36.
- ^ Скаллард 1989b , с. 39.
- ^ Бриско 1989 , с. 46.
- ^ Фронда 2011 , стр. 251–52.
- ^ Бриско 1989 , с. 47.
- ↑ Ливий , XXI.38, ссылается на Л. Цинция Алимента , который сообщил о личной беседе с Ганнибалом, в которой он сказал, что потерял 38 000 человек, перейдя через Альпы.
- ^ Бриско 1989 , с. 48.
- ^ «Scipione l'Africano» (на итальянском языке ) Проверено 12 августа 2023 г.
- ^ Sylloge Nummorum Graecorum, Великобритания, Том IX, Британский музей, Часть 2: Испания , Лондон, 2002, № 102.
- ^ Бриско 1989 , с. 51.
- ^ «Реджо-Эмилия, Миф и реальность в битве при Сильва-Литана» (на итальянском языке) . Проверено 12 августа 2023 г.
- ^ Бриско 1989 , стр. 52–53.
- ^ Бриско 1989 , стр. 49–50.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Бриско 1989 , с. 59.
- ^ Бриско 1989 , с. 55.
- ^ Бриско 1989 , с. 60.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Матышак 2004 , с. 47.
- ^ Экстайн 2012 , с. 42.
- ^ Экстайн 2012 , с. 43.
- ^ Матышак 2004 , с. 49.
- ^ Эррингтон 1989 , стр. 268–69.
- ^ Экстайн 2012 , с. 48.
- ^ Экстайн 2012 , с. 51.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Грант 1978 , с. 119.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Экстайн 2012 , с. 52.
- ^ Лейн Фокс 2006 , с. 326.
- ^ Экстайн 2012 , с. 55.
- ^ Циолковски 1988 , стр. 314 и далее, 316 и далее.
- ^ Дероу 1989 , с. 301.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2016 , с. 84.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2016 , стр. 90 и след.
- ^ Матышак 2004 , с. 53.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2016 , с. 105.
- ^ Дероу 1989 , с. 323, со ссылкой на Полиб. , 38.12.5..
- ^ Дероу 1989 , с. 323.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2001 , с. 338.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2001 , с. 339.
- ^ «Рим и Карфаген: борьба за господство» (на итальянском языке). 10 августа 2015 г. Проверено 14 августа 2023 г.
- ^ «Краткая история римского Карфагена (I век до н. э. – VII век нашей эры)» (на итальянском языке). 6 января 2023 г. Проверено 14 августа 2023 г.
- ^ Морштейн-Маркс и Розенштейн 2006 , с. 627, со ссылкой на Бранта 1971 г.
- ^ Морштейн-Маркс и Розенштейн 2006 , стр. 627–28, со ссылкой на Мейера 1997 . См. также о кризисе без альтернативы, Meier 1995 , стр. 491–496.
- ^ Морштейн-Маркс и Розенштейн 2006 , с. 628, со ссылкой на Gruen 1995 , с. 504.
- ^ Морштейн-Маркс и Розенштейн 2006 , с. 634.
- ^ Морштейн-Маркс и Розенштейн 2006 , стр. 634–635; Моуритсен 2017 , стр. 171–172.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Линтотт 1992a , стр. 25–26.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , с. 62.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , с. 66.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , с. 67.
- ^ Эбботт 2001 , с. 96.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , с. 68.
- ^ Roselaar 2010 , стр. 252–254.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , с. 72–73.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , с. 78.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , стр. 82–83.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , с. 84.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , с. 65.
- ^ «КРАССО, Луций Лициний» (на итальянском языке ) Проверено 14 августа 2023 г.
- ^ Кроуфорд 1974 , стр. 449–451.
- ^ Линтотт 1992a , стр. 28–29.
- ^ Матышак 2004 , с. 64.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , с. 88.
- ^ Линтотт 1992a , с. 30; Линтотт 1992b , с. 92.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , с. 94.
- ^ Приложение. BCiv. , 6.
- ^ Матышак 2004 , с. 75.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , с. [ нужна страница ] .
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , с. 96.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , стр. 96–97.
- ^ Габба 1992 , стр. 104–11.
- ^ Габба 1992 , стр. 113–14.
- ^ Борода 2015 , с. 238.
- ^ Борода 2015 , стр. 238–39.
- ^ Борода 2015 , с. 244.
- ^ Сигер 1992a , с. 171.
- ^ Борода 2015 , стр. 241–42.
- ^ Сигер 1992a , с. 178.
- ^ Сигер 1992a , с. 180.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Сигер 1992а , с. 182.
- ^ Сигер 1992a , с. 187.
- ^ Сигер 1992a , стр. 194–95.
- ^ Сигер 1992a , с. 197.
- ^ Seager 1992a , стр. 197–99, также цитирует древние источники о том, что около 80 сенаторов и 1600 всадников стали мишенью в первом раунде, а затем к ним присоединились два дополнительных раунда по 220 имен.
- ^ Борода 2015 , с. 246.
- ^ Сталь 2014 .
- ^ Сигер 1992a , стр. 205–07.
- ^ Сигер 1992b , стр. 208–10.
- ^ Сигер 1992b , стр. 210–11.
- ^ Сигер 1992b , с. 220, в котором управление Испанией Сертория описывается как «Рим в изгнании».
- ^ Сигер 1992b , с. 213.
- ^ Сигер 1992b , с. 222.
- ^ Сигер 1992b , стр. 221–22.
- ^ Сигер 1992b , стр. 224–25.
- ^ Сигер 1992b , стр. 225–26.
- ^ Шервин-Уайт 1992 , с. 229.
- ^ Матышак 2004 , с. 76.
- ^ Шервин-Уайт 1992 , стр. 234–35.
- ^ Шервин-Уайт 1992 , стр. 236, 239.
- ^ Шервин-Уайт 1992 , с. 244.
- ^ Шервин-Уайт 1992 , с. 252.
- ^ Шервин-Уайт 1992 , с. 253.
- ^ Шервин-Уайт 1992 , с. 254.
- ^ Шервин-Уайт 1992 , стр. 255–62.
- ^ Gruen 1995 , стр. 422–25 (сторонники), 429–31 (цели и неудачи).
- ^ Грюн 1995 , с. 432–33.
- ^ Wiseman 1992 , стр. 360–61.
- ^ Уайзман 1992 , с. 364.
- ^ Морштейн-Маркс 2021 , с. 120.
- ^ Грюн 1995 , с. 90; Уайзман 1992 , с. 364.
- ^ Грюн 1995 , с. 89.
- ^ Грюн 1995 , с. 91.
- ^ Грюн 1995 , с. 92.
- ^ Эбботт 2001 , с. 113.
- ^ Сантосуоссо 2008 , стр. 58.
- ^ Сантосуоссо 2008 , стр. 62.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2016 , с. 212.
- ^ Эбботт 2001 , с. 114.
- ^ Матышак 2004 , с. 133.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2016 , с. 214.
- ^ Эбботт 2001 , с. 115.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2016 , с. 217.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2016 , с. 218.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2016 , с. 227.
- ^ Лейн Фокс 2006 , с. 403.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Эбботт 2001 , с. 134.
- ^ Эбботт 2001 , с. 135.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Эбботт 2001 , с. 137.
- ^ Эбботт 2001 , с. 138.
- ^ Ролик 2010 , с. 175.
- ^ Уокер 2008 .
- ^ Эбботт 2001 , с. 133.
- ^ Голсуорси 2003 , с. 237.
- ^ Латтвак 1976 , с. 7.
- ^ Берд 1995 , с. 161.
- ^ Берд 1995 , с. 96.
- ^ Берд 1995 , с. 44.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Момильяно и Корнелл, 2012 .
- ^ Момильяно и Линтотт, 2012 ; Золотой 2013 , с. 148.
- ^ Эбботт 2001 , с. 251.
- ^ Эбботт 2001 , с. 257.
- ^ Тейлор 1966 , с. 7.
- ^ Эбботт 2001 , с. 196.
- ^ Линтотт 1999a , с. 101.
- ^ Линтотт 1999a , с. 95.
- ^ Линтотт 1999a , с. 97.
- ^ Линтотт 1999a , с. 113.
- ^ Берд 1995 , с. 24.
- ^ Суолахти, Дж. (1963) Римские цензоры: исследование социальной структуры (Хельсинки)
- ^ «цензура | Этимология, происхождение и значение цензуры» . этимонлин . Архивировано из оригинала 12 октября 2023 года.
- ^ Берд 1995 , с. 26.
- ^ Берд 1995 , с. 20.
- ^ Берд 1995 , с. 179.
- ^ Берд 1995 , с. 23.
- ^ Берд 1995 , с. 32.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2016 , с. 15.
- ^ Лейн Фокс 2006 , с. 312.
- ^ Секунда и Нортвуд 1995 , с. 17.
- ^ Секунда и Нортвуд 1995 , с. 18.
- ^ Секунда и Нортвуд 1995 , стр. 37–38.
- ^ Д.Б. Саддингтон (2011) [2007]. « Классы: эволюция римского императорского флота », Пол Эрдкамп (редактор), «Спутник римской армии» , 201–217. Молден, Оксфорд, Чичестер: Уайли-Блэквелл. ISBN 978-1-4051-2153-8 . Табличка 12.2 на стр. 204.
- ^ Коарелли, Филиппо (1987), Святилища Лацио в эпоху республиканцев . НИС, Рим, стр. 35–84.
- ^ Полиб. , Б6.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Сантосуоссо 2008 , стр. 18.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Вебстер 1994 , с. 156.
- ^ Сантосуоссо 2008 , стр. 11.
- ^ Вебстер 1994 , с. 143.
- ^ Сантосуоссо 2008 , стр. 29.
- ^ Латтвак 1976 , с. 14.
- ^ Вебстер 1994 , с. 116.
- ^ Латтвак 1976 , с. 15.
- ^ Латтвак 1976 , с. 43.
- ^ Корнелл 1995 , стр. 215–216.
- ^ Макгинн 1998 , стр. 65 и далее.
- ^ Драммонд 1989 , с. 126.
- ^ Cornell 1995 , стр. 238, 379–380, со ссылкой на Ливи , 9. 46. 13–14 для самых бедных граждан как forensis facto... humillimi («самый низкий из низких»)
- ^ Альфёлди 2014 , с. 17.
- ^ Гарднер 2008 .
- ^ Маклин 2018 , с. 2.
- ^ Остров 2023 , с. 31.
- ^ Корнелл 1995 , стр. 288–291.
- ^ Цветок 2004 , стр. 173–175. Флауэр описывает ограничения, наложенные на деловую деятельность сенаторов плебисцитумом Клаудиана 218 г. до н. э., и связанным с ним законодательством: возможно, они были предназначены для уменьшения возможностей взяточничества и коррупции или для того, чтобы помочь сенаторам сосредоточиться исключительно на своих задачах в правительстве.
- ^ Д'Армс 1980 .
- ^ Джонстон 1999 , стр. 33–34.
- ^ Frier & McGinn 2004 , стр. 20, 53, 54. Другие формы брака включают coemptio' (брак «по покупке») и usus (брак, признанный посредством «обычного сожительства пары»).
- ^ Корнелл 1995 , стр. 265–268, 283.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Бэннон, 2009 г. , стр. 5–10.
- ^ Драммонд 1989 , стр. 118–122, 135, 136.
- ^ Ливий , III.26–29.
- ^ Корнелл 1989b , стр. 412–413. Катон Старший подробно остановился на, вероятно, мифической бедности ведущих римлян, таких как Маний Дентатус и неподкупный Гай Фабриций Лусцин .
- ^ Розенштейн 2008 .
- ^ Корнелл 1995 , стр. 265–268.
- ^ Габба 1992 , стр. 197–198.
- ^ Линтотт 1992b , с. 55. Более позднее консульское расследование подобных посягательств на землю датировано 175 годом.
- ^ Корнелл 1995 , стр. 328–329.
- ^ Бэннон 2009 , 5–10, цитирует Ходжа 1989 , стр. 219 за обличительную речь Катона против злоупотребления водой из акведука Л. Фурия Пурпуреуса , консула в 196 г.
- ^ Николет 1992 , с. 619.
- ^ Розенштейн 2008 , стр. 2–16.
- ^ Николет 1992 , стр. 612–615. До этого времени римская элита предпочитала импортное греческое вино любому из отечественных римских вин.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Драммонд 1989 , стр. 118–122.
- ^ Габба 1992 , стр. 237–239.
- ^ Фаулер 1899 , стр. 202–204.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Рюпке 2007b , с. 4.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Beard, North & Price, 1998 , стр. 30–35.
- ^ Шиллинг 1992 , с. 115.
- ^ Орр 1978 , стр. 1557–1591.
- ^ Рюпке 2007b , с. 5.
- ^ Грюн 1996 , стр. 34 и далее.
- ^ Рюпке 2007c , с. 223.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Корнелл 1995 , с. 264.
- ^ Lott 2004 , стр. 31, 35, со ссылкой на Катона, «О сельском хозяйстве» , 5.3., и Дион. Хэл. Муравей. ПЗУ. , 4.14.2–4
- ^ Ovid, Fasti , v, 129–145
- ^ Кроуфорд 1974 , с. 312.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Липка 2009 , с. 171–172.
- ^ Розенбергер 2007 , с. 299. Auctoritas («авторитет») этимологически связан с авгуром : см. Cornell 1995 , p. 341
- ^ Брент 1999 , стр. 19–20, 21–25, цитируется Цицерон, «О природе богов» , 2.4.
- ^ Спэт 1996 , стр. 4, 6–13.
- ^ Калхэм 2004 , с. 155. См. также Beard 1980 и Parker 2004 .
- ^ « Байи, историческое место, Италия ». энциклопедия Британская По состоянию на 6 июня 2021 г.
- ^ Орлин 2002 , стр. 4–5.
- ^ Роллер 1999 , стр. 282–285.
- ^ Кроуфорд 1974 , стр. 487–495.
- ^ Орлин 2007 , с. 58.
- ^ Beard, North & Price 1998 , стр. 44, 59, 60, 143.
- ^ Джонс 2000 .
- ^ Грин 2000 , с. 39.
- ^ Чеккарелли, Л., в Белл, С., и Карпино, А., А, (редакторы) Спутник этрусков (Спутники Блэквелла по древнему миру), Blackwell Publishing, 2016, стр. 33
- ^ Воут 1996 , с. 215.
- ^ Цветок 1996 , с. 118: «Лучшей моделью для понимания римского законодательства о роскоши является модель аристократического самосохранения в высококонкурентном обществе, которое превыше всего ценило открытое проявление престижа».
- ^ Себеста и Бонфанте 1994 , стр. 62–68.
- ^ Габуччи 2005 , с. 168.
- ^ Брэдли 2011 , стр. 189, 194–195.
- ^ Эдмондсон и Кейт 2008 , стр. 28–30.
- ^ Воут 1996 , стр. 211, 212.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Эдмондсон и Кейт 2008 , с. 33.
- ^ Ведьмак 2016 , с. 8 .
- ^ Вульф 2007 , с. 388.
- ^ Далби 2003 , с. 270.
- ^ Стамбо 1988 , с. 149.
- ^ Бонфанте 2011 , с. 23.
- ^ Гарнси 1998 , стр. 237–238.
- ^ Мильорини, Бруно (2007). История итальянского языка (на итальянском языке) (XII изд.). Милан: Бомпиани. стр. 12–13. ISBN 978-88-452-4961-7 .
- ^ Паскаль 1984 .
- ^ ОКР 3 1996 .
- ^ Фаррелл 2001 , стр. 74–75.
- ^ Бауман 1994 , стр. 51–52.
- ^ Тойнби 1971 .
- ^ Смит, диджей (1983). «Мозаика» . В Мартине Хениге (ред.). Справочник римского искусства . Файдон. п. 26. ISBN 978-0-7148-2214-3 .
- ^ О 2016 году .
- ^ Гриффин 1986 , стр. 454–459.
- ^ Страбон , География , V, 3,8.
- ^ «Спорт и игры во времена Римской империи» (на итальянском языке) . Проверено 16 августа 2023 г.
- ^ «Комната LIV: Охота, рыбалка и кормление» (на итальянском языке) . Проверено 16 августа 2023 г.
- ^ Остин 1934 .
- ^ « Гладиаторы, колесницы и корабли. Шоу в Древнем Риме «Патриции Арены» (на итальянском языке). 24 марта 2020 г. Проверено 16 августа 2023 г.
Древние источники
[ редактировать ]- AppianАппиан война Гражданская
- Кассий Дион . Римская история - через LacusCurtius.
- Дионисий Галикарнасский Римские древности (Римские древности) – Via Lacus Curtius.
- Цветок. Воплощение – через Lacus Curtius.
- Ливи . История Рима .
- Плутарх . «Жизнь Пирра» . Параллельные жизни – через LacusCurtius.
- PolybiusПолибий История – Виа Лакус Курциус.
Цитируемые источники
[ редактировать ]- Эбботт, Фрэнк Фрост (2001) [1901]. История и описание римских политических институтов . Элиброн Классика. ISBN 0-543-92749-0 .
- Альфёлди, Геза (2014) [Впервые опубликовано на немецком языке в 1975 году]. Социальная история Рима . Возрождение Рутледжа. ISBN 978-1-317-66858-9 .
- Остин, Роланд (октябрь 1934 г.). «Римские настольные игры». Греция и Рим . 4 (10): 24–34. дои : 10.1017/S0017383500002941 . ISSN 0017-3835 . S2CID 162861940 .
- Бэннон, Синтия (2009). Сады и соседи: частные права на воду в римской Италии . Издательство Мичиганского университета. ISBN 978-0-472-03353-9 .
- Бауман, Ричард (1994) [1992]. Женщины и политика в Древнем Риме . Рутледж.
- Борода, Мэри; Норт, Джон; Прайс, SRF (1998). Религии Рима . Том. 1 (1-е изд.). Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 0-521-30401-6 .
- Борода, Мэри (1980). «Сексуальный статус весталок». Журнал римских исследований . 70 : 12–27. дои : 10.2307/299553 . JSTOR 299553 . S2CID 162651935 .
- Борода, Мэри (2015). SPQR: история Древнего Рима . Профильные книги. ISBN 978-1-8466-8380-0 .
- Бенко, Стивен (2004). Богиня-дева: исследования языческих и христианских корней мариологии . Брилл.
- Бонфанте, Лариса (2011). Варвары древней Европы: реалии и взаимодействие . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-0-521-19404-4 .
- Брэдли, Марк (2011). Цвет и значение в Древнем Риме . Кембриджские классические исследования. Издательство Кембриджского университета.
- Бреннан, Т. Кори (2000). Претура . Том. 1. Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-1951-3867-2 .
- Брент, Аллен (1999). Имперский культ и развитие церковного порядка: концепции и образы власти в язычестве и раннем христианстве до эпохи Киприана . Брилл. ISBN 978-90-04-11420-3 .
- Браун, Фрэнк (1961). Римская архитектура . Г. Бразиллер.
- Бротон, Томас Роберт Шеннон (1952–1986). Магистраты Римской республики .
- Брант, Питер (1971). Социальные конфликты в Римской республике . Чатто и Виндус.
- Берд, Роберт (1995). Сенат Римской республики . Документ Сената типографии правительства США 103-23.
- Корнелл, Тим (1995). Начало Рима . Рутледж. ISBN 978-0-415-01596-7 .
- Кроуфорд, Майкл (1974). Римская республиканская чеканка . Издательство Кембриджского университета.
- Крук, Дж.А.; Уолбанк, ФРВ; Фредериксен, MW; Огилви, Р.М., ред. (1989). Рим и Средиземноморье до 133 г. до н.э. Кембриджская древняя история. Том. 8 (2-е изд.). Издательство Кембриджского университета. дои : 10.1017/CHOL9780521234481 . ISBN 978-1-139-05436-2 .
- Скаллард, Х.Х. (1989b). «Карфагеняне в Испании». В ЦАГ 2 8 (1989) , стр. 17–43.
- Бриско, Джон. «Вторая Пуническая война». В ЦАГ 2 8 (1989) , стр. 44–80.
- Эррингтон, Р. М. «Рим против Филиппа и Антиоха». В ЦАГ 2 8 (1989) , стр. 244–89.
- Дероу, П.С. «Рим, падение Македонии и разграбление Коринфа». В ЦАГ 2 8 (1989) , стр. 290–323.
- Крук, Дж.А.; Линтотт, Эндрю ; Роусон, Элизабет, ред. (1992). Последний век Римской республики, 146–43 гг . до н.э. Кембриджская древняя история. Том. 9 (2-е изд.). Издательство Кембриджского университета. дои : 10.1017/CHOL9780521256032 . ISBN 978-1-139-05437-9 .
- Линтотт, А. (1992a). «Римская империя и ее проблемы в конце второго века». В ЦАГ 2 9 (1992) , стр. 16–39.
- Линтотт, А. (1992b). «Политическая история, 146–95 до н.э.». В ЦАГ 2 9 (1992) , стр. 40–103.
- Габба, Э. «Рим и Италия: социальная война». В ЦАГ 2 9 (1992) , стр. 104–28.
- Николет, Клод. «Экономика и общество, ок. 133–143 до н. э. ». В ЦАГ 2 9 (1992) , стр. 599–643.
- Сигер, Робин (1992a). «Сулла». В ЦАГ 2 9 (1992) , стр. 165–207.
- Сигер, Робин (1992b). «Возвышение Помпея». В ЦАГ 2 9 (1992) , стр. 208–228.
- Шервин-Уайт, А. Н. «Лукулл, Помпей и Восток». В ЦАГ 2 9 (1992) , стр. 229–273.
- Уайзман Т. П. «Сенат и народ ». В ЦАГ 2 9 (1992) , стр. 327–67.
- Далби, Эндрю (2003). «Поска». Еда в Древнем мире от А до Я. Рутледж. ISBN 978-0-415-23259-3 .
- Д'Армс, JB (1980). «Участие сенаторов в торговле в поздней республике: некоторые свидетельства Цицерона». Мемуары Американской академии в Риме . 36 (Морская торговля Древнего Рима: исследования по археологии и истории): 77–89. дои : 10.2307/4238697 . JSTOR 4238697 .
- Девелин, Р. (1978). « Провокация» и плебисциты. Раннее римское законодательство и историческая традиция». Мнемозина . 31 (1): 45–60. дои : 10.1163/156852578X00256 . JSTOR 4430760 .
- Экстайн, Артур М. (2012). Рим входит на греческий Восток: от анархии к иерархии в эллинистическом Средиземноморье, 230–170 гг . до н.э. Уайли-Блэквелл. ISBN 978-1-1182-5536-0 . LCCN 2007037809 .
- Эдмондсон, Дж. К.; Кейт, А., ред. (2008). Римское платье и ткани римской культуры . Университет Торонто Пресс. дои : 10.3138/9781442689039 . ISBN 978-1-4426-1079-8 .
- Эйланд, Мюррей (2023). Изображение римских систем верований: иконография монет в республике и Империи . Британские археологические отчеты (Оксфорд) Ltd. с. 31. дои : 10.30861/9781407360713 . ISBN 978-1-4073-6071-3 .
- Фэган, Гаррет (1999). Публичное купание в римском мире . Издательство Мичиганского университета.
- Фаррелл, Джозеф (2001). Латинский язык и латинская культура . Издательство Кембриджского университета.
- Флауэр, Харриет (1996). Маски предков и аристократическая власть в римской культуре . Издательство Оксфордского университета.
- Флауэр, Харриет, изд. (2004). Кембриджский спутник Римской республики (1-е изд.). Издательство Кембриджского университета.
- Калхэм, Филлис. «Женщины в Римской республике». В цветке (2004) , стр. 139–159.
- Форсайт, Гэри (2005). Критическая история раннего Рима . Издательство Калифорнийского университета. ISBN 978-0-520-22651-7 .
- Фаулер, В. Вард (1899). Римские праздники периода республики . Кенникат Пресс. стр. 202–204.
- Фриер, Брюс В.; Макгинн, Томас Эй Джей (2004). Сборник дел по римскому семейному праву . Издательство Оксфордского университета.
- Габуччи, Ада (2005). Словари цивилизации: Рим . Издательство Калифорнийского университета.
- Гарднер, Джейн Ф (2008). Женщины в римском праве и обществе . Рутледж. ISBN 978-1-134-93026-5 .
- Гарнси, Питер (1998). Шайдель, Уолтер (ред.). Города, крестьяне и еда в классической древности: Очерки социальной и экономической истории . Издательство Кембриджского университета. дои : 10.1017/cbo9780511585395 . ISBN 978-0-521-59147-8 .
- Голден, Грегори К. (2013). Кризисное управление в период Римской республики . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-1-107-05590-2 . OCLC 842919750 .
- Голсуорси, Адриан (2001). Пунические войны . Касселл. ISBN 0-3043-5967-Х .
- Голсуорси, Адриан (2003). Во имя Рима: Люди, которые завоевали Римскую империю . Вайденфельд и Николсон. ISBN 978-0-297-84666-6 .
- Голдсуорси, Адриан (2016) [Впервые опубликовано в 2003 г.]. Во имя Рима: люди, которые завоевали Римскую империю (1-е издание издательства Йельского университета). Издательство Йельского университета. ISBN 978-0-300-21852-7 .
- Грант, Майкл (1978). История Рима (1-е изд.). Сыновья Чарльза Скрибнера. ISBN 0-0234-5610-8 .
- Грин, Кевин (2000). «Технологические инновации и экономический прогресс в древнем мире: новый взгляд на М.И. Финли». Обзор экономической истории . Новая серия. 53 (1): 29–59. дои : 10.1111/1468-0289.00151 .
- Гриффин, Мириам (1986). «Цицерон и Рим». В Бордмане, Джон; Гриффин, Джаспер; Мюррей, Освин (ред.). Оксфордская история классического мира . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 0-19-285236-1 .
- Грюн, Эрих С. (1995). Последнее поколение Римской республики (1-е изд. в мягкой обложке). Издательство Калифорнийского университета.
- Грюн, Эрих С. (1996). «Дело о вакханалии». Исследования греческой культуры и римской политики . Издательство Калифорнийского университета.
- Ходж, Тревор (1989). Римские акведуки и водоснабжение . Дакворт.
- Хорнблауэр, Саймон; Спофорт, Энтони, ред. (1996). Оксфордский классический словарь (3-е изд.). Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-1986-6172-6 .
- Хорнблауэр, Саймон; и др., ред. (2012). Оксфордский классический словарь (4-е изд.). Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-19-954556-8 . OCLC 959667246 .
- Момильяно, Арнальдо; Корнелл, Тим. « Сенат, царственный и республиканский период ». В ОКР 4 (2012) .
- Момильяно, А; Линтотт, А. « Последняя консультация сената ». В ОКР 4 (2012) .
- Тревес, Пьеро. « Бренн (1), галльский вождь ». В ОКР 4 (2012) .
- Ойос, Декстер, изд. (2011). Спутник Пунических войн . Уайли-Блэквелл. ISBN 978-1-4051-7600-2 .
- Ойос, Декстер (2011a). «Карфаген в Африке и Испании, 241–218». В Ойосе (2011) , стр. 204–222.
- Фронда, Майкл П. «Ганнибал: тактика, стратегия и геостратегия». В Ойосе (2011) , стр. 242–259.
- Хмм, Мишель (2005). Аппий Клавдий Цек: состоявшаяся республика . Библиотека французских школ Афин и Рима (на французском языке). Публикации Французской школы Рима. ISBN 97-82728310265 .
- Джонстон, Дэвид (1999). Римское право в контексте . Издательство Кембриджского университета.
- Джонс, Марк Уилсон (2000). Принципы римской архитектуры . Издательство Йельского университета.
- Крута, Вацлав (2000). Кельты, история и словарь: от истоков до романизации и христианства (на французском языке). Роберт Лаффон. ISBN 2-221-05690-6 .
- Лейн Фокс, Робин (2006). Классический мир: эпическая история от Гомера до Адриана . Основные книги. ISBN 0-465-02496-3 .
- «Латинская лига» . Британника . Проверено 24 мая 2022 г.
- Линтотт, Эндрю (1999a). Конституция Римской республики . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-19-926108-6 .
- Линтотт, Эндрю (1999b). Насилие в республиканском Риме . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-19-815282-8 .
- Липка, М (2009). «Римские боги: концептуальный подход». В Верснеле, HS; Франкфуртер, Д.; Хан, Дж. (ред.). Религии в греко-римском мире . Брилл.
- Лотт, Джон (2004). Окрестности Августа Рима . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 0-521-82827-9 .
- Латтвак, Эдвард (1976). Великая стратегия Римской империи: от первого века до третьего . Издательство Университета Джонса Хопкинса. ISBN 978-0-8018-1863-9 .
- Макбейн, Брюс (1980). «Аппий Клавдий Слепой и Аппиев путь». Классический ежеквартальный журнал 30 (2): 356–372. дои : 10.1017/S0009838800042294 . JSTOR 638505 . S2CID 170803863 .
- Маклин, Роуз (2018). Освобожденные рабы и римско-имперская культура: социальная интеграция и трансформация ценностей . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-1-107-14292-3 .
- Матышак, Филипп (2004). Враги Рима . Темза и Гудзон. ISBN 978-0-500-25124-9 .
- Макгинн, Томас Эй Джей (1998). Проституция, сексуальность и закон в Древнем Риме . Издательство Оксфордского университета.
- Мейер, Кристиан (1995) [Впервые опубликовано на немецком языке Северином и Зидлером, 1982]. Цезарь . Перевод Маклинток, Дэвид. Основные книги. ISBN 0-465-00895-Х .
- Мейер, Кристиан (1997) [1966]. Res publica amissa (на немецком языке) (3-е изд.). Зуркамп. ISBN 978-3-518-57506-2 .
- Морштейн-Маркс, Роберт (2021). Юлий Цезарь и римский народ . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-1-108-94326-0 .
- Муритсен, Хенрик (2017). Политика в Римской республике . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-1-107-65133-3 .
- Орр, Д.Г. (1978). «Римская домашняя религия: свидетельства домашних святынь». Взлет и падение римского мира . Том II, том 16, 2.
- Орлин, Эрик М. (2002). «Иностранные культы в республиканском Риме: переосмысление поморского правления». Мемуары Американской академии в Риме . Том. 47.
- Паркер, Холт Н. (2004). «Почему весталки были девственницами? Или целомудрие женщин и безопасность Римского государства» (PDF) . Американский журнал филологии . 125 (4): 563–601. дои : 10.1353/ajp.2005.0009 . S2CID 154436702 .
- Паскаль, Нанетт (1984). «Наследие римского образования (на форуме)». Классический журнал . 79 (4).
- Роллер, Линн Эмрих (1999). В поисках Бога-Матери: Культ анатолийской Кибелы . Издательство Калифорнийского университета. ISBN 0-520-21024-7 .
- Роллер, Дуэйн В. (2010). Клеопатра: биография . Издательство Оксфордского университета . ISBN 978-0-19-536553-5 .
- Розелаар, Саския Т (2010). Общественная земля в Римской республике: социальная и экономическая история ager publicus в Италии . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-19-957723-1 .
- Розенштейн, Натан С; Морштейн-Маркс, Р., ред. (2006). Спутник Римской республики . Блэквелл. ISBN 978-1-4051-7203-5 .
- Морштейн-Маркс, Р.; Розенштейн, Н.С. «Преобразование республики». В Розенштейне и Морштейне-Марксе (2006) , стр. 625–637.
- Розенштейн, Натан (2008). «Аристократы и земледелие в Средней и Поздней республике» . Журнал римских исследований . 98 : 1–26. дои : 10.3815/007543508786239238 . JSTOR 20430663 .
- Ротфус, Массачусетс (2010). «Генс Тогата: изменение стилей и изменение идентичности». Американский журнал филологии . 131 (3): 425–452. дои : 10.1353/ajp.2010.0009 . S2CID 55972174 .
- Рюпке, Йорг , изд. (2007). Спутник римской религии . Уайли-Блэквелл. дои : 10.1002/9780470690970 . ISBN 978-0-470-69097-0 .
- Рюпке, Йорг (2007b). «Римская религия - Религии Рима». В Рюпке (2007) , стр. 1–9.
- Орлин, Эрик. «Городская религия в Средней и Поздней республике». В Рюпке (2007) , стр. 58–70.
- Розенбергер, Файт. « Дворяне -республиканцы : контроль над общественными делами ». В Рюпке (2007) , стр. 292–303.
- Рюпке, Йорг (2007c) [2001]. Религия римлян . Политическая пресса.
- Сантосуоссо, Антонио (2008). Штурм небес . Издательство Авалон. ISBN 978-0-7867-4354-4 .
- Шиллинг, Роберт (1992). «Упадок и выживание римской религии». Римская и европейская мифологии . Издательство Чикагского университета.
- Себеста, Джудит Линн; Бонфанте, Лариса, ред. (1994). Мир римского костюма . Висконсинские исследования классической литературы. Университет Висконсина Пресс. ISBN 978-0-2991-3850-9 .
- Секунда, Николай; Нортвуд, Саймон (1995). Ранние римские армии . Скопа. ISBN 1-85532-513-6 .
- Спэт, Барбетт Стэнли (1996). Римская богиня Церера . Издательство Техасского университета. ISBN 0-292-77693-4 .
- Стамбо, Джон Э (1988). Древний римский город . Издательство Университета Джонса Хопкинса. ISBN 978-0-8018-3574-2 .
- Сталь, Кэтрин (2014). «Римский сенат и постсулланская «res publica» » (PDF) . Historia: Журнал древней истории . 63 (3): 323–339. дои : 10.25162/история-2014-0018 . JSTOR 24432812 . S2CID 151289863 .
- Таагепера, Рейн (1979). «Размер и продолжительность существования империй: кривые роста-упадка, с 600 г. до н.э. по 600 г. н.э.». История социальных наук . 3 (3/4): 115–138. дои : 10.2307/1170959 . JSTOR 1170959 .
- Тейлор, Лили Росс (1925). «Мать Ларов». Американский журнал археологии . 29 (3): 299–313. дои : 10.2307/497560 . JSTOR 497560 . S2CID 192992171 .
- Тейлор, Лили Росс (1966). Римские избирательные собрания: от Ганнибаловой войны до диктатуры Цезаря . Издательство Мичиганского университета. ISBN 978-0-472-08125-7 .
- Тойнби, JMC (1971). «Римское искусство». Классический обзор . 21 (3): 439–442. дои : 10.1017/S0009840X00221331 . JSTOR 708631 . S2CID 163488573 .
- Воут, Кэролайн (1996). «Миф о тоге: понимание истории римской одежды» . Греция и Рим . 43 (2): 204–220. дои : 10.1093/gr/43.2.204 .
- Уолбанк, ФРВ ; Астин, А.Е.; Фредериксен, MW; Огилви, Р.М. , ред. (1989). Возвышение Рима до 220 г. до н.э. Кембриджская древняя история. Том. 7 очков. 2 (2-е изд.). Издательство Кембриджского университета. дои : 10.1017/CHOL9780521234467 . ISBN 978-1-139-05435-5 .
- Момильяно, А. «Происхождение Рима». В ЦАГ 2 7.2 (1989) , стр. 52–112.
- Драммонд, А. «Рим в пятом веке I: социальные и экономические рамки». В ЦАГ 2 7.2 (1989) , стр. 113–171.
- Корнелл, Ти Джей (1989a). «Восстановление Рима». В ЦАГ 2 7.2 (1989) , стр. 309–50.
- Корнелл, Ти Джей (1989b). «Завоевание Италии». В ЦАГ 2 7.2 (1989) , стр. 351–419.
- Франке, П. Р. «Пирр». В ЦАГ 2 7.2 (1989) , стр. 456–485.
- Скаллард, Х.Х. (1989a). «Карфаген и Рим». В ЦАГ 2 7.2 (1989) , стр. 486–569.
- Уокер, Сьюзен (2008). «Клеопатра в Помпеях?» . Документы Британской школы в Риме . 76 : 35–46 и 345–348 (стр. 35, 42–44). дои : 10.1017/S0068246200000404 .
- Вебстер, Грэм (1994). Римская императорская армия первого и второго веков нашей эры . Университет Оклахомы Пресс.
- Ведьмак, RE (2016). «Сельскохозяйственное производство в Римской Италии» (PDF) . Спутник Римской Италии . Спутники Блэквелла в древнем мире. Уайли-Блэквелл. стр. 459–482. дои : 10.1002/9781118993125.ch23 . ISBN 9781444339260 .
- Вульф, Грег (2007). Древние цивилизации: иллюстрированный справочник по вере, мифологии и искусству . Барнс и Ноубл. ISBN 978-1-4351-0121-0 .
- Заузмер, Джули (3 ноября 2016 г.). «Дональд Трамп, Цицерон 2016 года» . Вашингтон Пост .
- Циолковски, Адам (1988). «Храм Геркулеса Виктора Мумия и Круглый храм на Тибре». Феникс . 42 (4): 309–333. дои : 10.2307/1088657 . JSTOR 1088657 .
Внешние ссылки
[ редактировать ]- Римская республика из сериала «В наше время » ( BBC Radio 4 )
- Нова Рома – Образовательная организация работающая историческая реконструкция Римской республики
- История Римской Империи
- Римская республика
- Древняя итальянская история
- Итальянские государства
- Бывшие страны Европы
- Бывшие страны Африки
- Бывшие страны Западной Азии
- Страны древней Африки
- Государства и территории, основанные в VI веке до нашей эры.
- 509 г. до н.э.
- Заведения VI века до нашей эры в Италии
- Государства и территории, упраздненные в I веке до нашей эры.
- Разрушения I века до н.э.
- 27 г. до н.э.
- I тысячелетие до нашей эры в Италии.
- Бывшие республики



